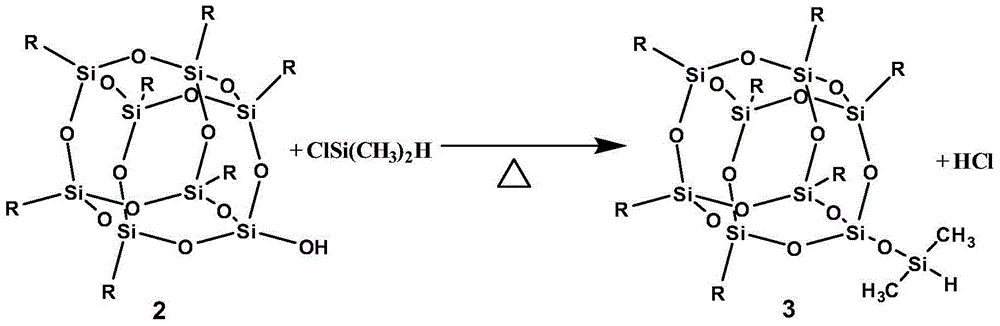
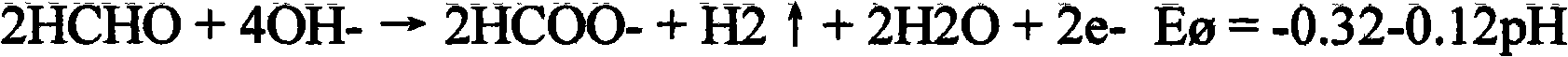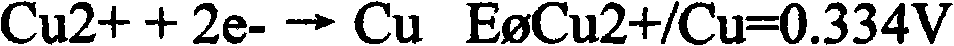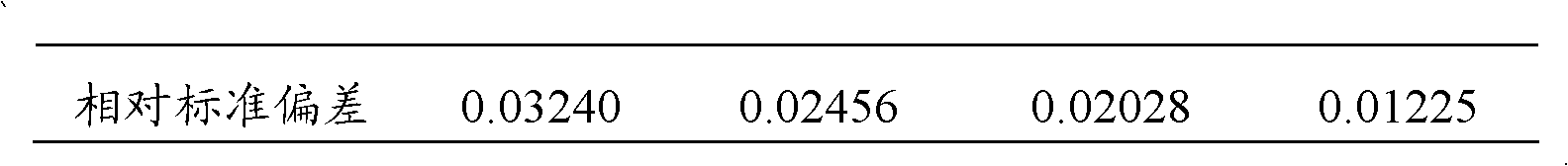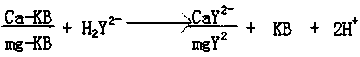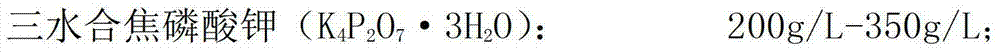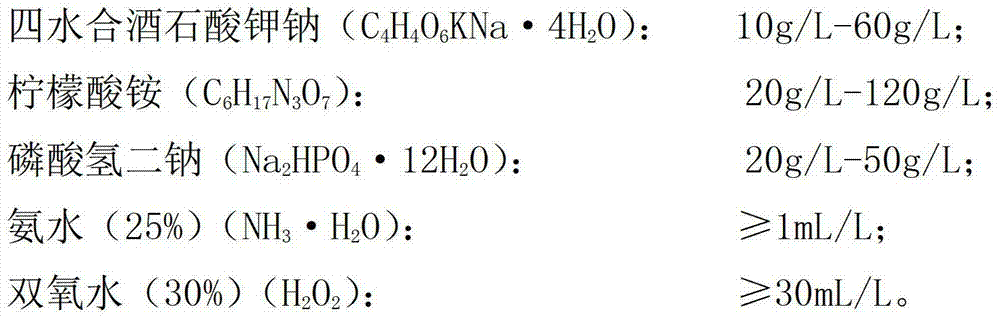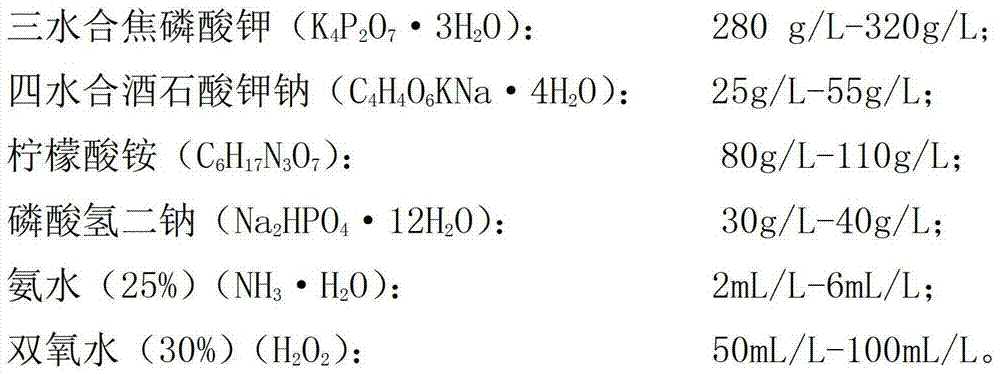Patents
Literature
446 results about "Potassium sodium tartrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Potassium sodium tartrate tetrahydrate, also known as Rochelle salt, is a double salt of tartaric acid first prepared (in about 1675) by an apothecary, Pierre Seignette, of La Rochelle, France. Potassium sodium tartrate and monopotassium phosphate were the first materials discovered to exhibit piezoelectricity. This property led to its extensive use in "crystal" gramophone (phono) pick-ups, microphones and earpieces during the post-World War II consumer electronics boom of the mid-20th Century. Such transducers had an exceptionally high output with typical pick-up cartridge outputs as much as 2 volts or more. Rochelle salt is deliquescent so any transducers based on the material deteriorated if stored in damp conditions.
Organic water soluble fertilizer
The invention relates to an organic water soluble fertilizer, which belongs to a novel, efficient and organic hyperconcentration chelate fertilizer and is prepared from plant source organic matters, potassium humate, citric acid, amino acid, vitamin, monosaccharide, fructose, dextrose, polysaccharide, potassium sodium tartrate, zinc sulfate, copper sulfate, manganese sulfate, boracic acid, ammonium molybdate, ethanediol, monoammonium phosphate, monopotassium phosphate, phosphoric acid and the like through the processes of acidification, chelation and concentration. The organic water soluble fertilizer is suitable for being used for all plants in modes of leaf surface spray application, root filling, seed soaking, flushing application, drip irrigation and spray irrigation. The product is nontoxic and does not have hormone or residue, the crop growth and development can be regulated in a balanced way, the metabolism and the photosynthesis of the plants can be promoted, the aging of the plants can be delayed, the quality is improved, the yield is increased, and certain drought resistance, cold resistance and disease resistance effects are realized. 20 percent to 40 percent of soil fertilizer consumption can be reduced through using the organic water soluble fertilizer for many times, and the yield of the crops can be increased by about 10 to 40 percent.
