Patents
Literature
359results about How to "Solve the low heat dissipation efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
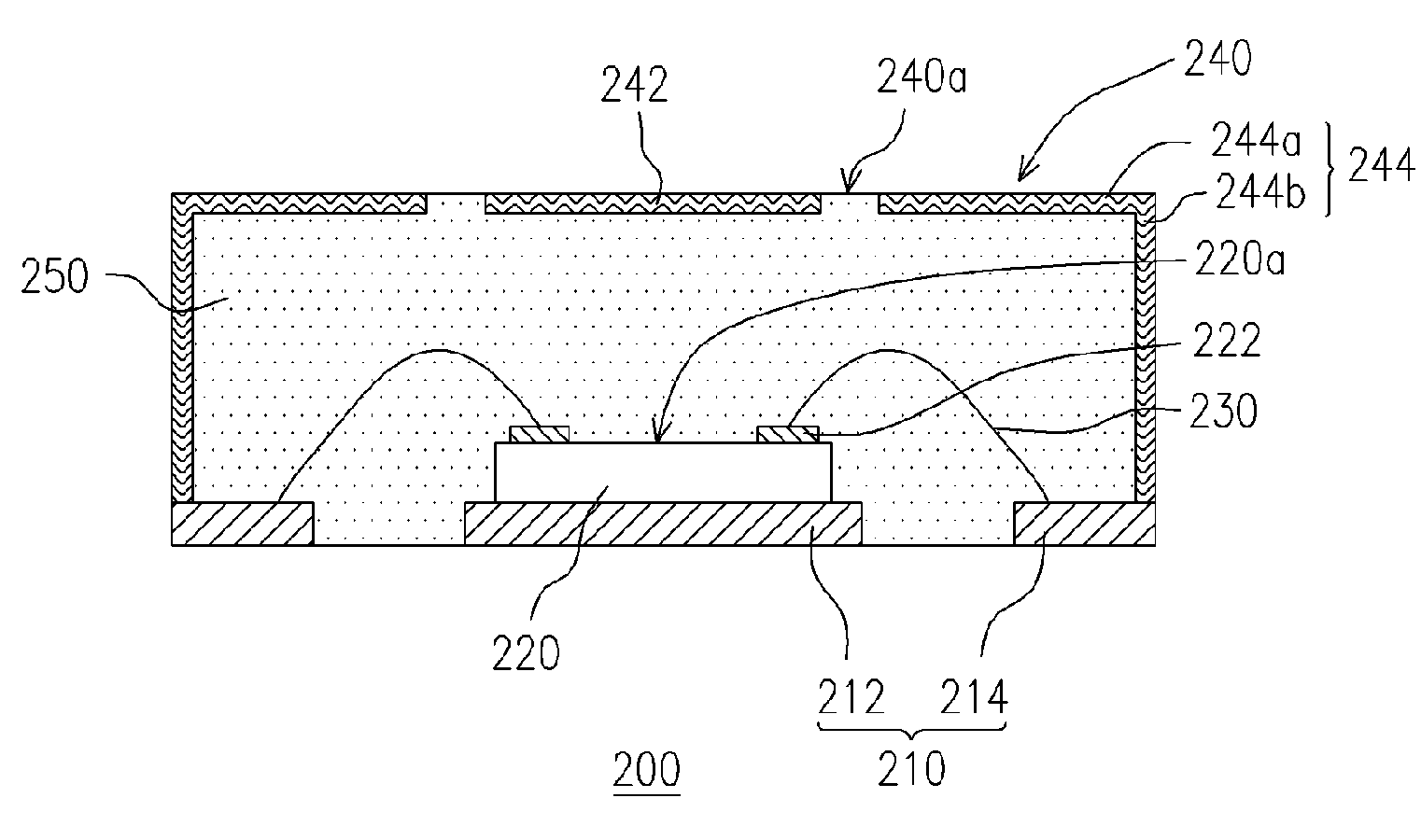
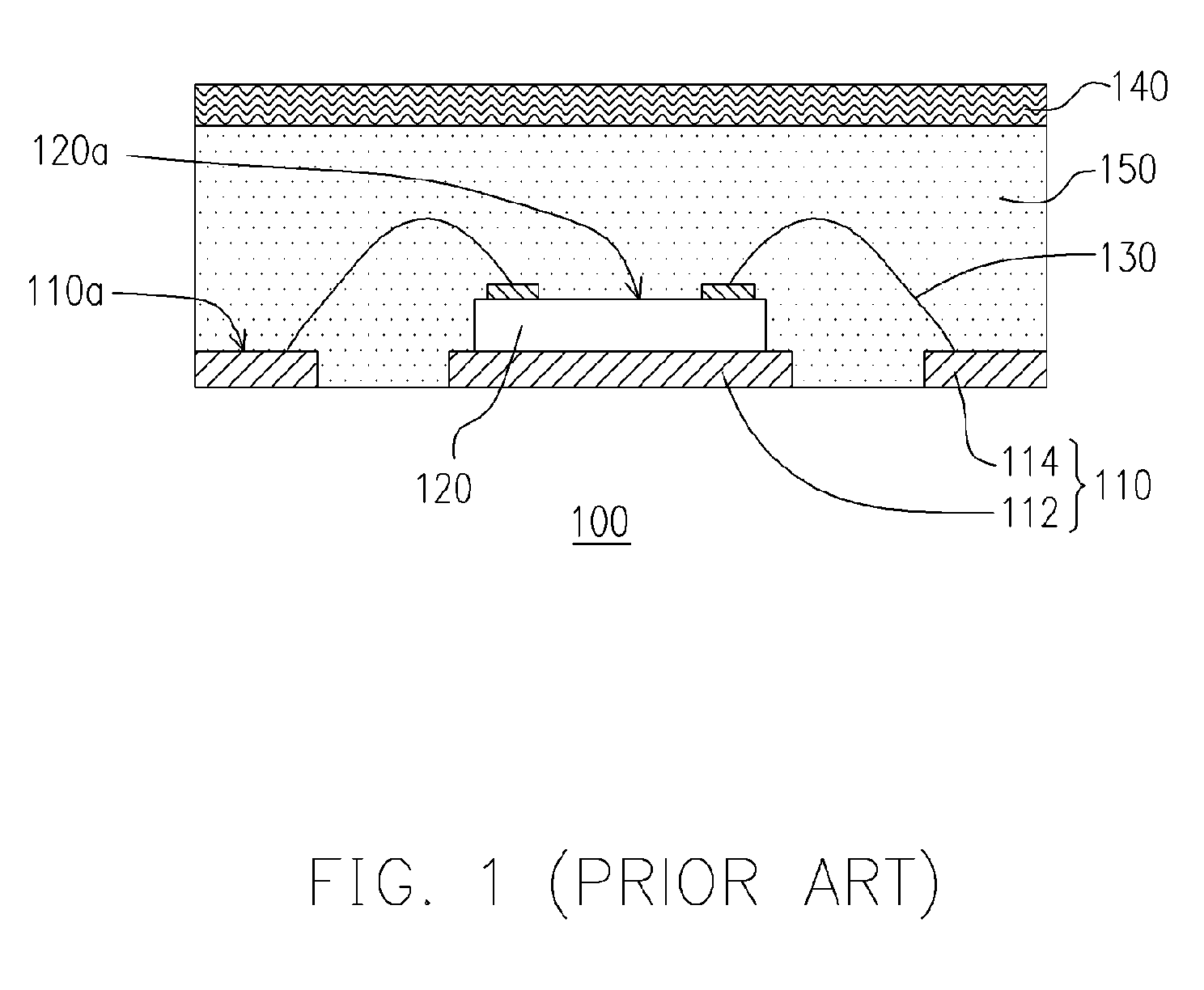
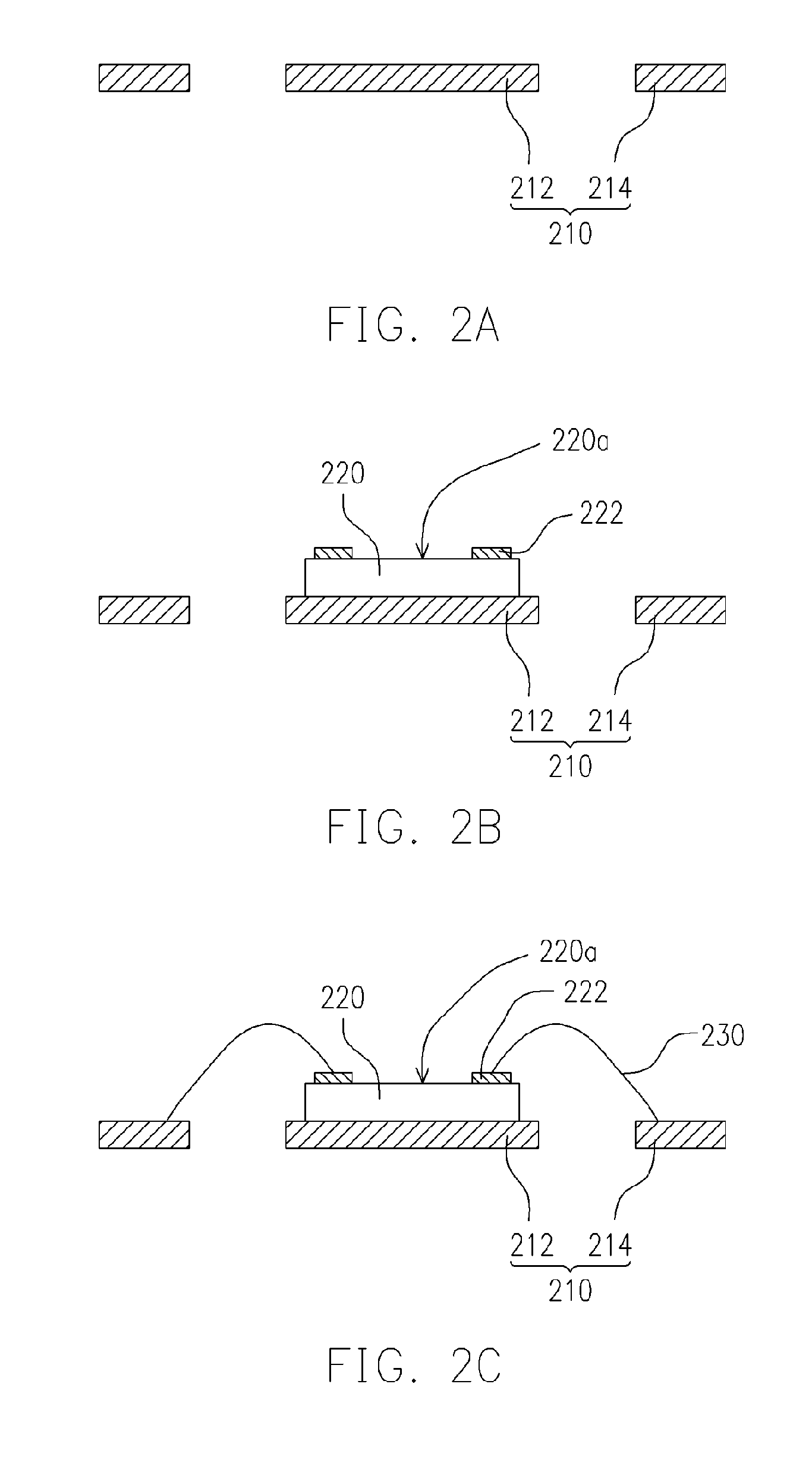
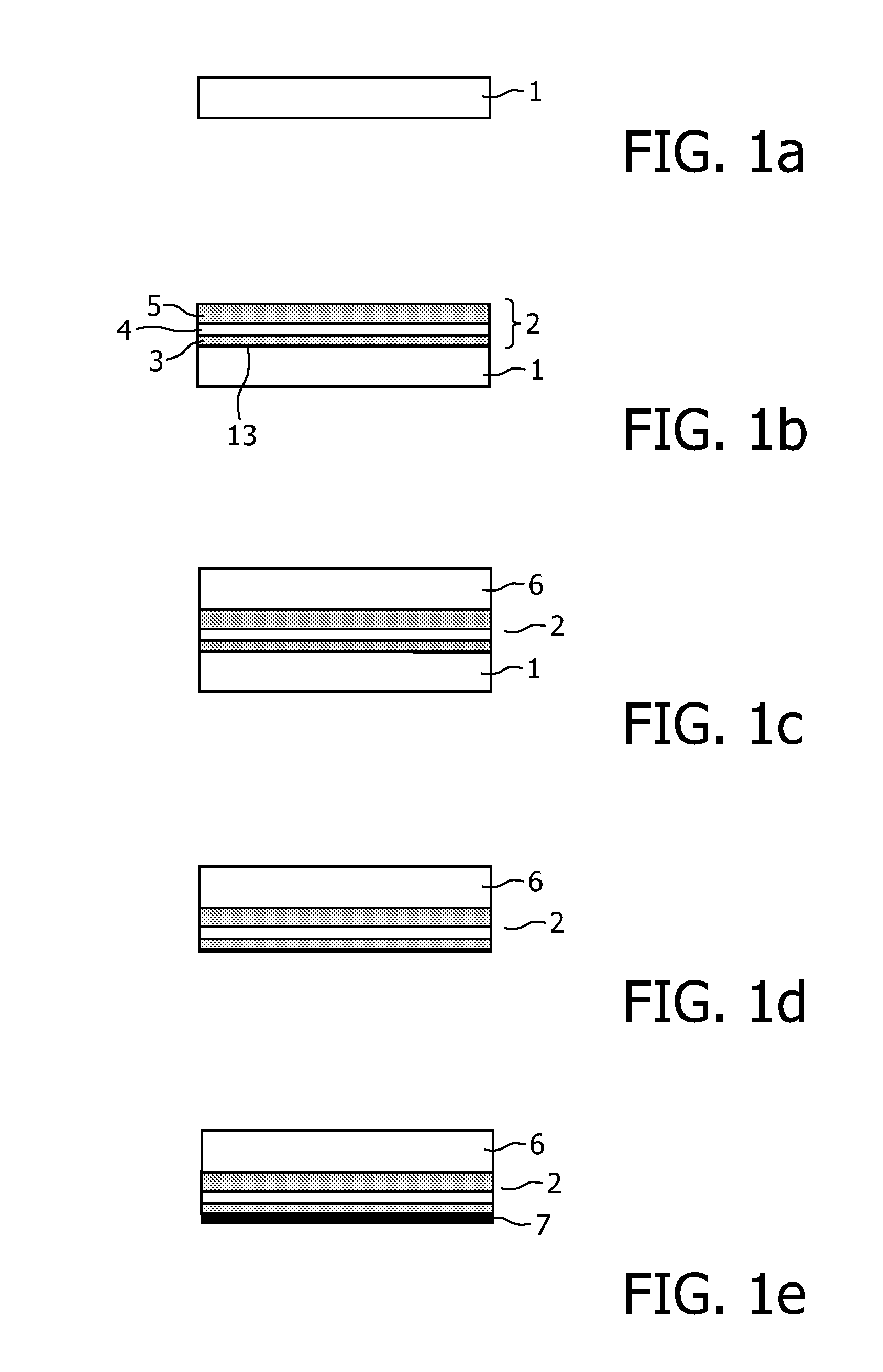
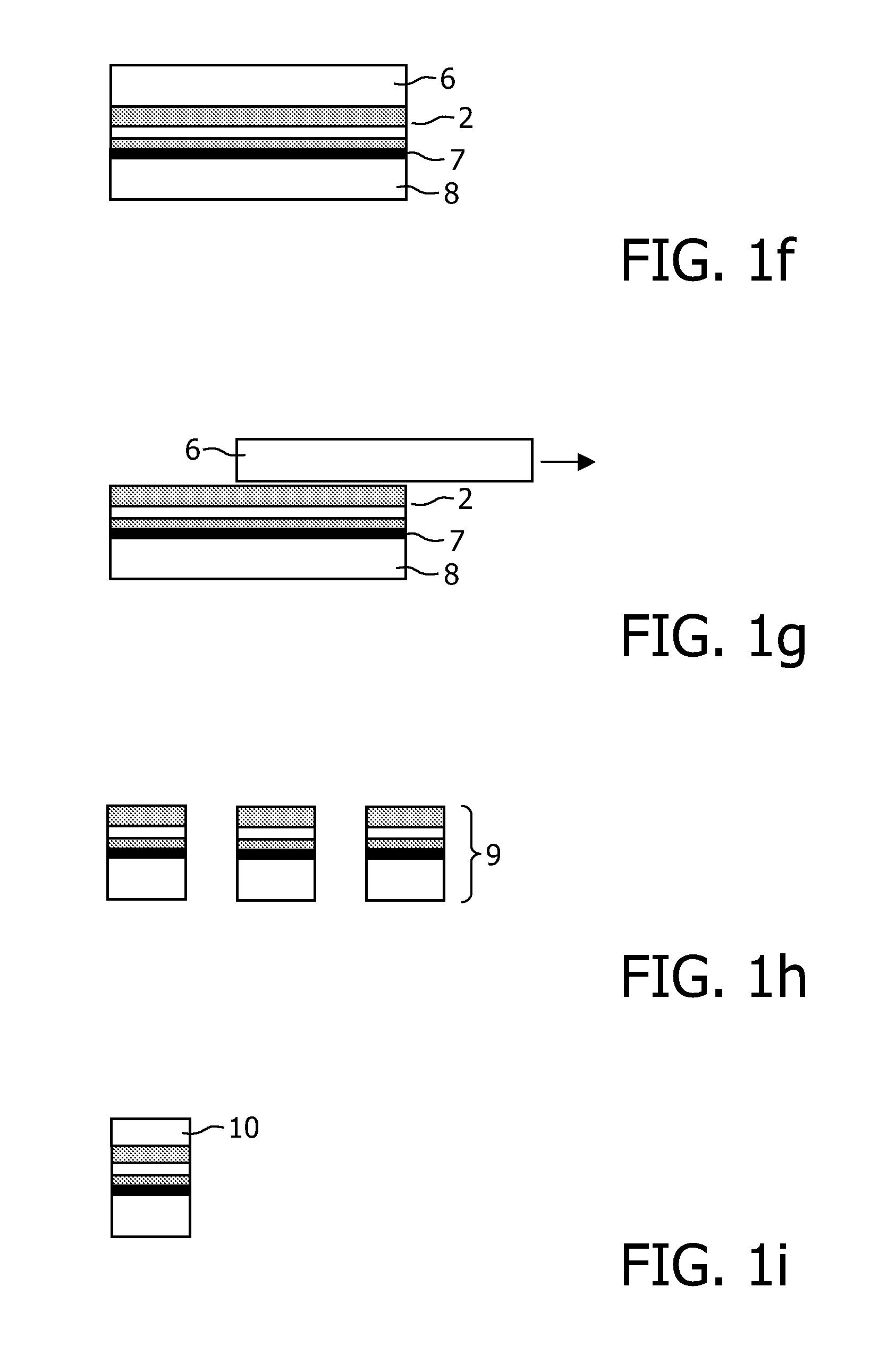
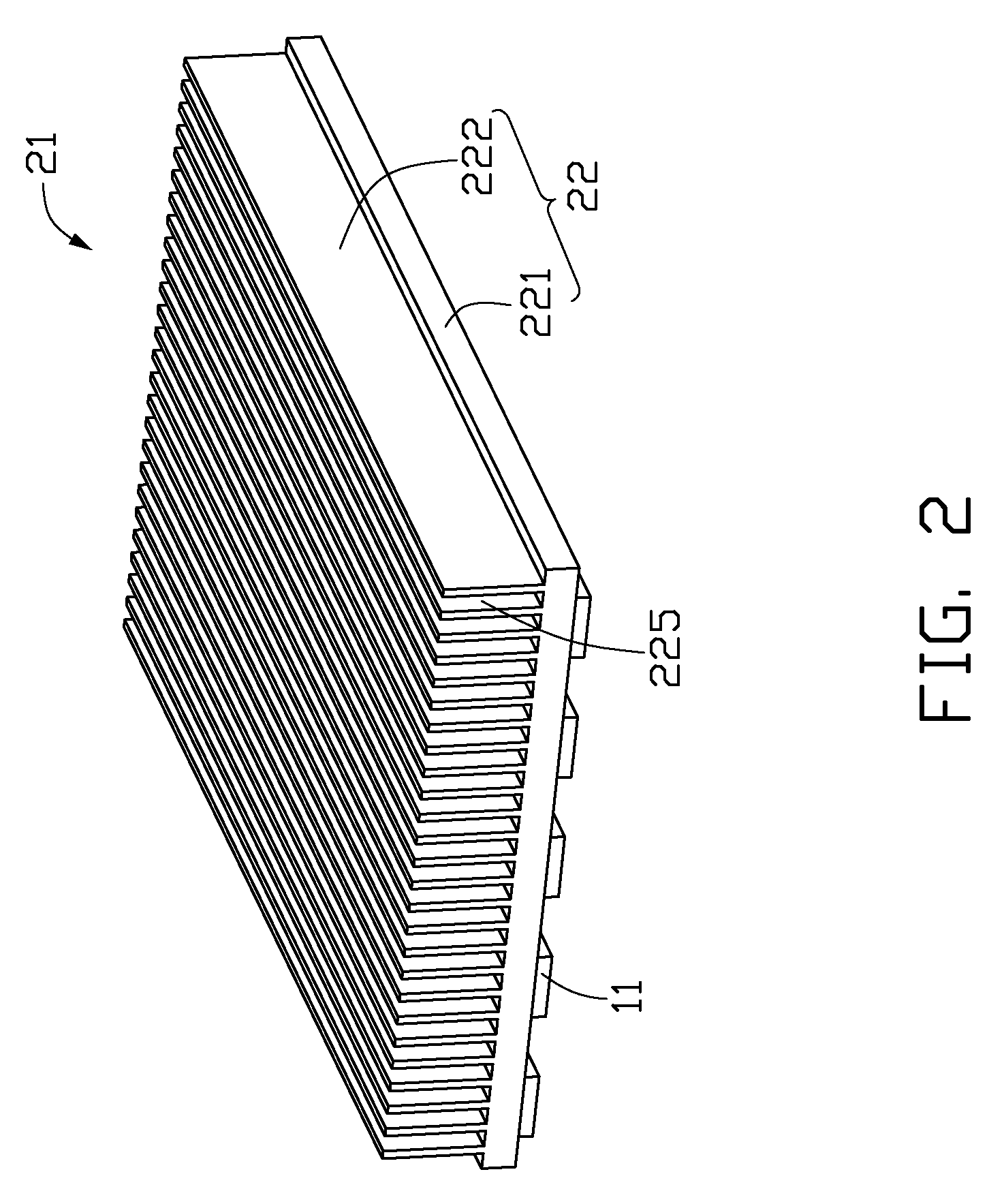
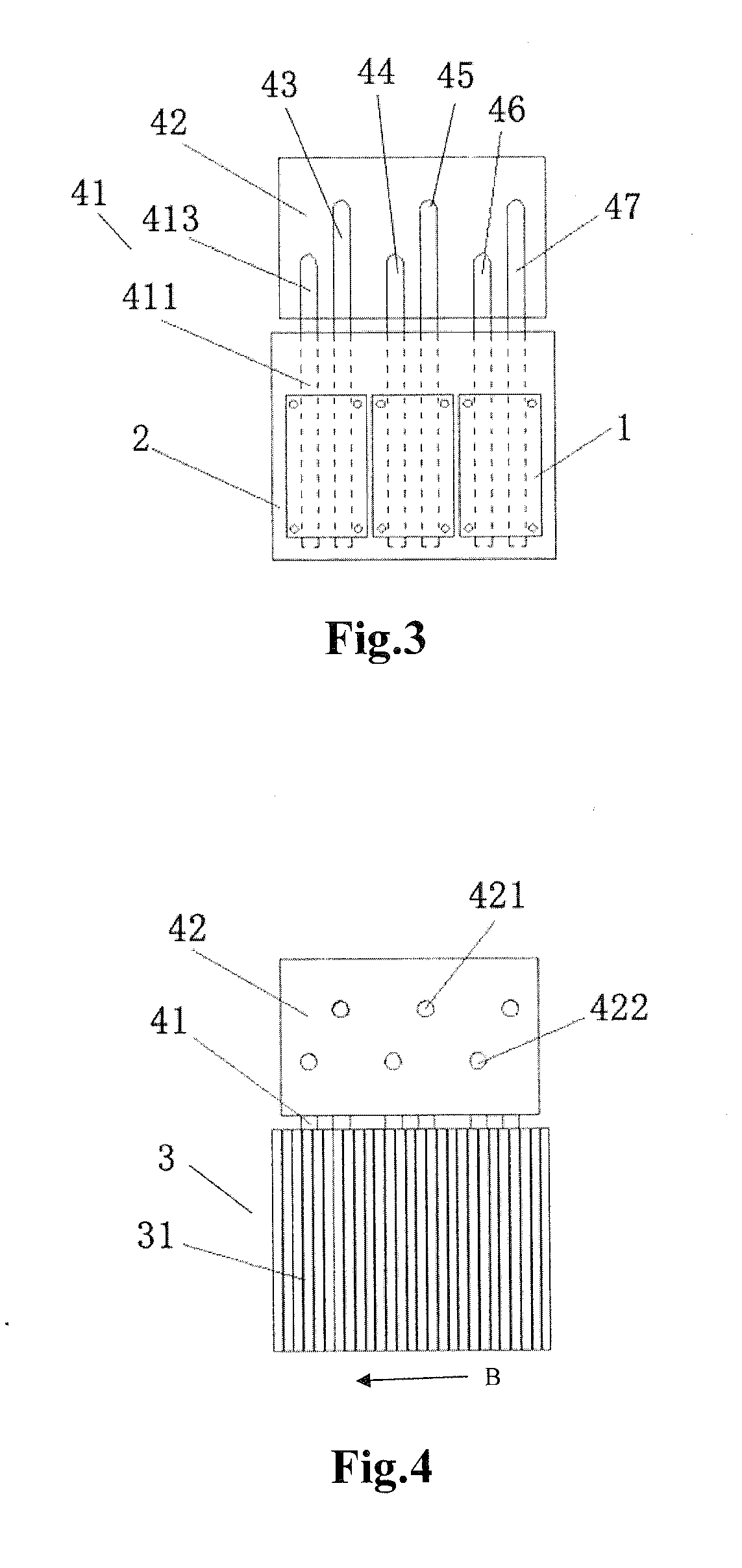
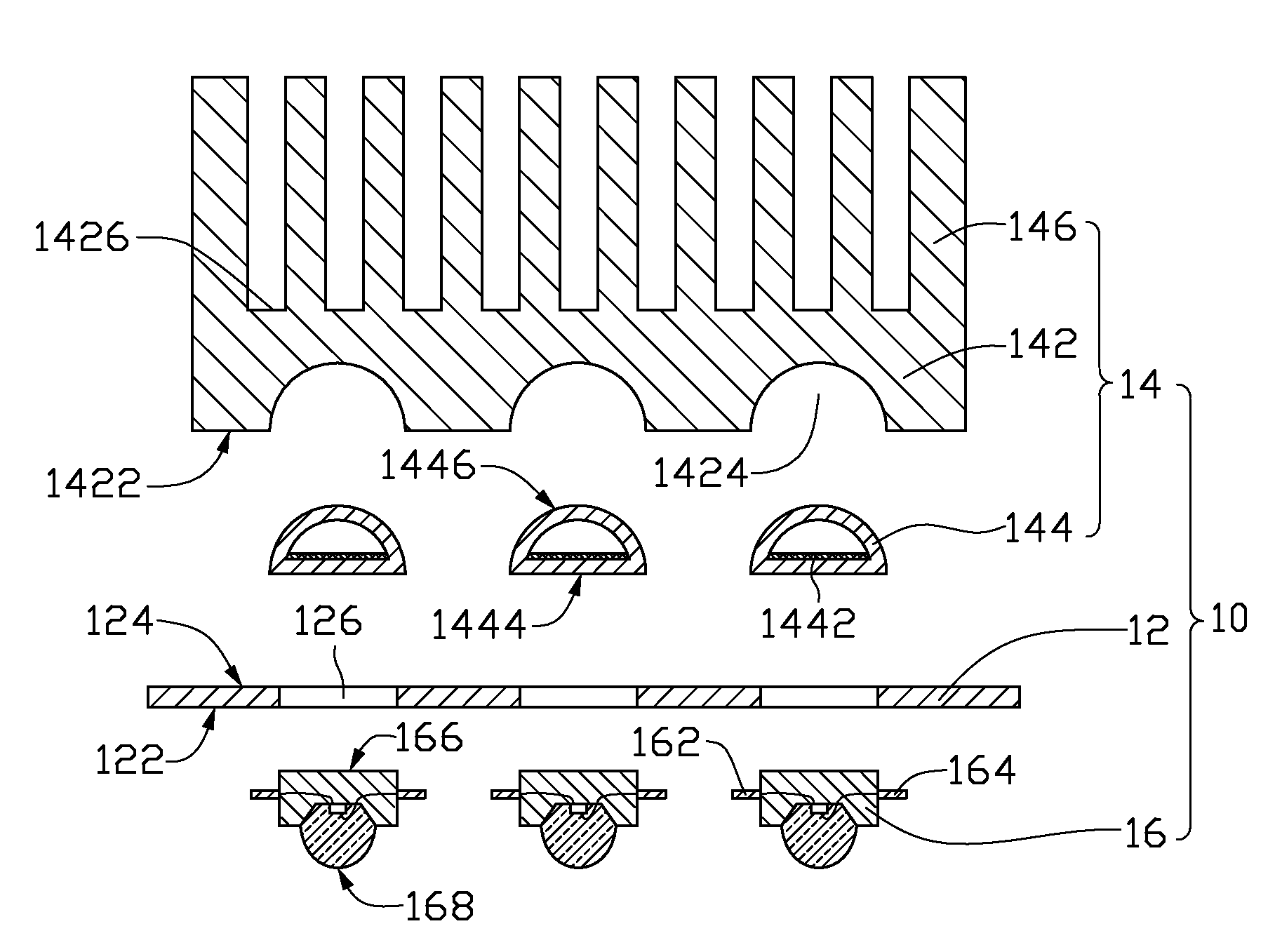
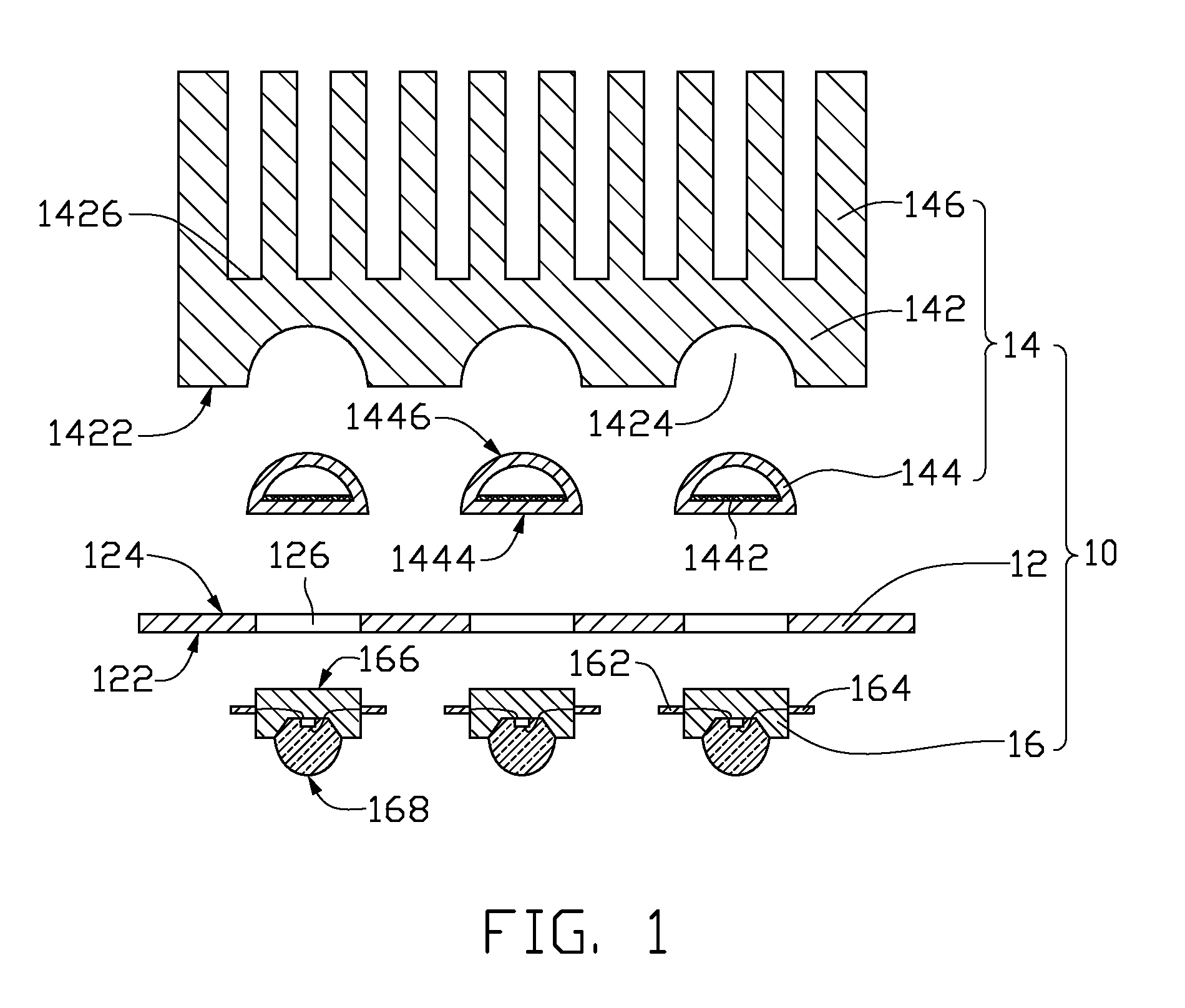
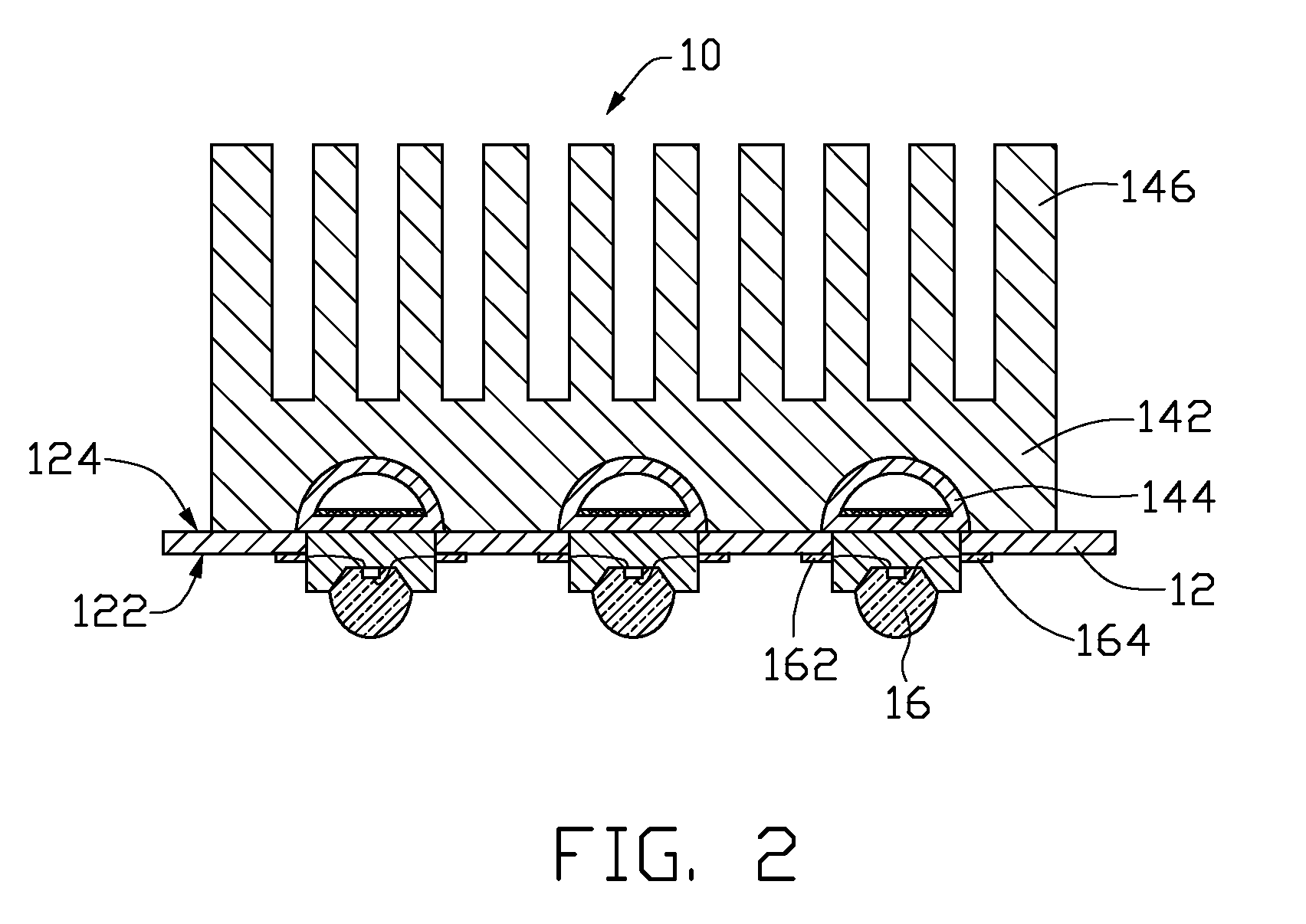
Chip package structure and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7061079B2Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyEasy to integrateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh heatHeat spreader
The present invention provides a chip package structure and the manufacturing method thereof, which affords higher heat dissipation efficiency and is suitable to fabricate the stack type package structure with a higher integration. The chip package structure comprises a carrier, at least a chip, a heat sink and a mold compound. The chip is disposed on the carrier, while the bonding pads of the chip are electrically connected to the leads of the carrier. The heat sink is disposed over the chip and includes at least a body and a plurality of connecting portions. The connecting portions are disposed around a periphery of the body and are electrically connected to the leads. By using a specially designed heat sink, the chip package structure can afford better heat dissipation and be suitable to form stack type package structures.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
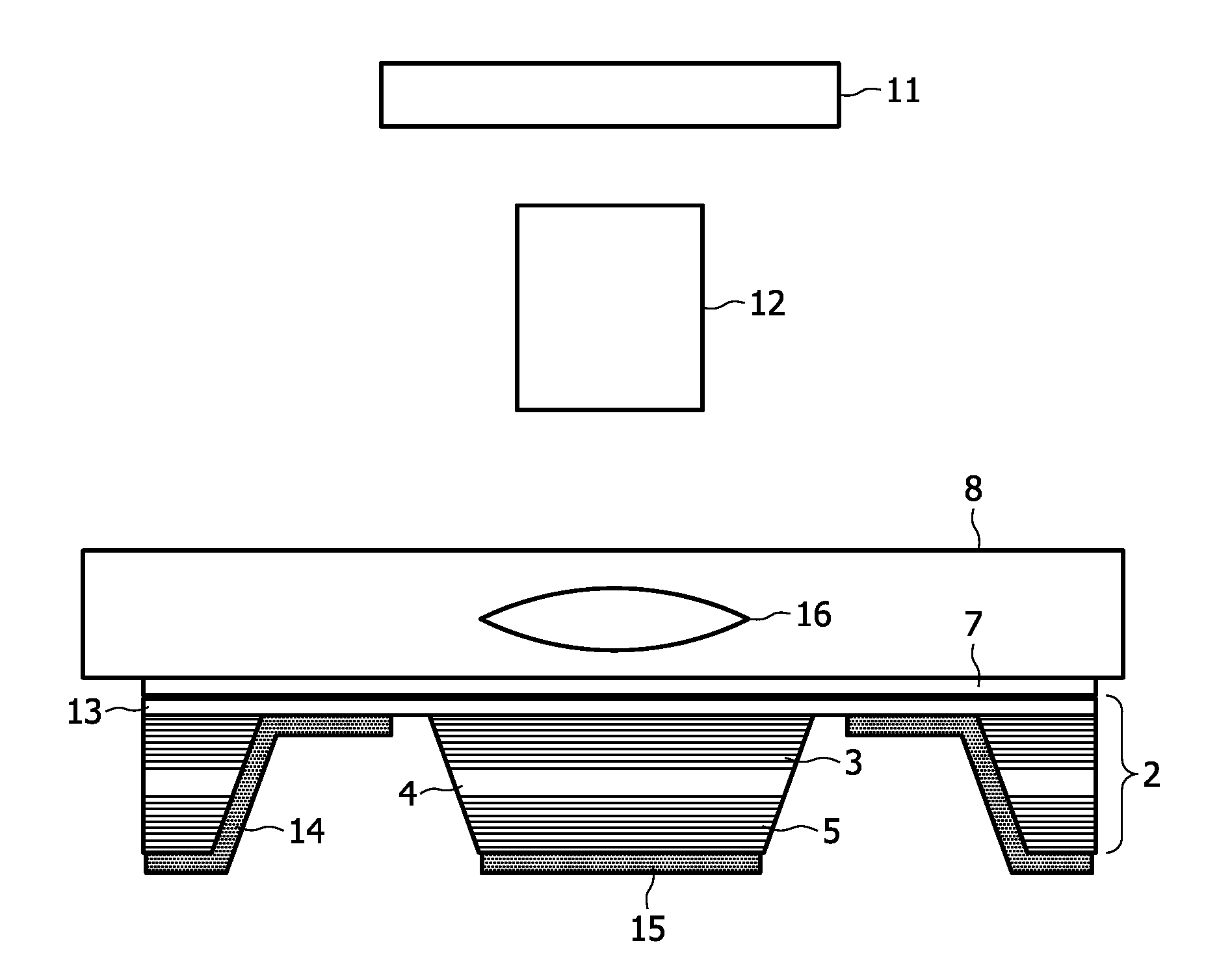
Vertical extended cavity surface emission laser and method for manufacturing a light emitting component of the same
ActiveUS20100195690A1Low thicknessSolve the low heat dissipation efficiencyLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionPhysicsSemiconductor
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing the light emitting component of a VECSEL and the corresponding VECSEL. In the method a layer stack (2) is epitaxially grown on a semiconductor substrate (1). The layer stack comprises an active region (4), an upper distributed Bragg reflector (5) and a n- or p-doped current injection layer (13) arranged between the active region (4) and the semiconductor substrate (1). A mechanical support (6) or submount is bonded to an upper side of the layer stack (2) and the semiconductor substrate (1) is subsequently removed. A metallization layer (7) is optionally deposited on the lower side of the layer stack (2) and an optically transparent substrate (8) is bonded to this lower side. The proposed method allows the manufacturing of such a component in a standard manner and results in a VECSEL with a homogenous current injection and high efficiency of heat dissipation.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
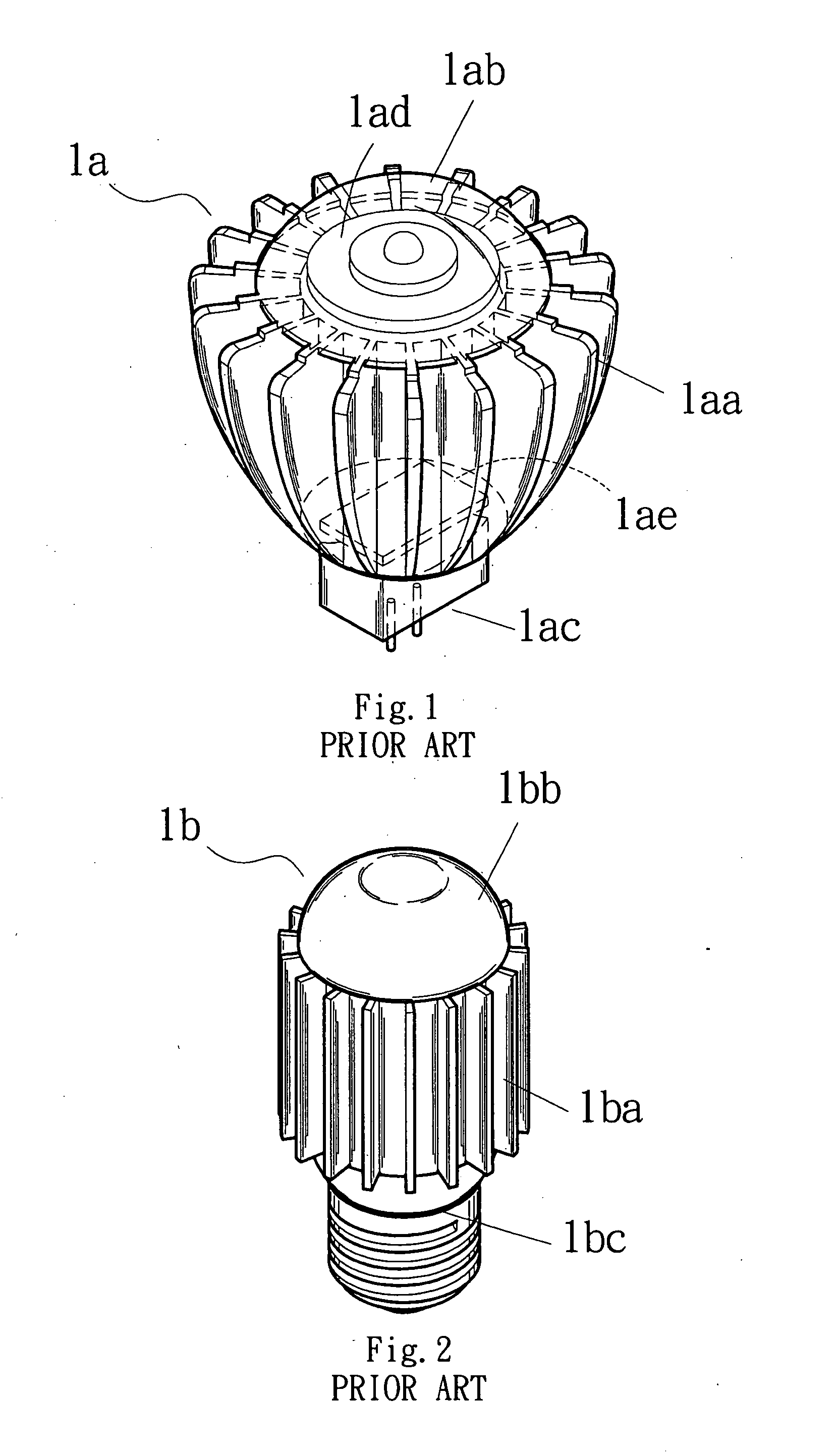
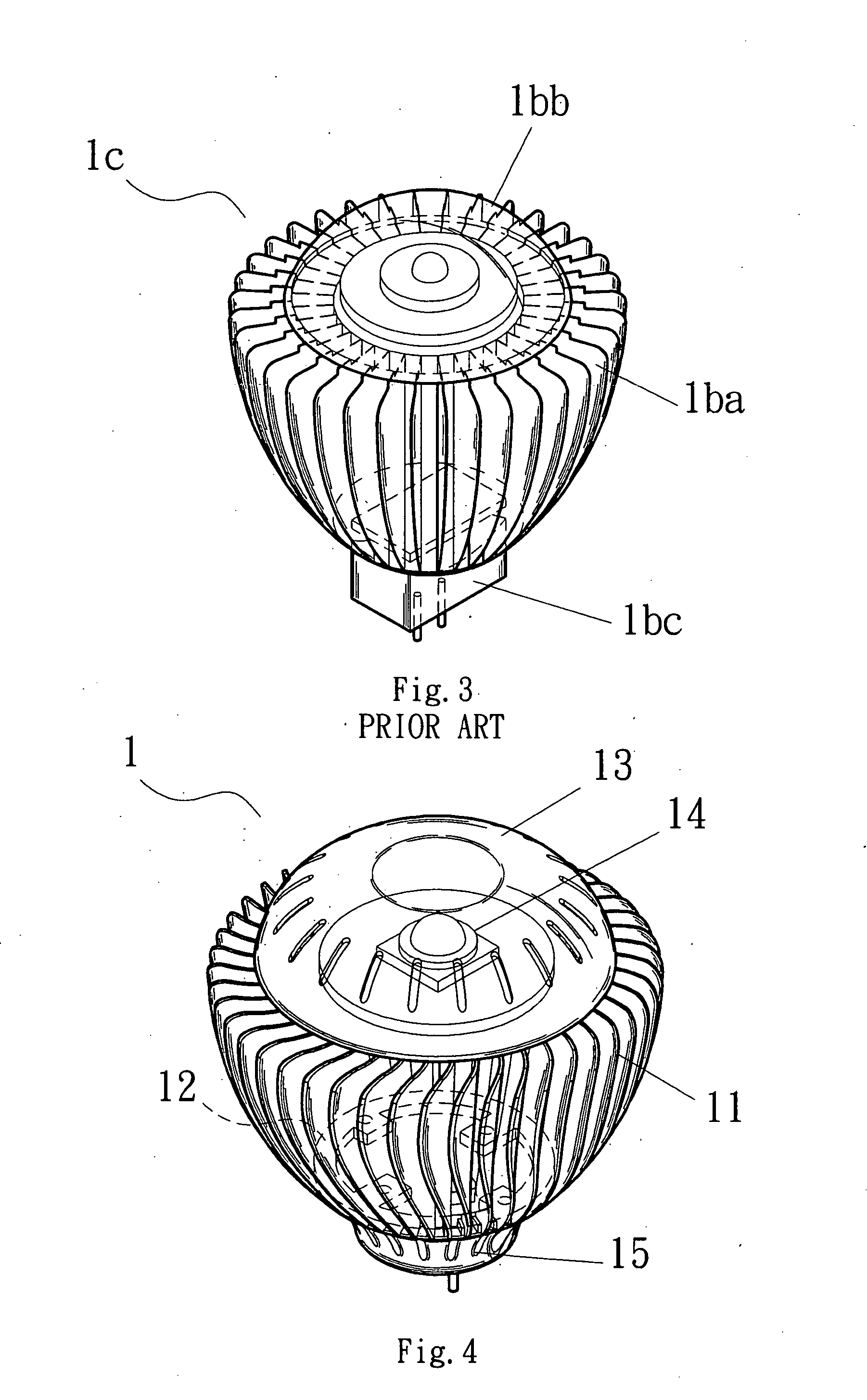
LED illuminating device and lamp unit thereof
InactiveUS7988335B2Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyWide areaLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceEngineeringAir exchange
An LED illuminating device includes a mounting module and a lamp unit mounted in the mounting module. The lamp unit includes a light-emitting module and a heat sink. The light-emitting module includes a light source having a plurality of LEDs, and a light penetrable cover located below the light source and defining a plurality of air venting holes therein. The heat sink includes an elongated base defining a plurality of air exchanging holes therein and a plurality of fins. The base has an outer convex surface and an opposite inner concave surface defining an elongated recess. The light source is received in the recess and thermally attached to the concave surface. Air flows into and out of a chamber defined between the base and the cover via the venting holes of the cover and the air exchanging holes of the base.
