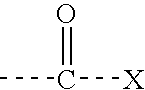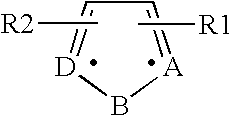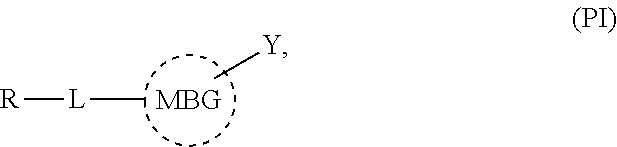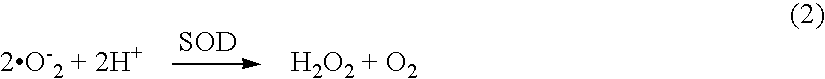Patents
Literature
80 results about "Metalloprotein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large proportion of all proteins are part of this category. For instance, at least 1000 human proteins (out of ~20,000) contain zinc-binding protein domains although there may be up to 3000 human zinc metalloproteins.
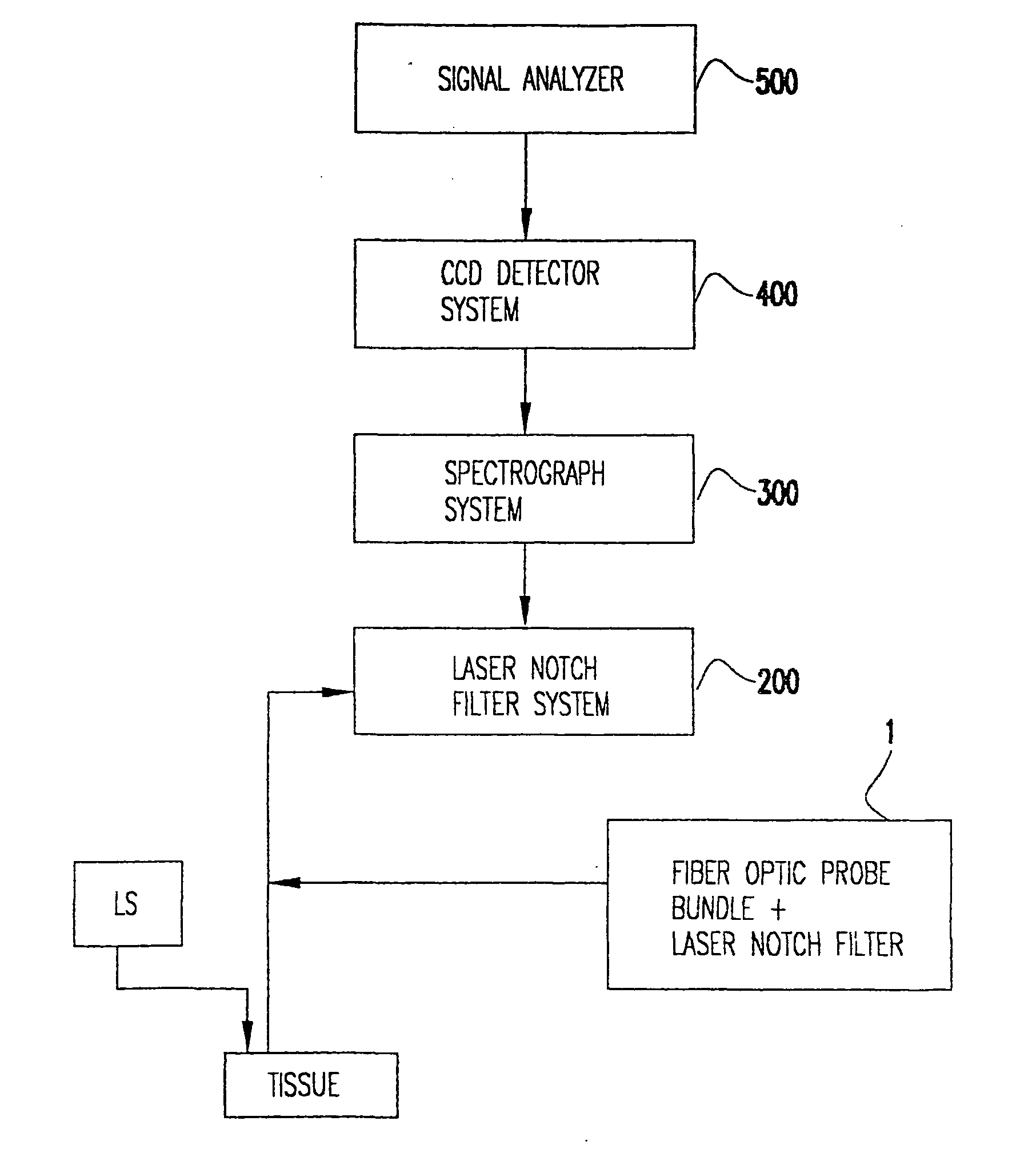
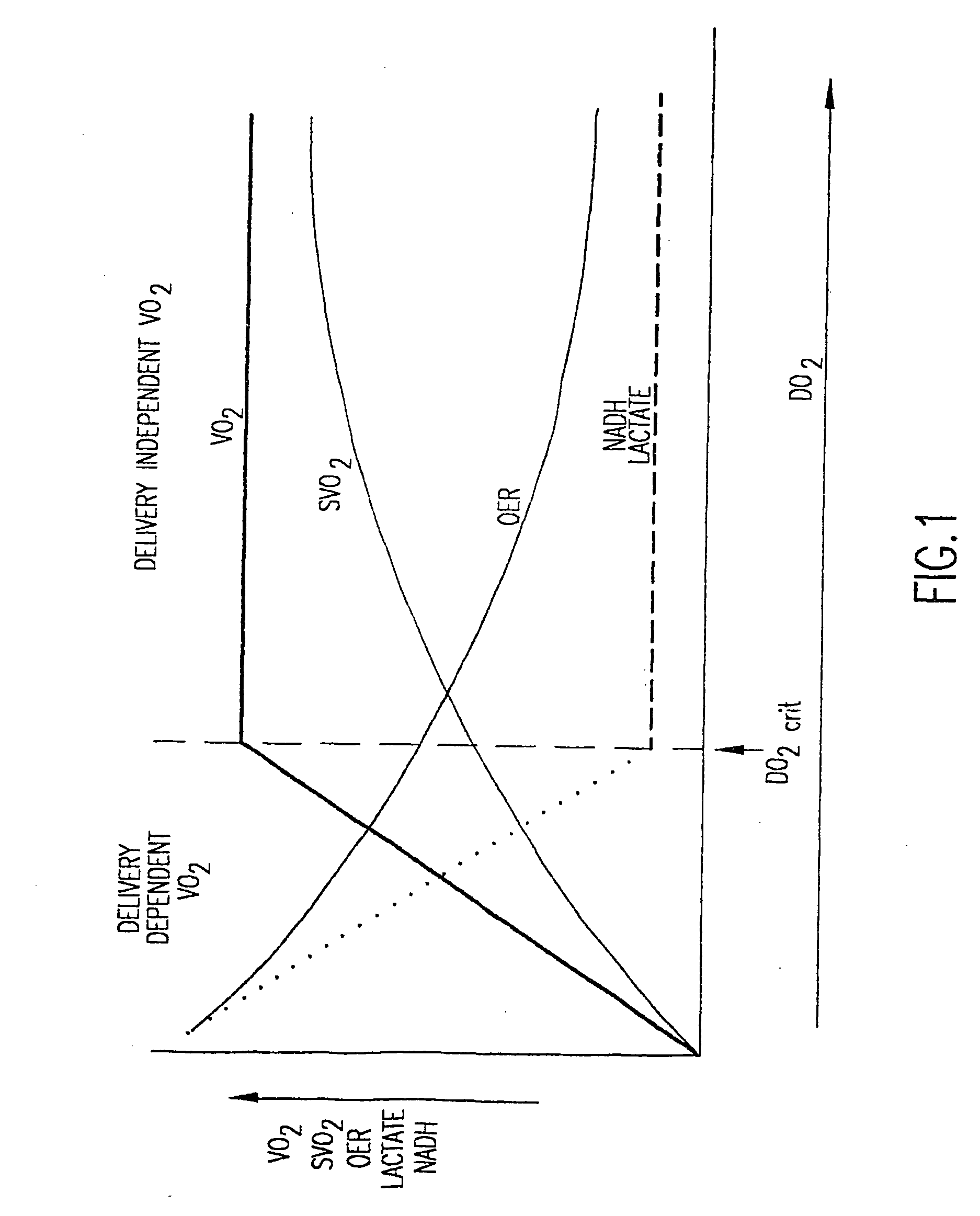
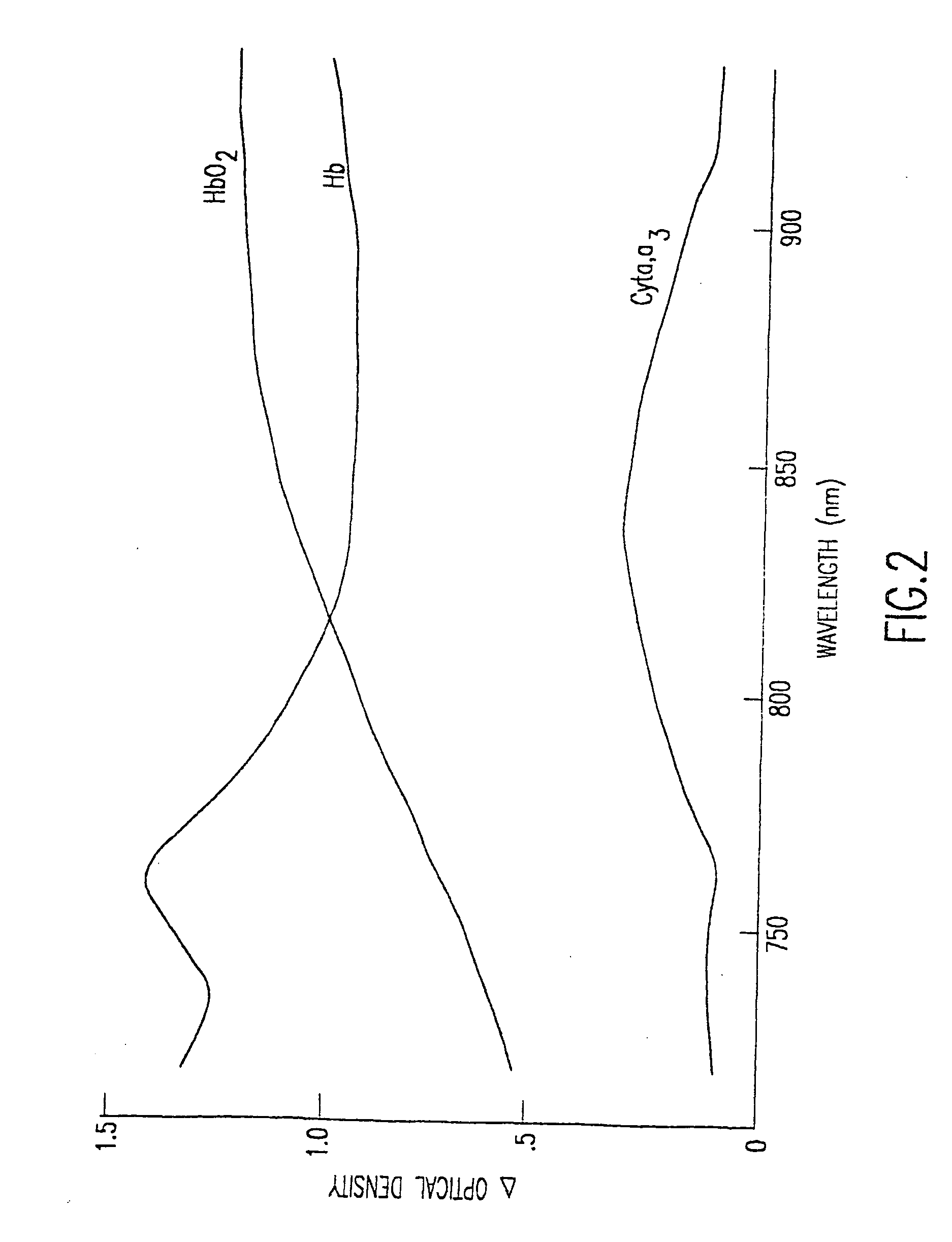
Nitric-oxide detection using Raman spectroscopy
InactiveUS20060074282A1Accurate conditionHigh precisionRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiseaseResonance Raman spectroscopy
In an emergency medicine patient, accurate measurement of change or lack thereof from non-shock, non-ischemimc, non-inflammation, non-tissue injury, non-immune dysfunction conditions is important and is provided, as practical, real-time approaches for accurately characterizing a patient's condition, using Raman spectroscopy with a high degree of accuracy, Resonance Raman spectroscopy is used to monitor tissue nitric oxide activity either in vivo or in vitro, especially as a function of its interaction with hemoglobin or other metalloproteins. Measurement times are on the order of seconds. High-accuracy measurement is achieved with Raman spectroscopy interrogation of tissue. Measurements may be non-invasive to minimally invasive. The invention may be used to monitor the effect of instituting therapies using nitric oxide or disease processes that produce nitric oxide.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Antibodies and pharmaceutical compositions containing same useful for inhibiting activity of metalloproteins
A method of producing a metalloprotein inhibitor, the method comprising generating antibodies directed at a composition including a metal ion-bound chelator, wherein the composition is selected having structural and electronic properties similar to a functional domain of the metalloprotein, thereby producing the metalloprotein inhibitor.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Two-dimensionally arrayed quantum device
InactiveUS7015139B2High gainMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsMetalloproteinInsulation layer
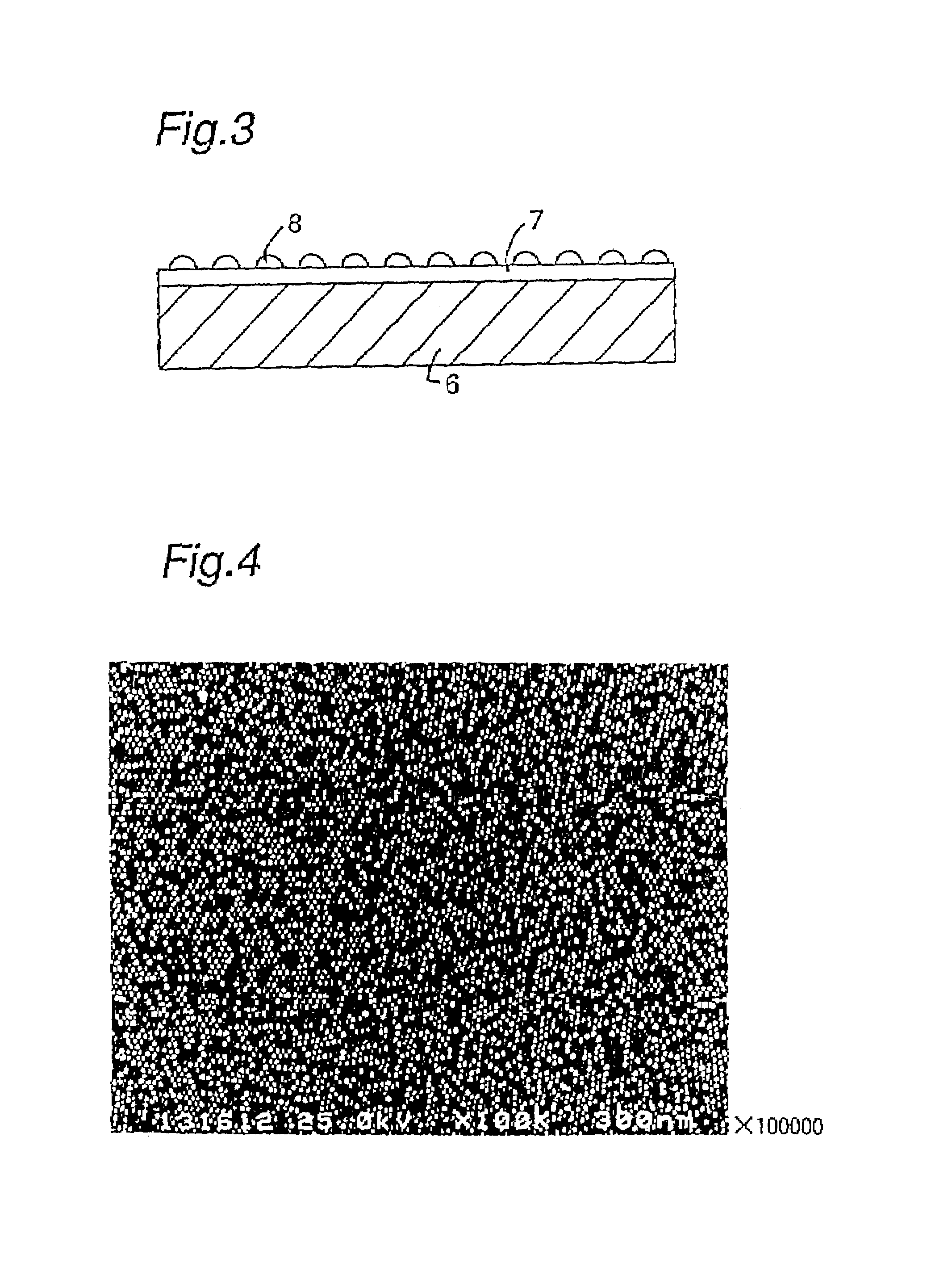
A quantum device is constituted from a two-dimensional array of quantum dots formed from metal atom aggregates contained in a metalloprotein complex. The metalloprotein is arranged on the surface of a substrate having an insulation layer with a pitch of the size of the metalloprotein complex. The diameter of the metal atom aggregates used in the quantum device is 7 nm or smaller, and the pitch of the metalloprotein complex is preferably from 11 to 14 nm.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Pharmacological agents and methods of treatment that inactivate pathogenic prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and viruses by attacking highly conserved domains in structural metalloprotein and metalloenzyme targets
The invention relates to the treatment of viral, bacterial, parasitic, proliferative diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, inflammatory diseases, immunological diseases, transplanted organ rejection, and diseases produced by intoxication with heavy metals. The invention relates to the use of specific metal chelating agents including, furoic acid, 2-thiophenecarboxylic acid and their derivatives, analogs and structurally related chemicals as pharmacological agents that can be used effectively to disrupt and inactivate specific transition metal ion containing zinc finger structural motifs in metalloproteins and specific transition metal ion containing catalytic sites in metalloproteinases, which in turn, inactivate the pathogenic virus, pathogenic prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells which produces disease conditions. The preparations can be administered topically or for systemic use. The preparations are novel wide-spectrum antibiotics which have antiviral, antiproliferative, antineoplastic, antiangiogenic, antibacterial, antiparasitic, antiinfective, and anti-inflammatory effects and can be used in the treatment and prevention of diseases such as AIDS, cancers, untoward angiogenesis, pulmonary anthrax, malaria, inflammatory responses, Alzheimer's disease and other diseases.