Owner:GUANGXI PENSHIBAO
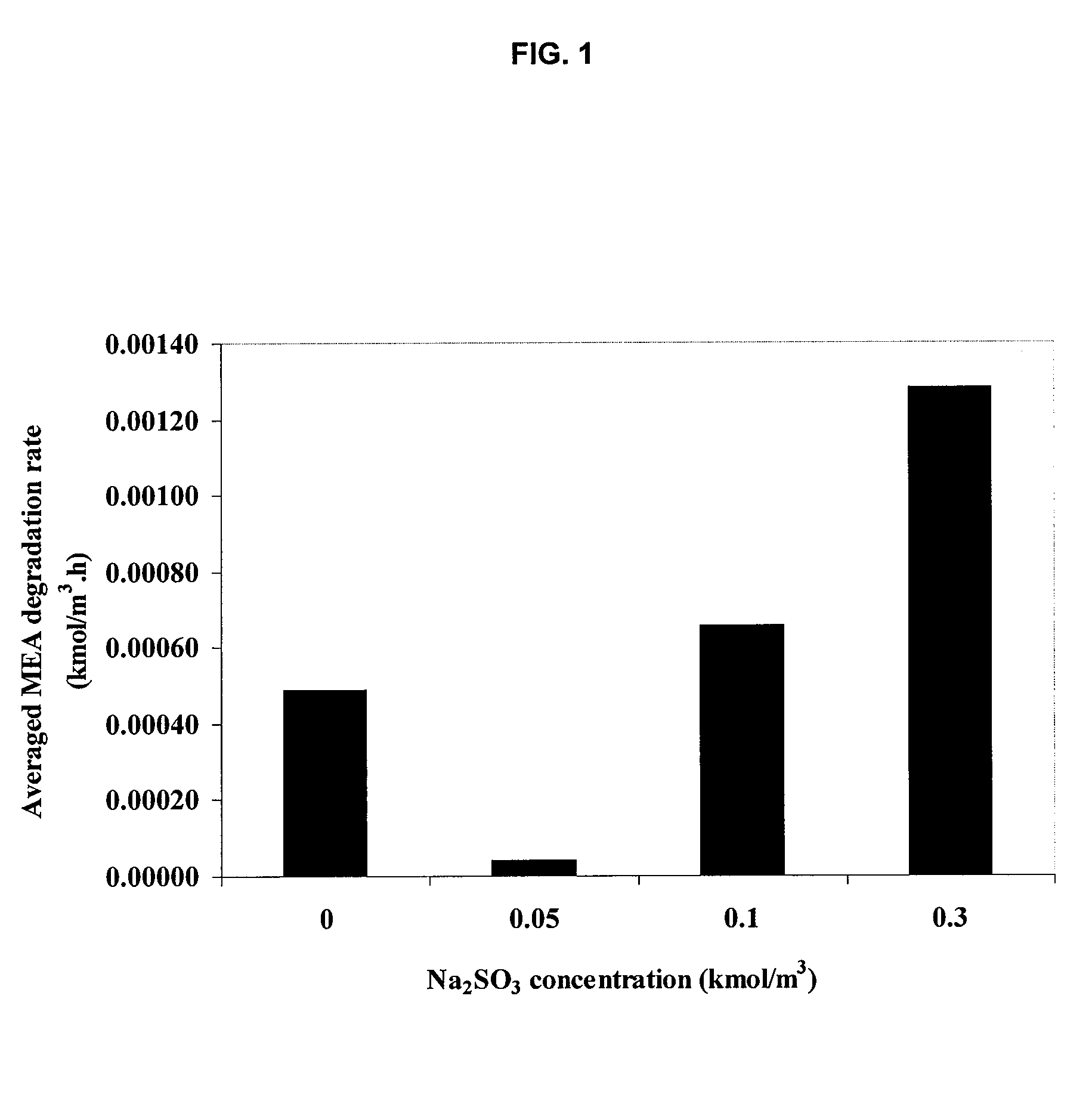
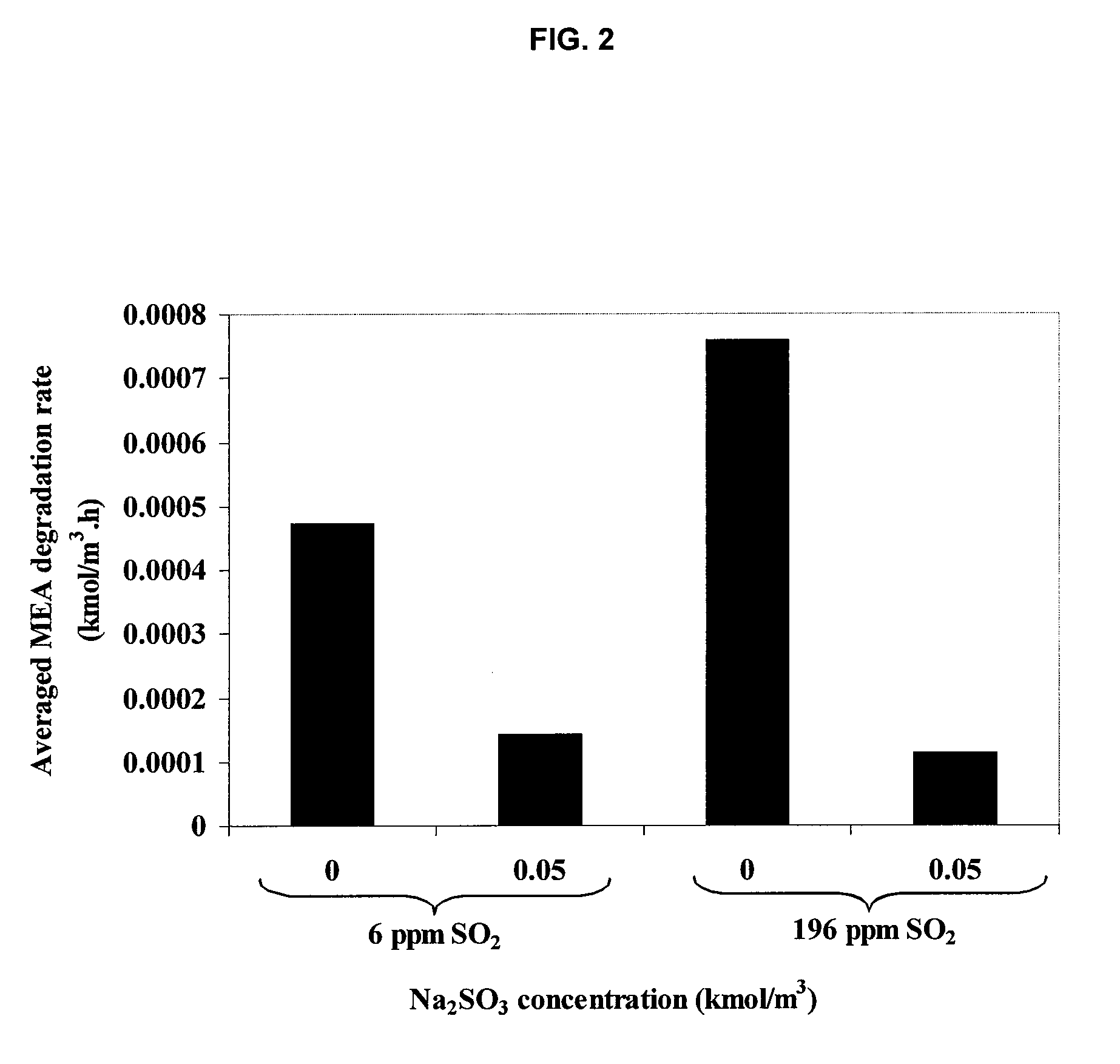
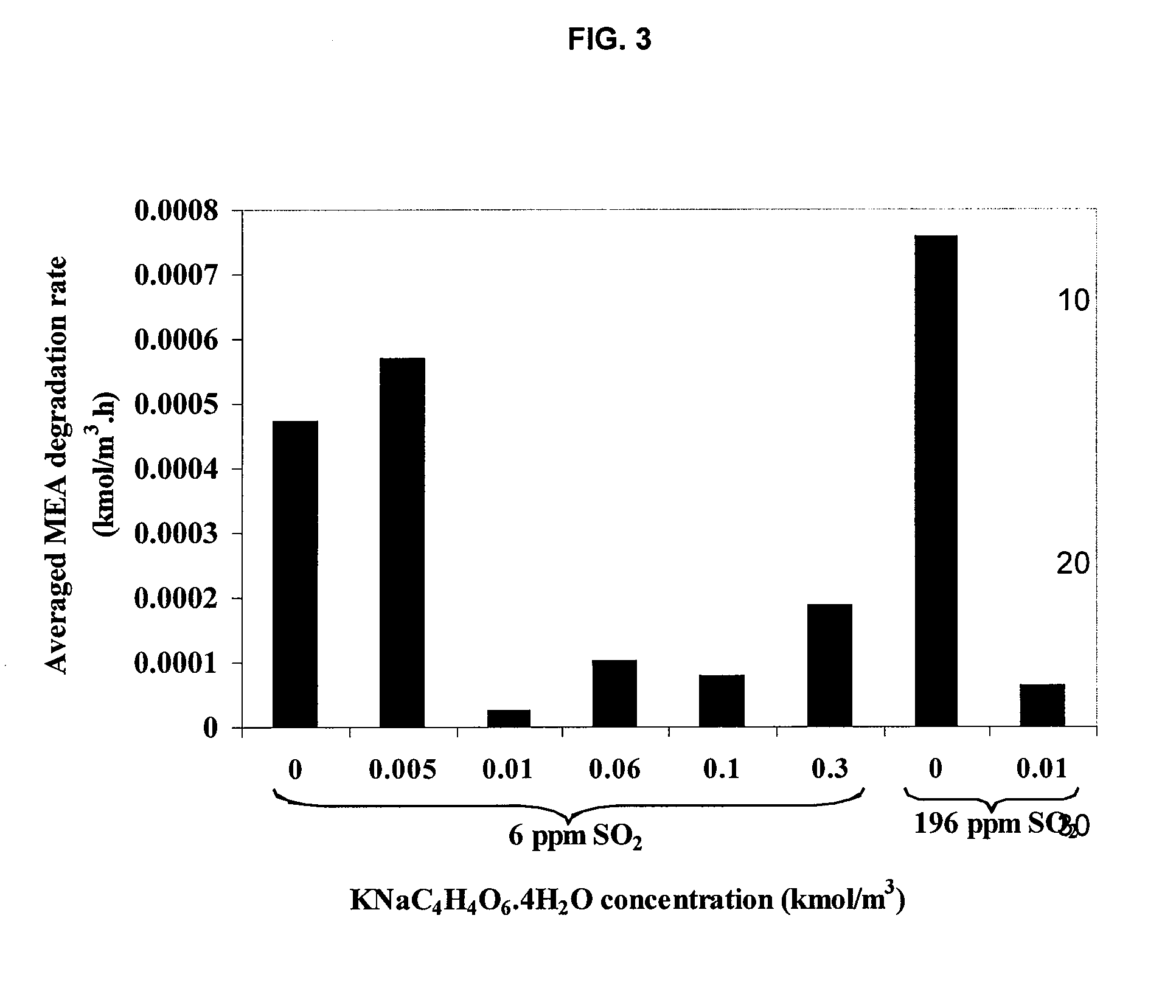
Method for inhibiting amine degradation during c02 capture from a gas stream
ActiveUS20090205496A1Induce degradationGas treatmentOther chemical processesHydroxylamineSulfite salt
The present application includes a method for inhibiting amine degradation during CO2 capture from flue gas streams. Particularly, the present disclosure relates to a method of inhibiting O2- and / or SO2-induced degradation of amines using sodium sulfite (Na2SO3), potassium sodium tartrate tetrahydrate (KNaC4H4O6.4H2O), ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) or hydroxylamine (NH2OH), or analogs or mixtures thereof during CO2 capture by amines.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF REGINA
Pottery plaster formulations for the manufacture of plaster molds
InactiveUS6398864B1Efficient processImprove water absorptionCeramic shaping apparatusPotassium sodium tartratePotassium sulfate
A plaster composition for making molds for reproduction by casting is disclosed. Calcium sulfate hemihydrate, potassium sulfate and potassium sodium tartrate are mixed together. The potassium sulfate and potassium sodium tartrate are in a ratio of from about 1:1 to about 10:1. Potassium sodium tartrate is present in an amount of from about 1 to about 10 pounds per ton of dry calcium sulfate hemihydrate, and the total of the potassium sulfate and potassium sodium tartrate is from about 2 to about 35 pounds per ton of calcium sulfate hemihydrate. Methods of making and using molds of this composition are also disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
Oxygen-absorbing compositions and method
An oxygen-absorbing composition including iron and a soluble tartrate. A method of absorbing oxygen from a closed environment including the steps of providing an oxygen-absorbing composition containing iron and a tartrate, injecting water into the composition, and placing the composition into the closed environment. An oxygen-absorbing packet containing iron and a tartrate. All of the foregoing-mentioned compositions preferably include an electrolyte. The tartrates may be selected from the group which may include sodium acid tartrate, potassium acid tartrate, potassium sodium tartrate tetrahydrate and sodium tartrate dihydrate, but are not limited thereto.
