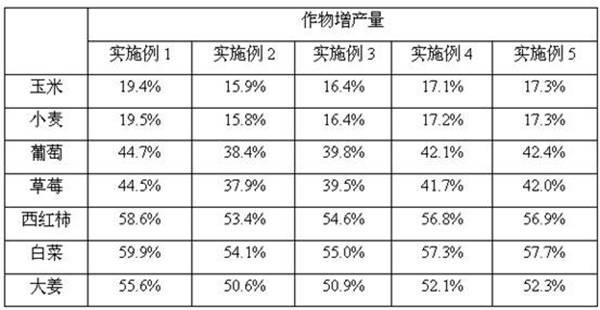
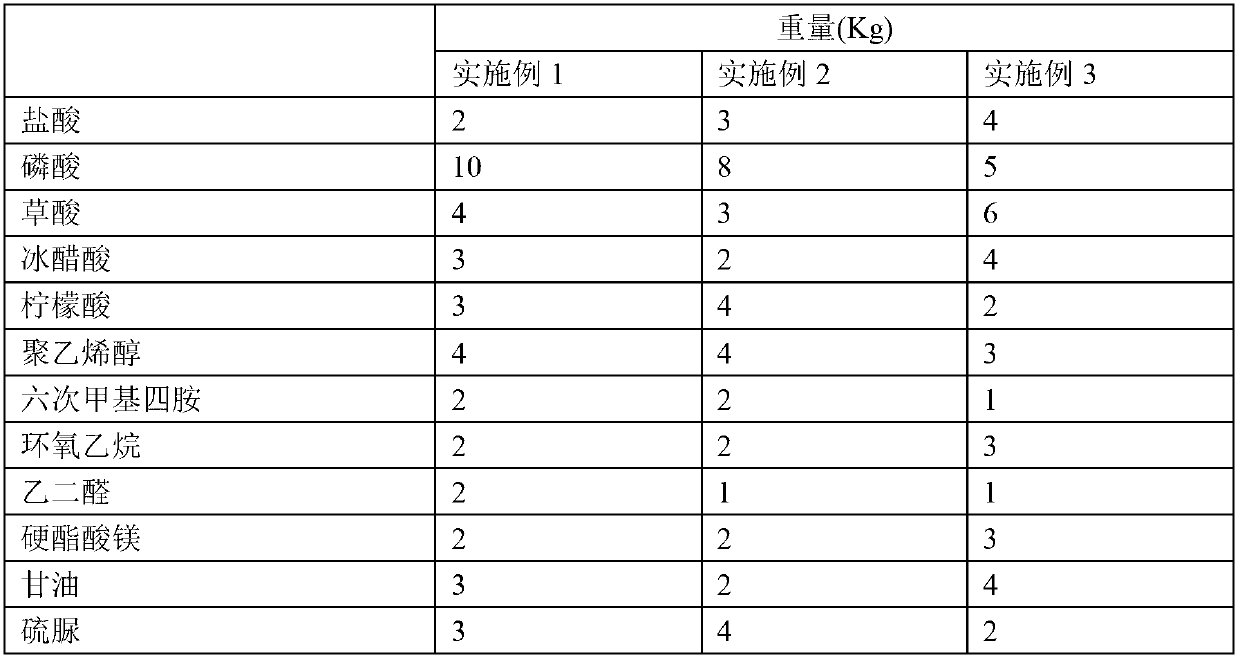
Patents
Literature
5154 results about "Ammonium molybdate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ammonium molybdate can refer to: Ammonium orthomolybdate, (NH₄)₂MoO₄ Ammonium heptamolybdate, (NH₄)₆Mo₇O₂₄, usually encountered as the tetrahydrate
Amino acid compound leaf fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102219610APromote absorptionNutritional diversityFertilizer mixturesMonopotassium phosphateAmino acid
The invention discloses an amino acid compound leaf fertilizer and a preparation method thereof, relating to the technical field of production of agricultural fertilizer. The amino acid compound leaf fertilizer is prepared by the following components according to parts by weight: 1-2 parts of zinc sulphate, 1-2 parts of borax, 2-3 parts of magnesium sulfate, 1-1.5 parts of surfactant, 2-3 parts of monopotassium phosphate, 15-20 parts of compound amino acid, 1-2 parts of potassium humate, 1-2 parts of ammonium molybdate, 3-5 parts of calcium chloride, 5-8 parts of urea, 10-15 parts of citric acid, and 15-20 parts of chelant; the amino acid compound leaf fertilizer has the characteristics of being complete in nutrient, high in utilization rate, good in absorption, fast in effect and the like, and can be widely applied to crops such as tobacco, oranges and tangerines, vegetables, melon and fruits and the like.
Owner:HUNAN ZHONGKE AGRI
Liquid fertilizer with pyroligneous liquor and oxalacetic liquor and production thereof
InactiveCN1778773AMagnesium fertilisersFertilisers by pryogenic processesRare-earth elementPlant regulators
A liquid fertilizer containing wood vinegar liquid or oxalic vinegar liquid and its production are disclosed. The liquid fertilizer consists of urea 1í½20.0%, potassium phosphate 1í½20.0%, potassium nitrate 1í½20.0%, lime nitrate 0.1í½10.0%, magnesium sulfate 0.1í½5.0%, ferrous sulfate 0.1í½5.0%, manganous sulfate 0.1í½5.0%, zinc sulfate 0.1í½5.0%, cupric sulfate 0.1í½5.0%, boron sand or boric acid 0.1í½2.0%, sodium molybdate or ammonium molybdate 0.1í½1.0%, plant hormone or plant regulator, rare earth element or humus acid or pesticide auxiliaries etc. The process is carried out by proportioning and mixing. It can improve bacterium inhibiting and plant growth regulating functions.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIANZHONG BAMBOO IND
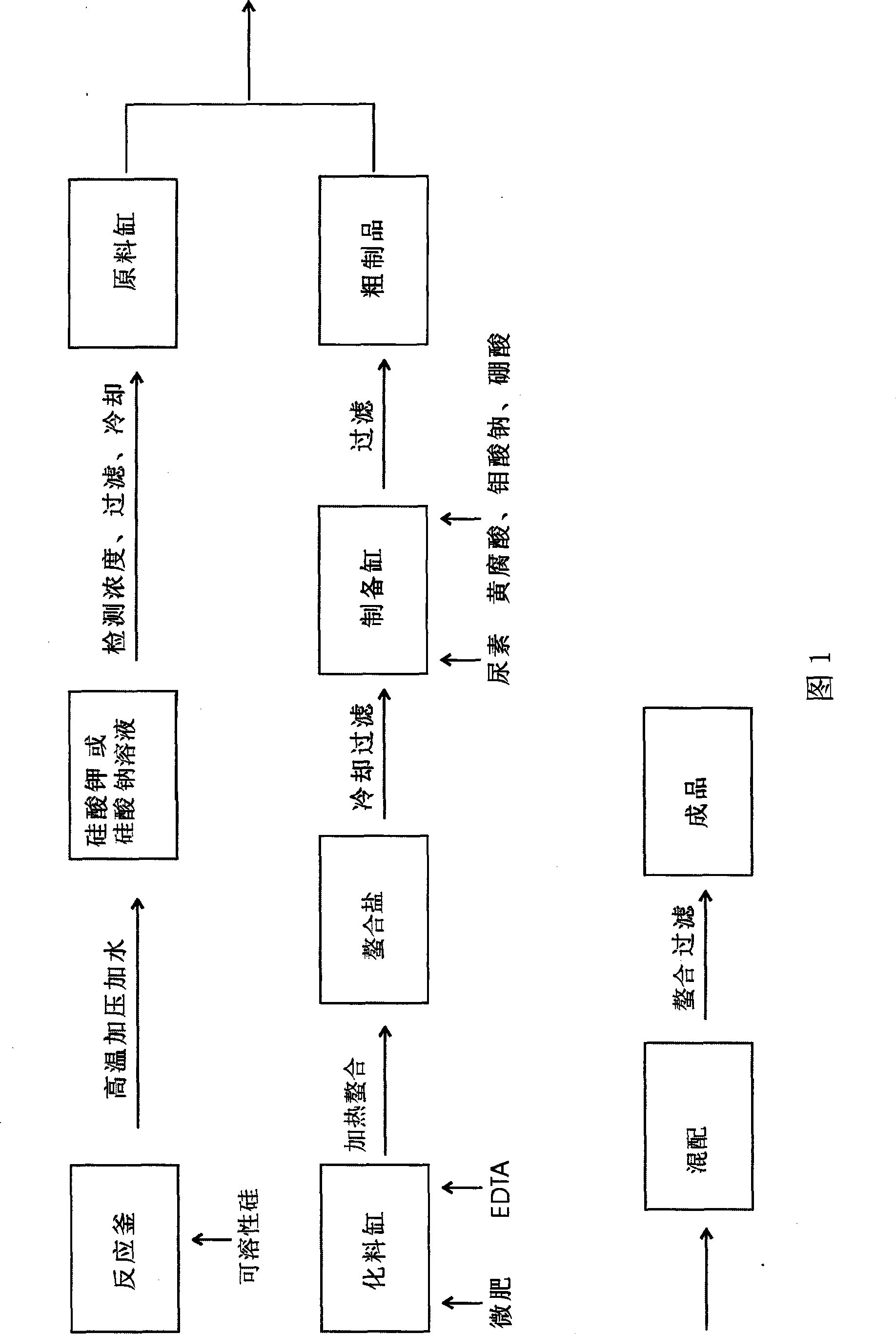
Liquid silicon fertilizer and technique for producing the same
InactiveCN101440001APromote growthIncrease resistanceOrganic fertilisersUrea compound fertilisersMetasilicateSilicic acid
The invention relates to a liquid silicon fertilizer and a production technique thereof, and belongs to the technical field of fertilizer. The liquid silicon fertilizer is characterized in that raw materials comprise soluble silicon, urea, trace elements, chelate and fulvic acid, which are prepared into the balanced compound fertilizer. The production technique comprises the following steps: 1, dissolving solid potassium metasilicate; 2, dissolving sulfate of the trace elements in water, and adding EDTA into the mixture to obtain the chelate of the EDTA trace elements; and adding boric acid, ammonium molybdate, the urea and the fulvic acid into the mixture after cooling and filtration; and 3, blending the chelate into the mixture to obtain the liquid silicon fertilizer. The production technique is characterized in that (1) the production technique uses water glass and the fulvic acid chelate, has better buffer action for alkali, and can effectively improve stability of SiO3; and (2) the trace elements are chelated twice by using the EDTA and the fulvic acid to form chelated metal ions, so as to prevent silicic acid radicals and the metal ions reacting to form silicate difficult to be dissolved in water, and influence utilization rate of silicon element. The production technique uses the liquid potassium metasilicate and large amount of elements, trace elements and organic substances to establish a balanced compound system, and can effectively improve utilization rate of the silicon element and various nutrient elements for the crops.
