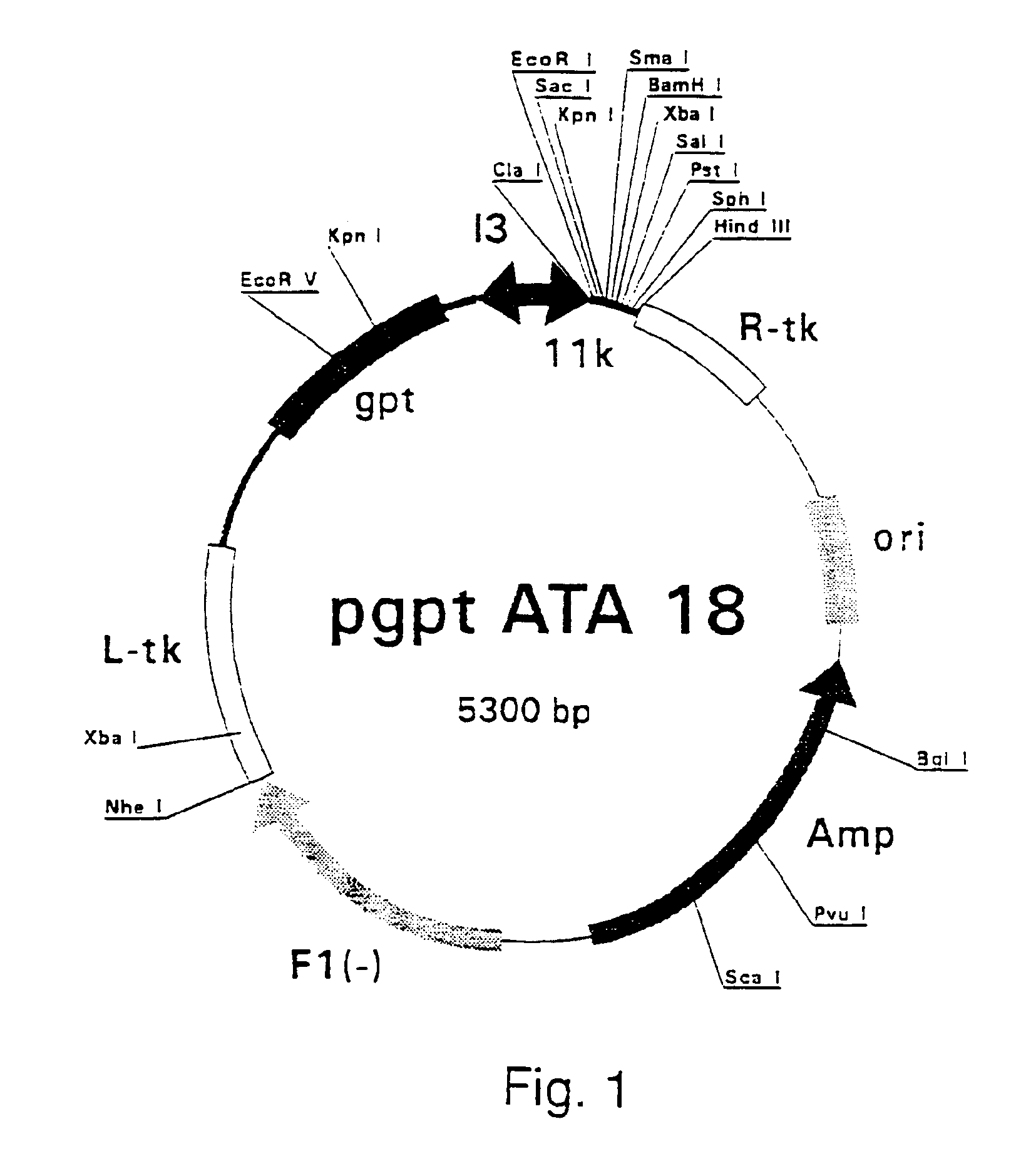
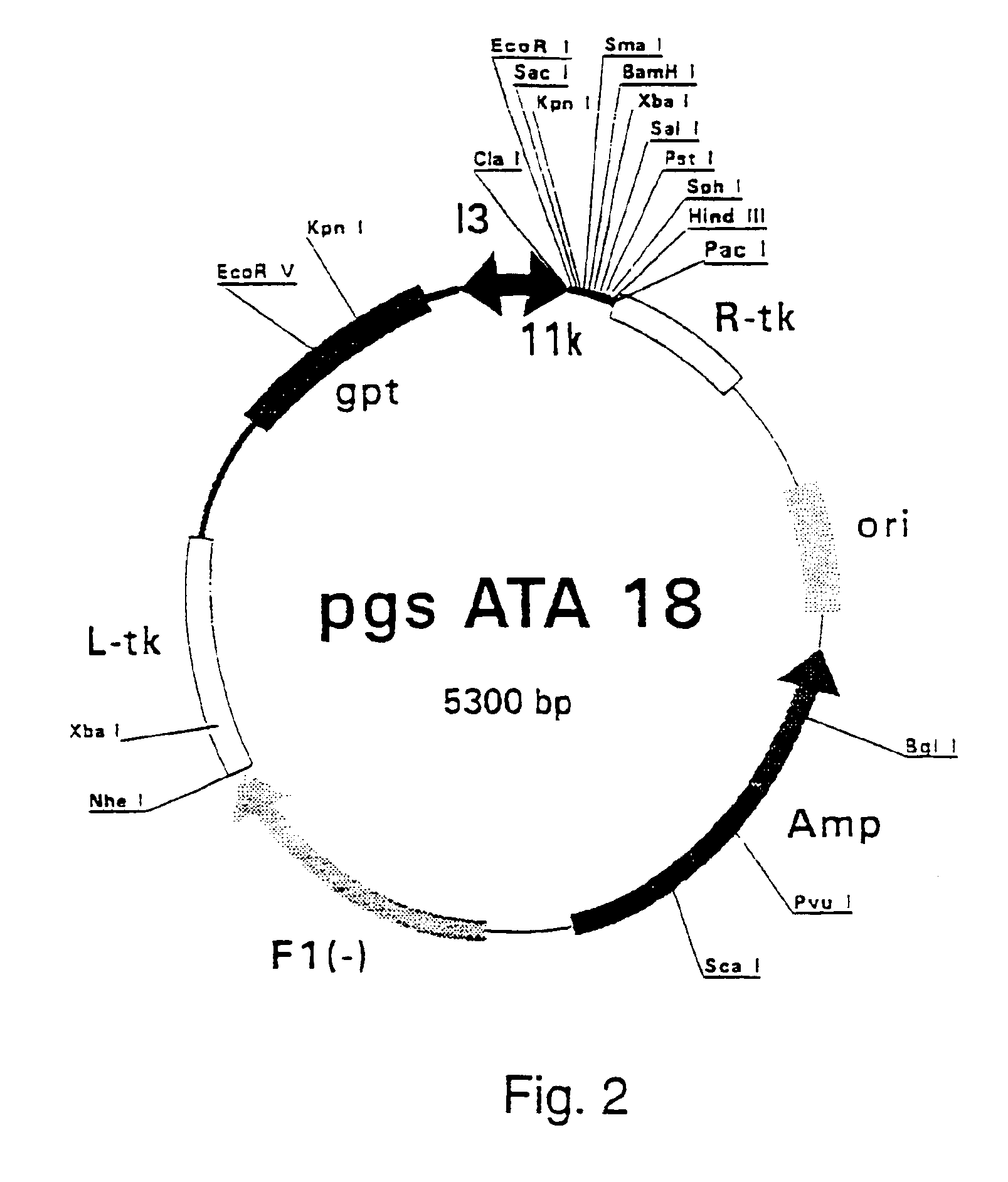
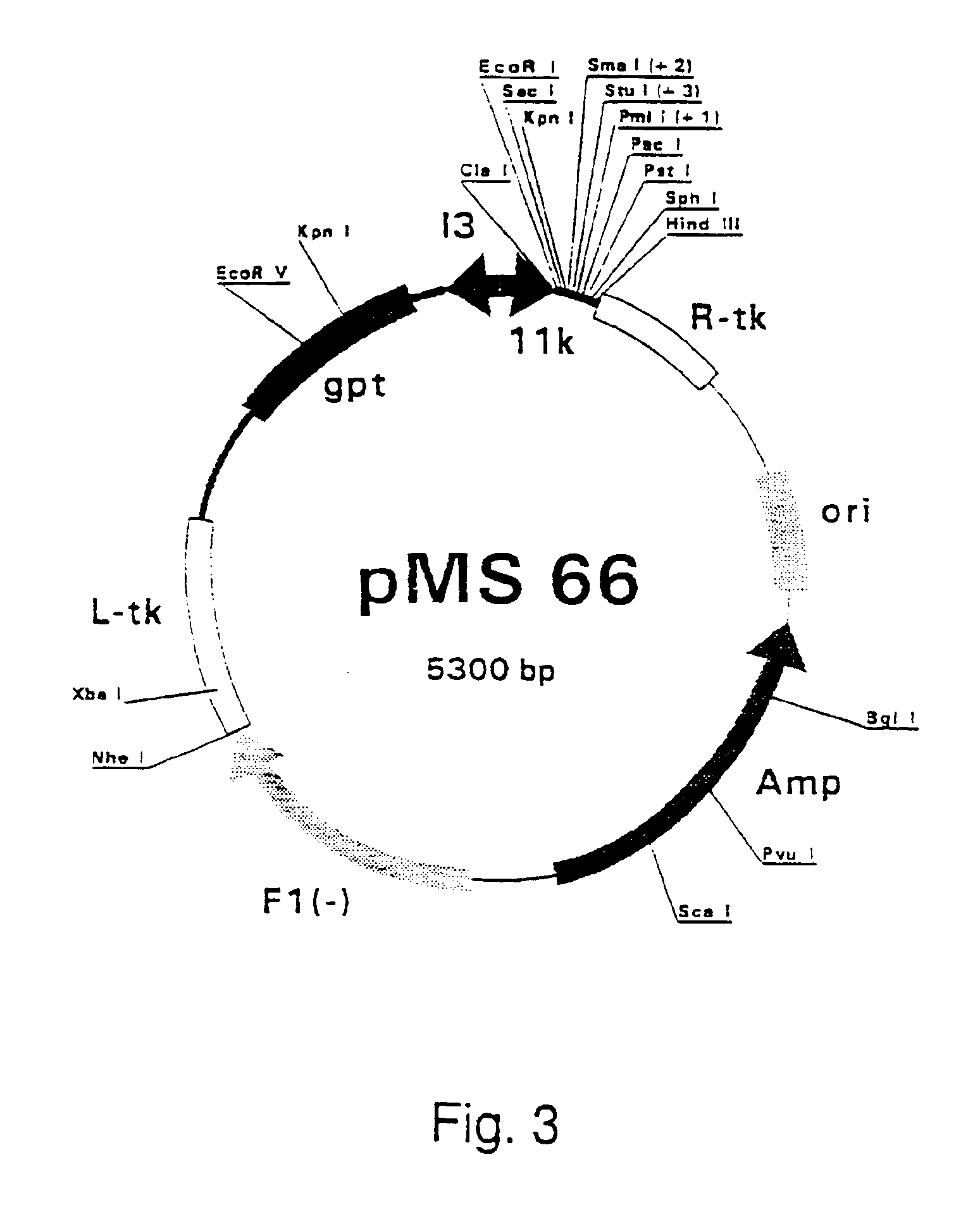
