Nucleic acid aptamer of epithelial cell adhesion molecule and preparation method thereof
A technology for adhesion molecules and epithelial cells, applied in the field of nucleic acids, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory clinical test results, poor antibody specificity, and low binding force, and achieve the effect of simple and fast screening and detection, small molecular weight, and good permeability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1 In vitro screening of nucleic acid aptamers that specifically bind to the epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM
[0047] 1) Dissolve the synthesized 5nmol single-stranded DNA nucleic acid library in binding buffer (12mmol / L PBS, 0.55mmol / LMgCl 2 ), conduct heat treatment: heat at 95°C for 5 minutes, place on ice for 10 minutes, and then place at room temperature for 10 minutes;
[0048] 2) Incubate the processed single-stranded DNA nucleic acid library with Ni microbeads, and collect the liquid that is not bound to Ni microbeads;
[0049] 3) Incubate the liquid not bound to Ni microbeads with EpCAM Ni microbeads at 37°C for 40min;
[0050] 4) Wash the incubated EpCAM Ni microbeads with binding buffer, and then perform PCR reaction on the EpCAM Ni microbeads bound to oligonucleotides;
[0051] The PCR reaction program was: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 3min, 30s at 94°C, 30s at 53°C, 30s at 68°C, 10 cycles of amplification, and final extension at 68°C for 5m...
Embodiment 2
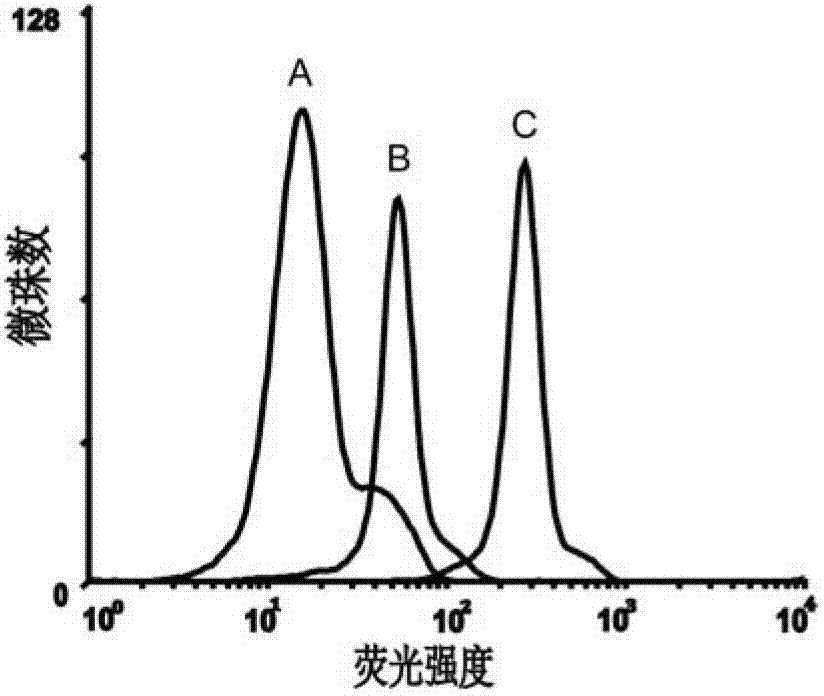
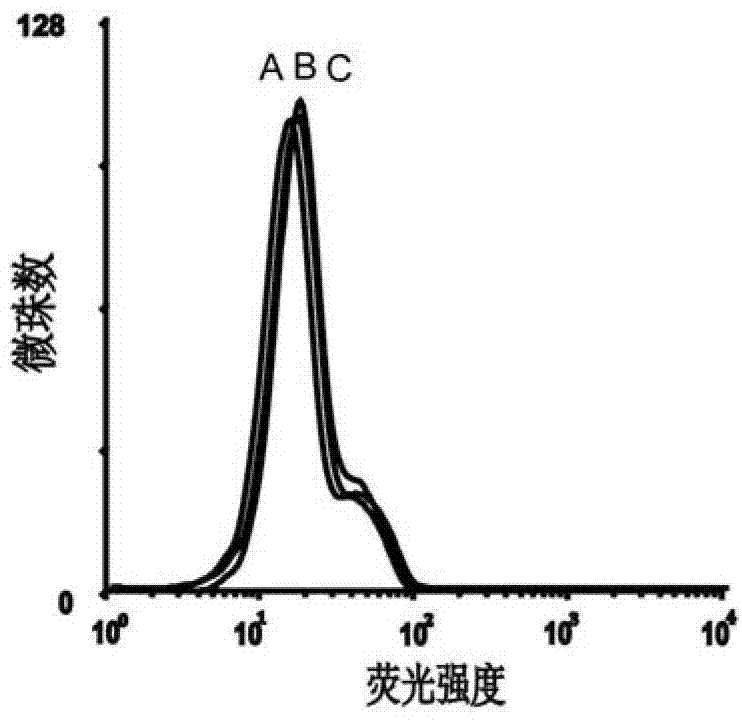
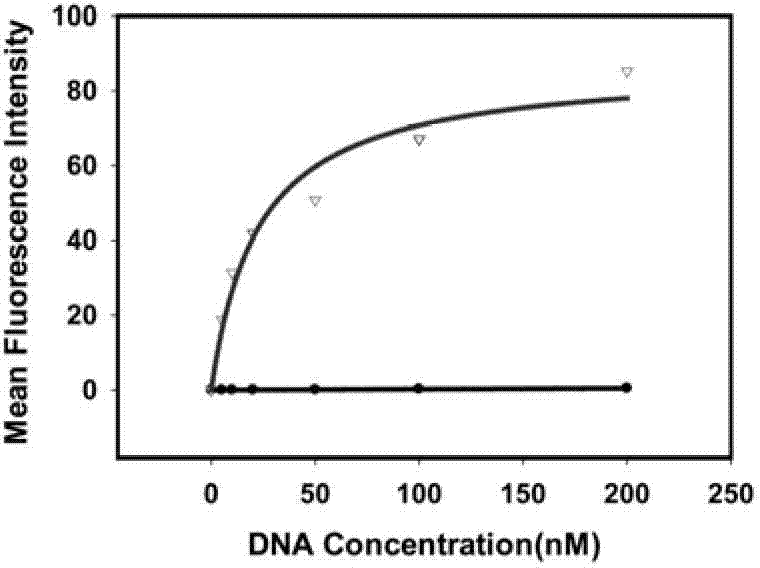
[0056] Example 2 Detection of the Binding Ability of the Obtained Single-Stranded DNA to the Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule EpCAM by Flow Cytometry