Owner:POLS LAB BIOTECH
New application of collagen chelate
InactiveCN101773663AIncrease bone densityStimulationPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderMetalloproteinBone density
The invention relates to application of collagen chelate in the preparation of medicament or food for enhancing bone quality. The medicament or food can enhance bone strength, can enhance bone strength and bone density at the same time and can be used for curing and / or preventing osteoporosis. The collagen chelate is a metalloprotein conjugate; compared with calcium carbonate (CaCO3) with the same calcium concentration, the collagen chelate can enhance the bone density by 4.4 percent and enhance the bone strength by 9.9 percent; and compared with a mixture of collagen and calcium carbonate (CaCO3) with the same concentration of collagen and calcium carbonate, the collagen chelate has a more obvious effect.
Owner:顾凌洁 +1
Serum-free culture fluid for culture of salivary gland epidermal cell and salivary gland stem cell of mammals
ActiveCN102399742AProliferation effect is goodGood biological propertiesArtificial cell constructsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsCulture fluidAntioxidant
The invention provides serum-free culture fluid for culture of salivary gland epidermal cells and salivary gland stem cells of mammals, which is prepared by using MCDB153HAA as basic culture medium and adding amino acid, vitamins, salts, lipid, trace elements, buffer fluid, hormone-like compounds, transgenic metalloprotein, antioxidants, seralbumin, glucide, purine, pyrimidine base substances and pH value indicators. The serum-free culture fluid has the advantages that salivary gland epidermal cells of the mammals can vigorously grow, good cell activity and physiological properties are maintained, in addition, the serum-free culture fluid is also suitable for the salivary gland epidermal cell culture, is particularly suitable for the field of study relevant to biological tissue engineering and belongs to the commercial cell culture fluid.
Owner:INST OF DONGGUAN SUN YAT SEN UNIV
High purity ulinastatin and its prepn process and medicine composition
ActiveCN1931875AHigh purityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticMetalloproteinPhosphate
The present invention relates to high purity ulinastatin and its medicine composition and their preparation process. Specially, the high purity ulinastatin in 50,000 U / ml concentration has optical absorption value at 405 nm not exceeding 0.05 and human urea kininogenase content not exceeding 0.0003 PNAU. The present invention purifies ulinastatin product through adsorption with hydrophobic column, purification in hydrophilic column, combination with metalloprotein in metal chelating column and elution with buffering phosphate solution.
Owner:GUANGDONG TECHPOOL BIO-PHARMA CO LTD
Antibodies and pharmaceutical compositions containing same useful for inhibiting activity of metalloproteins
An antibody comprising an antigen recognition region which comprises CDR amino acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
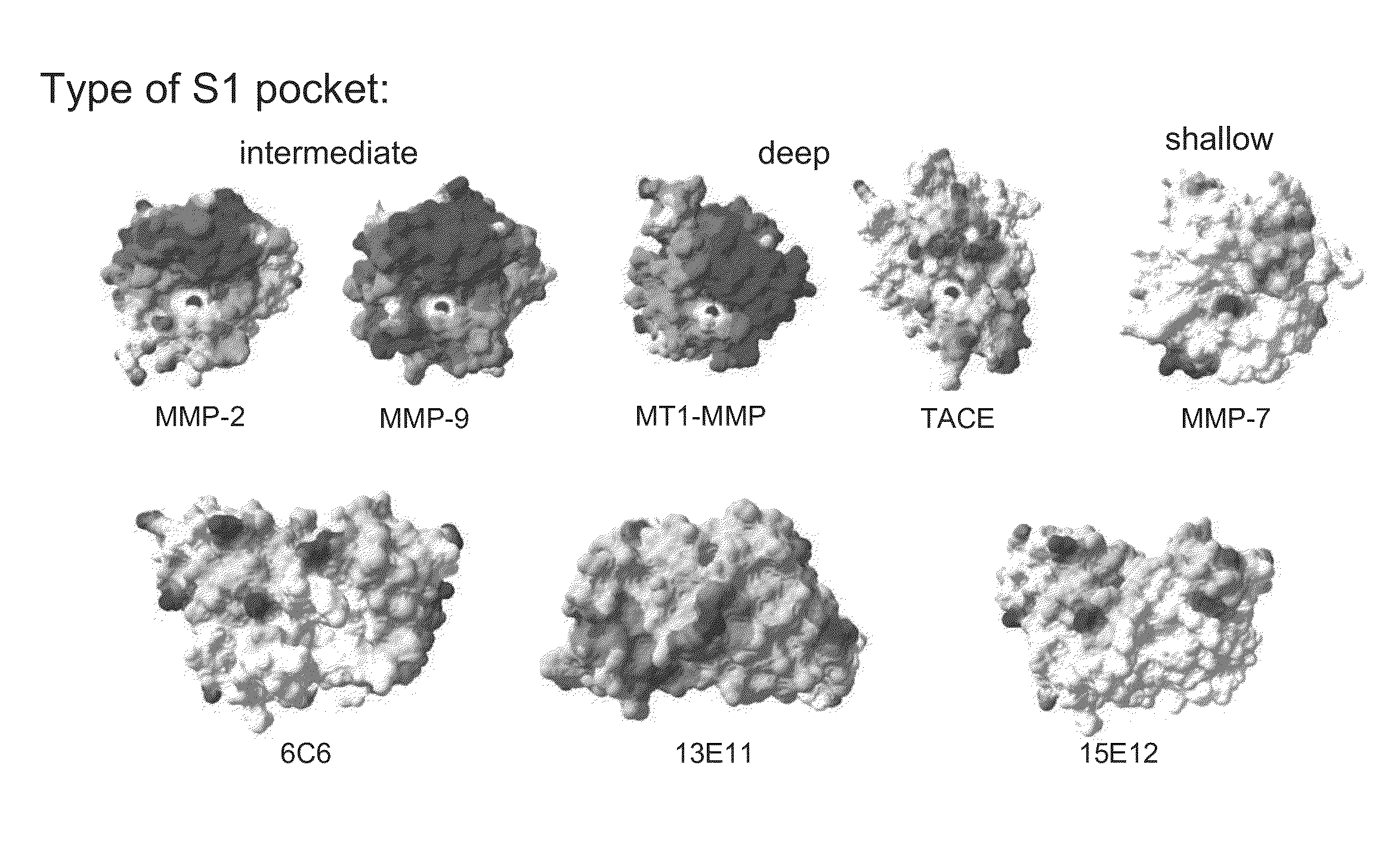
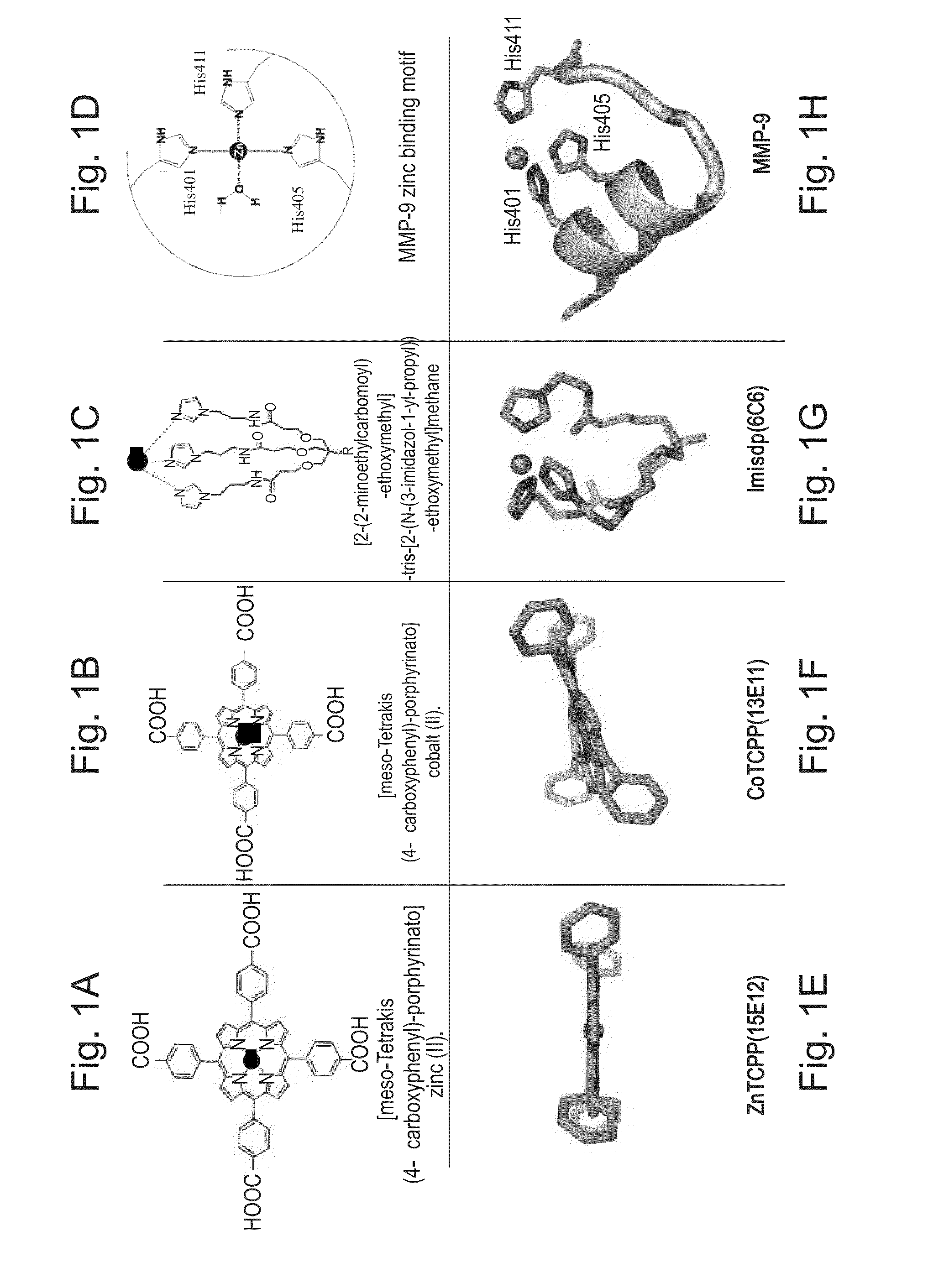
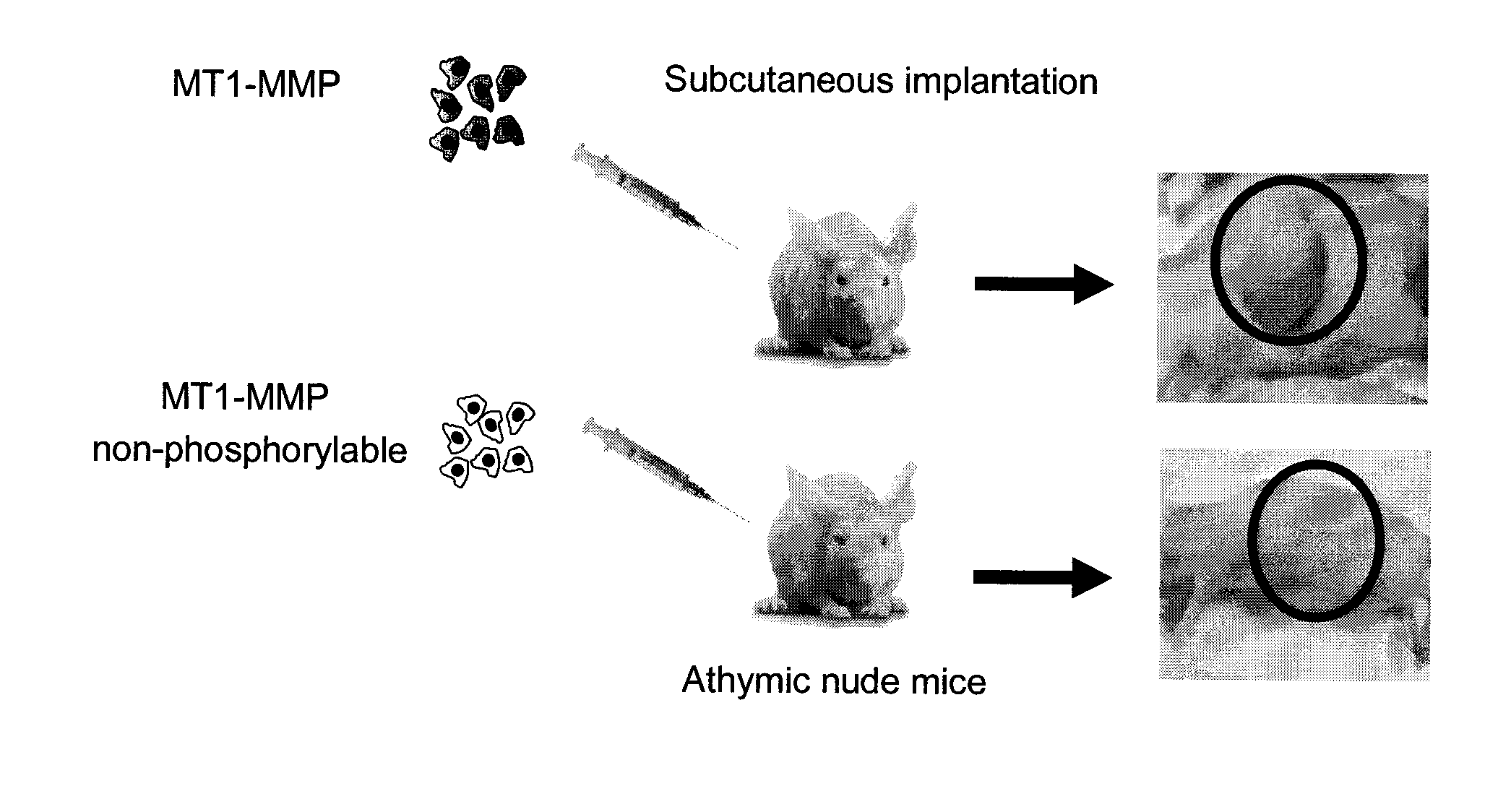
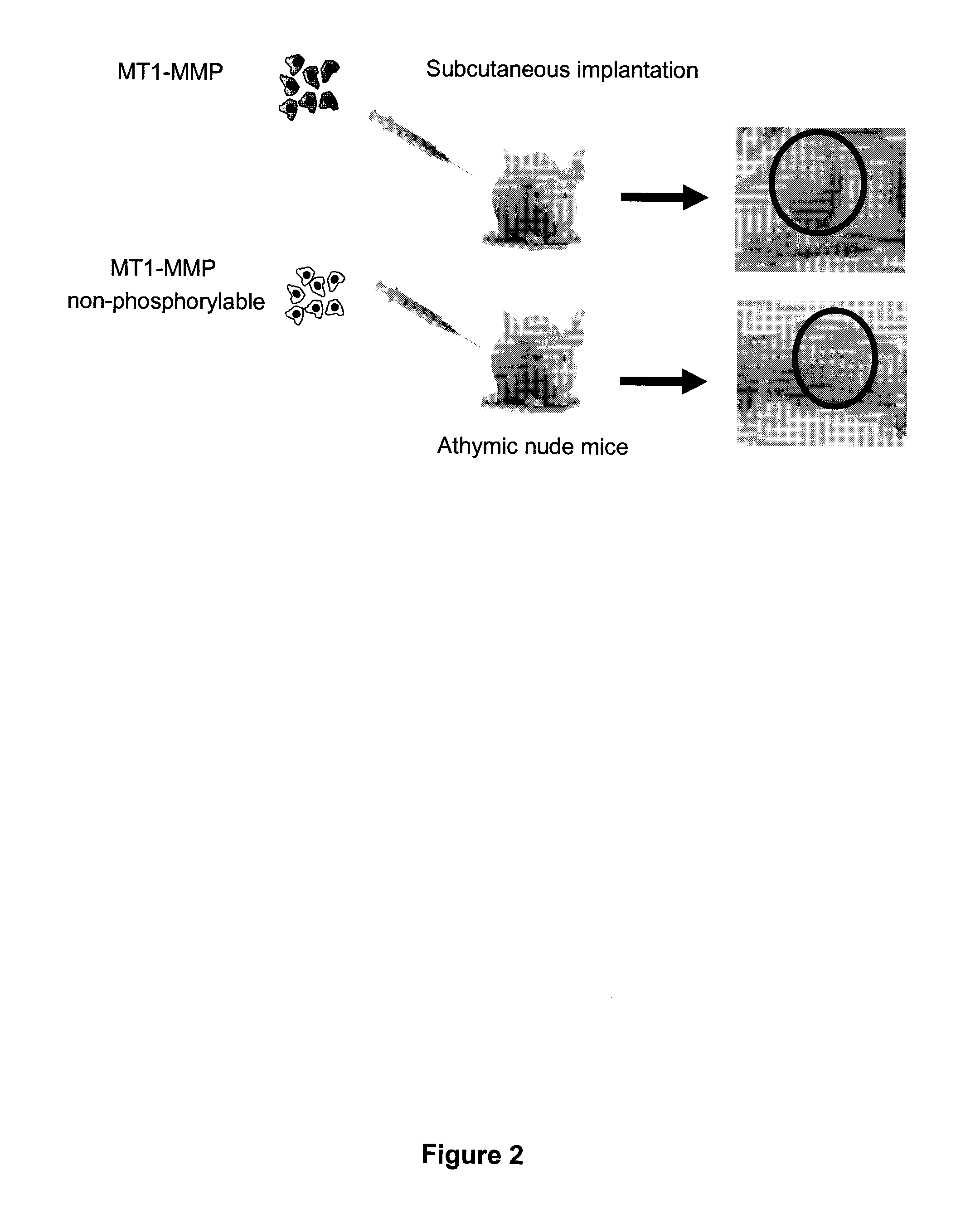
Membrane type-1 matrix metalloprotein inhibitors and uses thereof
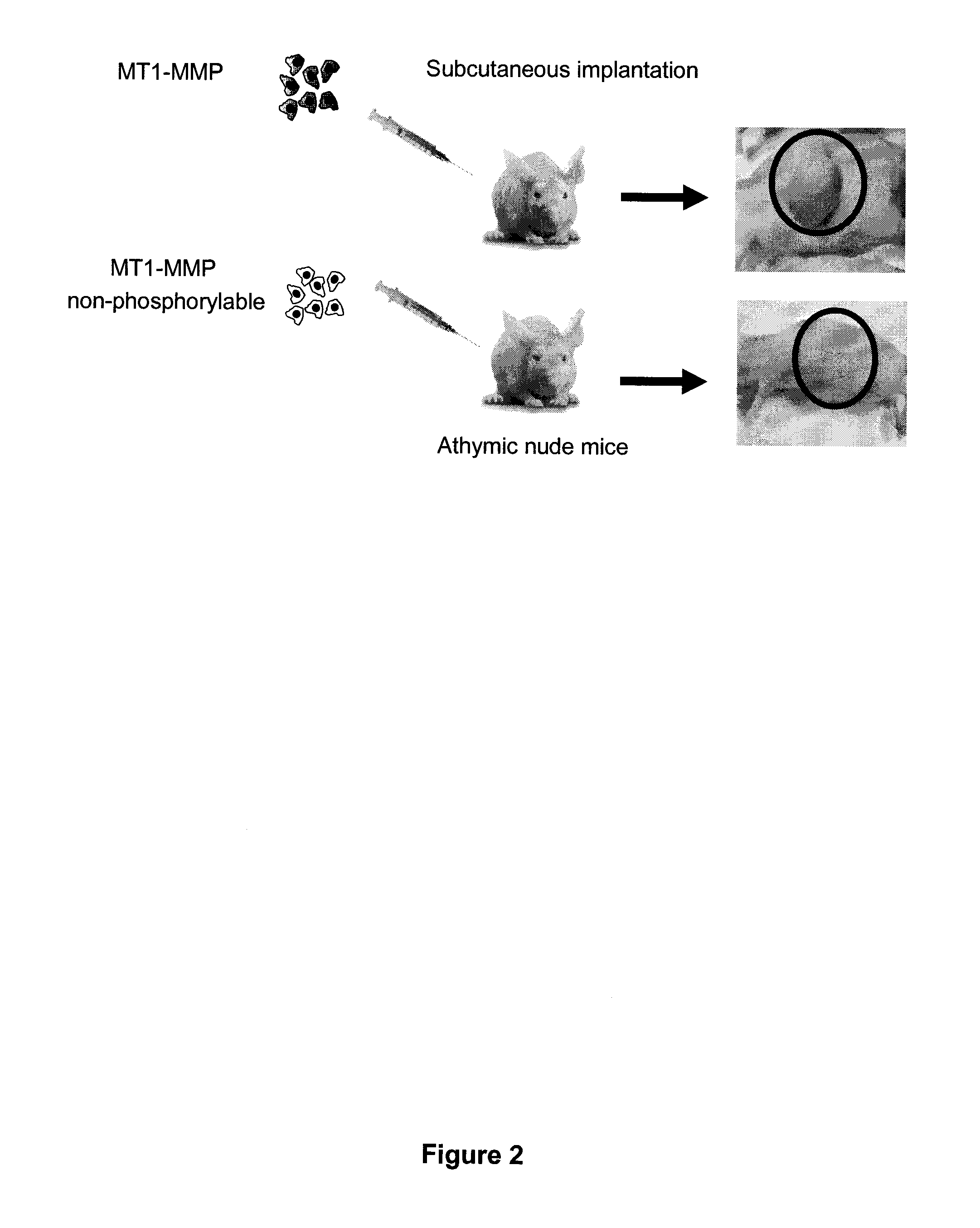
InactiveUS20110305750A1Reduce the frequency of occurrenceReduce severityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticDiseasePhosphorylation
Based on the discovery that a soluble polypeptide including a nonphosphorylatable form of the cytoplasmic domain is capable of inhibiting in a dominant negative manner, the present invention provides compositions including MT1-MMP inhibitors such as peptide inhibitors, and methods for treating diseases associated with MT1-MMP activity. Such diseases include cancer, arthritis, and heart disease, and vascular disease.
Owner:ANGLACHEM INC
Antibodies and pharmaceutical compositions containing same useful for inhibiting activity of metalloproteins
A method of producing a metalloprotein inhibitor, the method comprising generating antibodies directed at a composition including a metal ion-bound chelator, wherein the composition is selected having structural and electronic properties similar to a functional domain of the metalloprotein, thereby producing the metalloprotein inhibitor.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Homogeneous Chemiluminescent Immunoassay for Analysis of Iron Metalloproteins
The present invention relates to assays and kits for detecting or quantifying iron metalloprotein in test samples.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Inhibitors of lpxc
Provided herein, inter alia, are compounds and methods for treating infectious diseases. The compounds provided herein are, inter alia, useful for the treatment of bacterial infections. The compounds provided herein are, inter alia, useful inhibitors of metalloproteins, e.g. UDP-3-O—(R-3-hydroxymyristoyl)-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase (LpxC).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
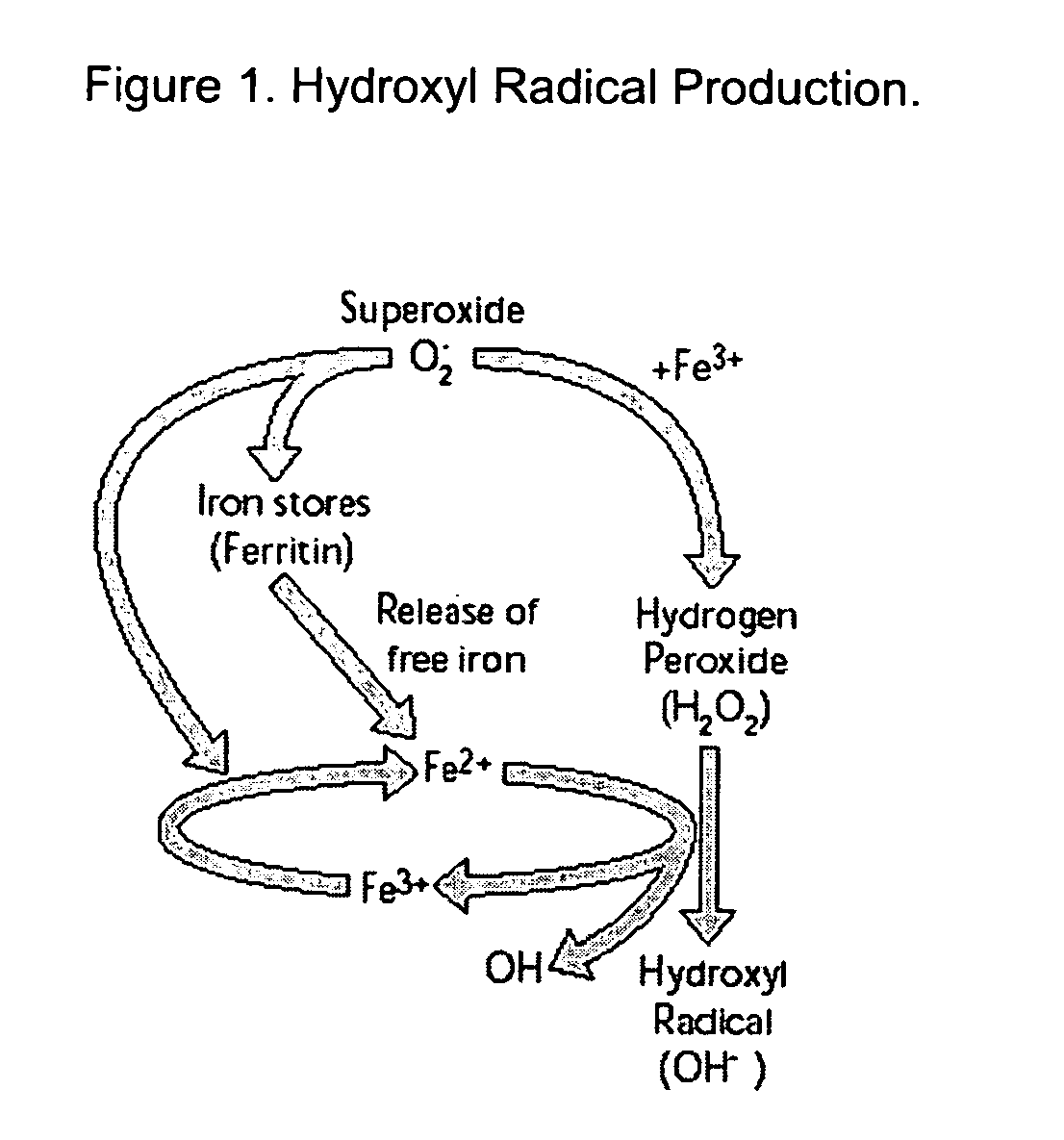
Method of treatment and composition for inhibiting the production of toxic free radical and reactive oxygen species using metalloproteins found in bacteria
PendingUS20050267015A1Preventing tissueAvoid cell damageBiocideSenses disorderThiobacillus ferrooxidansMetalloprotein
Compositions and methods for treating, reducing the risk of, or slowing the onset of a neurological disorder or pathological condition in a subject are provided. An inhibitor of the formation of free radical or reactive oxygen species is administered in an effective amount to the subject and the inhibitor prevents tissue and cellular damage and / or necrosis by inhibiting the release of free radicals or reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can cause such damage in the subject. The inhibitor may be a bacterial metalloprotein. An exemplary free radical production inhibitor is the metalloprotein rusticyanin, a type I blue-copper metalloprotein found in the aerobic acidophilic iron-oxidizing bacterium Thiobacillus ferrooxidan. A composition containing the inhibitor of the formation of free radical or reactive oxygen species includes a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:BATARSEH KAREEM I
Membrane type-1 matrix metalloprotein inhibitors and uses thereof
InactiveUS8853353B2Easy to transportReduce frequencyHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseasePhosphorylation
Based on the discovery that a soluble polypeptide including a nonphosphorylatable form of the MT1-MMP cytoplasmic domain is capable of inhibiting MT1-MMP in a dominant negative manner, the present invention provides compositions including MT1-MMP inhibitors such as peptide inhibitors, and methods for treating diseases associated with MT1-MMP activity. Such diseases include cancer, arthritis, and heart disease, and vascular disease.
