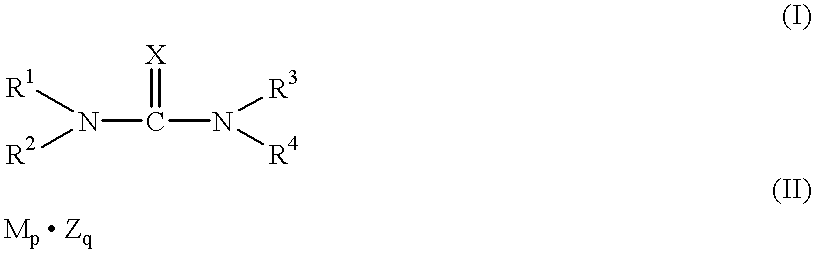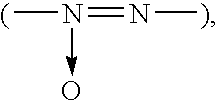Patents
Literature
874results about "Deferred-action cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
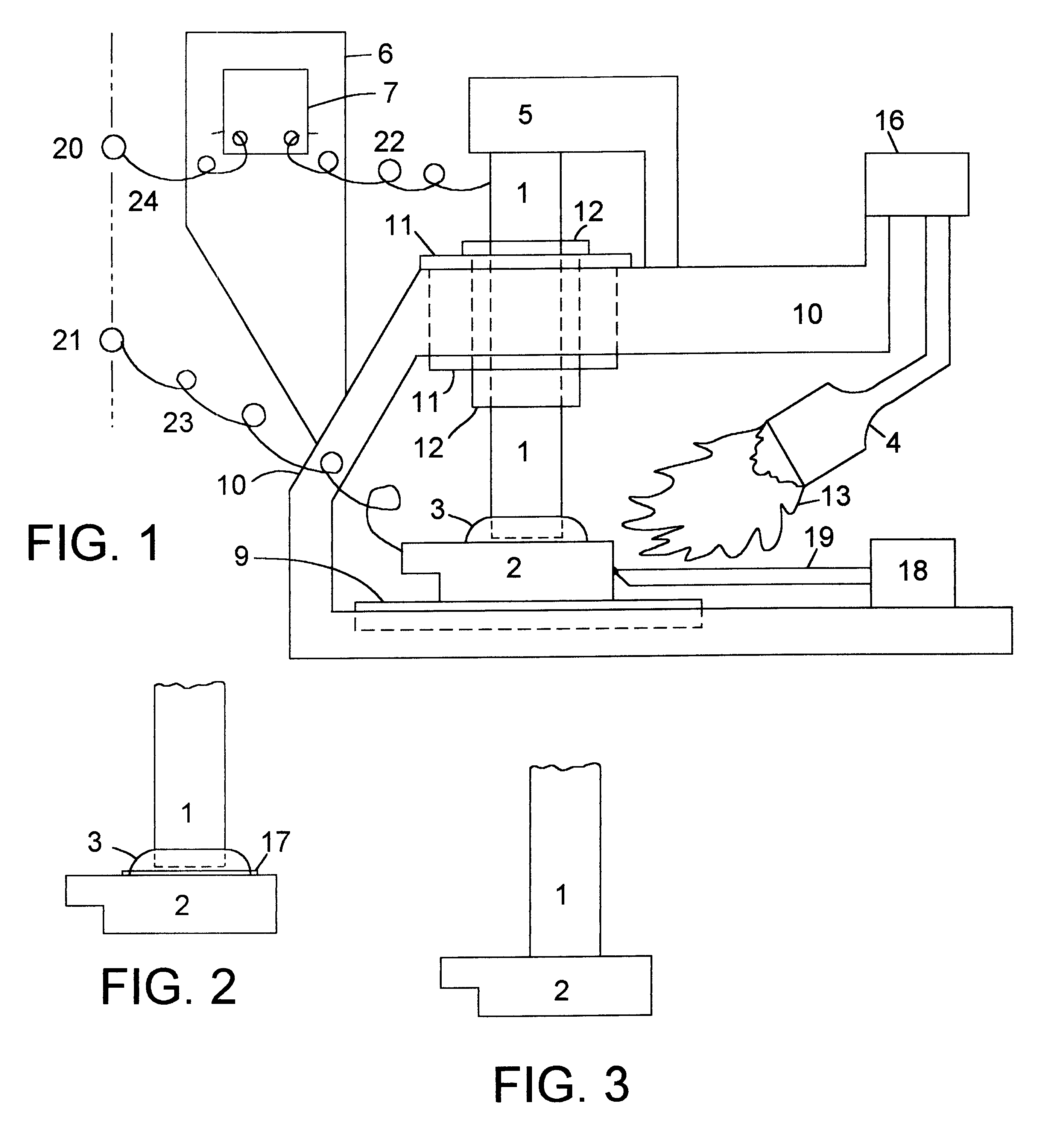
Devices for testing fluid
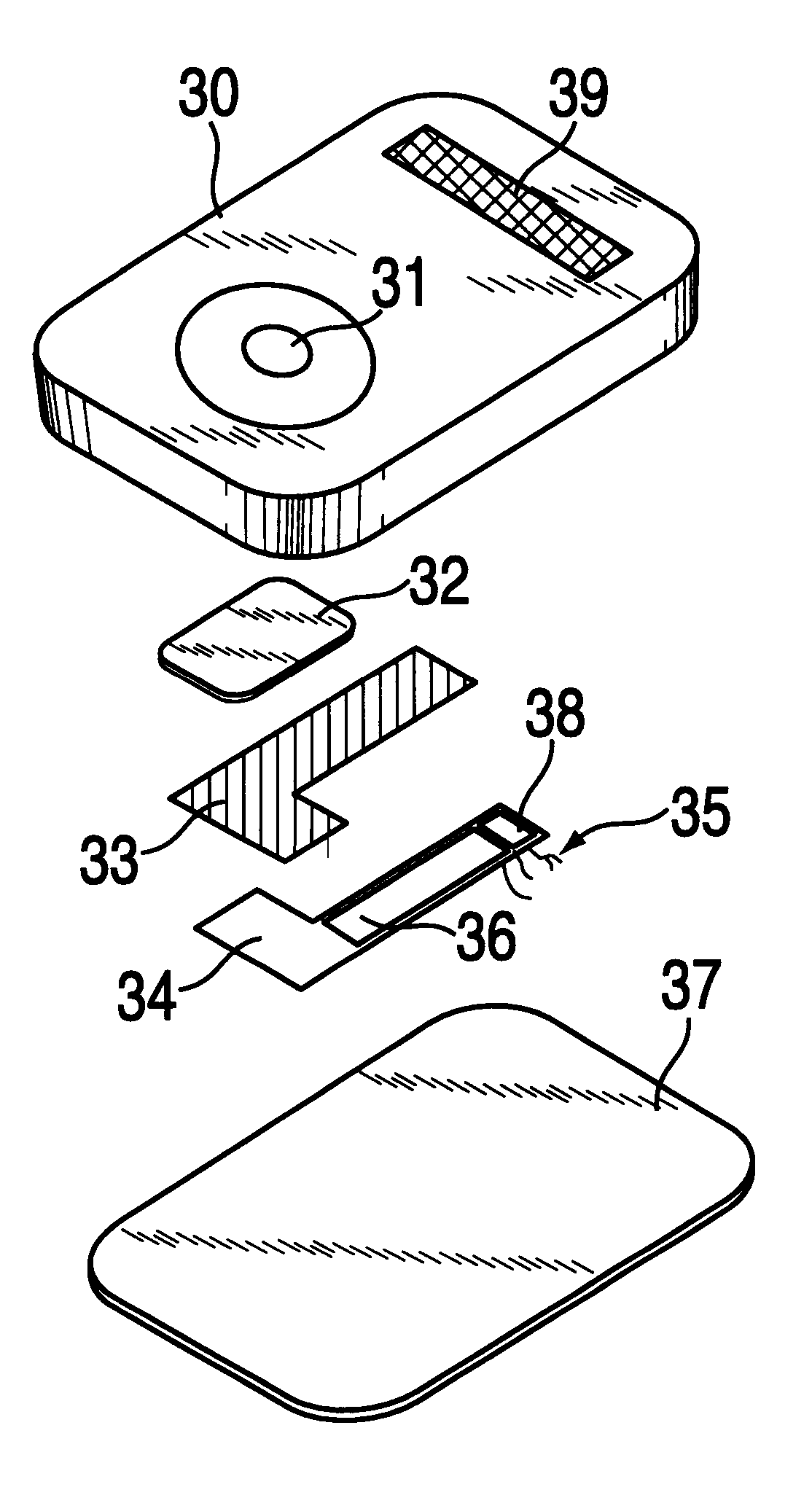
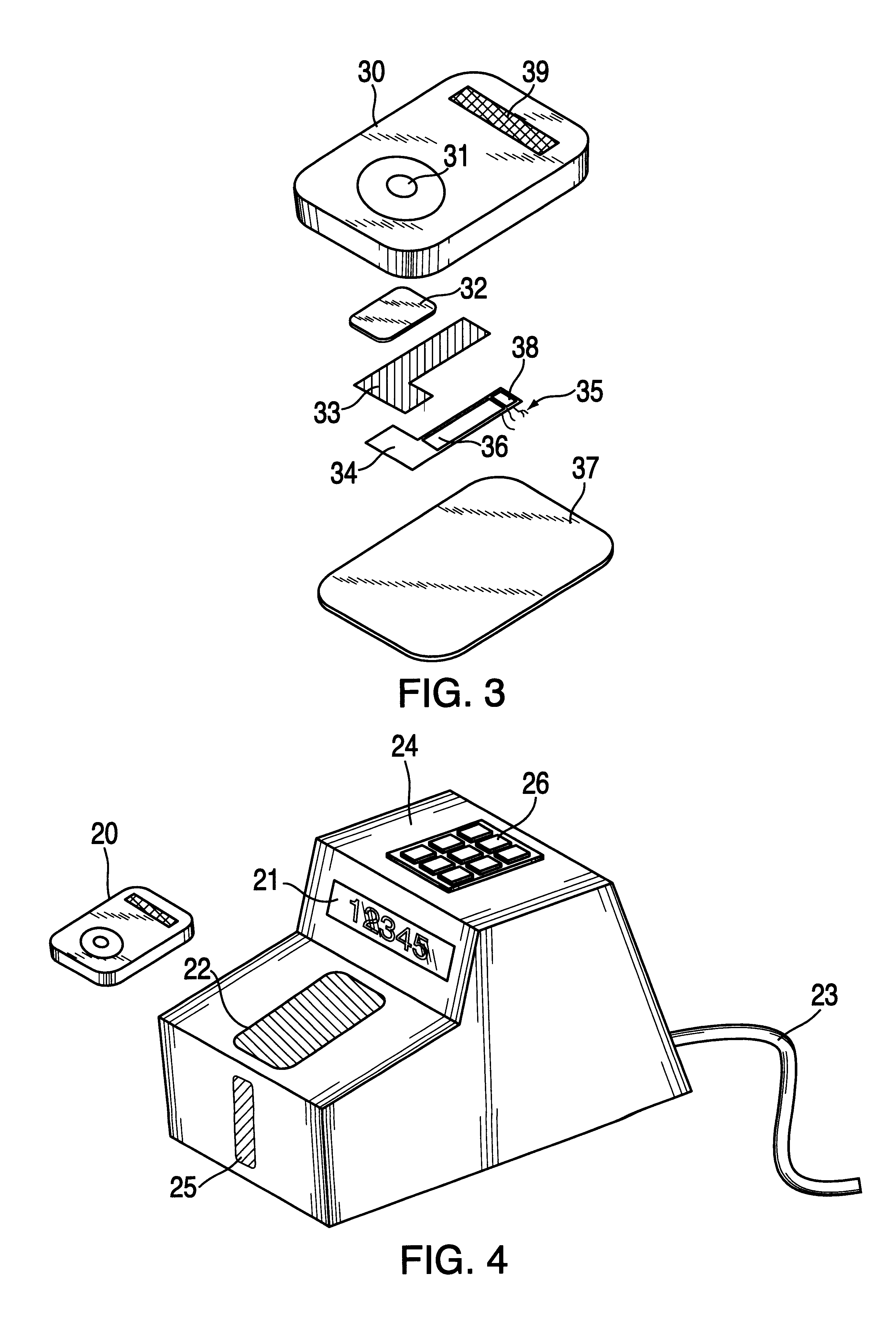
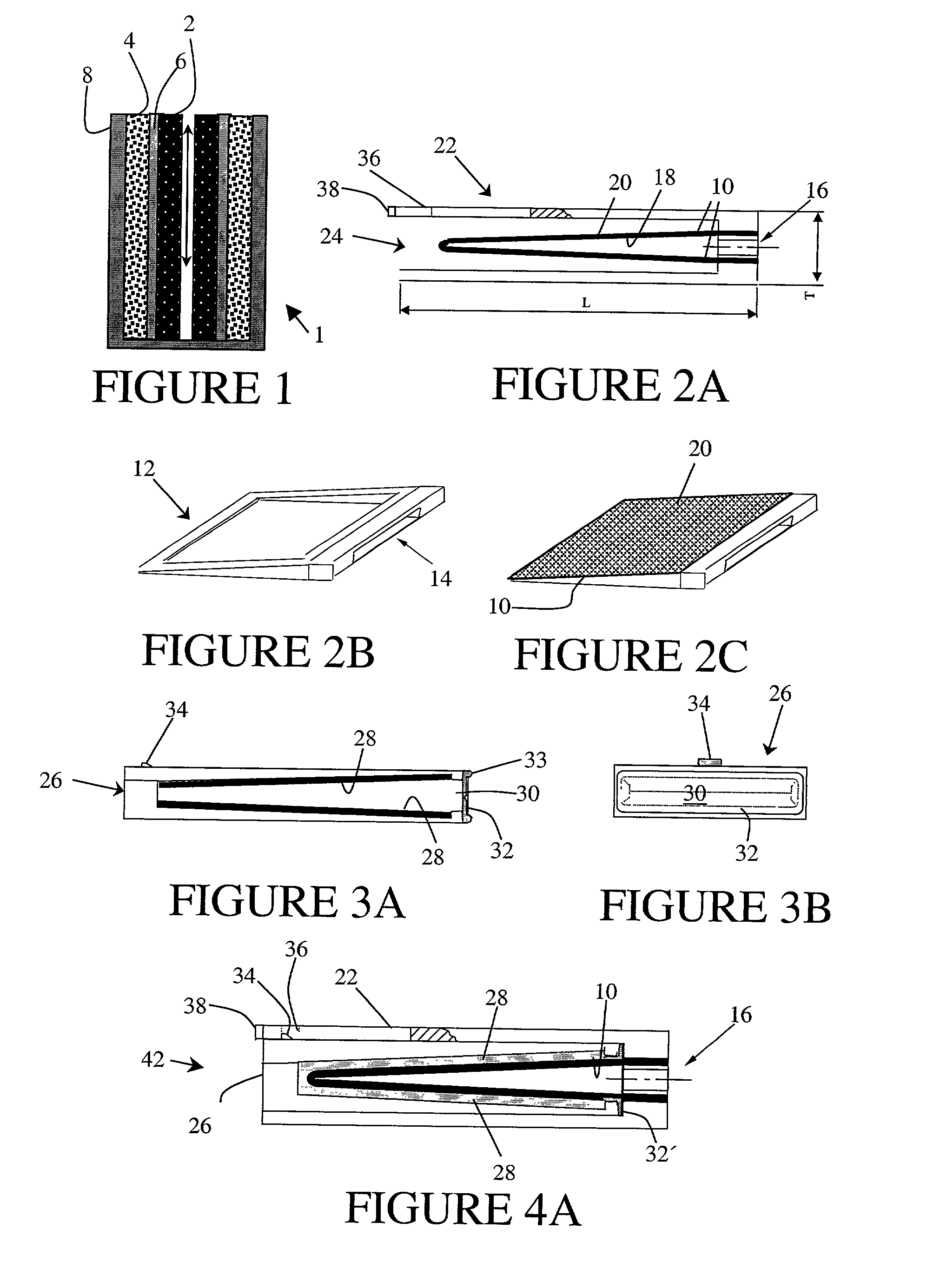
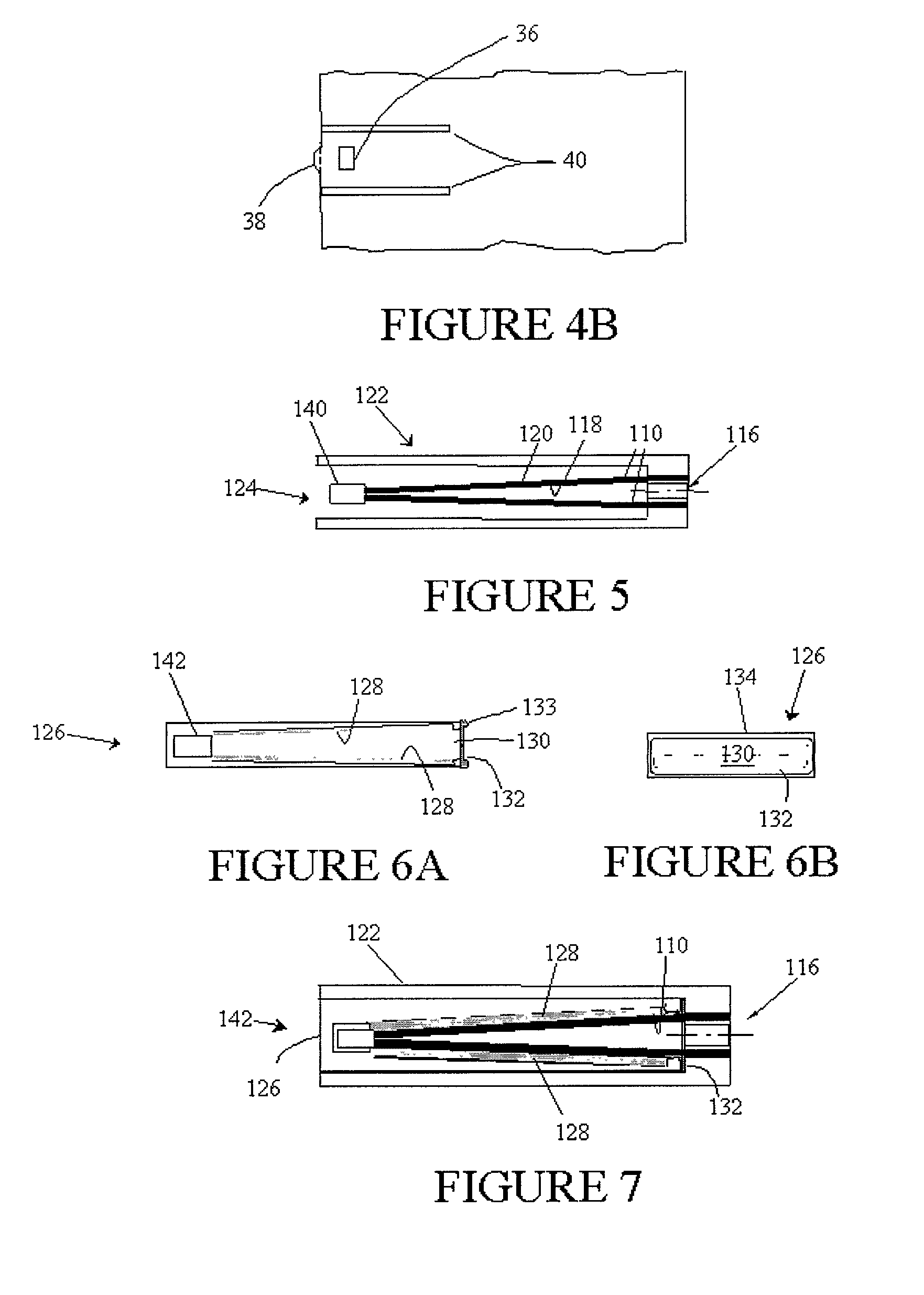
An improvement is described to disposable devices for performing chemical or biological tests on a sample of fluid, and the method by which such devices perform tests. The power for the device comes from an electrochemical battery, where a portion of the fluid sample itself provides the electrolyte for the battery. Furthermore, the time of diffusion of the fluid into the battery provides the timing signal for activation of the system. Communication between the improved device and an information system is provided by a transponder system built into the device which requires no direct electrical connection. Rather, the device is placed in proximity with a reader which can interrogate the device, obtain the results of the test and if necessary provide power for the device to perform the test, and / or communicate the information. The improvements and methods are particularly applicable to devices for performing in vitro diagnostic tests on a sample of body fluid.
