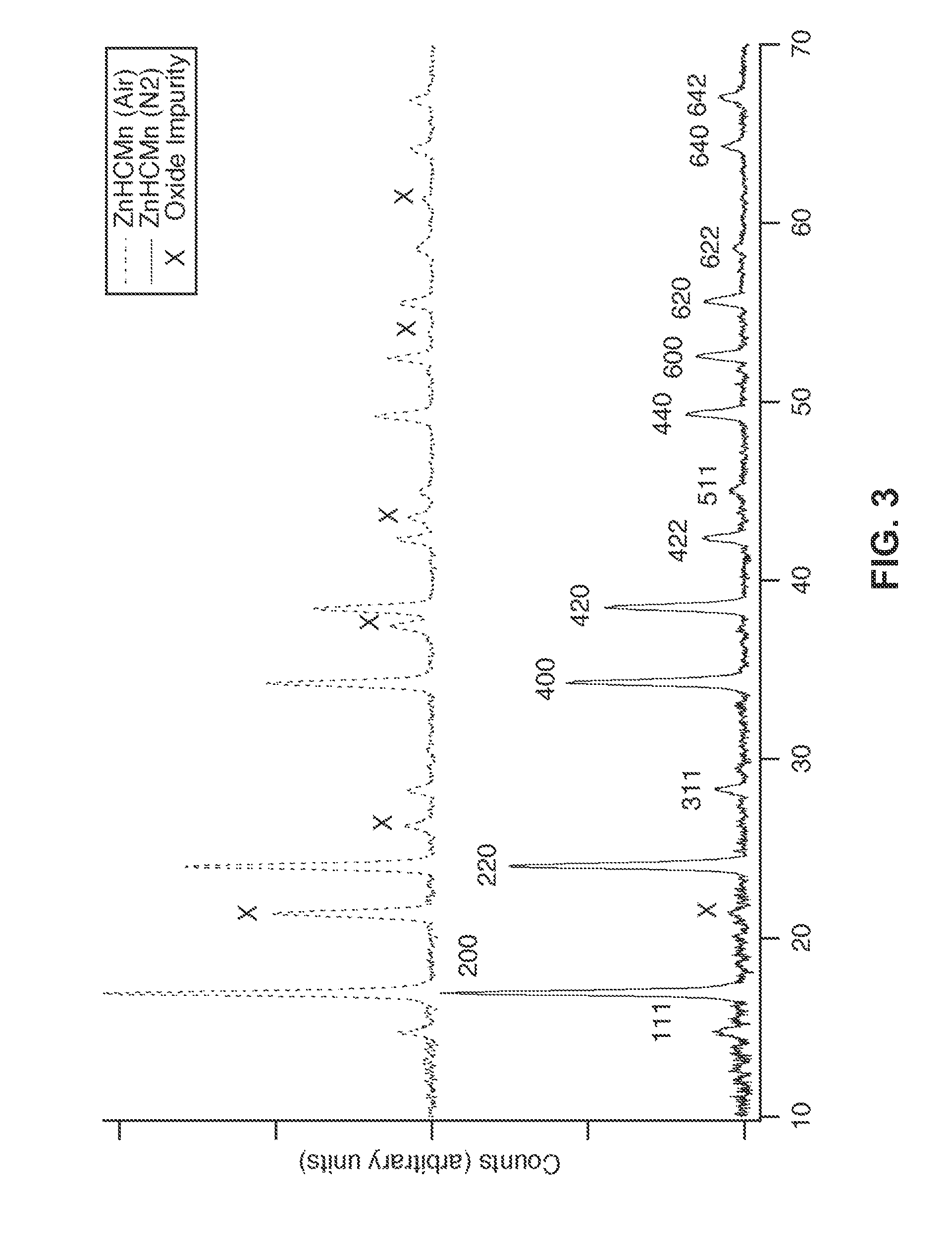
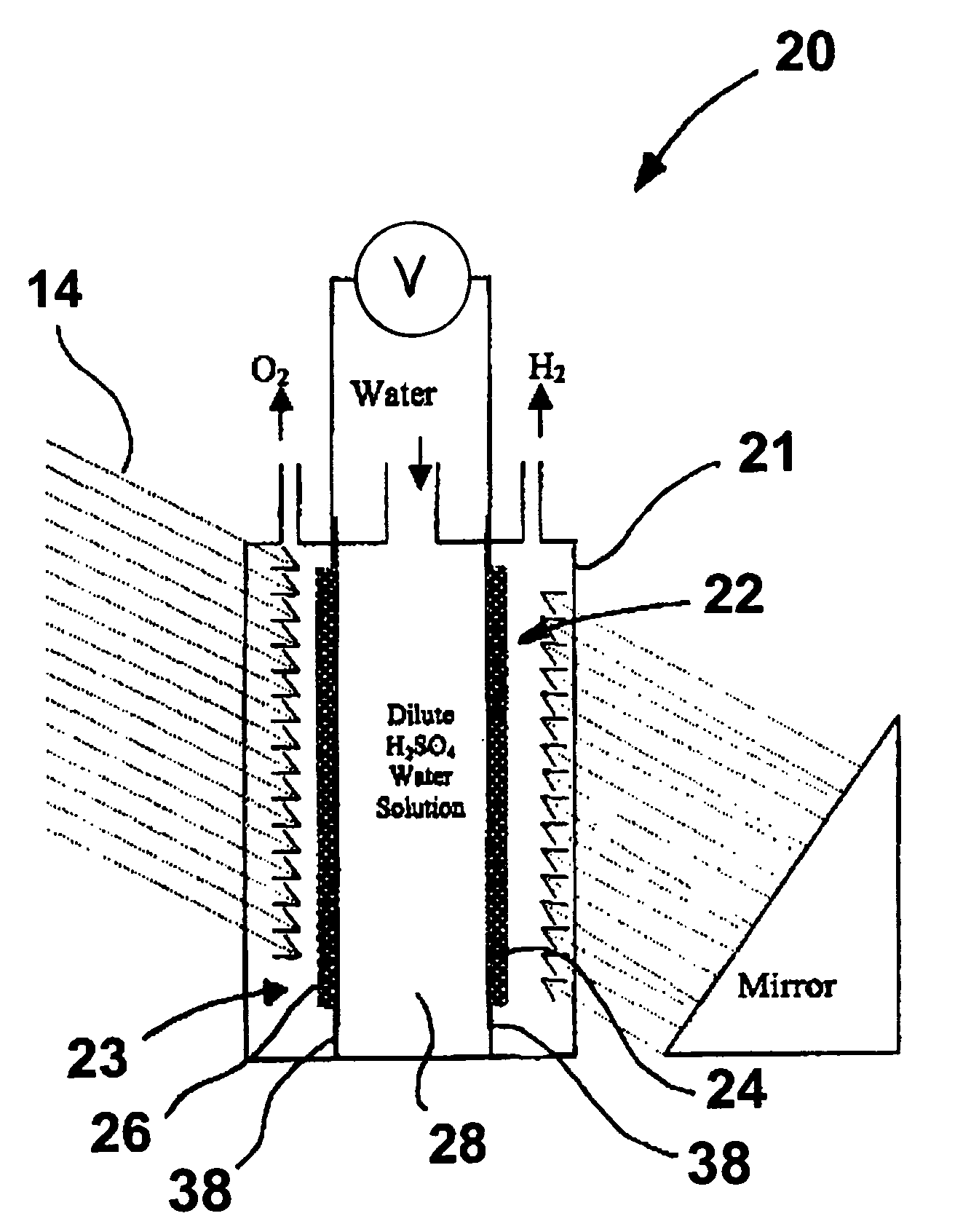
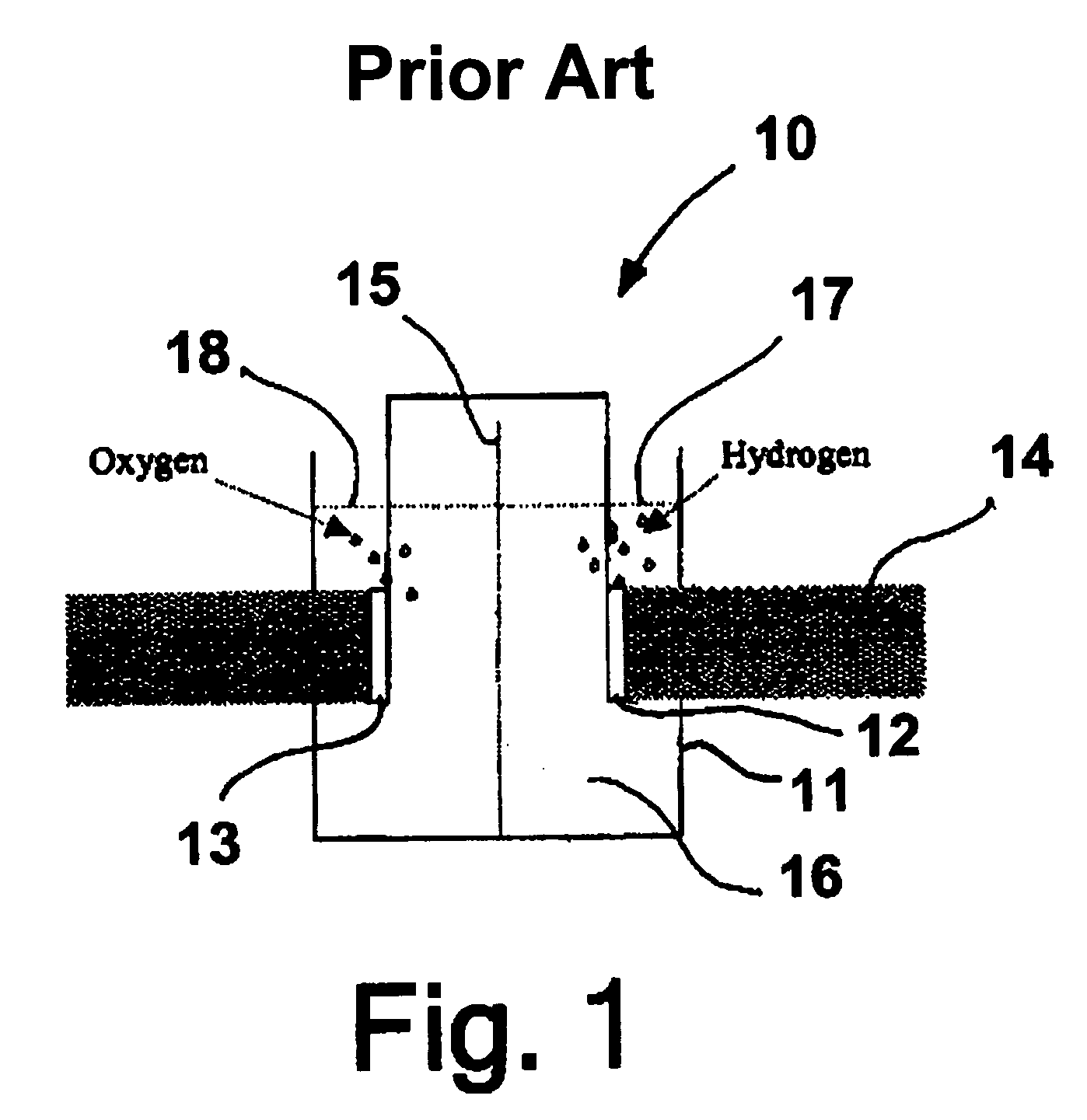
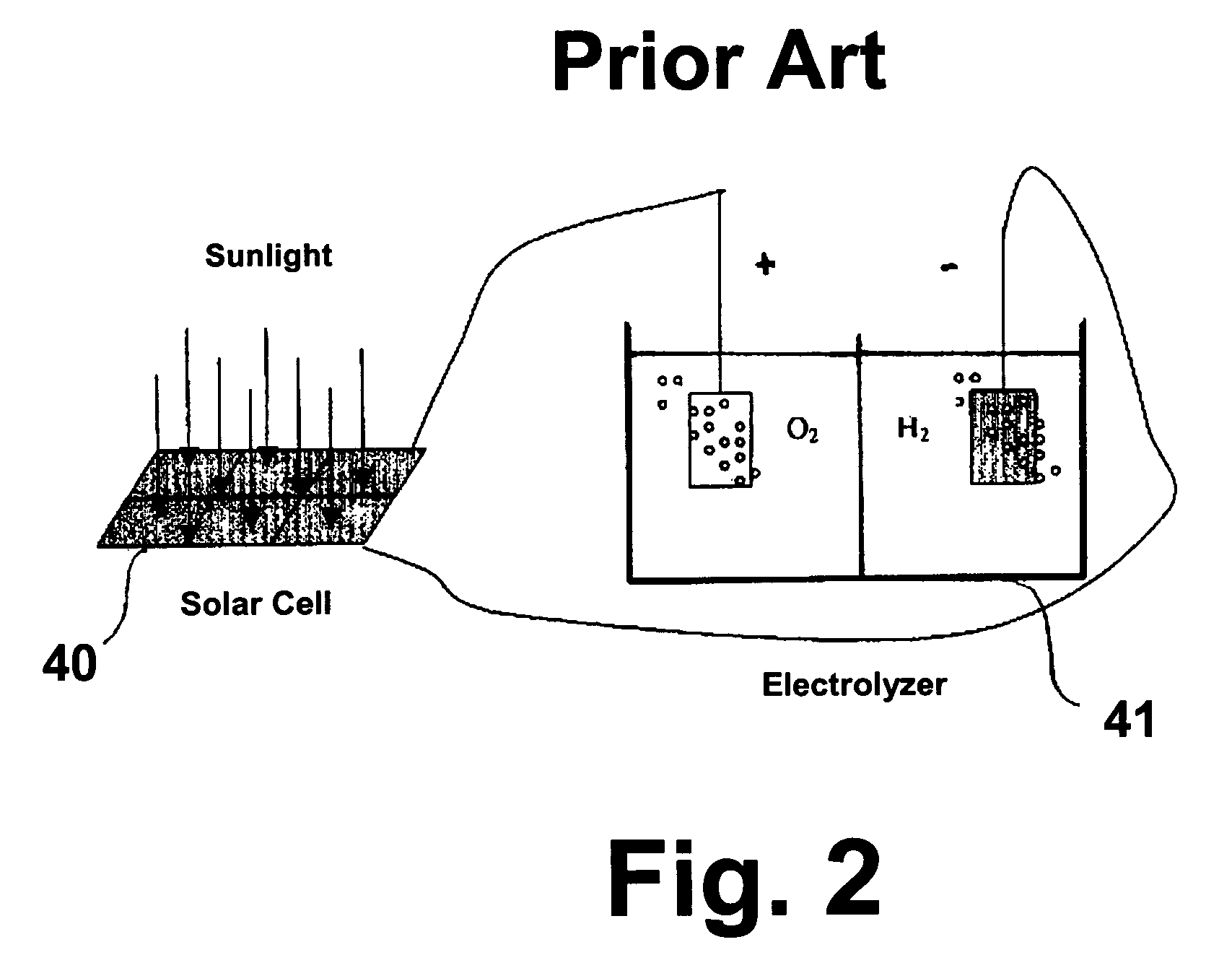
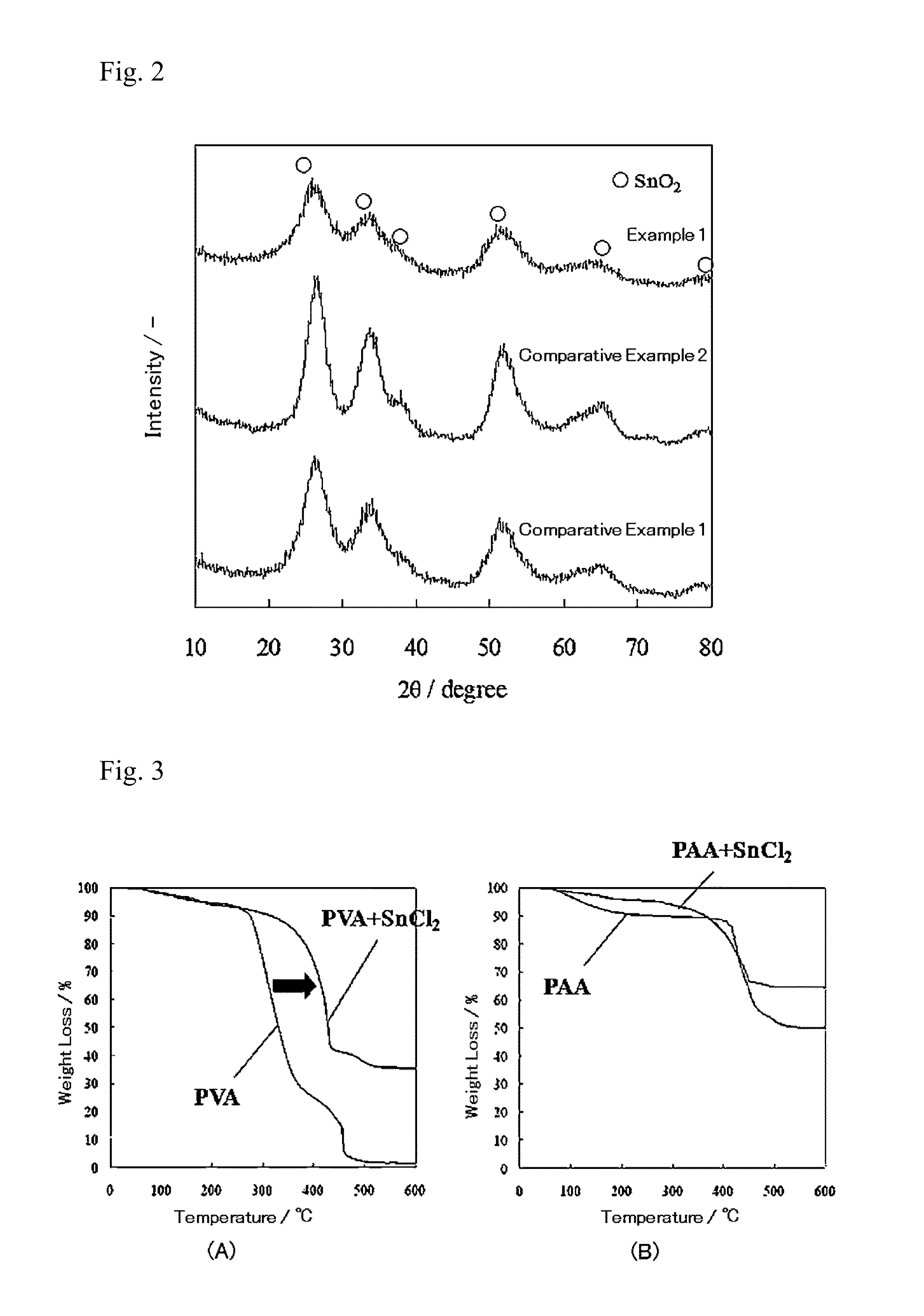
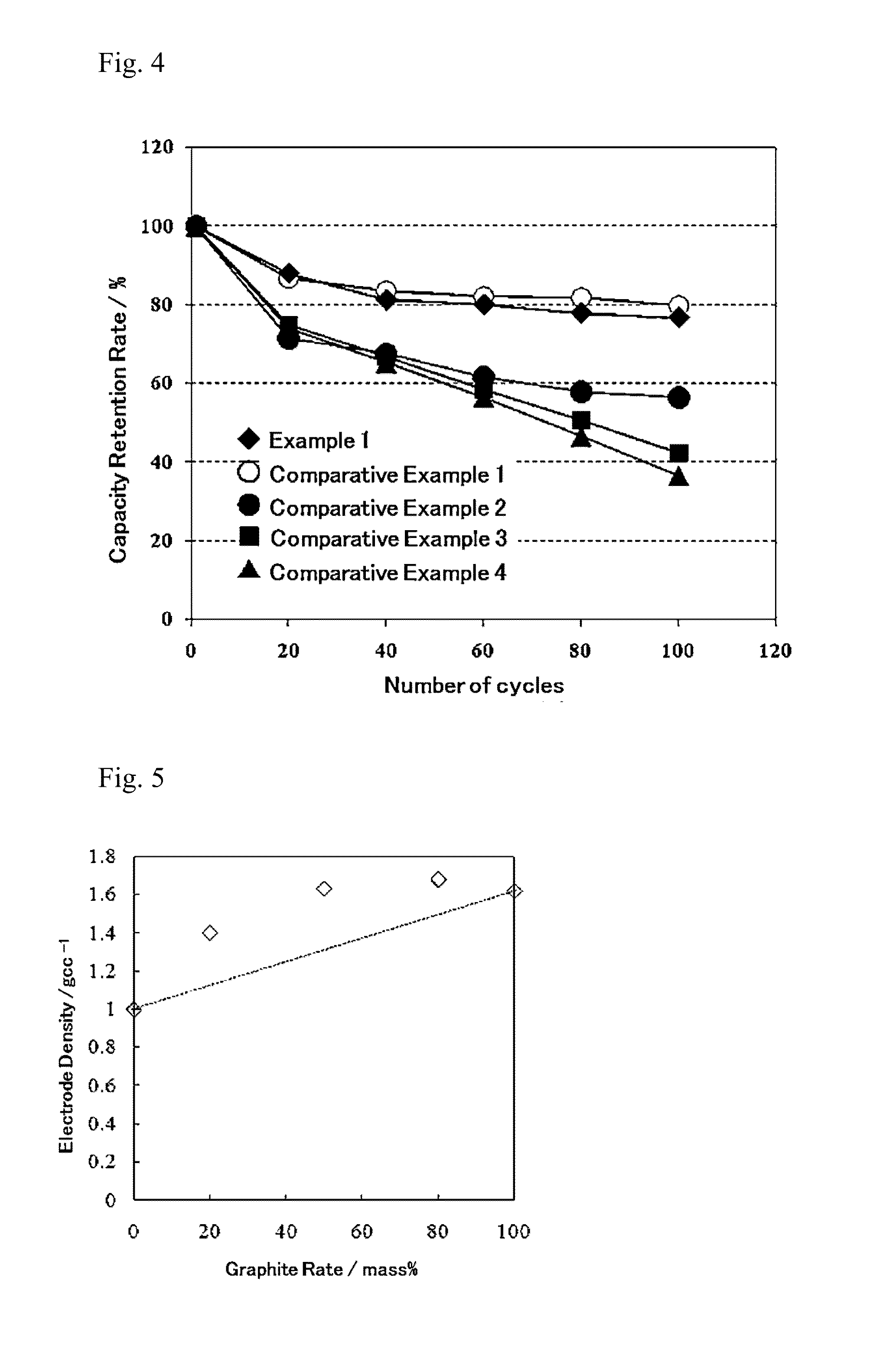
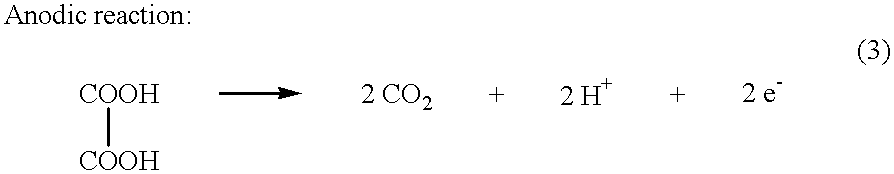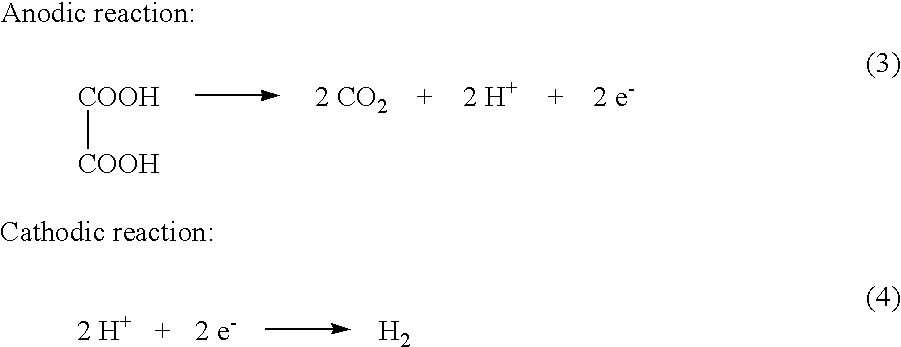Patents
Literature
128 results about "Electrochemical decomposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
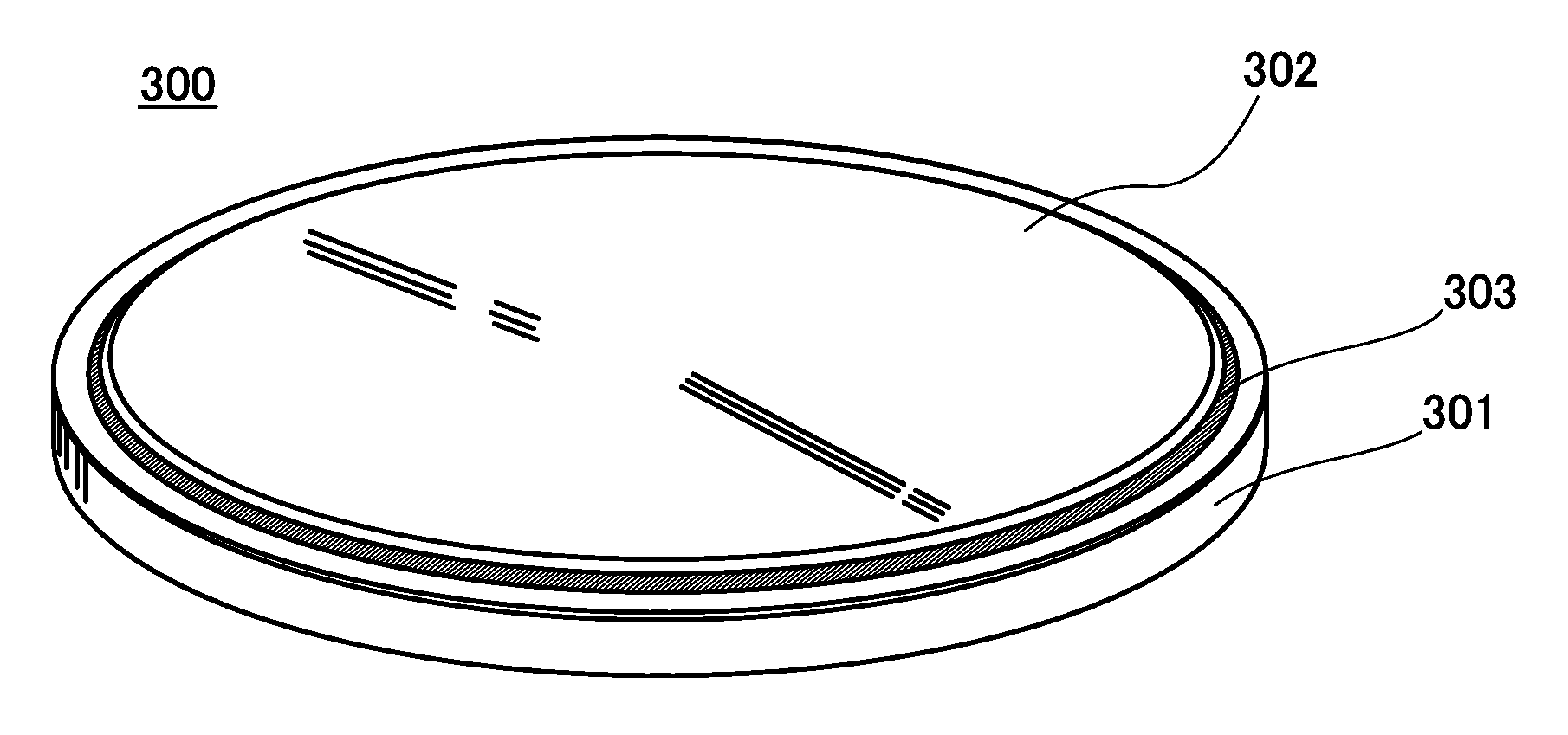
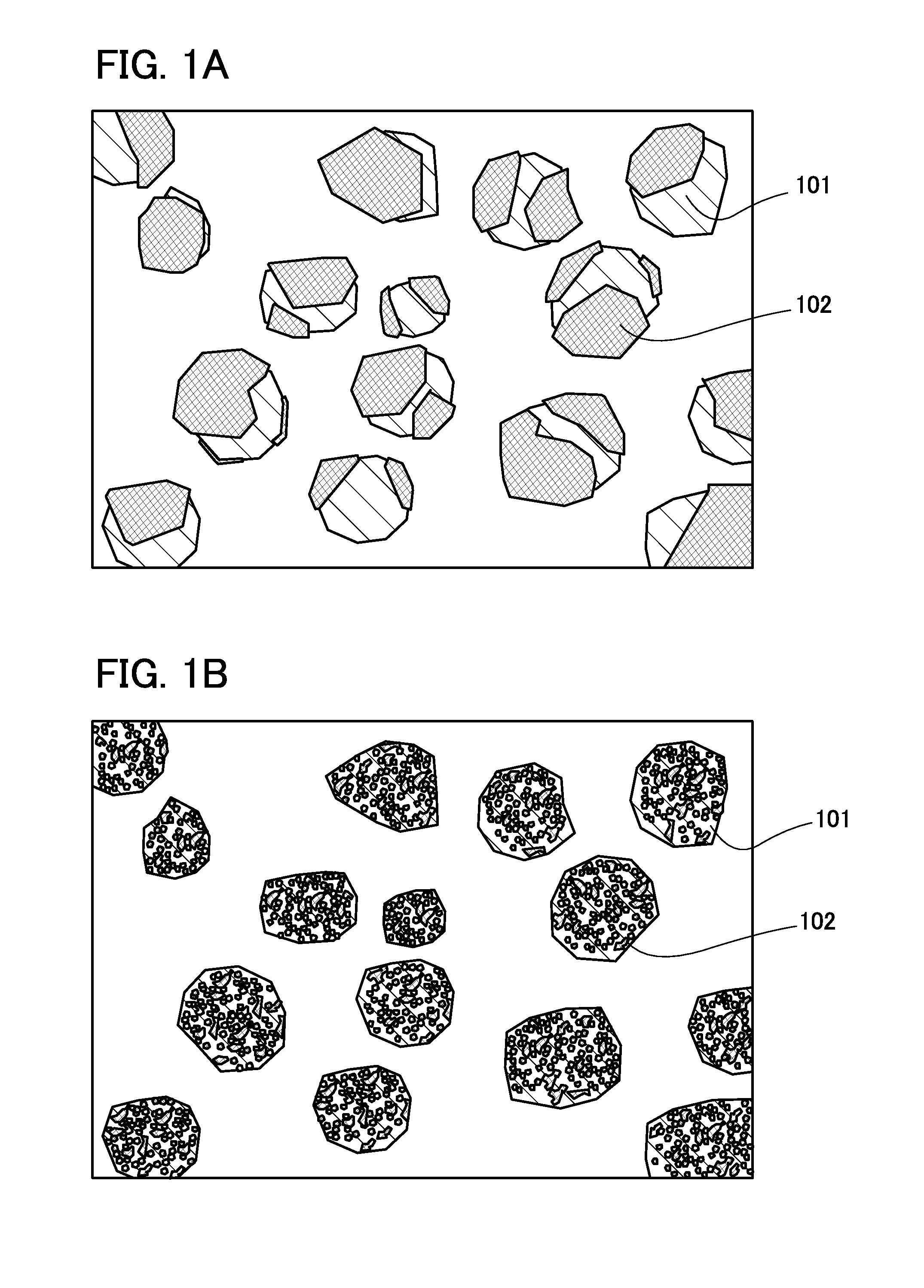
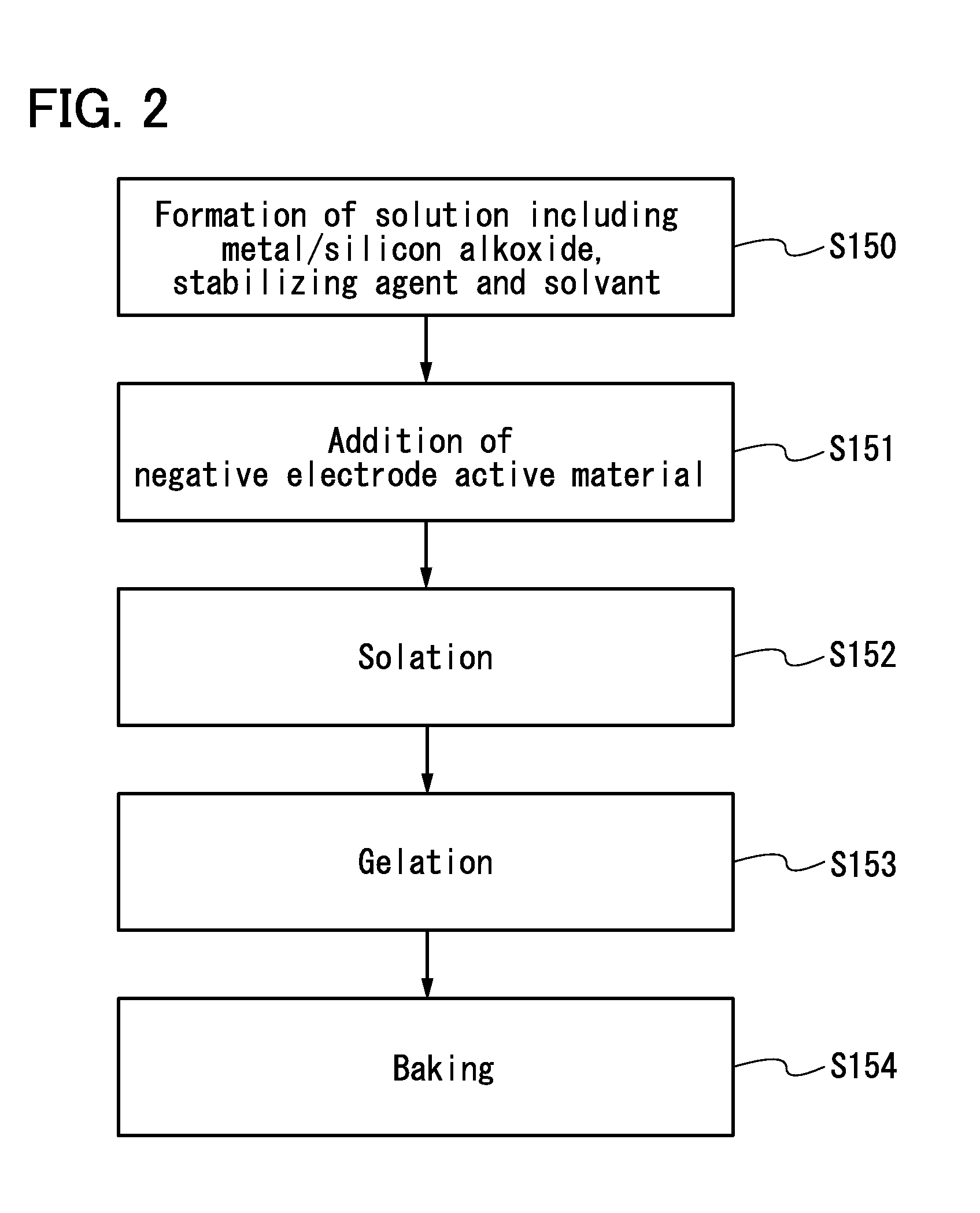
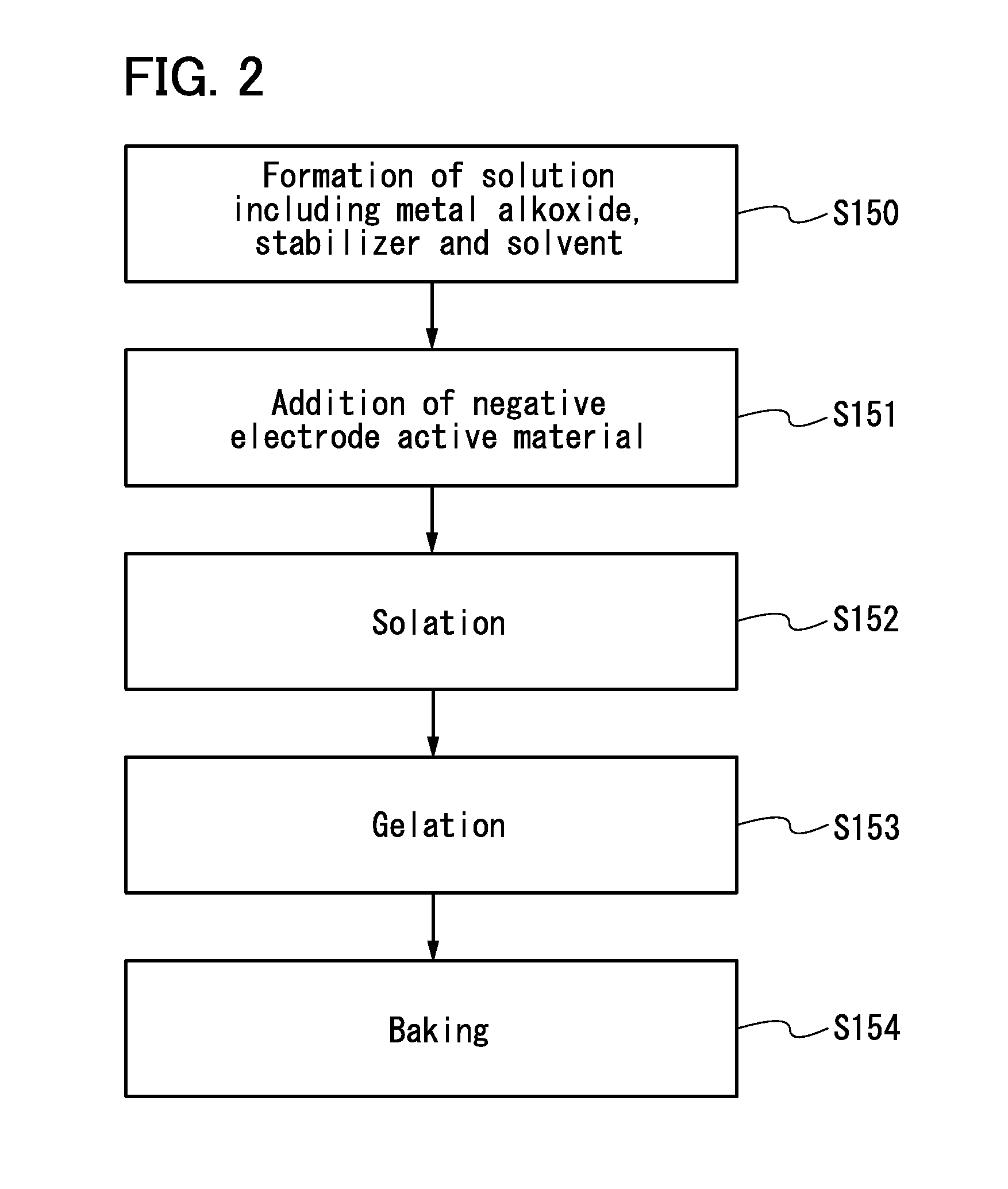
Negative electrode for power storage device, method for forming the same, and power storage device
ActiveUS20130266858A1Improve cycle performanceDecrease in capacity in chargeElectrode thermal treatmentGraphiteElectrical batteryEngineering
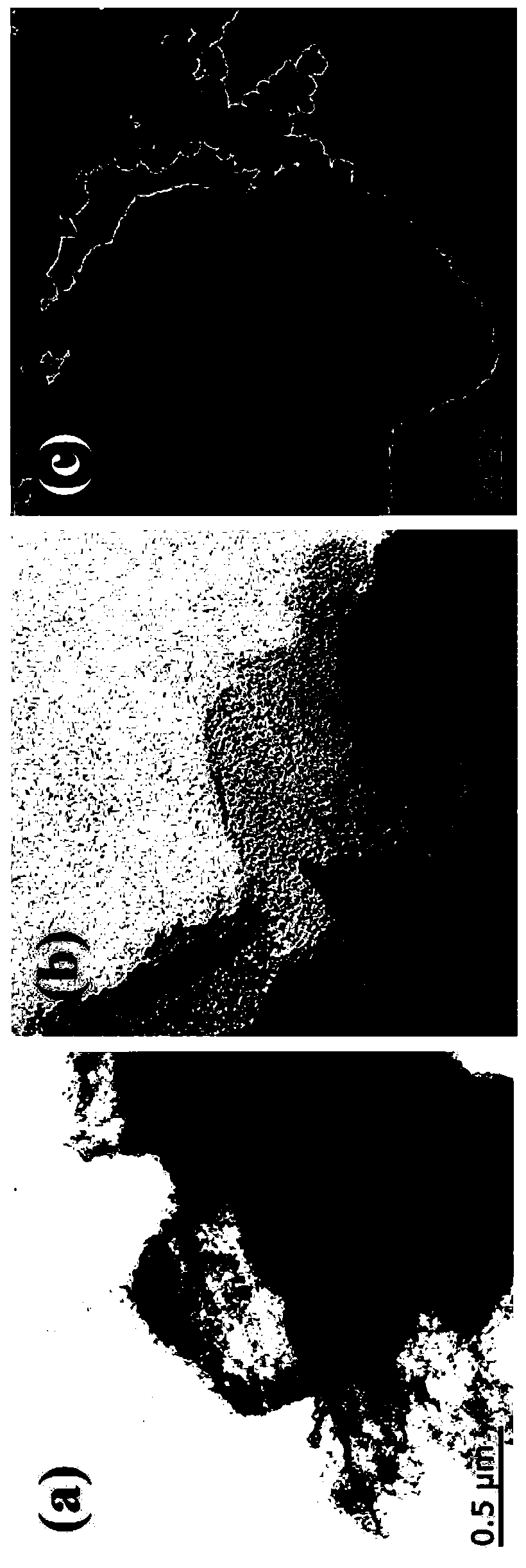
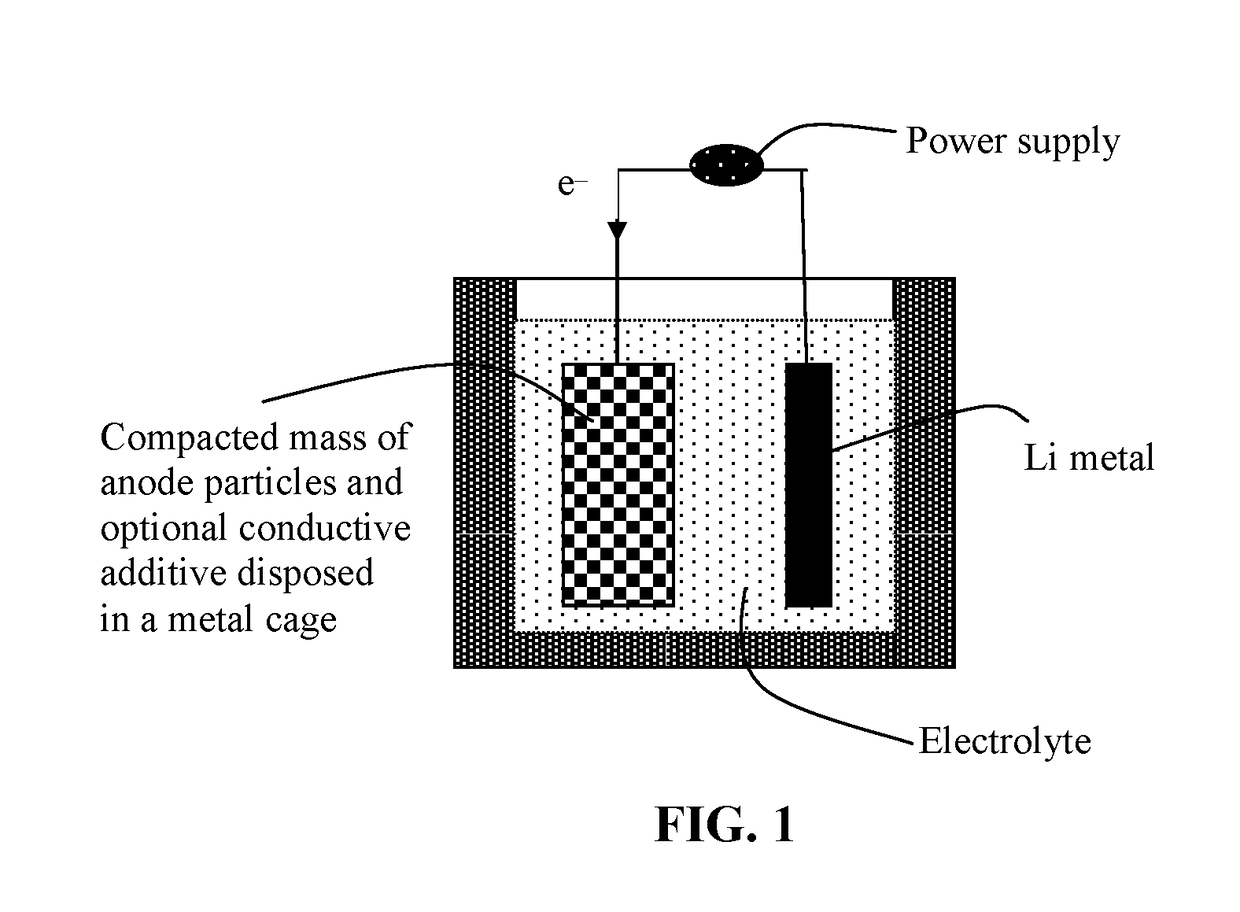
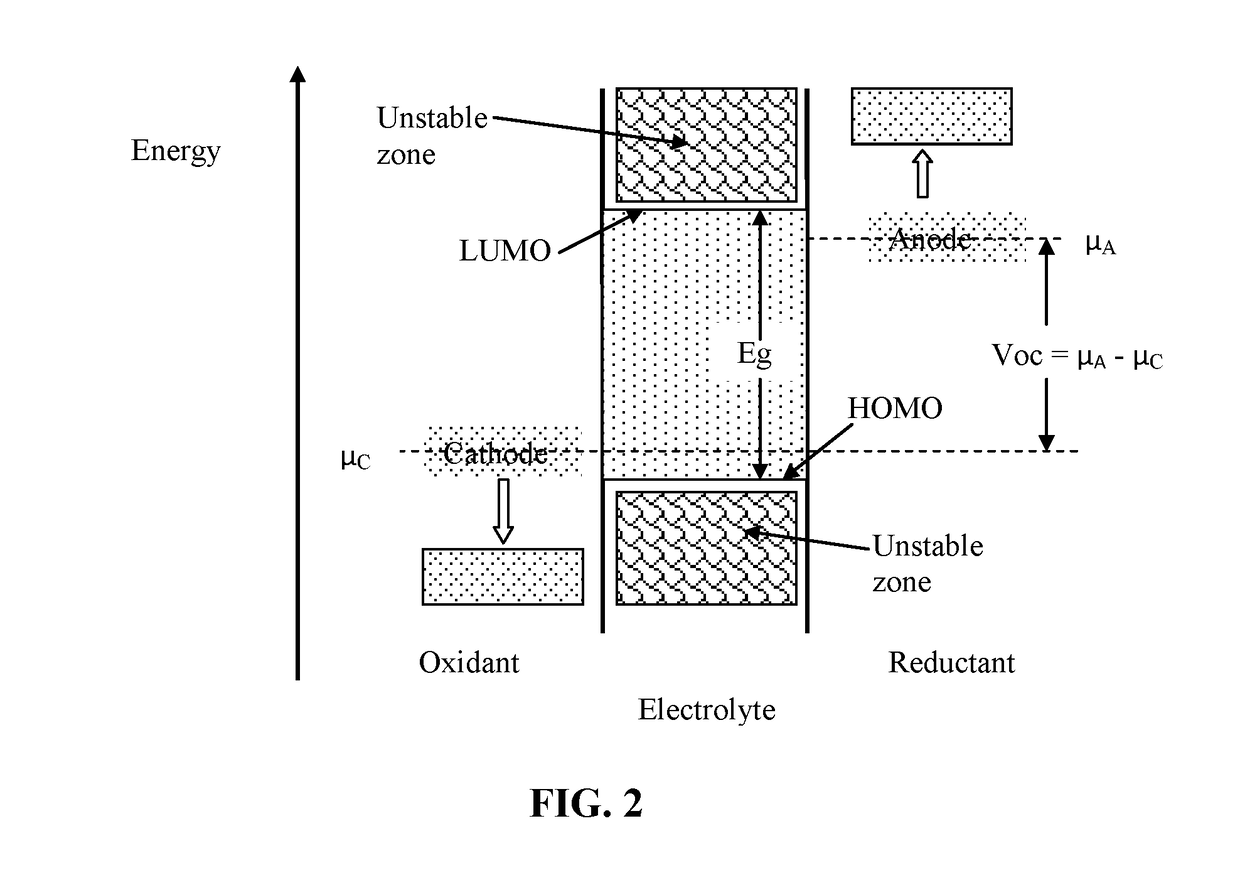
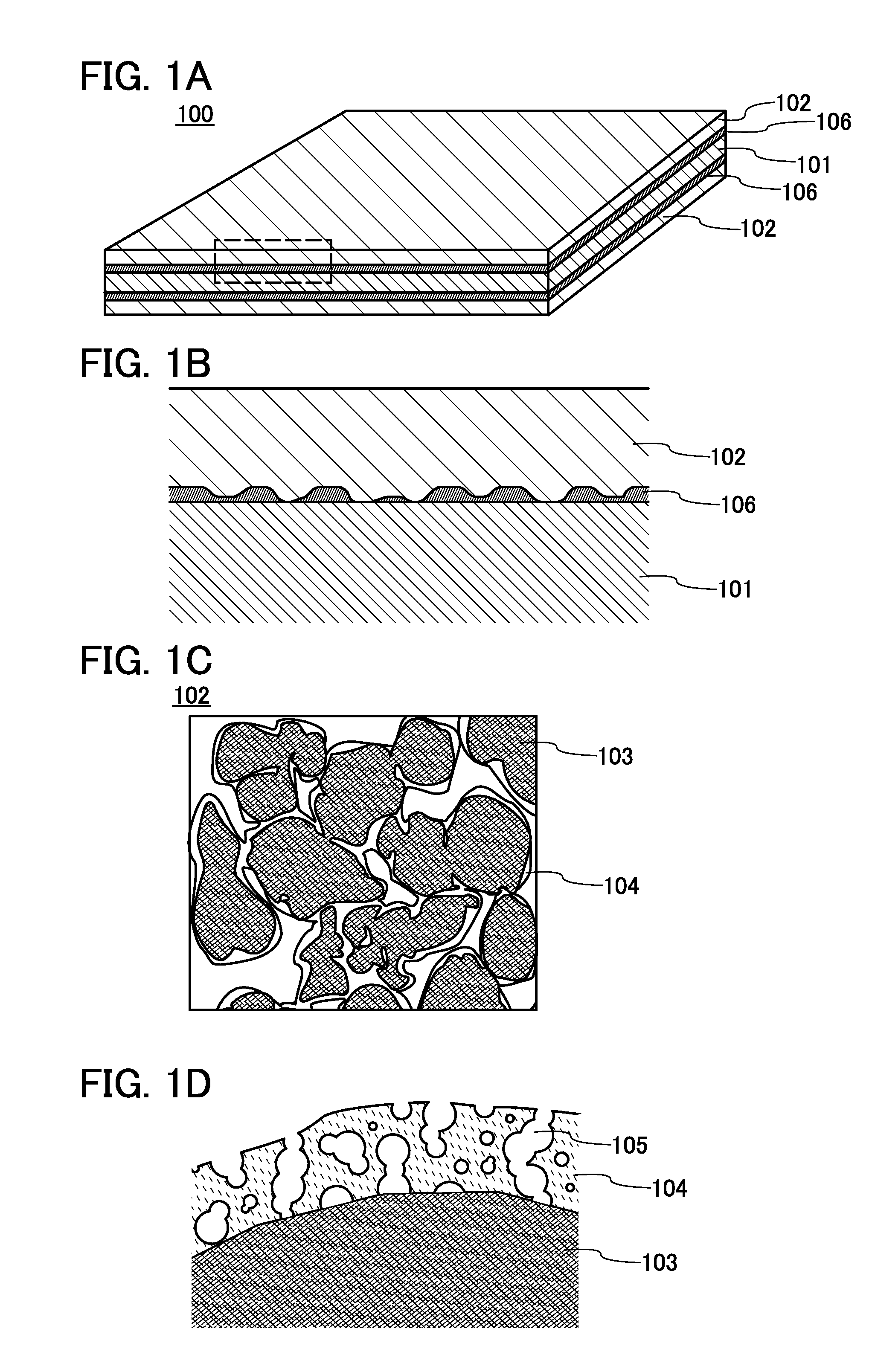
An object is to suppress electrochemical decomposition of an electrolyte solution and the like at a negative electrode in a lithium ion battery or a lithium ion capacitor; thus, irreversible capacity is reduced, cycle performance is improved, or operating temperature range is extended. A negative electrode for a power storage device including a negative electrode current collector, a negative electrode active material layer which is over the negative electrode current collector and includes a plurality of particles of a negative electrode active material, and a film covering part of the negative electrode active material. The film has an insulating property and lithium ion conductivity.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
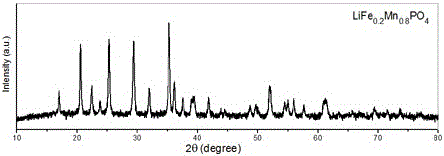
Water system high-voltage mixed ion secondary battery based on zinc-lithium ferric manganese phosphate
InactiveCN105826520AIncrease capacityExcellent rate performanceCell electrodesSecondary cellsElectrolytic agentElectrical battery