[0057] First PCR amplifies the fluorescently labeled single-stranded DNA, using primer 2: 5'-Biotin-CTG ACC ACG AGC TCC ATT AG-3' and primer 3: 5'-FAM-AGC GTC GAA TAC CAC TAC AG-3' , the PCR product is a double-stranded DNA with FAM at the 5' end and biotin at the 3' end, add streptavidin microbeads, react for 30min, then use 0.1mol / L NaOH for single-stranded DNA, and purify by desalting column That is, the FAM-labeled single-stranded DNA for flow analysis is obtained.
[0058] The dissociation constant (Kd=22.8 ±6.0). Use 200 μl of binding buffer to prepare DNA solutions of the above concentrations, heat at 95°C for 5 minutes, place on ice for 10 minutes, and then place at room temperature for 10 minutes. Add 155nmol / L EpCAM microbeads and incubate at 37°C for 40min. Wash the beads 3 times with binding buffer, then resusp...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3 Screening to obtain nucleic acid aptamers that specifically bind to various cell lines
[0061] 1) Dissolve the synthesized 5nmol single-stranded DNA nucleic acid in the binding buffer (12mmol / L PBS, 0.55mmol / L MgCl 2 ), conduct heat treatment: heat at 95°C for 5 minutes, place on ice for 10 minutes, and then place at room temperature for 10 minutes;
[0062] 2) Incubate the processed single-stranded DNA nucleic acid with 10,000 cells in a 24-well plate for 24 hours, at 37°C for 30 minutes or at 4°C for 40 minutes.
[0063] 3) After incubation, remove the buffer solution and wash twice, then scrape off the cells and dissolve them in 200 μL buffer solution, and use BD’s FACSAria flow cytometer to measure the fluorescence of the microbeads (see Figure 5 and6 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com