Owner:CROSBY PETER
Electrolyte composition, photoelectric conversion device and photo-electrochemical cell
InactiveUS6376765B1Improve rendering capabilitiesIncreased durabilityLight-sensitive devicesOrganic chemistryPhotoelectrochemical cellHydrogen atom
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Photoelectric conversion device and method for producing same
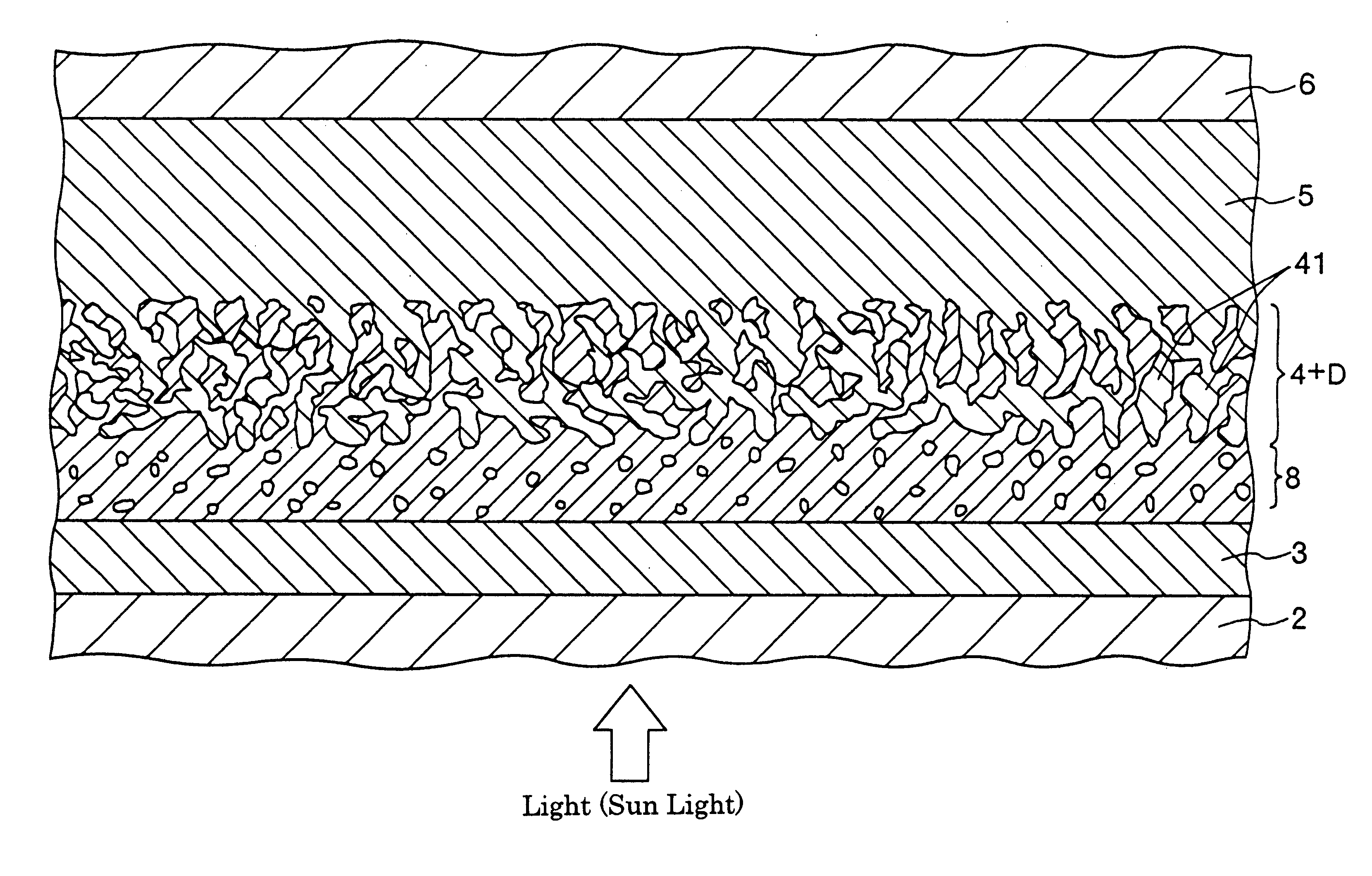
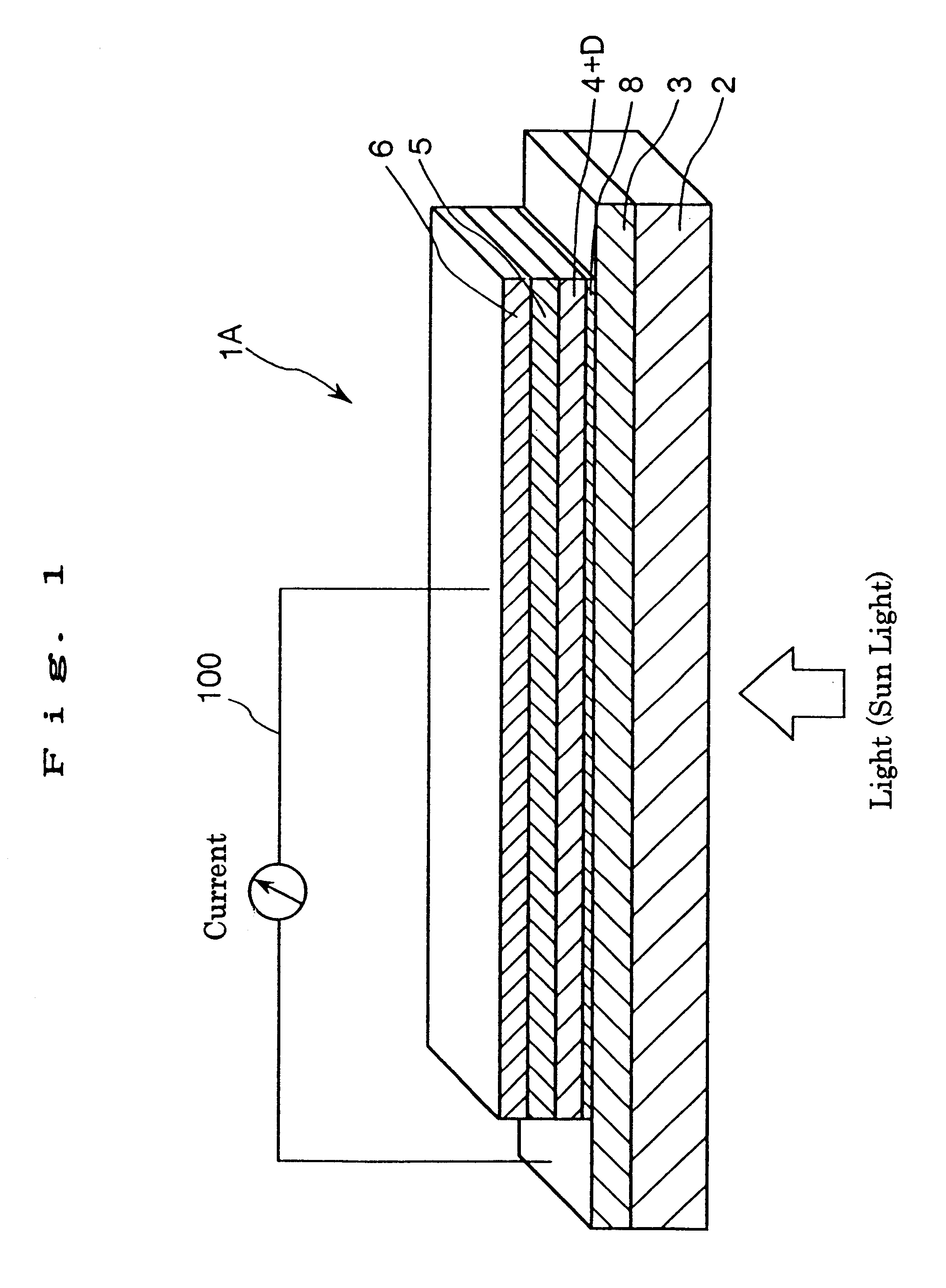
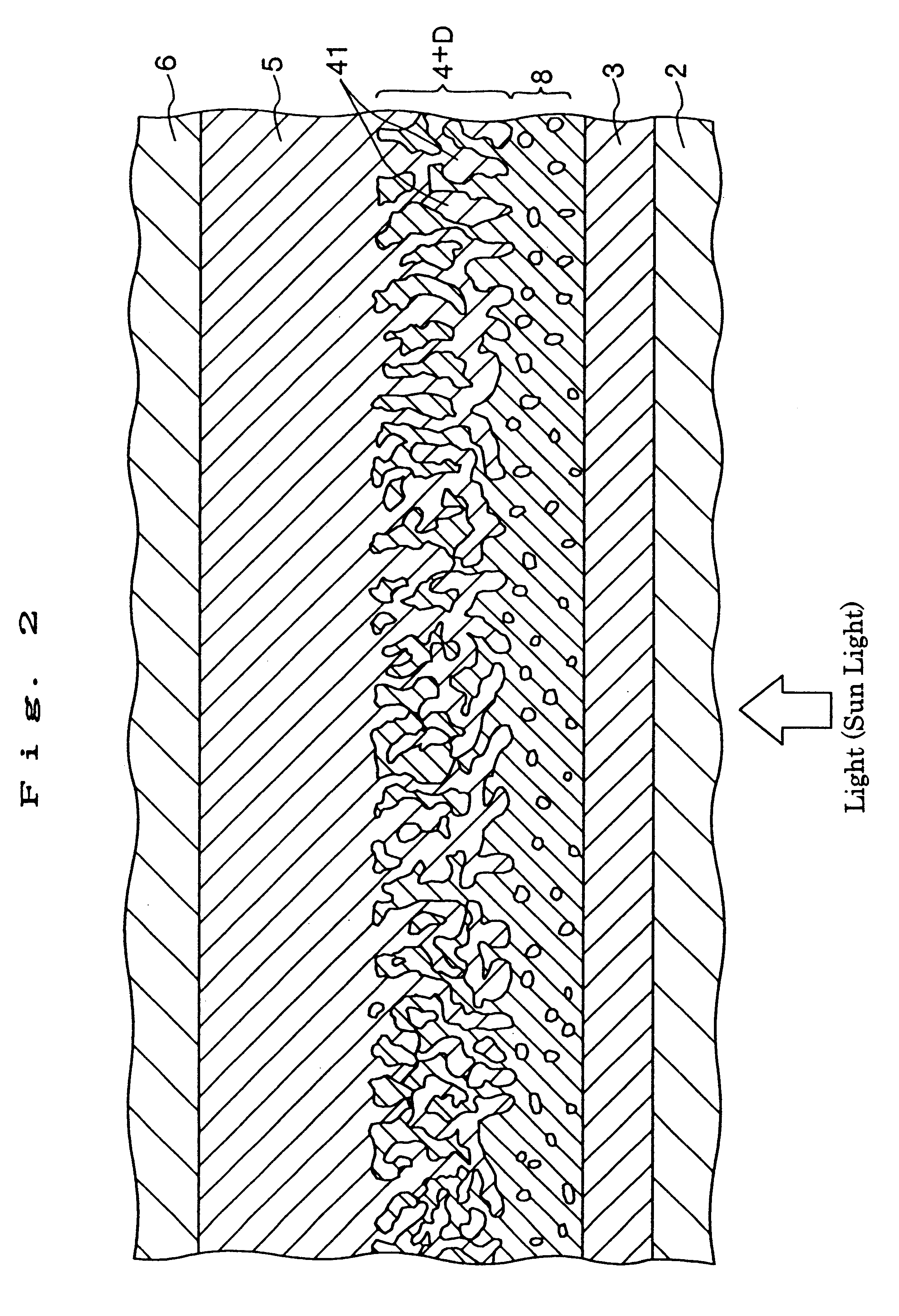
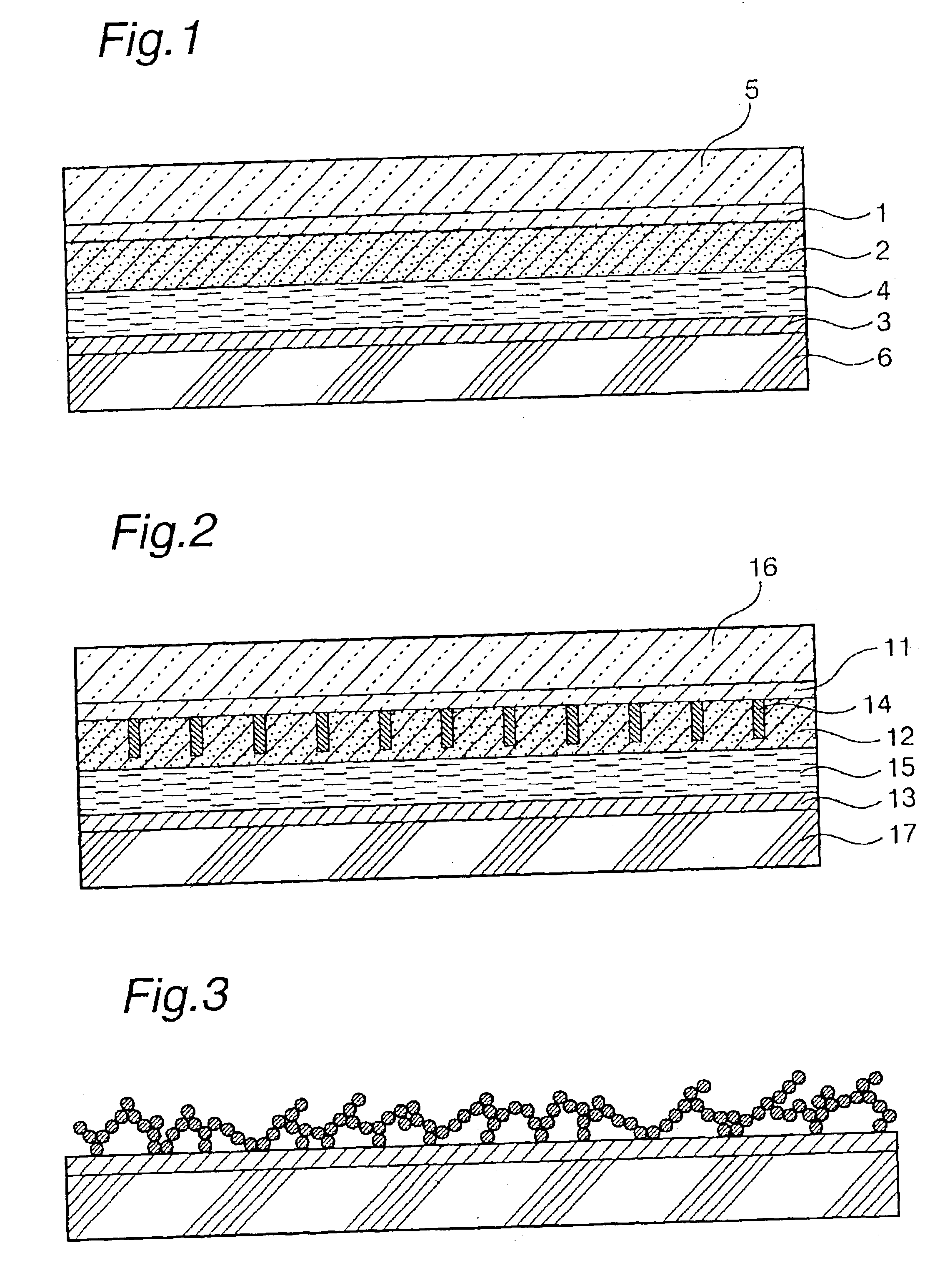
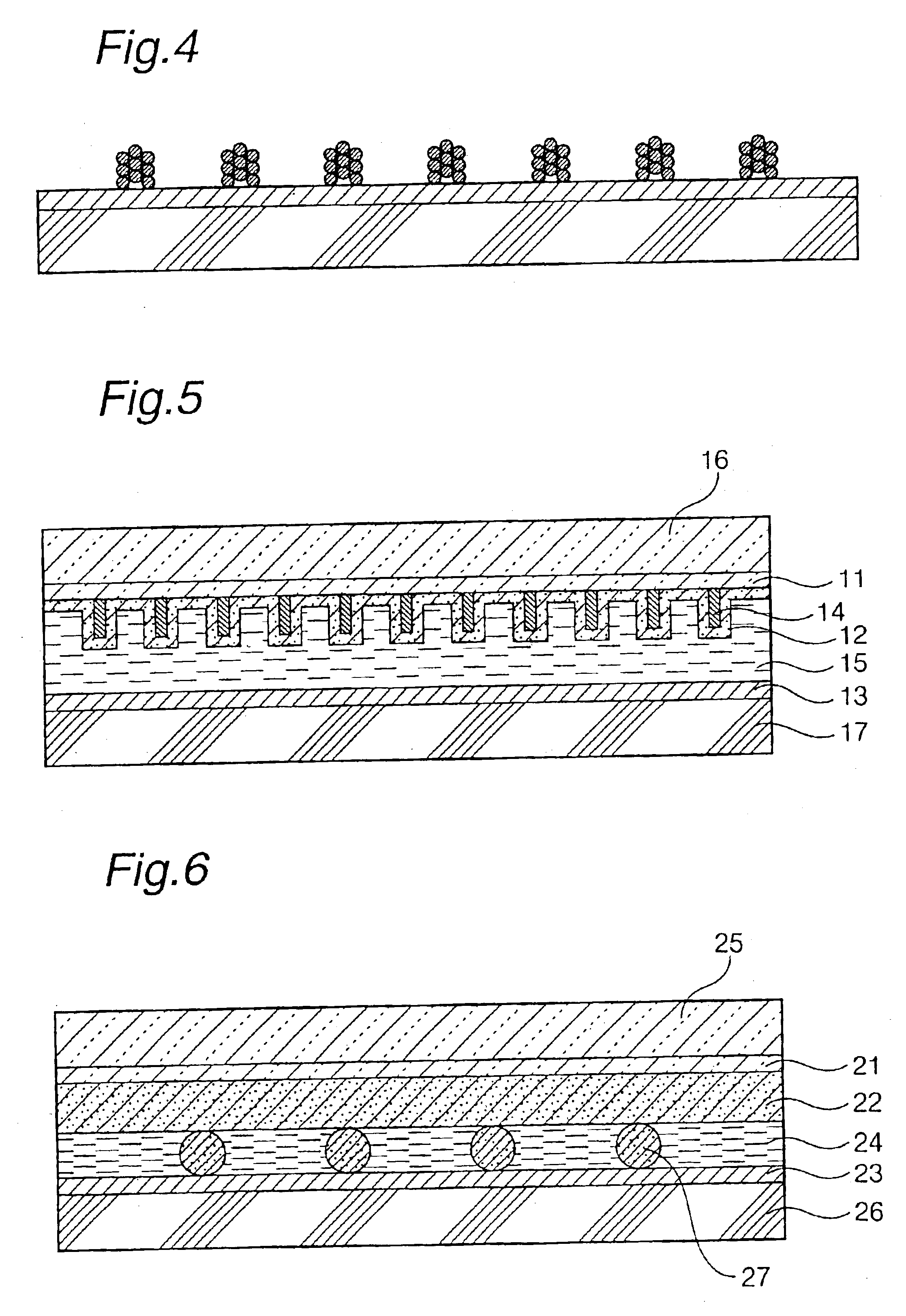
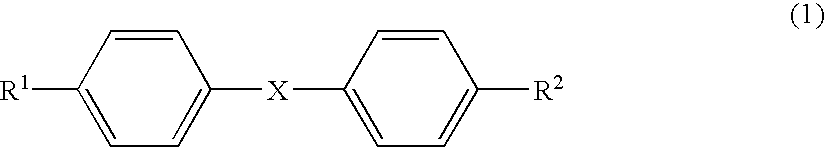
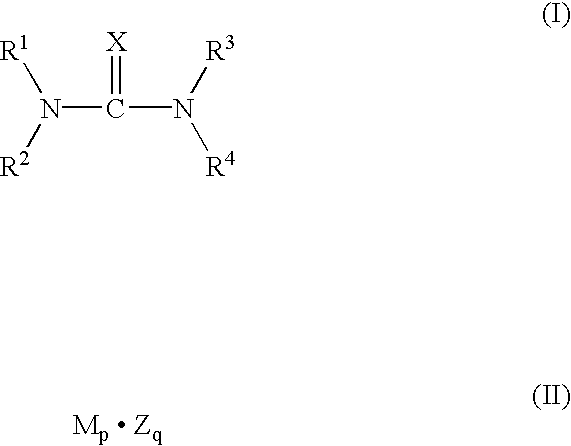
InactiveUS20020040728A1Promote conversionPrevent deterioration and volatilityLight-sensitive devicesDeferred-action cellsArylHydrogen atom
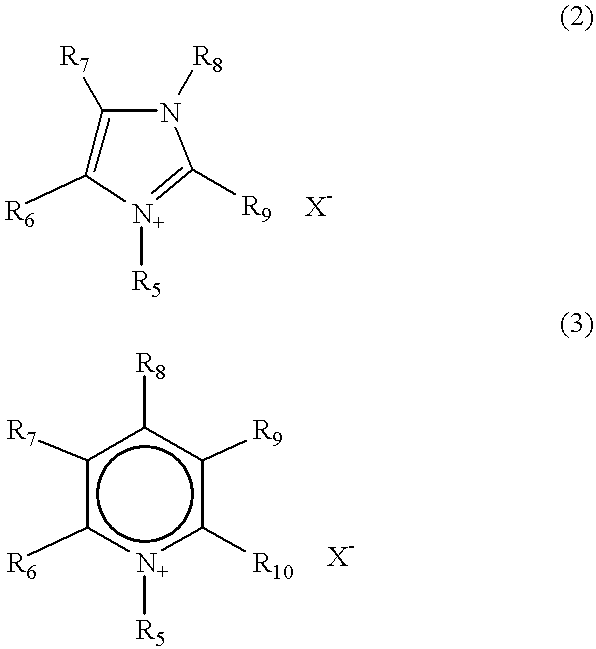
A method for producing a photoelectric conversion device comprising a conductive support and a photosensitive layer containing a semiconductor fine particle on which a dye is adsorbed, wherein the semiconductor fine particle is treated with a compound represented by the following general formula (I): wherein X represents an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom, a selenium atom or NY, in which Y represents a hydrogen atom, an aliphatic hydrocarbon group, a hydroxyl group or an alkoxy group; R1, R2, R3 and R4 independently represent a hydrogen atom, an aliphatic hydrocarbon group, an aryl group, a heterocyclic group, -N(R5)(R6), -C(=O)R7, -C(=S)R8, -SO2R9 or -OR10; R5 and R6 few independently have the same meaning as the R1, R2, R3 and R4; R7, R8 and R9 independently represent a hydrogen atom, an aliphatic hydrocarbon group, an aryl group, a heterocyclic group, -N(R5)(R6), -OR10 or -SR11; and R10 and R11 independently represent a hydrogen atom or an aliphatic hydrocarbon group.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Photoelectric conversion element
InactiveUS6683244B2Improve photoelectric conversion efficiencyPrevent and suppressLight-sensitive devicesDeferred-action cellsPorosityPhotoelectric conversion
