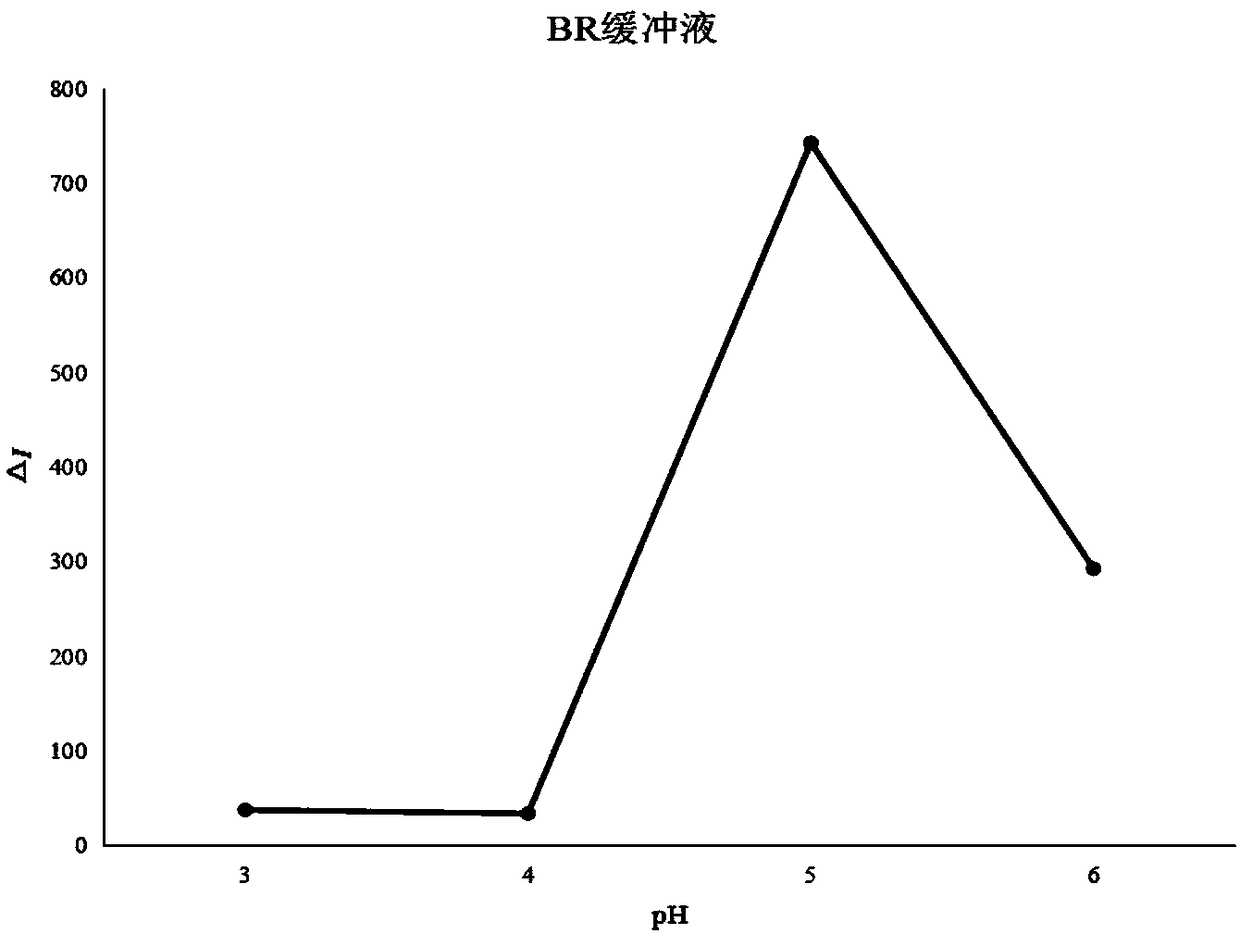
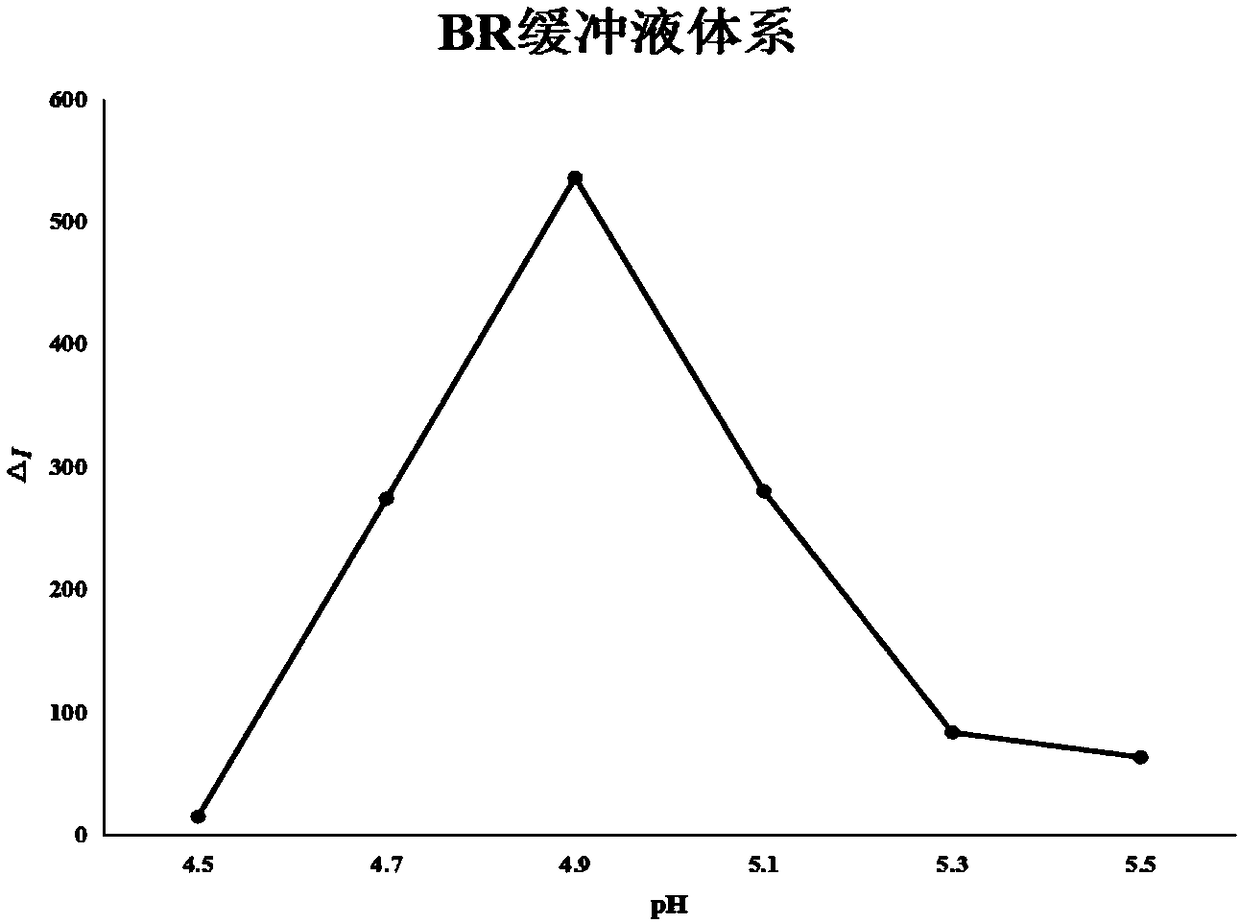
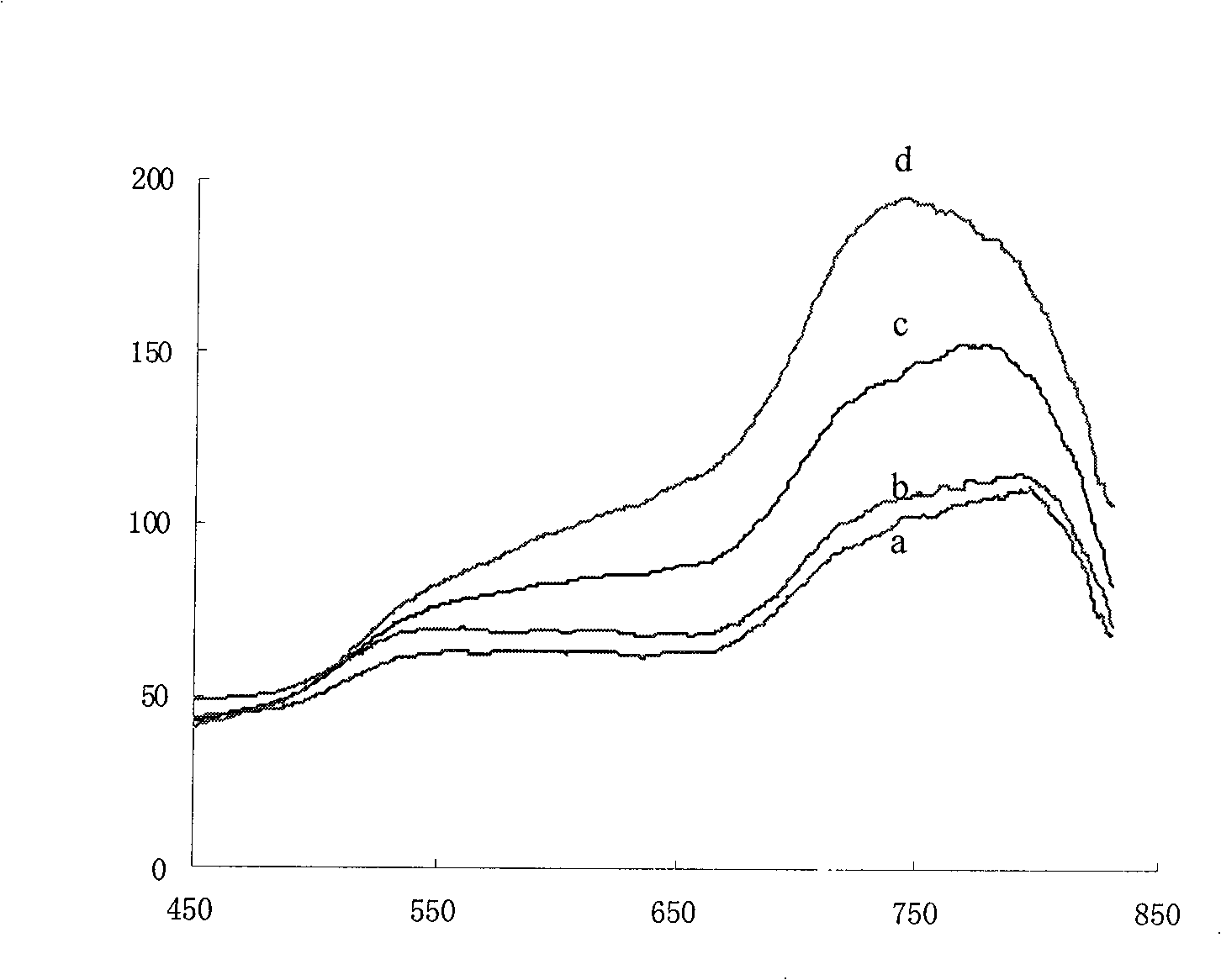
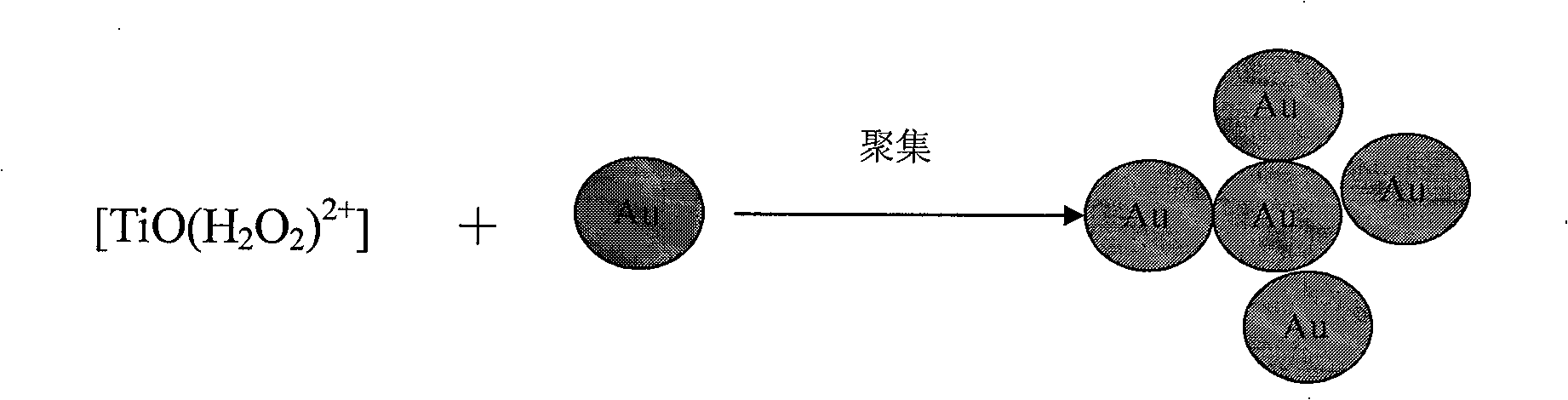
Patents
Literature
56 results about "Resonance scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
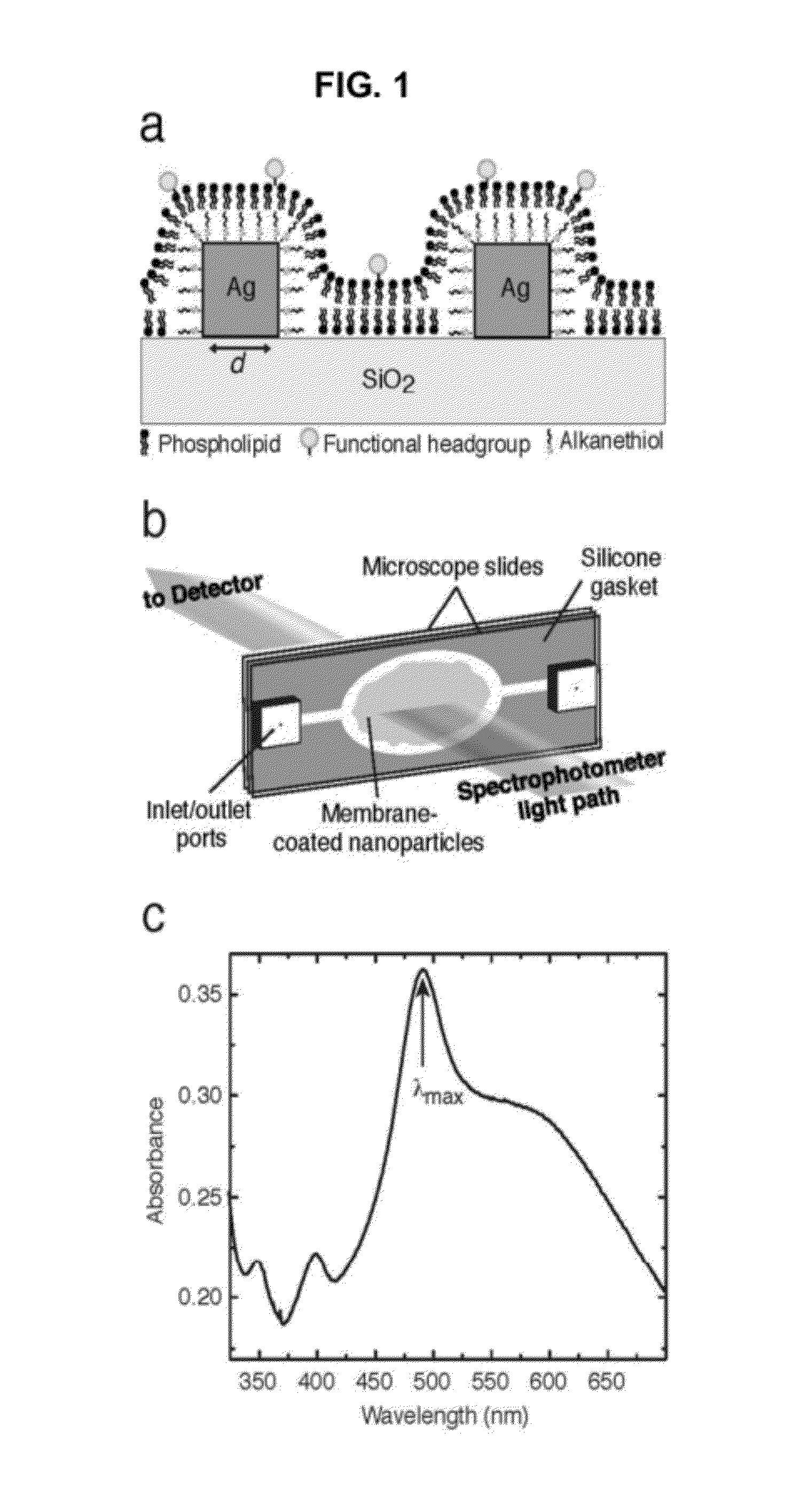
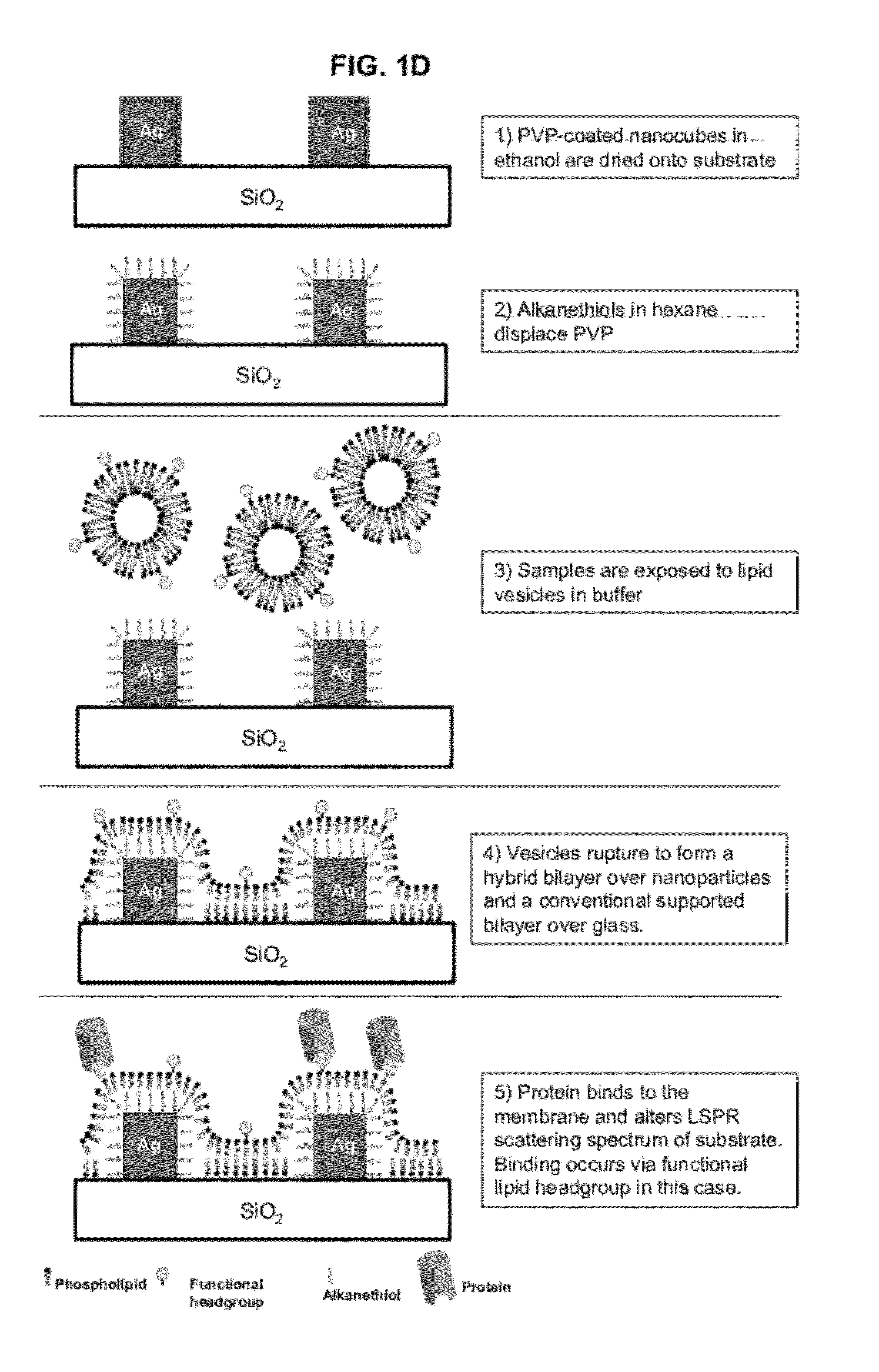
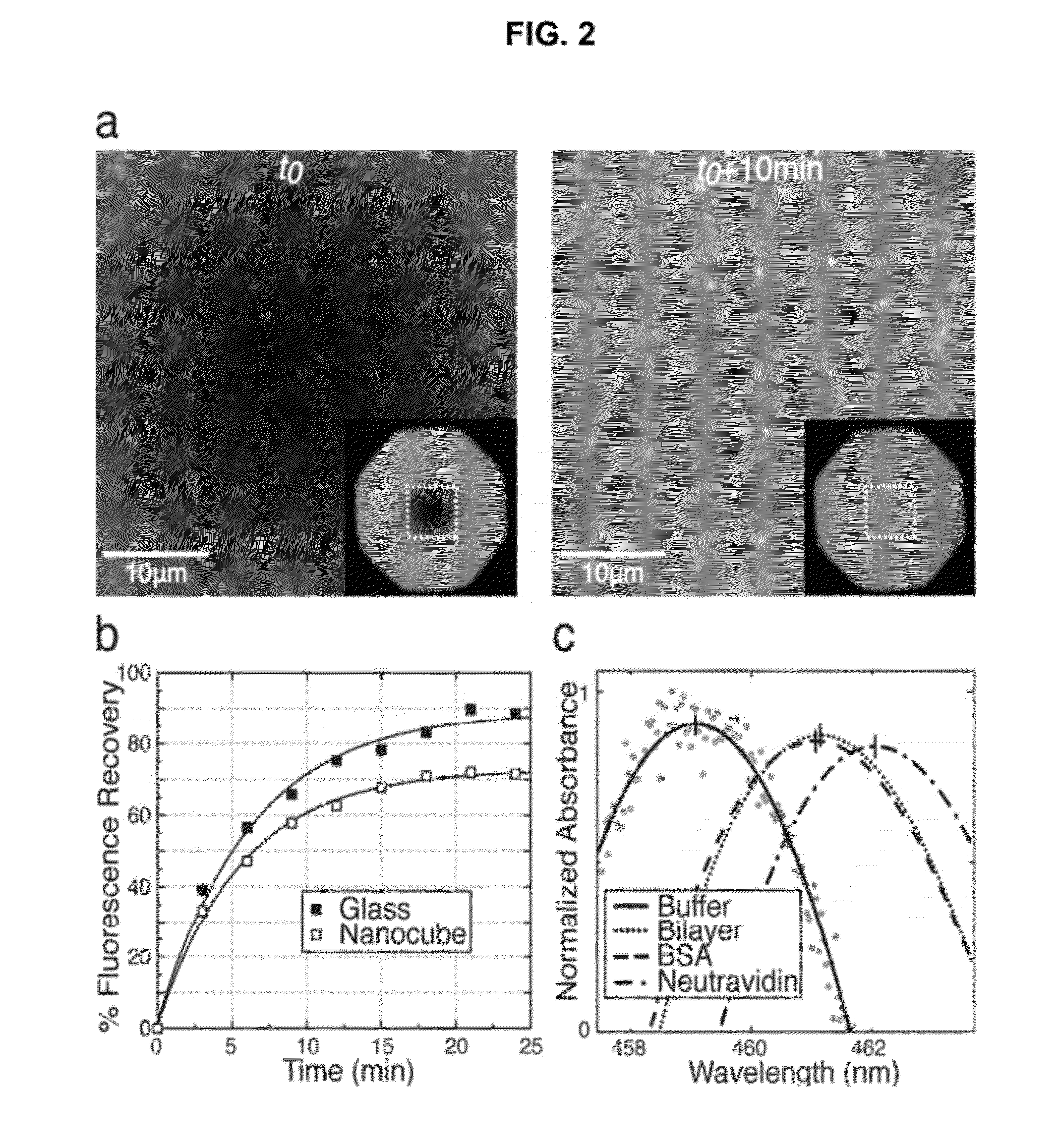
Plasmonic System for Detecting Binding of Biological Molecules
InactiveUS20120208174A1Simplicity of fabricationEasy to parallelizeMicrobiological testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsProtein insertionNanoparticle
Detection and characterization of molecular interactions on membrane surfaces is important to biological and pharmacological research. In one embodiment, silver nanocubes interfaced with glass-supported model membranes form a label-free sensor that measures protein binding to the membrane. The present device and technique utilizes plasmon resonance scattering of nanoparticles, which are chemically coupled to the membrane. In contrast to other plasmonic sensing techniques, this method features simple, solution-based device fabrication and readout. Static and dynamic protein / membrane binding are monitored and quantified.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of catalytic resonance scattering spectral determination of mercury by using aptamer modified nanogold
InactiveCN101726473AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityPreparing sample for investigationScattering properties measurementsHigh concentrationAnalysis data
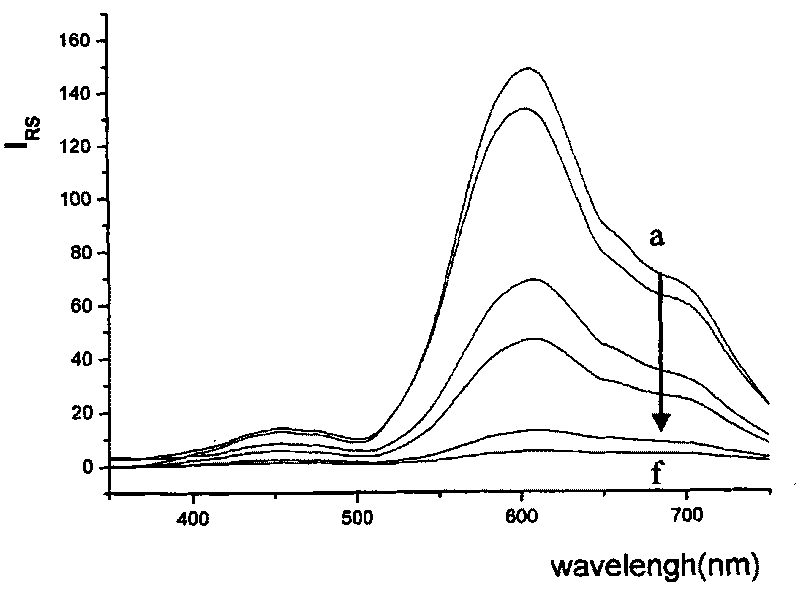
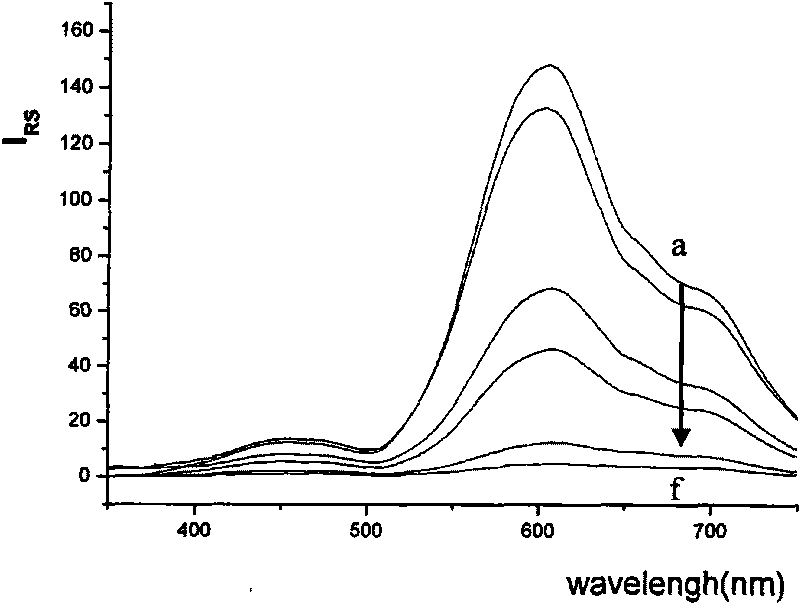
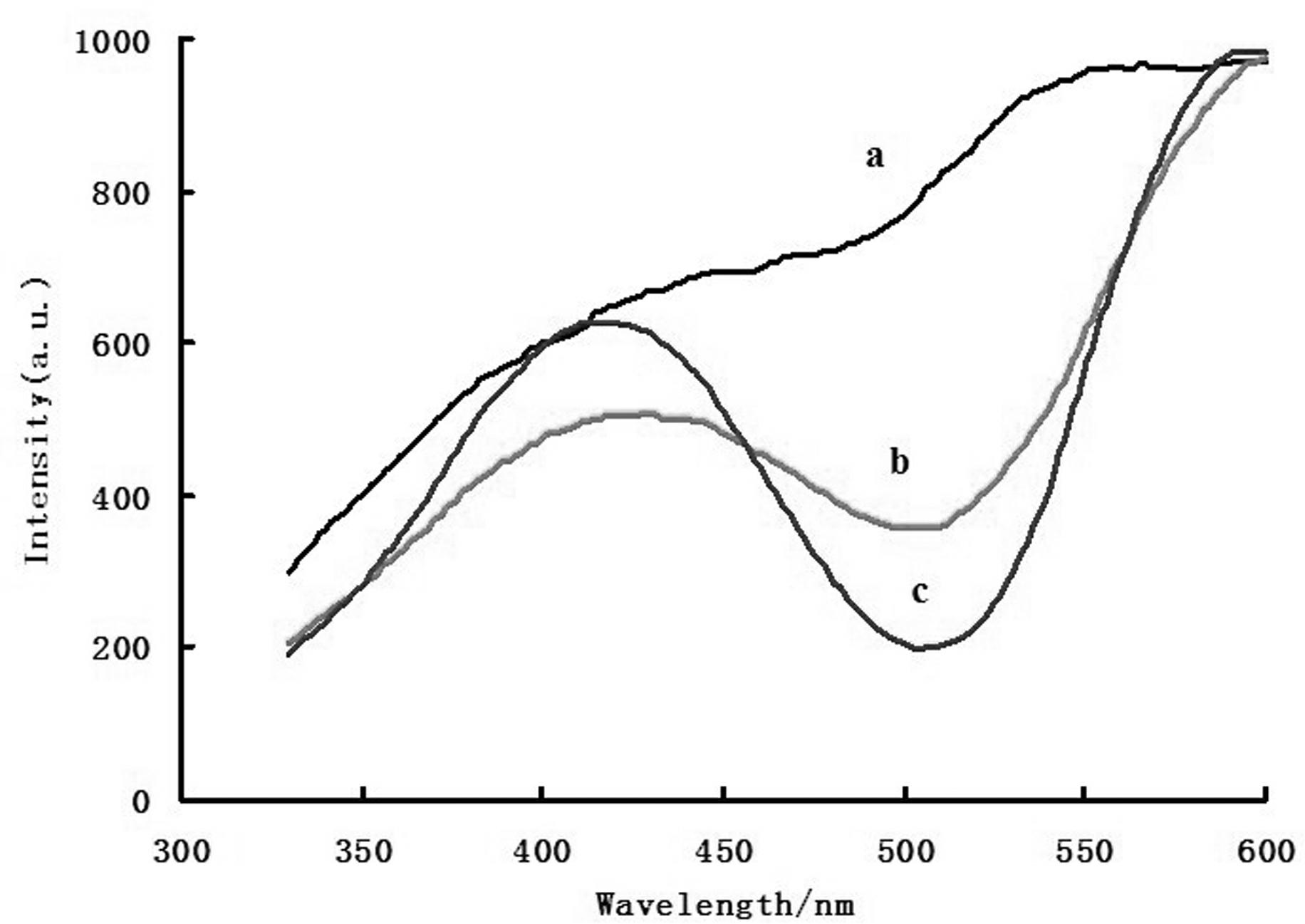
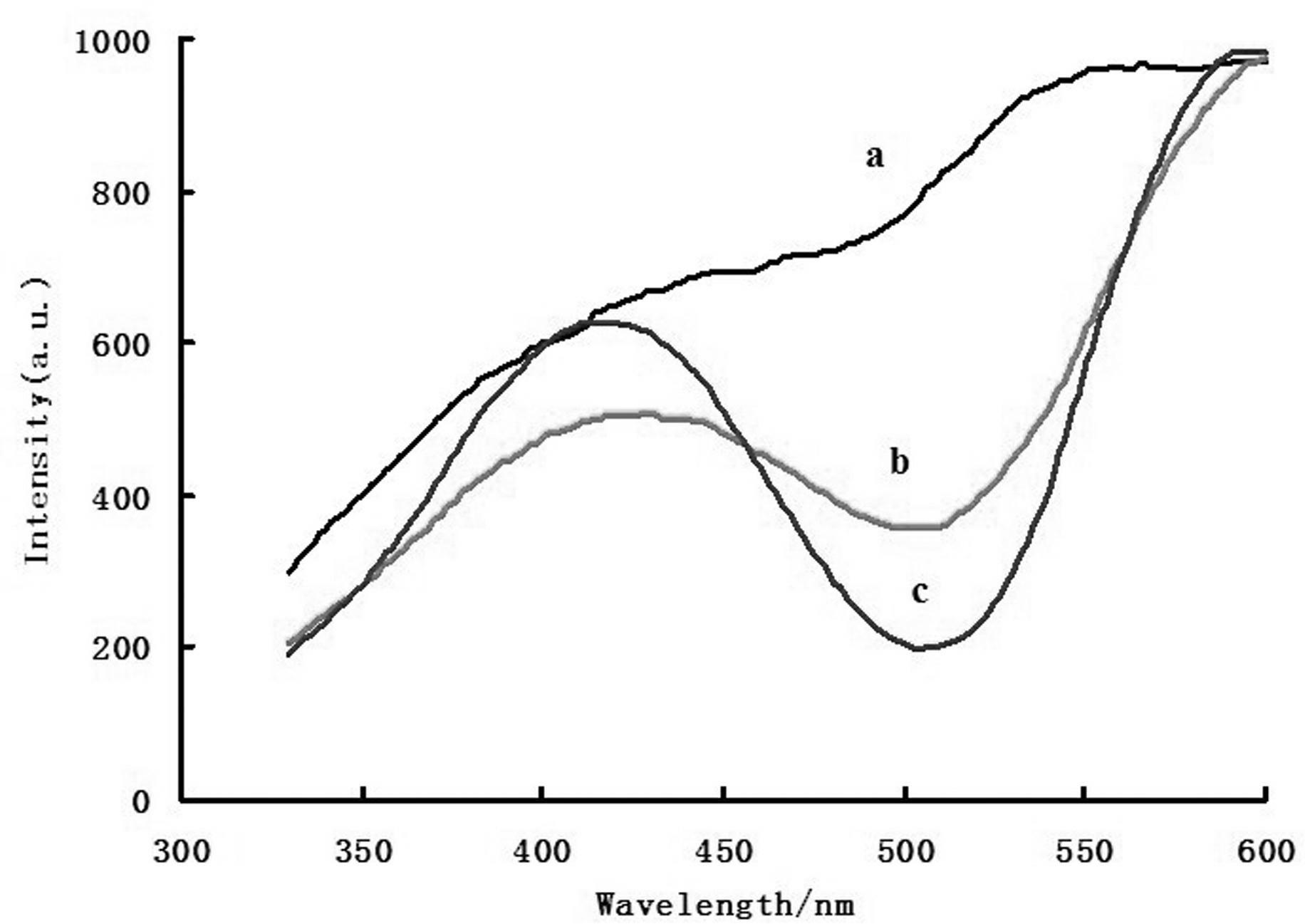
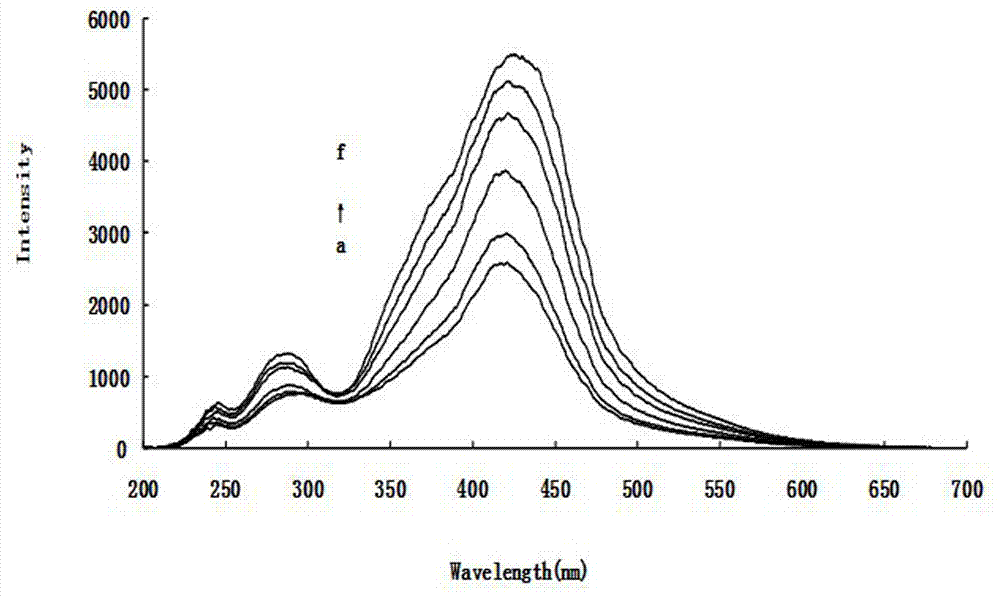
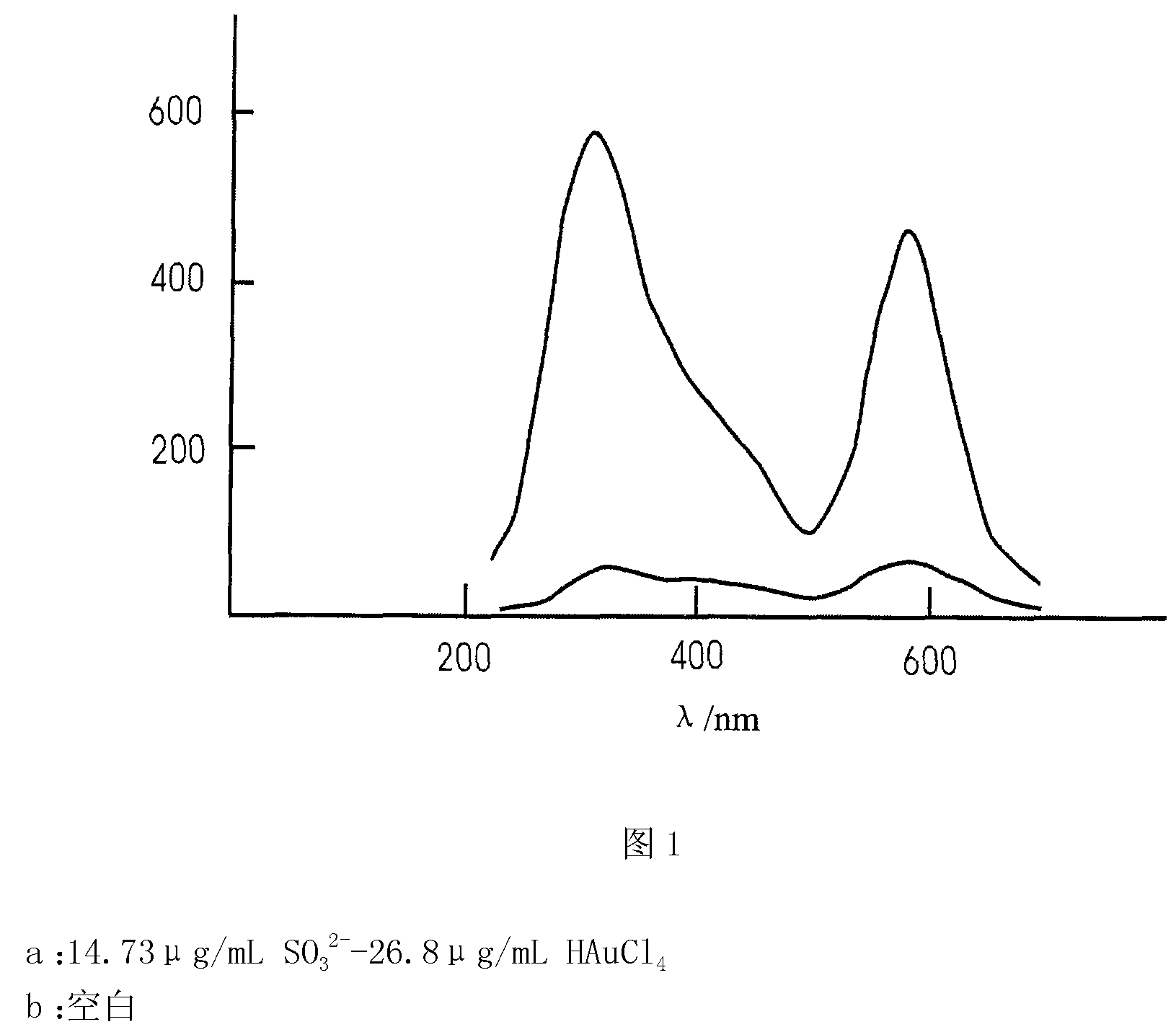
The invention discloses a method of catalytic resonance scattering spectral determination of mercury by using aptamer modified nanogold, which comprises the following steps: Hg2+ aptamer ssDNA and nanogold are combined to form nanogold AussDNA modified by DNA, stable Hg2+aptamer-Hg2+compound is generated by T-T mismatching when Hg2+ and AussDNA coexist, nanogold is gathered under the action of high-concentration NaCl, redundant AussDNA in filtrate after membrane filtration is taken as a nano catalytic seed crystal to catalyze the reaction of Cu2+ and furfural so as to reduce Cu2+ into Cu+, Cu+ reacts with OH- in solution to generate CuOH, and finally generate Cu2O particles. From the above preparation method, a determined system and a reagent blank system of mercury concentration can be known, resonance scattering strength of the two systems are measured at the 605nm part, drawn into a standard curve, and then prepared into a sample detection system, a deltaI sample is solved, the mercury content in the sample is calculated on the standard curve. The invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity, wide determination range, simple equipment, and convenient operation, is suitable for determining various samples containing mercury, and provides reliable analysis data for environment monitoring, foods, cosmetics and other fields.From the above method, a determined system and a reagent blank system of which the mercury concentration is known can be prepared, resonance scattering strength of the two systems are measured at the 605nm part and drawn into a standard curve, and then a sample detection system is prepared, delta I sample is calculated, the mercury content in the sample is calculated by the standard curve.The invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity, wide determination range, simple equipment, and convenient operation, and is suitable for determining various samples containing mercury.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Method for measuring trace Hg2+ by using aptamer modified nano gold rhenium catalysis-tellurium particle resonance scattering spectrum
InactiveCN101776608ASimple and fast operationHigh sensitivityAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh concentrationRhenium
The invention discloses a method for detecting trace Hg2+ by using aptamer modified nano gold rhenium catalysis-tellurium particle resonance scattering spectrum. T-T mismatch in an ssDNA sequence can be stabilized by using Hg2+ so that the ssDNA cannot stabilize AuRe composite nano particles and the AuRe composite nano particles are gathered under the high-concentration electrolyte condition, and the phenomenon and a nano gold rhenium catalysis reaction are organically combined; and the tellurium particles generated by the catalytic reaction have resonance scattering; and the Hg2+ and the resonance scattering strength are in linear relation. A test system with known mercury concentration and a reagent vacant system are first prepared during the measurement; the resonance scattering strength with wavelengths of 734nm of the two systems are measured; a working curve is drawn; then, a sample detection system is prepared; a delta I sample is obtained; and the content of the mercury in the sample is calculated according to the working curve. Compared with the conventional method, the detection method of the invention has the advantages of simple instrument, simple and convenient operation, high sensitivity, good selectivity and easily reached reaction condition; the nucleic aptamer and the Hg2+ solution used in the method have low concentrations, little reagent is used, and the cost is low.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
