Patents
Literature
170 results about "Cell adhesion molecule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) are a subset of cell adhesion proteins located on the cell surface involved in binding with other cells or with the extracellular matrix (ECM) in the process called cell adhesion. In essence, cell adhesion molecules help cells stick to each other and to their surroundings. Cell adhesion is a crucial component in maintaining tissue structure and function. In fully developed animals, these molecules play an integral role in creating force and movement and consequently ensure that organs are able to execute their functions. In addition to serving as "molecular glue", cell adhesion is important in affecting cellular mechanisms of growth, contact inhibition, and apoptosis. Oftentimes aberrant expression of CAMs will result in pathologies ranging from frostbite to cancer.
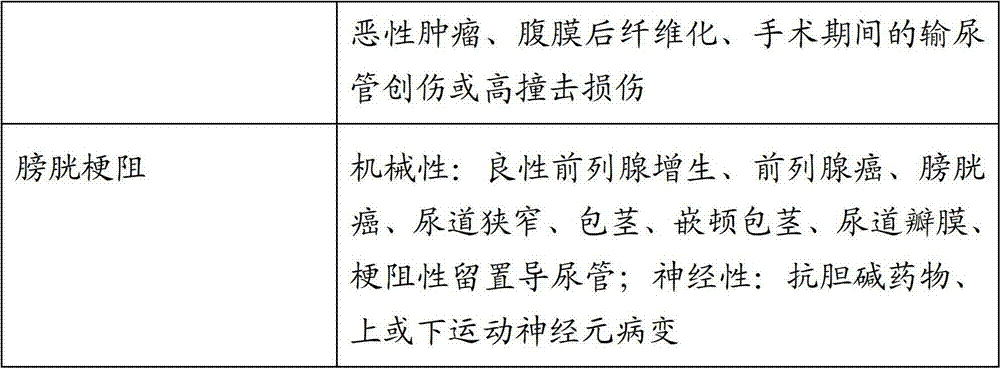
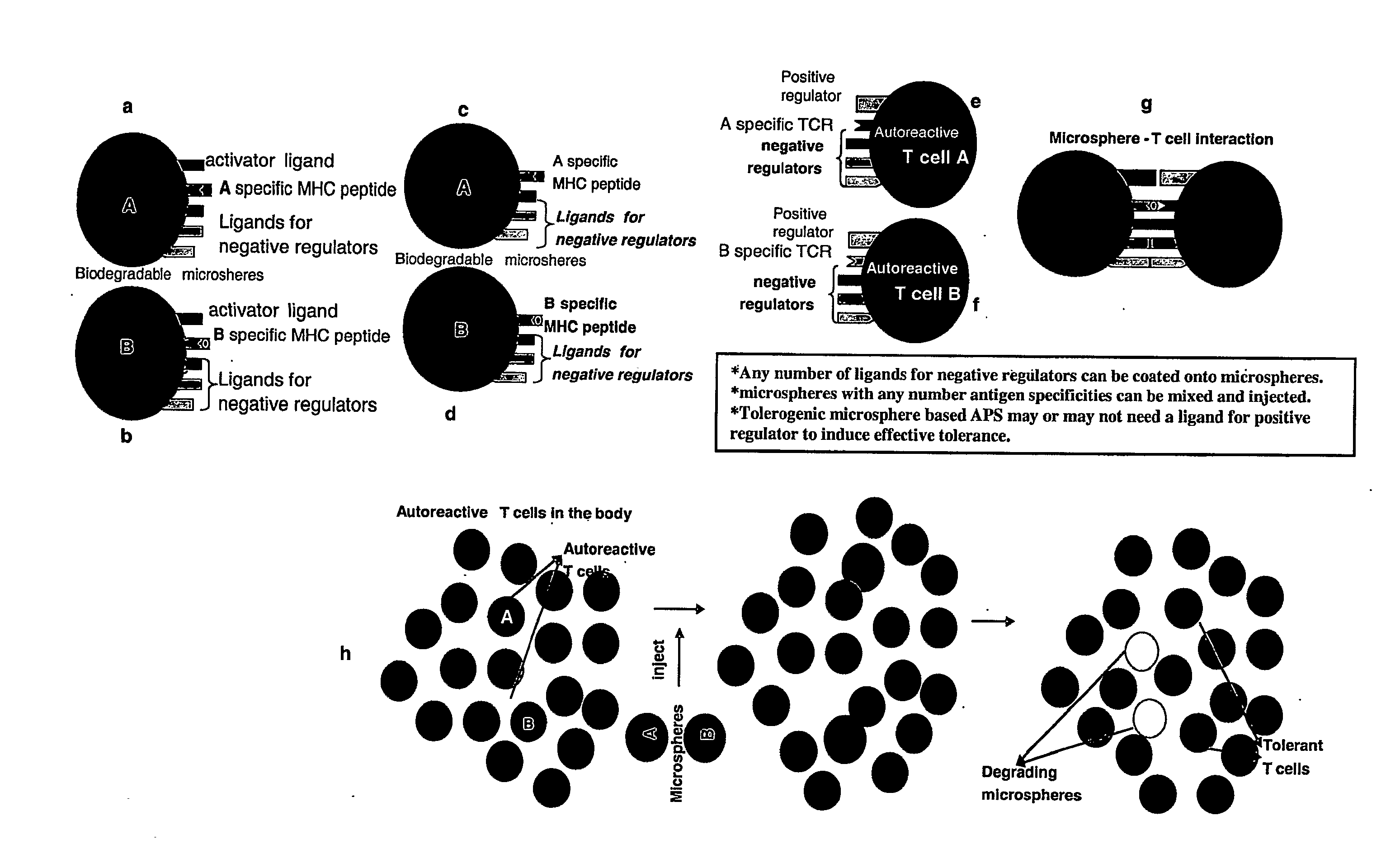
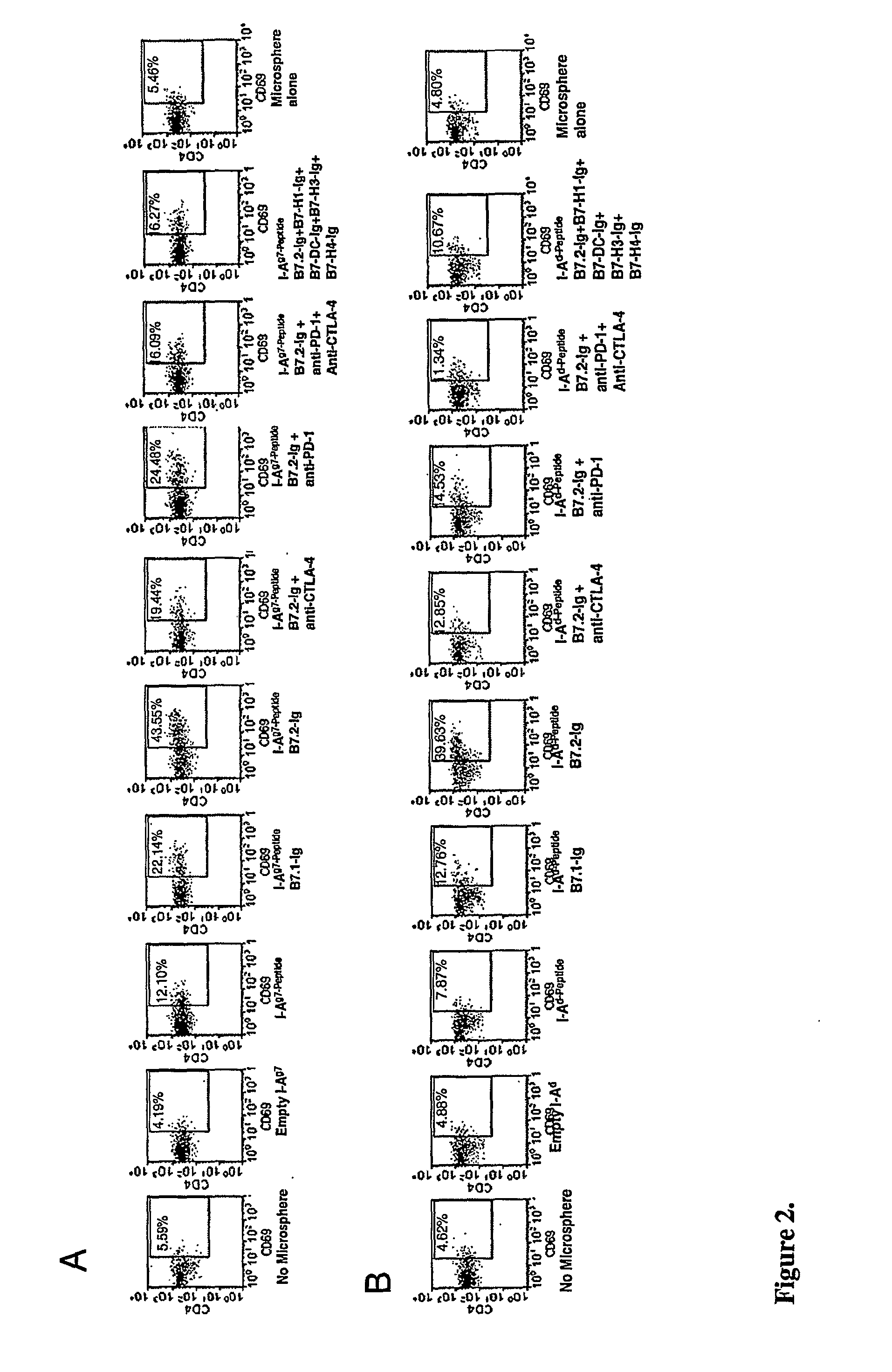
Tolerogenic biodegradable artificial antigen presenting system
InactiveUS20100028450A1Improve standardizationWide range of applicationsPowder deliveryBiocideCell adhesion moleculeMolecular biology
An artificial antigen presenting system is presented. The herein presented microspheres combine negative regulators individually or at varying combinations along with MCH molecules and can induce antigen specific tolerance. The herein described methods provide for the construction of artificial biodegradable microsomes containing MHC: peptide complexes, accessory molecules, co-stimulatory molecules, adhesion molecules, and other molecules relevant to T cell binding or modulation. Additionally, the present invention is directed to compositions and methods for treating conditions which would benefit from modulation of T cell response, for example, autoimmune disorders, allergies, cancers, viral infections, and graft rejection.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
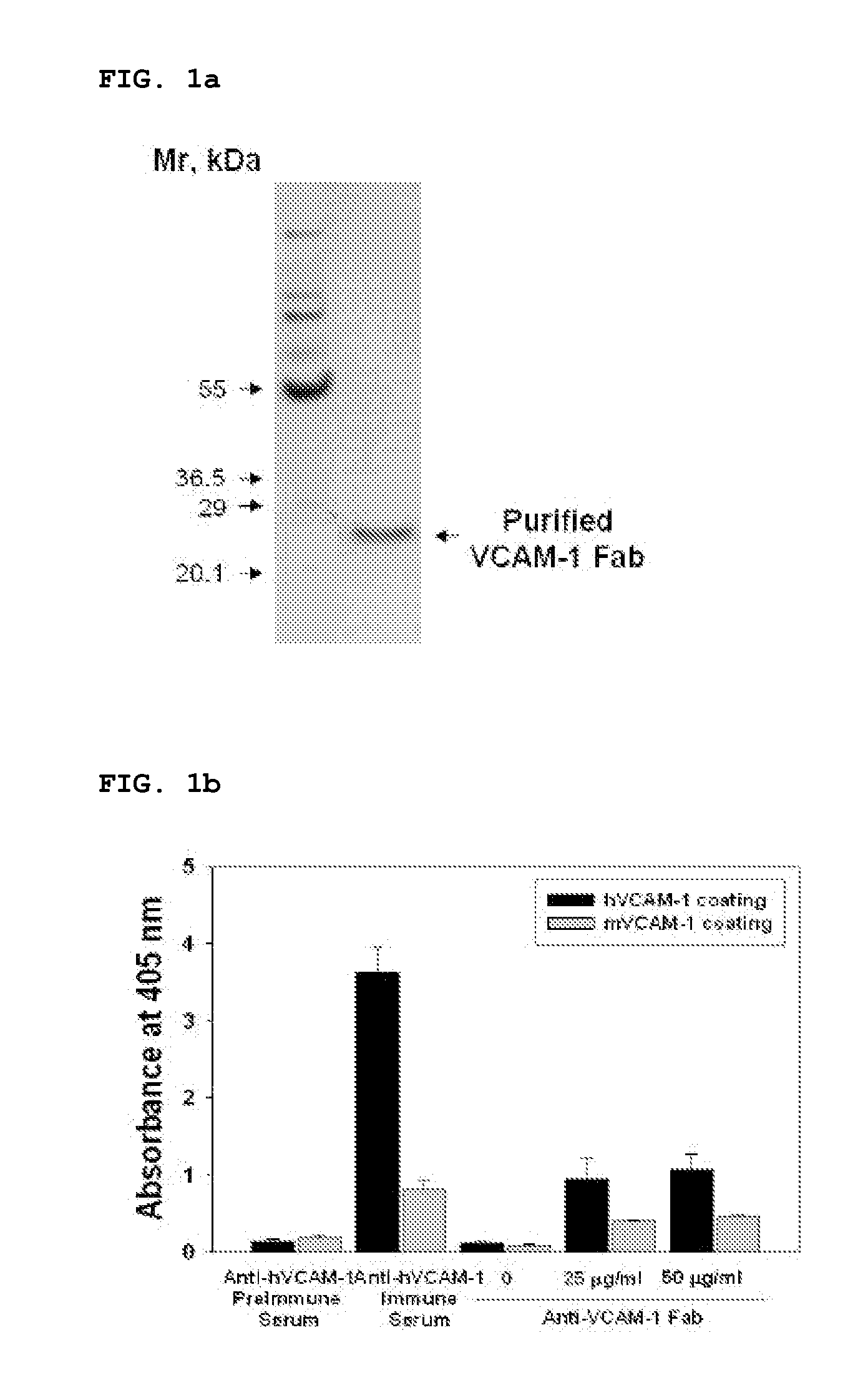
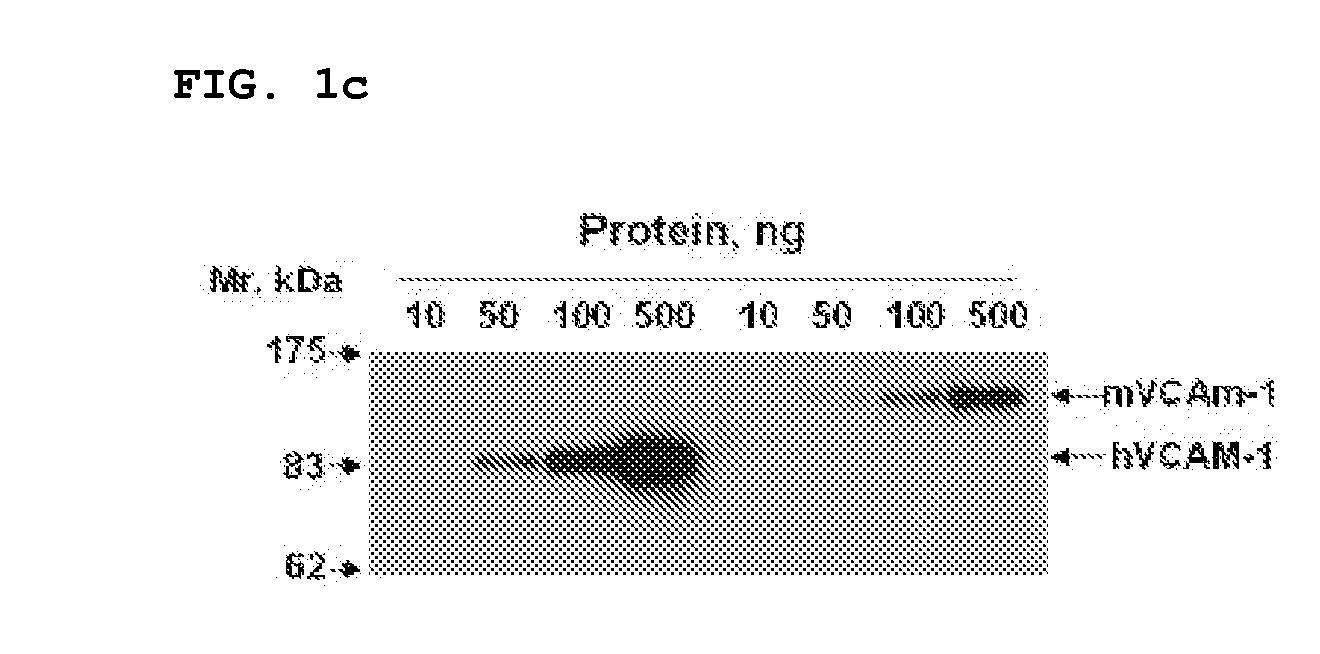
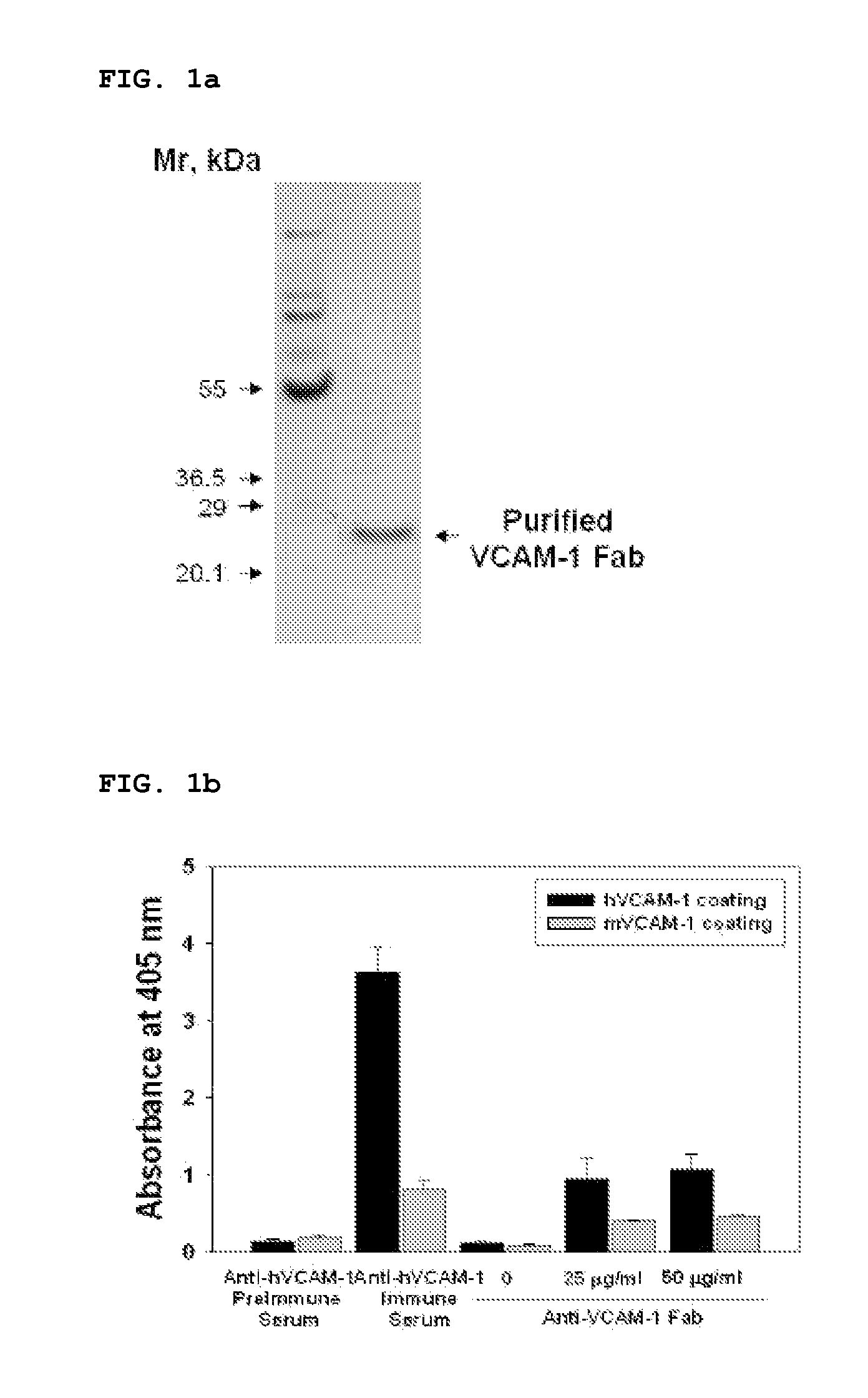
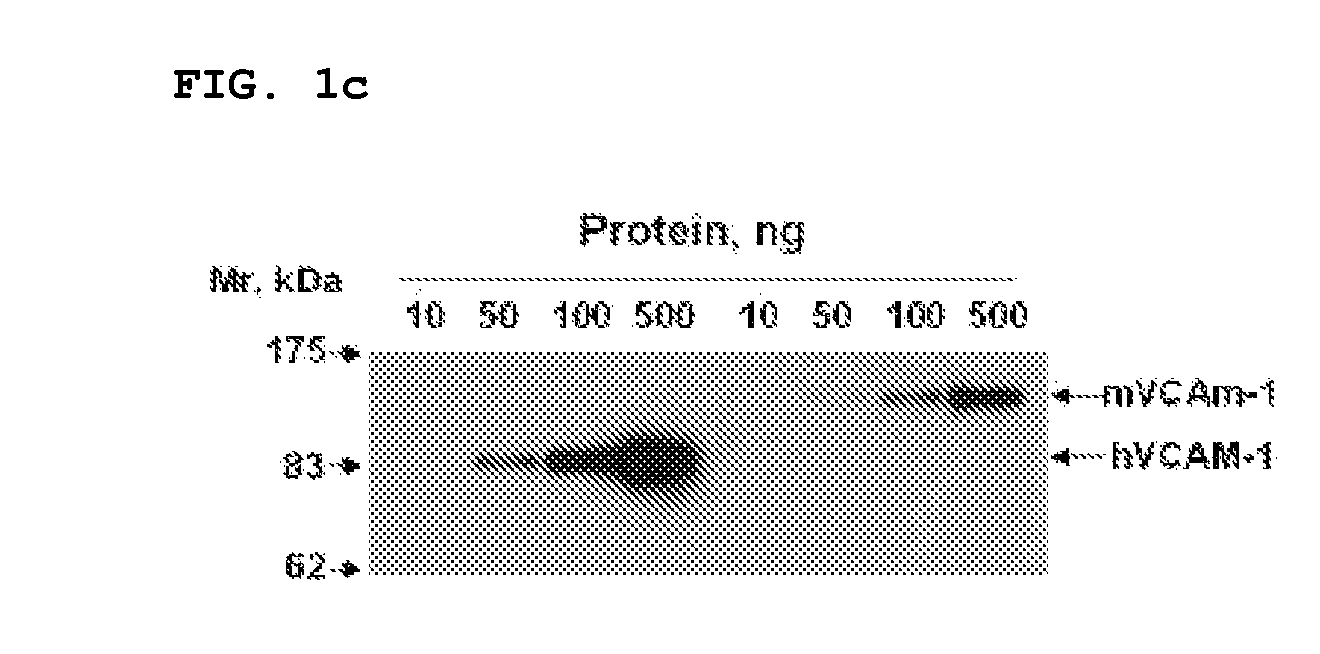
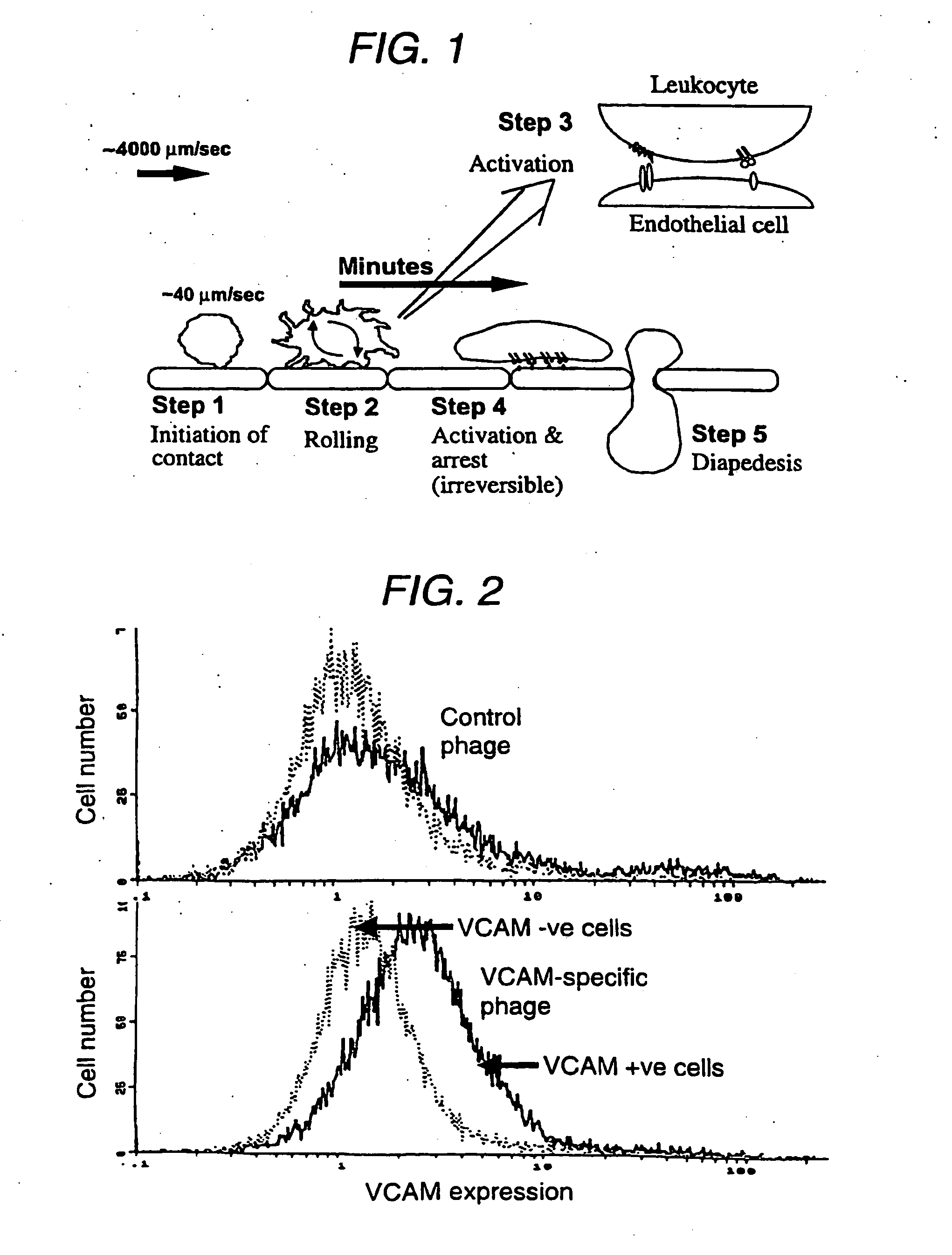
Vcam-1 specific monoclonal antibody
The present invention relates to a monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1 or CD106). Specifically, the present invention relates to an antibody that specifically binds to both human and mouse vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), a method for producing the same, a composition for diagnosis or treatment comprising them and a method for diagnosis or treatment using them. The monoclonal antibody of the present invention is the first recombinant monoclonal antibodies that is specific to human and mouse VCAM-1. In addition, the monoclonal antibody of the present invention shows a strong affinity to VCAM-1 expressed in rat skeletal muscle and porcine endothelial cells as well as human and mouse endothelial cells and is found to strongly inhibit the interaction between leukocytes and activated endothelial cells. Accordingly, the monoclonal antibody of the present invention can inhibit a VCAM-1 mediated adhesion of leukocytes to endothelial cells and potently treat VCAM-1 mediated disease, especially inflammatory disease or cancer.