Owner:于春开
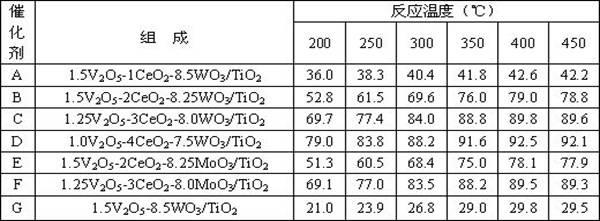
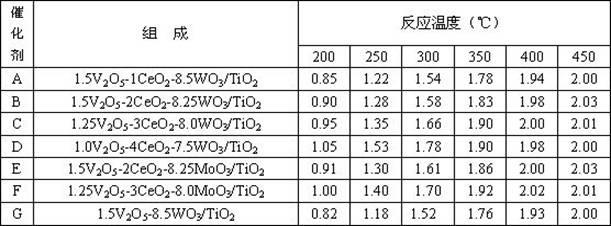
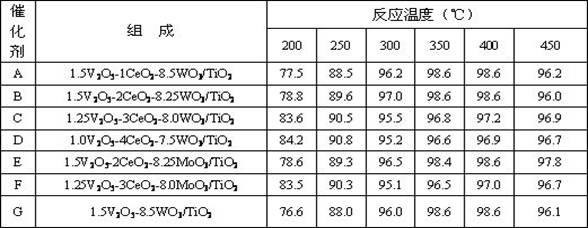
Composite smoke denitration catalyst capable of oxidizing zero-valence mercury
ActiveCN102350340AImprove oxidation capacityRealize collaborative controlDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystVanadate
The invention provides a composite smoke denitration catalyst capable of oxidizing zero-valence mercury. The catalyst is composite oxide V2O5-CeO2-WO3 / TiO2 or V2O5-CeO2-MoO3 / TiO2 based on TiO2 as a carrier, wherein the weight proportion is as follows: the weight percent of TiO2 is 75-100, the weight percent of V is 1-1.5, the weight percent of Ce is 1-5, and the weight percent of W or Mo is 7.5-8.5. The preparation method comprises the following steps: depositing Ce(OH)3 on nano TiO2; dipping ammonium vanadate / ammonium molybdate; and drying and roasting so as to obtain the catalyst; or dipping a commercial SCR (selective catalytic reduction) catalyst in a cerous nitrate aqueous solution, and then drying and roasting. The catalyst provided by the invention maintains the denitraiton efficiency of the original SCR catalyst and simultaneously the oxidation rate of zero-valence mercury is obviously improved, and divalent mercury ions are captured in subsequent dedusting equipment and wet desulphurization system; and the application temperature range of the catalyst is wide, the combination control of emission amounts of nitrogen oxides and mercury in smoke of a fuel coal power plant can be achieved on the promise that the smoke purification facility of the fuel coal power plant is not added.
Owner:GUODIAN SCI & TECH RES INST
Plant nutrient liquid fertilizer
InactiveCN102701861AImprove stress resistanceSolve the problem of lack of nutrientsFertilizer mixturesSucrosePhosphate
The invention relates to a plant nutrient liquid fertilizer. In order to solve the problem of over fertilization, the plant nutrient liquid fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials in proportion by weight: aqua brassin 12-36, gibberellin 1-4, indoleacetic acid 30-80, abscisic acid 10-20, naphthaleneacetic acid 50-90, salicylic acid 80-180, vitamin C 1-3, cane sugar 40-100, chitin 20-80, 0.05-0.2 percent triacontanol 400-1,000, hydrolyzed protein 2-5, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 300-400, thiourea 40-120, cobalt chloride 5-12, borax 50-100, sodium silicate 30-55, urea 300-500, ammonium molybdate 50-80, copper sulfate 30-65, zinc sulfate 120-200, magnesium sulfate 100-150, calcium chloride 50-120, manganese sulfate 40-80 and water in the amount of 3-8 times the total amount of all the raw materials or water in the amount capable of dissolving all the raw materials, wherein the water is de-ionized water or micro cluster water; and the preparation method is that all the materials are prepared into aqueous solution. The plant nutrient liquid fertilizer has the advantages of favorably solving the problems of over fertilization and shortage of nutrient elements in soil, obviously improving the plant adverse resistance, improving the photosynthesis and the accumulation efficiency of nutritive materials and improving the yield and the quality.
Owner:魏玉芳
Method for preparing catalyst for acrolein and acrylic acid
InactiveCN101690900AOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationTrace elementActive component
The invention discloses a method for preparing a catalyst for acrolein and acrylic acid, which is characterized in that: the catalyst consists of an active component supporter and an inert alumina carrier; the main composition elements of the active component are selected from Mo, Bi, Co and / or Ni and Fe, and the active component also contains trace elements such as K, Na, Rb, Cs, Mg, Ca, Zn, B, P and W; the active component supported on the carrier accounts for 5 to 70 percent of the total weight of the catalyst; and the active component supporter is not prepared by coprecipitation, instead, initial raw materials of the elements of the above expression formula containing the active component are precipitated in aqua ammonia of ammonium molybdate step by step to prepare an active component precursor with core-shell distribution, and the active component precursor is dried and baked to prepare the active component.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