Owner:ANGLACHEM INC
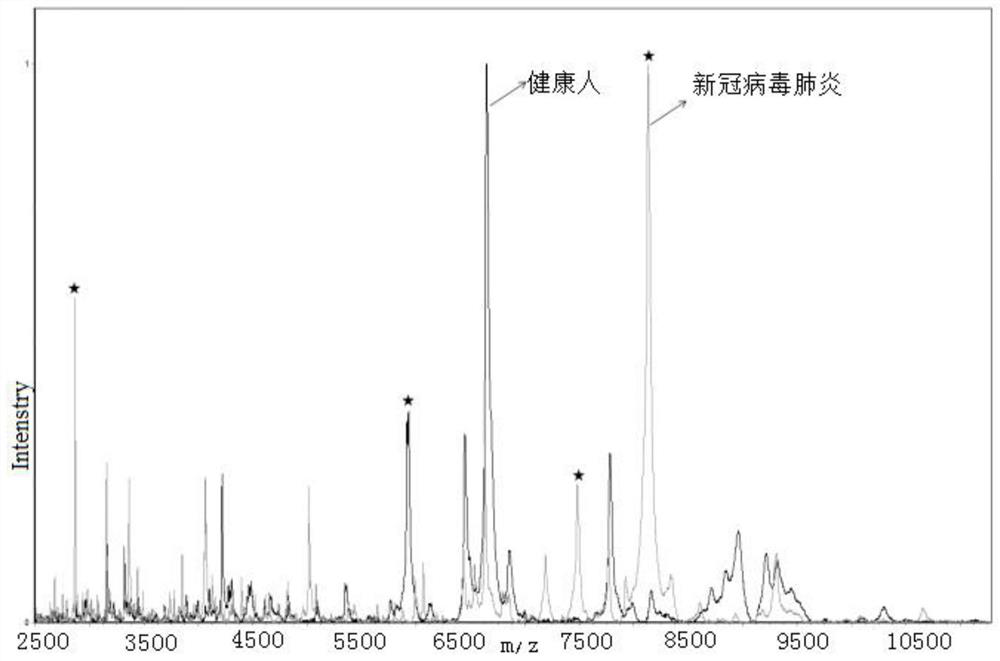
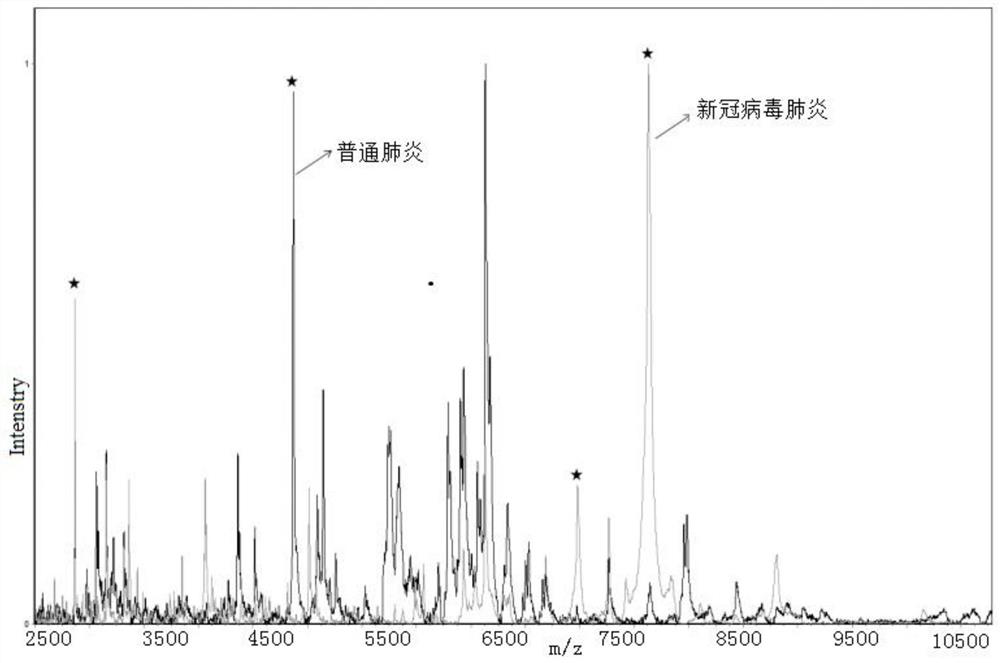
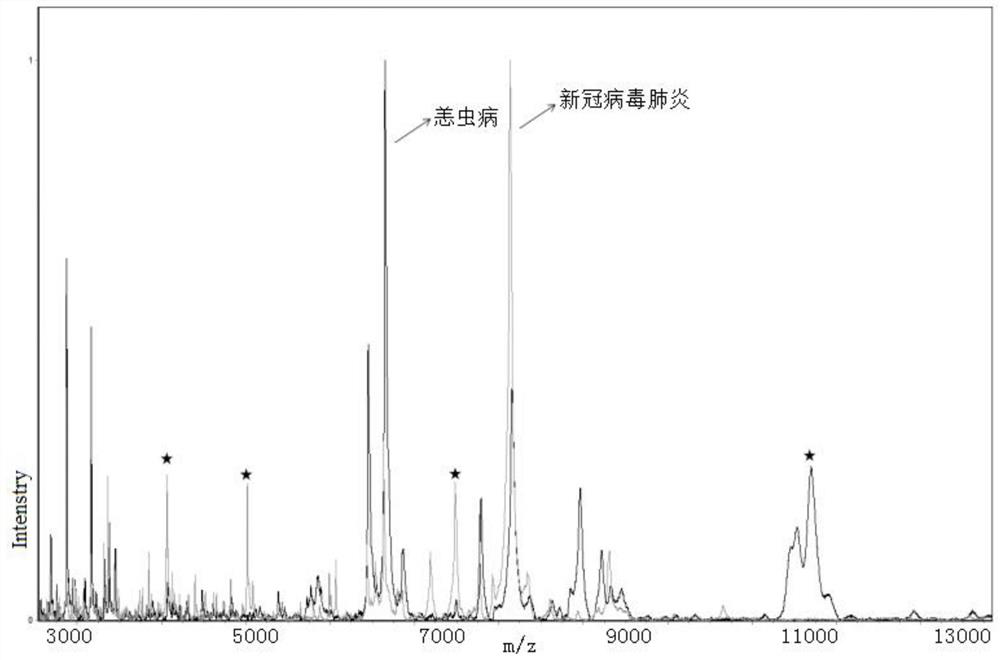
Kit for identifying new coronavirus by applying mass spectrum system and using method thereof
ActiveCN111830120AFast and effective comprehensive detectionAccurate detectionPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSodium acetateMetalloprotein
The invention discloses a kit for identifying a new coronavirus by applying a mass spectrum system and a use method of the kit. The kit comprises the following components: a U9 buffer solution, a U1 buffer solution and a sodium acetate buffer solution. The using method of the kit comprises the following steps: S1, activating a metalloprotein chip target plate; S2, pretreating a serum sample; S3, extracting protein in the serum sample by using the metalloprotein chip target plate; and S4, acquiring and processing a spectrogram by using an MALDI-TOF mass spectrum system, and analyzing the read spectrogram by using software. Therefore, the kit is high in sensitivity, good in accuracy, simple and convenient to operate, short in consumed time and very suitable for clinical diagnosis.
Owner:北京东西分析仪器有限公司
Metalloprotein Inhibitors
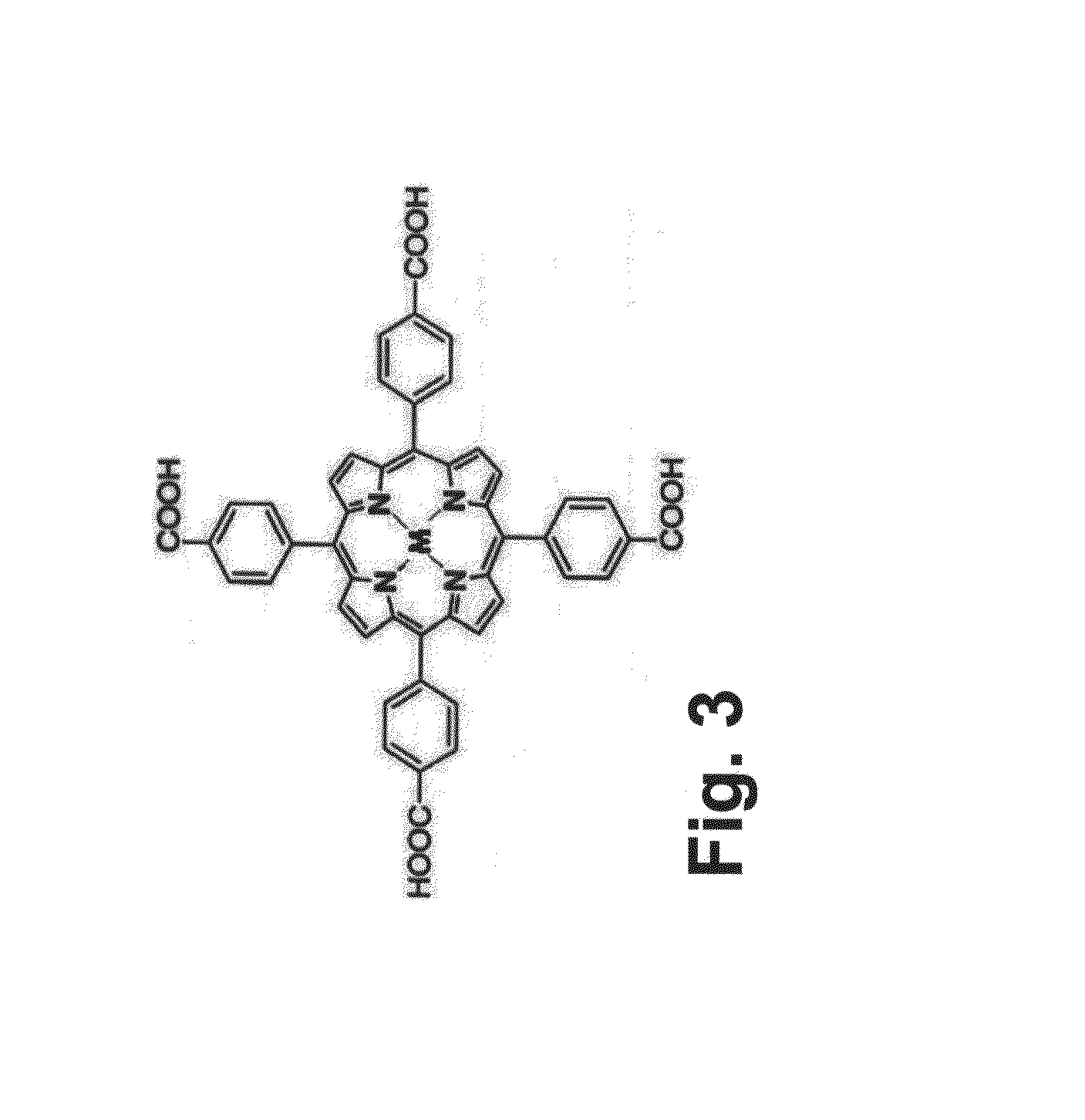
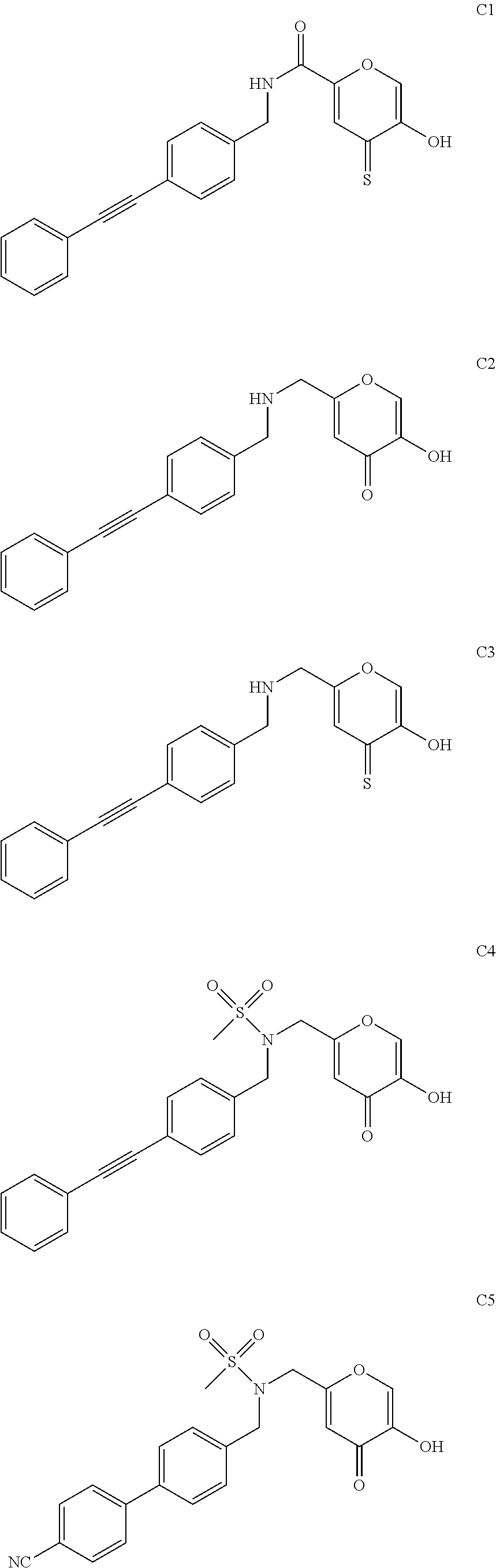
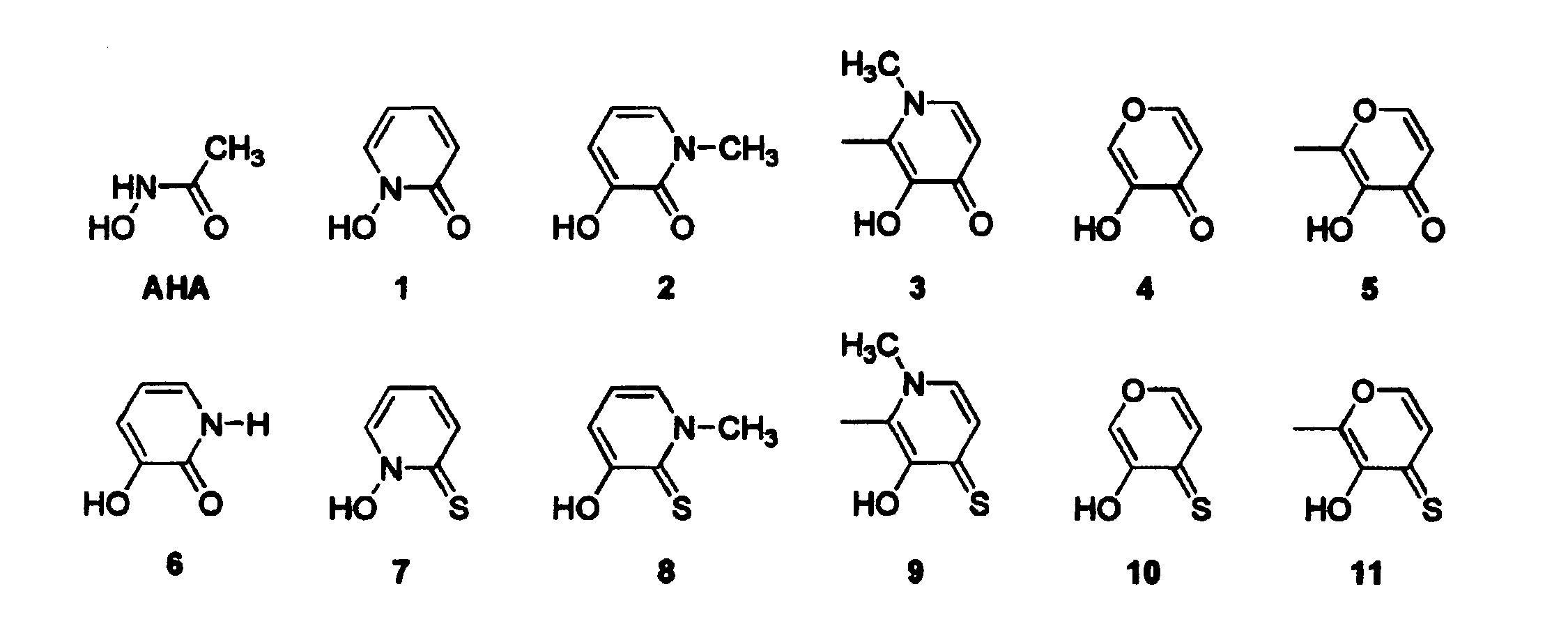
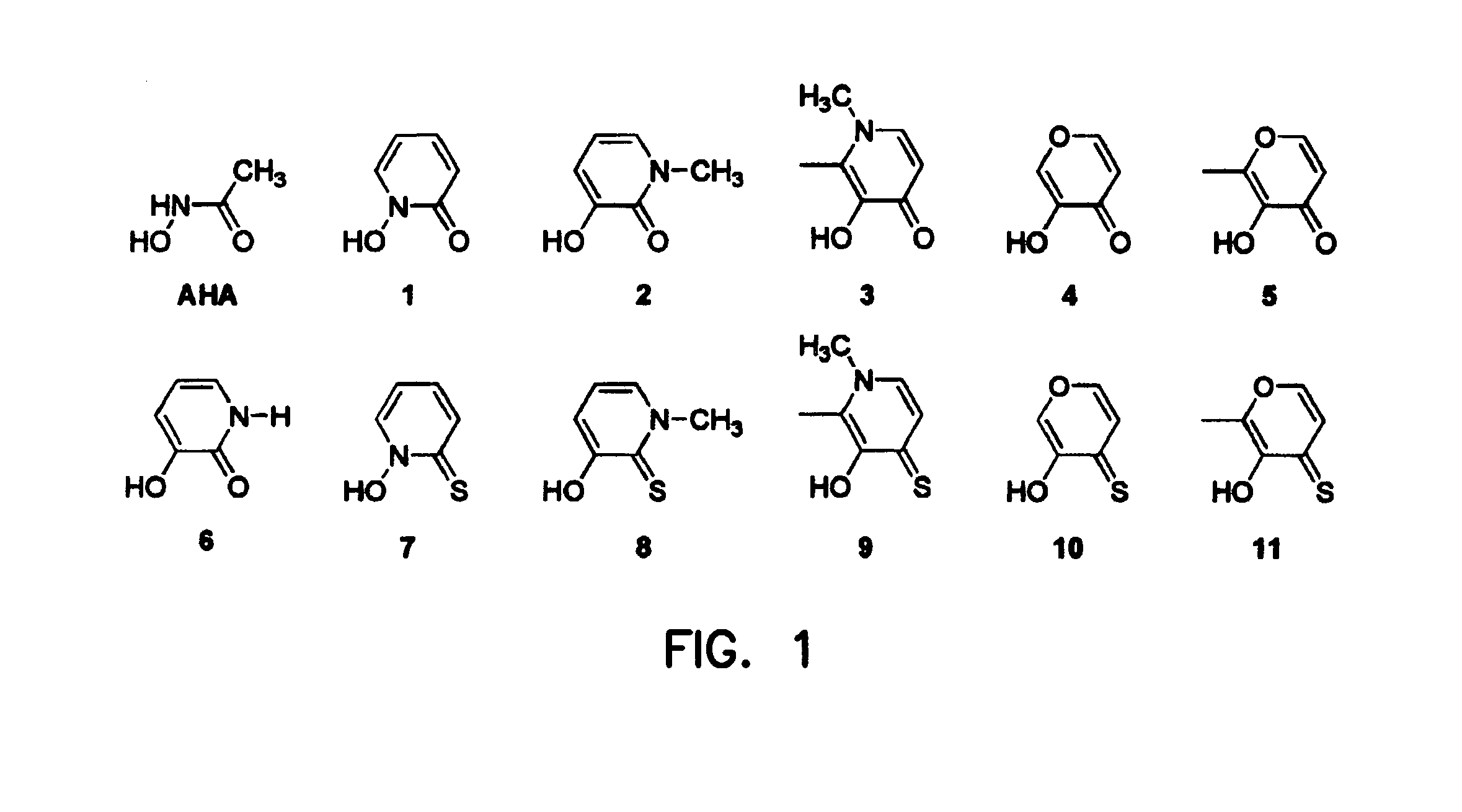
The present invention relates to metalloprotein inhibitors comprising: a. an organic substituent and at least one zinc binding group (ZBG) covalently attached thereto; or b. a ZBG substituted by a side chain wherein the ZBG is of formula (I): wherein X is O or S and each R1, R2, R3, and R4 is individually