Owner:FU ZHUN PRECISION IND SHENZHEN +1
Lightemitting device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050073846A1Improve efficiencyRaise the ratioSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLight emitting deviceMetallic substrate
A light emitting apparatus includes a metallic substrate having at least one recess on the surface and at least one projection opposing the recess on the back surface thereof, a light emitting element mounted in the recess of the metallic substrate, the light emitting element having a pair of positive and negative electrodes formed on one side thereof, and electrically conductive members formed via an insulating member on the surface of the metallic substrate, the electrically conductive members being electrically connected with the pair of positive and negative electrodes of the light emitting element.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
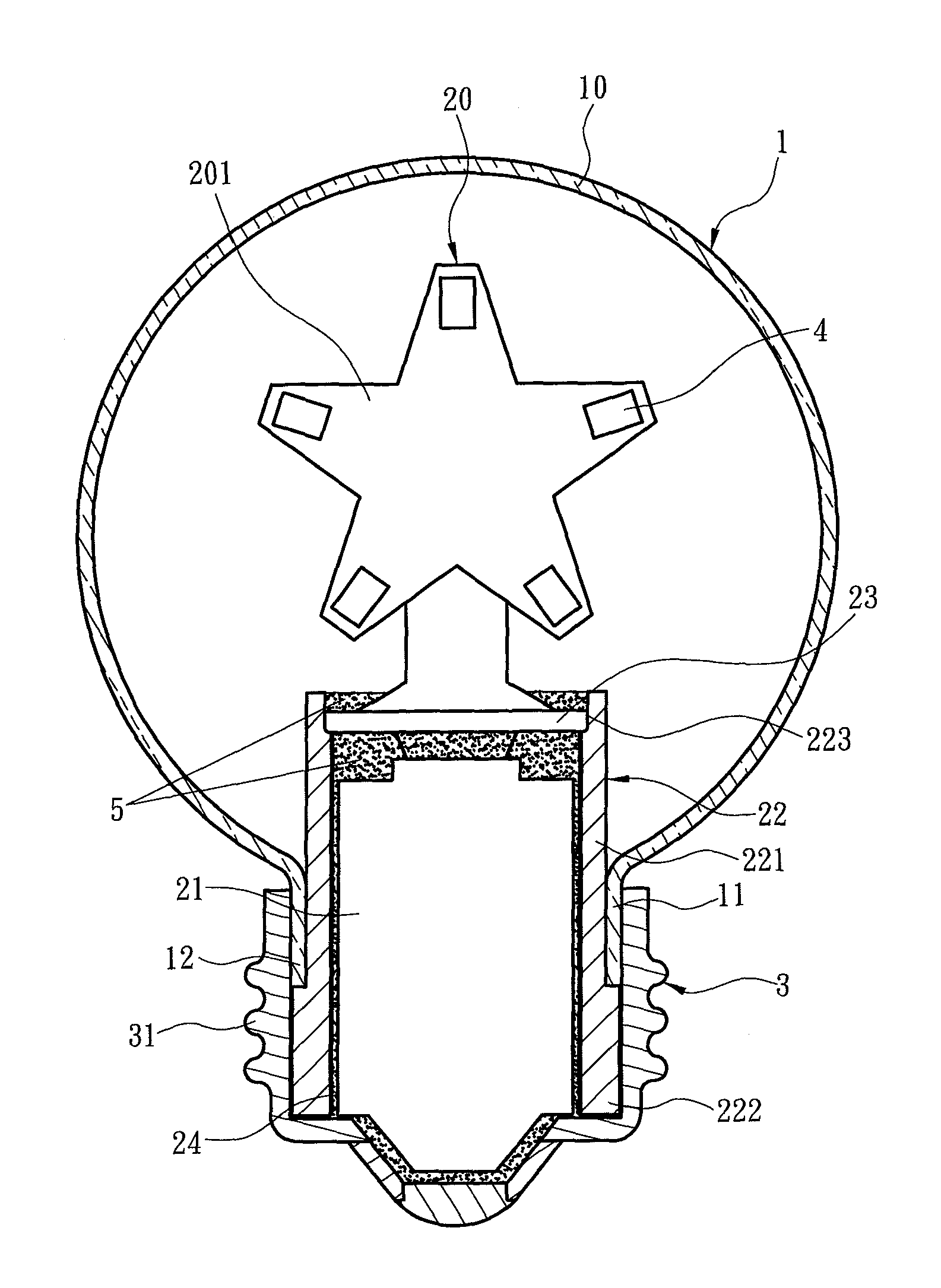
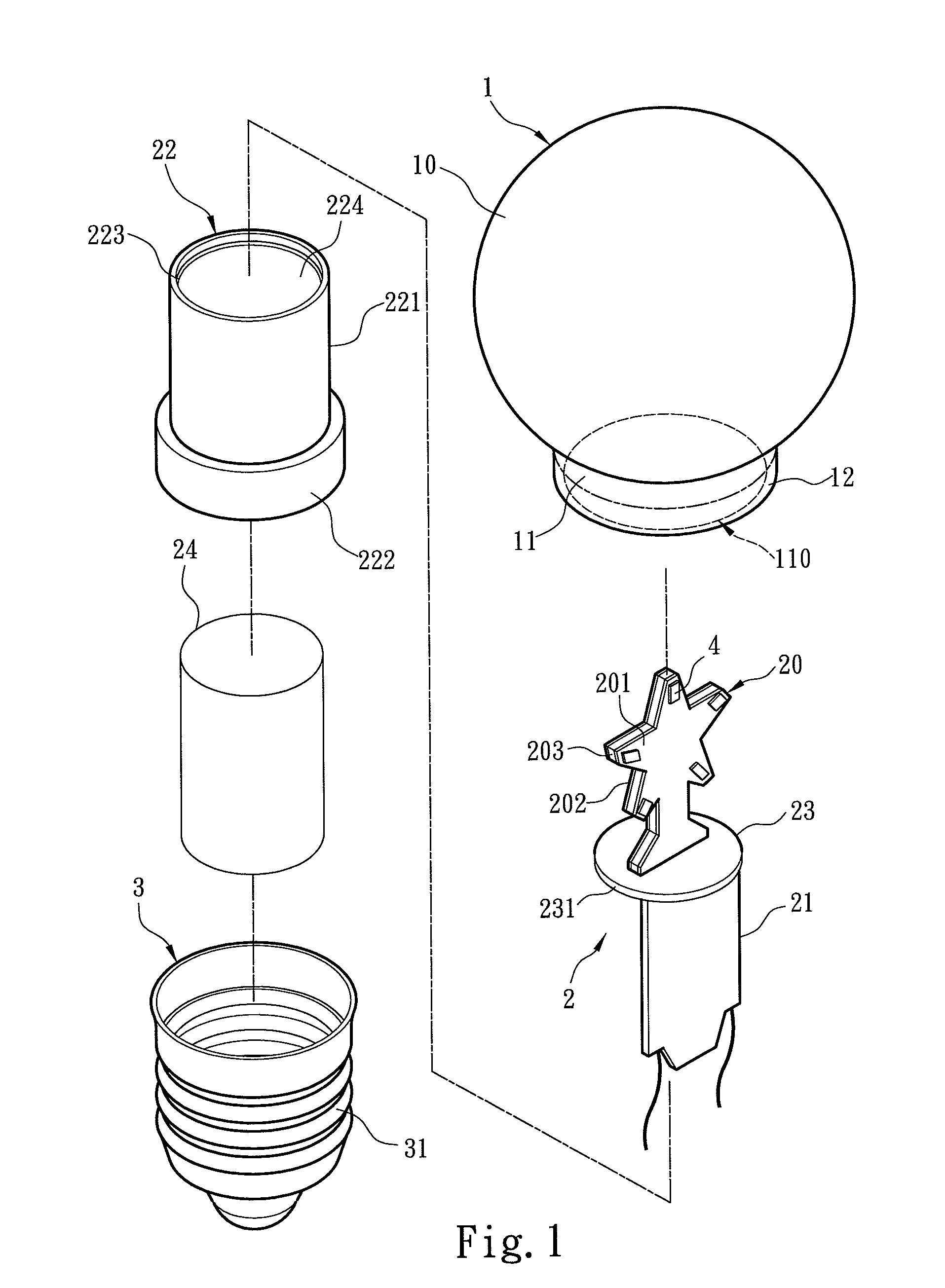
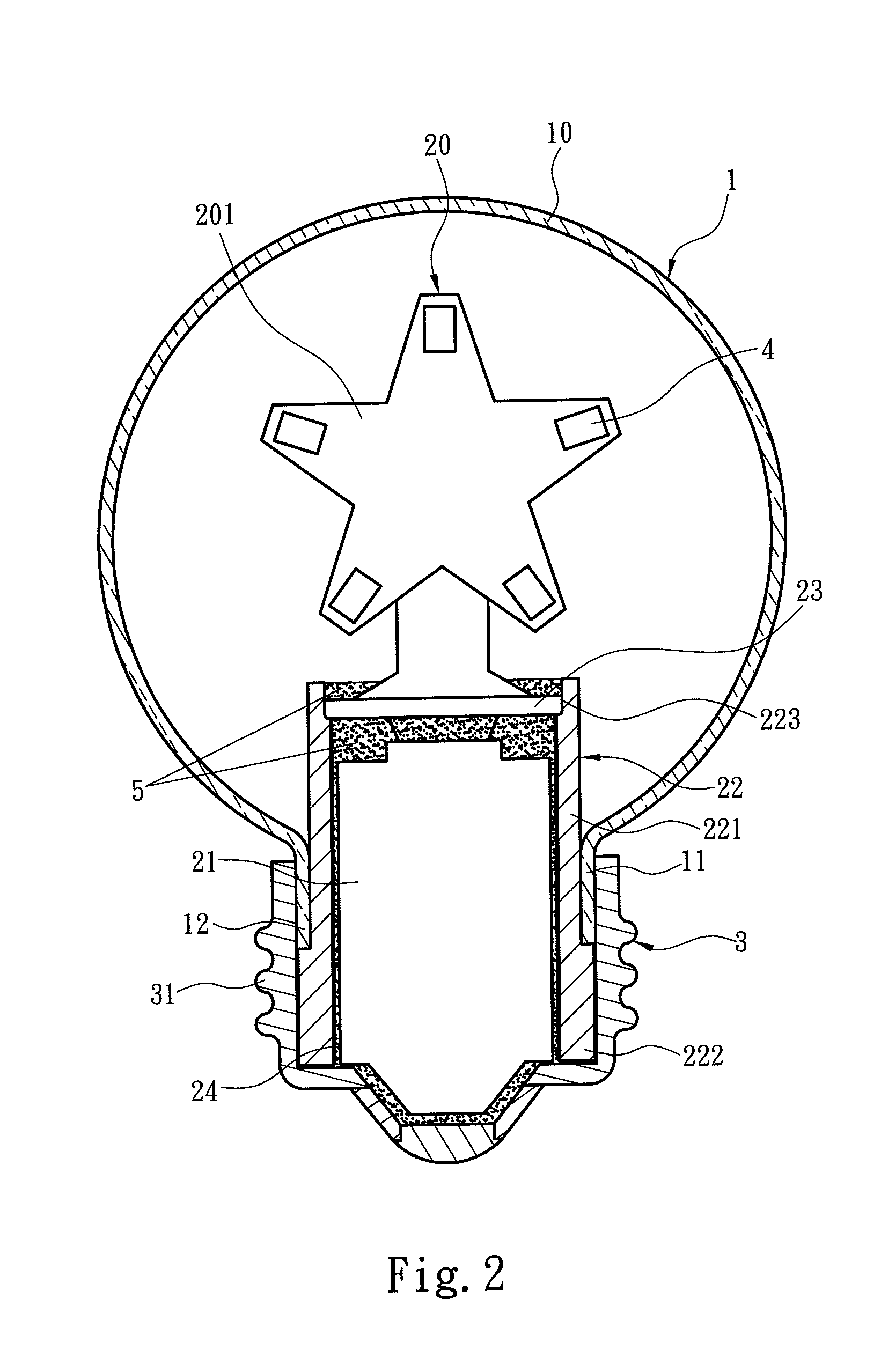
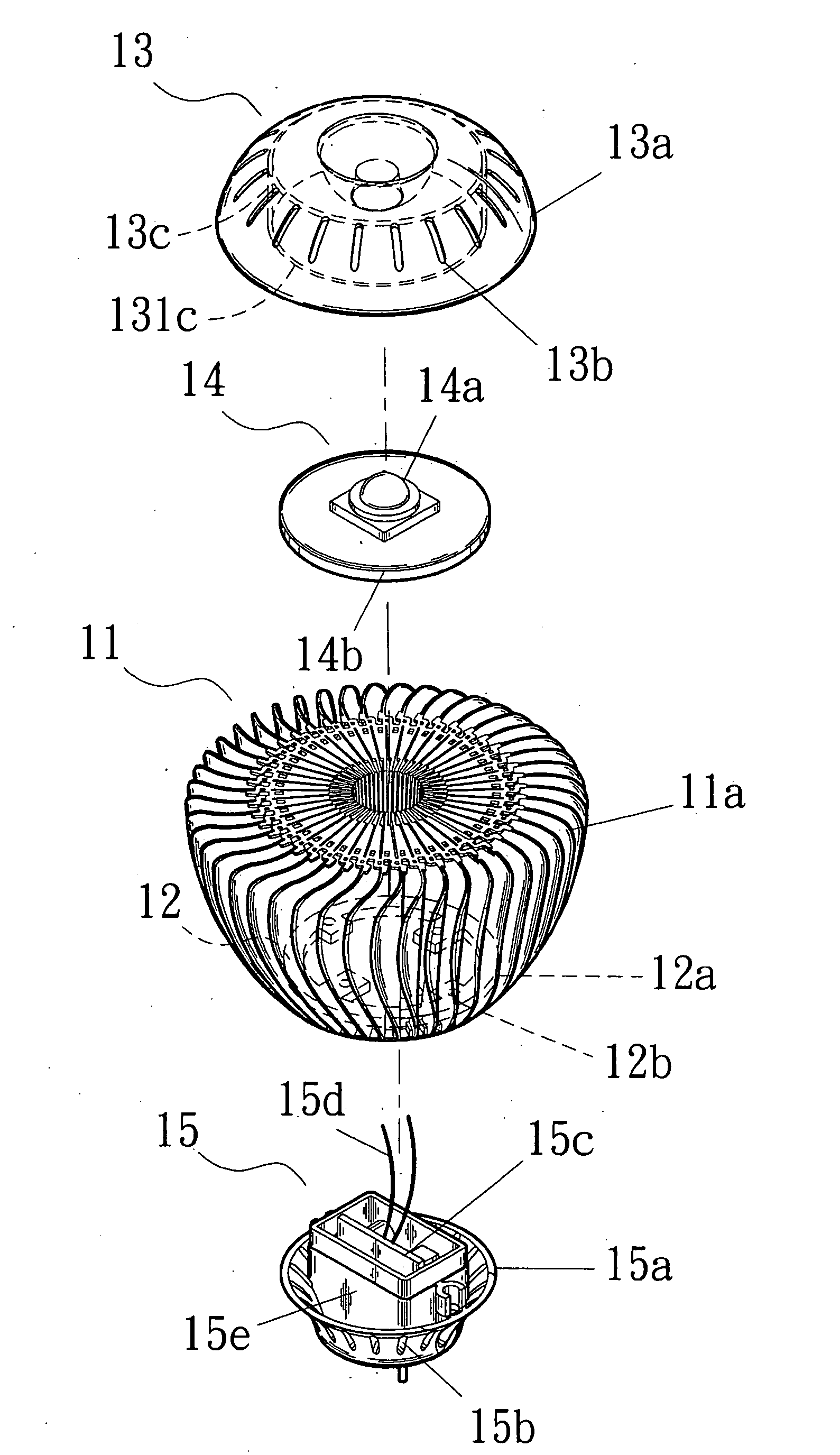
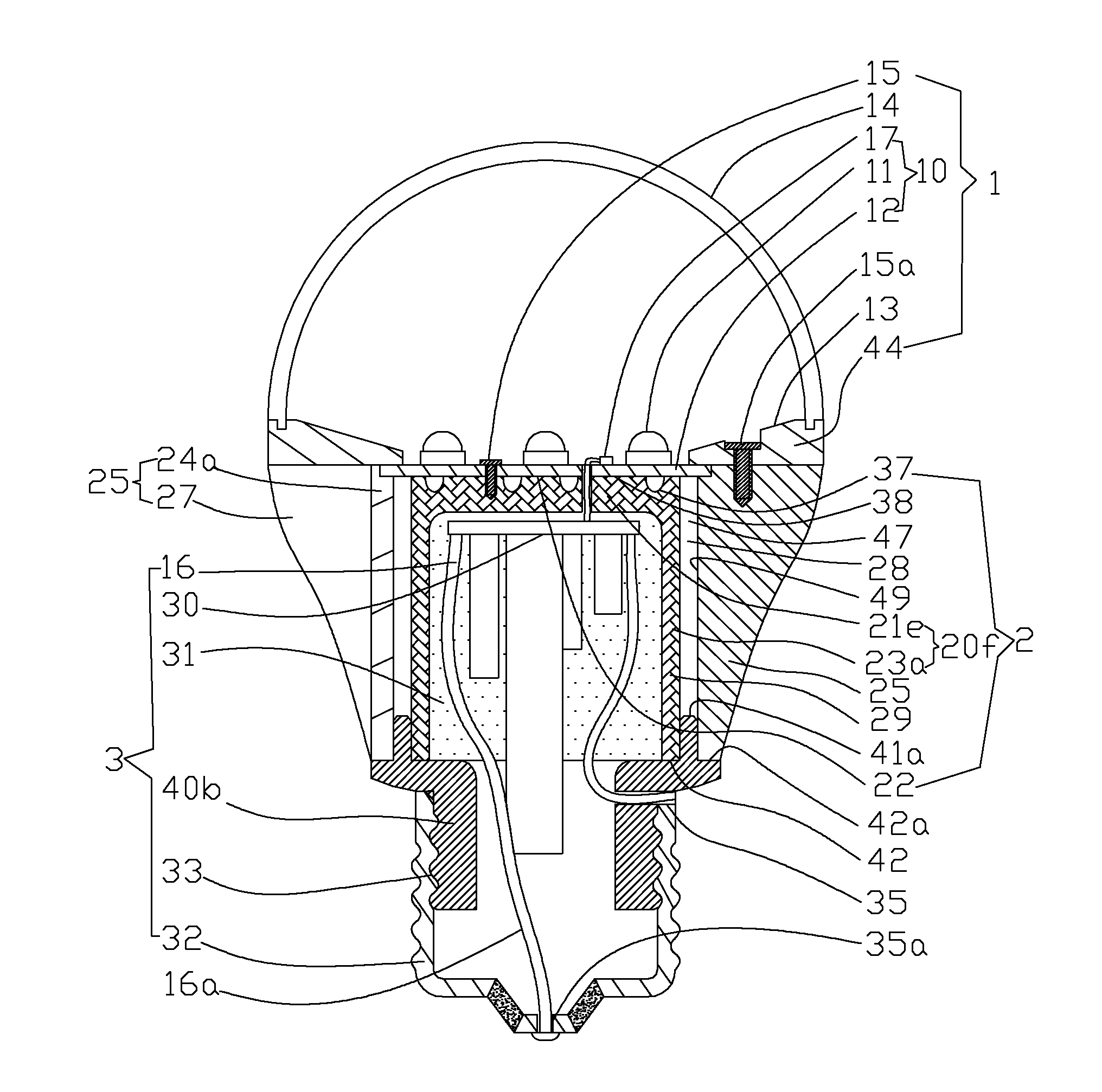
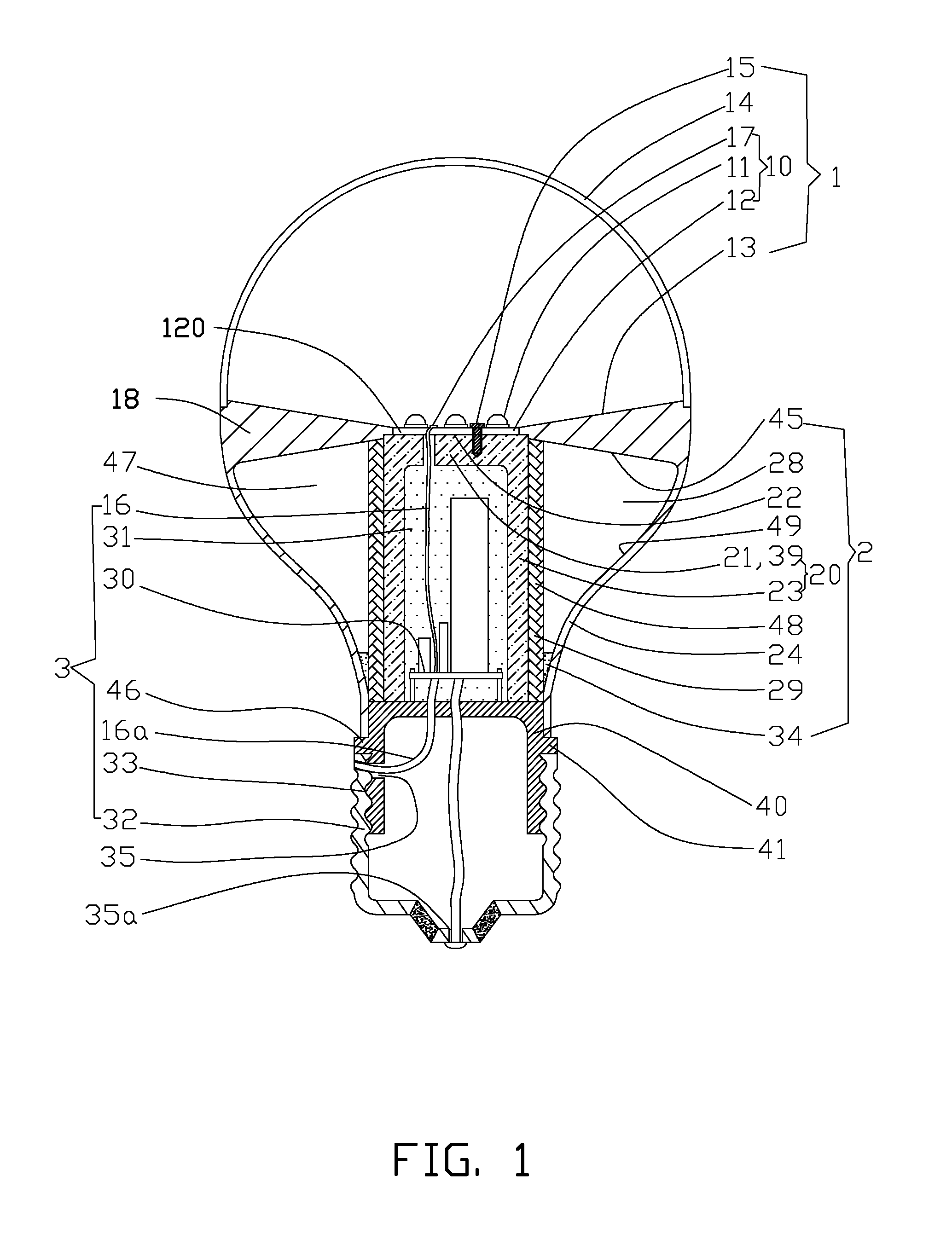
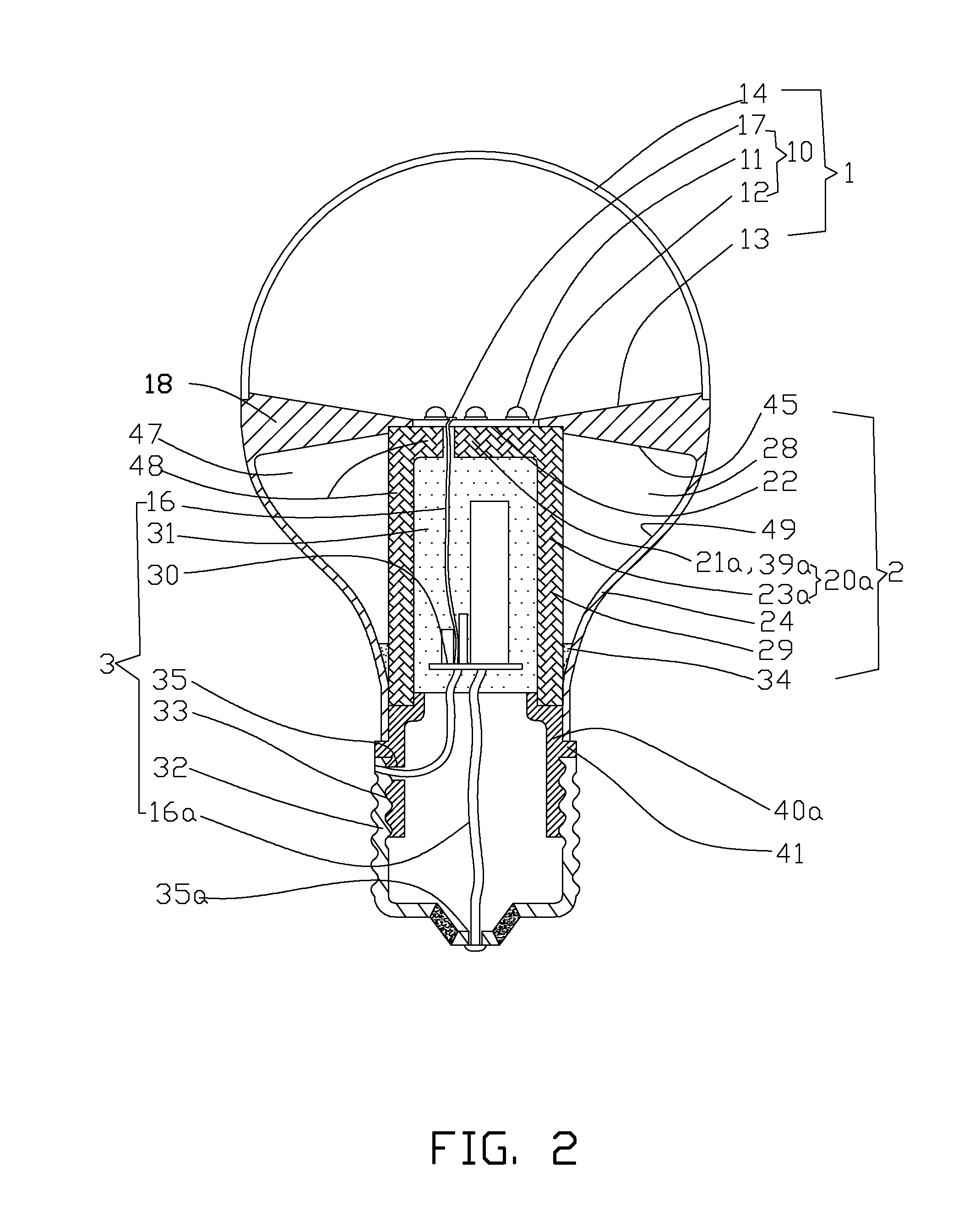
LED light bulb providing high heat dissipation efficiency
InactiveUS8641237B2Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyHigh voltagePlanar light sourcesLighting support devicesEngineeringLamp shell
An LED light bulb includes a lamp shell, a light emitting assembly and a power receiving base. The lamp shell includes a light transmissive portion and a holding portion. The light emitting assembly includes a light source baseboard located in the light transmissive portion and a circuit board connecting to the light source baseboard. The circuit board is surrounded by a heat sink. The heat sink includes a heat collecting section and a holding section extended from the heat collecting section into the power receiving base such that the power receiving base fully encases the heat sink without exposing. The inner surface of the power receiving base connects to the outer surface of the holding section so that heat generated by the light source baseboard is absorbed by the heat collecting section and transmitted via the holding section to the power receiving base for dissipating.
Owner:HSU WEI LIN
Heat dissipation structure of LED light
InactiveUS20100026158A1Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyHeat dissipation surface area is thus increasedPoint-like light sourceElectric discharge tubesHeat sinkLED lamp
A heat dissipation structure of LED light, including a ventilation lampshade, a ventilation power supply seat module and a streamlined curved-surface thermal module. The ventilation lampshade and the ventilation power supply seat module are formed with ventilation holes for expediting fluid convection and enhancing heat dissipation efficiency. The thermal module is composed of multiple radiating fins, which are adjacently annularly stacked to form the thermal module. The radiating fins are formed with streamlined curved surfaces, whereby fluid can more smoothly flow through the radiating fins to greatly enhance heat dissipation ability of the thermal module.
Owner:WU YA LI
Integrated, multi-chip, thermally conductive packaging device and methodology
InactiveUS6075287AImproved compactness and shortness of connectionImprove electrical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsAdhesive
Electrically conductive lamina are attached by an electrically insulating, thermally conductive adhesive and / or solder to one or more semiconductor devices such as chips and extend beyond the periphery of the chip or chips to form heat sink fins. Electrical connections may be made between such chips through holes (e.g. by a wire or plated through hole) in the electrically conductive lamina lined with an insulating material such as the electrically insulating adhesive to provide a structurally robust assembly. Surface pads and connections may overlie patterns of insulator on the lamina. A further lamina can be wrapped around lateral sides of the assembly to provide further heat sink area and mechanical protection for other heat sink fins. A graphite / carbon fiber composite matrix material is preferred for the lamina and the coefficient of thermal expansion of such materials may be matched to that of the semiconductor material attached thereto. Conductivity of the lamina also provides shielding against electrical noise to improve the noise immunity of short connections between chips made through the lamina as well as that of surface connections which may be formed on the lamina.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
LED lamp
InactiveUS20100264800A1Ensure adequate heatingControl areaPoint-like light sourceSolid-state devicesHeat conductingEngineering
An LED lamp includes a hollow lamp housing, a front optical part, a rear electrical part, and a middle heat dissipation part. The heat dissipation part includes a heat sink, a mounting seat in front of the heat sink, and a heat conducting member connecting the mounting seat with the heat sink. The lamp housing defines a plurality of air exchanging holes corresponding to the fins. The mounting seat includes a small top surface, an opposite large bottom surface, and a plurality of sloping heat absorbing surfaces between the top surface and the bottom surface. The optical part includes a plurality of light sources arranged on the heat absorbing surfaces, a light reflector located between the heat sink and the mounting seat and surrounding the heat conducting member, an optical lens located in front of the light reflector and the mounting seat.
Owner:FU ZHUN PRECISION IND SHENZHEN +1
Cooling apparatus for flat display device
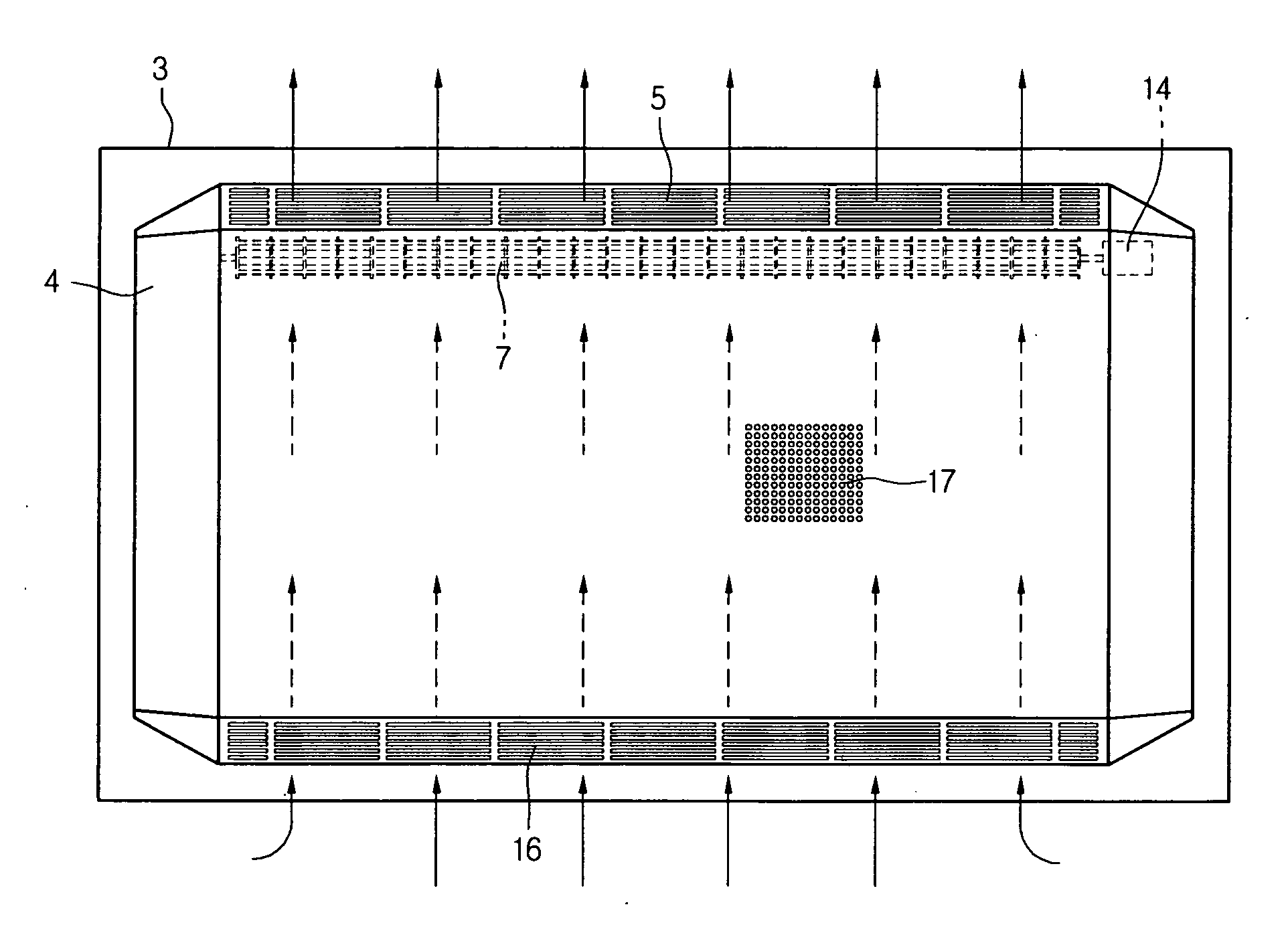
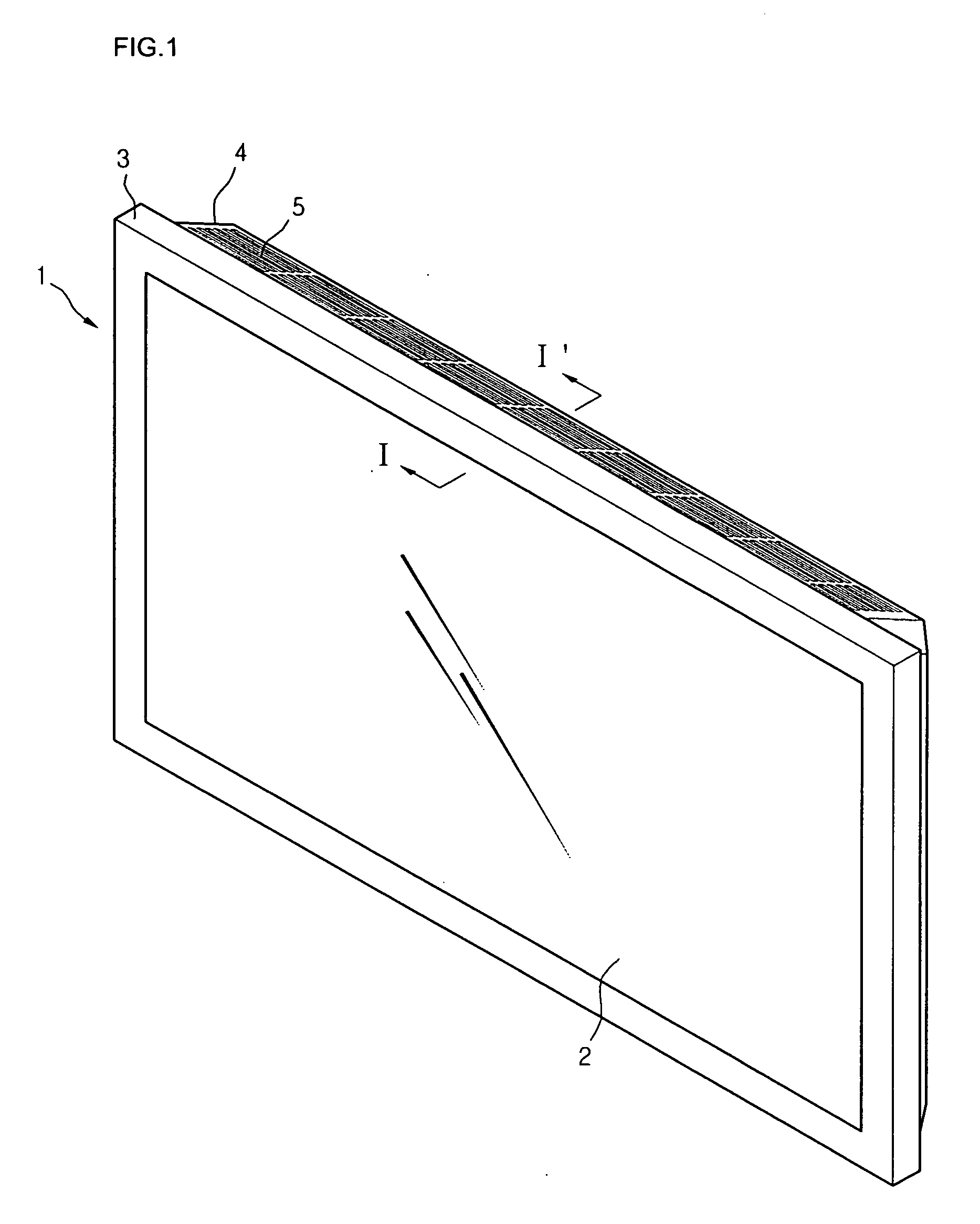
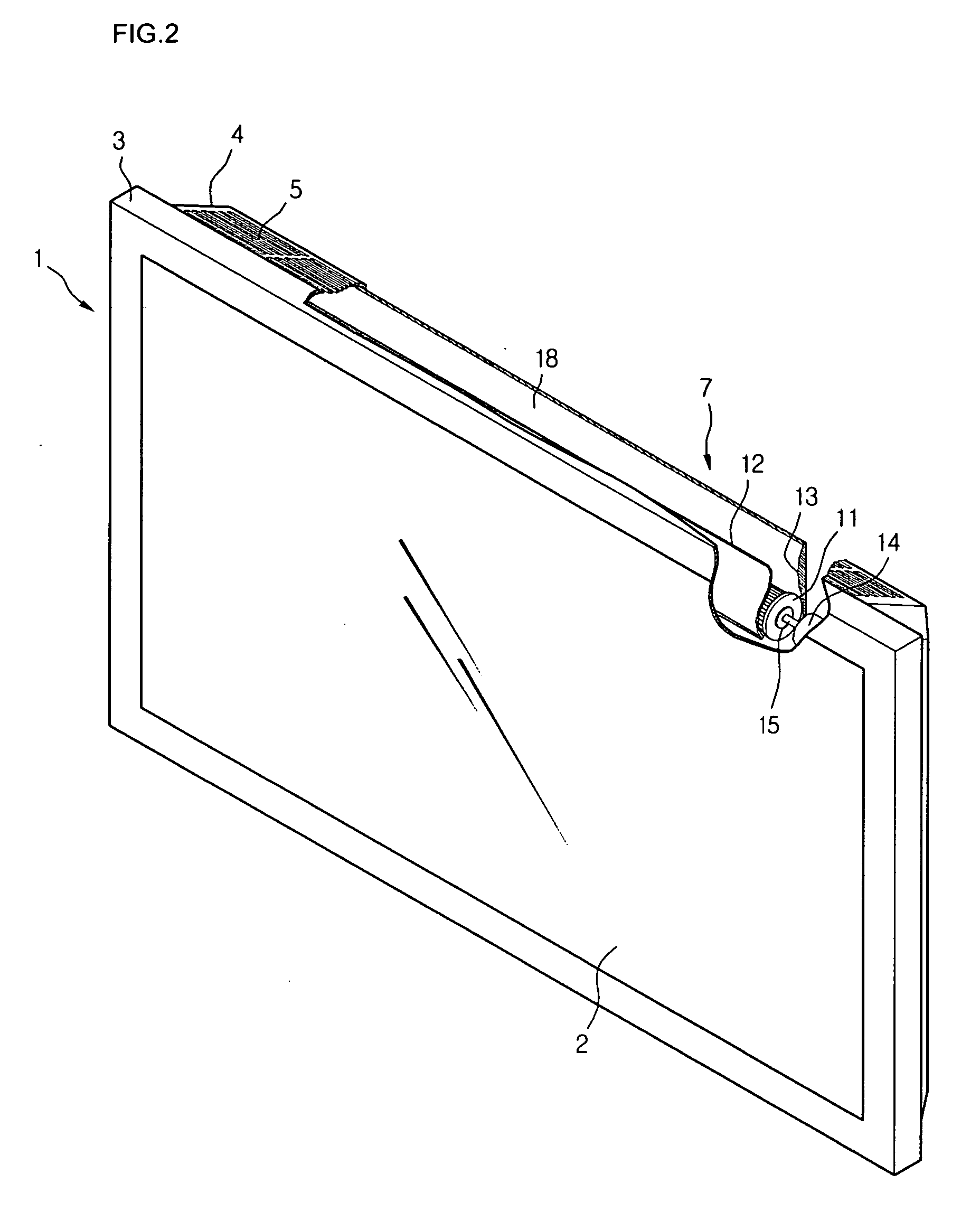
InactiveUS20070103863A1Efficiently dissipatedThin display deviceCircumferential flow pumpsStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
There is provided a cooling apparatus for a flat display device. The cooling apparatus includes a flat display module, a front cover for protecting a front portion of the flat display module, a back cover for protecting a rear portion of the flat display module, an air inlet formed on a portion of the back cover to allow external air to be introduced into the back cover, an air outlet formed on another portion of the back cover and extending along a longitudinal length of the flat panel display module; a fan disposed inside the back cover and aligned with the air outlet formed on the back cover, and an air outlet channel formed in the back cover and aligned with the air outlet formed on the back cover, the air outlet having an effective exhaust area having a longitudinal length extending in a longitudinal direction of the flat display module.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
LED illuminating device and lamp unit thereof
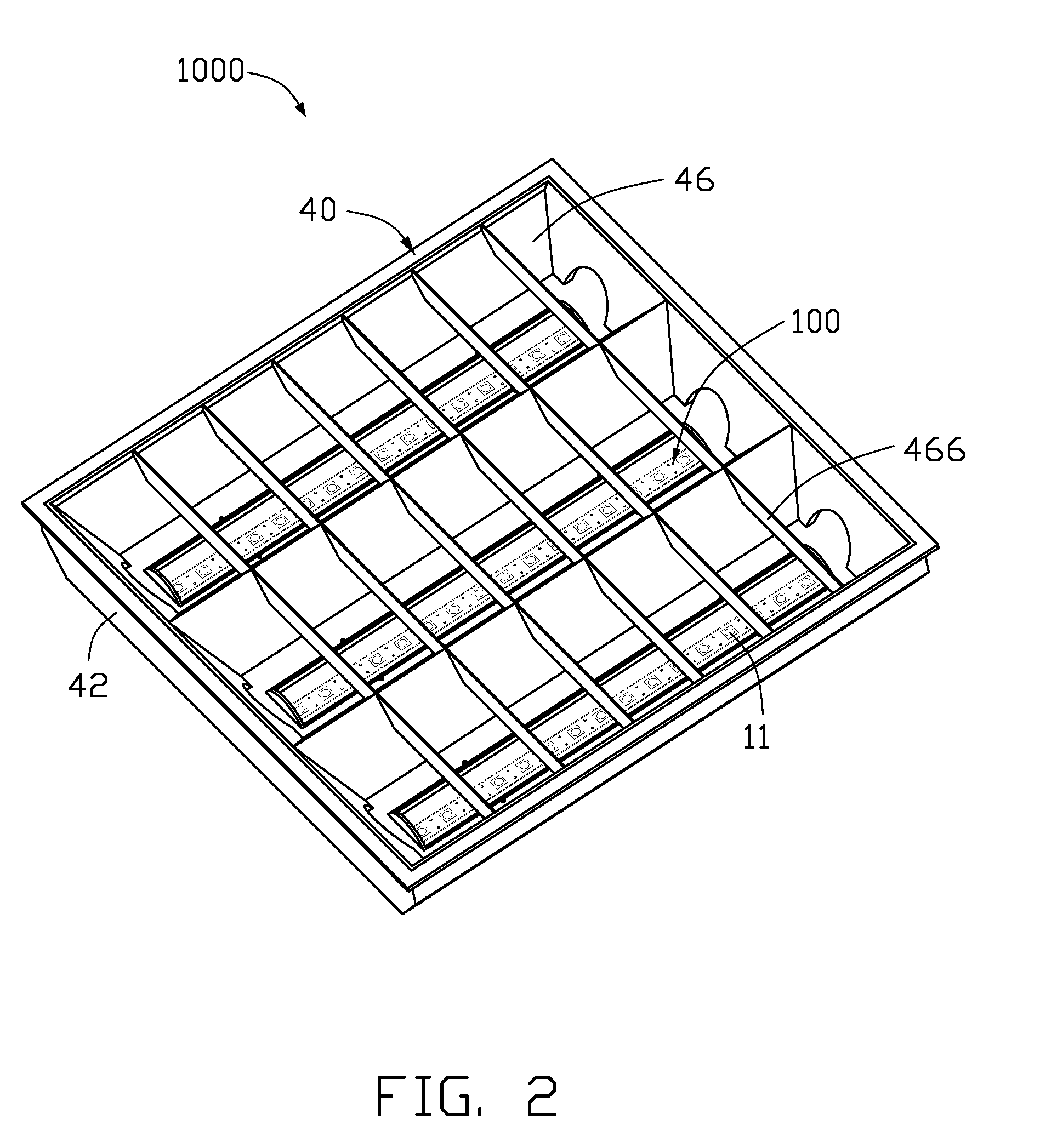
InactiveUS20100177514A1Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyWide areaPoint-like light sourceLighting support devicesEngineeringTroffer
An LED illuminating device includes a mounting module and a lamp unit mounted in the mounting module. The lamp unit includes a light-emitting module and a heat sink. The light-emitting module includes a light source having a plurality of LEDs, and a light penetrable cover located below the light source and defining a plurality of air venting holes therein. The heat sink includes an elongated base defining a plurality of air exchanging holes therein and a plurality of fins. The base has an outer convex surface and an opposite inner concave surface defining an elongated recess. The light source is received in the recess and thermally attached to the concave surface. Air flows into and out of a chamber defined between the base and the cover via the venting holes of the cover and the air exchanging holes of the base.
