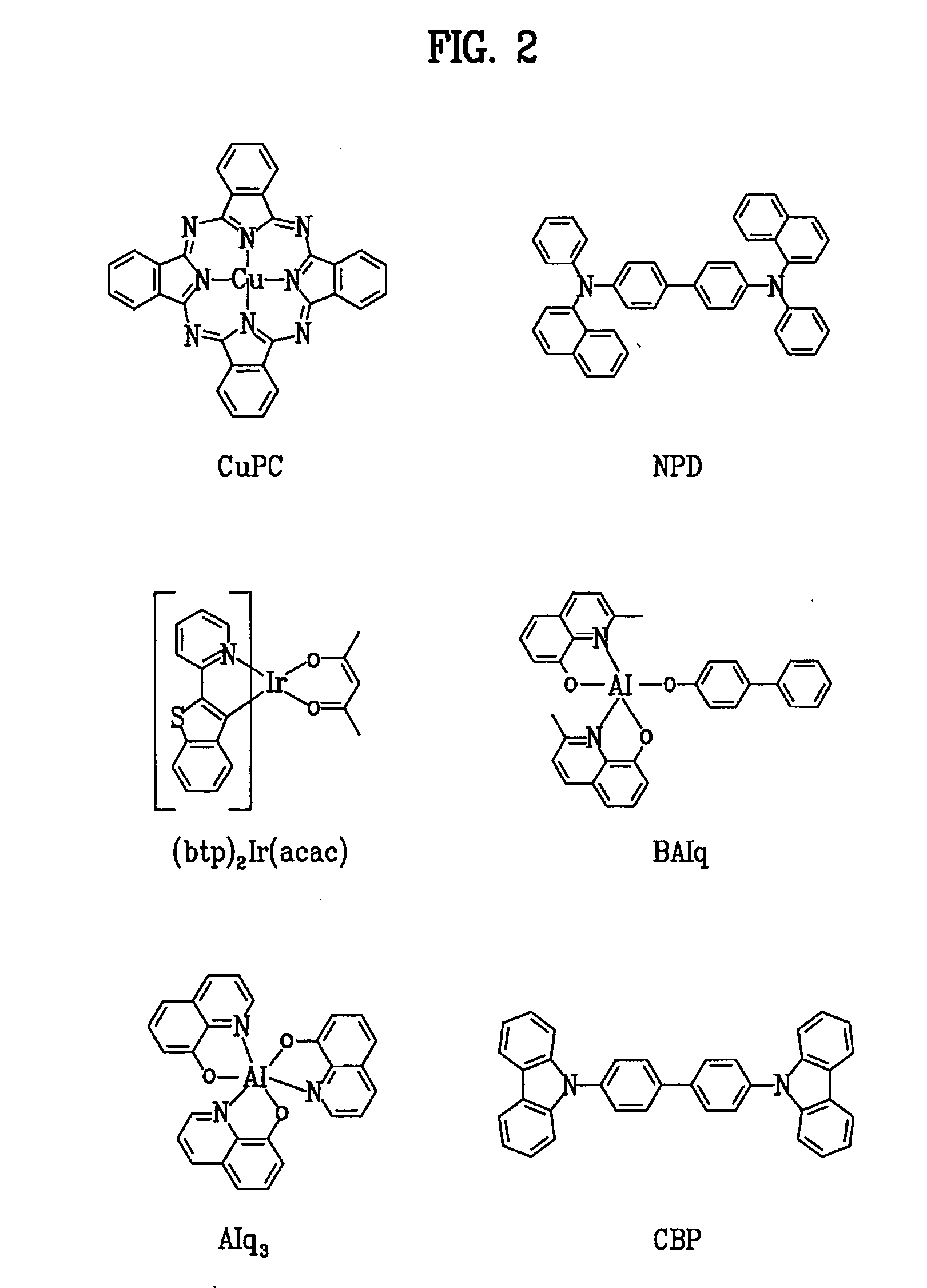
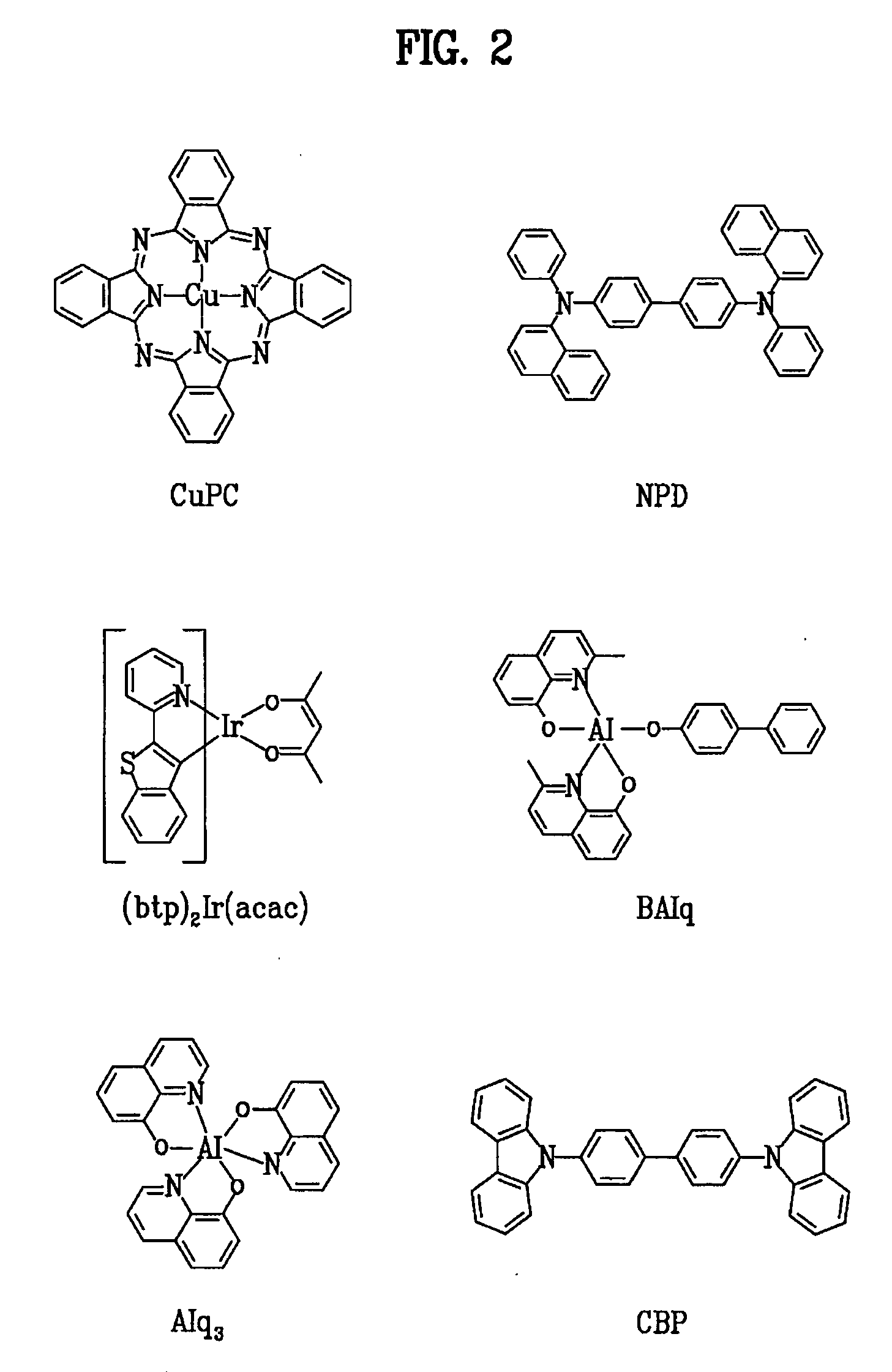
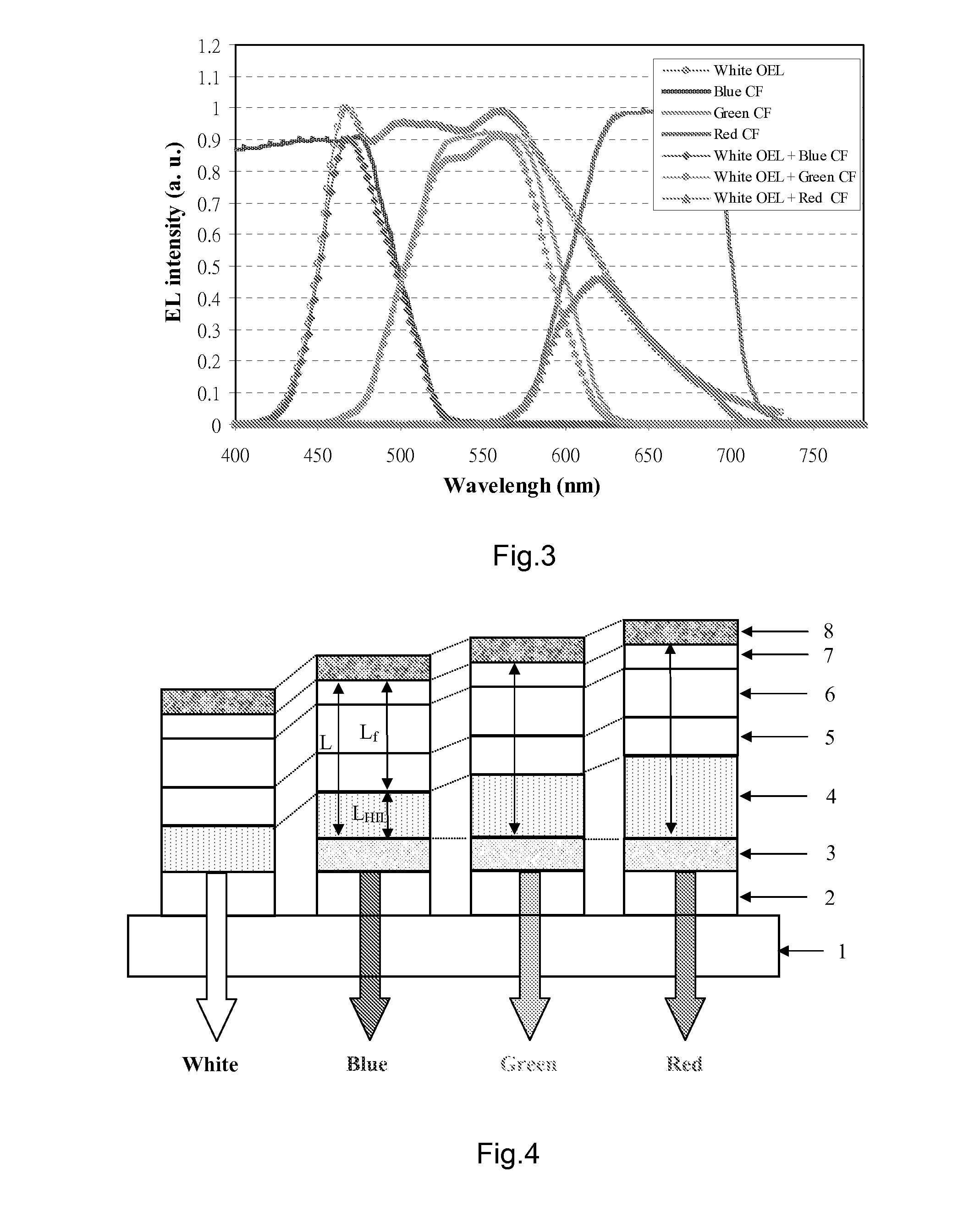
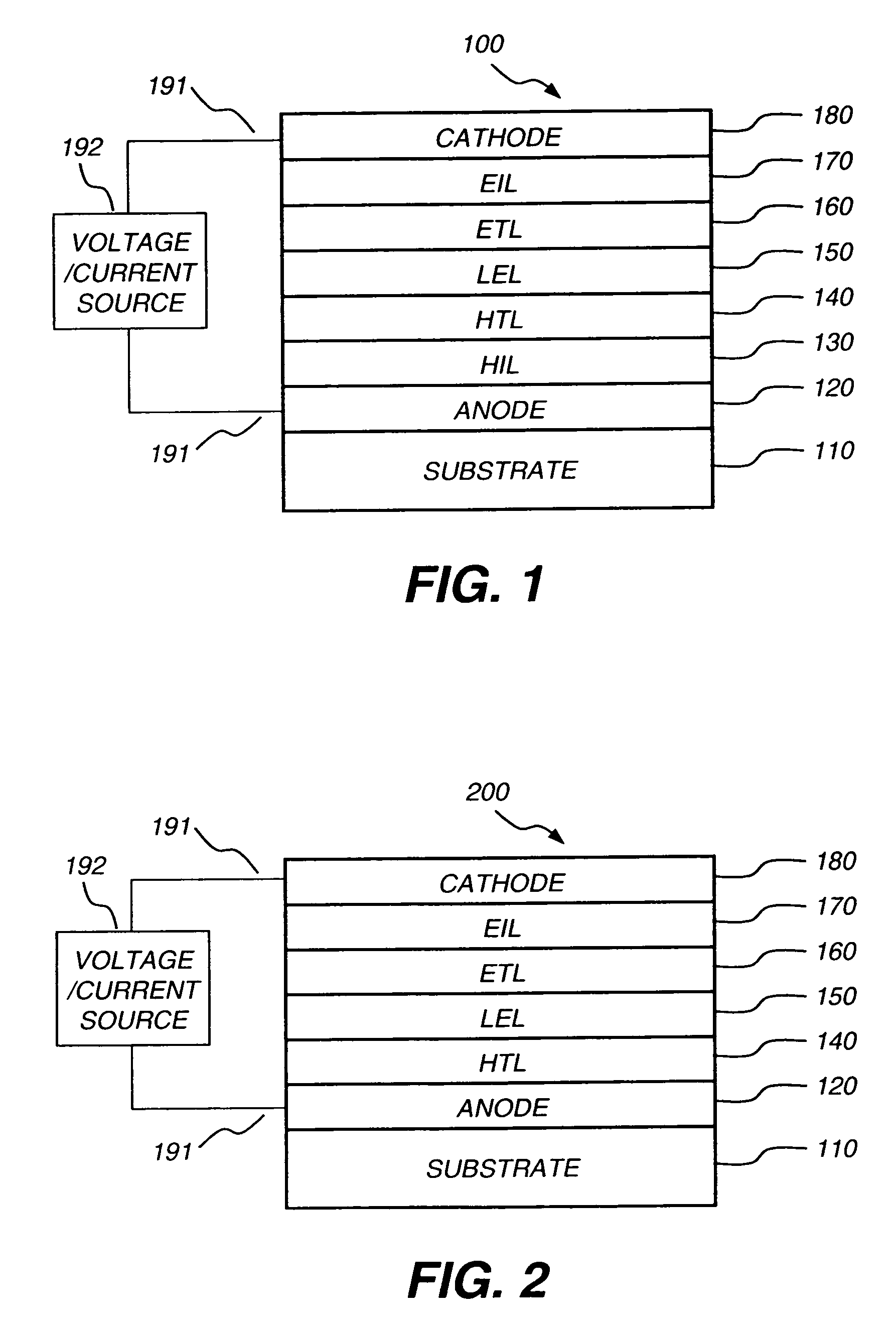
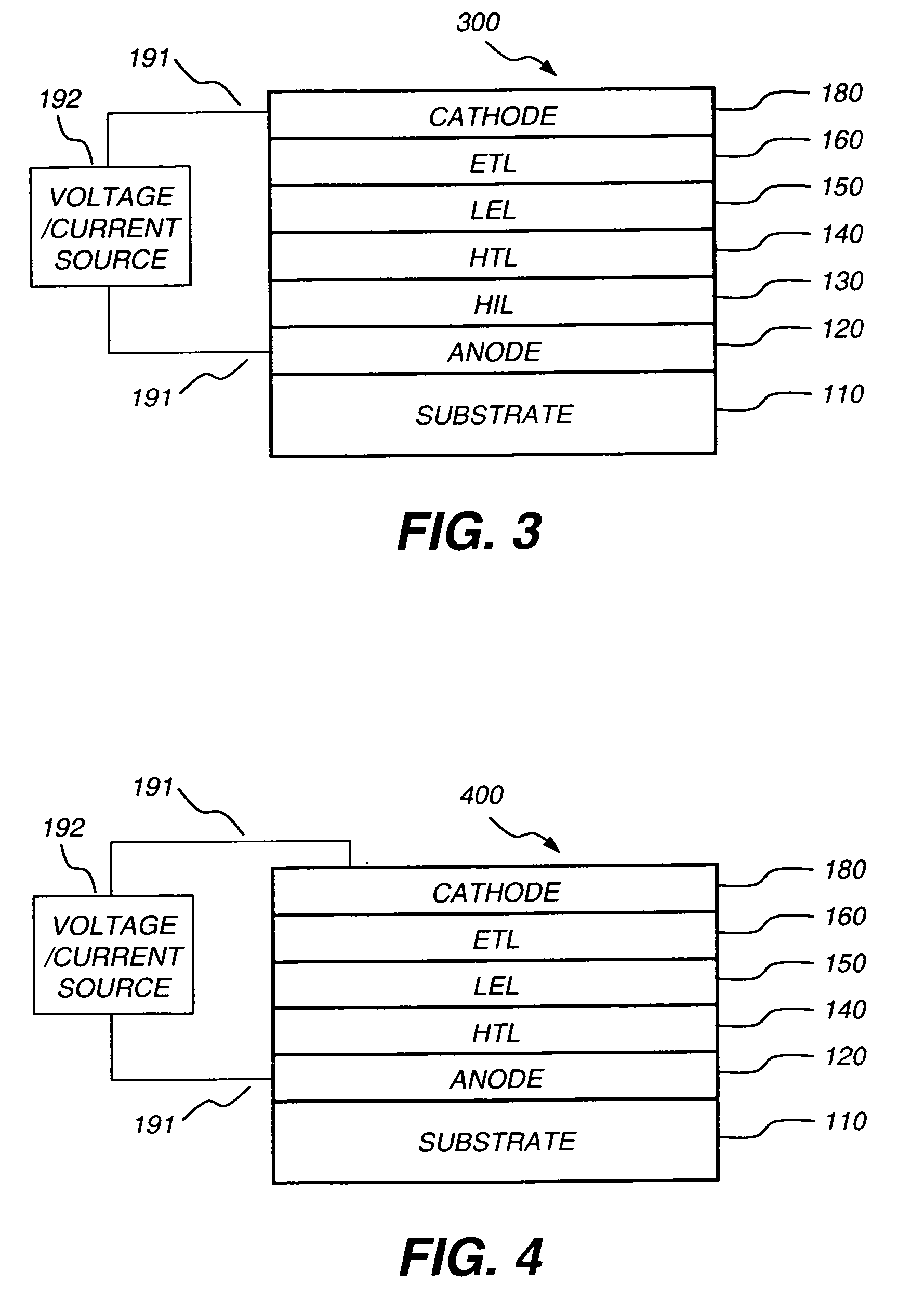
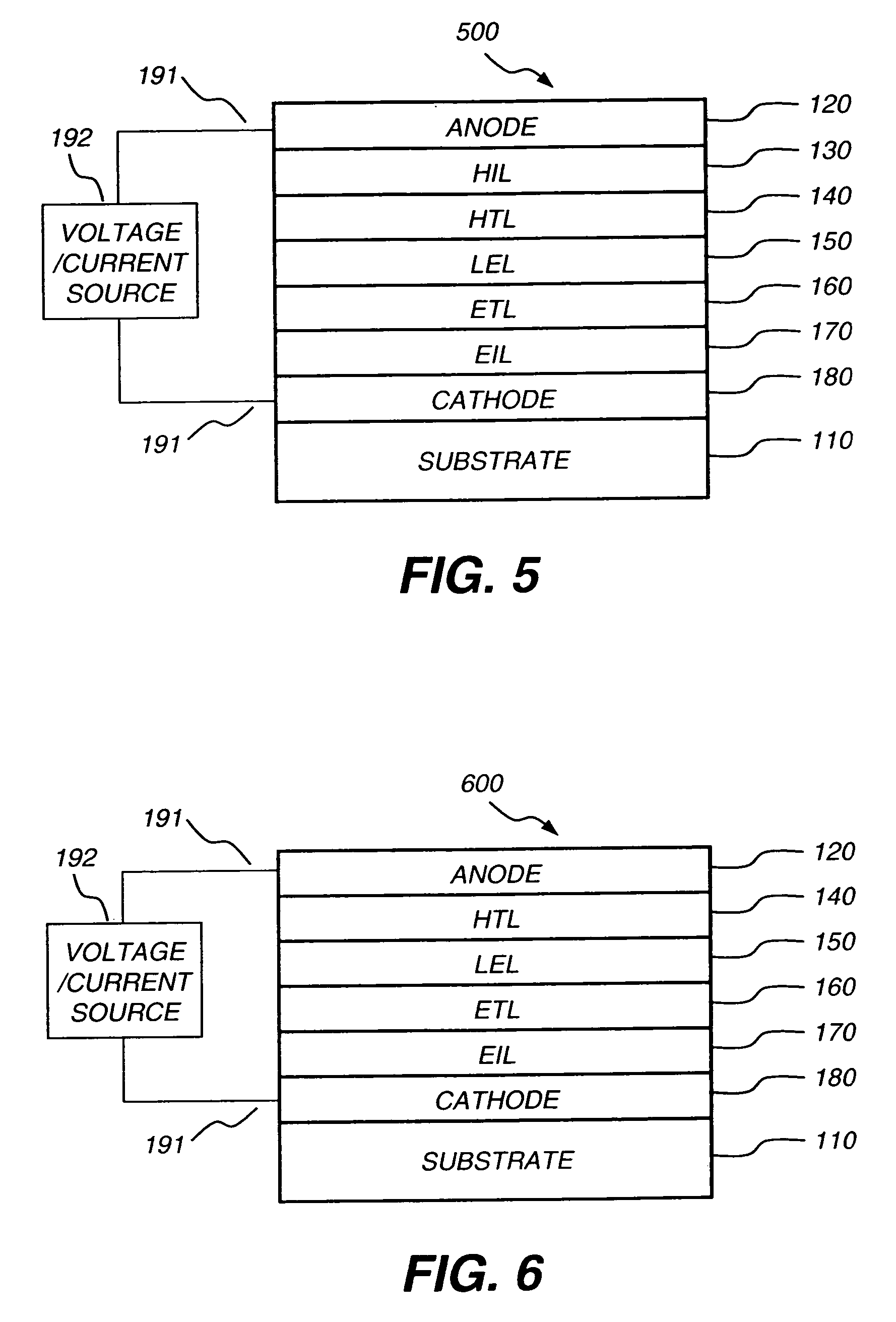
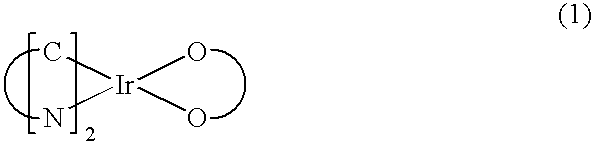Patents
Literature
3112 results about "Electron transport layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
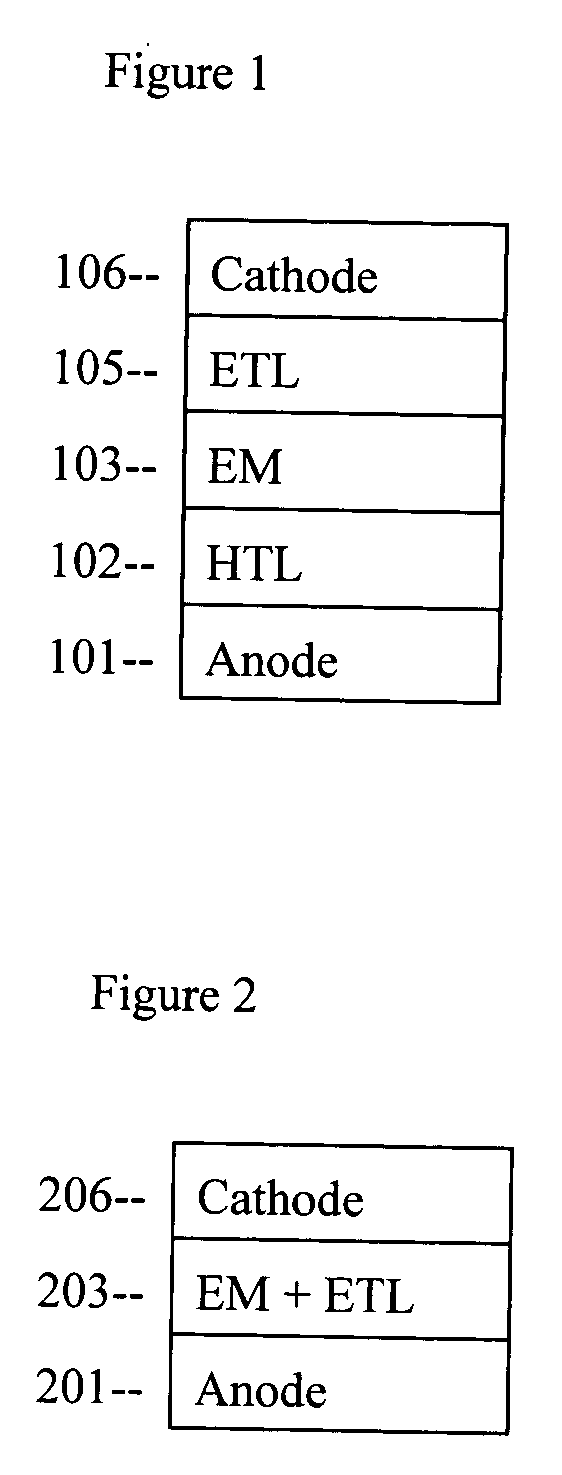
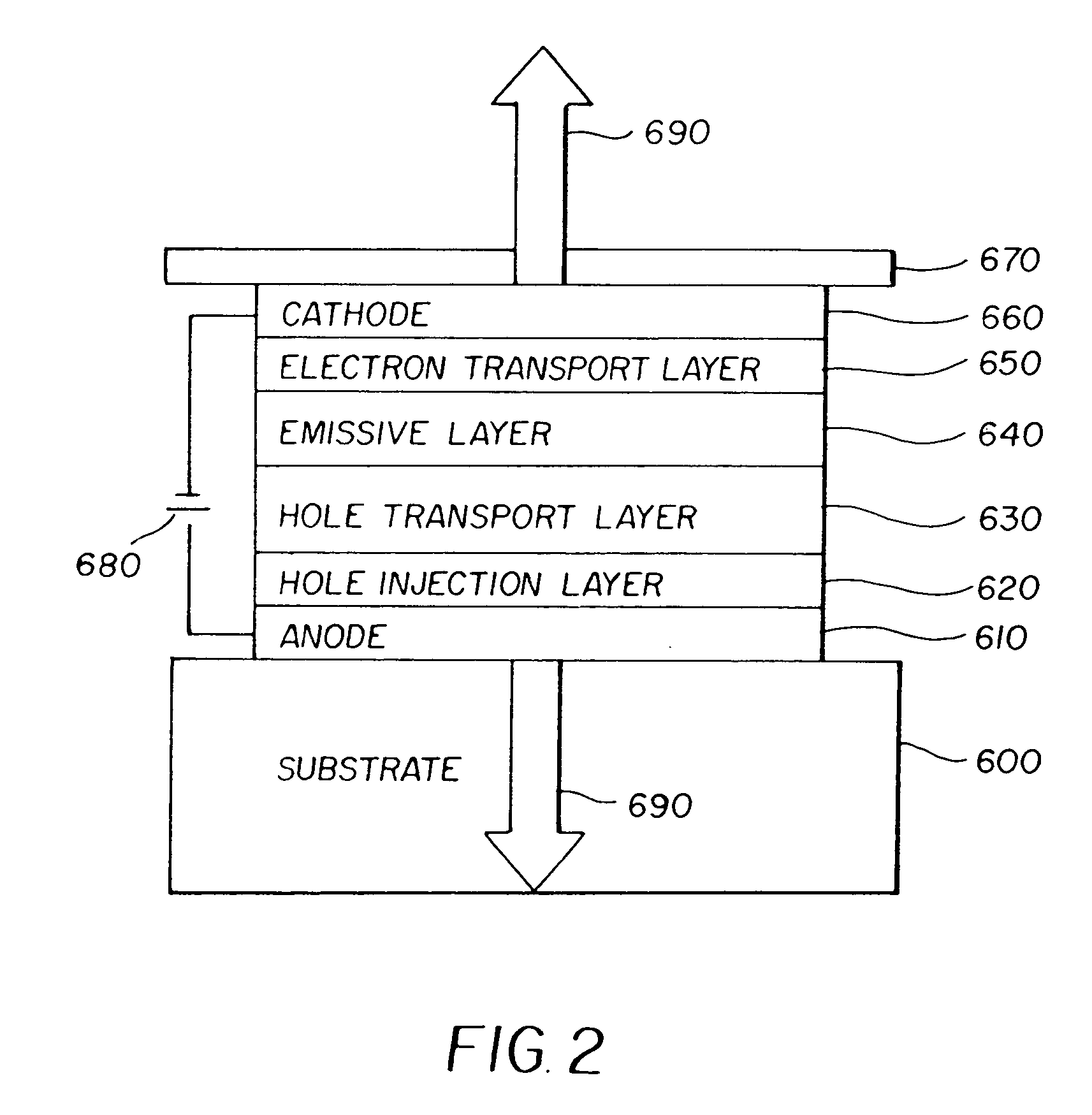
Electron transport layer (ETL) is a layer which has high electron mobility and high electron affinity. Thus in this layer holes are blocked and cannot go through while electrons can flow through. Hole transport layer (HTL) do the opposite of (ETL) behavior it blocks electrons to fllow through .
Charge transport layers and organic electron devices comprising same
InactiveUS20070181874A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsTransport layerHole transport layer
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
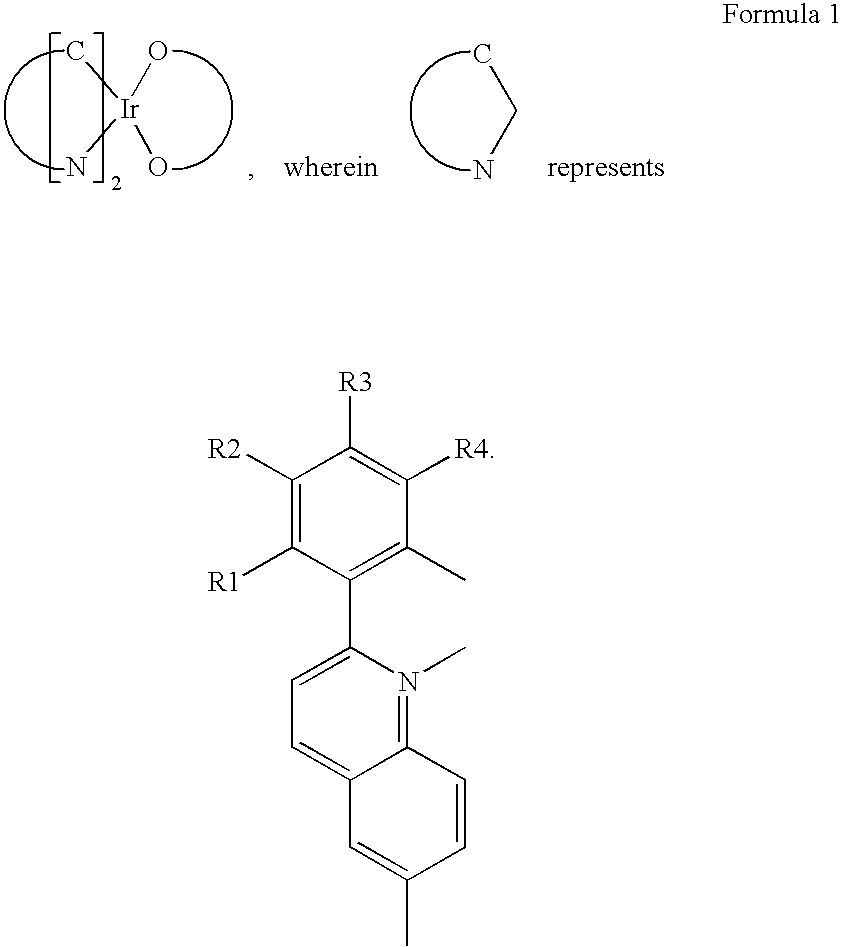
Red phosphorescent compounds and organic electroluminescent devices using the same
ActiveUS20070104980A1High color purityLong life-timeIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensDopantHydrogen
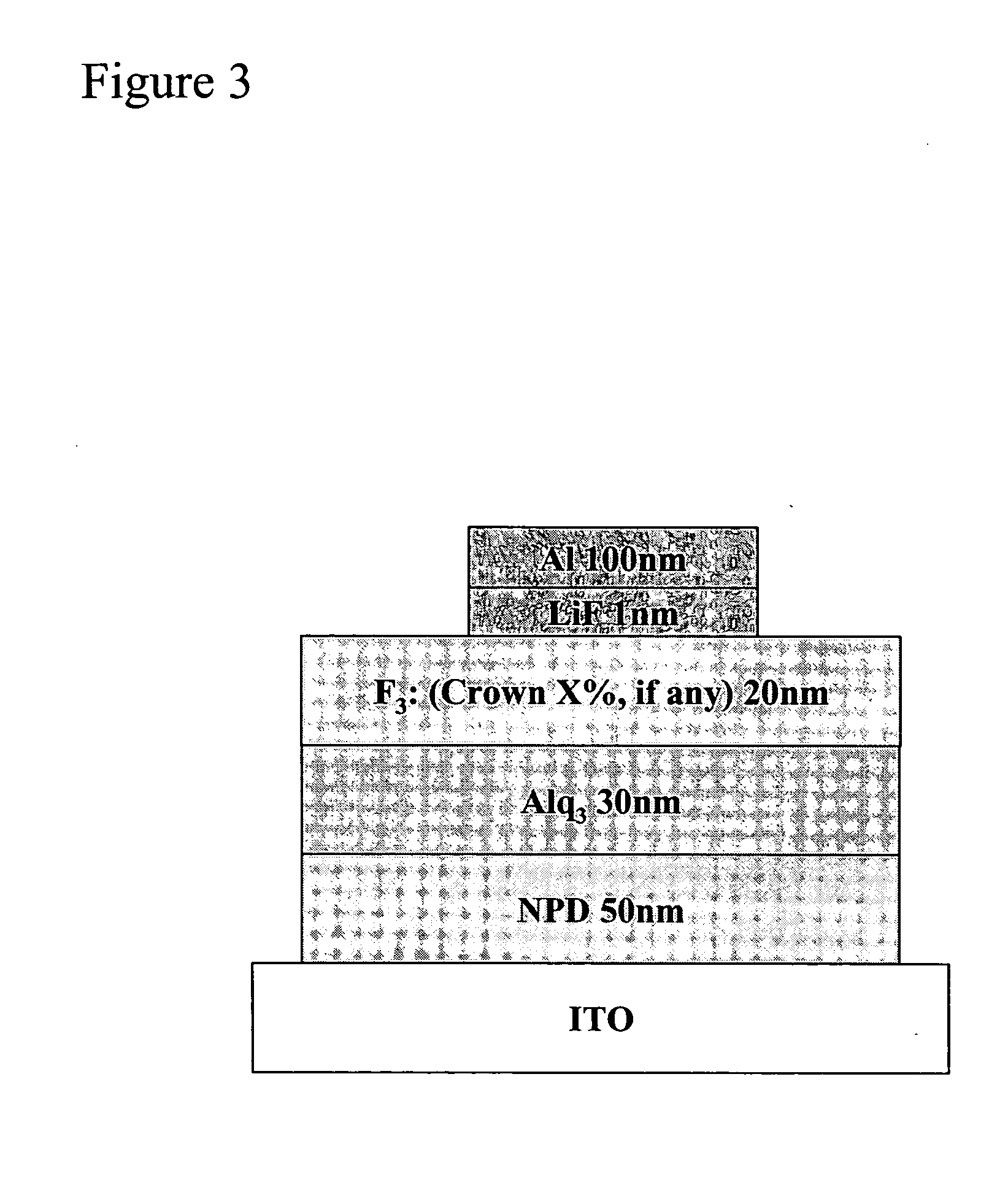
Disclosed herein are red phosphorescent compounds of the following Formulas 1 to 4: wherein is R1, R2 and R3 are independently a C1-C4 alkyl group, R4, R5, R6 and R7 are independently selected from hydrogen, C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, and is selected from 2,4-pentanedione, 2,2,6,6,-tetramethylheptane-3,5-dione, 1,3-propanedione, 1,3-butanedione, 3,5-heptanedione, 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentanedione, 1,1,1,5,5,5-hexafluoro-2,4-pentanedione, and 2,2-dimethyl-3,5-hexanedione; wherein is R1 and R2 are independently selected from C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are independently selected from hydrogen, C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, and is selected from 2,4-pentanedione, 2,2,6,6,-tetramethylheptane-3,5-dione, 1,3-propanedione, 1,3-butanedione, 3,5-heptanedione, 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentanedione, 1,1,1,5,5,5-hexafluoro-2,4-pentanedione and 2,2-dimethyl-3,5-hexanedione; wherein is R1 and R2 are independently selected from C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are independently selected from hydrogen, C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, and is selected from 2,4-pentanedione, 2,2,6,6,-tetramethylheptane-3,5-dione, 1,3-propanedione, 1,3-butanedione, 3,5-heptanedione, 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentanedione, 1,1,1,5,5,5-hexafluoro-2,4-pentanedione and 2,2-dimethyl-3,5-hexanedione; and wherein is R1 and R2 are independently selected from C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are independently selected from hydrogen, C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, and is selected from 2,4-pentanedione, 2,2,6,6,-tetramethylheptane-3,5-dione, 1,3-propanedione, 1,3-butanedione, 3,5-heptanedione, 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentanedione, 1,1,1,5,5,5-hexafluoro-2,4-pentanedione and 2,2-dimethyl-3,5-hexanedione. Further disclosed herein is an organic electroluminescent (EL) device comprising an anode, a hole injecting layer, a hole transport layer, a light-emitting layer, an electron transport layer, an electron injecting layer, and a cathode laminated in this order wherein one of the red phosphorescent compounds is used as a dopant of the light-emitting layer.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Red phosphorescent compound and organic electroluminescent device using the same
ActiveUS20070104979A1High color purityLong life-timeIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensDopantHydrogen
Disclosed herein is a red phosphorescent compound of the following Formula 1: wherein is R1 is a C1-C4 alkoxy group, R2, R3, R4 and R5 are independently selected from hydrogen, C1-C4 alkyl groups and C1-C4 alkoxy groups, and is selected from 2,4-pentanedione, 2,2,6,6,-tetramethylheptane-3,5-dione, 1,3-propanedione, 1,3-butanedione, 3,5-heptanedione, 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentanedione, 1,1,1,5,5,5-hexafluoro-2,4-pentanedione, and 2,2-dimethyl-3,5-hexanedione. Further disclosed herein is an organic electroluminescent (EL) device comprising an anode, a hole injecting layer, a hole transport layer, a light-emitting layer, an electron transport layer, an electron injecting layer, and a cathode laminated in this order wherein one of the red phosphorescent compounds is used as a dopant of the light-emitting layer.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Red phosphorescence compounds and organic electroluminescence device using the same
ActiveUS7740957B2High color purityLong durabilityIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensDopantOrganic electroluminescence
Red phosphorescence compounds and organic electro-luminescence device using the same are disclosed. In an organic electroluminescence device including an anode, a hole injecting layer, a hole transport layer, a light emitting layer, an electron transport layer, an electron injecting layer, and a cathode serially deposited on one another, the organic electroluminescence device may use a compound as a dopant of the light emitting layer.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS20070104977A1Improve efficiencyHigh color purityDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDopantAryl
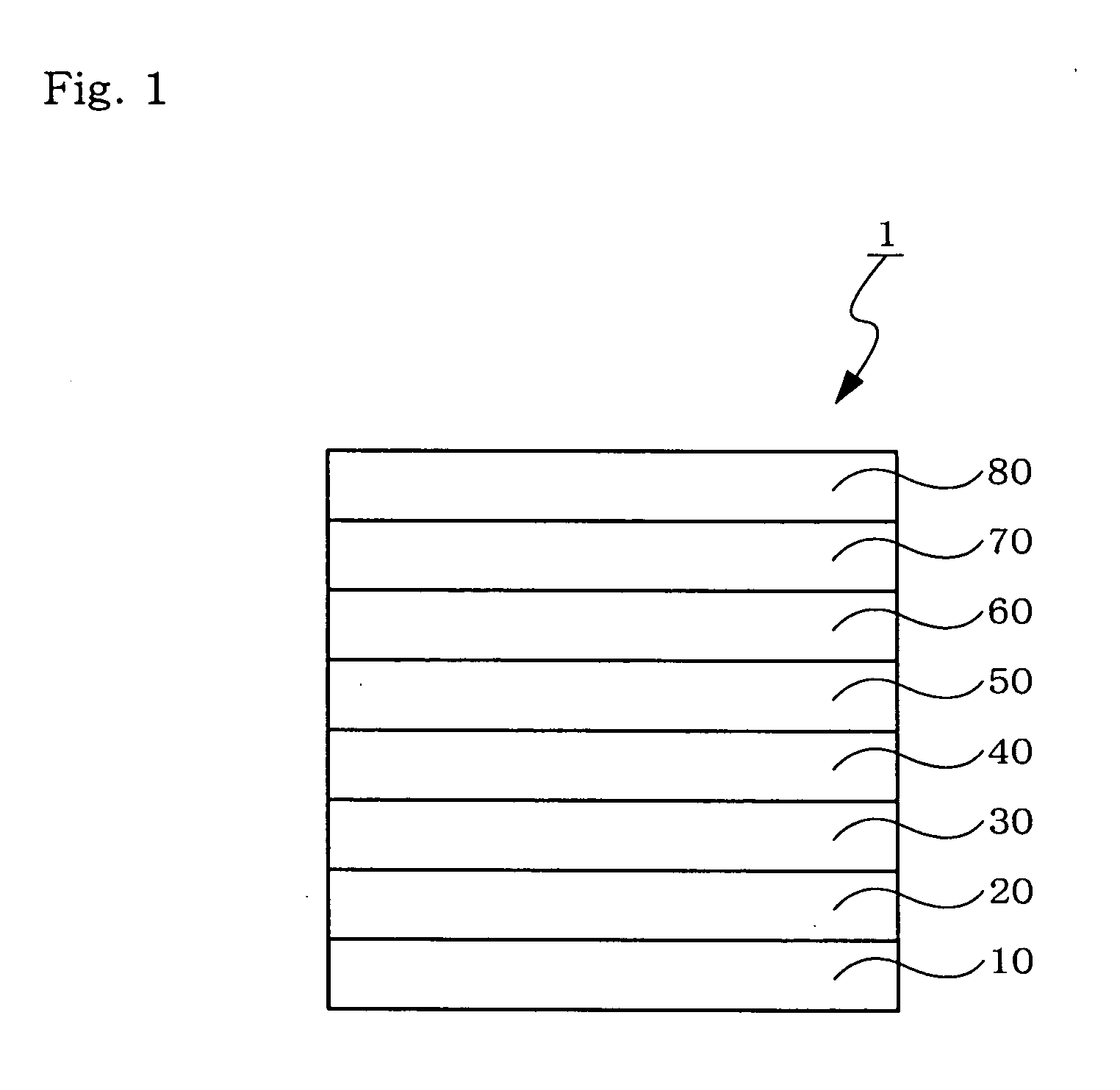
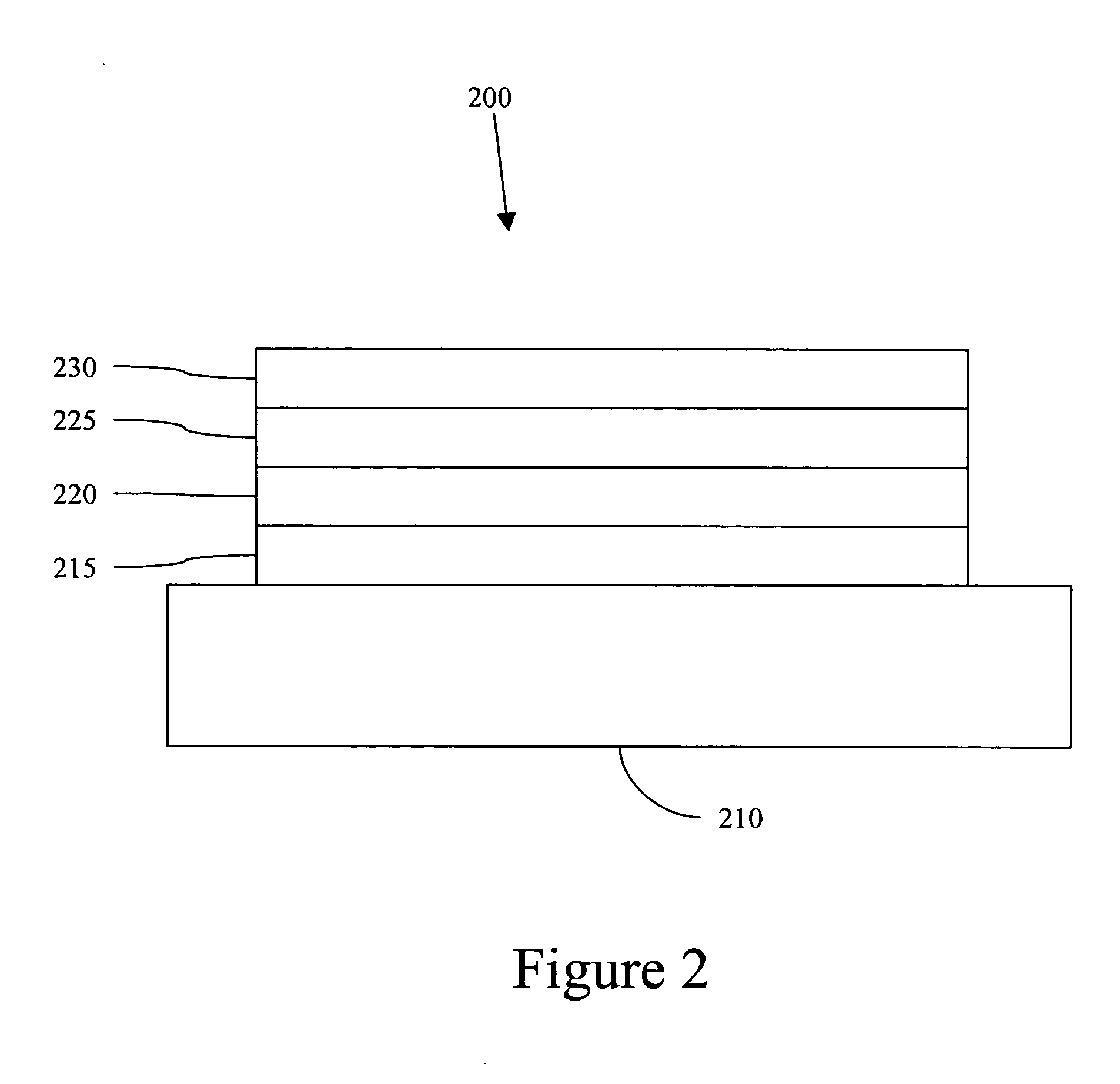
An organic electroluminescent device 1 comprising, an emitting layer (50) and an electron-transporting layer (60) between a cathode (80) and an anode (20), the electron-transporting layer (60) comprising a compound represented by formula (1), the emitting layer (50) comprising a host material which is a compound with an energy gap of 2.8 eV or less represented by formula (2) and a dopant which is an indenoperylene derivative, A-B (1) wherein A is an aromatic hydrocarbon group with three or more carbocycles and B is a substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclic group, X—(Y)n (2) wherein X is a condensed aromatic ring group with three or more carbocycles, Y is a group selected from substituted or unsubstituted aryl, substituted or unsubstituted diarylamino, substituted or unsubstituted arylalkyl and substituted or unsubstituted alkyl groups, and n is an integer of 1 to 6, provided that Ys may be the same or different when n is 2 or more.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Light emitting element
InactiveUS20130105787A1Improve light emission efficiencySufficient durability lifeOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesSilyleneAlkaline earth metal
Provided is an organic thin film light emitting element which has achieved all of improved luminous efficiency, improved driving voltage and improved durability life. Specifically provided is a light emitting element which comprises a hole transport layer and an electron transport layer between a positive electrode and a negative electrode and emits light by means of electrical energy. The light emitting element is characterized in that: the hole transport layer of the light emitting element contains a compound represented by general formula (1); the electron transport layer contains a donor compound; and the donor compound is an alkali metal, an inorganic salt containing an alkali metal, a complex of an alkali metal and an organic substance, an alkaline earth metal, an inorganic salt containing an alkaline earth metal, or a complex of an alkaline earth metal and an organic substance. (In the formula, R1-R20 each represents one group selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, deuterium, an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group, an amino group, an aryl group, a heterocyclic group, a heteroaryl group, an alkenyl group, a cycloalkenyl group, an alkynyl group, analkoxy group, an alkylthio group, an arylether group, an arylthioether group, a halogen, a cyano group, a —P(═O)R24R25 group and a silyl group; R24 and R25 each represents an aryl group or a heteroaryl group; and these substituents may be further substituted, or adjacent two substituents may combine together to form a ring. Meanwhile, R21-R23 may be the same or different and each represents one group selected from the group consisting of an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group, an aryl group and a heteroaryl group; and these substituents maybe further substituted.)