Owner:HANWHA CHEMICAL CORPORATION
N, N-disubstituted amides that inhibit the binding of integrins to their receptors
A method for the inhibition of the binding of .alpha..sub.4.beta..sub.1 integrin to its receptors, for example VCAM-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule-1) and fibronectin; compounds that inhibit this binding; pharmaceutically active compositions comprising such compounds; and the use of such compounds either as above, or in formulations for the control or prevention of diseases states in which .alpha..sub.4.beta..sub.1 is involved.
Owner:ENCYSIVE PHARMA INC
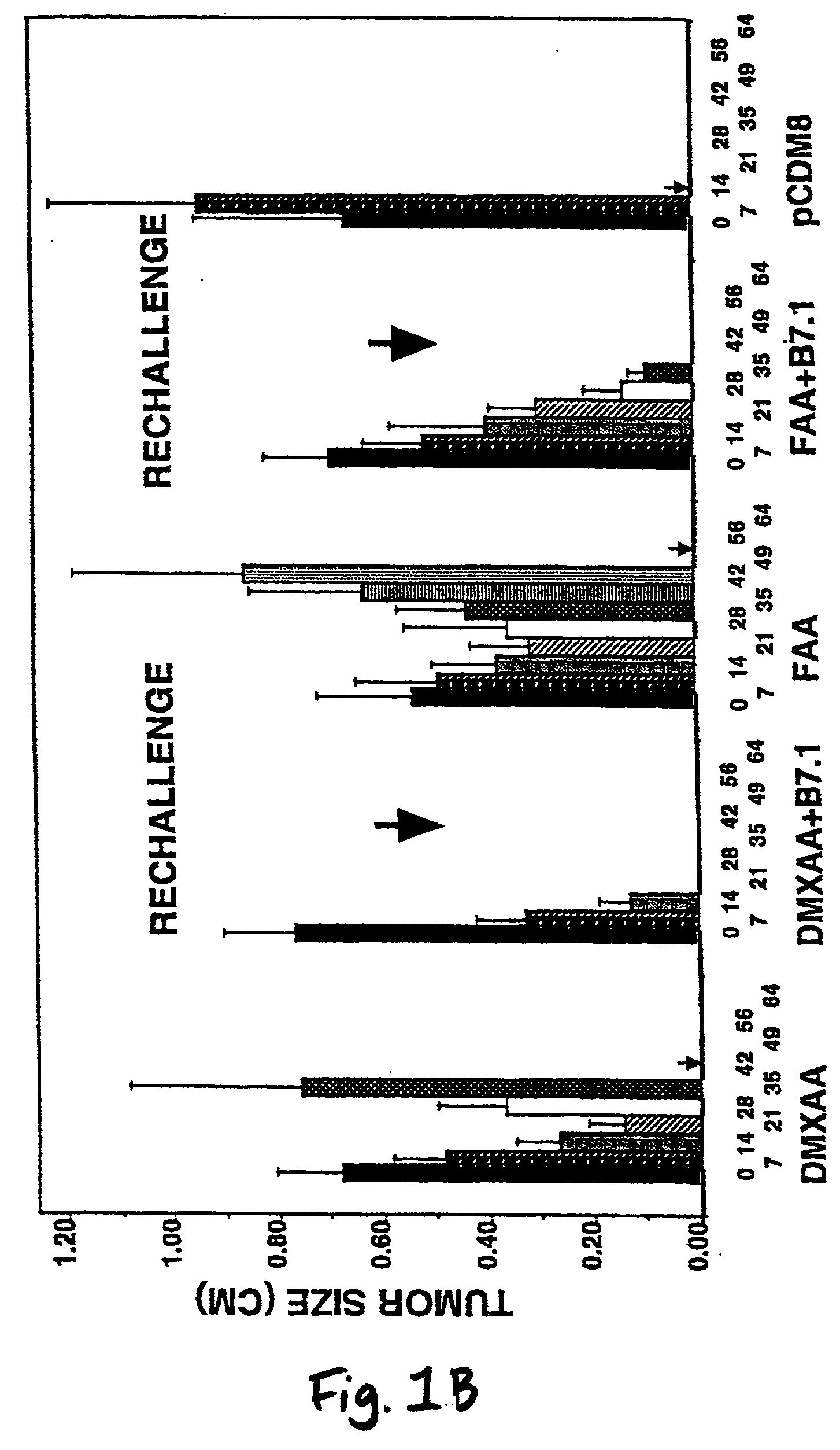
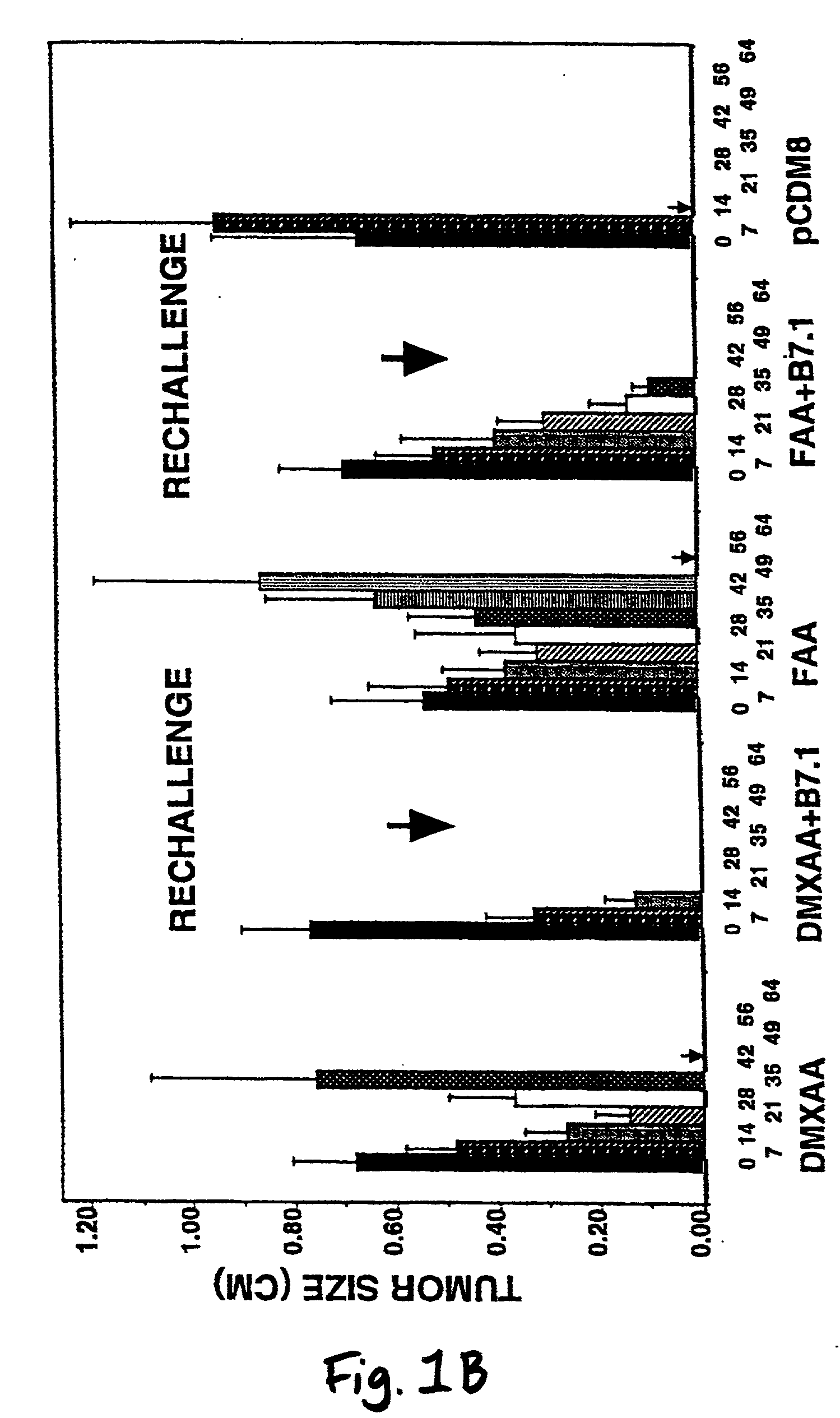
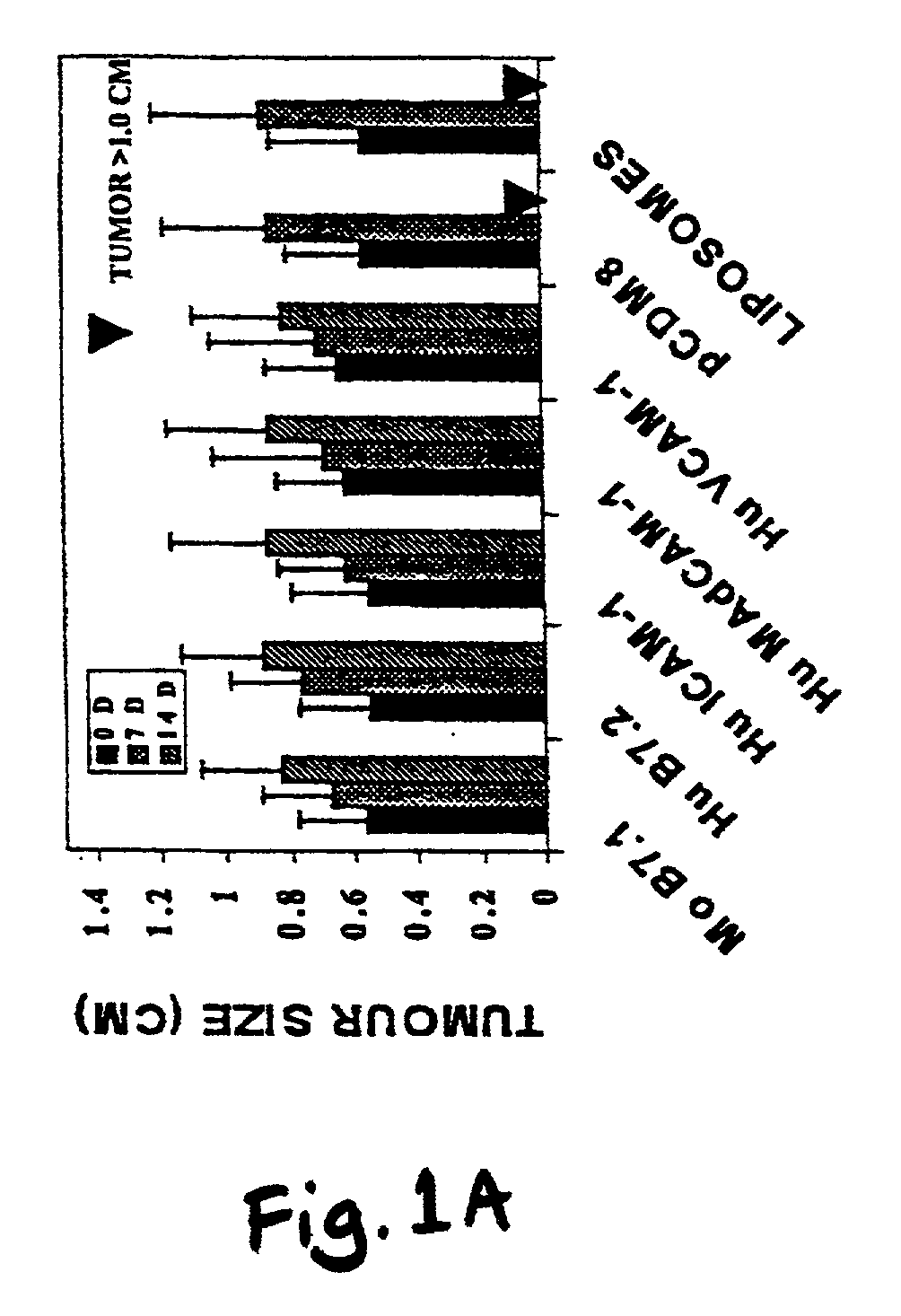
Cancer therapy
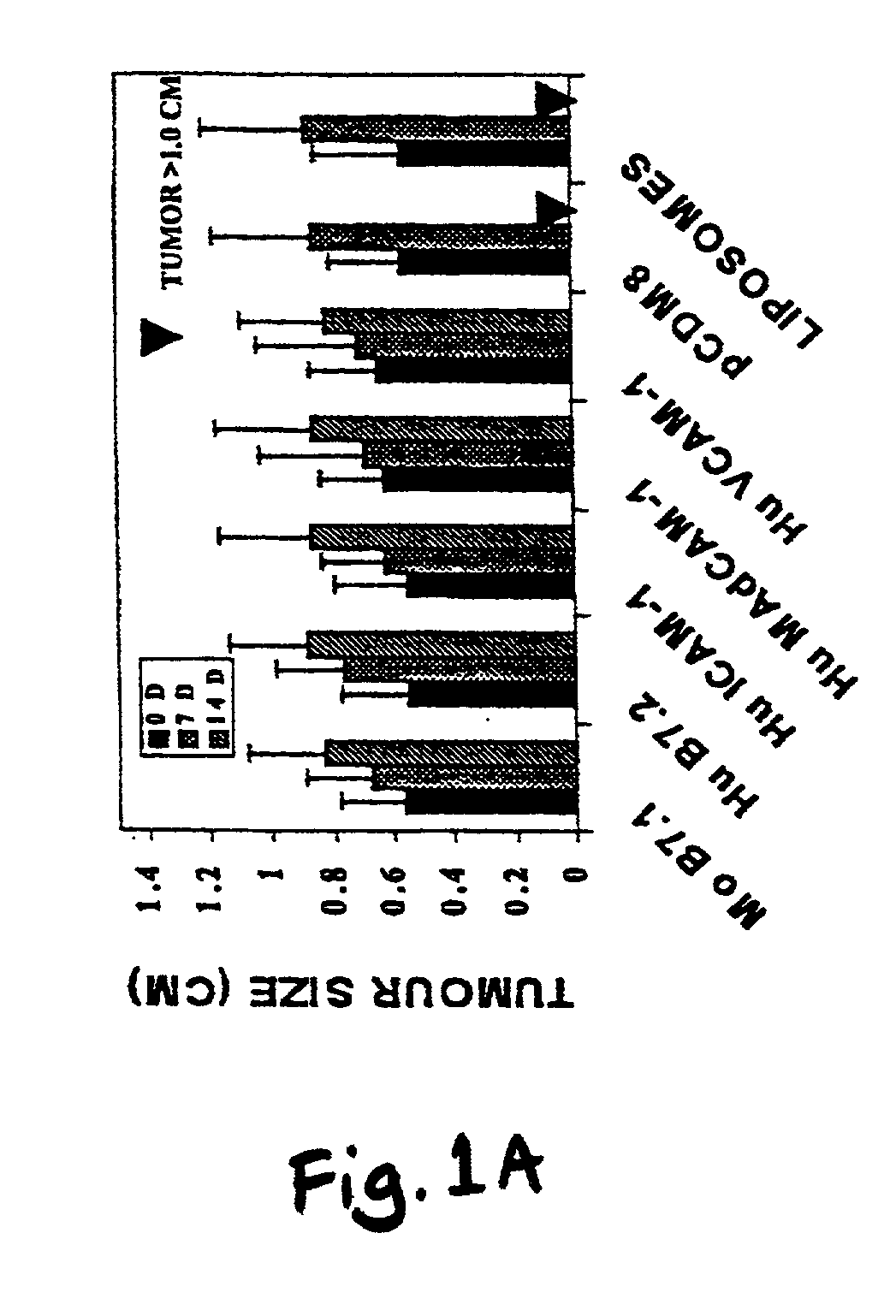
A method is provided for treating mammals, including humans, with advanced or large-tumour burdens. The method involves administering an immunotherapeautic agent in conjunction with a tumour growth restricting agent, in amounts effective to eradicate any advanced or large tumours present. In preferred embodiments, the immunotherapeautic agent comprises a T-cell co-stimulatory cell adhesion molecule (CAM) or a mammalian expression vector containing DNA which encodes a T-cell co-stimulatory CAM, such as B7.1, and the tumour growth restricting agent is flavone acetic acid, 5,6-dimenthyl-xanthenone-4-acetic acid, or an agent which disrupts the expression or activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1).
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD +1
VCAM-1 specific monoclonal antibody
The present invention relates to a monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1 or CD106). Specifically, the present invention relates to an antibody that specifically binds to both human and mouse vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), a method for producing the same, a composition for diagnosis or treatment comprising them and a method for diagnosis or treatment using them. The monoclonal antibody of the present invention is the first recombinant monoclonal antibodies that is specific to human and mouse VCAM-1. In addition, the monoclonal antibody of the present invention shows a strong affinity to VCAM-1 expressed in rat skeletal muscle and porcine endothelial cells as well as human and mouse endothelial cells and is found to strongly inhibit the interaction between leukocytes and activated endothelial cells. Accordingly, the monoclonal antibody of the present invention can inhibit a VCAM-1 mediated adhesion of leukocytes to endothelial cells and potently treat VCAM-1 mediated disease, especially inflammatory disease or cancer.