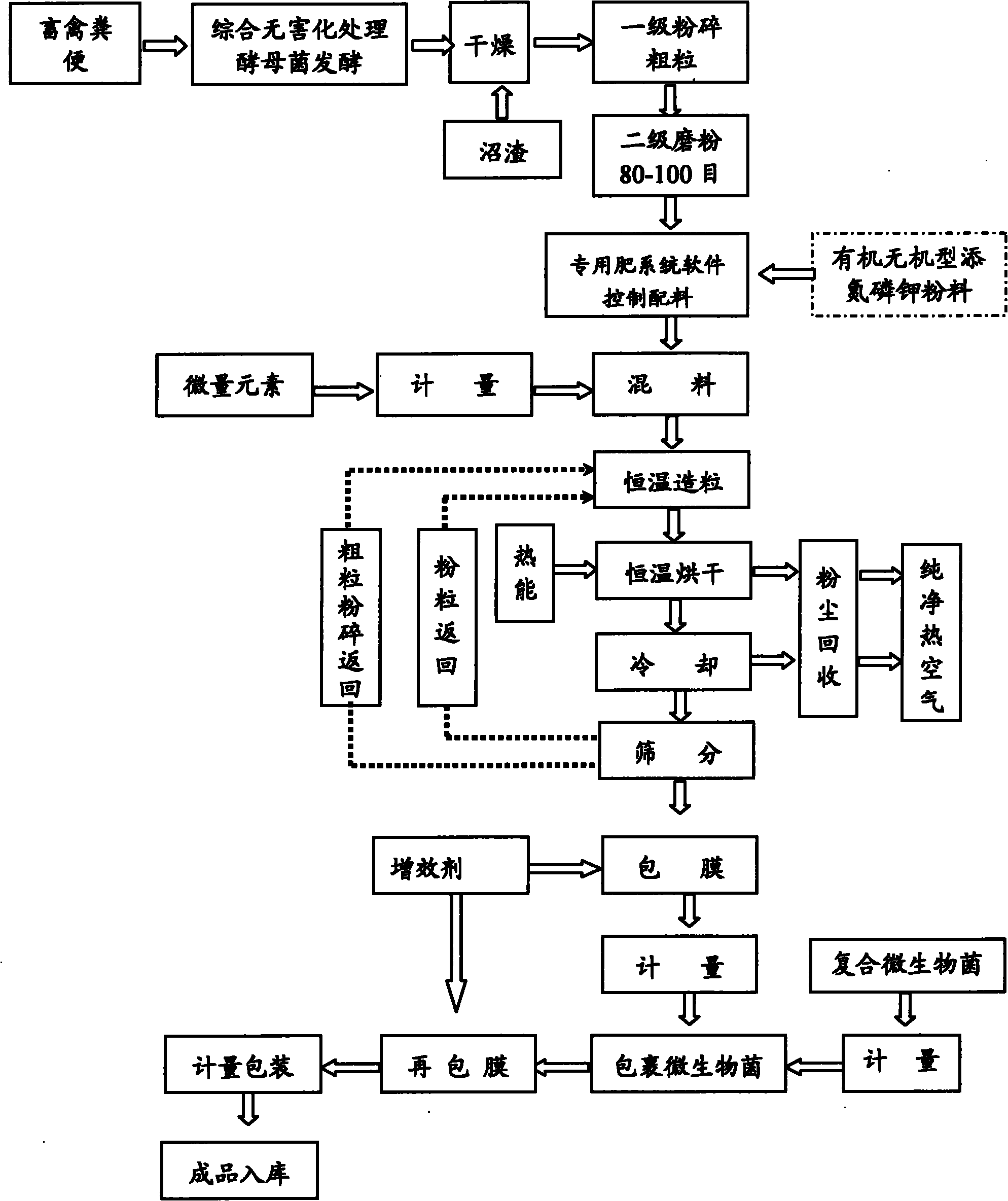
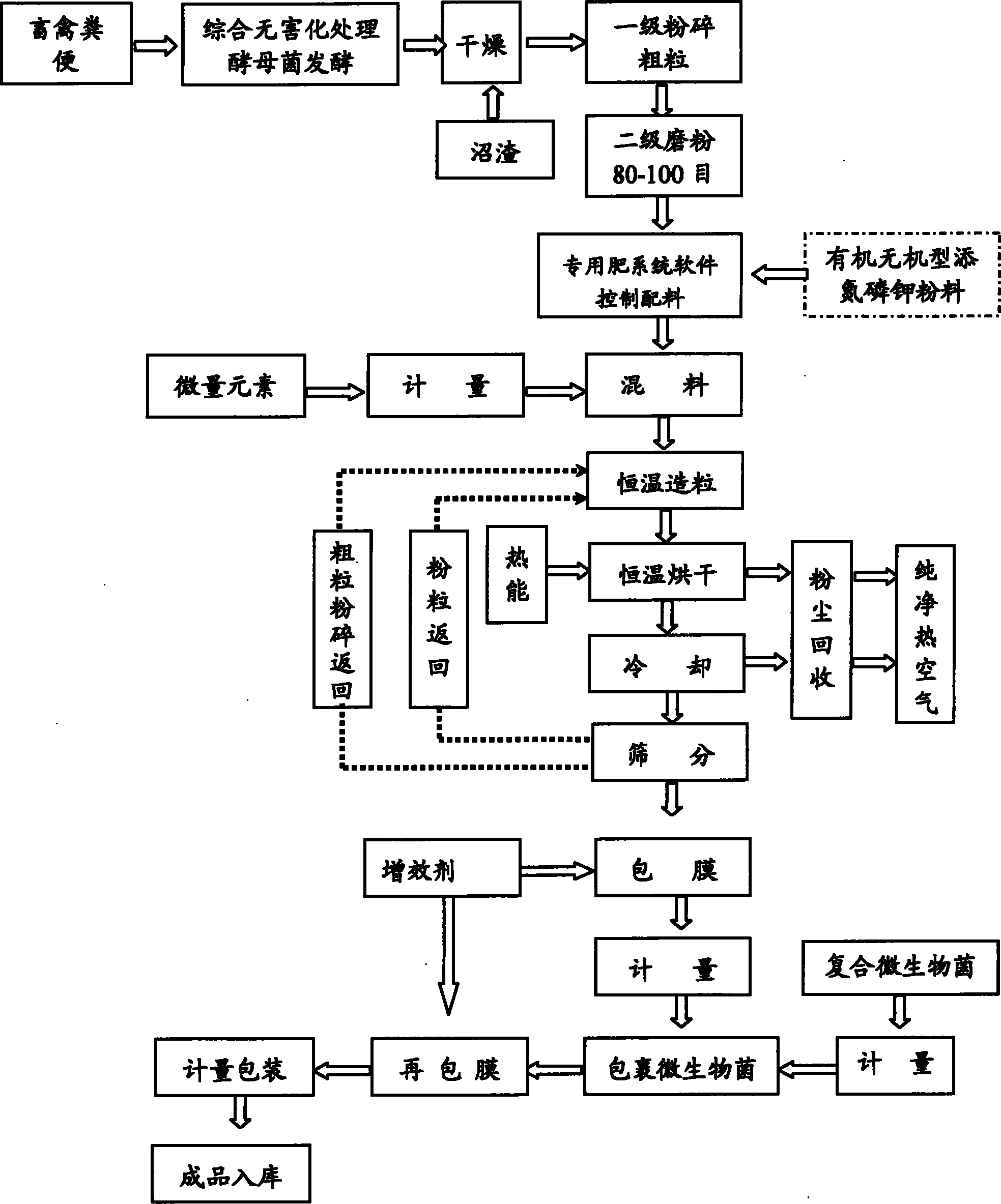
Functional bioorganic and semi-organic fertilizers and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101891544AIncrease enzyme activityIncrease profitFertilizer mixturesEcological environmentLivestock manure
The invention discloses a functional bioorganic fertilizer and a semi-organic fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: adding microzyme into livestock manure to perform anaerobic and aerobic fermentation; deodorizing, drying and crushing (after biogas slurry of residues after fermentation in a methane tank is separated, the biogas dregs are dried and crushed); adding a certain amount of humic acid, amino acid, borax, ammonium molybdate and zinc sulfate, or also adding nitrogen, phosphor and kalium inorganic nutrients; automatically blending materials by using a computer according to a proportion; after uniformly stirring, granulating by using a granulator, and drying, cooling and screening the grains; and coating a synergist and nitrogen-fixing, phosphorous-dissolving and potassium-releasing composite bacteria on qualified grains to prepare the functional bioorganic and semi-organic fertilizers. The product has the functions of preserving moisture and fertility, resisting drought, coldness, plant diseases and insect pests and the like, improves the soil structure, promoting the proliferation of beneficial microorganisms in soil, jointly participating substance circulation of a soil ecosystem and the like, has quick response and long effect, is mainly used as a base fertilizer for crops to save time and manpower, can realize waste recycling, protects ecological environment, integrates land utilization, land nourishment and land protection, and ensures constant soil productivity.
Owner:杨泉胜
Preparation method of few-layer MoS2/graphene electrochemical storage lithium composite electrode
ActiveCN102683648AGood dispersionHigh electrochemical lithium storage specific capacityCell electrodesActive agentOrganosolv
The invention relates to a preparation method of a few-layer MoS2 / graphene electrochemical storage lithium composite electrode. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: ultrasonically dispersing graphene oxide in de-ionized water; adding octaalkyl trimethyl ammonium bromide cationic surfactant, then adding ammonium thiomolybdate and dropwise adding hydrazine hydrate with stirring; performing reflow reaction at 95 DEG C to reduce the ammonium thiomolybdate and graphene oxide into MoS2 and graphene at the same time respectively; centrifugally collecting a solid product; washing with de-ionized water; drying; thermally treating in a nitrogen / hydrogen mixed atmosphere to obtain the few-layer (two to four layers) MoS2 / graphene composite nanomaterial; mixing the few-layer MoS2 and graphene composite nanomaterial and acetylene black as well as polyvinylidene fluoride into paste; and coating on a copper foil for rolling. The method provided by the invention has a simple process, and an organic solvent is not consumed. The few-layer MoS2 / graphene composite material is used as the electrochemical storage lithium composite electrode and has high electrochemical storage lithium specific capacity, superior circulation performance and superior high-power charging and discharging characteristic.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Liquid agent multielement fertilizer and its production method
InactiveCN1410395AChange physiologyPromote absorptionOrganic fertilisersFertilizer mixturesManganesePlant cell
A multi-element liquid fertilizer contains active components, additive and water. Its active components includes 13 components, such as potassium sulfate, borax, copper sulfate, manganese sulfate, zinc sulfate, etc.. The additives include 9 components, such as disodium hydrogen phosphate, nitric acid, useful bacteria, useful enzyme, etc.. It can improve the activity of plant cells, change physiological mechanism of plant, increase yield, and make plant robust.