A solar cell including a first electrode, a second electrode arranged opposite to the first electrode, an electron transport layer arranged between the first electrode and the second electrode, a dye layer D which is in contact with the electron transport layer, a hole transport layer arranged between the electron transport layer and the second electrode and being in contact with the dye layer D, and a barrier layer, and these elements are provided on a substrate. The barrier layer prevents or suppresses short-circuit between the first electrode and the hole transport layer. The porosity of the barrier layer is made smaller than that of the electron transport layer. The barrier layer is formed into a film-like shape and arranged between the first electrode and the electron transport layer. The solar cell can accomplish excellent photoelectric conversion efficiency by the provision of such a barrier layer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
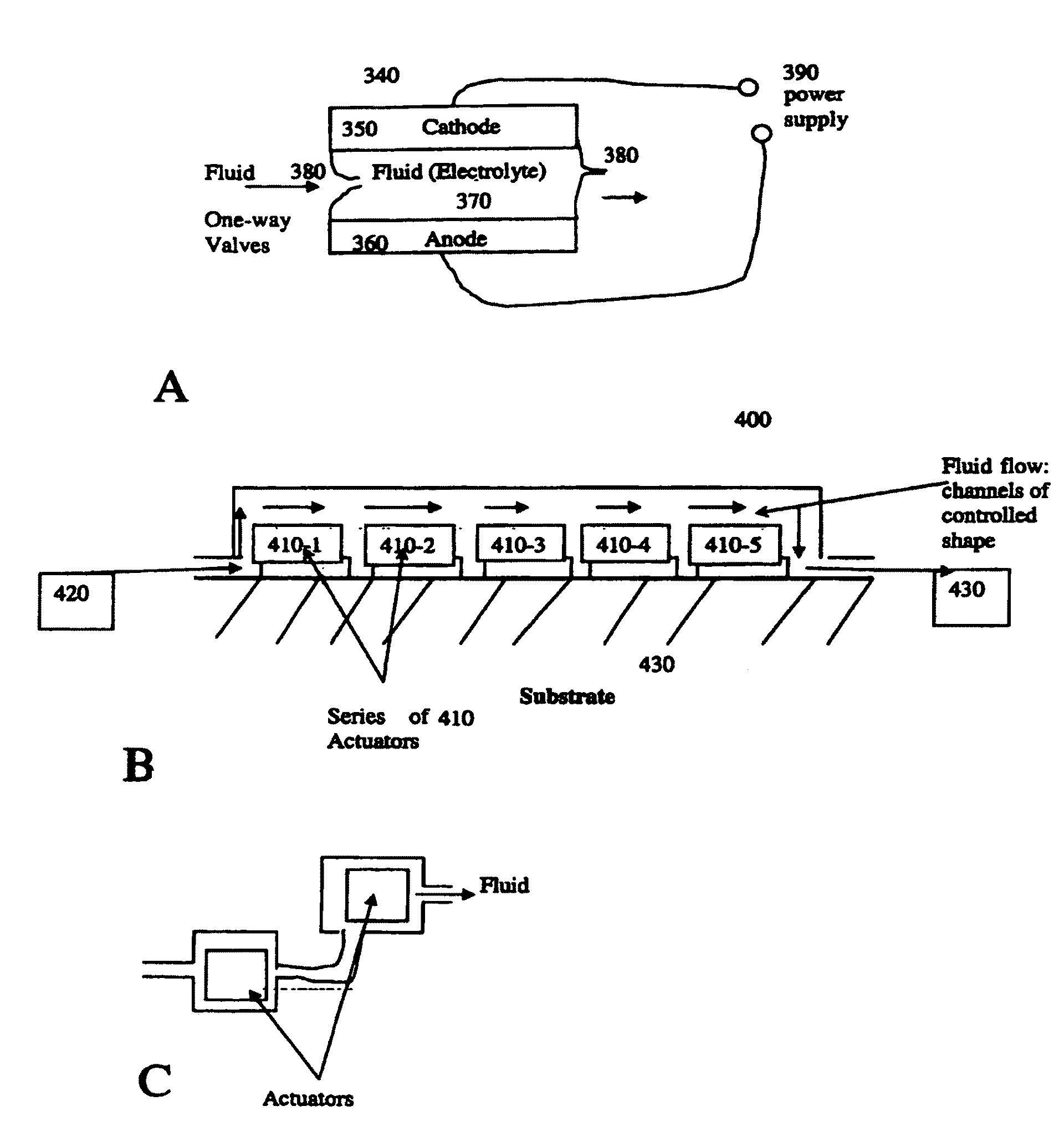
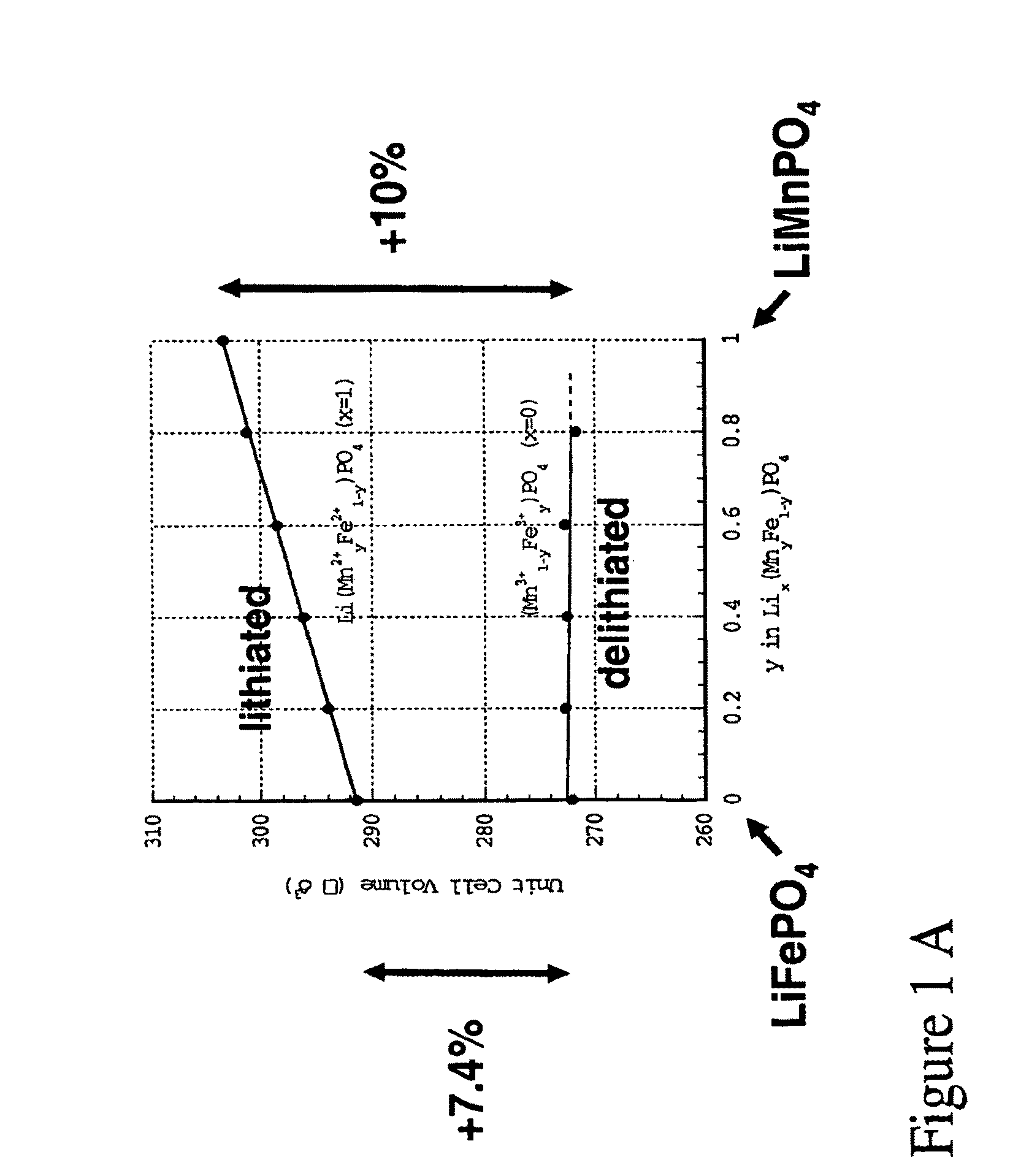
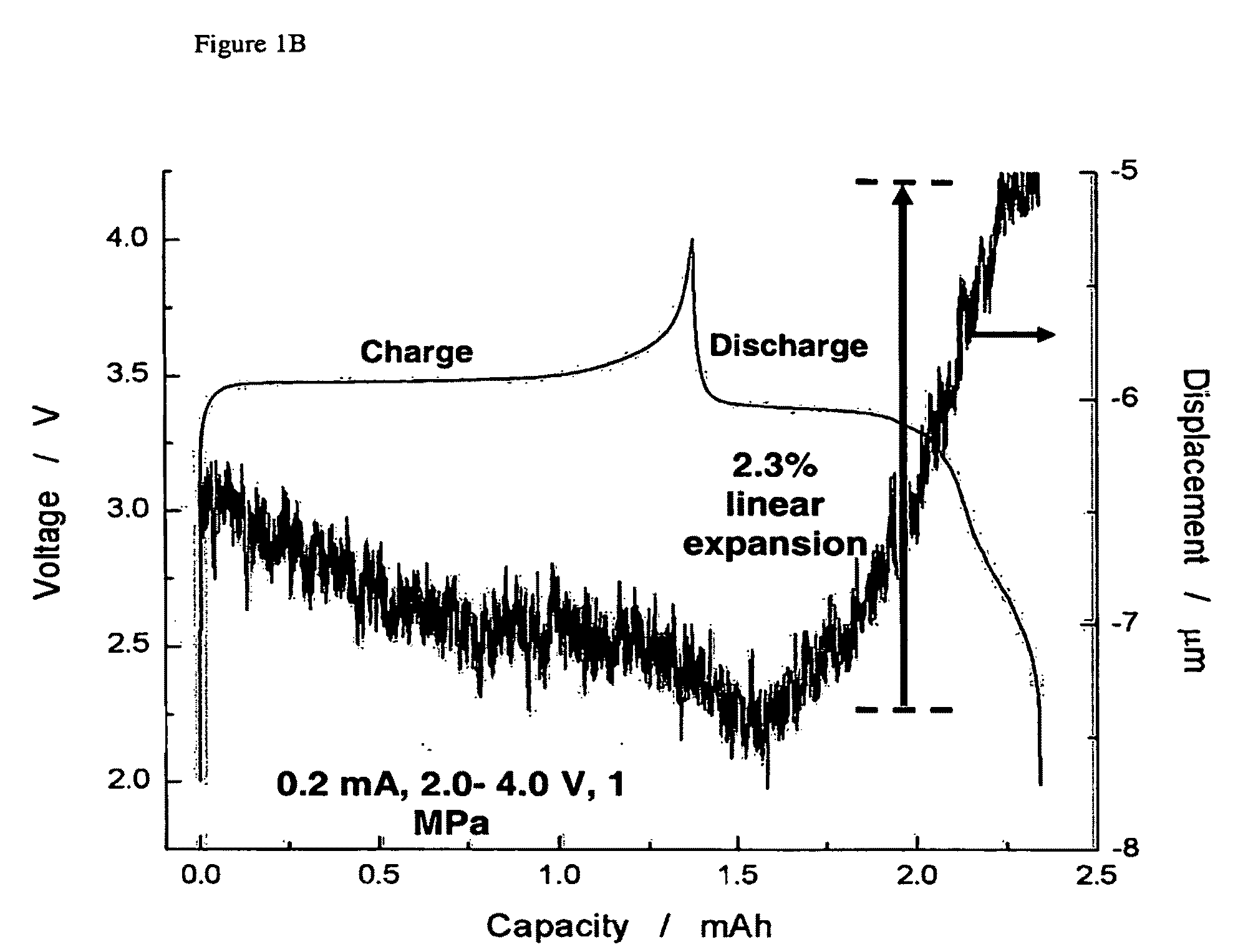
Electrochemical methods, devices, and structures
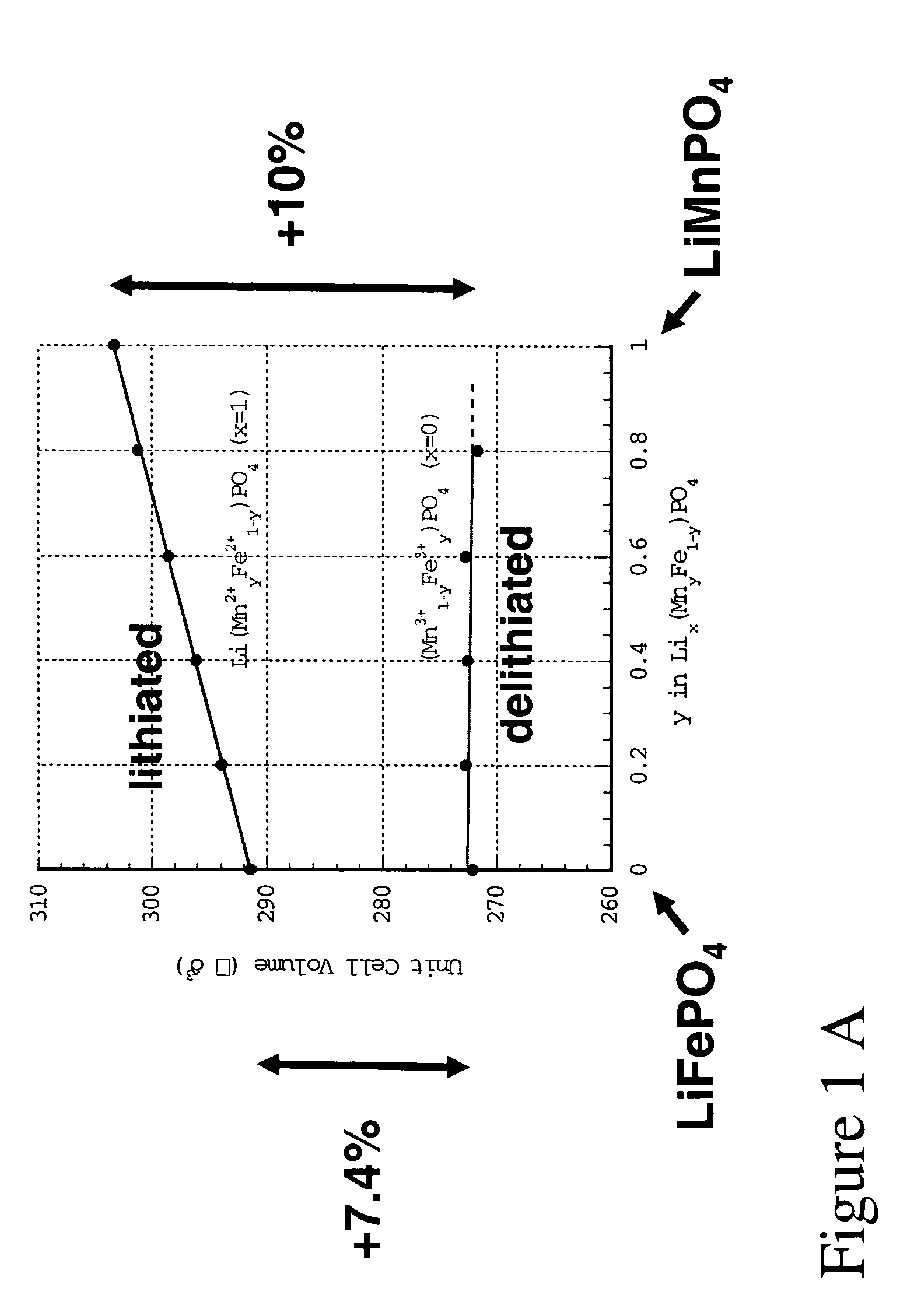
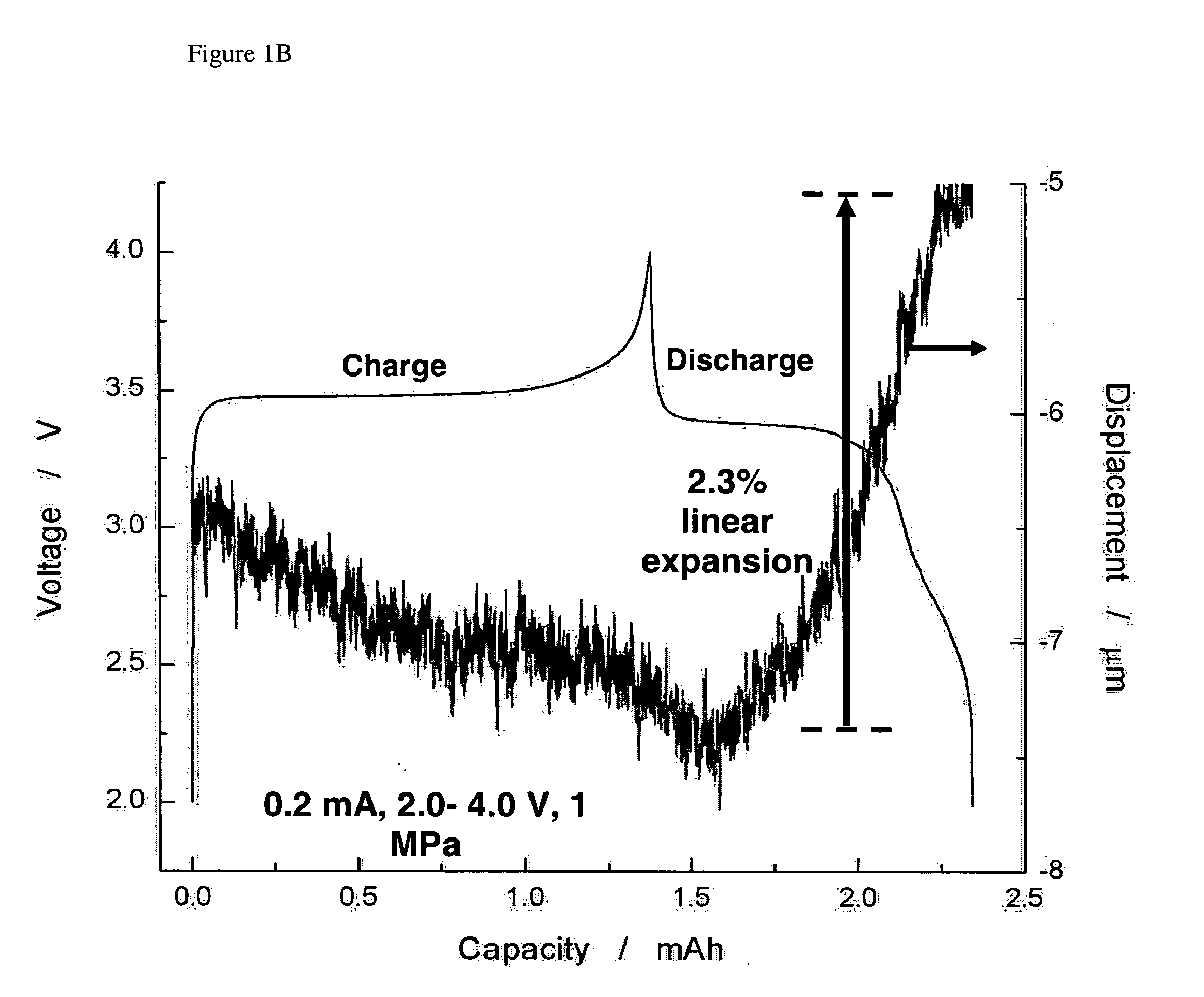
ActiveUS20060102455A1Increase strainDeferred-action cellsCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersInorganic compoundElectrochemistry
The present invention provides devices and structures and methods of use thereof in electrochemical actuation. This invention provides electrochemical actuators, which are based, inter-alia, on an electric field-driven intercalation or alloying of high-modulus inorganic compounds, which can produce large and reversible volume changes, providing high actuation energy density, high actuation authority and large free strain.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Packaging for primary and secondary batteries
InactiveUS20050112461A1Extended calendar lifeDeferred-action cellsSynthetic resin layered productsMetal foilEngineering
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
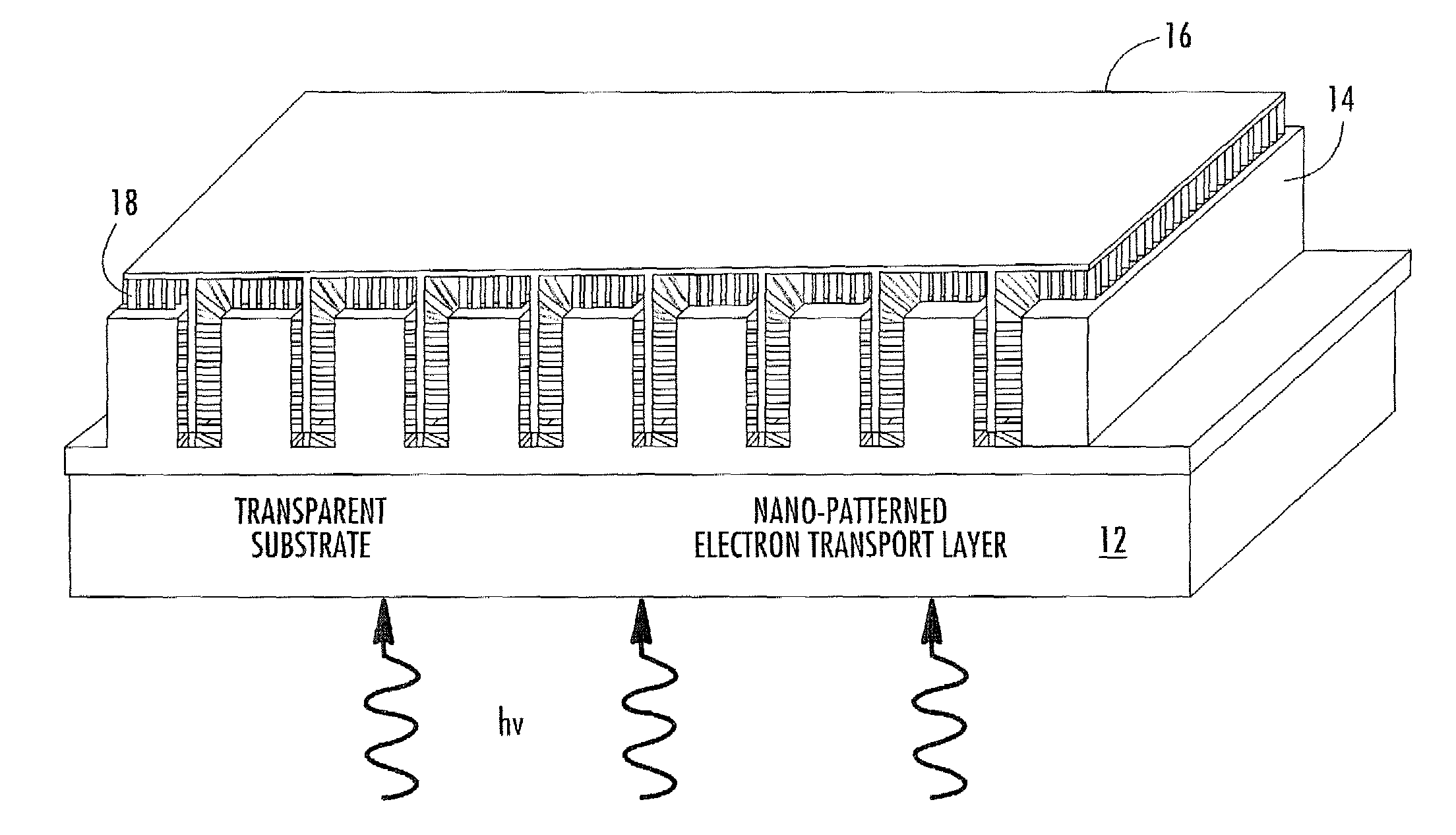
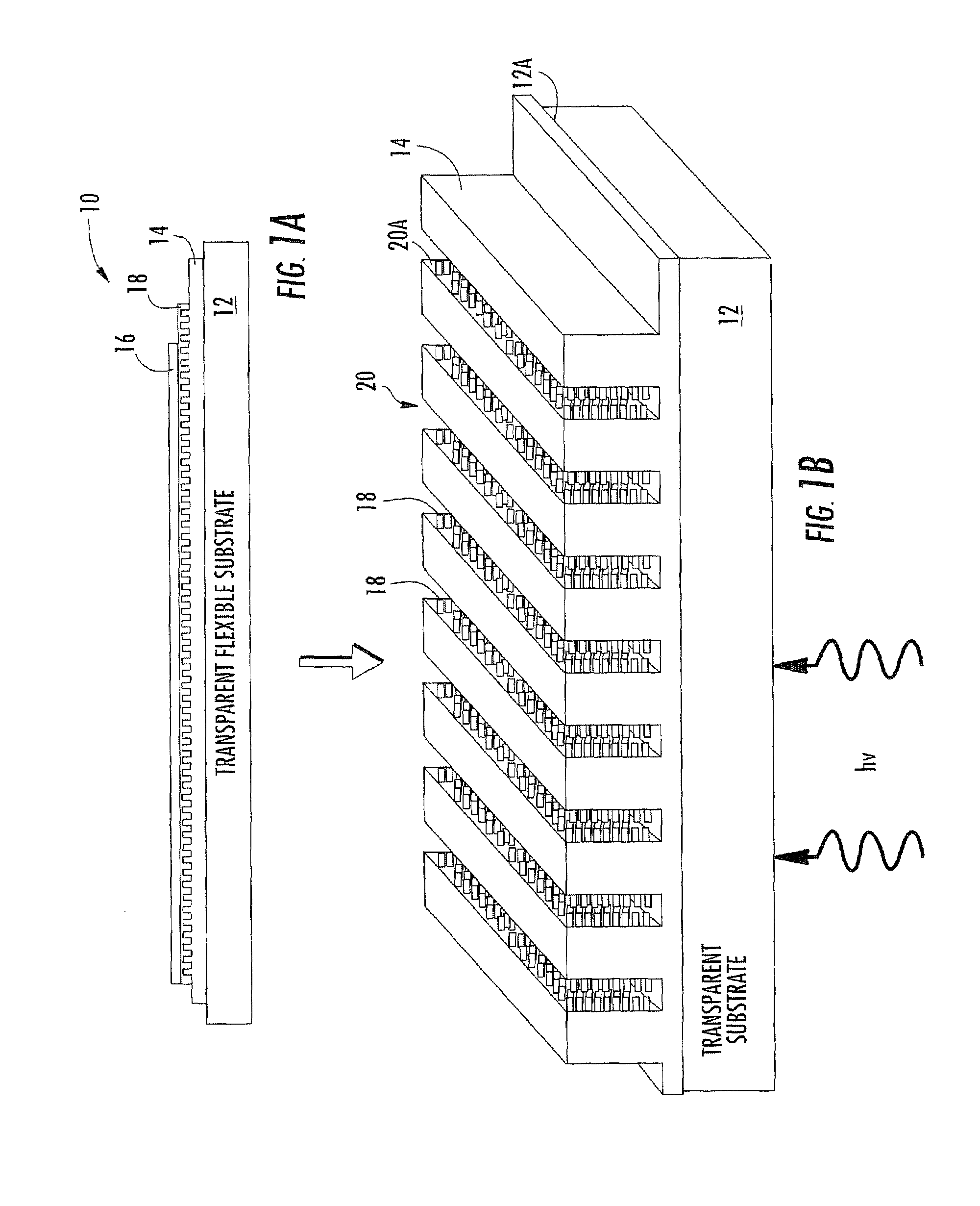
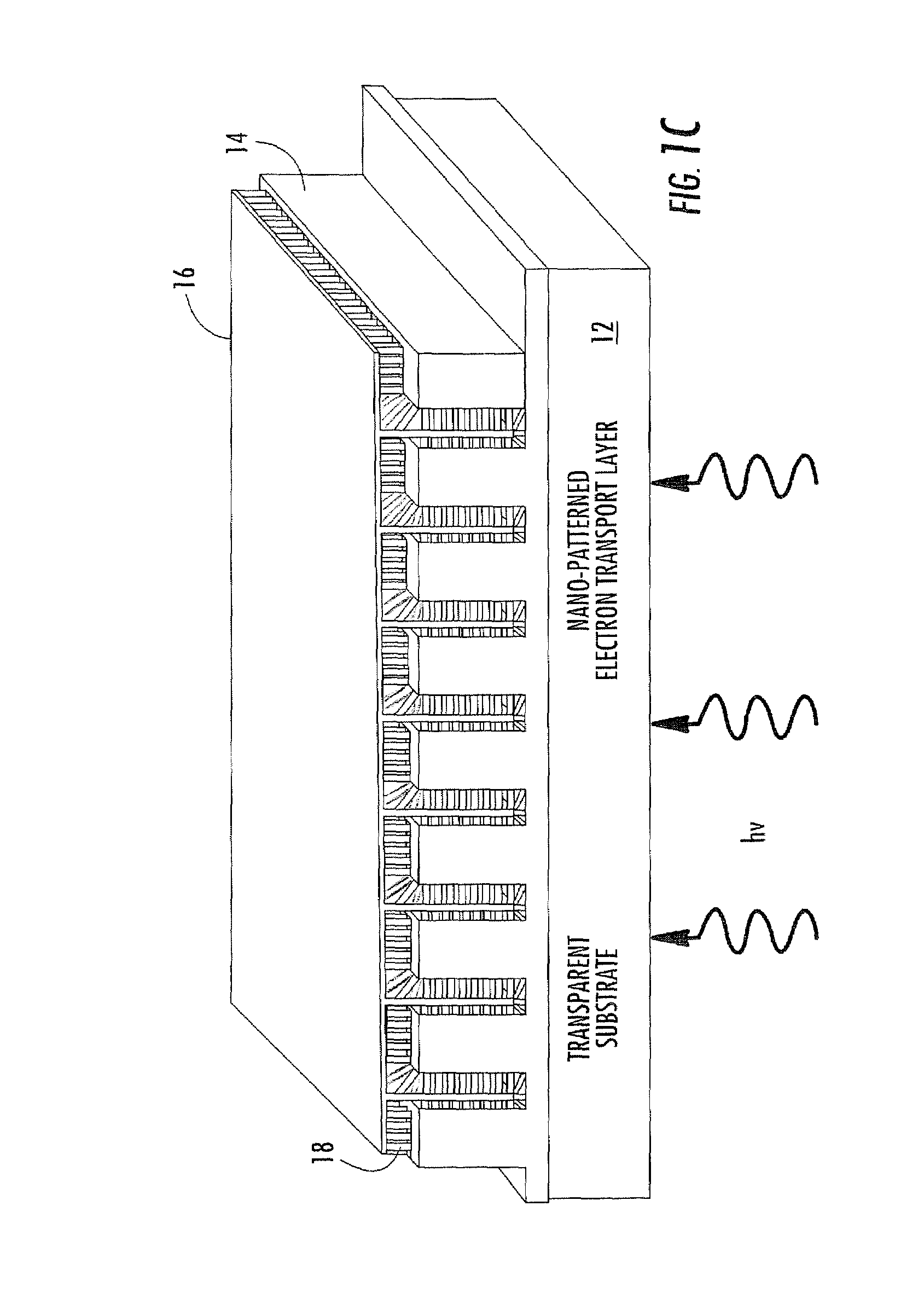
Nano-structured photovoltaic solar cell and related methods
A solar cell includes a substrate having a horizontal surface, and an electrode layer on the substrate. The electrode has a plurality of vertical surfaces substantially perpendicular to the horizontal surface, and light-harvesting rods are coupled to the vertical surface of the electrode.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Photo-catalytic reactor