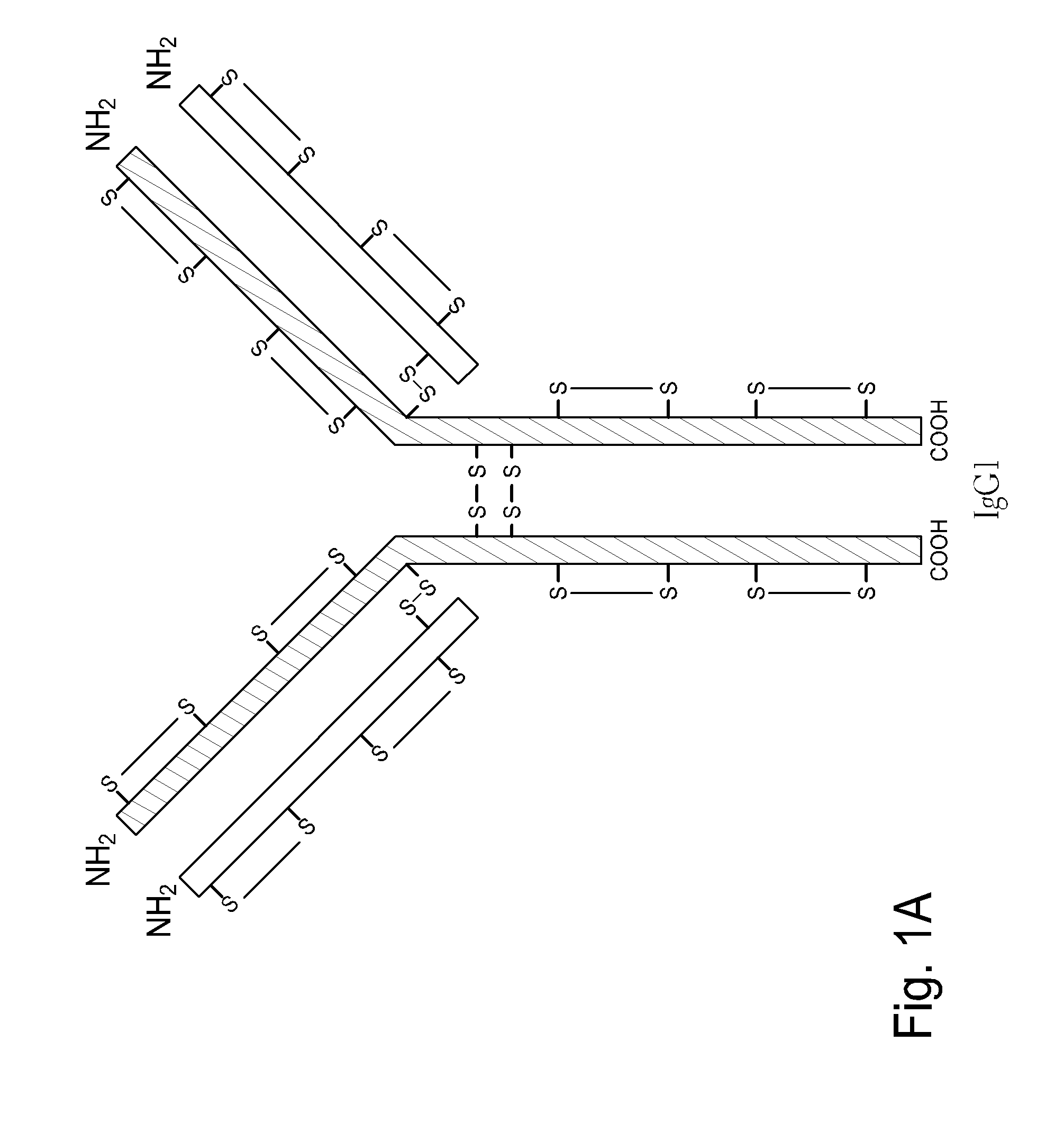
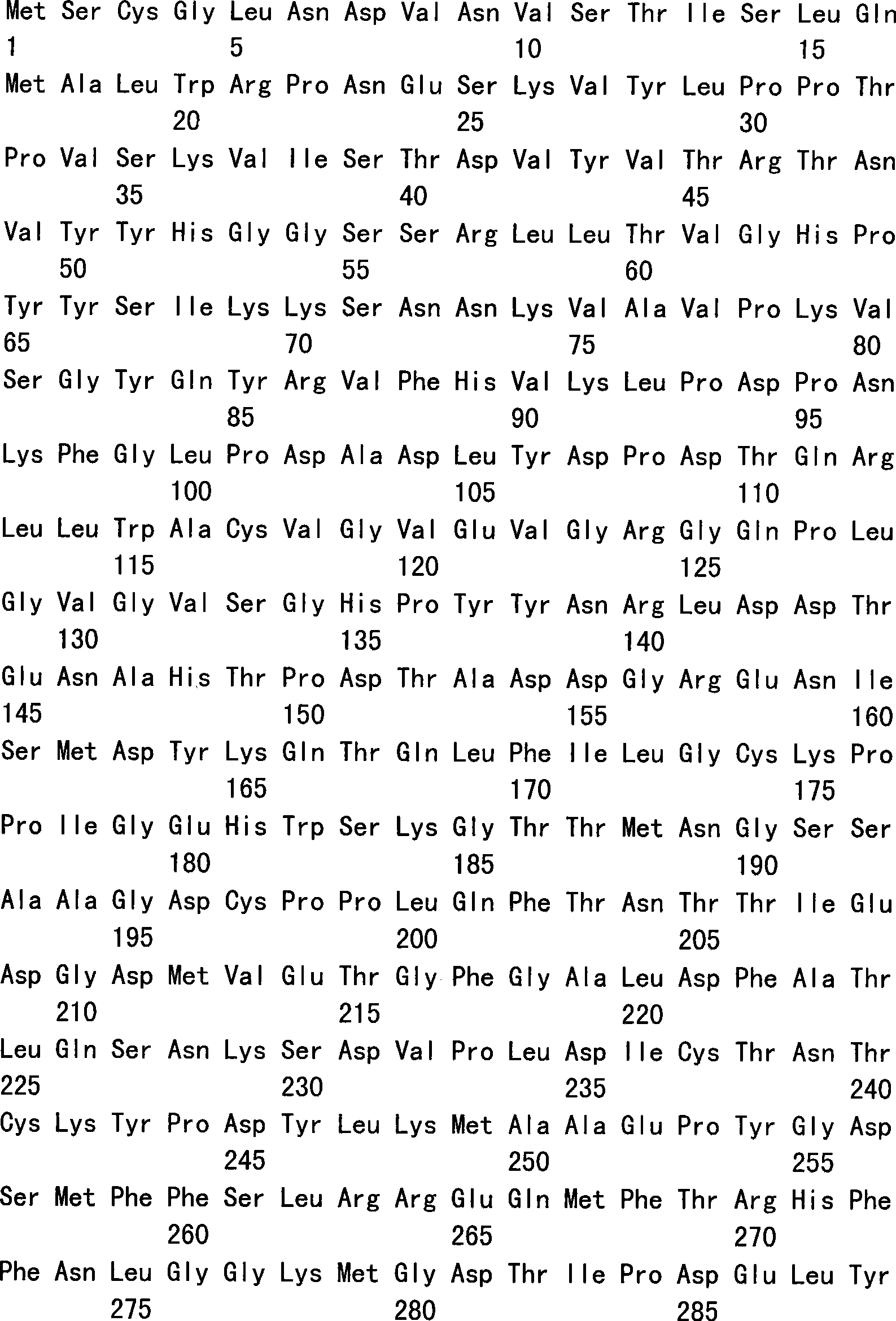Patents
Literature
135 results about "Disulphide