Owner:MULTISORB TECH INC
Tea polyphenol detecting test paper, standard color comparison card and usage thereof
InactiveCN101294912AEasy to detectLong storage timeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsPhenolic content in teaPotassium sodium tartrate
The invention provides tea polyphenol test paper, which is prepared by using transition metal, such as iron, as a color development agent; using tartaric acid, citric acid, oxalic acid, hydrofluoric acid and salicylsulfonic acid, or any of sylvite, sodium salt and potassium sodium tartrate thereof as a complexing agent; and using soluble starch, polyvinyl alcohol, agaragar, polyacrylamide gel or gelatin as a bonding agent. Meanwhile, a standard tea polyphenol concentration color card is prepared. The tea polyphenol content can be quickly and visually observed according to the contrast between the color development of a sample to be tested on the detecting test paper and the standard color card. The test paper is suitable for quickly measuring the tea polyphenol content in plants or plant products, particularly suitable for the measurement of tea polyphenol content in tea. The test paper has the advantages of simple method, convenience, rapidness, low cost and easy popularization.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Surface pretreating method of dry method spray sand type neodymium iron boron permanent magnetic material
ActiveCN101373650AImprove bindingImprove adhesionInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsEthylenediamineCopper plating
The invention provides a surface preprocessing method of a dry-process sand-spraying type NbFeB permanent magnet material. The method comprises the following steps: chamfering, polishing, spraying sand, and chemical plating. Under the condition of room temperature, a natural sand blasting material is adopted to apply sand blasting on the surface of the NbFeB permanent magnet material; the pressure of a sand blasting machine is 0.16 to 8MP; the partial pressure of a spray gun is 0.16 to 6MP; and the sand blasting angle is 10 degree to 60 degree. A copper plating bath comprises copper sulfate of 0.03-0.5m / L, sulfite of 0.10-0.3m / L, fluoride of 0.05-0.7m / L and one or more components selected from EDTA, sodium citrate, potassium sodium tartrate and quadrol. The pH of 6.5-8.0 is achieved through adjustment, and the copper plating temperature is 10-65DEG C. The invention improves the binding force of a plating layer and a substrate, changes the roughness of the plating layer and improves the cohesive force of the plating layer.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONG KE SAN HUAN HI TECH +1
Copper ion test paper and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101545867ARealize detectionEasy to makeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSteepingPotassium sodium tartrate
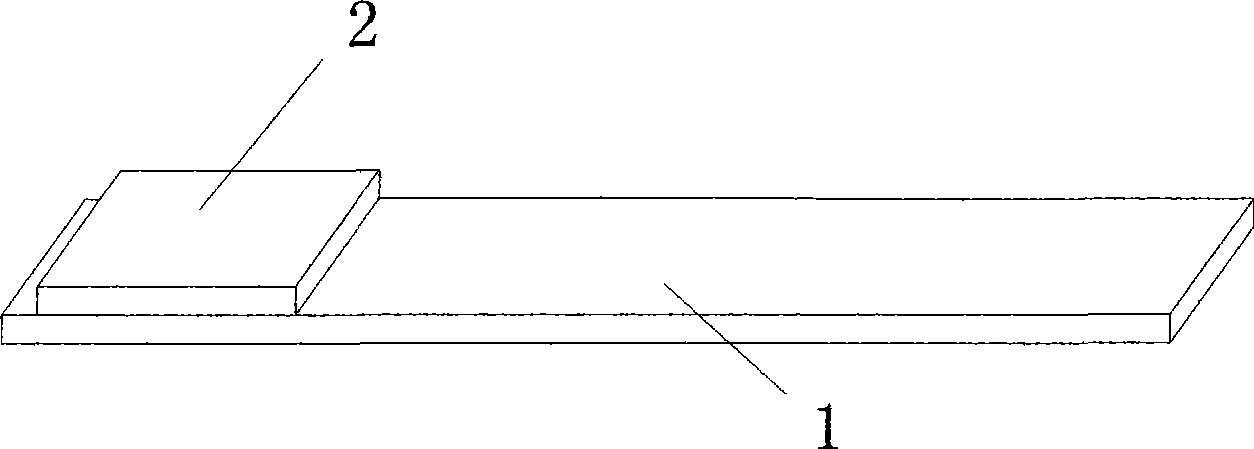
The invention discloses a copper ion test paper, which comprises a substrate (1) and chromogenic test paper (2) fixed on the substrate (1), and is characterized in that the chromogenic test paper (2) is prepared by steeping filter paper in a steeping fluid, taking out the filter paper from the steeping fluid and drying the filter paper, wherein the steeping fluid consists of the following components by weight: 0.07 to 1.4 percent of sodium diethyl dithiocarbamate, 5.7 to 11.4 percent potassium sodium tartrate, 0.036 to 0.71 percent of soluble starch, and 86.49 to 94.194 percent of distilled water. The invention also provides a method for preparing the copper ion test paper. The test paper has the advantages of simple fabrication, low cost, convenient use, no pollution to the environment, and favorability for environmental protection; and besides, the test paper has wide test range, is not required to be operated by a professional, and is particularly applicable to quick field test of copper content.
Owner:KUNMING BOYIN SCIANDTECH CO LTD
Non-cyanide alkaline copper plating bath, preparation and use method thereof
The present invention is a new non-cyanide alkaline copper plating bath, preparation and use method thereof. In the copper plating bath, using copper sulfate or basic copper carbonate as main salt, using hydroxy-ethylidene diphosphonic acid as main complexant, using trisodium citrate, potassium citrate or potassium sodium tartrate as auxiliary complexant, using sodium nitrate or potassium nitrate as conductive salt, using sodium hydroxide or potassium hydrate as pH value regulator; the operation conditions are: cathode current density is 0.5-3.0 A / dm [2], pH of plating bath controlled between 12 and 13, plating bath temperature is 50-70 DEG. Comparing with the prior known technology, the invention has following advantages or positive effects: simple plating bath formula, easy control and operation, wide temperature range of plating bath using, high current efficiency, fine crystallization coating, good appearance color, stable plating bath, strong uniform plating and covering ability, low cost, easy wastewater treatment. The invention can be used for pre copper plating or direct electro-coppering instead of virulent cyaniding electro-coppering process.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of silver-coated aluminum powder
InactiveCN102248159AFully coveredReduce dosageLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingAluminum IonCopper plating
