Method for detecting alpha-amylase activity by soluble starch resonance scattering spectrometry
A resonance scattering and amylase technology, which is applied in the measurement of scattering properties, color/spectral properties, Raman scattering, etc. Simple equipment and low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
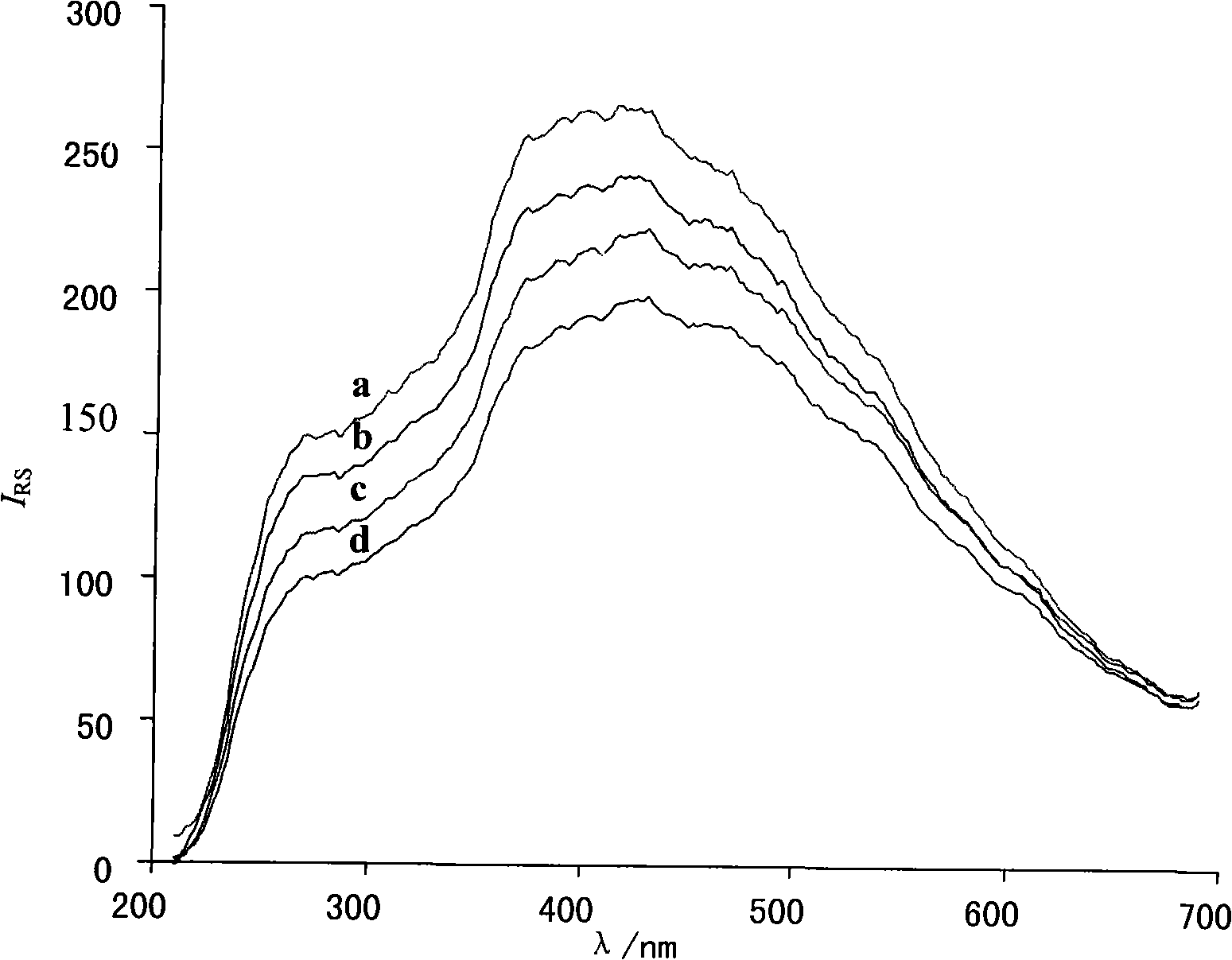
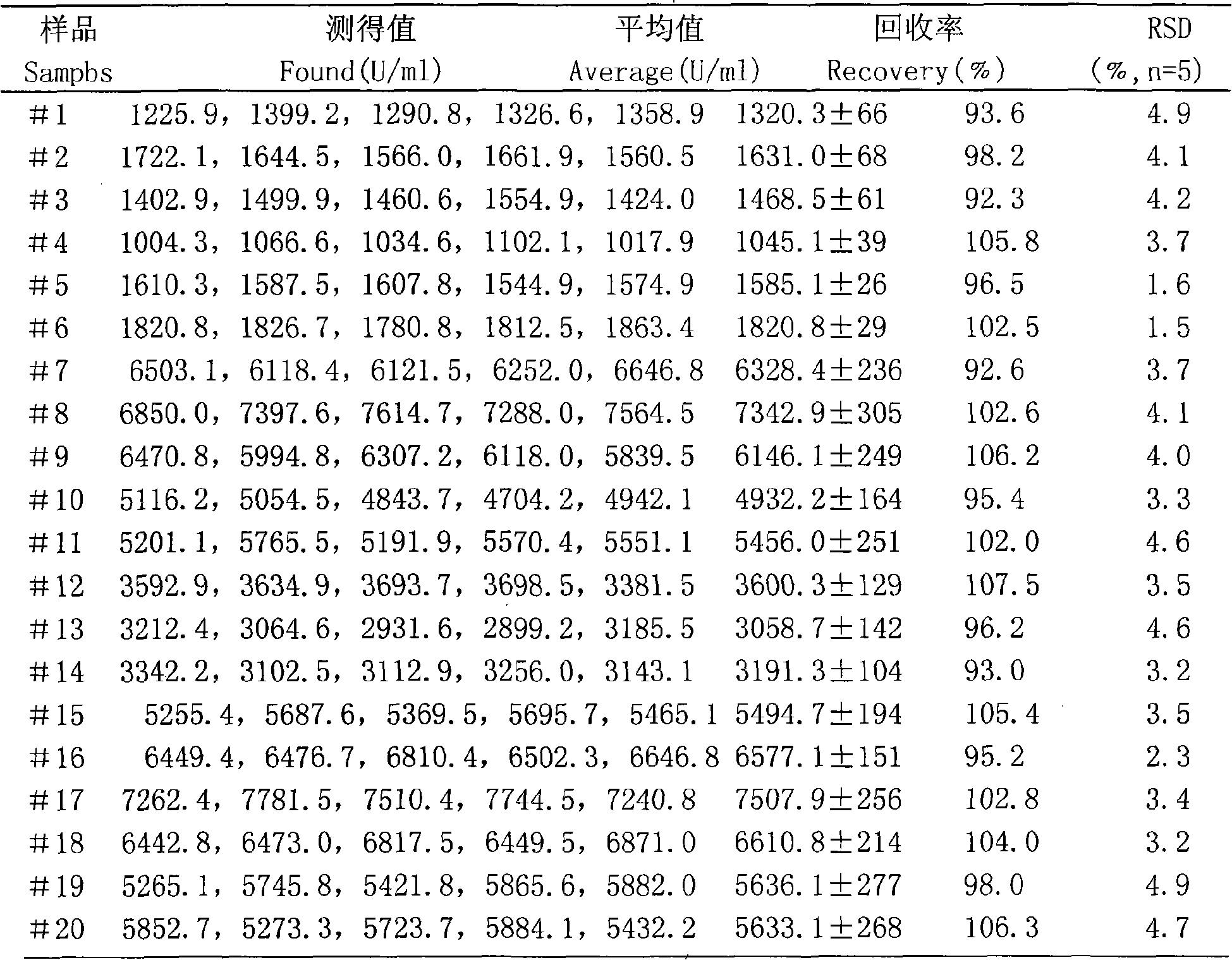
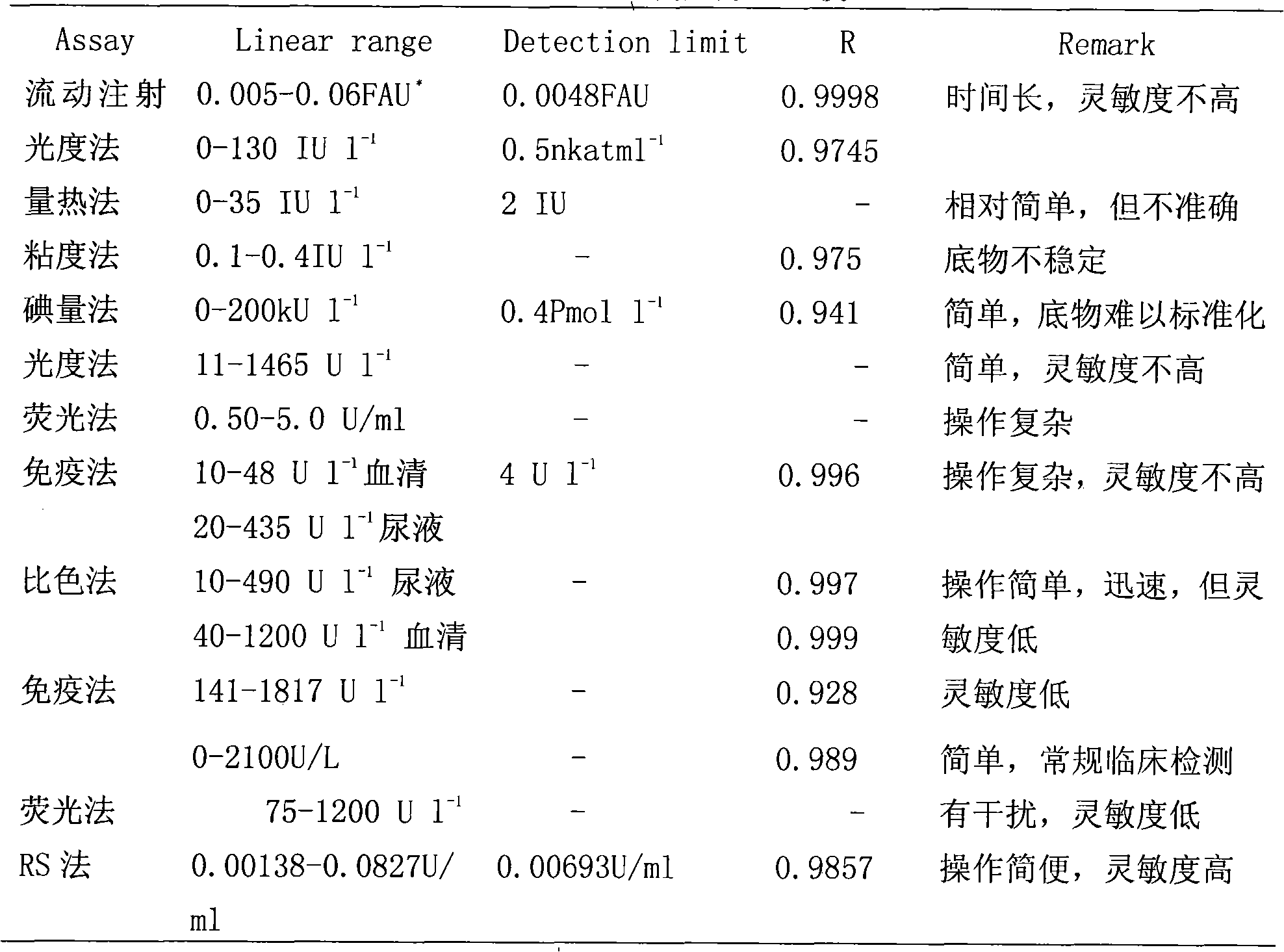
[0025] Detect the content of α-amylase in the saliva of 20 people with the method of the present invention:
[0026] 1. Instruments used for reagents:
[0027] Cary Eclipse spectrophotometer (Varian Company, Palo Alto, CA), HH-S 2 Electric constant temperature water bath (Jintan Dadi Automation Instrument Factory), TGL-16G centrifuge (Shanghai Anting Scientific Instrument Factory);
[0028] Soluble starch (China Pharmaceutical Group Shanghai Chemical Reagent Company), α-amylase (165,000U / g Fontes Chemical Reagent Company), polyacrylamide (molecular weight above 5 million, Shanghai Chemical Reagent Purchasing and Supply Station Subpackage Factory); Soluble starch solution: Take 0.25g of soluble starch in a small beaker, add about 5mL of water and mix well, slowly pour it into a 50ml beaker filled with 20ml of boiling water while stirring, and use a washing bottle to transfer all the starch in the small beaker to 50ml In a beaker, continue to stir and heat, boil slowly for 2mi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com