The invention relates to a water system high-voltage mixed ion secondary battery. A positive pole material of the battery is a high-voltage battery positive pole material, namely zinc-lithium ferric manganese phosphate (LiFe1-xMnxPO4), the element zinc serves as the majority of a negative pole material, and electrolyte is a liquid-state or gel-state material which is formed by lithium bis(trifluoromethane sulfonimide) (LiTFSI) and soluble zinc salt as solute and water as solvent and has ionic conductivity. The battery is based on the energy storage mechanisms of a dissolution-out / deposition reaction of zinc ions (Zn2+) on a negative pole and a reversible embedding / ejection reaction of the zinc ions (Zn2+) on a positive pole, meanwhile, through the water-in-salt electrolyte formed by high-concentration LiTFSI, the electrochemical water decomposition process is inhibited, a potential window of the water system electrolyte is remarkably broadened, the zinc-lithium mixed ion secondary battery has the advantages of being high in capacity, long in cycling life, safe, environmentally friendly, low in cost and the like, and the battery can be applied to the fields such as consumer electronic equipment, electromobiles and large-scale energy storage.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Electrochemical generation of carbon dioxide and hydrogen from organic acids
InactiveUS6387228B1Dissolution rateControllably operatedCellsPressure infusionOrganic acidElectricity
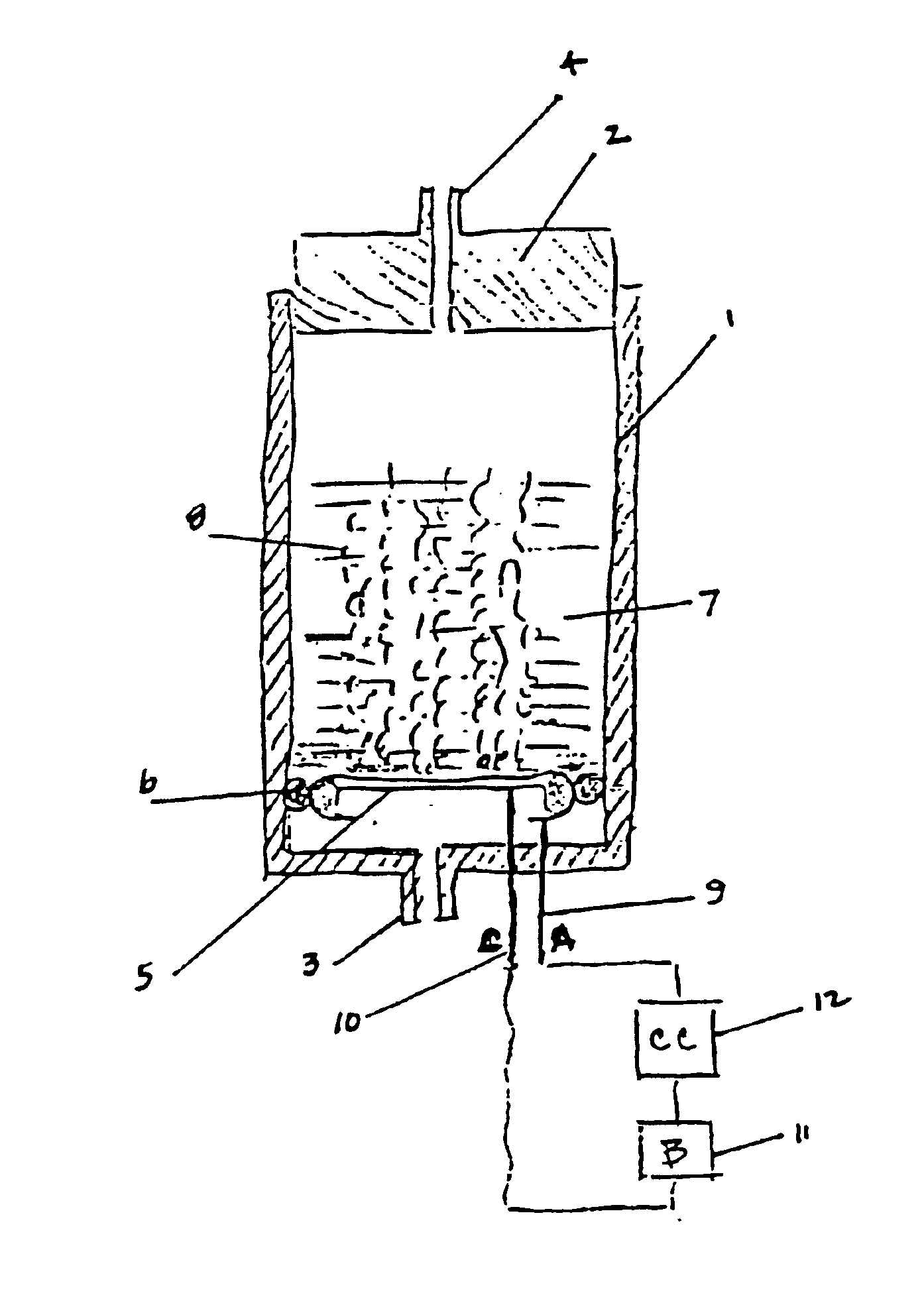
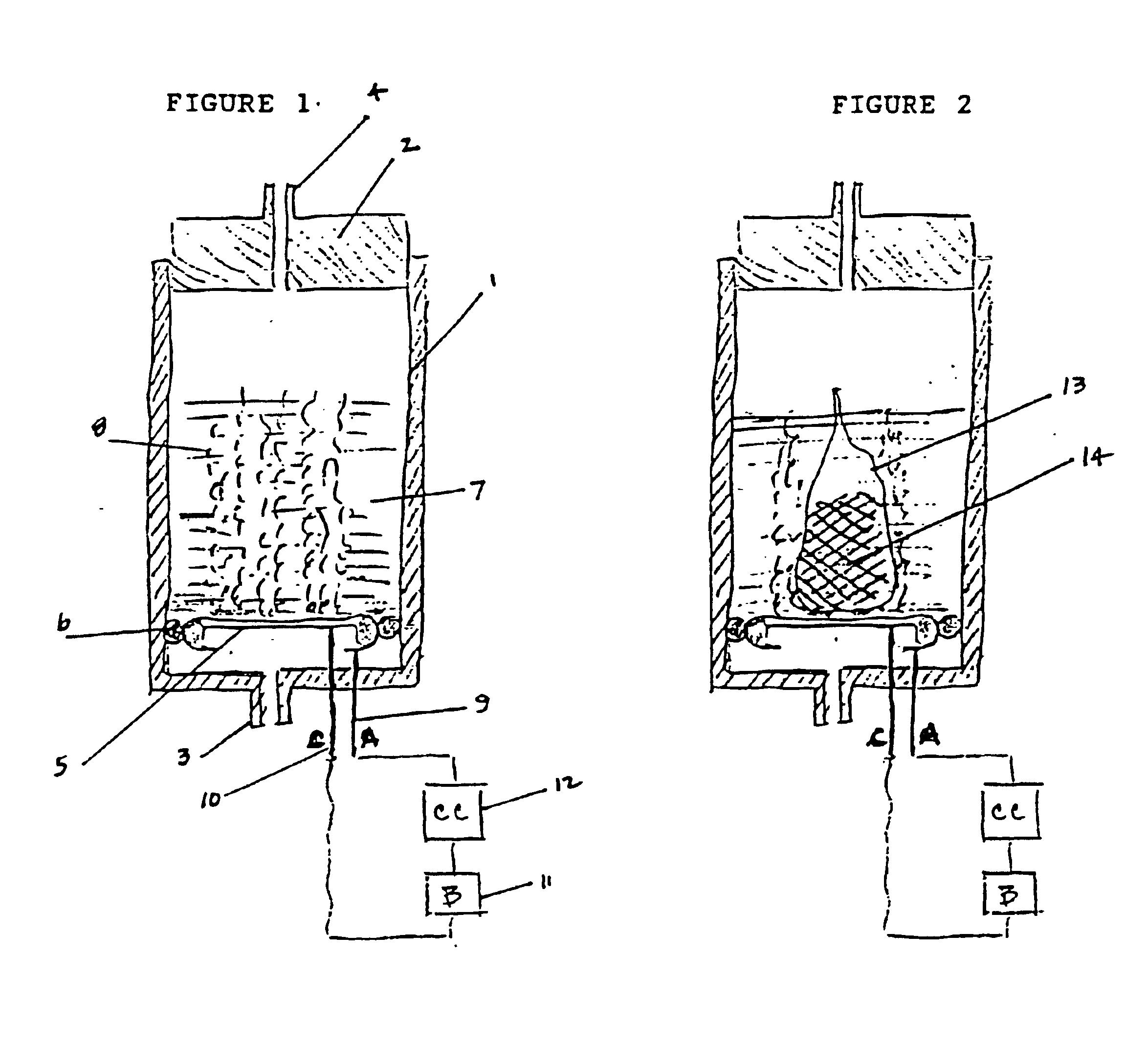
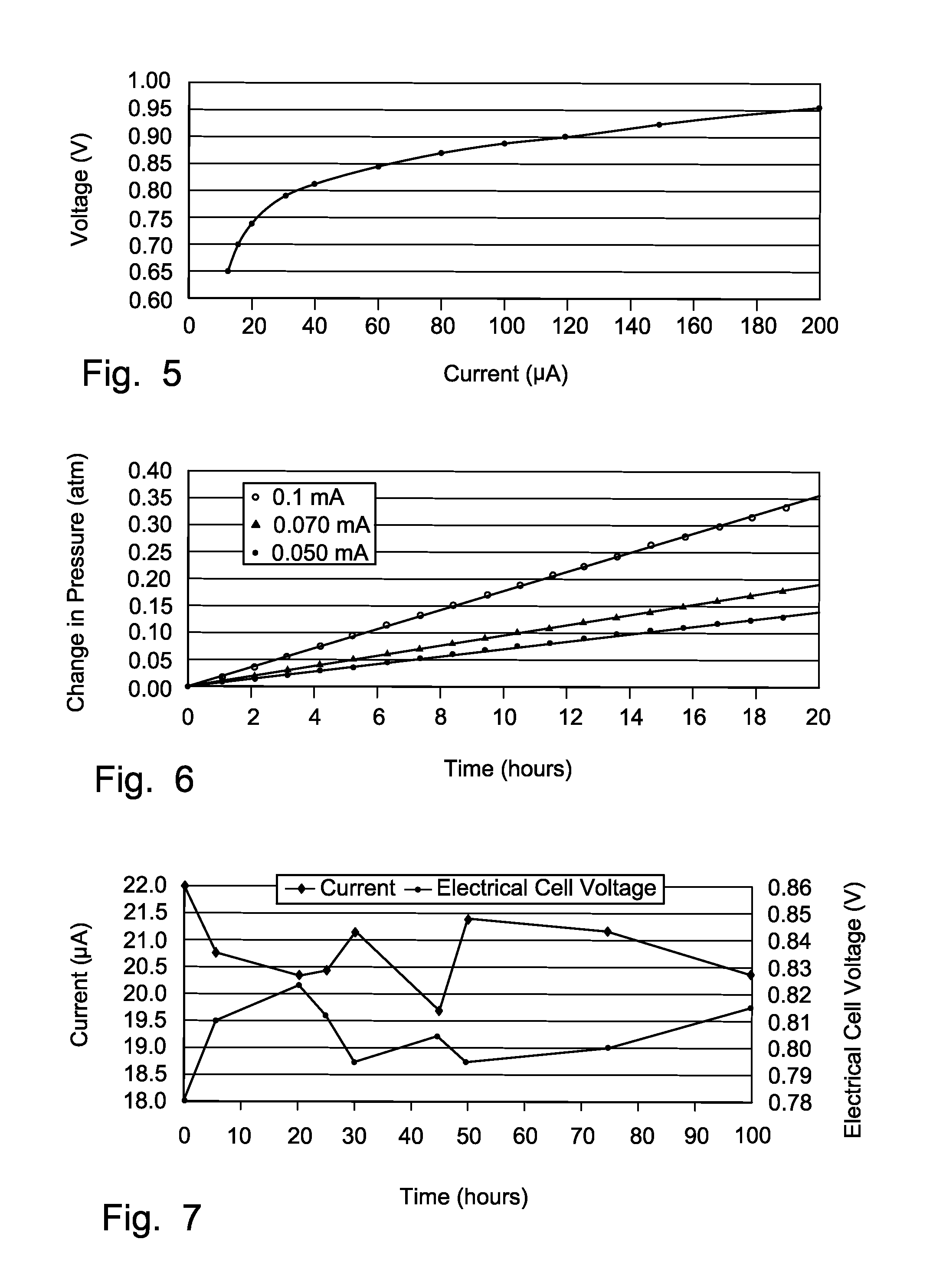
A device as described for the generation of high purity carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen (H2) by electrochemical decomposition of aqueous solutions of liquid and solid organic acids. A d.c. power source is used to apply a preselected current to an electrochemical cell, consisting of an ion permeable membrane and two electrodes. The generation rate of CO2 and H2 is continuous and proportional to the applied current; it can be stopped instantaneously by interrupting the current. Small Battery operated generators can produce propellant CO2 and H2 to deliver fluids from containers. Other uses include the creation of anaerobic environments in incubation chambers.