Owner:FU ZHUN PRECISION IND SHENZHEN +1
Packaging method for light emitting diode module that includes fabricating frame around substrate
InactiveUS7919339B2Increase brightnessSolve the low heat dissipation efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFluorescenceSilica gel
A packaging method for light emitting diode module that includes fabricating frame around substrate, wherein the method comprises the steps of: fabricating a printed circuit layer with a plurality of staggered nodes on a substrate; fabricating a frame around the substrate; fabricating a protruding inclined pier around the bottom rim of the inner wall of the frame; fabricating a plurality of convex reflecting microstructure points on the surface of the printed circuit layer; positioning chips and wire bonding; spraying reflecting paint on the surface of the substrate and the inner wall of the frame except the chips; filling a silica gel diffusion layer formed by mixing the silica gel and the diffusion powder into the frame; and evenly coating a fluorescent glue layer formed by evenly mixing another silica gel and fluorescent powder on the silica gel diffusion layer.
Owner:HSU CHI YUAN +1
Light emitting diode module
InactiveUS6914261B2Improve cooling efficiencyIncrease the areaStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringLight-emitting diode
A light emitting diode (LED) module illuminates under application of an electrical current for use in an electrical device as a light source. The LED module includes a plurality of epitaxy chips, an electrode set, and a substrate having good electrical insulation and good heat dissipation. The epitaxy chips, formed by cutting an epitaxy wafer, are mounted on the substrate. The LED module has good heat dissipation properties, thereby improving its illumination performance. The electrodes are arranged so that the illuminating area of the LED module is not shielded and can achieve full-area illumination through a large illumination area.
Owner:LEATEC FINE CERAMICS
SMD(surface mount device)-type light emitting diode with high heat dissipation efficiency and high power
ActiveUS7081645B2Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyHighly conductive materialSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricitySurface mounting
A SMD-type LED with high heat dissipation efficiency and high power includes a base with a post arranged and integrated on the center thereof and a slot on top of the post. At least one contact hole is arranged on bottom of the base for connecting with an external heat sink so as to achieve better heat dissipation. The slot is used for accommodating a LED chip that is electrically connected with a circuitry extension device through two electrical contacts. The LED chip is electrically connected with the circuitry extension device directly while it also connects with the base for heat dissipation, thus the structure for electricity conduction is separated from the structure for heat dissipation.
Owner:BRIGHT LED ELECTRONICS CORP
LED illumination device
InactiveUS8029169B2Increase cooling areaA large amountMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceEngineeringAmbient air
An LED illumination device includes a lamp housing, a heat sink, a cooling fan, and a light source. The heat sink, the cooling fan and the light source are received in the lamp housing. The heat sink includes a base and a plurality of fins extending from the base. The light source is attached to the base of the heat sink. The cooling fan causes ambient air to enter into the lamp housing and flow through the heat sink. A plurality of air-disturbing plates extends from the lamp housing towards the heat sink. The air-disturbing plates disturb the air in the lamp housing and guide the disturbed air into air passageways defined between adjacent fins of the heat sink.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
LED illumination device
InactiveUS20090323361A1Increase cooling areaA large amountMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceEngineeringAmbient air
An LED illumination device includes a lamp housing, a heat sink, a cooling fan, and a light source. The heat sink, the cooling fan and the light source are received in the lamp housing. The heat sink includes a base and a plurality of fins extending from the base. The light source is attached to the base of the heat sink. The cooling fan causes ambient air to enter into the lamp housing and flow through the heat sink. A plurality of air-disturbing plates extends from the lamp housing towards the heat sink. The air-disturbing plates disturb the air in the lamp housing and guide the disturbed air into air passageways defined between adjacent fins of the heat sink.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Divided LED lamp
InactiveUS20100315824A1Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyGuaranteed uptimePlanar light sourcesLighting support devicesLED lampElectronics
A divided LED lamp includes an LED assembly, a casing assembly, LED electronics, power and signal cables, a control panel including a display screen and operation buttons, and a bracket for mounting the lamp. The casing assembly includes a first casing member and a second casing member. At least one cable tube is formed between the first casing member and the second casing member. The power and signal cables that connect the LED assembly received in the first casing member and the LED electronics received in the second casing member are received through the cable tube. This arrangement allows the LED assembly and the LED electronics to be received in individual and independent casing members and are associated with respective individual heat dissipation fins or heat radiators, so as to realize high efficiency of heat dissipation, stabilized operation, and extended lifespan.
Owner:GUANGZHOU YAJIANG PHOTOELECTRIC EQUIP CO LTD
Thermoduct
InactiveUS20060283574A1Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyIncrease surface areaIndirect heat exchangersCopperMaterials science
A thermoduct comprises a metallic tube with multiple trenches, cupric powder and a metallic net, wherein the metallic net and the cupric powder are disposed inside the metallic tube and function as a capillary texture. The cupric powder is sintered to adhere to recesses of trenches, and the metallic net is sintered to adhere to the inner wall of the metallic tube. In the present invention, the metallic net can confine the cupric powder inside the gap between the metallic net and the inner wall of the metallic tube, which enables the cupric powder to be sintered to firmly adhere to the recesses of the trenches; thus, the thermoduct can simultaneously have capillarity, permeability and thermal conductivity, and the backflow of the liquid working fluid is speeded up.
Owner:LEE TING WEI
Light Emitting Device Mounting Substrate, Light Emitting Device Housing Package, Light Emitting Apparatus, and Illuminating Apparatus
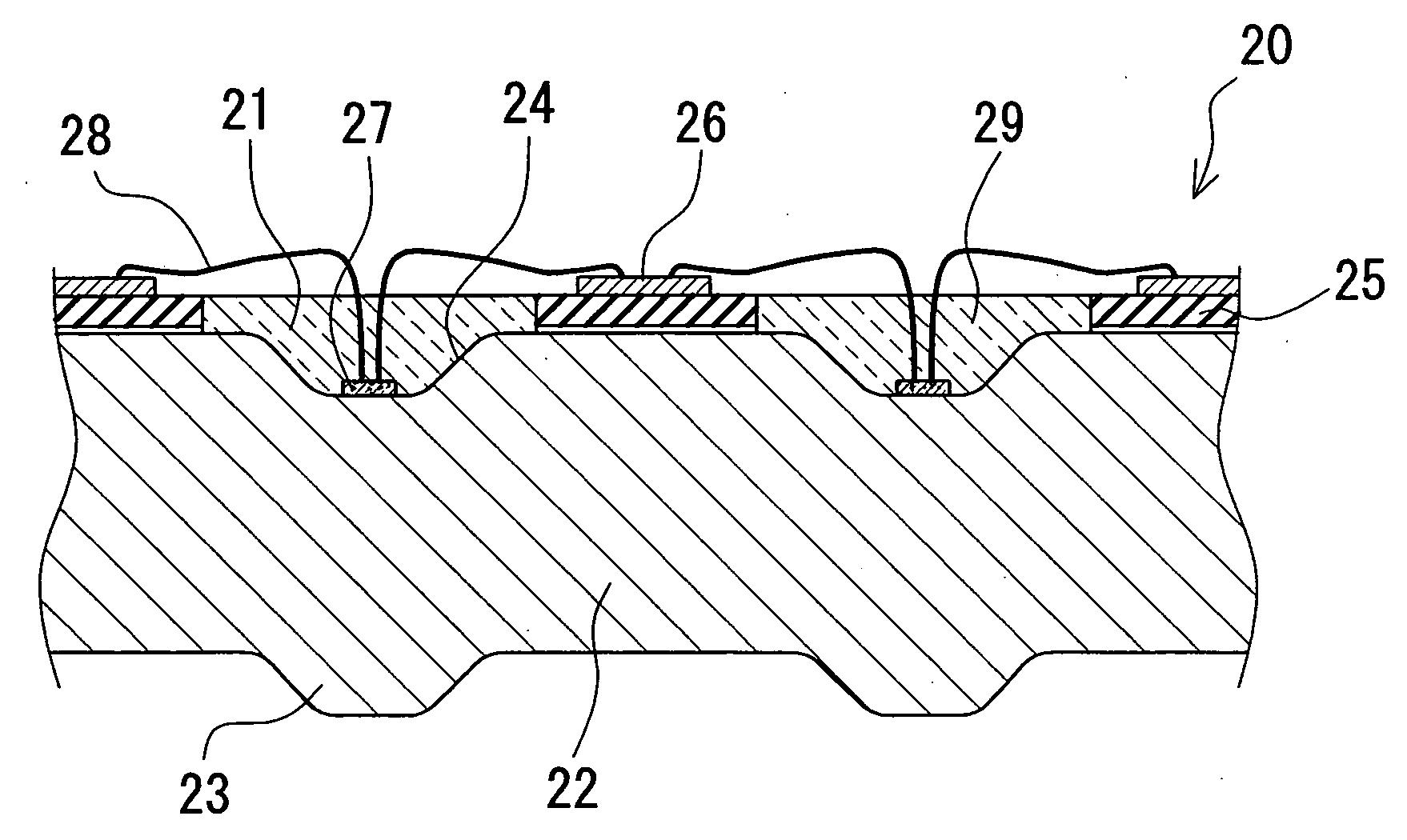
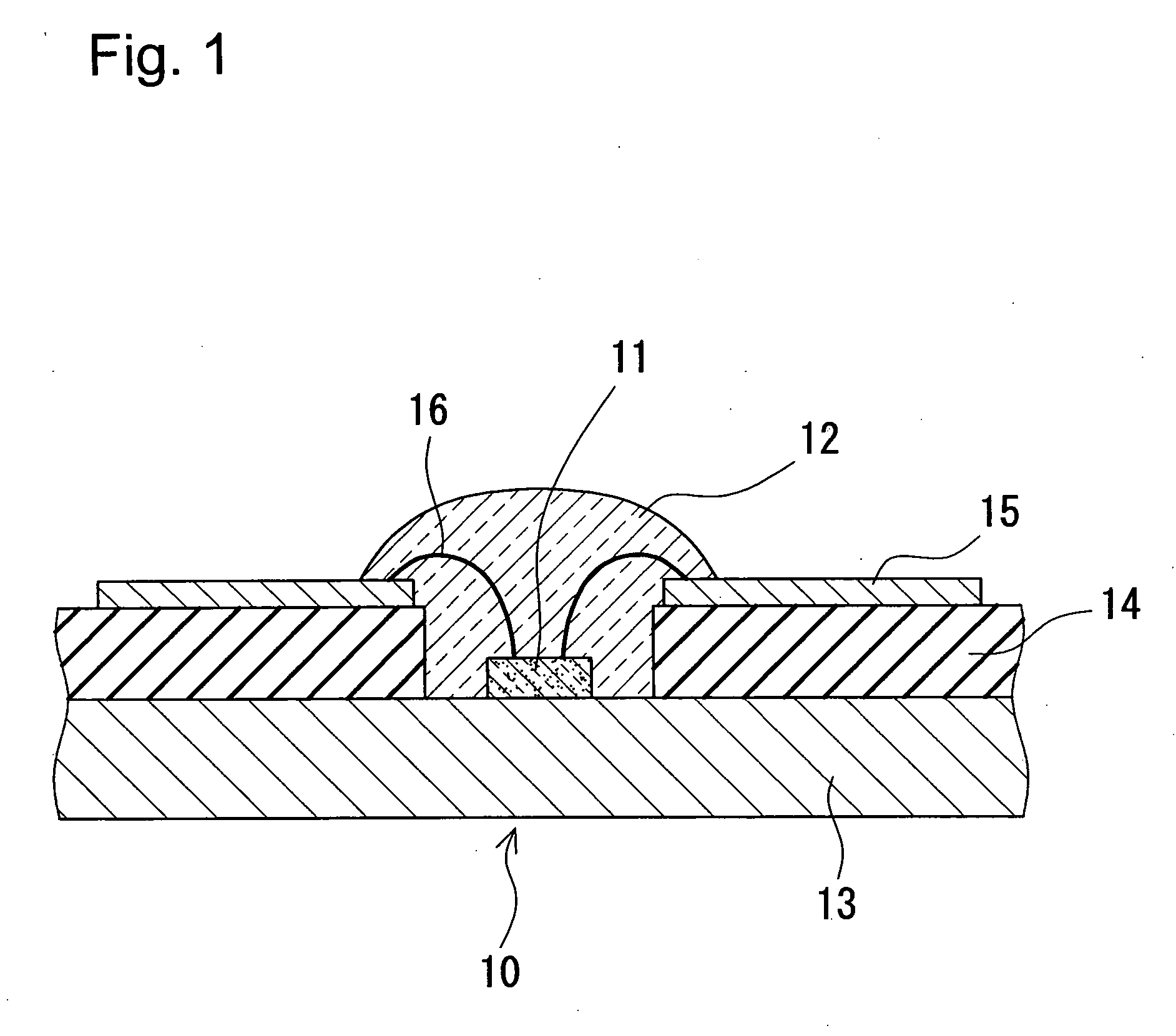
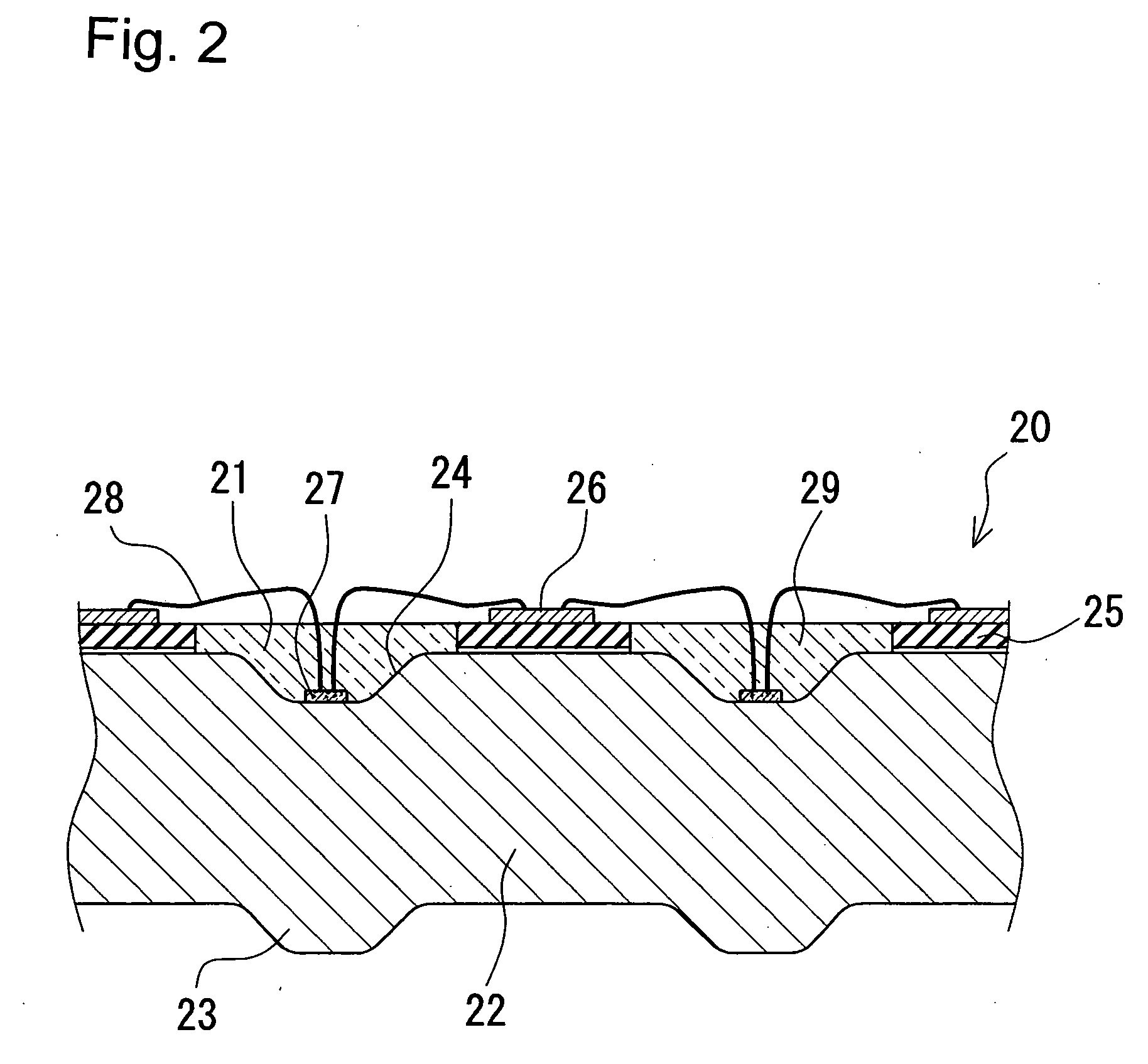
InactiveUS20090200570A1Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyHeat dissipationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringLight-emitting diode
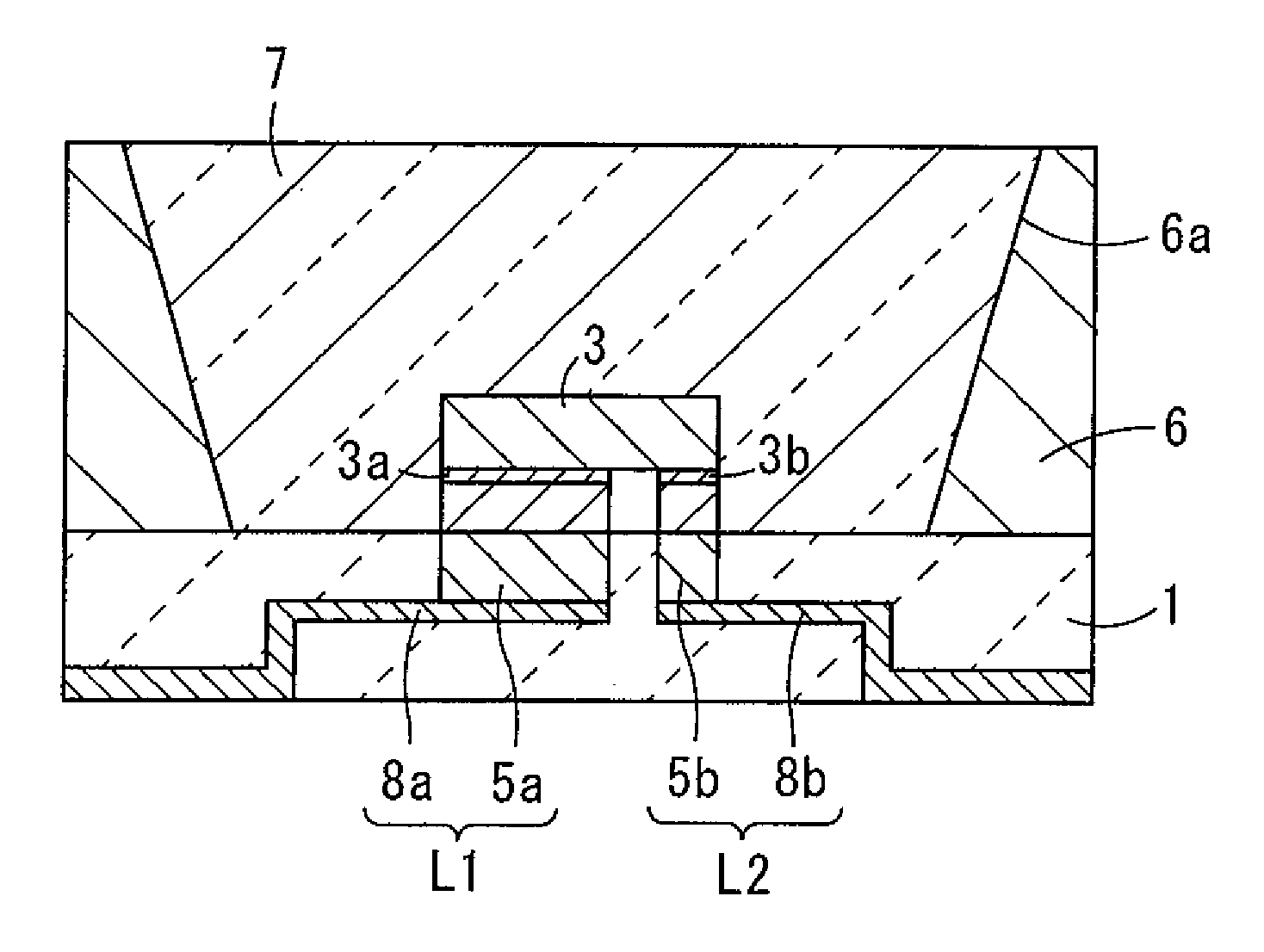
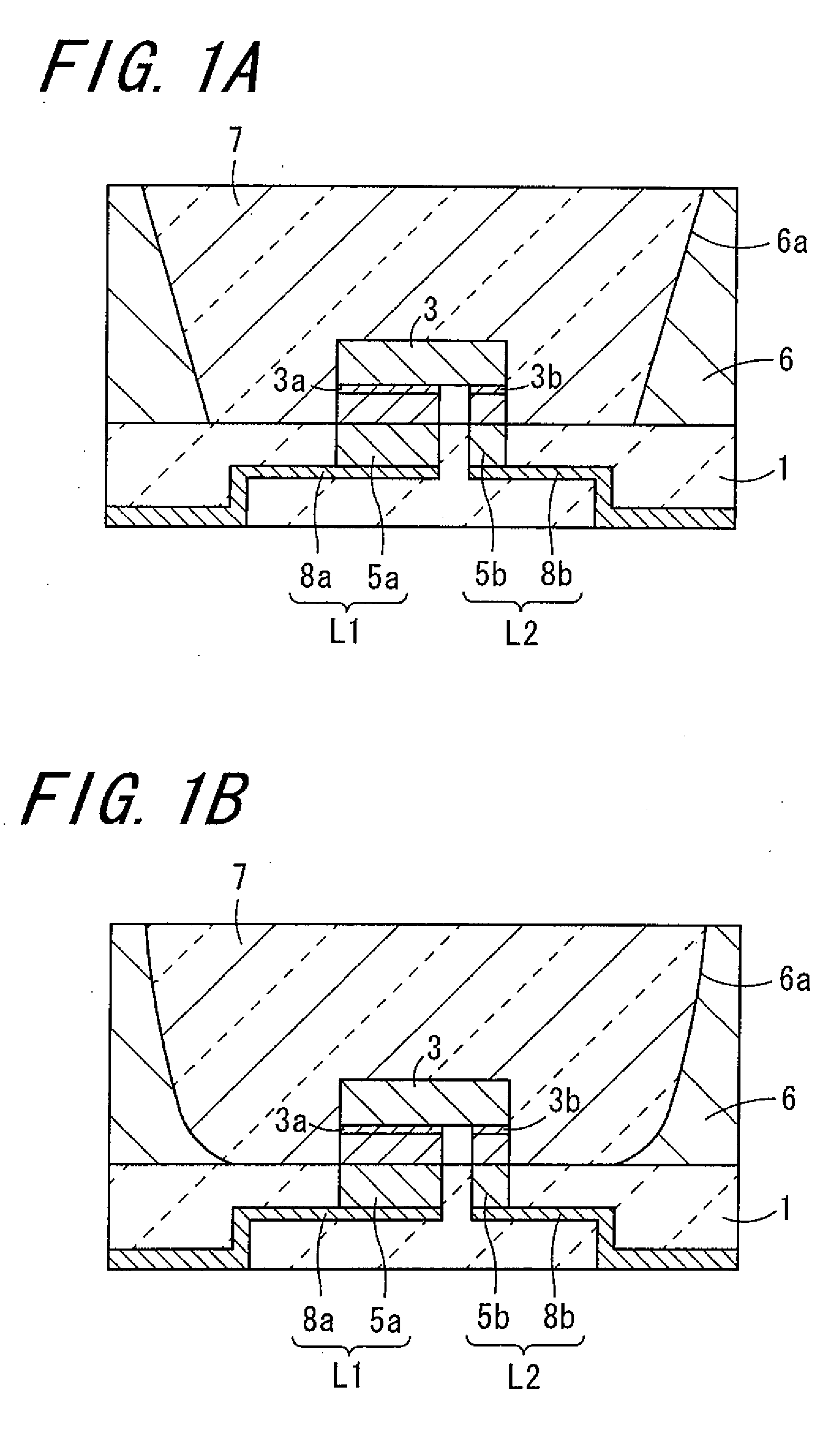
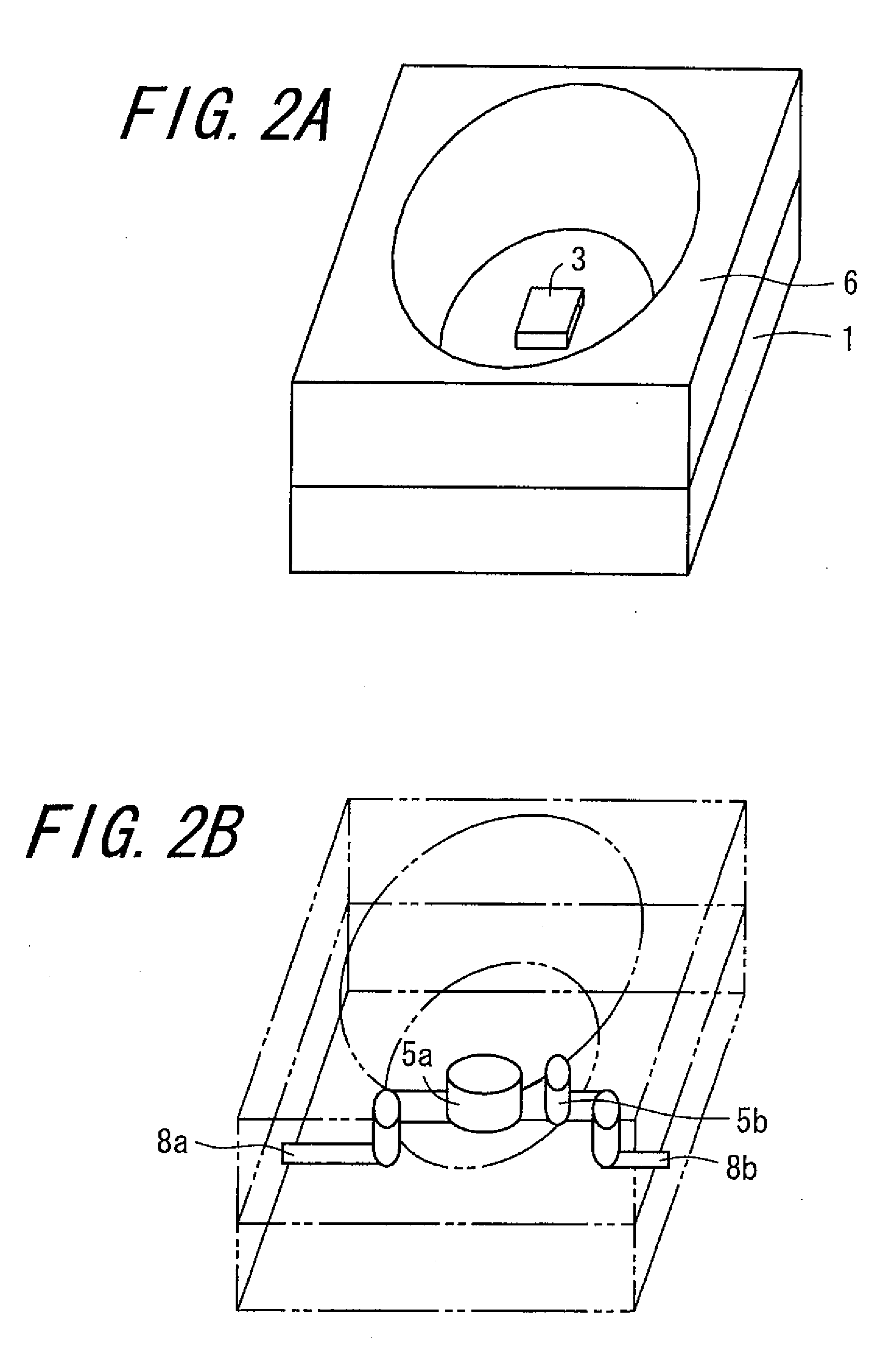
A light-emitting apparatus with improved dissipation efficiency of heat transmitted to a specific electrode of a light-emitting device is provided. A light-emitting device mounting substrate used for the light emitting apparatus include a base body (1) which mounts thereon a light-emitting device (3); a first electrically conductive path (L1) formed within the base body (1), one end thereof being electrically connected to a first electrode (3a) of the light-emitting device (3) and the other end thereof being led out to a surface of the base body (1); and a second electrically conductive path (L2) formed in the base body (1), one end thereof being electrically connected to a second electrode (3b) of the light-emitting device (3), and the other end thereof being formed on the surface of the base body (1). The first electrically conductive path (L1) is made smaller in thermal resistance than the second electrically conductive path (L2).