hydrogen or an organic radical. The metalloprotein inhibitors are useful for preventing or treating a pathological disease, condition, or symptom that is associated with pathological metalloprotein activity and / or that is alleviated by inhibition of said activity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
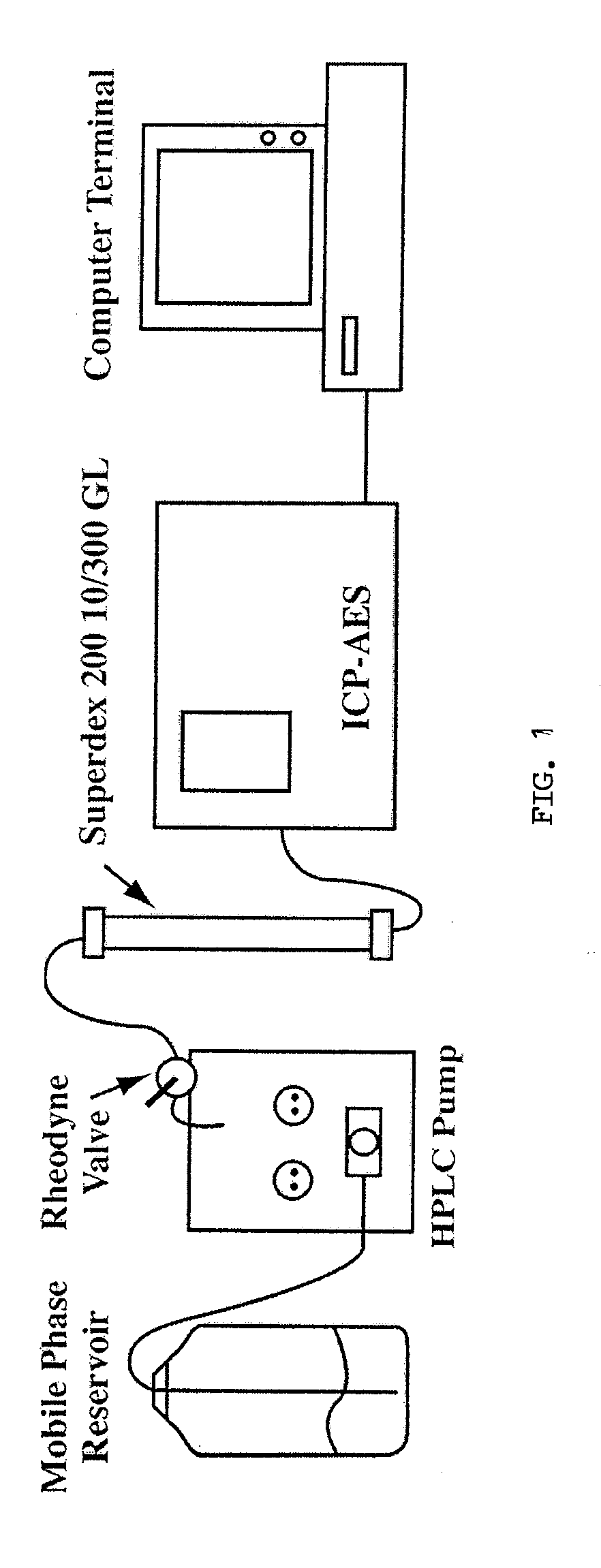
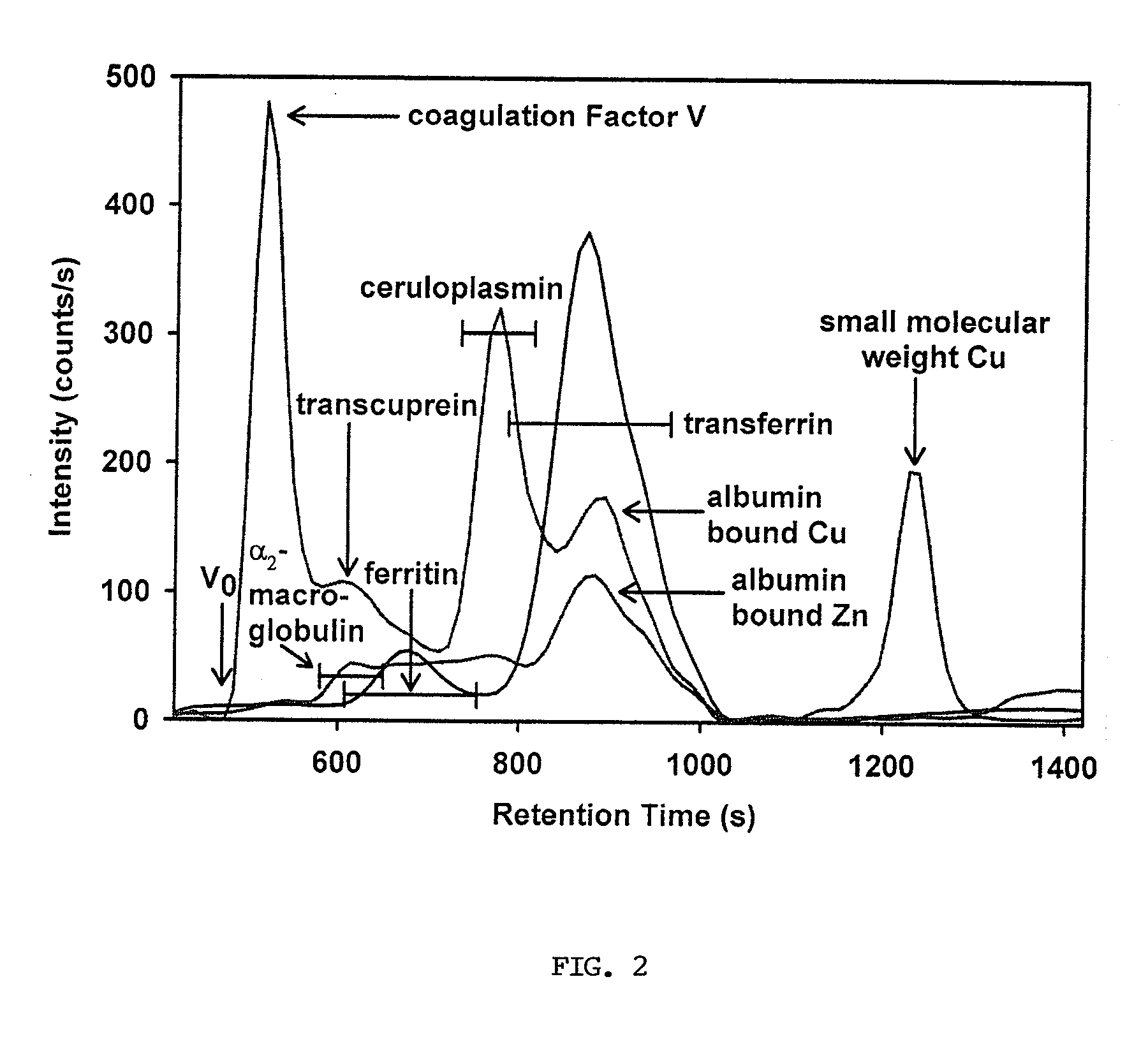
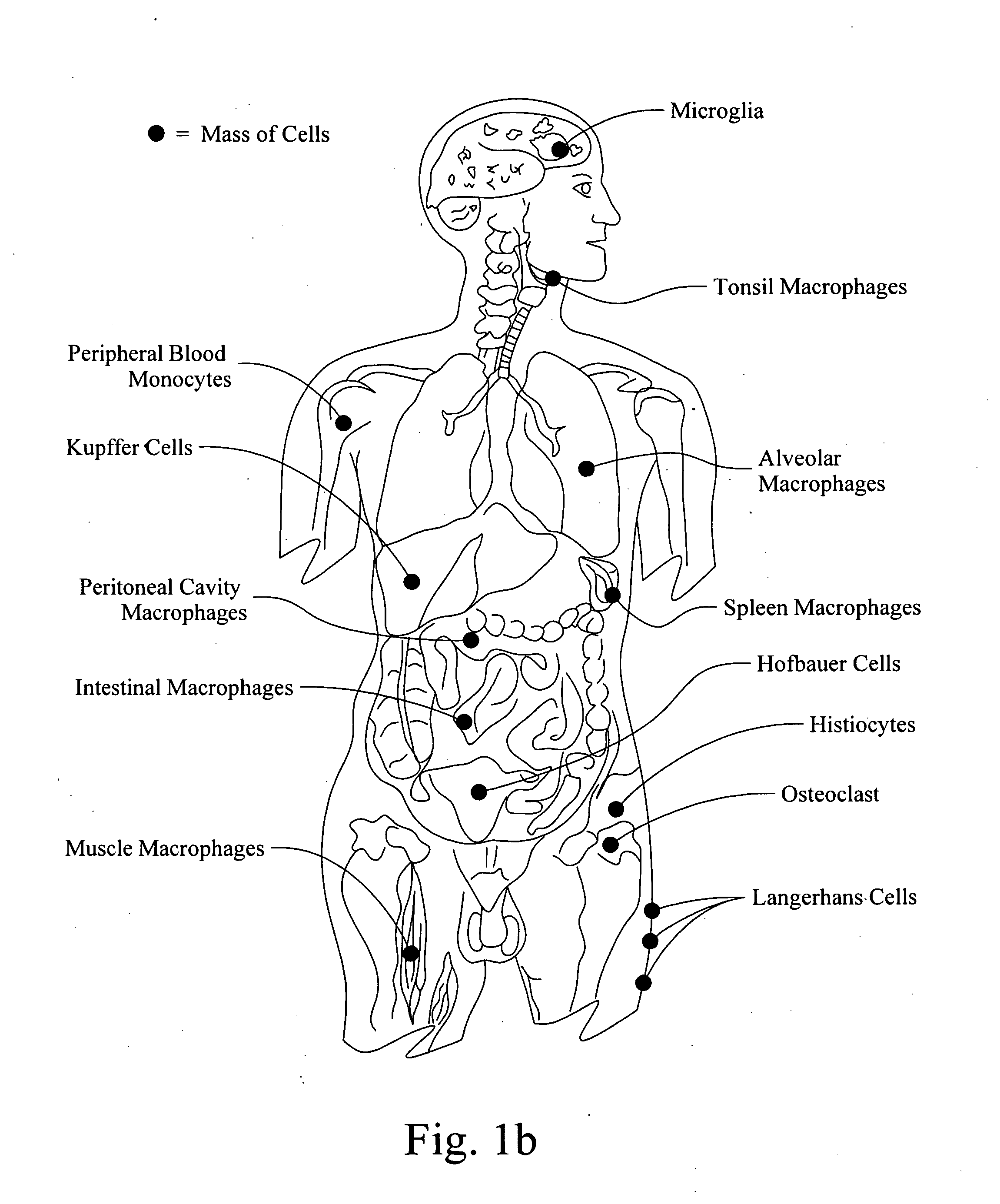
Method for Assessing Trace Element Related Disorders in Blood Plasma
InactiveUS20080299543A1Component separationMicrobiological testing/measurementMetalloproteinTrace element
Owner:UTI LLP
Method to control dengue viruses in humans by picolinic acid and derivatives thereof
A method treats and then prevents a virus for afflicting an animal or a human as a metalloprotein mediates the virus. The method administers systemically a therapeutic pharmacological agent of picolinic acid either singly or with interferons, chemokines or cytokines to fight dengue fever virus. The picolinic acid inactivates the metalloprotein that allows replication of the virus. The picolinic acid has the structure of:where R1, R2, R3, and R4 are mutually exclusive. The viral proteins disintegrate by macrophage proteolytic enzymes stimulated by the picolinic acid.
Owner:FERNANDEZ POL JOSE ALBERTO +1
Formative agent of protein complex
The present invention proposes formative agent of protein complex, in which a polyphenol is useful component, and the agent is useful as gene complex, cell adhesion inhibitor or immune tolerogen. The polyphenol of forming the agent is selected from catechin group consisting of epigallocatechin-gallate, tannic acids, or proanto-dianisidine, a