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device
ActiveUS20160336519A1Long life-timeImprove emission efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesFluorescenceHost material
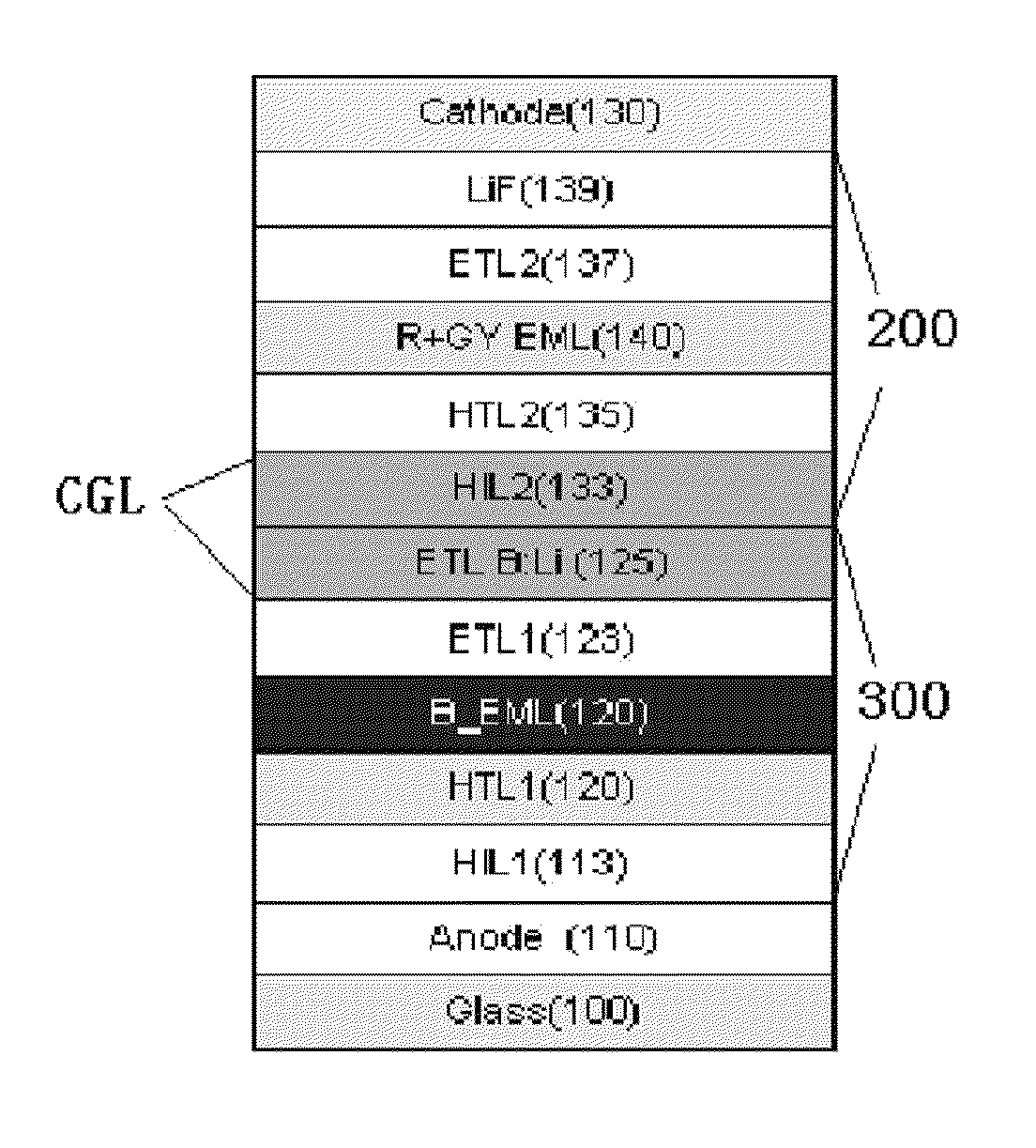
Provided is a novel light-emitting element, a light-emitting element with a long lifetime, or a light-emitting element with high emission efficiency. The light-emitting element includes an EL layer between a pair of electrodes. The EL layer includes at least a light-emitting layer containing a fluorescent substance and a host material, a first electron-transport layer containing a first electron-transport material, and a second electron-transport layer containing a second electron-transport material, which are in contact with each other and in this order. The LUMO level of each of the host material and the second electron-transport material is higher than the LUMO level of the first electron-transport material.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Solid state photosensitive devices which employ isolated photosynthetic complexes
ActiveUS20050098726A1Radiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementPhotosynthetic ComplexesSemiconductor materials
Solid state photosensitive devices including photovoltaic devices are provided which comprise a first electrode and a second electrode in superposed relation; and at least one isolated Light Harvesting Complex (LHC) between the electrodes. Preferred photosensitive devices comprise an electron transport layer formed of a first photoconductive organic semiconductor material, adjacent to the LHC, disposed between the first electrode and the LHC; and a hole transport layer formed of a second photoconductive organic semiconductor material, adjacent to the LHC, disposed between the second electrode and the LHC. Solid state photosensitive devices of the present invention may comprise at least one additional layer of photoconductive organic semiconductor material disposed between the first electrode and the electron transport layer; and at least one additional layer of photoconductive organic semiconductor material, disposed between the second electrode and the hole transport layer. Methods of generating photocurrent are provided which comprise exposing a photovoltaic device of the present invention to light. Electronic devices are provided which comprise a solid state photosensitive device of the present invention.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Photoelectric conversion element
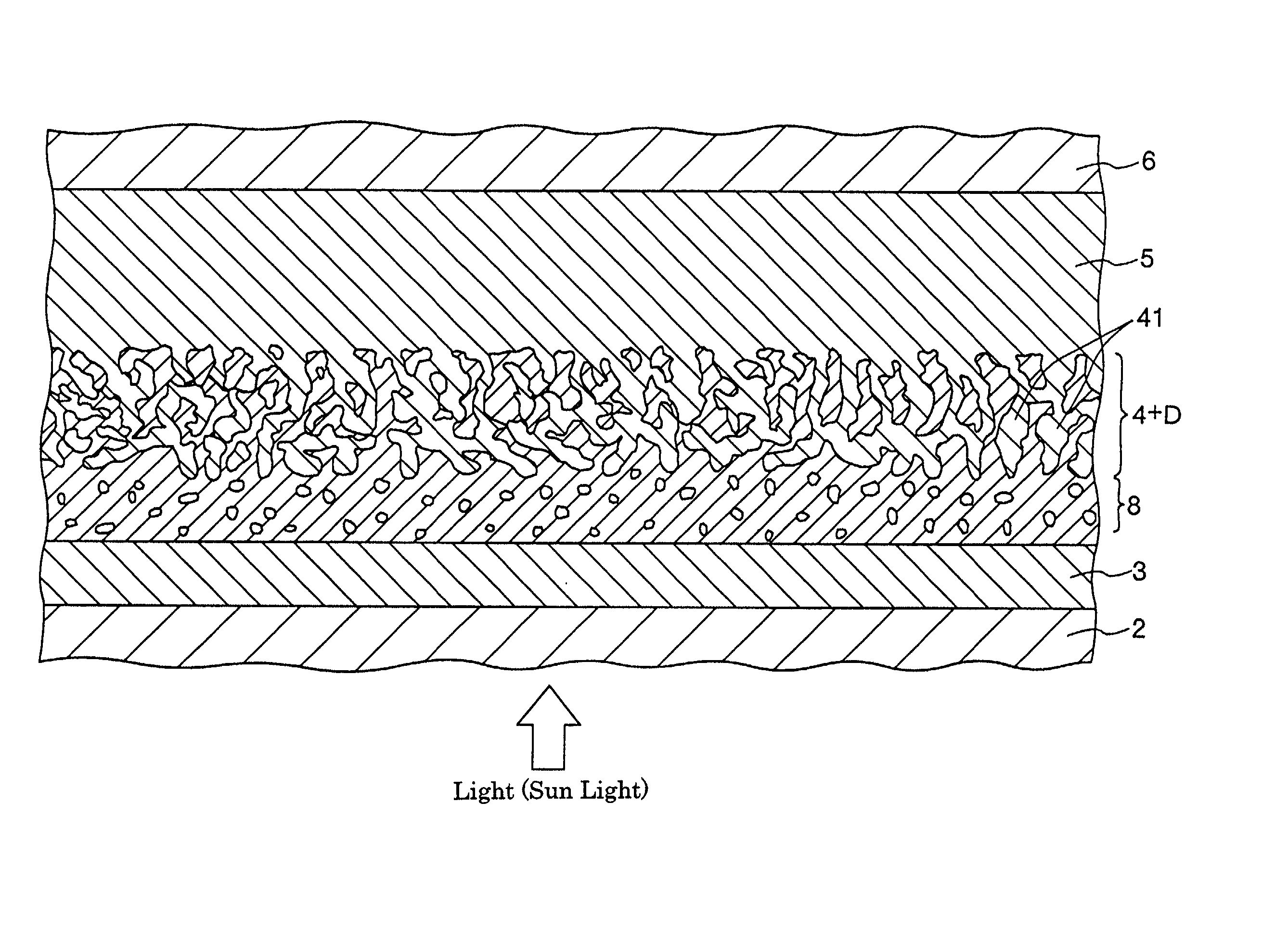
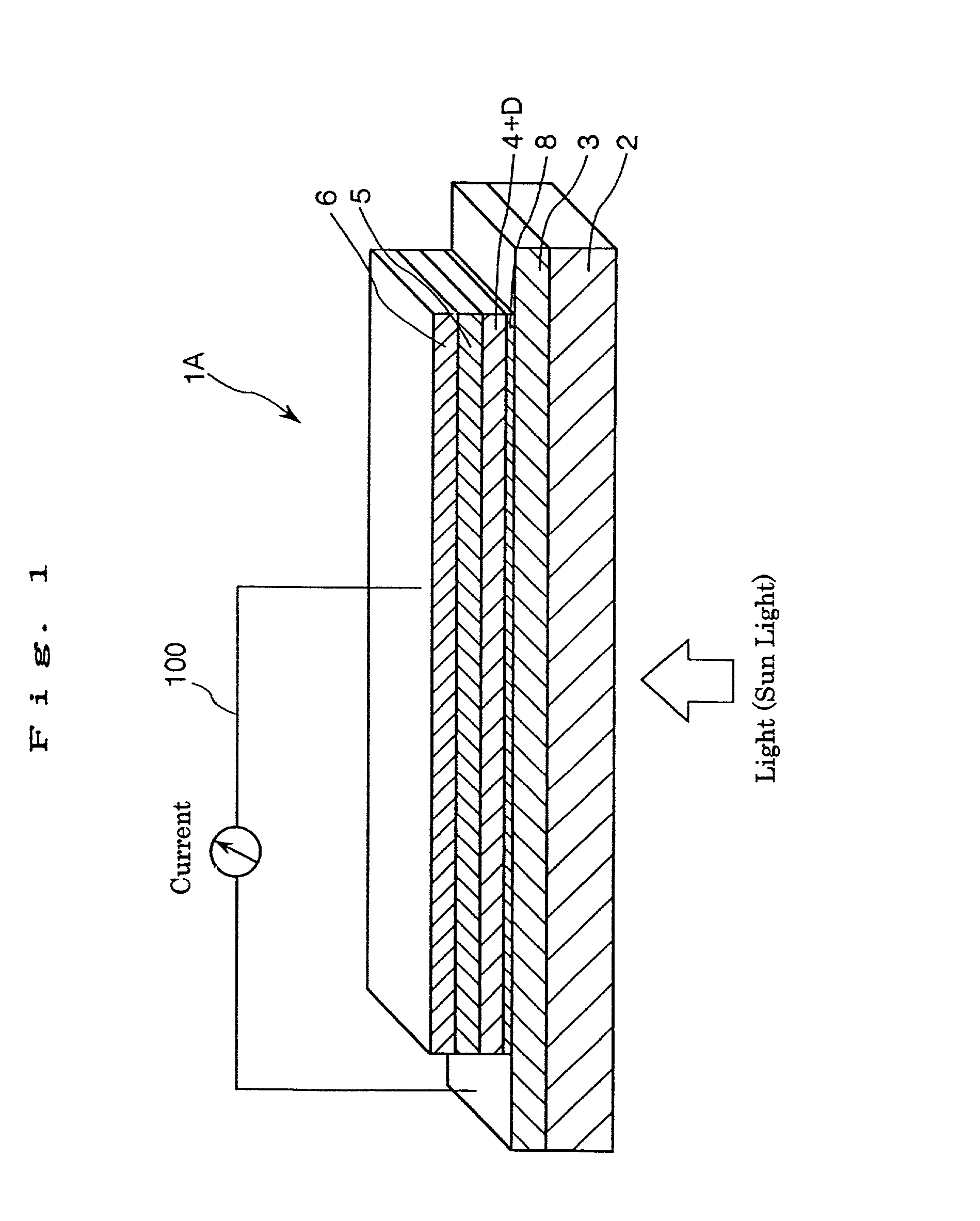
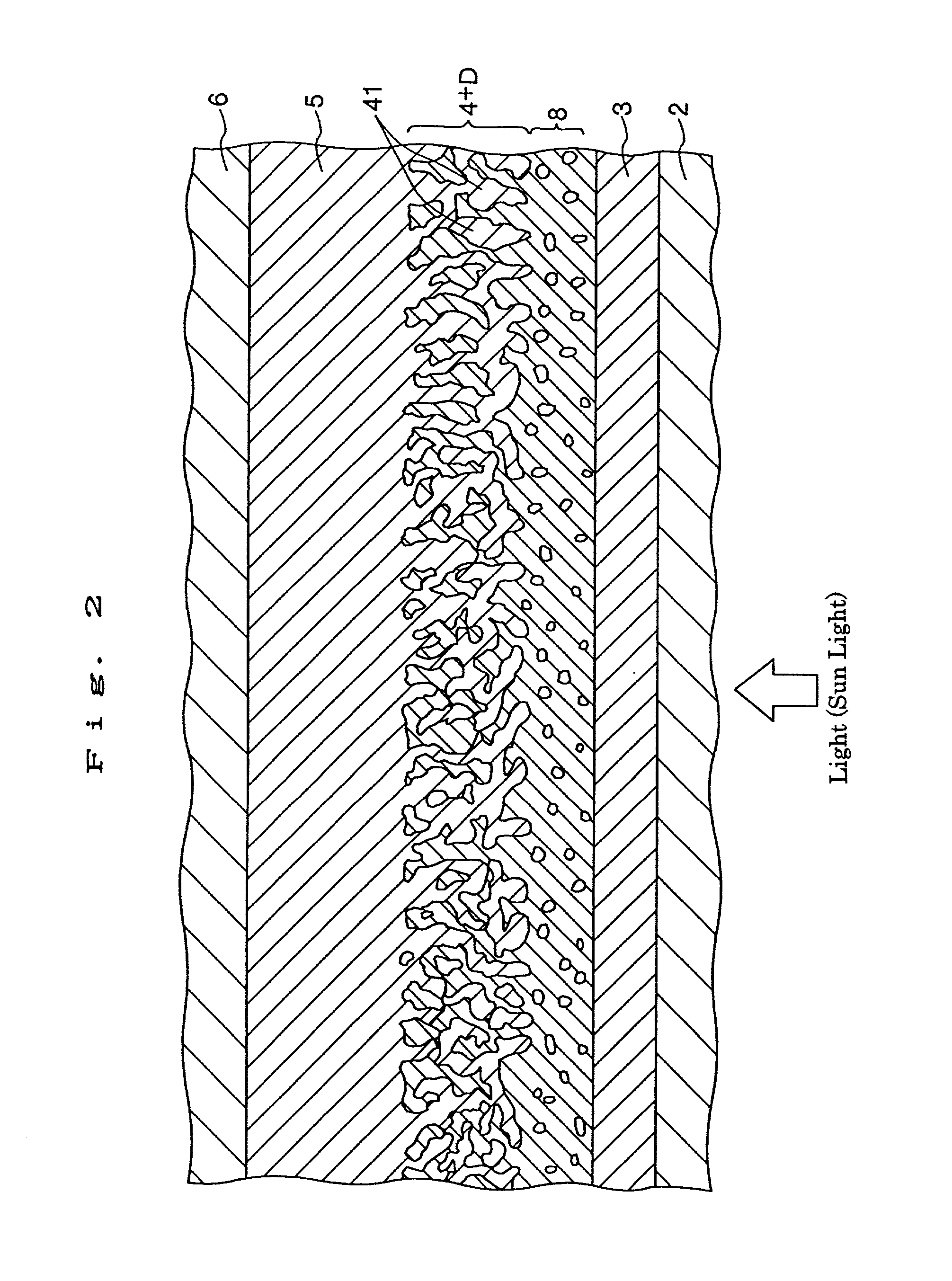
InactiveUS6683244B2Improve photoelectric conversion efficiencyPrevent and suppressLight-sensitive devicesDeferred-action cellsPorosityPhotoelectric conversion
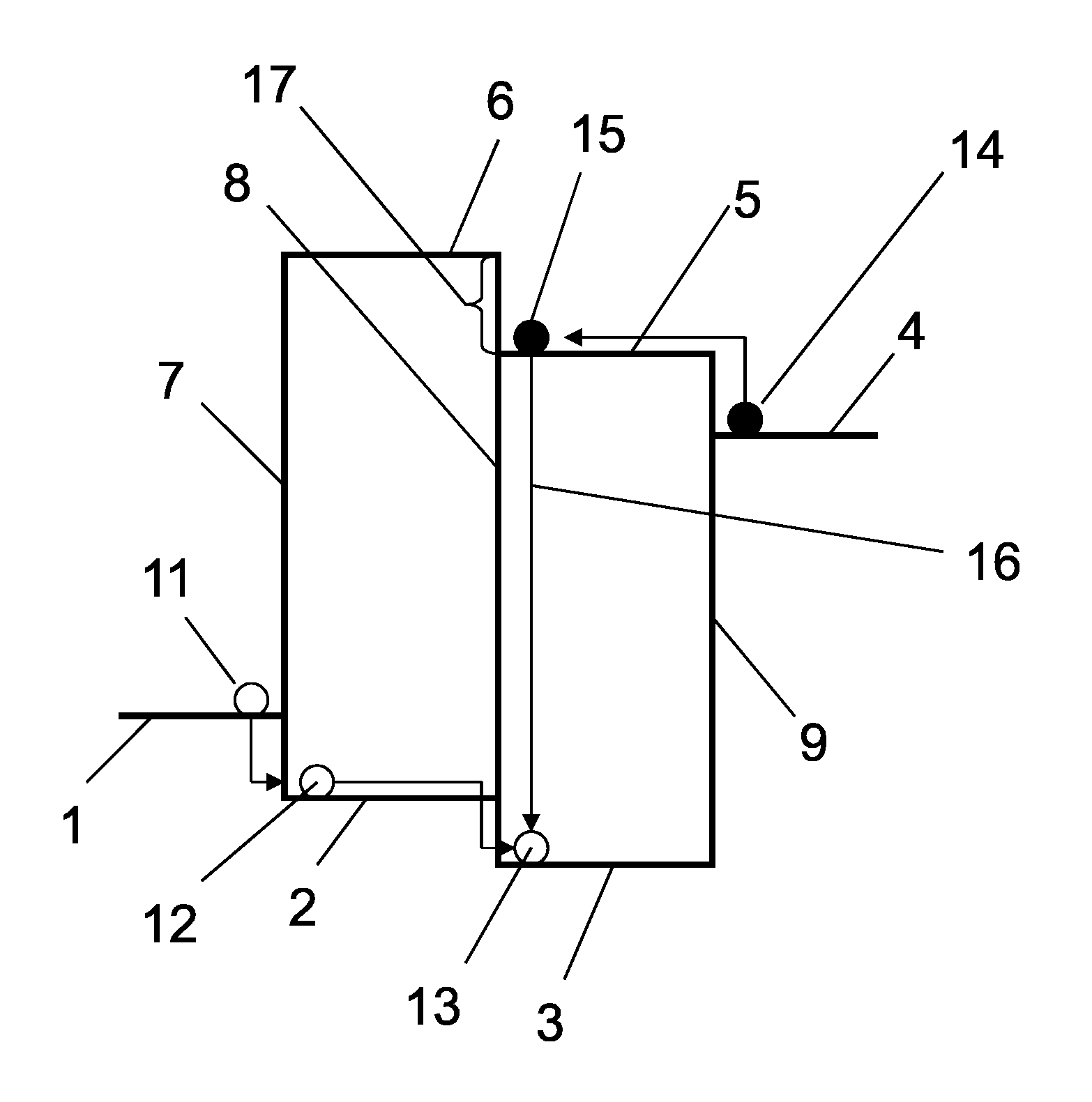
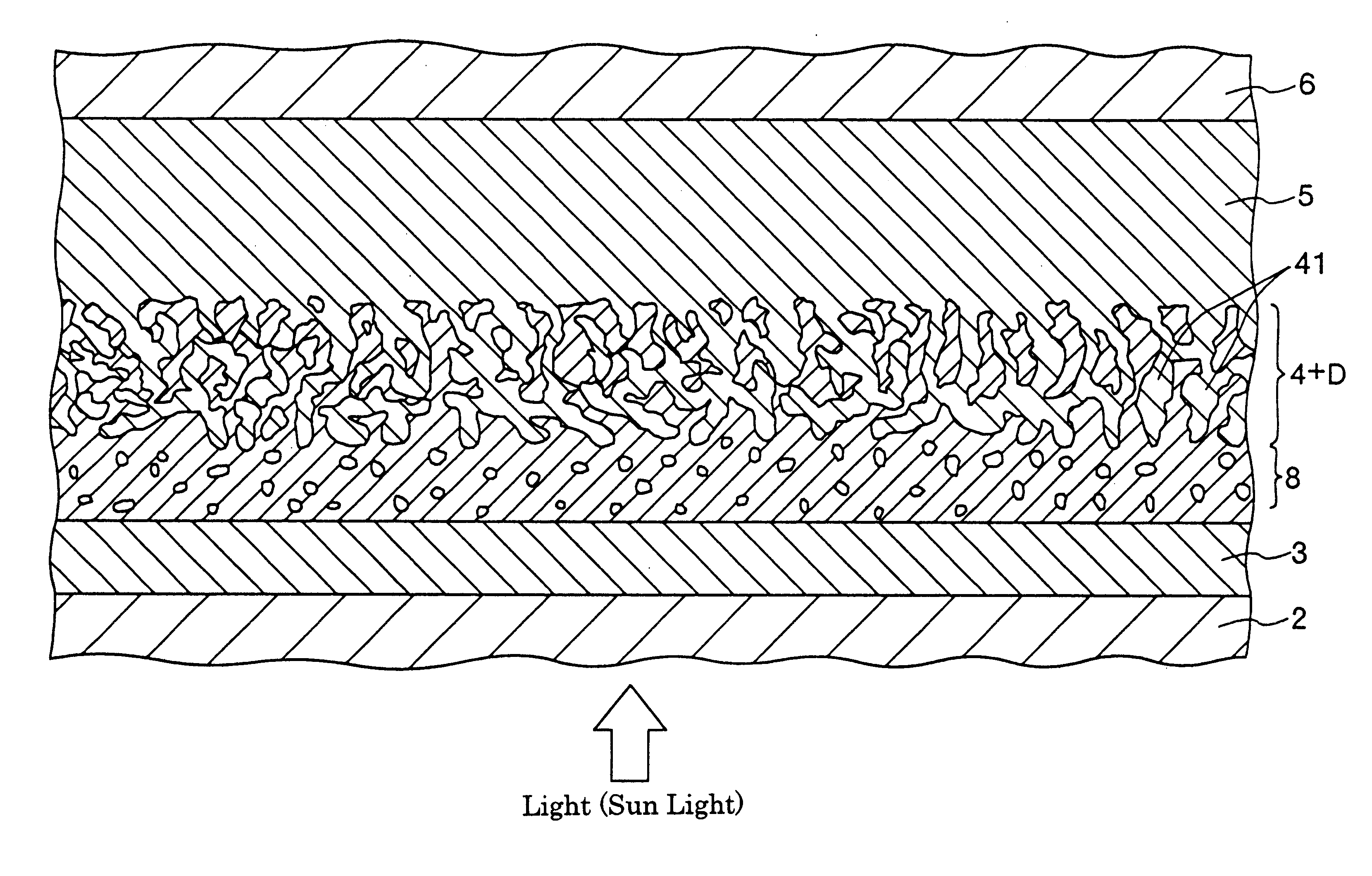
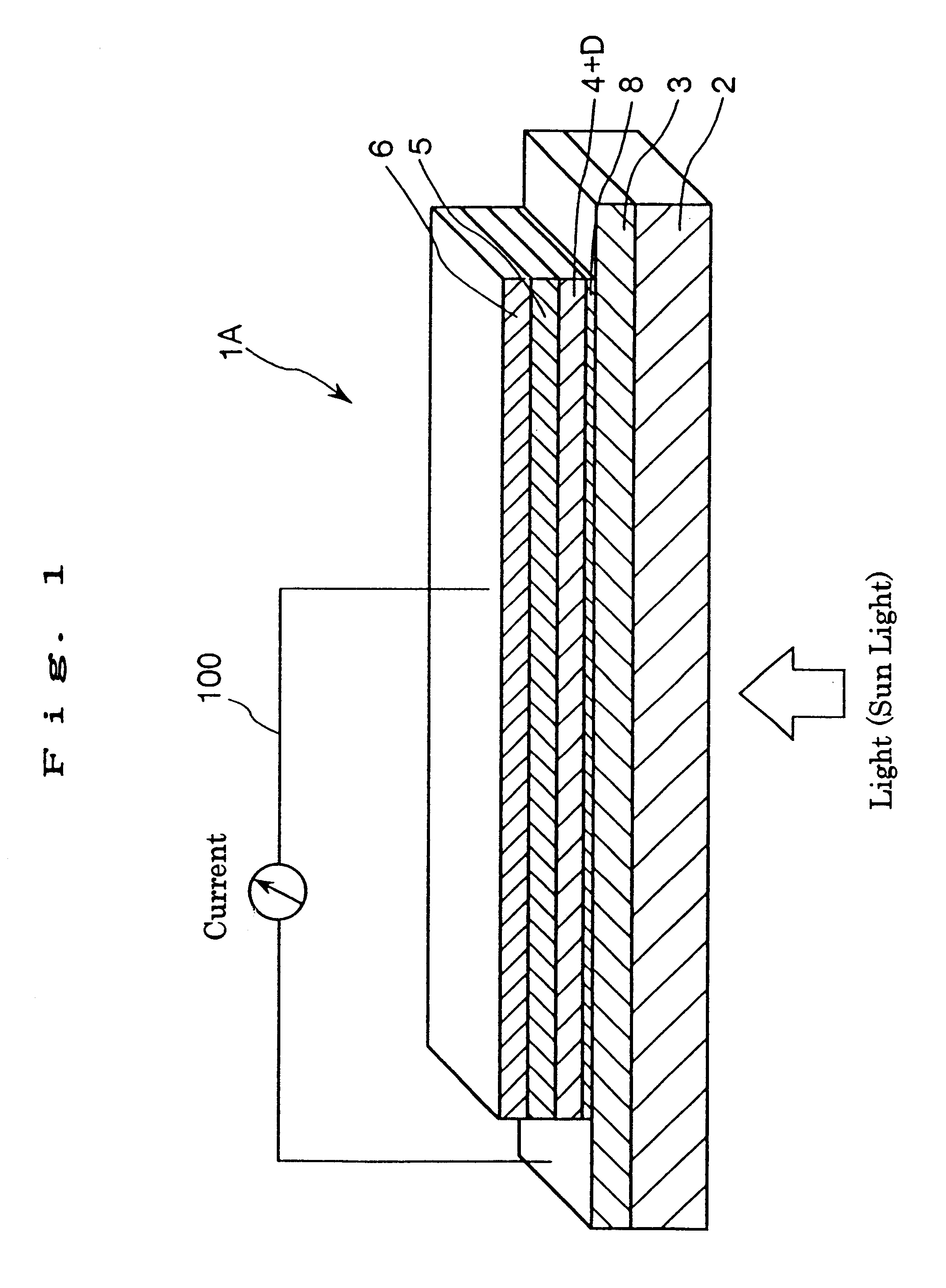
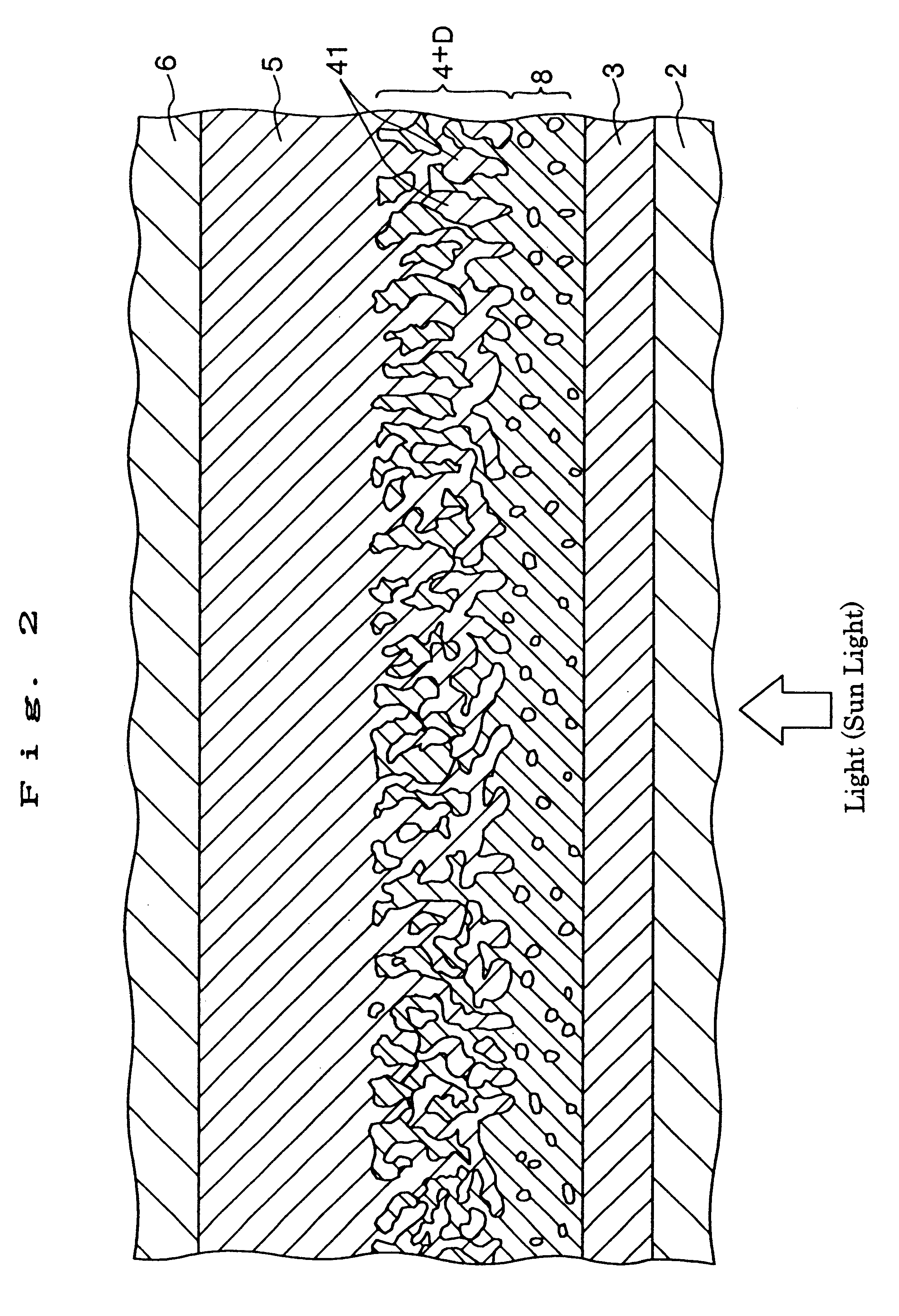
A solar cell including a first electrode, a second electrode arranged opposite to the first electrode, an electron transport layer arranged between the first electrode and the second electrode, a dye layer D which is in contact with the electron transport layer, a hole transport layer arranged between the electron transport layer and the second electrode and being in contact with the dye layer D, and a barrier layer, and these elements are provided on a substrate. The barrier layer prevents or suppresses short-circuit between the first electrode and the hole transport layer. The porosity of the barrier layer is made smaller than that of the electron transport layer. The barrier layer is formed into a film-like shape and arranged between the first electrode and the electron transport layer. The solar cell can accomplish excellent photoelectric conversion efficiency by the provision of such a barrier layer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
White organic light emitting device
