Patents
Literature
3218results about How to "Avoid warping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
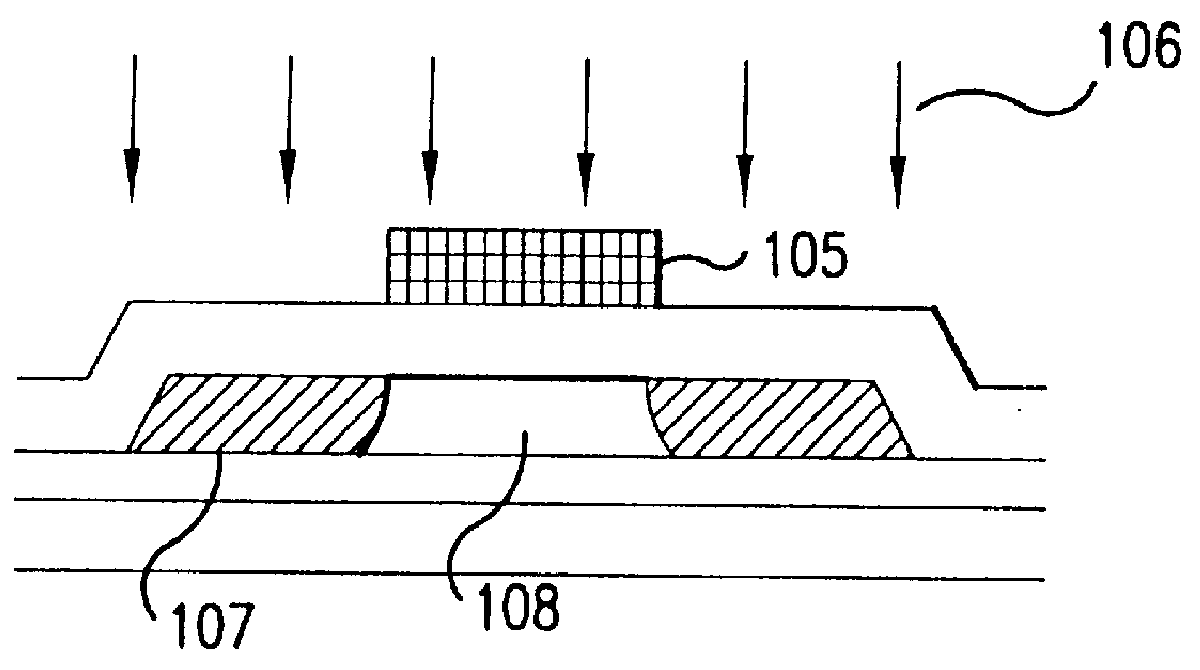
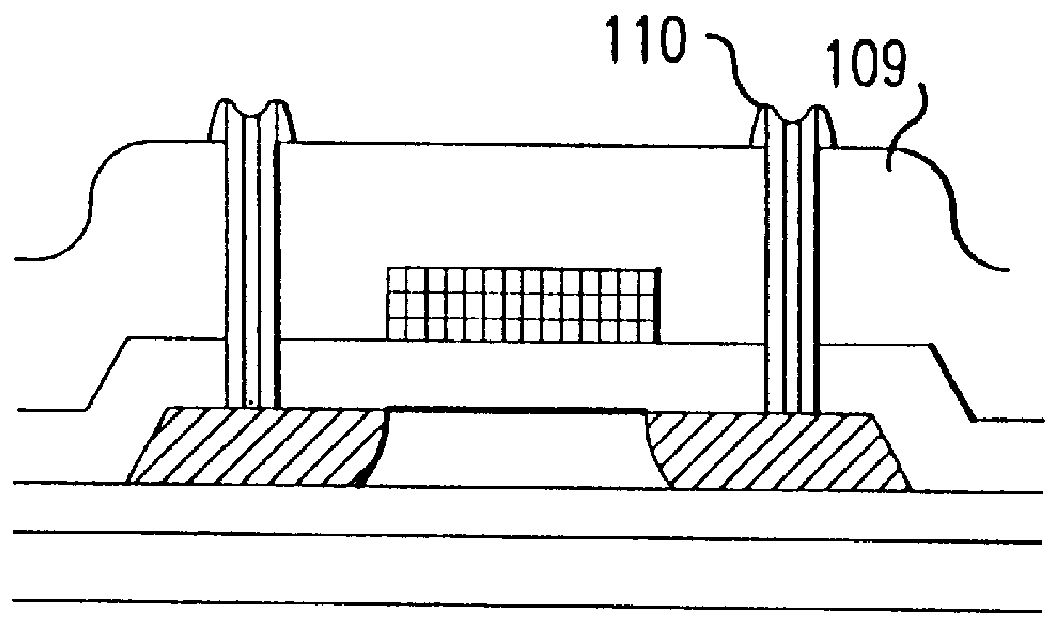
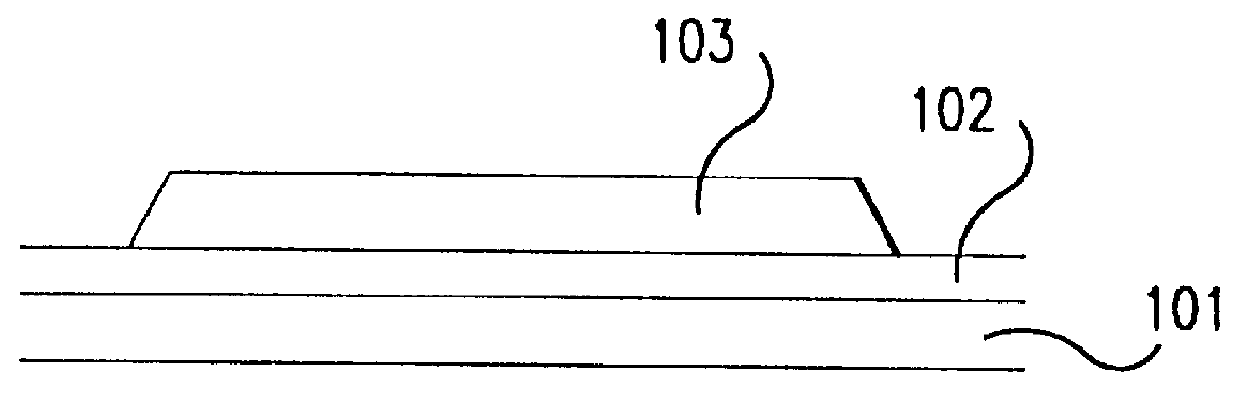
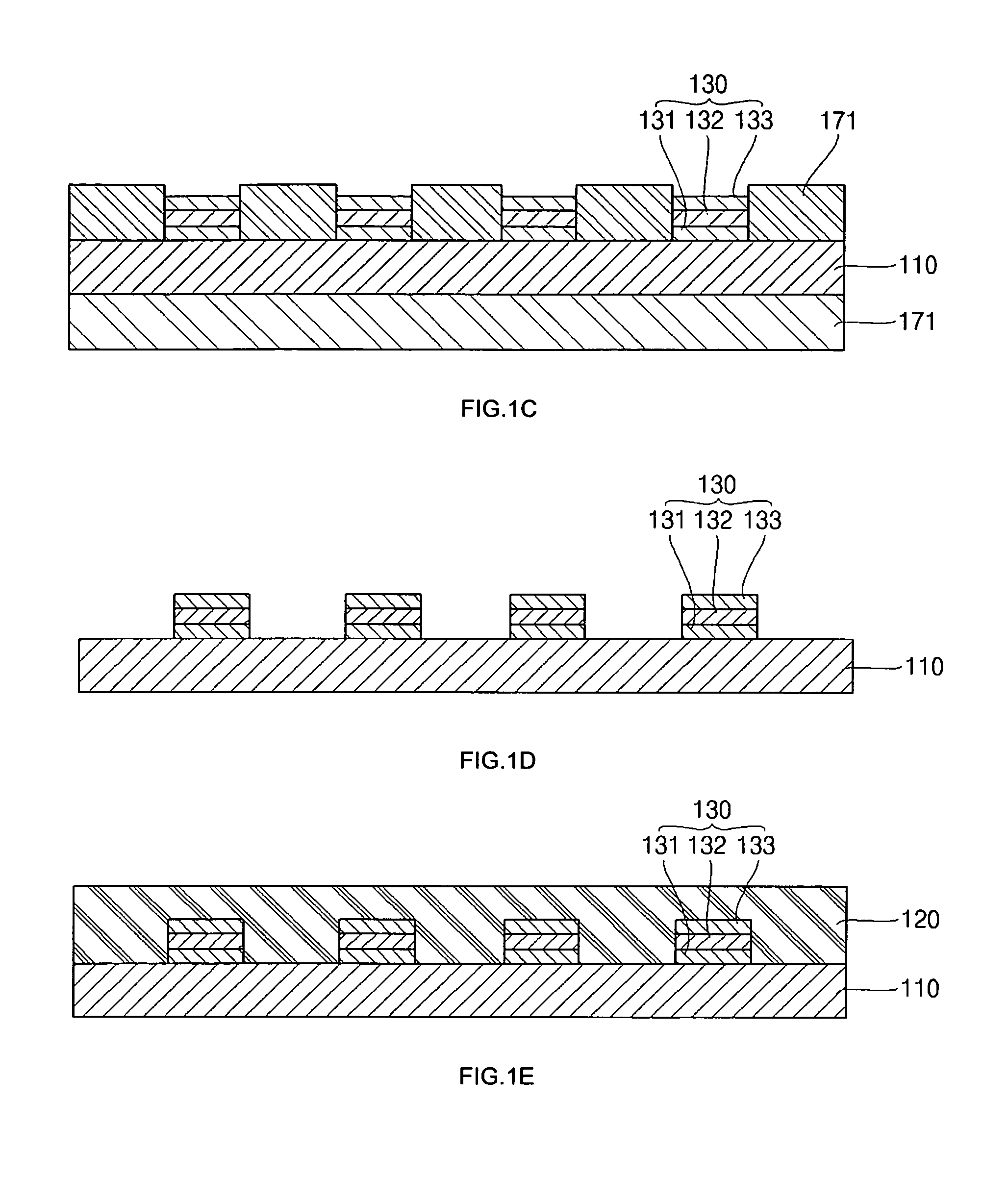
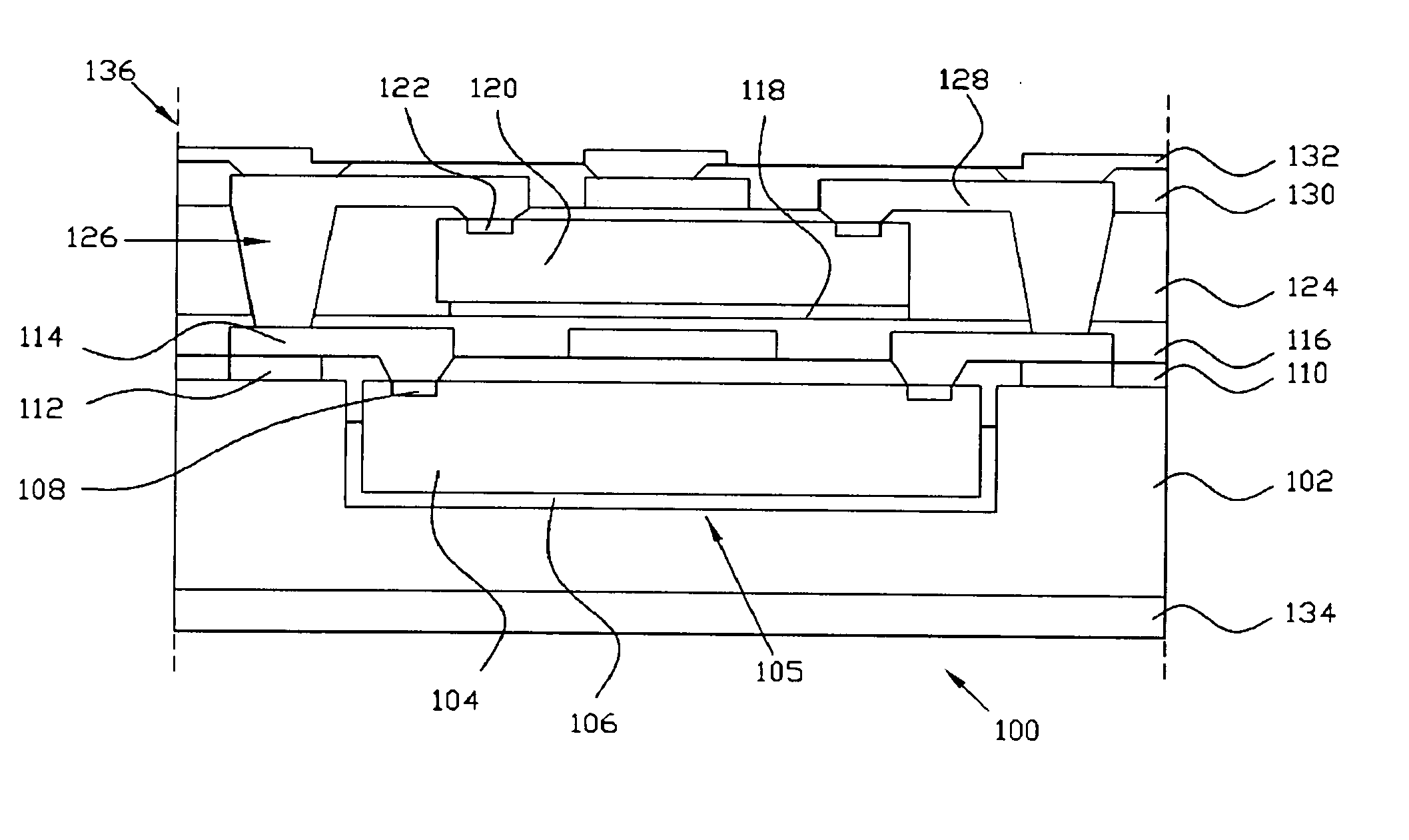
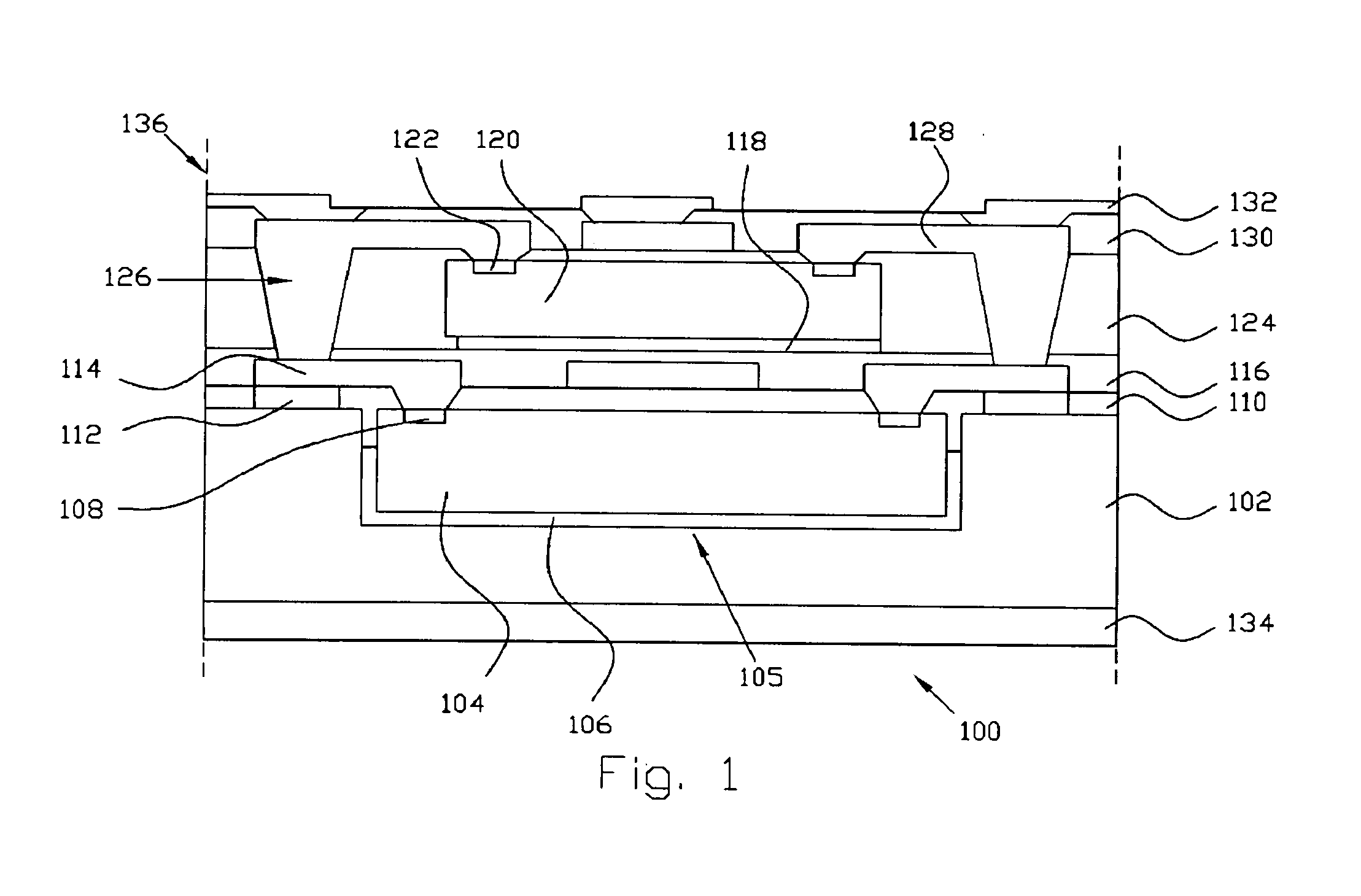
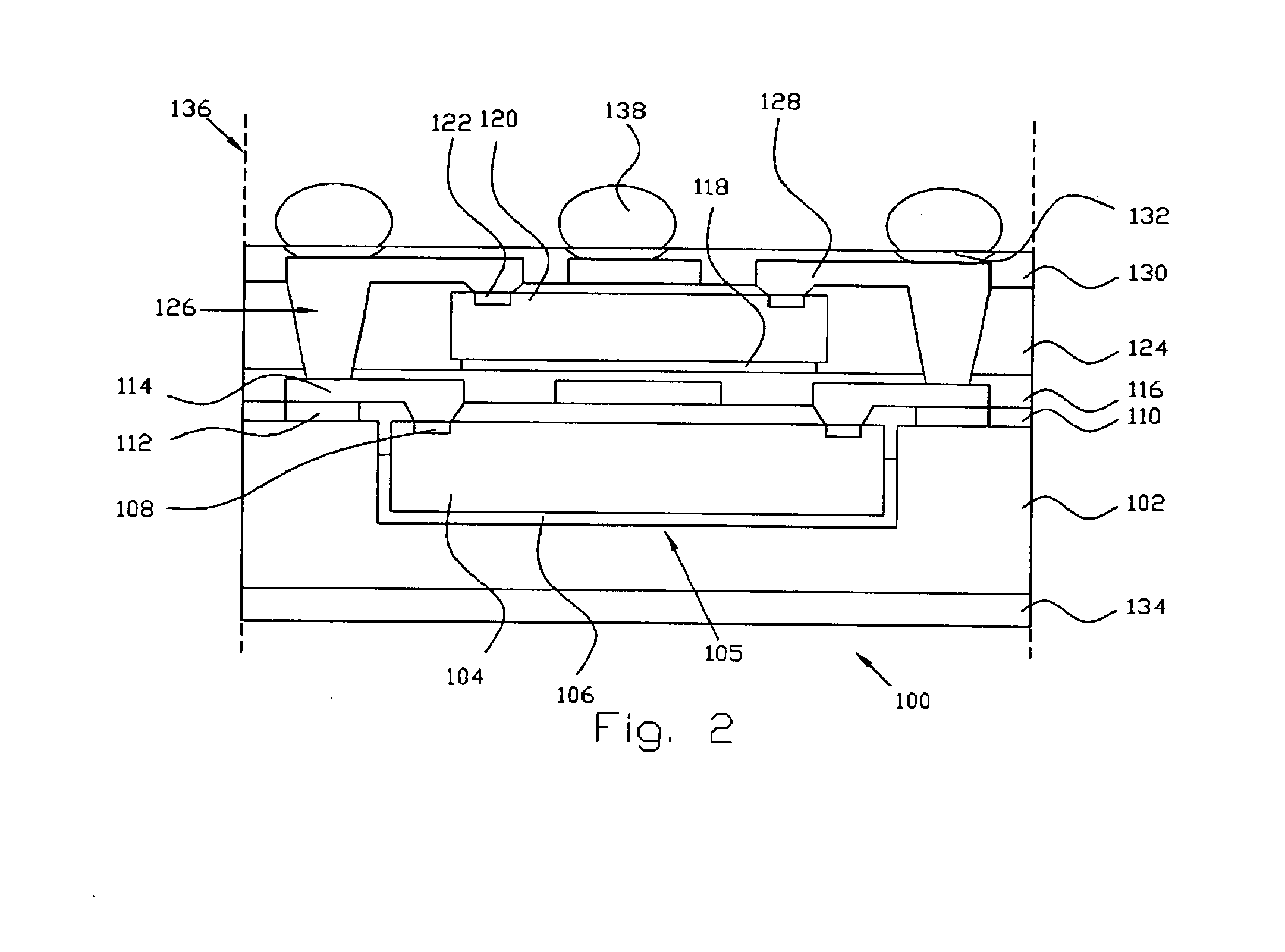
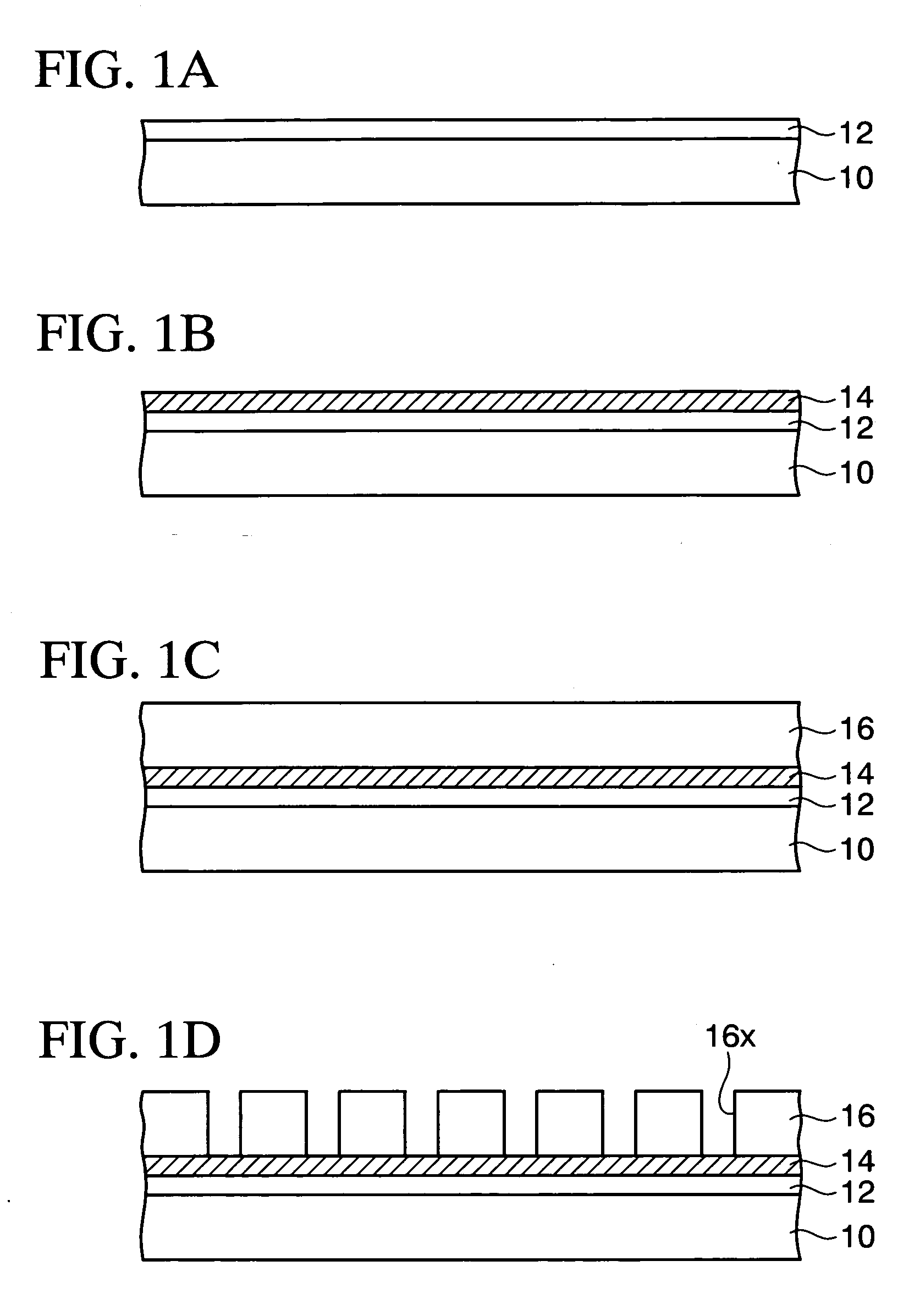
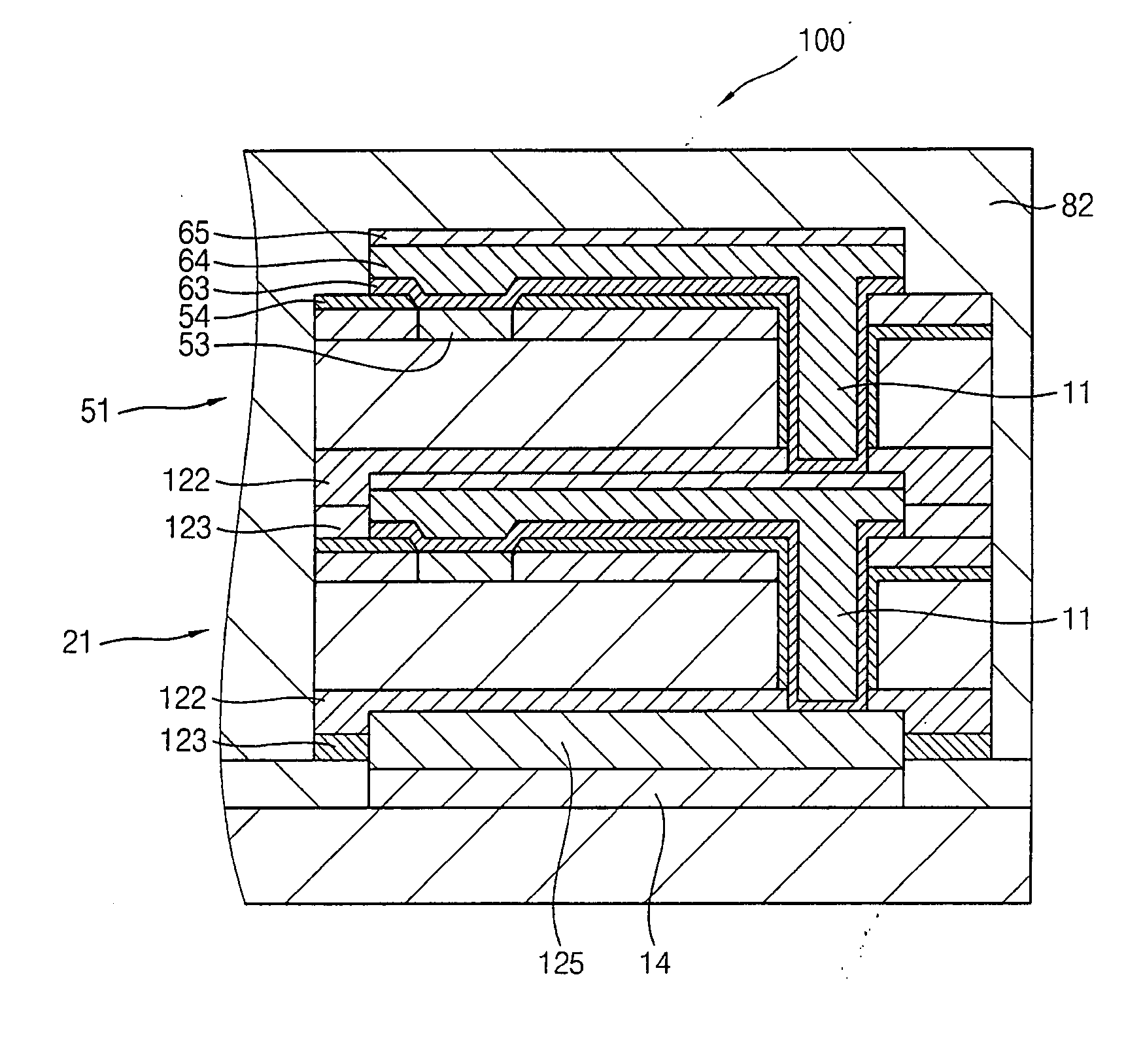
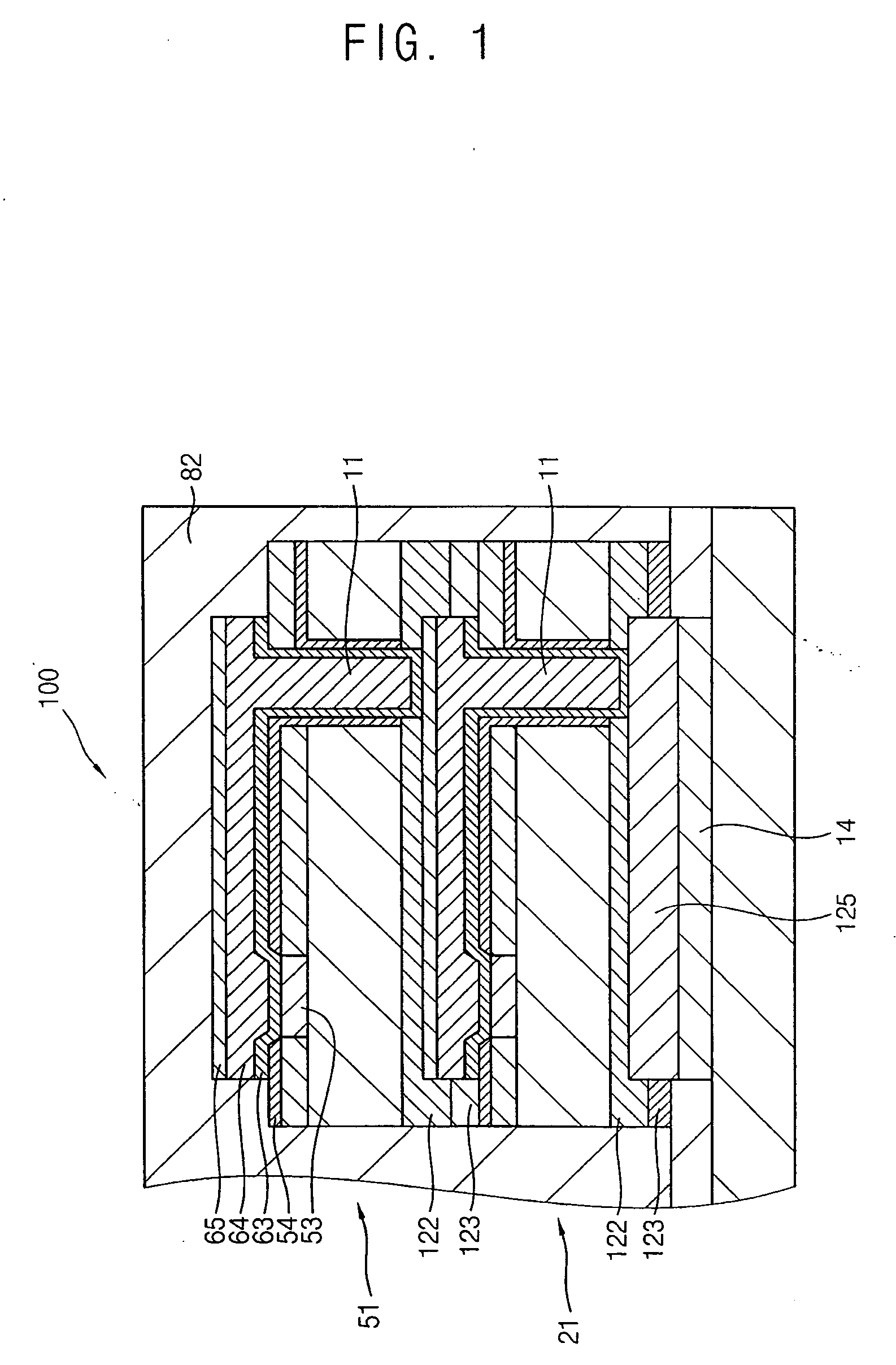
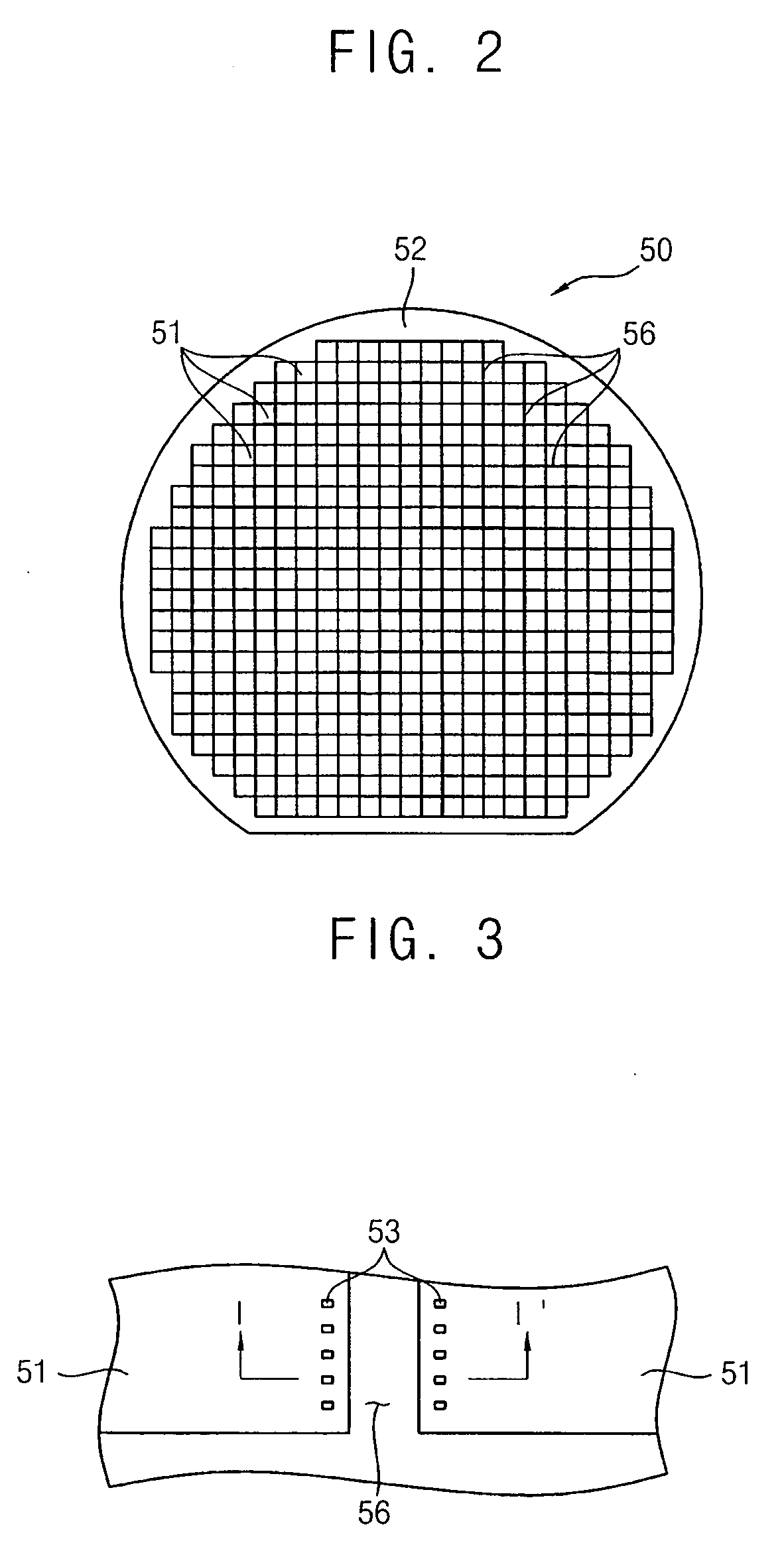
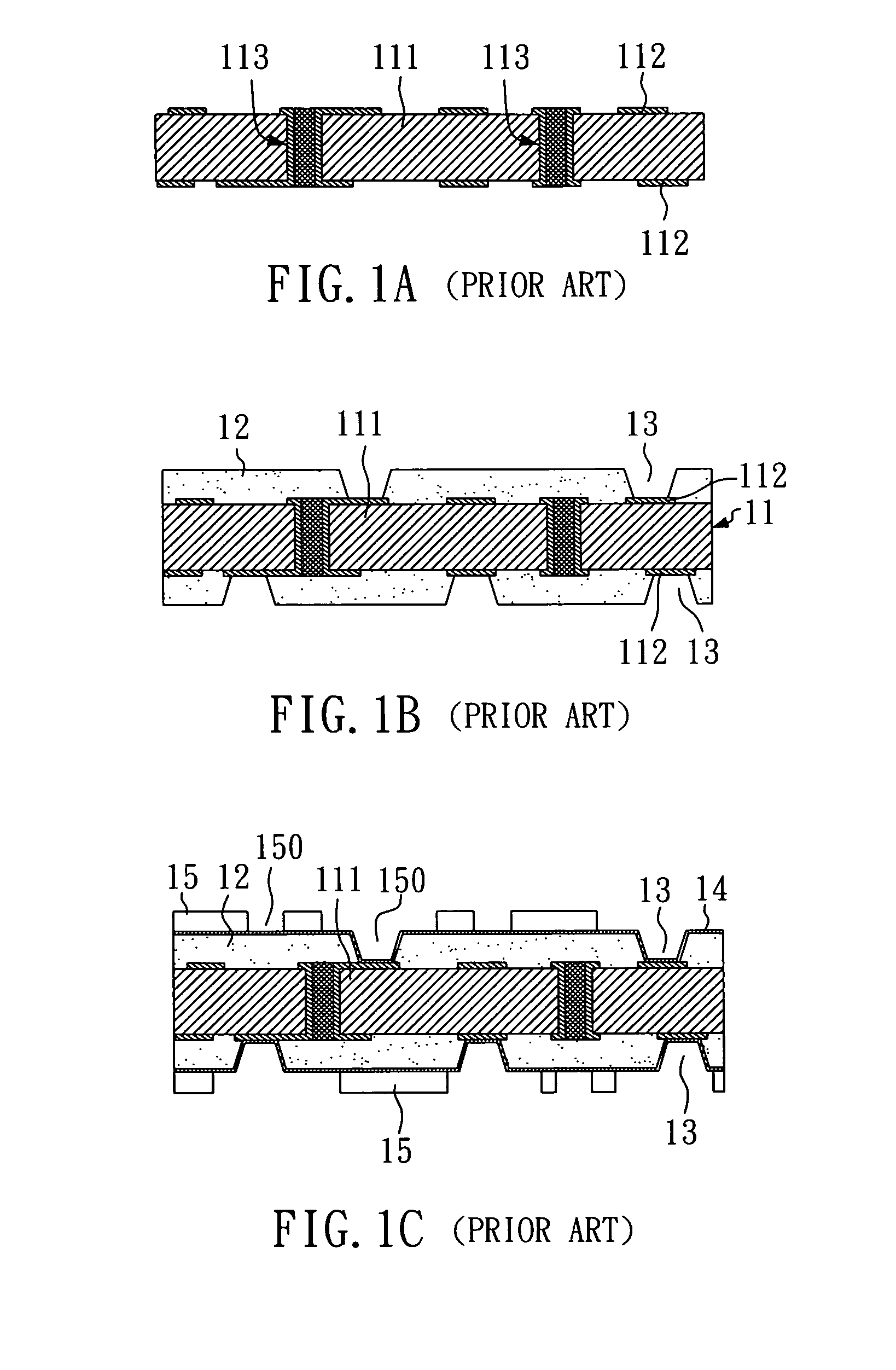
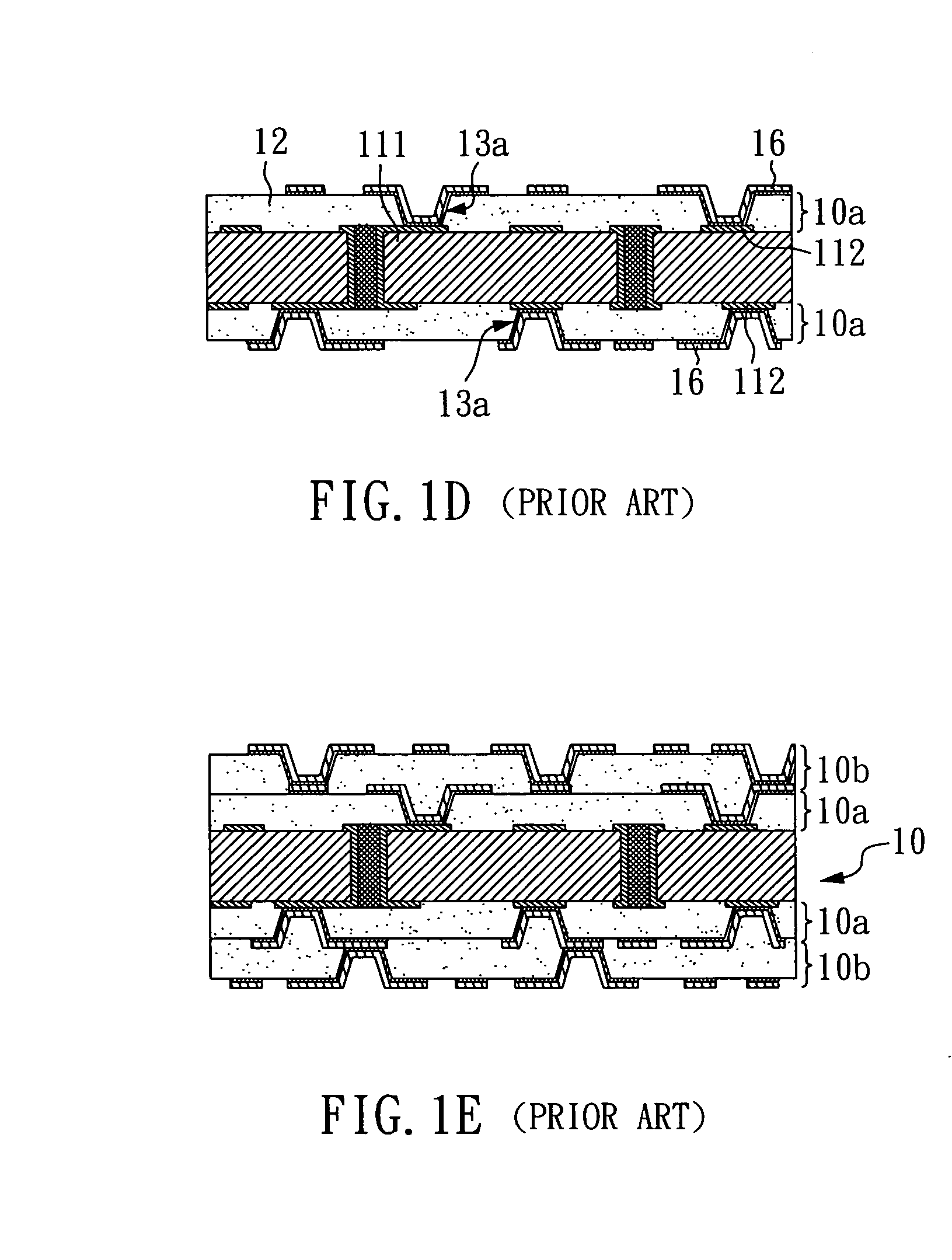
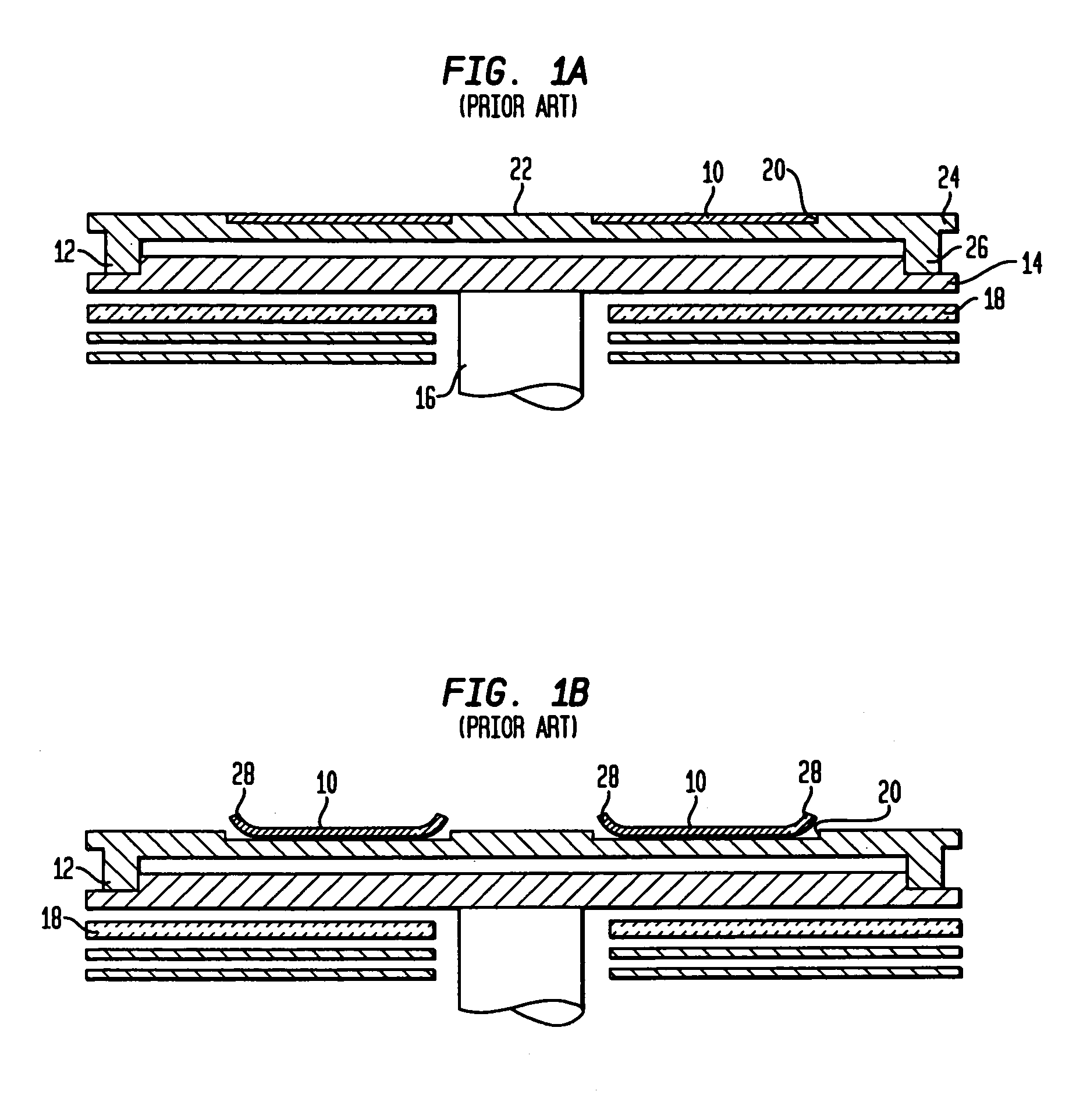
Fabrication method for a thin film semiconductor device, the thin film semiconductor device itself, liquid crystal display, and electronic device
InactiveUS6017779AImprove propertiesWell formedTransistorLinear bearingsElectronic circuitLiquid-crystal display
In order to fabricate a high performance thin film semiconductor device using a low temperature process in which it is possible to use low price glass substrates, a thin film semiconductor device has been fabricated by forming a silicon film at less than 450 DEG C., and, after crystallization, keeping the maximum processing temperature at or below 350 DEG C. In applying the present invention to the fabrication of an active matrix liquid crystal display, it is possible to both easily and reliably fabricate a large, high-quality liquid crystal display. Additionally, in applying the present invention to the fabrication of other electronic circuits as well, it is possible to both easily and reliably fabricate high-quality electronic circuits.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL KEYSTONE TECH