protein of the protein complex is selected from proteins consisting of animal proteins composed of polypeptide chain of peptide-combined amino acids, vegetative proteins, nucleus proteins, glycogen proteins, lipo-proteins and metal proteins, the gene complex comprises by compositing genes by polyphenol catechins in order to introduce genes to cells of animals or human bodies, a cell composed of the cell adhesion inhibitor is selected from cells consisting of an animal cell including a stem cell, skin cell, mucosa cell, hepatocyte, islet cell, neural cell, cartilage cell, endothelial cell, epidermal cell, osteocyte or muscle cell isolated from human or animal organism, or sperm, ovum or fertilized egg of domestic animals or fishes and a tissue or an organ for transplantation of the immune tolerogen is selected from the tissue or the organ consisting of skin, blood vessel, cornea, kidney, heart, liver, umbilical cord, bowels, nerve, lung, placenta or pancreas.
Owner:BERTELSMANN MUSIC GROUP
Method for assessing trace element related disorders in blood plasma
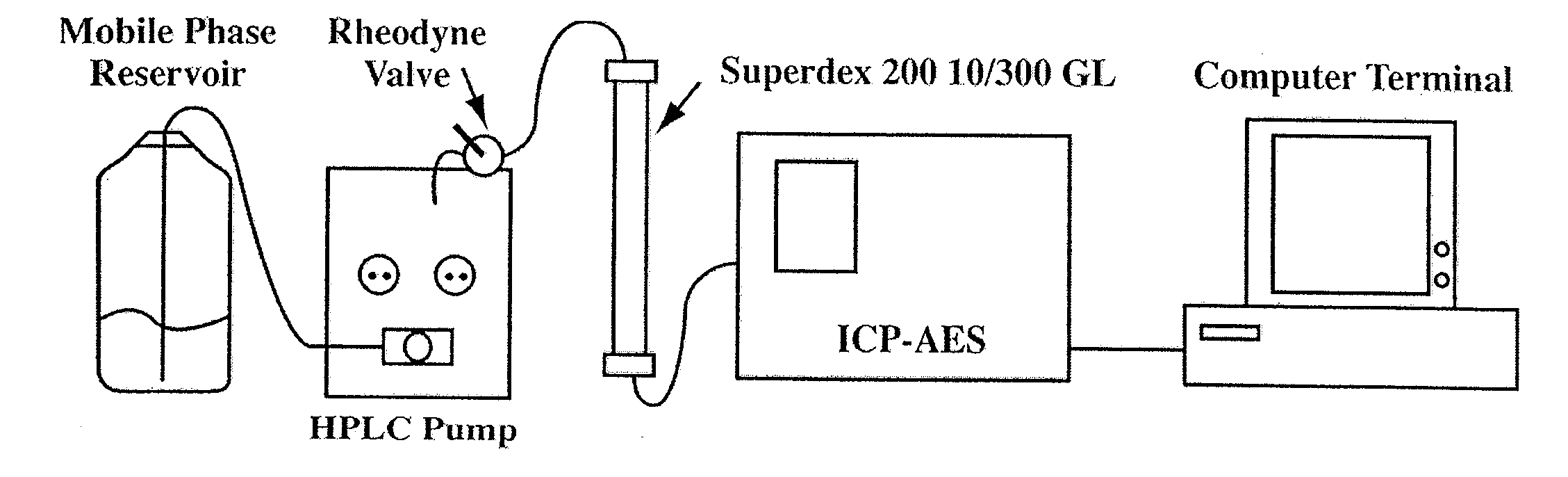
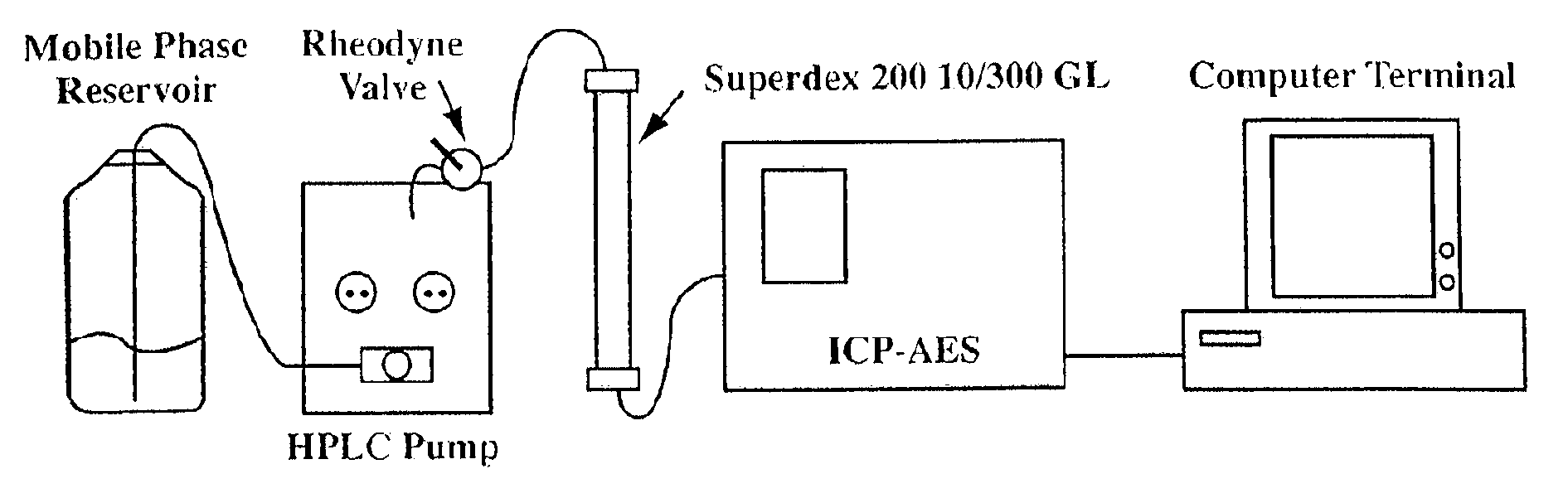
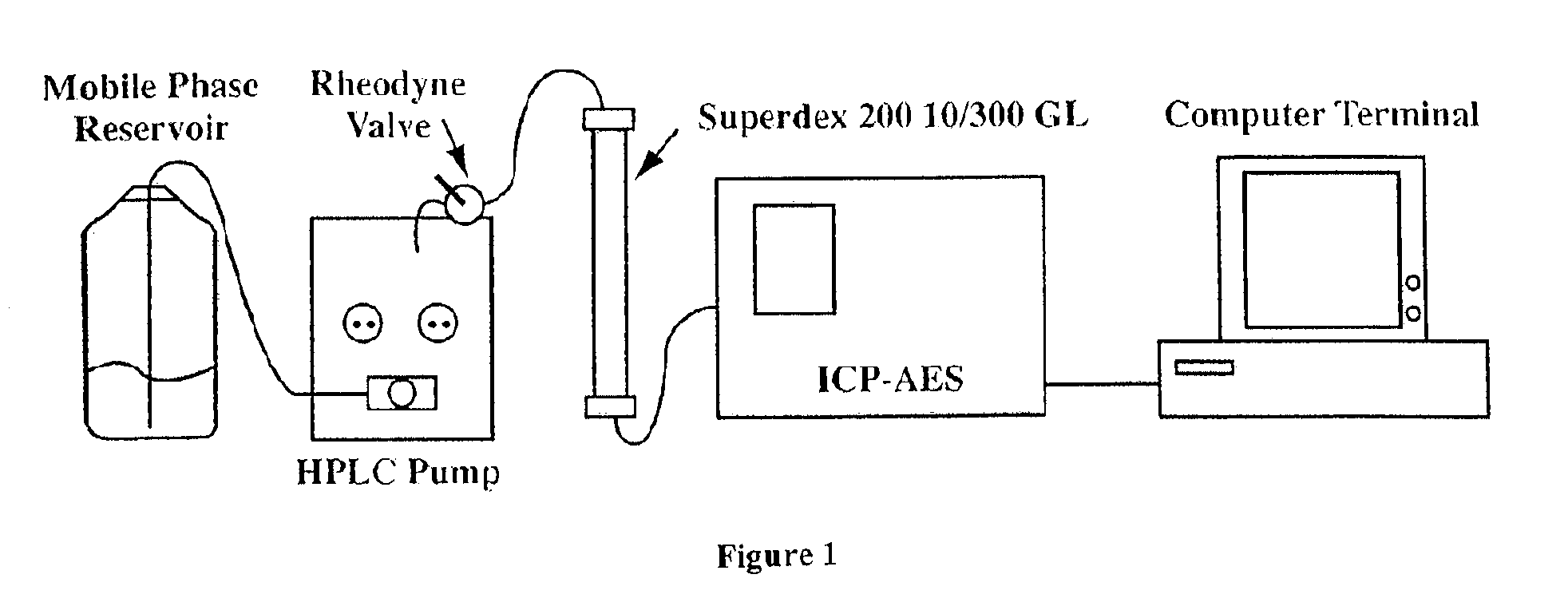
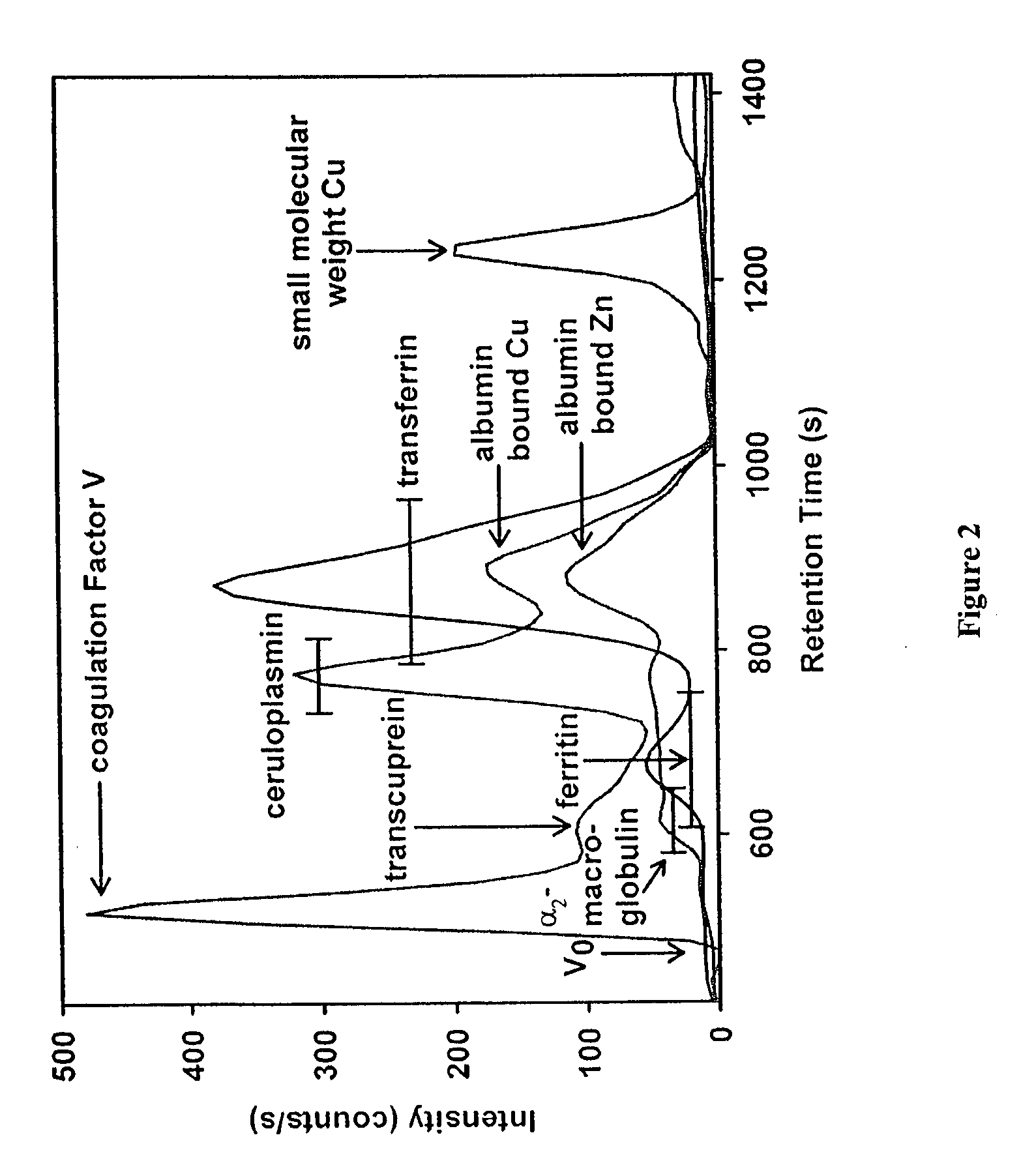
The present invention provides for spectrometric methods of analyzing blood plasma or serum for metal distribution in metalloproteins by subjecting the sample to size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) and determining the metal content of the separated protein fractions by inductively-coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES). The methods can be used to assess such conditions as toxicity and disease in subjects.