The invention relates to a preparation method of silver-coated aluminum powder and belongs to the technical field of powder surface treatment. The preparation method comprises the steps of performing copper displacement plating and then performing silver displacement plating. In the step of performing copper displacement plating, fluoride serves as a complexing agent of aluminum ions, so that reaction of removing an oxide film from the surface of aluminum powder can be performed in a nearly neutral environment, dissolution of the aluminum powder is inhibited and deposition of the copper on the aluminum powder is promoted. In the step of performing silver displacement plating, ammonium sulfate solution serves as activating solution, potassium sodium tartrate serves as a complexing agent ofcopper, and a copper platting layer is removed by replacing silver by copper, so that the silver can be deposited on the aluminum powder. The final silver-coated aluminum powder does not contain interlayer copper and the aluminum powder is coated completely. The procedures of plating the interlayer copper and then plating the silver are adopted, so the difficulty of coating the silver on the aluminum powder is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Acid and odor removal agent for dosidicus gigas
InactiveCN102366127AEasy to handleReduce amine odorFood preparationPotassium sodium tartrateTrehalose
The invention discloses an acid and odor removal agent for dosidicus gigas. The acid and odor removal agent comprises the following raw material components in percentage by weight: 5-15% of sodium erythorbate, 20-30% of trisodium citrate, 5-15% of sodium polyphosphate, 15-25% of potassium sodium tartrate, 2-3% of calcium disodium edetate, 15-25% of trehalose, 1-3% of mannitol and the balance of modified starch. The acid and odor removal agent is made by mixing and evenly stirring the raw material components. The acid and odor removal agent has the advantages of availability at normal temperature, short soakage time within 10 hours, better acid removal effect, fast acid and odor removal speed and capability of reducing and even preventing amine odor generated during the heat treatment process of the dosidicus gigas, thus being convenient for use.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
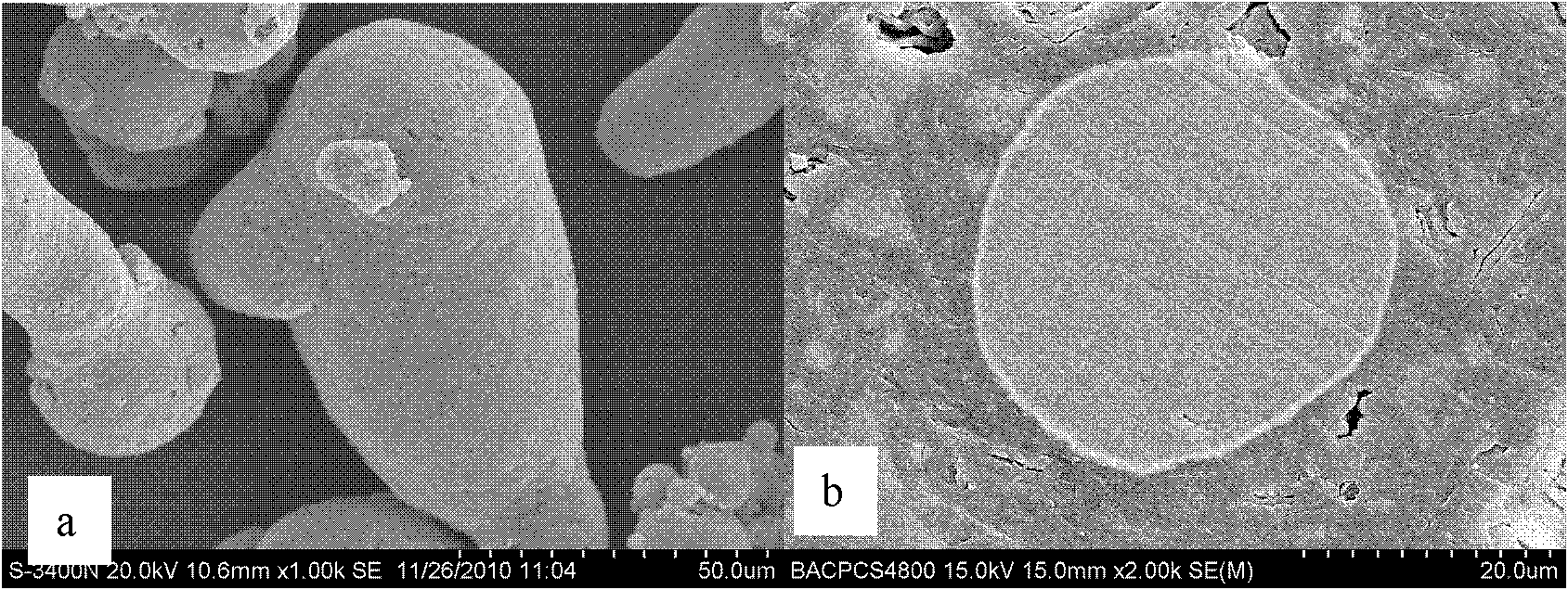
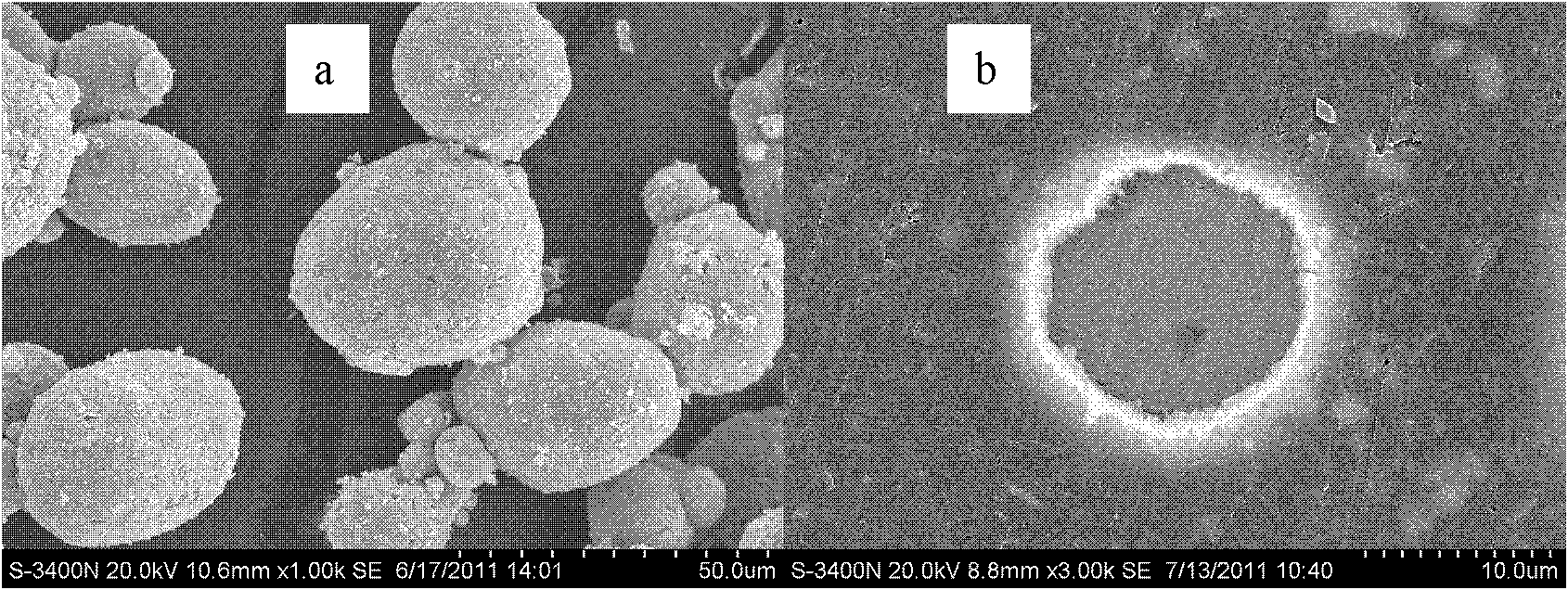
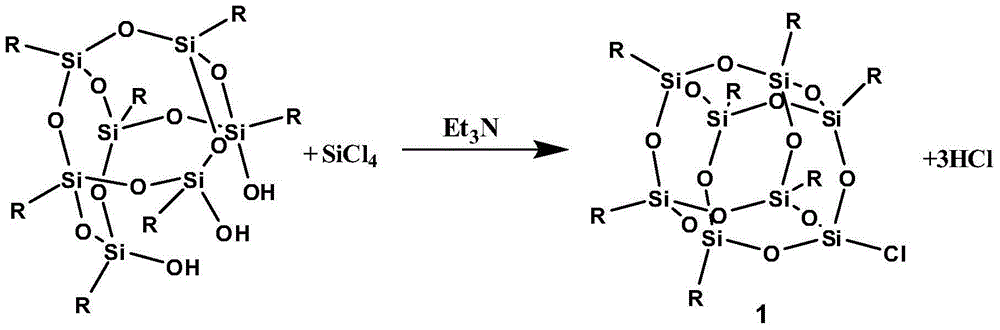
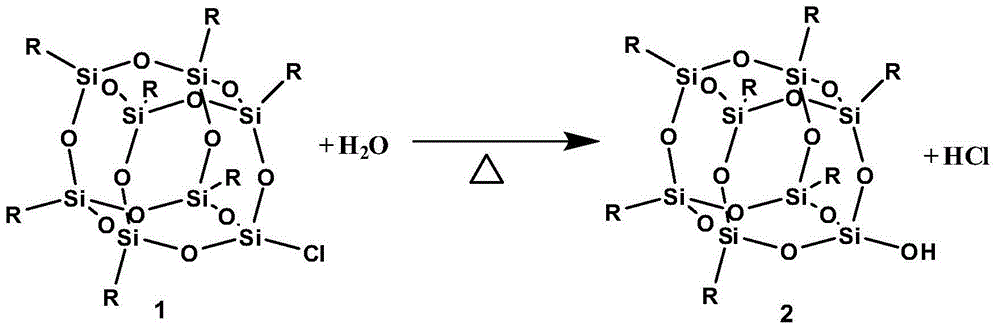
Preparation method of POSS modified polyurethane resin
InactiveCN104592473AImprove mechanical propertiesHigh tensile strengthPolyesterTetrahydrophthalamic acid
A preparation method of POSS (polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane) modified polyurethane resin comprises the following steps: preparing POSS diol by using trihydroxy cage-like siloxane heptamer, triethylamine, tetrahydrofuran, SiCl4, dimethylchlorosilane, tetrahydrophthalic anhydride, LiAlH4 and potassium sodium tartrate; and polymerizing the POSS diol, polyether diol, polyester diol and isocyanate to obtain the POSS modified polyurethane resin. The method allows the novel POSS modified polyurethane resin to be obtained by using the POSS diol, and can effectively overcome the compatibility problem existing in the modification of common inorganic substances; and the obtained POSS modified polyurethane resin has large tensile strength, impact strength, shearing strength and other mechanical performances, and also has the advantages of low surface energy, good heat resistance and good wear resistance.
Owner:JIAXING HEXIN CHEM IND
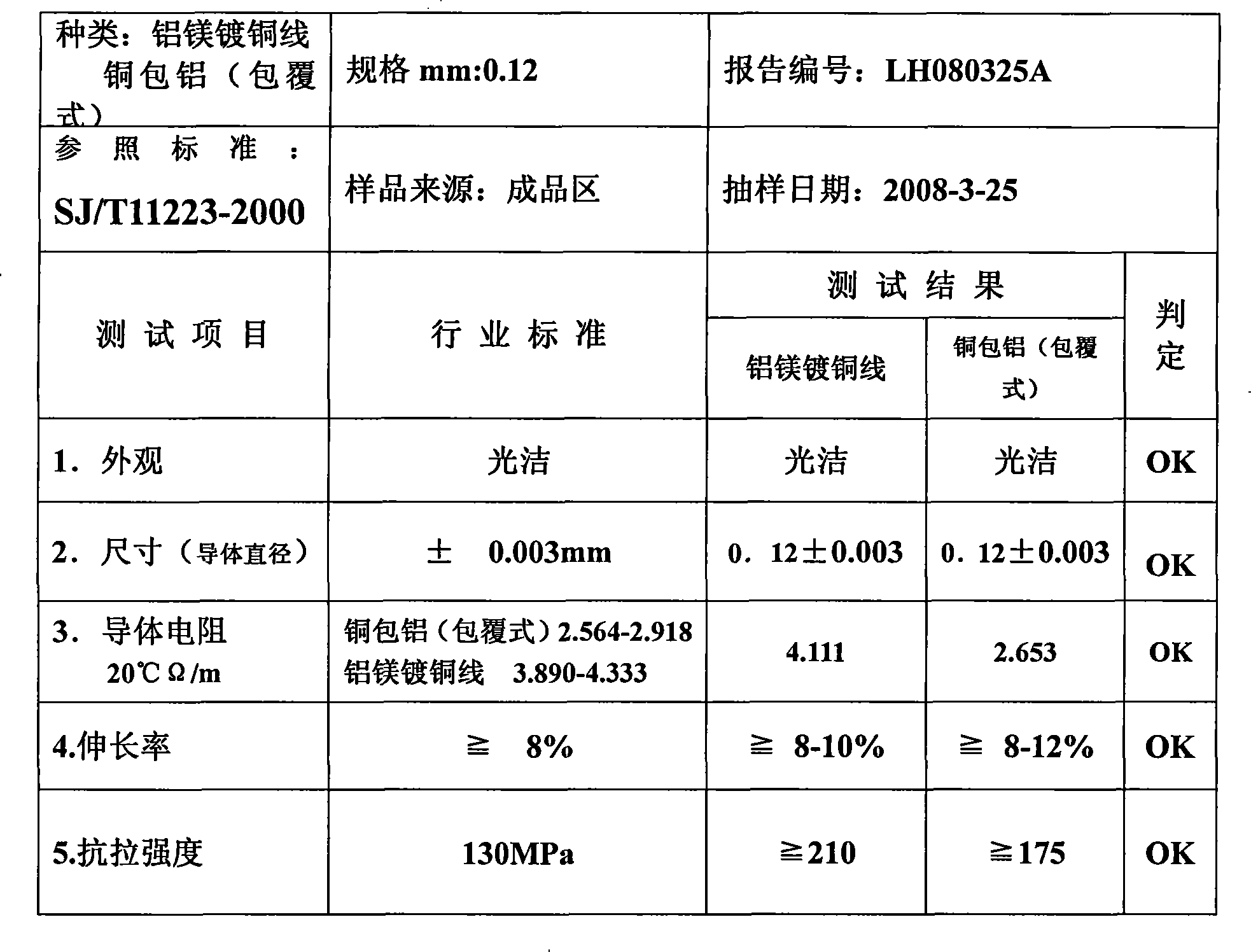
Technique for producing aluminum magnesium plating copper wire copper-coating
A manufacturing process of plating copper by using aluminum-magnesium copper-plating wire comprises the following steps: arranging wire, cleaning by alkali, cleaning by water, cleaning by sulfuric acid, cleaning by water, cleaning by alkali, cleaning by water, a first time soaking zinc, cleaning by water, removing the zinc by nitric acid, cleaning by water, a second time soaking zinc, cleaning by water, cleaning by hot water, pre-plating nickel, cleaning by water, activating, acidicly plating copper, cleaning by water, carrying out the anti-oxidation treatment, cleaning by hot water, drying and taking out the wire. The manufacturing process is characterized in that the process of the first time zinc soaking is that completing the first time zinc soaking in solution with temperature of 12-27DEG C for 30-60 sec after mixing with 60 parts water, 7 parts zinc oxide, 31 parts superalkali, 2 parts potassium sodium tartrate and 0.06 parts iron trichloride. By adopting the manufacturing process of the invention, the aluminum-magnesium copper-plating wire has the double advantages that aluminium conductor has light weight and low cost, copper conductor has high conductivity and good chemical stability, wherein the specific weight of copper is about 18-19%, mean density is 2.8g / cm3, the length of aluminum-magnesium copper plating wire whose size and weight are the same with that of pure copper wire is 3.1 times than that of the pure copper wire, tensile strength is more than or equal to 210, which enables the aluminum-magnesium copper plating wire uneasily to break and improves the quality of the products.