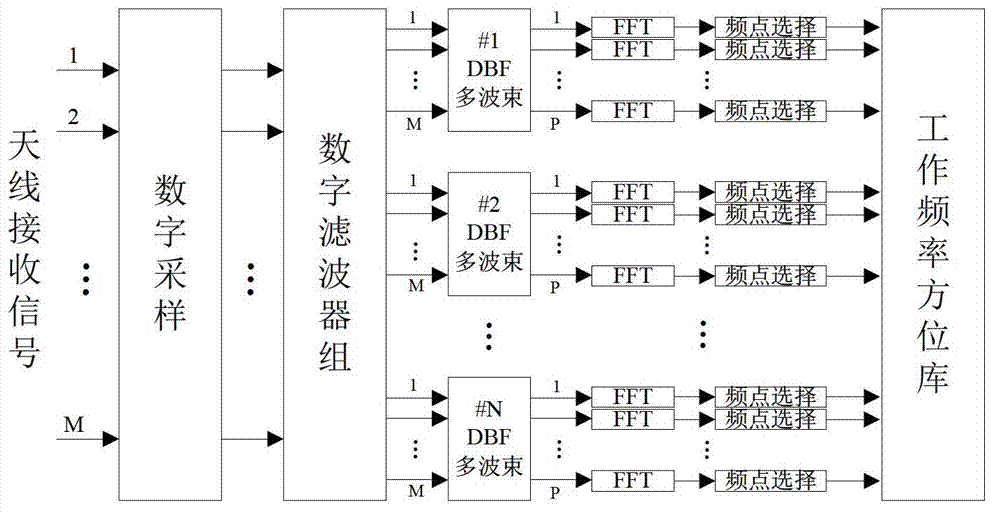
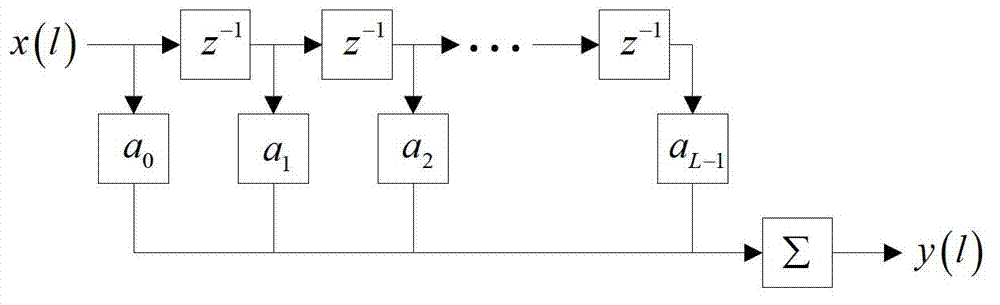
Metrewave radar self-adaption frequency selection method based on spatial filtering
ActiveCN103033797AEasy to detectImprove real-time performanceWave based measurement systemsFrequency spectrumElectromagnetic environment
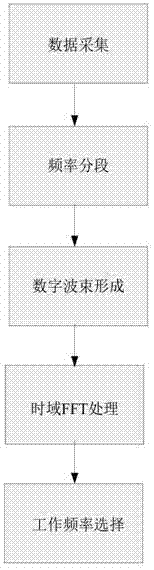
The invention relates to a metrewave radar self-adaption frequency selection method based on spatial filtering. The metrewave radar self-adaption frequency selection method based on the spatial filtering carries out frequency subsection, digital beam formation and time domain fast fourier transform (FFT) algorithm process on metrewave radar according to the character that a metrewave radar similarly has a low-frequency stage, finally creates an optimum working frequency base through frequency spectrum comparison, and selects working frequency according to different requirements of users. The metrewave radar self-adaption frequency selection method based on the spatial filtering adopts a process procedure which is not preset with an optimum working frequency band, carries out demodulator band filter (DBF) spatial filtering process on data of all frequency bands, meanwhile takes the character that resonance scattering of a conventional target occurs in a metrewave frequency band into consideration, about criterions, selection of working frequency is carried out by creating the optimum working frequency base and combining the optimum working frequency base and a resonant frequency data base instead of using a criterion that output average power is minimum, and therefore the best detection performance of the metrewave radar is ensured. The metrewave radar self-adaption frequency selection method based on the spatial filtering is applicable to self-adaption and resisting external disturbance of the metrewave radar under complex electromagnetic environment.
Owner:CNGC INST NO 206 OF CHINA ARMS IND GRP
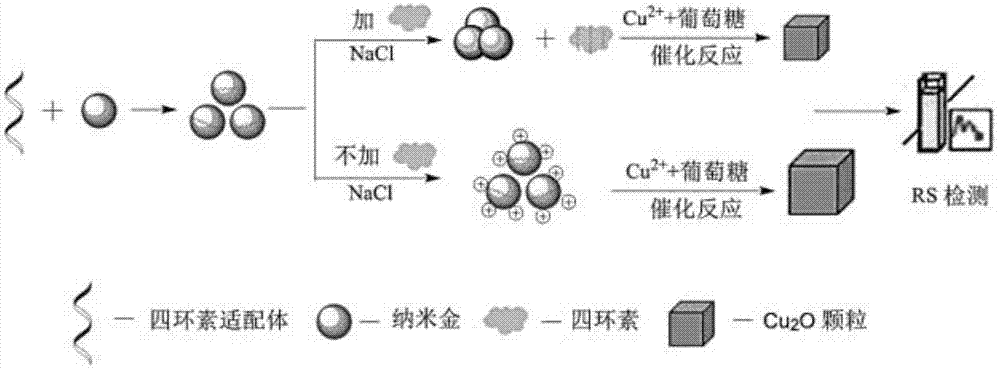
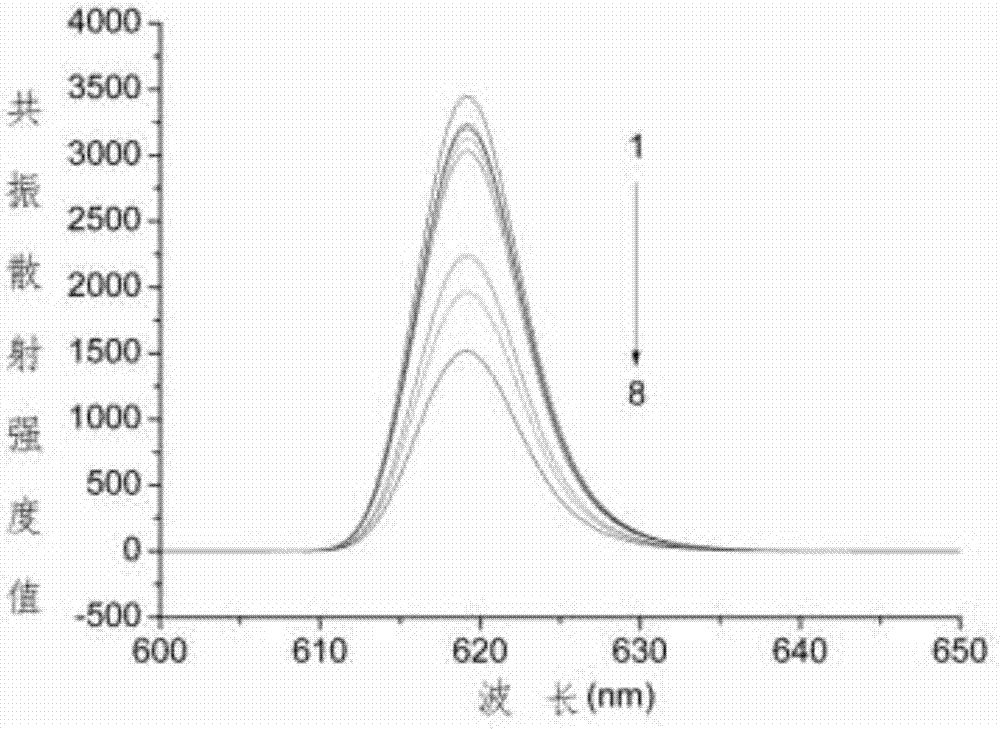
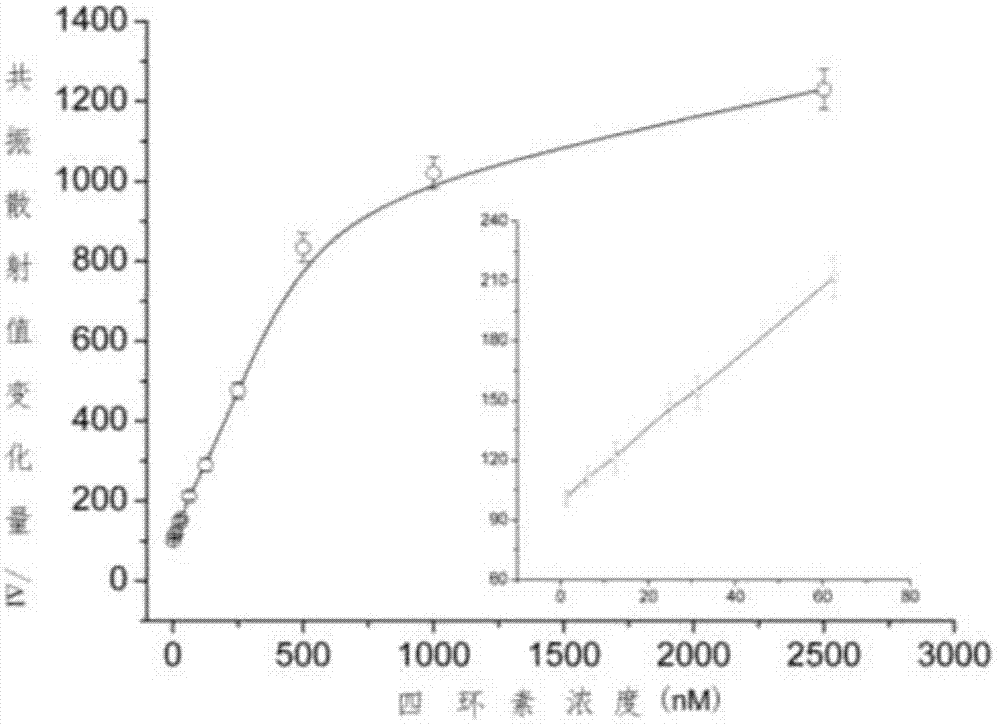
Resonance scattering spectral detection method for tetracycline based on nano-gold catalysis
ActiveCN103196875AHigh detection sensitivityGood choiceFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescencePotassium sodium tartrate
The invention provides a resonance scattering spectral detection method for tetracycline based on nano-gold catalysis. The method comprises the following steps: constructing detection systems containing tetracycline with known concentration; carrying out resonance scattering spectral signal scanning by using a fluorophotometer so as to obtain a resonance scattering signal variable standard curve; respectively adding a to-be-detected object and ultrapure water, i.e., a control sample, into a mixed liquor containing a tetracycline aptamer and nano-gold, and adding a sodium chloride solution for an agglomeration reaction; and carrying out mixing with a solution containing copper sulfate, sodium hydroxide and potassium sodium tartrate and carrying out resonance scattering spectral signal scanning by using the fluorophotometer to obtain a resonance scattering signal variable curve so as to obtain the concentration of tetracycline in the to-be-detected object. The detection method provided by the invention overcomes the defects that a nucleic acid aptamer needs modification, a detection line is non-ideal and the like and has the advantages of sensitivity, good selectivity, low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
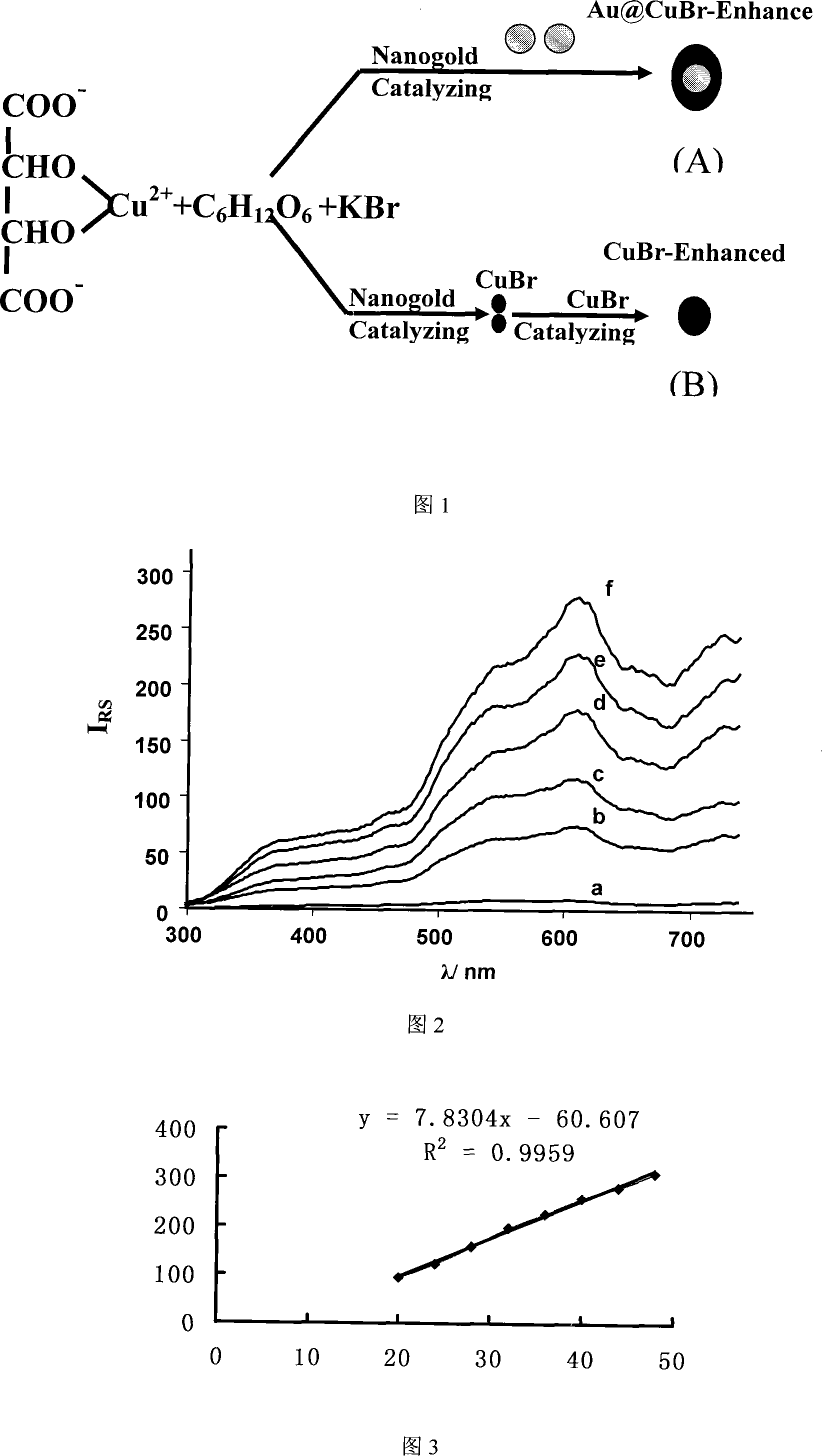
Nano gold catalysis resonance scattering spectrometry for measuring grape-sugar
InactiveCN101226151AHigh sensitivityLow detection limitScattering properties measurementsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionLinear relationshipMicroparticle
The invention discloses a nanometer gold catalysis resonance scattering spectrum method for testing amylaceum, which is based on the catalysis of nanometer gold on the copper bromide particles generated by Cu(II)-amylaceum-KBr, and the linear relationship between amylaceum in some density and delta I610nm. The invention has the advantages that compared with prior art, the invention combines catalysis reaction with resonance scattering spectrum technique, with high analysis sensitivity, low check limit, ug / mL level, better selectivity, simple operation, simple device, easily accessible agents and low cost, which only needs fluorescence spectrometer.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Resonance scattering spectrometry for measuring ammonia nitrogen in water rapidly
InactiveCN101551328AThe instrument is simpleSimple and fast operationScattering properties measurementsAmmonium MuriateUltimate tensile strength