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
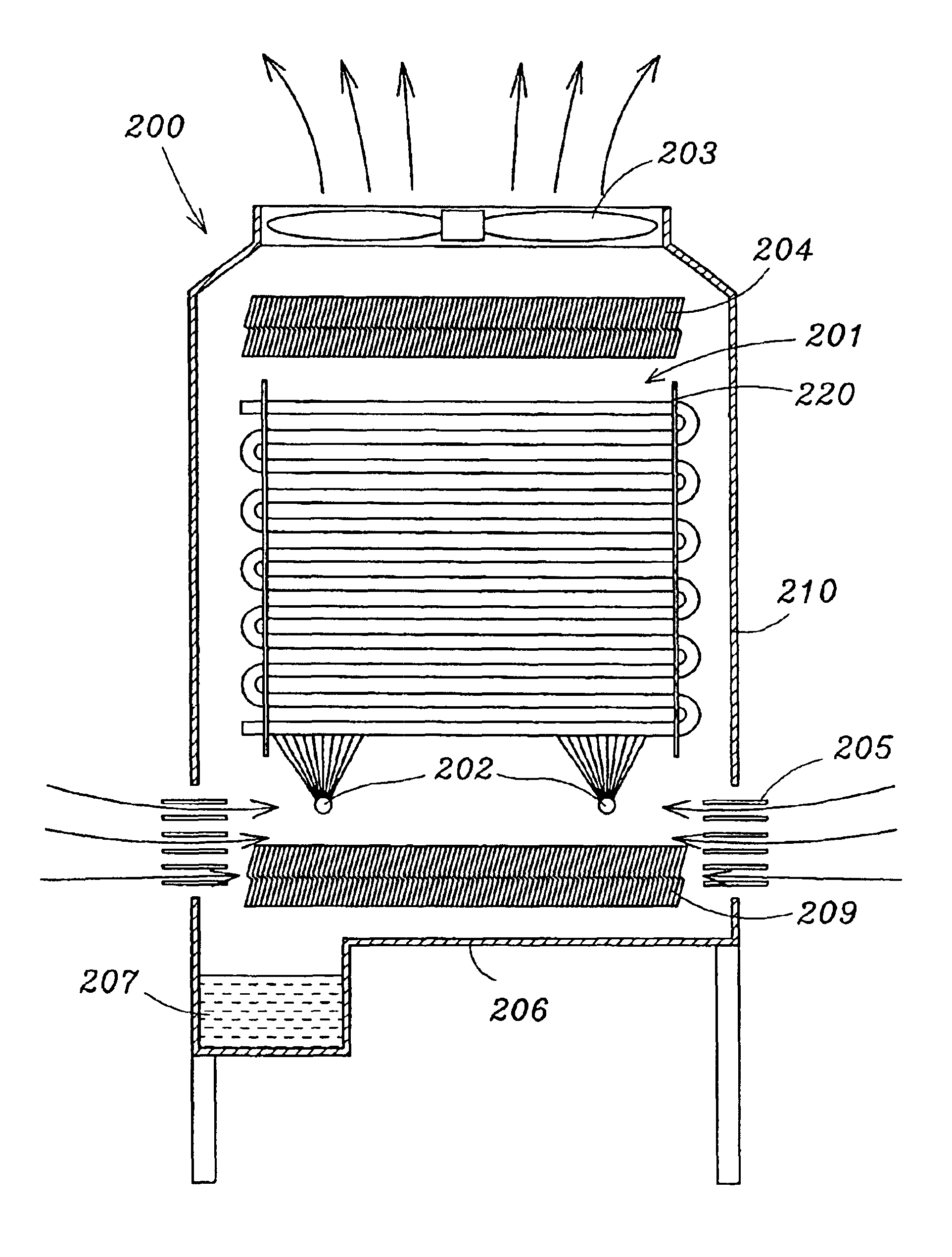
Evaporative condenser without cooling fins
InactiveUS6766655B1Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyLong lastingEvaporators/condensersSteam/vapor condensersEvaporative coolerEvaporation
An evaporative type medium condenser without the using of conventional cooling fins comprises: characteristically a plurality of streamline cross sectional bare metal tubes disposed in parallel for medium coils to instead the conventional round sectional tubes thereof; a recycling water supply system having a plurality of water spray nozzles for spraying fine water particles onto the surface of coil tubes formed a water film continuously held thereon; a fan system to provide a wind flow blowing over the streamline tubes in a direction from a large head front portion of the streamline cross section to a gradual reduced rear portion thereof and to provide a low pressure area thereat so as to speedy the evaporation of the water film on the surface of the coils tubes for improving a high cooling efficiency to reach a high E.E.R. therefore.
Owner:WU HO HSIN
Divided LED lamp
InactiveUS8425091B2Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyGuaranteed uptimePlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceEngineeringLED lamp
A divided LED lamp includes an LED assembly, a casing assembly, LED electronics, power and signal cables, a control panel including a display screen and operation buttons, and a bracket for mounting the lamp. The casing assembly includes a first casing member and a second casing member. At least one cable tube is formed between the first casing member and the second casing member. The power and signal cables that connect the LED assembly received in the first casing member and the LED electronics received in the second casing member are received through the cable tube. This arrangement allows the LED assembly and the LED electronics to be received in individual and independent casing members and are associated with respective individual heat dissipation fins or heat radiators, so as to realize high efficiency of heat dissipation, stabilized operation, and extended lifespan.
Owner:GUANGZHOU YAJIANG PHOTOELECTRIC EQUIP CO LTD
LED illuminating device
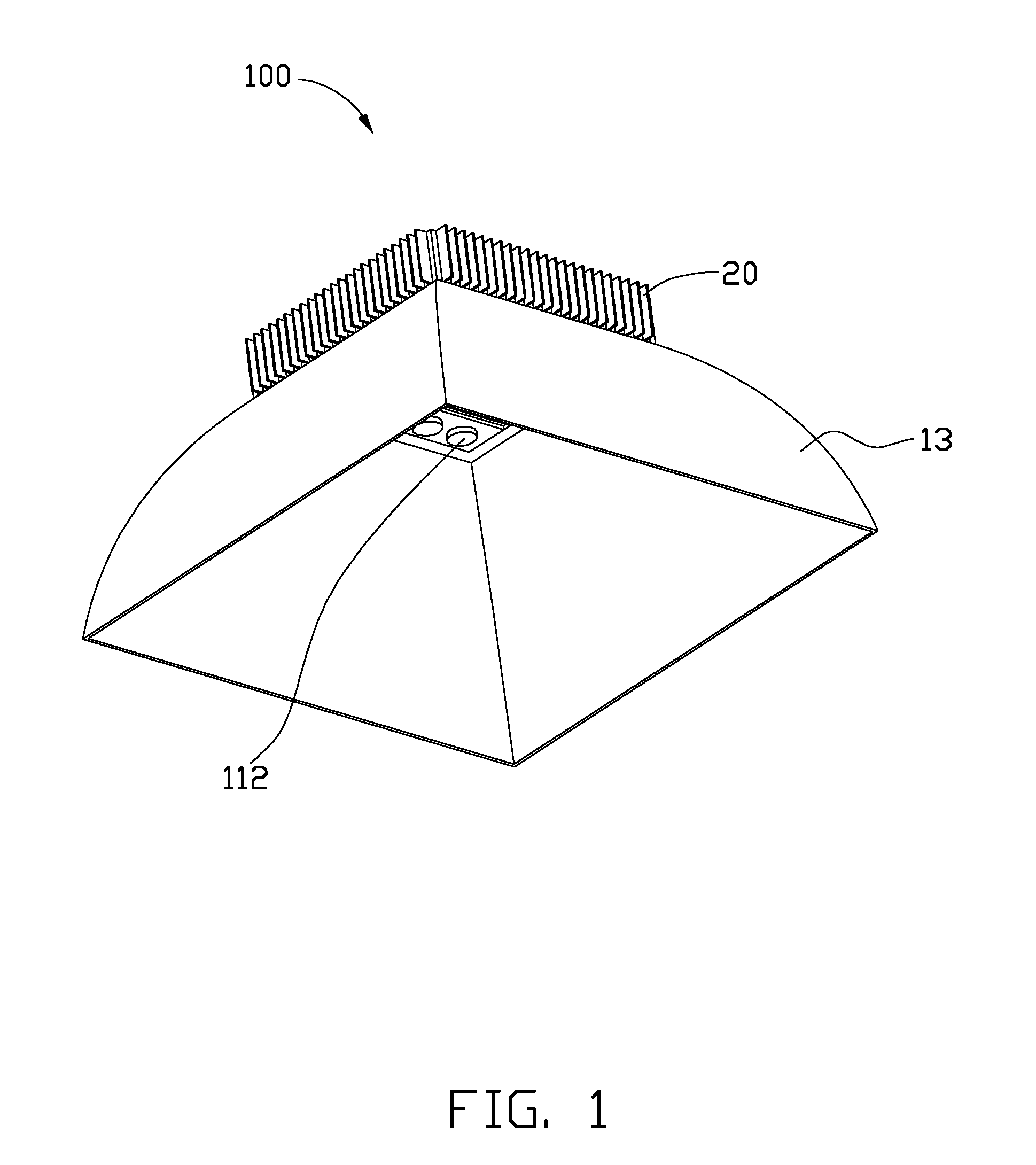
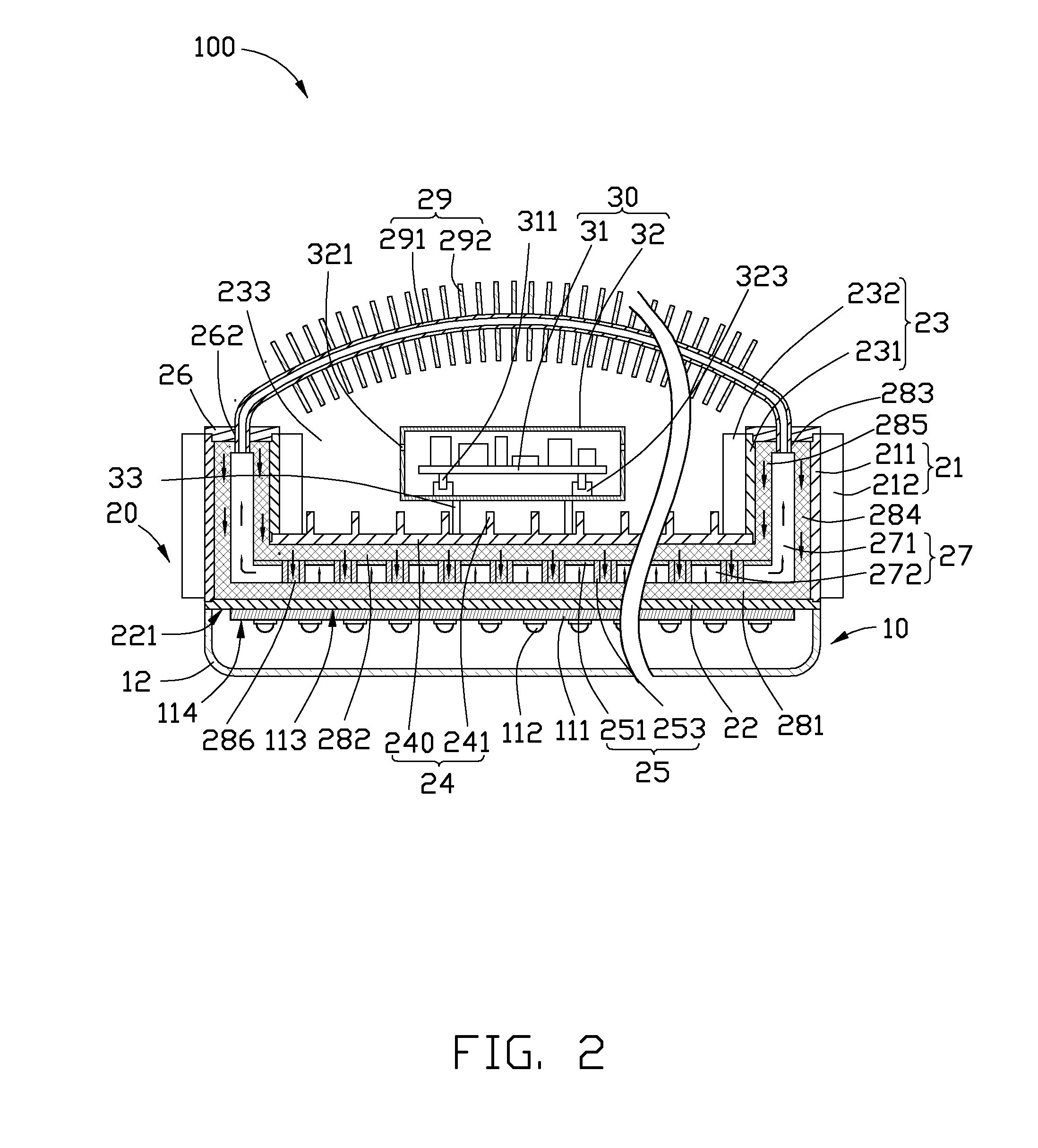
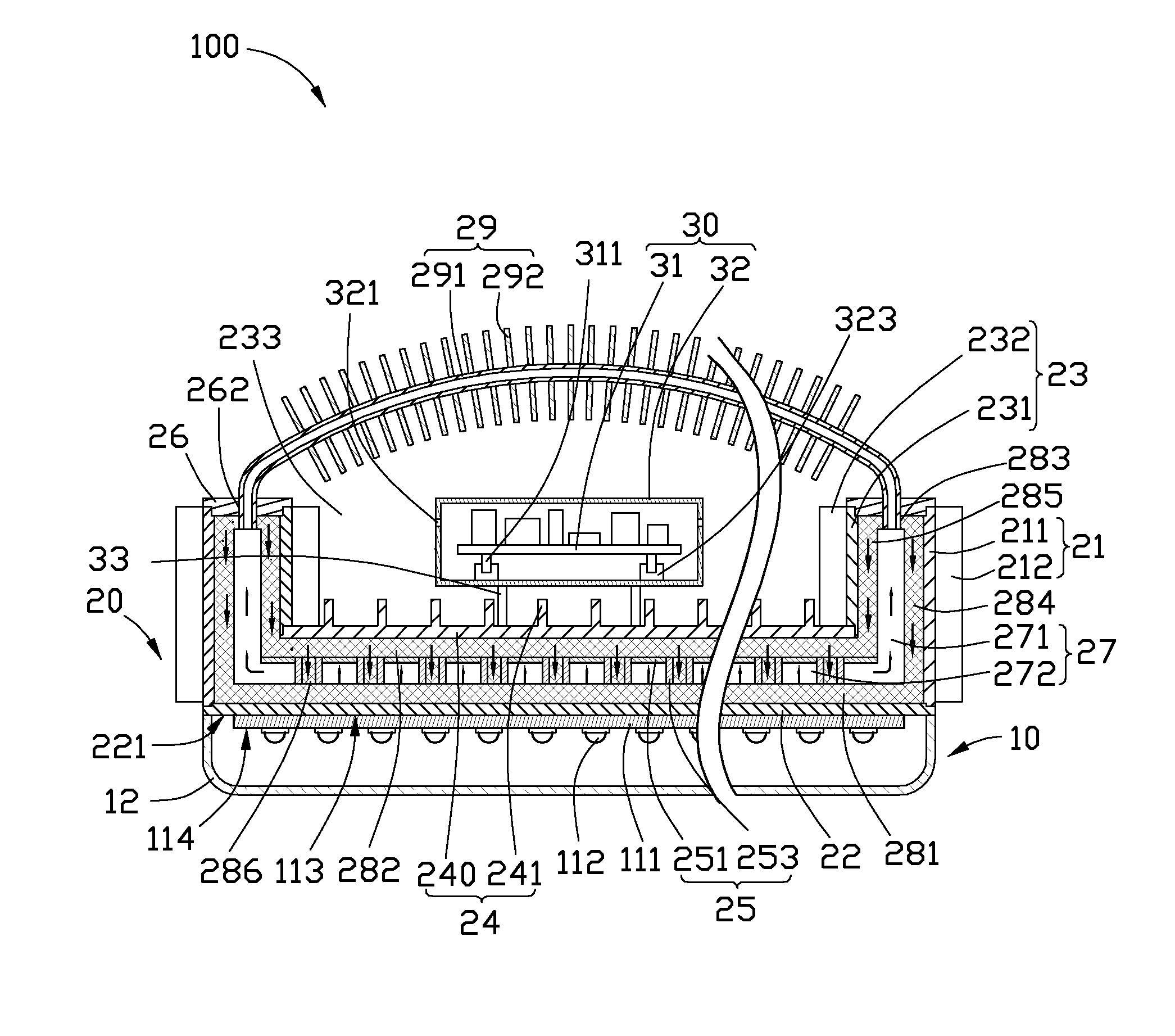
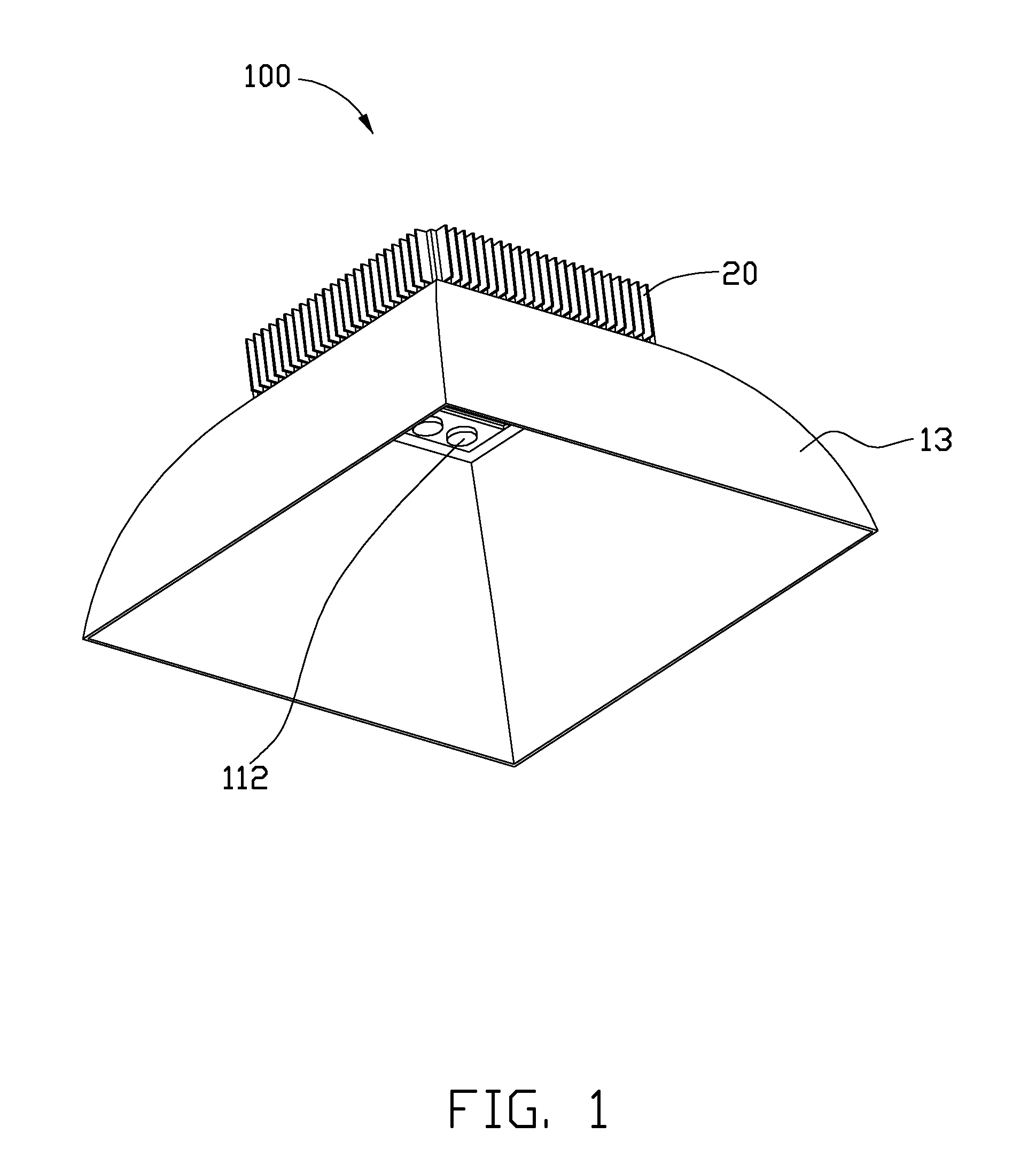
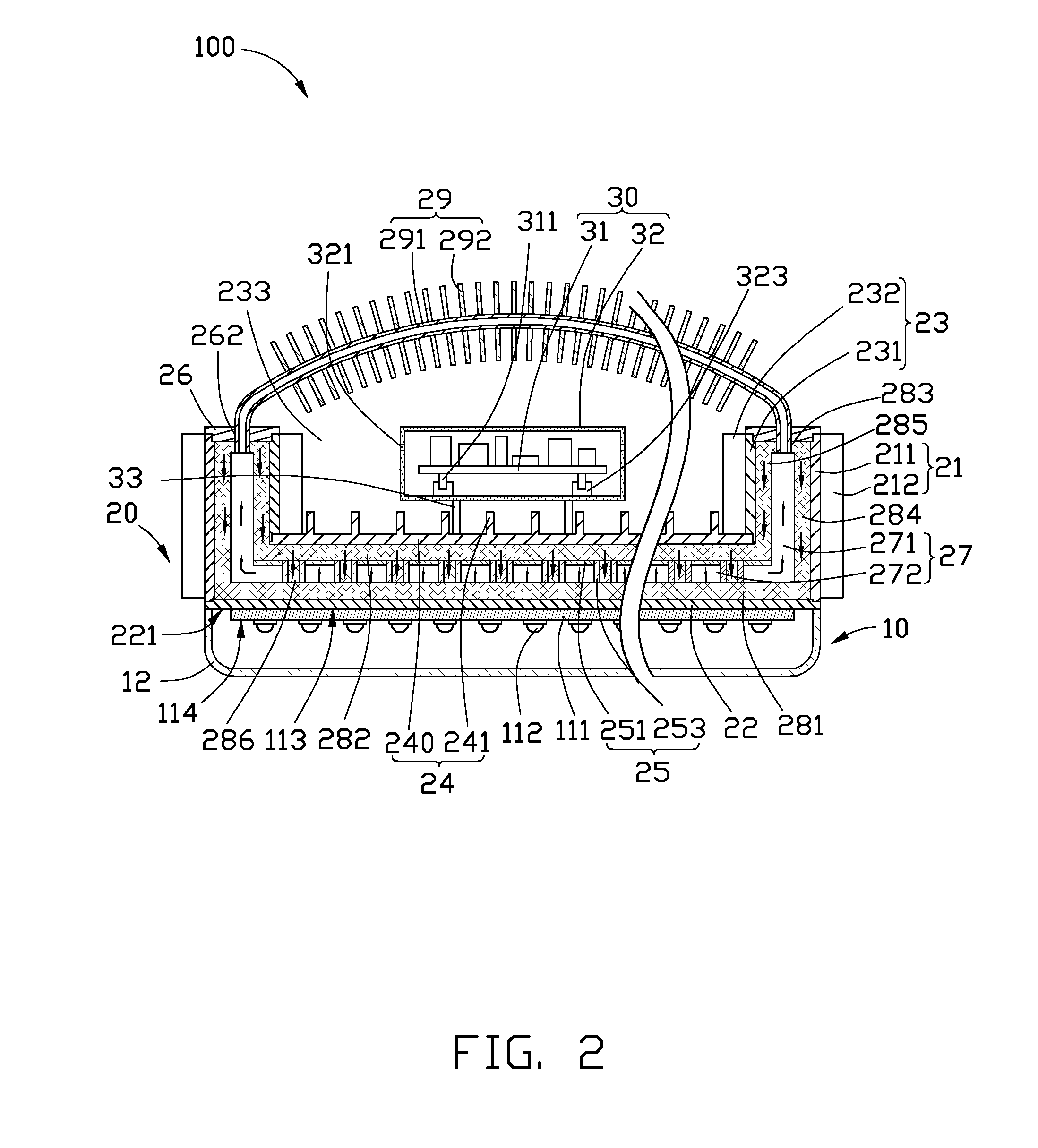
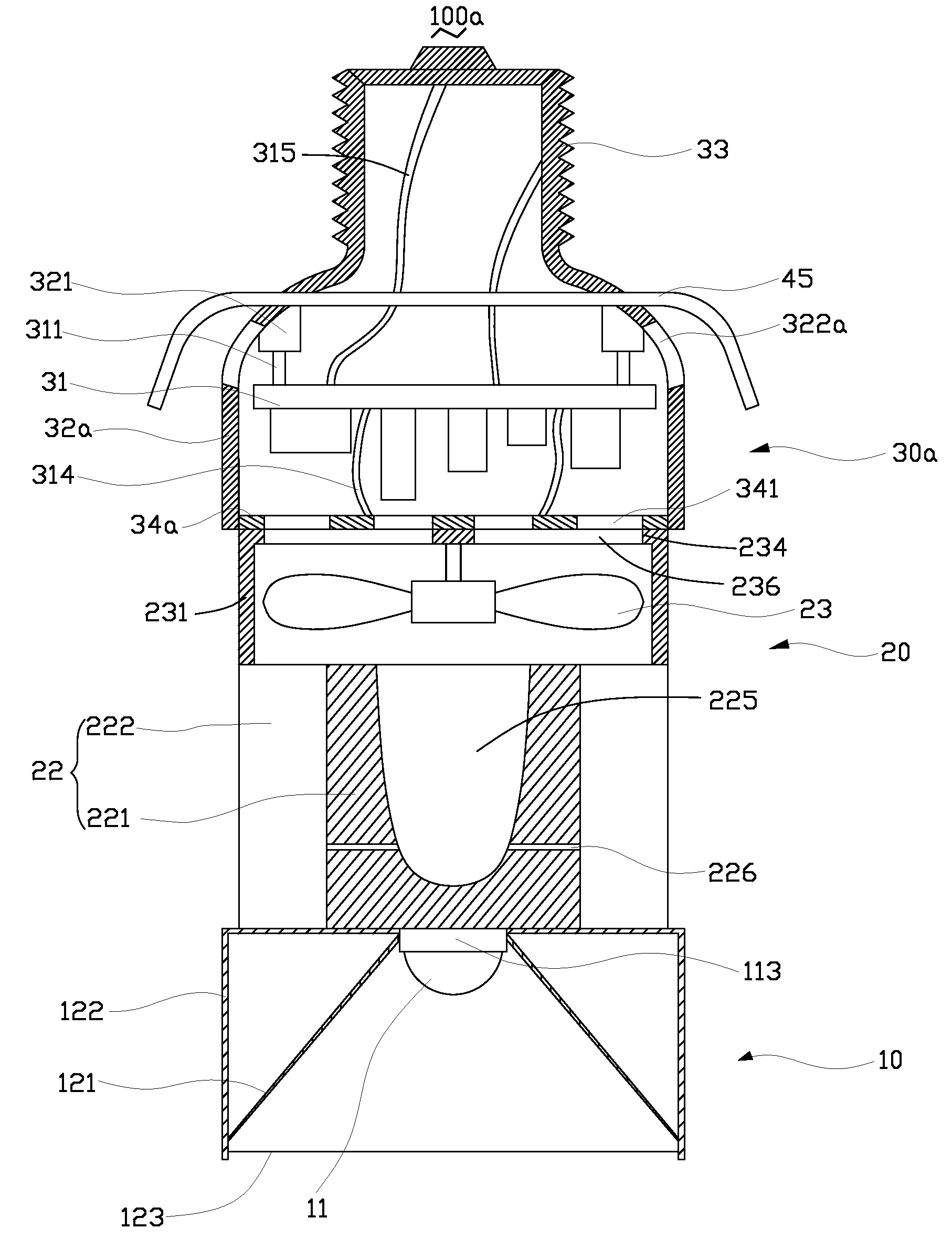
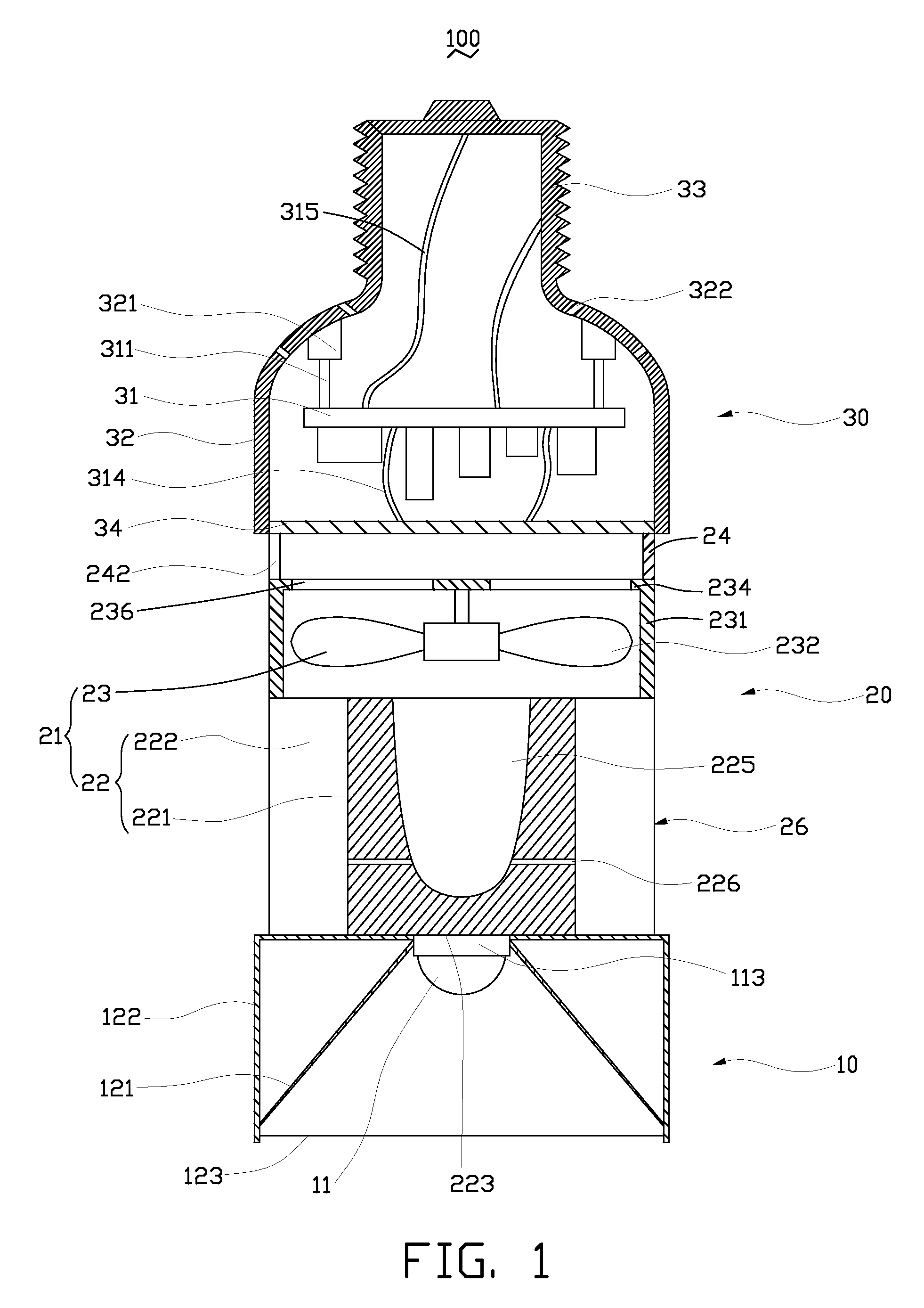
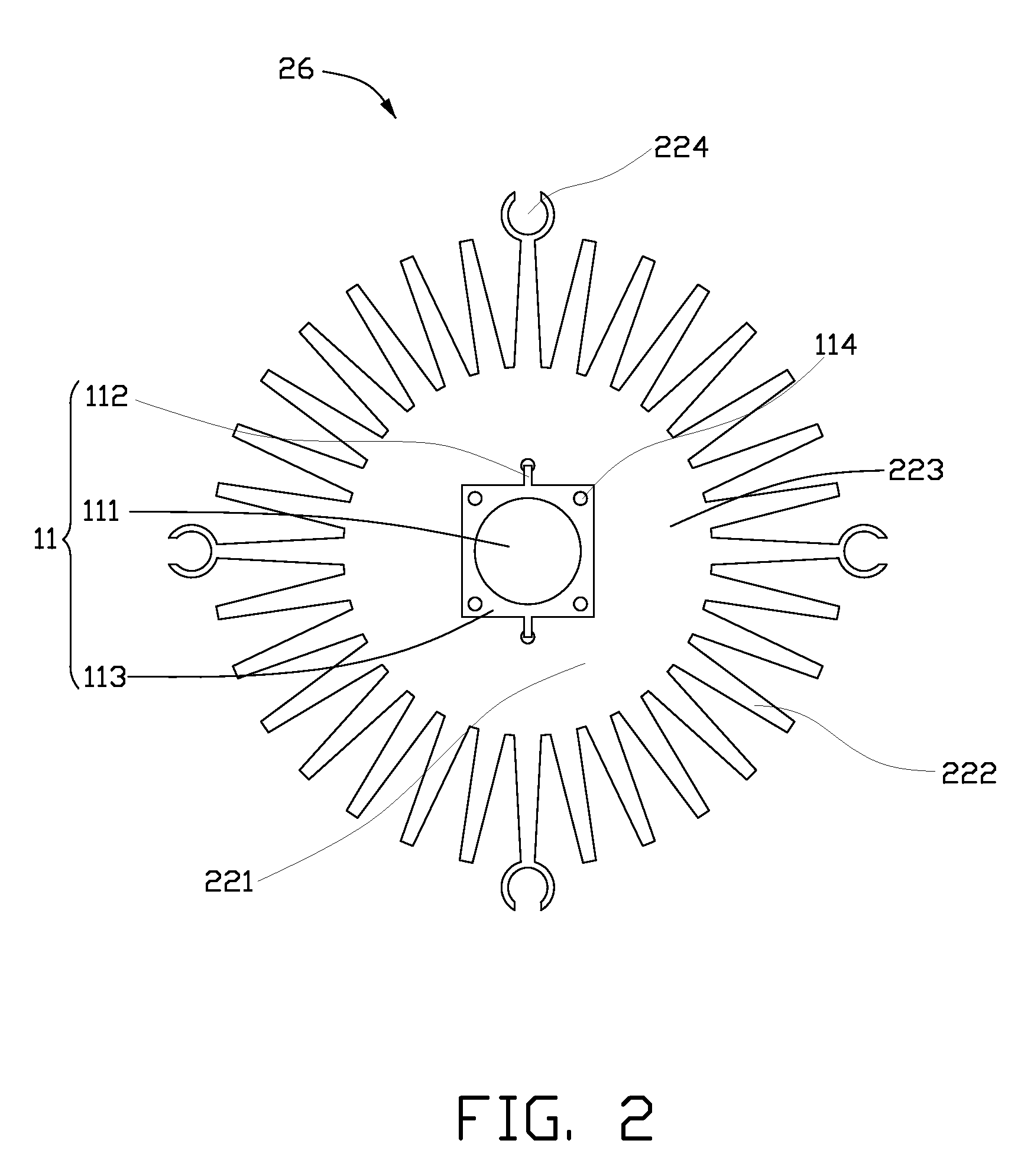
InactiveUS20100265709A1Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyIncrease brightnessPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceOptical ModuleWorking fluid
An LED illuminating device includes an optical module and a heat dissipation device. The optical module includes a plurality of LEDs. The heat dissipation device includes a housing and a heat sink. The heat sink includes a base and a plurality of spaced fins formed on the base. The LEDs are thermally attached to a heat absorbing surface formed at a bottom of a bottom plate of the housing. The heat sink and the housing cooperatively define a hermetical chamber therebetween. A closed sidewall of the chamber is sandwiched between the base of the heat sink and the bottom plate of the housing. A wick structure is received in the chamber and attached to the heat dissipation device at a periphery of the chamber. A working fluid is filled in the chamber and saturated in the wick structure.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