Owner:孙国庆 +1
Modified cobalt-molybdenum based sulfide catalyst and its preparation method
InactiveCN1569331ASolve the problem of unstable catalytic activityWide variety of sourcesCatalyst activation/preparationCobaltInorganic sulfide
The invention is a modified cobalt and molybdenum base sulfide catalyst and its manufacturing method, which belongs to catalyst field. the component of the catalyst is: Mo: 30-40wt%, Co: 20-30wt%, Mn, V, Cr, Cu or Fe: 0.1-10.0wt%, K: 15-25wt%, S: 15-30wt%, through confecting sulph ammonium molybdate liquid, the molybdenum, cobalt and the third transition metal are deposited, filtered, cleaned, dried, grinded, baked, and acquires the product. The activity of the catalyst is stable.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Plant nutrient solution and application in plant cultivation
InactiveCN101062877AImprove survival rateDoes not affect life cycleMagnesium fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserManganeseMonopotassium phosphate
The invention discloses a plant nutrition liquid, which is characterized by the following: comprising potassium nitrate, calcium nitrate, magnesium sulfate, ammonium phosphate, potassium sulfate, monopotassium phosphate and so on a good deal of element; comprising edetate disodium, ferrosi sulfas, boric acid, manganese sulfate, zinc sulfate, copper sulfate, ammonium molybdate and so on microelement; comprising azophoska fertilizer and fertilizer booster; including diverse nutritious element of vegetation development; providing nourishing element for large and medium scale bush and small arbor. This invention also discloses a utility scheme in large and medium scale woody plant soilless culture.
Owner:成都市第二农业科学研究所 +1
Polypeptide-ammonium polyphosphate trace element liquid chelated fertilizer and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a polypeptide-ammonium polyphosphate trace element liquid chelated fertilizer and a preparation method of the liquid chelated fertilizer. The polypeptide-ammonium polyphosphate trace element liquid chelated fertilizer comprises the components by weight percent: 5-25% of urea, 5-15% of ammonium polyphosphate, 5-25% of potassium nitrate, 0.2-3% of potassium silicate, 0.8-5% of potassium chloride, 0.008-0.1% of polyaspartic acid, 0.8-5% of ammonium sulfate, 0.8-5% of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) calcium, 0.2-3% of EDTA magnesium, 0.02-1.5% of EDTA boron, 0.005-0.1% of EDTA zinc, 0.005-0.1% of EDTA iron, 0.005-0.05% of EDTA copper, 0.005-0.05% of EDTA manganese, 0.001-0.01% of nickel sulfate, 0.001-0.01% of ammonium molybdate, 0.0008-0.01% of cobaltous sulfate, 0.008-0.1% of polyacrylamide and the balance of water. The polypeptide-ammonium polyphosphate trace element liquid chelated fertilizer disclosed by the invention is simple in technology, scientific in proportion, balanced in fertilization, low in cost and good in effect.
Owner:张朝晖
Graphene-supported layered MoS2 (molybdenum disulfide) nanocomposite and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104226337AImprove catalytic performanceHigh crystallinityPhysical/chemical process catalystsThioureaCrystallinity
The invention relates to a graphene-supported layered MoS2 (molybdenum disulfide) nanocomposite and a preparation method thereof, belongs to the technical field of preparation of nano materials, and is used for solving the problem that graphene-supported MoS2 nanoparticles prepared in the prior art are poorer in catalytic performance due to small composite areas between the nanoparticles and graphene. Ammonium molybdate and thiourea are taken as initiators, and layered nano MoS2 can be supported on the surface of graphene oxide under the hydrothermal condition; after roasting treatment, the graphene-supported layered MoS2 has the higher crystallinity, and the photocatalytic efficiency is more than 1.7 times that of commercial nano titanium oxide. The method is simple and easy to operate; MoS2 nanosheets are uniformly distributed on the surface of the graphene and have larger contact areas with the graphene, so that the nanocomposite has the high catalytic performance and is widely applied to fields of electro-catalysis, photo-catalysis, hydrogen evolution catalysis and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for separating and extracting tungsten-molybdenum from mixed solution of tungstate-molybdate
InactiveCN101880780AEfficient separationRealize recyclingProcess efficiency improvementMagnesium saltDecomposition
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Metal surface oil and rust removal agent
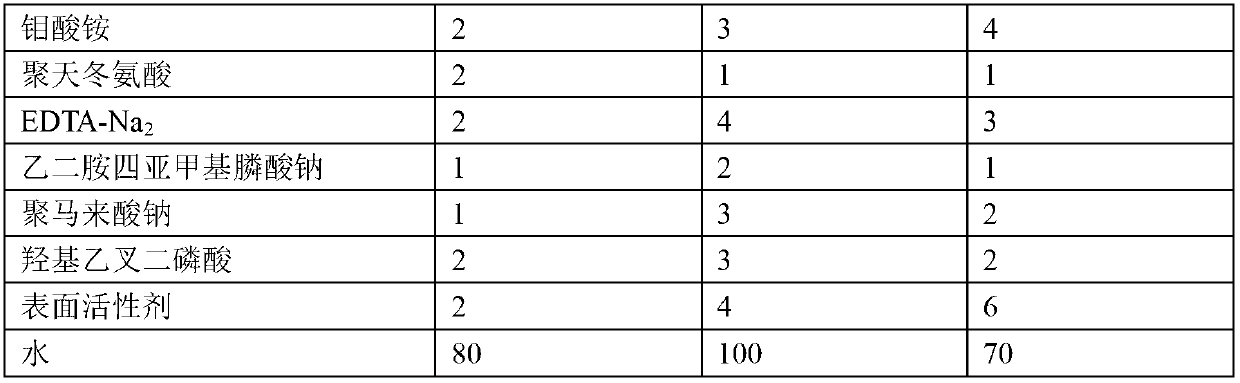
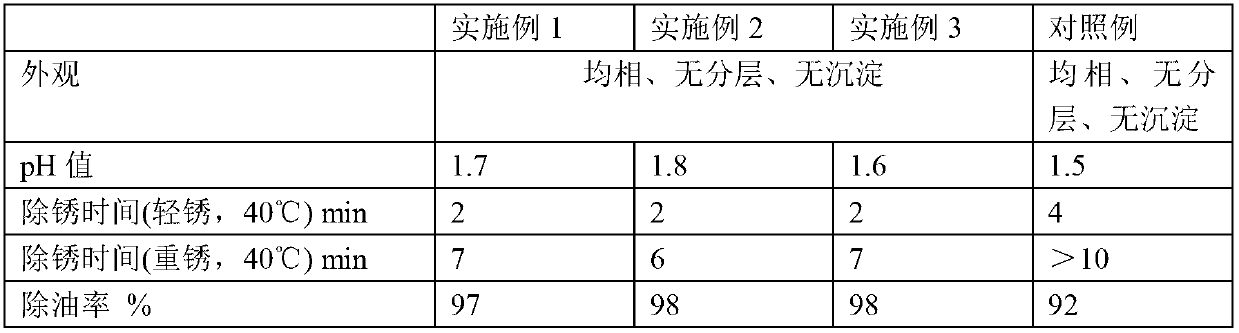
The invention provides a metal surface oil and rust removal agent, and belongs to the technical field of cleaning agents. The metal surface oil and rust removal agent comprises the following components by weight: 2 to 4 parts of hydrochloric acid, 5 to 10 parts of phosphoric acid, 3 to 6 parts of oxalic acid, 3 to 5 parts of glacial acetic acid, 2 to 4 parts of citric acid, 3 to 4 parts of polyvinyl alcohol, 1 to 2 parts of hexamethylene tetramine, 2 to 3 parts of ethylene oxide, 1 to 2 parts of glyoxal, 2 to 3 parts of magnesium stearate, 2 to 4 parts of glycerol, 2 to 4 parts of thiourea, 2 to 4 parts of ammonium molybdate, 1 to 2 parts of polyaspartic acid, 2 to 4 parts of EDTA-Na2, 1 to 2 parts of ethylene diamine tetra sodium, 1 to 3 parts of poly maleic acid sodium, 2 to 3 parts of HEDPA, 2 to 6 parts of surface active agent and 70 to 100 parts of water. The metal surface oil and rust removal agent is convenient to use, and removes light rust for about 2 minutes and heavy rust for 6 to 7 minutes, and the oil removal rate can reach more than 97%.