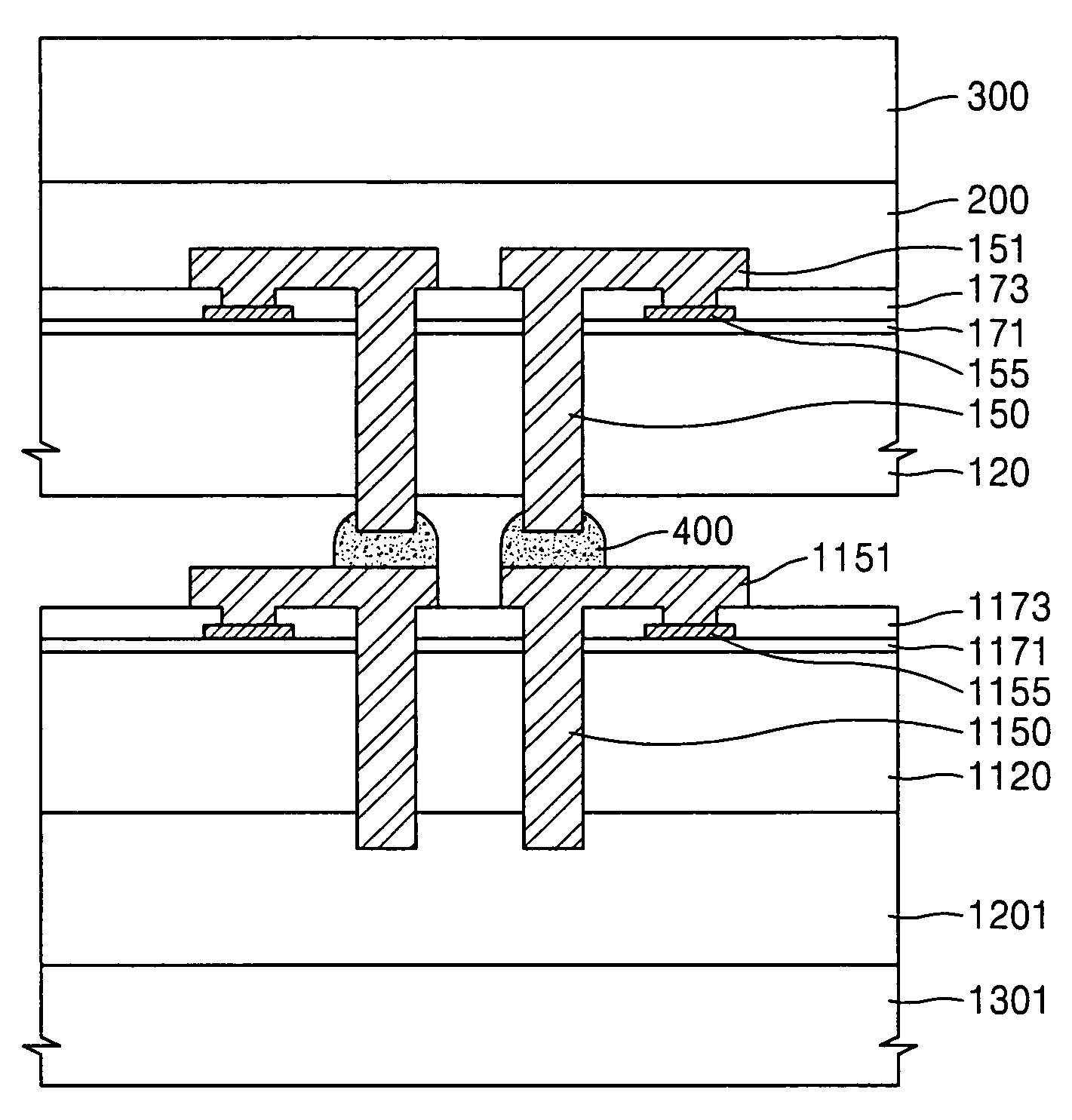
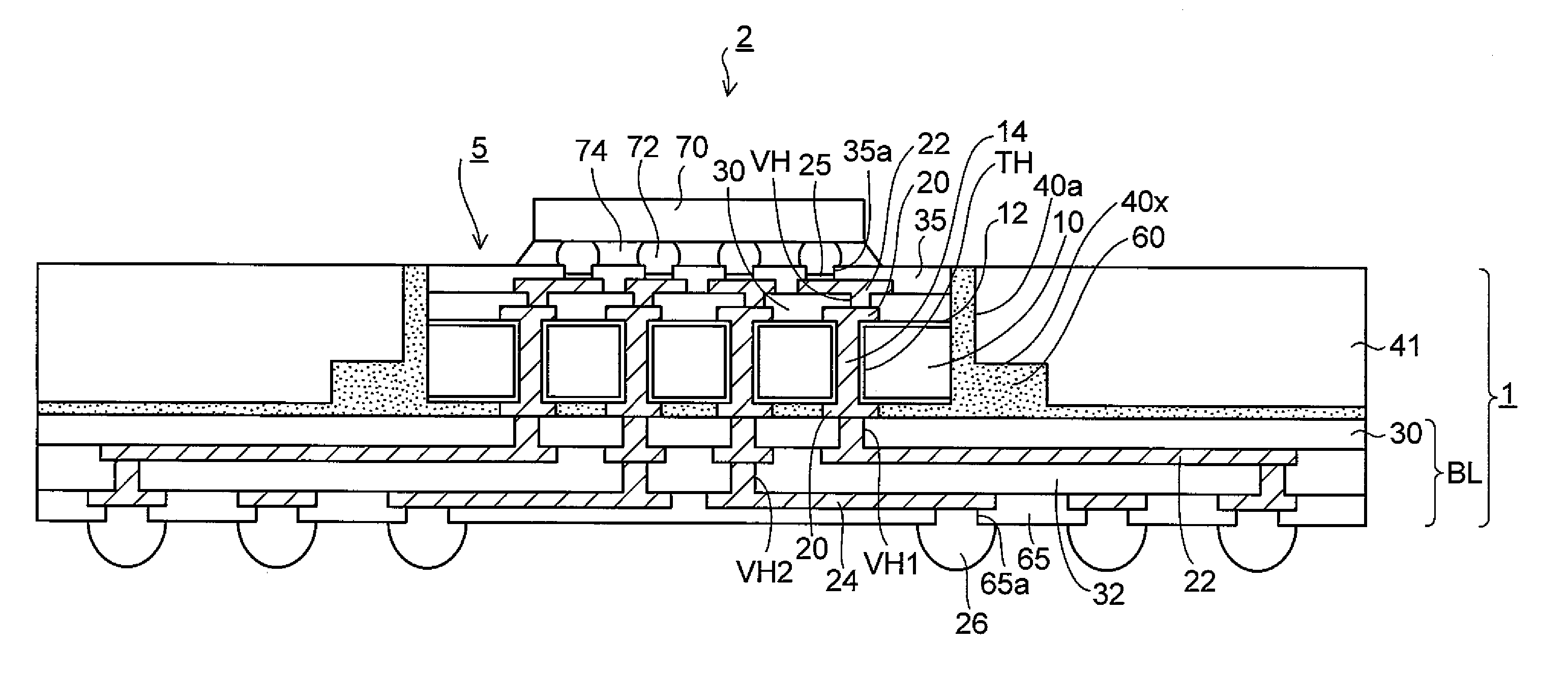
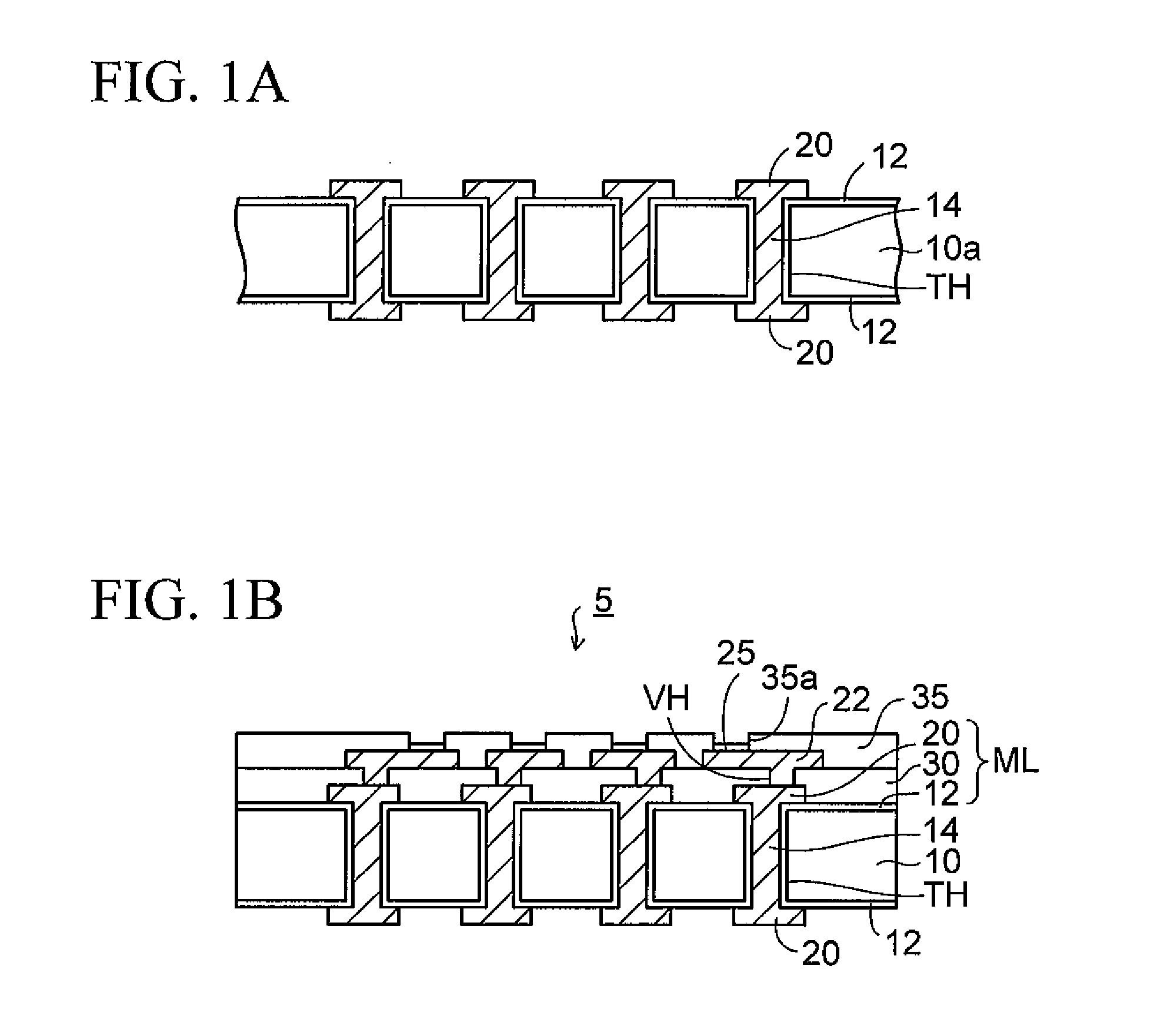
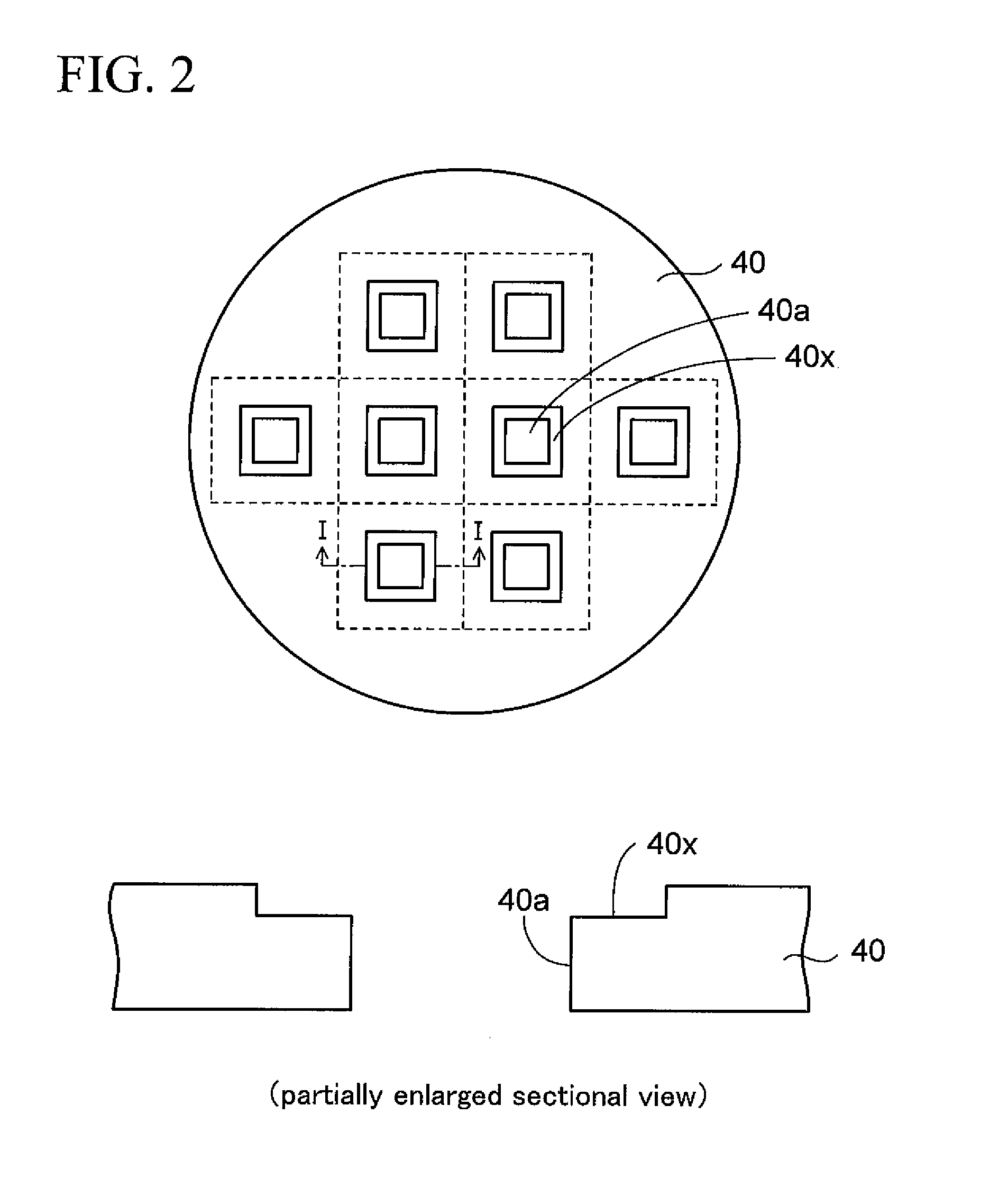
Method of forming a thin wafer stack for a wafer level package
InactiveUS7494845B2Reduce warpageTrend downSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaferingUltraviolet
A method of forming a stack of thin wafers provides a wafer level stack to greatly reduce process time compared to a method where individually separated chips are stacked after a wafer is sawed. A rigid planar wafer support member stabilizes and planarizes each wafer while it is thin or its thickness is reduced and during subsequent wafer processing. Thinned wafers are stacked and the external support members are removed by applying heat or ultraviolet (UV) light to an expandable adhesive layer between the support members and the thin wafers. The stacked wafers then can be further processed and packaged without thin-wafer warping, cracking or breaking. A wafer level package made in accordance with the invented method also is disclosed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Substrate for semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7902660B1Thin thicknessAvoid warpingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricitySolder ball
A substrate for a semiconductor device and a manufacturing thereof, and a semiconductor device using the same and a manufacturing method thereof are disclosed. For example, in the substrate according to the present invention, a core is eliminated, so that the substrate has a very thin thickness, as well, the length of electrically conductive patterns becomes shorter, whereby the electrical efficiency thereof is improved. Moreover, since a carrier