Owner:M & R CONSULTING SERVICES
Photoelectrode for producing hydrogen and oxygen by photoelectro-chemically decomposing water, preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN104762634AEasy to separateImprove transmission performanceEnergy inputElectrode shape/formsHydrogenPhotocathode
A photoelectrode for producing hydrogen and oxygen by photoelectro-chemically decomposing water is characterized in that the photoelectrode is composed of a photocathode and a photoanode, wherein the photocathode and a photoanode are provide with quantum dots being assembled with assistance of a double-functional molecule. The invention achieves the establishment and the application of the photoelectrode for producing hydrogen and oxygen on the basis of semiconductors, quantum dots and catalysts. The photoelectrode is high in stability, is free of a sacrificial agent, is simple in operation, is good in repeatability, is strong in universality and is high in utilization rate on visible light. In addition, the catalyst is free of requirement of noble metals, is low in cost and is easy to obtain.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
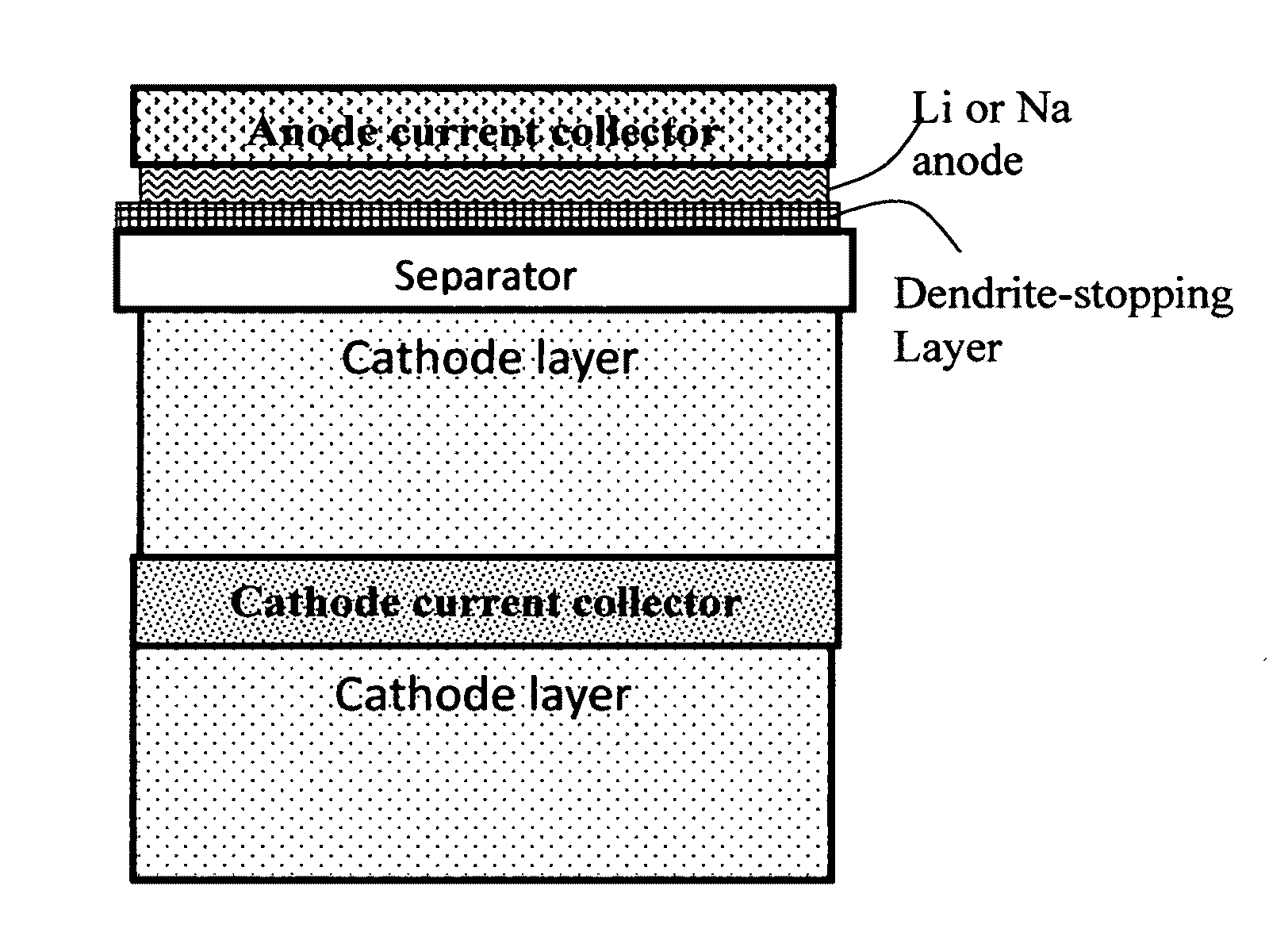
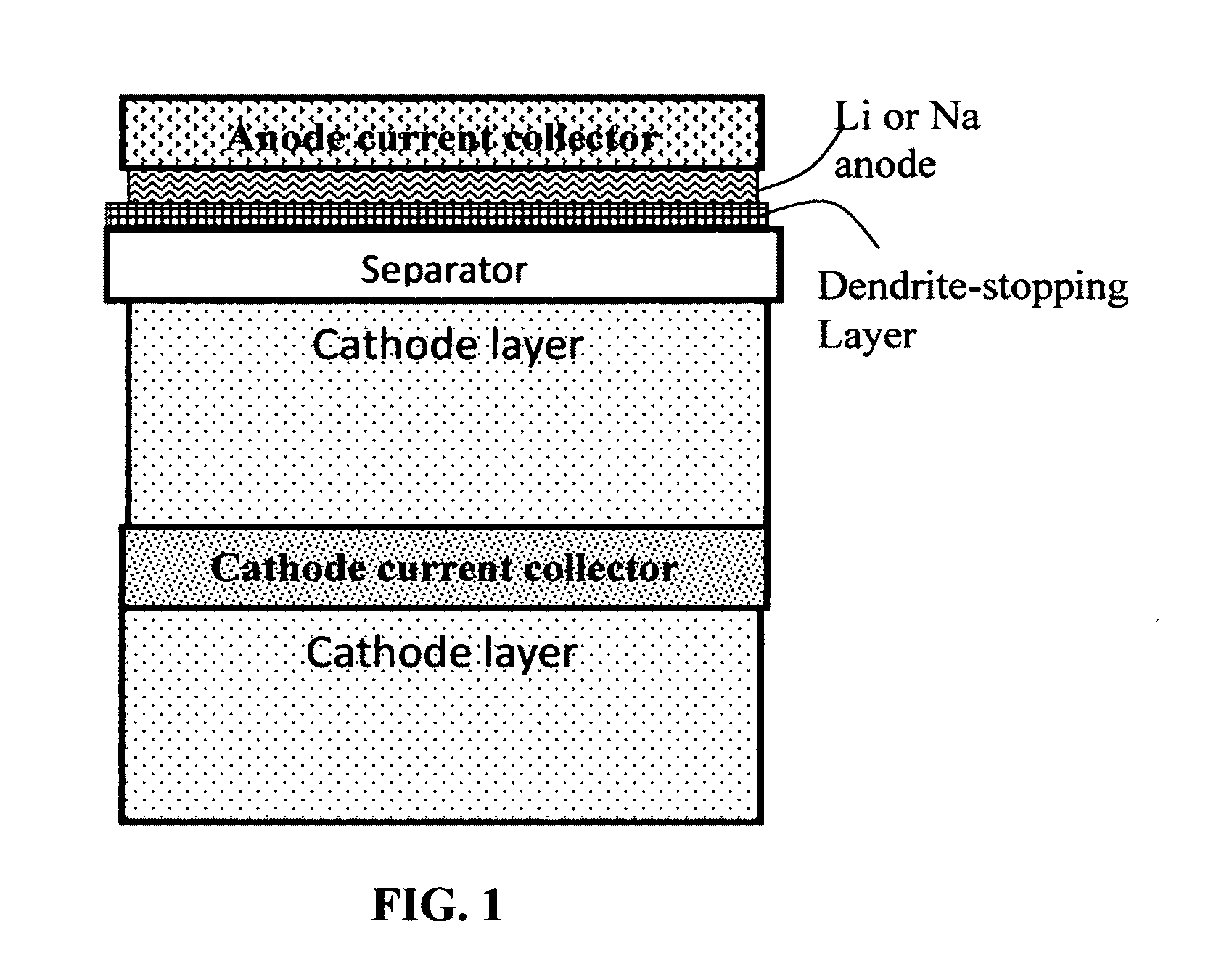
Carbon matrix-and carbon matrix composite-based dendrite-Intercepting layer for alkali metal secondary battery
ActiveUS20160344010A1Increase energy densityReduce material costsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsElectrolytic inorganic material coatingPhysical chemistryGraphite
A dendrite penetration-resistant layer for a rechargeable alkali metal battery, comprising an amorphous carbon or polymeric carbon matrix, an optional carbon or graphite reinforcement phase dispersed in this matrix, and a lithium- or sodium-containing species that are chemically bonded to the matrix and / or the optional carbon or graphite reinforcement phase to form an integral layer that prevents dendrite penetration through this integral layer in the alkali metal battery, wherein the lithium- or sodium-containing species is selected from Li2CO3, Li2O, Li2C2O4, LiOH, LiX, ROCO2Li, HCOLi, ROLi, (ROCO2Li)2, (CH2OCO2Li)2, Li2S, LixSOy, Na2CO3, Na2O, Na2C2O4, NaOH, NaiX, ROCO2Na, HCONa, RONa, (ROCO2Na)2, (CH2OCO2Na)2, Na2S, NaxSOy, or a combination thereof, wherein X=F, Cl, I, or Br, R=a hydrocarbon group, x=0-1, y=1-4; and wherein the lithium- or sodium-containing species is derived from an electrochemical decomposition reaction.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
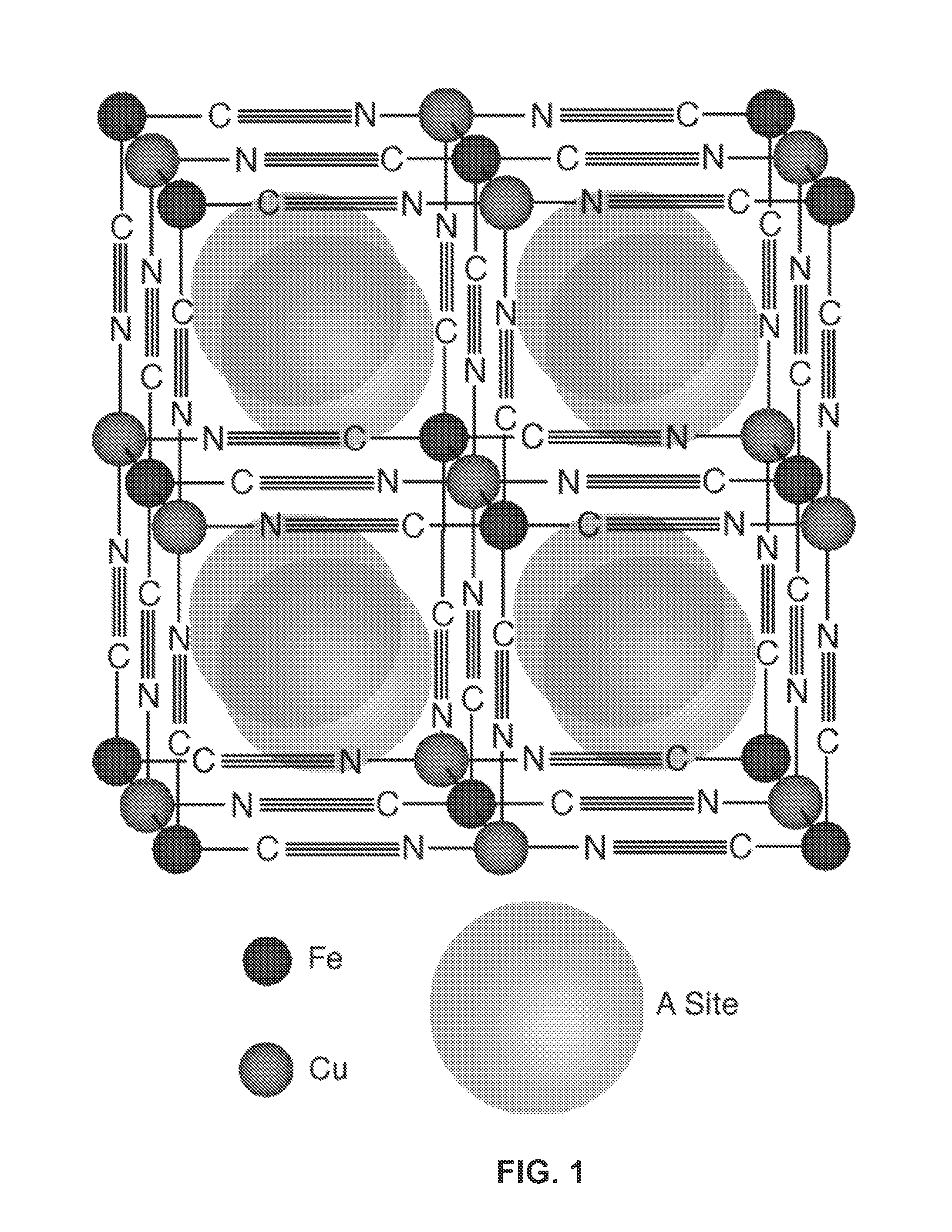
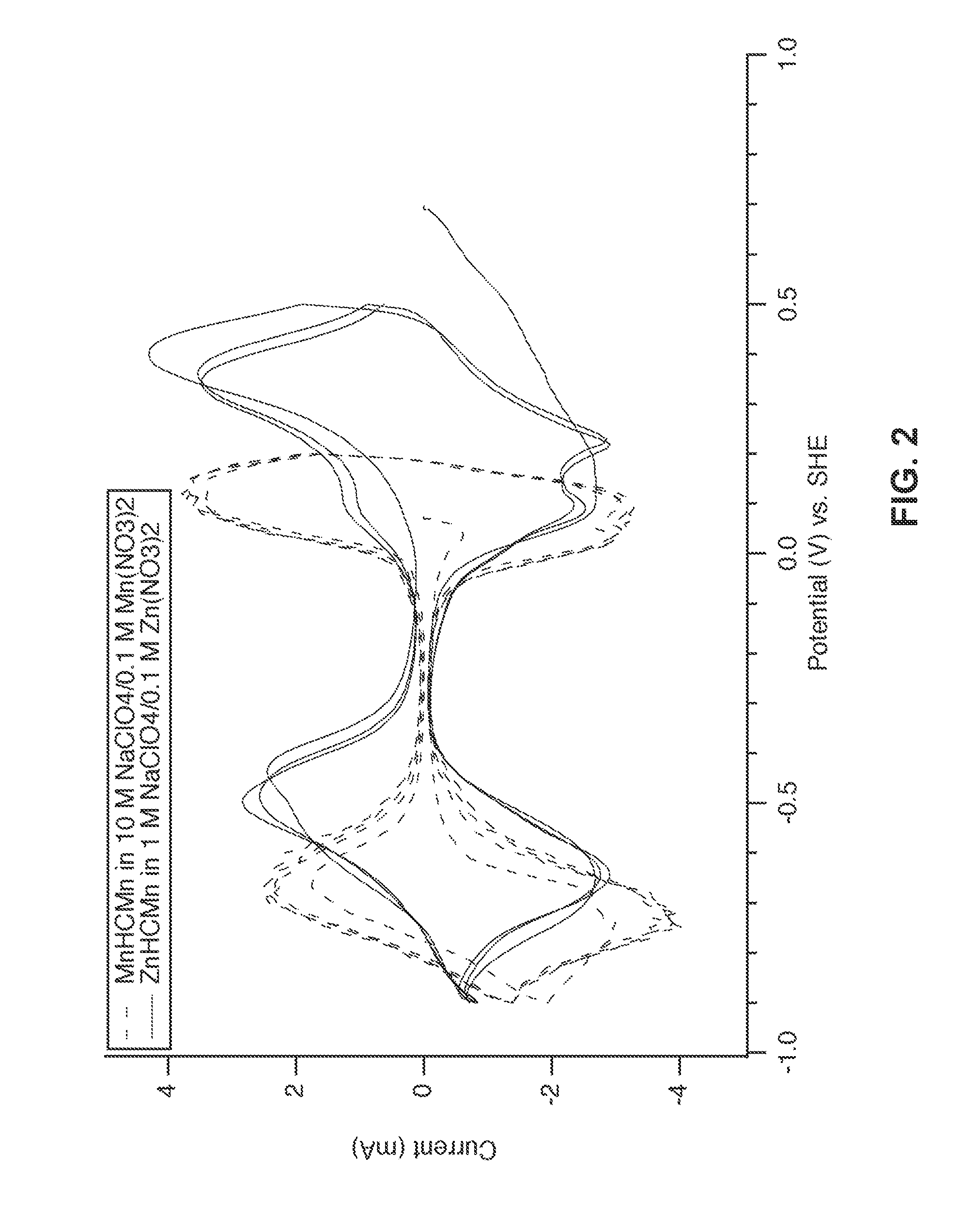
Prussian Blue Analogue Anodes for Aqueous Electrolyte Batteries
InactiveUS20140220392A1Maximizes energy storageReduces electrochemical decompositionIron cyanidesComplex cyanidesRedoxPrussian blue
A system and method producing electrodes in an aqueous electrolyte battery that maximizes energy storage, reduces electrochemical decomposition of the electrolyte, and uses Prussian Blue analogue materials for both electrodes, with an anode electrode including an electrochemically active hexacyanometalate group having two possible redox reactions of different potentials. These potentials may be tuned by substituting different electrochemically inactive components.