ActiveUS8963127B2Convenient lightingImprove display efficiencyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDopantGreen yellow
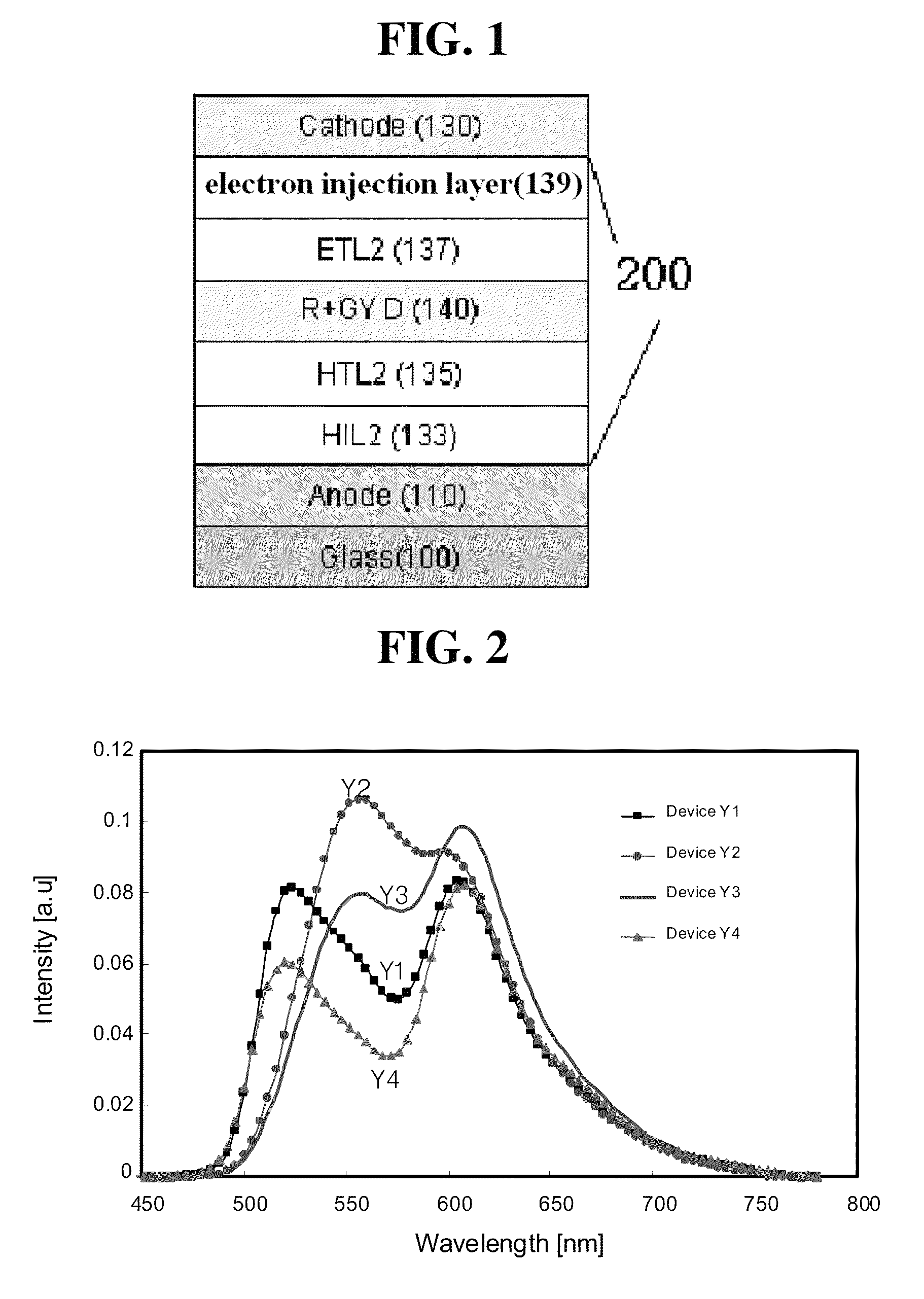
A white organic light emitting device having a dual stack structure is disclosed, in which an electron transport layer adjacent to a blue light emitting layer includes an electron transport catalyst layer including metal to improve blue light emitting efficiency, and a greenish yellow dopant is used to improve white display efficiency, increase lifespan, and reduce power consumption.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
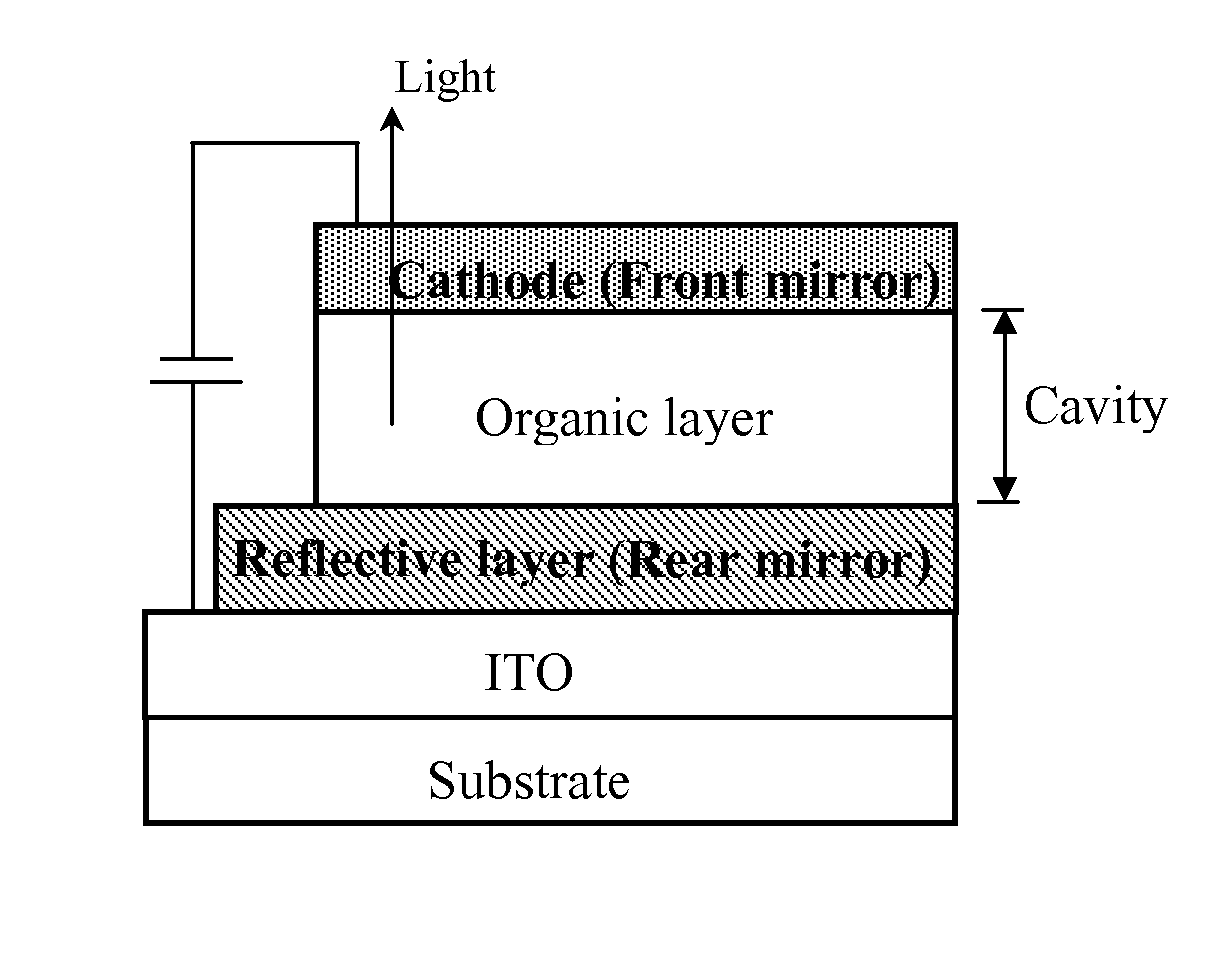
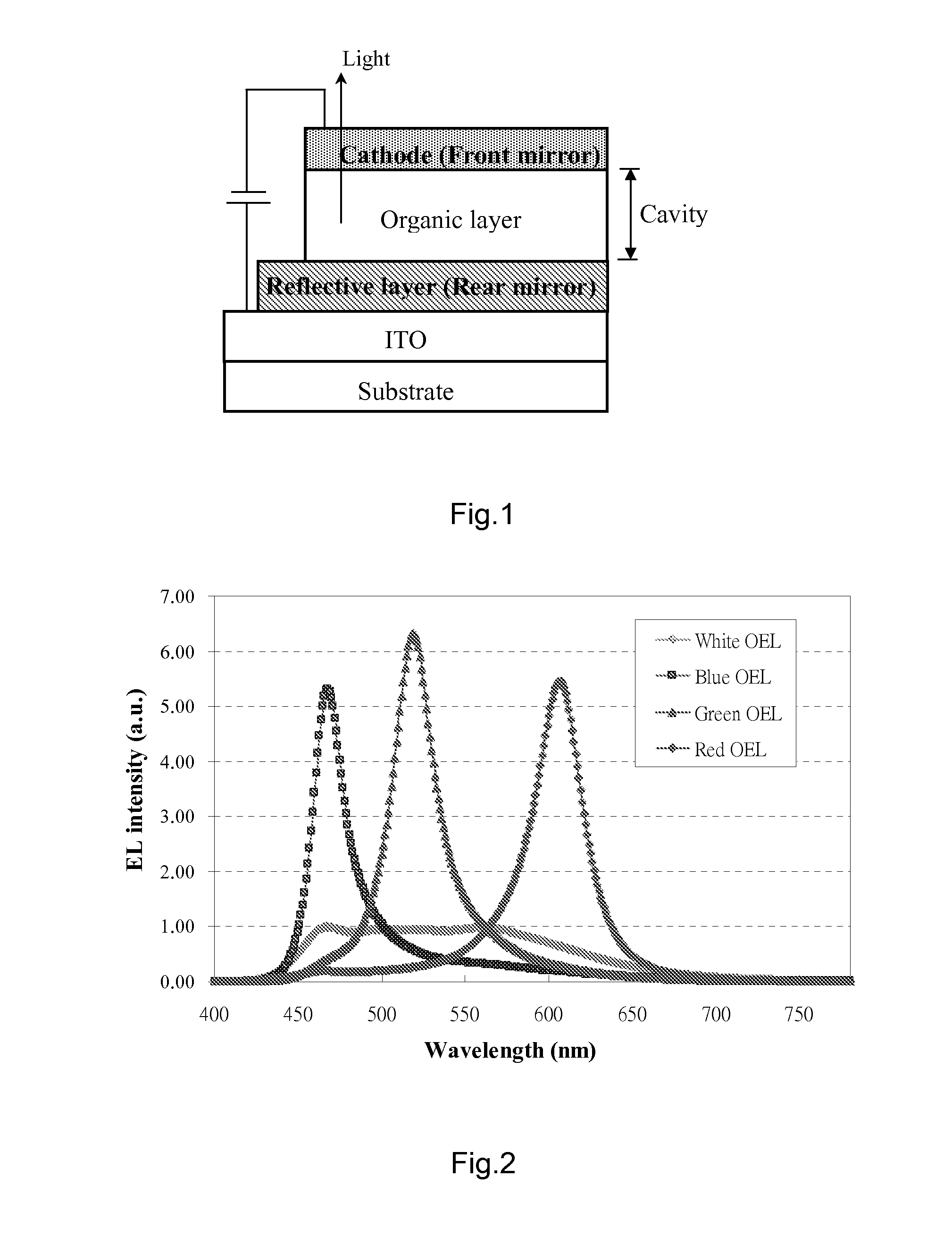
Fabrication of full-color OLED panel using micro-cavity structure
Methods of making top-emitting or bottom-emitting full-color OLED flat panel using micro-cavity structure for primary colors are disclosed. The primary colors are realized by setting a different thickness for the hole injection layer of the OLEDs for each primary color, while keeping the thickness of the hole transport layer, the emission layer, the electron transport layer the same for all the OLEDs. Steps for predetermining the respective thickness of the hole injection layer for each primary color are also disclosed.
Owner:ITC LIMITED
Photovoltaic devices having metal oxide electron-transport layers
Optoelectronic devices in both traditional and inverted configurations are provided that include an electron-transport layer. The electron-transport layer includes a metal oxide layer and a monolayer. Methods for making and using the devices are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
White light-emitting organic-inorganic hybrid electroluminescence device comprising semiconductor nanocrystals
InactiveUS20060043361A1Material nanotechnologyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLiquid-crystal displayLuminophore
A white light-emitting organic-inorganic hybrid electroluminescence device which has nanocrystals as illuminants. According to the device, a semiconductor nanocrystal layer composed of at least one kind of nanocrystals, a hole transport layer and / or an electron transport layer simultaneously emit light to produce white light, or a semiconductor nanocrystal layer composed of at least two kinds of nanocrystals emits light at different wavelengths to produce white light. The device can be used as a backlight unit for a liquid crystal display, or can be used to manufacture an illuminator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Organic electroluminescence device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20070020483A1Improve efficiencyProlong lifeDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsInorganic compound
An organic electroluminescent (EL) device having improved efficiency and service life is provided. The organic electroluminescent device has a stack structure including an emitting layer and an electron-transport layer positioned between an anode and a cathode. The electron-transport layer includes a first layer adjacent to the emitting layer which may be a mixture of at least two materials, and a second layer adjacent to the cathode which may be a mixture of at least two materials. The mixture of at least two materials may be a mixture of an organic compound and one or more other organic compounds, or may be a mixture of a metal or inorganic compound and one or more other metal or inorganic compounds, or may be a mixture of one or more organic compounds and one or more metal or inorganic compounds.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Organic electroluminescence element
InactiveUS20080241518A1Solid-state devicesRecord information storageOrganic layerOrganic electroluminescence
An organic electroluminescence element having at least one organic layer including a light-emitting layer between a pair of electrodes, wherein the organic electroluminescence element has an electron transport layer containing a phosphine oxide compound and an electron transport layer that does not substantially contain the phosphine oxide compound between the light-emitting layer and a cathode, the electron transport layer containing the phosphine oxide compound is nearer to the cathode, and the electron transport layer that does not substantially contain the phosphine oxide compound is nearer to the light-emitting layer. An organic EL element that exhibits high light-emission efficiency and is excellent in drive durability is provided.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Organic electroluminescent element and device