bonds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
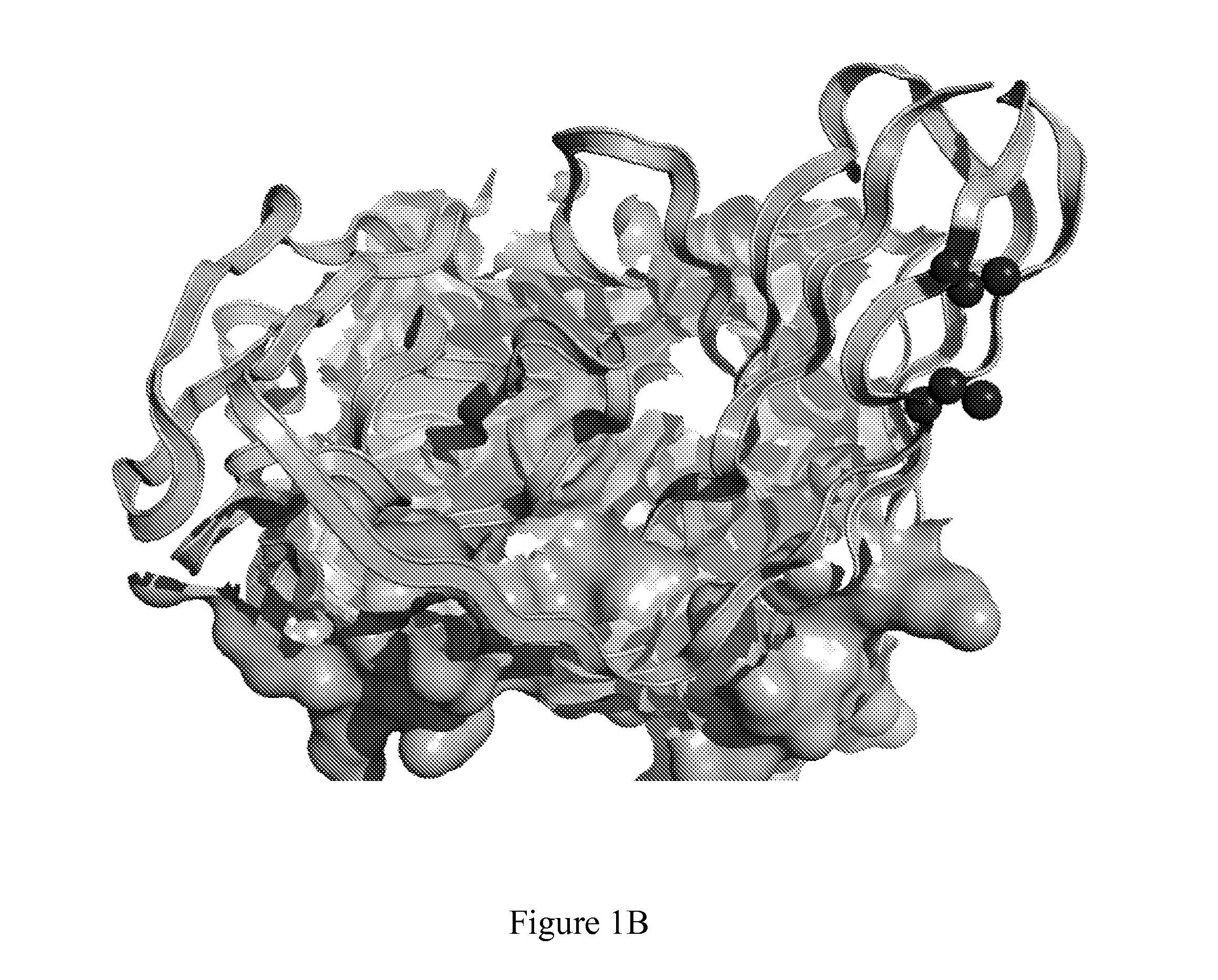
Disulphide bond. Definition. noun. (chemistry) (1) The single covalent bond formed from the coupling of thiol groups, especially of cysteine residues. (2) The linkage formed by the oxidation of two SH groups, each attached to a cysteine, stabilizing the structure of many protein molecules (during protein synthesis).