Owner:NATRON ENERGY INC
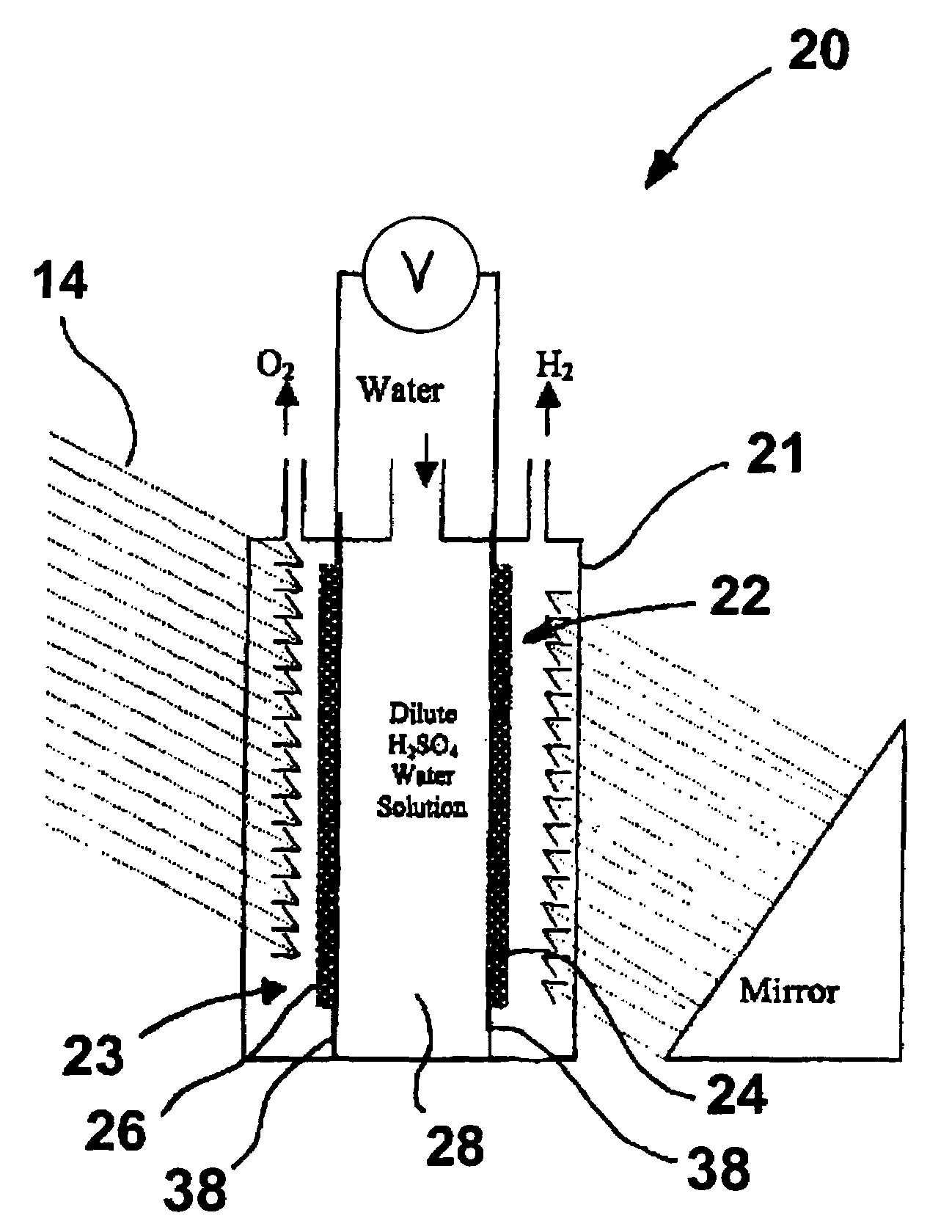
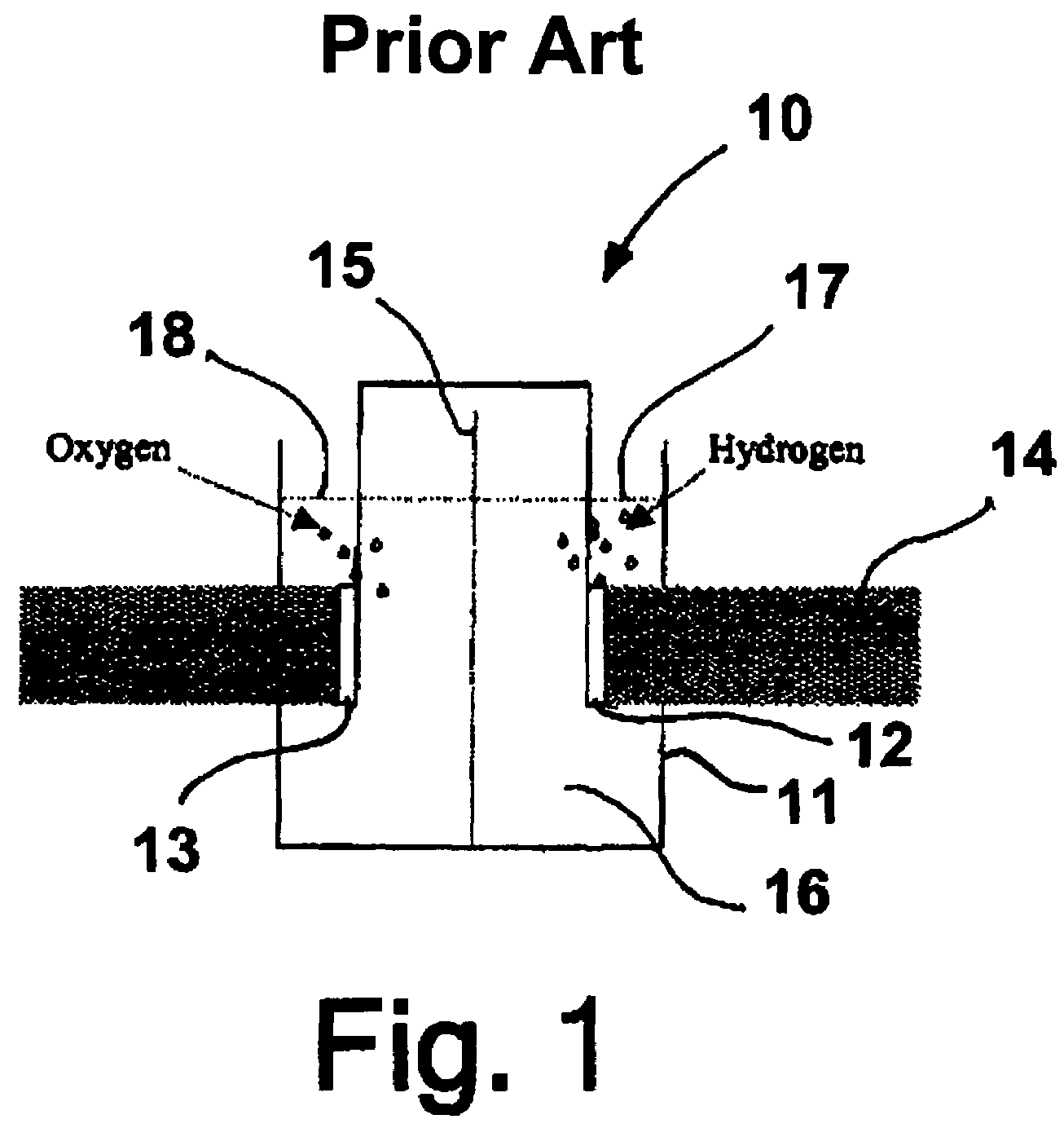
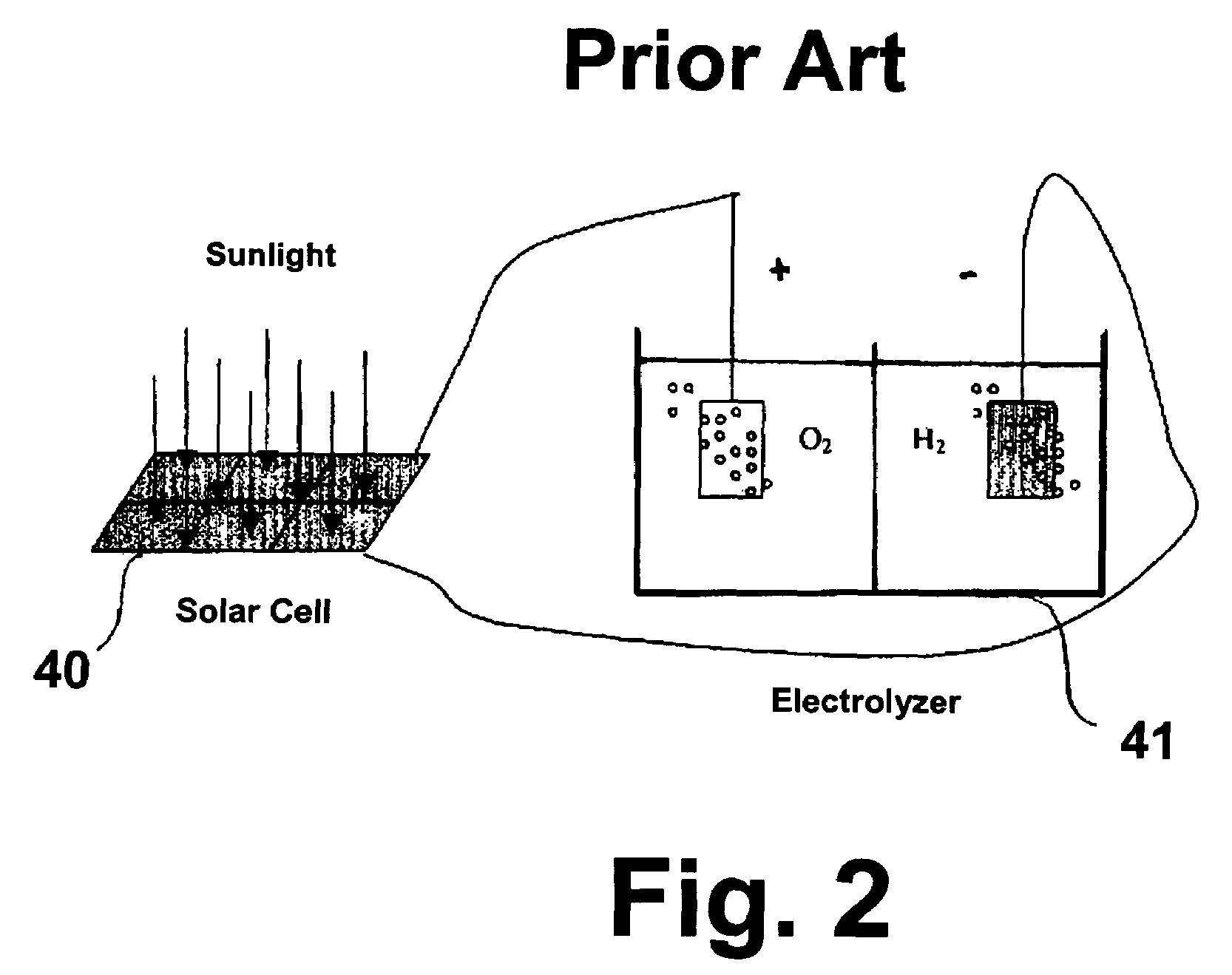
Solar cell electrolysis of water to make hydrogen and oxygen
InactiveUS20050194041A1Improve efficiencyIncreased durabilityCellsDeferred-action cellsSolar cellElectrochemical decomposition
A water permeable electrode for electrochemical splitting of water having a light sensitive catalytic material layer which includes a light sensitive catalytic material and a semiconductor, a polymer electrolyte membrane layer, a metallic substrate layer disposed there between adjacent the polymer electrolyte membrane layer, and at least one photovoltaic device connected in series to the light sensitive catalytic material layer and disposed between the light sensitive catalytic material layer and the metallic substrate layer.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
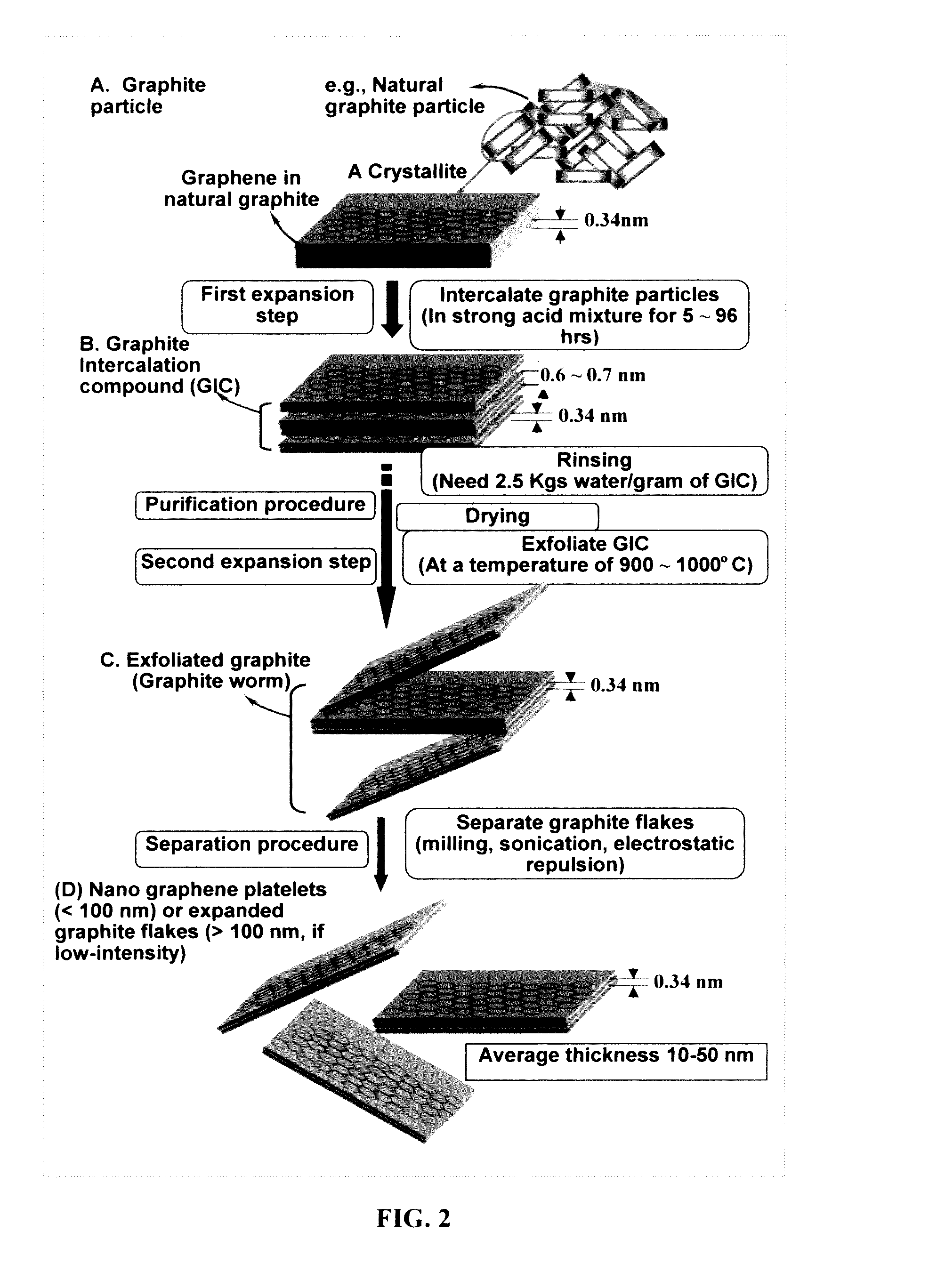
Surface-stabilized and prelithiated anode active materials for lithium batteries and production method
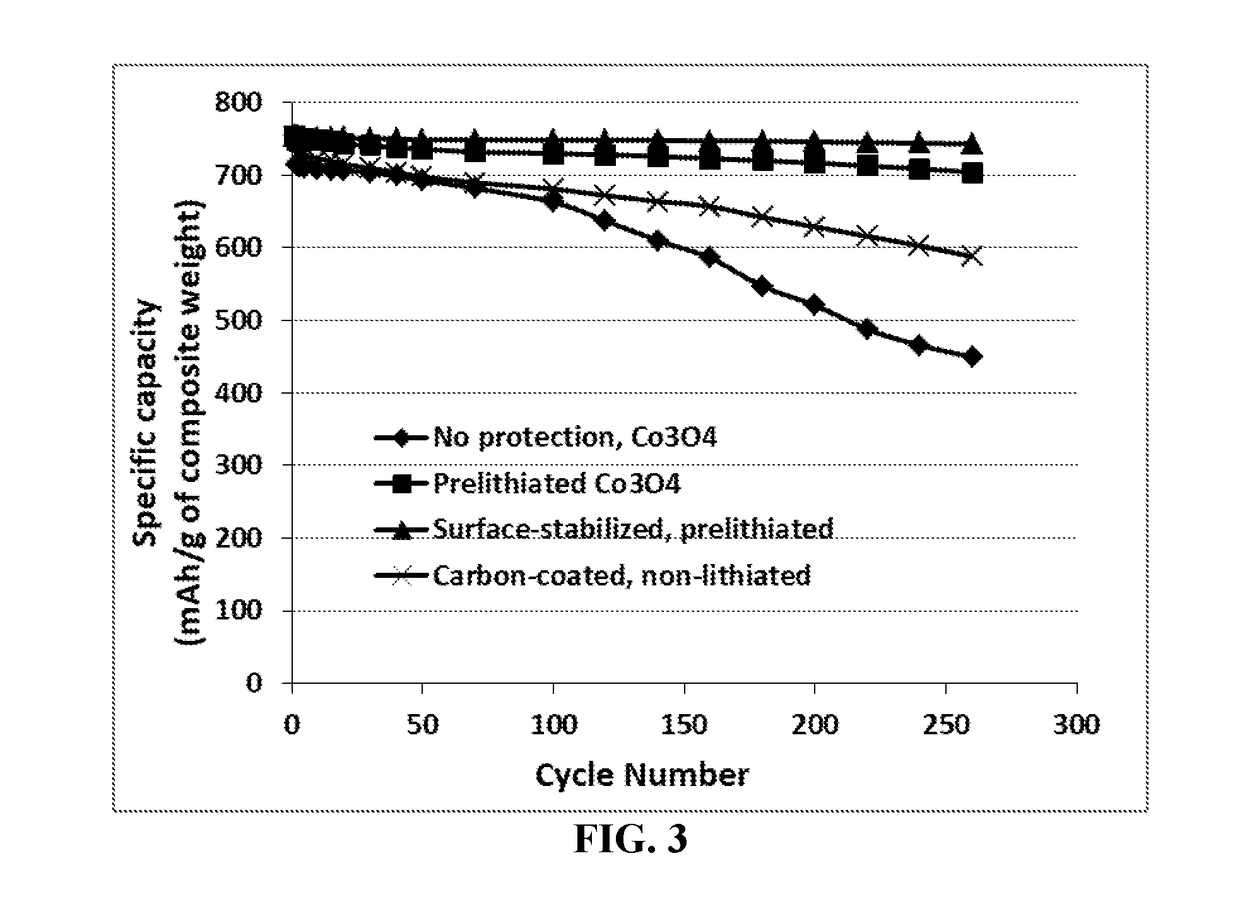
ActiveUS20190088930A1High specific capacityLong charge-discharge cycle lifeCell electrodesLi-accumulatorsPhysical chemistryElectrochemical decomposition
A prelithiated and surface-stabilized anode active material for use in a lithium battery, comprising a protected anode active material particle comprising a surface-stabilizing layer embracing a core particle, wherein the surface-stabilizing layer comprises a lithium- or sodium-containing species chemically bonded to the core particle and the lithium- or sodium-containing species is selected from Li2CO3, Li2O, Li2C2O4, LiOH, LiX, ROCO2Li, HCOLi, ROLi, (ROCO2Li)2, (CH2OCO2Li)2, Li2S, LixSOy, Li4B, Na4B, Na2CO3, Na2O, Na2C2O4, NaOH, NaiX, ROCO2Na, HCONa, RONa, (ROCO2Na)2, (CH2OCO2Na)2, Na2S, NaxSOy, or a combination thereof, wherein X=F, Cl, I, or Br, R=a hydrocarbon group, 0<x≤1, and 1≤y≤4; wherein the lithium- or sodium-containing species is preferably derived from an electrochemical decomposition reaction and the core particle is prelithiated to contain an amount of lithium from 1% to 100% of the maximum lithium content that can be included in the core particle of anode active material.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
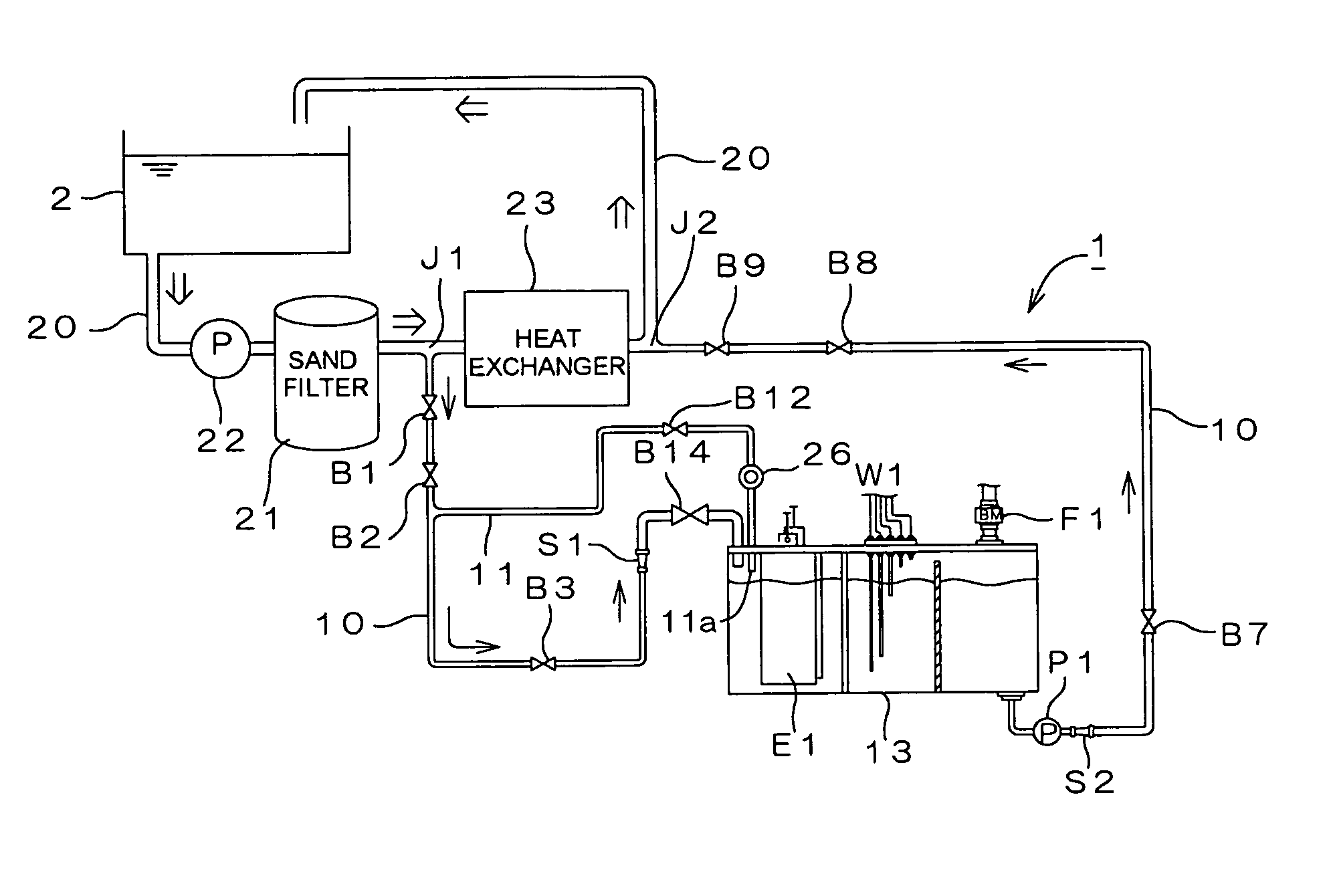
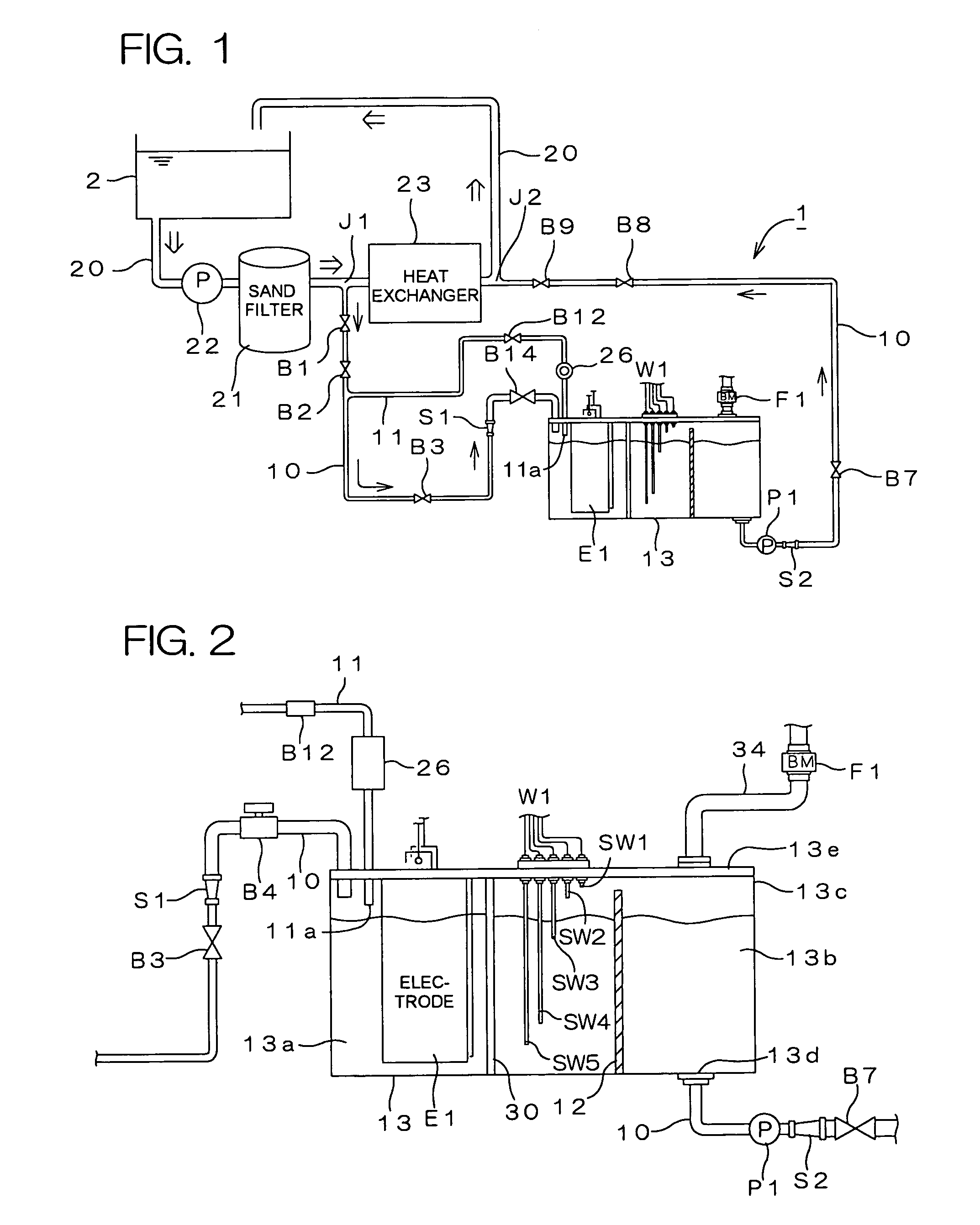
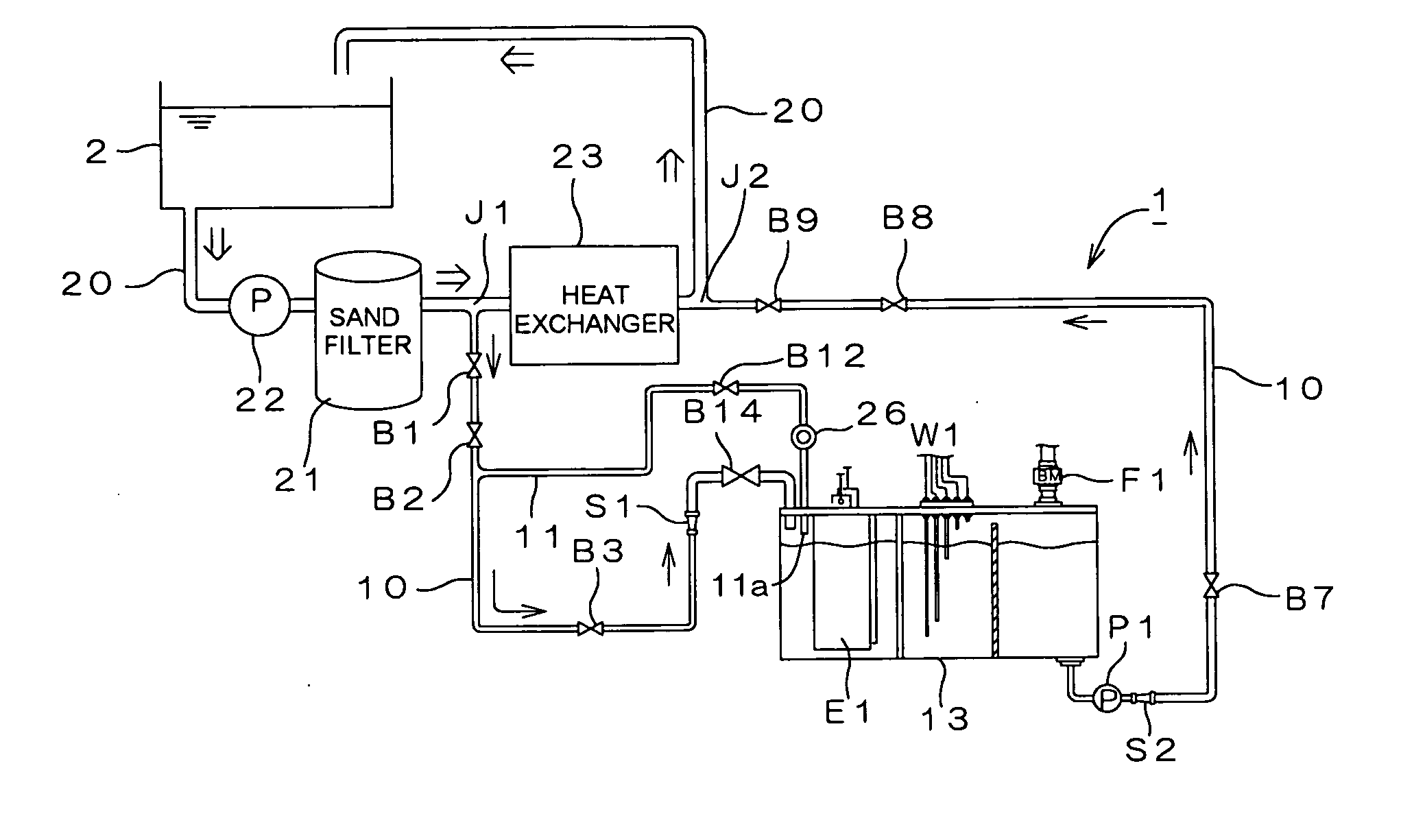
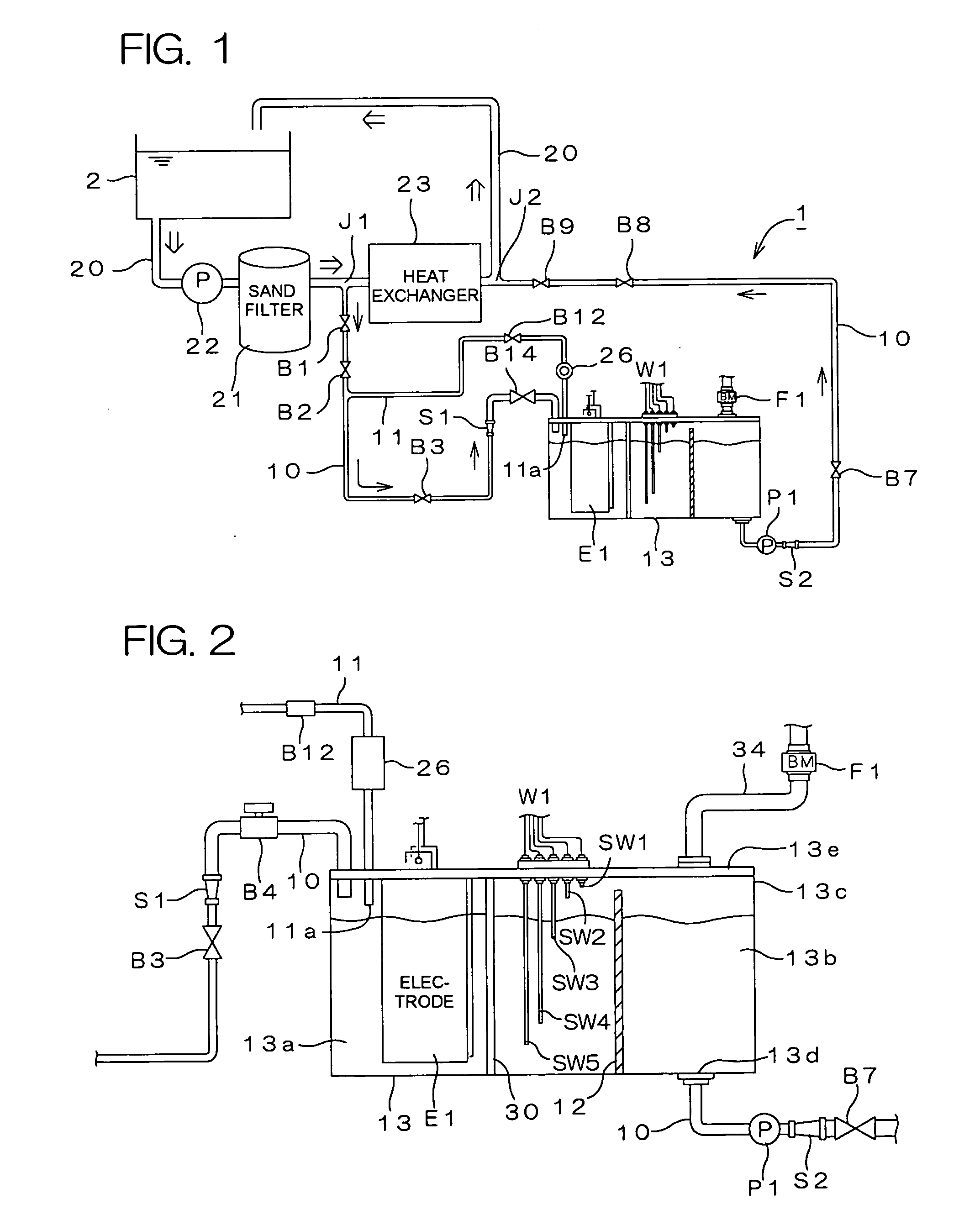
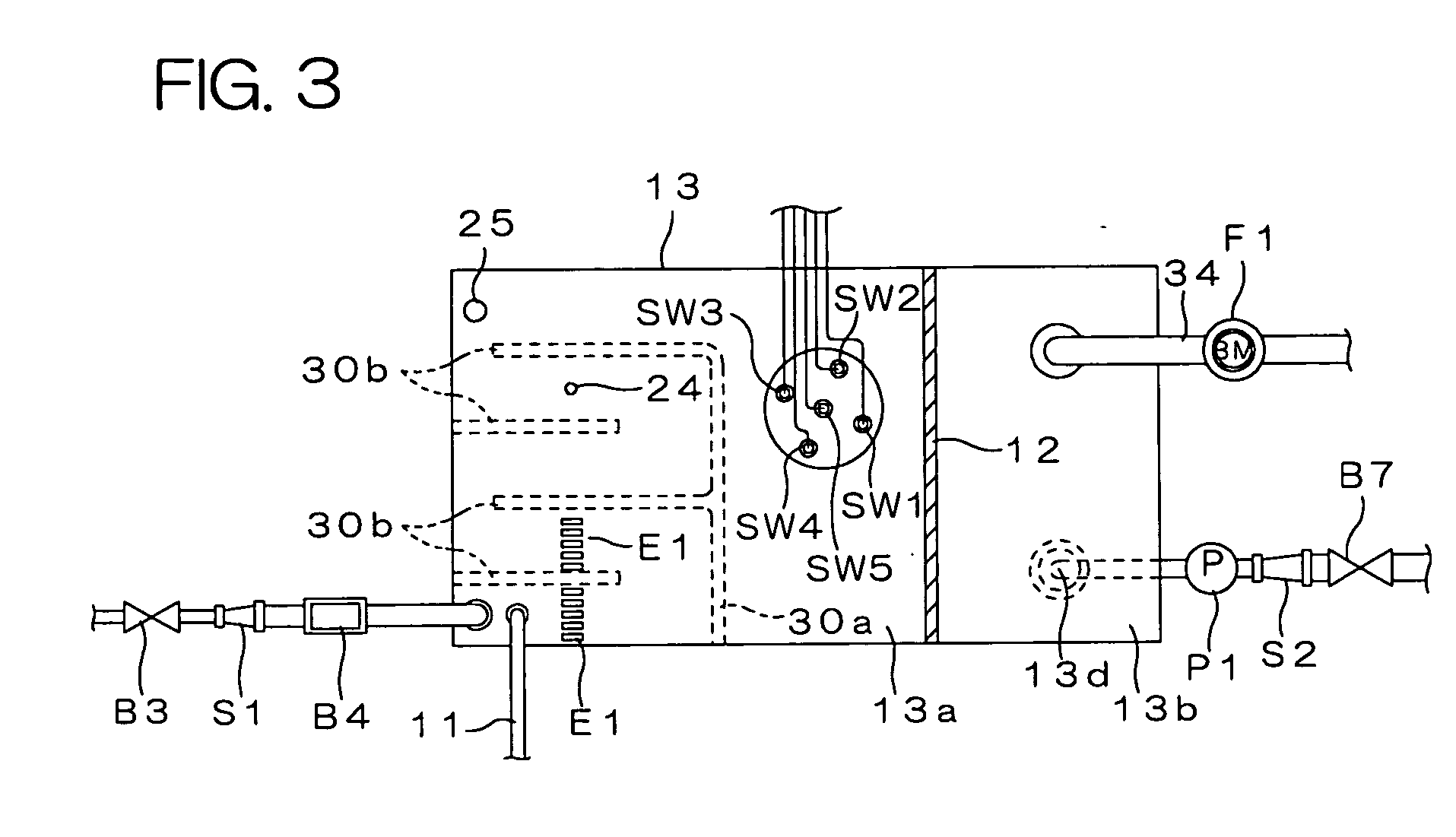
Water treating device
InactiveUS7008529B2Safely and properly performingSludge treatmentElectrostatic separatorsElectrochemical decompositionResidual chlorine
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
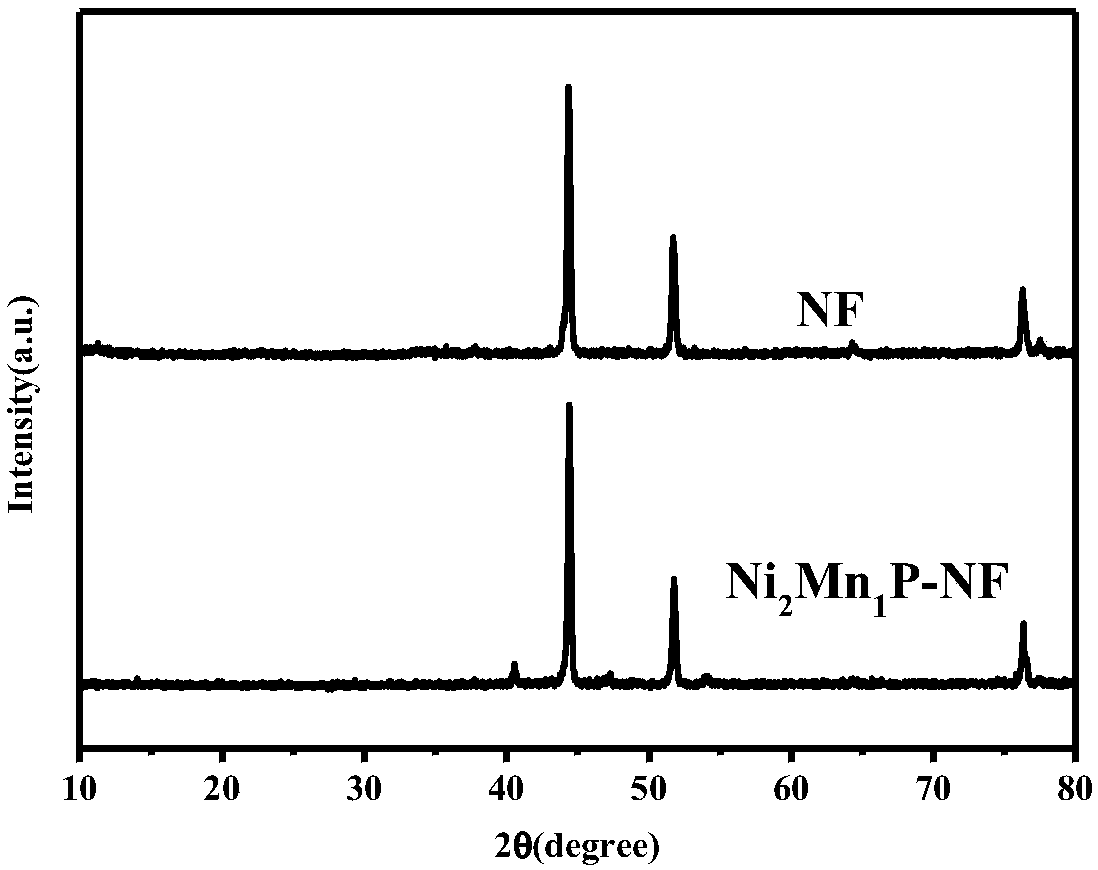
Bi-metal phosphide electrocatalyst as well as preparation method thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN108588750ASimple stepsShort reaction timeLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectrodesHydrogenElectrochemical decomposition
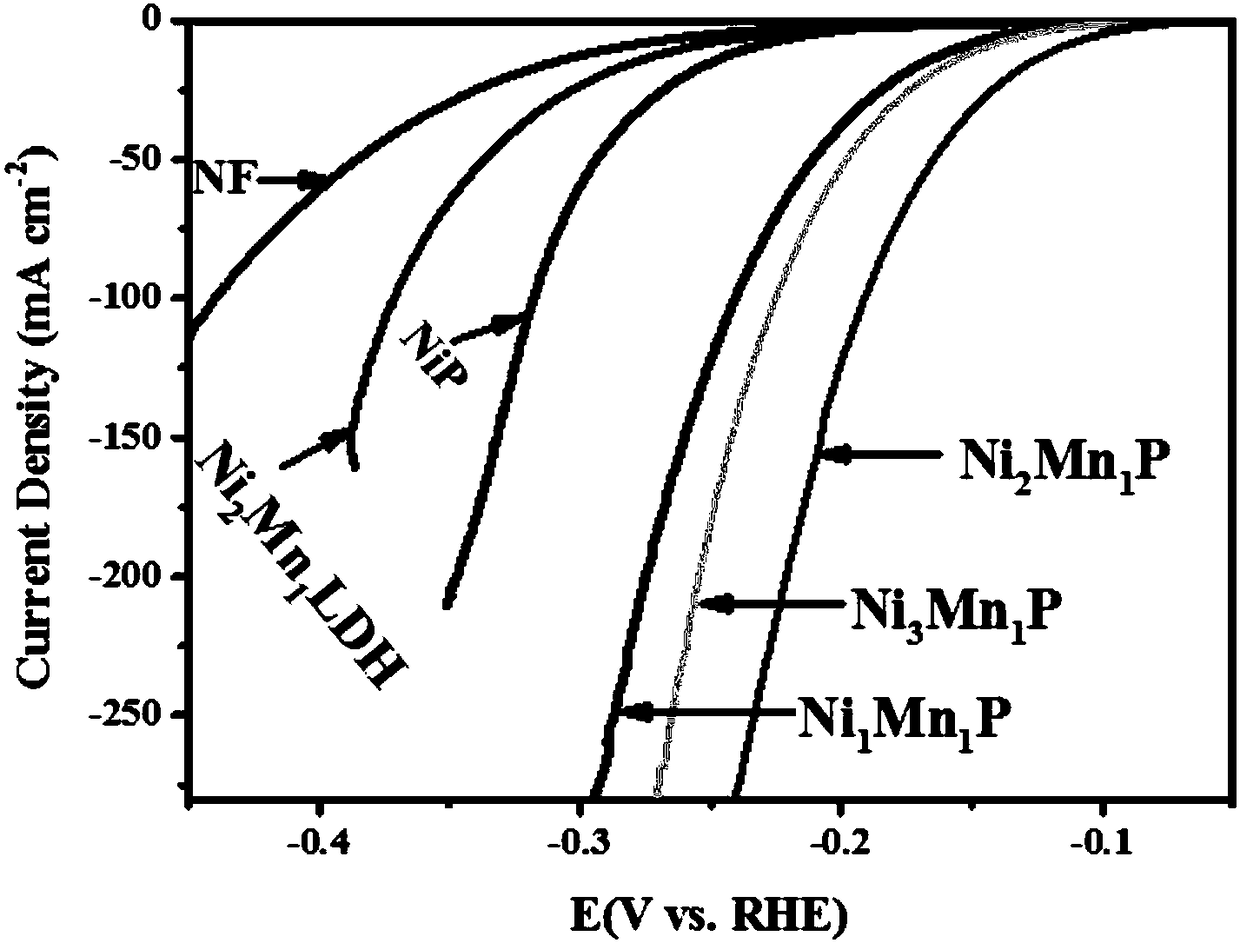
The invention belongs to the field of electrocatalysts, and specifically relates to a preparation method and application of a mesoporous bi-metal phosphide electrocatalyst for electrochemically decomposing water to generate hydrogen with high performance. A hydroxide precursor is synthesized through hydrothermal reaction and is further subjected to low-temperature phosphating reaction to obtain aNixMn1P porous nanosheet array electrocatalyst. The series of bi-metal phosphides have relatively low charge transfer resistance and reaction barrier of hydrogen evolution reaction, and have excellentperformances in electro-catalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. The catalyst is low in cost, is simple and convenient in operation, is simple in process, is excellent in catalysis performance, and provides basic application research, in the electro-catalysis field, of the materials.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Water treating device
InactiveUS20040149663A1Reduce system costLow costElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentReclaimed waterElectrochemical decomposition