ActiveUS20080054799A1Significant valueSmall valueDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesHigh densityOptoelectronics
An organic electroluminescent (EL) element includes at least a positive hole transport layer, a light emitting layer and an electron transport layer between at least a pair of electrodes, wherein the light emitting layer contains therein at least two light emitting materials having different Ea values or Ip values and emitting phosphorescence having the same color as each other, and among the two light emitting materials, a light emitting material having a larger Ea value or Ip value is contained at a higher density in a region of the light emitting layer in the vicinity of the positive hole transport layer, while a light emitting material having a smaller Ea value or Ip value is contained at a higher density in a region of the light emitting layer in the vicinity of the electron transport layer.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Photoelectric conversion element
InactiveUS20020108649A1Improve photoelectric conversion efficiencyPrevent and suppressLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesPorosityTransport layer
A solid type dye-sensitized photoelectric conversion element which is excellent in photoelectric conversion efficiency and which can be manufactured at a low cost is disclosed. The photoelectric conversion element can be applied to a so-called wet type solar cell which does not use any electrolyte. The solar cell comprises a first electrode 3, a second electrode 6 arranged opposite to the first electrode 3, an electron transport layer 4 arranged between the first electrode 3 and the second electrode 6, a dye layer D which is in contact with the electron transport layer 4, a hole transport layer 5 arranged between the electron transport layer 4 and the second electrode 6 and being in contact with the dye layer D, and a barrier layer 8, and these elements are provided on a substrate 2. The barrier layer 8 constitutes short-circuit preventing or suppressing means for preventing or suppressing short-circuit between the first electrode 3 and the hole transport layer 5. The porosity of the barrier layer is made smaller than that of the electron transport layer 4. The barrier layer is formed into a film-like shape and arranged between the fist electrode 4 and the electron transport layer 4. The solar cell can accomplish excellent photoelectric conversion efficiency by the provision of such a barrier layer 8.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Red phosphorescene compounds and organic electroluminescence device using the same
ActiveUS20060204785A1High color purityLong durabilityIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensDopantHole transport layer
Red phosphorescene compounds and organic electro-luminescence device using the same are disclosed. In an organic electroluminescence device including an anode, a hole injecting layer, a hole transport layer, a light emitting layer, an electron transport layer, an electron injecting layer, and a cathode serially deposited on one another, the organic electroluminescence device may use a compound as a dopant of the light emitting layer.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
OLEDs having n-type doping
ActiveUS20050123793A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesAlkaline earth metalOrganic light emitting device
The present invention provides an organic light emitting device comprising an anode, a cathode, and an organic layer disposed between the anode and the cathode, wherein the organic layer comprises a host material, an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal, and a metal binding agent. In a preferred embodiment, the organic layer is an electron transport layer in which the metal binding agent may confine the alkali metal or the alkaline earth metal.
