Wet process of extracting vanadium and/or molybdenum from waste catalyst
A technology of waste catalyst and wet method, which is applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of difficult solid-liquid separation of slurry, small catalyst processing capacity, and large investment in equipment, and achieves the advantages of extraction and molybdenum extraction, easy solid-liquid separation, and mechanization high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
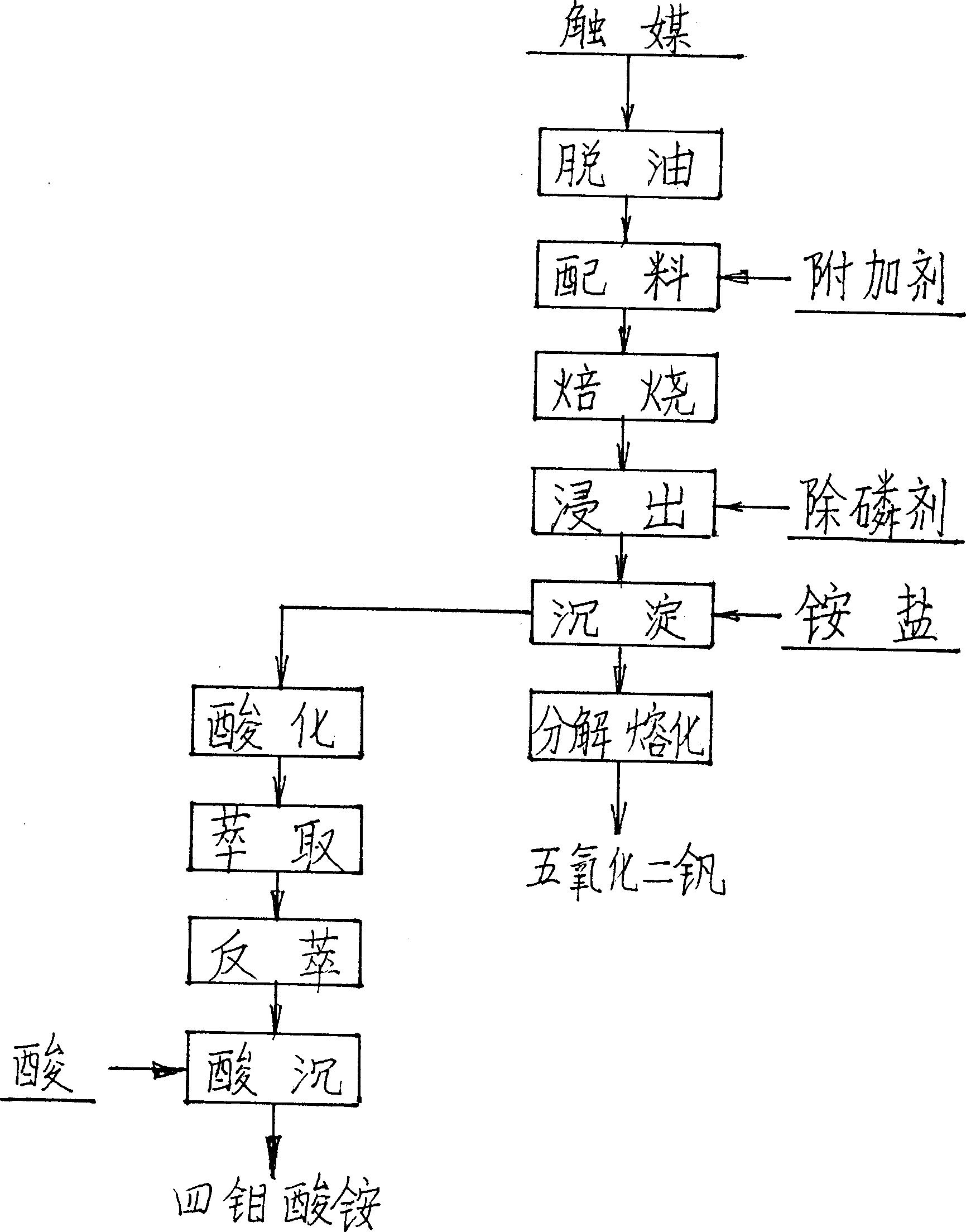
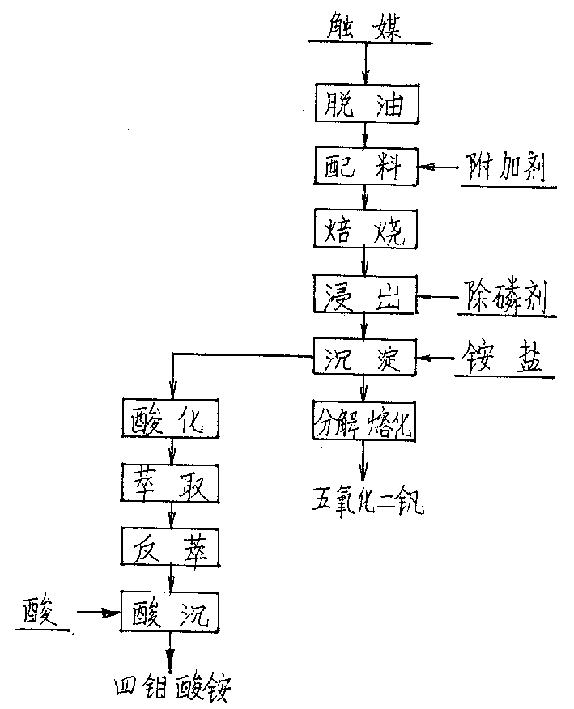
[0042] Embodiment 1, a kind of technique of wet extraction vanadium and / or molybdenum from waste catalyst, it carries out according to the following steps:
[0043] 1. The oil-containing waste catalyst with natural particle size is sent to the rotary kiln to remove oil at high temperature, and the air flow is used to flow with the material in the kiln to make full use of the heat energy contained in the catalyst. The temperature is controlled at 600 ° C for 4 hours;
[0044] 2. The catalyst after deoiling is added with an additive composed of soda ash, and the catalyst (according to V 2 o 5 meter) and additives in a weight ratio of 1:1;
[0045] 3. The prepared materials are again oxidized and roasted in a rotary kiln at a temperature of 700°C for 5 hours, and the conversion rate of vanadium and molybdenum is greater than 90%;
[0046] 4. The roasted clinker is sent to the leaching tank, and it is immersed in static countercurrent water at a temperature of 25°C for 5 hours, ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Embodiment 2, a kind of technique of wet extracting vanadium and / or molybdenum from spent catalyst, it carries out according to the following steps:
[0059] 1. The oil-containing waste catalyst with natural particle size is sent to the rotary kiln to remove oil at high temperature, and the airflow is used to flow with the material in the kiln to make full use of the heat energy contained in the catalyst. The temperature is controlled at 750 ° C for 3 hours;
[0060] 2. The catalyst after deoiling is added with an additive consisting of soda ash and salt (the weight ratio is 1:0.1), and the catalyst (according to V 2 o 5 The weight ratio of the additive) to the additive is 1:2;
[0061] 3. The prepared materials are roasted again by high-temperature sodium oxidation in a rotary kiln at a temperature of 850°C for 3.5 hours, and the conversion rate of vanadium and molybdenum is greater than 90%;
[0062] 4. The roasted clinker is sent to the leaching tank, and is immers...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Embodiment 3, a kind of technique of wet extraction vanadium and / or molybdenum from waste catalyst, it carries out according to the following steps:
[0075] 1. The oil-containing waste catalyst with natural particle size is sent to the rotary kiln to remove oil at high temperature, and the air flow is used to flow with the material in the kiln to make full use of the heat energy contained in the catalyst. Control the temperature to 800°C for 3 hours;
[0076] 2. The catalyst after deoiling is added with an additive consisting of soda ash and salt (the weight ratio is 1:0.2), and the catalyst (according to V 2 o 5 The weight ratio of the additive) to the additive is 1:3;
[0077] 3. The prepared materials are roasted again by high-temperature sodium oxidation in a rotary kiln at a temperature of 950°C for 3 hours. The low-valence vanadium and molybdenum in the catalyst are oxidized to a high-valence state, and react with sodium to form water-soluble sodium vanadate a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com