Owner:丹阳利华电子有限公司
Stainless steel electrolytic etching technique
The invention provides a stainless steel electrolytic etching process, which mainly comprises the following steps of: (a) pre-treatment: cleaning the surface of a stainless steel workpiece by washing, deoiling, etc.; (b) application: applying a photosensitive adhesive on the surface of the workpiece and carrying out exposure, developing, hardening, etc.; (c) electrolytic etching: disposing the workpiece in an electrolysis tank containing a stainless steel electrolytic etching solution and electrifying for electrolysis, wherein the stainless steel electrolytic etching solution mainly contains copper chloride 200 to 400 g / L, hydrochloric acid 20 to 80 g / L, thiourea 1 to 5 g / L and potassium sodium tartrate 10 to 20 g / L; and (d) demolding: removing the residual adhesive film on the surface after electrolysis and cleaning to obtain the product. Accordingly, the stainless steel electrolytic etching process provided by the invention can achieve very high etching speed and higher accuracy under the low pressure condition, and has the advantages of simple process, low power consumption, high etching speed and wide application prospect.
Owner:MITAC PRECISION TECH CO LTD SHUNDE DISTRICT FOSHAN CITY
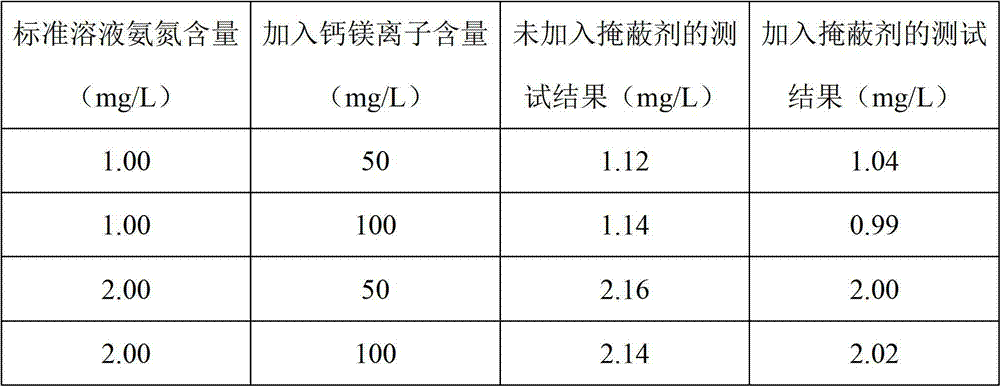
Spectrophotometric method for determining ammonia nitrogen content in water
InactiveCN102735627AAvoid interferenceImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsFiltrationRelative standard deviation
The invention discloses a spectrophotometric method for determining the ammonia nitrogen content in water. The method comprises the steps that: (1) an original water sample requiring analyzing is fetched; (2) pre-treatment of the original water sample is carried out, wherein residual chlorine is removed, suspended solids are removed by filtration, and a masking agent which is potassium sodium tartrate is added for eliminating the interference of magnesium ions; (3) the absorbance of the water sample is tested by using a spectrophotometer; (4) a blank test is carried out by using distilled water, such that a blank absorbance is obtained; and (5) the blank absorbance obtained in the steps (4) is subtracted from the absorbance obtained in the step (3), such that a corrected absorbance is obtained; a standard curve is drawn, and the ammonia nitrogen content in water is calculated. The method provided by the invention is advantaged in that: with the method provided by the invention, the ammonia nitrogen content in water can be rapidly and conveniently tested. Through the pre-treatment upon the original water sample, interferences of the suspended solids, the residual chlorine, the calcium ions and the magnesium ions upon testing results can be avoided, and the accuracy of testing results can be effectively improved. The method is also advantaged in good repeatability and low relative standard partial.
Owner:SUZHOU GUOHUAN ENVIRONMENT DETECTION
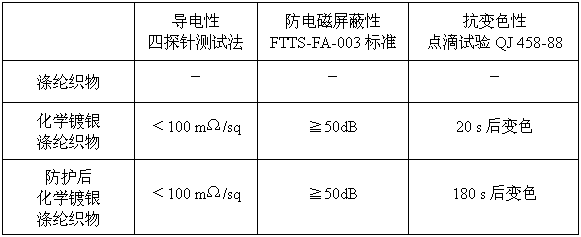
Silver plating solution for chemical silvering of polyester fabrics, silver plating method of silver plating solution and anti-tarnishing protection method of plating layer
The invention relates to a silver plating solution for chemical silvering of polyester fabrics, a silver plating method of the silver plating solution and an anti-tarnishing protection method of a plating layer. The silver plating solution is divided into a silver salt solution and a reducing agent solution, wherein constituents and concentrations of the silver salt solution are as follows: 5 to 10g / L of AgNO3, 55 to 65mL / L of ammonia water, 15 to 25mL / L of ethidene diamine, 5 to 10g / L of sodium thiosulfate and 5 to 10g / L of potassium hydroxide; and the constituents and the concentrations of the reducing agent solution are as follows: 5 to 10g / L of glucose, 1 to 5g / L of potassium sodium tartrate, 35 to 45mL / L of ethanol, and 70 to 80mg / L of polyethylene glycol 1000. The polyester fabrics with the plating layer prepared by the invention is durable in conductivity, excellent in anti-electromagnetic shielding capacity, and good in anti-tarnishing property, thereby being applied to preparation of conductive foam, conductive adhesive tapes, conductive hasps, shielding clothes and shielding caps and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Non-cyanide copper plating solution
Cyanogen-free preplated copper solution belongs to the technical field of surface treatment electroplating. The solution adopts a nontoxic organic phosphine compound to replace cyanide as a complexing agent for the preplated copper, and is particularly suitable for preplated copper used to electroplate steel, aluminum, magnesium, zinc, titanium and titanium alloy. The cyanogen-free preplated copper solution has the following main technical characteristic that the solution consists of (a) one sort of copper sulphate, basic cupric carbonate or copper nitrate with the volume concentration of between 30 and 60 g / L; (b) one sort or two sorts of compounds selected from methylene diphosphonic acid, 1-hydroxyethylidene 1.1 diphosphonic acid and 1-hydroxybutyleneidene 1.1 diphosphonic acid with the volume concentration of between 120 and 160 g / L; (c) one sort or two sorts of compounds selected from methylamino dimethylene diphosphonic acid, hexamethylene diamine tetramethylene phosphonic acid and ethylenediamine tetramethylene phosphonic acid with the volume concentration of between 2 and 5 g / L; (d) one sort of potassium citrate, amine citrate or seignette salt with the volume concentration of between 6 and 12 g / L, and (e) polyethyleneimine alkyl slat or aliphatic amine ethoxy sulfonated substance (AESS) with the volume concentration of between 0.02 and 0.05 g / L. The cyanogen-free preplated copper solution has the characteristics of stable service performance, simple solution compositions, convenient maintenance, high safety, environmental protection, reliable plating coat binding and the like.
Owner:江南工业集团有限公司
Method for plating copper on surface of carbon nanotube
InactiveCN101311306ALow priceEasy to operateLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingCopper platingGlycerol
The invention discloses a preparation method for plating copper on the surface of a carbon nano-tube, which is characterized by adopting Cu2+ as the source of the elementary substance copper and adopting Zn or HCHO as a reducing agent. When adopting Zn as the reducing agent, the main reagents are: CuSO4.5H2O, Zn powder, glycerol, glycol, potassium sodium tartrate, FeSO4.7H2O and HNO3. When adopting the HCHO as the reducing agent, the main reagents are: CuSO4.5H2O, HCHO, EDTANa2, FeCl3.7H2O, triethanolamine, a, a-bipyridine, NaOH and HNO3. The technological process of the plating copper on the surface of the carbon nano-tube is as follows: carbon nano-tube oxidation, water scrubbing, plating, water scrubbing and drying. The preparation method of the plating copper on the surface of the carbon nano-tube of the invention not only changes the traditional way of palladium catalysis but also has the advantages of low price and convenient operation, which simplifies process and is simple.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH LIAONING
Composite microbial fertilizer for controlling soil-borne disease and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105732195AImprove micro-ecological environmentIncrease diversityBio-organic fraction processingAnimal corpse fertilisersBiosphereResource pool
The invention discloses a composite microbial fertilizer for controlling soil-borne disease and a preparation method thereof. The composite microbial fertilizer for controlling soil-borne disease is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: waste livestock / fowl feather, rice bran, dry manure, weathered coal, biochar, a composite microbial inoculant, humic acid, bentonite, potassium sodium tartrate, citric acid, copper sulfate and ferrous sulfate. The composite microbial inoculant is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus mucilagimosus krassilm and Paenibacillus sabinae. The composite microbial fertilizer contains abundant various microbes, and the composite microbial inoculant is added to increase the beneficial bacterium content, so that the composite microbial fertilizer becomes a microbe resource pool. After being applied by drip irrigation and spraying, the composite microbial fertilizer can adjust the phytoedaphon structure, enhance the soil microbe diversity, improve the microecological environment of the soil and reduce the biosphere of the phytopathogen, thereby achieving the goal of controlling soil-borne disease.