having a stiffness of a predetermined strength is bonded on the substrate, it can prevent a warpage phenomenon during the manufacturing process of the semiconductor device. Furthermore, the carrier is removed from the substrate, whereby a solder ball fusing process or an electrical connecting process of the semiconductor die can be easily performed.
Owner:AMKOR TECH SINGAPORE HLDG PTE LTD
Firing furnace, porous ceramic member manufacturing method using the same, and porous ceramic member manufactured by the manufacturing method
ActiveUS20060029898A1Avoid warpingEnsuring spaceMuffle furnacesIncreasing energy efficiencyPorous ceramicsMaterials science
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Flat panel display manufacturing apparatus
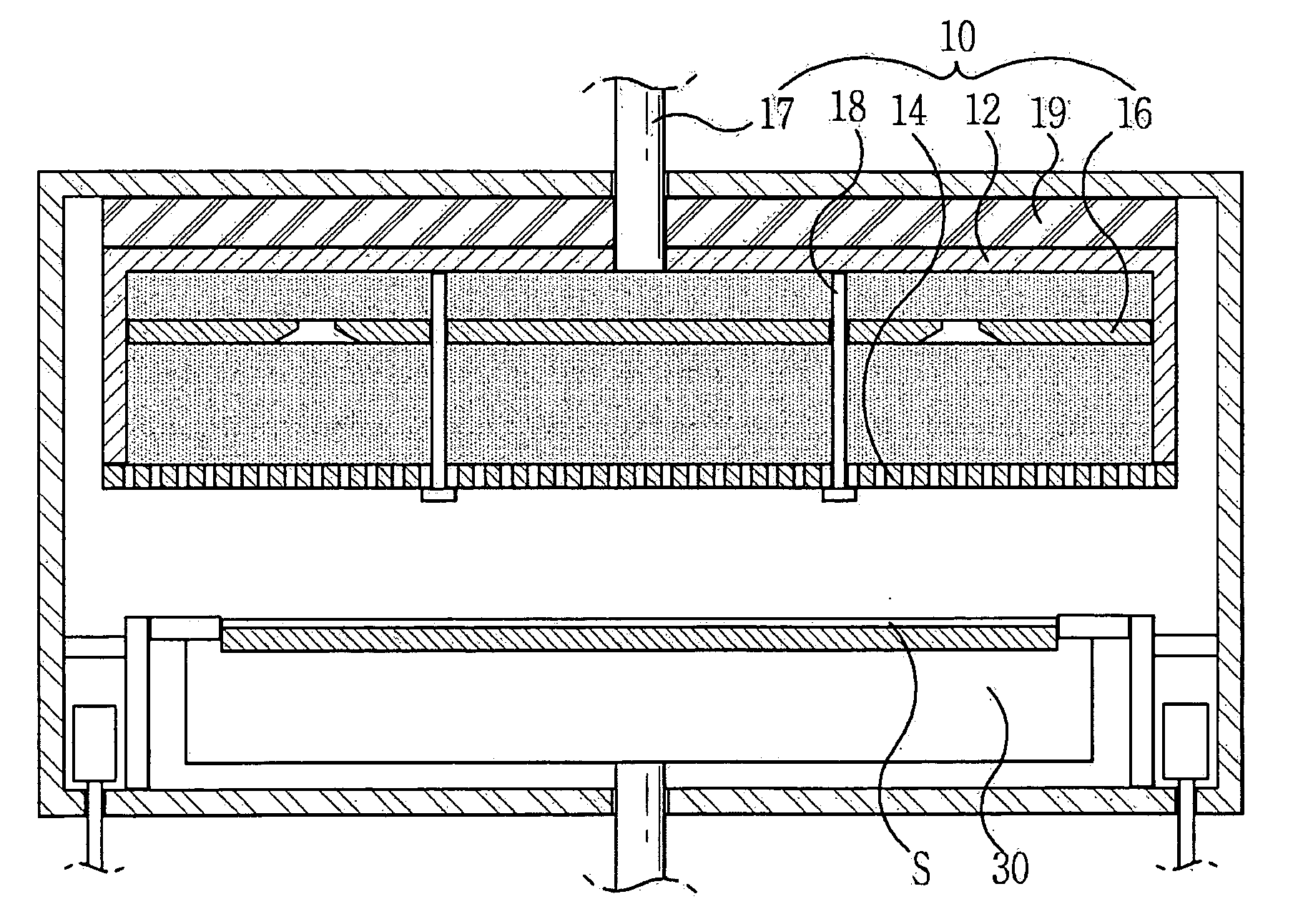
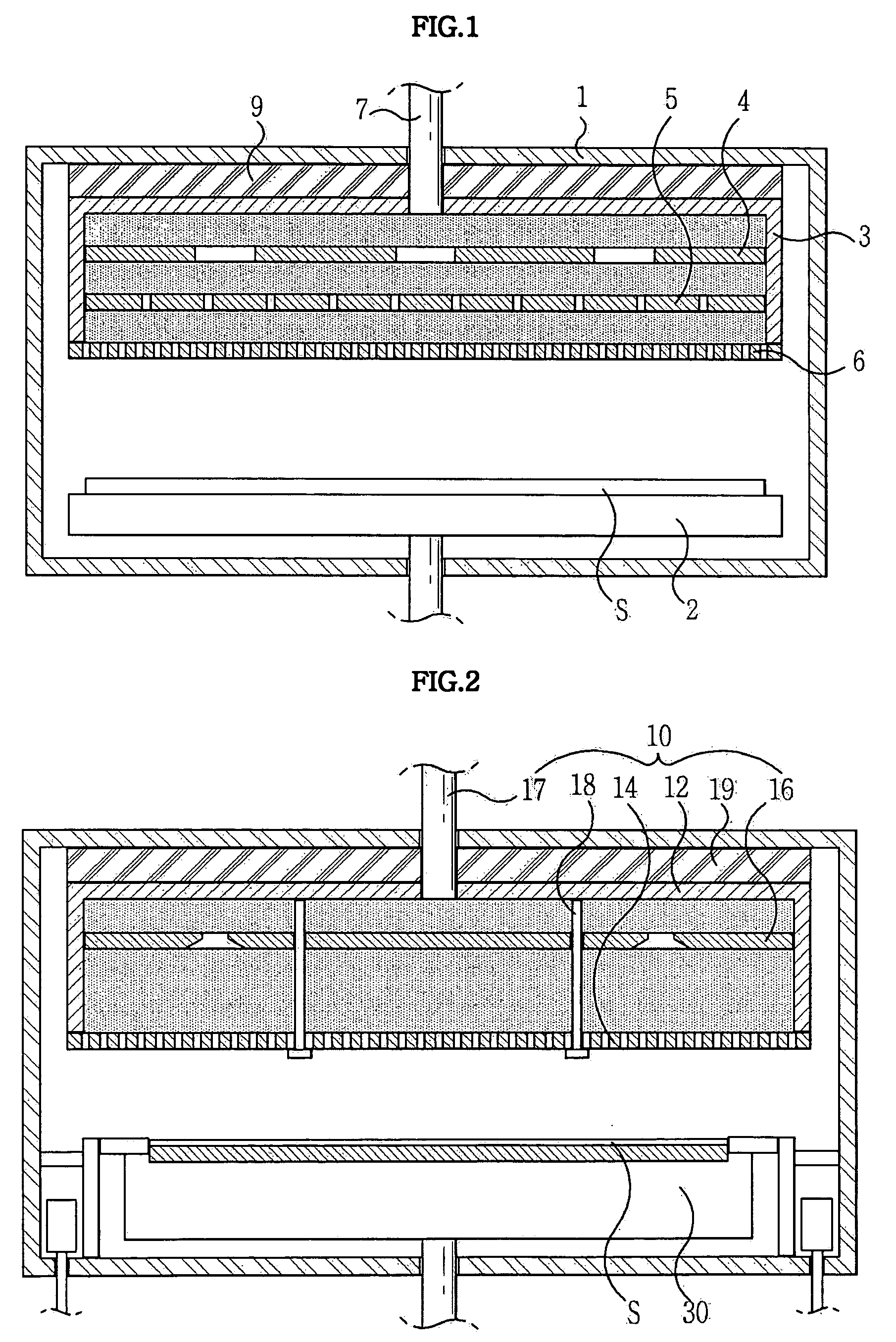
InactiveUS20050103267A1Simple structureEasy to manufactureElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInterior spaceDisplay device
Disclosed herein is a flat panel display manufacturing apparatus in a predetermined process is performed using plasma generated therein. In such a flat panel display manufacturing apparatus, a process gas is supplied into a chamber in an evenly diffused state to generate even plasma inside a symmetrical interior space of the chamber. Consequently, the flat panel display manufacturing apparatus can appropriately control flow rate of the plasma, thereby being capable of performing even processing on a large-scale substrate. In the flat panel display manufacturing apparatus, a substrate pedestal thereof is provided with a combination of vertical and horizontal shielding members, thereby being entirely protected from attack of the plasma, resulting in an increased life-span.