The present invention provides a water treating device, which comprises: a water container for containing water to be treated; an electrolyzing chamber for sterilizing the to-be-treated water by way of electrochemical decomposition through energization of an electrode set consisting of at least two electrode plates; a water treatment line through which the to-be-treated water is introduced into the electrolyzing chamber from the water container and fed back into the water container after the sterilization of the water in the electrolyzing chamber; a residual chlorine sensor for measuring the residual chlorine concentration of the to-be-treated water before the water is introduced into the electrolyzing chamber; and control means for controlling the amount of the to-be-treated water to be electrochemically decomposed in the electrolyzing chamber on the basis of the residual chlorine concentration measured by the residual chlorine sensor to keep the residual chlorine concentration of the water to be fed back into the water container within a predetermined range; wherein a bypass line is provided which is branched from the water treatment line at a position upstream of the electrolyzing chamber for sampling the to-be-treated water, introducing the sampled to-be-treated water into the residual chlorine sensor for the measurement of the residual chlorine concentration thereof, and discharging the sampled to-be-treated water into the electrolyzing chamber after the measurement. With this arrangement, the to-be-treated water subjected to the measurement of the residual chlorine concentration in the bypass line is returned into the electrolyzing chamber, so that no waste water is produced. Further, the to-be-treated water returned into the electrolyzing chamber is sterilized in the electrolyzing chamber, and then fed back into the water container. Therefore, water yet to be sterilized is not fed back into the water container.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Lithium secondary battery
InactiveUS20020018926A1Avoid emissionsLarge capacityNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsOrganic electrolyte cellsOrganic solventDecomposition
A lithium secondary battery exhibiting very high safety, which is ensured by restraining both the generation of flammable gas caused by the decomposition of an electrolyte, and the emission of oxygen from a positive active material even during overcharging. The lithium secondary battery includes a positive electrode of which an active material is a lithium transition metal composite oxide, a negative electrode of which an active material is a carbon material, and a nonaqueous electrolyte containing an organic solvent in which a lithium salt is dissolved. The nonaqueous electrolyte contains at least one kind of conductive polymer-forming monomers which have an alkyl group and is electrochemically polymerizable on the positive electrode within a battery operation voltage, and at least one kind of film-forming agents which electrochemically decompose within the battery operation voltage to form films on a surface of the negative electrode.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Electrochemical generation of carbon dioxide and hydrogen from organic acids
InactiveUS6780304B1Controllably operatedReduce processing stepsCellsPressure infusionElectricityOrganic acid
A device as described for the generation of high purity carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen (H2) by electrochemical decomposition of aqueous solutions of liquid and solid organic acids. A d.c. power source is used to apply a pre-selected current to an electrochemical cell, consisting of an ion permeable membrane and two electrodes. The generation rate of CO2 and H2 are continuous and proportional to the applied current; it can be stopped instantaneously by interrupting the current. Small battery operated generators can produce propellant CO2 and H2 to deliver fluids from containers other uses include the creation of anaerobic environments in incubation chambers.
Owner:MAGET HENRI J R
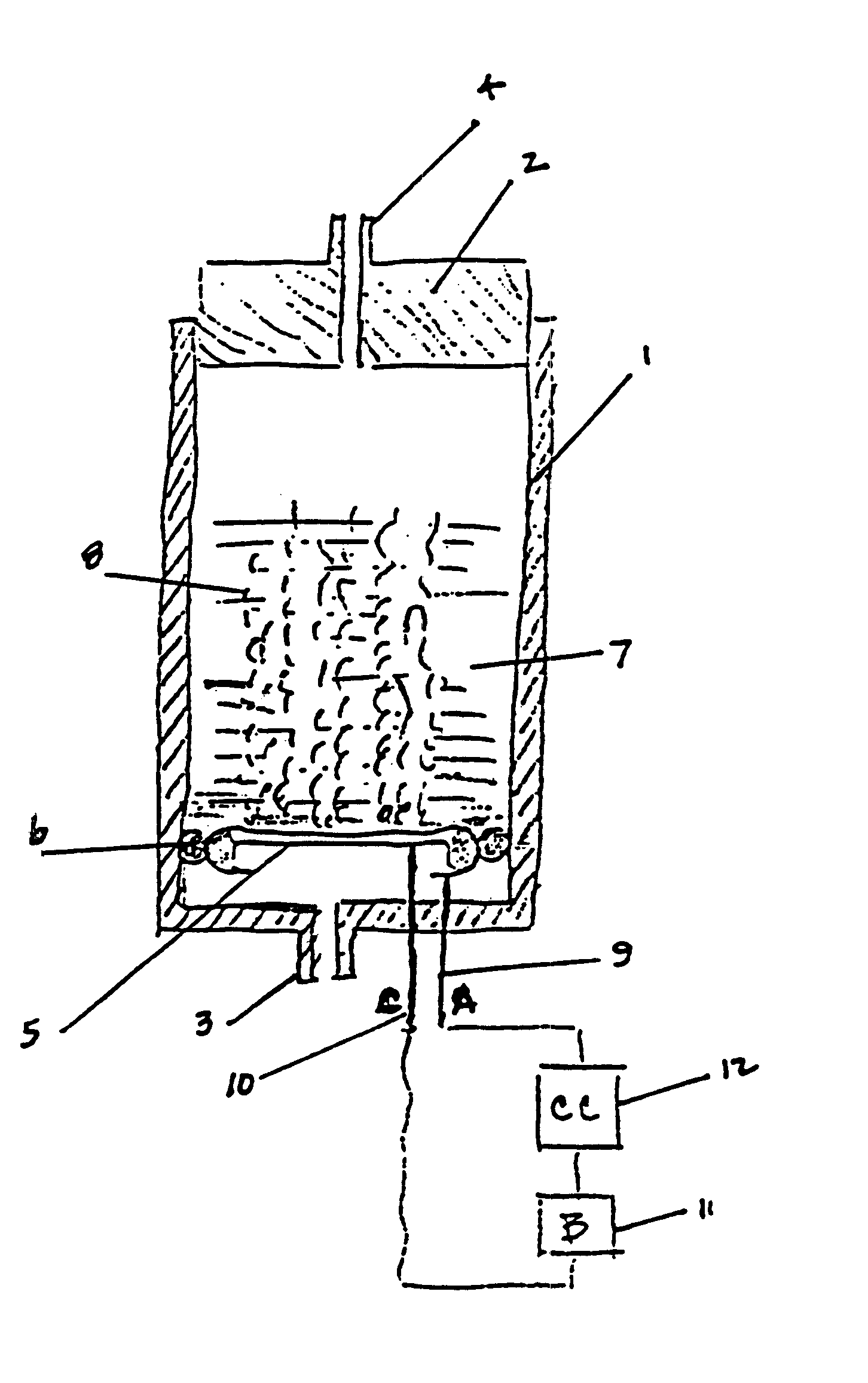
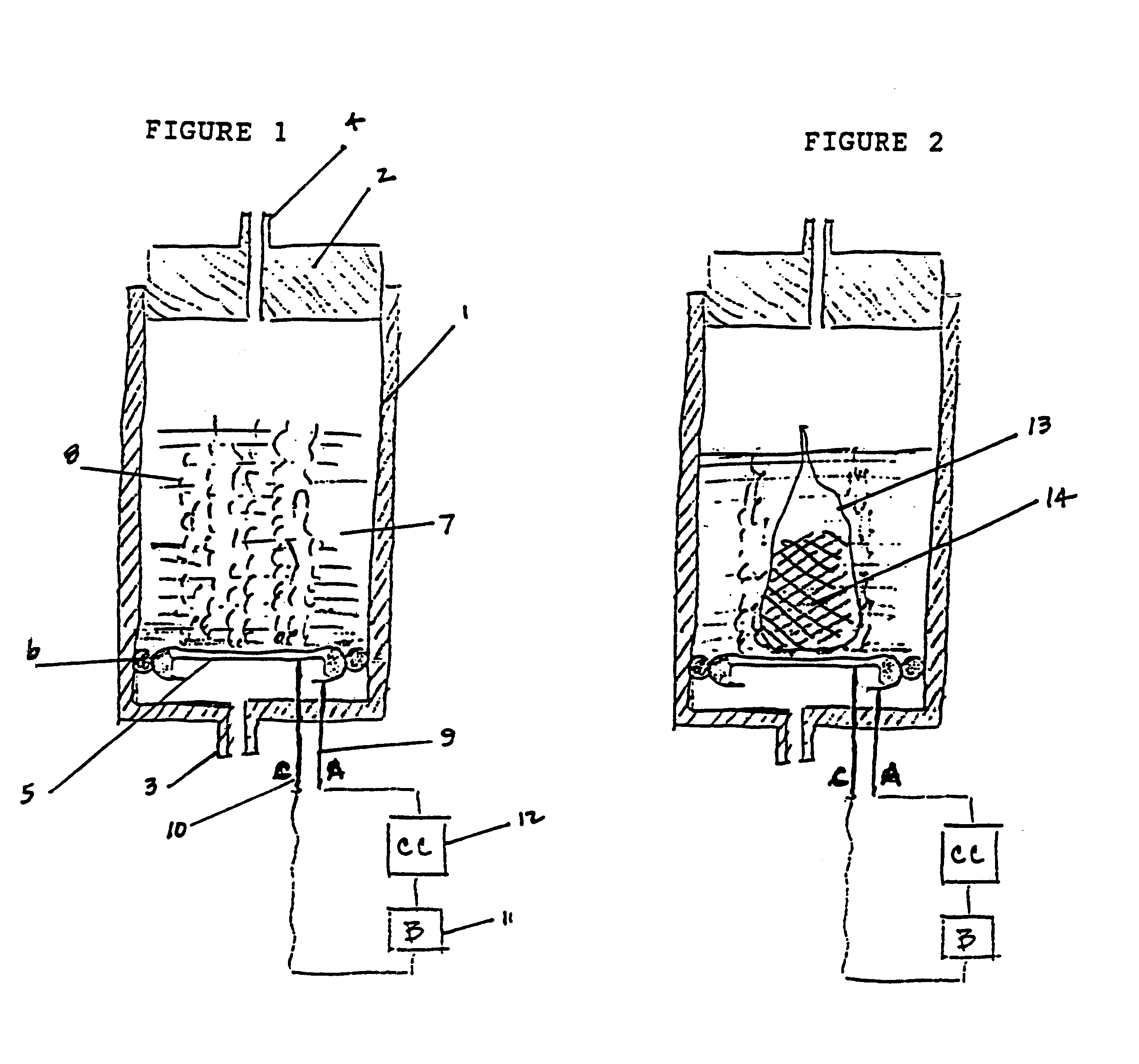
Miniature electrochemical gas generator and power source
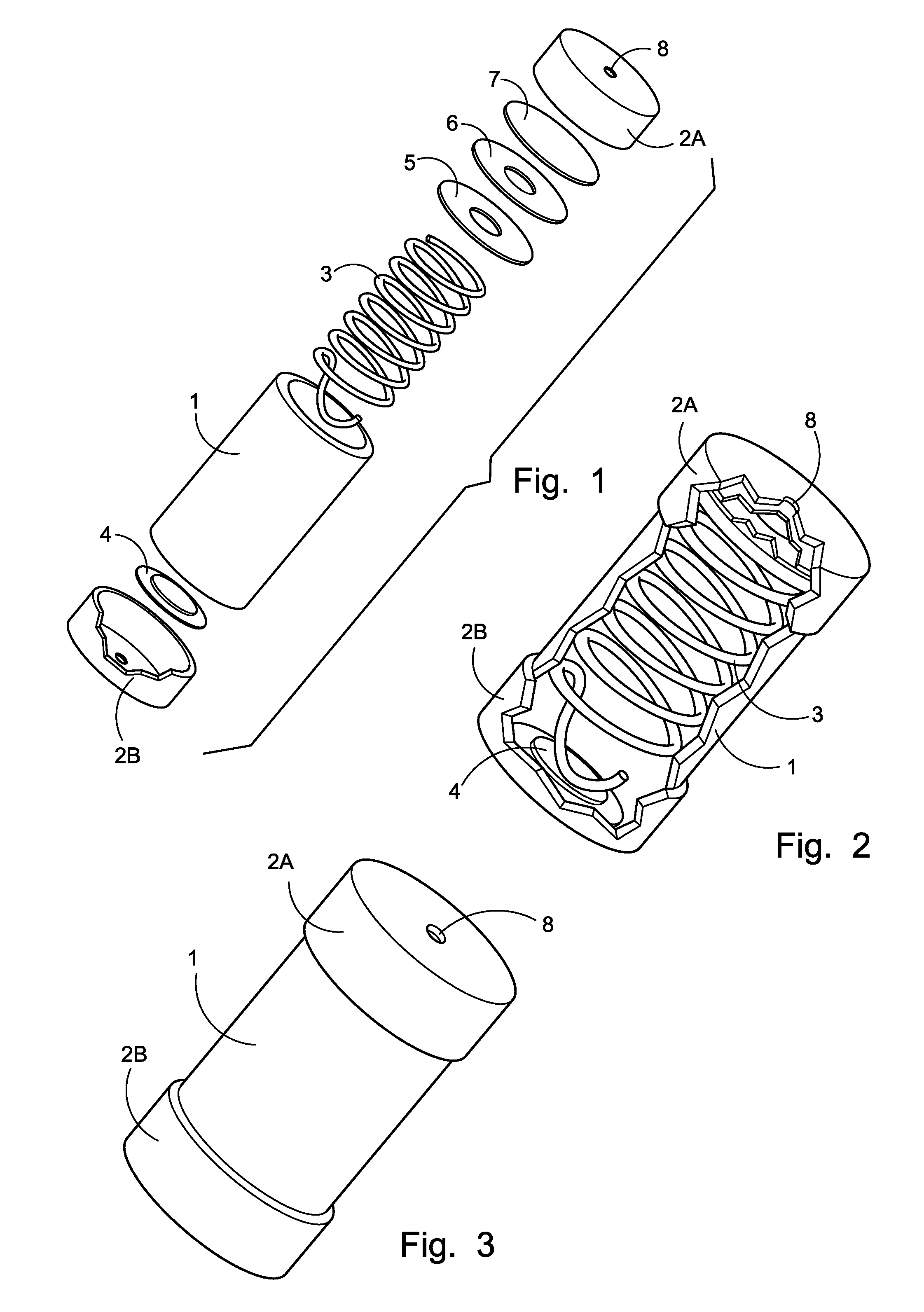
InactiveUS7316857B1Practical and convenientLong period of timeCellsReactant parameters controlElectrical batteryEngineering
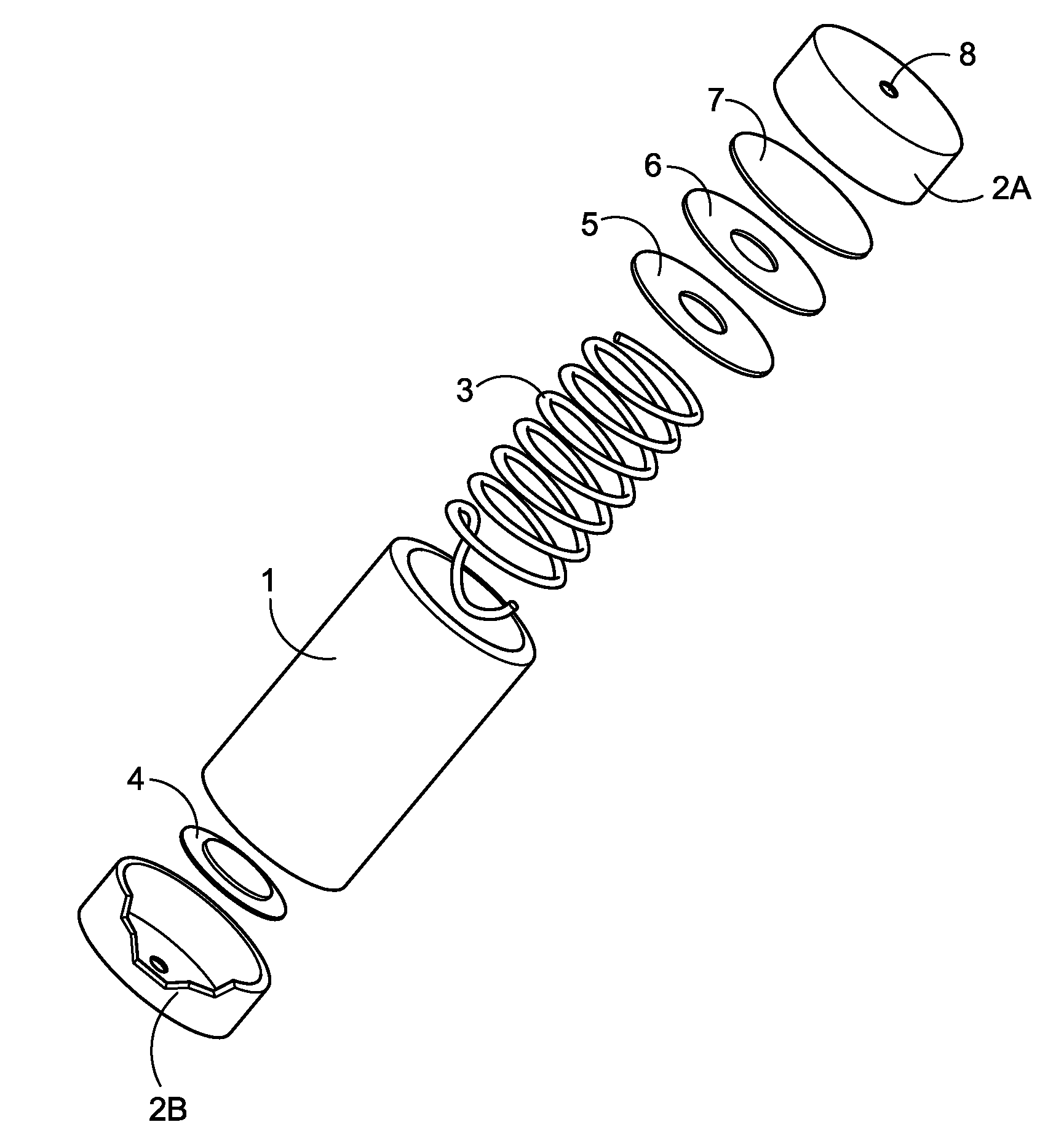
A miniature, battery-like device is described for the generation of gases or as a power source or battery. The generation of carbon dioxide and hydrogen by electrochemical decomposition of an aqueous oxalic acid solution is detailed. One of the electrodes of the internally located electrochemical cell is in intimate contact with the cathode cap of the device, while the other electrode is under compression from an internal spring of variable length which is in electrical contact with the anode cap. The low-cost device is easy to fill and assemble. It can be used for the controlled release of small quantities of fluid, delivered at low flow rates for long periods of time, such as pheromones, fragrances, insecticides, pesticides. It can also be used as power source using liquid fuels such as methanol and ambient air as a source of oxygen.