Owner:GUANGXI WEILIDA BIOTECH CO LTD
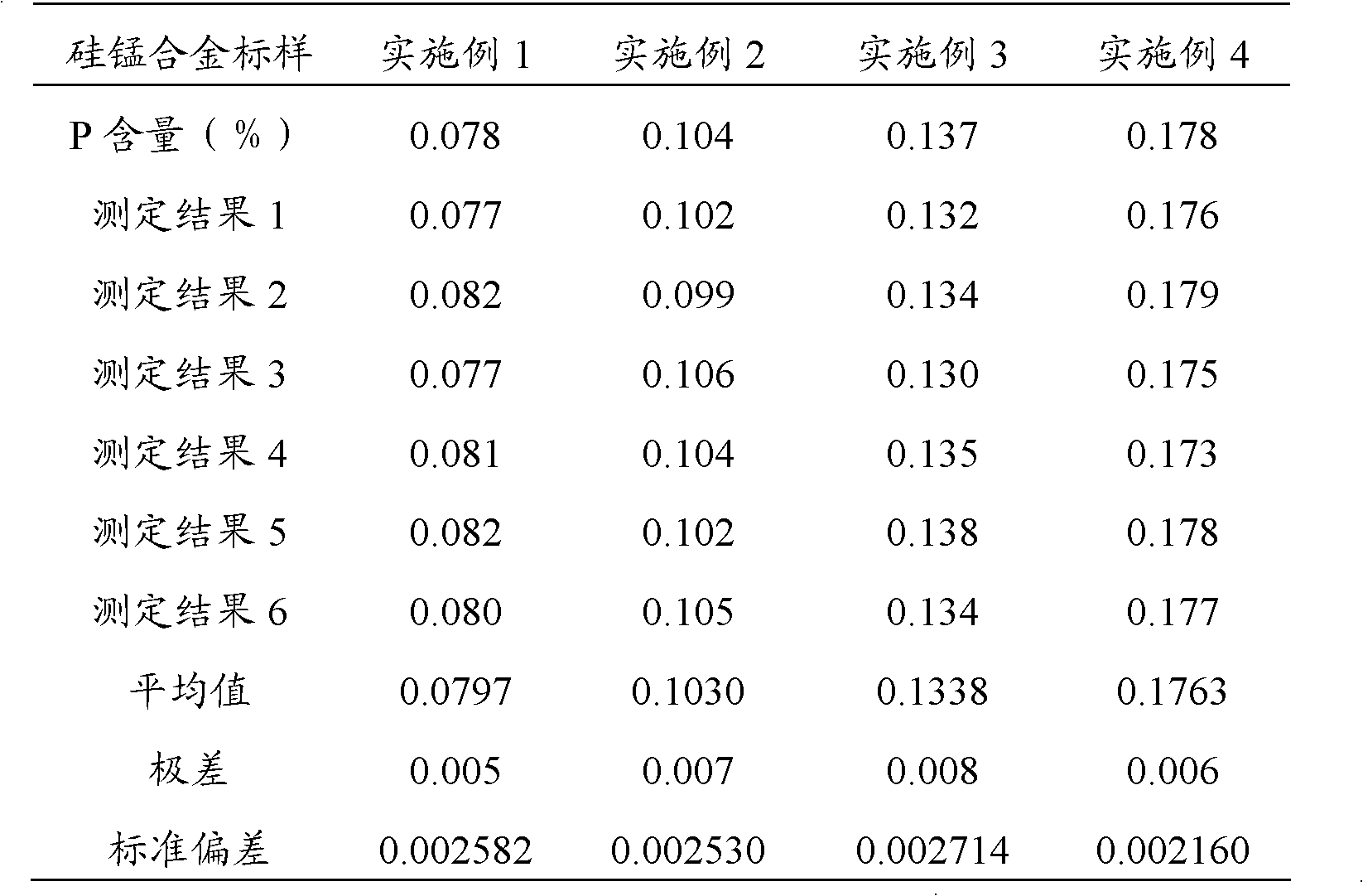
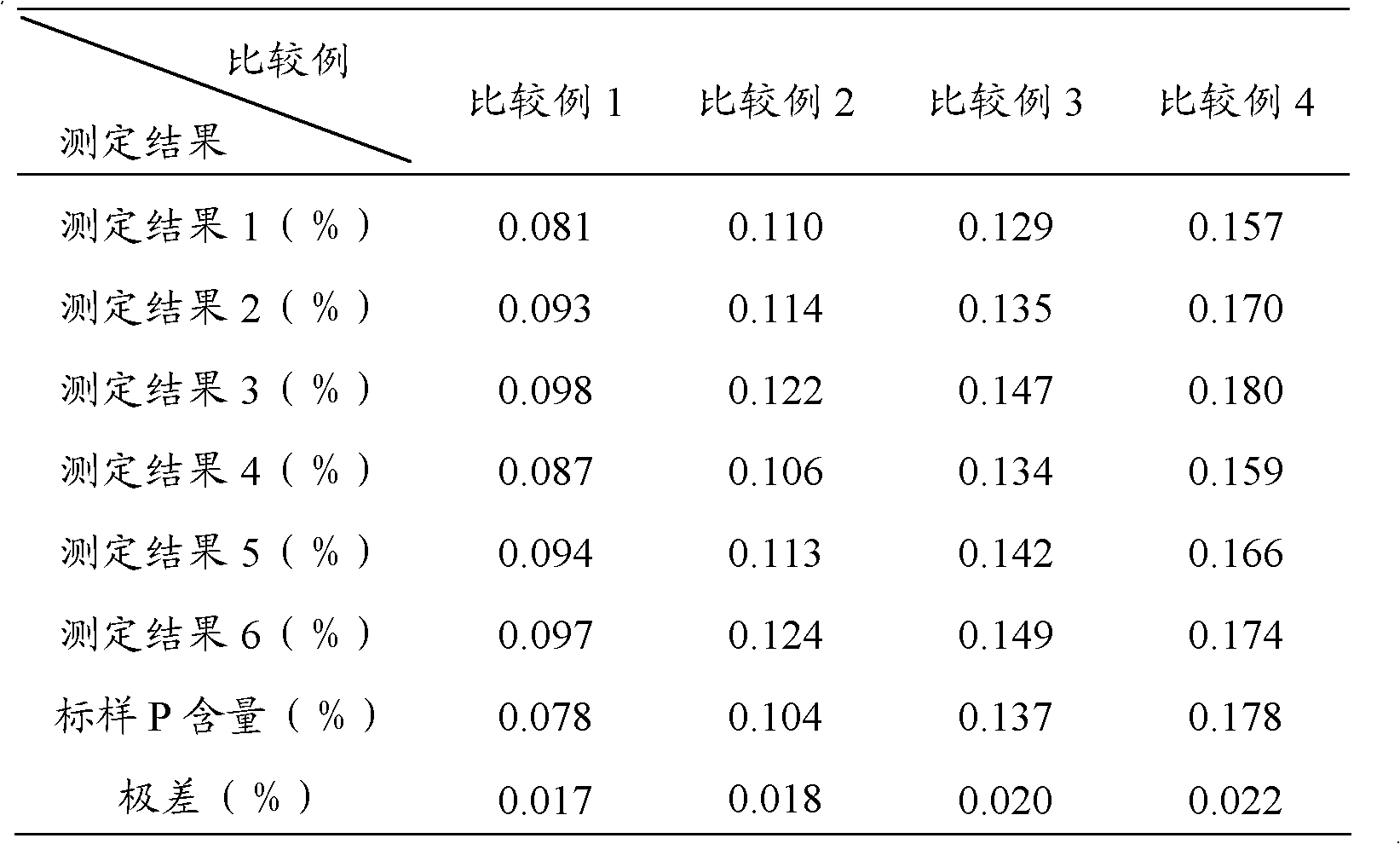
Method for determining phosphorus in silicon-manganese alloy
InactiveCN102539426AShort analysis timeImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFistHeteropoly acid
The invention discloses a method for determining phosphorus in silicon-manganese alloy, which comprises the steps of: dissolving a test sample by using nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid and adding perchloric acid to convert phosphorus in the test sample into orthophosphoric acid to obtain fist mixed solution; adding sodium sulfite into the first mixed solution to reduce manganese in the silicon-manganese alloy to obtain second mixed solution; and adding bismuth nitrate solution, ammonium molybdate solution, potassium sodium tartrate solution, sodium fluoride and stannous chloride into the second mixed solution, wherein ammonium molybdate can convert the orthophosphoric acid in the first mixed solution into phosphorus-molybdenum heteropoly acid, using stannous chloride to reduce the formed phosphorus-molybdenum heteropoly acid into blue phosphomolybdenum blue and finally using a spectrophotometric method to determine the content of the phosphorus. Compared with the prior art, by using the stannous chloride as the reducing agent, since the stannous chloride has the characteristics of high reducing speed, good reducing effect and the like, the analysis time of the determination method is shorter, the accuracy and the stability of the determination result are improved and the method is suitable for field mass production analysis.
Owner:吉林建龙钢铁有限责任公司
Environment-friendly stainless steel substrate plating stripping agent
The invention discloses an environment-friendly stainless steel substrate plating stripping agent. Nitrate is optimally selected as an oxidizing agent for stripping nickel, chromium, copper, tin, and other plating on a stainless steel substrate, and as generally, nitrate is relatively stable in property and relatively low in toxicity, so that when the stripping agent provided by the invention is used, exhaust gases and waste water are not generated, and the stripping agent is non-corrosive to a device and highly friendly to the environment; at the same time nitrate is matched with citrate, potassium sodium tartrate and a proper amount of polyhydroxyl aldehyde, so that the speed for stripping the nickel plating on the stainless steel substrate is effectively increased, the plating stripping is achieved in a short time, and the production cycle is shortened while the substrate is not damaged; and the stripping rate of the nickel plating on the stainless steel substrate can be effectively increased through the combination of mannitol and sodium diacetate. Relative to the prior art, the stripping agent has the advantages of being free of corrosion, poisonous gases and pollution, high in efficiency, environment-friendly in use, easy and convenient to maintain, and the like.
Owner:HUIZHOU CITY HIROMI CHEM CO LTD
Method for rapidly detecting ammonia nitrogen removal rate
InactiveCN104483280AReduce usageHarm reductionColor/spectral properties measurementsPotassium sodium tartrateAmmonia nitrogen
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting an ammonia nitrogen removal rate. The method comprises steps of preparation of a potassium sodium tartrate solution with the concentration of 50%, preparation of a Nessler reagent, preparation of ammonia nitrogen standard working solutions, establishment of standard curves and sample measurement. According to the method, the ammonia nitrogen standard working solutions with high, medium and low concentrations are set; when the ammonia nitrogen concentration in the sample cannot be ensured, the ammonia nitrogen standard working solutions with different concentrations can be simultaneously used, different standard curves are established for determining the ammonia nitrogen concentration of a detected sample, and the ammonia nitrogen removal rate is obtained through formula computing. The toxic reagent use amount is effectively reduced, harm to an operator and environmental pollution are reduced, the detecting speed is high, and the application range is wide.