The present invention discloses a resonance scattering spectrometry for measuring ammonia nitrogen in water rapidly, the measurement steps is that 1. a standard system of ammonium muriate is prepared, and a scattering intensity I is mensurated at a point of 447m; 2. a blank system without ammonium muriate is prepared, and a scattering intensity I0 is mensurated; 3. calculation of Delta I447m = I-I0; 4. a working curve is made according to the concentration relation of the Delta I447m to the ammonium muriate; 5. a detection system is prepared by adding a measuring object containing ammonium muriate with ignorance concentration, and Delta I447M of the measuring system is obtained; 6. according to the working curve, the ammonium muriate concentration of the measuring object is calculated. Comparing with the existing method, the instrument of the method of the invention is simple, operation is easy, reagent is obtained easily, sensitivity is high, measurement range is wide, and cost is low.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
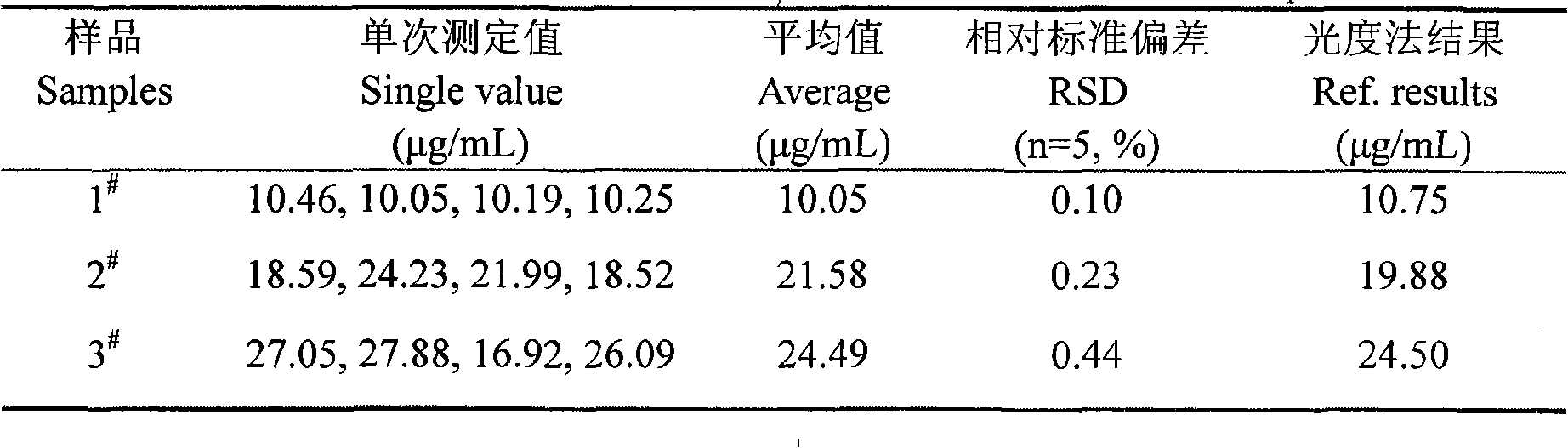
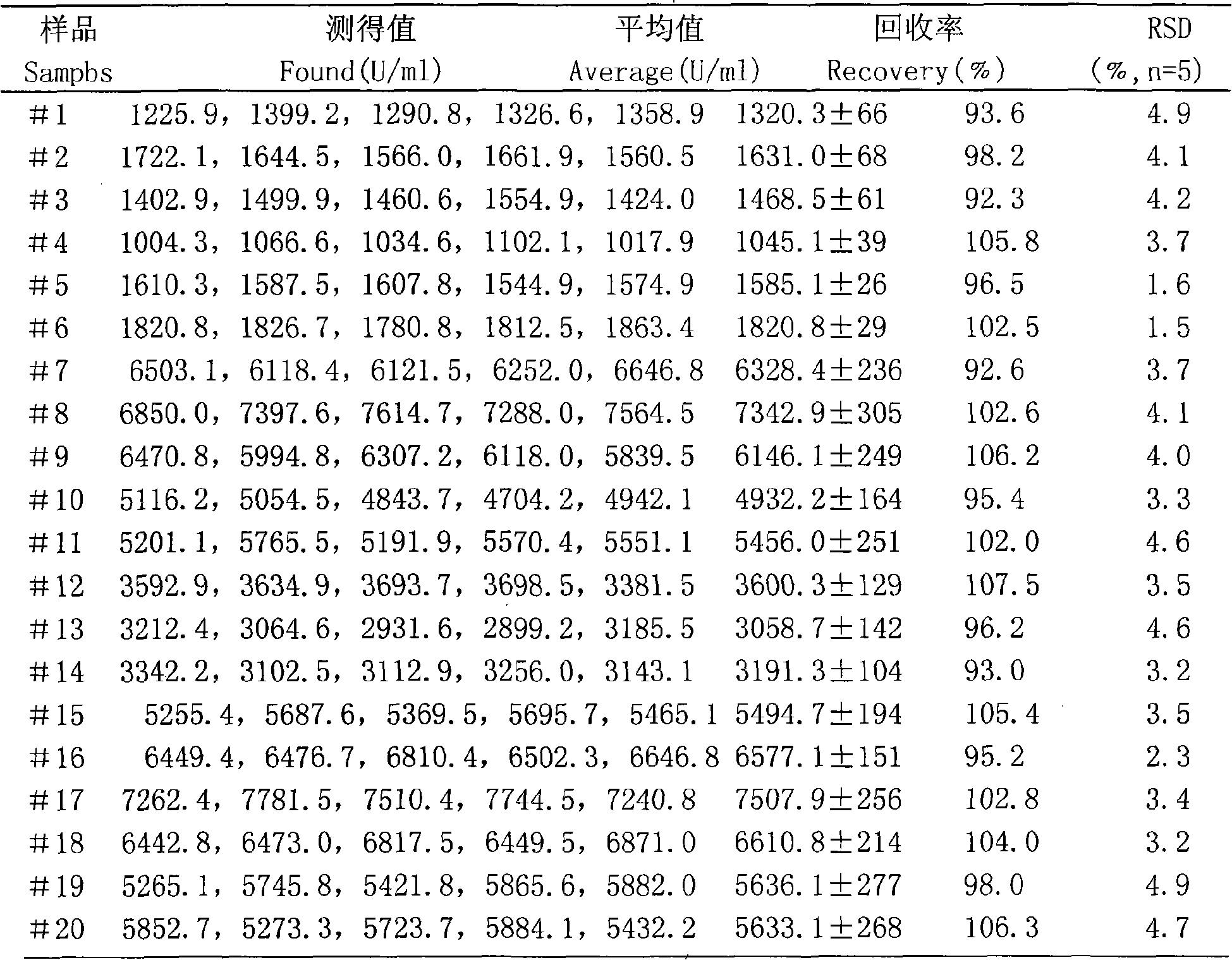
Method for determining activity of endotrypsin A
InactiveCN102590167ALow detection limitHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceChaffSpectrofluorometer
The invention discloses a method for determining the activity of endotrypsin A, belonging to the field of fermentation engineering. The invention relates to a novel method for determining the activity of the endotrypsin A by using a resonance light scattering technology. According to the method, trichloroacetic acid and trace amount of protein can form associated-particles; according to the principle that the concentration of micro particles and the resonance scattering light intensity form a a proportional relationship under certain conditions, the trichloroacetic acid is associated with protein in a solution before and after the endotrypsin A reacts with casein protein; the light intensity of the protein is determined by using a fluorospectro photometer; and the activity of the endotrypsin A is obtained according to the degradation amount of casein. The method has the advantages of low detection limit, favorable sensitivity, high stability, wide linear range, little influence from a chaff interference, quickness, simpleness and convenience, low detection cost and greater potential; and the requirements for determining the activity of trace amount of endotrypsin A in fermentation broth and beer can be met and reliable base for deeply researching the endotrypsin A is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for rapidly determining nitrite in water through nanogold resonance scattering spectrometry
InactiveCN102435587AThe instrument is simpleSimple and fast operationPreparing sample for investigationScattering properties measurementsNitriteControl system
The invention discloses a method for rapidly determining nitrite in water through a nanogold resonance scattering spectrometry, which comprises the following determination steps: 1, preparing an analysis solution of known-concentration nitrite, and determining the resonance scattering intensity of the analysis solution to be I at the point of 510 nm; 2, preparing a blank control system without the nitrite, and determining the resonance scattering intensity of the blank control system to be I0; 3, calculating delta I = I0-I; 4, making a work curve by delta I to the concentration C of the nitrite; 5, preparing an analysis solution of a sample to be determined, determining the resonance scattering intensity of the analysis solution to be I, and calculating delta I=I0-I; and 6, calculating the concentration of the nitrite in the determined sample according to working curve. Compared with the existing method, the determination method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the instruments are simple and easy to operate, and reagents are easy to obtain and have high sensitivity, good selectivity and low cost.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
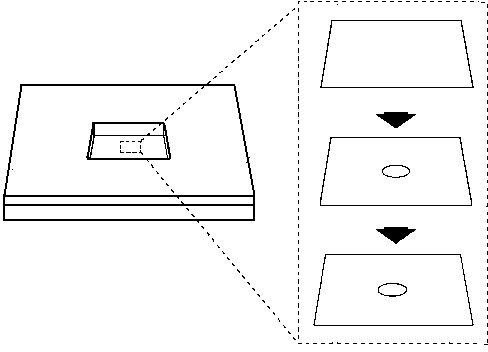
Preparation method of nanopore chip with plasmon resonance scattering response function
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nanopore chip with a plasmon resonance scattering response function. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a chip substrate: selecting a silicon chip as a substrate, and depositing an insulating material on the front surface of the silicon chip, without the insulating material on the back surface; (2) etching a square area on the back surface of the silicon chip by a wet etching method until a nanopore chip film is exposed on the back surface; (3) etching nanopores: forming the nanopores on the nanopore chip film by using a focused ion beam or a focused electron beam to bomb the nanopore chip film; (4) modifying noble metal: coating a noble metal layer on the surface of the nanopore chip film by using a magnetron sputtering instrument. The preparation method is simple in steps; the prepared nanopore chip is controllable in size and relatively low in cost; through noble metal modification on the nanopores, the nanopore chip with a photoelectric response function is prepared; the nanopore chip can cause a plasmon resonance coupling phenomenon so as to amplify a spectral signal, and can be applied to many fields such as electrochemical detection of the nanopores.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Device for detecting biological chips based on resonance light scattering
InactiveCN103115901AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh detection sensitivityAnalysis by material excitationAngle of incidenceOpto electronic
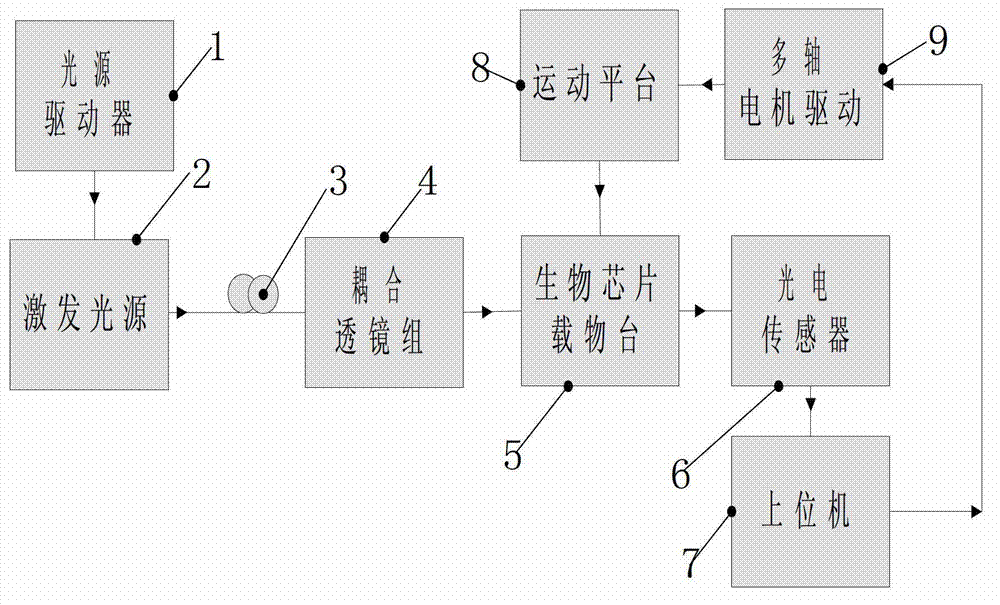
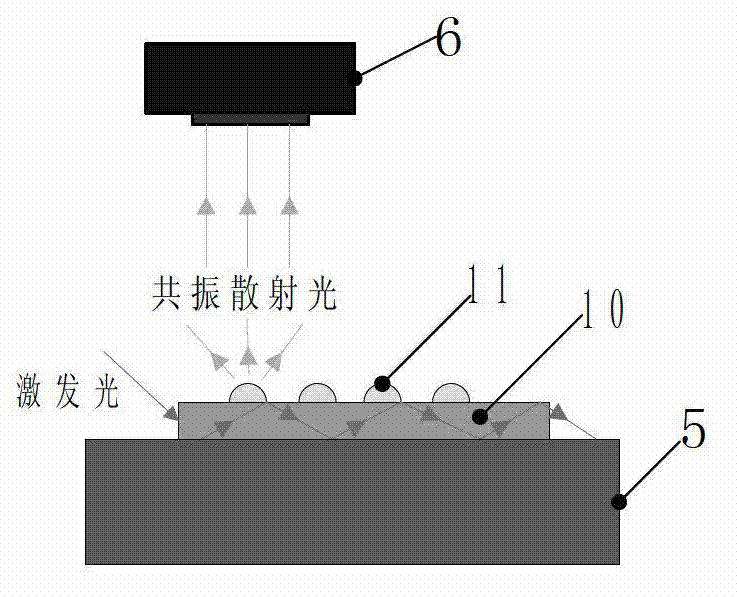