Owner:HANWHA CHEMICAL CORPORATION
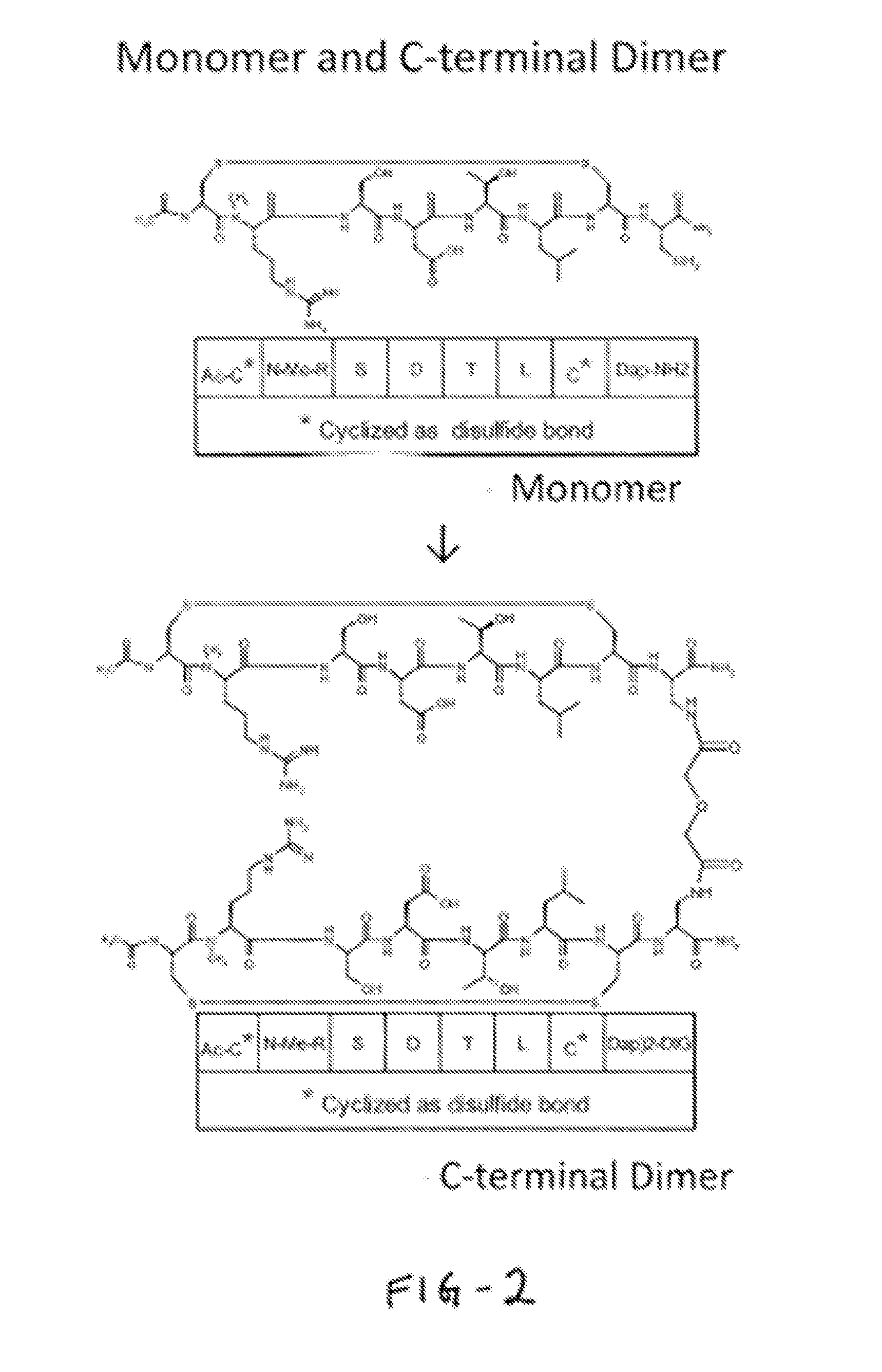
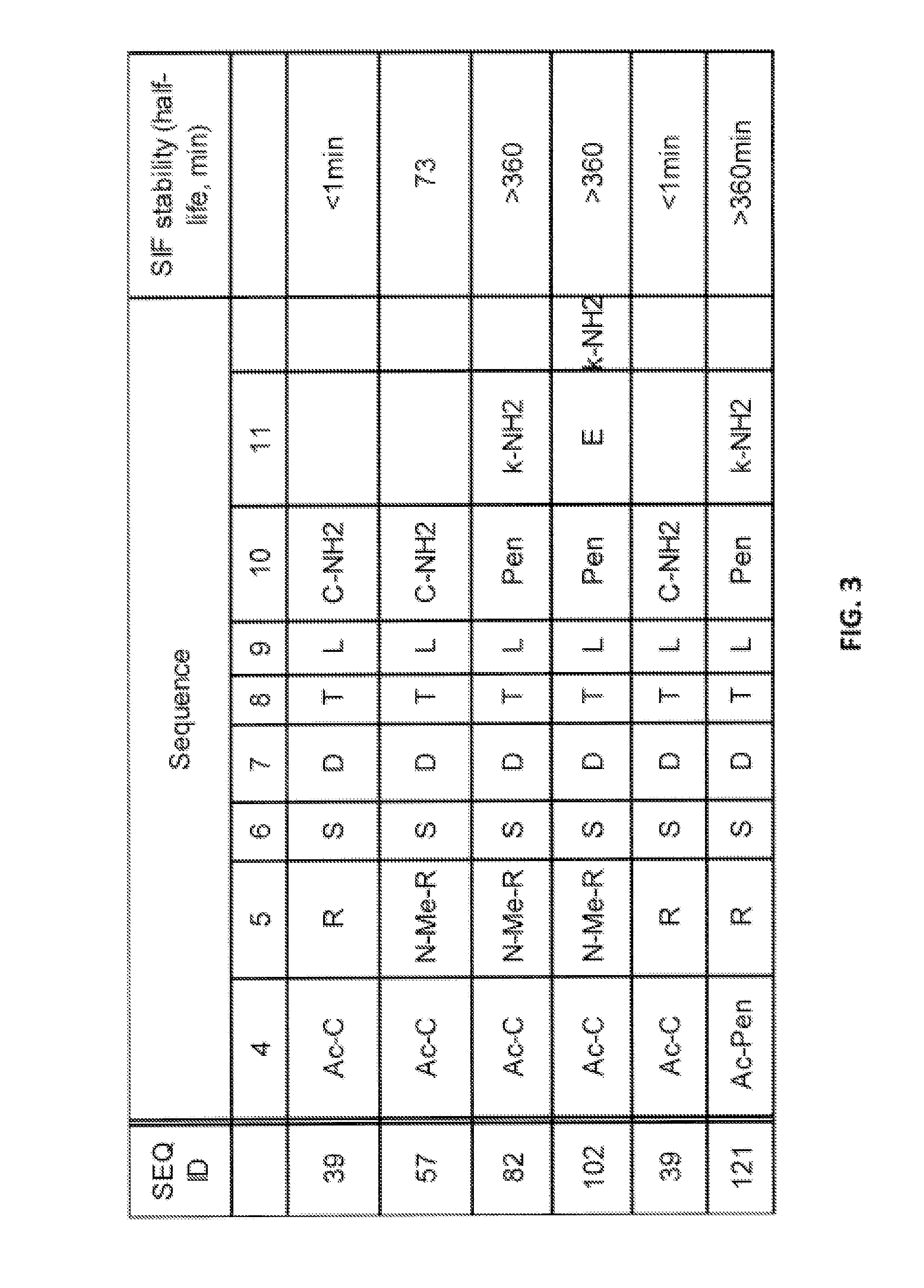
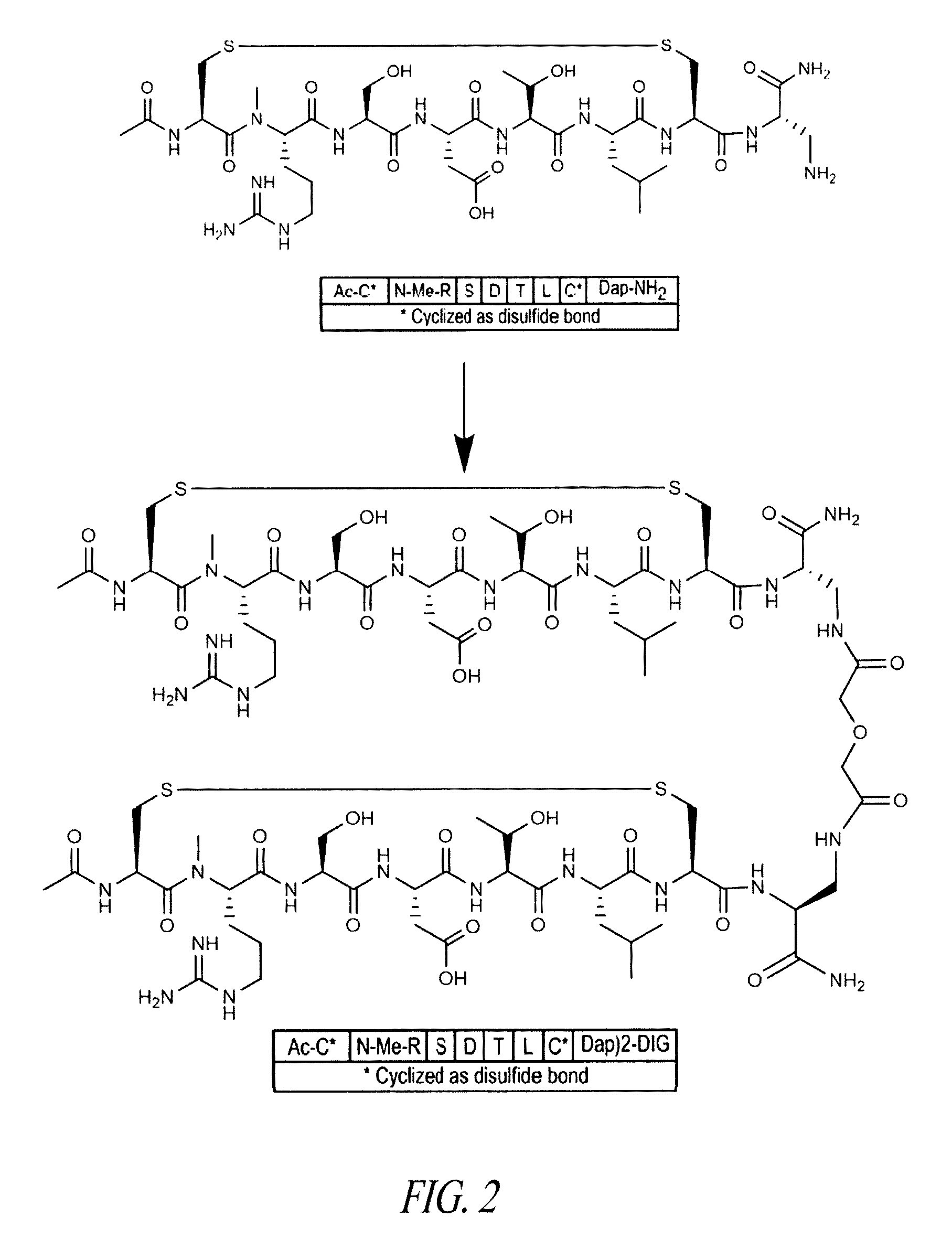
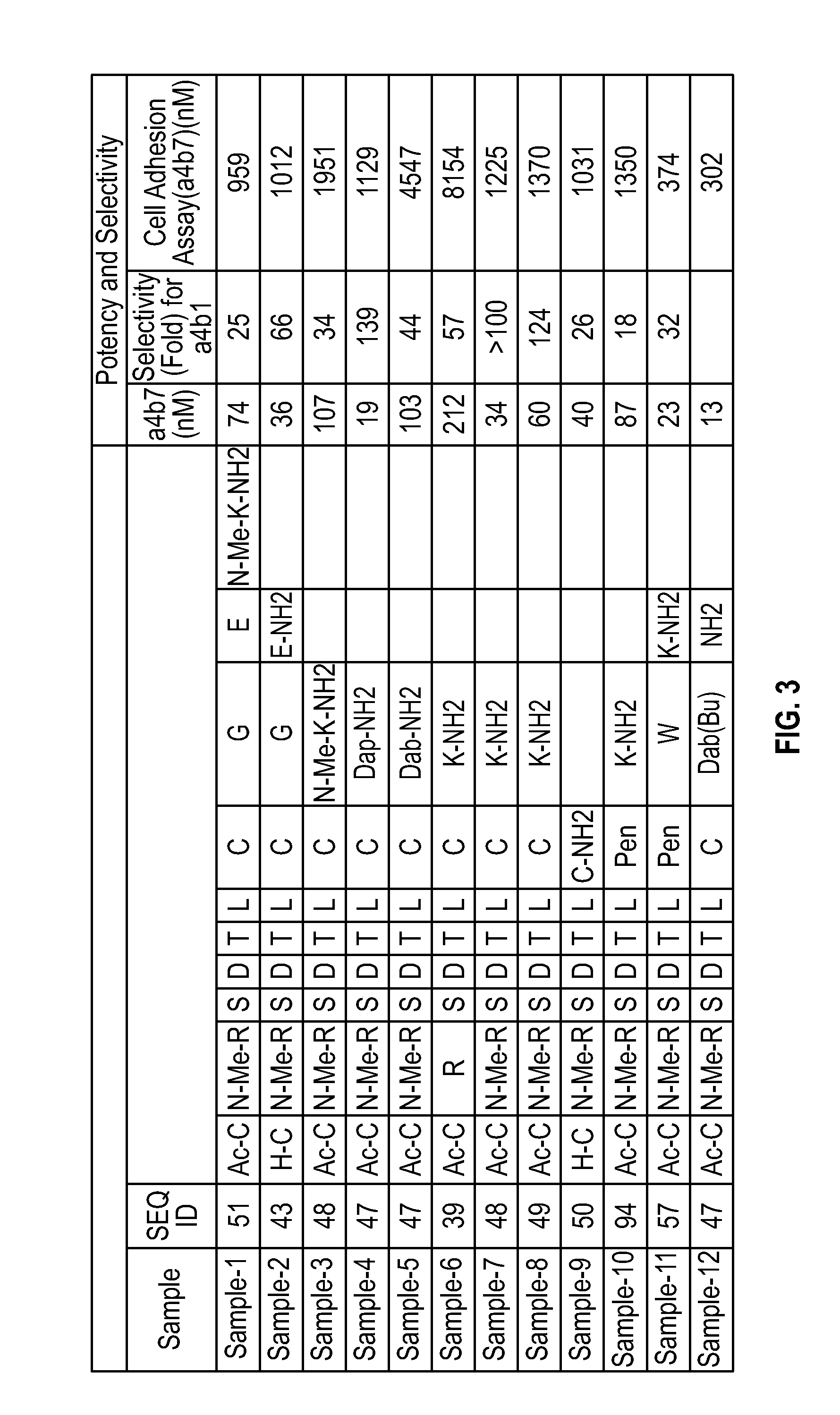
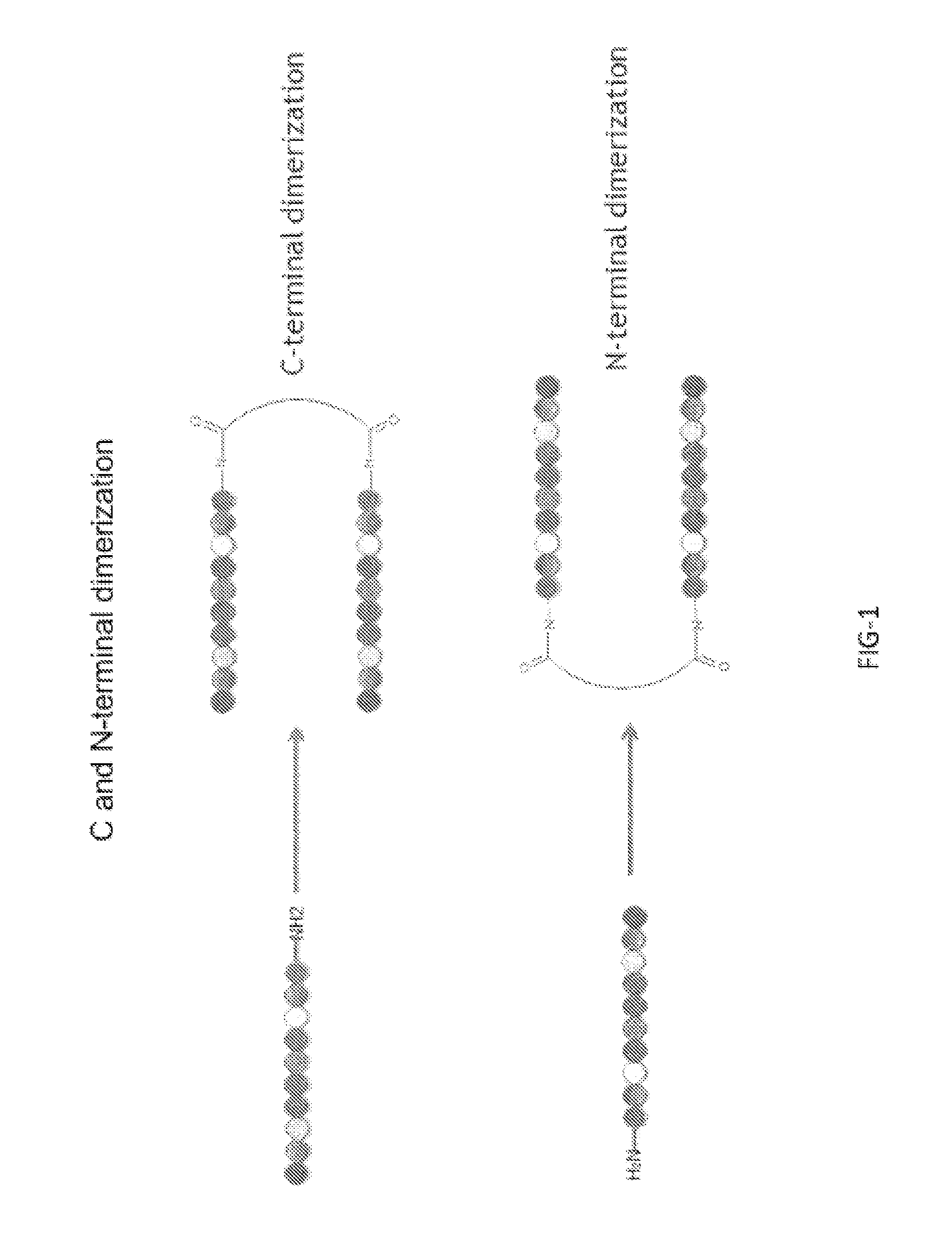
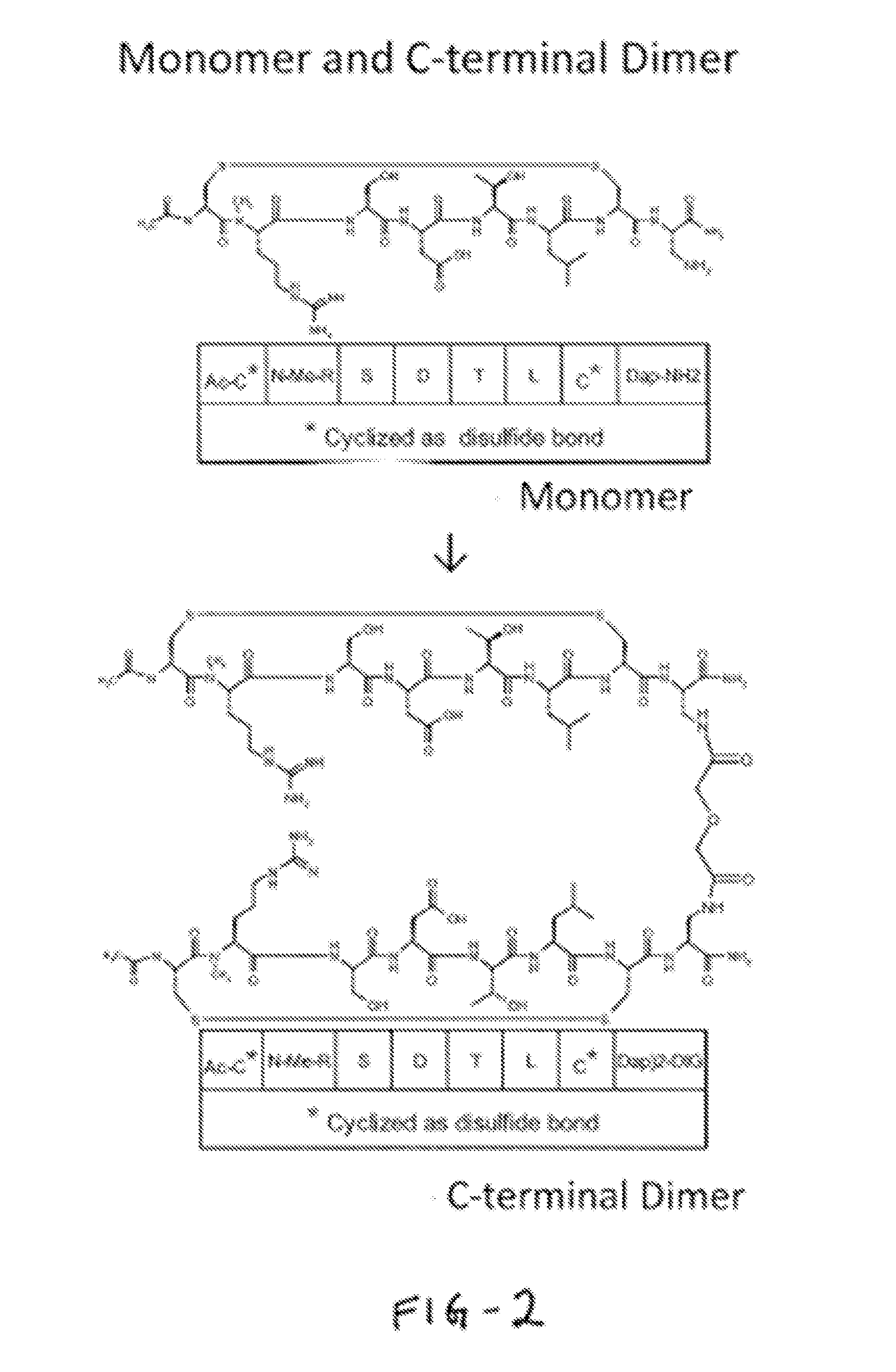
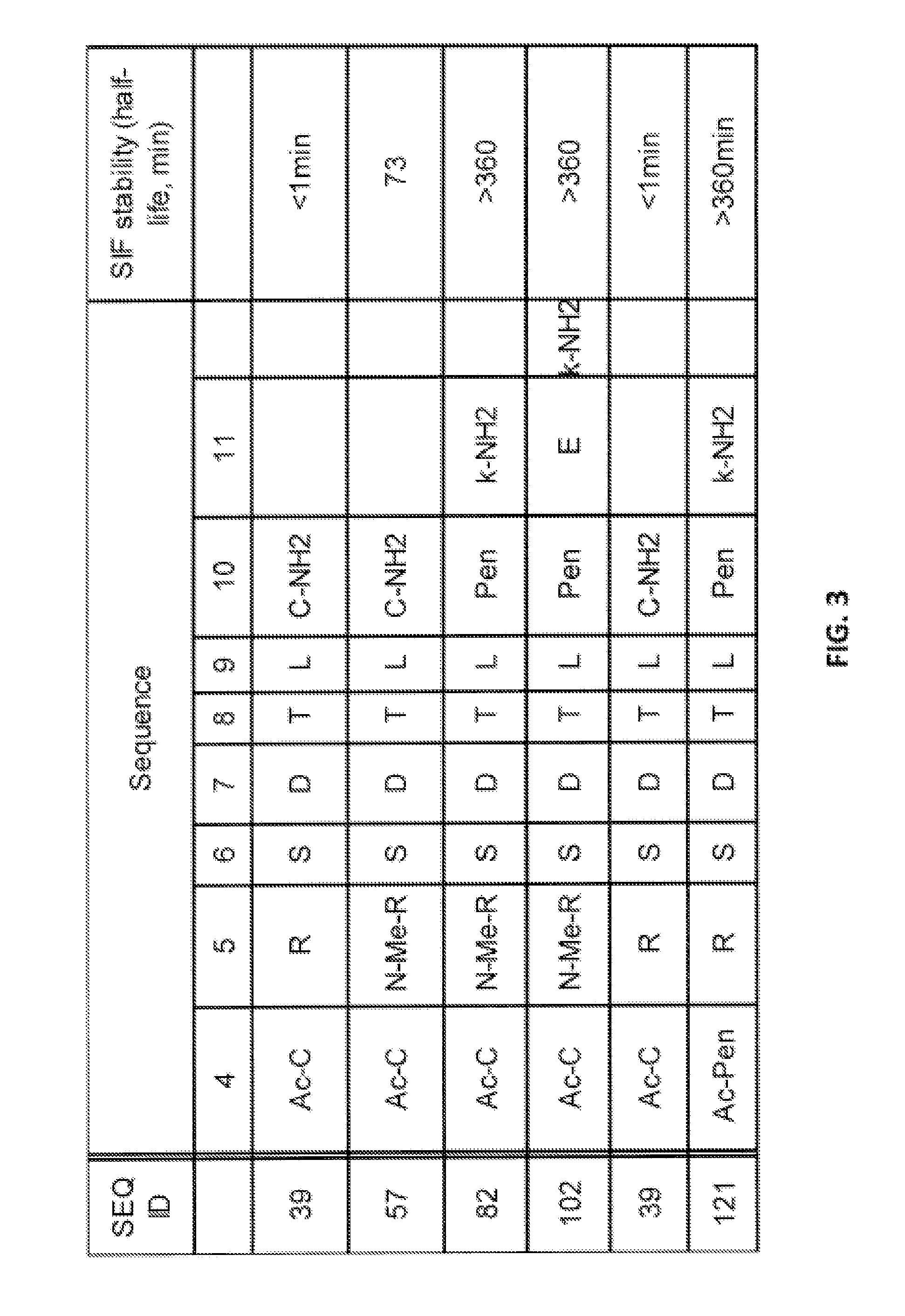
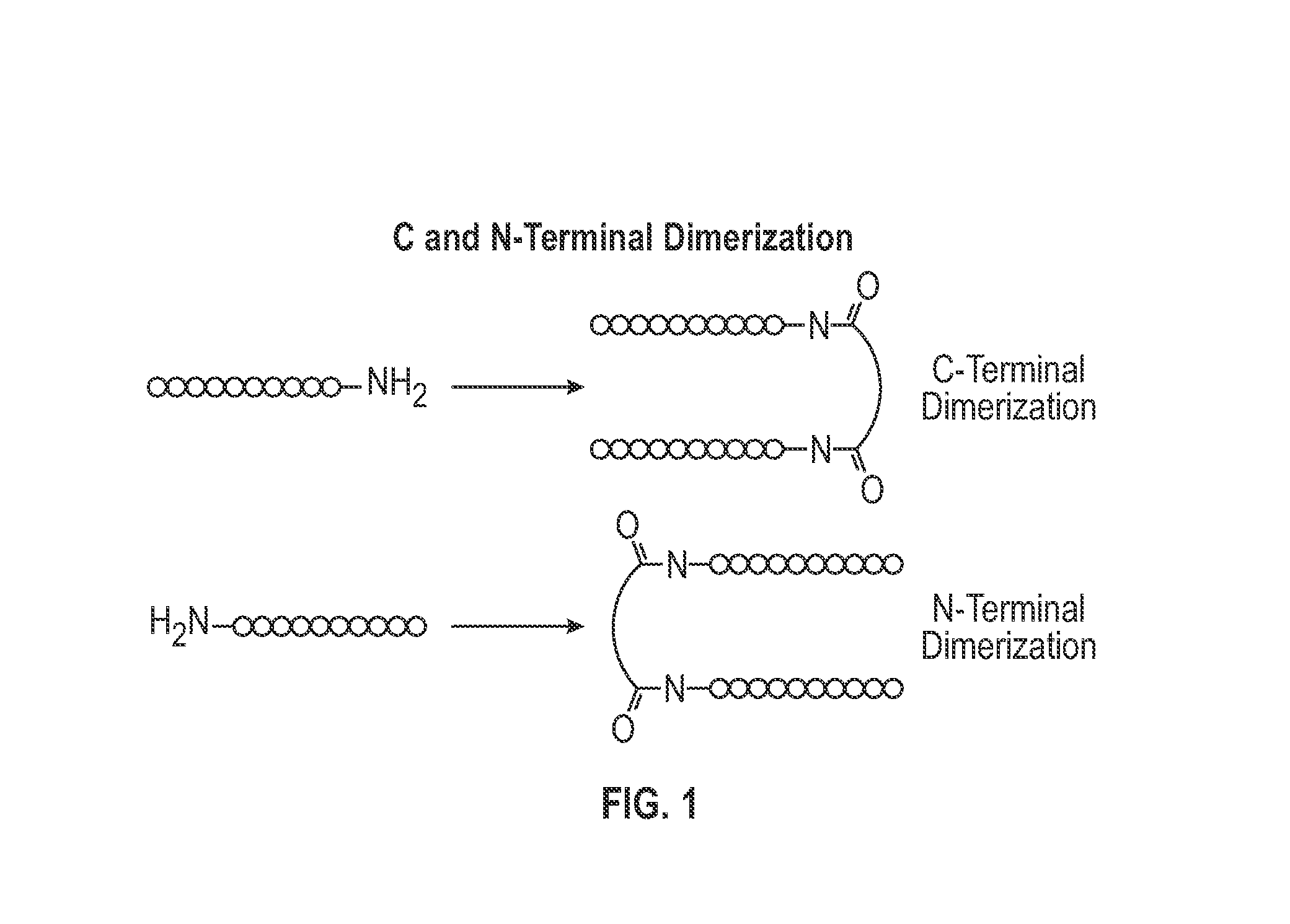
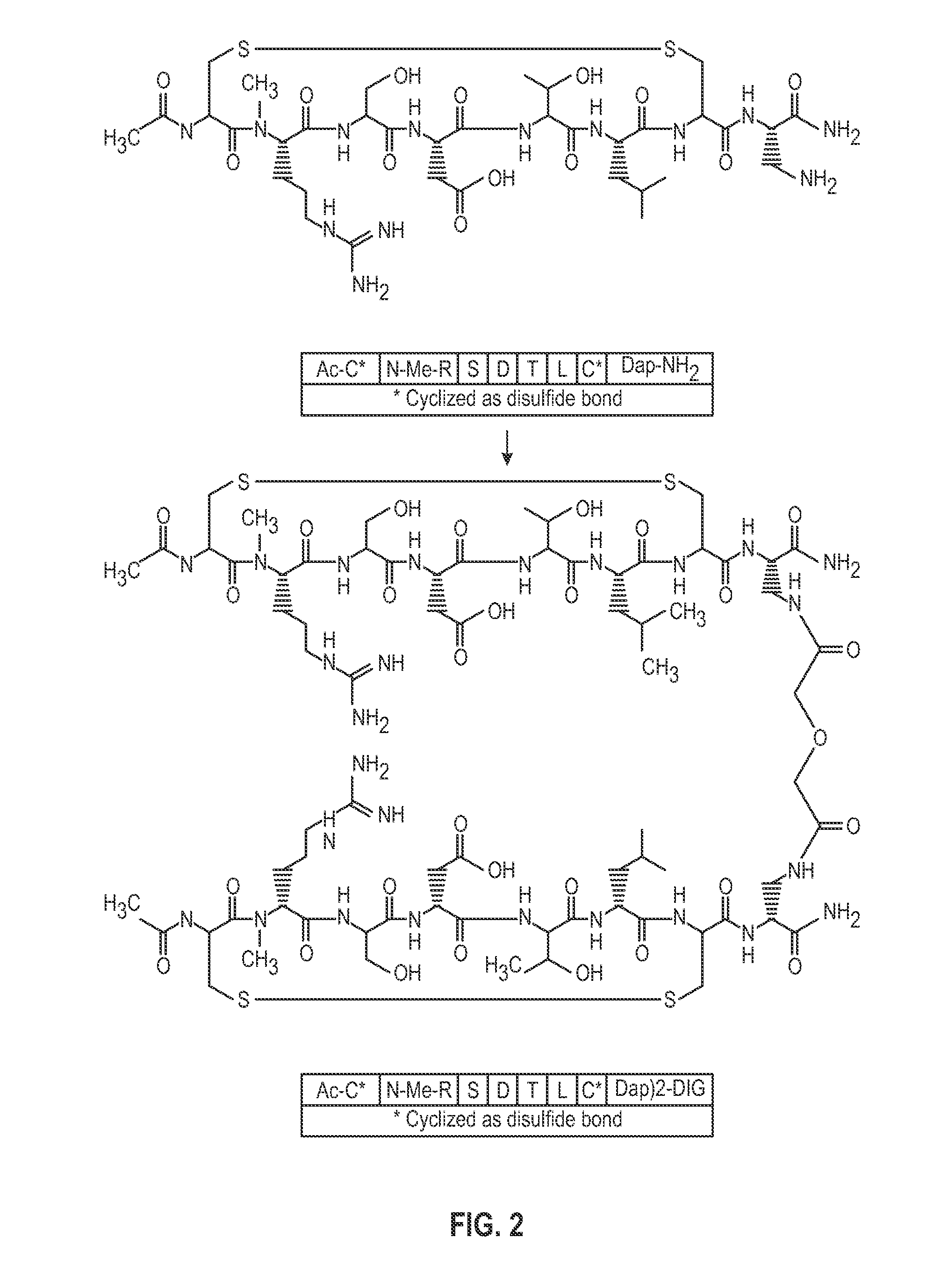
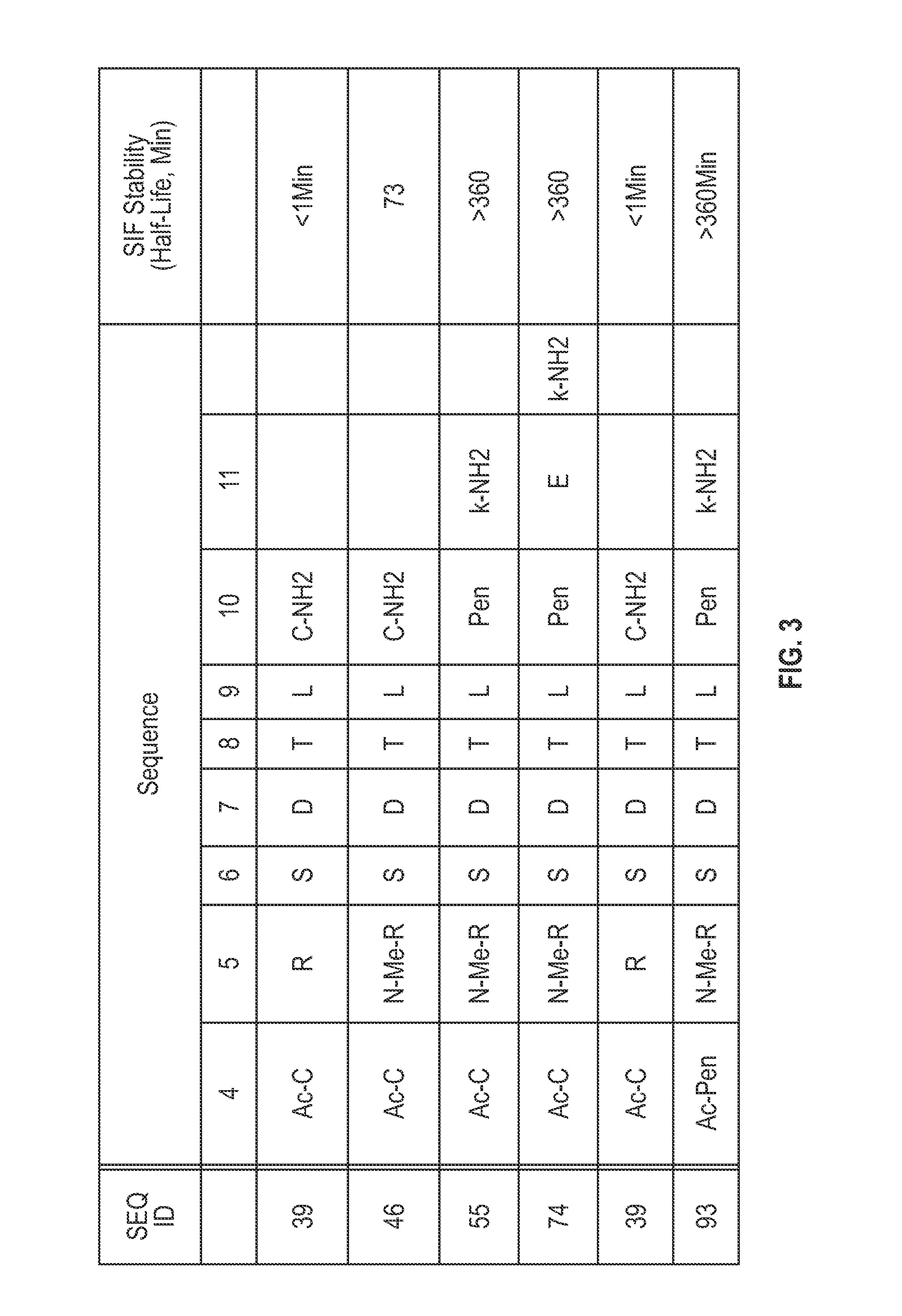
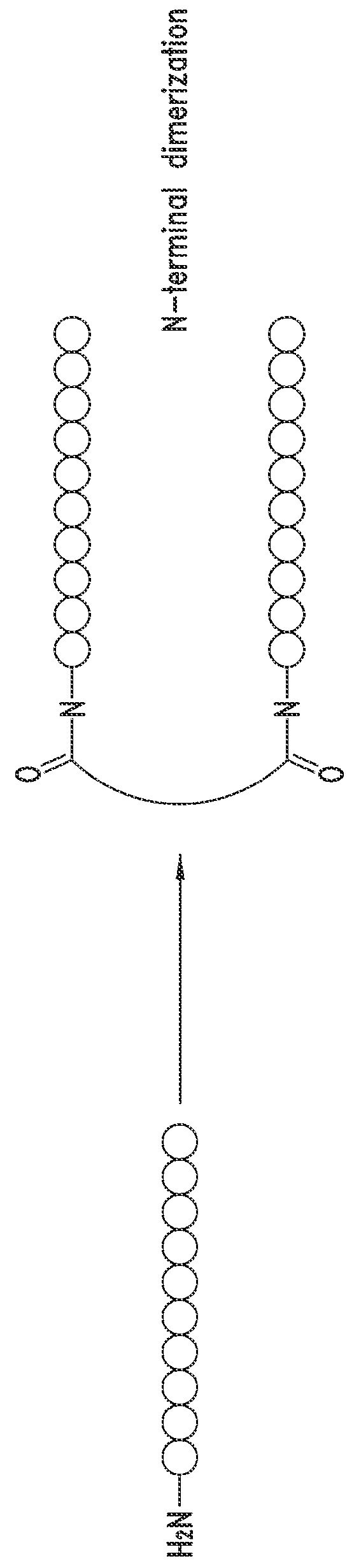
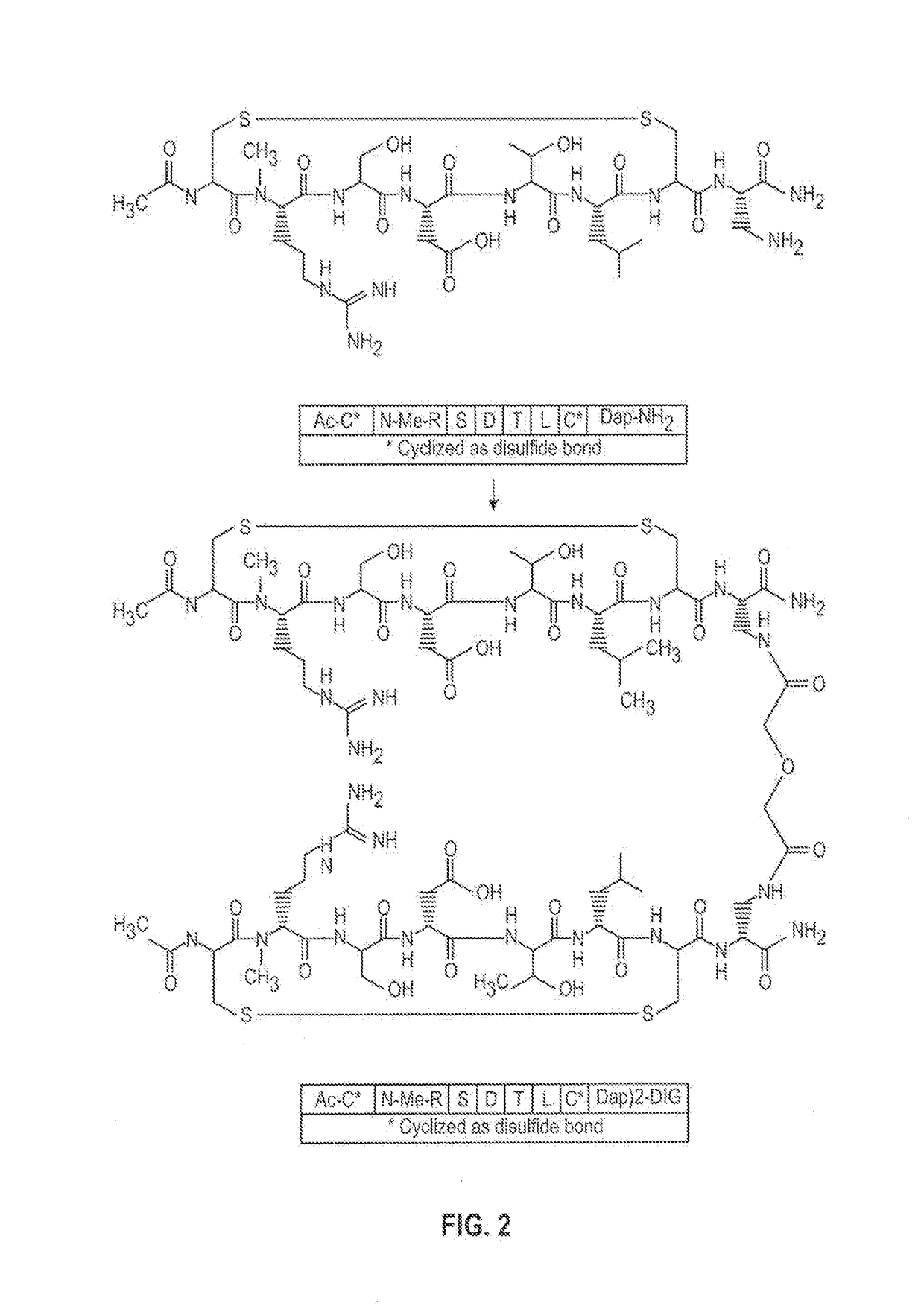
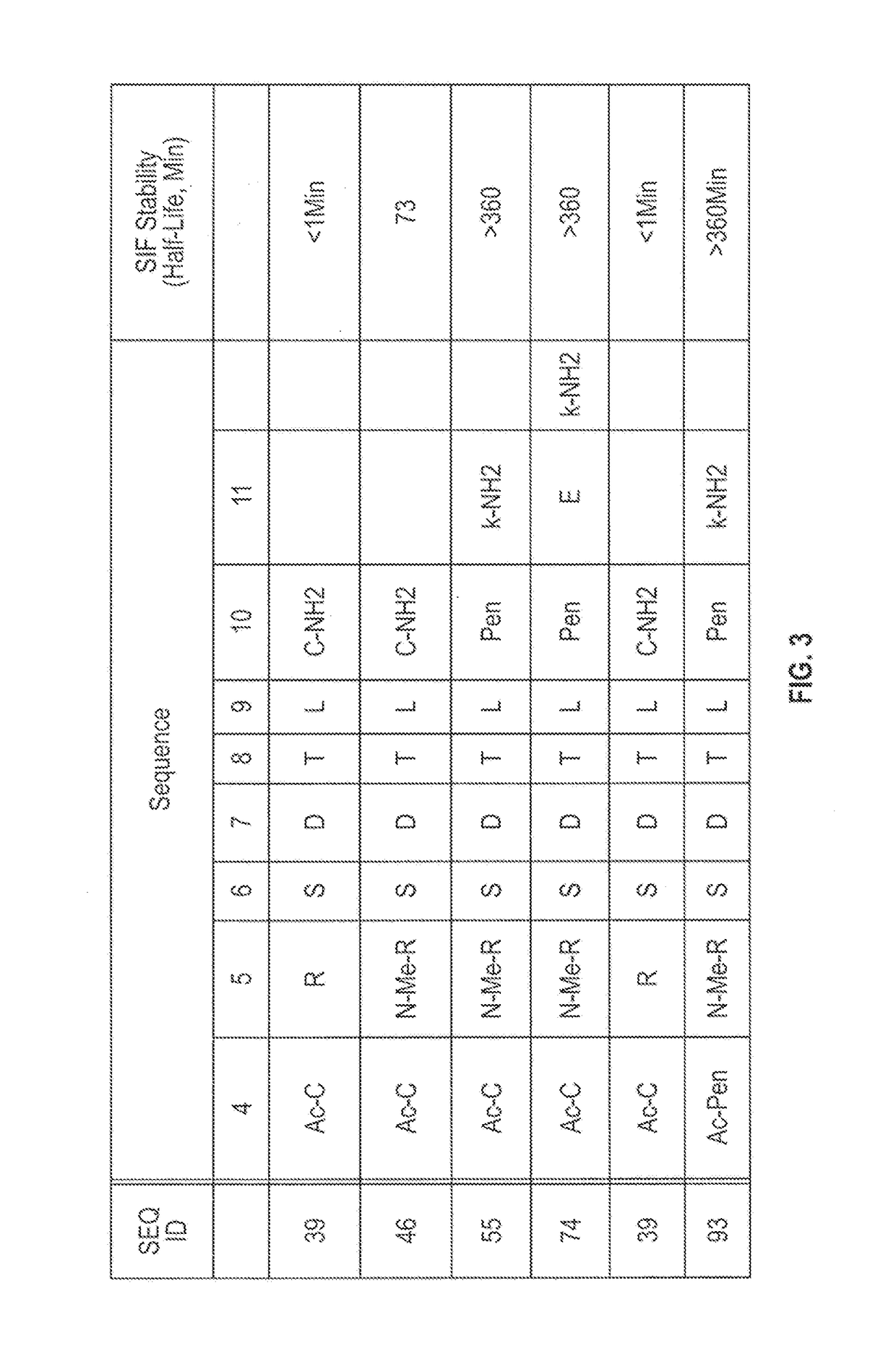
NOVEL a4B7 PEPTIDE DIMER ANTAGONISTS
ActiveUS20140193465A1Strong specificityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticBiochemistryIn vivo
The invention relates to disulfide-rich dimer molecules which inhibit binding of α4β7 to the mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule (MAdCAM) in vivo, and show high selectivity against α4β1 binding.
Owner:PROTAGONIST THERAPEUTICS INC
A4B7 peptide monomer and dimer antagonists