Owner:FUYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Hypophosphite system plating Ni-P alloy electroplating solution and electroplating method
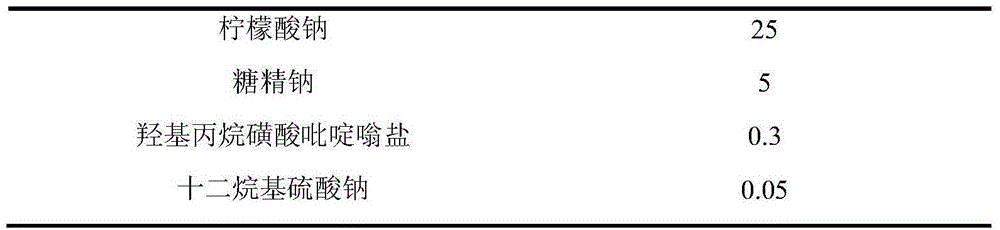
The invention discloses a hypophosphite system plating Ni-P alloy electroplating solution and an electroplating method. The electroplating solution comprises the following components by content: 200-260 g / L of NiSO4.6H2O, 30-70 g / L of NiCl2.6H2O, 30-70 g / L pf hypophosphite, 40-70 g / L of H3PO4, 25-50 g / L of potassium sodium tartrate, 5-10 g / L of saccharinate, 0.3-0.5 g / L of pyridinium hydroxy propyl sulfobetaine and 0.05-0.2 g / L of a cationic surfactant. The hypophosphite system plating Ni-P alloy electroplating solution and the electroplating method have the advantages that potassium sodium tartrate is selected as a coordination agent, so that Ni-P co-deposition is facilitated; pyridinium hydroxy propyl sulfobetaine and saccharinate are compositely selected as brightening agents, so that the rigidity, abrasion resistance and corrosion resistance of Ni-P alloy plating can be high.
Owner:WUXI QINGYANG MACHINERY MFG
Magnesium-lithium alloy surface electrocoppering solution and magnesium-lithium alloy surface electrocoppering treatment method
InactiveCN102776535AImprove manufacturing speedImprove corrosion resistanceCopper platingPhytic acid
The invention provides magnesium-lithium alloy surface electrocoppering solution and a magnesium-lithium alloy surface electrocoppering treatment method. The method comprises the following steps that (1) the magnesium-lithium alloy surface is subjected to pretreatment; (2) the activation is carried out under the room temperature and ultrasonic conditions; (3) the zinc galvanizing is carried out at the temperature being 40 to 60 DEG C; and (4) the electrocoppering is carried out in copper plating solution; the electrocoppering solution consists of 50 to 70g / L of cupric pyrophosphate, 300g / L of potassium pyrophosphate, 40g / L of dipotassium phosphate, 40g / L of potassium sodium tartrate, 0.1 g / L of citric acid, 0.1g / L of phytic acid, 0.02 g / L of vanillin and the balance water; and the electrocoppering comprises the following conditions that the pH is 8 to 9, the temperature is 30 to 50 DEG C, the voltage is 2 to 4V, the current is 0.02 to 0.04 A, and the time is 20 to 40 minutes. The plating layer has the performance which is not reached by the existing magnesium-lithium alloy surface treatment method, meanwhile, the plating layer forming is fast, the plating layer forming speed is accelerated, the surface treatment efficiency is improved, the operation is simple and convenient, the production efficiency is high, and the large-scale popularization and the application are favorably realized.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Fireproof foam brick and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104402494AImprove fire resistanceImprove high temperature resistanceCeramicwareBrickPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention discloses a fireproof foam brick, which is characterized by being prepared from the following raw materials by weight part: 60-70 of waste glass, 10-15 of asbestos powder, 5-10 of quartz sand, 5-10 of semi-hydrated gypsum, 3-5 of antimony trioxide, 2-4 of aluminium tripolyphosphate, 2-4 of silicon nitride, 1-2 of oxalic acid, 1-2 of zinc borate, 1-2 of potassium sodium tartrate, 0.5-1 of isopropyl myristate, 0.2-0.4 of isooctyl palmitate, 0.5-1 of polyvinyl alcohol, 2-4 of fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate, 2-4 of a modification additive, and 50-60 of water. The foam brick provided by the invention has excellent fireproofness and high temperature resistance, and good heat insulation, and can effectively prevent potential safety hazards.
Owner:HEFEI KANGLING HEALTH TECH
Method for quickly measuring content of MgO by calcium-magnesium total subtraction process
InactiveCN103645188AThe titration process is shortenedSave operating timeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPotassium sodium tartrateColor changes
The invention provides a method for quickly measuring the content of MgO by a calcium-magnesium total subtraction process, which specifically comprises the following steps: 1) measuring the content of Ca in a sample according to GB / T176-2008; 2) preparing a sample to be measured according to a method offered by the GB / T176-2008; 3) fetching the solution of the sample to be measured; adding water for diluting, sequentially adding potassium sodium tartrate and triethanolamine and mixing uniformly; adding an EDTA standard solution to complex all CaO in the sample while ensuring excessive EDTA; finally, adding an indicator and titrating with the EDTA standard solution to the end point; calculating the content of MgO according to a calcium-magnesium total subtraction process. By adopting the method provided by the invention, the titration time can be shortened, the color change is sharp and easy to observe, the working efficiency is greatly improved, and the measurement accuracy is improved.
Owner:GEZHOUBA DANGYANG CEMENT
Stripping agent for stainless steel electroplating rack
The invention relates to the technical field of electroplating processes, in particular to a stripping agent for a stainless steel electroplating rack. The stripping agent for the stainless steel electroplating rack is prepared from sodium nitrate, potassium sodium tartrate tetrahydrate, boric acid, triethanolamine, glacial acetic acid, thiourea and water and is characterized in that a concentrated solution of the stripping agent comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 6 to 30 percent of sodium nitrate, 0.1 to 8 percent of potassium sodium tartrate tetrahydrate, 5 to 10 percent of triethanolamine, 0.01 to 0.05 percent of thiourea, 1 to 4 percent of boric acid, 0.1 to 2 percent of glacial acetic acid and the balance of water. The process is advanced, and the combined concentrated solution of the stripping agent is colorless and tasteless. During use, the concentrated solution of the stripping agent and water are mixed. During operation, the rack is used as an anode, and a stainless steel plate is used as a cathode; the stripping voltage is 4 to 6V; the hooking and electroplating layer of the rack can be stripped completely in 3 to 5 minutes, harmful gas is not produced, and a hook point is not corroded; and after the rack is stripped completely, the hook point is bright, and limb insulating glue is not damaged.