The invention discloses a device for detecting biological chips based on resonance light scattering, which comprises a light source driver, an optical fiber, an excitation light source, a coupling lens group, a biological chip objective table, a photoelectric sensor, an upper computer, a motion platform and a multi-axle motor drive, wherein the light source driver controls the excitation light source to generate excitation light; the excitation light is outputted to the coupling lens group through the optical fiber, subjected to beam shaping, and transmitted to the biological chip objective table, and the excitation light is transmitted from the side edge of a biological chip under the condition that an angle of incidence is greater than a critical angle; a sample after being excited by the excitation light produces resonance light scattering, and radiates resonance scattering light with a specific wavelength outwards; the resonance scattering light is transmitted to the inside of the photoelectric sensor; the upper computer receives converted electric signals and carries out acquisition and analysis on the converted electric signals through software of the upper computer, thereby obtaining scanning images; and the software of the upper computer controls the multi-axle motor drive to operate and drives the motion platform to move, in such a way, the biological chip objective table is driven to move, so that the whole point sample area of the biological chip is scanned. The device disclosed by the invention is low in background noises and high in detection sensitivity.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for measuring pipemidic acid by using resonance scattering spectrum
InactiveCN102645422AThe instrument is simpleSimple and fast operationAnalysis by material excitationPipemidic acidSodium acetrizoate
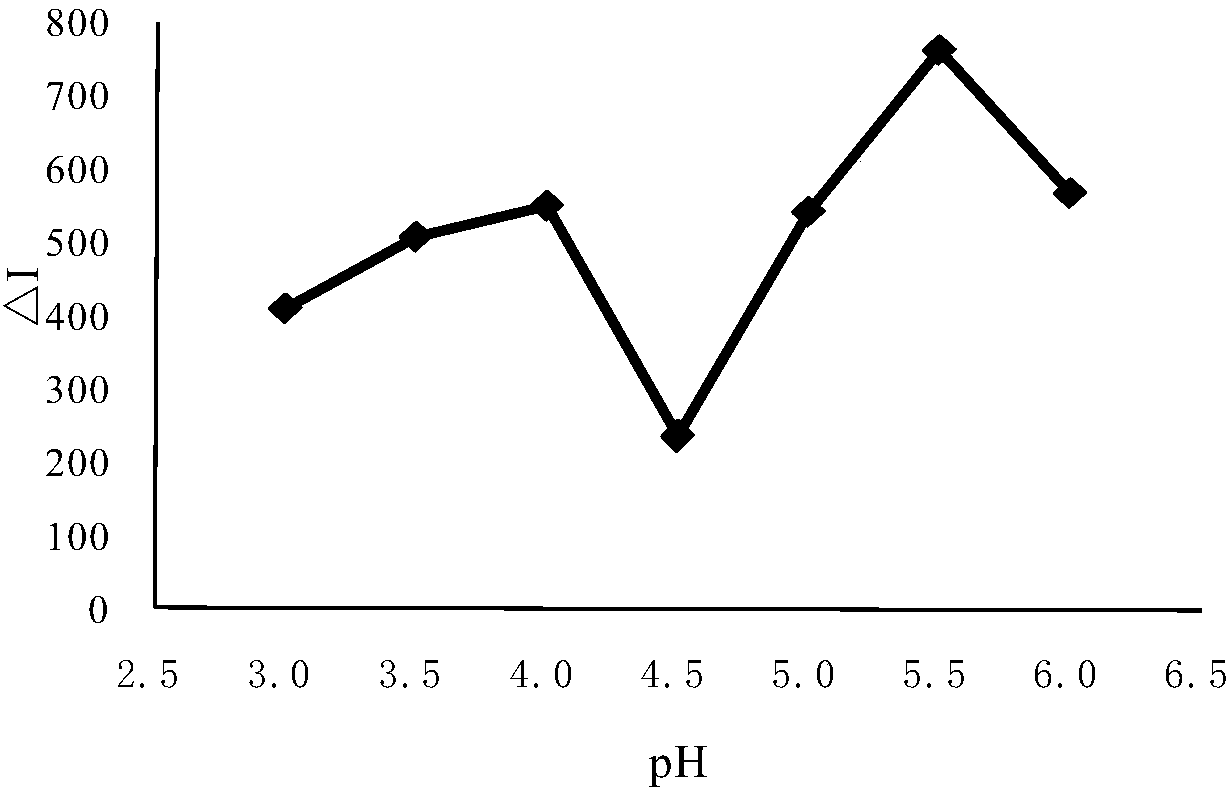
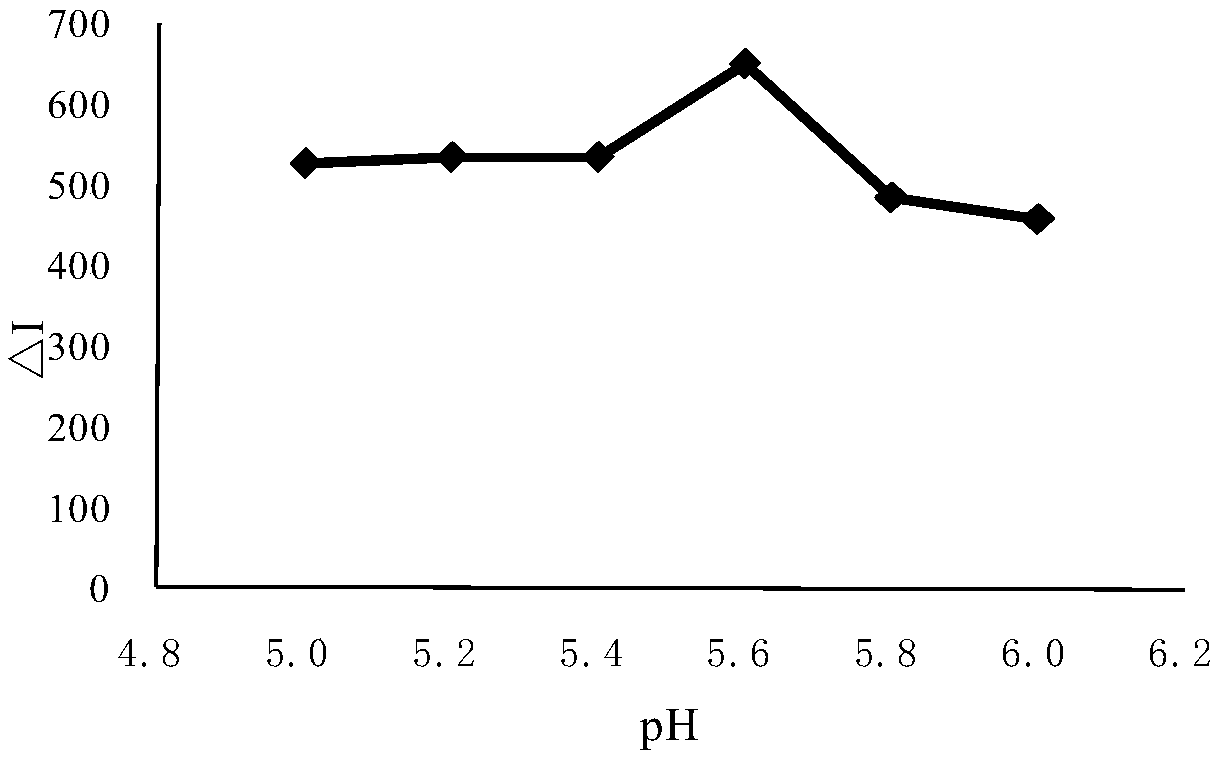
The invention discloses a method for measuring pipemidic acid by using a resonance scattering spectrum. Pipemidic acid and tetraphenylboron sodium react in acetic acid-acetic acid buffer solution with the pH value being 3.6 to form ionic associate particles, wherein the particles generate a resonance scattering spectrum peak at the wavelength being 480nm, and the resonance scattering intensity is linearly related to the concentration of the pipemidic acid so as to provide a new method for measuring the content of the pipemidic acid by using the resonance scattering spectrum. In comparison with the conventional method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple instrument, convenience in operation, rapidness, easily obtained reagent and high sensitivity.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Catalytic reaction-resonance scattering spectroscopic method for detecting trace molybdenum
InactiveCN101576490AConvenient amountReduce dosageScattering properties measurementsNon toxicityControl system
The invention discloses a catalytic reaction-resonance scattering spectroscopic method for detecting trace molybdenum. The method is characterized by including the following steps: (1) preparing a standard molybdenum system; (2) preparing a blank control system; (3) right amount of components are taken to be arranged in a quartz cell and then are put on a fluoro spectrophotometer to be synchronously scanned (lambdaem is equal to lambdaex), the resonance scattering light intensity I540nm of a 540nm part is detected, the blank value of a blank system is I540nmb, and the expression that delta 540nm is equal to 540nm minus I540nmb is calculated; (4) the delta 540nm is used for making the working curve of the concentration relationship of molybdenum; (5) a detection system is prepared according to the method of step one so as to obtain the delta I540nm of a tested object by calculation; and (6) according to the working curve of step four, the concentration of molybdenum of the tested object is calculated. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, favorable selectivity, simple operation, high safety, non-toxicity, low-cost reagent needed, etc.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
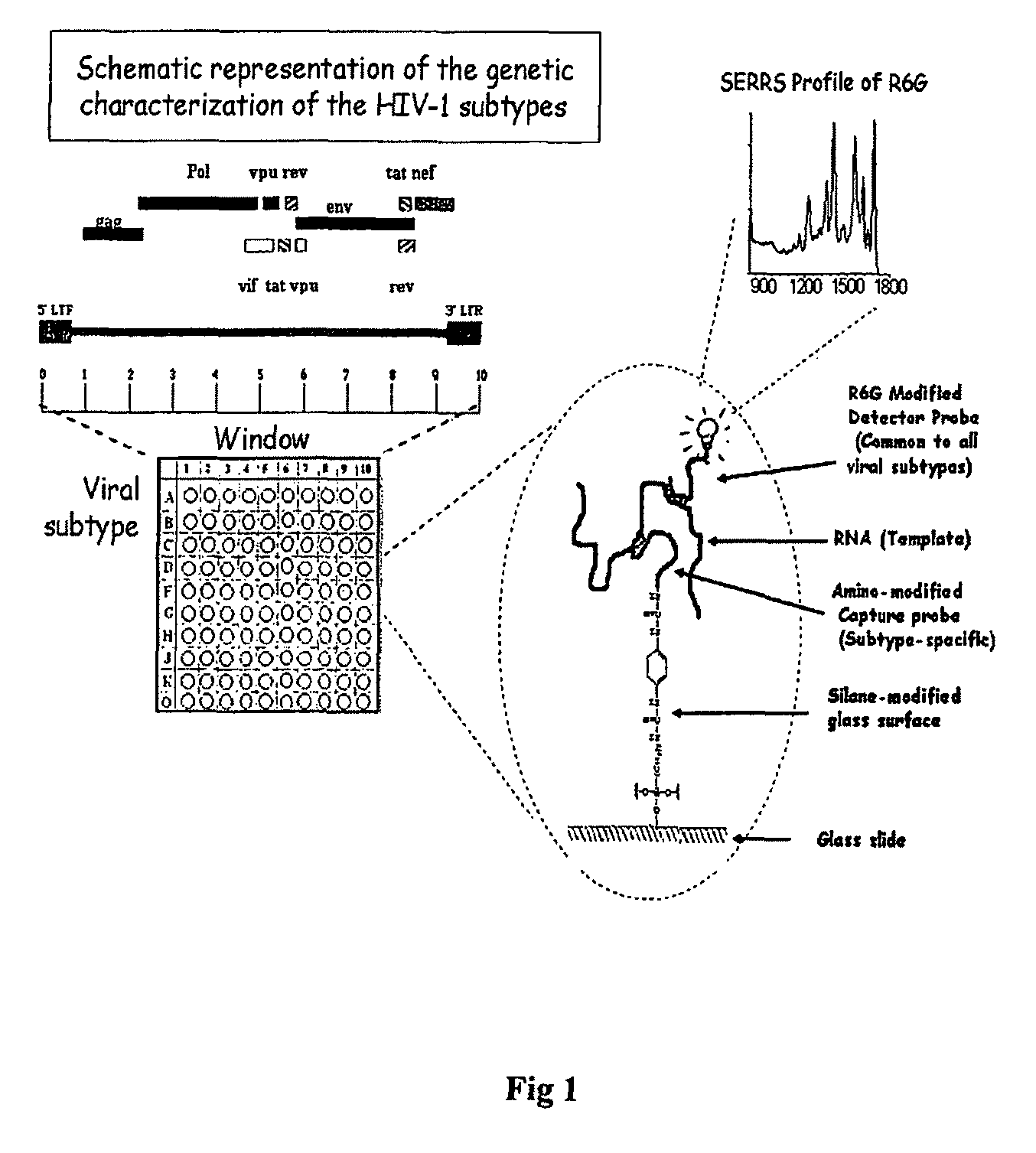
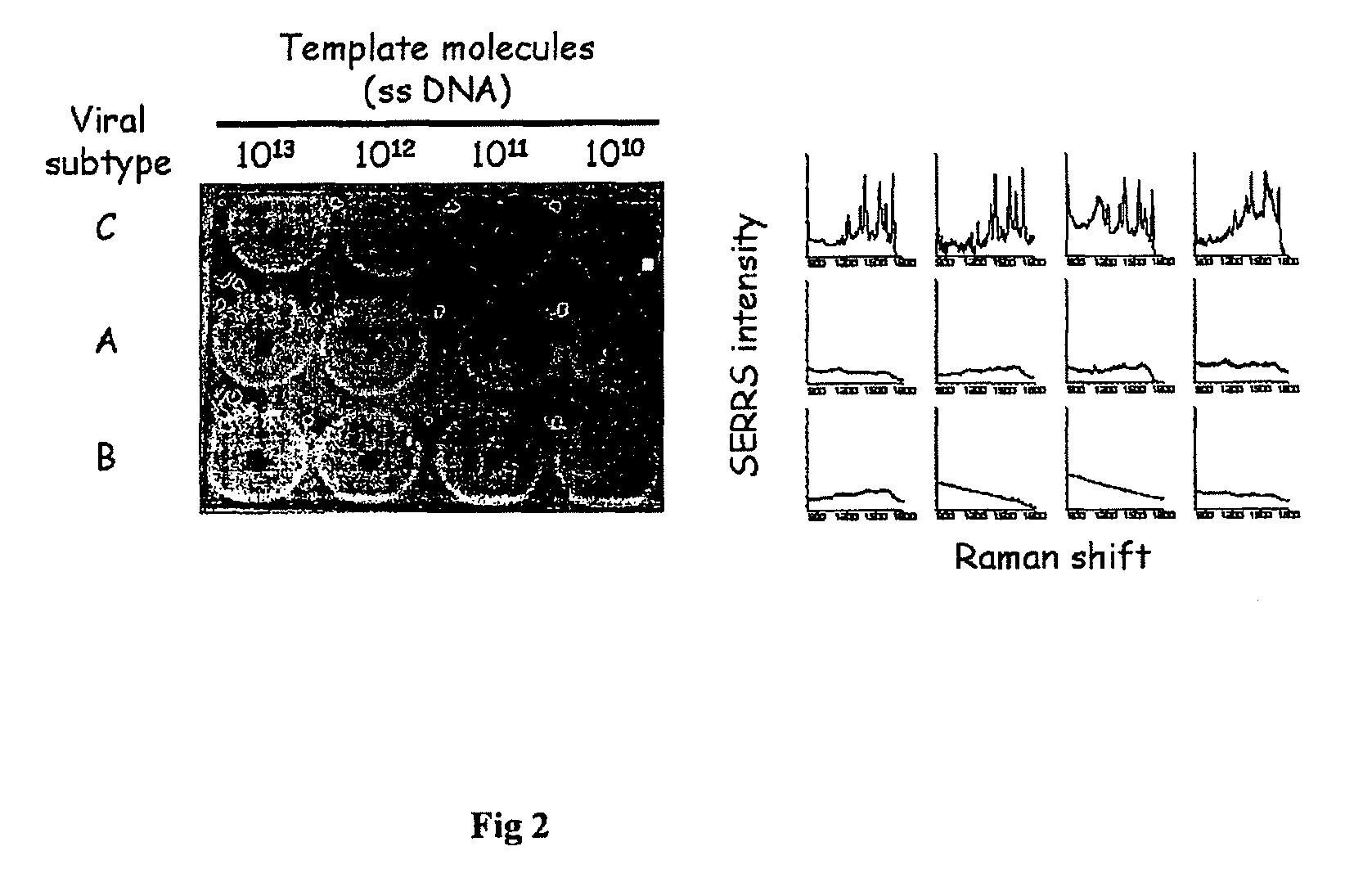
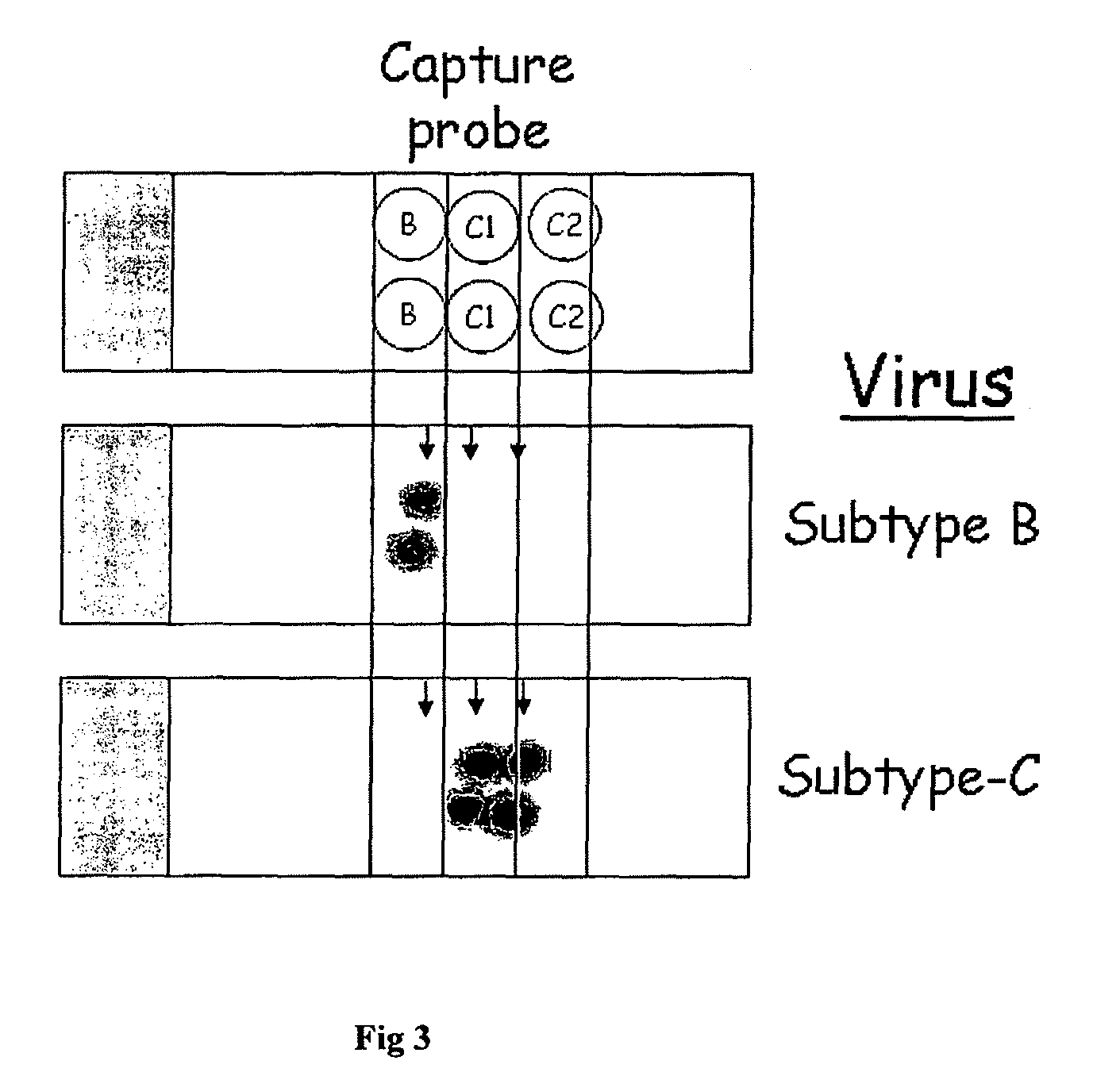
High sensitivity assay for molecular typing of biological sample, probes and a kit thereof
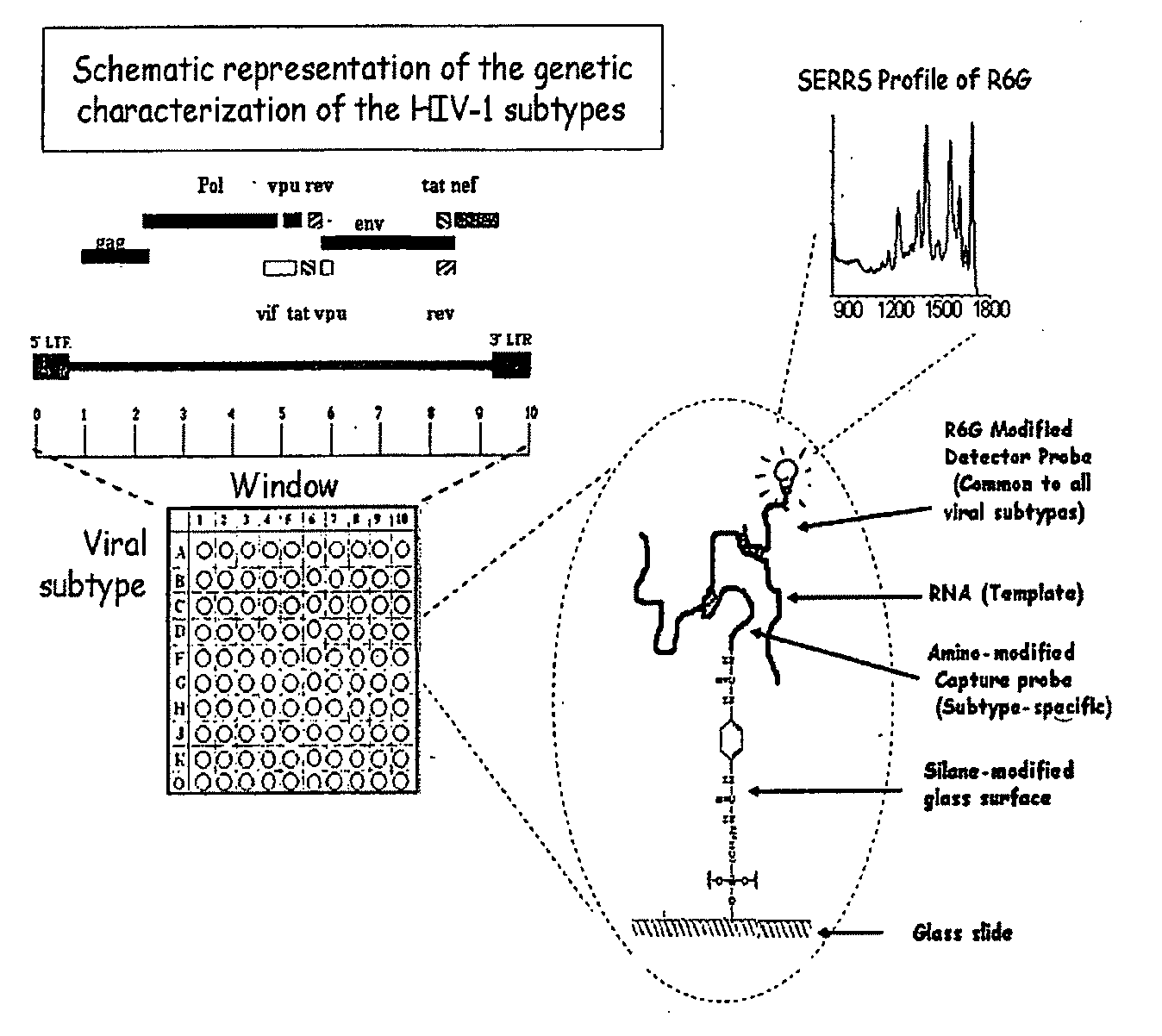
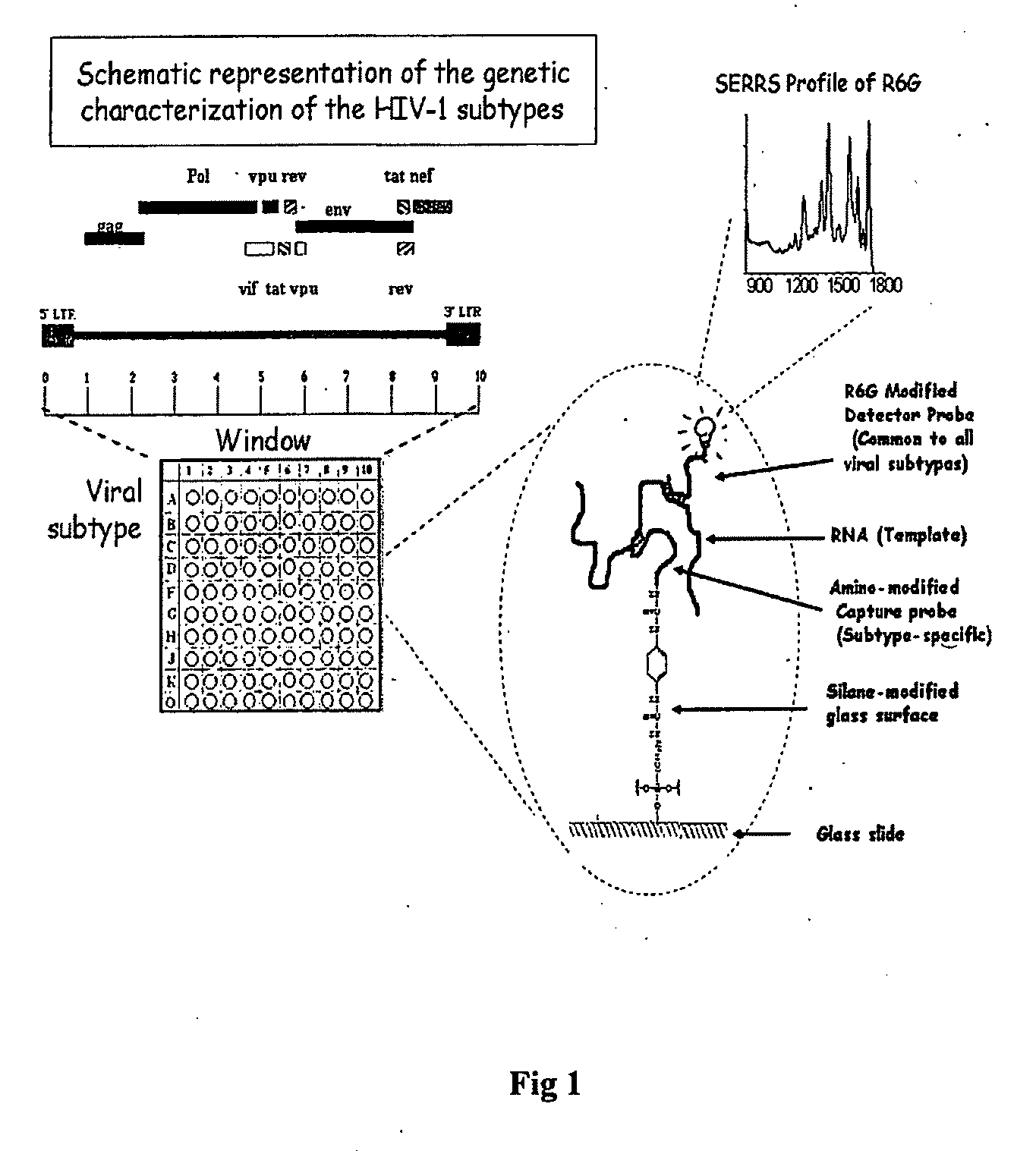
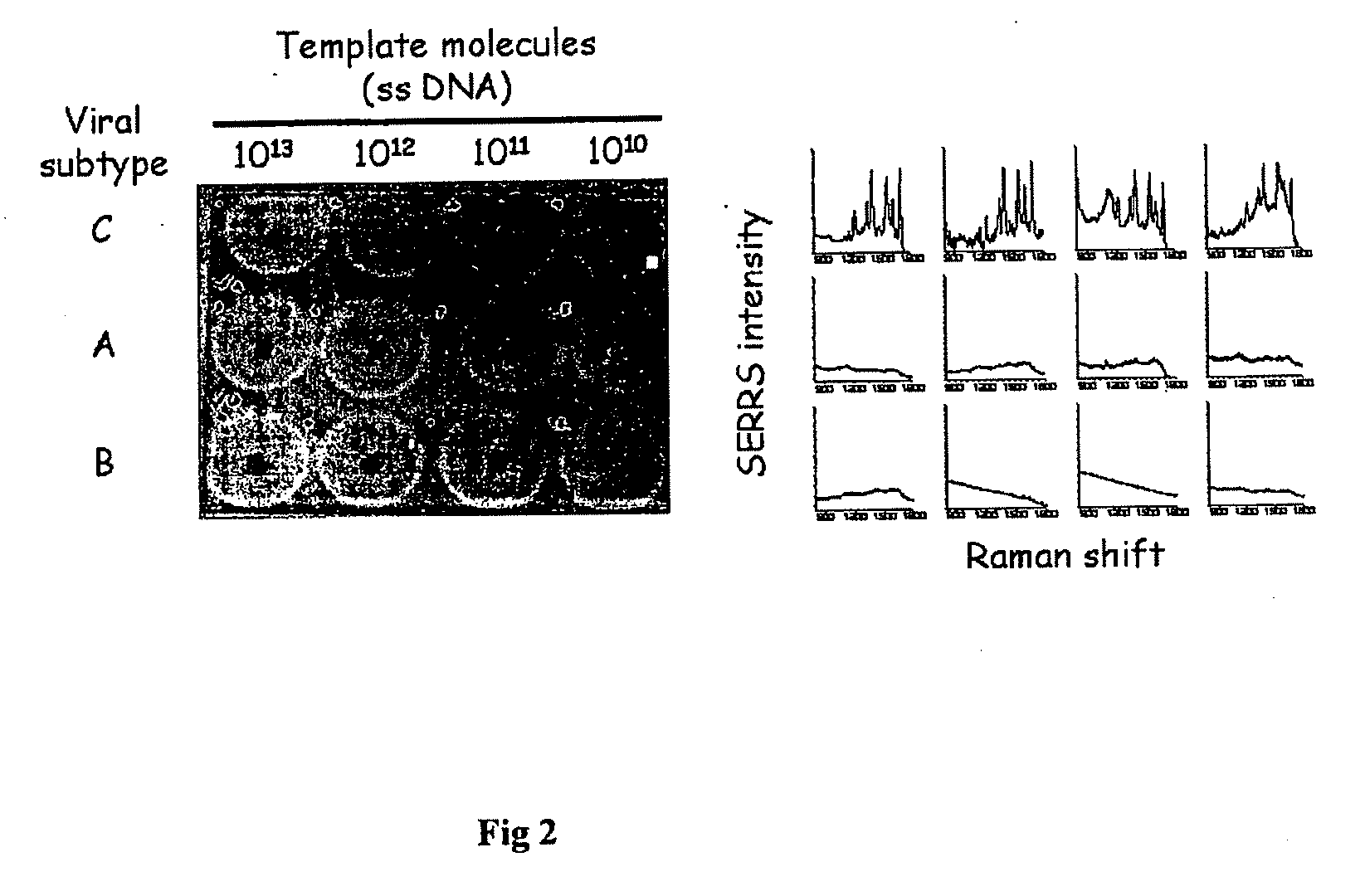
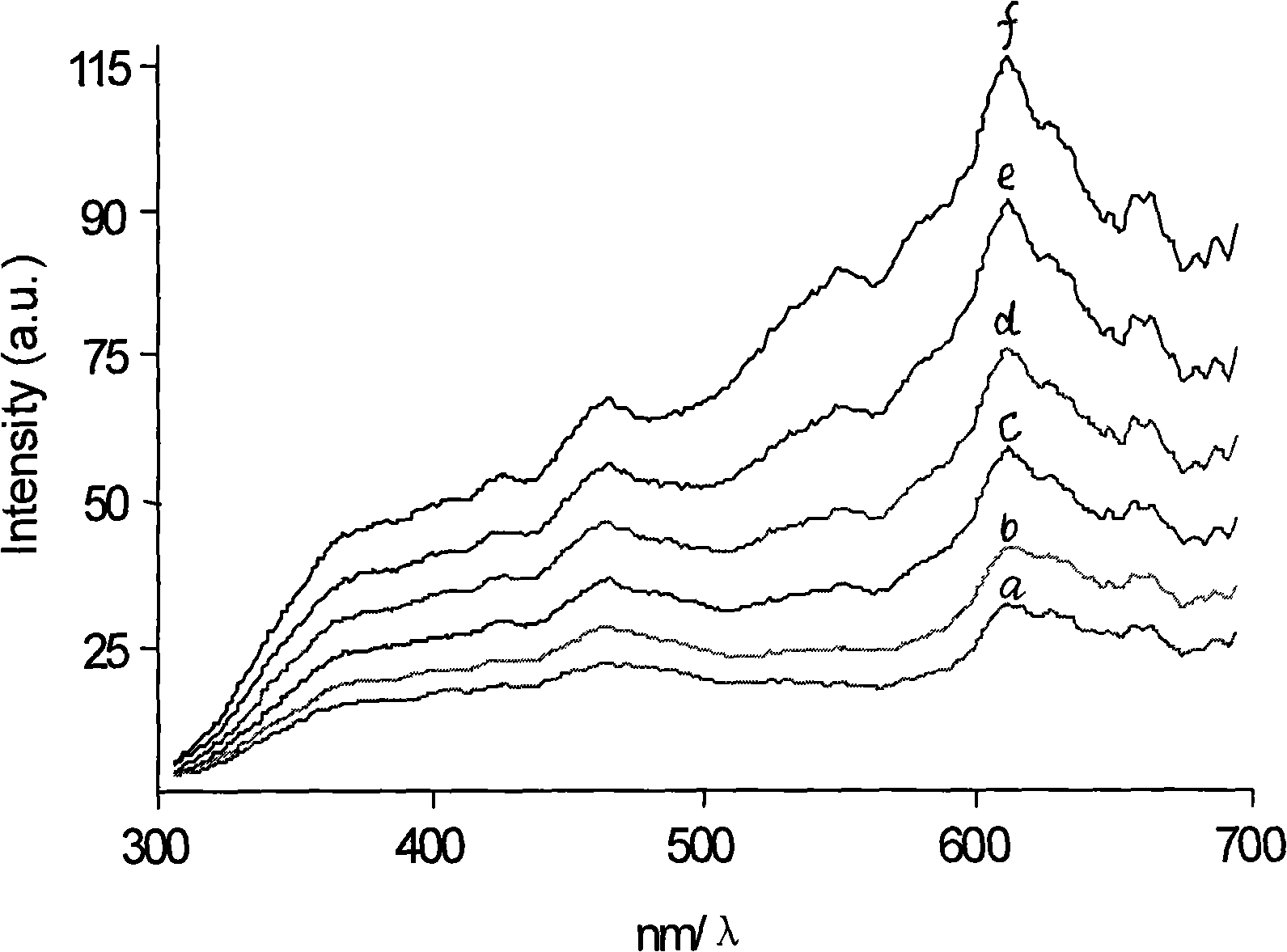
InactiveUS20100028858A1Avoids false-positive/false-negative resultHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayMolecular typing
The present invention relates to a high sensitivity assay for molecular typing of a biological sample using surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) including resonance scattering (SERRS); capture probes for capturing nucleic acid; a detector probe to detect captured nucleic acid; a kit for molecular typing of biological sample using surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) including resonance scattering (SERRS); and lastly a method of manufacturing said kit.
Owner:MICROTEST INNOVATIONS PVT +1
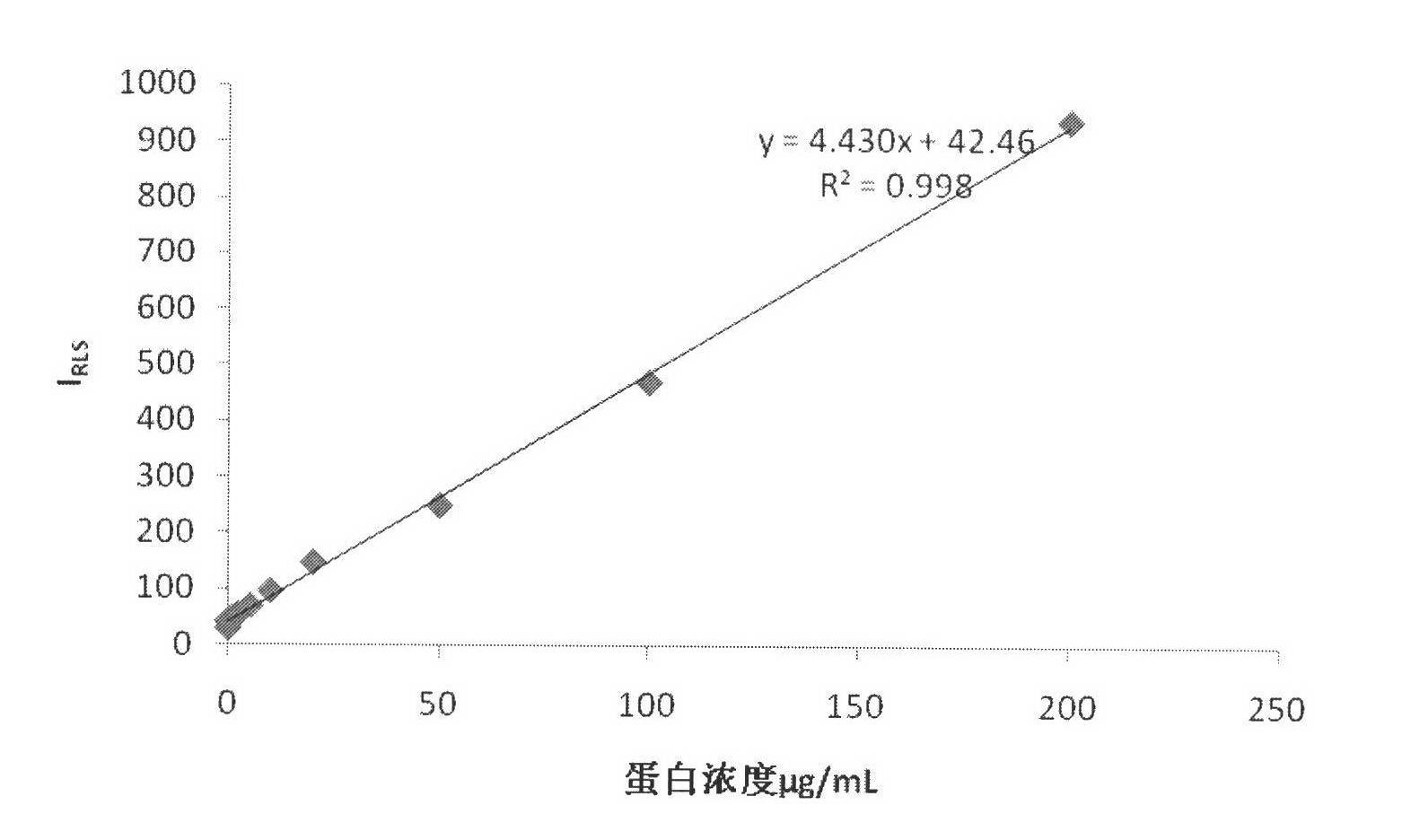
Method for quantitative detection of ultramicro-protein based on principle of biomineralization
InactiveCN102230896ALow equipment requirementsLow costAnalysis by electrical excitationNanosensorsDendrimerMicroparticle