LED illuminating device
InactiveUS20110026251A1Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyPlanar light sourcesLighting support devicesOptical ModuleWorking fluid
An LED illuminating device includes a boiling room, an optical module, a heat insulating member and a heat exchanging member communicating with the boiling room. The boiling room defines a horizontal room and an annular, vertical room having a bottom end surrounding the horizontal room. A wick structure is received in the boiling room. Working fluid is received in the boiling room and saturated in a bottom portion of the wick structure. The optical module includes a plurality of LEDs attached to a heat absorbing member connecting with the bottom portion of the wick structure. The heat insulating member is received in the boiling room and attached to a middle portion of the wick structure for thermally insulating the middle portion of the wick structure from vaporized working fluid in the horizontal room of the boiling room.
Owner:FU ZHUN PRECISION IND SHENZHEN +1
LED illuminating device
InactiveUS8348470B2Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceOptical ModuleWorking fluid
An LED illuminating device includes a boiling room, an optical module, a heat insulating member and a heat exchanging member communicating with the boiling room. The boiling room defines a horizontal room and an annular, vertical room having a bottom end surrounding the horizontal room. A wick structure is received in the boiling room. Working fluid is received in the boiling room and saturated in a bottom portion of the wick structure. The optical module includes a plurality of LEDs attached to a heat absorbing member connecting with the bottom portion of the wick structure. The heat insulating member is received in the boiling room and attached to a middle portion of the wick structure for thermally insulating the middle portion of the wick structure from vaporized working fluid in the horizontal room of the boiling room.
Owner:FU ZHUN PRECISION IND SHENZHEN +1
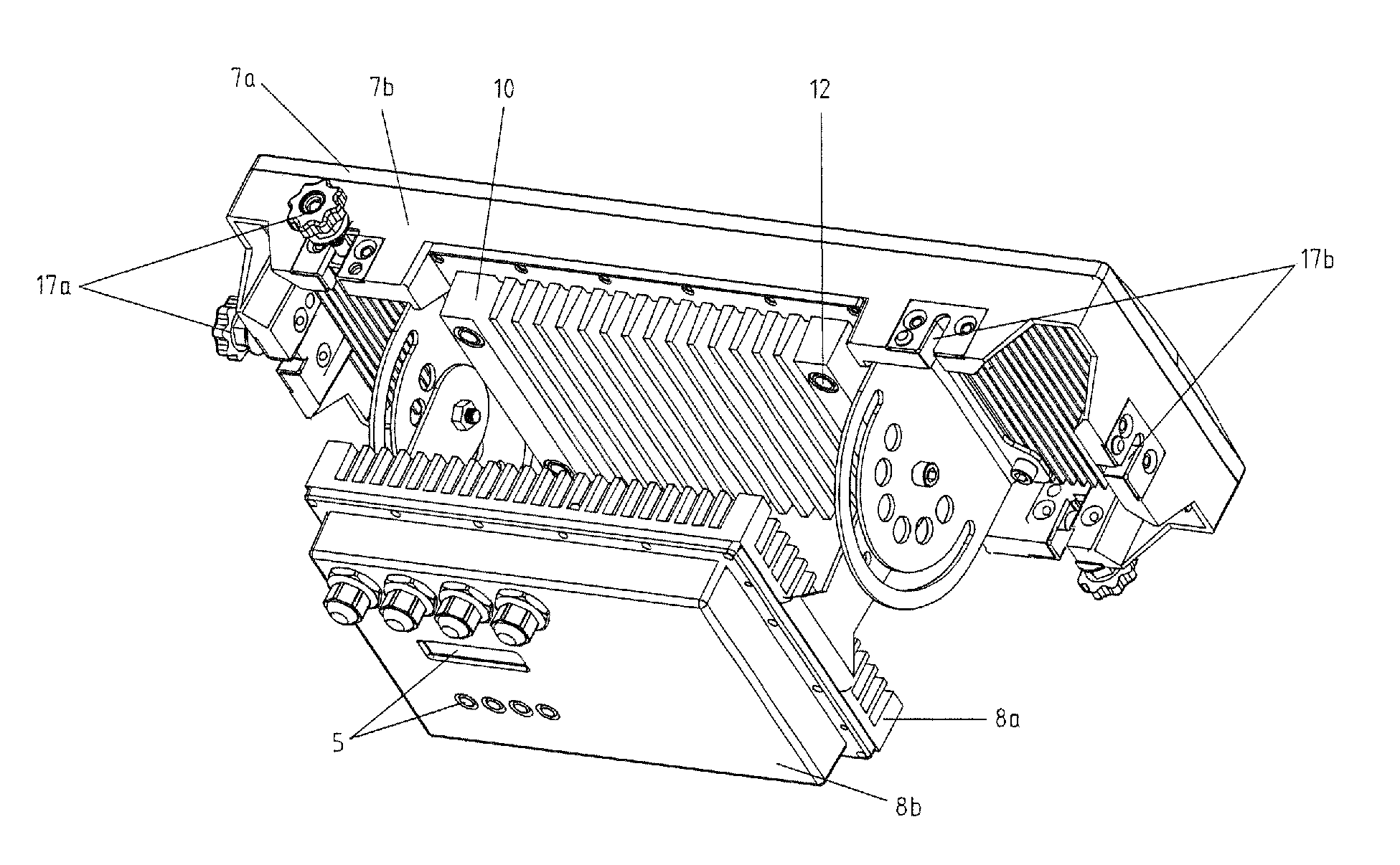
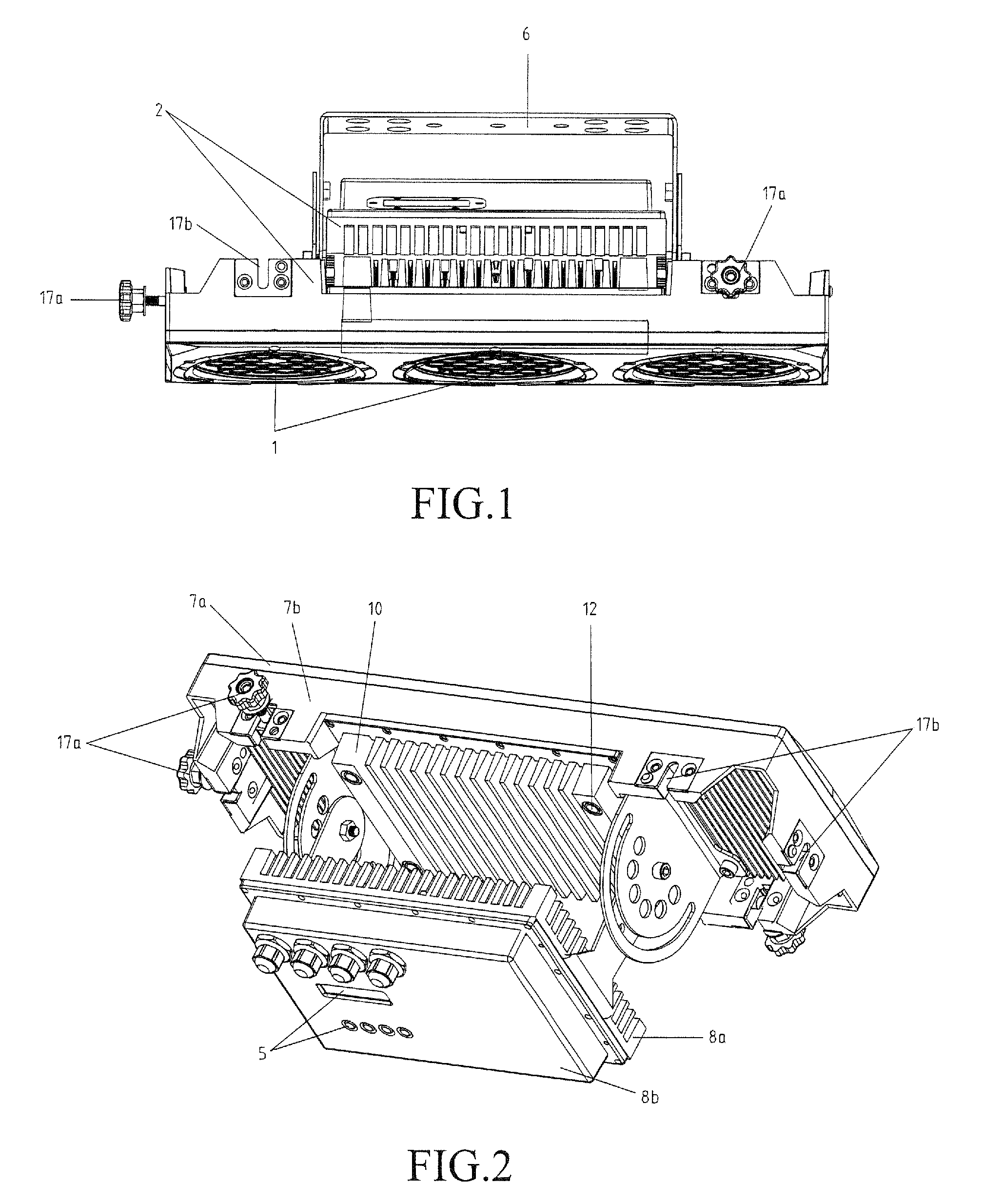
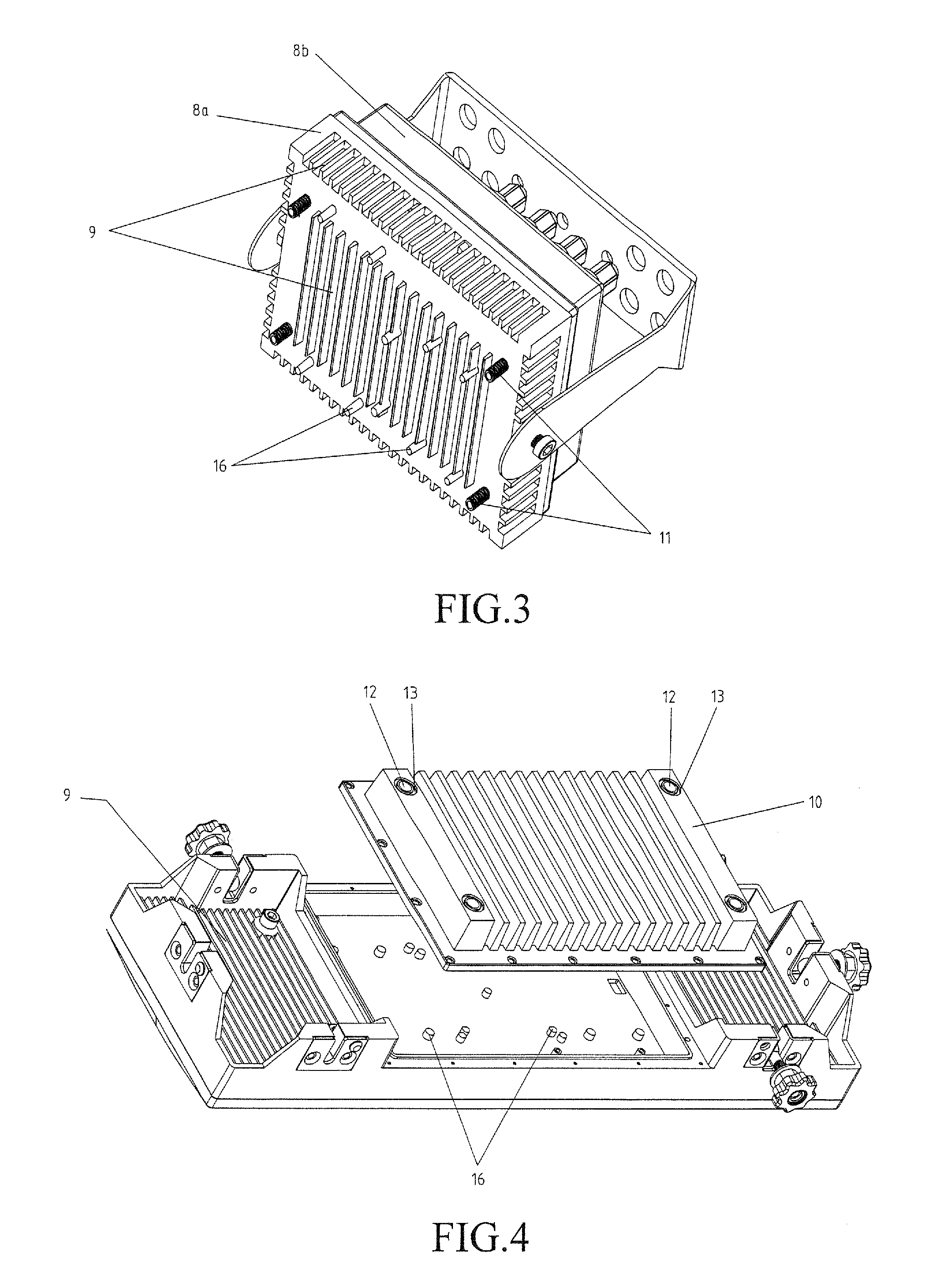
LED illuminating device and light engine thereof
InactiveUS20090268468A1Heat dissipationImprove cooling effectCoupling device connectionsPoint-like light sourceEngineeringHeat spreader
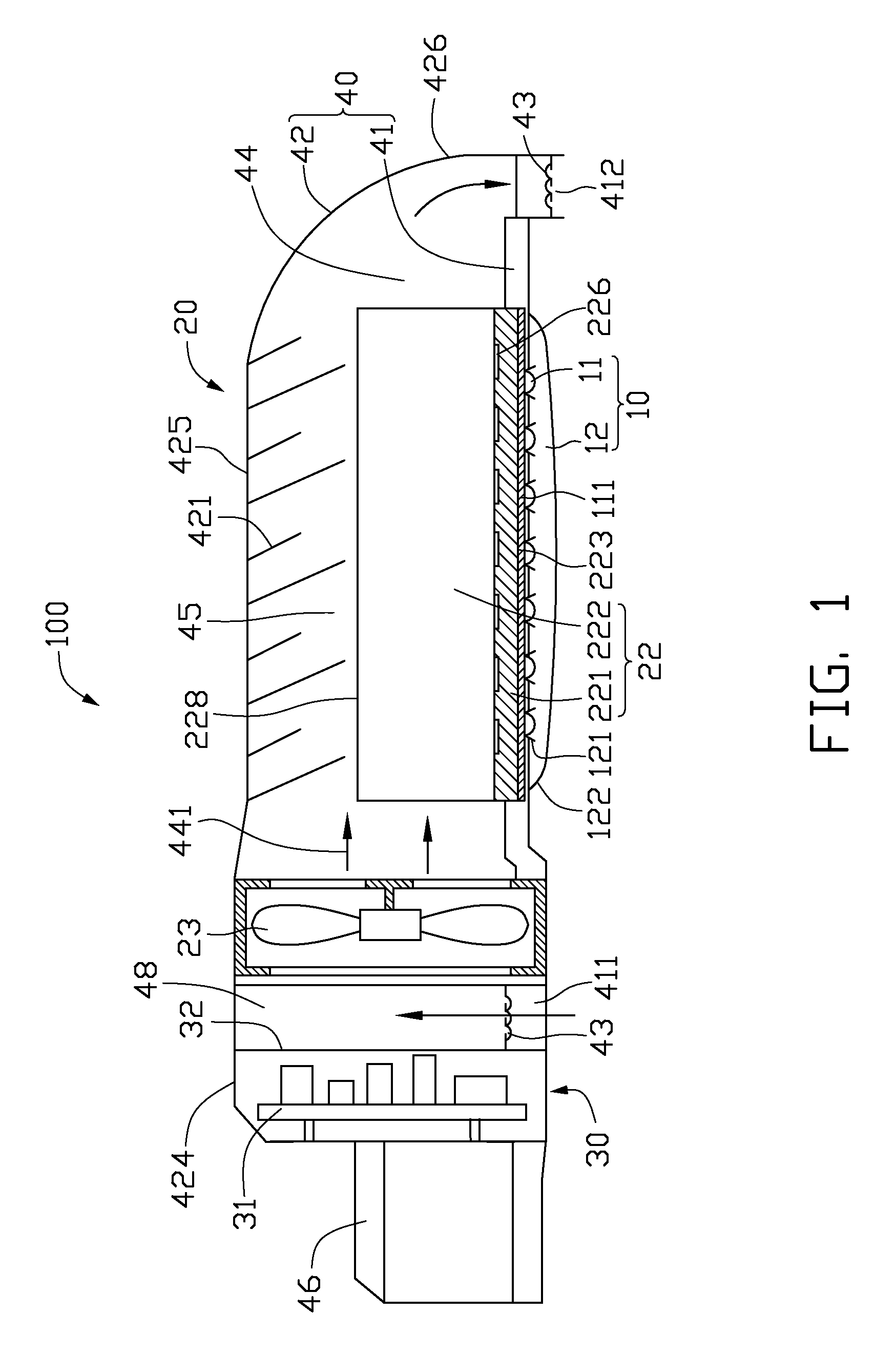
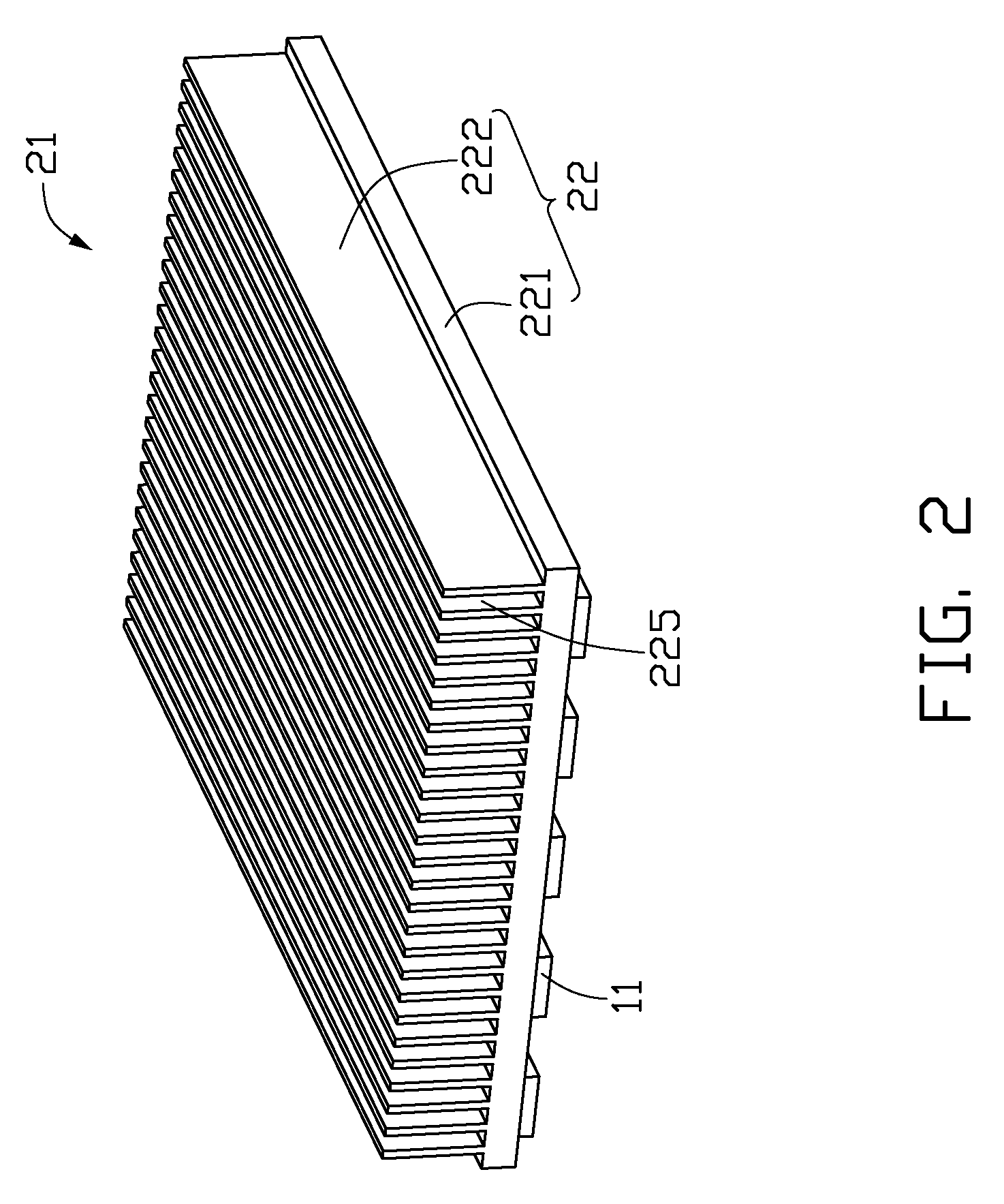
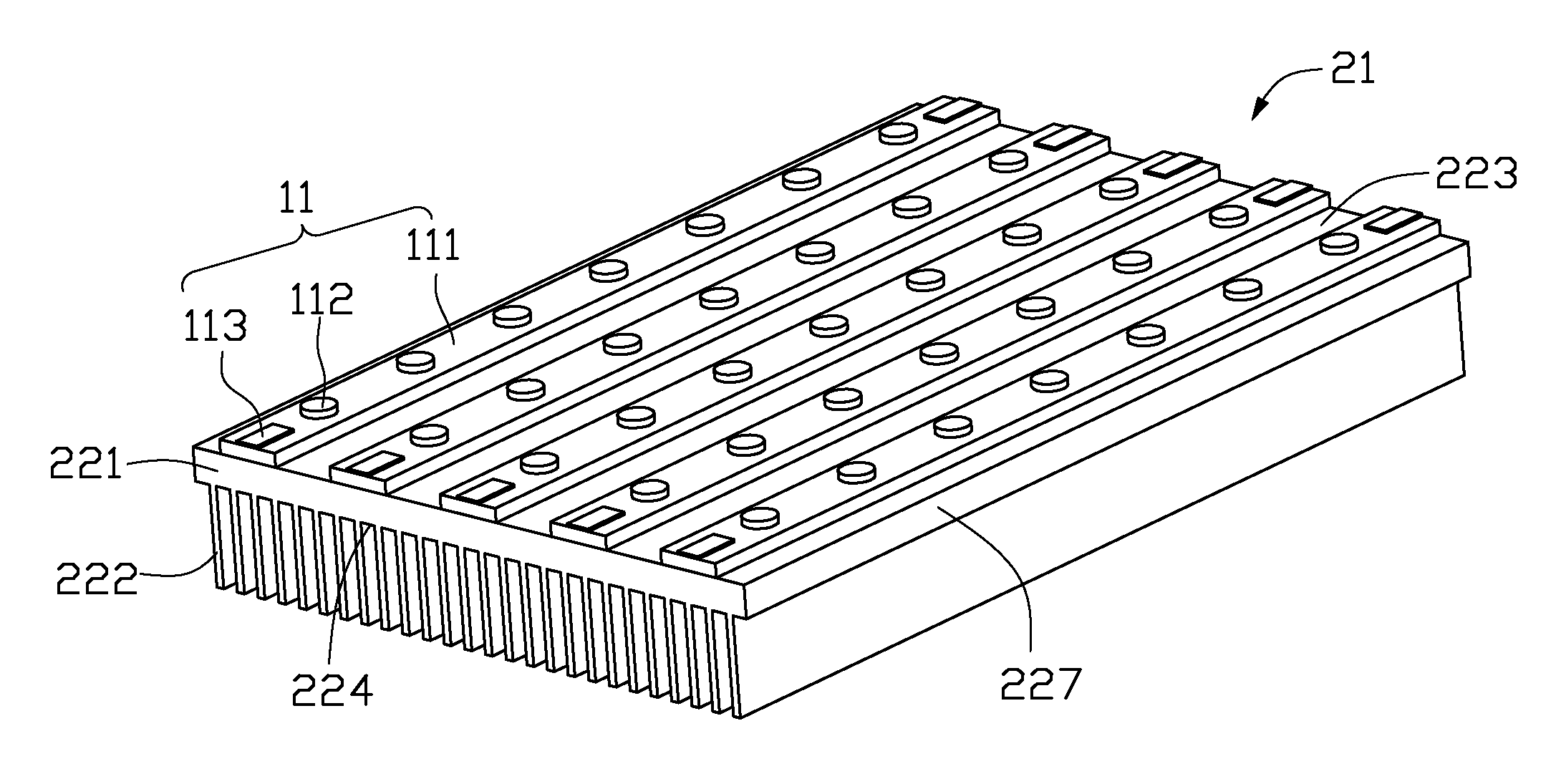
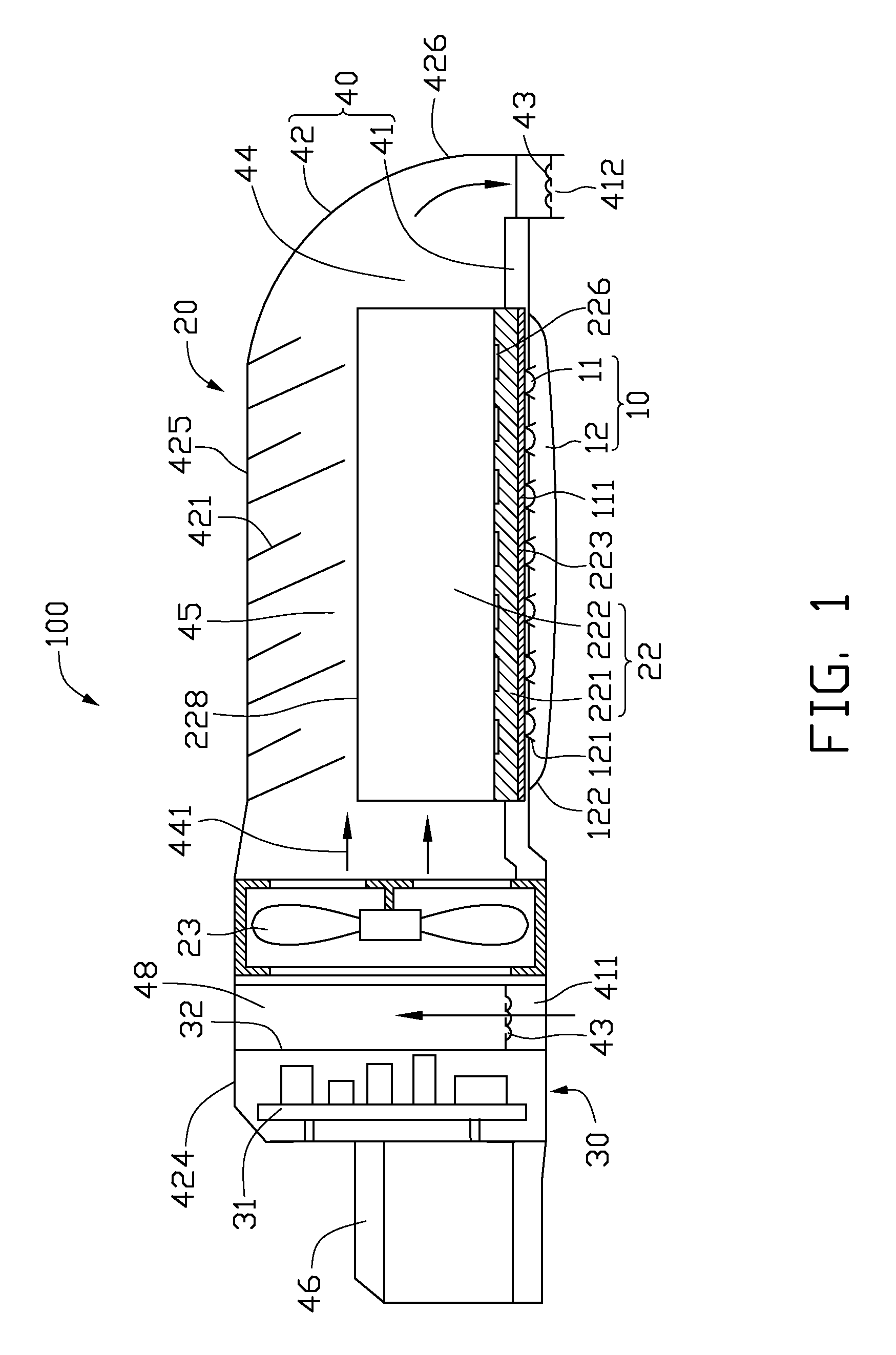
An LED illuminating device includes an optical section (10), an electrical section (30), and a heat dissipation section (20). The heat dissipation section is provided with a heat dissipation device (21) which includes a heat sink (22) and a cooling fan (23) provided over the heat sink. The heat sink includes a solid base (231) and a plurality of fins (222) extending radially and outwardly from the base. A blind hole (225) is axially provided in the base. A plurality of air passage holes (226) are radially defined through the base and communicate the blind hole with an outside of the base. The cooling fan provides an airflow towards the heat sink. A portion of the airflow flows through the blind hole and the air passage holes of the base.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