Owner:DONGGUAN DAOGU ELECTRONICS MATERIAL TECH
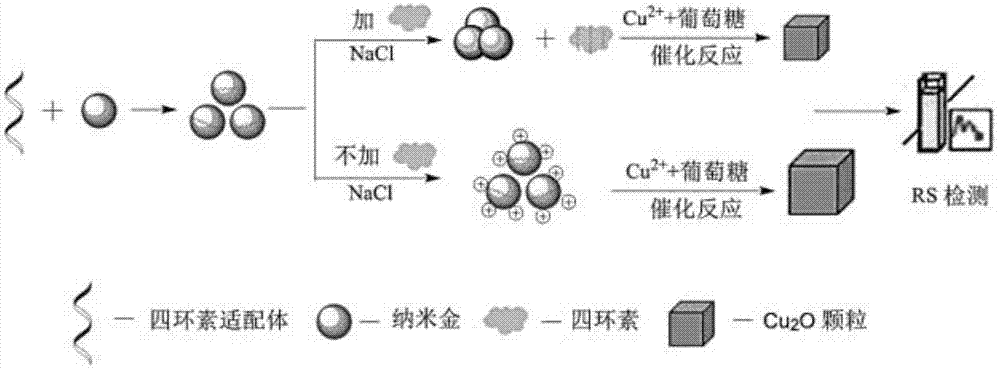
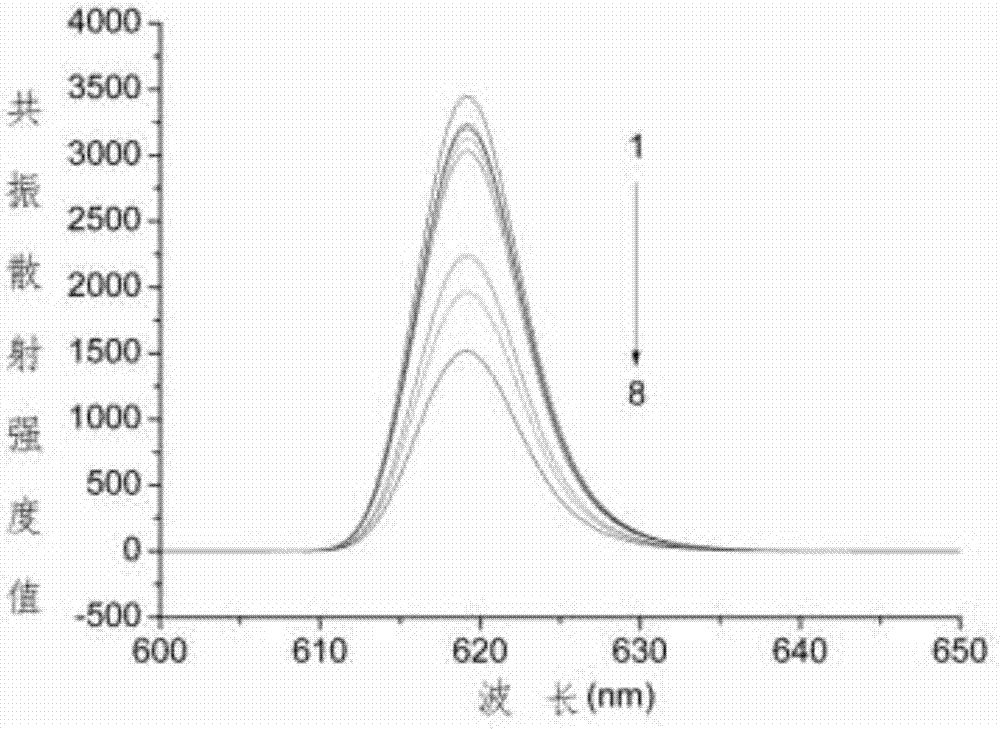
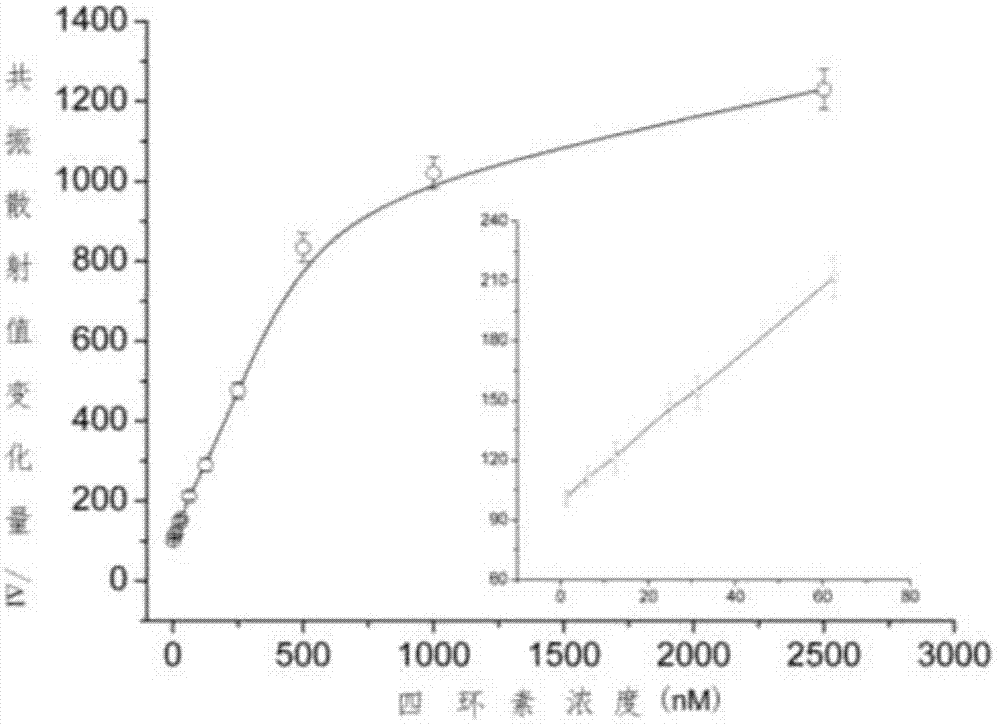
Resonance scattering spectral detection method for tetracycline based on nano-gold catalysis
ActiveCN103196875AHigh detection sensitivityGood choiceFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescencePotassium sodium tartrate
The invention provides a resonance scattering spectral detection method for tetracycline based on nano-gold catalysis. The method comprises the following steps: constructing detection systems containing tetracycline with known concentration; carrying out resonance scattering spectral signal scanning by using a fluorophotometer so as to obtain a resonance scattering signal variable standard curve; respectively adding a to-be-detected object and ultrapure water, i.e., a control sample, into a mixed liquor containing a tetracycline aptamer and nano-gold, and adding a sodium chloride solution for an agglomeration reaction; and carrying out mixing with a solution containing copper sulfate, sodium hydroxide and potassium sodium tartrate and carrying out resonance scattering spectral signal scanning by using the fluorophotometer to obtain a resonance scattering signal variable curve so as to obtain the concentration of tetracycline in the to-be-detected object. The detection method provided by the invention overcomes the defects that a nucleic acid aptamer needs modification, a detection line is non-ideal and the like and has the advantages of sensitivity, good selectivity, low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Environment-friendly de-plating liquid of copper plating layer and de-plating process of reproducible de-plating liquid
The invention relates to the technical field of electroplating, and particularly relates to a de-plating liquid and a de-plating process. The environment-friendly de-plating liquid of the copper plating layer is prepared from the raw materials of the de-plating liquid: potassium pyrophosphate, sodium potassium tartrate tetrahydrate, ammonium citrate, disodium hydrogen phosphate, 25% ammonia water and 30% hydrogen peroxide. According to the de-plating process of the reproducible de-plating liquid, copper in the de-plating liquid is recovered by electro-deposition, so that copper ions in the de-plating liquid are reduced, and the de-plating liquid is reproduced and can be recycled by appropriately supplementing hydrogen peroxide. By adopting the technical scheme, compared with the prior art, the de-plating liquid provided by the invention is stable, free from corrosion to the surface of a plate matrix, free from harmful gases, reproducible and recyclable, long in service period and cost-saving, and satisfies the purpose of environment-friendliness and conservation with more social demands.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
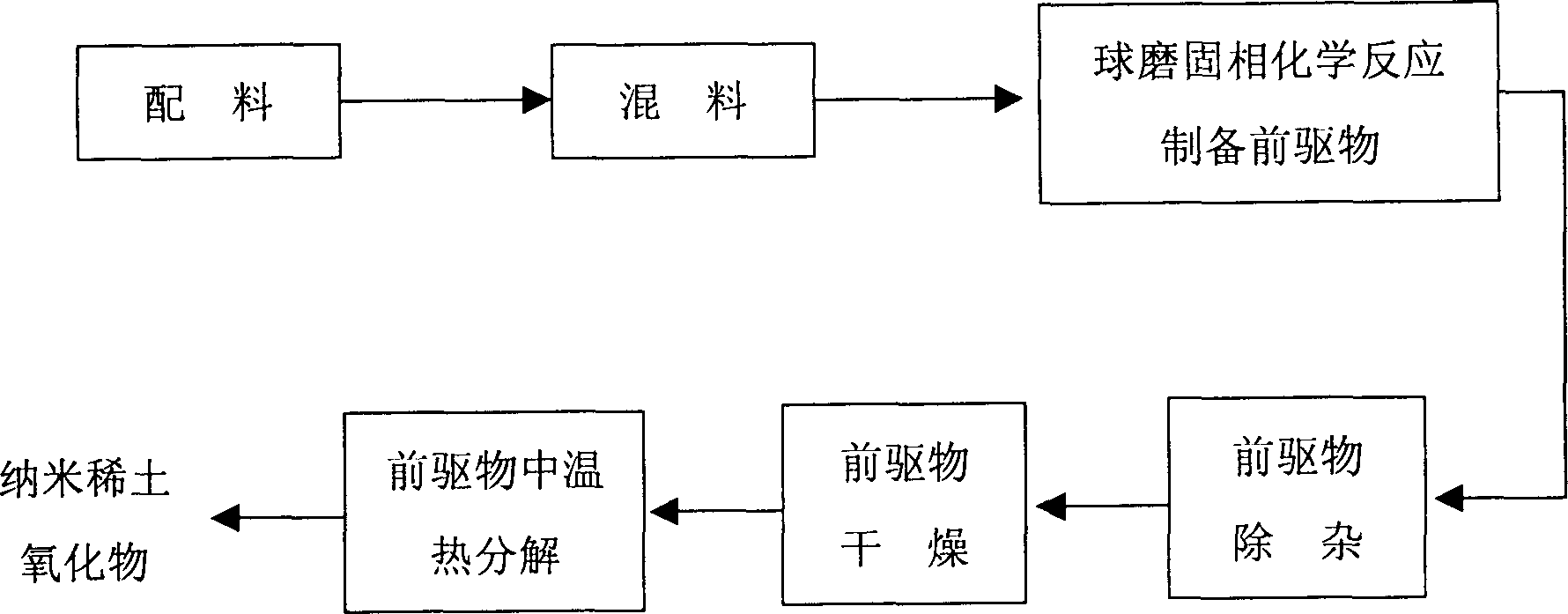
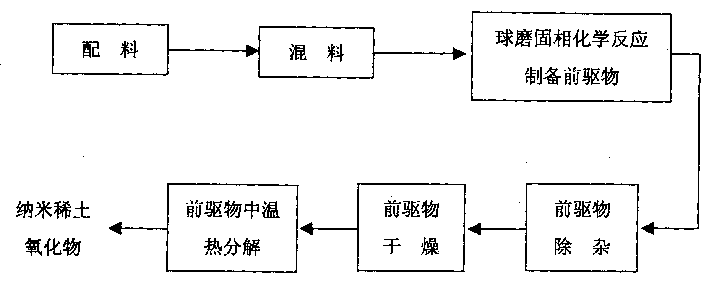
Process for preparing rare-earth nano oxide by ball grinding and solid-phase chemical reaction
InactiveCN1386706AQuick smashIncrease surface areaRare earth metal compoundsSodium acetrizoateRare-earth element
A nano rare-earth oxide is prepared from the inorganic salt of rare-earth element (Ce, La, Pr, Nd, or Tb) and ligand (oxalic acid, sodium oxalate, dicarbonate, 8-hydroxyquinoline, complexon, etc) through proportioning, mixing, and ball grinding while solid-phase chemical reaction to obtain precursor, removing impurities, drying, and medium-temp thermal decomposition. Its advantages are simple process, low cost, saving energy, high purity (more than 99%) and narrow size distribution (10-30 nm).
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
High-quality and low-cost modified active carbon air filtering material for air conditioner and preparation method of air filtering material
The invention discloses a high-quality and low-cost modified active carbon air filtering material for an air conditioner. The high-quality and low-cost modified active carbon air filtering material is characterized by being prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 130-140 parts of active carbon, 24-29 parts of corn cobs, 2-3 parts of isopropanol, 1-2 parts of camellia seed oil acid, 1-2 parts of potassium sodium tartrate, 2-3 parts of citric acid, 2-3.5 parts of potassium iodide, 11-12 parts of kieselguhr, 2.5-4 parts of acetic acid, 0.5-1 part of thiourea, 0.8-1.3 parts of sodium tripolyphosphate, 0.5-0.8 part of potassium sorbate, 4-6 parts of an adsorption auxiliary and a property amount of water. According to the high-quality and low-cost modified active carbon air filtering material, corn cob powder and the kieselguhr carry out activation on active carbon; by the adding of the adsorption auxiliary, the material is of various hole structures and has a large specific surface area, so that harmful gas such as formaldehyde and benzene which are free in air can be effectively removed, and the effect of purifying the air is achieved. A technology is simple, and the cost is low; the prepared active carbon filtering material is high in quality and can be repeatedly used.
Owner:MINGGUANG JIAYI ELECTRIC CONTROL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com