The invention discloses a method for quantitative detection of ultramicro-protein based on the principle of nano gold particle biomineralization, which comprises the following steps: firstly, by taking the first generation of PPIHA dendrimer and chloroauric acid (HAuCl4) as raw materials, preparing nano gold colloid with surface modified by amine by means of a microwave reflux heating method, andcombining the nano gold colloid with to-be-detected protein to form conjugate at a normal temperature; secondly, carrying out biomineralization on the nano gold-protein conjugate in a sodium citrate-chloroauric acid system; and then carrying out resonance scattering spectral analysis on the biomineralization product by using a fluorescence spectrum spectrograph. Because of the linear relation between the peak strength of the resonance scattering spectrum of the product at the characteristic wavelength and the protein concentration, the ultramicro-protein can be quantitatively detected. The method is easy and quick and has high sensitivity, high specificity and high accuracy. In addition, the method has a good portability and can be used for early tumor diagnosis, quick food safety detection, water quality monitoring and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Resonance scattering spectrometry for detecting trace of albumin in human urine
InactiveCN101320044AThe instrument is simpleSimple and fast operationScattering properties measurementsRaman scatteringHorizontal axisSpectroscopy methods
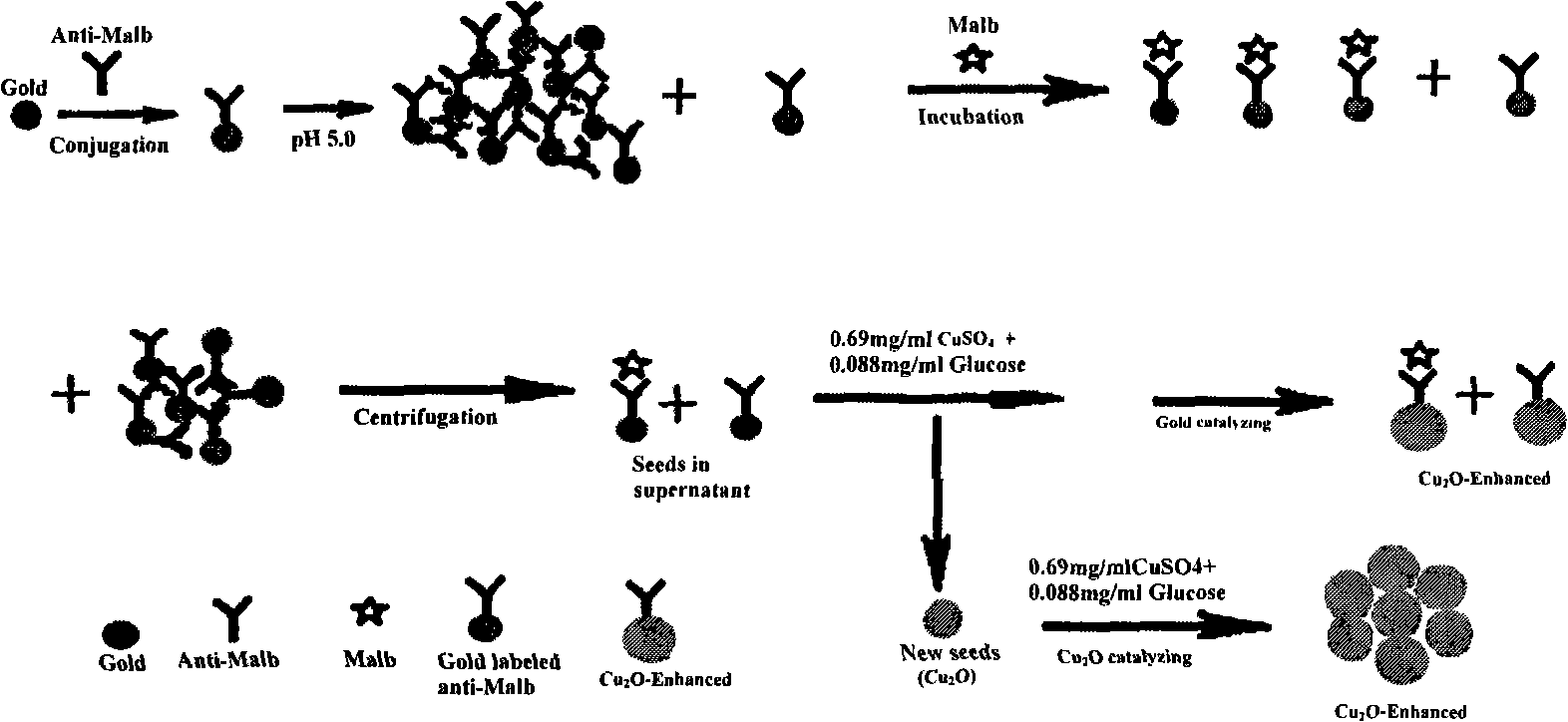
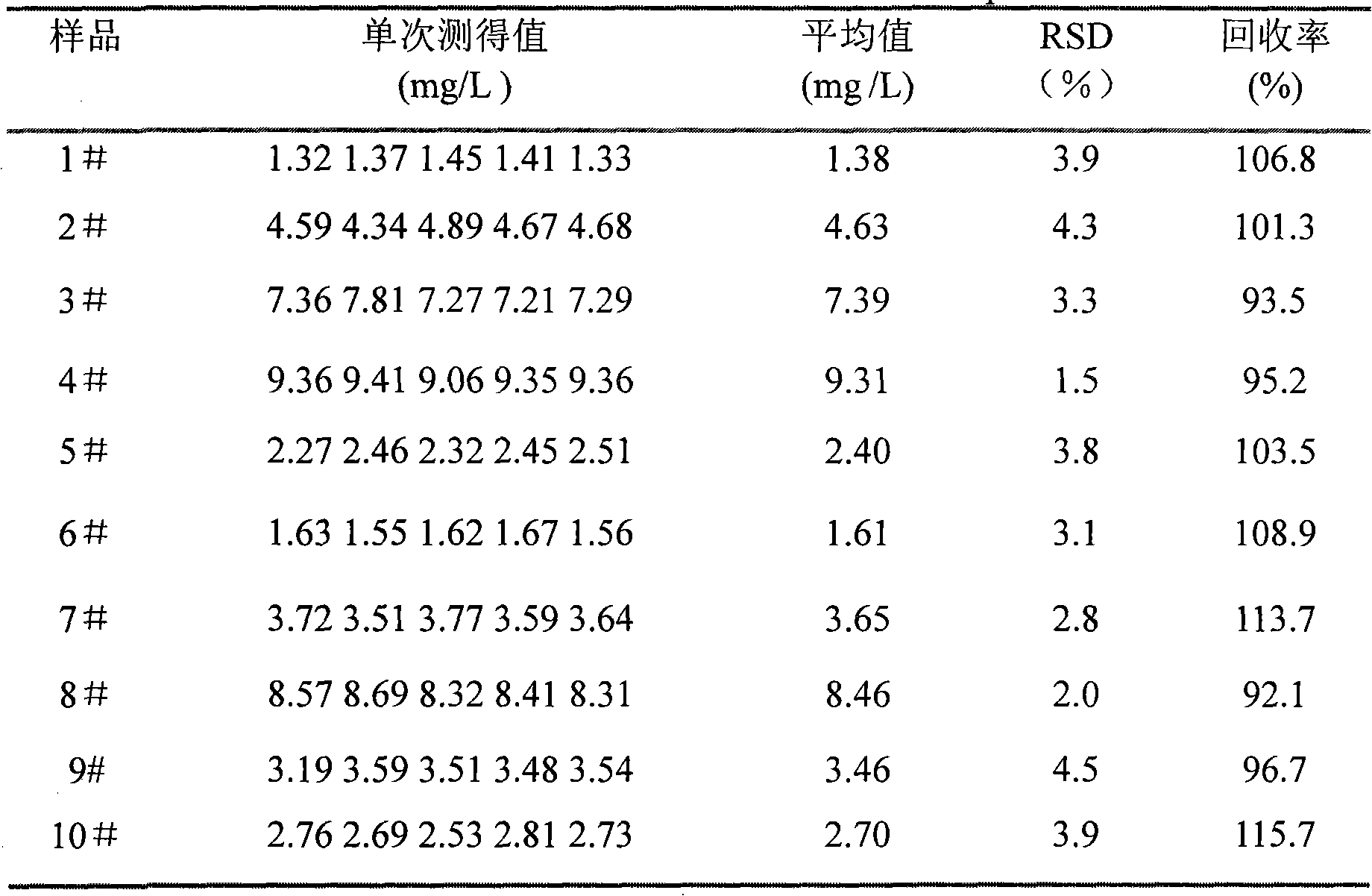
The utility model discloses a resonance scattering spectroscopy method for quickly and sensitively detecting microalbumin in human urine. According to the method provided by the utility model, the detection system of Malb the concentration of which is known is firstly prepared to work out the resonance scattering spectroscopy I 610nm of Malb; and then Mabl can be taken as a blank and the blank value (I 610) b can be measured, and Delta I can be worked out according to the equation: Delta I is equal to I 610nm subtracting (I 610) b; a working curve can be drawn by taking the concentration of added Malb solution as a horizontal axis, and taking Delta I as a vertical axis; and then, the system to be detected of a detecting sample can be prepared, and the Delta I of a sample to be detected can be worked out; and the Malb concentration of the sample can be also worked out according to the working curve. The method provided by the utility model has the advantages that instruments included in the method are simple and can be operated easily; film regent is stable and suitable for storage; colloidal gold can be prepared easily; catalysis performance is excellent and quick; and the sensitivity is high.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
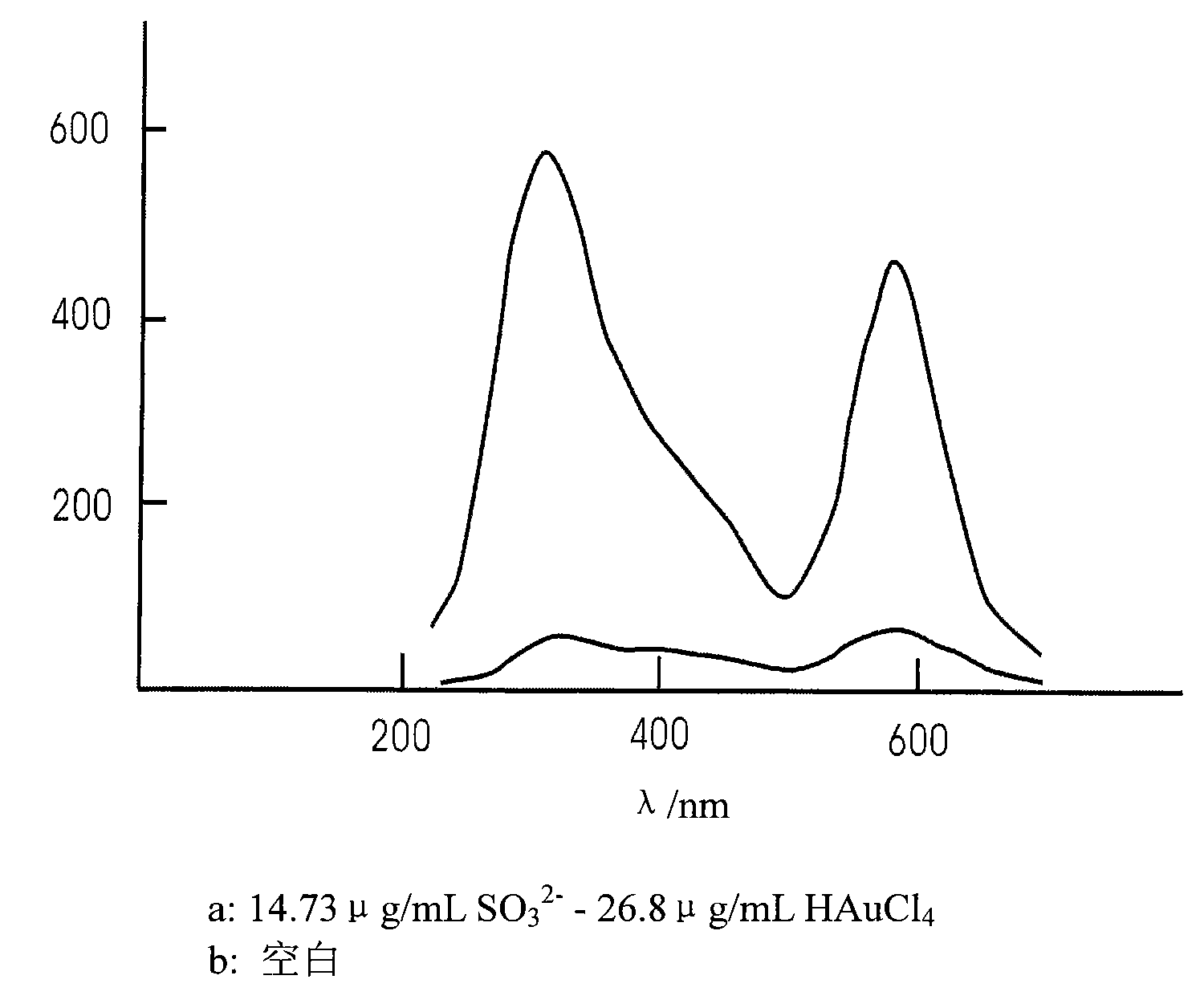
Method for measuring sulphite in food using chlorauric acid resonance scattering spectrometry
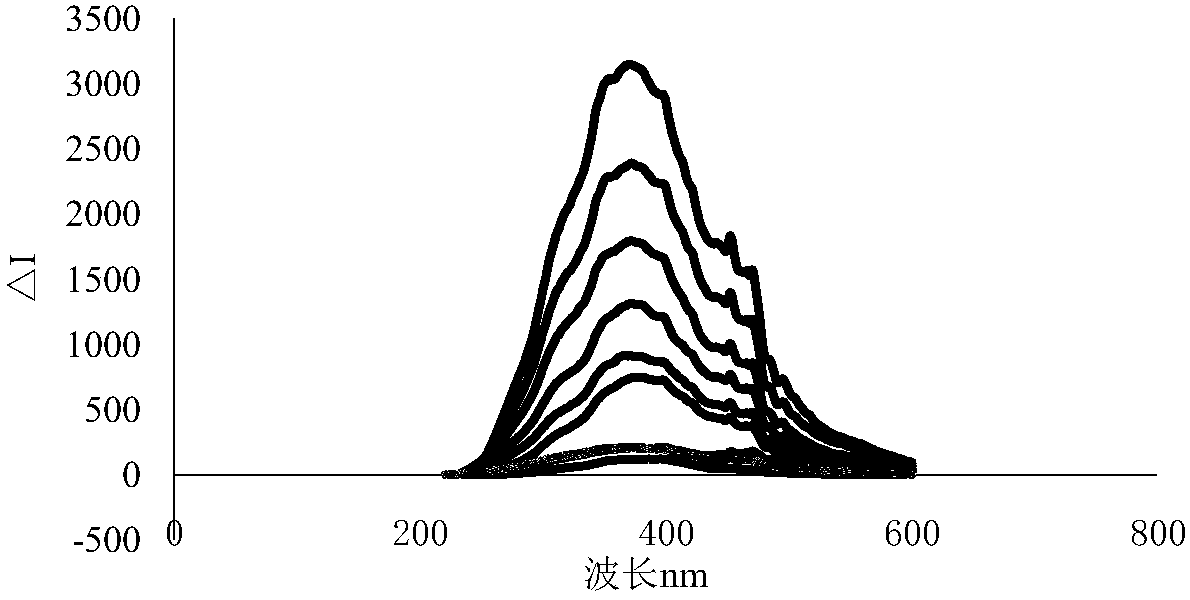
The present invention discloses a method for measuring the sulfite in the food with a chlorauric acid resonance scattering spectrometric determination. A 5mL color comparison tube is sequentially added with a 223.2 mu g / mL (calculated with Au(III)) HAuCl4 for 0.10-1.50mL, 1.0% aminosulfonic solution for 0.05-0.5mL and 116.0 mu g / mL sodium sulfite for 0.05-1.50mL, shaking up, adding the secondary distilled water to volume, swaying to uniform, and placing for 5-180min. On a fluorospectrophotometer, a synchronous scanning in which the inspiring wavelength is equal to the transmission wavelength is adopted, and the resonance scattering spectrometric of the system is obtained. The intensity I583nm of scattering light and reagent vacancy I0 are measured at 583nm. The value of delta I583nm is calculated with the equation: delta I583nm=I583nm-I0. Additionally the white sugar with right amount is added and is dissolved in water. The value of intensity delta I583nm is measured according to the method, and then the content of sulfite in the white sugar can be calculated out. The measuring method according to the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, easiness and shortcut.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for accurately measuring content of chitosan oligosaccharide according to resonance rayleigh scattering method
ActiveCN108088830AGood linear relationshipImprove linearityFluorescence/phosphorescenceRayleigh scatteringLinearity
The invention relates to a method for accurately measuring the content of chitosan oligosaccharide according to a resonance rayleigh scattering method, and belongs to the field of macromolecule detection. The chitosan oligosaccharide and rubylith are combined to form ionic associate under the certain condition, then the resonance scattering strength is obviously increased, and lauryl sodium sulfate serving as a sensitizer is added to improve the sensitivity. The resonance scattering strength and the chitosan oligosaccharide form a linear relation within certain concentration range, the linearrelation is taken as a quantitative basis of the chitosan oligosaccharide, and the resonance rayleigh scattering method for measuring the chitosan oligosaccharide is established. The measurement of the method is affected by the ionic concentration and the interferent, a standard product with the ionic concentration controlled to 0.05 mol / L to 0.20 mol / L is taken as a quantitative standard in the actual measurement of a sample, and the method has the advantages of cheap agents, high sensitivity, good repeatability, simplicity and convenience in operation, and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Nanometer gold resonance scattering spectrometry for simply and rapidly measuring trace amount Ti