Owner:ADVANCED DISPLAY PROCESS ENG
Conductive plastic compositions and method of manufacture thereof
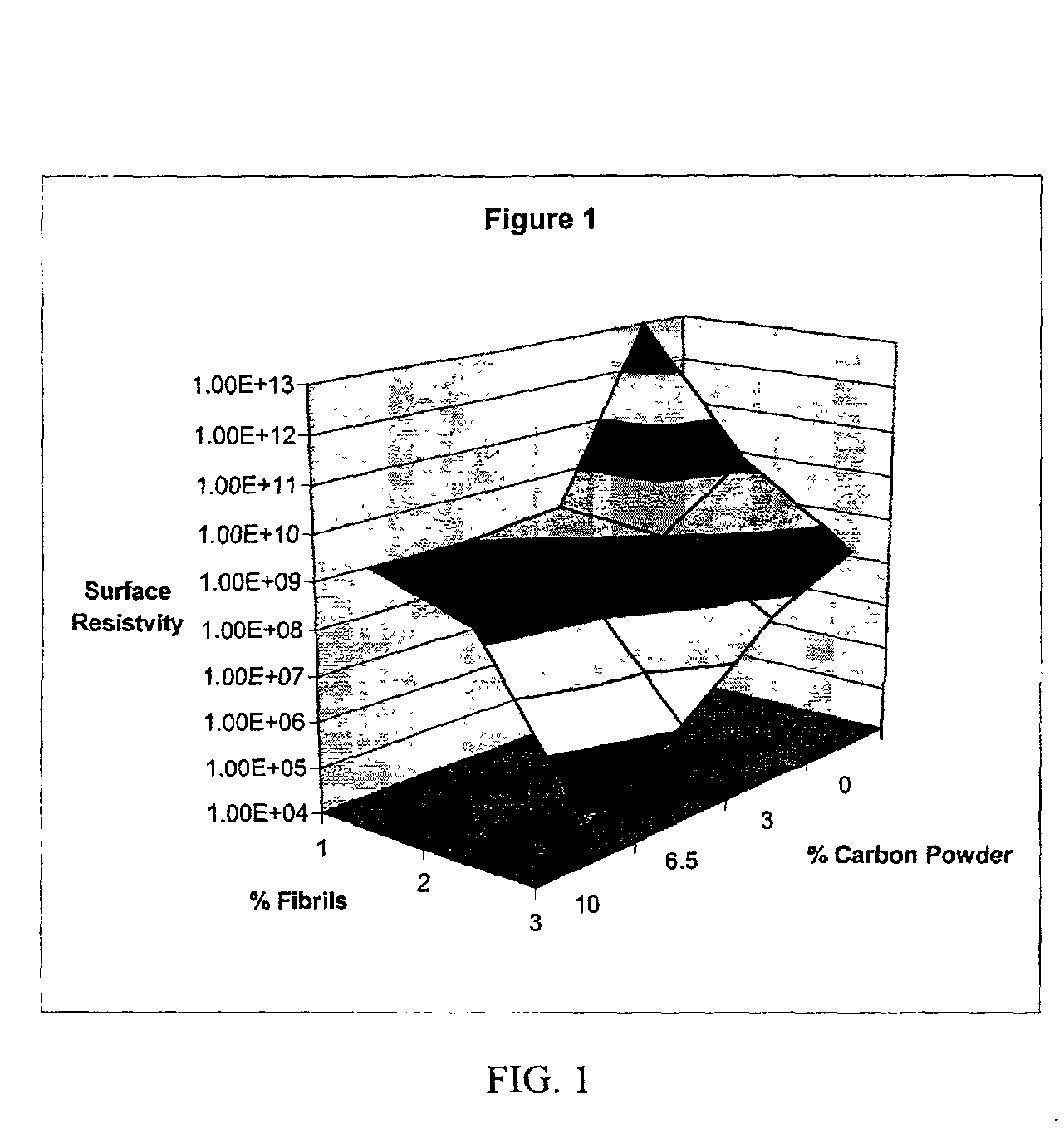
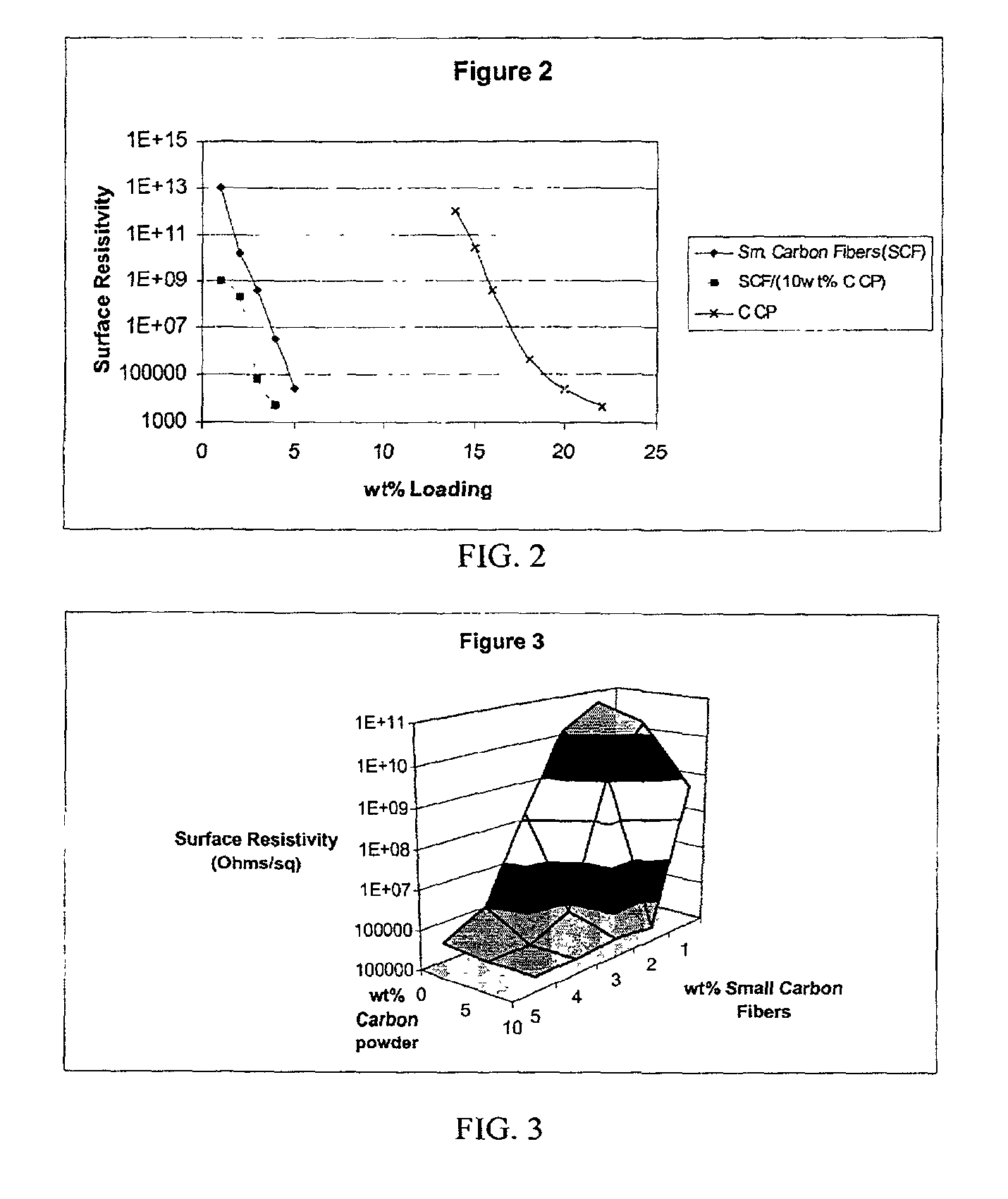
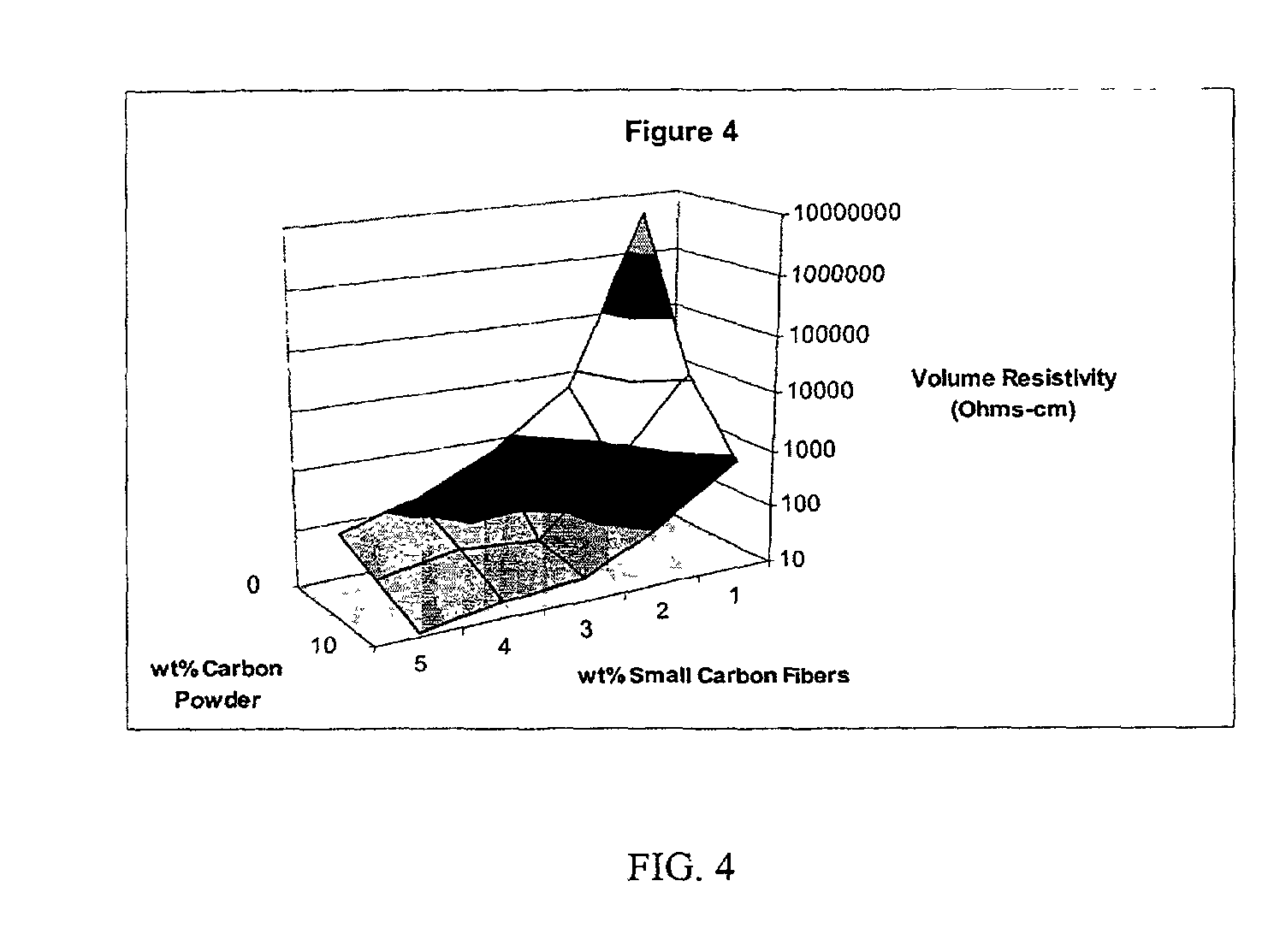
InactiveUS20020183438A1Reduce concentrationSame surface resistivitySpecial tyresNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialFiberCarbon fibers
An improved, conductive, polymeric composition comprises a polymeric resin; an electrically conductive filler system comprising small carbon fibers and either carbon powder or fibrous non-conductive filler or a combination of both. The amount of the conductive filler system utilized is dependent upon the desired electrical conductivity (surface and volume conductivity or resistivity) while preferably preserving intrinsic properties of the polymeric resin such as impact, flex modulus, class A finish, and the like. The conductive articles made from these compositions can therefore be used for electromagnetic shielding, electrostatic dissipation or antistatic purposes in packaging, electronic components, housings for electronic components and automotive housings.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
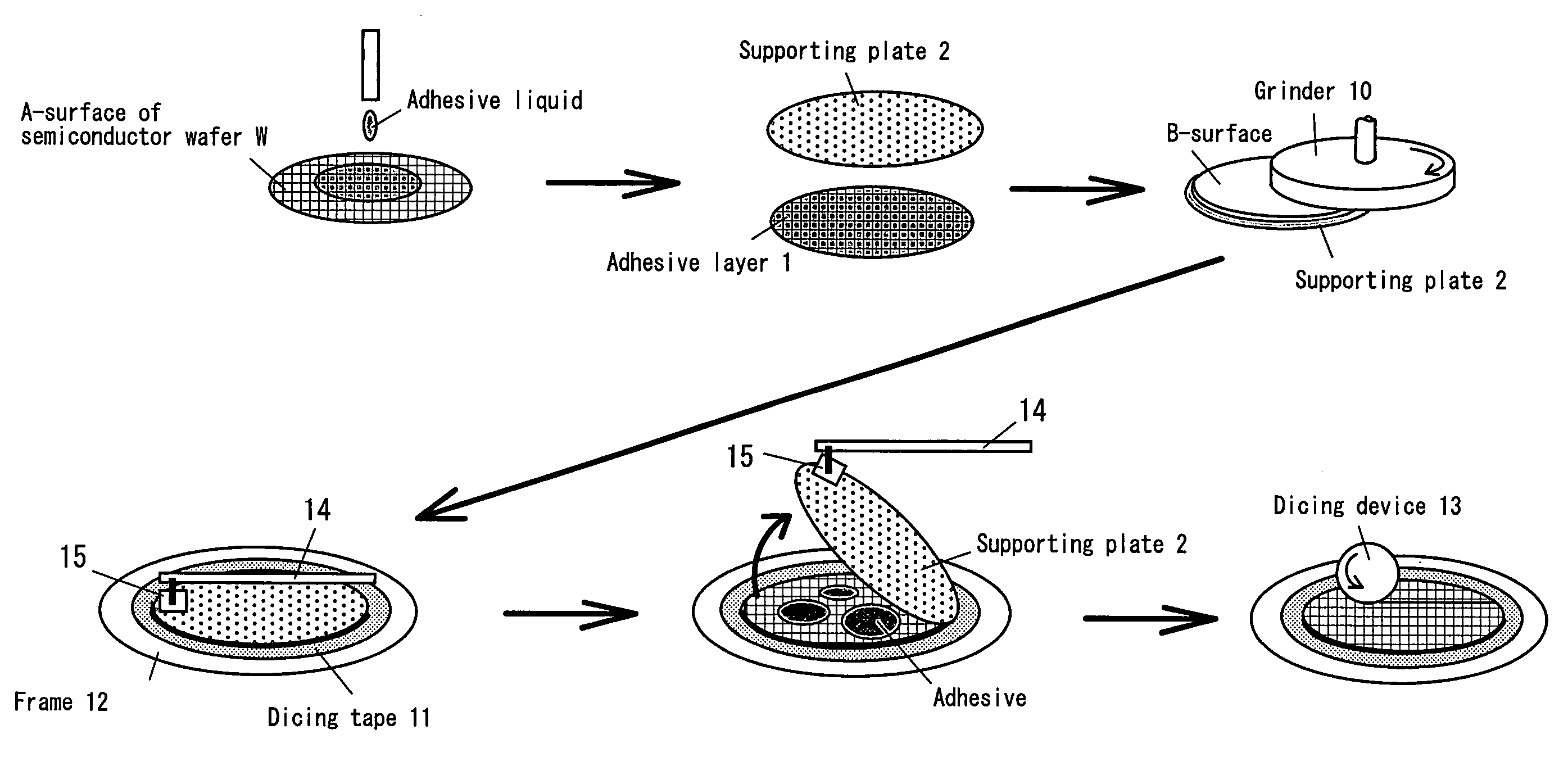
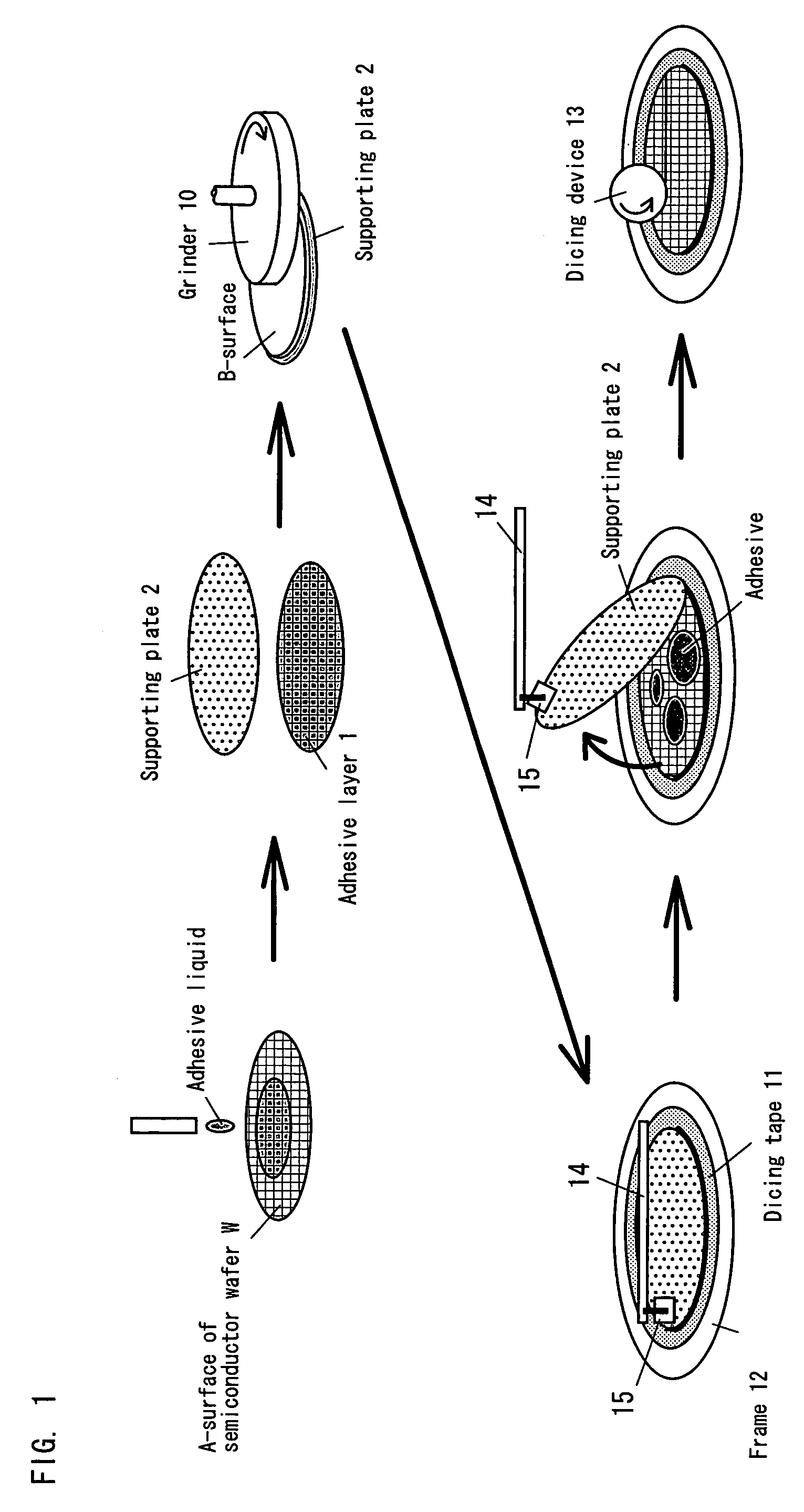
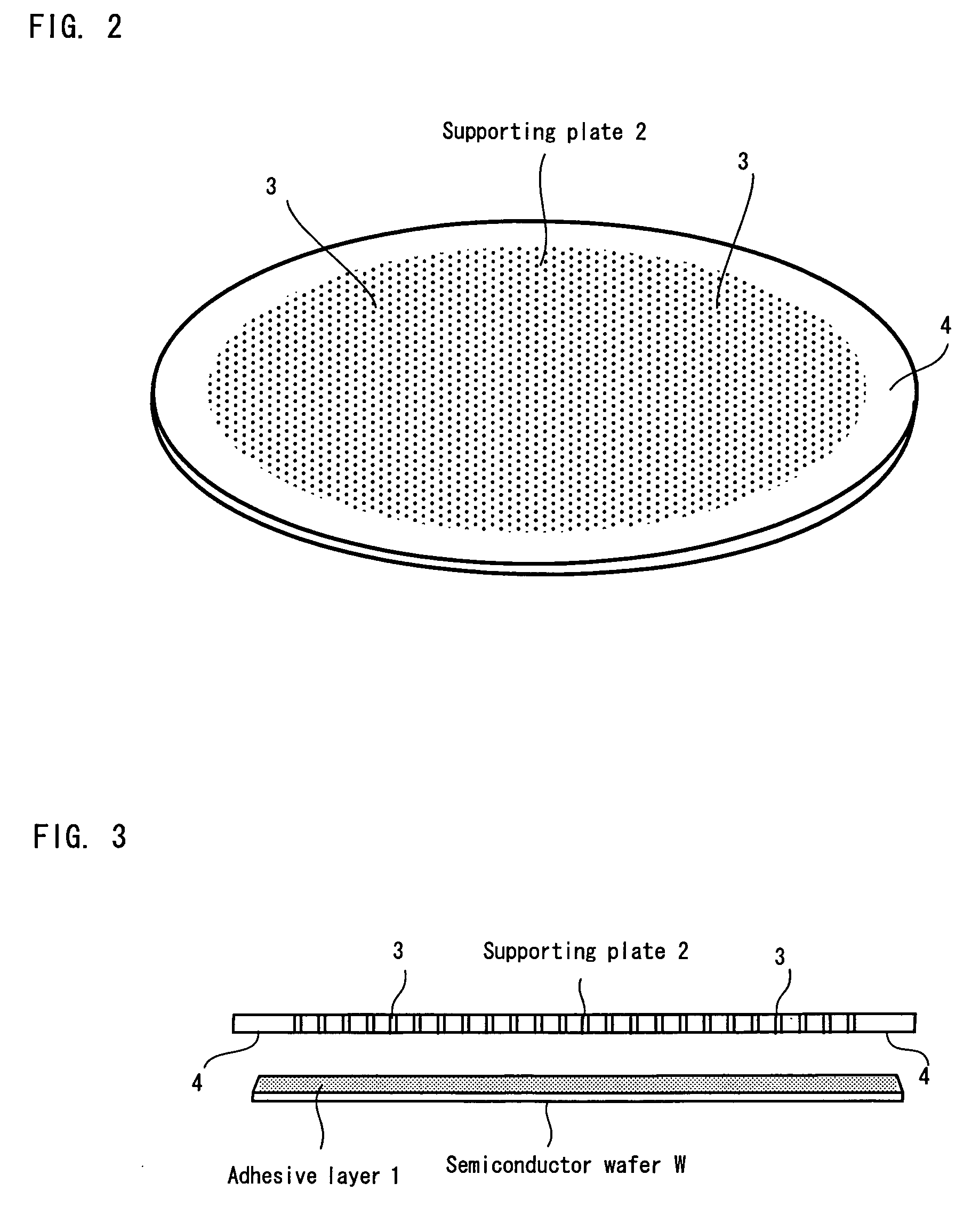
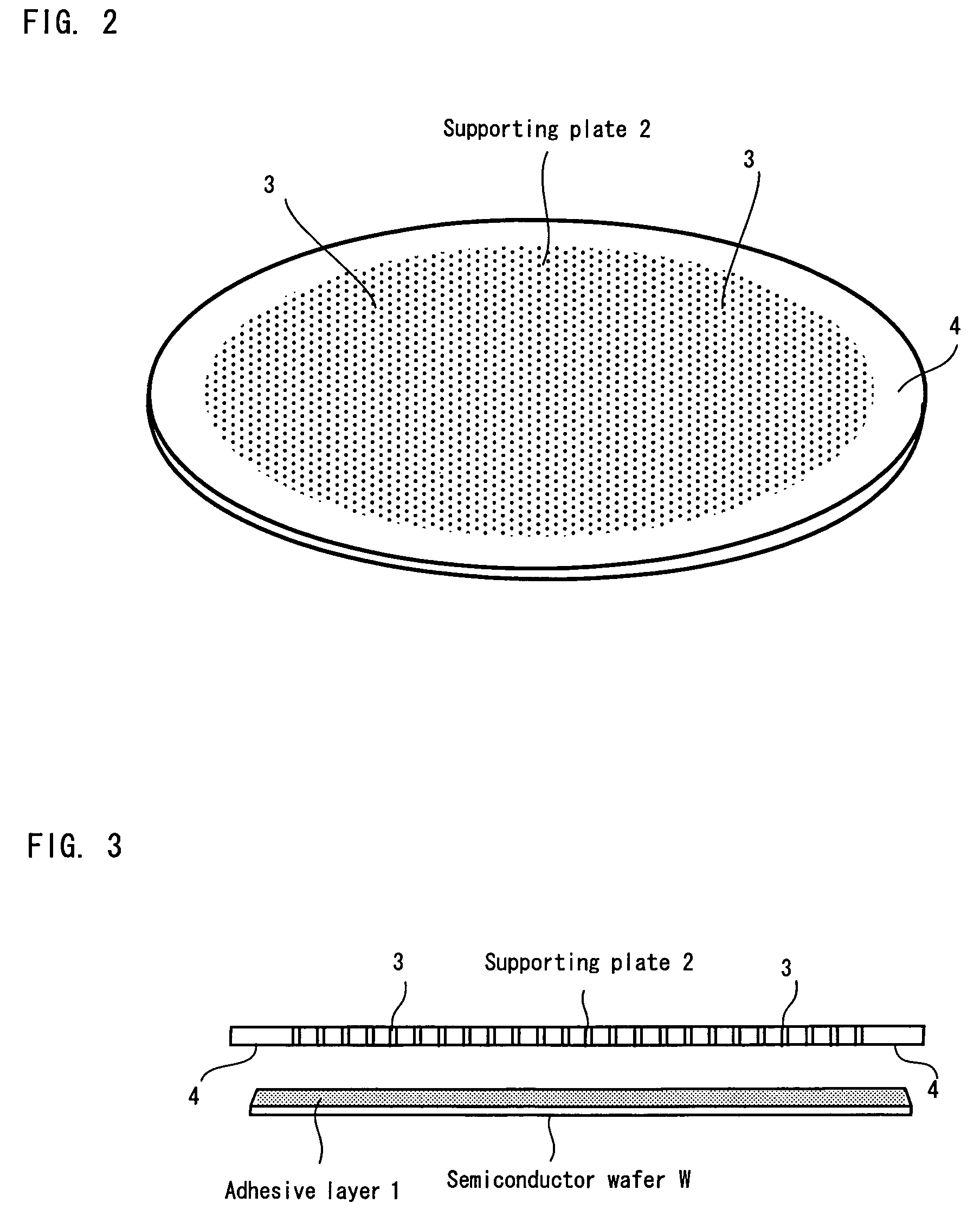
Substrate supporting plate and stripping method for supporting plate
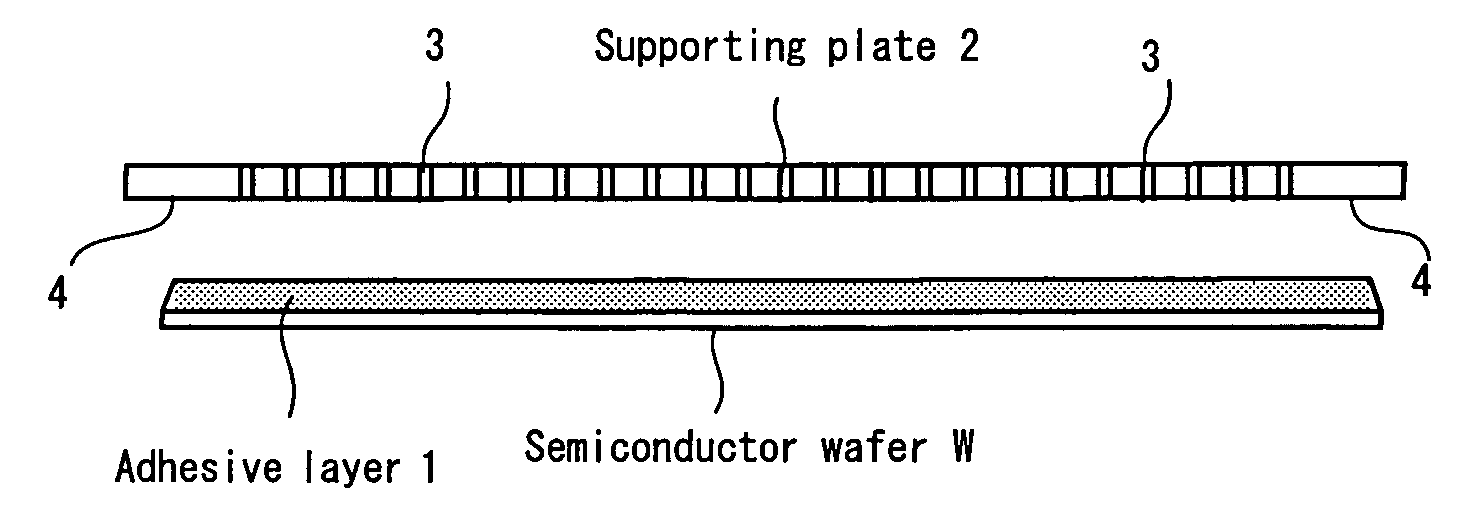
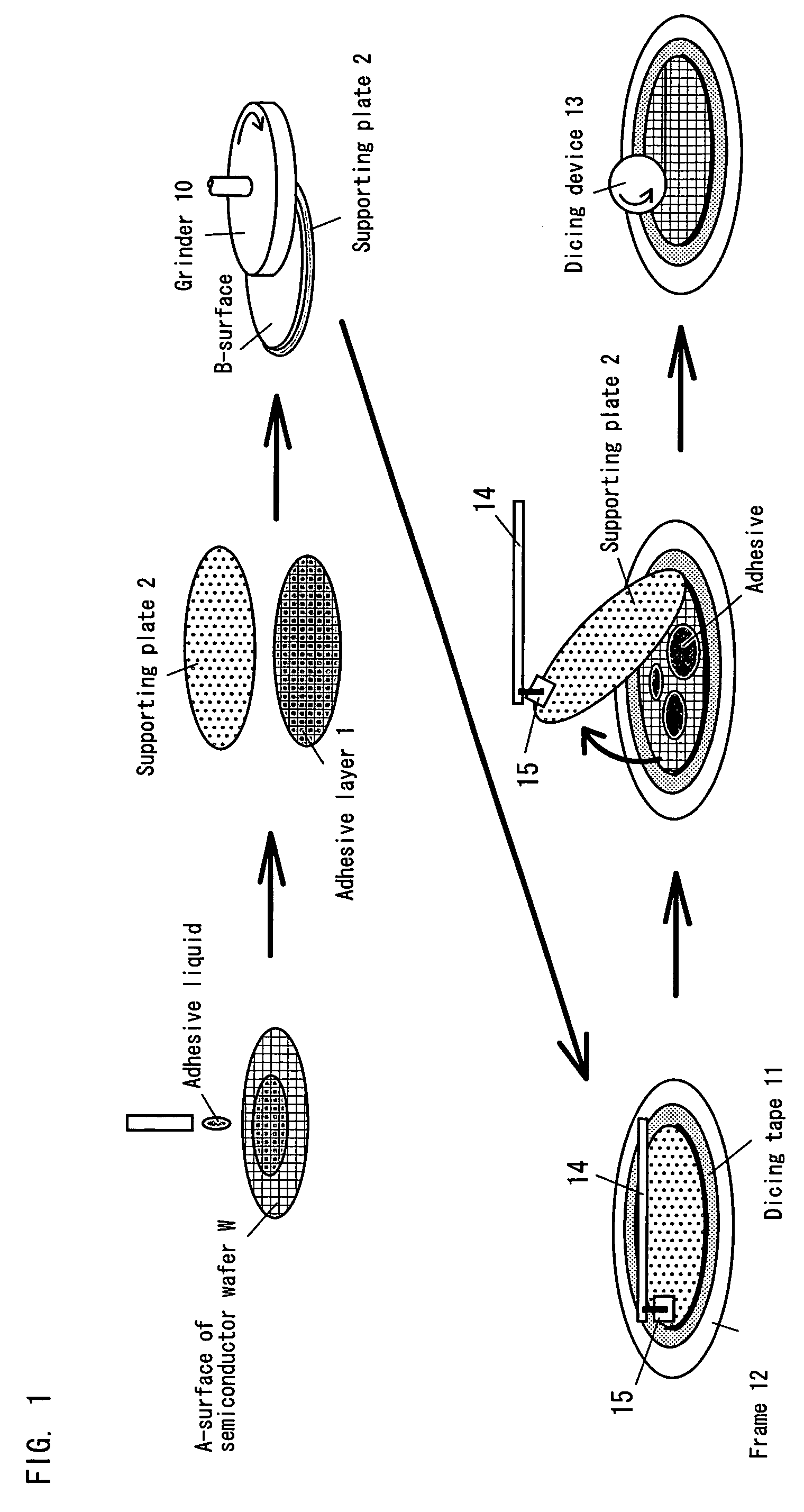
There is provided a supporting plate having a structure in which a solvent can be supplied to an adhesive layer between the supporting plate and a substrate such as a semiconductor wafer in a short period of time after the substrate is thinned, and also a method for stripping the supporting plate. The supporting plate may have a larger diameter than the semiconductor wafer, and penetrating holes are formed in the supporting plate. The outer peripheral portion of the supporting plate is a flat portion in which no penetrating hole is formed. When alcohol is poured from above the supporting plate, the alcohol reaches the adhesive layer through the penetrating holes, dissolves and removes the adhesive layer.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Method of forming a thin wafer stack for a wafer level package