Owner:盐城创咏新能源投资有限公司
Water culture nutrient solution prescription of lettuce and preparation method of water culture nutrient solution prescription
InactiveCN103172431ASmooth changeMeet the changeFertilizer mixturesPhosphoric acidMonopotassium phosphate
The invention discloses a water culture nutrient solution prescription of a lettuce and a preparation method of the water culture nutrient solution prescription, and belongs to the technical field of plant soilless culture of the agricultural science. The nutrient solution prescription of the lettuce comprises the following components: a fertilizer A composed of 584.23g / T of calcium nitrate, 421.34g / T of potassium nitrate and 47.8g / T of ammonium nitrate; a fertilizer B composed of 182.4g / T of monopotassium phosphate and, 256.23g / T of magnesium sulfate; a fertilizer C composed of 16.8g / T of FeEDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid), 3g / T of boric acid, 2g / T of manganese sulfate, 0.25g / T of zinc sulfate, 0.85g / T of copper sulfate, and 0.38g / T of ammonium molybdate; hormone composed of 0.1g / T indolebutyric acid of or 0.1g / T of naphthylacetic acid; a bactericide composed of 15g / T of carbendazim; and nutrient solution pH (Potential Of Hydrogen) adjusting acid composed of 200ml / T of phosphoric acid or 150g / T of citric acid. The prescription is nutritionally balanced, so that the demand of the lettuce to nutrition can be met, the amount of used nutrient elements is decreased at the same time, the output of the lettuce is increased, and the fertilizers are saved; and the prescription effectively decreases the contents of nitrates in the lettuce under the water culture, improves the quality of the lettuce, enables the simplification of the complicated processes in preparation based on the demand of the actual operation, and is suitable for being used for meeting the requirements of industrialization production.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Antitranspirant foliar fertilizer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101913941AThe ratio is scientific and reasonableImprove solubilityFertilizer mixturesMicrobial agentMonopotassium phosphate
The invention discloses an antitranspirant foliar fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The antitranspirant foliar fertilizer comprises the raw materials of copper sulfate, ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, monopotassium phosphate, zinc sulfate, ferrous sulphate, manganese sulphate, ammonium molybdate, composite rare earth, boric acid, sodium dodecyl sulphonate, urea, fulvic acid, hexanoic acid 2-(diethylamino) ethyl ester, compound amino acid, magnesium sulfate, calcium nitrate, ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, microbial agent, azone and ammonia water. The antitranspirant foliar fertilizer provides nutrient elements and microbial agents which are required by the growth of plants, the rare earth and amino acid and other beneficial elements, can promote the growth of the plants, improve the yield, the quality, the stress resistance of the plants and the absorbing and operating capabilities on trace elements, simultaneously can effectively reduce the transpiration of the plants and is applied to afforesting in arid regions.
Owner:SHENZHEN TECHAND ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT CO LTD