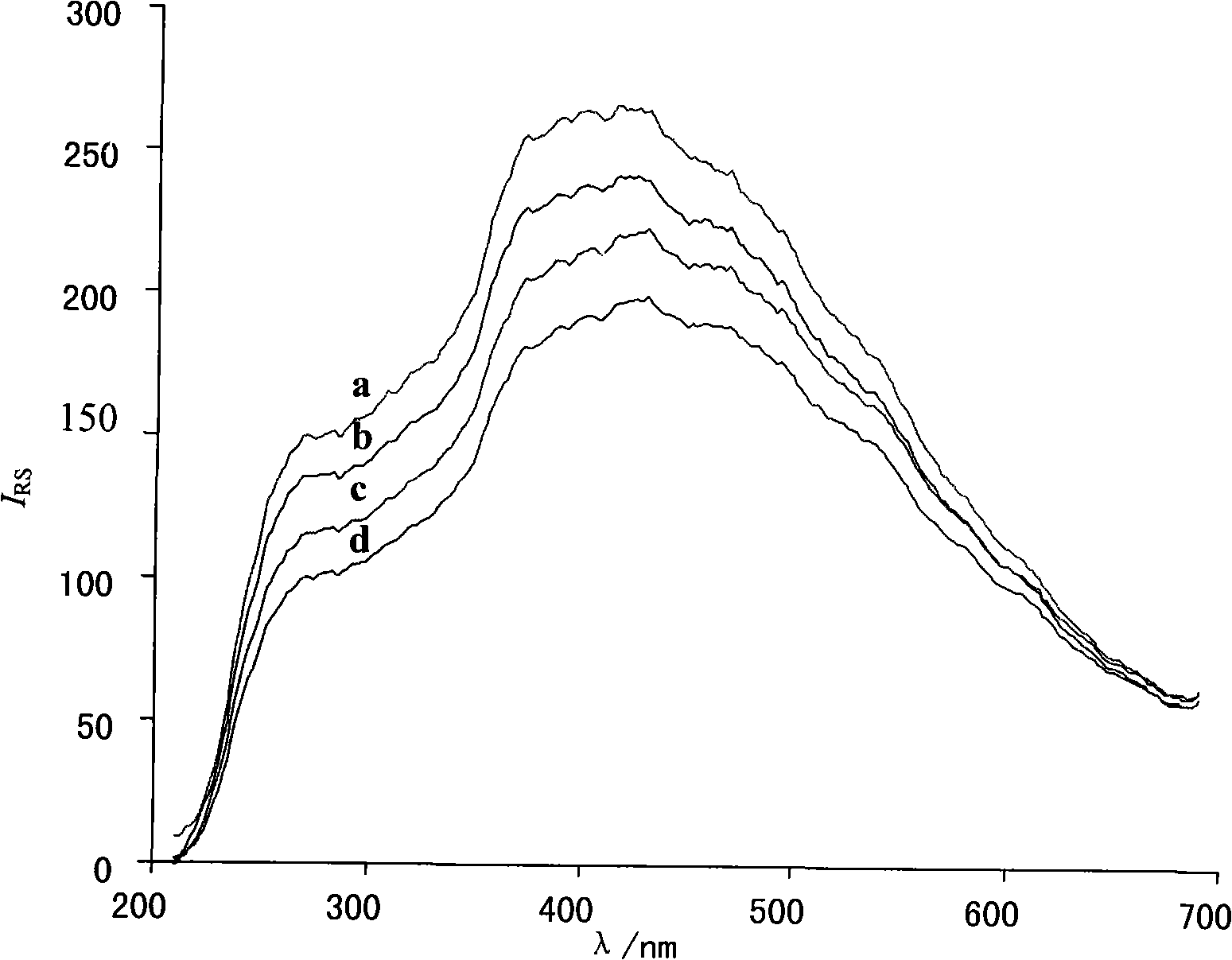
InactiveCN101324531AEasy to operateLow costMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorScattering properties measurementsWastewaterTitanium
The invention discloses a nano-Au resonance scattering spectrographic method for conveniently and rapidly detecting trace titanium, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a measuring system with the known titanium concentration, and measuring the resonance scattering intensity (IRS) thereof; (2) preparing a reagent blank system, and measuring the resonance scattering light intensity (IRS)0 without adding the Ti(SO4)2 solution as the blank,; (3) calculating based on that Delta IRS is equal to IRS minus (IRS)0; (4) plotting a work curve with the concentration of the added Ti(SO4)2 solution as the abscissa and the Delta IRS as the ordinate; (5) preparing a detecting system, measuring the titanium content in the industrial wastewater and obtaining Delta IRS of the sample to be measured; and (6) obtaining the titanium concentration of the sample to be measured according to the work curve. The method has the advantages of simple device, convenient operation, easily-accessible reagent and low cost, and can be carried out by only a fluorescence spectrophotometer.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Resonance scattering spectrometry method for determining NH<4+> by using sodium tetraphenylborate ligand for adjusting and controlling nano-silver catalytic activity
InactiveCN107356579ASimple methodFast wayFluorescence/phosphorescenceSodium tetraphenylborateUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a resonance scattering spectrometry method for determining NH<4+> by using a sodium tetraphenylborate ligand for adjusting and controlling nano-silver catalytic activity. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) preparing a NH<4+> standard solution system with known concentration; (2) preparing a blank control solution system not containing NH<4+>; (3) calculating according to the equation that delta I is equal to I minus I0; (4) making a working curve according to a relationship between the delta I and NH<4+> concentration; (5) preparing a to-be-measured sample solution, determining the resonance scattering peak intensity value of the to-be-measured sample solution as an I sample, and calculating according to the equation that delta I sample is equal to I sample minus I0; (6) calculating out the NH<4+> content of the sample solution according to the working curve of step (4). The method of the invention uses the ligand for adjusting and controlling nano-enzyme catalytic activity, and is simple, convenient, quick and high in sensitivity.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
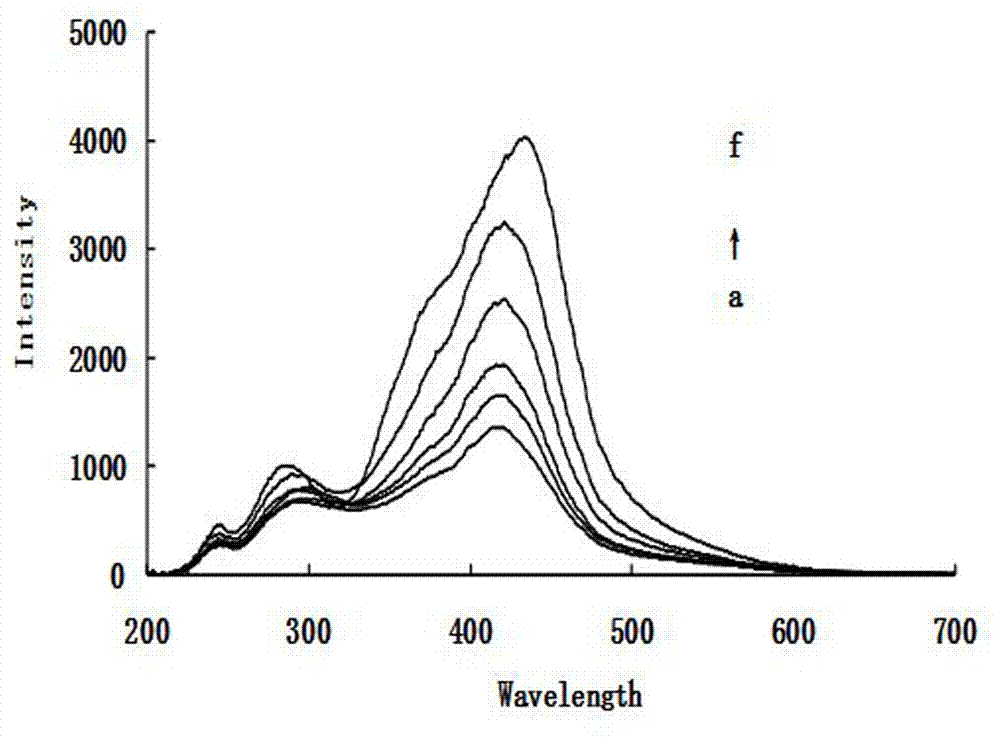
Method for detecting alpha-amylase activity by soluble starch resonance scattering spectrometry
InactiveCN101320000AEasy to operateLow costMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorScattering properties measurementsAlpha-amylase activityUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a soluble starch resonance scattering spectra method for detecting Alpha-amylase activity. The resonance scattering strength I423nm of Alpha-amylase with known enzyme activity and the resonance scattering strength I0 of reagent blank are utilized for working out Delta I423nm which is equal to the difference between I423nm and I0 and is used as a standard curve. Then, Delta I of Alpha-amylase with unknown concentration is determined. The concentration of Alpha-amylase of an object to be determined is worked out according to a working curve. The soluble starch resonance scattering spectra method has the advantages of simple equipment, convenient operation, easily obtained reagent and low cost. And the method can be finished just through a spectrophotometer. The soluble starch of substrates is nontoxic.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Immune syntony scattering spectrometry for rapid measuring copper blue protein
InactiveCN101158690ASimple and fast operationStrong anti-interferenceAnalysis by material excitationBiological testingWater bathsImmune complex deposition
The present invention discloses a simple and rapid immune resonance scattering spectroscopy for the determination of ceruloplasmin, which mainly makes use of the specific immune binding reaction between goat anti-human ceruloplasmin and ceruloplasmin under the condition of PEG in the 37 DEG C water bath for production of immune complex particles. The resonance scattering is existed in the complex particles. The concentration of the ceruloplasmin is linear with the strength of the resonance scattering when the concentration of ceruloplasmin is in a certain range, thereby establishing a novel method for the rapid determination of the ceruloplasmin. The present invention has the advantages that: compared with the prior art, the determination method has simple instrument, easy operation, high sensitivity and selectivity, and easy achievement of the reaction conditions. The dosage of the goat anti-human CER reagent is less and the cost is low.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Surface plasma resonance absorption spectrometry method for determining NH<4+> by using sodium tetraphenylborate ligand for adjusting and controlling nano-silver catalytic activity