InactiveUS20050282374A1Wafer thickness reductionAvoid warpingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringWafer stacking
A method of forming a stack of thin wafers provides a wafer level stack to greatly reduce process time compared to a method where individually separated chips are stacked after a wafer is sawed. A rigid planar wafer support member stabilizes and planarizes each wafer while it is thin or its thickness is reduced and during subsequent wafer processing. Thinned wafers are stacked and the external support members are removed by applying heat or ultraviolet (UV) light to an expandable adhesive layer between the support members and the thin wafers. The stacked wafers then can be further processed and packaged without thin-wafer warping, cracking or breaking. A wafer level package made in accordance with the invented method also is disclosed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
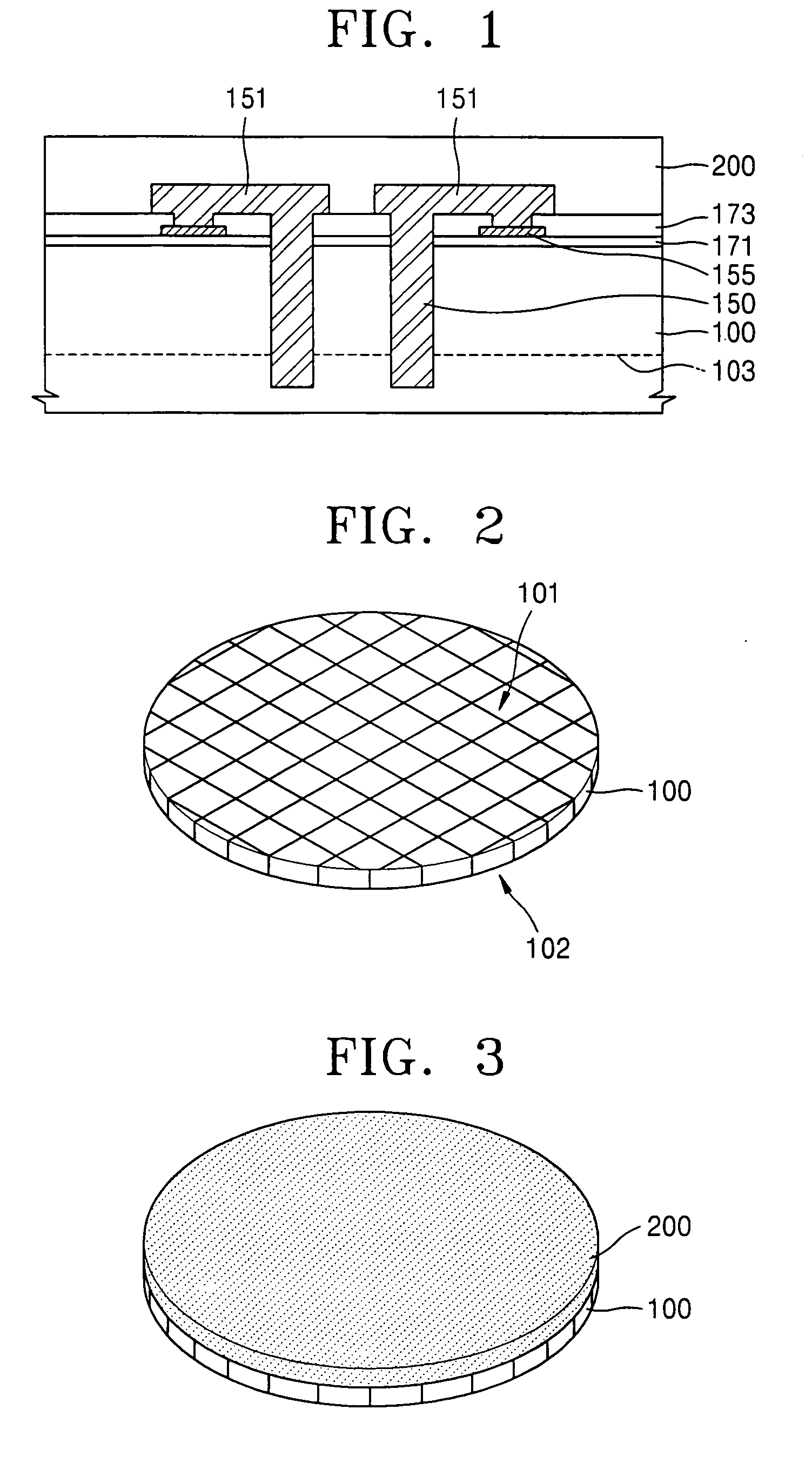
Structure of semiconductor device package and method of the same
InactiveUS20080217761A1Avoid warpingReduce processing stepsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringDielectric layer
The present invention provides a semiconductor device package comprising a substrate with at lease a pre-formed die receiving cavity formed and terminal contact metal pads formed within an upper surface of the substrate. At lease a first die is disposed within the die receiving cavity. A first dielectric layer is formed on the first die and the substrate and refilled into a gap between the first die and the substrate to absorb thermal mechanical stress there between. A first re-distribution layer (RDL) is formed on the first dielectric layer and coupled to the first die. A second dielectric layer is formed on the first RDL, and then a second die is disposed on the second dielectric layer and surrounded by core pastes having through holes thereon. A second re-distribution layer (RDL) is formed on the core pastes to fill the through holes, and then a third dielectric layer formed on the second RDL.