High-quality strawberry planting dedicated slow-release compound fertilizer
InactiveCN104030800AImprove the phenomenon of single fixationGood release effectFertilizer mixturesMicrobial agentGluconates
The invention relates to the compound fertilizer field, and particularly relates to a high-quality strawberry planting dedicated slow-release compound fertilizer. The fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 10-15 parts of a 1250-2000 mesh diatomite, 4-5 parts of borax, 2-3 parts of ammonium molybdate heptahydrate, 10-12 parts of sodium humate, 20-25 parts of urea, 18-22 parts of potassium nitrate, 25-28 parts of organic compost, 2-4 parts of fish meal, 1-3 parts of sesame leaves, 8-10 parts of alfalfa meal, 15-18 parts of corn distiller grains, 2-4 parts of brine, 8-10 parts of an erythromycin fungi residue, 1-2 parts of an EM microbial agent, 4-6 parts of a fern root residue, 1-3 parts of nano silver, 1-2 parts of a semen ginkgo powder, 4-6 parts of 1,6-hexanediol diacrylate, 10-12 parts of an acrylic resin dispersion liquid, 1-2 parts of isocyanate, 1-2 parts of calcium stearoyl lactate, 2-4 parts of zinc gluconate, 6-8 parts of table vinegar, and 4-5 parts of an auxiliary agent. The compound fertilizer has multiple nutrients, is low in production cost and good in slow-release effect, allows double coating to be formed on the nutrients by utilizing diatomite and a coating agent in the process, also contains various trace elements, has no toxicity and no pollution, and is excellent in quality of planted strawberry and obvious in yield and income increasing effects.
Owner:ANHUI SUNSON CHEM
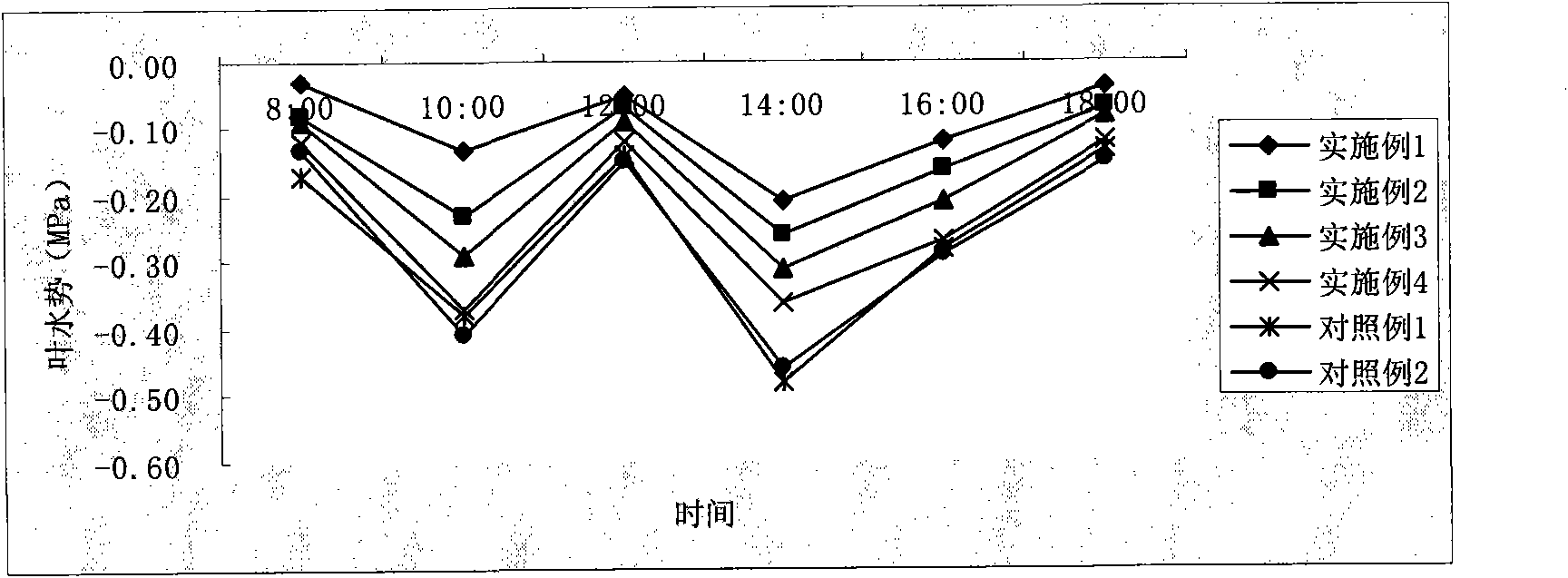
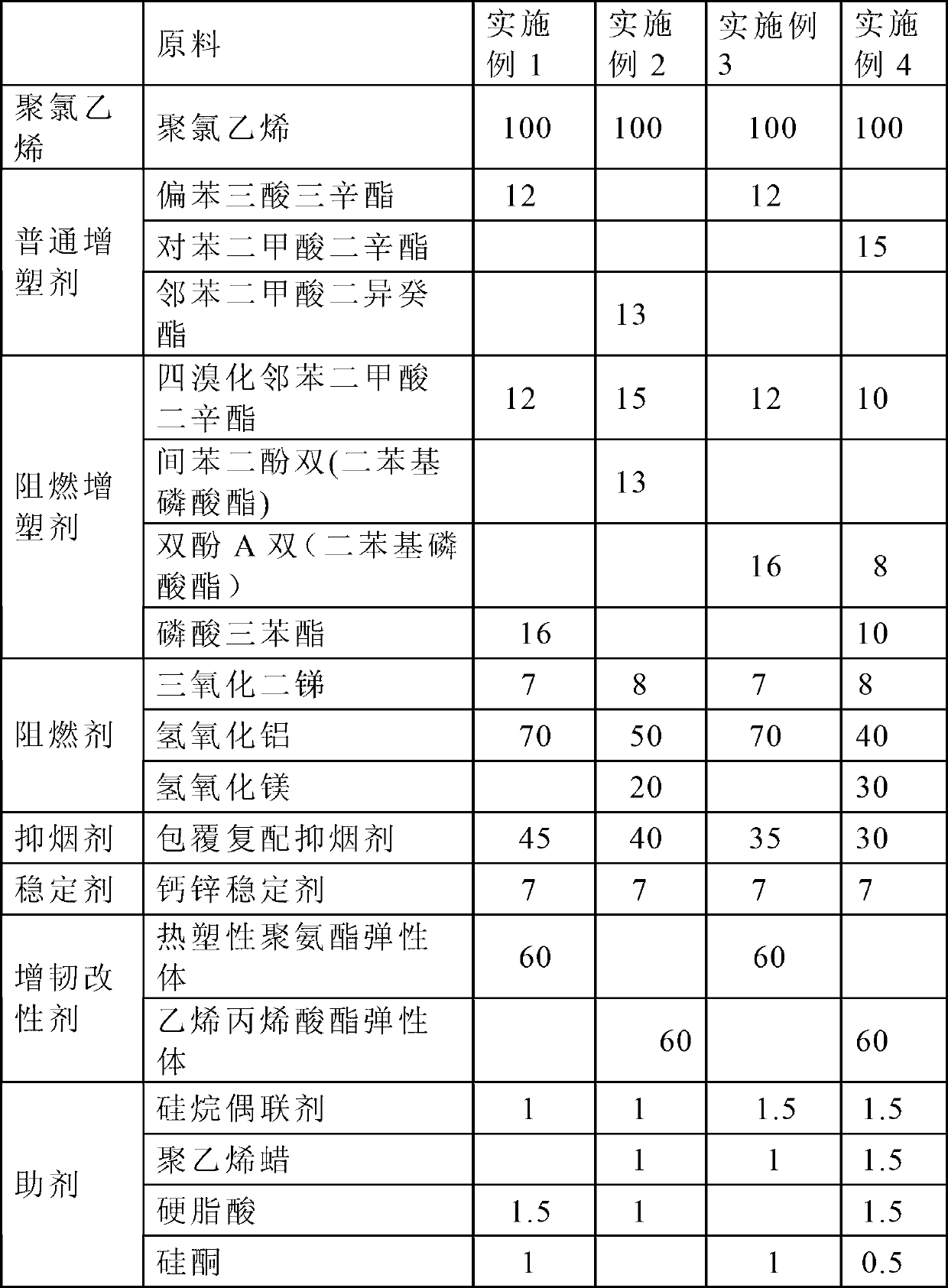
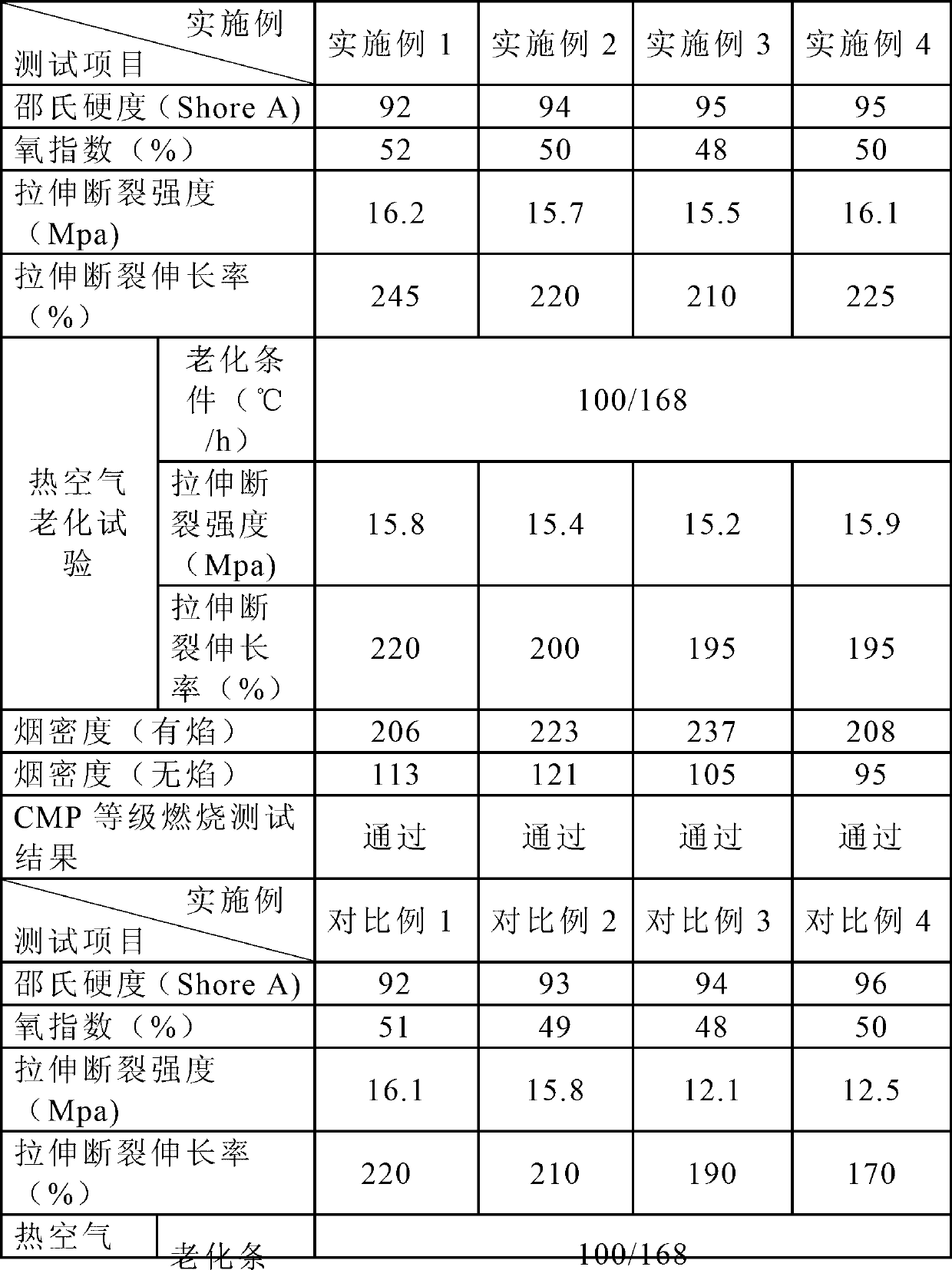
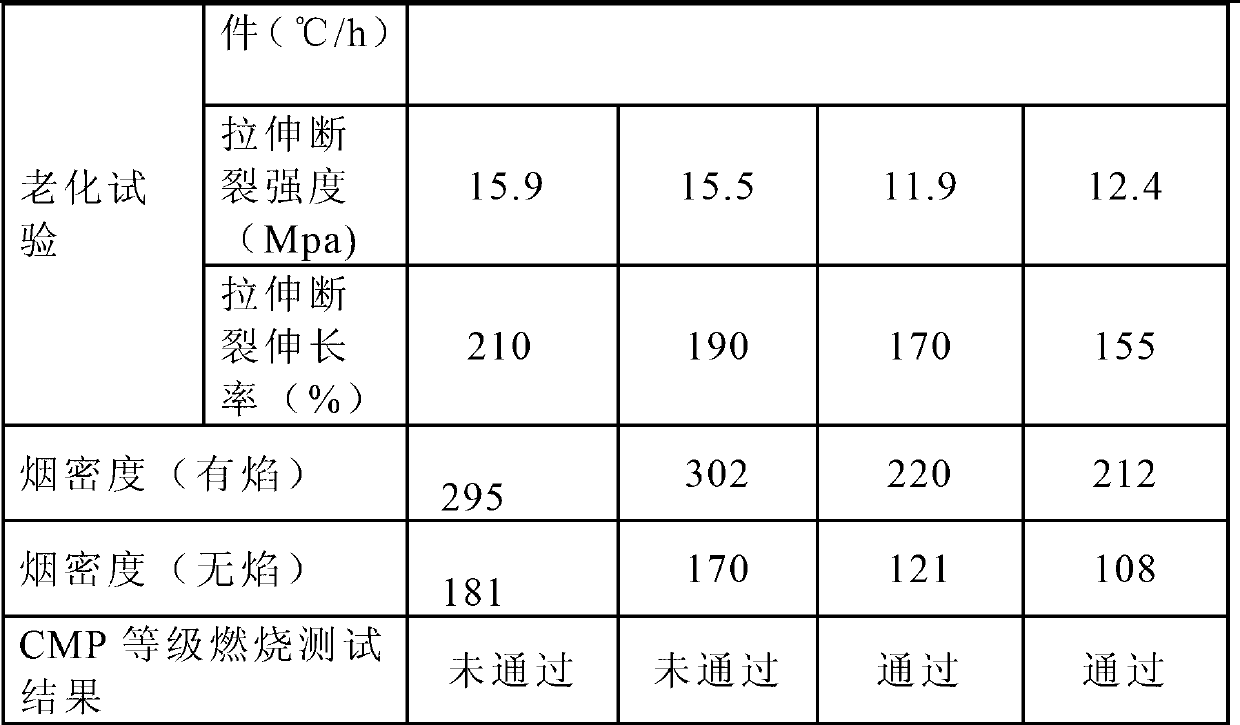
Corrugated metal pipe (CMP) grade flame-retardant smoke-suppressing polyvinyl chloride cable sheath material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102993602AReasonable cooperationImprove flame retardant and smoke suppression performanceInsulated cablesInsulated conductorsAluminium hydroxidePolyvinyl chloride
The invention provides a corrugated metal pipe (CMP) grade flame-retardant smoke-suppressing polyvinyl chloride cable sheath material and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of material. The invention solves the problem that in the prior art, the flame-retardant and smoke-suppressing effects and the mechanical property and the physical property of the cable sheath material are all good. The raw materials thereof comprise the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of polyvinyl chloride, 5-15 parts of common plasticizer, 20-50 parts of flame-retardant plasticizer, 40-100 parts of fire retardant, 20-50 parts of smoke-suppressing agent, 5-10 parts of stabilizer, 40-80 parts of toughening modification agent and 1-5 parts of promoter; wherein the smoke-suppressing agent comprises ammonium octamolybdate, zinc molybdate and zinc borate which are compounded according to the proportion of 1:1 to 3:1 to 3 and coated by aluminium hydroxide the grain size of which is 1-5mu m according to the proportion of 1:1 to 3. The CMP grade flame-retardant smoke-suppressing polyvinyl chloride cable sheath material has the advantages of good flame-retardant and smoke-suppressing effect, mechanical property and physical property.