Owner:M & R CONSULTING SERVICES
Electrode material for power storage device, electrode for power storage device, and power storage device
InactiveUS20140087251A1Reduce capacityActive material electrodesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesElectrochemical decompositionSide reaction
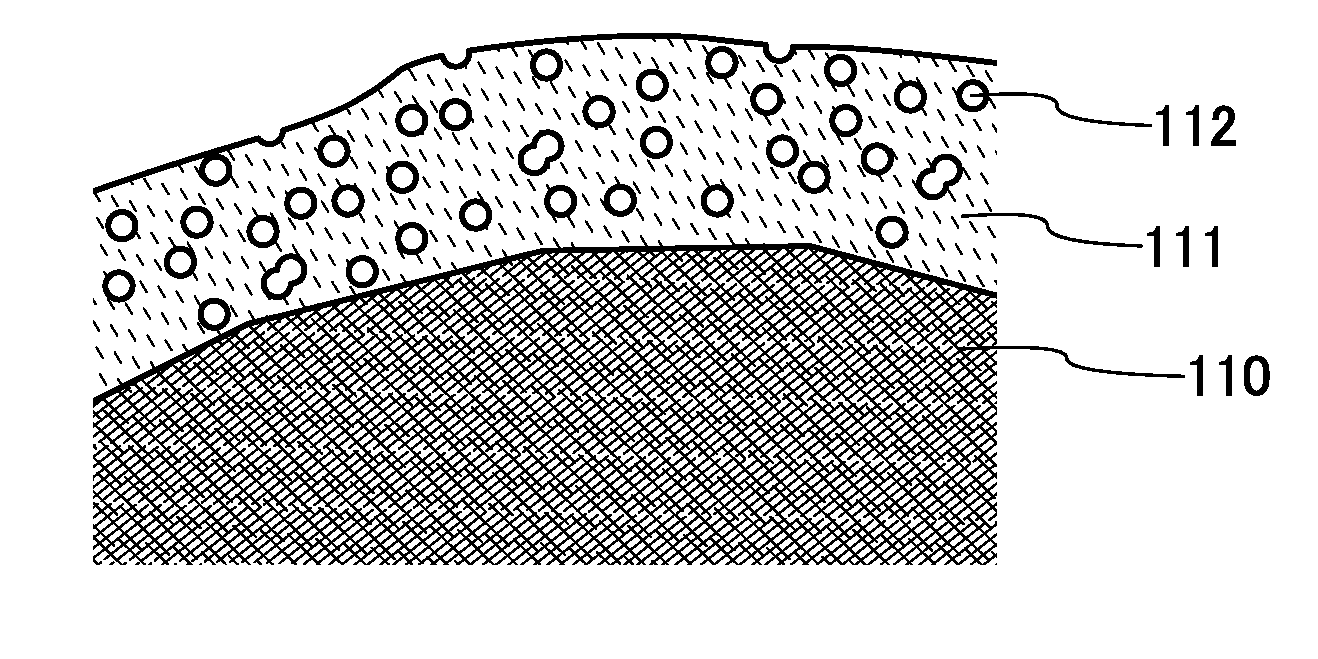
Irreversible capacity which causes a decrease in the initial capacity of a power storage device is reduced and the electrochemical decomposition of an electrolytic solution is suppressed. The decomposition reaction of an electrolytic solution as a side reaction of a power storage device is reduced or suppressed to improve the cycle performance of the power storage device. An electrode material for a power storage device includes active material particles and coating films covering part of surfaces of the active material particles. Carrier ions used for the power storage device can pass through the coating film. The product of the electric resistivity and the thickness of the coating film at 25° C. is greater than or equal to 20 Ωm·m.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Solar cell electrolysis of water to make hydrogen and oxygen
InactiveUS7241950B2Improve efficiencyIncreased durabilityCellsDeferred-action cellsElectrochemical decompositionSolar cell
A water permeable electrode for electrochemical splitting of water having a light sensitive catalytic material layer which includes a light sensitive catalytic material and a semiconductor, a polymer electrolyte membrane layer, a metallic substrate layer disposed there between adjacent the polymer electrolyte membrane layer, and at least one photovoltaic device connected in series to the light sensitive catalytic material layer and disposed between the light sensitive catalytic material layer and the metallic substrate layer.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
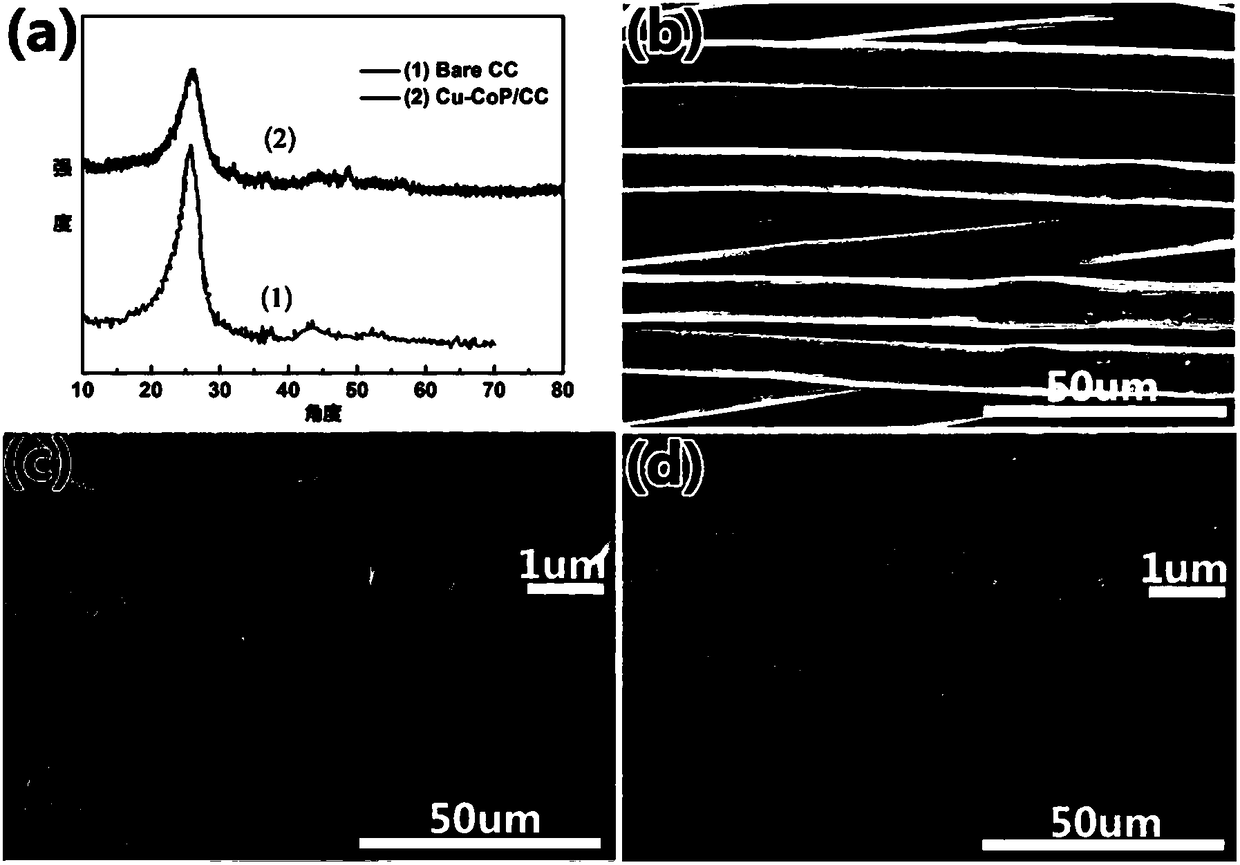
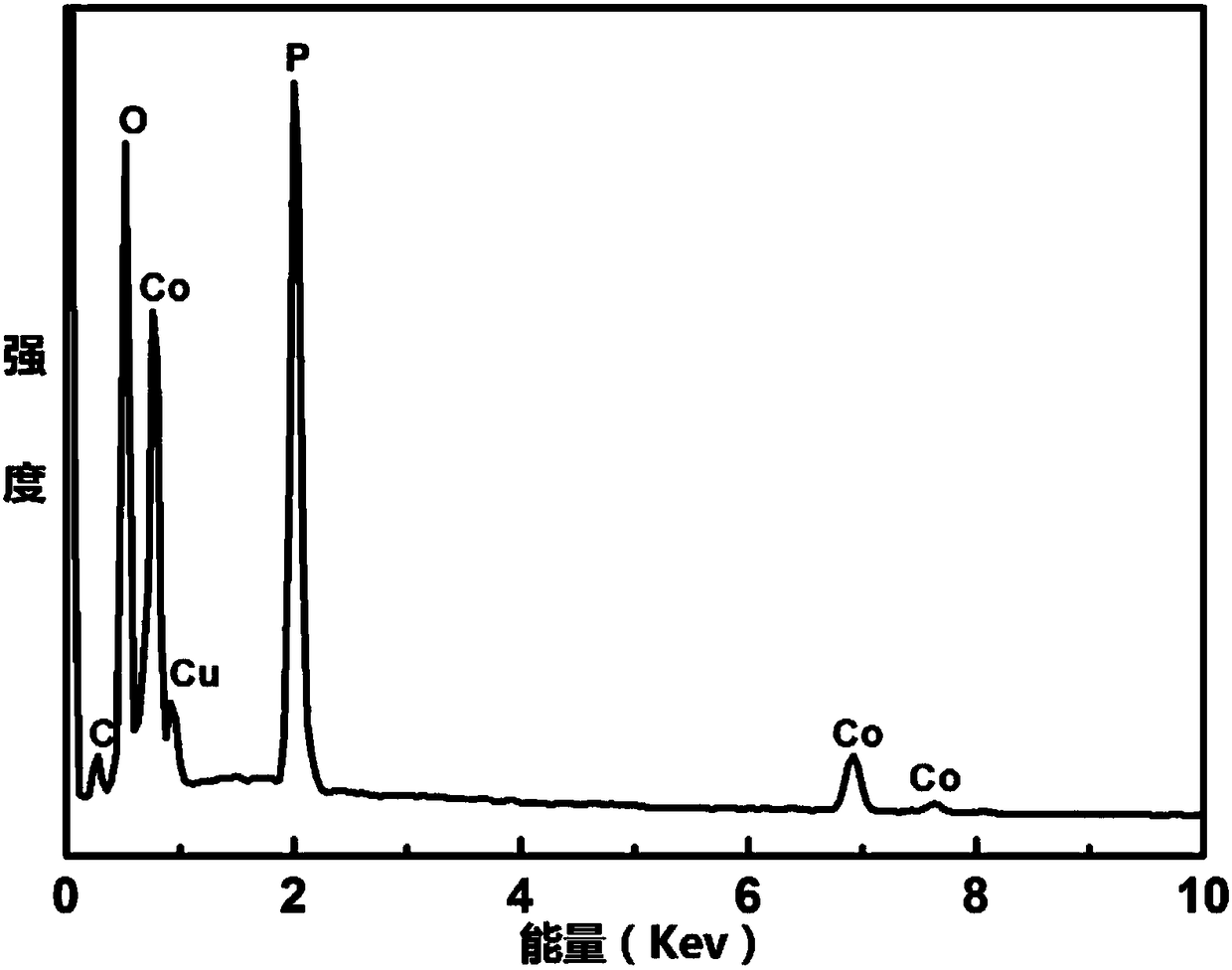
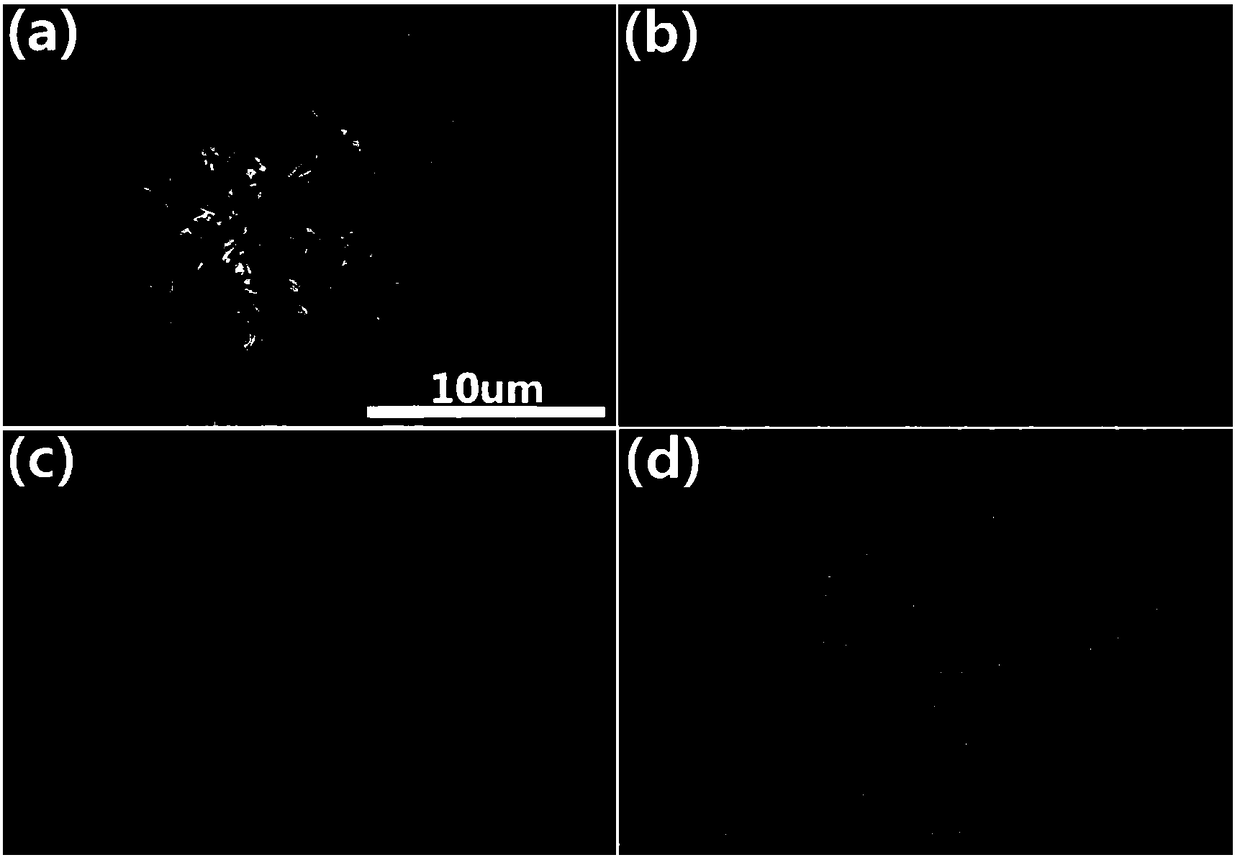
Ternary Cu-Co-P (copper-cobalt-phosphor) nanorod as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108325544ALow costSimple preparation processPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesUreaHydrotalcite
The invention discloses a ternary Cu-Co-P (copper-cobalt-phosphor) nanorod as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of mixing copper nitrate, cobalt nitrate, urea and ammonia fluoride in water, so as to prepare a precursor mixed solution; placing a substrate into the precursor mixed solution, reacting for 480 to 600min in a high-pressure kettle at the temperature of 100 to 120 DEG C, and preparing a CuCo-LDH (hydrotalcite) nanorod on the substrate; placing the dried substrate and the CuCo-LDH nanorod into a ceramic boat withsodium hypophosphite; transferring into a tubular furnace, and heating for 0.5 to 2h at the temperature of 300 to 350 DEG C, so as to obtain the ternary Cu-Co-P nanorod. The ternary Cu-Co-P nanorod can be directly used as a working electrode for electrochemically decomposing water. The ternary Cu-Co-P nanorod has the advantages that compared with the existing transition metal phosphide, the waterhydrolyzing catalyzing cavity is higher in the pH (potential of hydrogen) electrolytes; the cost is low, the preparation technology is simple, the environment-friendly and non-pollution effects are realized, and the ternary Cu-Co-P nanorod is suitable for large-scale industrialized production.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
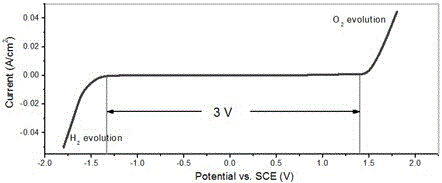
A high working voltage super capacitor and its making method
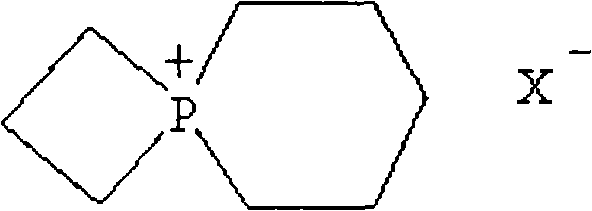
InactiveCN101261899AIncrease working voltageImprove power densityHybrid capacitor electrolytesHybrid capacitor electrodesHigh energySupercapacitor
The invention provides a high-working voltage super capacitor and the manufacturing method, which include: a positive polarizing electrode and a negative polarizing electrode, a multihole isolating film and an electrolyte; the electrolyte is a high-working voltage electrolyte, the electrolyte salt can be ring quaternary alkylphosphonium salt and the solvent of the electrolyte can be ethylene carbonate (EC) or propylene carbonate (PC) and so on. The electrolyte concentration is 0.5-5.0 mol / L; the electrolyte has an electrochemical window of more than 4.6v. The invention adopts the high-working voltage super capacitor electrolyte which has a wider electrochemical window; the high-working voltage super capacitor made by utilizing the high electrochemical decomposition voltage can not only keep the characteristics of high power density and better cycle performance, but also have higher working voltage (3.0v-3.5v) and higher energy density.