ActiveUS20060246342A1Reduce deliveryEasy to demonstrateDeferred-action cellsFuel cells groupingElectron holePhotocatalytic reaction
A photocatalytic reactor, capable of generating an electric current by consumption of a fuel containing organic material, comprises a direct oxidation fuel cell including an anode and a cathode. The anode is a photocatalysis-assisted anode which comprises a photocatalyst on a surface of an electrically-conductive substrate so arranged as to be receptive to light. A light-transmissive proton-conductive membrane is arranged between the anode and the cathode, such that light passes through said membrane as a final stage in the optical path to the photocatalyst. The photocatalyst promotes oxidation of organic material and generates electron-hole pairs. The reactor, configured to support multiple cells in a stacked array, is provided with inlet(s) for introducing said fuel and connector(s) for connection to an external electrical circuit.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF ABERDEEN REGENT WALK
Low temperature interconnection of nanoparticles
A polymeric linking agent enables the manufacture of photovoltaic cells on flexible substrates, including, for example, polymeric substrates. Photovoltaic cells may be fabricated by a relatively simple continuous manufacturing process, for example, a roll-to-roll process, instead of a batch process.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Electric connection of electrochemical and photoelectrochemical cells
InactiveUS6657119B2Equipment is cheapReduce needLight-sensitive devicesPV power plantsPhotoelectrochemical cellEngineering
Owner:FORSKARPATENT I UPPSALA
Solid electrolyte thermoelectrochemical system
InactiveUS20060141346A1Improve efficiencyNegligible effect of impurityDeferred-action cellsSecondary cellsConcentration cellMembrane configuration
A solid electrolyte thermoelectrochemical system which employs a non-porous solid electrolyte as membrane between an anode compartment and a cathode compartment. The system utilizes the principles of a concentration cell using a non-porous inorganic solid electrolyte membrane and ionic solutions of differing concentration.