Owner:江西一舟数据技术有限公司
Organic water soluble fertilizer
The invention relates to an organic water soluble fertilizer, which belongs to a novel, efficient and organic hyperconcentration chelate fertilizer and is prepared from plant source organic matters, potassium humate, citric acid, amino acid, vitamin, monosaccharide, fructose, dextrose, polysaccharide, potassium sodium tartrate, zinc sulfate, copper sulfate, manganese sulfate, boracic acid, ammonium molybdate, ethanediol, monoammonium phosphate, monopotassium phosphate, phosphoric acid and the like through the processes of acidification, chelation and concentration. The organic water soluble fertilizer is suitable for being used for all plants in modes of leaf surface spray application, root filling, seed soaking, flushing application, drip irrigation and spray irrigation. The product is nontoxic and does not have hormone or residue, the crop growth and development can be regulated in a balanced way, the metabolism and the photosynthesis of the plants can be promoted, the aging of the plants can be delayed, the quality is improved, the yield is increased, and certain drought resistance, cold resistance and disease resistance effects are realized. 20 percent to 40 percent of soil fertilizer consumption can be reduced through using the organic water soluble fertilizer for many times, and the yield of the crops can be increased by about 10 to 40 percent.
Owner:GUANGXI PENSHIBAO
Method for recycling vanadium and molybdenum from waste petroleum catalyst
InactiveCN105274344AReduce pollutionAchieve recyclingProcess efficiency improvementPtru catalystPorphyrin
The invention relates to a method for recycling vanadium and molybdenum from a waste petroleum catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of petrochemical industry. The method comprises air-burning and ball-removing, ball-milling, soda roasting-water leaching, aluminum removing, molybdenum precipitating and enriching molybdenum by ion exchange. The method specifically comprises the following steps: firstly, igniting sticky oil in the waste catalyst in air to burn carbon and oils in the waste catalyst; then, oxidizing the vanadium and nickel in the forms of porphyrin compounds in the waste catalyst into vanadium oxide and nickel oxide, converting most of the molybdenum into molybdenum oxide, wherein the waste catalyst subjected to air-burning and oil-removing is more beneficial for crushing, and the crushed waste catalyst and a certain proportion of sodium carbonate are mixed, and are roasted at a high temperature; leaching roasted materials by hot water, dissolving sodium salts of the vanadium and the molybdenum into water to obtain a solution, filtering the solution, introducing the filtered solution into a leaching solution, introducing a little aluminum into the leaching solution, regulating the pH value of the solution to remove aluminum; regulating the pH value of the solution to 8-9, adding ammonium chloride, precipitating and separating out the vanadium in the form of ammonium vanadate; and concentrating vanadium-precipitated solution by adopting an ion exchange process and enriching an ammonium molybdate solution.
Owner:刘楚玲
Method for separating tungsten and molybdenum
ActiveCN105200246AEasy to separateThe operation process is easy to controlProcess efficiency improvementTungstateIon-exchange resin
The invention relates to a method for separating tungsten and molybdenum. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding acid into a tungsten-molybdenum mixed solution and adjusting pH value to obtain mixed sediment of tungsten acid and molybdenum acid; (2) adding hydrogen peroxide and acid into the mixed sediment to form peroxide tungsten acid and peroxide molybdenum acid; (3) heating an obtained mixed solution, adding tungsten powder, reacting and filtering to obtain tungsten acid sediment and a molybdenum-containing acid solution; (4) calcining the prepared tungsten acid to prepare tungsten trioxide or dissolving by using ammonium hydroxide to obtain an ammonium tungstate solution and then evaporating and crystallizing to prepare APT; (5) extracting the molybdenum in the obtained molybdenum-containing acid solution by using an extraction agent / ion exchange resin; and (6) reversely extracting molybdenum-containing organic phase / resin by using ammonium hydroxide to obtain the ammonium molybdate solution, and carrying out acid precipitation to obtain ammonium tetramolybdate. The production process of tungsten-molybdenum products is taken into account in the method, so that the separated tungsten acid or molybdenum can be directly used for preparing the products thereof; the separation effect is excellent; the operation process is simple and is liable to control; the industrial popularization and application are liable to implement.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Flame-retardant and environmentally-friendly polyurethane cable material and its preparation method
ActiveCN102977585AImprove flame retardant performanceExcellent non-flammabilityElastomerDecabromodiphenyl ether
The invention provides an flame-retardant and environmentally-friendly polyurethane cable material. The cable material is prepared from the following raw materials, by weight, 20-30 parts of chloroprene rubber, 60-80 parts of a polyurethane thermoplastic elastomer, 8-10 parts of acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber, 8-10 parts of chlorinated paraffin, 0.5-1.0 part of stearic acid, 1-3 parts of barium stearate, 4-6 parts of iron oxide, 0.5-1.0 part of ammonium trimolybdate, 30-50 parts of precipitated silica, 10-13 parts of modified argil, 0.5-1.0 part of capsaicin, 0.1-0.3 parts of an antioxidant AW, 0.5-1.5 parts of a promoter TMTD, 0.2-0.5 parts of sulfur, 8-10 parts of decabromodiphenyl oxide, 12-15 parts of antimony (III) oxide and 6-8 parts of zinc borate hydrate. The cable material has the advantages of excellent flame retardation, very less smoke in combustion, no generation of toxic gases or corrosive gases, good low temperature resistance, good oil resistance, and good abrasion resistance, and the cables processed through using the cable material can prevent the harms of mice and termites and simultaneously have the efficacies of low smoke, environmental protection and flame retardation.
Owner:蚌埠尚维知识产权运营有限公司
Method for reclaiming metals from molybdenum-containing waste catalyst
ActiveCN102051483APrevents the problem of easy leachingSolve pollutionProcess efficiency improvementFiltrationImpurity
The invention discloses a method for reclaiming metals from a molybdenum-containing waste catalyst, which comprises the following steps of: mixing the waste catalyst and a magnesium-containing compound, roasting, degreasing, removing carbon, then crushing, mixing the powder and sodium carbonate, roasting the mixture, and leaching the roasted materials by using aqueous solution, wherein ammonium salt or aqueous ammonia is added in the aqueous solution leaching step, the molybdenum in the waste catalyst enters the solution in a form of sodium molybdate or ammonium molybdate, the impurities such as silicon, phosphorus and the like entering the aqueous solution form sediment, and the sediment is kept in solid residue in a filtration step; and after the solid is separated, performing acidification, extraction, re-extraction and the like to reclaim the molybdenum and other metals. The method solves the pollution problem caused by sulfur dioxide in the discharged gas in the roasting, degreasing and carbon removal processes; and the salts formed by the reclaimed sulfur and magnesium can play a role in removing impurities in the subsequent steps so as to save the consumption of chemical reagents in the metal reclaiming process and reduce the cost. In addition, the method reduces the operation steps, reduces equipment, improves the operation effect, and also can improve the molybdenum yield.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Dry farm cultivating agent
The dry-land planting agent refers to a kind of droughtresistance crop's nutrient specific to the growth of the plants. The invention is composed of the following components: AU absorber with super strength, carbamide, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, ammonium dibasic phosphate, calcium nitrate, bitter salt, ammonium molybdate, zinc sulfate, manganese sulfate, boracic acid or borax, ferrous sulphate, fulvic acid potassium, disodium edta, fatty alcohol polyethenoxy ether, 6- benzyl aminopurine, melissyl alcohol, potassium naphthylacetic acid, indolebutyric acid, gibberellin, santobrite, potassium sorbate, ketotriazole, penta azole alcohol., thiram, carbendazim, acid brilliant scarlet, humic acid, bluestone, potassium permanganate, potassium chloride, polyethylene glycol, bentonite or water. The invention is featured by sopping, molding moisture, molding fertilizer, withering resistance, disinsection, sterilization, strengthening the effects of the pesticide, accelerating the burgeon of the plants, increasing roots, innocuity, no pollution and low cost.