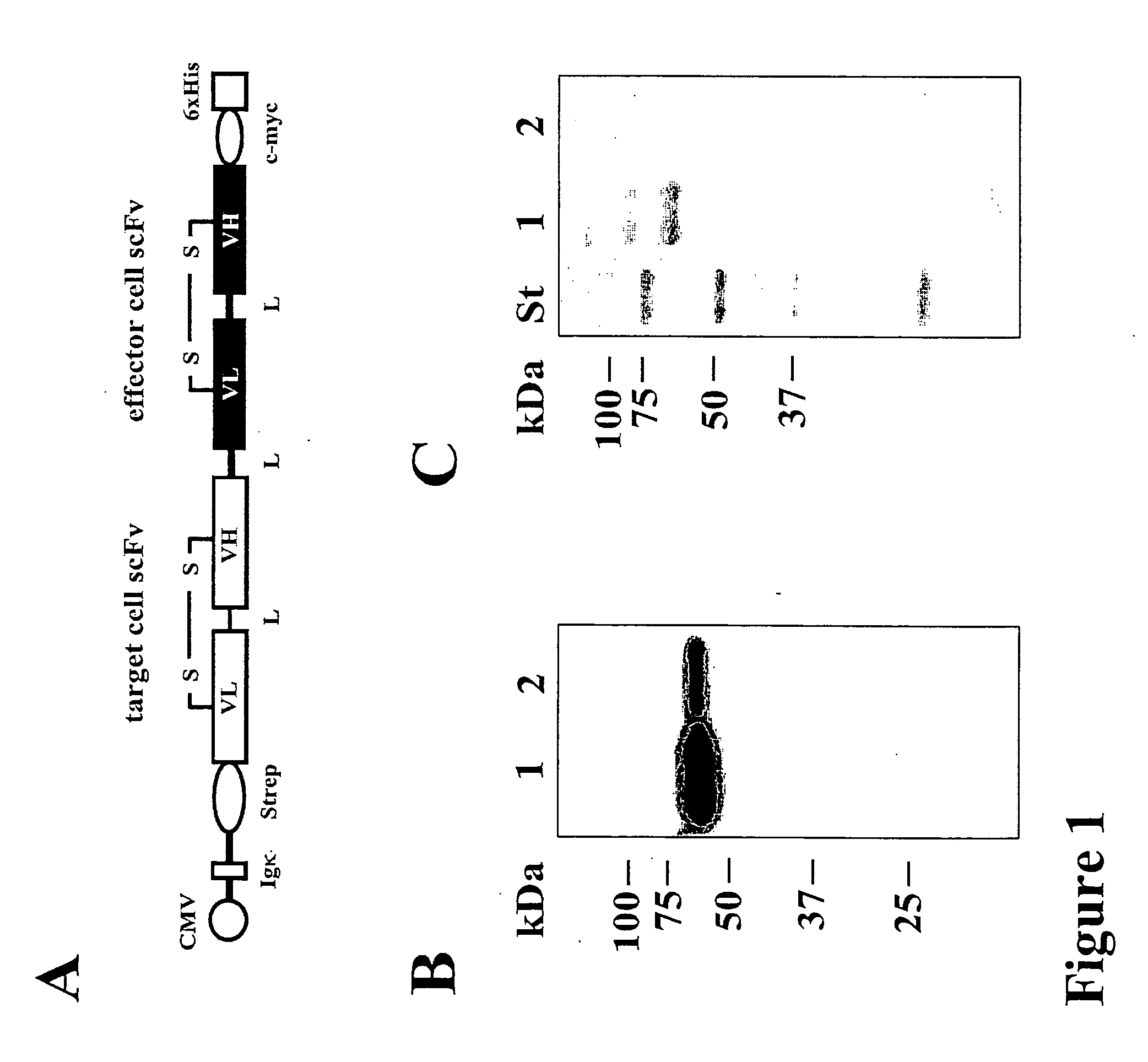
Bispecific antibody devoid of Fc region and method of treatment using same
InactiveUS20060263367A1Efficient productionAvoids undesirable effector functionHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBispecific antibodyAntigen binding
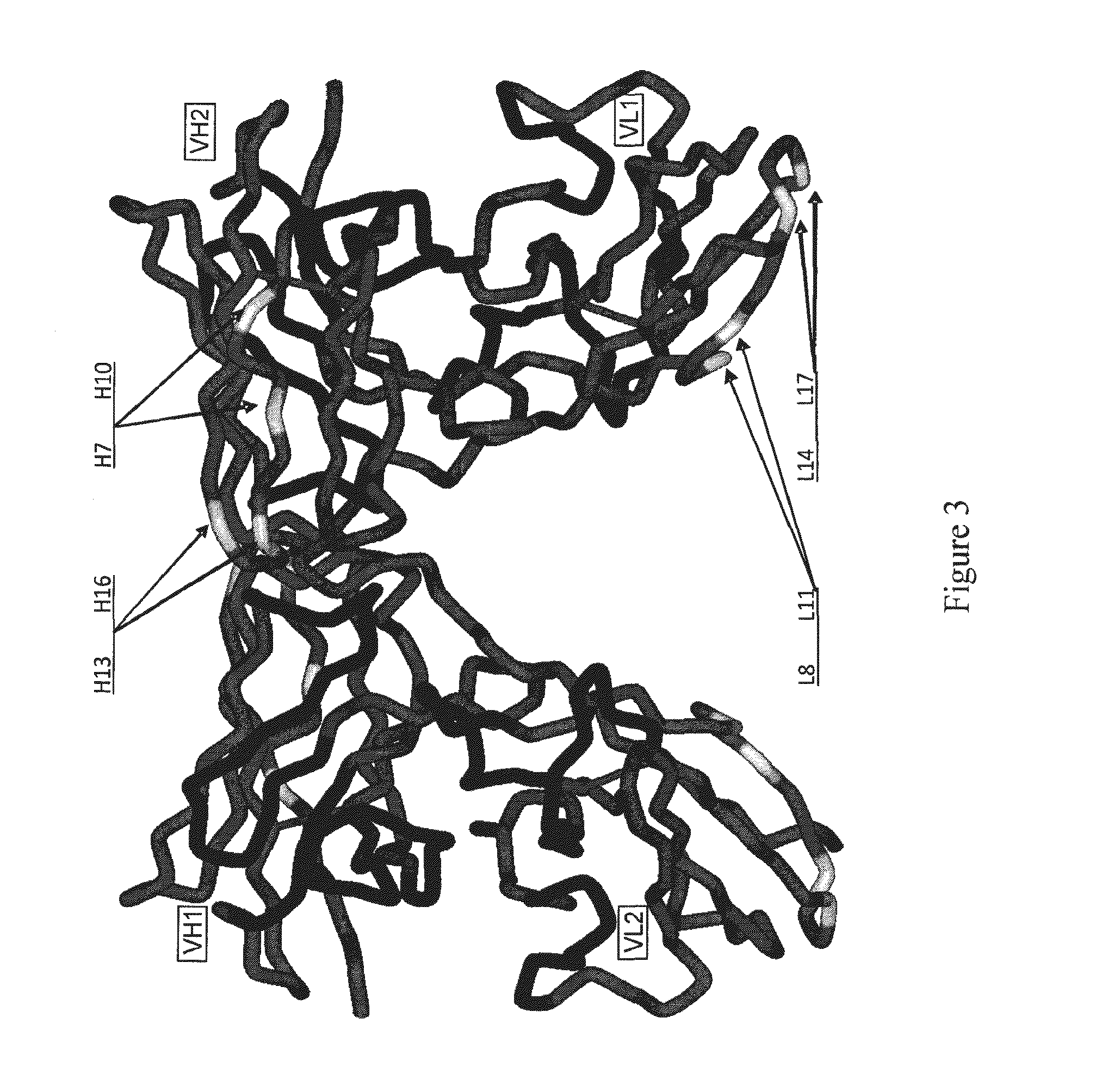
Bispecific antibody derivatives are disclosed which are comprised of a first region which binds to a first antigen and a second region which binds to a second antigen different from the first antigen. The first and second regions of the bispecific antibody are each stabilized by an additional internal disulfide bridge, and connected by a flexible polypeptide linker. The bispecific antibody is devoid of an Fc portion and is encoded as a single chain-sequence.