Owner:SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA THE UNIV OF
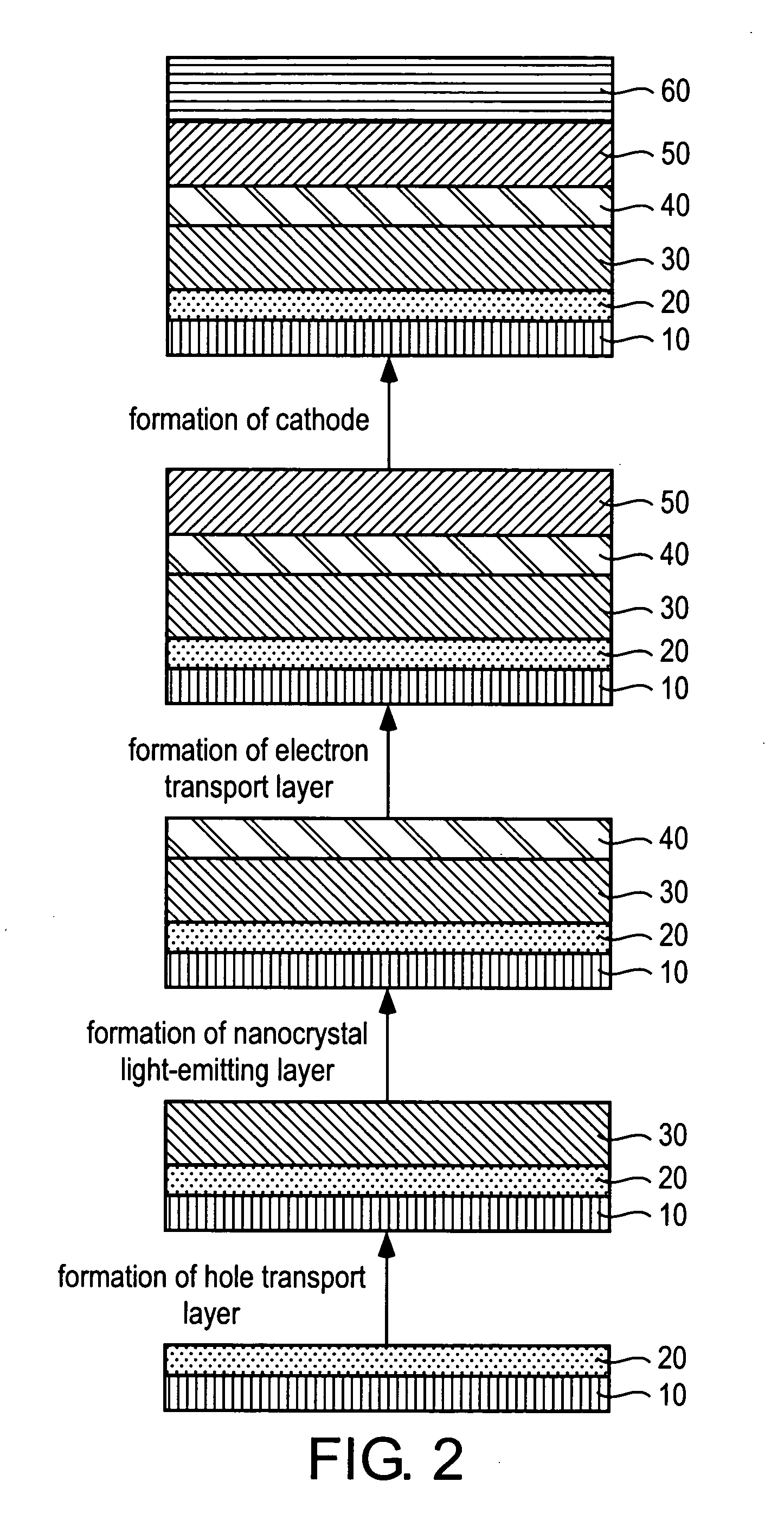
Nanocrystal electroluminescence device and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20050274944A1High color purityNanostructure manufactureElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic layerHole transport layer
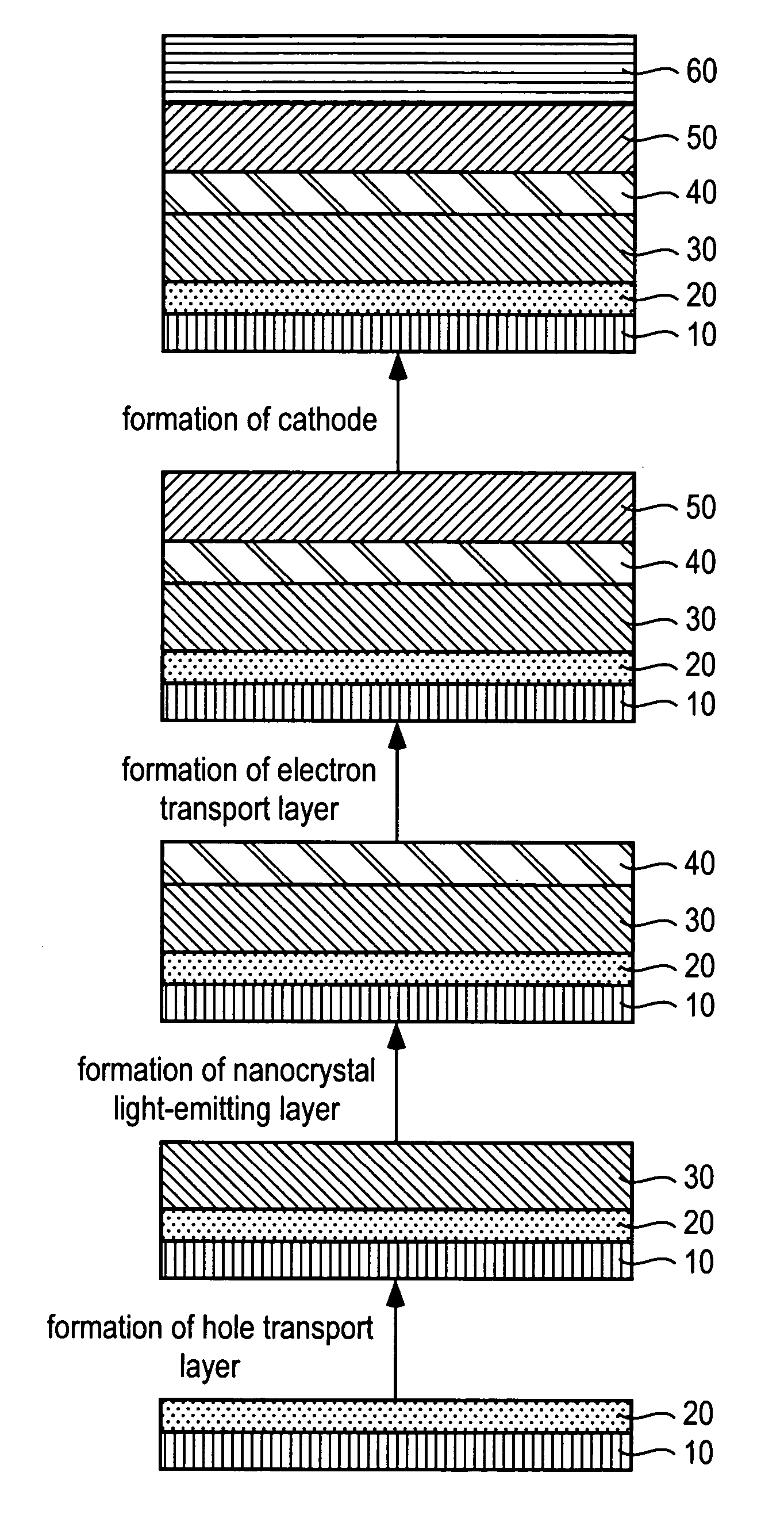
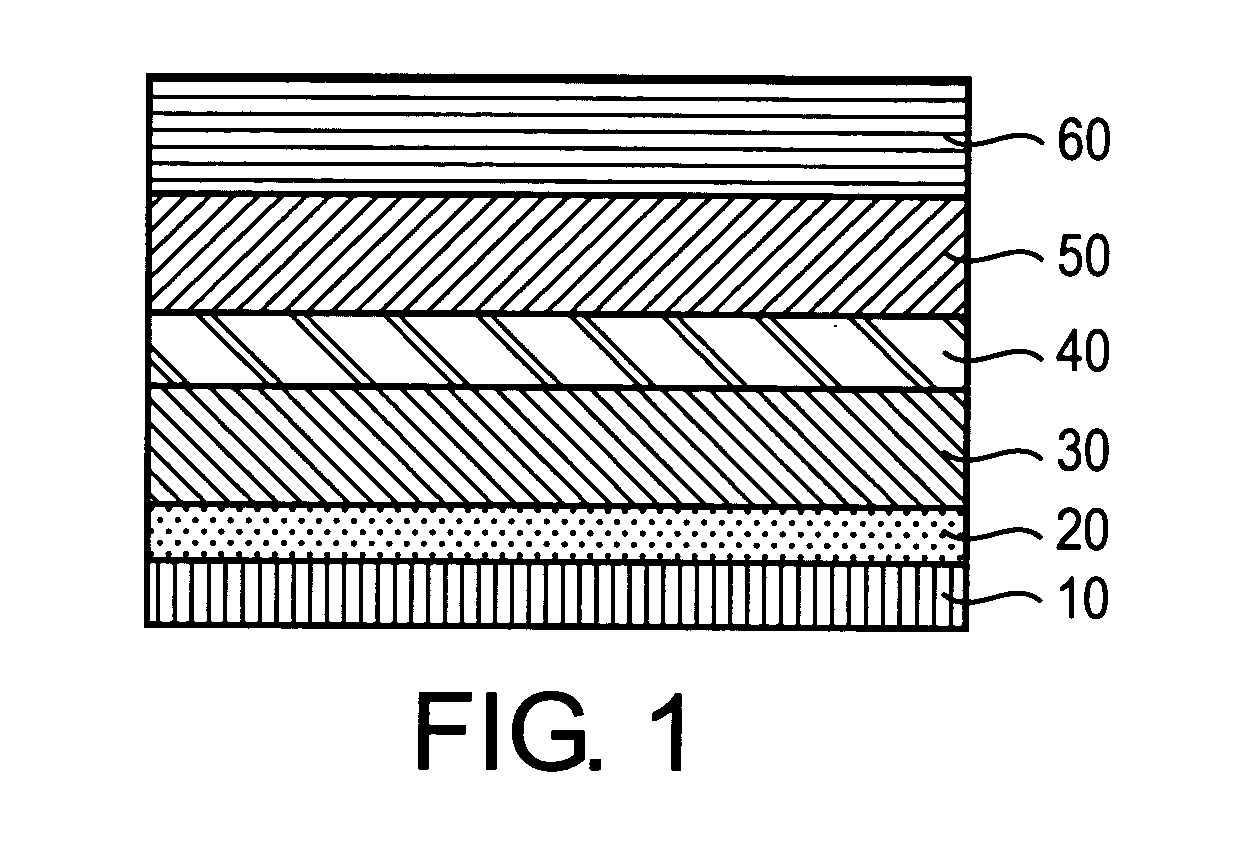
A nanocrystal electroluminescence device comprising a polymer hole transport layer, a nanocrystal light-emitting layer and an organic electron transport layer wherein the nanocrystal light-emitting layer is independently and separately formed between the polymer hole transport layer and the organic electron transport layer. According to the nanocrystal electroluminescence device, since the hole transport layer, the nanocrystal light-emitting layer and the electron transport layer are completely separated from one another, the electroluminescence device provides a pure nanocrystal luminescence spectrum having limited luminescence from other organic layers and substantially no influence by operational conditions, such as voltage. Further, a method for fabricating the nanocrystal electroluminescence device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
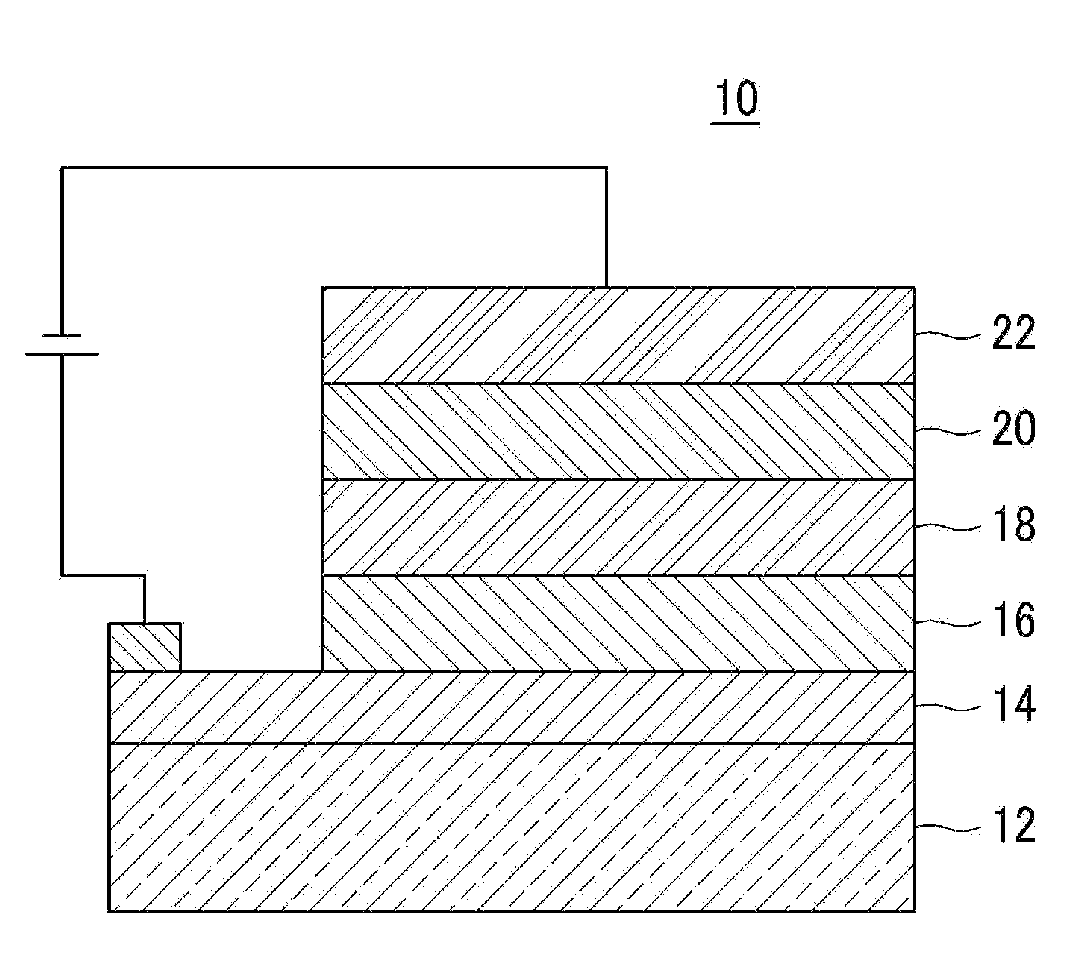
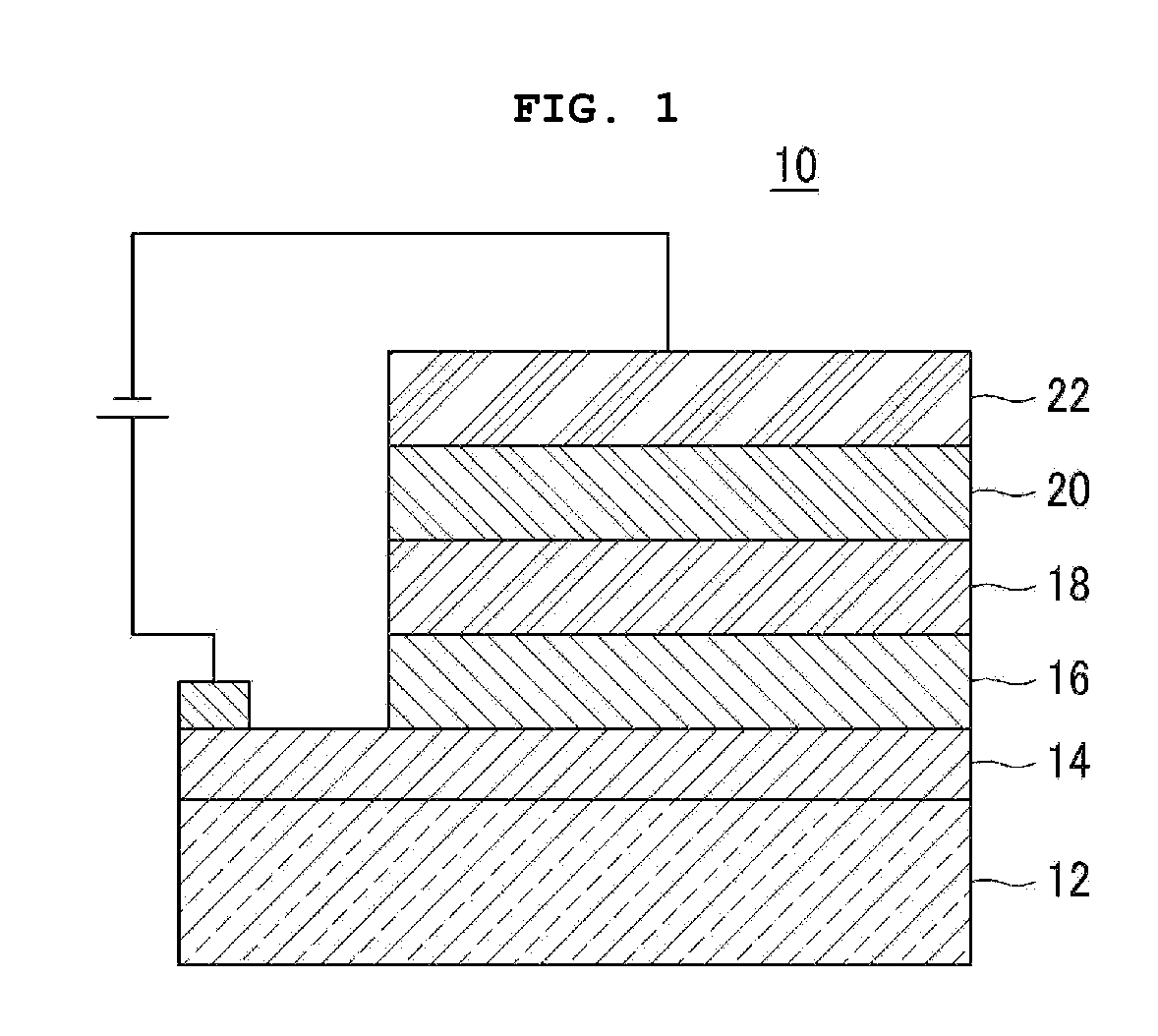
Quantum dot electroluminescent device and method for fabricating the same
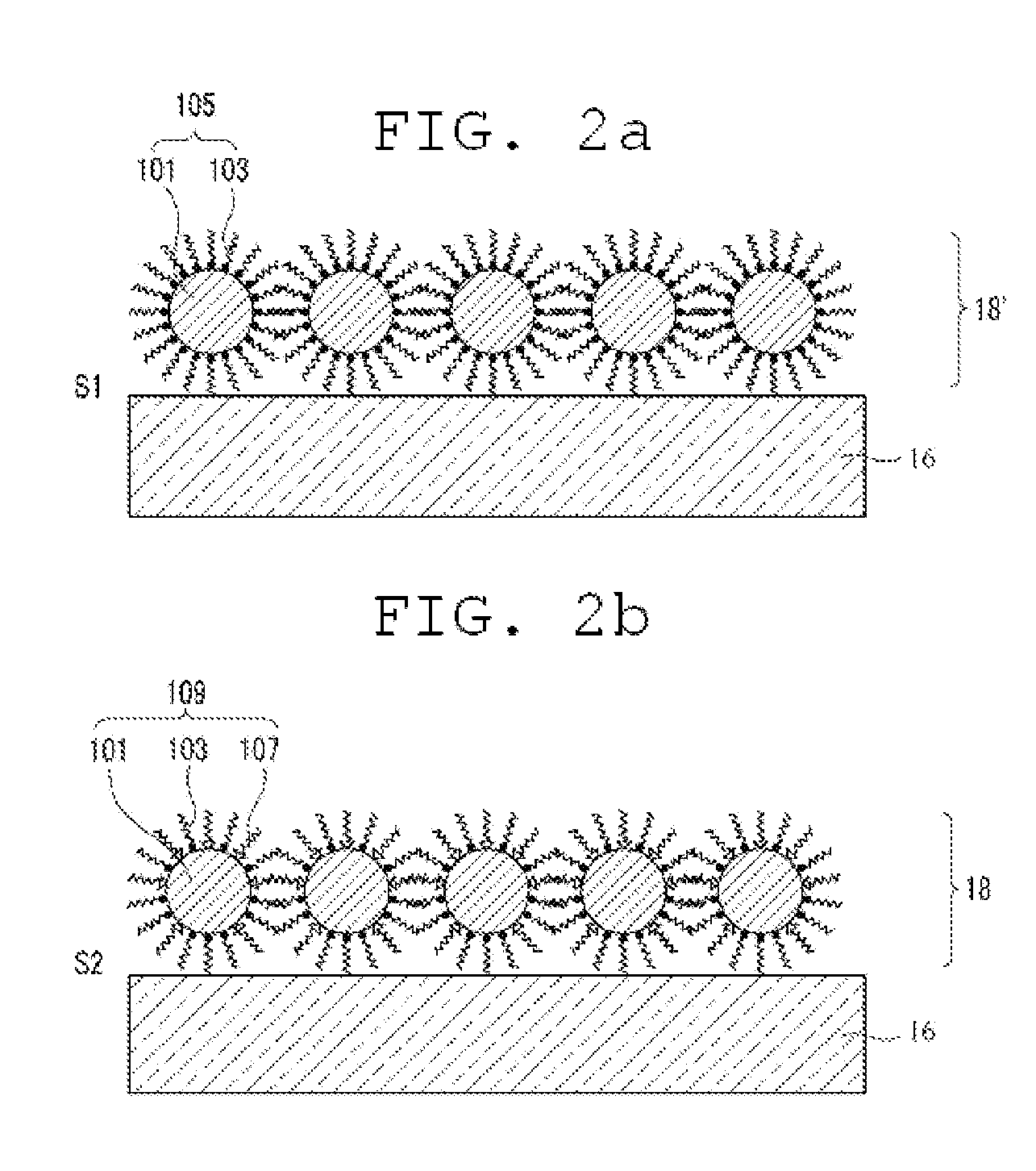
A quantum dot electroluminescent device that includes a substrate, a quantum dot light-emitting layer disposed on the substrate, a first electrode which injects charge carriers into the quantum dot light-emitting layer, a second electrode which injects charge carriers, which have an opposite charge than the charge carriers injected by the first electrode, into the quantum dot light-emitting layer, a hole transport layer disposed between the first electrode and the quantum dot light-emitting layer, and an electron transport layer disposed between the second electrode and the quantum dot light-emitting layer, wherein the quantum dot light-emitting layer has a first surface in contact with the hole transport layer and a second surface in contact with an electron transport layer, and wherein the first surface has an organic ligand distribution that is different from an organic ligand distribution of the second surface.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Organic electroluminescent device and manufacuring method thereof
InactiveUS20050274961A1Improve stabilityStable maintenanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantHole injection layer
An organic electroluminescent device comprises an anode, a hole injection layer as CFx formed on the anode, a first hole transport layer formed on the hole injection layer and the first hole transport layer doped with a P-type dopant, a second hole transport layer formed on the first hole transport layer, a light emitting layer formed on the second hole transport layer, an electron transport layer formed on the light emitting layer, and a cathode formed on the electron transport layer. According to the structure of the organic electroluminescent device disclosed in the present invention, the hole injection layer and the first hole transport layer provide the function of increasing the efficiency of the hole injection so as to improve the operating life and stability of the device.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
OLEDS with improved efficiency
InactiveUS20070126347A1Improved luminescence yieldHigh yieldDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDopantTrapping
An organic light-emitting device, comprising a substrate; an anode and a cathode; a first hole-transport layer provided over the anode and having at least a first material; a second hole-transport layer provided over the first hole-transport layer, and having at least a second material; at least one light-emitting layer disposed over the second hole-transport layer wherein the light-emitting layer(s) includes a host, a dopant, and a hole-trapping material; an improved electron-transport layer disposed between the light-emitting layer(s) and the cathode.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