ActiveUS9518091B2Strong specificityImprove stabilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsIn vivoOrganic chemistry
Owner:PROTAGONIST THERAPEUTICS INC
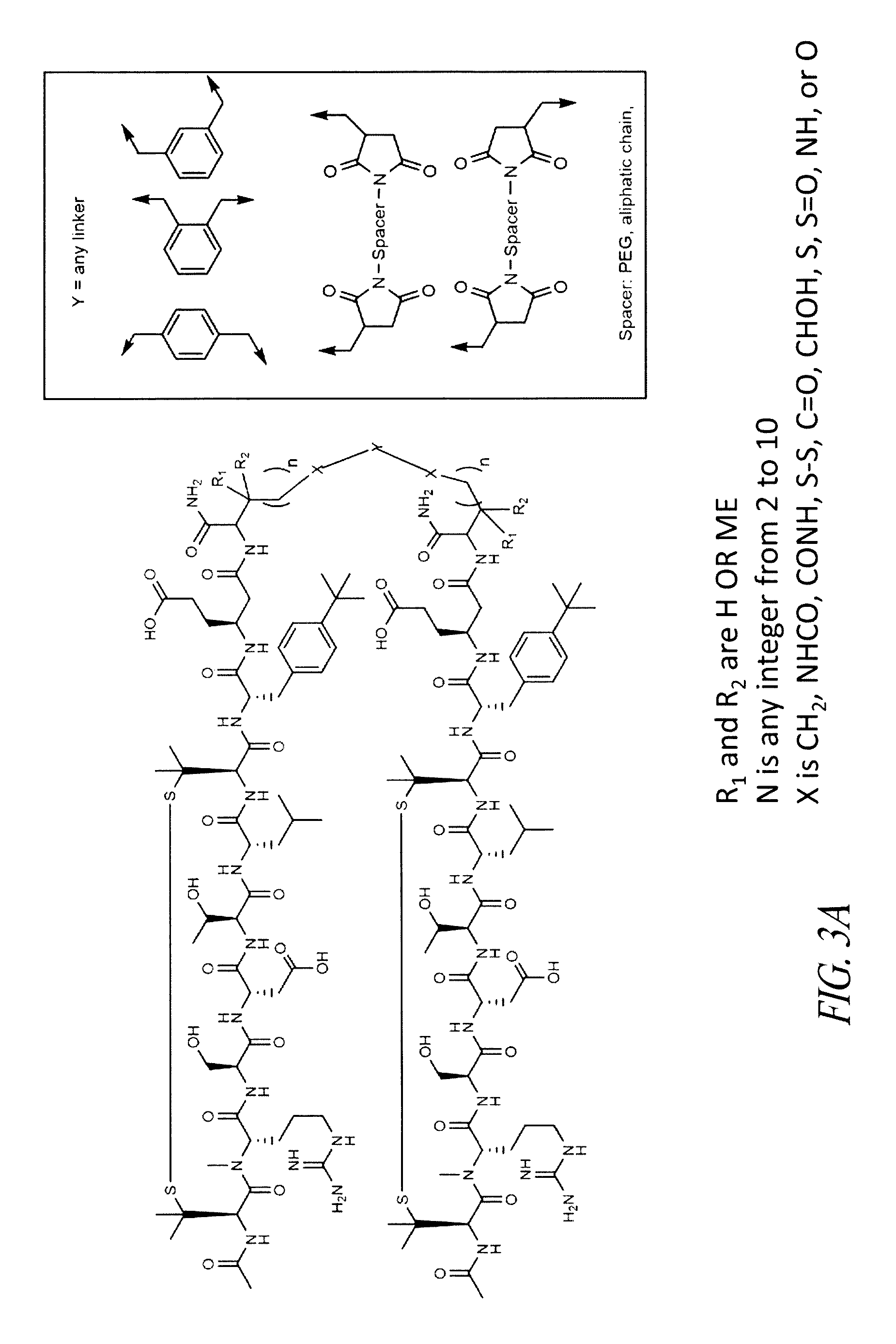
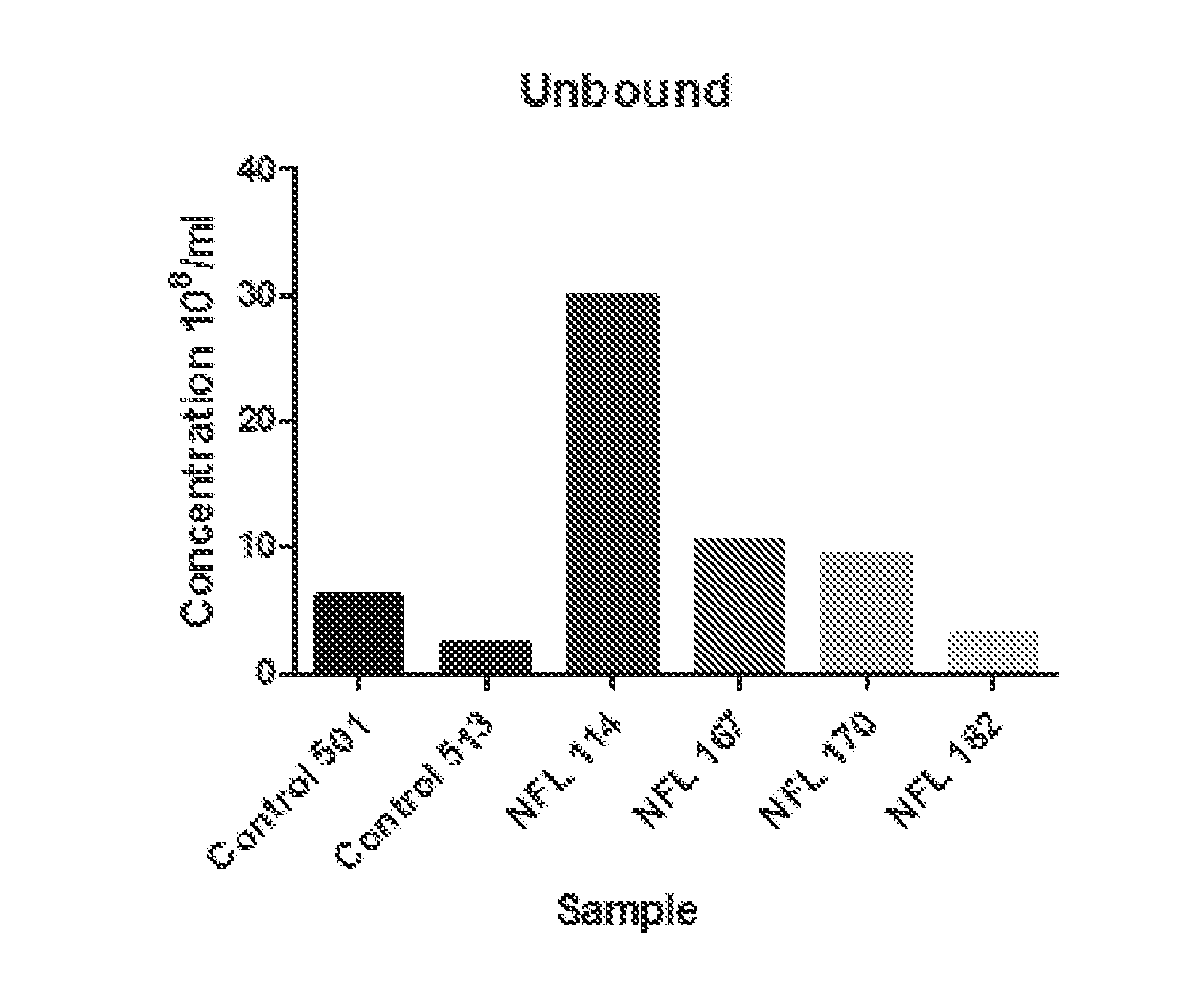
Brain specific exosome based diagnostics and extracorporeal therapies
InactiveUS20170014450A1Reliable and inexpensive and portable and rapid and simple approachMinimally invasive, inexpensive, portable, and reliableCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPsa ncamPhosphorylation
Disclosed are methods, compositions, devices, and kits for the isolation of brain-specific exosomes. Specifically, methods, compositions, devices, and Unbound kits comprising an isolated brain-specific extracellular vesicle or exosome joined to a first binding agent that is specific for tau, β-amyloid, SlOO β, neuron-specific enolase, glycoprotein A2B5, CD133, NQ01, synaptophysin, neuronal nuclei, MAB 1569, polysialic acid-neural cell adhesion molecule (PSA-NCAM), or neurogenic differentiation 1 (NeuroD or Beta2), or glycosylated or phosphorylated forms of these molecules, are provided.