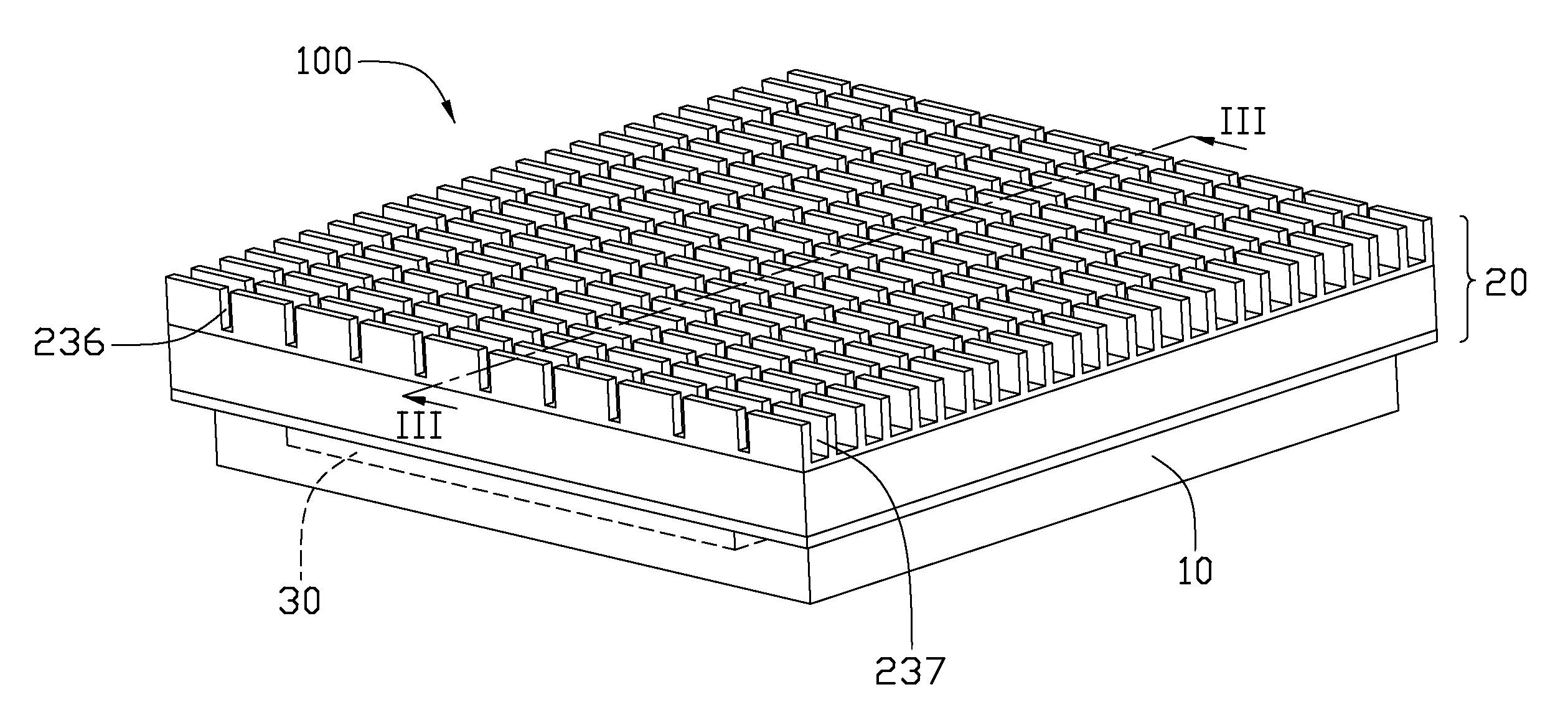
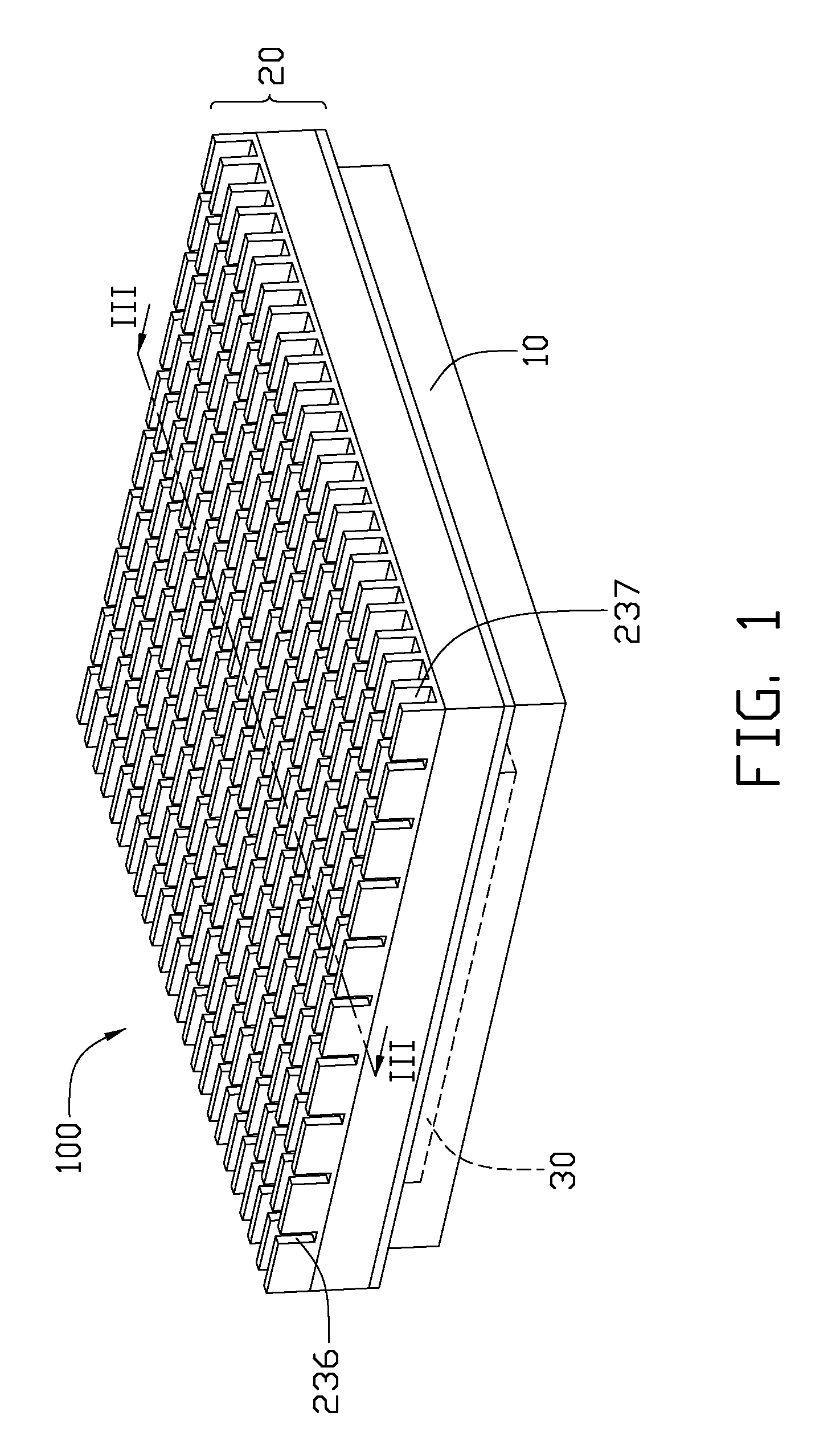
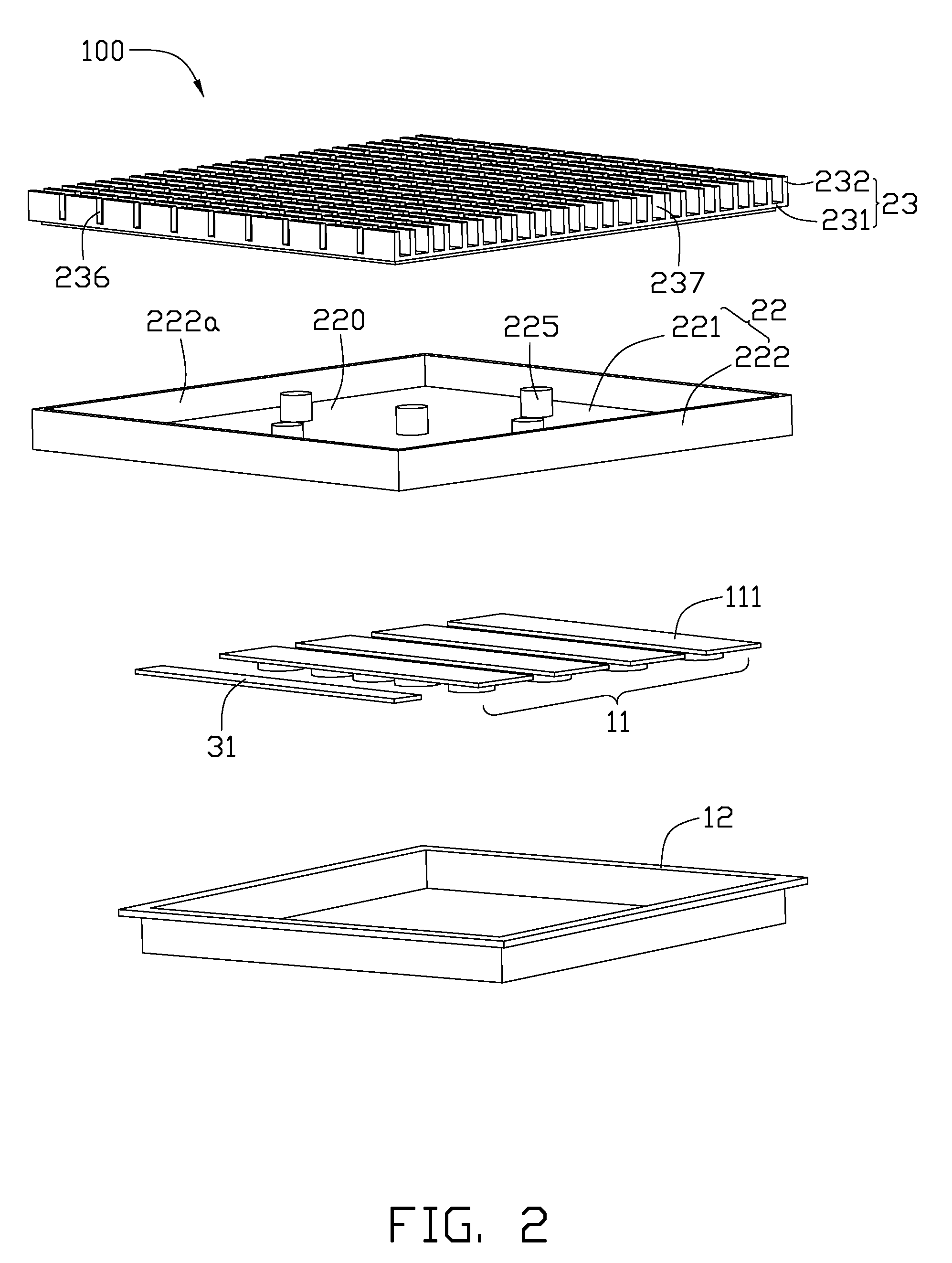
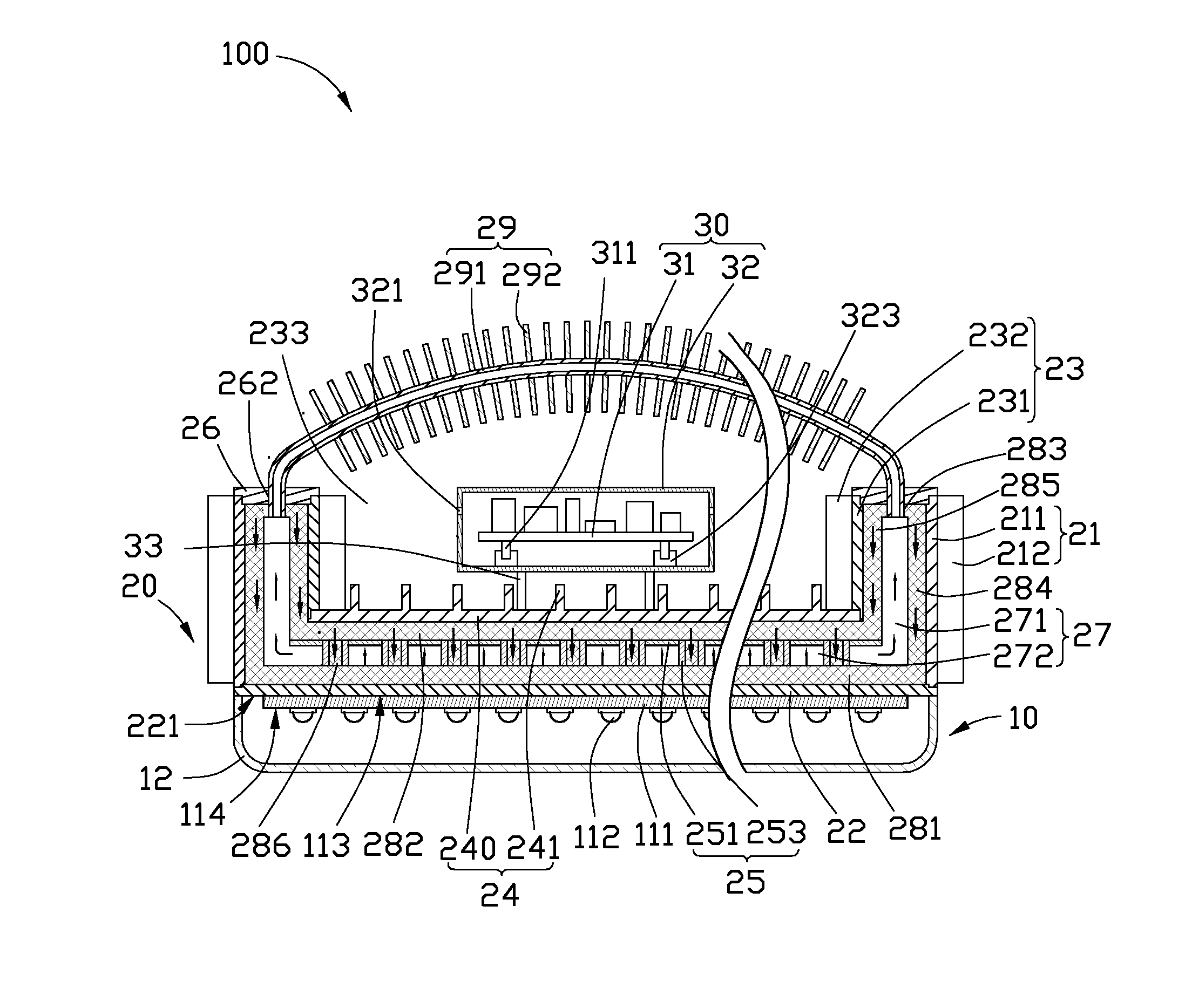
Heat sink
InactiveUS20050199376A1Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyIncrease heat loadIndirect heat exchangersHeat exhanger finsHeat spreaderEngineering
A heat sink including a main body and a plurality of porous structures is disclosed. The main body has a plurality of hollow fins and a base. The fins and the base form a closed room. The porous structures are set on the interior surfaces of different fins, and are connected to the base. Each porous structure defines a vapor chamber.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Hybrid heat sink and hybrid heat sink assembly for power module
ActiveUS20130155616A1Increase cooling areaCompact structureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesComputer moduleEngineering
Disclosed are a hybrid heat sink and a hybrid heat sink assembly for a power module. The hybrid heat sink comprises a base provided with at least one power module on one side thereof, a first heat dissipation unit being a first heat dissipation fin group which is composed of a plurality of heat dissipation fins intervally arranged and is located on the other side of the base, and a second heat dissipation unit comprising a plurality of heat pipes and a second heat dissipation fin group. Each of the heat pipes comprises an evaporating section provided in the base and close to the power module, a condensing section, and an adiabatic section located between the evaporating section and the condensing section and comprises an extension portion and a folding portion, the second heat dissipation fin group is provided on the condensing sections.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
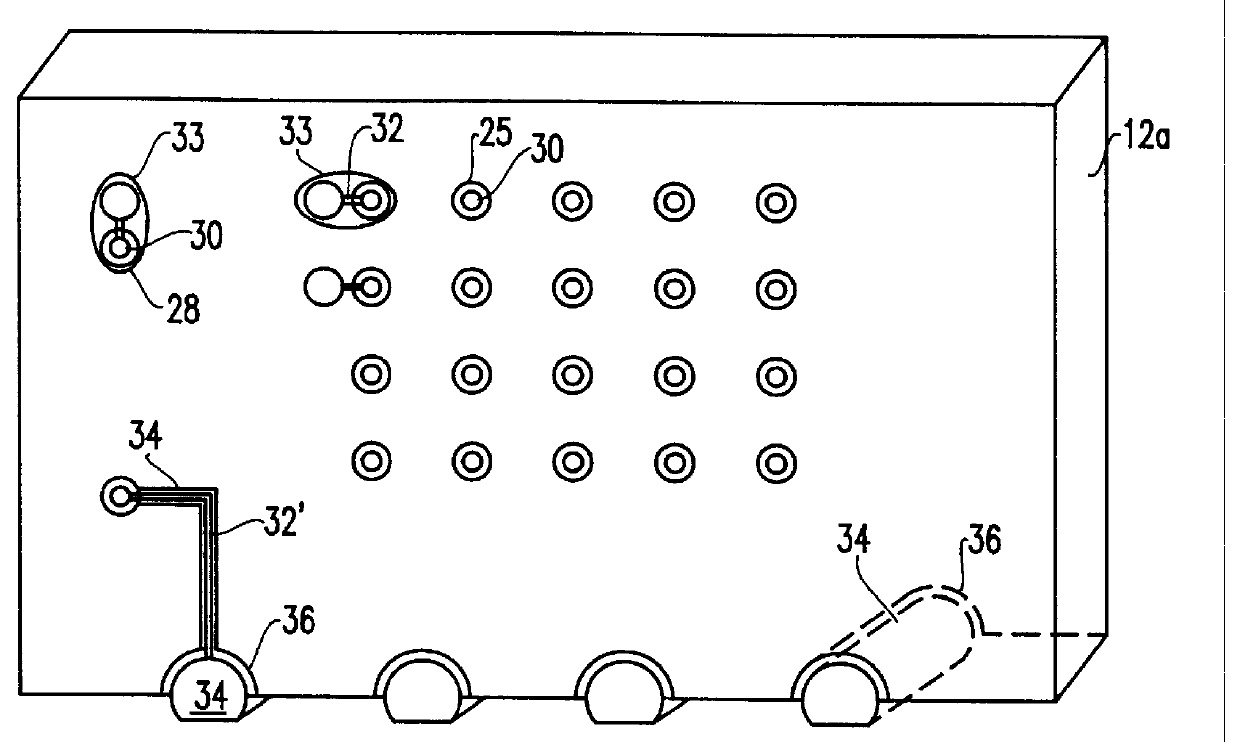
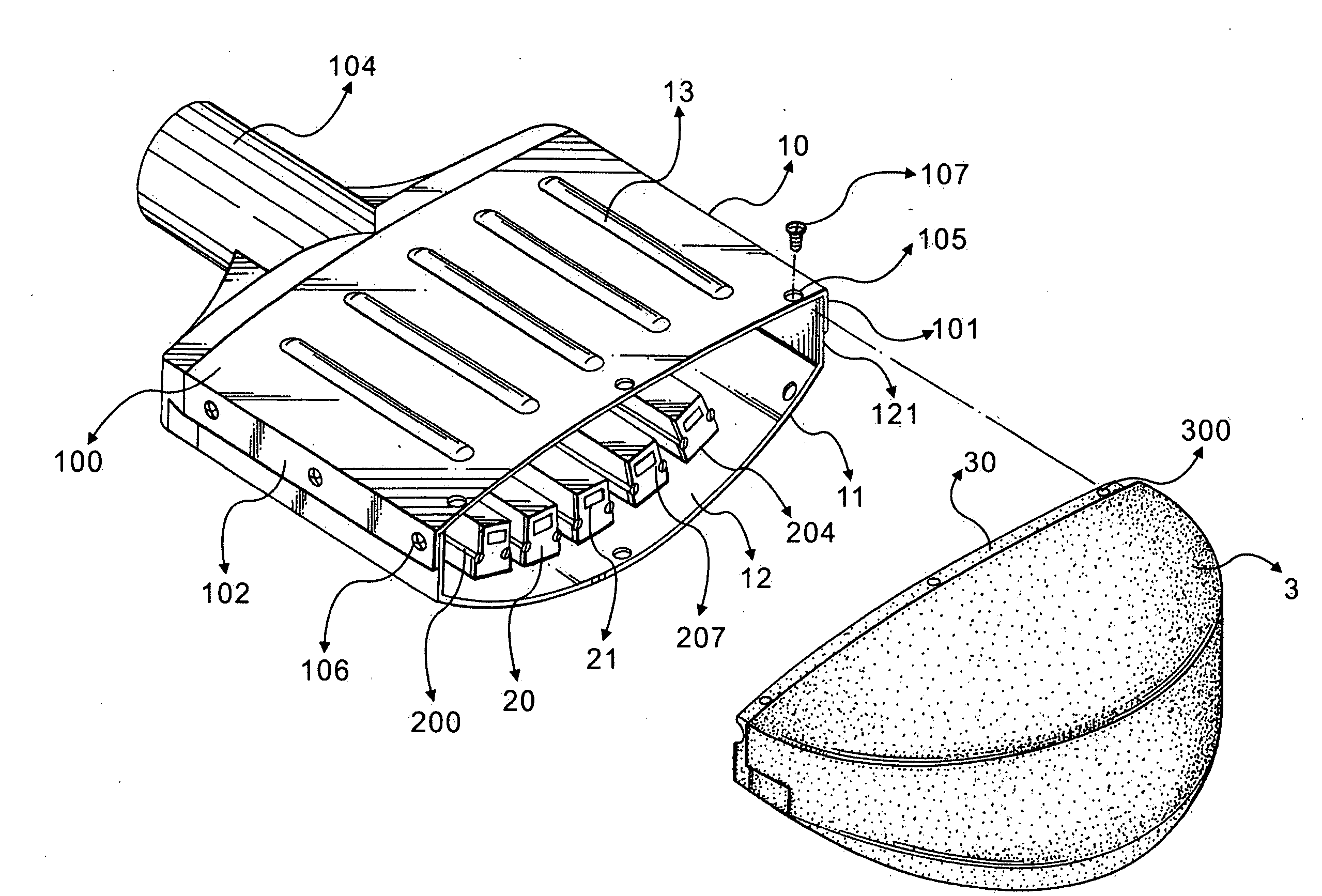
Light source module with high heat-dissipation efficiency
InactiveUS7572033B2Increase the areaSolve the low heat dissipation efficiencyPoint-like light sourceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityHeat conducting
An exemplary light source module includes a printed circuit board (PCB), a heat-dissipating assembly, and a number of light emitting elements. The PCB includes a first surface, an opposite second surface, and a number of through holes. The heat-dissipating assembly is located adjacent to the second surface and includes a base, a number of heat-conducting elements, and a number of heat dissipation fins. The base includes a third surface defining a number of cavities therein and an opposite fourth surface. The heat dissipation fins extend from the fourth surface. Each of the heat-conducting elements is inlaid in a corresponding cavity. Each of the light emitting elements is placed in a corresponding through hole and thermally contacts a corresponding heat-conducting element. Each light emitting element electrically connects with the PCB and defines a respective light emitting surface located outside the corresponding through hole.