InactiveCN107356562ASimple methodFast wayMaterial analysis by optical meansPlasma resonanceSodium tetraphenylborate
The invention discloses a surface plasma resonance absorption spectrometry method for determining NH<4+> by using a sodium tetraphenylborate ligand for adjusting and controlling nano-silver catalytic activity. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) preparing a NH<4+> standard solution system with known concentration; (2) preparing a blank control solution system; (3) calculating according to the equation that delta A is equal to A minus A0; (4) making a working curve according to a relationship between the delta A and NH<4+> concentration; (5) preparing a to-be-measured sample solution, determining the resonance scattering peak intensity value of the to-be-measured sample solution as an A sample, and calculating according to the equation that delta A sample is equal to A sample minus A0; (6) calculating out the NH<4+> content of the sample solution according to the working curve. The method of the invention uses the ligand for adjusting and controlling nano-enzyme catalytic activity, and is simple, convenient, quick and high in sensitivity.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
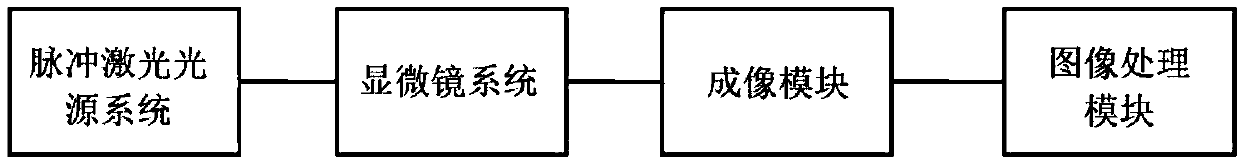
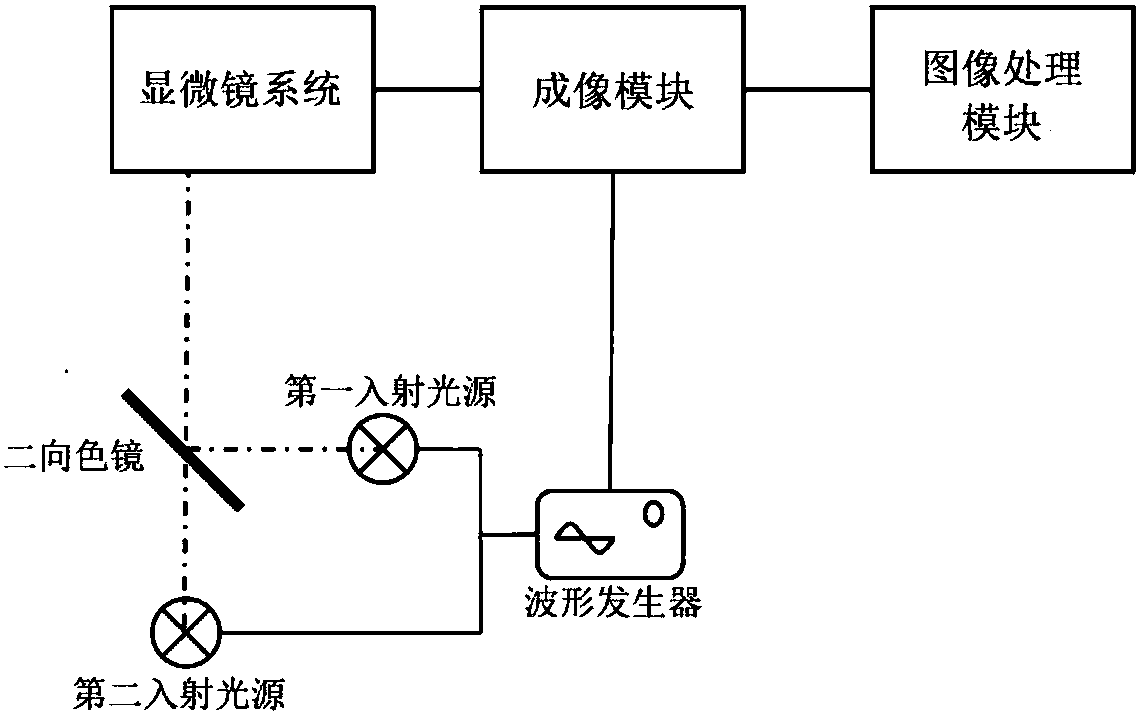
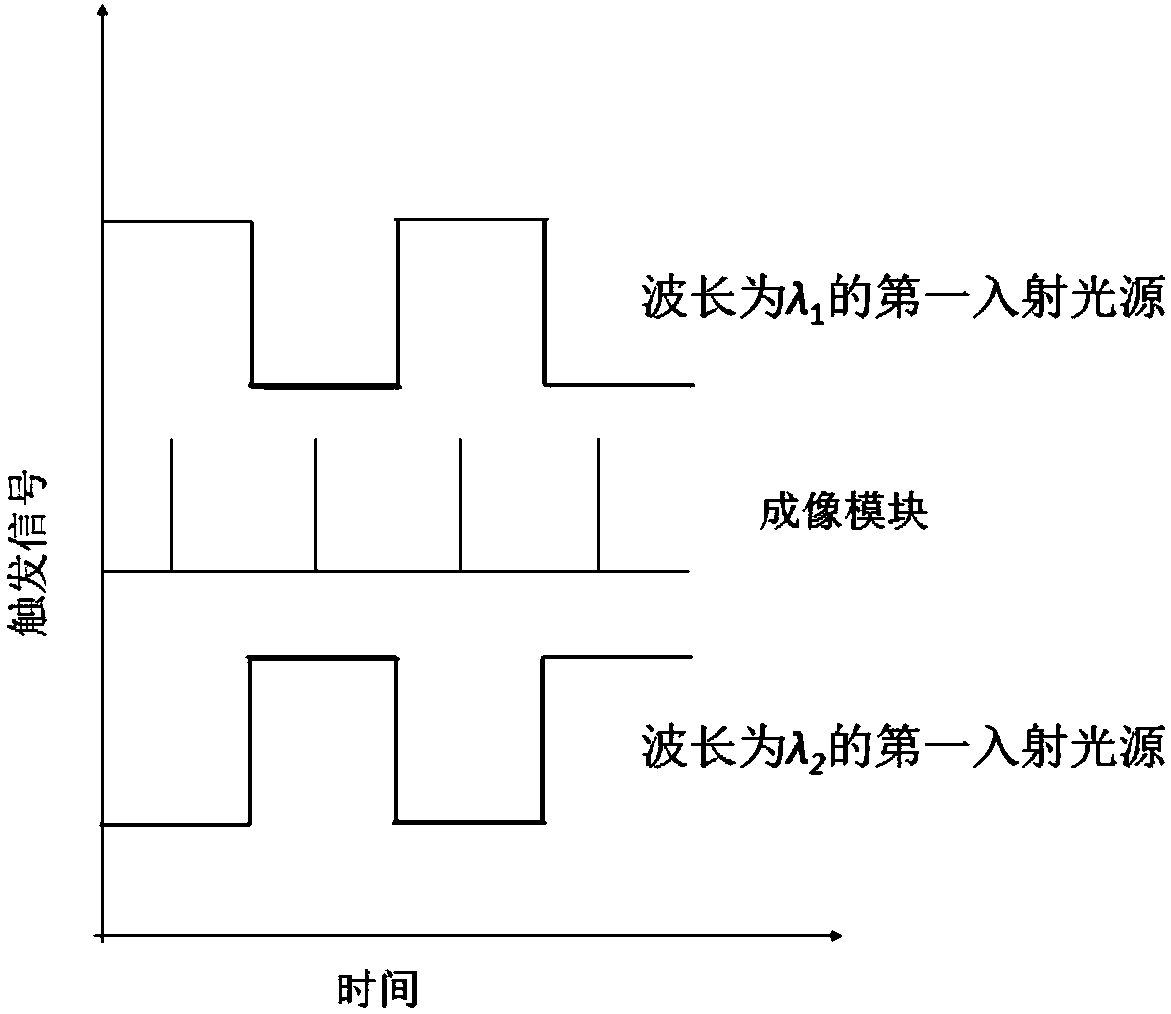
Space-time resolved spectral imaging system
ActiveCN107727614AOvercoming the defect of low sampling throughputOvercome the disadvantage of strong scattering backgroundMaterial analysis by optical meansTemporal resolutionManufacturing technology
The invention belongs to the technical field of an optical micro-instrument manufacturing technology and a spectral imaging technology and particularly relates to a space-time resolved spectral imaging system. The system comprises a pulsed laser light source system, a microscope system, an imaging module and an image processing module. The pulsed laser light source system emits pulsed laser lightbeams with wavelengths lambda 1 and lambda 2 changed alternately. The microscope system and the imaging module are arranged on an output light path of the pulsed laser light source system. The image processing module extracts images of the imaging module. Through calculating processing on image scattering light intensity, images of resonance wavelength of plasmas on the local surface of a target sample are acquired and space-time resolved spectral imaging is realized. The space-time resolved spectral imaging system can simultaneously detect resonance scattering wavelength of plasmas on the local surfaces of the multiple target samples, reduce spectrum temporal resolution to the millisecond level from the second level and significantly improve the spatial resolution.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
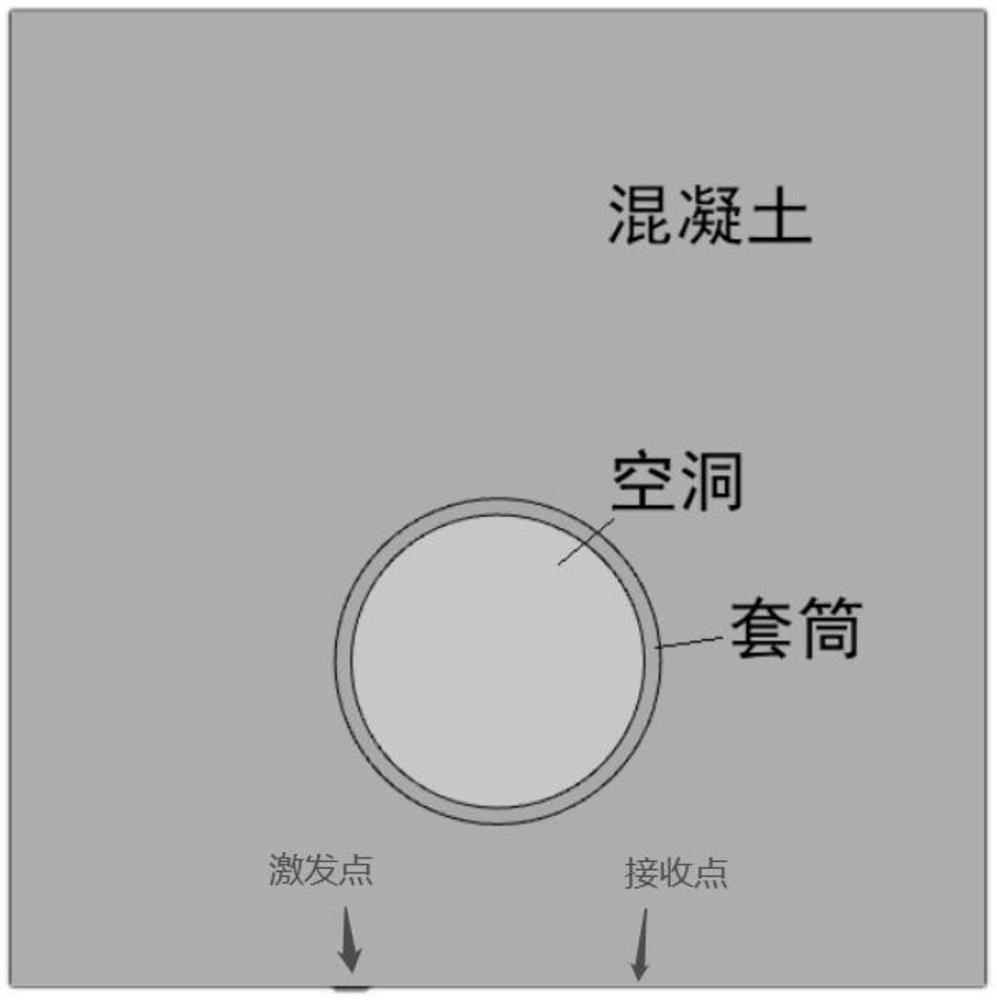
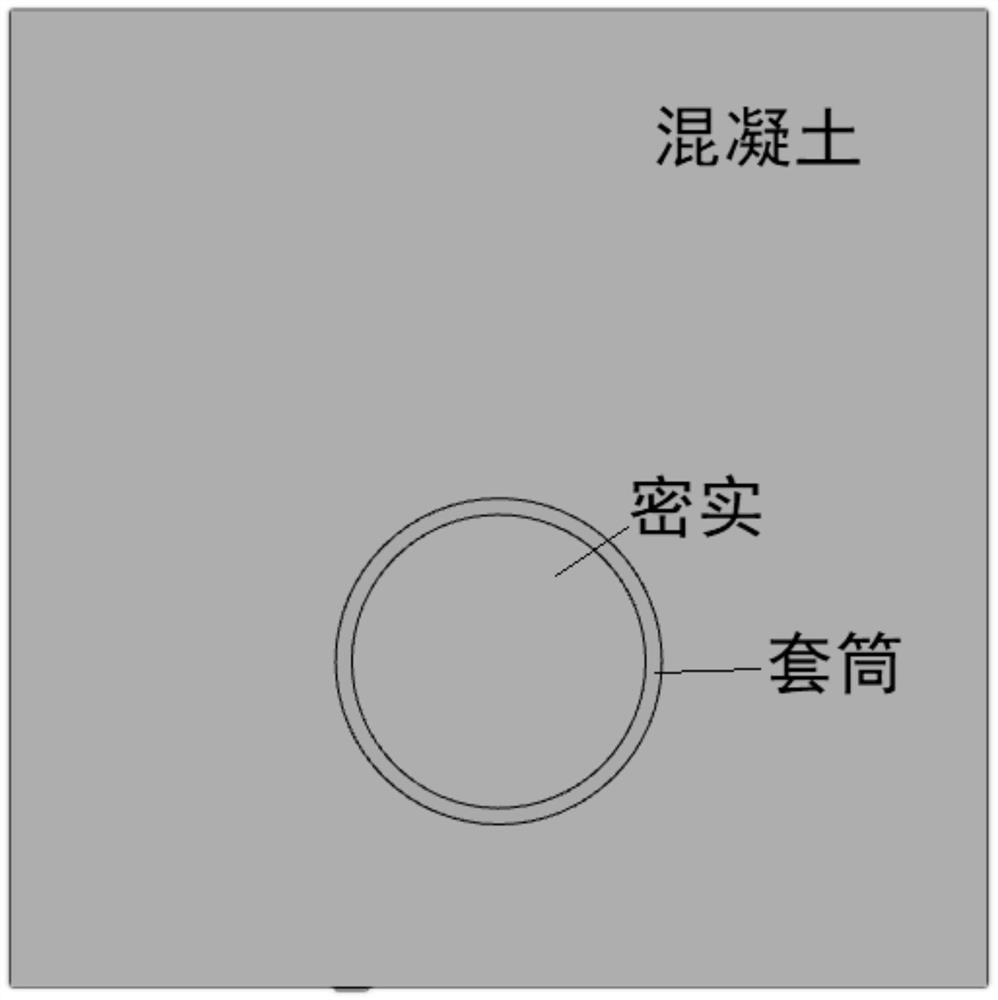
Grouting sleeve grouting defect detection method based on sound wave local resonance scattering characteristics
ActiveCN112098512AReduce labor intensityReduce the amount of configurationMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWater resource assessmentScattering attenuationEngineering
The invention discloses a grouting sleeve grouting defect detection method based on sound wave local resonance scattering characteristics, which comprises the following steps: carrying out sound wavedetection outside a to-be-detected part on the same side of a grouting sleeve, and carrying out data processing on an obtained original echo signal to obtain a pulse upper envelope diagram; and extracting a sound wave local resonance scattering attenuation characteristic parameter alpha after data formula fitting, so that whether void or void exists in the sleeve or not is judged. Compared with the prior art, the detection method provided by the invention has the advantages that the process is simple, the labor intensity of workers is effectively reduced, the personnel allocation amount is reduced, the tedious working process is reduced, the detection method is different from the traditional detection of void sound velocity and sound time angle, the detection is carried out from the perspective of energy attenuation, and the measurement accuracy can be improved.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Resonance scattering method for controlling catalytic activity of graphene oxide nanoribbon by using sodium tetraphenylborate ligand to measure K<+>
InactiveCN107389614ASimple methodFast wayScattering properties measurementsSodium tetraphenylborateComputational chemistry