Owner:ADVANCED CHIP ENG TECH
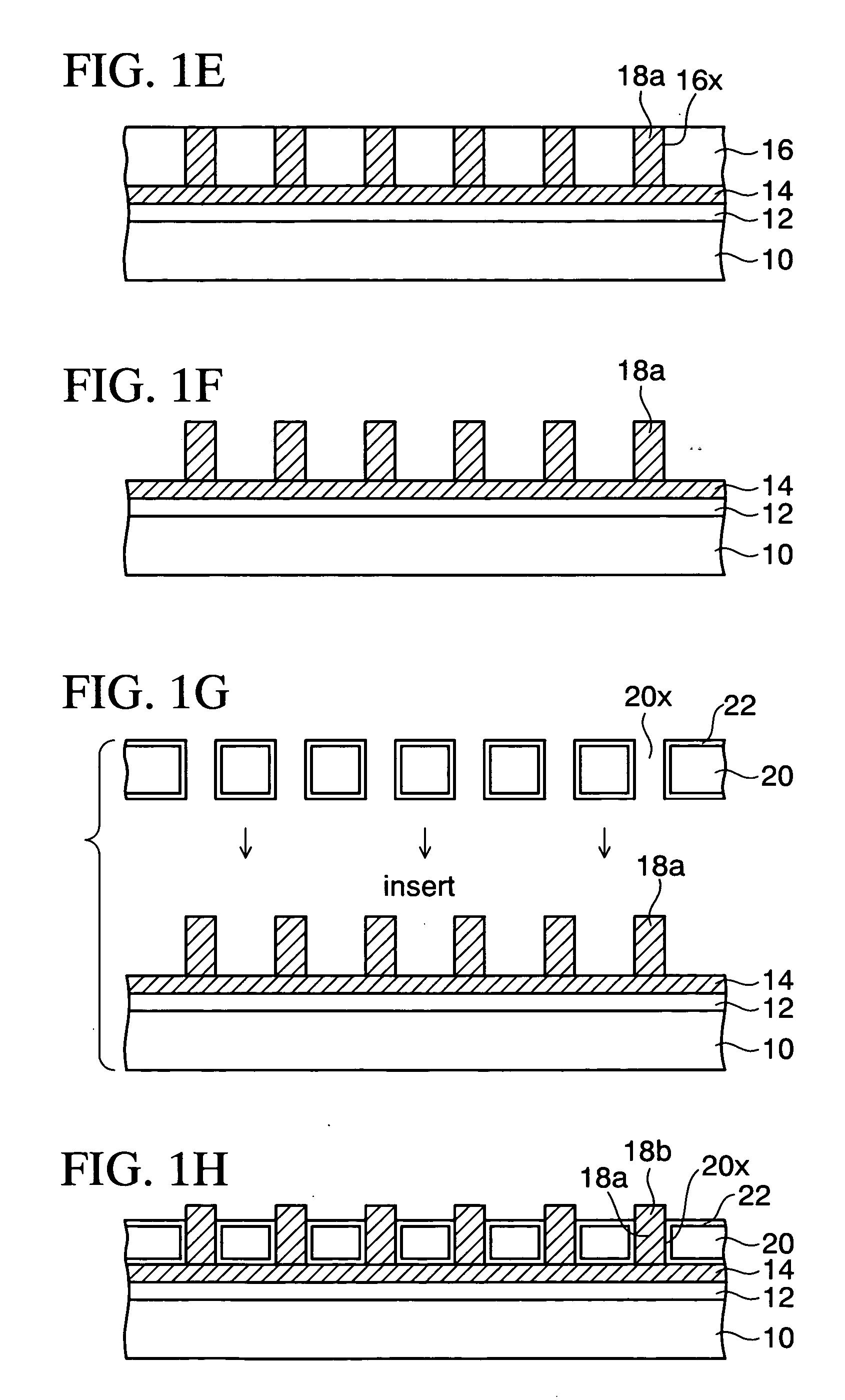
Method of manufacturing a substrate with through electrodes
InactiveUS20060073701A1Avoid warpingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOptoelectronicsMetal
A method of manufacturing a substrate with through electrodes of the present invention, includes the steps of forming a metal post over a temporal substrate in a state that the metal post is peelable from the temporal substrate, placing a normal substrate in which a through hole is provided in a position corresponding to the metal post over the temporal substrate, whereby inserting the metal post on the temporal substrate into the through hole in the normal substrate, and obtaining a through electrode that is formed of the metal post passing through the normal substrate by peeling the temporal substrate from the metal post.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
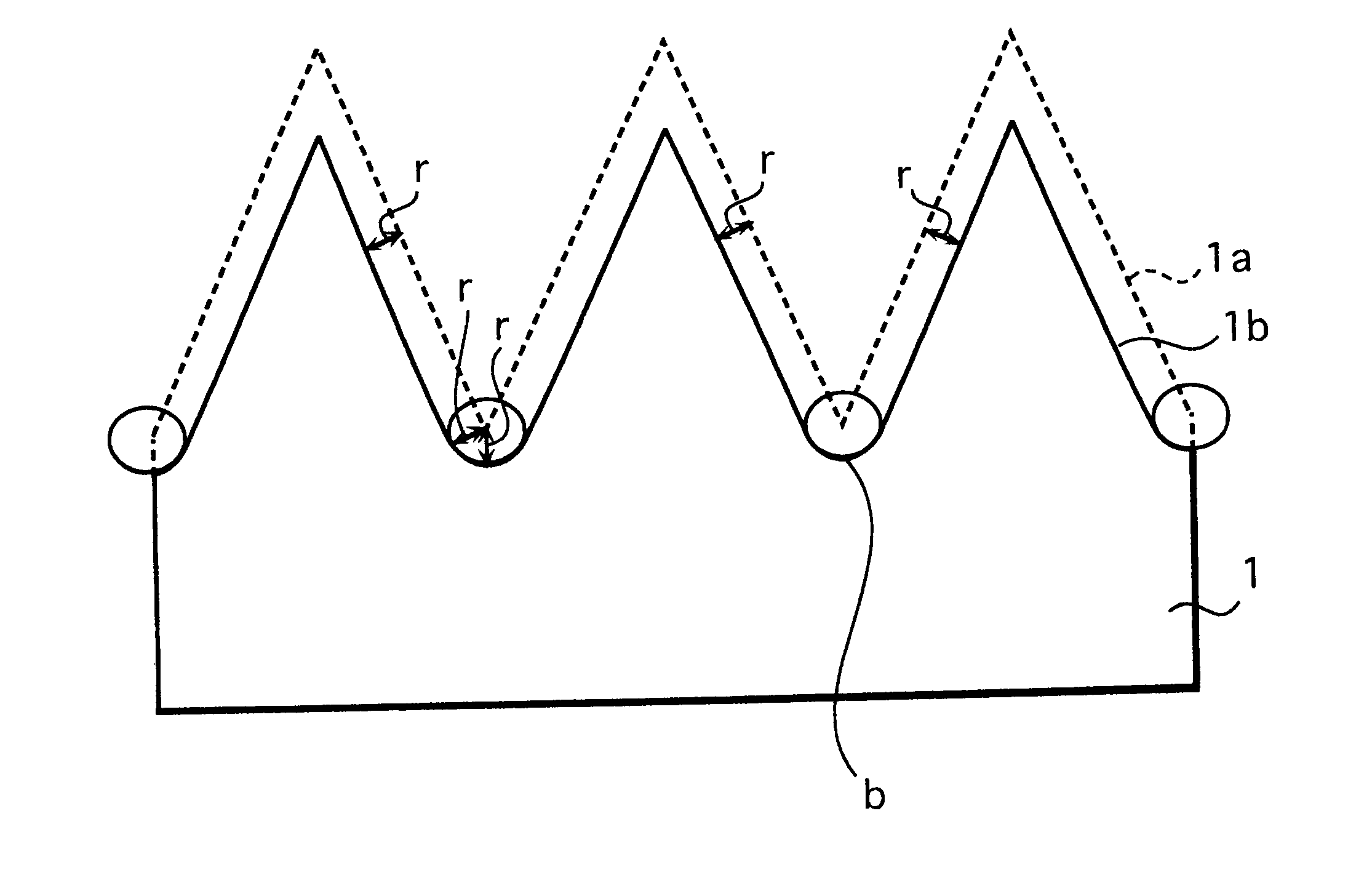
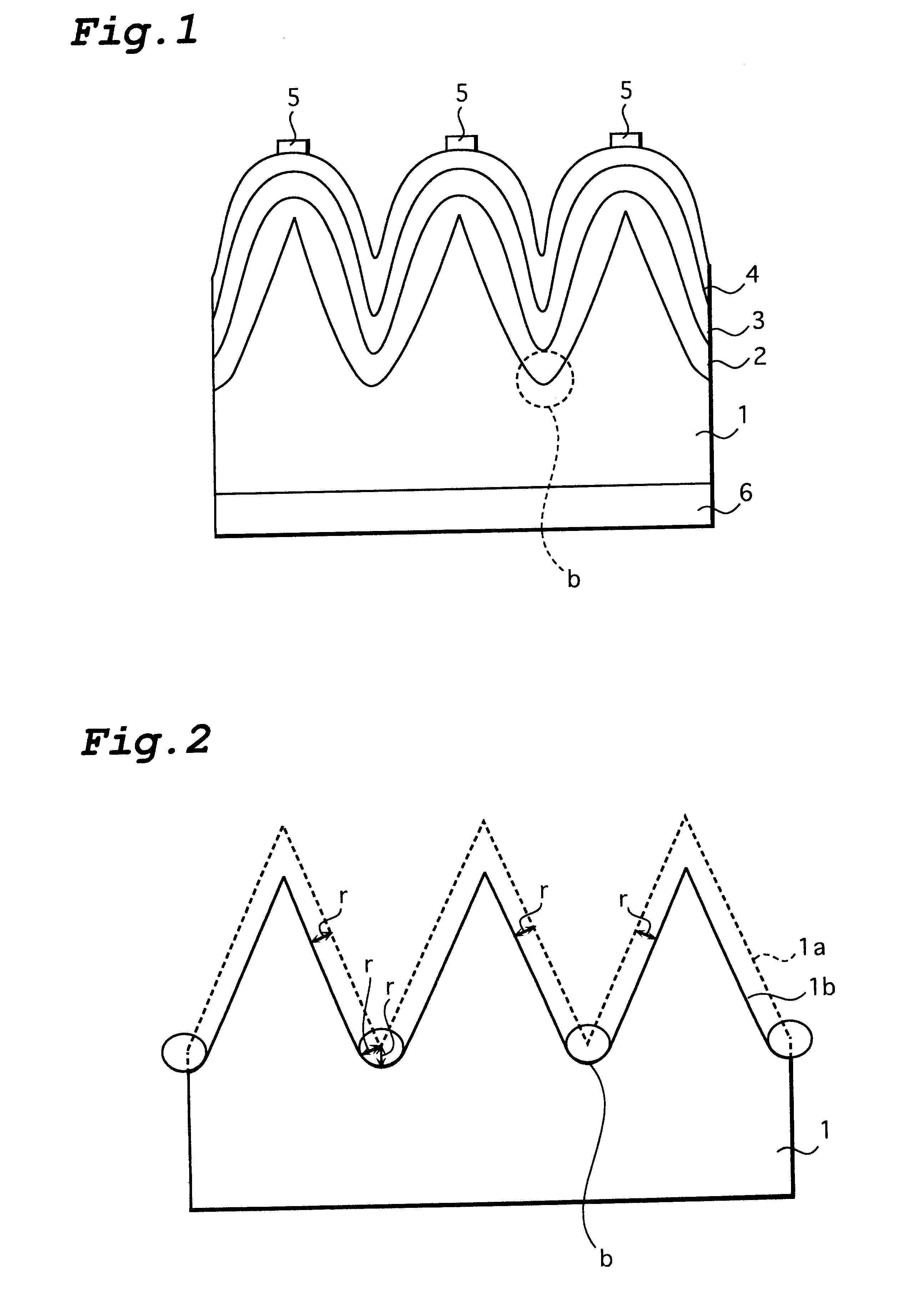
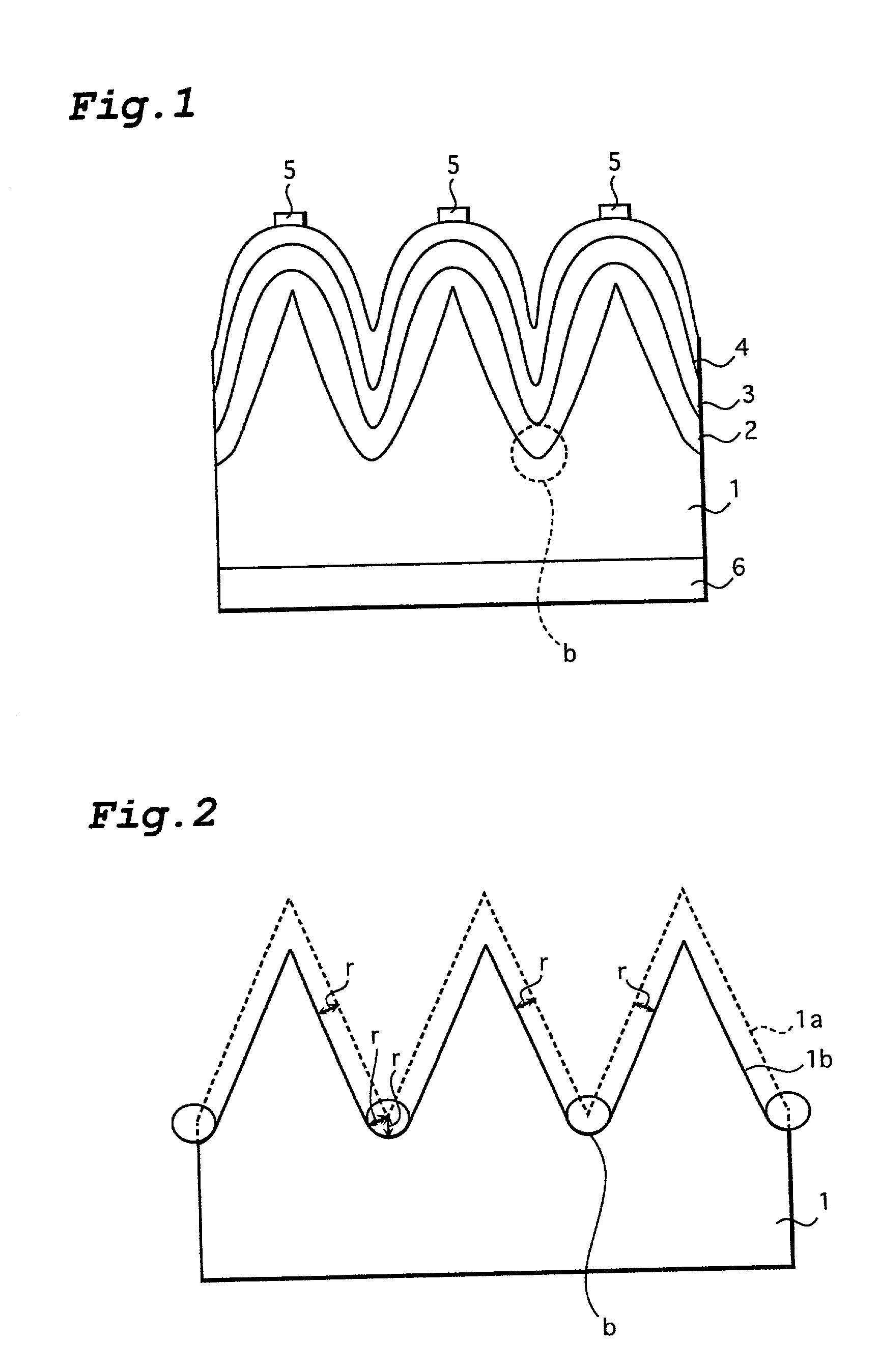
Photovoltaic element and method for manufacture thereof
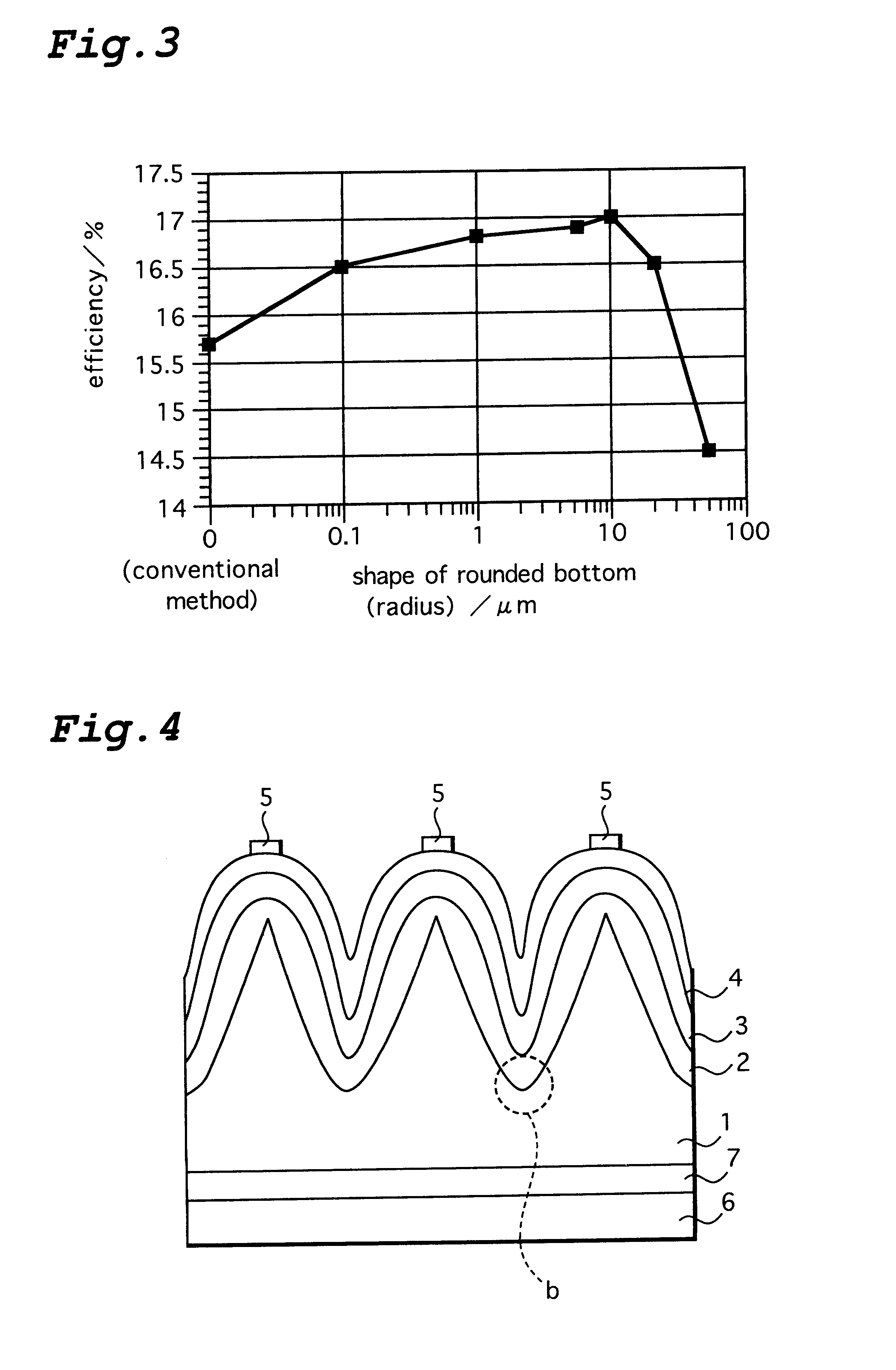
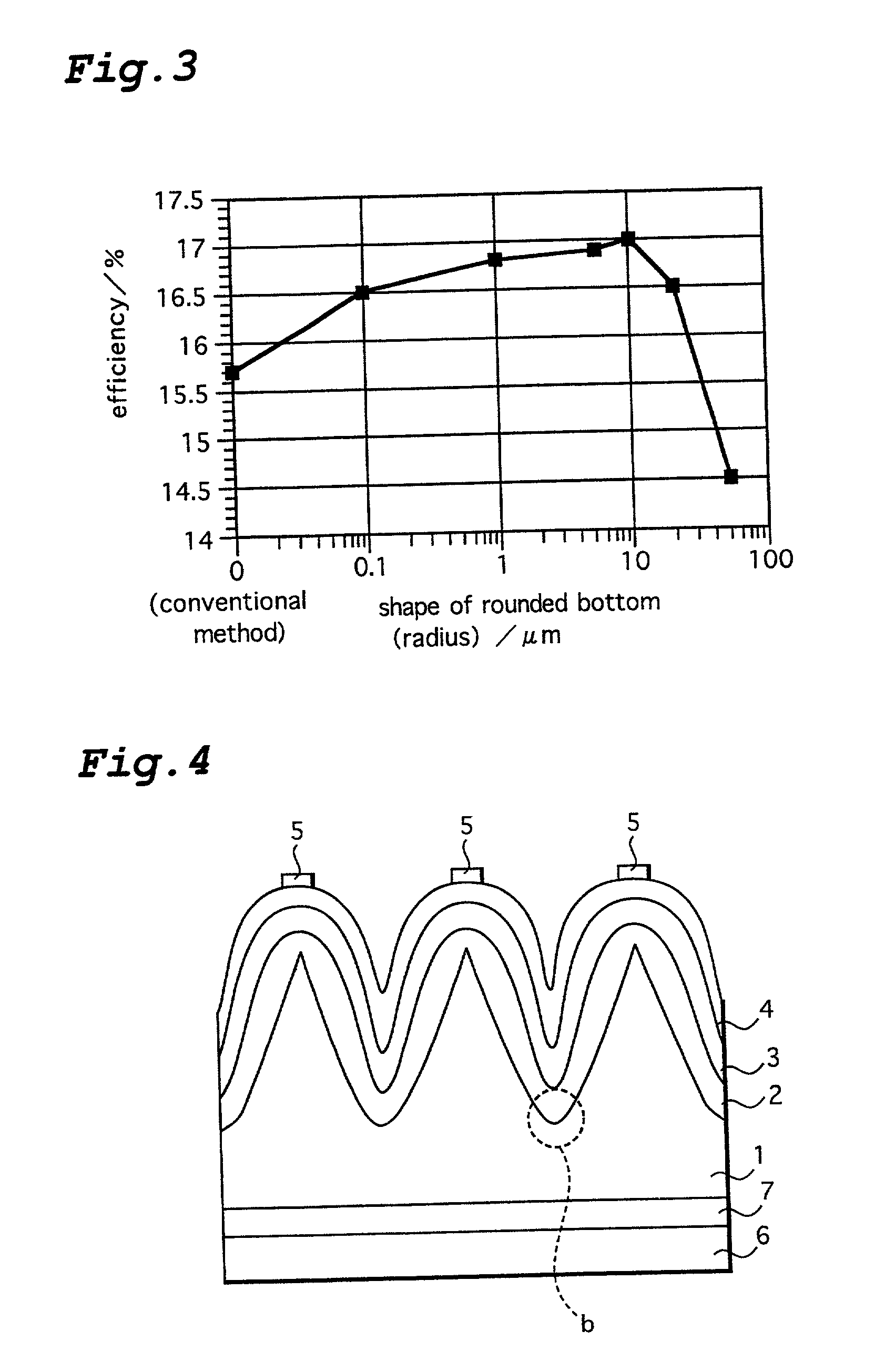
InactiveUS6207890B1Lowered open circuit voltage circuitLowered circuit short circuitPV power plantsSolid-state devicesSolar lightAmorphous silicon
A photovoltaic element which directly converts an optical energy such as solar light into an electric energy. After many uneven sections are formed on the surface of an n-type crystalline silicon substrate (1), the surface of the substrate (1) is isotropically etched. Then the bottoms (b) of the recessed sections are rounded and a p-type amorphous silicon layer (3) is formed on the surface of the substrate (1) through an intrinsic amorphous silicon layer (2). The shape of the surface of the substrate (1) after isotropic etching is such that the bottoms of the recessed sections are slightly rounded and therefore the amorphous silicon layer can be deposited in a uniform thickness.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Wave soldering fixture
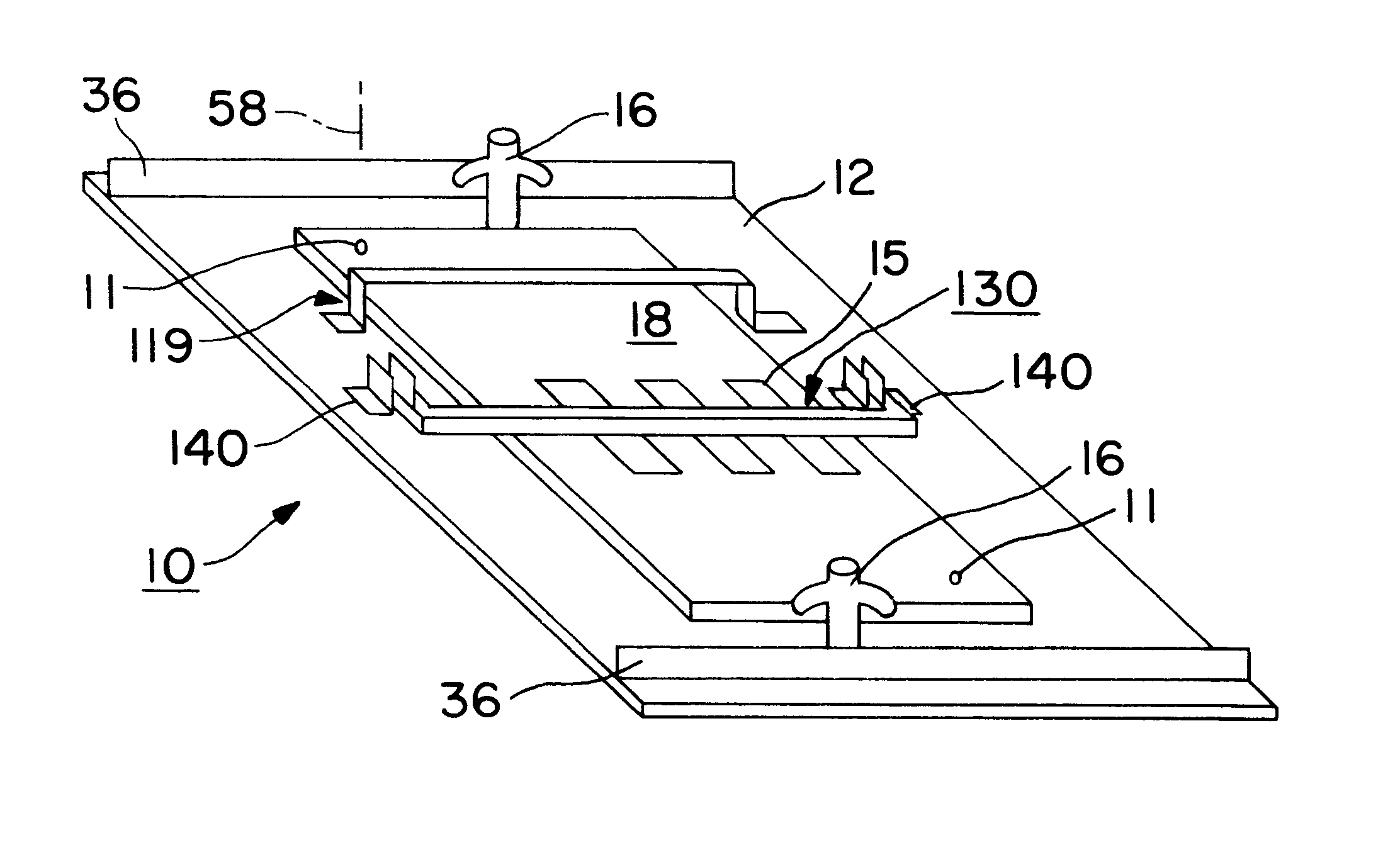
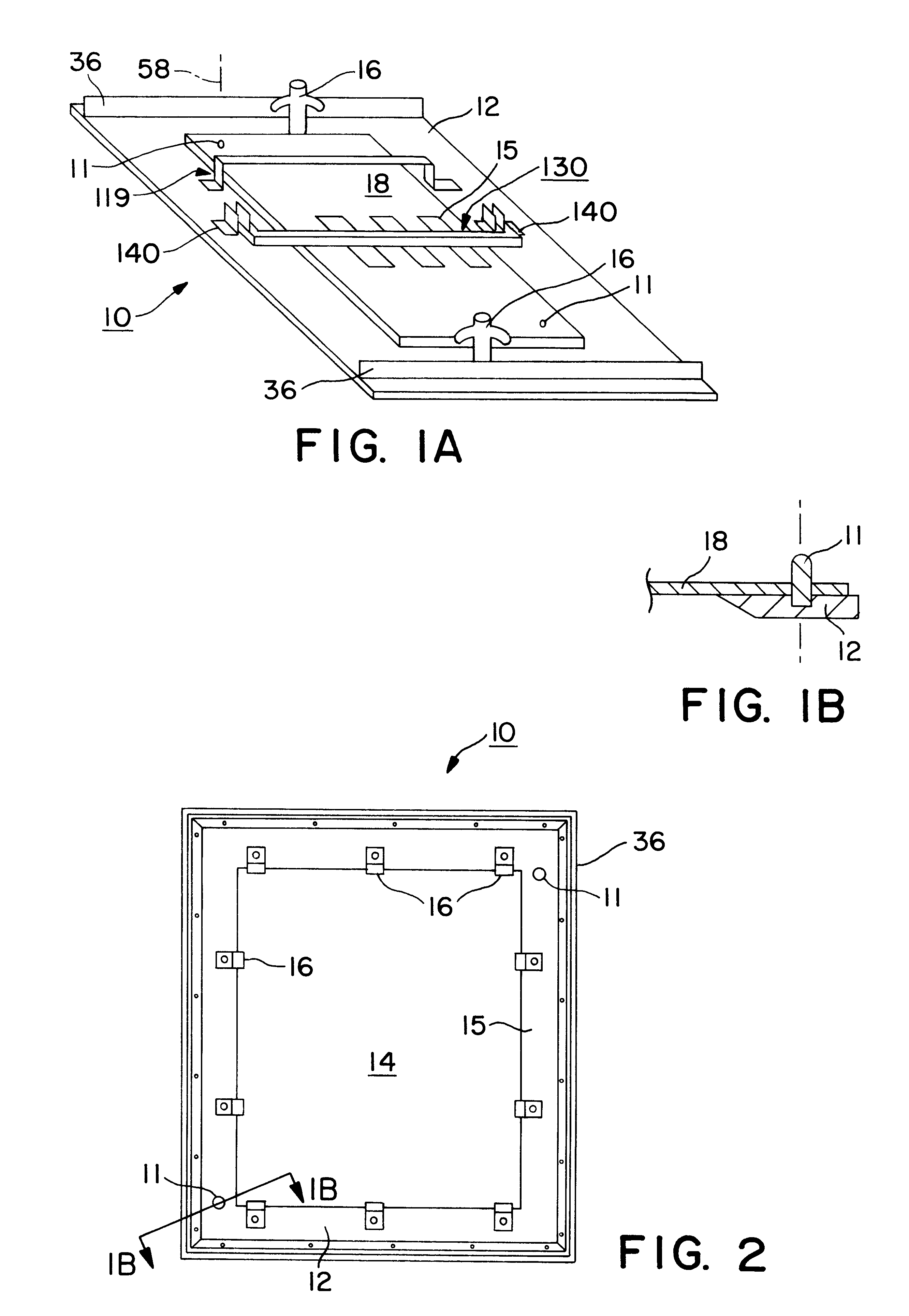
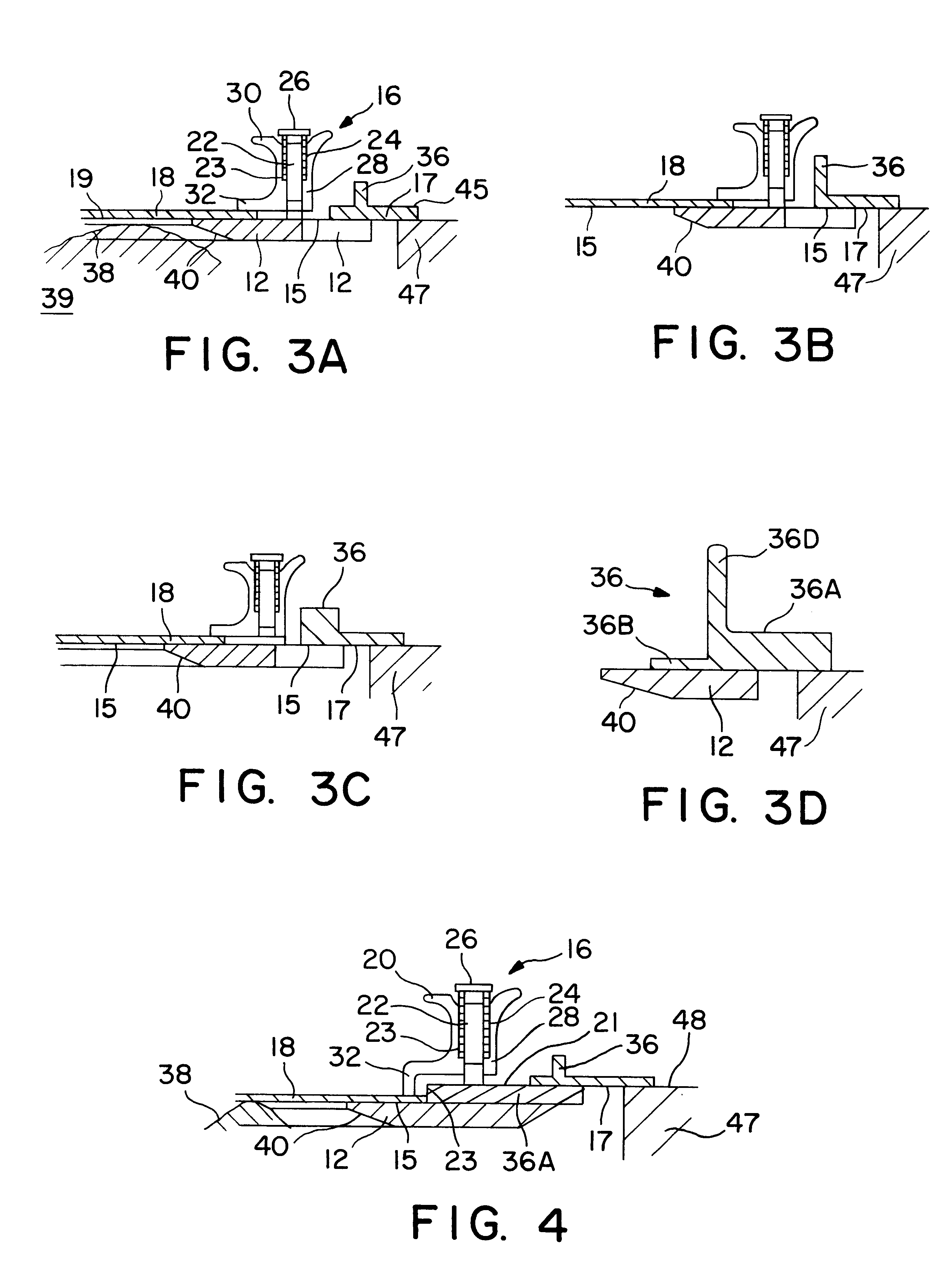
InactiveUS6237832B1Minimizing conductionMinimizing warpage/bowingWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesEngineeringAluminum extrusion
An apparatus used in a process for supporting a printed circuit board during a wave soldering operation including a frame with a frame opening in which a surface of the frame supports the board and also serves as a reference surface for vertically positioning the board above the solder pool. The board is secured against the reference surface with spring loaded clamps. Stiffeners preferably being an aluminum extrusion having a Tee or angle cross section is mounted along the outside edge of the reference surface of the frame and has a second reference surface facing in a direction opposite the reference surface of the frame. The second reference surface on the extrusion is accessible for support by a slide rail so that the height of the reference surface of the frame above the surface of the pool is independent of the thickness of the board or frame. A board support bar for minimizing warpage of the board from heat is disclosed as well as a hold down bar that secures components on the board so that they do not float away when contacted by the solder wave.
Owner:CHUNG HENRY
Stacked chip package using warp preventing insulative material and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20070045836A1AdhesionHigh mechanical reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMechanical reliabilityPhotosensitive polymer
In a stacked chip configuration, and manufacturing methods thereof, the gap between a lower chip and an upper chip is filled completely using a relatively simple process that eliminates voids between the lower and upper chips and the cracking and delamination problems associated with voids. The present invention is applicable to both chip-level bonding and wafer-level bonding approaches. A photosensitive polymer layer is applied to a first chip, or wafer, prior to stacking the chips or stacking the wafers. The photosensitive polymer layer is partially cured, so that the photosensitive polymer layer is made to be structurally stable, while retaining its adhesive properties. The second chip, or wafer, is stacked, aligned, and bonded to the first chip, or wafer, and the photosensitive polymer layer is then cured to fully bond the first and second chips, or wafers. In this manner, adhesion between chips / wafers is greatly improved, while providing complete fill of the gap. In addition, mechanical reliability is improved and CTE mismatch is reduced, alleviating the problems associated with warping, cracking and delamination, and leading to an improvement in device yield and device reliability.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Card cartridge