Owner:CERAMTEC
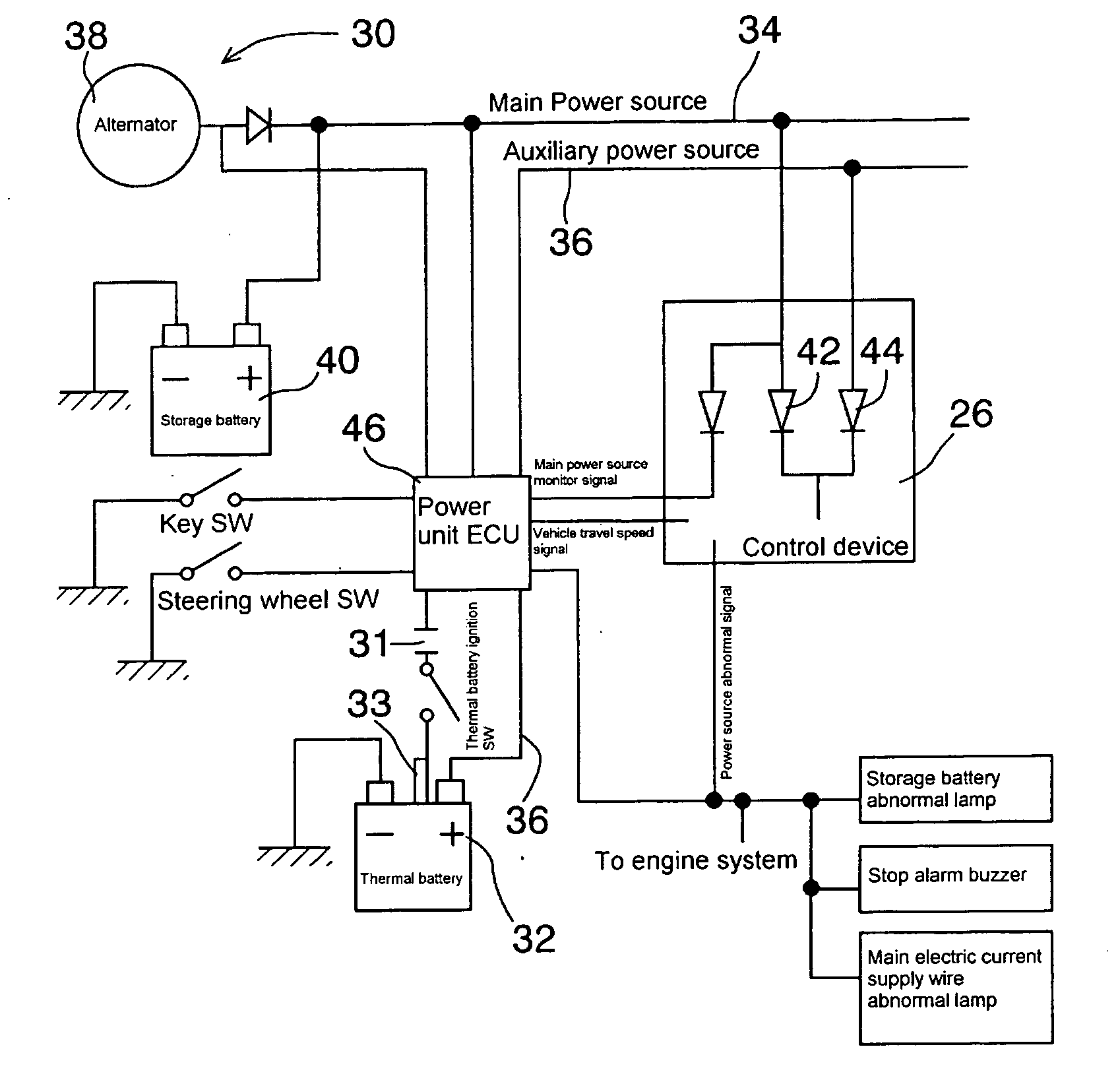
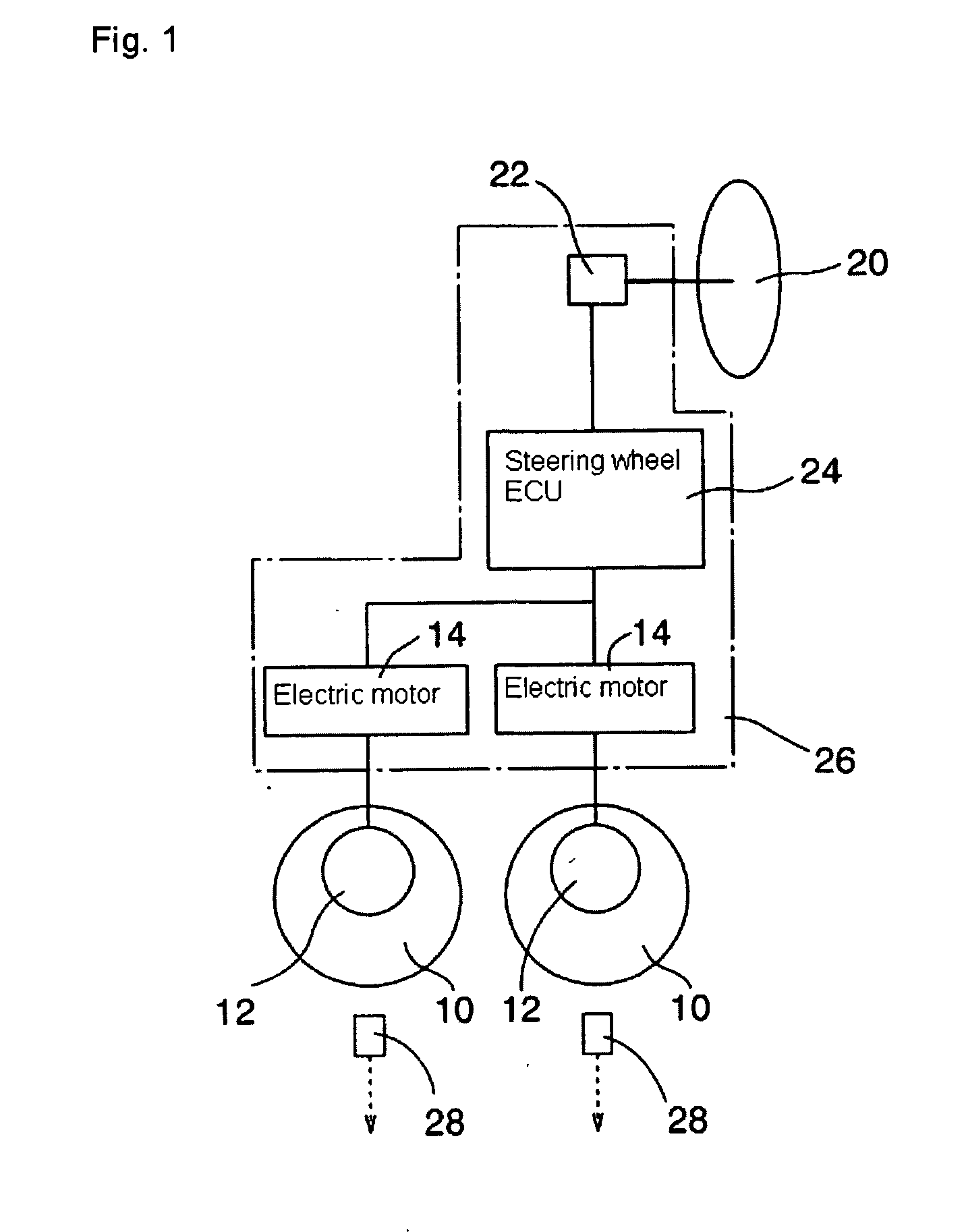
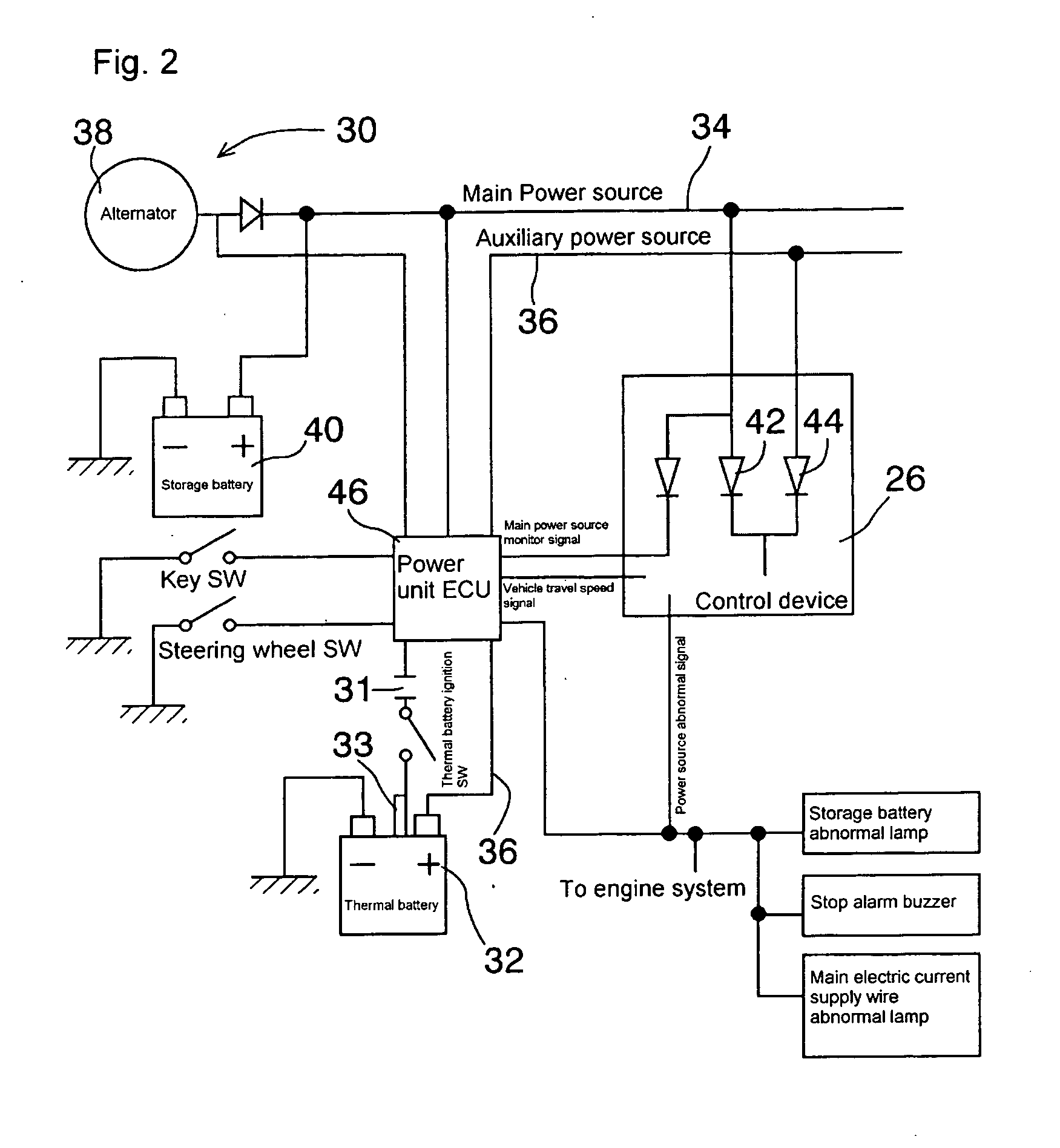
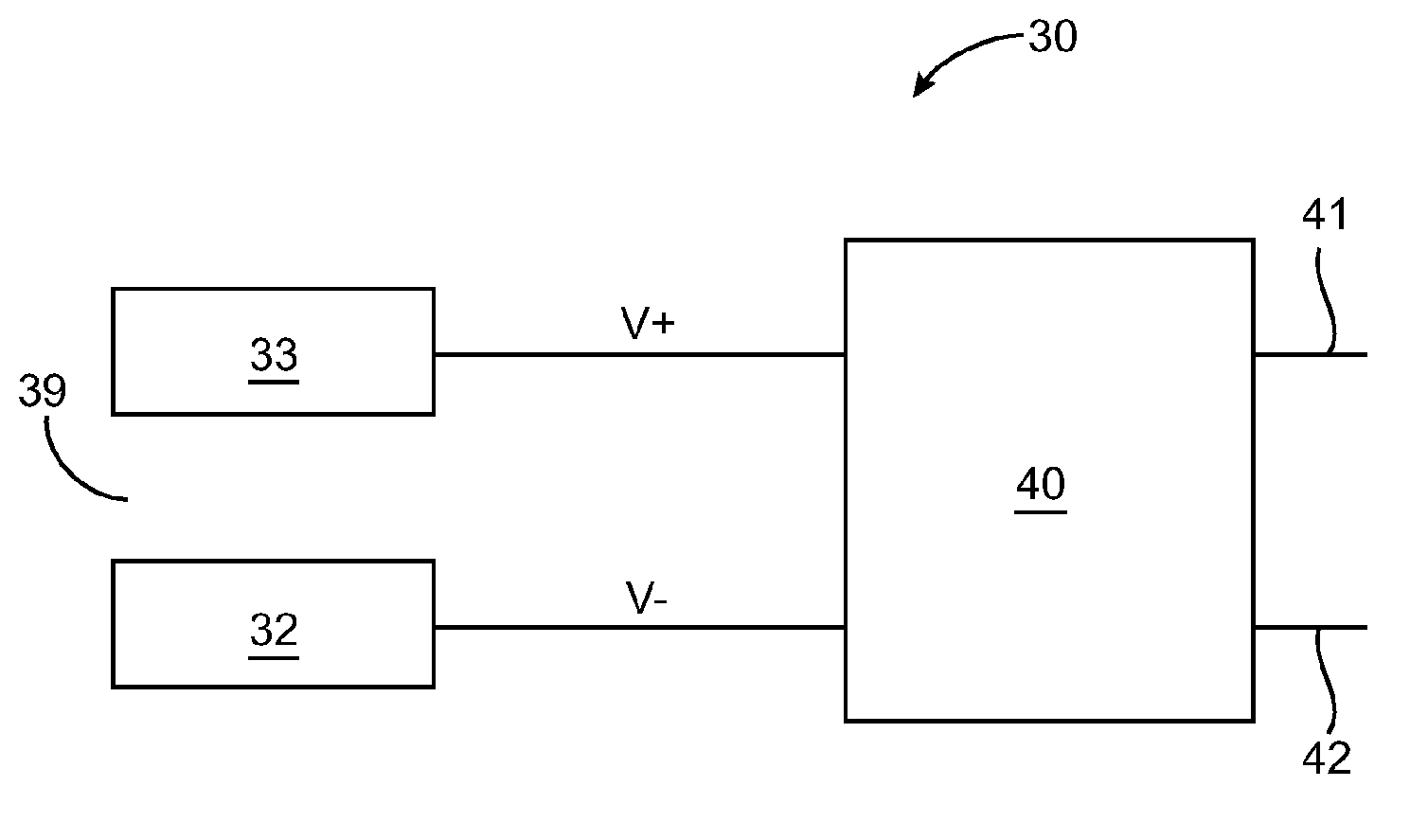
Power unit for conveyance and conveyance provided with the power unit
InactiveUS20050253458A1Avoid startingSimple structureBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric devicesControl systemElectronic control system
This invention aims to improve the reliability of an electronic control system which drives an actuator on conveyance operation based on an electrical signal to make adjustments such as acceleration / deceleration and movement direction of a conveyance, by achieving a power unit for conveyances having a power source with no need of charge and with little performance deterioration, thereby allowing for practical application of high-performance conveyances. The present invention relates to a power unit for conveyance comprising a main power source and a stand-by power source, which is characterized in that a thermal battery is provided as the stand-by power source, and a conveyance which is provided with an electronic control system and the power unit for conveyance of the present invention, is constituted so that electric power for operating the electronic control system is supplied to the electronic control system from the power unit for conveyances. By employing a thermal battery as the stand-by power source as thus, the stand-by power source does not require to be charged and the long-term reliability of the stand-by power source is also ensured.