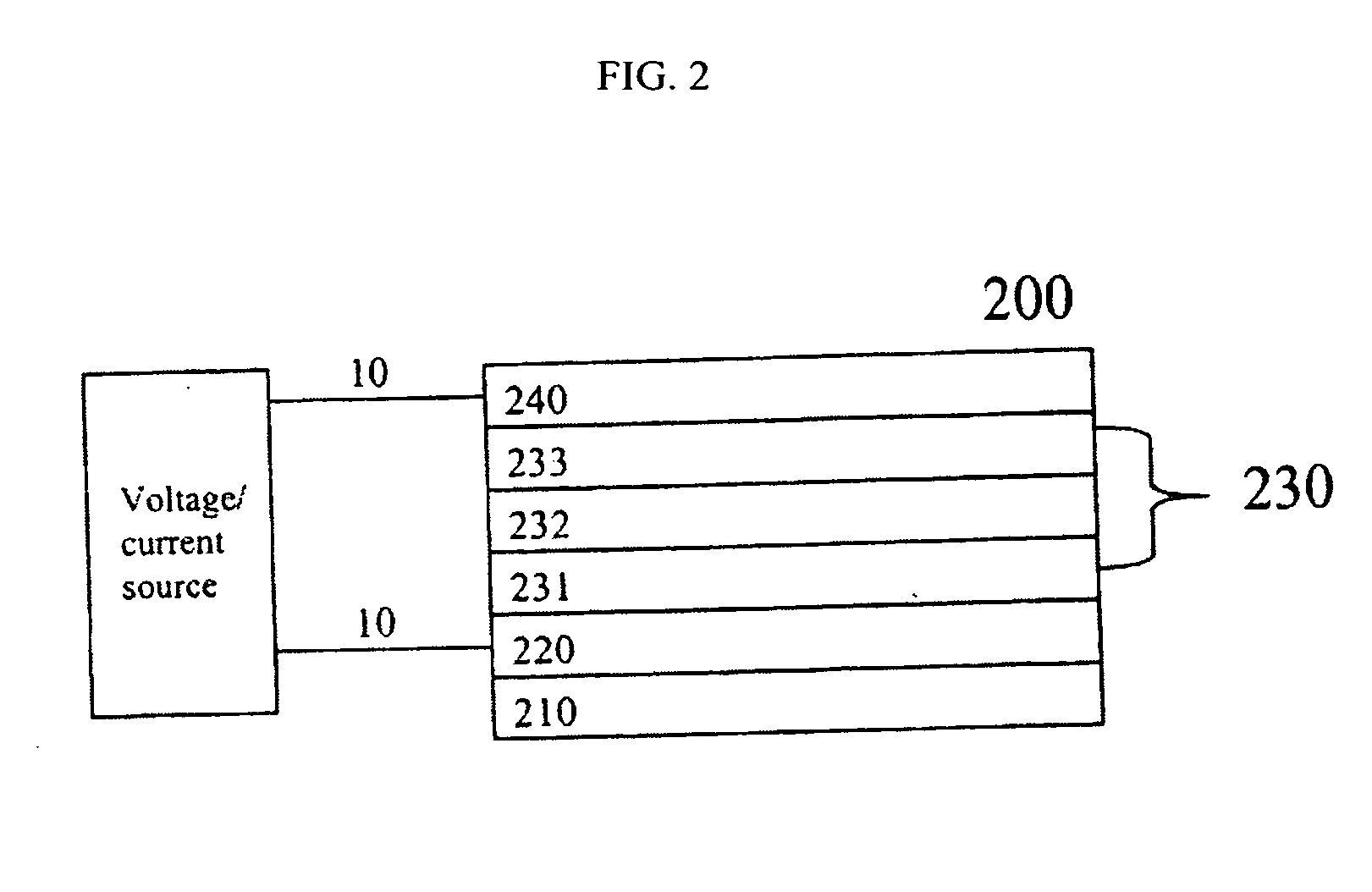
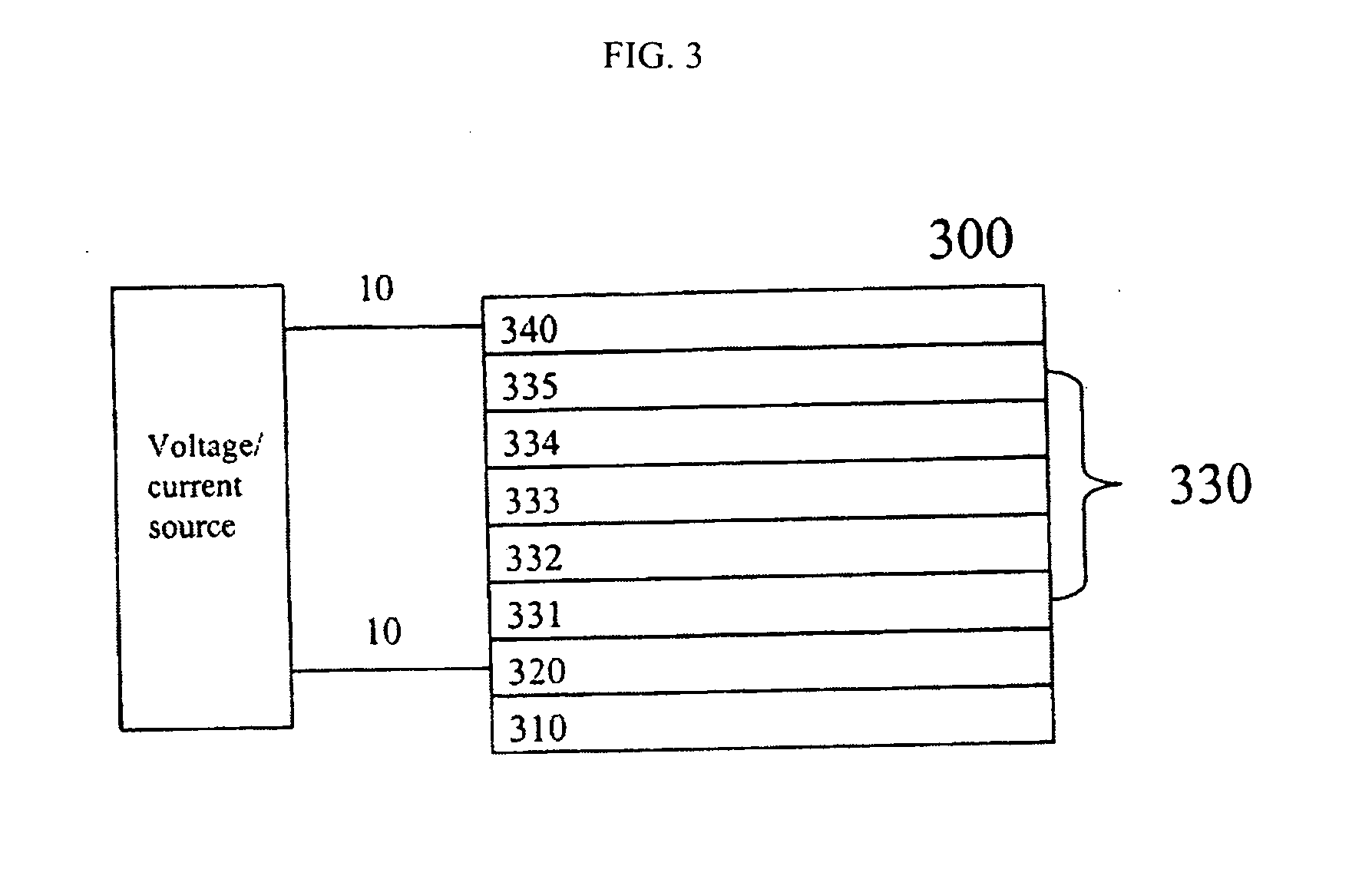
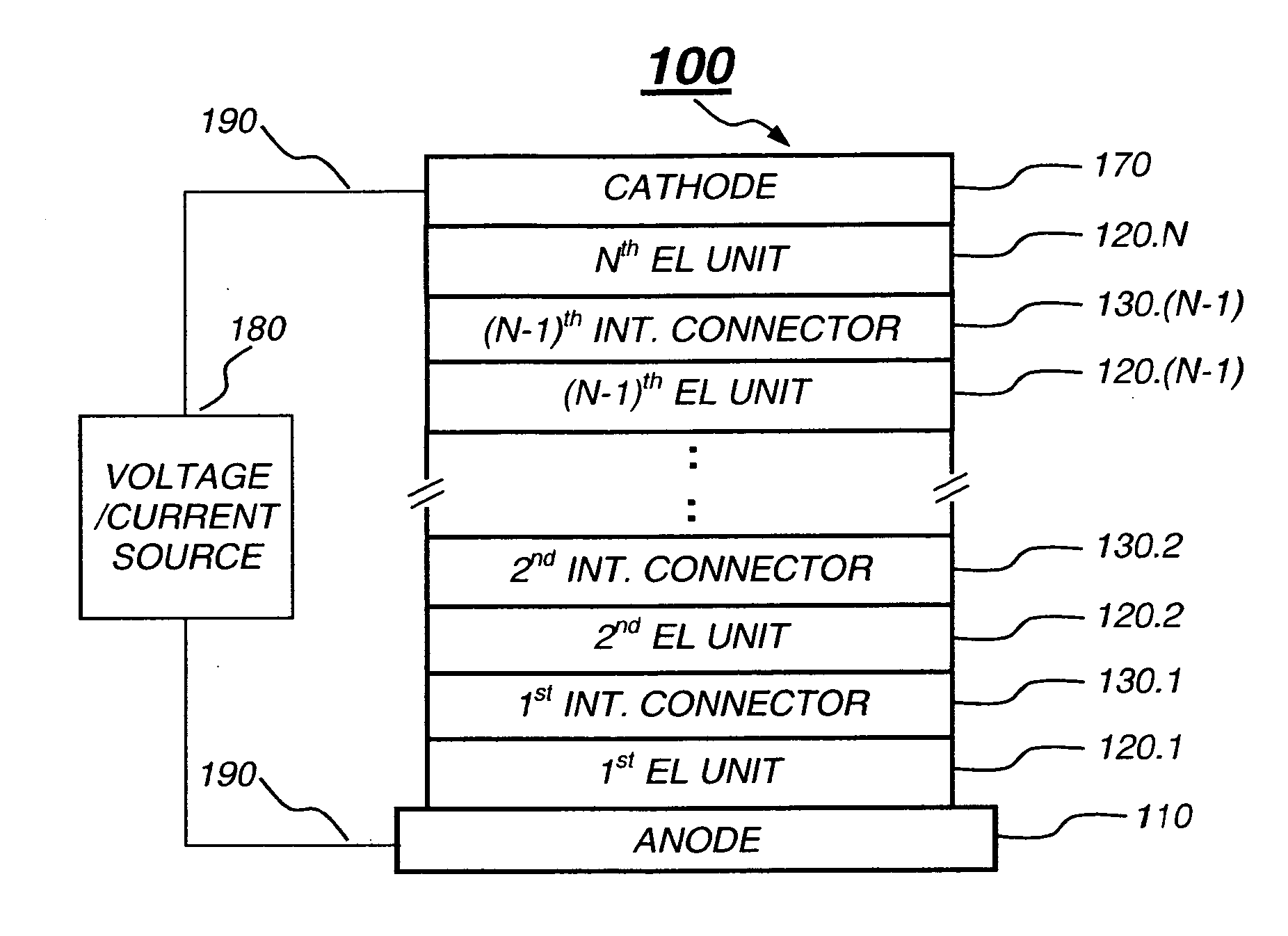
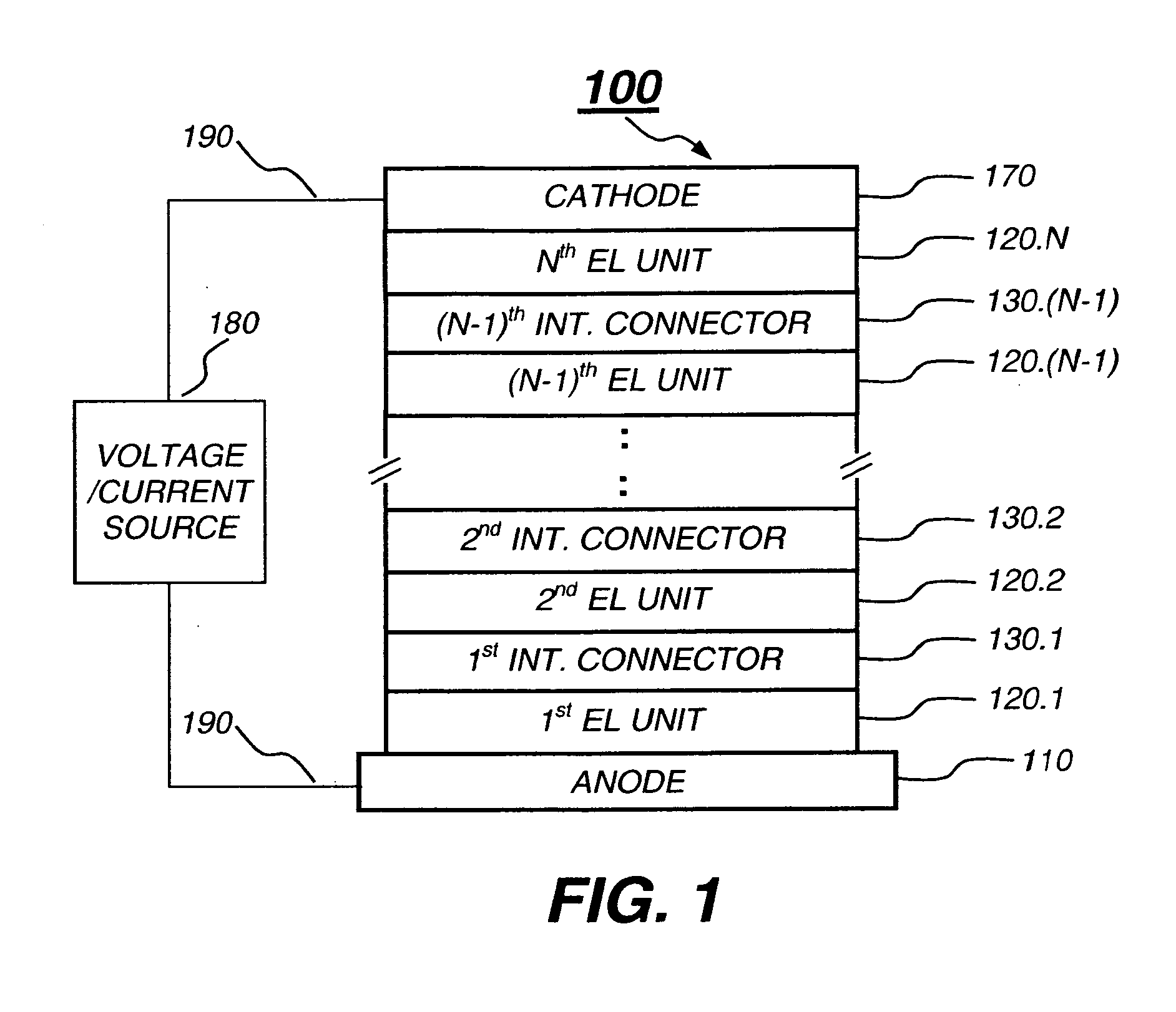
Tandem OLED device
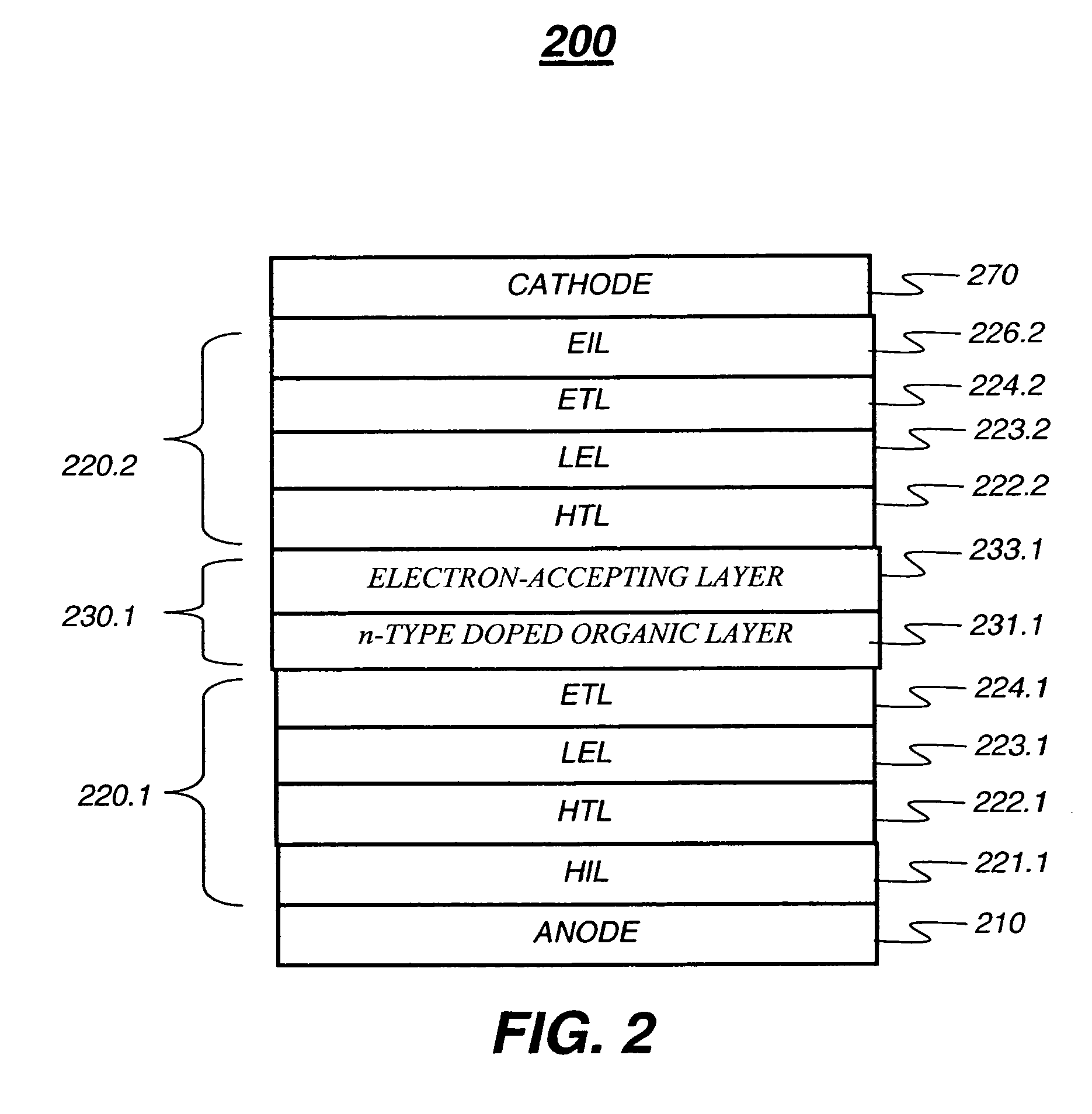
InactiveUS20060240277A1Reduce the driving voltageImprove efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDopantOrganic layer
A tandem OLED device includes an anode, a cathode, first and second electroluminescent units disposed between the anode and the cathode, and an intermediate connector disposed between the first and second electroluminescent units. Each of the electroluminescent units include at least one individually selected organic light-emitting layer, and the first electroluminescent unit includes a first electron-transporting layer disposed between the cathode and the light-emitting layer of the first electroluminescent unit, wherein the first electron-transporting layer includes a first electron-transporting material. The intermediate connector includes a first n-type doped organic layer disposed in contact with the first electron-transporting layer, and wherein the first n-type doped organic layer includes an n-type dopant and an electron-transporting material that is different from the first electron-transporting material.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Organic electroluminescent device based on pyrene derivatives
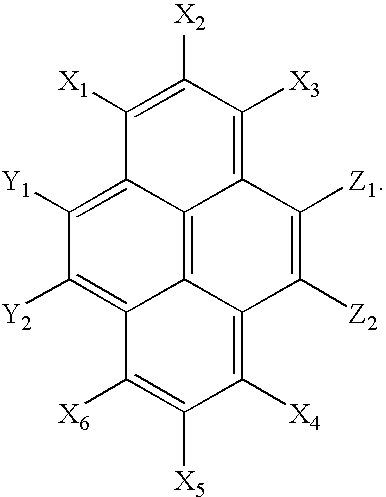
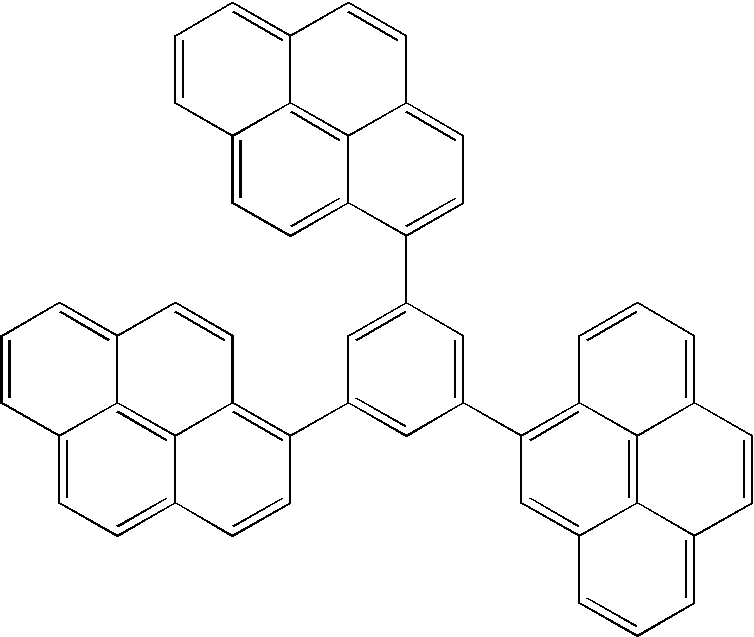
InactiveUS20050031898A1Reduce decreaseHigh puritySilicon organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensHole transport layerPyrene
A pyrene based compound and its use in an organic light emitting device (OLED) according to the following formula: In the above formula, Z1 represents a hydrogen atom, deuterium atom, oxygen atom, silicon atom, selenium atom, substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group, substituted or unsubstituted aryl amine or a combination thereof, and Z2 represents a hydrogen or deuterium atom. One of Y1 and Y2 represents a hydrogen atom, deuterium atom, oxygen atom, silicon atom, selenium atom, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group, substituted or unsubstituted aryl amine or a combination thereof, and the other of Y1 and Y2 represents a hydrogen or deuterium atom. X1 through X6 independently represent hydrogen atoms, deuterium atoms, alkyl groups or aryl groups, and at least one of X1 through X6 represents a bulky alkyl group or bulky aryl group. Also, at least one of X1 through X6, Y1, Y2, Z1, and Z2 represents a deuterium atom. The pyrene based compounds of this invention are useful in emissive layers, hole transport layers, or electron transport layers of an organic light emitting device (OLED). Within these layers, the pyrene based compound can serve directly to constitute the layers or as a host and / or dopant.
Owner:CANON KK
OLED electron-transporting layer
InactiveUS20060269782A1Improved LEL/ETL interfaceLower potentialDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDopantOrganic light emitting device
An organic light-emitting device (OLED) includes an anode, a cathode, and a light-emitting layer disposed between the anode and the cathode, wherein the light-emitting layer includes a dominant host and a dopant. The device also includes an electron-transporting layer disposed in direct contact with the light-emitting layer on the cathode side, wherein the electron-transporting layer includes an electron-transporting material having the same chromophore as that of the dominant host in the light-emitting layer, wherein the electron-transporting material constitutes more than 50% by volume of the electron-transporting layer, and wherein the electron-transporting material has a greater reduction potential than that of the dominant host in the light-emitting layer.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Compound semiconductor substrate