Owner:EXOSOME SCI
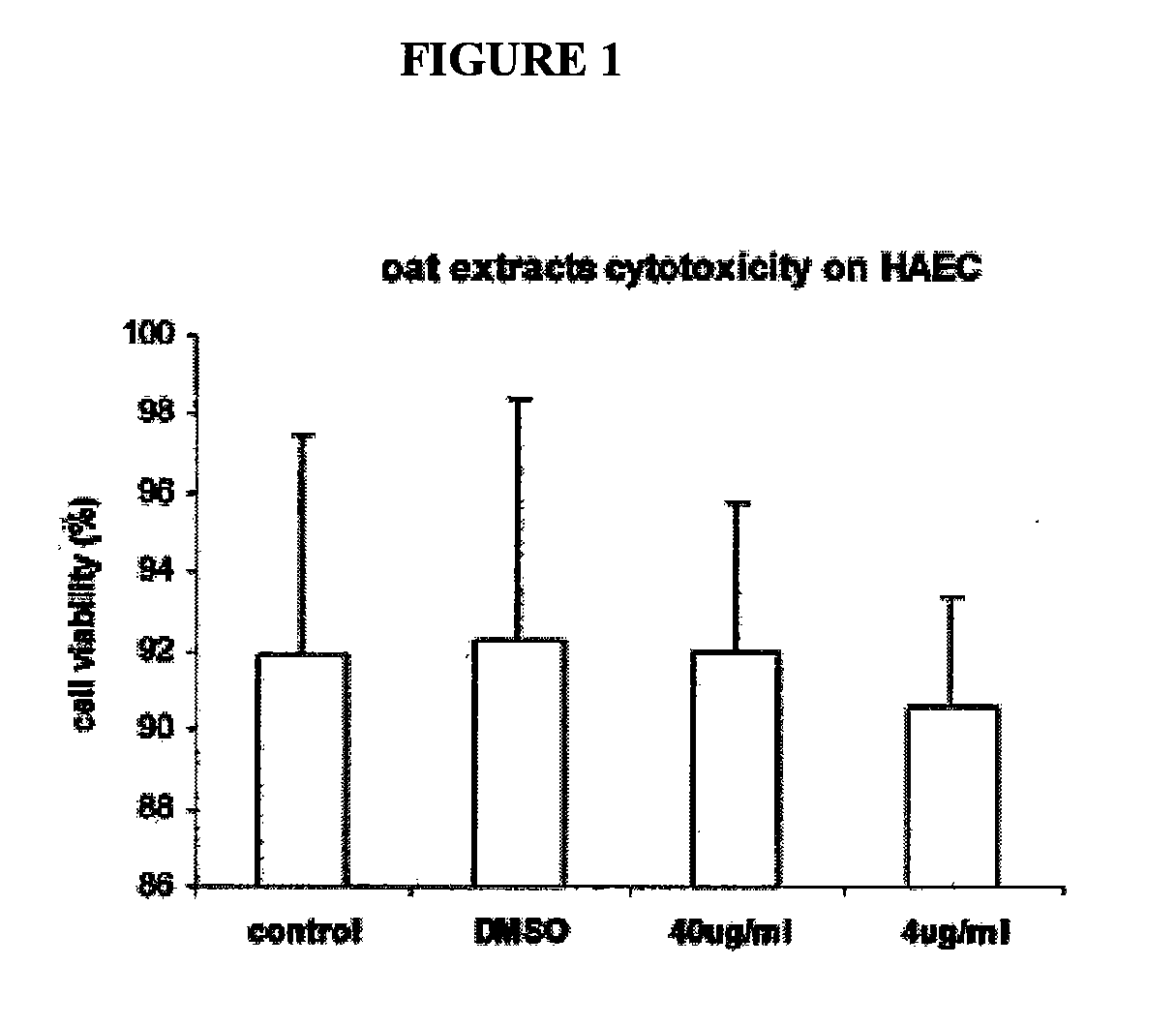
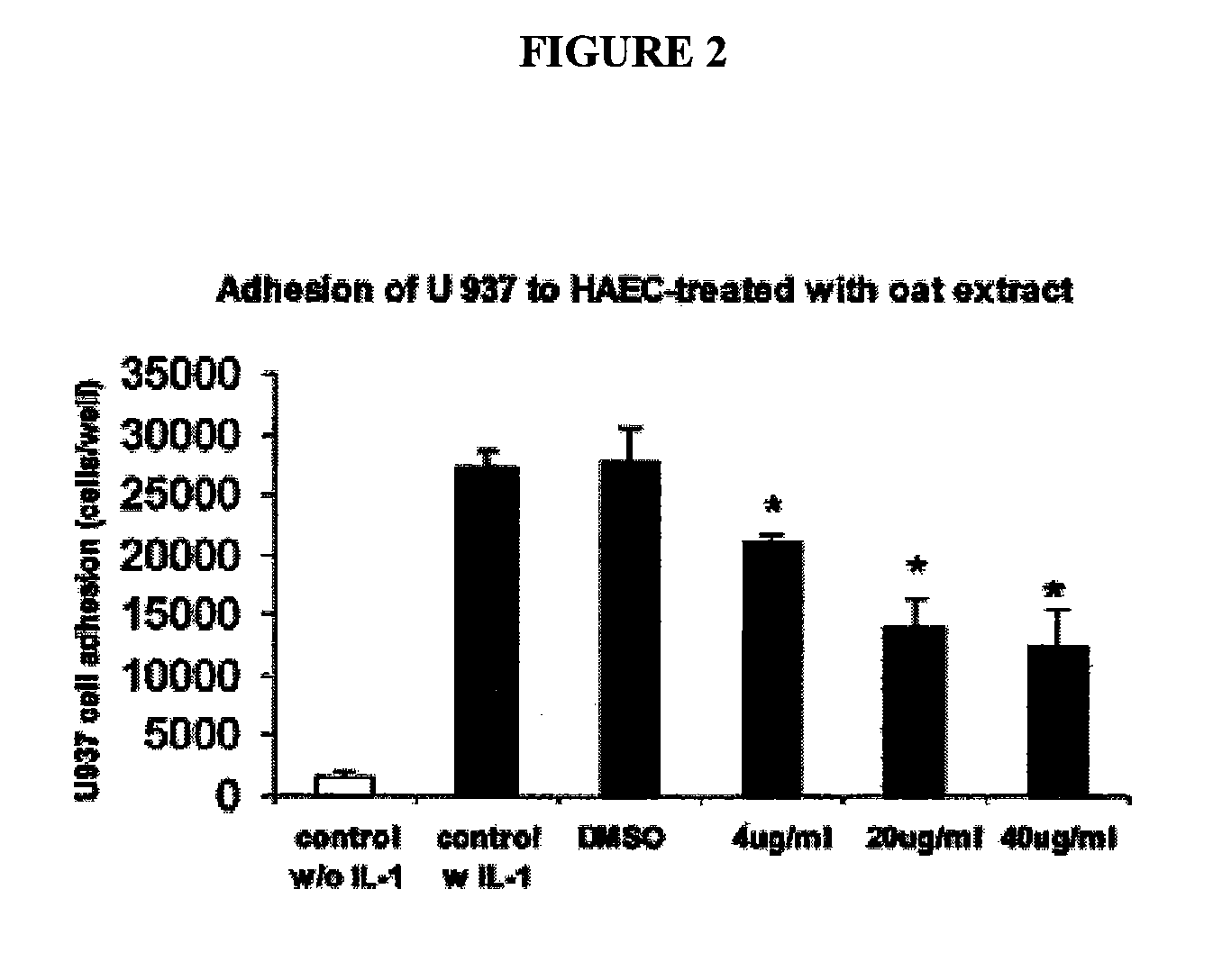
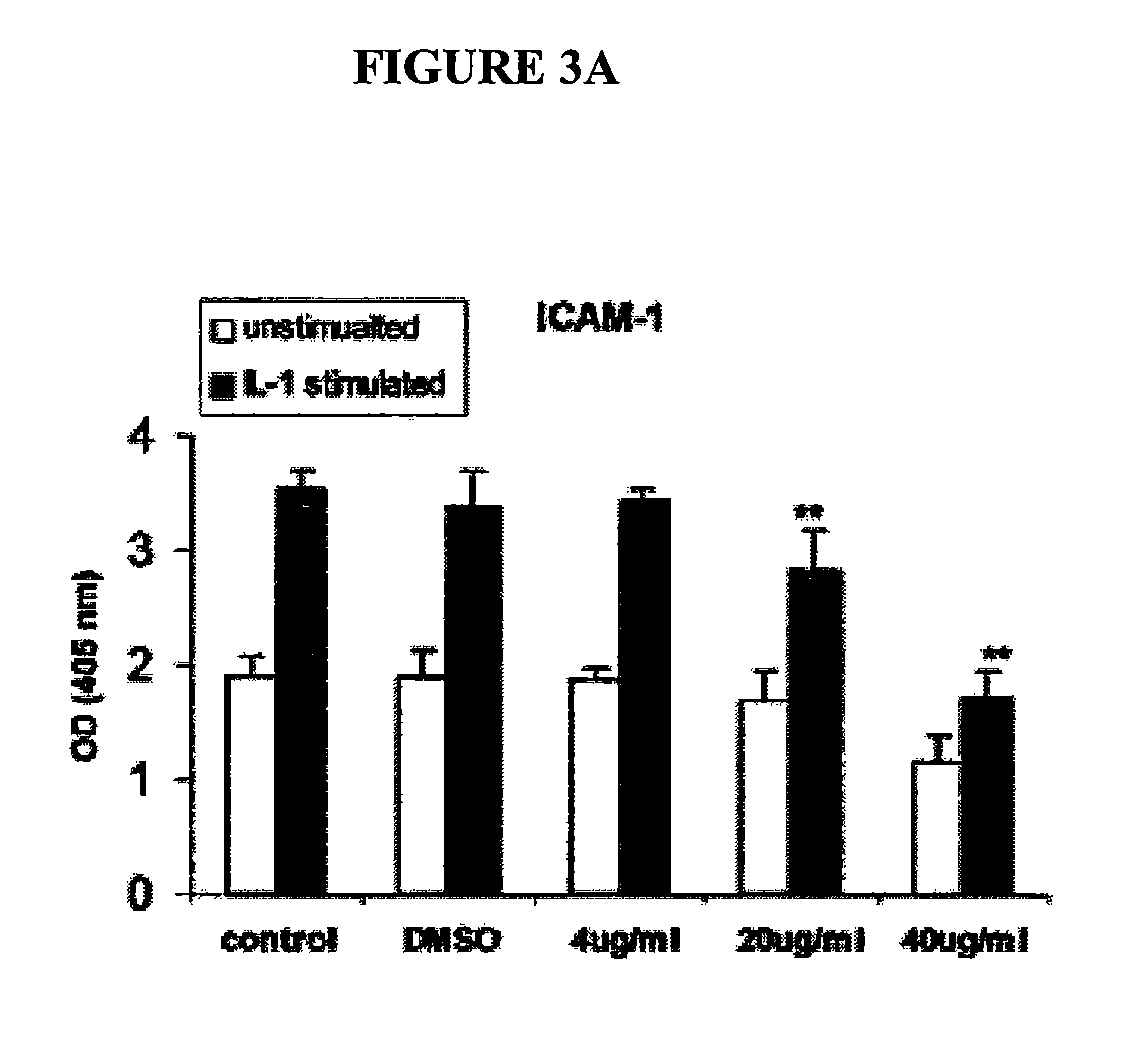
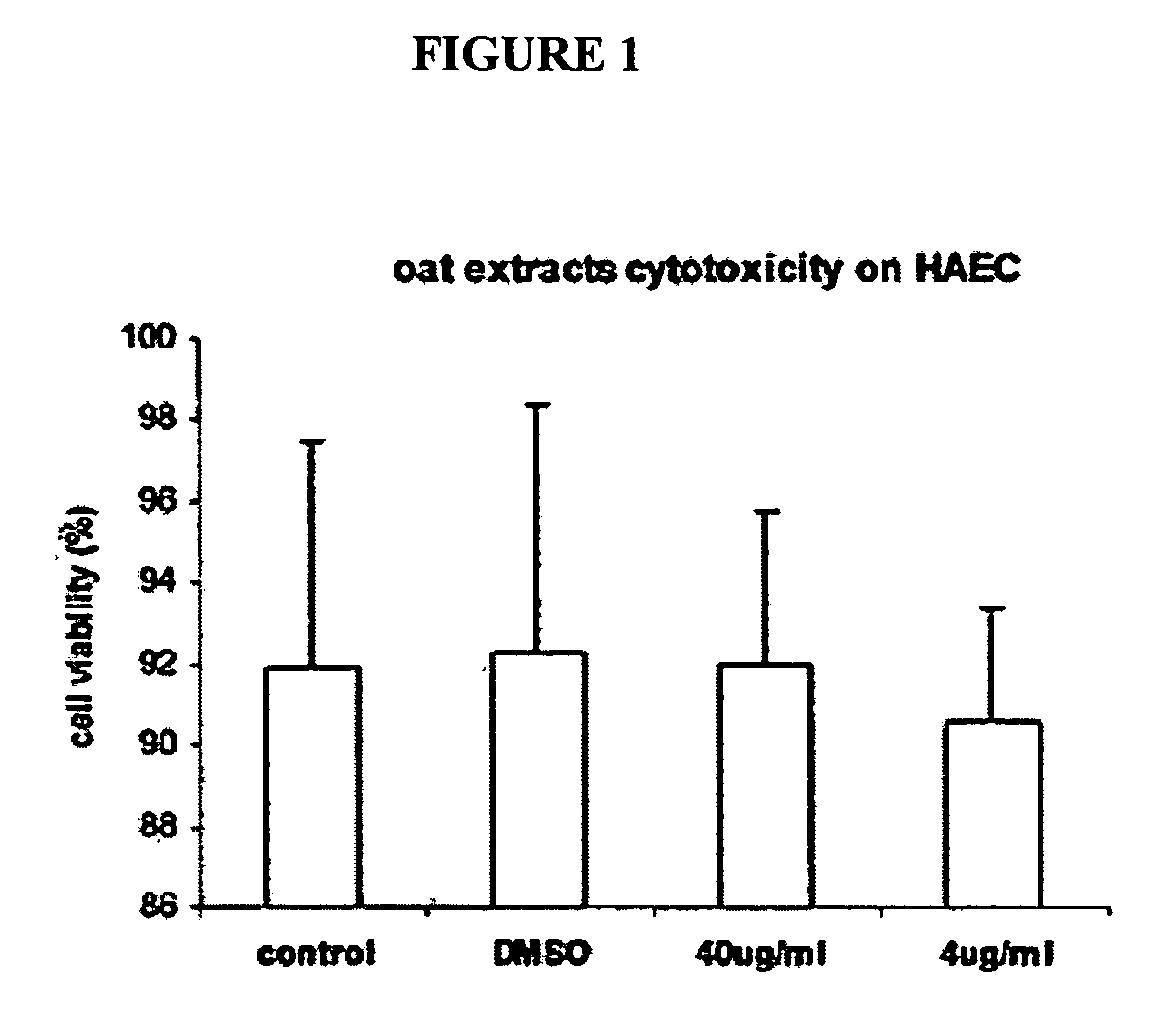
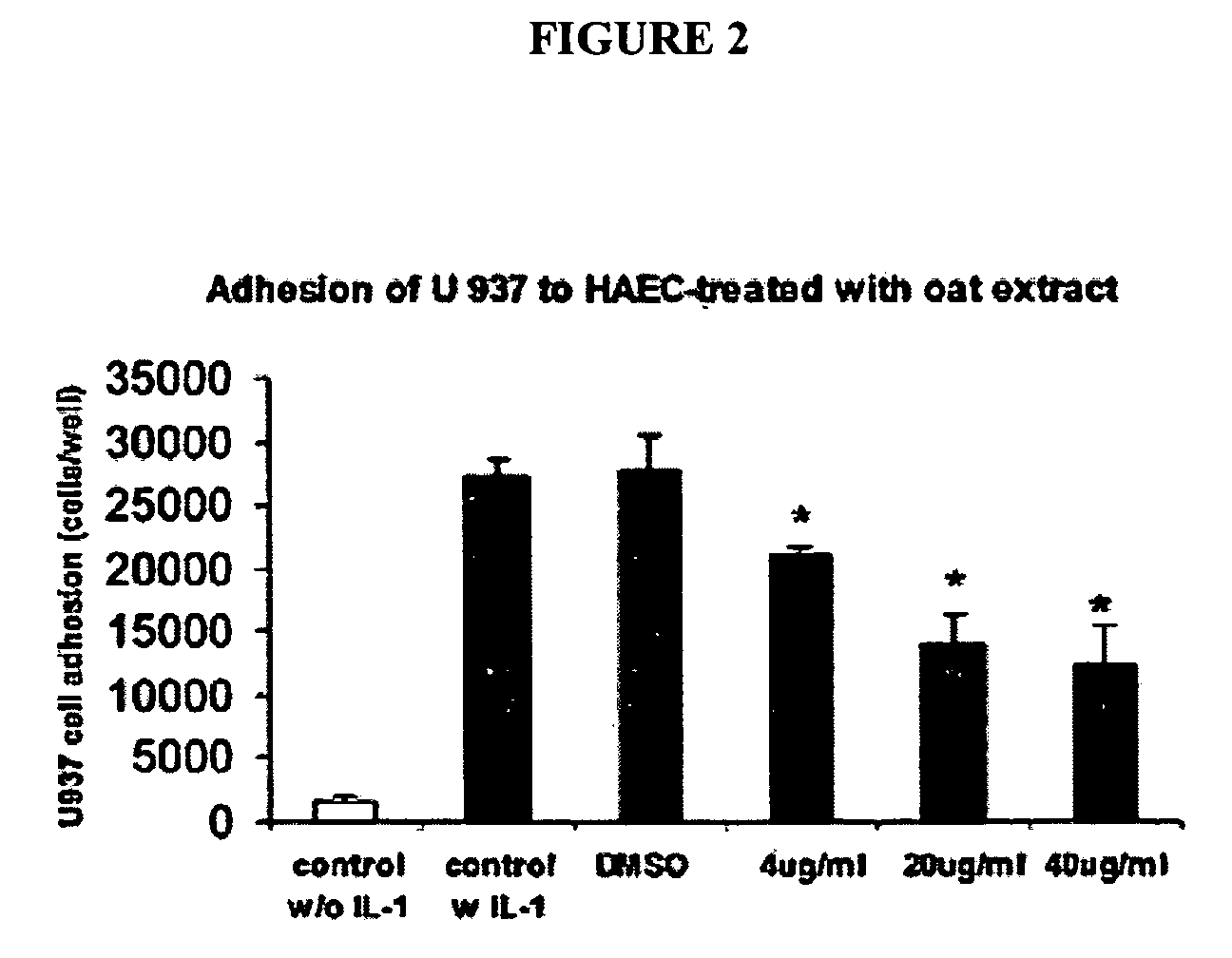
Therapeutic Avenanthramide Compounds
InactiveUS20070254055A1Delay disease progressionAvoid formingOrganic active ingredientsBiocideArteriolar VasoconstrictionCell adhesion
Methods and compositions are disclosed for inhibiting proliferation of human colon adenocarcinoma cells, reducing pro-inflammatory molecules, adhesion molecules, and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, and for increasing NO production. The present invention describes the use of phenolic compositions, purified from oats or synthetically produced, to decrease the effective amount of pro-inflammatory molecules and / or cell adhesion molecules. Alternatively, an alcoholic extract or concentrate from oats can be used. The methods of the present invention can be used as a treatment or prophylaxis of a wide variety of disorders associated with inflammatory states and / or with a lack of or need for nitric oxide (NO), such as inflammatory conditions, pain, free radical associated disorders, cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune disorders, pathological platelet aggregation, pathological vasoconstriction, vascular effects of diabetes, stroke, atherosclerosis, hypertension, abnormal vasospasm, and restenosis after angioplasty.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE D B A TUFTS UNIV
Combination products with carboxylic acid derivatives that inhibit the binding of integrins to their receptors and other therapeutic compounds
A composition, method and kit comprising a compound for the inhibition of the binding of α4β1 integrin to its receptors, for example VCAM-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule-1) and fibronectin and other therapeutic compounds for the control or prevention of diseases states in which α4β1 is involved.
Owner:ENCYSIVE PHARMA INC +1
Novel a4b7 peptide antagonists
InactiveUS20140294902A1Strong specificityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticDisulphide bondsAntagonist
The invention relates to disulfide-rich peptide molecules which inhibit binding of α4β7 to the mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule (MAdCAM) in vivo, and show high selectivity against α4β1 binding.
Owner:PROTAGONIST THERAPEUTICS INC
Α4β7 peptide dimer antagonists
ActiveUS9273093B2Strong specificityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticBiochemistryIn vivo
The invention relates to disulfide-rich dimer molecules which inhibit binding of α4β7 to the mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule (MAdCAM) in vivo, and show high selectivity against α4β1 binding.
Owner:PROTAGONIST THERAPEUTICS INC
Novel a4b7 peptide dimer antagonists
InactiveUS20140294901A1Strong specificityImprove stabilityAntipyreticAnalgesicsDimerDisulphide bonds
The invention relates to disulfide-rich dimer molecules which inhibit binding of α4β7 to the mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule (MAdCAM) in vivo, and show high selectivity against α4β1 binding.
Owner:PROTAGONIST THERAPEUTICS INC
a4B7 integrin thioether peptide antagonists
ActiveUS9714270B2Improve stabilityIncreased specificity and potencyAntipyreticAnalgesicsIn vivoIntegrin
Owner:PROTAGONIST THERAPEUTICS INC
Carboxylic acid derivatives that inhibit the binding of integrins to their receptors
A method for the inhibition of the binding of α4β1 integrin to its receptors, for example VCAM-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule-1) and fibronectin; compounds that inhibit this binding; pharmaceutically active compositions comprising such compounds; and to the use of such compounds either a above, or in formulations for the control or prevention of diseases states in which α4β1 is involved.
Owner:ENCYSIVE PHARMA INC
Herbal composition for treating various disorders including psoriasis, a process for preparation thereof and method for treatment of such disorders
InactiveUS20030194456A1Safe and well-toleratedMinimal effectBiocideAntipyreticPhosphodiesteraseEnzyme inhibition
The invention provides a novel herbal composition containing the extracts of the leaves and / or stem of <italic>Argemone mexicana < / highlight>plant, optionally containing the extracts of the fruits of <italic>Cuminum cyminum< / highlight>, which exhibits useful in vitro, in vivo and interesting immunological and pharmacological activities; a process for preparation thereof; and a method of treatment of psoriasis and related immunological and biological disorders by administration of the said novel herbal composition. The useful in vitro, in vivo and interesting immunological and pharmacological activities exhibited by the extracts and fractions of the leaves and / or stem of <italic>Argemone mexicana < / highlight>plant include immunosuppression, lymphoproliferation inhibition, cytokine modulation such as IL-2 inhibition, IFNgamma inhibition, IL-10 induction, keratinocyte proliferation inhibition, keratolytic activity, endothelial cell proliferation inhibition, inhibition of cell adhesion molecule expression such as ICAM-1, MEST inhibition, and enzymes inhibition such as p60src Tyrosine kinase, which are known to be involved in anti-psoriatic activity. The novel herbal composition(s) is useful in the treatment of various disorders, such as psoriasis including plaque psoriasis, gutatte psoriasis, pustular psoriasis and psoriasis of the nails; dermatitis and scleroderma; eczema; inflammatory disorders and other autoimmune diseases like psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, multiple sclerosis, irritable bowel disease, ankylosing spondilitis, systemic lupus erythremetosus and Sjogren's syndrome; allergies like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and is safe, well-tolerated, non-toxic, with minimal and reversible adverse reactions or side effects, and most importantly, with minimal relapse or recurrence of the disease following completion of a treatment regimen. The invention also describes the presence of phosphodiesterase (III, IV and V) inhibition and 5-Lipoxygenase inhibition in the aqueous, ethanolic or aqueous-ethanolic extracts of fruits of <italic>Cuminum cyminum < / highlight>plant.