Owner:GS YUASA INT LTD
Controlled activation ingestible identifier
Controlled activation identifiers for use in ingestible compositions, such as pharma-informatics enabled compositions, are provided. The identifiers include a controlled activation element that provides for activation of the identifier in response to the presence of a predetermined stimulus at a target site of interest. The invention finds use in a variety of different applications, including but not limited to, monitoring of therapeutic regimen compliance, tracking the history of pharmaceutical agents, etc.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
Photoelectrochemical Cell
InactiveUS20080286643A1Reduced current efficiencyCurrent efficiency downElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic capacitorsPhotoelectrochemical cellChemical species
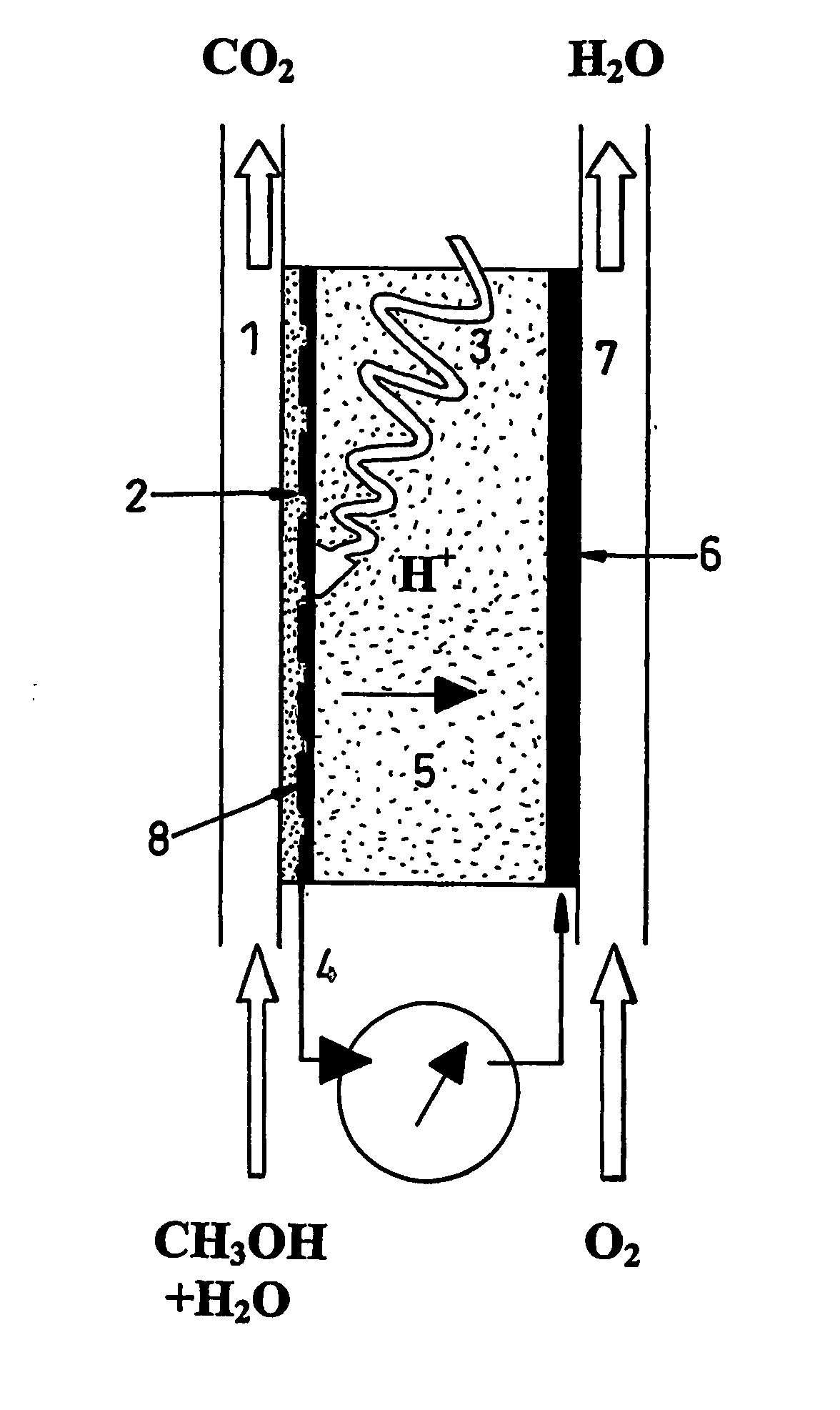
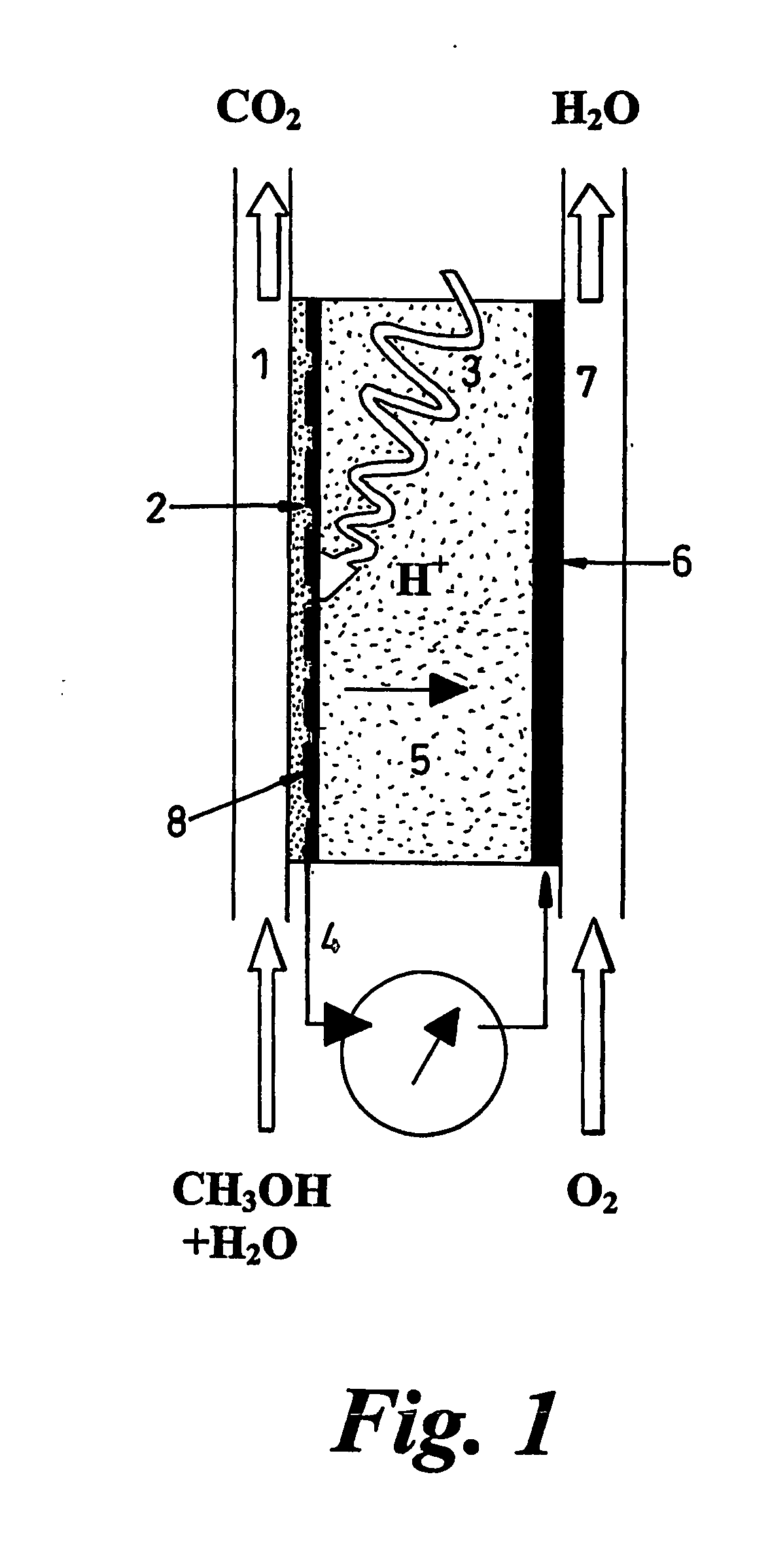
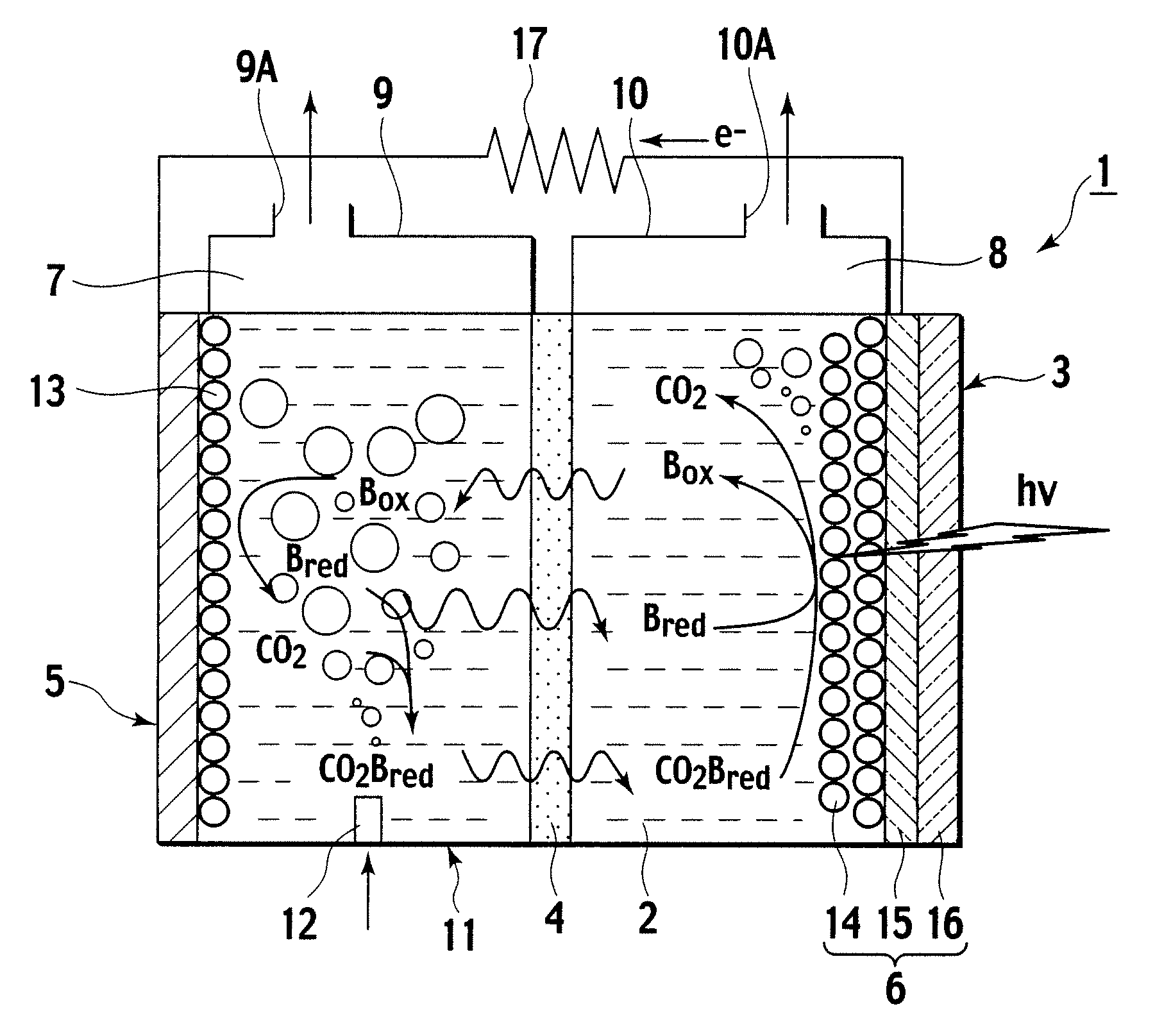
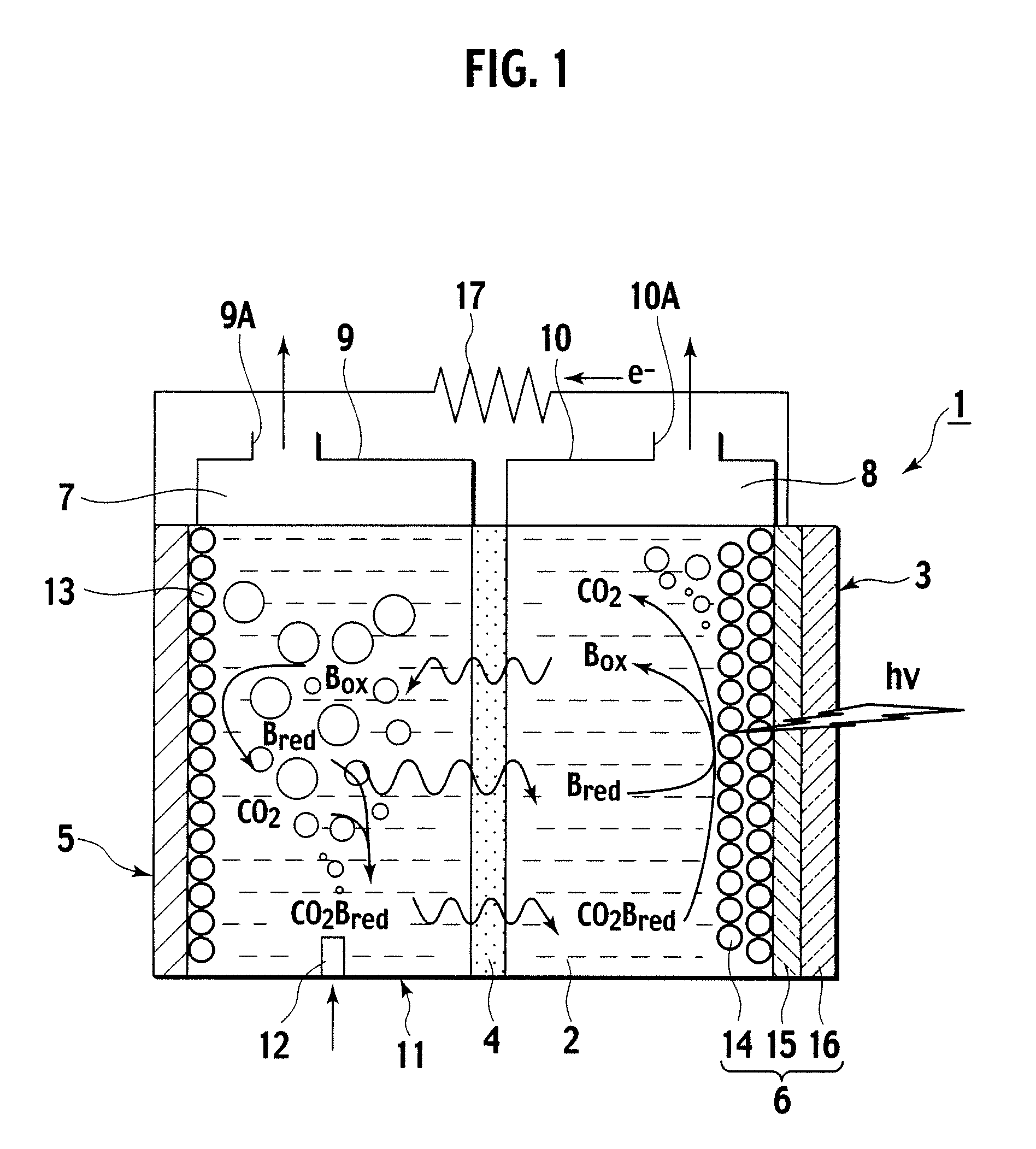
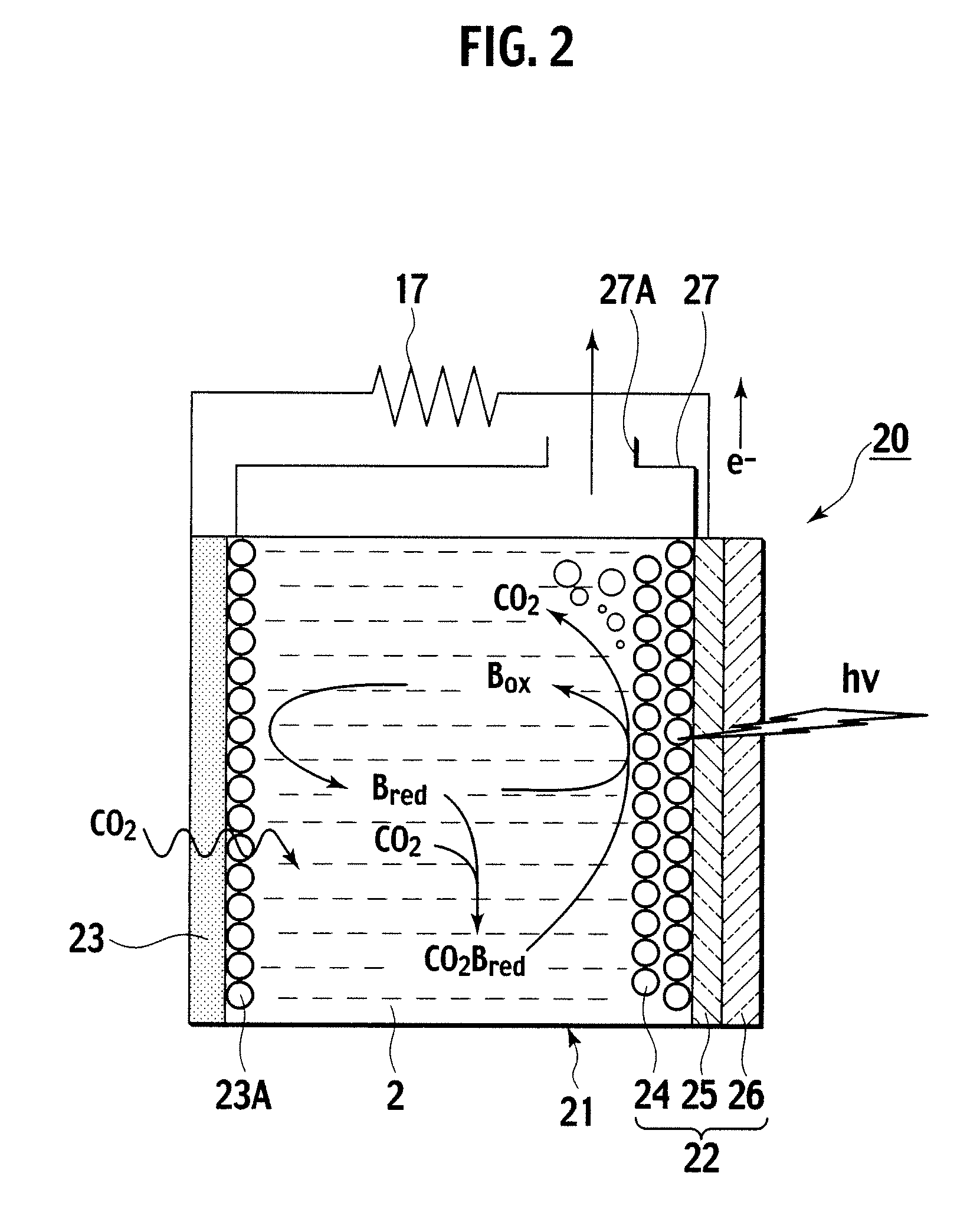
A photoelectrochemical cell (1) includes an electrolyte container (3) containing an ionic liquid (2), and a partitioning membrane (4) dividing an interior of the electrolyte container (3) into two being a CO2 capturing chamber (7) and a CO2 releasing chamber (8), having side walls opposing each other, with the partitioning membrane (4) in between, either as a carbon electrode (5) and the other as a photoelectrode (6). A redox mediator (B) has different bonding forces to carbon dioxide, as it appears as an oxidant Box and a reductant Bred, of which that one which has a greater bonding force serves as an intermediary chemical species carrying carbon dioxide to one of the paired electrodes (5, 6). Over the CO2 releasing chamber (10), an upper wall portion (10) is formed, which has a CO2 take-out port (10A) formed therein, for making use of oxidation and reduction of the redox mediator to achieve separation and concentration of carbon dioxide, converting photo energy of sunlight into electric power.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Redox flow cell rebalancing
A redox cell rebalance system is provided. In some embodiments, the rebalance system includes electrochemical cell and a photochemical cell. In some embodiments, the photochemical cell contains a source of ultraviolet radiation for producing HCl from H2 and Cl2 generated by the system. The HCl product may be collected or circulated back through the system for the rebalancing of electrolytes. A rebalance cell for use in a rebalance system is also provided. In some embodiments, the rebalance cell is the combination of an electrochemical cell and a photochemical cell. In some embodiments, a source of ultraviolet radiation is housed in the cathode compartment of the rebalance cell. In some embodiments, the source of ultraviolet radiation is used to effect the formation of HCl from H2 and Cl2 present in the rebalance cell. The HCl is dissolved in aqueous electrolytes contained in the rebalance cell, which can subsequently be circulated through a rebalance system for the rebalancing of redox cells.
Owner:IMERGY POWER SYST
Solar cell device
InactiveUS7737356B2Low-gradeMechanical apparatusLight-sensitive devicesElectrical batteryEngineering
A photovoltaic cell for converting a light source into electricity, including: (a) a housing for the photovoltaic cell, including: (i) an at least partially transparent cell wall; (b) at least one electrically-conductive element, disposed at least partially within the photovoltaic cell, for boosting collection of a current generated by the cell; (c) a conductive coating, electrically associated with the electrically-conductive element, and disposed on a surface within the photovoltaic cell; (d) an electrolyte, disposed within the cell wall, the electrolyte containing a redox species, and (e) a current collection element, disposed on a side of the cell wall, wherein the current collection element is electrically connected to the electrically-conductive element, so as to remove the current produced by the cell.
Owner:3GSOLAR PHOTOVOLTAICS
Light-receiving device and image sensor
InactiveUS20030013008A1Increase ratingsAccurate informationLight-sensitive devicesDeferred-action cellsSemiconductor electrodeResponse type
A differential response-type light-receiving device comprising: a semiconductor electrode comprising an electrically conductive layer and a photosensitive layer containing a semiconductor sensitized by a dye; an ion-conductive electrolyte layer; and a counter electrode, the differential response-type light-receiving device making time-differential response to quantity of light to output a photoelectric current. A composite light-receiving device comprising the differential response-type light-receiving device and a stationary response-type light-receiving device, and an image sensor using the differential response-type light-receiving device or the composite light-receiving device are also provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Controlled activation ingestible identifier
Controlled activation identifiers for use in ingestible compositions, such as pharma-informatics enabled compositions, are provided. The identifiers include a controlled activation element that provides for activation of the identifier in response to the presence of a predetermined stimulus at a target site of interest. The invention finds use in a variety of different applications, including but not limited to, monitoring of therapeutic regimen compliance, tracking the history of pharmaceutical agents, etc.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
Photoelectric cell and process for producing metal oxide semiconductor film for use in photoelectric cell
A photoelectric cell that includes a first insulating base, having on its surface a first electrode layer, which has on its surface a metal oxide semiconductor film, which includes anatase titanium oxide particles, on which a photosensitizer is absorbed and a second insulating base having on its surface a second electrode layer and an electrolyte sealed between the metal oxide semiconductor film and the second electrode layer. The first electrode layer and the second electrode layer are arranged opposite from each other. At least one of the first and second insulating bases with an electrode layer is transparent.
Owner:CATALYSTS & CHEM
Gel electrolytes for dye sensitized solar cells
Replacing liquid electrolytes with solid or quasi-solid electrolytes facilitates the production of photovoltaic cells using continuous manufacturing processes, such as roll-to-roll or web processes, thus creating inexpensive, lightweight photovoltaic cells using flexible plastic substrates.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS6849797B2Expansion quantityWithdrawing electrical energyLight-sensitive devicesDeferred-action cellsPhotosensitizerEngineering
A photovoltaic cell includes a first substrate having on its surface a first electrode layer having on its surface a semiconductor film on which a photosensitizer is adsorbed, and a second substrate having on its surface a second electrode layer. The first and second substrates are arranged so that the first electrode layer overlaid with the semiconductor film and the second electrode layer are opposite each other with an electrolyte disposed therebetween. Spacer particles are interposed between the semiconductor film and the second electrode layer, and at least one of the electrode-layer-having substrates is transparent. A coating liquid for forming the semiconductor film includes both a component for forming the semiconductor film as well as the spacer particles, dispersed in a dispersion medium.