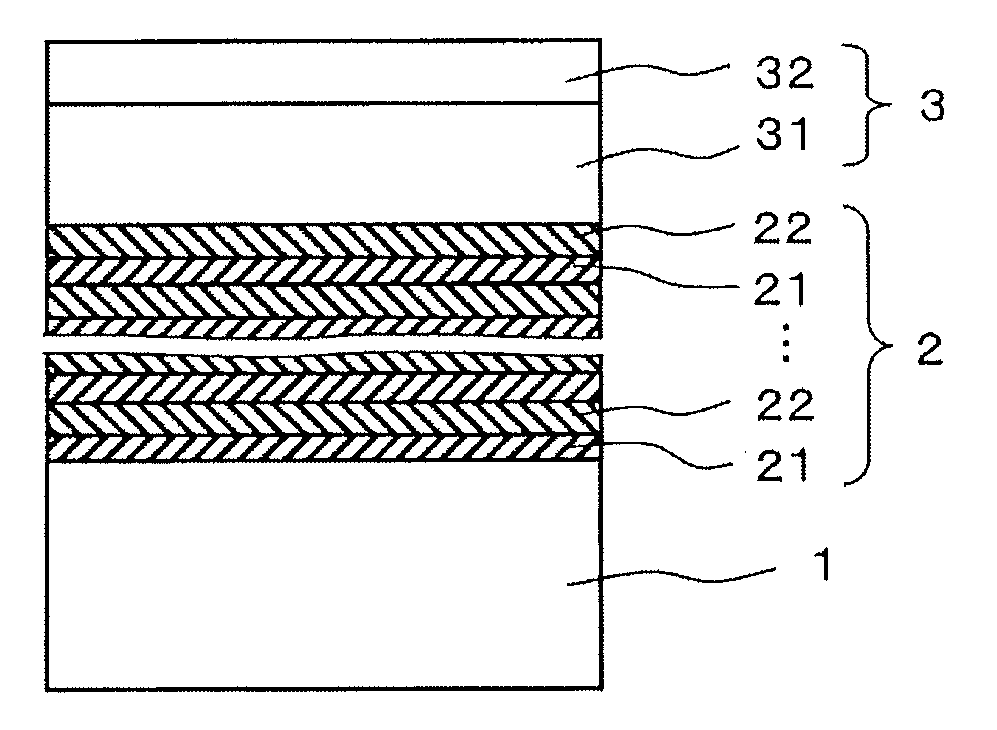
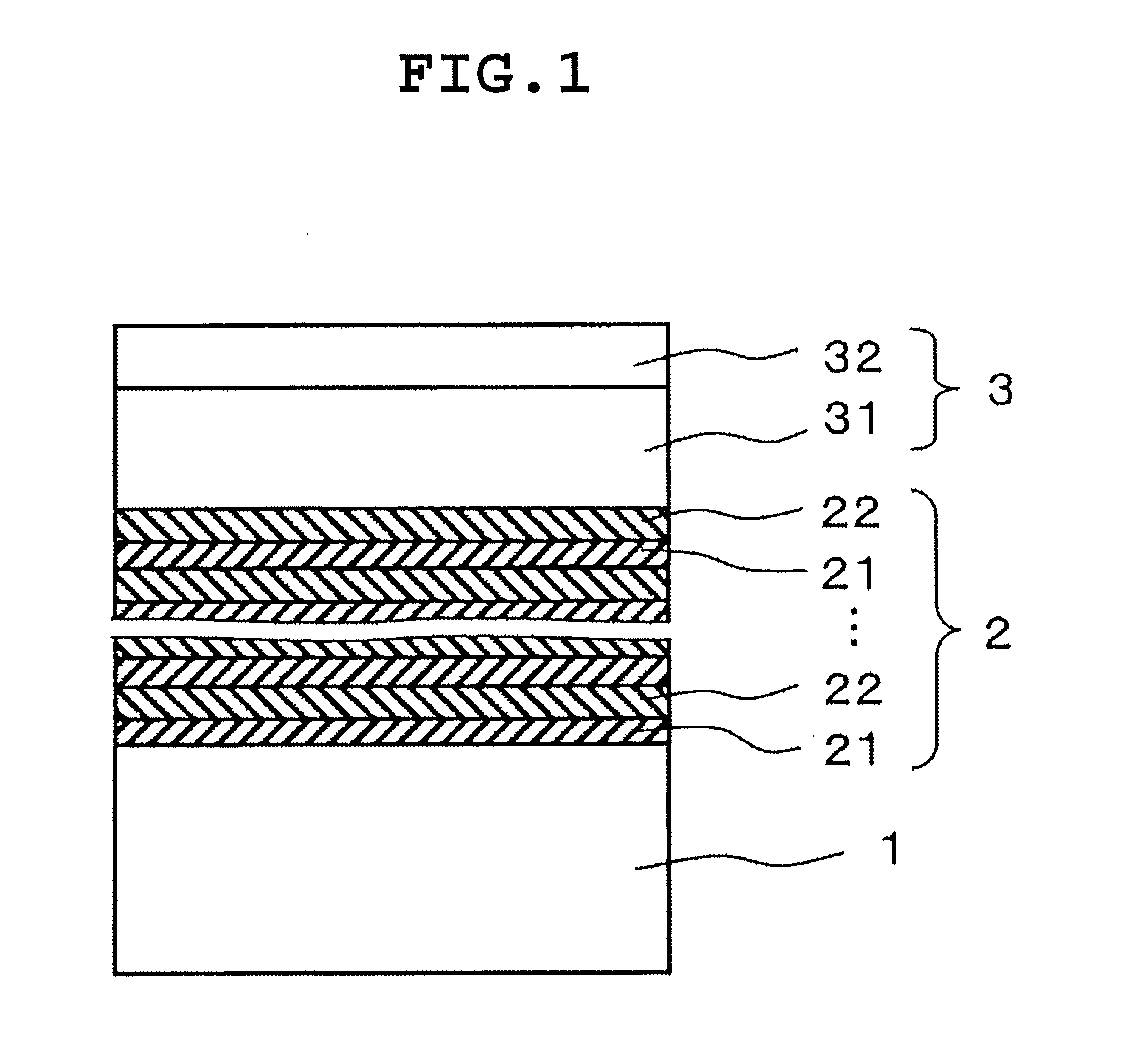
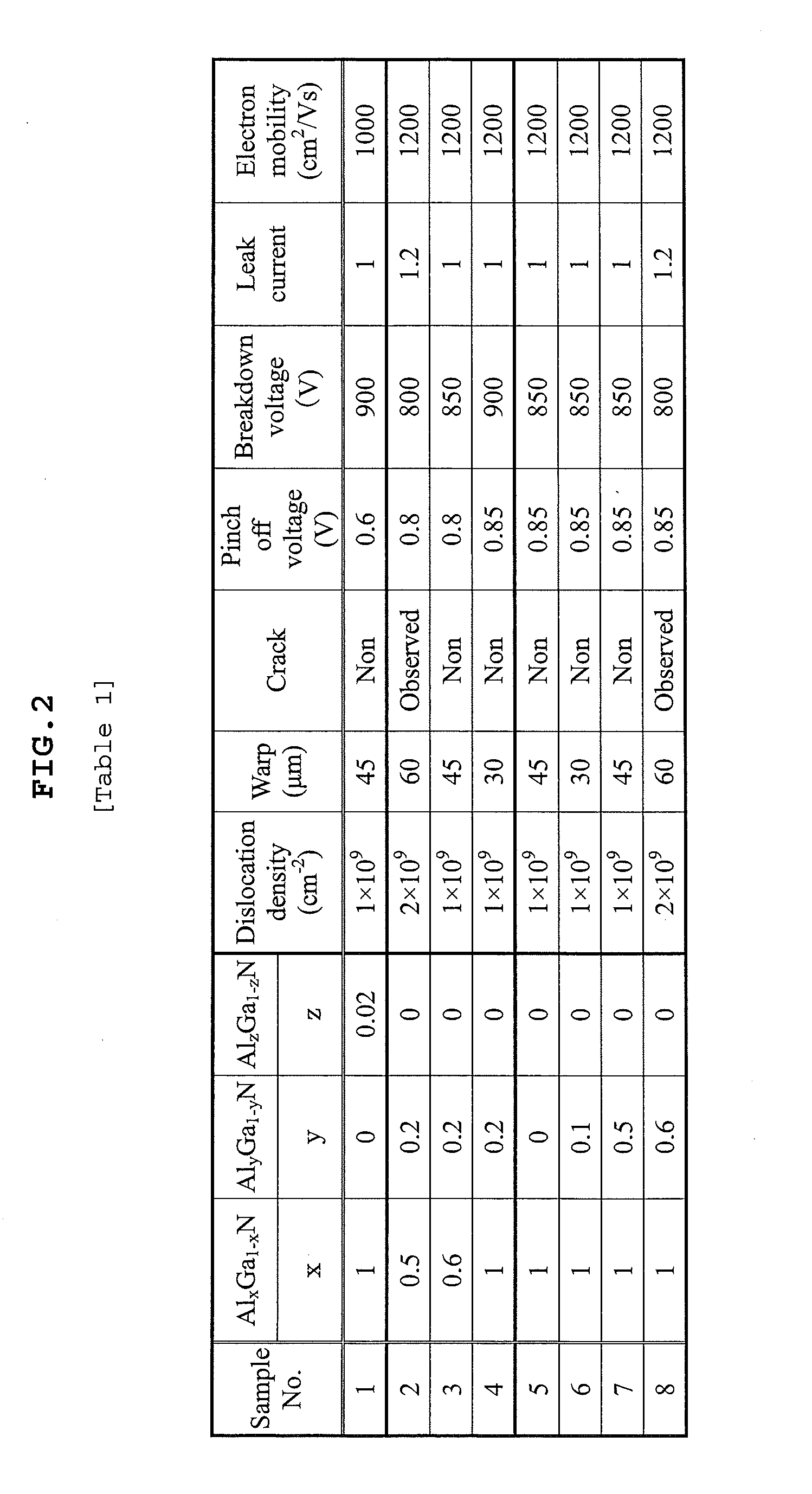
ActiveUS20110062556A1Avoid crackingAvoid warpingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSingle crystal substrateSingle crystal
A compound semiconductor substrate which inhibits the generation of a crack or a warp and is preferable for a normally-off type high breakdown voltage device, arranged that a multilayer buffer layer 2 in which AlxGa1-xN single crystal layers (0.6≦X≦1.0) 21 containing carbon from 1×1018 atoms / cm3 to 1×1021 atoms / cm3 and AlyGa1-yN single crystal layers (0.1≦y≦0.5) 22 containing carbon from 1×1017 atoms / cm3 to 1×1021 atoms / cm3 are alternately and repeatedly stacked in order, and a nitride active layer 3 provided with an electron transport layer 31 having a carbon concentration of 5×1017 atoms / cm3 or less and an electron supply layer 32 are deposited on a Si single crystal substrate 1 in order. The carbon concentrations of the AlxGa1-xN single crystal layers 21 and that of the AlyGa1-yN single crystal layers 22 respectively decrease from the substrate 1 side towards the above-mentioned active layer 3 side. In this way, the compound semiconductor substrate is produced.
Owner:COORSTEK INC
Method for manufacturing a display device with low temperature diamond coatings
InactiveUS20060017055A1Increase powerEasy to operateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
A display device with multiple low temperature diamond coatings, including a substrate as a base; an anode layer residing on the diamond substrate for emitting holes; a hole drift layer that includes a doped diamond coating residing on the anode layer; an emissive layer for emitting light and residing on the hole drift layer. The display device also includes an electron transport layer that includes a doped diamond coating residing on the light emitting layer; a cathode layer, residing on the electron transport layer, for emitting electrons that will drift towards the light emitting layer; and a diamond coated encapsulation layer for sealing the display device from atmospheric moisture; wherein the multiple low temperature diamond coatings are all formed below 750° C. on the display device.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
OLEDs having n-type doping
InactiveUS7070867B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesAlkaline earth metalOrganic light emitting device
The present invention provides an organic light emitting device comprising an anode, a cathode, and an organic layer disposed between the anode and the cathode, wherein the organic layer comprises a host material, an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal, and a metal binding agent. In a preferred embodiment, the organic layer is an electron transport layer in which the metal binding agent may confine the alkali metal or the alkaline earth metal.
Owner:SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA THE UNIV OF
Organic electroluminescent element
InactiveUS20060051615A1Improve balanceImprove luminous efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesElectron holeHole injection layer
In an organic electroluminescent element in which a light emitting layer is disposed between a hole injection electrode and an electron injection electrode, and a hole injection layer is provided between the hole injection electrode and the light emitting layer, and an electron transport layer is provided between the electron injection electrode and the light emitting layer, the organic electroluminescent element is characterized in that a fluorocarbon layer is provided between the hole injection layer and the light emitting layer, and the electron transport layer is formed from a phenanthroline compound.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com