InactiveUS6932527B2Avoid warpingHand manipulated computer devicesPayment architectureEngineeringSoftware engineering
A card cartridge includes a housing having a pair of opposing side walls, a top, a front wall, a back wall opposite the front wall, and a base. The housing includes an interior cavity that is sized to accommodate a stack of cards, a card access, and a card output slot. The card access allows a card transport mechanism to engage a lead card contained in the housing and feed the lead card through the card output slot.
Owner:ASSA ABLOY AB
Selective laser melting forming device and method of medical magnesium alloy metal part
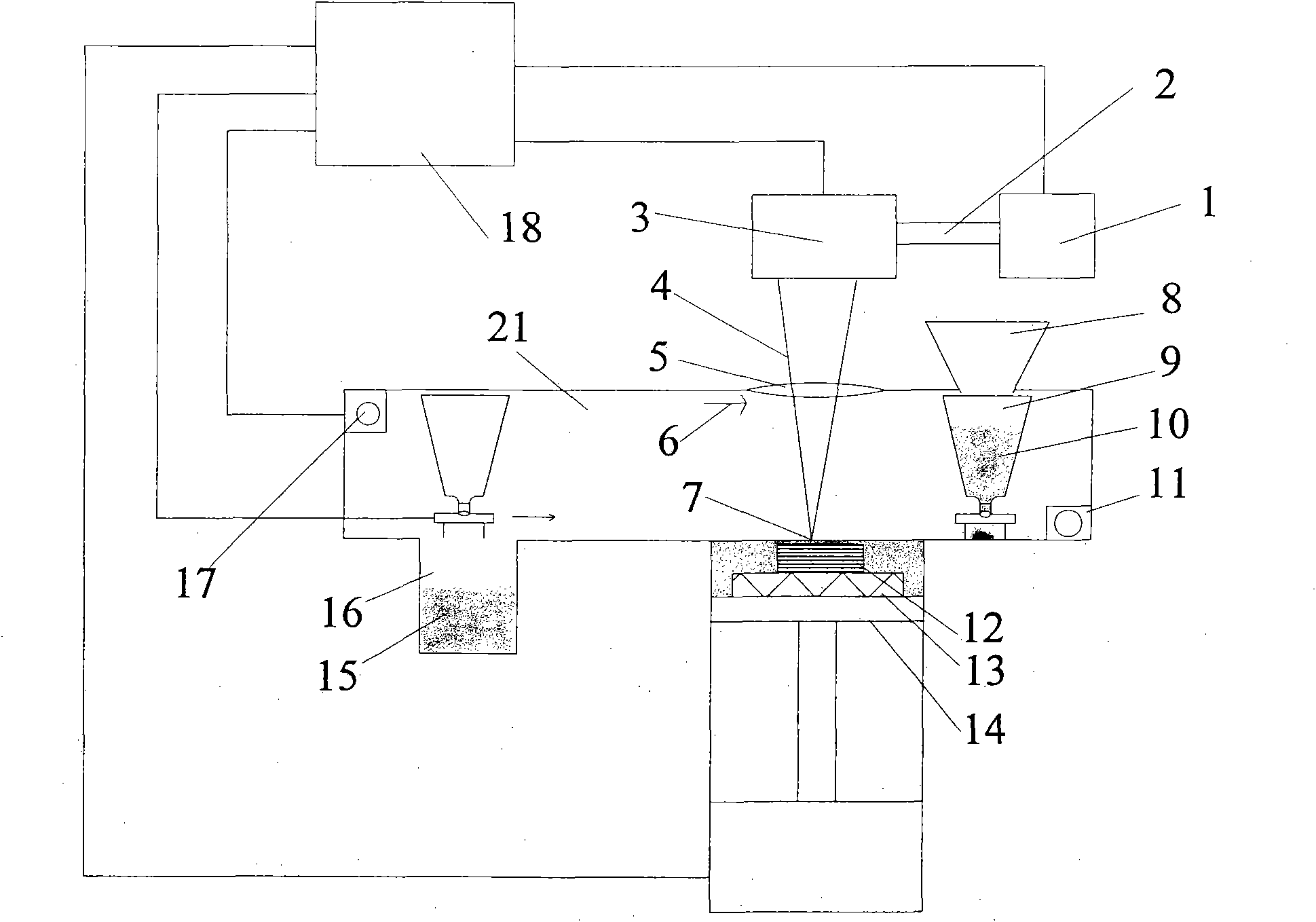
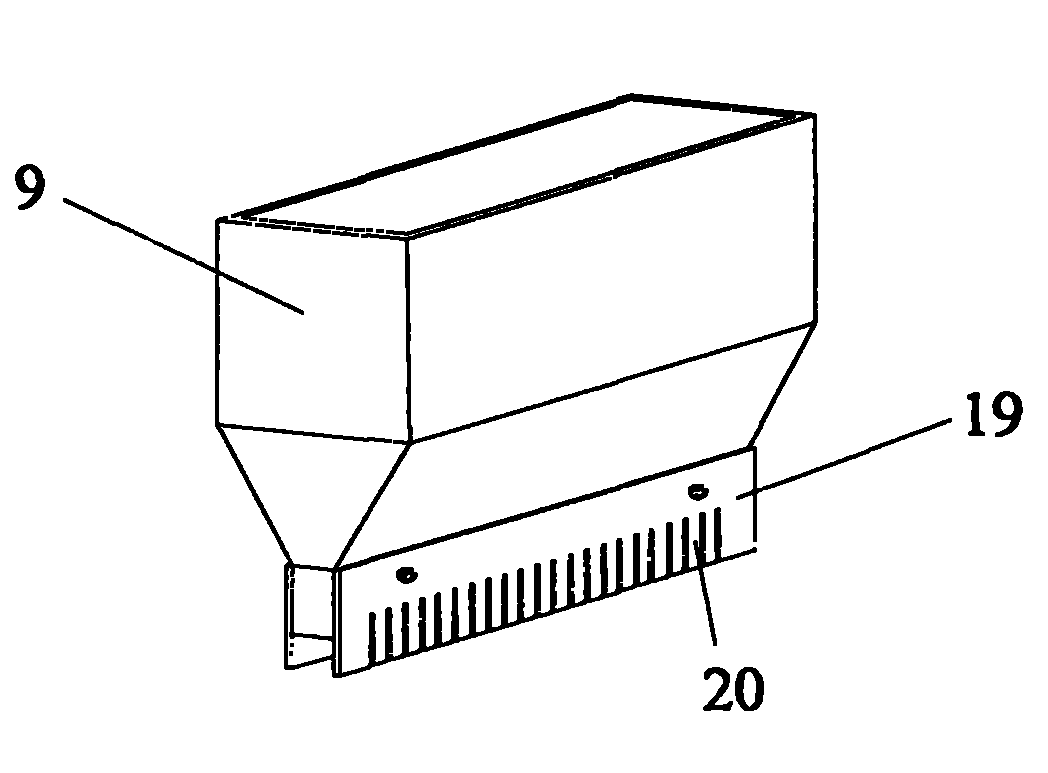
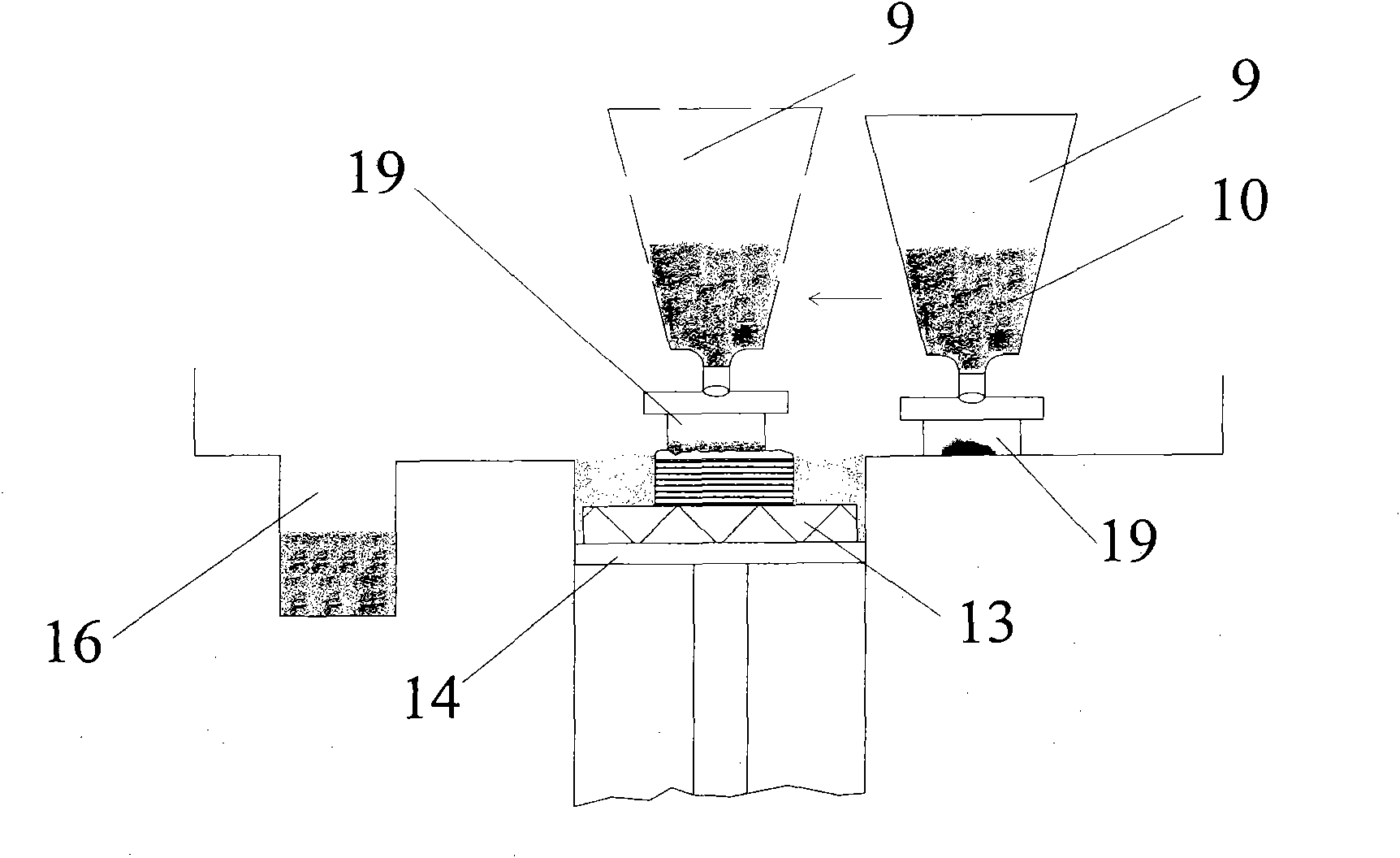
ActiveCN101856724ASatisfies complex spatial shape requirements with high degrees of freedomMeet complex space shape requirementsSelective laser meltingOptoelectronics
The invention provides a selective laser melting forming device of a medical magnesium alloy metal part, which comprises a control device, a powder delivering and spreading device, a laser transmission mechanism, an air purification device and a closed forming chamber, wherein the powder delivering and spreading device comprises a hopper and powder spreading brushes arranged on two sides below the hopper, the upper part of the hopper is arranged in a way of corresponding to a feeding opening on the upper part of the forming chamber, and the lower parts of the powder spreading brushes horizontally correspond to the upper surface of a forming cylinder; the laser transmission mechanism is arranged outside and above the forming chamber and is arranged in a way of corresponding to the forming cylinder; the side wall of the forming chamber is provided with an air inlet and an air outlet, and the air purification device is connected with the air inlet and the air outlet respectively; and the control device is connected with the powder delivering and spreading device, the laser transmission mechanism, the forming cylinder and the air purification device respectively. The invention also provides a selective laser melting forming method of the medical magnesium alloy metal part. The device and the method can manufacture parts which have complex shapes required in the medical field directly, and have the advantages of high forming efficiency and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Process for fabricating an integrated circuit package with reduced mold warping
InactiveUS7371610B1Avoid warpingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal stripsElectrical connection
Owner:UTAC HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
Process and structure for semiconductor package
ActiveUS7005327B2Reduce pollutionGood surface smoothnessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesResistSemiconductor chip
A packaging process for a semiconductor chip that includes the following steps. A carrier having an upper surface and a corresponding lower surface is provided. A photoresist layer is formed on the upper surface of the carrier. A plurality of photoresist openings that expose the carrier is formed in the photoresist layer. A plurality of openings that connects with the photoresist openings are formed in the carrier. A tape is attached to the lower surface of the carrier. The body is filled into the openings of the carrier. A chip is mounted onto the upper surface of the carrier and electrically connected therewith. Finally, the tape is removed from the lower surface of the carrier.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
Flip chip substrate structure and the method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080060838A1Reduce substrate thicknessReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsSolder maskElectrical contacts
A flip chip substrate structure and a method to fabricate thereof are disclosed. The structure comprises a build up structure, a first solder mask and a second solder mask. Plural first and second electrical contact pads are formed on the first and second surface of the build up structure, respectively. A first solder mask having plural openings is formed on the first surface of the build up structure, and the openings expose the first electrical contact pads, wherein the aperture of the openings of the first solder mask are equal to the outer diameter of the first electrical contact pads. A second solder mask having plural openings is formed on the second surface of the build up structure, and the openings expose the second electrical contact pads, wherein the aperture of the openings of the second solder mask are smaller than the outer diameter of the second electrical contact pads.