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD
Photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20030201010A1Improve long-term stabilityWithdrawing electrical energyLight-sensitive devicesDeferred-action cellsPhotosensitizerEngineering
A photovoltaic cell includes a first substrate having on its surface a first electrode layer having on its surface a semiconductor film on which a photosensitizer is adsorbed, and a second substrate having on its surface a second electrode layer. The first and second substrates are arranged so that the first electrode layer overlaid with the semiconductor film and the second electrode layer are opposite each other with an electrolyte disposed therebetween. Spacer particles are interposed between the semiconductor film and the second electrode layer, and at least one of the electrode-layer-having substrates is transparent. A coating liquid for forming the semiconductor film includes both a component for forming the semiconductor film as well as the spacer particles, dispersed in a dispersion medium.
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD
Lithium-sulfur battery and cathode therefore
ActiveUS20090226809A1Increase energy densityIncrease specific energyDeferred-action cellsCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersHigh energyLithium sulfur
An improved cathode suitable for lithium-sulfur batteries, a battery including the cathode, and a battery including a separator containing inorganic fillers are disclosed. The cathode includes sulfur and a metal oxide and optionally includes an additional polymeric material. The metal oxide reduces dissolution of sulfur at the cathode and reduces sulfur-containing deposits on the battery anode, thereby providing a battery with relatively high energy density and good partial discharge performance. The separator also reduces unwanted diffusion of sulfur species.
Owner:EAGLE PICHER TECH LLC
Interconnected Photoelectrochemical Cell
InactiveUS20080223439A1Light-sensitive devicesElectrolysis componentsHydrogenPhotoelectrochemical cell
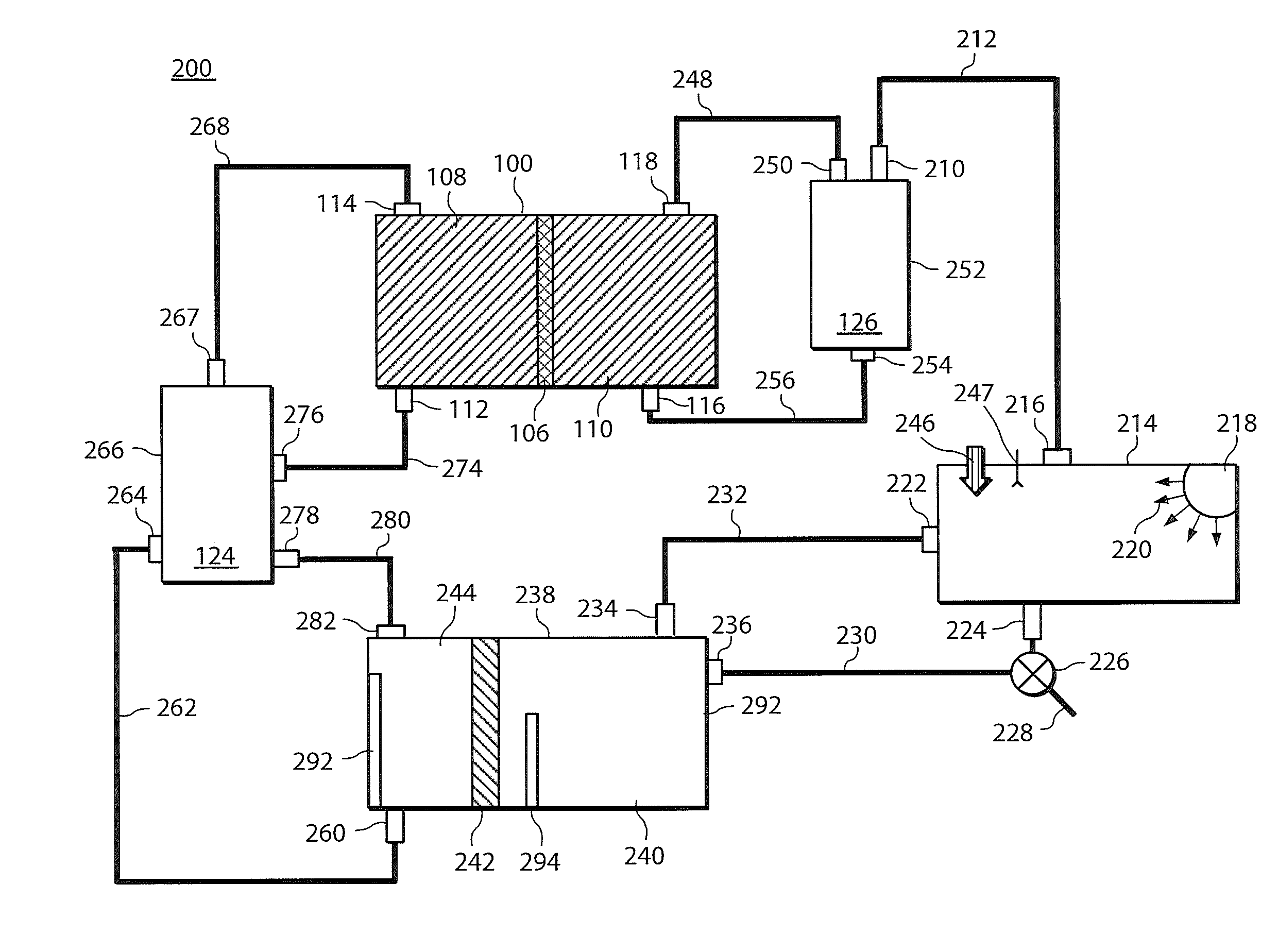
An interconnected photoelectrochemical (PEC) cell (1) generates hydrogen and oxygen from water while being illuminated with radiation such as sunlight. The photovoltaic structure in the photoelectrode is deposited on a transparent and insulating substrate (also called superstrate) (3) that is covered with a transparent conducting layer (front electrode) (4). The front electrode is electrically connected to the back side of the photovoltaic structure such that the PLC cell can be made with high efficiency and high durability and at low cost. Three types of photoelectrodes and phtoelectrochemical cells are illustrated as examples.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO +1
High temperature battery and electrolytes
A high temperature battery of one or more cells is disclosed in which each cell is made by holding an anode electrode and a cathode electrode, of different metallic substances, together through a fused flux wetted to an electrode, which fused flux is an electrolyte, to make an anode-to-cathode contact, and the anode-to-cathode contact is heated, by a heat source, to a high temperature above a threshold temperature to generate voltaic voltage, in excess of any thermoelectric voltage; such batteries with electrodes of various configurations are disclosed. The heat-activated flux and electrolyte, such as borax, may have, vegetable-growth ashes or chemical constituents of ashes, such as lithium carbonate, added to the heat-activated flux and electrolyte to catalyze or improve the current-generating capability of the battery. The preferred anode substance is aluminum, and the preferred cathode substance is copper. With the preferred cathode and anode substances and a heat-activated flux and electrolyte of fused borax between the cathode and anode, the open circuit voltage generated per cell when heated increases from 0.05 volts at 304° C. to 1.3 volts at 651° C.; the threshold temperature in this case is 279° C. Also disclosed is means to move the anode metal with respect to the cathode metal, when the heat-activated flux and electrolyte is fluid, for changing the battery characteristics and for replacing depleted heat-activated flux and electrolyte.
Owner:WILSON JOHN T R
Photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20030196692A1Smooth movementImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyLight-sensitive devicesDeferred-action cellsPhotosensitizerDecomposition
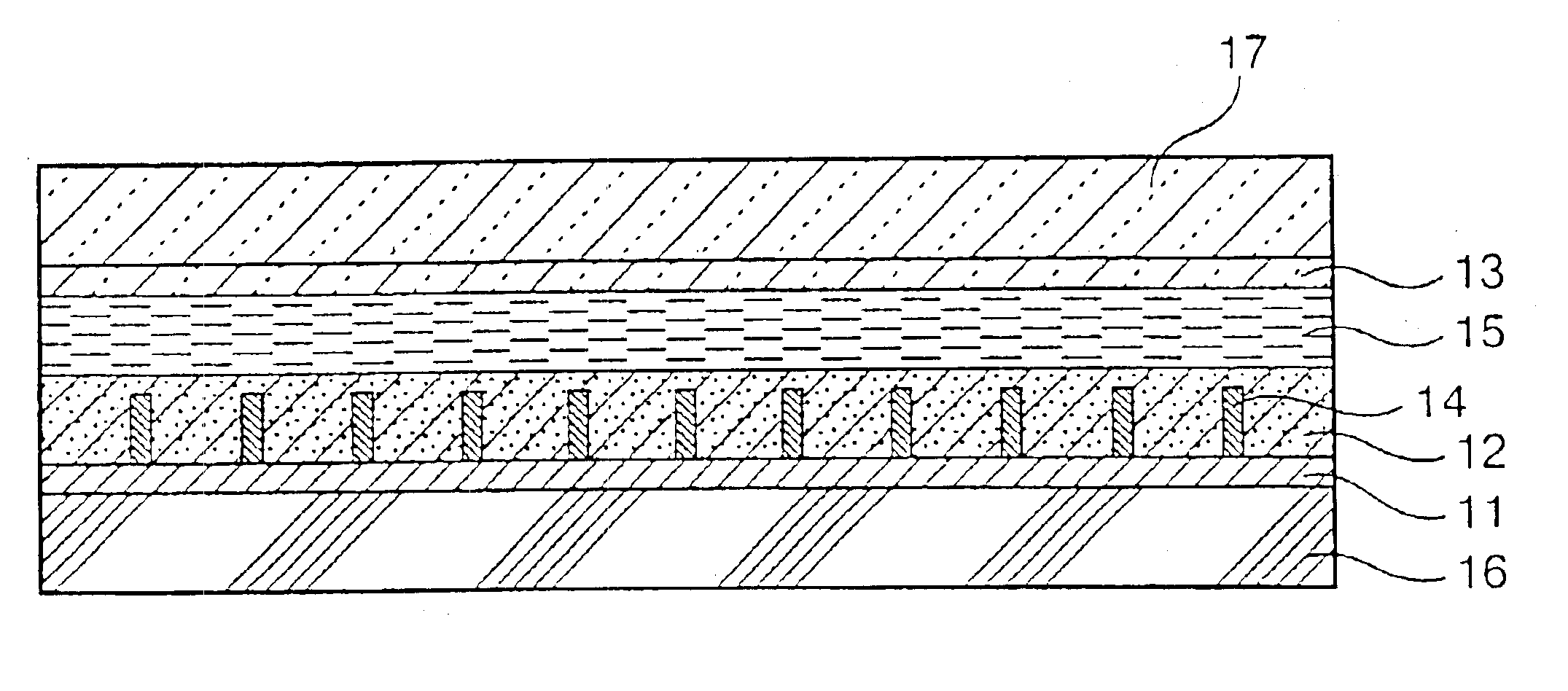
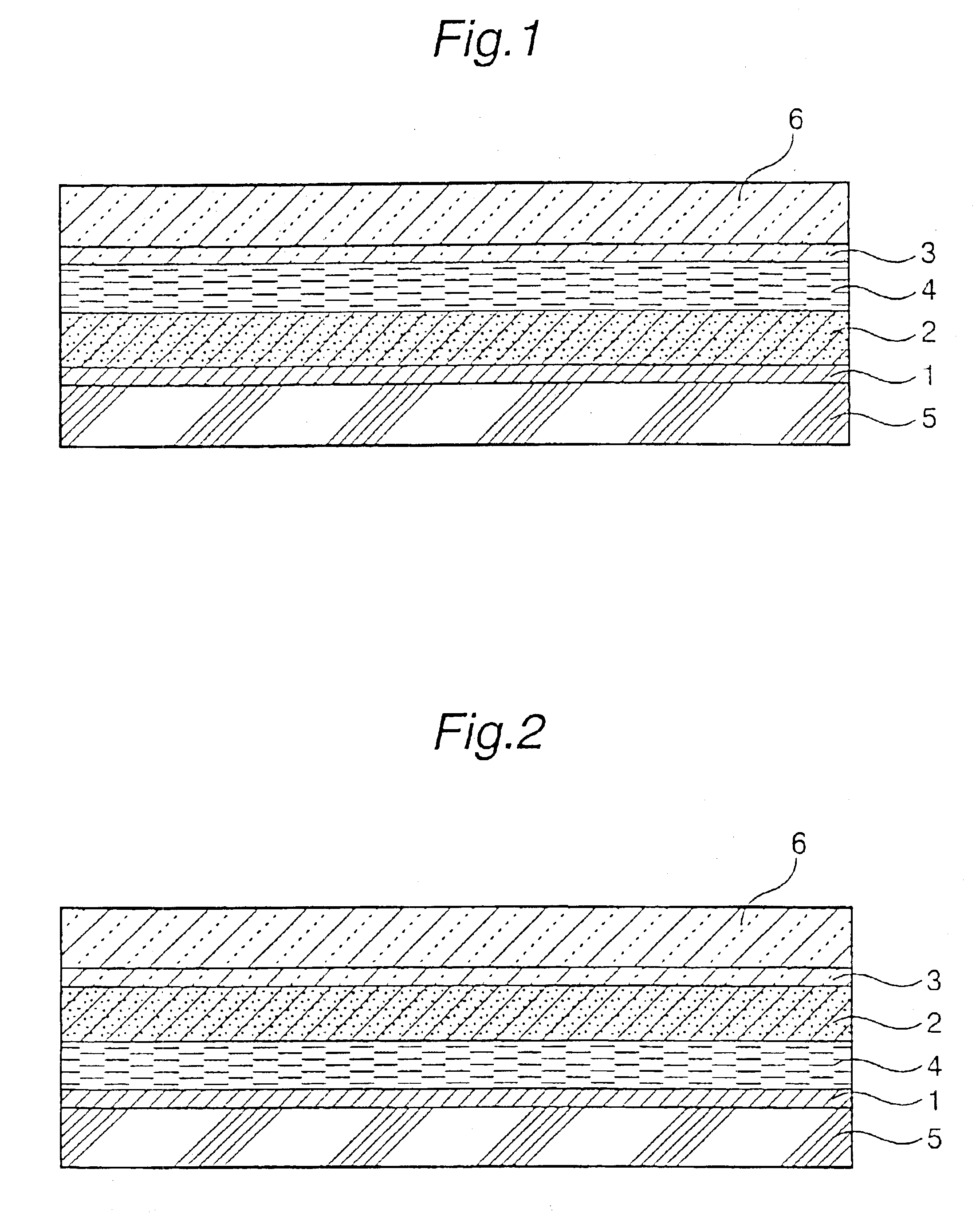
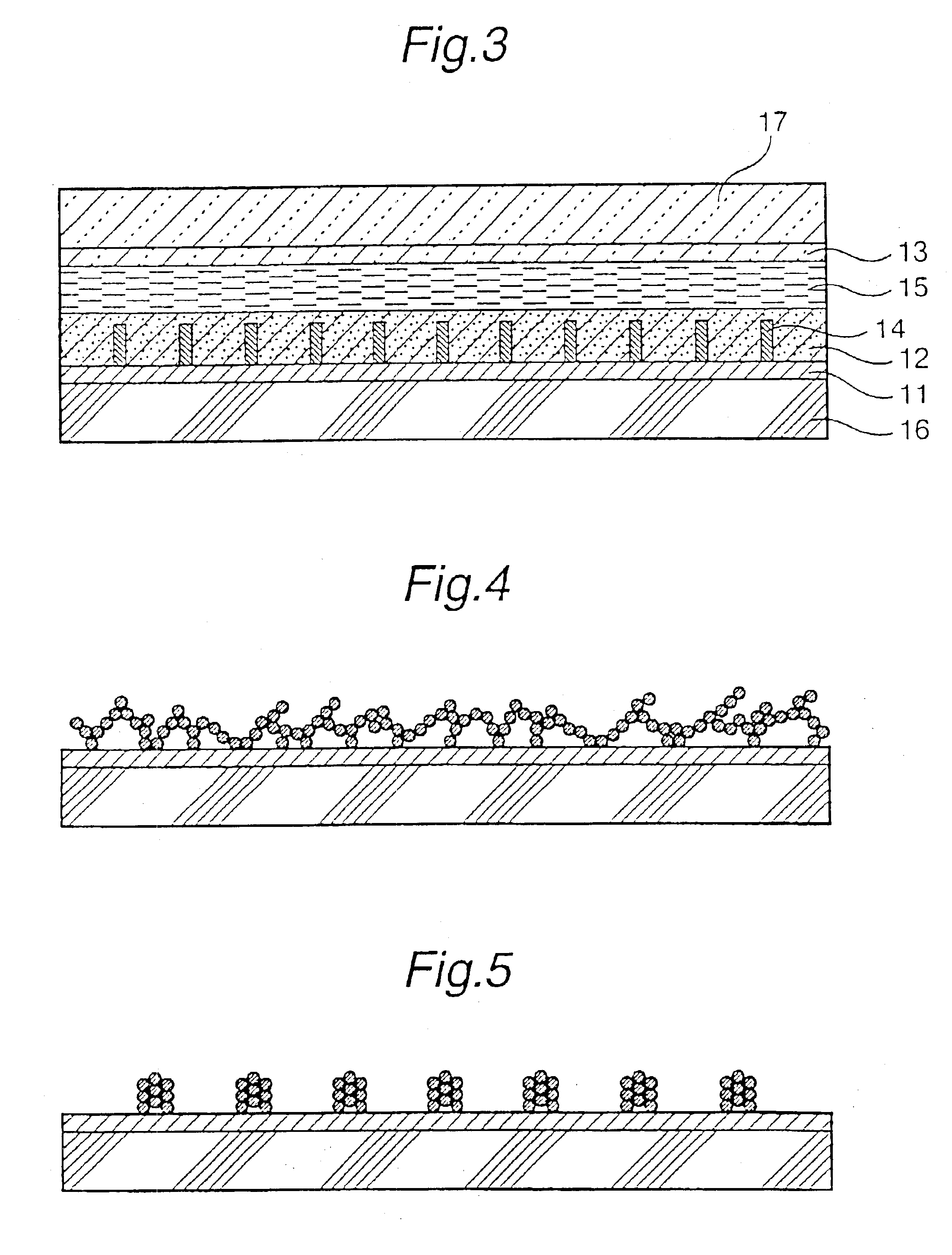
Disclosed is a photovoltaic cell comprising a substrate having an electrode layer (1) on the surface and having a porous metal oxide semiconductor film (2) which is formed on the electrode layer (1) and on which a photosensitizer is adsorbed, a substrate having an electrode layer (3) on the surface, both of said substrates being arranged in such a manner that the electrode layer (1) and the electrode layer (3) face each other, and an electrolyte layer provided between the semiconductor film (2) and the electrode layer (3), wherein the semiconductor film (2) contains an inhibitor of back current, and at least one pair of substrate and electrode layer thereon have transparency. The photovoltaic cell is capable of inhibiting back current and decomposition of a spectrosensitizing dye caused by the ultraviolet rays, has high photoelectric conversion efficiency and is capable of generating high electromotive force.