Owner:SHANDONG SHENGONGHAITE ELECTRONICS TECH
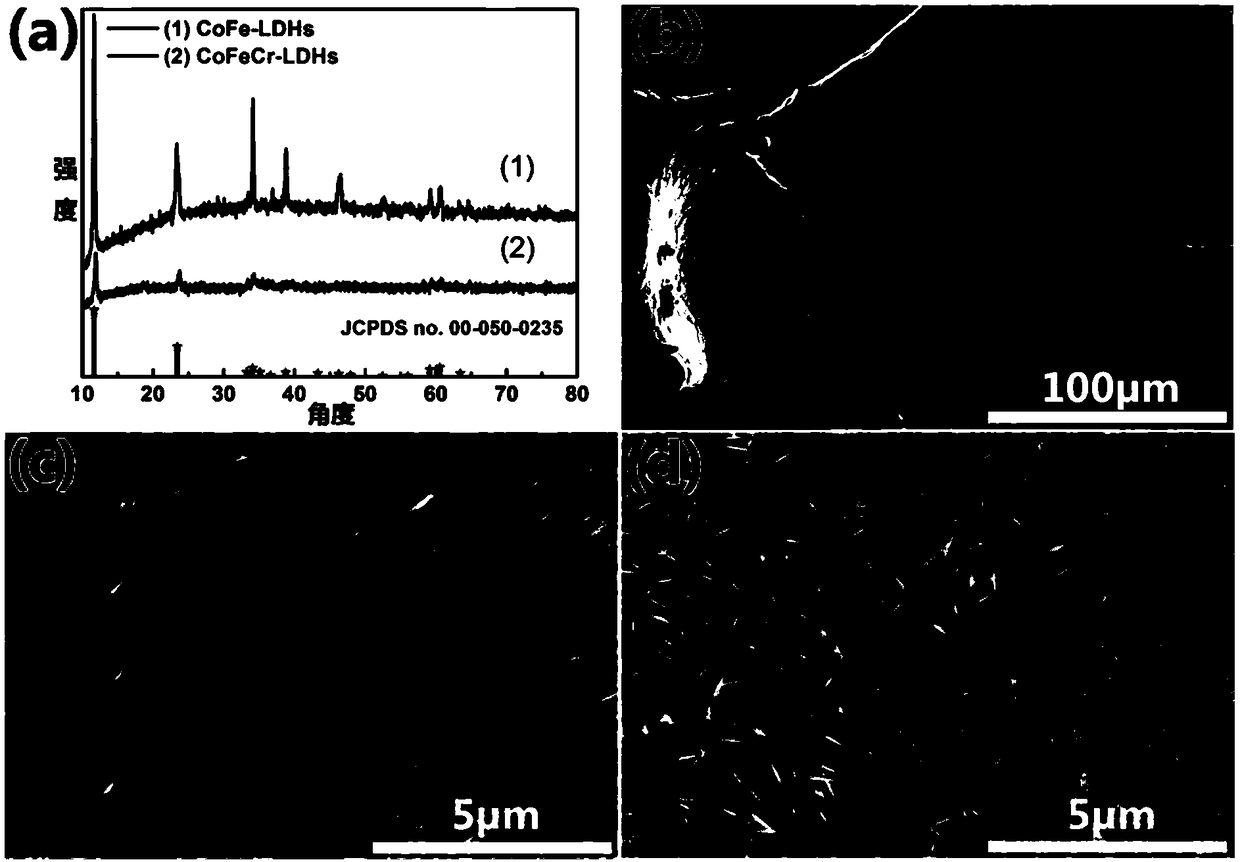
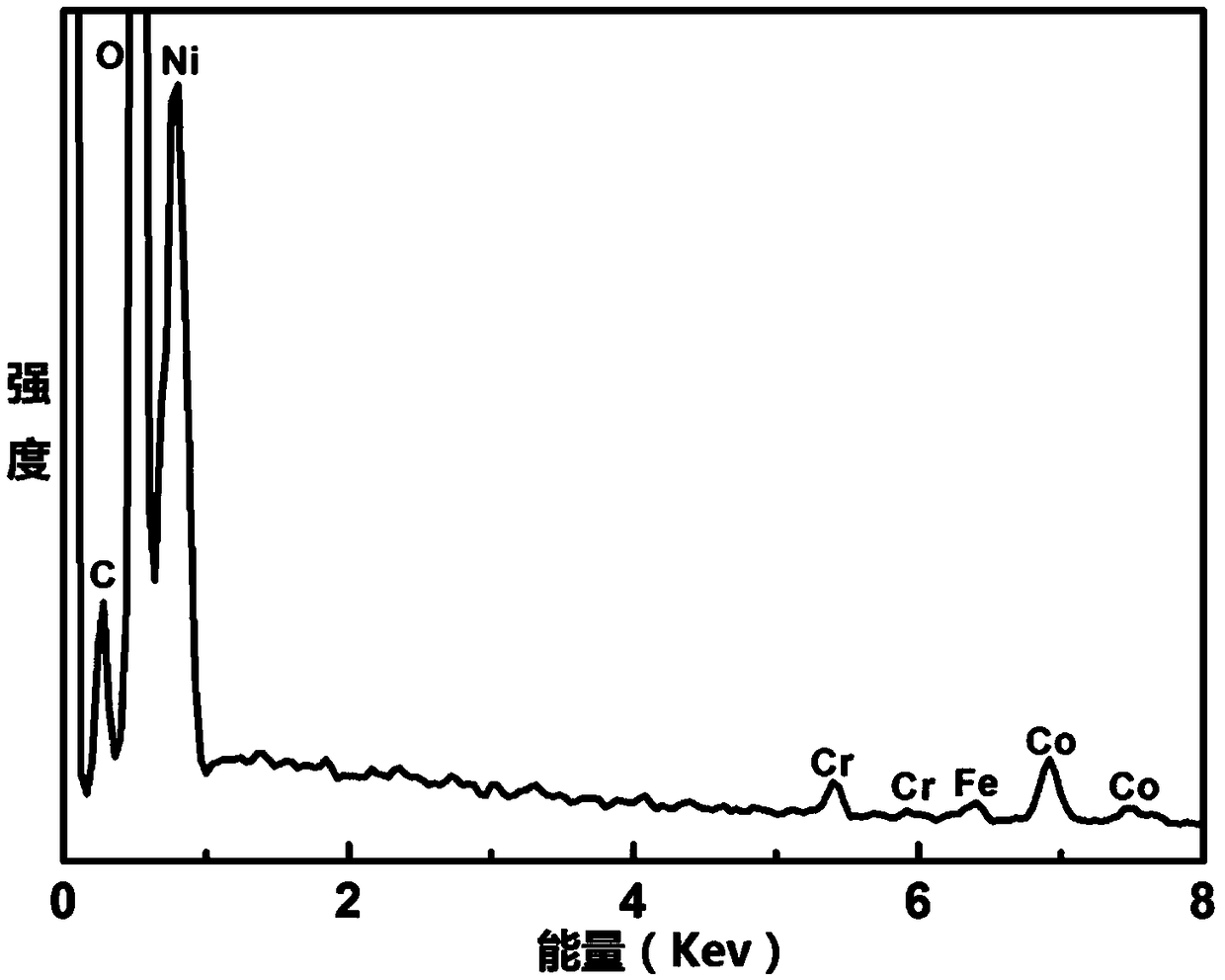
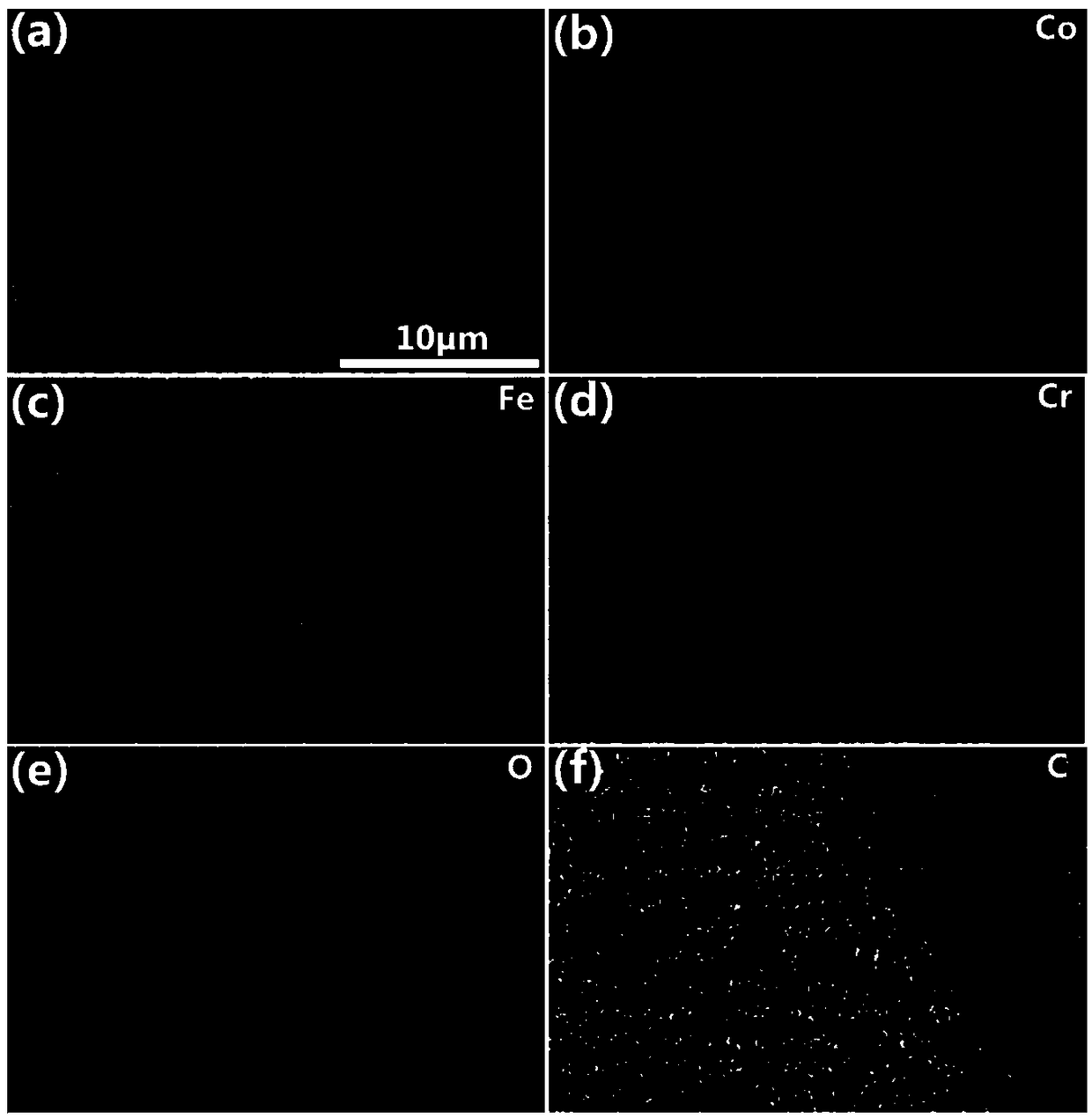
Ternary CoFeCr hydrotalcite nanorod and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108910962ALower overpotentialLow costNanotechnologyCobalt compoundsElectrolysisElectrochemical decomposition
The invention discloses a ternary CoFeCr hydrotalcite nanorod and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps: mixing cobalt nitrate, iron nitrate, chromium nitrate, urea and ammonium fluoride in water so as to prepare a precursor mixed solution, placing a substrate in the precursor mixed solution, transferring the substrate together with the precursormixed solution to an autoclave, and then performing a reacting at 110-130 DEG C for 360-600 minutes so as to prepare the ternary CoFeCr hydrotalcite nanorod on the substrate. The ternary CoFeCr hydrotalcite nanorod together with the substrate is directly used as a working electrode for electrochemical decomposition of water. Not only the ternary CoFeCr hydrotalcite nanorod has better performance of water electrolysis and oxygen evolution than transition metal oxide in the prior art, but also the preparation process is simple, fast and efficient, has low production energy consumption, low production cost, environmental protection and no pollution, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Negative electrode active material, method for producing the negative electrode active material, and lithium ion secondary battery using the negative electrode active material
InactiveUS20140017570A1Improve discharge performanceReduced initial irreversible capacityMaterial nanotechnologyNon-metal conductorsLithiumGraphite
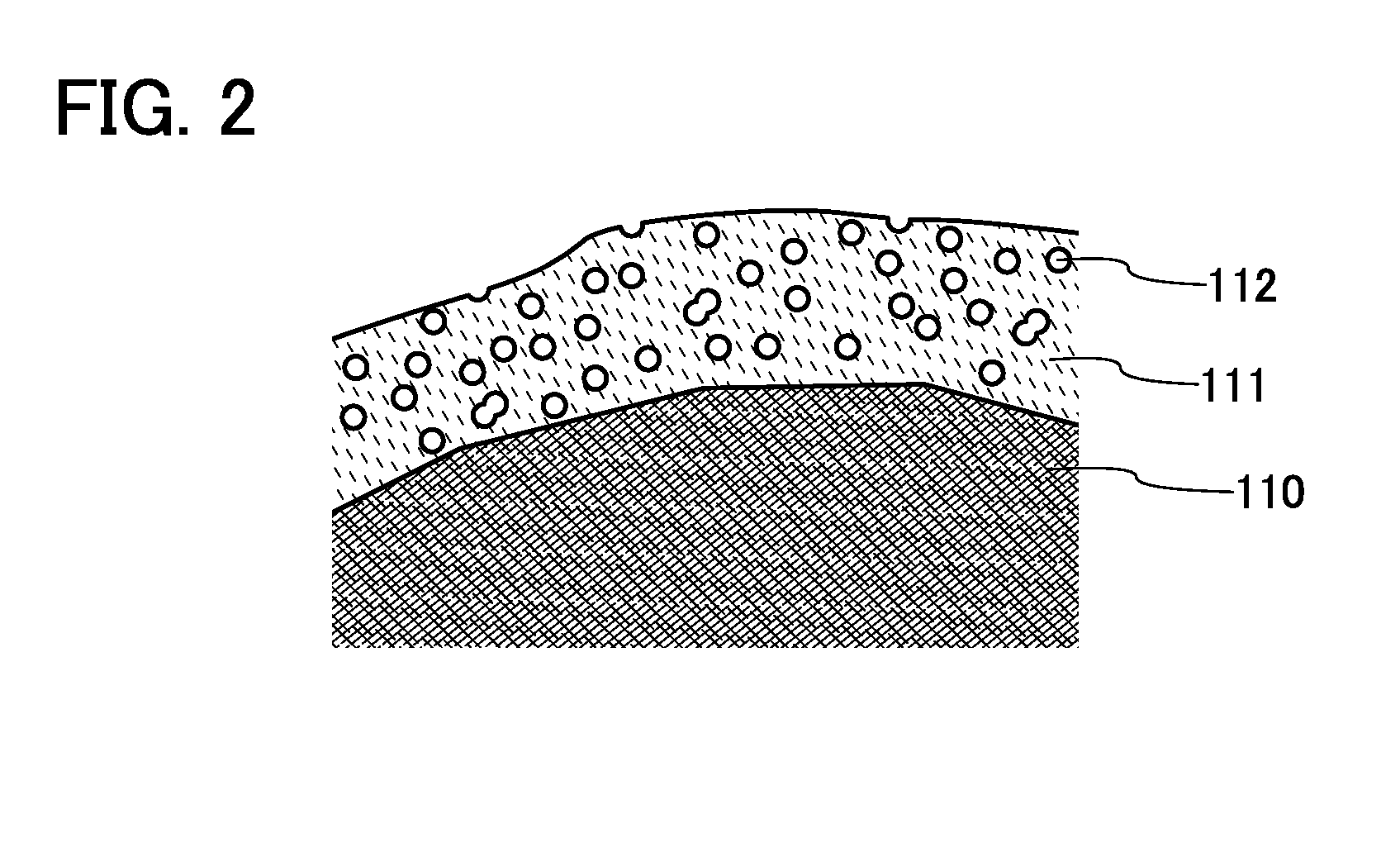
Disclosed is a negative electrode active material which is capable of occluding and releasing lithium, and has high reversible capacity and reduced initial irreversible capacity. This negative electrode active material includes a granulated substance, in which a composite containing nanosize conductive carbon powder and tin oxide powder contacting the surface of the conductive carbon powder in a highly dispersed state and an aggregate selected from the group consisting of graphite and nongraphitizable carbon are aggregated. The electrochemical decomposition of electrolytic solution is suppressed due to a reduction in the area where the carbon material in the granulated substance and the electrolytic solution are in contact, resulting in a significant reduction in the initial irreversible capacity of the negative electrode active material.
Owner:NIPPON CHIMI CON CORP
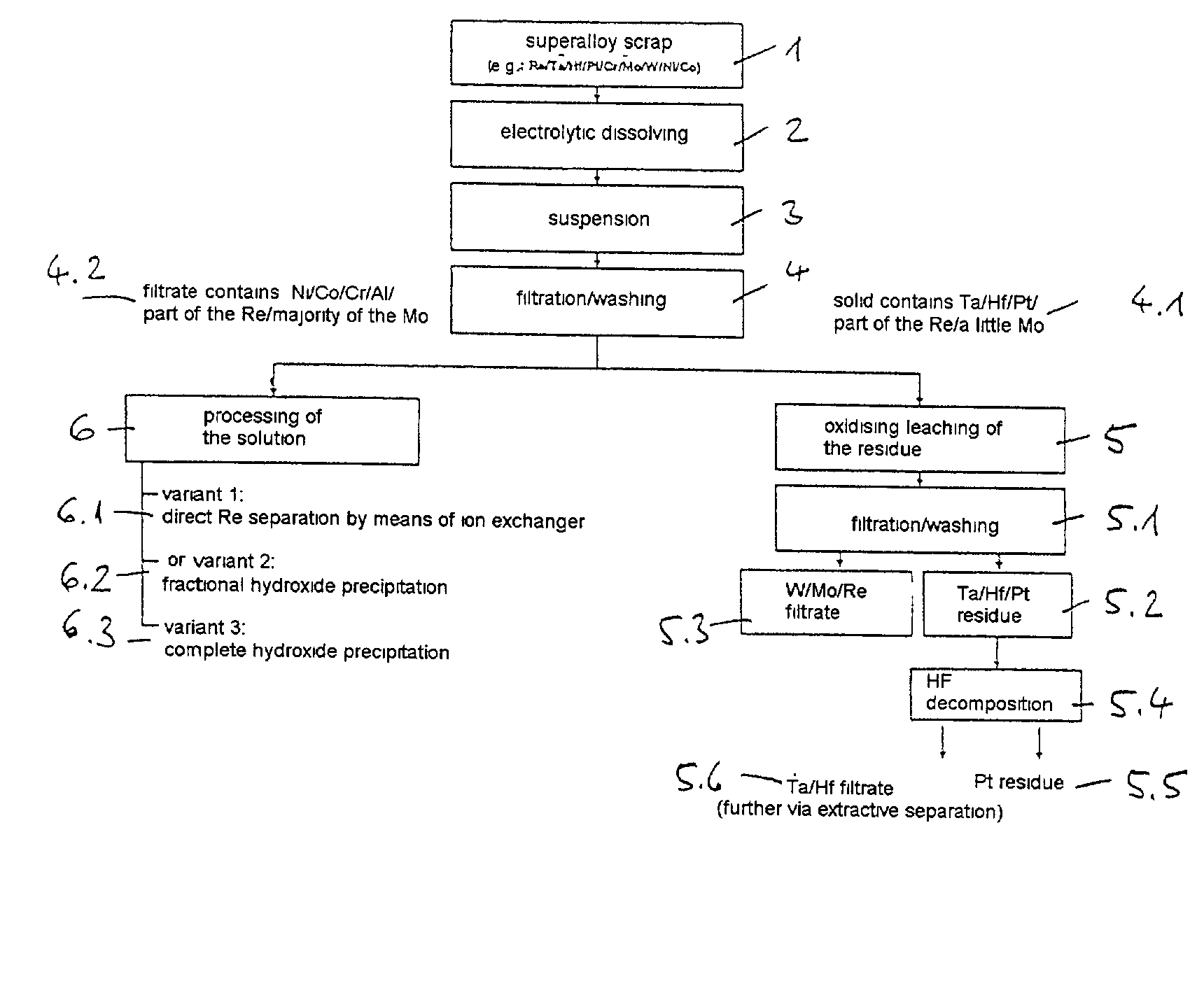
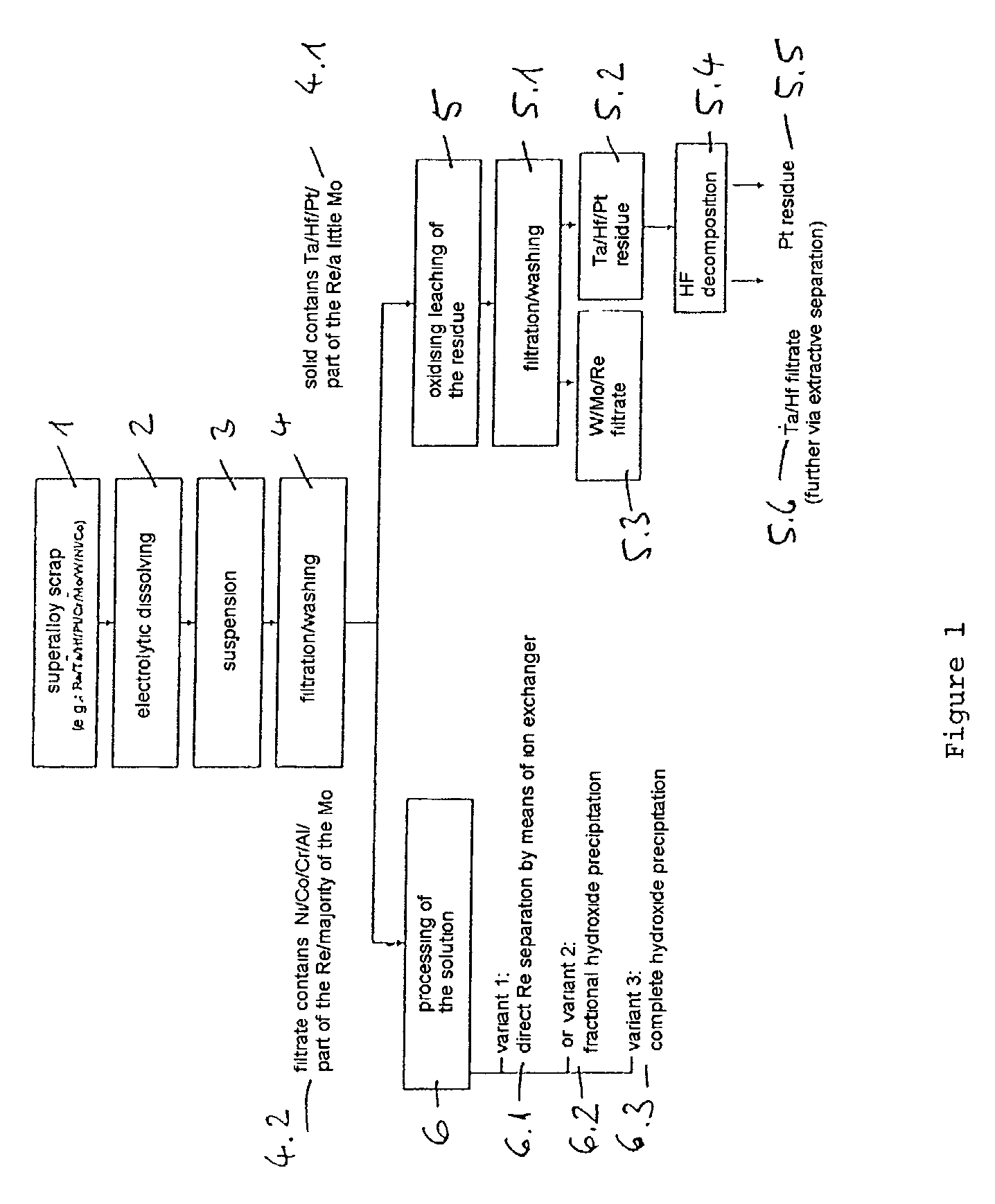
Process for electrochemical decomposition of superalloys
InactiveUS20030136685A1Polycrystalline material growthElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisElectrical polarity
A process for recovery of valuable metals from superalloys by electrochemical decomposition is described, both electrodes being formed by the superalloy and the polarity of the electrolysis current being reversed with a frequency of from 0.005 to 5 Hz.
Owner:H C STARCK GMBH
Manufacturing carbon-based combustibles by electrochemical decomposition of co2
InactiveUS20120055804A1Organic diaphragmsMultiple component coatingsPhysical chemistryElectrochemical decomposition
Provided is a method for the electrochemical conversion of carbon dioxide to fuels. The method employs reducing CO2 in an electrochemical cell using an aerogel carbon electrode and an ionic liquid membrane, thereby providing a carbon-based combustible.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
Preparation method and application of iron doped cobalt diselenide compound nitrogen doped carbon material
ActiveCN108374179ALower overpotentialImprove utilization efficiencyElectrodesCarbon fibersPorous carbon
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of an iron doped cobalt diselenide compound nitrogen doped carbon material. The method is characterized in that a metal organic framework ZIF-67 is used as the precursor, ferric ion is utilized to perform etching to obtain iron modified Fe-ZIF-67, selenium steam is used to perform carbonization and selenylation on the Fe-ZIF-67 to obtaina nitrogen doped porous carbon loaded iron doped cobalt diselenide (Fe-CoSe2@NC) powdered electrode material. The Fe-CoSe2@NC is prepared into slurry, and conductive carbon fiber paper is coated withthe slurry to obtain a Fe-CoSe2@NC / CFP electrode. The electrochemical catalysis hydrogen production performance indexes of the Fe-CoSe2@NC / CFP electrode include: the Tafel slope is 40.9mV / decade; overpotential for reach the current density of 10mA / cm<2> is -0.143V(vs RHE). Meanwhile, the assembled electrode is excellent in electrochemical stability and does not have evident voltage fluctuation ina 48-hour constant-current stability test. The synthesizing method of the compound electrode is simple, efficiency, green, environmentally friendly, low in raw material and synthesizing costs, suitable for industrial application using electrochemical water decomposition to produce hydrogen and extensive in scientific significance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
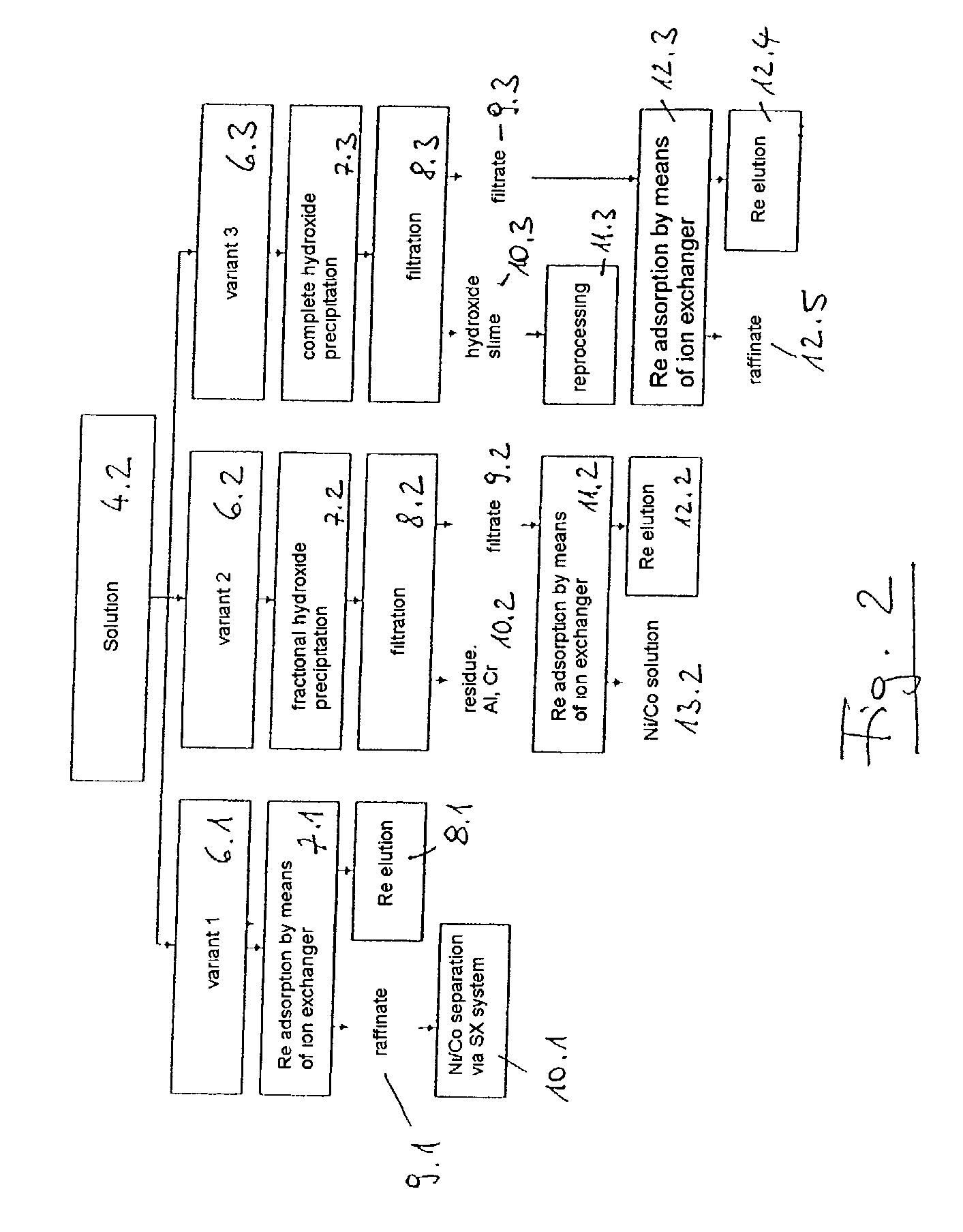
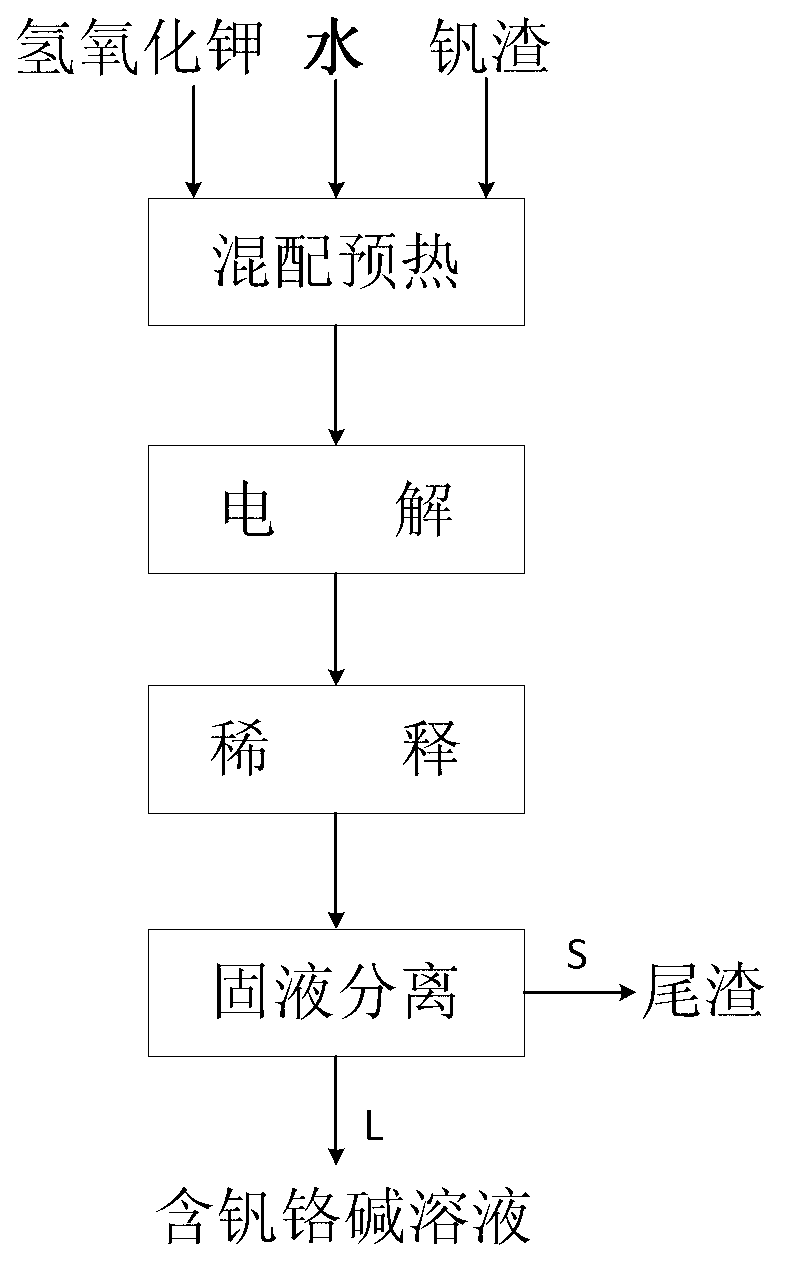
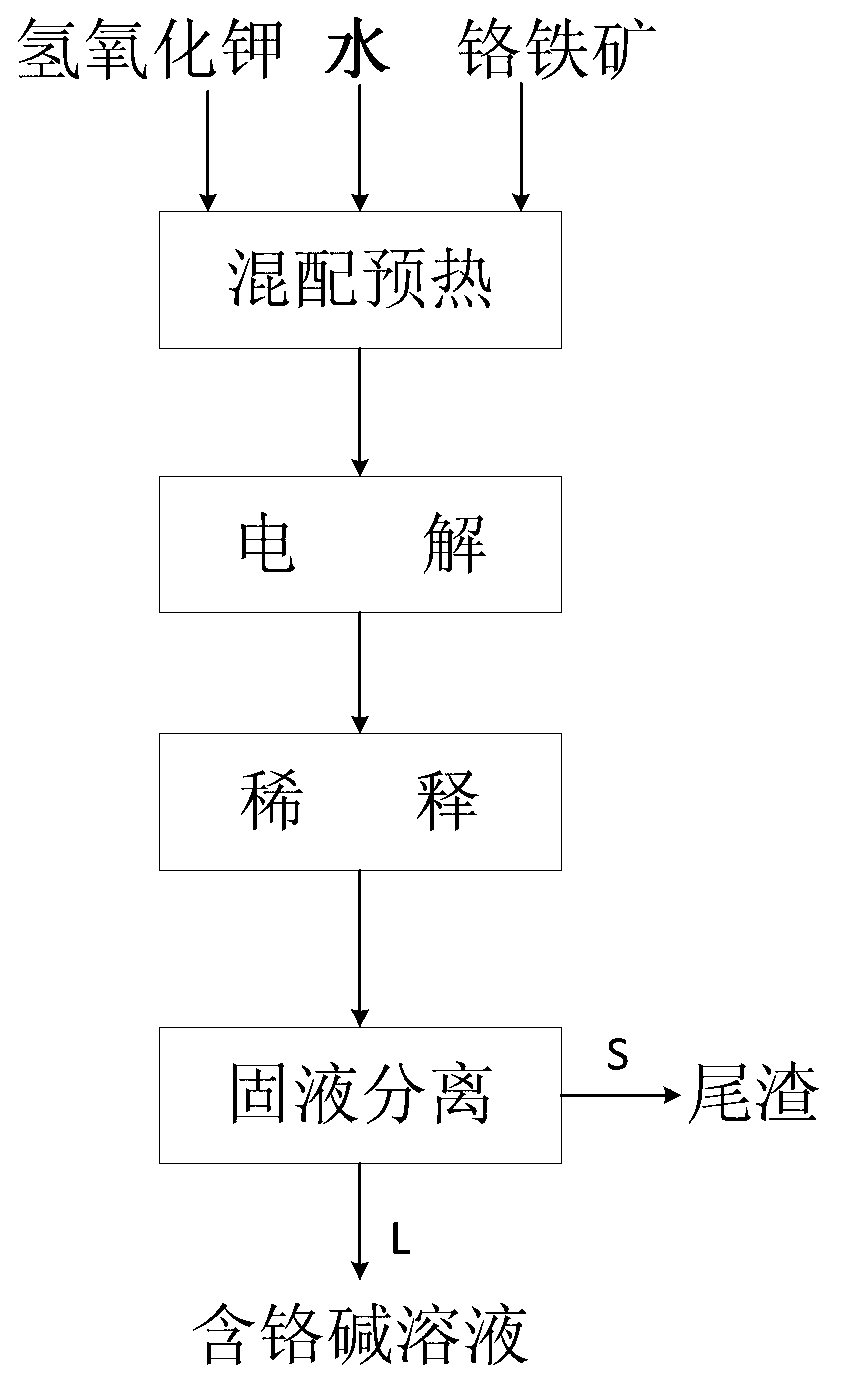
Method for synchronously extracting vanadium and chromium by electrochemically decomposing vanadium slag in potassium hydroxide solution
ActiveCN103060843AReduce concentrationEfficient extractionPhotography auxillary processesRecovering materialsSlagPotassium hydroxide
The invention relates to a method for synchronously extracting vanadium and chromium by electrochemically decomposing vanadium slag in a potassium hydroxide solution. The method comprises the steps as follows: introducing oxidizing gas into mixed slurry containing the vanadium slag, potassium hydroxide and water; carrying out electrochemical oxidization reaction; and after the reaction, carrying out solid-liquid separation on the mixed slurry to obtain tailings and a vanadium and chromium alkali solution. The method is low in cost, high in extraction efficiency, pollution-free and moderate in process conditions, and can be used for efficiently and synchronously extracting vanadium and chromium; the vanadium extraction rate can reach 85-99%; and the chromium extraction rate can reach 80-95%.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
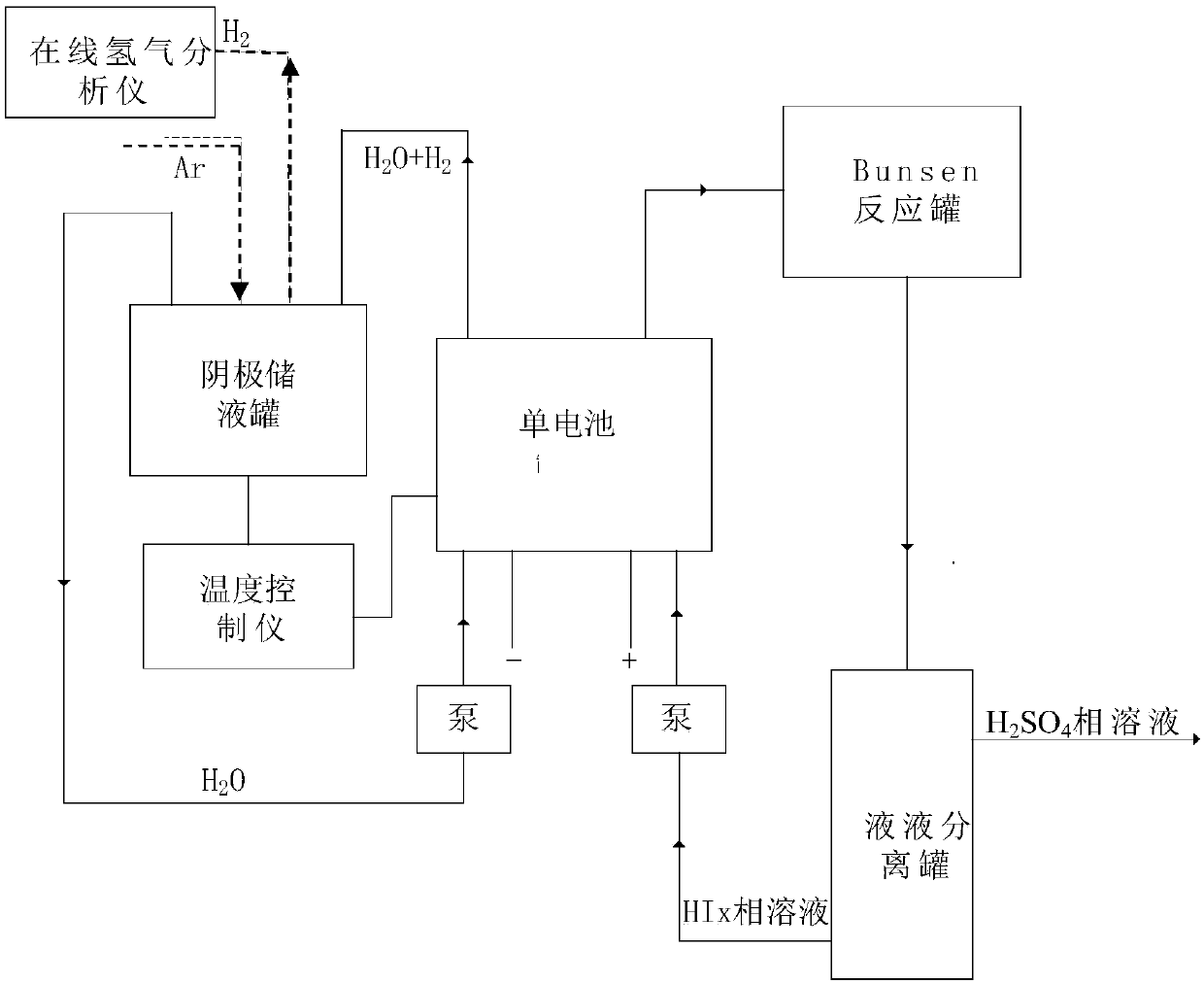
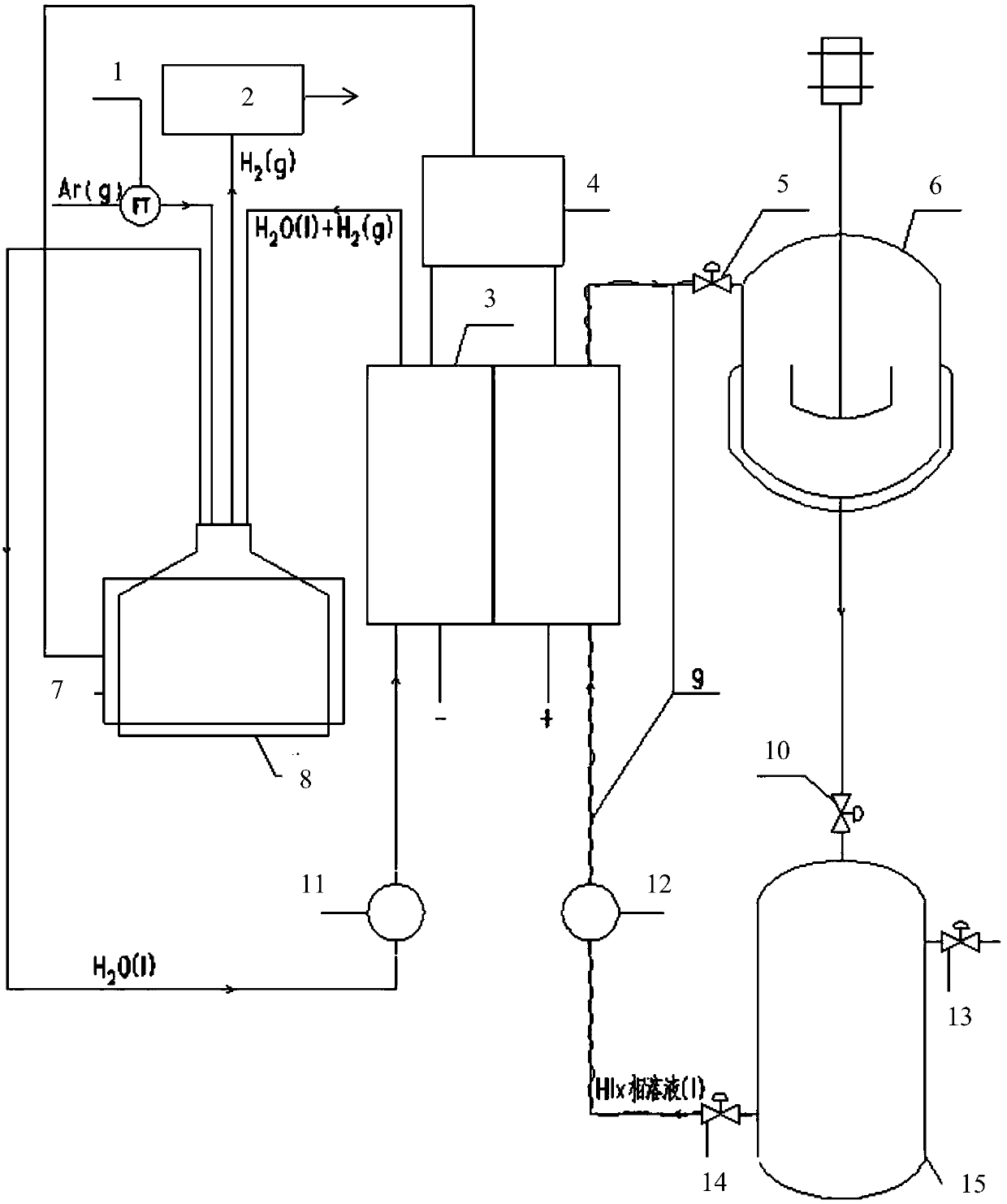
Hydrogen production method adopting electrochemistry to disintegrate HI in sulphur and iodine circulation hydrogen production and device
ActiveCN107904617AOmit enrichmentEliminate the distillation processCellsDiaphragmsElectrolysisDistillation