Owner:PHOENIX PRECISION TECH CORP
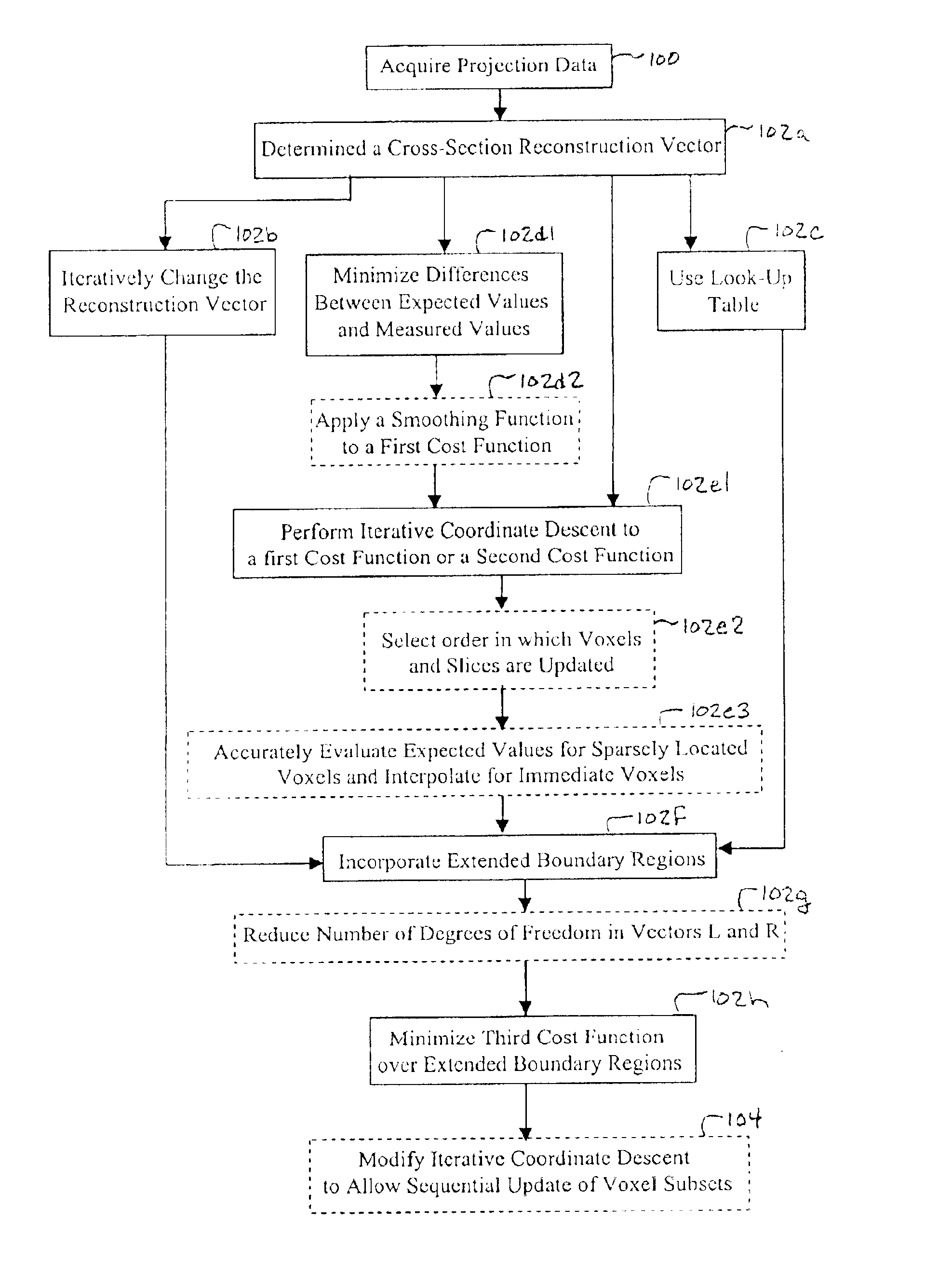
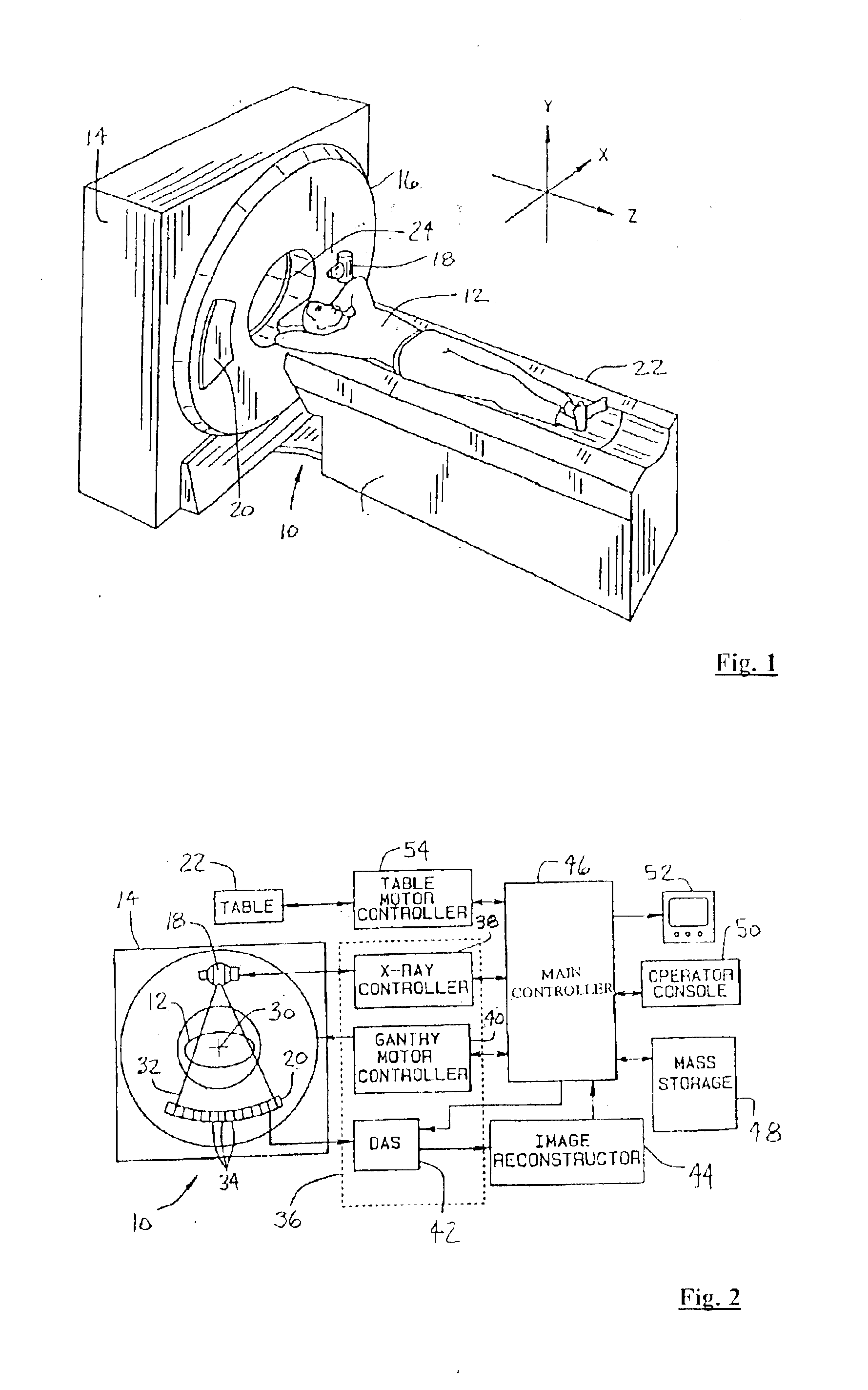
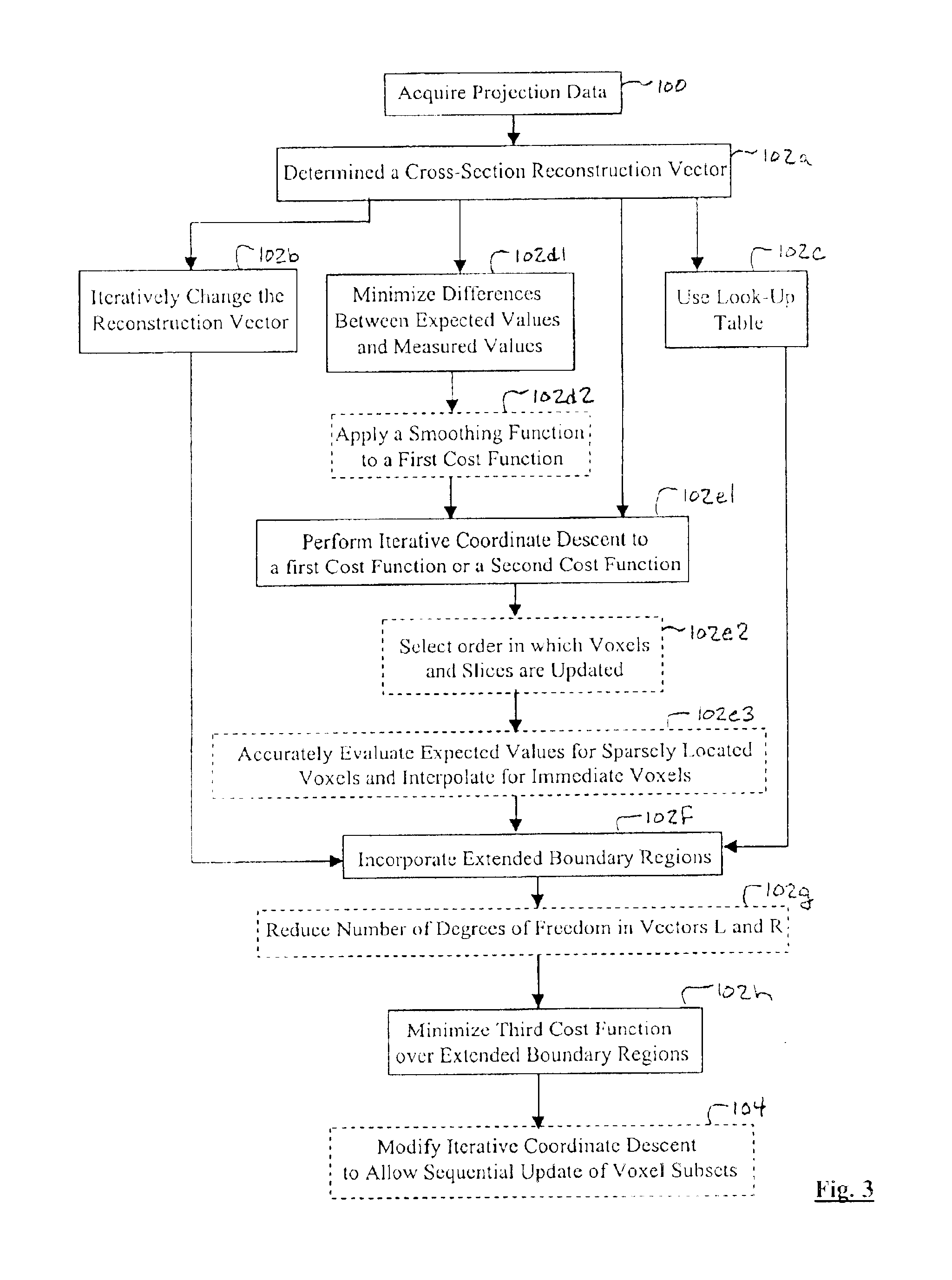
Iterative reconstruction methods for multi-slice computed tomography
InactiveUS6907102B1Avoid warpingError minimizationReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHelical scanMulti slice
A multi-slice computed tomography imaging system is provided including a source that generates an x-ray beam and a detector array that receives the x-ray beam and generates projection data. A translatable table has an object thereon and is operable to translate in relation to the source and the detector array. The source and the detector array rotate about the translatable table to helically scan the object. An image reconstructor is electrically coupled to the detector array and reconstructs an image in response to the projection data using a computed tomography modeled iterative reconstruction technique. The iterative reconstruction technique includes determining a cross-section reconstruction vector, which approximately matches the projection data via a computed tomography model. Methods for performing the same are also provided including accounting for extended boundary regions.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +2
Flanging press
ActiveUS9776234B2Firmly connectedStrong pressing forcePositioning apparatusMetal-working holdersEngineeringFlanging
Owner:FFT PRODIONSSYST
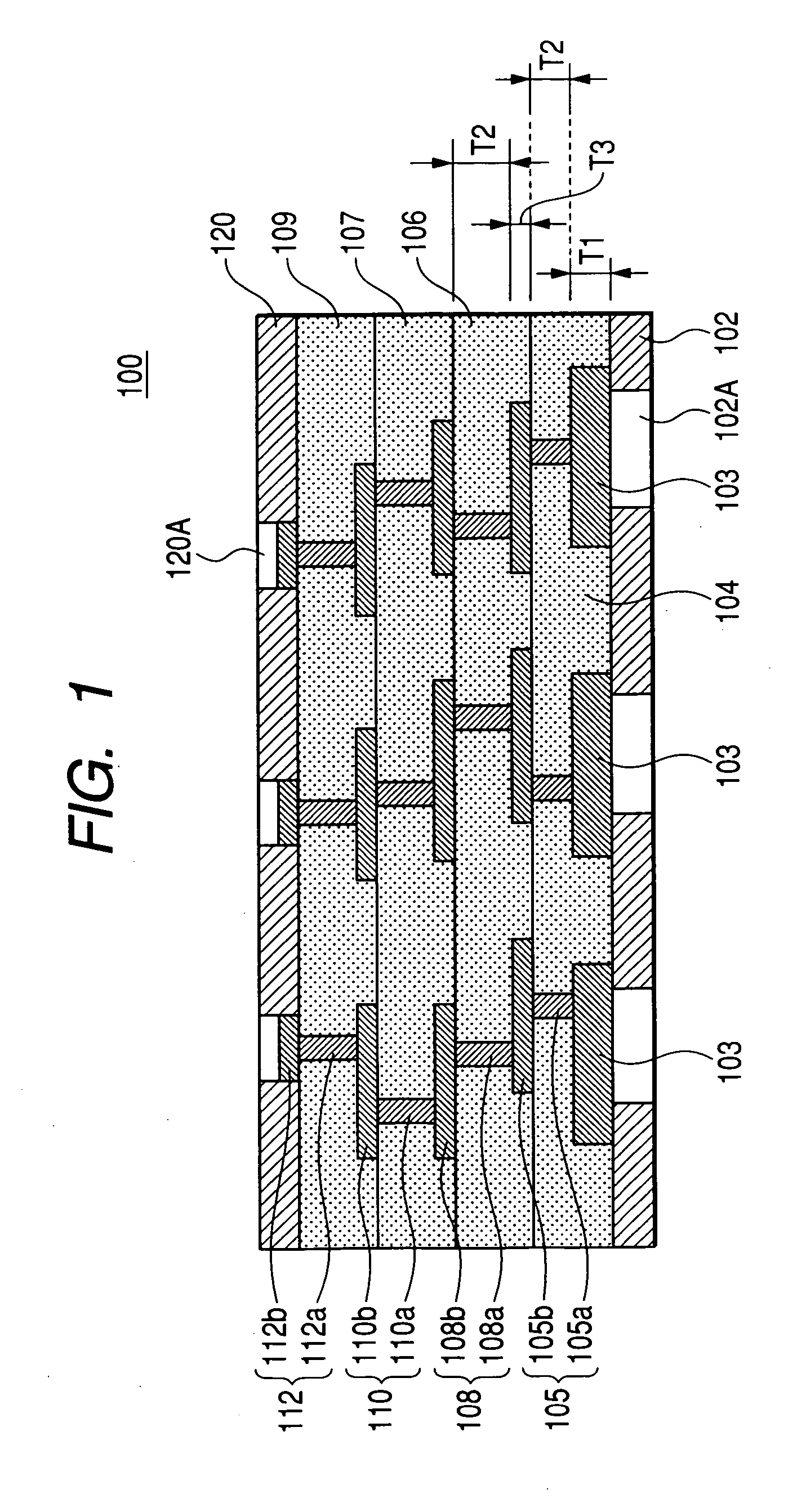
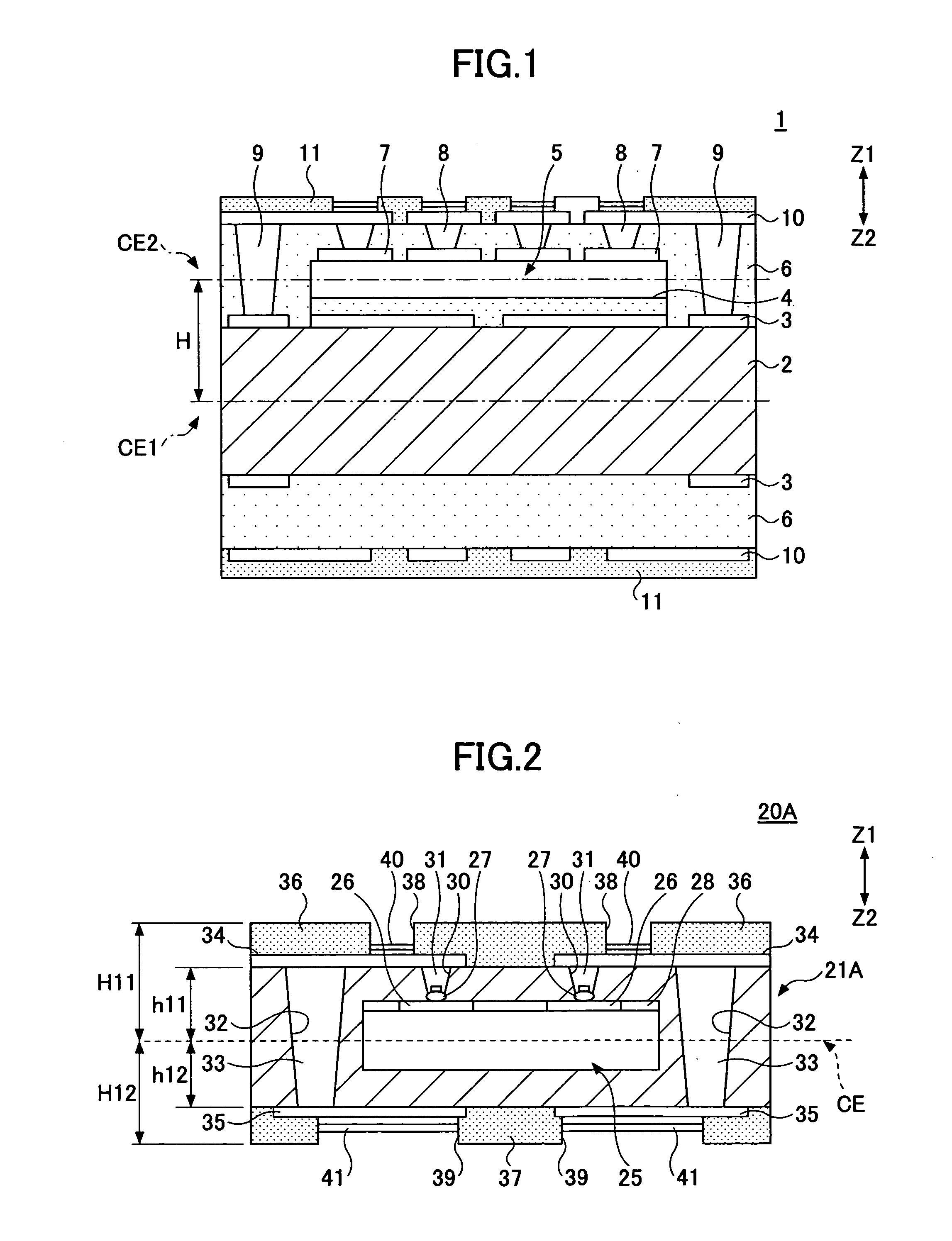
Wiring substrate and electronic component device
InactiveUS20100025081A1OccurrenceImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted electric component incorporationInterposerElectronic component
A wiring substrate includes a frame-shaped reinforcing plate in which an opening portion is provided in a center portion, an interposer arranged in the opening portion of the reinforcing plate and having such a structure that a wiring layer connected mutually via a through electrode is formed on both surface sides of a substrate respectively, a resin portion filled between a side surface of the interposer and a side surface of the opening portion of the reinforcing plate, and coupling the interposer and the reinforcing plate, and an n-layered (n is an integer of 1 or more) lower wiring layer connected the wiring layer on the lower surface side of the interposer to extend from the interposer to an outer area.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Photovoltaic element and method for manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20010029978A1Improve featuresReduce defectsPV power plantsSolid-state devicesSolar lightAmorphous silicon
A photovoltaic element which directly converts an optical energy such as solar light into an electric energy. After many uneven sections are formed on the surface of an n-type crystalline silicon substrate (1), the surface of the substrate (1) is isotropically etched. Then the bottoms (b) of the recessed sections are rounded and a p-type amorphous silicon layer (3) is formed on the surface of the substrate (1) through an intrinsic amorphous silicon layer (2). The shape of the surface of the substrate (1) after isotropic etching is such that the bottoms of the recessed sections are slightly rounded and therefore the amorphous silicon layer can be deposited in a uniform thickness.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Substrate supporting plate and stripping method for supporting plate
InactiveUS7211168B2Avoid warpingLamination ancillary operationsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSolvent
There is provided a supporting plate having a structure in which a solvent can be supplied to an adhesive layer between the supporting plate and a substrate such as a semiconductor wafer in a short period of time after the substrate is thinned, and also a method for stripping the supporting plate.The supporting plate may have a larger diameter than the semiconductor wafer, and penetrating holes are formed in the supporting plate. The outer peripheral portion of the supporting plate is a flat portion in which no penetrating hole is formed. When alcohol is poured from above the supporting plate, the alcohol reaches the adhesive layer through the penetrating holes, dissolves and removes the adhesive layer.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Structure of semiconductor device package and the method of the same
InactiveCN101261984ARoughness is easy to controlThickness is easy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageEngineering
The present invention provides a semiconductor device package comprising a substrate with at lease a pre-formed die receiving cavity formed and terminal contact metal pads formed within an upper surface of the substrate. At lease a first die is disposed within the die receiving cavity. A first dielectric layer is formed on the first die and the substrate and refilled into a gap between the first die and the substrate to absorb thermal mechanical stress there between. A first re-distribution layer (RDL) is formed on the first dielectric layer and coupled to the first die. A second dielectric layer is formed on the first RDL, and then a second die is disposed on the second dielectric layer and surrounded by core pastes having through holes thereon. A second re-distribution layer (RDL) is formed on the core pastes to fill the through holes, and then a third dielectric layer formed on the second RDL.
Owner:ADVANCED CHIP ENG TECH INC
Electronic component mounting base board having heat slug with slits and projections
InactiveUS6232558B1Avoid it happening againAvoid warpingPrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHeat sinkElectrical conductor
An electronic component mounting base board has an insulating substrate provided with a conductor circuit and a mount portion for an electronic component, and a heat slug adhered to the insulating substrate, wherein the heat slug is comprised of a flat main body and a projection portion extending vertically from a side face of the main body, and provided with a slit deforming portion absorbing deformation of the insulating substrate.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD +1
Multilayered wiring substrate and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070057363A1Suppress generationReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsEngineering
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Electronic component embedded substrate and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20060021791A1Easy to produceAvoid warpingPrinted circuit assemblingPrinted electric component incorporationElectronic componentEngineering
An electronic component embedded substrate and a method for manufacturing the substrate are disclosed. The electronic component embedded substrate includes a substrate main body and an electronic component embedded in the substrate main body. The center plane of the electronic component in the thickness direction thereof and the center plane of the substrate main body in the thickness direction thereof generally match each other.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Flip-chip semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060249852A1Avoid warpingAvoid distortionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDistortionHeat sink
A flip-chip semiconductor device is proposed, including a substrate, a plurality of stiffeners disposed at peripheral areas of the substrate, with a gap formed between each of the adjacent stiffeners; at least a semiconductor chip mounted on an area of the substrate surrounded by the stiffeners via flip-chip technique; and a beat sink attached to the semiconductor chip. By such arrangement, warpage of the semiconductor device may be prevented. As an opening is formed at an appropriate position of the stiffener structure, distortion of the stiffener may be avoided. Further, as the beat sink is not attached to the stiffener, solder bumps may be free from thermal stress due to mismatch in coefficient of thermal expansion between the heat sink and the substrate while preventing delamination of the heat sink caused by thermal stress.
Owner:SILICONWARE PRECISION IND CO LTD
Semiconductor chip assembly with post/base heat spreader with ESD protection layer
InactiveUS20110089465A1Low costNot easy to layerSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsSignal routingAdhesive
A semiconductor chip assembly includes a semiconductor device, a heat spreader, a conductive trace and an adhesive. The heat spreader includes a post, a base, an ESD protection layer and an underlayer. The conductive trace includes a pad and a terminal. The semiconductor device is electrically connected to the conductive trace, electrically isolated from the underlayer and thermally connected to the heat spreader. The post extends upwardly from the base into an opening in the adhesive, the base extends laterally from the post and the ESD protection layer is sandwiched between the base and the underlayer. The conductive trace provides signal routing between the pad and the terminal.
Owner:BRIDGE SEMICON
Wafer carrier for growing GaN wafers
InactiveUS7235139B2Avoid direct heat transferEliminate needLiquid surface applicatorsDiffusion/dopingEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com