Owner:FOXSEMICON INTEGRATED TECH INC
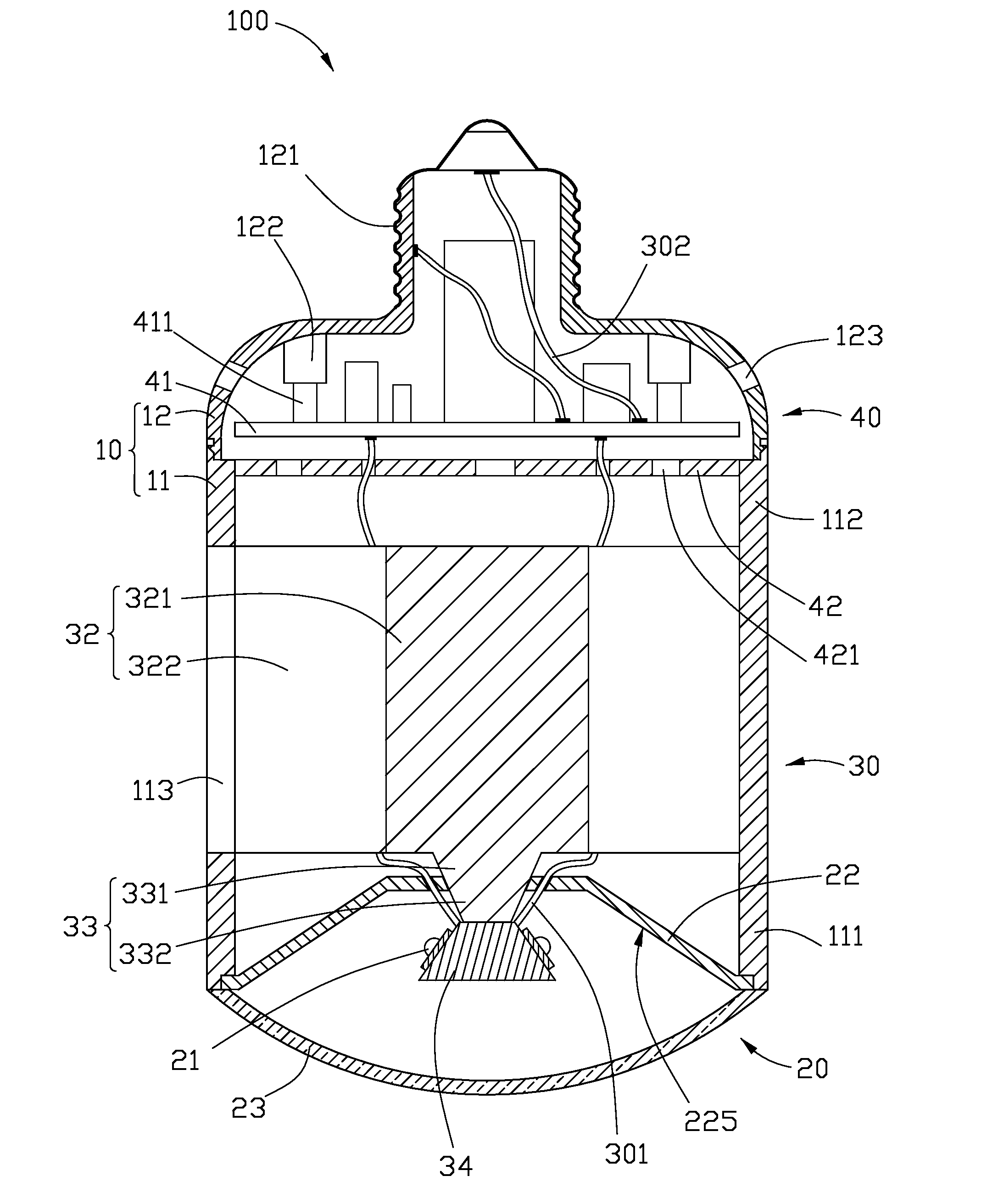
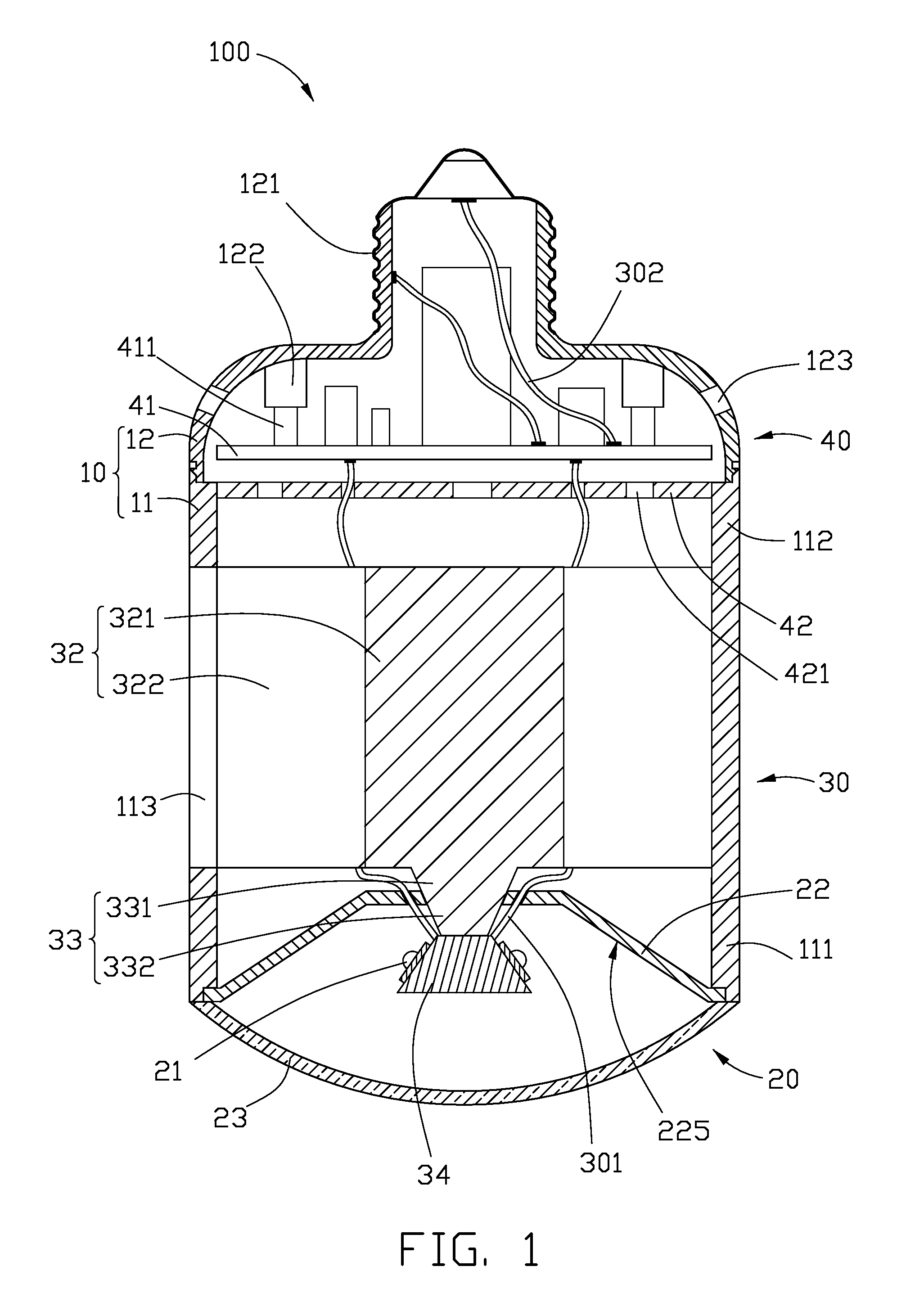
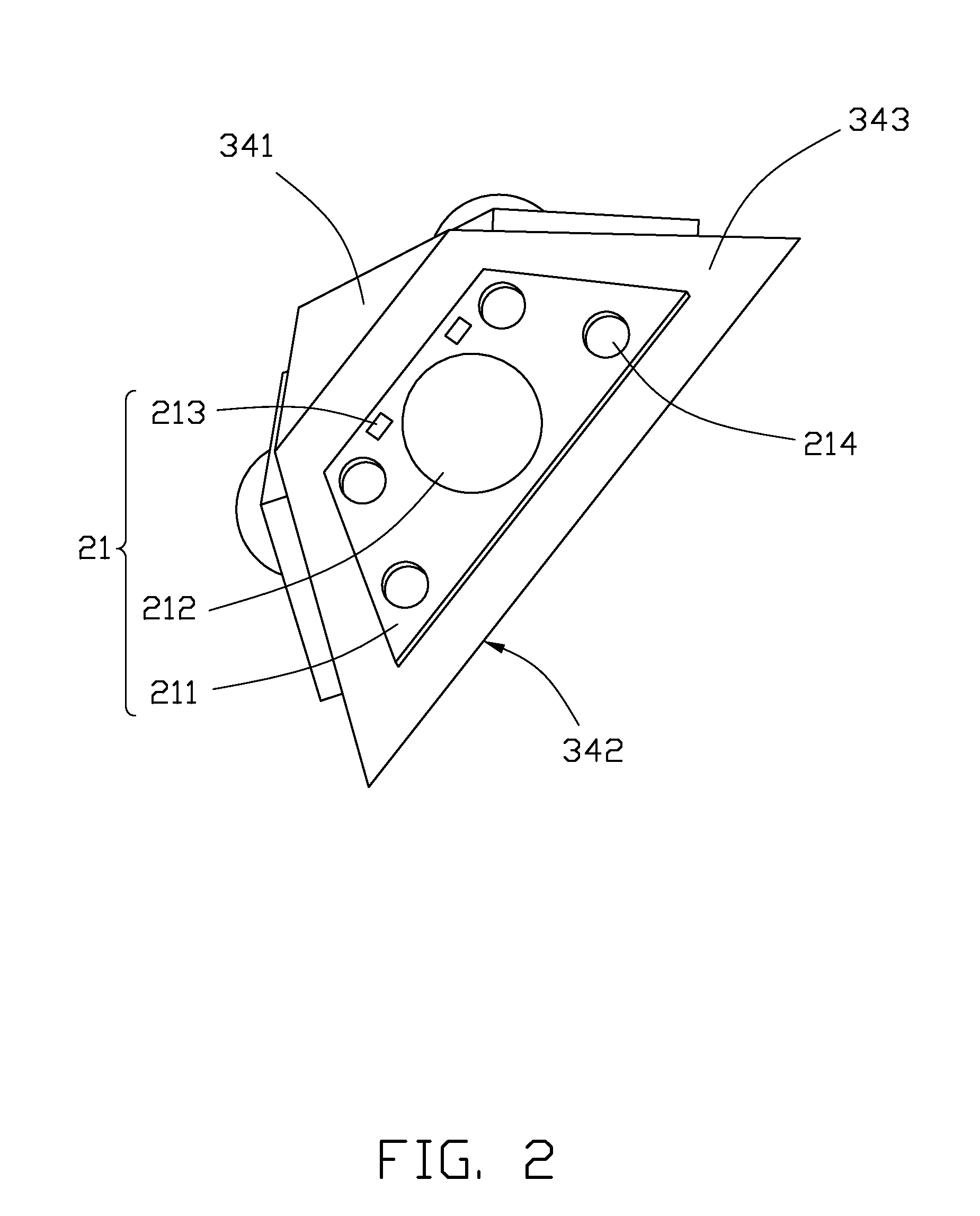
Light emitting diode bulbs with high heat dissipating efficiency
InactiveUS20130162139A1Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyLow reliabilityPoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsEngineeringLED lamp
An exemplary LED bulb includes a top optical section, a middle heat dissipation section, and a bottom electrical section. The optical section includes a light source and a light guider. The light source further includes a substrate and at least one LED arranged on the substrate. The heat dissipation section includes a sleeve at a rear of the optical section and a chamber. The sleeve has a tube portion and a sealed end with a heat absorbing surface thermally contacting the substrate. A porous wick structure is arranged on the outer sidewall of the tube portion and contains working fluid therein. The chamber has an annular configuration defined between an inner side surface of an LED bulb shell and an outer side surface of the sleeve. The electrical section includes a threaded cap arranged at a bottom portion of the LED bulb, and a circuit board received in the sleeve.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
LED streetlight with heat-dissipating structure
InactiveUS20100135008A1Heat dissipation fastSolve the low heat dissipation efficiencyMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceInterior spaceEngineering
An LED streetlight with heat-dissipating structure. The LED streetlight includes a light housing composed of an upper cover and a lower cover connected therewith to define an opening, a common rail assembly fixedly attached to an inner face of a bottom of the light housing, and a gas-permeable shade. The common rail assembly includes multiple common rail base seats connected with multiple LED light bulbs and multiple circuit boards. The gas-permeable shade is fitted with the end of the light housing to seal the opening thereof. The heat generated by the LED light bulbs are conducted by the common rail base seats and dissipated to internal space and outer side of the light housing. The heat on outer side of the light housing is carried away by external cold air. The heat in the internal space of the light housing is quickly dissipated through the gas-permeable shade to outer side of the light housing by way of thermal convection.
Owner:UNITE STAND ELECTRONICS
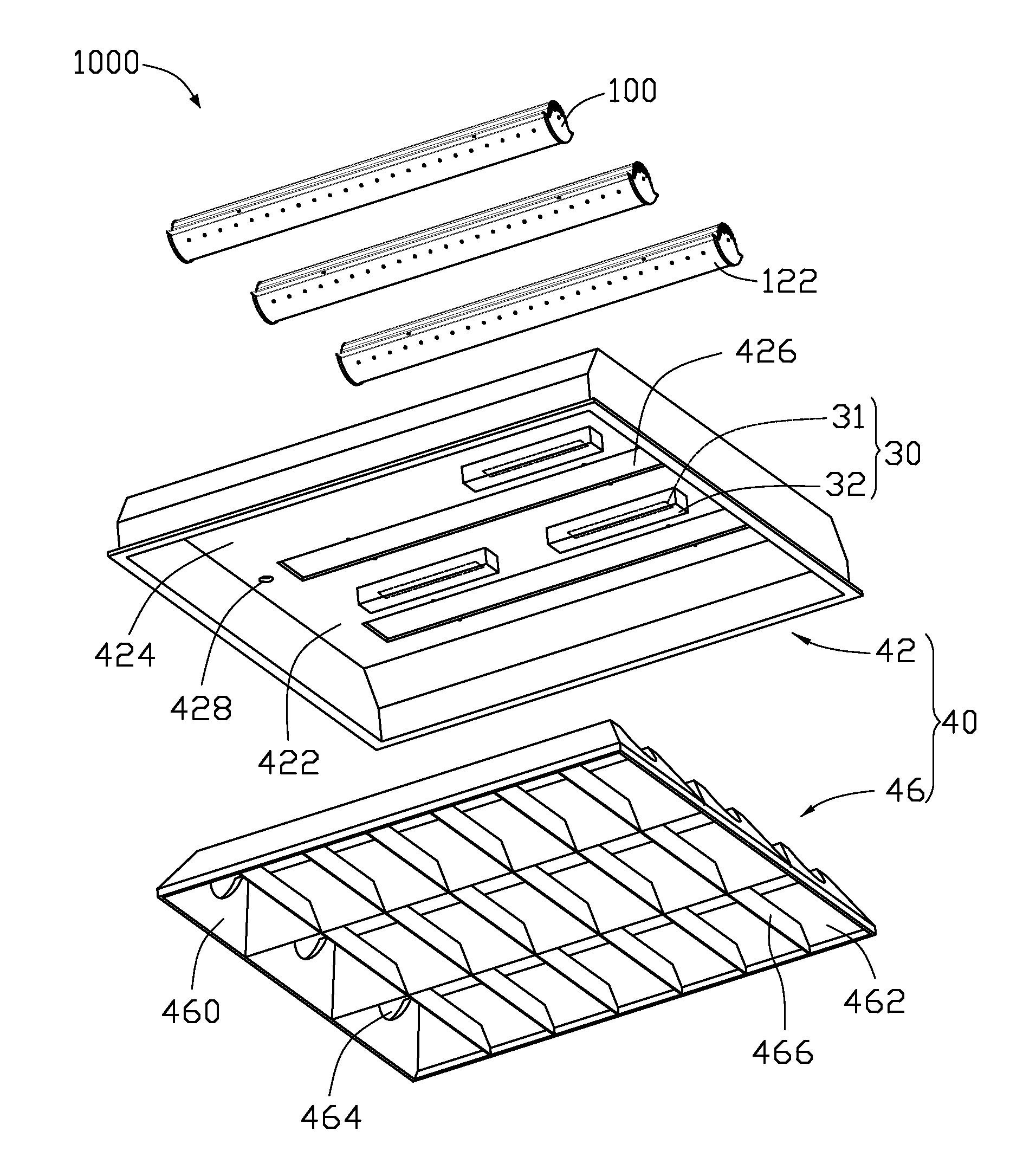
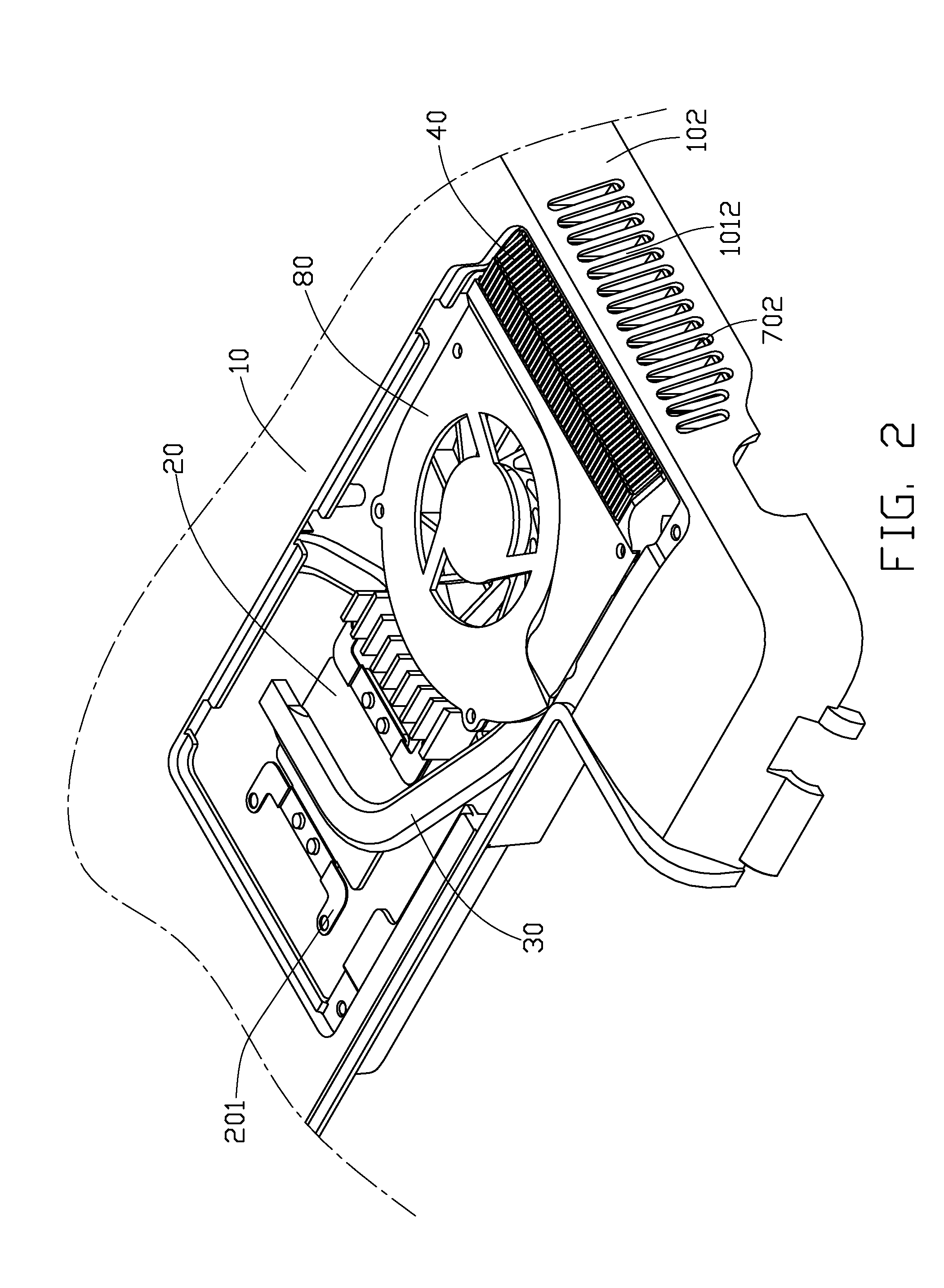
Thermal module and electronic assembly incorporating the same
InactiveUS20080151500A1Solve the low heat dissipation efficiencyEasy transferAir heatersIndirect heat exchangersEngineeringHeat sink
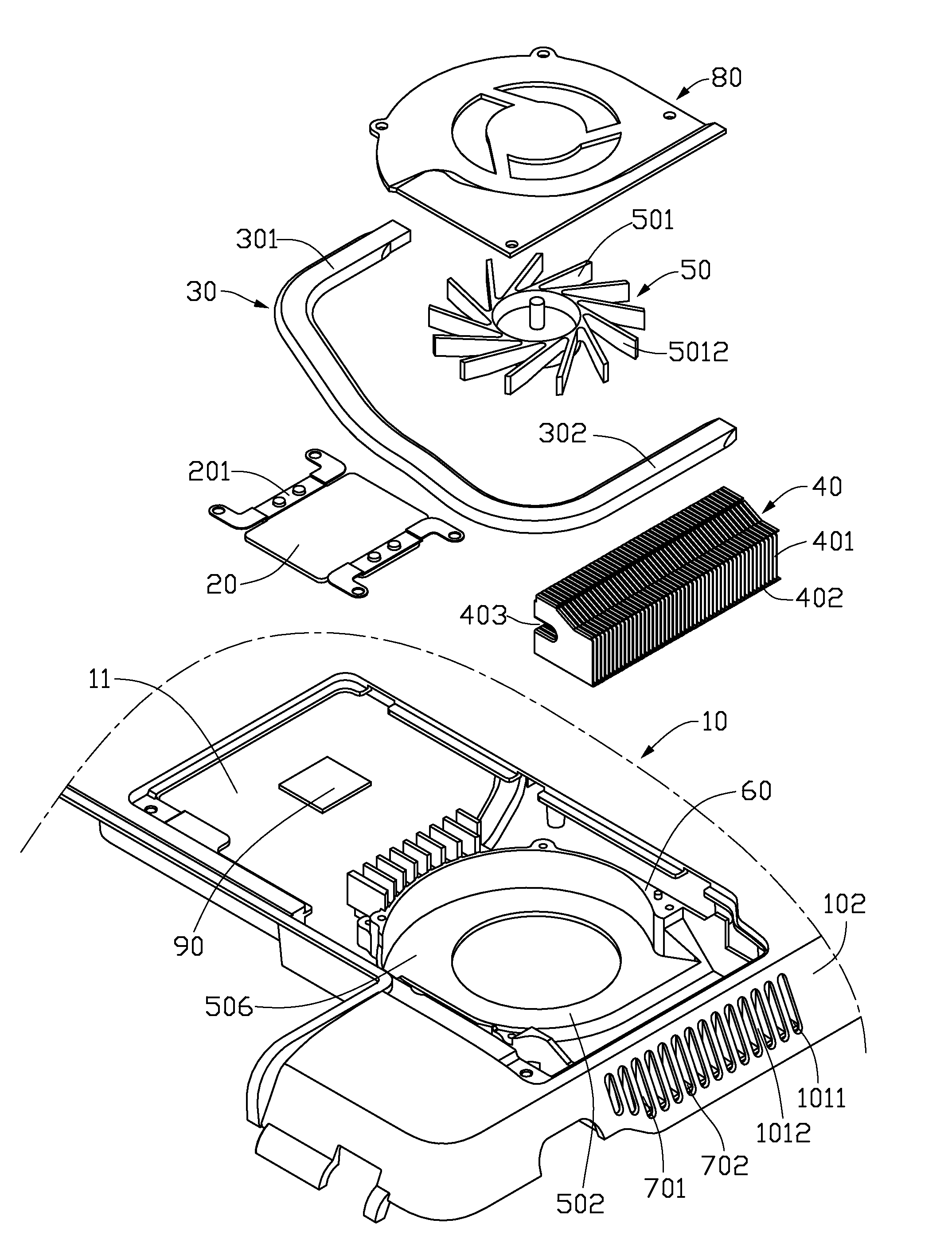
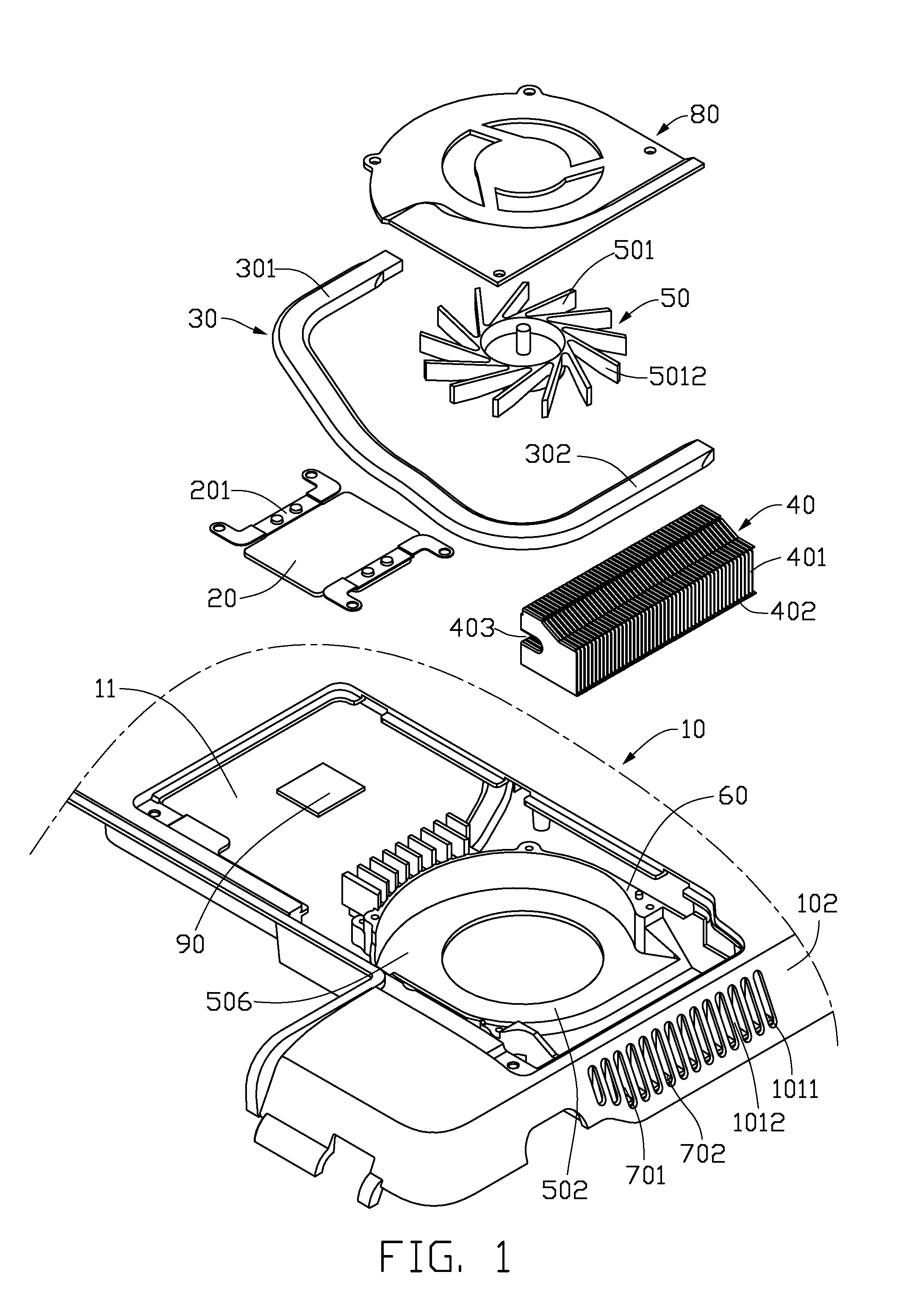
An electronic assembly includes a casing (10) of an electronic product, and a thermal module disposed in the casing. The casing has a sidewall (102) defining a plurality of slots (1011) therein. The thermal module includes a centrifugal blower (50), a fin assembly (40) and a plurality of sub-fins (701). The centrifugal blower defines an air outlet (502) therein. The fin assembly is disposed at the air outlet of the centrifugal blower and includes a plurality of fins (401) and has a plurality of air passages (402) formed between adjacent fins. The sub-fins are located between the fin assembly and the sidewall of the casing, and forming a plurality of air channels (702) therebetween. The air channels of the sub-fins communicate the air passages of the fin assembly with the slots of the sidewall of the casing.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com