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD
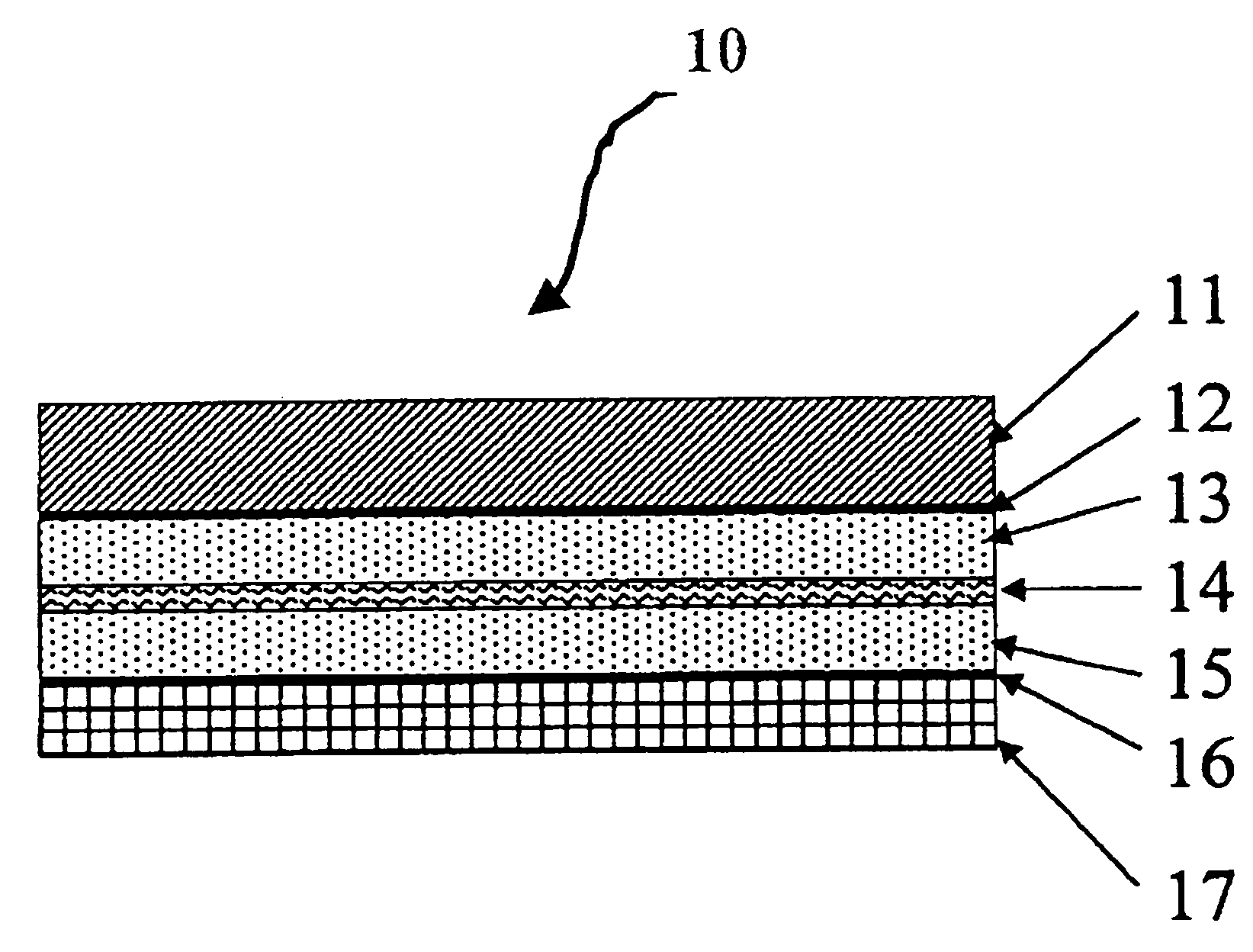
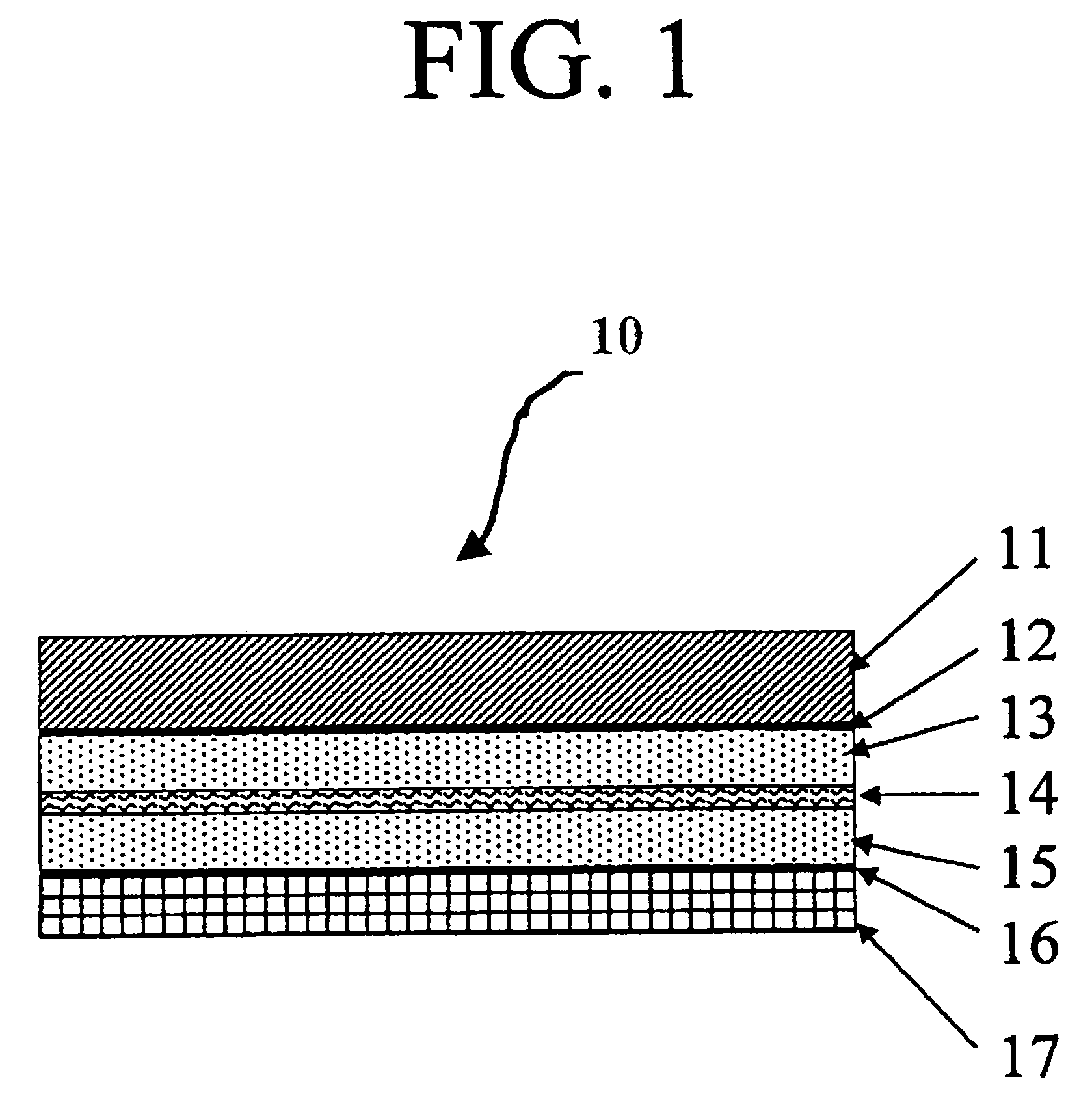
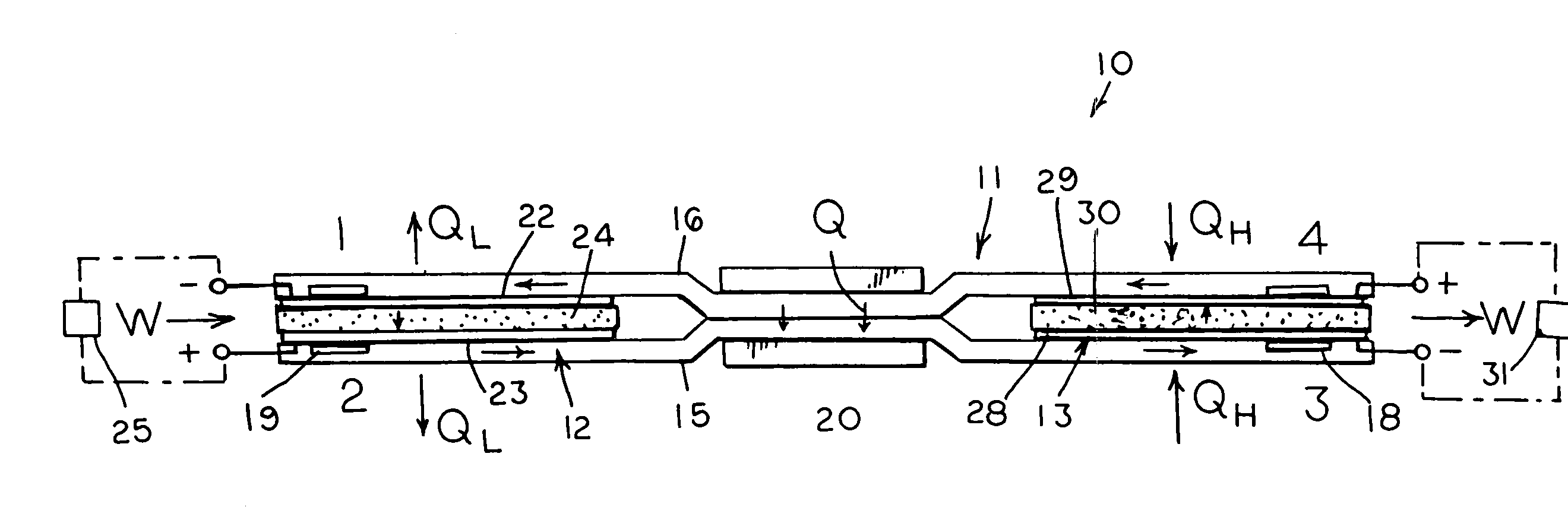
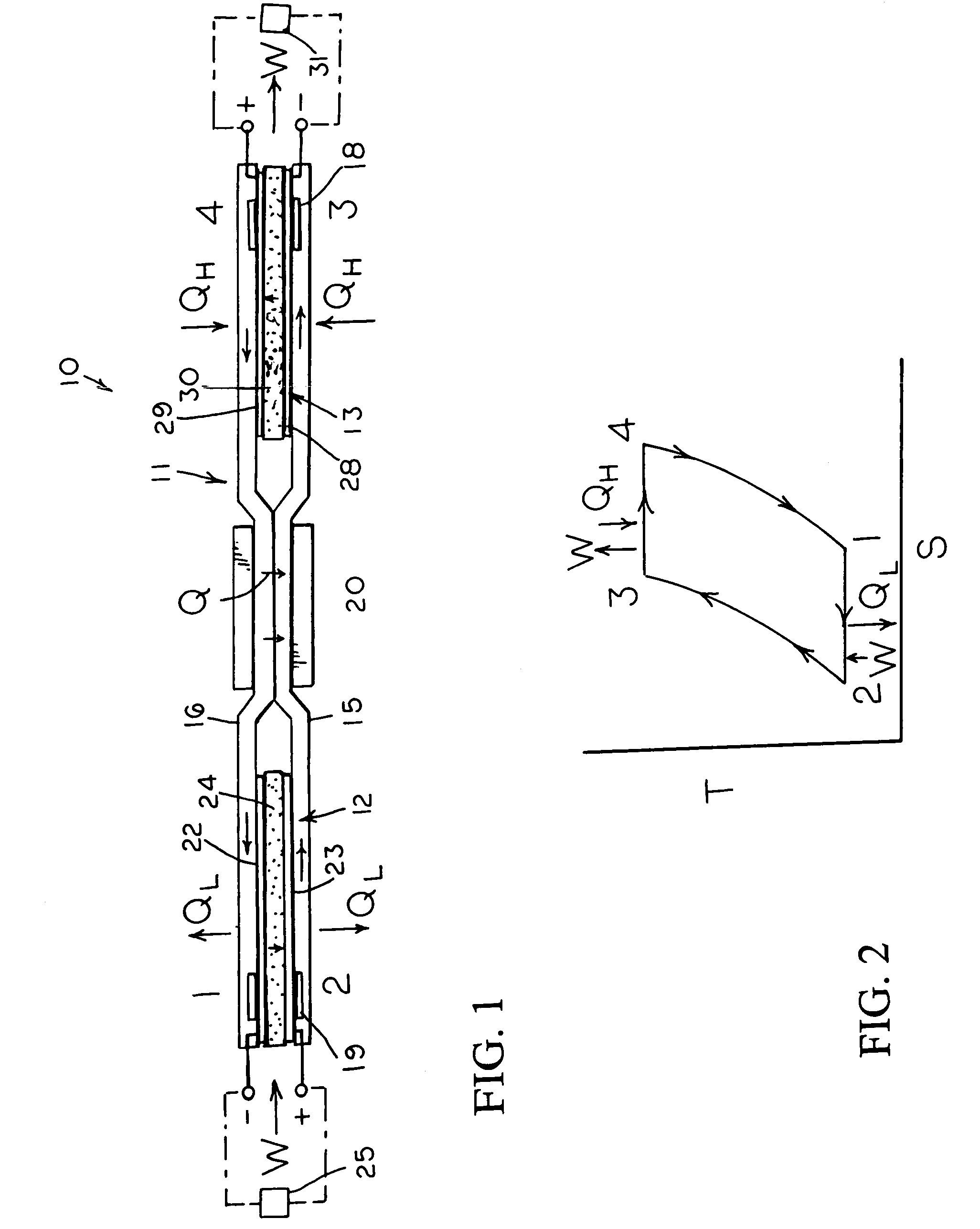
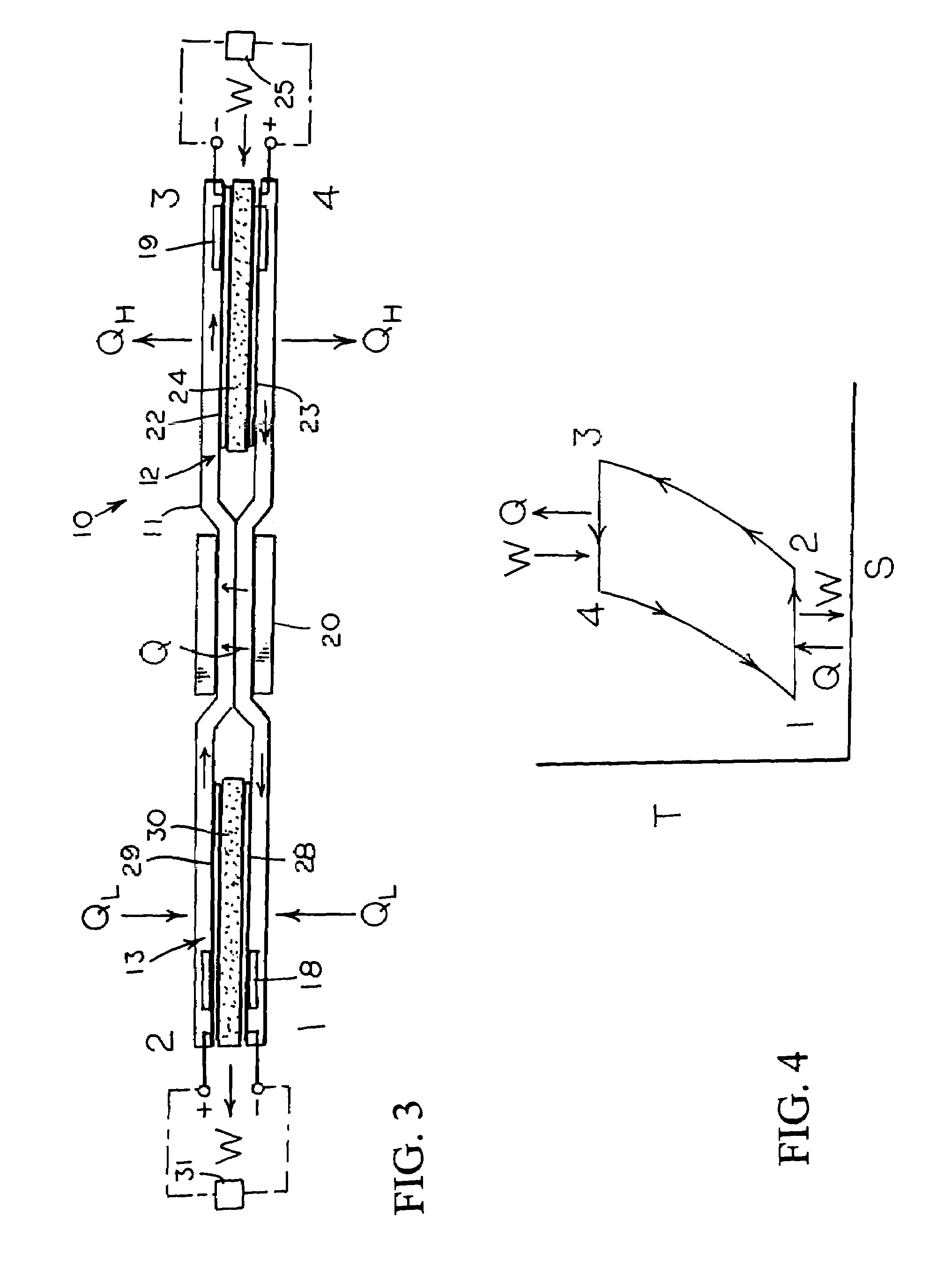
Johnson reversible engine
InactiveUS7160639B2Increase pressureReduce pressureHeat pumpsFuel cell heat exchangeEngineeringElectrochemical cell
An reversible engine (10) is disclosed having a conduit system (11), a first electrochemical cells (12), and a second electrochemical cell (13). The conduit system (11) includes a first conduit (15) extending from the first electrochemical cell (12) to the second electrochemical cell (13), and a second conduit (16) extending from the second electrochemical cell (13) to the first electrochemical cell (12). The heat engine (10) also includes a heater (18) mounted in thermal communication with the conduit system (11) adjacent the second electrochemical cell (13), a cooler (19) mounted in thermal communication with the conduit system (11) adjacent the first electrochemical cell (12), and a regenerative heat exchanger (20) thermally coupled to the first and second conduits (15) and (16) for the transfer of heat therebetween.
Owner:JTEC ENERGY INC
Photoelectric conversion device and method for producing same
InactiveUS6586670B2Promote conversionPrevent deterioration and volatilityLight-sensitive devicesDeferred-action cellsArylHydrogen atom
A method for producing a photoelectric conversion device comprising a conductive support and a photosensitive layer containing a semiconductor fine particle on which a dye is adsorbed, wherein the semiconductor fine particle is treated with a compound represented by the following general formula (I):wherein X represents an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom, a selenium atom or NY, in which Y represents a hydrogen atom, an aliphatic hydrocarbon group, a hydroxyl group or an alkoxy group; R1, R2, R3 and R4 independently represent a hydrogen atom, an aliphatic hydrocarbon group, an aryl group, a heterocyclic group, -N(R5)(R6), -C(=O)R7, -C(=S)R8, -SO2R9 or -OR10; R5 and R6 independently have the same meaning as the R1, R2, R3 and R4; R7, R8 and R9 independently represent a hydrogen atom, an aliphatic hydrocarbon group, an aryl group, a heterocyclic group, -N(R5)(R6), -OR10 or -SR11; and R10 and R11 independently represent a hydrogen atom or an aliphatic hydrocarbon group.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Electrochemical methods, devices, and structures
ActiveUS7541715B2Increase strainDeferred-action cellsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesInorganic compoundActuator
The present invention provides devices and structures and methods of use thereof in electrochemical actuation. This invention provides electrochemical actuators, which are based, inter-alia, on an electric field-driven intercalation or alloying of high-modulus inorganic compounds, which can produce large and reversible volume changes, providing high actuation energy density, high actuation authority and large free strain.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Metal air cell system
A metal air cell system is provided. The system includes a cathode having a pair of oxidant sides and anode sides. An anode is provided in two parts, each part having a side complementary each anode side of the cathode. A separator is disposed between the anode and cathode to electrically isolate the anode and the cathode. Electrolyte is disposed between the cathode and the anode, the electrolyte provided within the anode, separately at the interface between the cathode and the anode, or both within the anode and separately at the interface between the cathode and the anode. This configuration generally allows a single oxidant flow to be exposed to both portions of the cathode due to the central passage of the oxidant.
Owner:EVIONYX INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com