Owner:LUPIN LTD
Methods of surface modification to enhance cell adhesion
InactiveUS20050059140A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyCell adhesionChemistry
The current invention relates to methods of producing a surface with enhanced cell-adhesive properties comprising treating a pre-formed surface such that at least one intermediate reactive group is exposed on the surface. The exposed intermediate reactive group is then reacted to create a self-assembled monolayer, comprising at least one reactive group. The self-assembled monolayer is created non-mechanically. The reactive group is then coupled to at least one cell-adhesive molecule. The current invention also relates to cell culture devices comprising at least one oxygen-sensing compound and a cell-adhesive molecule.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
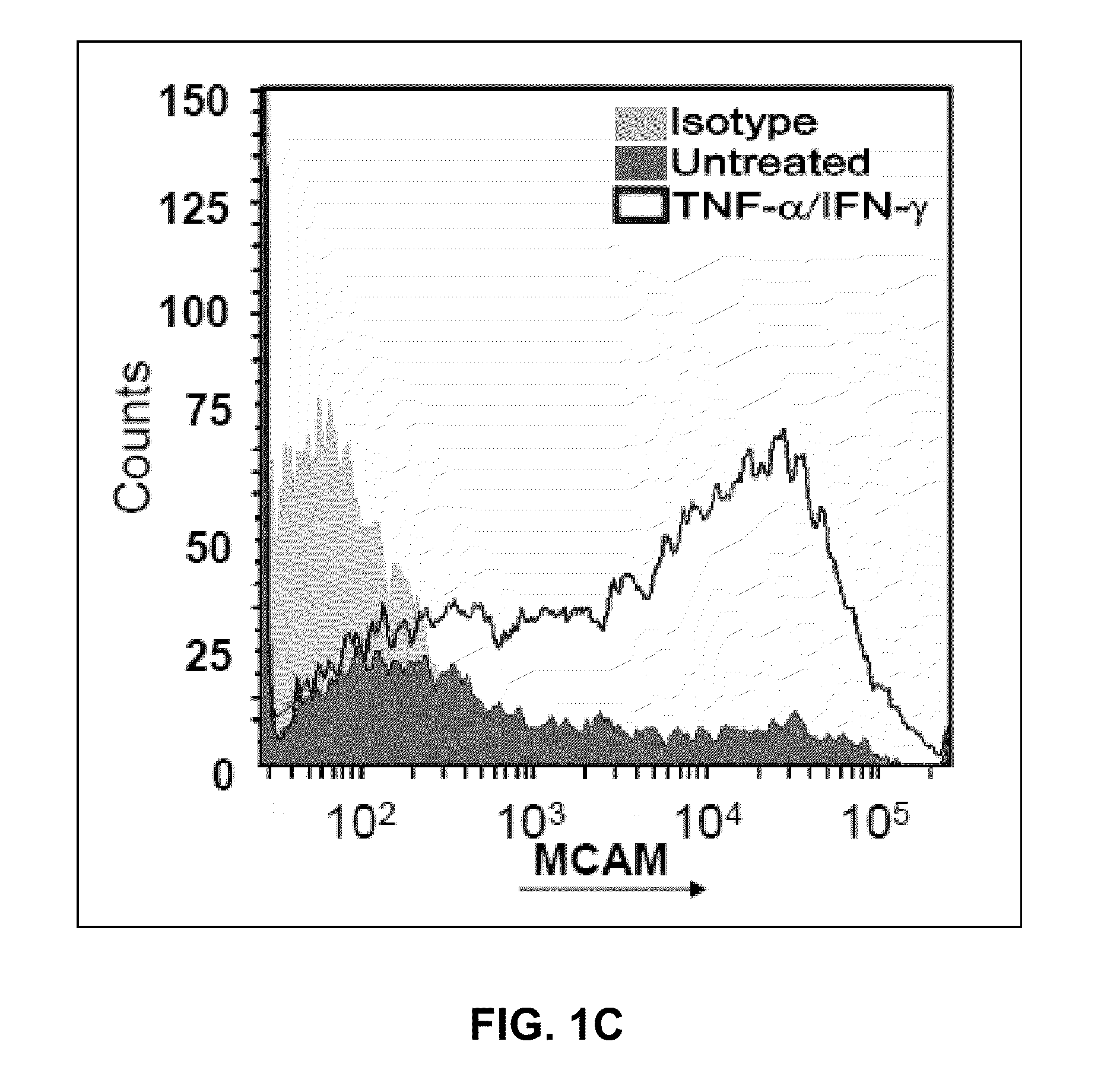
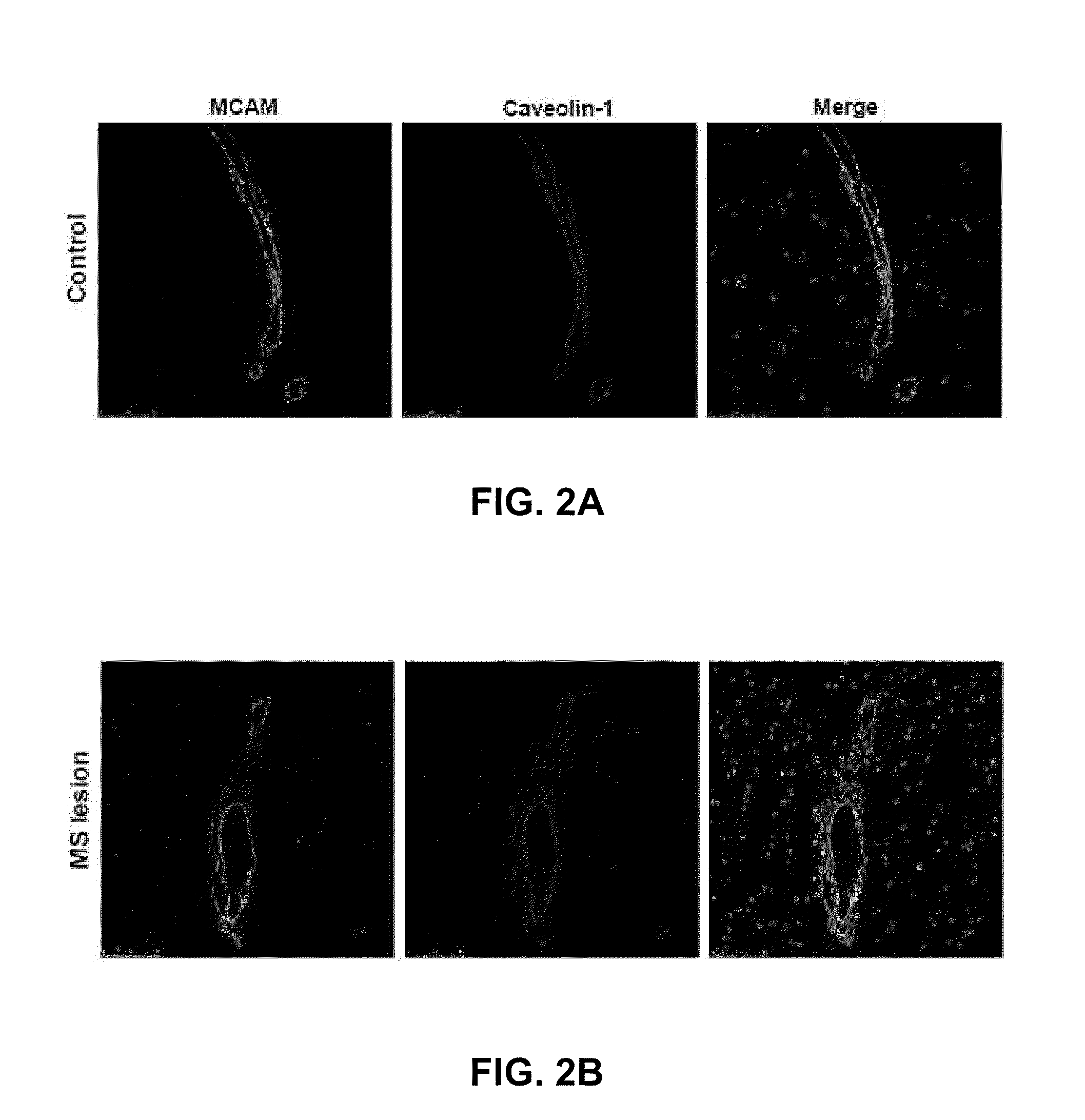
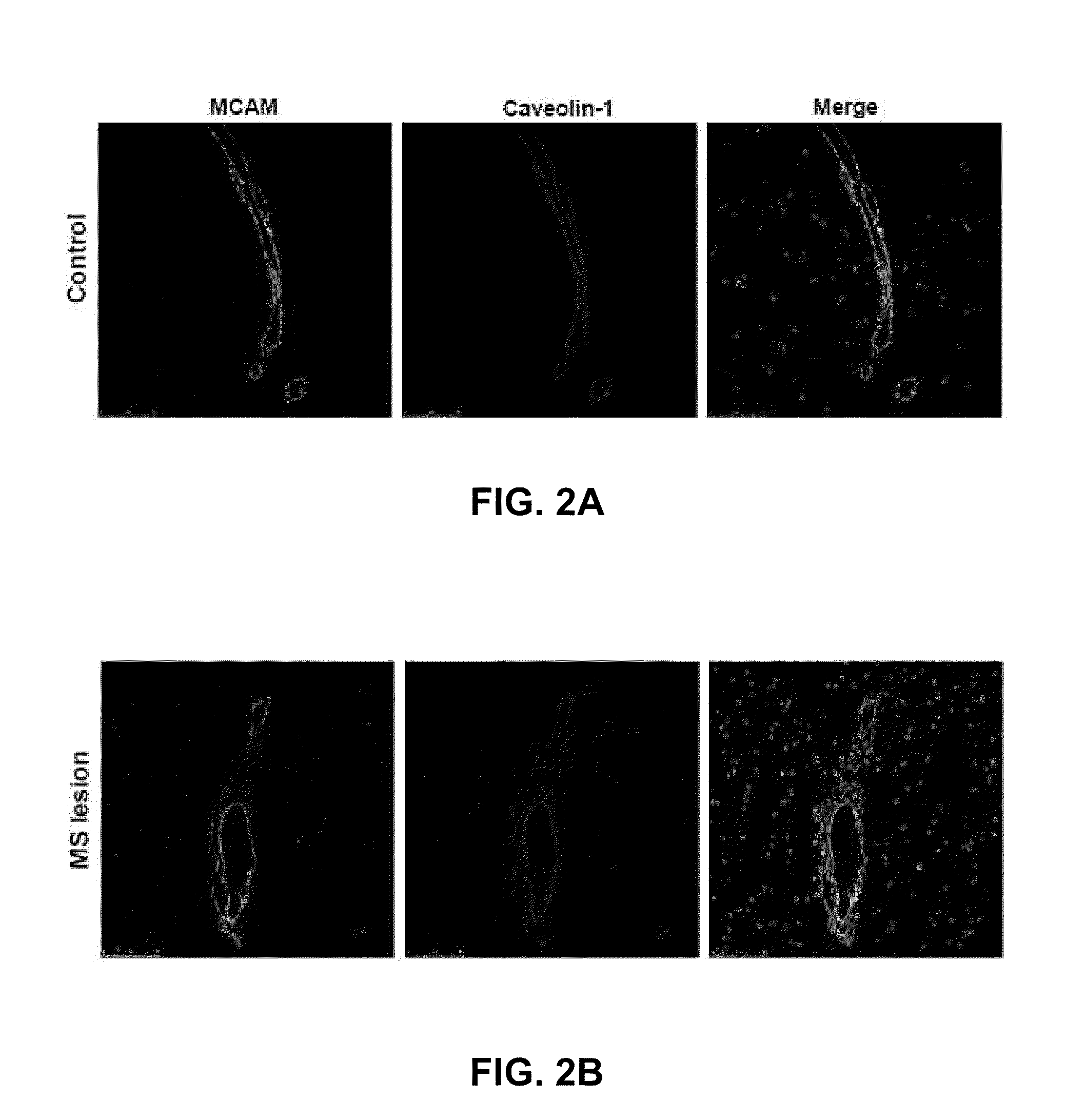
Mcam modulation and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110014183A1High activityHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseMelanoma Cell Adhesion Molecule
Methods, uses, agents and compositions useful for the diagnosis, prevention and / or treatment of inflammatory conditions, such as neuroinflammatory conditions such as multiple sclerosis, and for the identification and selection of inflammatory cytokine-secreting T cell or a precursor thereof, based on the expression and / or modulation of melanoma cell adhesion molecule (MCAM) are disclosed.
Owner:VAL CHUM PARTNERSHIP
Suppression of xenotransplant rejection
InactiveUS20070157328A1Sufficient supplyFacilitate transmigrationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsMedicineBiochemistry
This invention relates to the suppression of graft rejection, particularly to the suppression of xenograft rejection. In particular, the invention relates to biological tissues that contain endothelial cells that may be induced to generate a compound which down-regulates the expression of a cell adhesion molecule in these cells.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
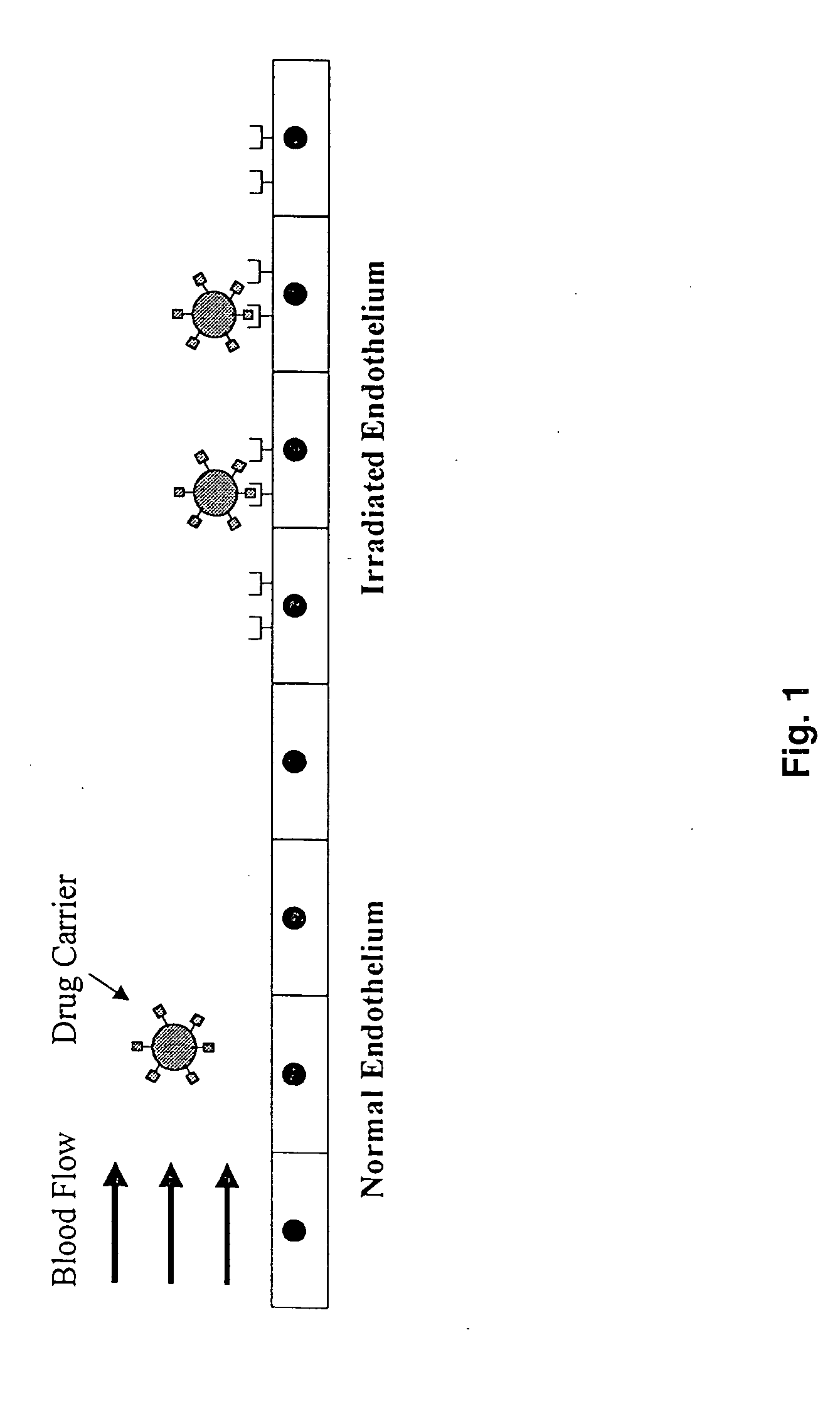
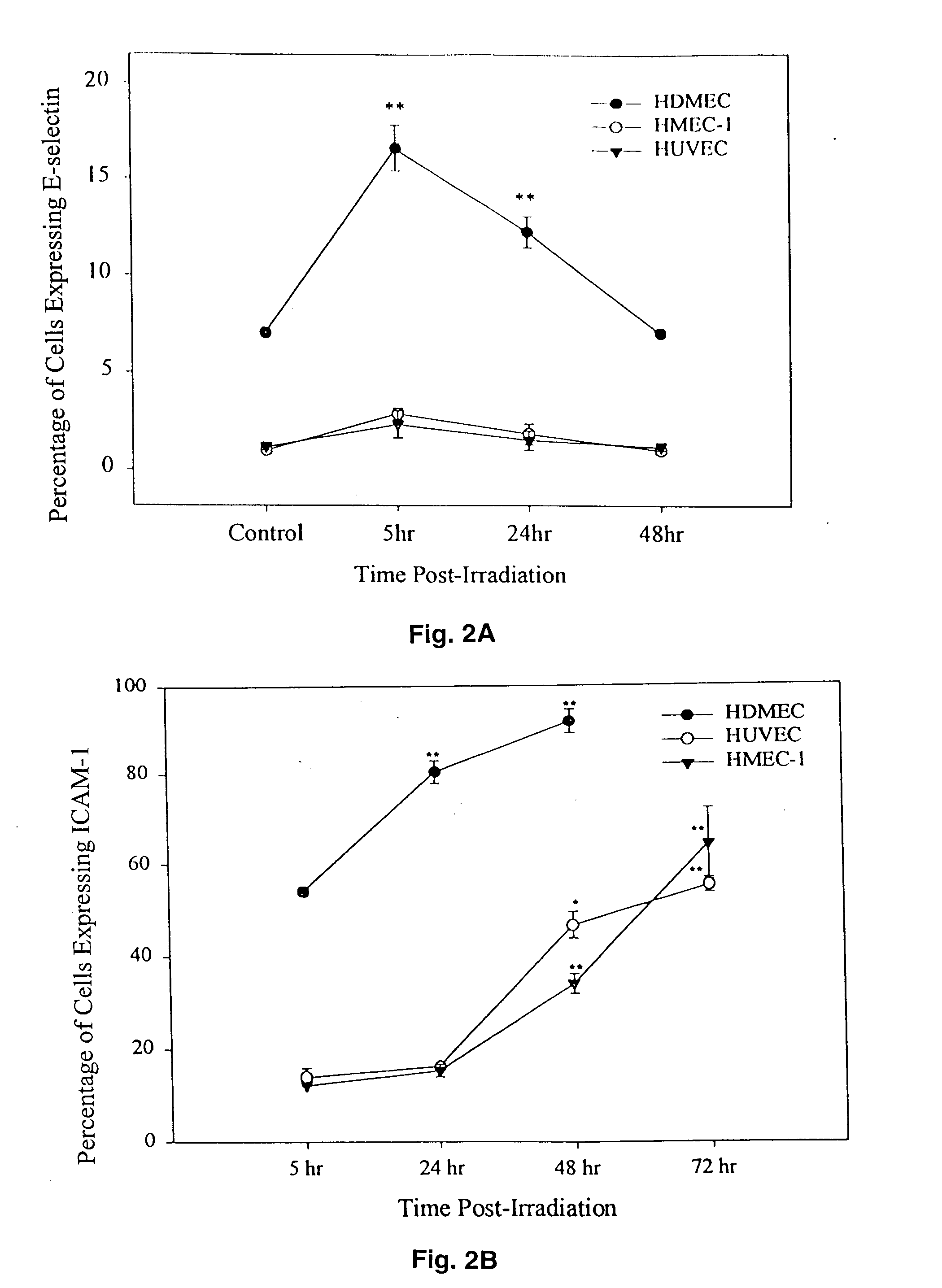
Targeting drug/gene carriers to irradiated tissue
InactiveUS20050186264A1Low magnificationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsMedicineLiposome
The present invention provides targeted delivery systems to deliver pharmaceuticals to irradiated tissue comprising a biomolecule carrier, a targeting moiety to cellular adhesion molecules and a pharmaceutical. The present invention also provides methods of selectively targeting endothelial tissue for delivery of a pharmaceutical thereto and of treating a pathophysiological state in an individual using the targeted delivery systems disclosed herein. Further provided is a method of optimizing an immunoliposome for specific targeting of a pharmaceutical encapsulated therein to irradiated tissue by selecting a liposome that has a greater rate of adhesion to the irradiated tissue than a rate of uptake by the reticuloendothelial system.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF OHIO UNIV THE +1
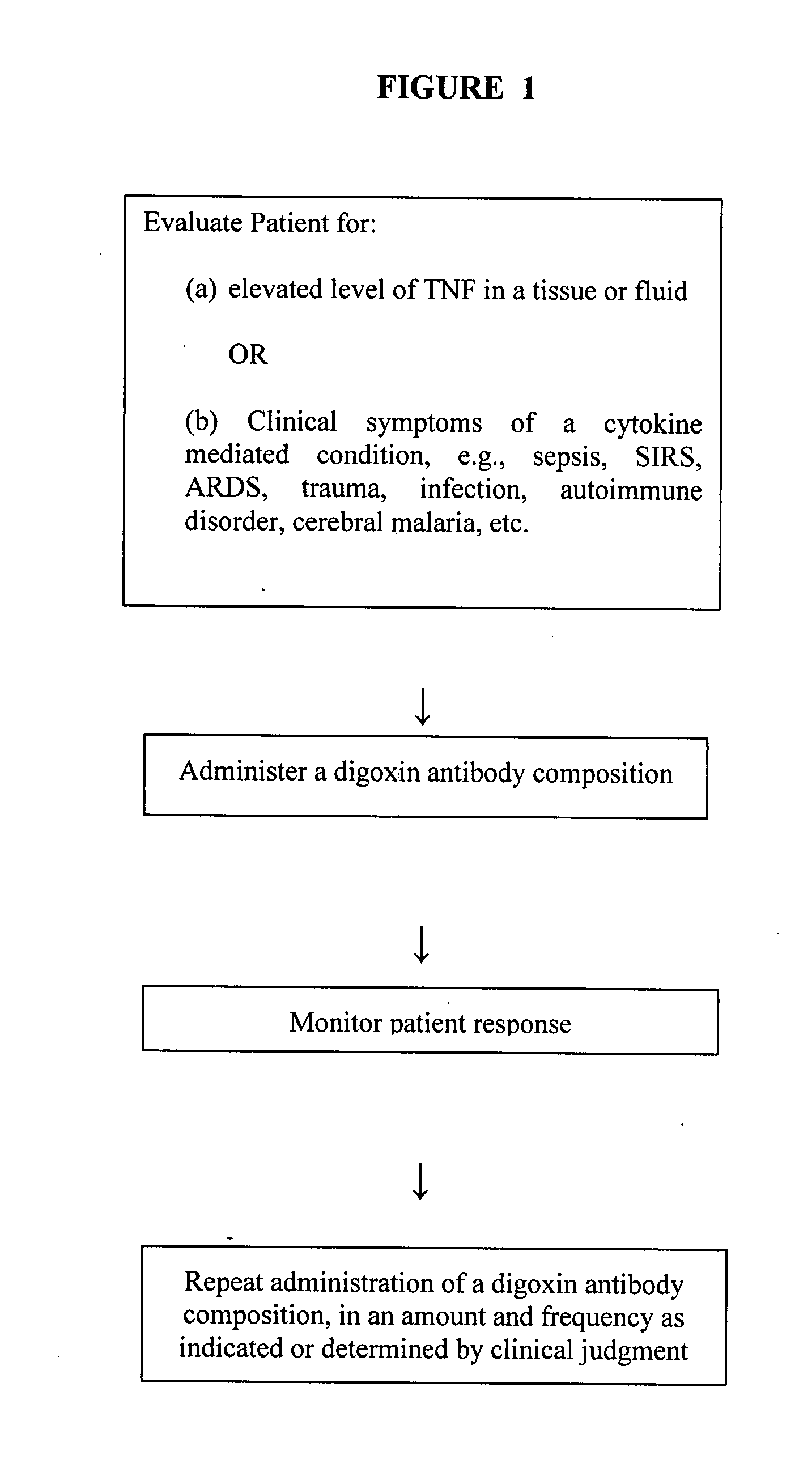
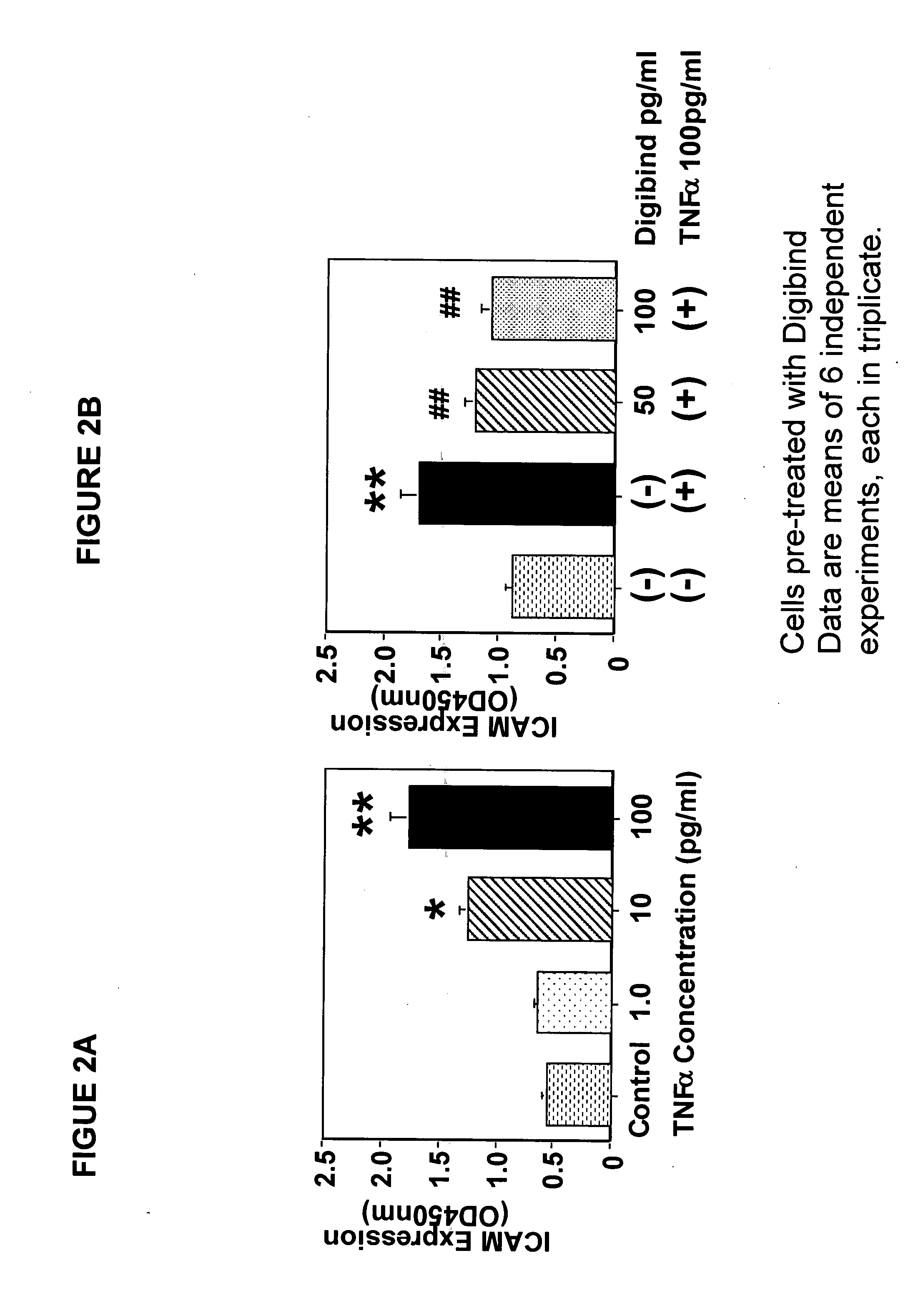
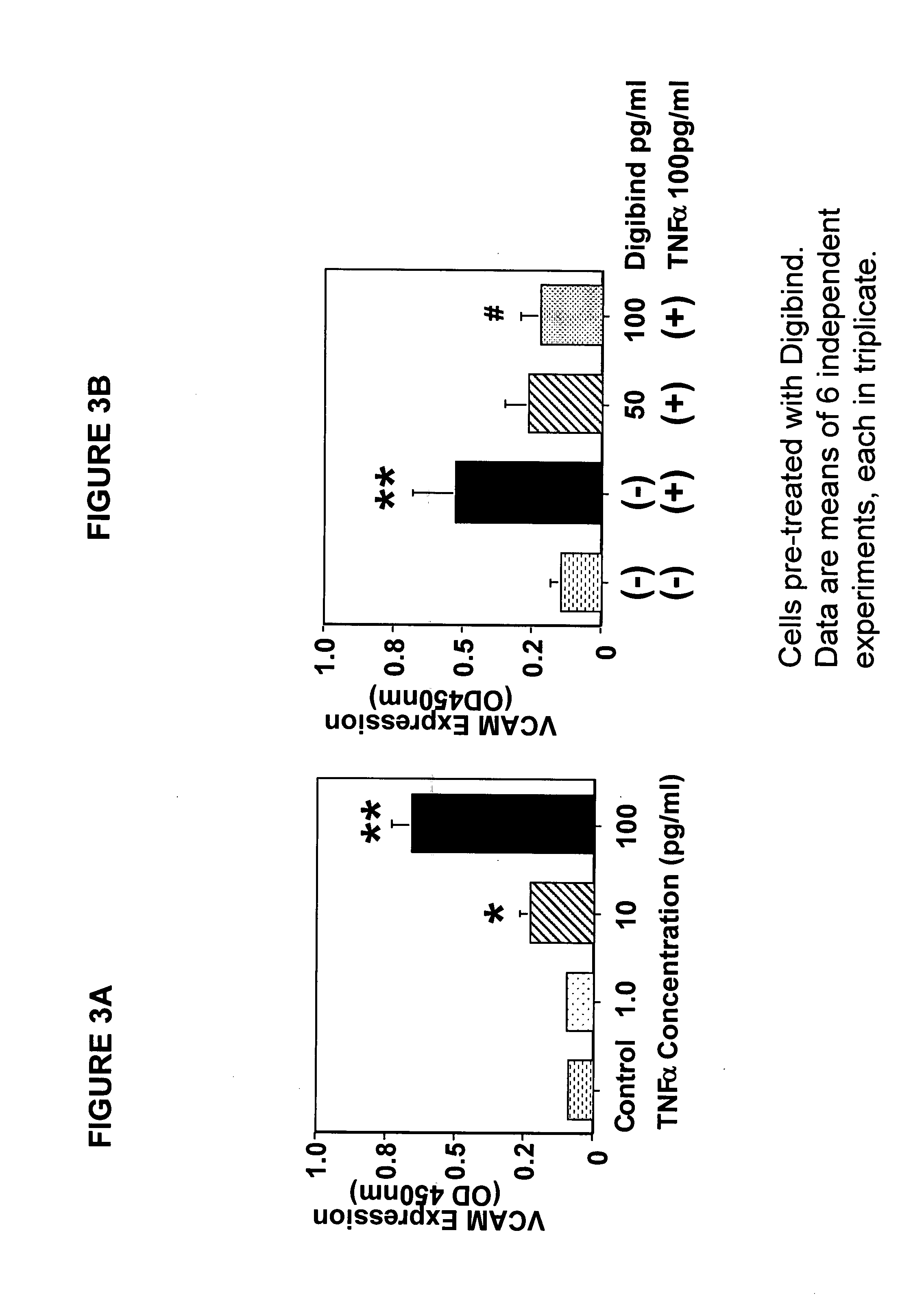
Composition for modulating the expression of cell adhesion molecules
InactiveUS20080003230A1Adverse side-effectIncreased riskAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticCell adhesionAdhesion process
A composition is provided for modulating or attenuating the cytokine induced cell surface expression of cell adhesion molecules, comprising an antibody that binds digoxin. There is also provided a method of modulating or attenuating the cytokine induced cell surface expression of a cell adhesion molecule in a patient by administering to a digoxin antibody composition to a patient in need of such treatment.