Owner:王亚玲
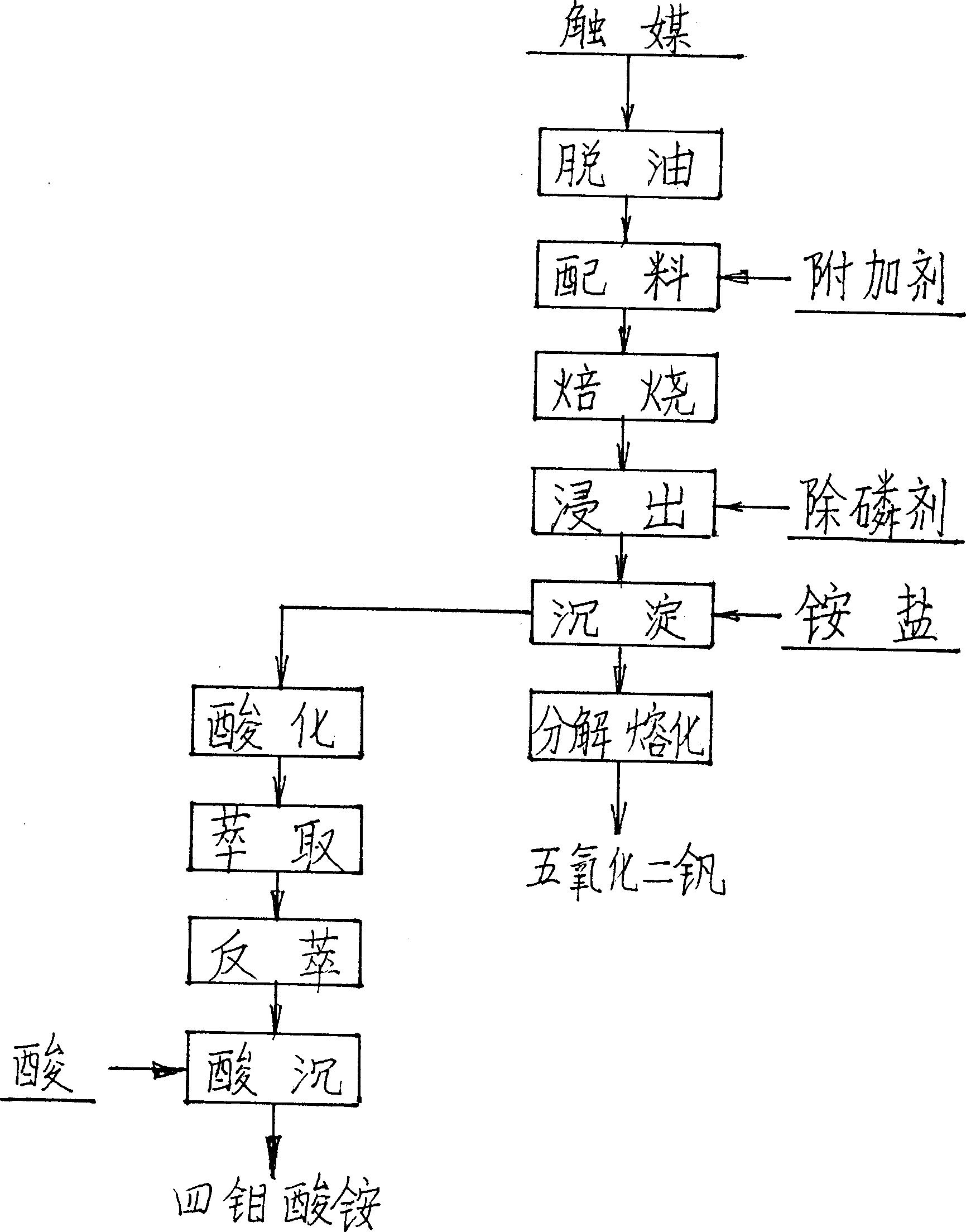
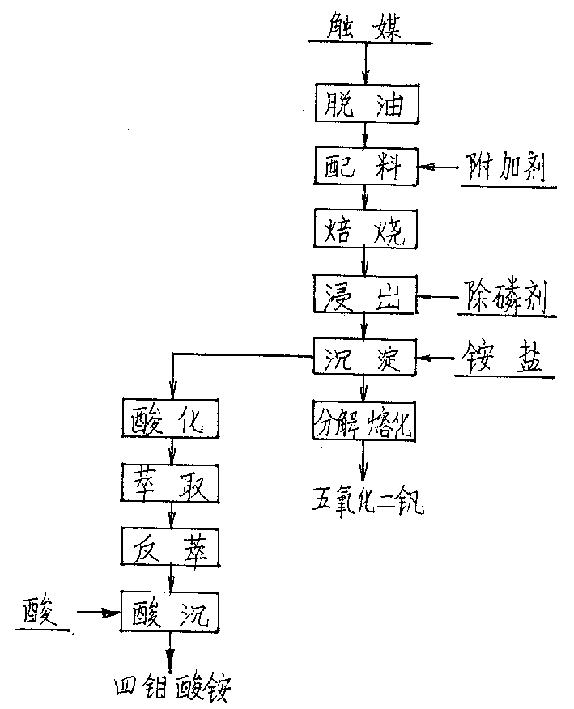
Wet process of extracting vanadium and/or molybdenum from waste catalyst
InactiveCN1453379ALess investmentReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementMagnesium saltAmmonium metavanadate
The present invention is wet process of extracting vanadium and / or molybdenum form waste petrochemical catalyst alumina carrier containing V, Mo and other elements. The wet process includes high-temperature deoiling the catalyst in natural granularity, mixing with sodium carbonate, high-temperature oxidation and roasting in a kiln or furnace to obtain water soluble sodium vanadate and sodium molybdate; countercurrent water soaking of the chamotte to obtain solution containing V and Mo in certain concentration, adding calcium salt and magnesium salt to eliminate P and other impurities, addingammonium salt solution into the clear solution to obtain ammonium metavanadate, decomposing and melting ammonium metavanadate to obtain V2O5 product; adding acid to the supernatant and organic phase extraction of Mo, ammonia water reverse extraction to obtain ammonium molybdate, and adding acid to precipitate ammonium tetramolybdate or molybdate product.
Owner:CITIC JINZHOU METAL
Method for preparing denitration catalyst
InactiveCN102357359AImprove conversion rateGood dispersionDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystTungstate
The invention discloses a preparation method of a denitration catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: (1) with an intermediate product of metatitanic acid from a titanium dioxide factory as a raw material, washing with dilute nitric acid, weak aqua ammonia, deionized water respectively to remove impurity ions so as to prepare metatitanic acid slurry; (2) orderly adding ammonium tungstate, ammonium molybdate and ammonium metavanadate into the metatitanic acid slurry, beating the mixture by ultrasonic wave, adjusting the pH of the slurry to 4.0-6.5 by an acid; (3) allowing the mixed slurry to stand, drying to obtain the catalyst powder; (4) compacting and molding the catalyst powder into honeycomb by a mold, performing heat treatment at 200-600 DEG C for 4-10 hours to obtain the denitration catalyst of the invention. The method for preparing the denitration catalyst of the invention has low cost and simple process, and the denitration catalyst can increase the conversion rate of NO. The denitration catalyst of the invention can realize a conversion rate of NO in power plant flue gas flue gas components of up to above 97% at a reaction temperature of 350 DEG C.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for recycling metal from waste catalyst containing molybdenum and nickel
ActiveCN102041388AReduce the introductionIncrease valueProcess efficiency improvementOperabilityAmmonia
The invention relates to a method for recycling metals from a waste catalyst containing molybdenum and nickel, which comprises the following steps of: roasting and smashing the waste catalyst containing the molybdenum and nickel; mixing with an alkaline substance and roasting; leaching by using a mixed acid liquid; depositing by using an alkaline solution, wherein molybdenum is deposited out in the form of ammonium molybdate; further dissolving the ammonium molybdate by using ammonia water; regulating a pH value to obtain ammonium molybdate deposition; and drying to obtain an ammonium molybdate product. The method is particularly suitable for extracting high-purity ammonium molybdate from the aluminum-based waste catalyst containing the molybdenume, and has the advantages of simple process, strong operability, low energy consumption, and stable produced product quality.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Carbon-based ginseng soil conditioner and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102604645ASimple production processSimple production equipmentOrganic fertilisersSoil-working methodsEcological environmentPhosphate
The invention relates to the field of agricultural chemistry, in particular relates to a carbon-based ginseng soil conditioner and a preparation method thereof. The carbon-based ginseng soil conditioner comprises biomass particle carbon, wood vinegar and an adhesion agent, and further comprises other fertilizers, such as urea, monoammonium phosphate powder, potassium chloride, zinc sulfate, boric fertilizer, manganese sulfate, ammonium molybdate, ferrous sulfate and copper sulfate. The biomass particle carbon is black carbon powder particles (biomass carbon) generated by incompletely combusting biomasses under a low-oxygen condition and has the advantages of stable property, strong adsorptive capacity and good moisture and fertility preservation effects. The soil conditioner prepared from the biomass particle carbon and the wood vinegar can improve the structure of the soil, optimize a soil ecological environment and improve the utilization efficiency of the fertilizer; when production increasing and synergism of ginsengs can be accelerated, the carbon is effectively stored in the soil, so as to realize agricultural emission reduction; and therefore an application prospect is wide.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Slow-release organic fertilizer for tea leaves and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103351219AWith fertilizer effect controlled releaseApplicable growthFertilizer mixturesPotassiumCopper oxide
Owner:ANHUI INNOVATIVE AGRI TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com