Owner:UTI LLP
Diagnostic Agents Selective Against Metalloproteases
ActiveUS20110117015A1High affinityOptimal diagnostic visualizationAntibacterial agentsBiocideArylMetalloprotein
The invention relates to aryl-sulphonamido compounds endowed with affinity against metallo proteases MMP, having formula (I) below wherein R, R1, R2, R3, G and n have the meanings reported in the specification, properly labelled with diagnostic imaging moieties or even radiotherapeutic moieties. The invention also refers to the process for their preparation, to pharmaceutical compositions comprising them and to their use as diagnostic imaging agents or radiotherapeutic agents.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
High purity ulinastatin and its prepn process and medicine composition
The present invention relates to high purity ulinastatin and its medicine composition and their preparation process. Specially, the high purity ulinastatin in 50,000 U / ml concentration has optical absorption value at 405 nm not exceeding 0.05 and human urea kininogenase content not exceeding 0.0003 PNAU. The present invention purifies ulinastatin product through adsorption with hydrophobic column, purification in hydrophilic column, combination with metalloprotein in metal chelating column and elution with buffering phosphate solution.
Owner:GUANGDONG TECHPOOL BIO-PHARMA CO LTD
Method for measuring content of metallic ion in metal protein
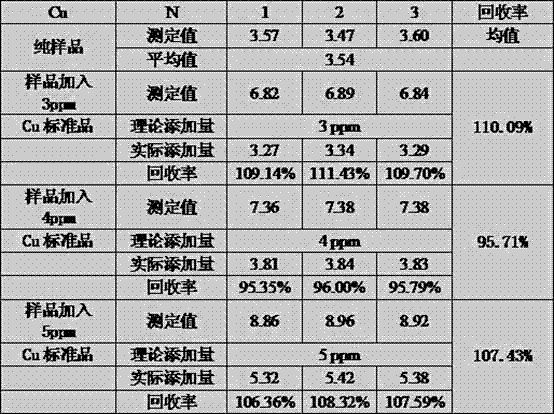
ActiveCN102393365AImprove accuracyHigh precisionPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsMetalloproteinOptical spectrometer
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of a metallic ion in a metal protein, which comprises the following steps of: pretreating a sample, preparing or treating the sample with an acid material and enabling the pH value of a sample solution to be smaller than 5; and then measuring by a metallic element measuring spectrum (an atomic absorption spectroscopy or an atomic emission spectrometer). According to the method, the problems of low accuracy, poor precision, poor reproducibility, poor specificity and the like in the method for measuring the content of the metallic ion in the metal protein are solved; the detection time can be shortened; the analysis efficiency is improved and the analysis cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING TIDE PHARMA
Use of one or more metal carriers to selectively kill mammalian cells
InactiveUS20100137557A1High affinityImprove accuracyHeavy metal active ingredientsPowder deliveryMetalloproteinCancer cell
Owner:ZOLTAN LAB
Purified ustading and its preparation method and medicinal composition containing said ustading
ActiveCN100425286CHigh purityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticMetalloproteinPhosphate
A purified ulinastatin is prepared through adsorbing by hydrophobic column, separating by gel column, combining metalloprotein by metallic chelating column, and eluting with phosphate buffering liquid. A composite medicine containing the purified ulinastatin also disclosed.
Owner:GUANGDONG TECHPOOL BIO-PHARMA CO LTD
Cholic acid modified amphiphilic pyrene derivative fluorescent probe as well as synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN106047339AGood biocompatibilityGood chemical stabilitySteroidsFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein detectionFluorescence
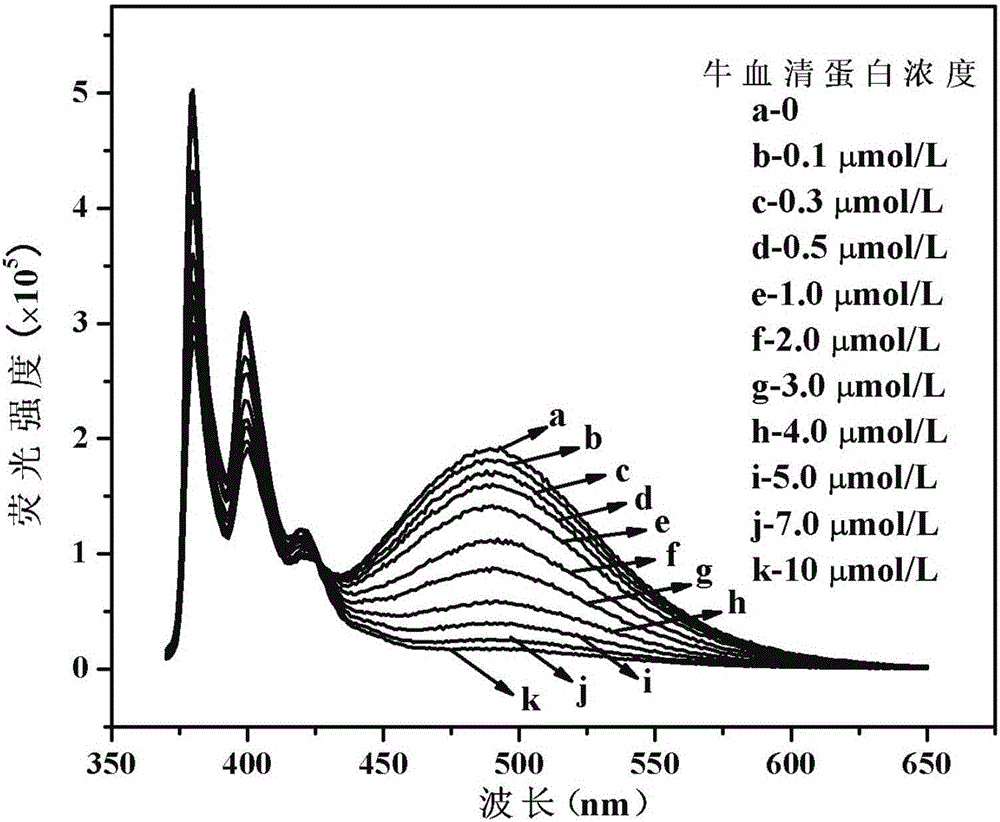
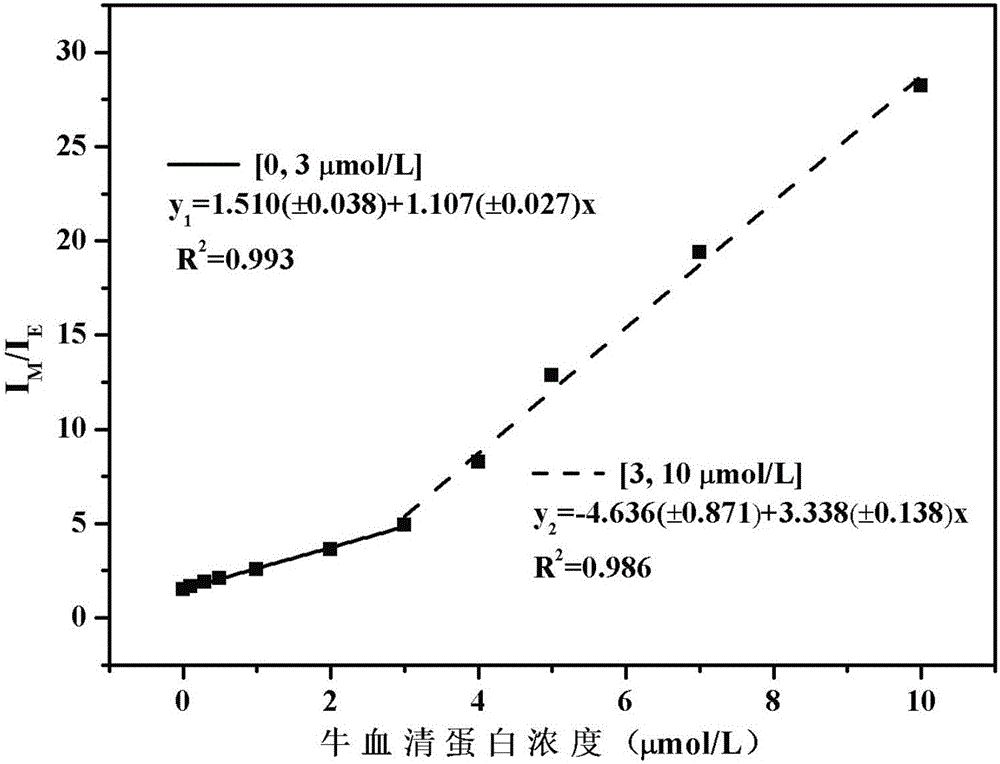
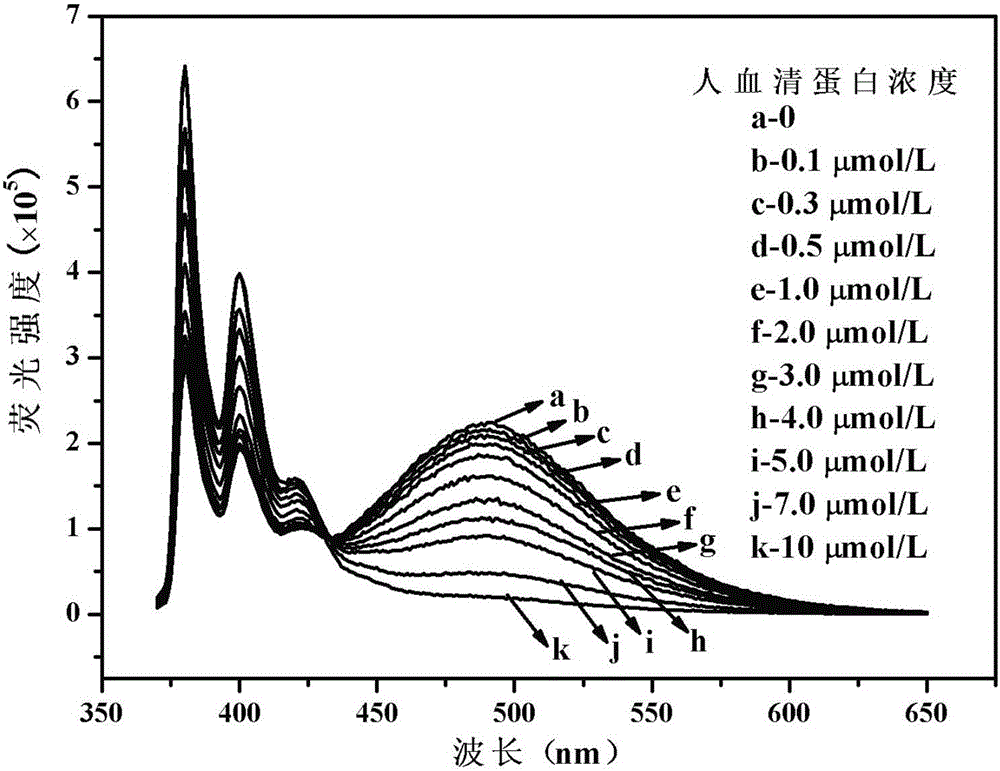
The invention discloses a cholic acid modified amphiphilic pyrene derivative fluorescent probe as well as a synthesis method and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of protein detection. The fluorescent probe has the advantages of good chemical stability, good biocompatibility, high response speed, high sensitivity, wide response range, low detection limit and the like, and can be used for determining protein in time in an online manner. The fluorescent probe can be used for selectively detecting bovine serum albumin (BSA) and human serum albumin (HAS) in non-metal protein and the detection limits can reach 19.8nmol / L (1.32Mug / mL) and 24.5nmol / L (1.64Mug / mL).