Owner:GLENVEIGH PHARMA
NOVEL a4B7 PEPTIDE DIMER ANTAGONISTS
InactiveUS20190002500A1Strong specificityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticBiochemistryIn vivo
The invention relates to disulfide-rich dimer molecules which inhibit binding of α4β7 to the mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule (MAdCAM) in vivo, and show high selectivity against α4β1 binding.
Owner:PROTAGONIST THERAPEUTICS INC
MCAM modulation and uses thereof
ActiveUS8293468B2Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderMelanoma Cell Adhesion MoleculeNeural cell adhesion molecule
Methods, uses, agents and compositions useful for the diagnosis, prevention and / or treatment of inflammatory conditions, such as neuroinflammatory conditions such as multiple sclerosis, and for the identification and selection of inflammatory cytokine-secreting T cell or a precursor thereof, based on the expression and / or modulation of melanoma cell adhesion molecule (MCAM) are disclosed.
Owner:VAL CHUM PARTNERSHIP
Cancer therapy
A method is provided for treating mammals, including humans, with advanced or large-tumour burdens. The method involves administering an immunotherapeautic agent in conjunction with a tumour growth restricting agent, in amounts effective to eradicate any advanced or large tumours present. In preferred embodiments, the immunotherapeautic agent comprises a T-cell co-stimulatory cell adhesion molecule (CAM) or a mammalian expression vector containing DNA which encodes a T-cell co-stimulatory CAM, such as B7.1, and the tumour growth restricting agent is flavone acetic acid, 5,6-dimenthyl-xanthenone-4-acetic acid, or an agent which disrupts the expression or activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1).
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD +1
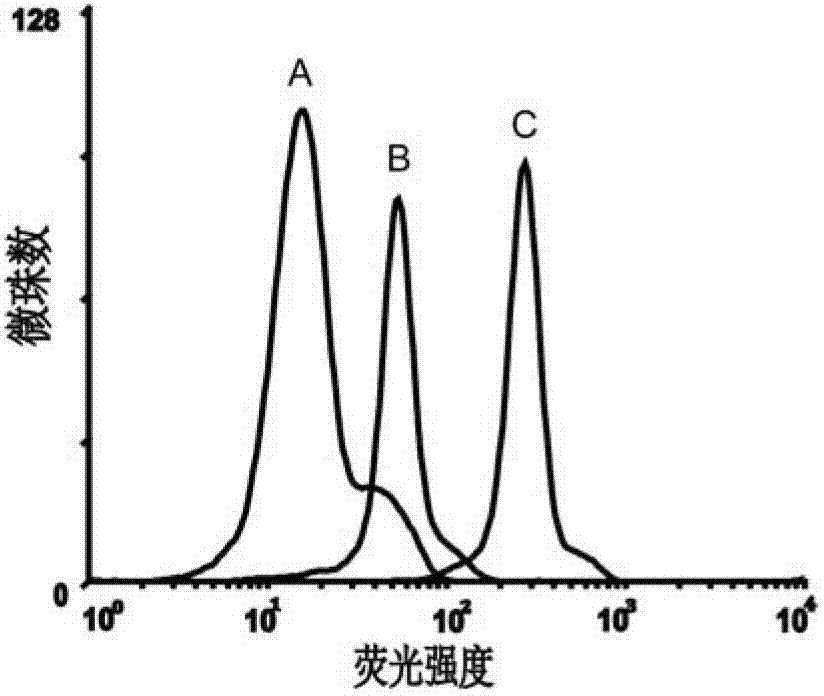
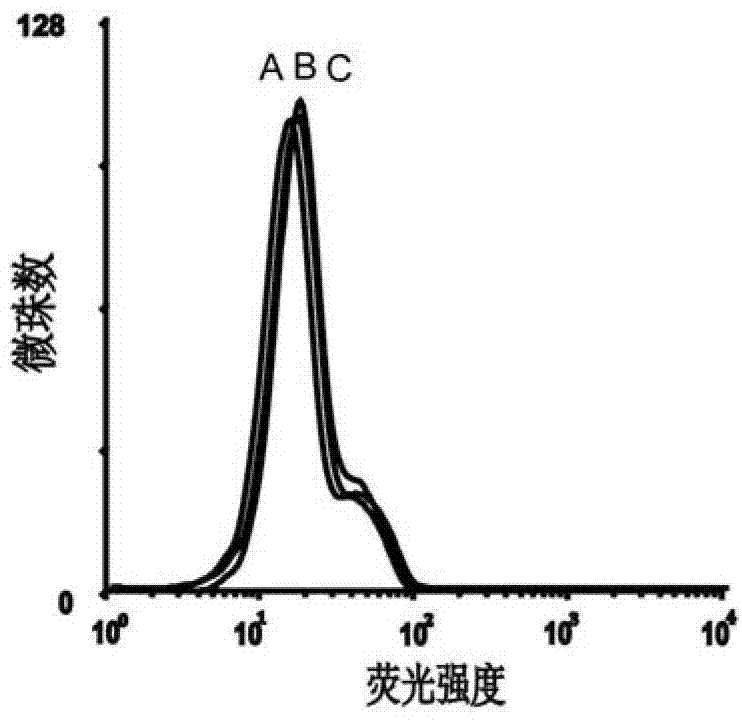
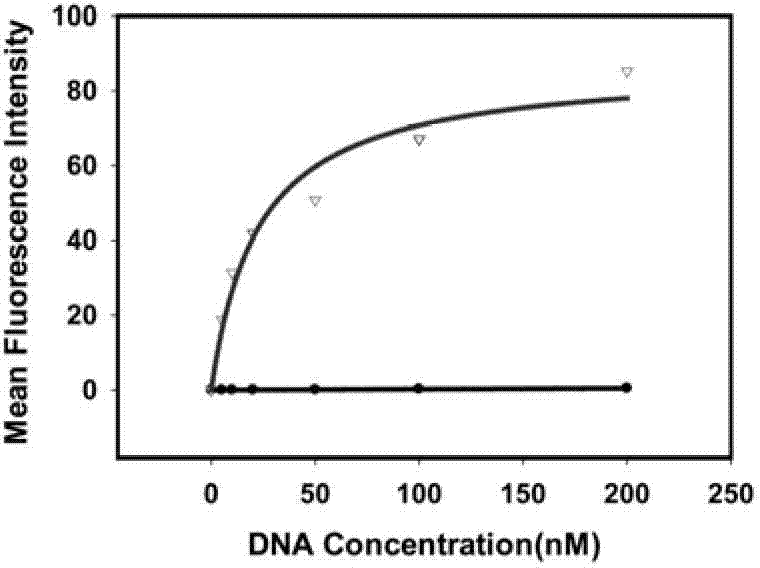
Aptamer EpCAM (epithelial cell adhesion molecule) Ccut of EpCAM and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103387988AMaintain native conformationNo toxicityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationProtein targetNeural cell adhesion molecule
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Therapeutic avenathramide compounds
InactiveUS20050239892A1Delay disease progressionAvoid formingOrganic active ingredientsBiocideArteriolar VasoconstrictionCell adhesion
Methods and compositions are disclosed for reducing pro-inflammatory molecules, adhesion molecules, and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, and for increasing NO production. The present invention describes the use of phenolic compositions, purified from oats or synthetically produced, to decrease the effective amount of pro-inflammatory molecules and / or cell adhesion molecules. Alternatively, an alcoholic extract or concentrate from oats can be used. The methods of the present invention can be used as a treatment or prophylaxis of a wide variety of disorders associated with inflammatory states and / or with a lack of or need for nitric oxide (NO), such as inflammatory conditions, pain, free radical associated disorders, cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune disorders, pathological platelet aggregation, pathological vasoconstriction, vascular effects of diabetes, stroke, atherosclerosis, hypertension, abnormal vasospasm, and restenosis after angioplasty.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
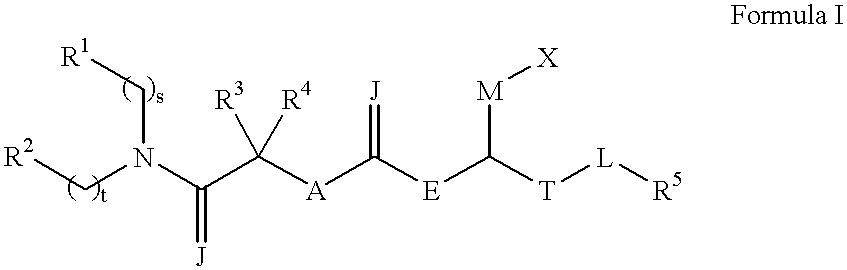
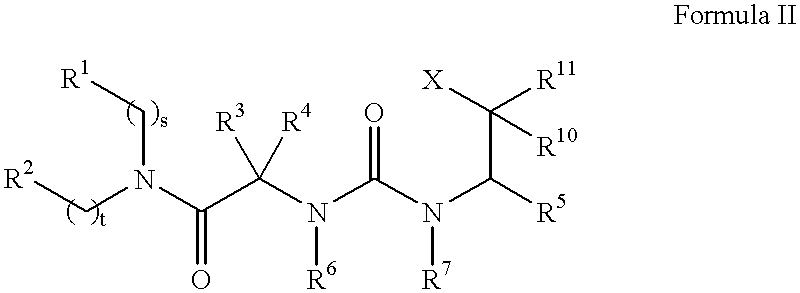
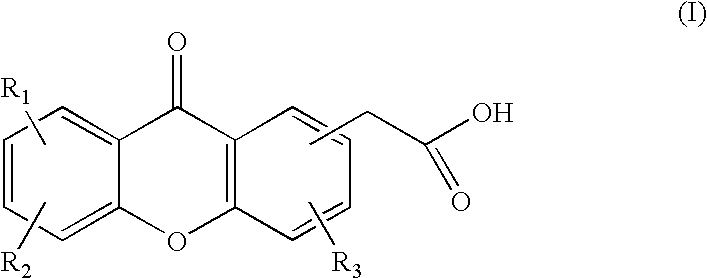
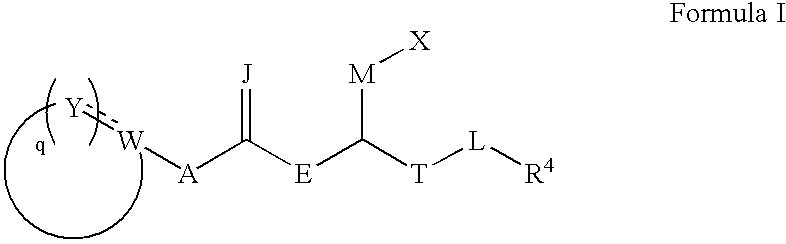
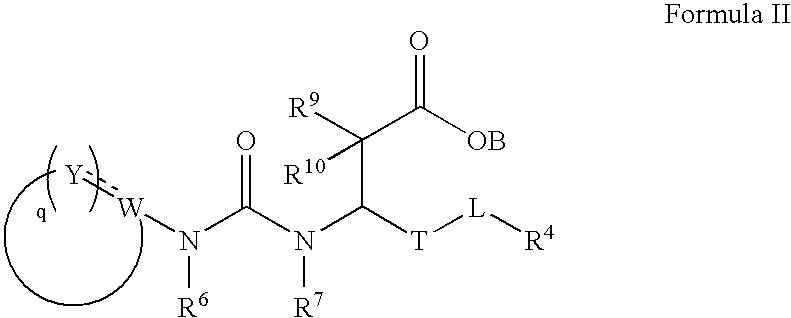
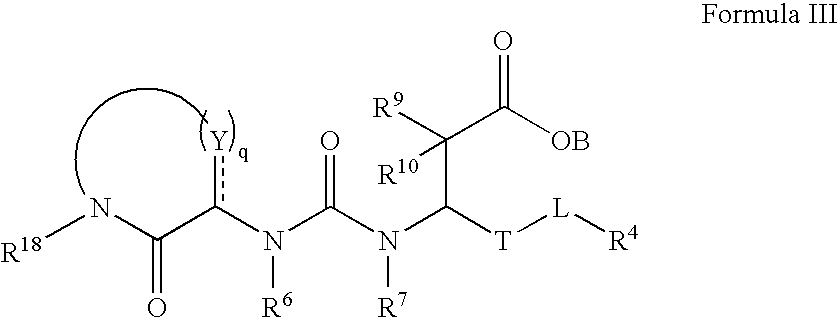
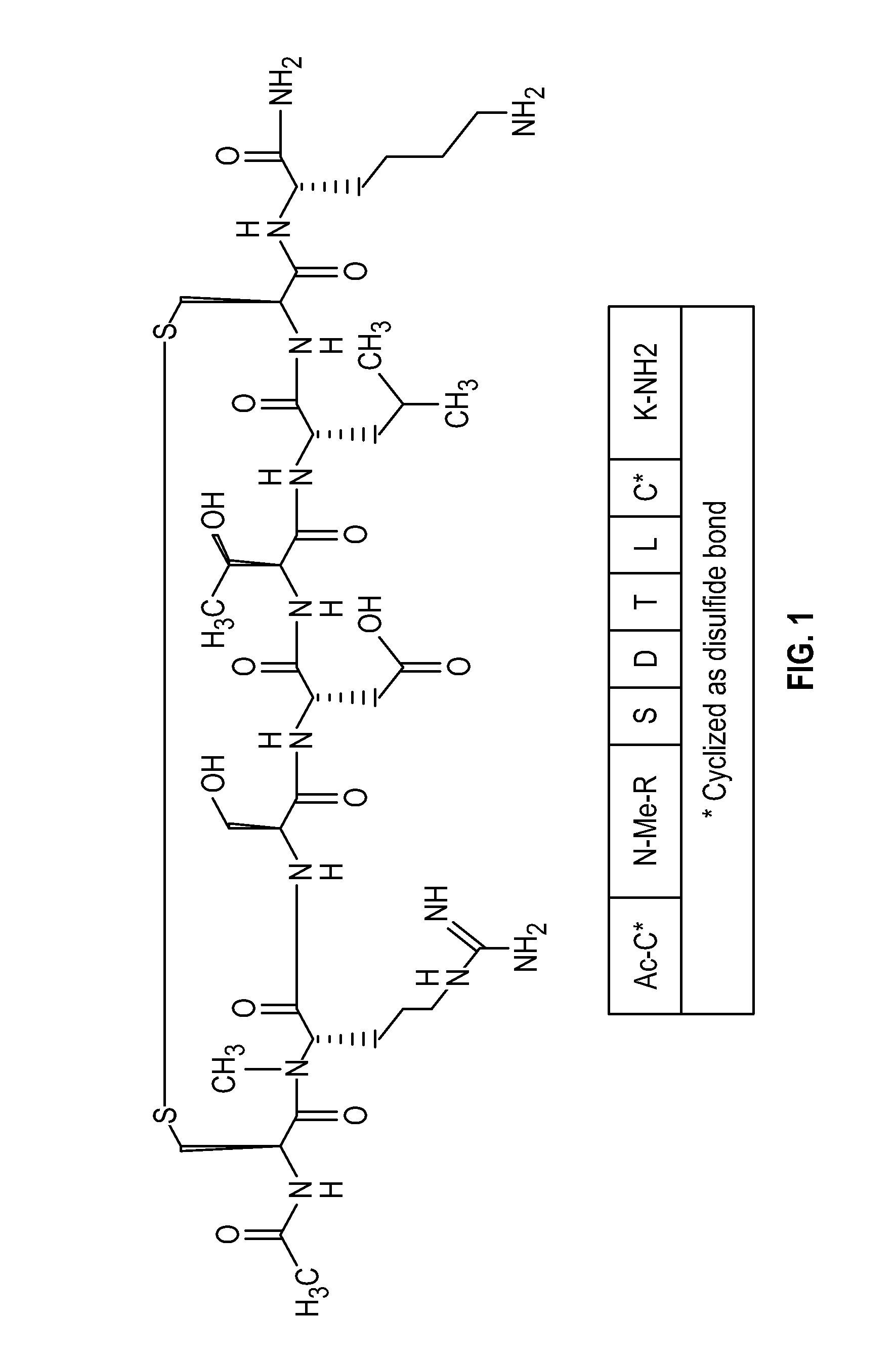
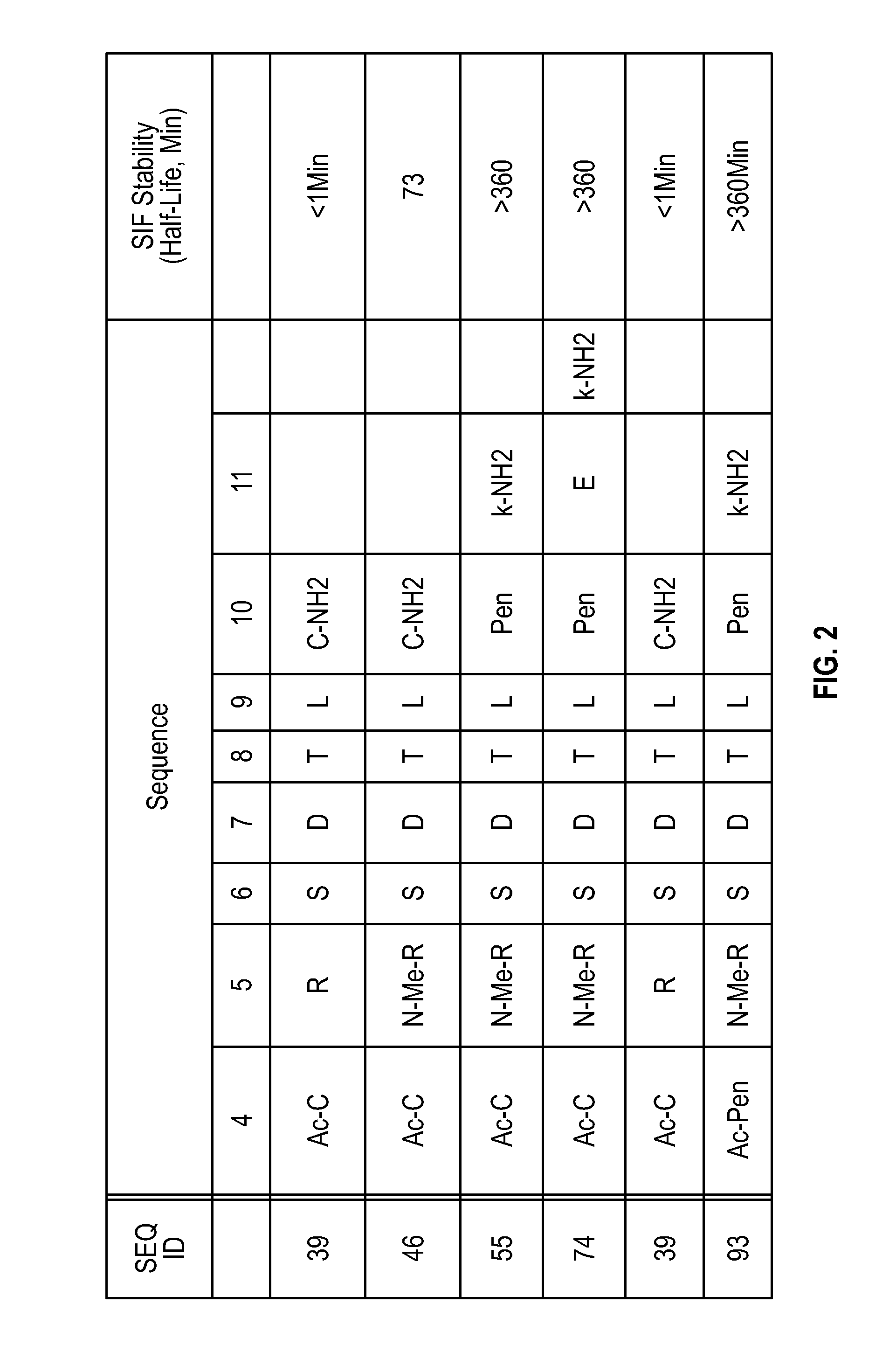
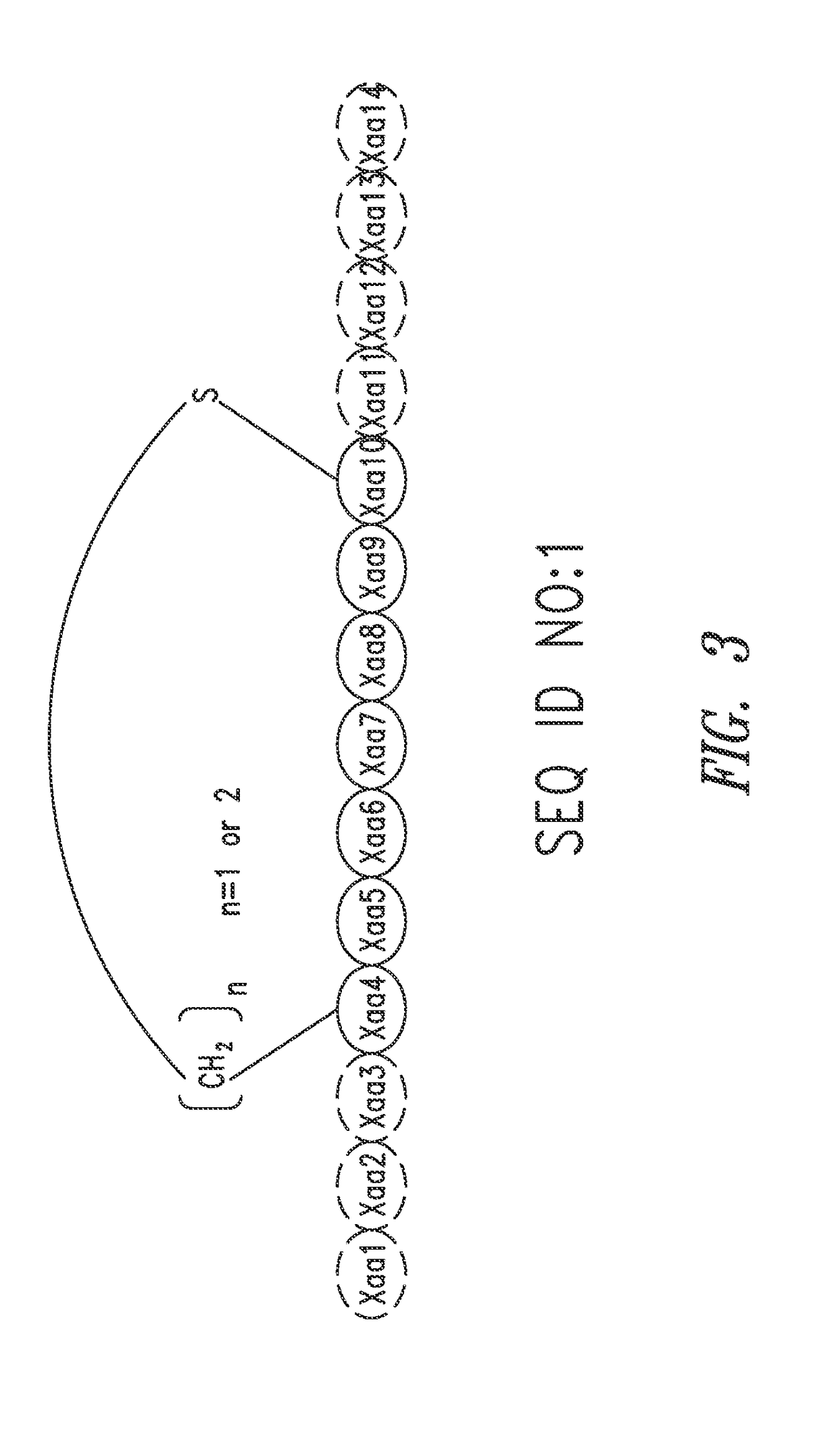
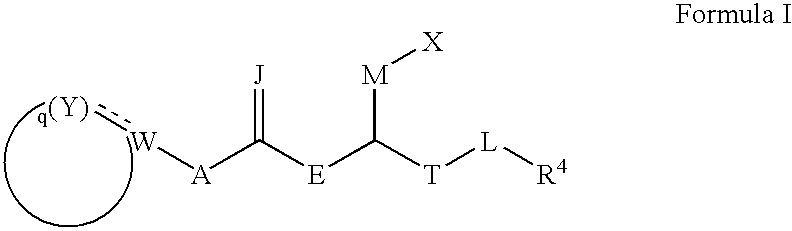