The invention discloses a resonance scattering method for controlling the catalytic activity of a graphene oxide nanoribbon by using a sodium tetraphenylborate ligand to measure K<+>. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of (1) preparing a K<+> standard solution system with known concentration; (2) preparing a bank control solution system; (3) calculating deltaI=I-I0; (4) making a work curve for a concentration relationship of the K<+> by using deltaI; (5) calculating deltaIsample=Isample-I0; and (6) calculating the content of the K<+> of the sample solution according to the work curve in the step (4). According to the measurement method, the catalytic activity of a nano-enzyme is controlled by adopting the ligand, and the method is simple, convenient, fast and high in sensitivity.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Radar target recognition method based on resonance scattering echo signal
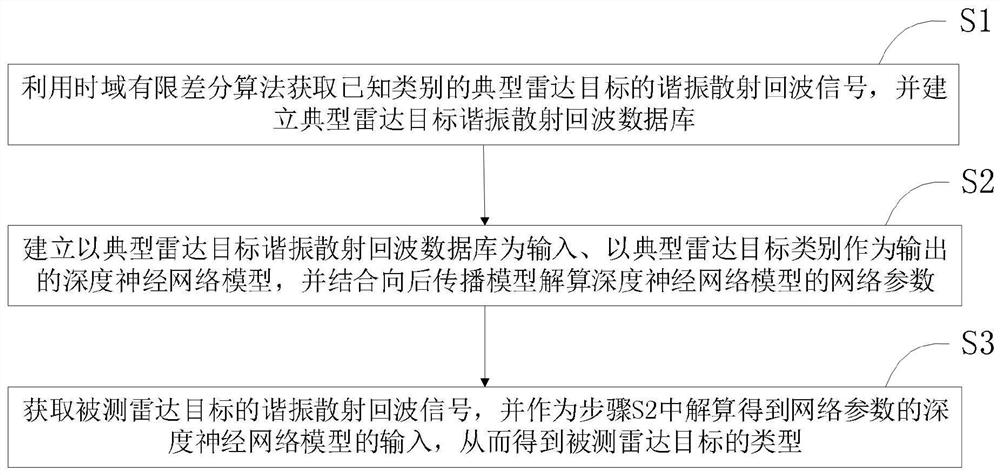
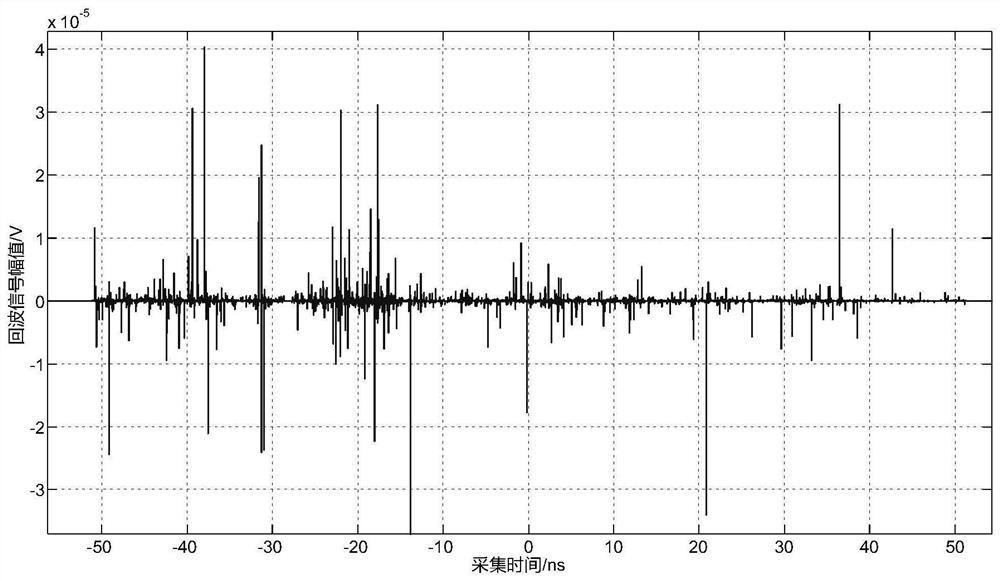
PendingCN112526476AResolve identifiabilitySolve the speed problemWave based measurement systemsTime domainRadar
The invention discloses a radar target recognition method based on a resonance scattering echo signal. The method comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining the resonance scattering echo signal of atypical radar target of a known type through employing a time domain finite difference algorithm, and building a typical radar target resonance scattering echo database; S2, establishing a deep neural network model taking the typical radar target resonance scattering echo database as input and the typical radar target category as output, and calculating network parameters of the deep neural network model in combination with a backward propagation model; and S3, obtaining the resonance scattering echo signal of the measured radar target, and taking the resonance scattering echo signal as the input of the deep neural network model of the network parameters calculated in the step S2 so as to obtain the type of the measured radar target. According to the invention, the radar target with low observability can be rapidly identified.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
High sensitivity assay for molecular typing of biological sample, probes and a kit thereof
InactiveUS8227590B2High sensitivityAvoids false-positive/false-negative resultsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayMolecular typing
The present invention relates to a high sensitivity assay for molecular typing of a biological sample using surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) including resonance scattering (SERRS); capture probes for capturing nucleic acid; a detector probe to detect captured nucleic acid; a kit for molecular typing of biological sample using surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) including resonance scattering (SERRS); and lastly a method of manufacturing said kit.
Owner:MICROTEST INNOVATIONS PVT +1
Method for determining chitosan content by resonance Rayleigh scattering method sensitized by sodium dodecyl sulfate
InactiveCN108181281AGood linear relationshipImprove linearityPreparing sample for investigationScattering properties measurementsRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
The invention relates to a method for determining chitosan content by a resonance Rayleigh scattering method sensitized by sodium dodecyl sulfate, and belongs to the field of macromolecule detection.Under certain conditions, chitosan can be combined with red amaranth to form an ionic associate to remarkably enhance resonance scattering intensity, and the sodium dodecyl sulfate is added as a sensitizer to improve the sensitivity. In a certain concentration range, the resonance Rayleigh scattering intensity and the chitosan content keep a linear relation in the certain concentration range, andthe resonance Rayleigh scattering intensity and the chitosan content keeping the linear relation are taken as a quantitative basis of the chitosan for establishment of the resonance Rayleigh scattering method of the chitosan. The method for determining the chitosan content is influenced by the molecular weight and the degree of deacetylation of the chitosan, and has the advantages of low cost, high sensitivity, good reproducibility and simple operation, and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Method for measuring sulphite in food using chlorauric acid resonance scattering spectrometry
The present invention discloses a method for measuring the sulfite in the food with a chlorauric acid resonance scattering spectrometric determination. A 5mL color comparison tube is sequentially added with a 223.2 mu g / mL (calculated with Au(III)) HAuCl4 for 0.10-1.50mL, 1.0% aminosulfonic solution for 0.05-0.5mL and 116.0 mu g / mL sodium sulfite for 0.05-1.50mL, shaking up, adding the secondary distilled water to volume, swaying to uniform, and placing for 5-180min. On a fluorospectrophotometer, a synchronous scanning in which the inspiring wavelength is equal to the transmission wavelength is adopted, and the resonance scattering spectrometric of the system is obtained. The intensity I583nm of scattering light and reagent vacancy I0 are measured at 583nm. The value of delta I583nm is calculated with the equation: delta I583nm=I583nm-I0. Additionally the white sugar with right amount is added and is dissolved in water. The value of intensity delta I583nm is measured according to the method, and then the content of sulfite in the white sugar can be calculated out. The measuring method according to the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, easiness and shortcut.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com