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
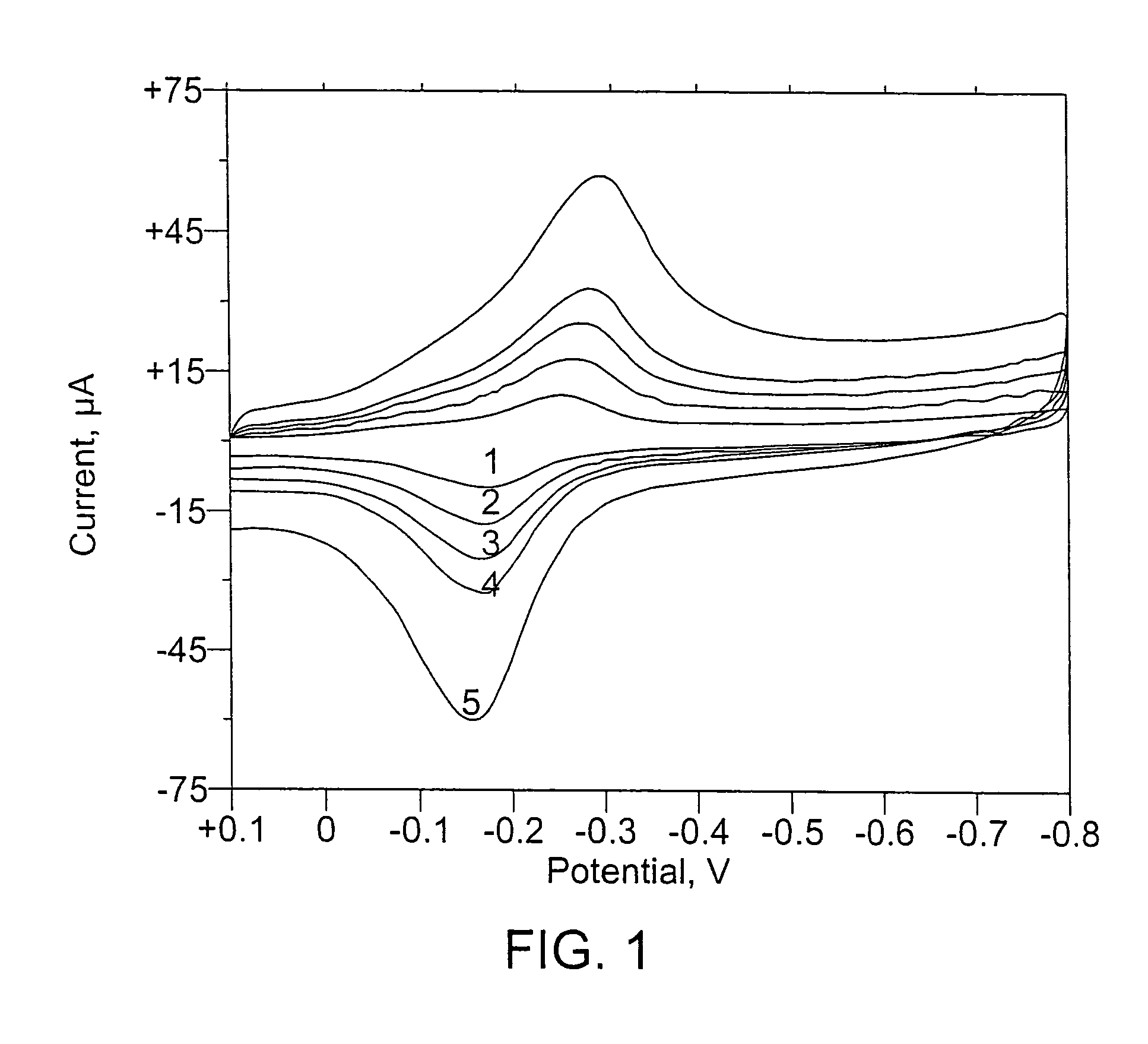
Magnetically modified electrodes containing at least one catalyst component that mediates a subatomic particle transfer process
Disclosed are magnetically modified electrodes containing at least one catalyst component that mediates a subatomic particle transfer process. Also disclosed are magnetically modified electrodes containing metalloproteins (metalloenzymes).
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Method for separating copper proteome by using copper-chelated magnetic beads
InactiveCN105085606AGuaranteed separation effectImprove acquisition efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsPlant peptidesProtein solutionCoboglobin
The invention discloses a method for separating copper proteome by using copper-chelated magnetic beads, and relates to the technical field of protein chemistry. The method comprises the following steps: taking a biological tissue or cell, after fully grinding with liquid nitrogen, adding protein extracting liquid, and after uniformly mixing, carrying out low-temperature centrifugation, so as to obtain a denatured protein solution; mixing the copper-chelated magnetic beads with the denatured protein solution, and incubating to obtain a magnetic bead protein mixed solution; adding a buffer solution 1 with the volume 1 time of that of the magnetic bead protein mixed solution into the magnetic bead protein mixed solution for suspension, pouring half of the supernate under the external magnetic field, and repeating for 4-5 times to obtain a mixed solution A; adding a buffer solution 2 with the volume 1 time of that of the mixed solution A into the mixed solution A, separating all the specific copper-binding proteins, namely, the copper proteome, and collecting the copper proteome under the external magnetic field. According to the method, the metalloproteome is separated under a denaturing condition by using magnetic bead-IDA, so that the procedures are greatly simplified, and the obtaining efficiency of metalloproteins is improved; a method suitable for separating the metalloproteome from the tissue or cell under the excess heavy metal treatment condition is established.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Lepidoptera pest ground substance metalloprotein gene mmp and application thereof
InactiveCN101210252AReduce the ratioHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementMetalloproteinNucleotide
The invention discloses a matrix metalloproteinase gene (mmp) derived from a Lepidoptera pest, whic has the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also discloses a protein encoded by the gene mmp, which has an amoni acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention further discloses the use of the gene mmp in regulation of allergic reaction of Lepidoptera pests.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
RNA INTERFERENCE MEDIATED INHIBITION OF MATRIX METALLOPROTEINASE 13 (MMP13) GENE EXPRESSION USING SHORT INTERFERING NUCLEIC ACID (siNA)
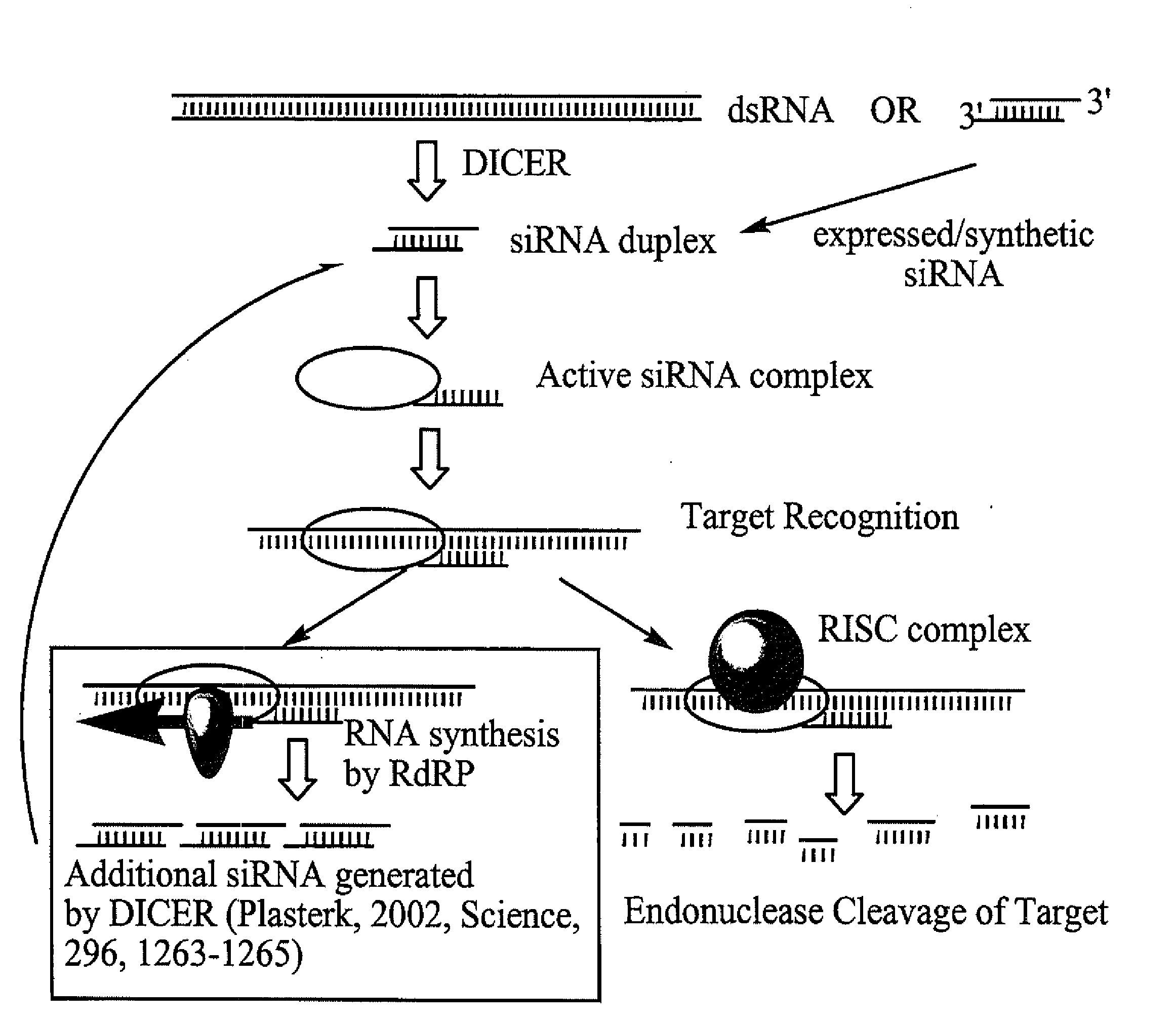
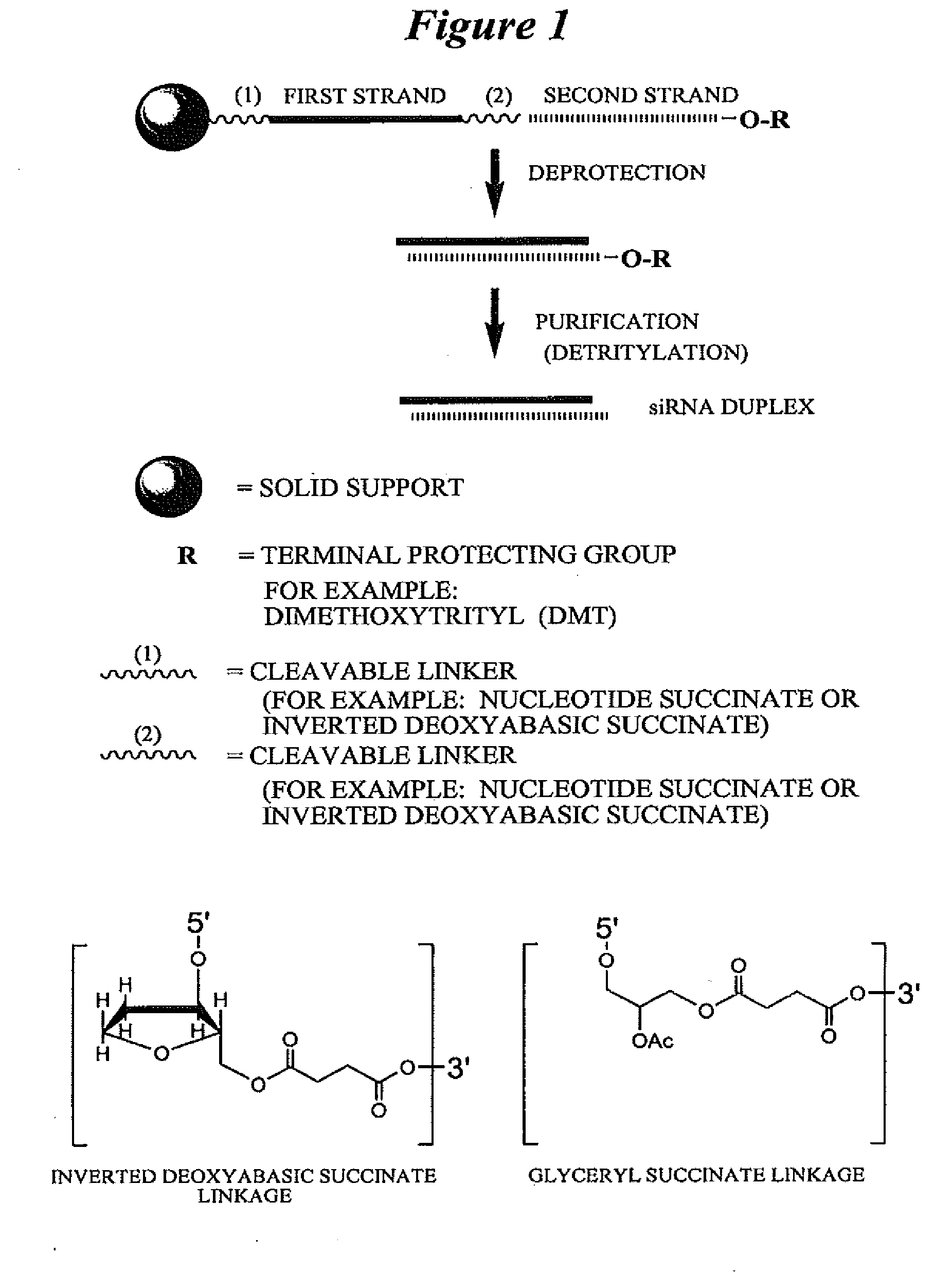
InactiveUS20090099121A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesMetalloproteinDouble stranded rna
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating matrix metalloproteinase (e.g., MMP13) gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of MMP13 genes.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com