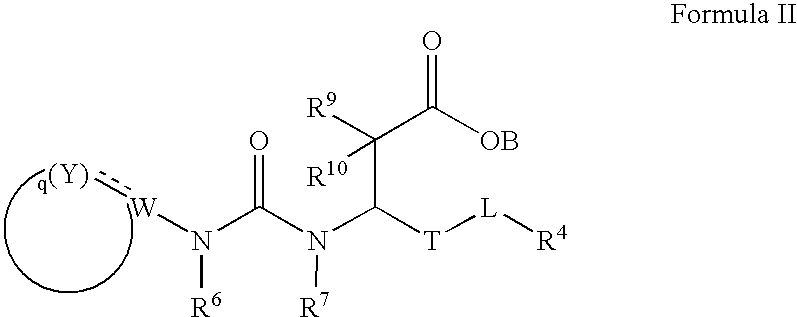
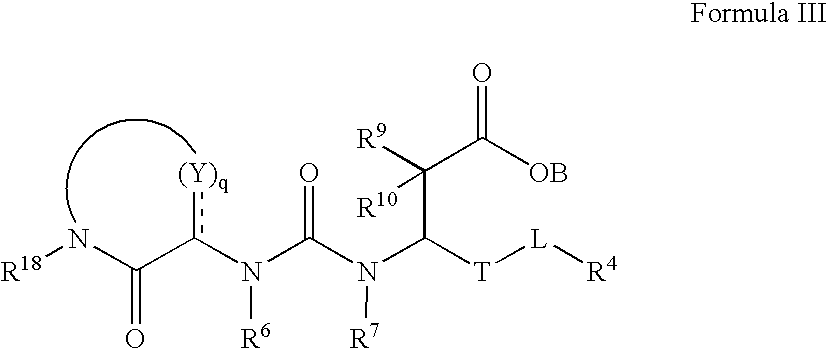
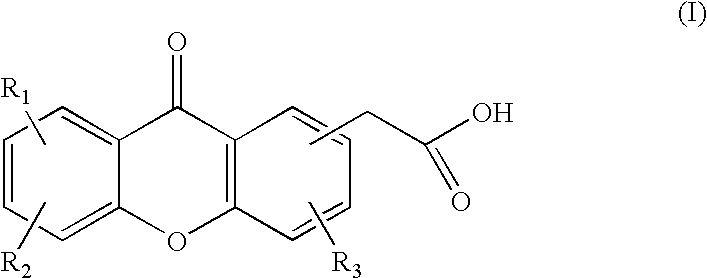
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising thieno[2,3-c]pyridine derivatives and use thereof
Owner:RIMONYX PHARMA
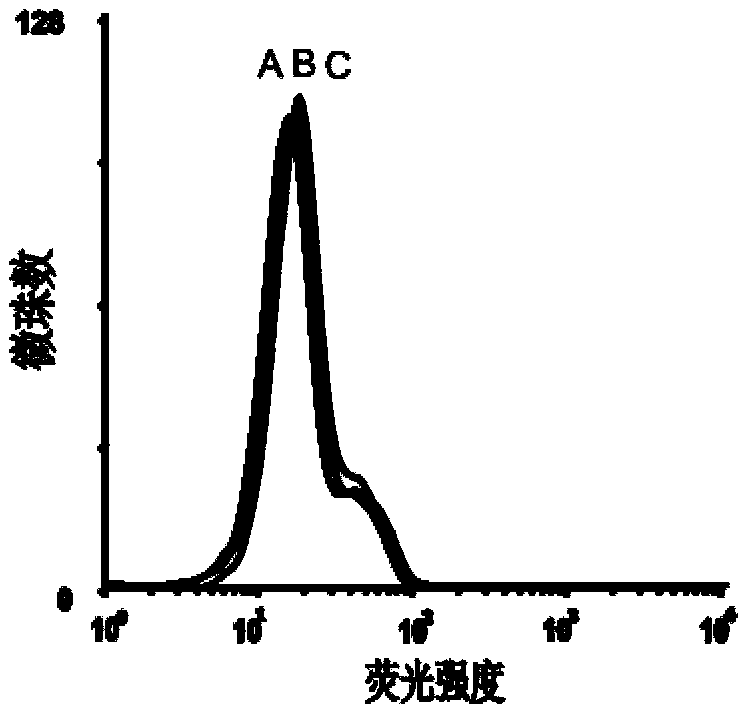
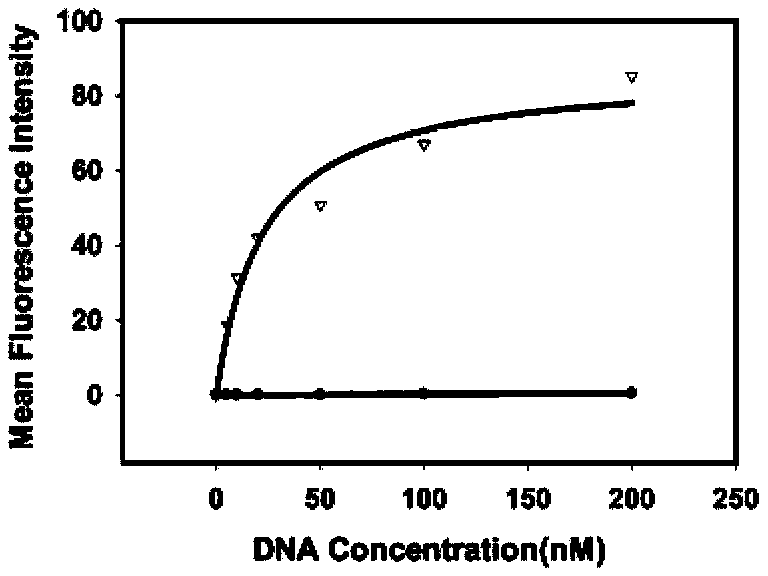
Nucleic acid aptamer of epithelial cell adhesion molecule and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102827845AMaintain native conformationNo toxicityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein targetSingle strand dna
The invention relates to a nucleic acid, in particular to a nucleic acid aptamer of the epithelial cell adhesion molecule and a preparation method thereof. The invention provides a high-specificity and high-affinity nucleic acid aptamer of the epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM and a preparation method and applications thereof. The nucleic acid aptamer of the epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM is of the G-quadruplex structure or the stem-loop structure. The preparation method comprises the following steps: designing and synthetizing a single-stranded DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) random oligonucleotide library, screening the target oligonucleotide sequence, and identifying the binding specificity and affinity of the sequence to the target protein through the flow cytometry. The screened nucleic acid aptamer is non-toxic, has small molecular weight and good permeability, is easy in synthesis and marking and can only perform specific identification to the EpCAM protein and perform specific identification and specific expression to the cell line of the EpCAM protein; and the nucleic acid aptamer can not identify the cell line which does not express the protein.
Owner:苏州德运康瑞生物科技有限公司
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
InactiveCN102792161AEasy to understandDisease diagnosisBiological testingBCL2 ANTAGONISTCell adhesion
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for monitoring, diagnosis, prognosis, and determination of treatment regimens in subjects suffering from or suspected of having a renal injury. In particular, the invention relates to using assays that detect one or more biomarkers selected from the group consisting of Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1OB, Cadherin-16, Caspase-9, Bcl2 antagonist of cell death, Caspase-1, Cadherin-1, Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1, Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1, Cadherin-5, Myoglobin, Apolipoprotein A-II, Mucin-16, Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5, and Cellular tumor antigen p53 as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker assays in renal injuries.
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

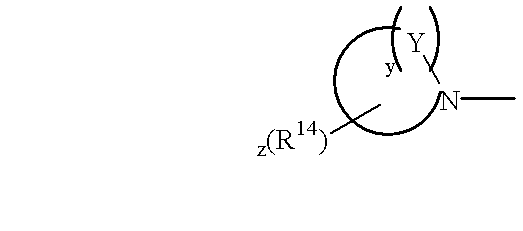

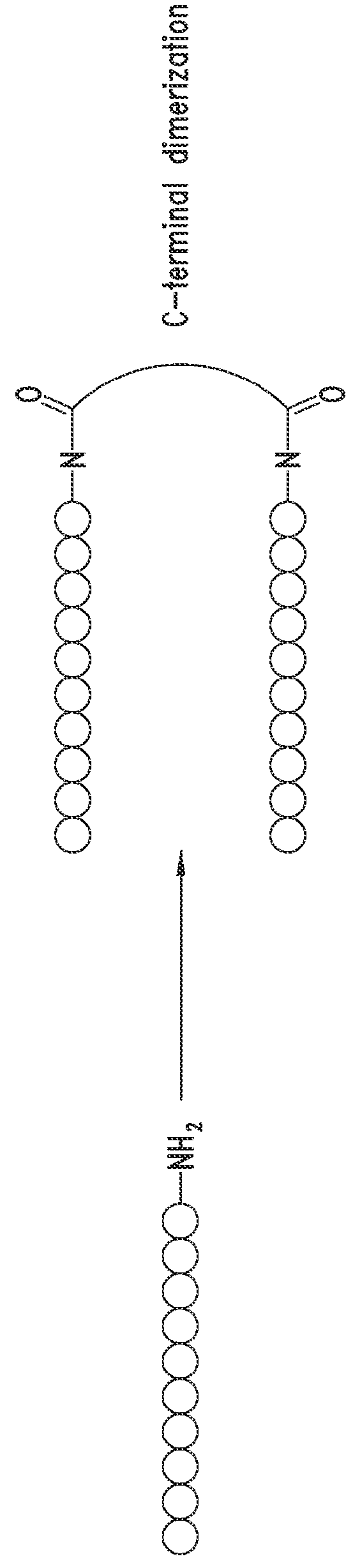
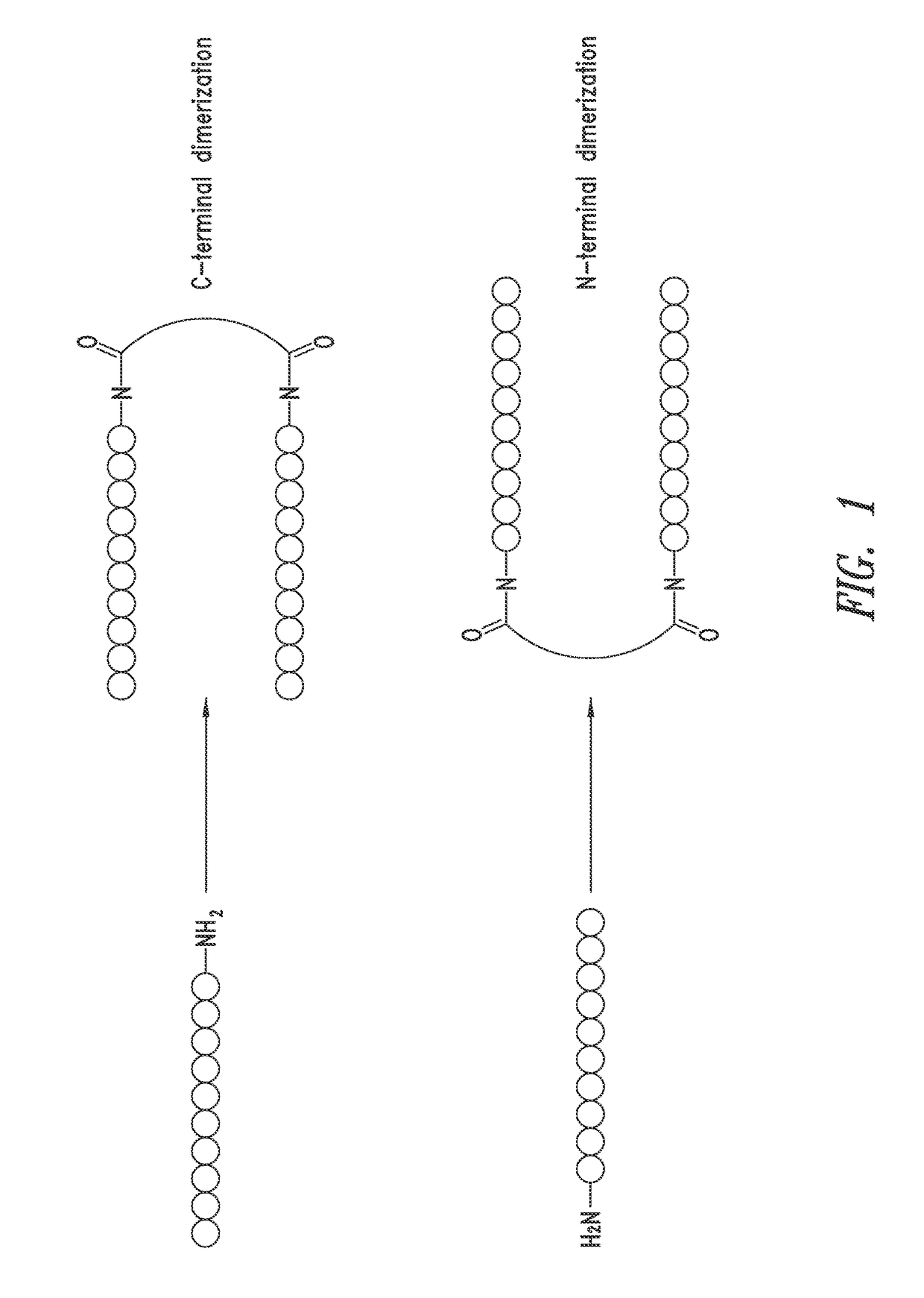

![Pharmaceutical compositions comprising thieno[2,3-c]pyridine derivatives and use thereof Pharmaceutical compositions comprising thieno[2,3-c]pyridine derivatives and use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/024957e9-86f4-47e0-9129-7e635a2abbe3/US07365080-20080429-D00001.png)
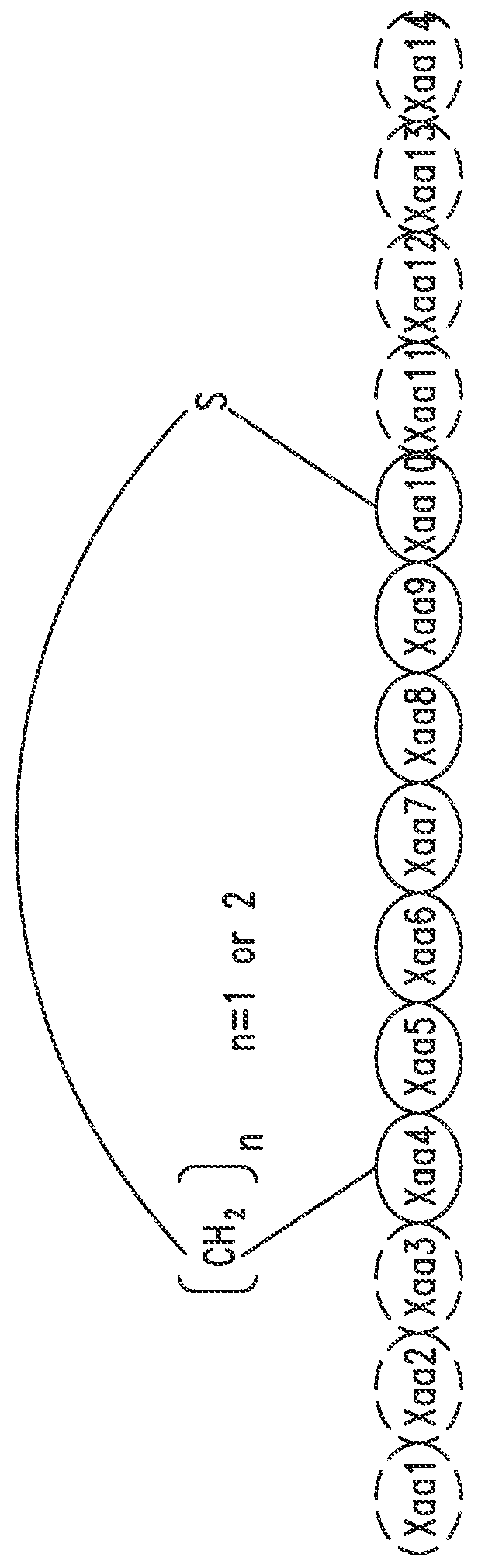
![Pharmaceutical compositions comprising thieno[2,3-c]pyridine derivatives and use thereof Pharmaceutical compositions comprising thieno[2,3-c]pyridine derivatives and use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/024957e9-86f4-47e0-9129-7e635a2abbe3/US07365080-20080429-D00002.png)
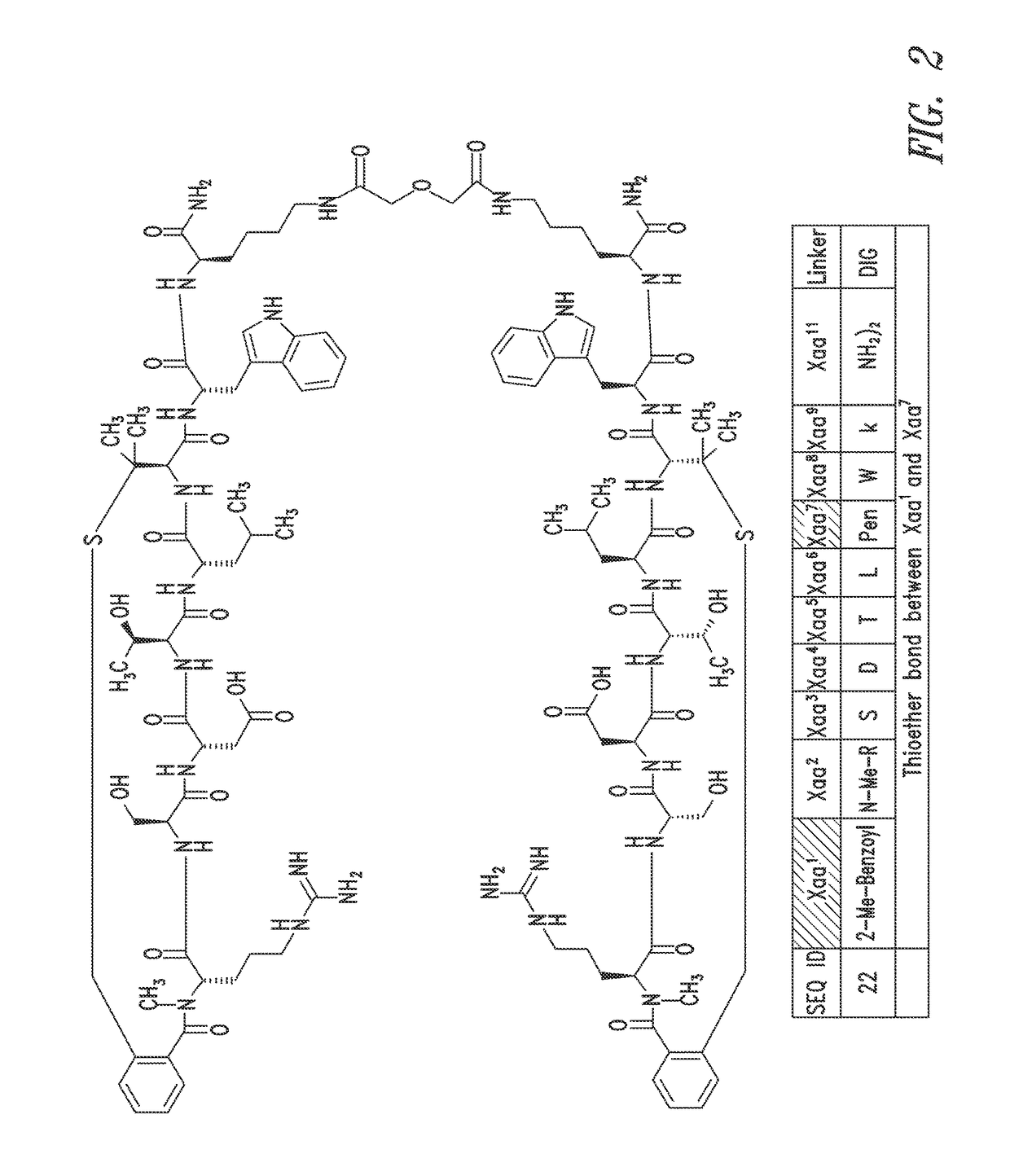
![Pharmaceutical compositions comprising thieno[2,3-c]pyridine derivatives and use thereof Pharmaceutical compositions comprising thieno[2,3-c]pyridine derivatives and use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/024957e9-86f4-47e0-9129-7e635a2abbe3/US07365080-20080429-D00003.png)