The invention relates to the technology of sulphur and iodine circulation hydrogen production, and particularly provides a hydrogen production method adopting electrochemistry to disintegrate HI in sulphur and iodine circulation hydrogen production and a device. The method includes the steps that a monocell is used as a reactor, the monocell has anode graphite electrode and cathode graphite electrode, and a proton exchange membrane is used as a diaphragm; HIx homogeneous solution in the sulphur and iodine circulation hydrogen production system is injected into the anode side, and deionized water is injected into the cathode side; power supply is turned on to carry out decomposition reaction, I- of the anode side HIx homogeneous solution is oxidized to I2, and generated H+ passes through proton exchange membrane to reach the cathode side and is reduced to hydrogen; HIx homogeneous solution of the anode side enters a Bunsen reactor to be Bunsen reaction raw material in a circulating modeafter electrolytic reaction, and hydrogen generated from cathode side is sent out. According to the hydrogen production method adopting electrochemistry to disintegrate HI in sulphur and iodine circulation hydrogen production, an HIx solution is directly decomposed adopting electrochemistry method, the original process of concentration and distillation is omitted, and the process and the device are greatly simplified. Hydrogen is generated from cathode, and the separation problem with HI gas does not need to be considered.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Transition metal based catalyst electrode of honeycomb macroporous structure as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107008461AHigh catalytic efficiencyAvoid reunionPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrolysis componentsMicrospherePolystyrene
The invention relates to a transition metal based catalyst electrode of a honeycomb macroporous structure as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: S1, synthesizing a polystyrene sub-microsphere aqueous solution; S2, preparing a transition metal salt solution, mixing the transition metal salt solution and the polystyrene sub-microsphere aqueous solution to obtain a mixed solution, spraying the mixed solution onto a conductive substrate for forming a film, and calcining at a high temperature so as to obtain an oxide film with a honeycomb macroporous structure; and S3, performing sulfidizing or selenizing or phosphating treatment on the oxide film at the high temperature in an inert atmosphere, thereby obtaining the transition metal based catalyst electrode of the honeycomb macroporous structure. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the operation is simple, the macroporous structure of the catalyst is easily maintained, the reproducibility is high, and a large-area electrode is conveniently prepared. Moreover, the catalyst electrode prepared by the invention has high specific surface area and capable of exposing more active sites and can be applied to dye-sensitized solar cells, electrochemical decomposition of water and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Power storage device electrode, method for manufacturing the same, power storage device, and electronic device
InactiveUS20150111101A1Increase powerReduce and inhibit reactionFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsEngineeringElectrochemical decomposition
To provide a highly reliable power storage device. To provide a long-life power storage device. To provide a power storage device electrode having high adhesion with a current collector. To reduce or inhibit electrochemical decomposition of an electrolytic solution or the like on a surface of an electrode. The power storage device electrode includes a current collector and a second electrode layer provided over the current collector and including a second binder and an active material. A first electrode layer including a first binder and conductive particles is provided between the current collector and the second electrode layer. At least part of a surface of the active material is provided with a coating film, and the coating film is porous.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
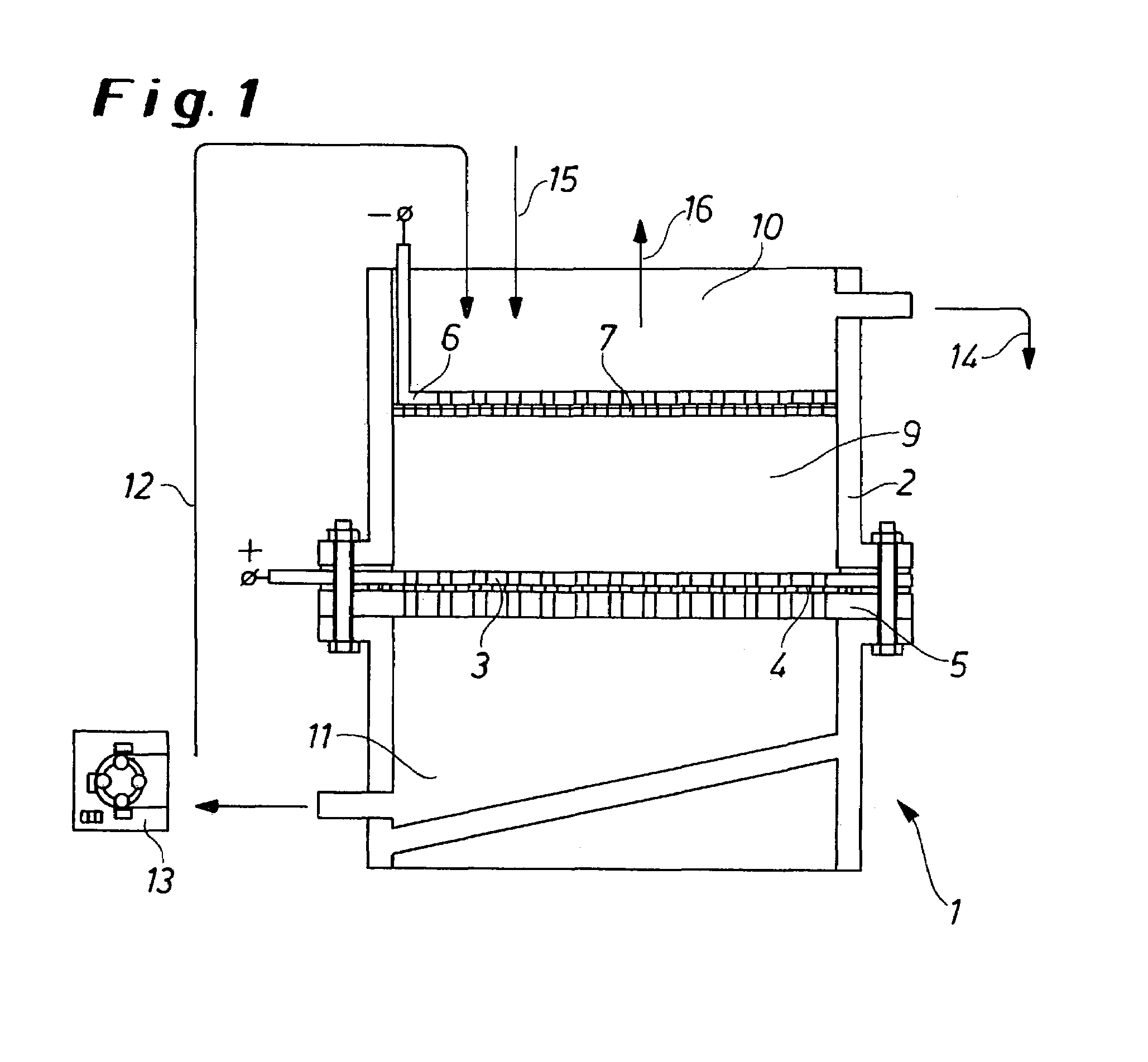
Process for the electrochemical decomposition of powders and electrolysis cells suitable therefor
InactiveUS7144493B2From normal temperature solutionsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisElectrochemical decomposition
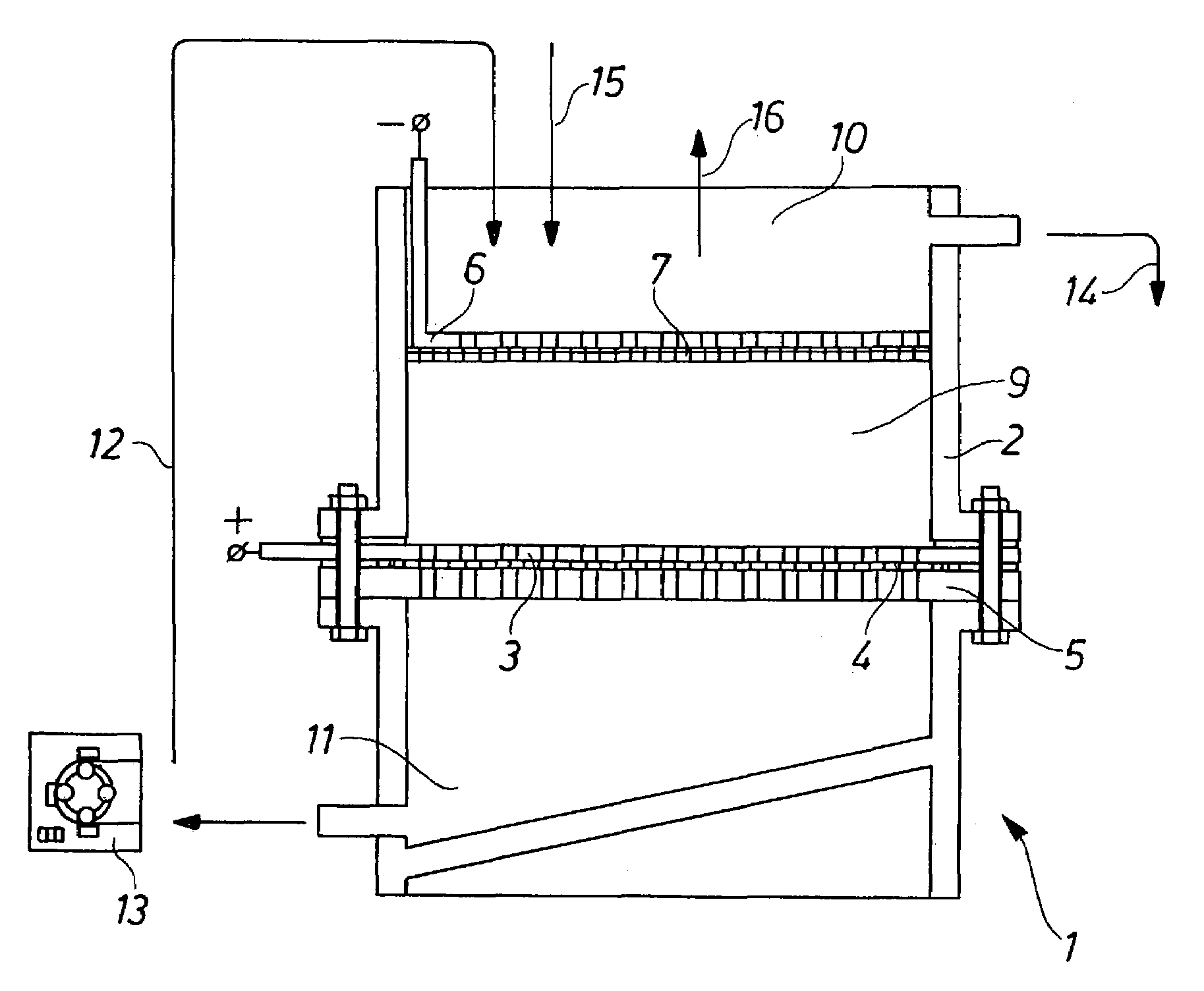
Process for the electrochemical decomposition of precursors in powder form by introducing a powder batch between two electrodes of an electrolysis cell, electrodes being designed to be liquid-permeable, and the electrolyte flowing through the powder batch perpendicularly to the electrode surfaces, and electrolysis cell suitable therefor, which is essentially characterized in that at least one electrode has a structure which consists of a supporting pierced plate (5), an electrode plate (3) provided with perforations, and a filter cloth (4) arranged between the supporting pierced plate (5) and the electrode plate (3), and in that the cathode (6) is shielded from the cell by means of a liquid-permeable separator (7).
Owner:H C STARCK GMBH
Method for extracting chromium by electrochemically decomposing chromite in potassium hydroxide solution
InactiveCN103060838ASubsequent separation is simpleLow reaction temperatureElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic productionPotassium hydroxideSlurry
The invention relates to a method for extracting chromium by electrochemically decomposing chromite in a potassium hydroxide solution. The method comprises the steps as follows: filling oxidizing gas into mixed slurry containing chromite, potassium hydroxide and water; carrying out electrochemical oxidization reaction; and after the reaction, carrying out solid-liquid separation on the mixed slurry to obtain tailings and a chromium alkali solution. The method is low in cost, high in extraction efficiency, pollution-free and moderate in process conditions, and the chromium extraction rate can reach more than 95%.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
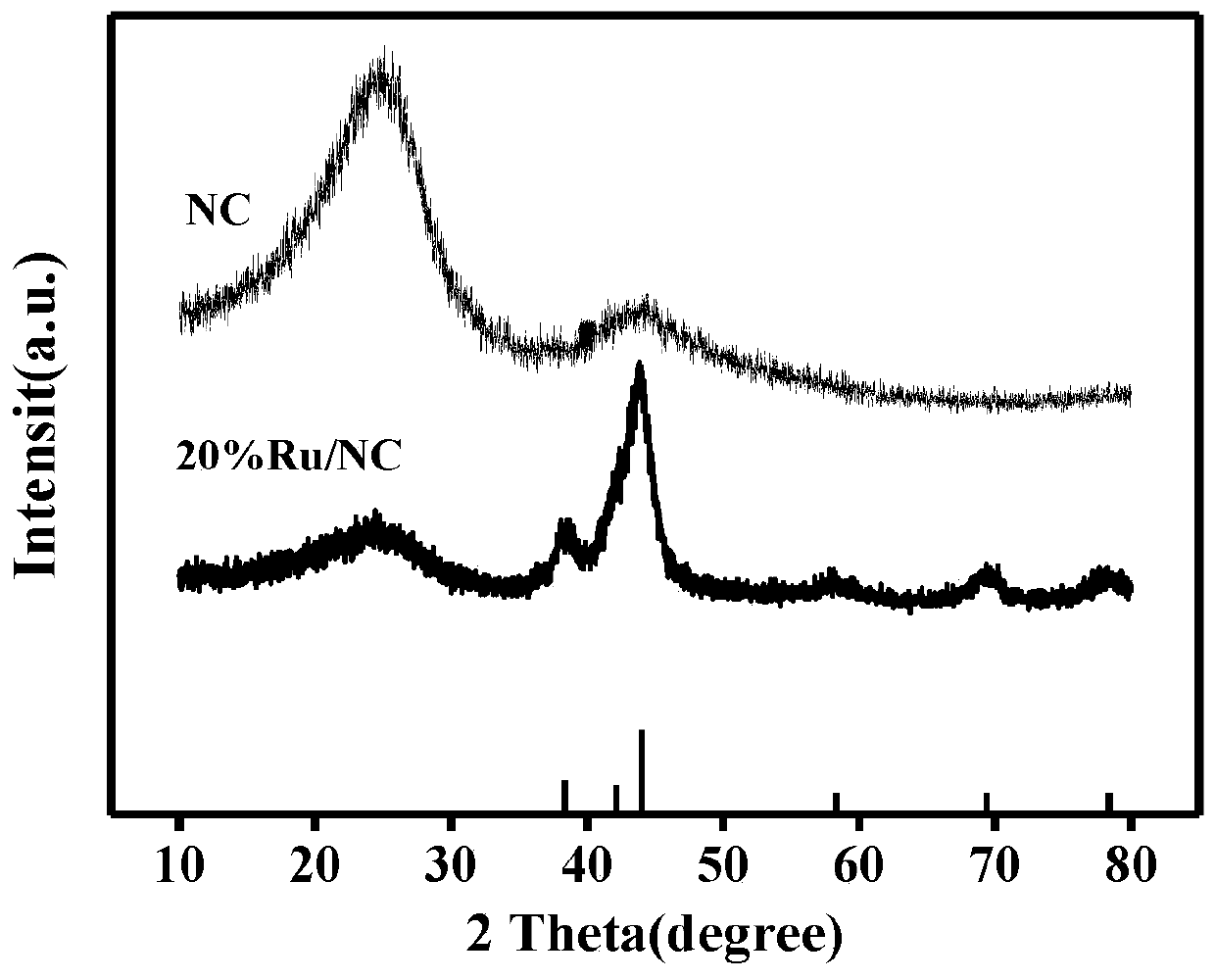
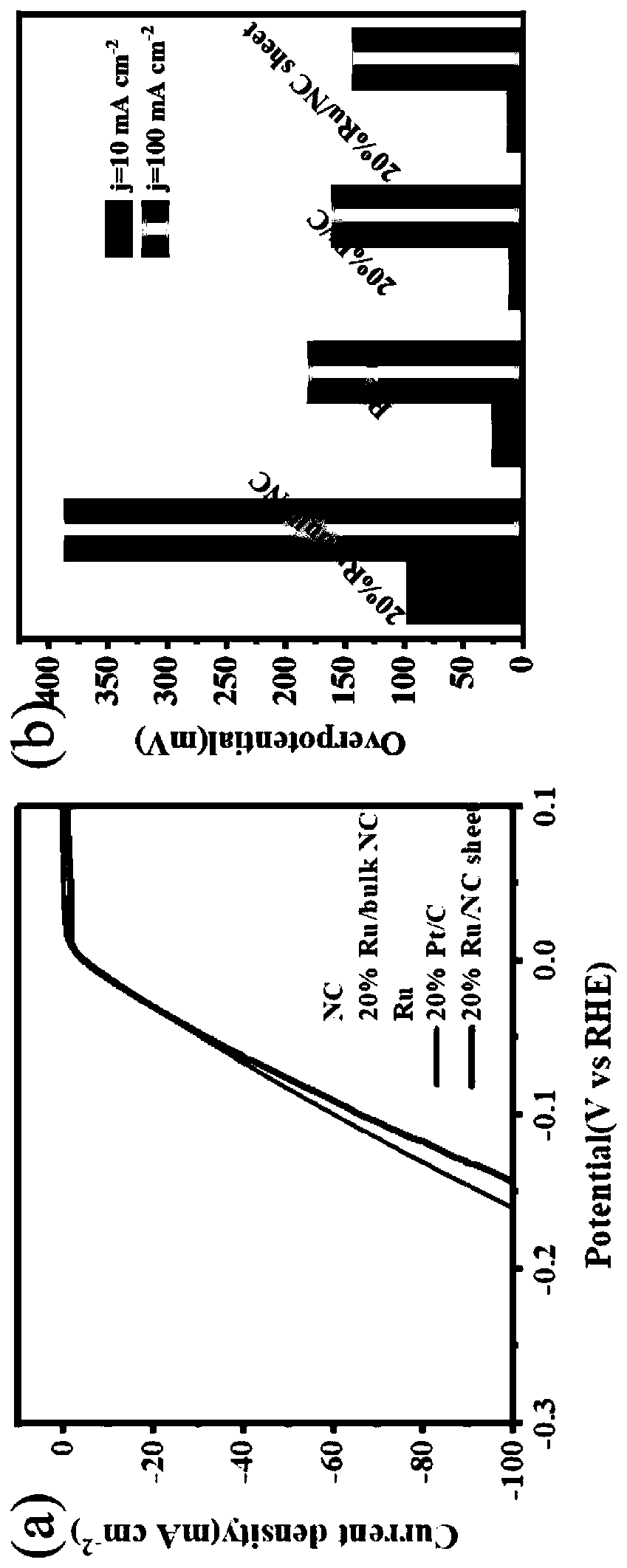
Carbon-based composite electrocatalyst, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN110813350ASimple stepsShort reaction timePhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesPtru catalystElectrochemical decomposition
The invention belongs to the field of electrocatalysts, and particularly relates to a preparation method and applications of a high-performance carbon-based composite catalyst for producing hydrogen by electrochemically decomposing water, wherein the Ru / NC electrocatalyst is obtained by using nitrogen-doped carbon (NC) synthesized through complexing, calcining and acid washing as a substrate material and using ethylene glycol as a reducing agent under a reflux condition. According to the invention, the electrocatalyst material has low charge transfer resistance and reaction barrier of hydrogenevolution reaction, and has excellent performance in electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reactions; Ru has the lowest price in Pt series precious metal materials, so that the catalyst is low in cost;and the obtained catalyst is simple and convenient in experimental operation, simple in process and excellent in catalytic performance, and provides the basic application research for the materials in the field of electro-catalysis.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com