Owner:FRIEDRICH ALEXANDER UNIV ERLANGEN NURNBERG
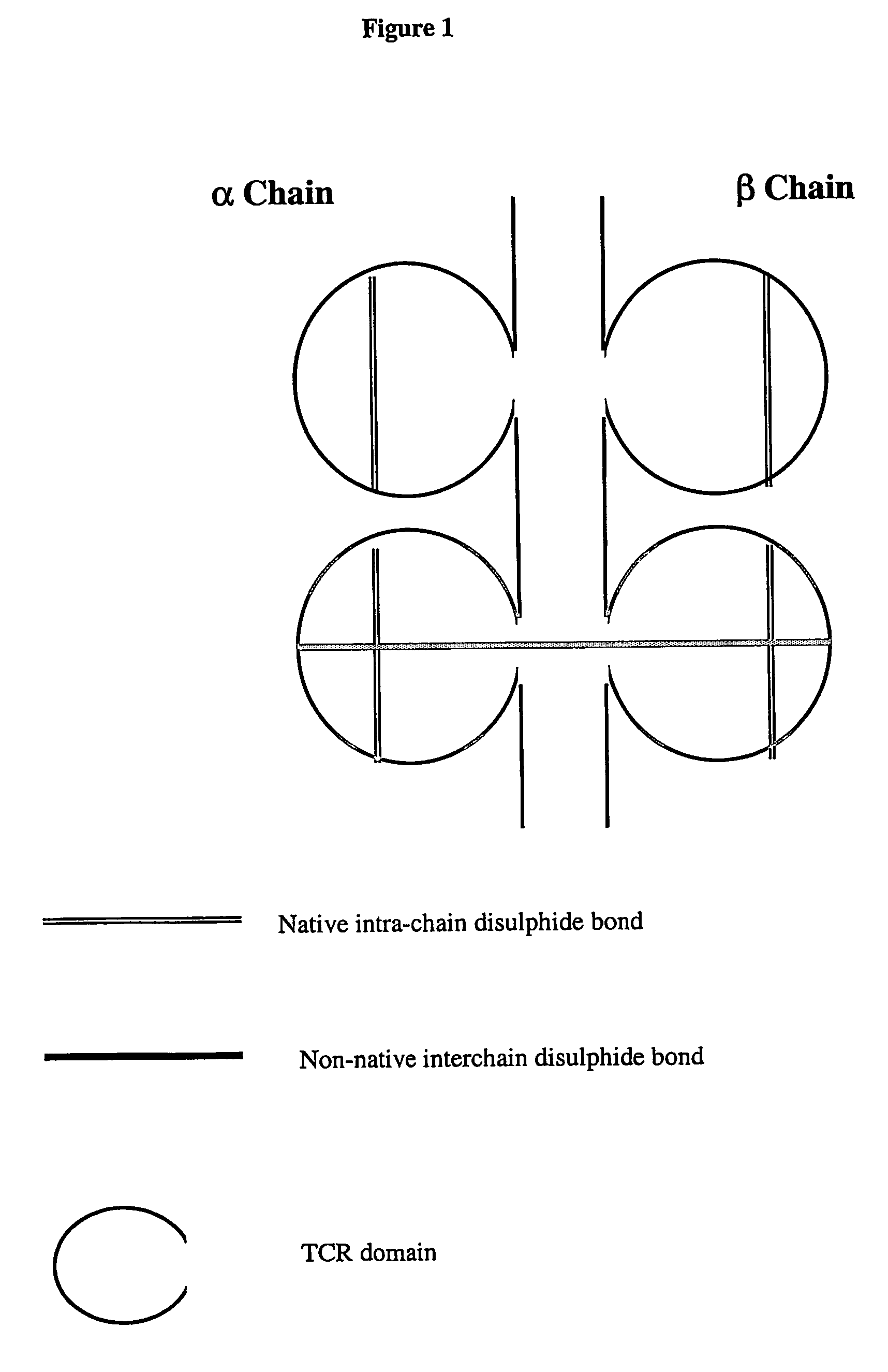
Modified soluble T cell receptor
The present invention provides a soluble T cell receptor (sTCR), which comprises (i) all or part of a TCR $g(a) chain, except the transmembrane domain thereof, and (ii) all or part of a TCR $g(b) chain, except the transmembrane domain thereof. (i) and (ii) each comprise a functional variable domain and at least a part of the constant domain of the TCR chain, and are linked by a disulphide bond between constant domain residues which is not present in native TCR, characterized in that the sTCR recognizes a CD1-antigen complex, a bacterial superantigen or a peptide-MHC / superantigen complex.
Owner:IMMUNOCORE LTD +1
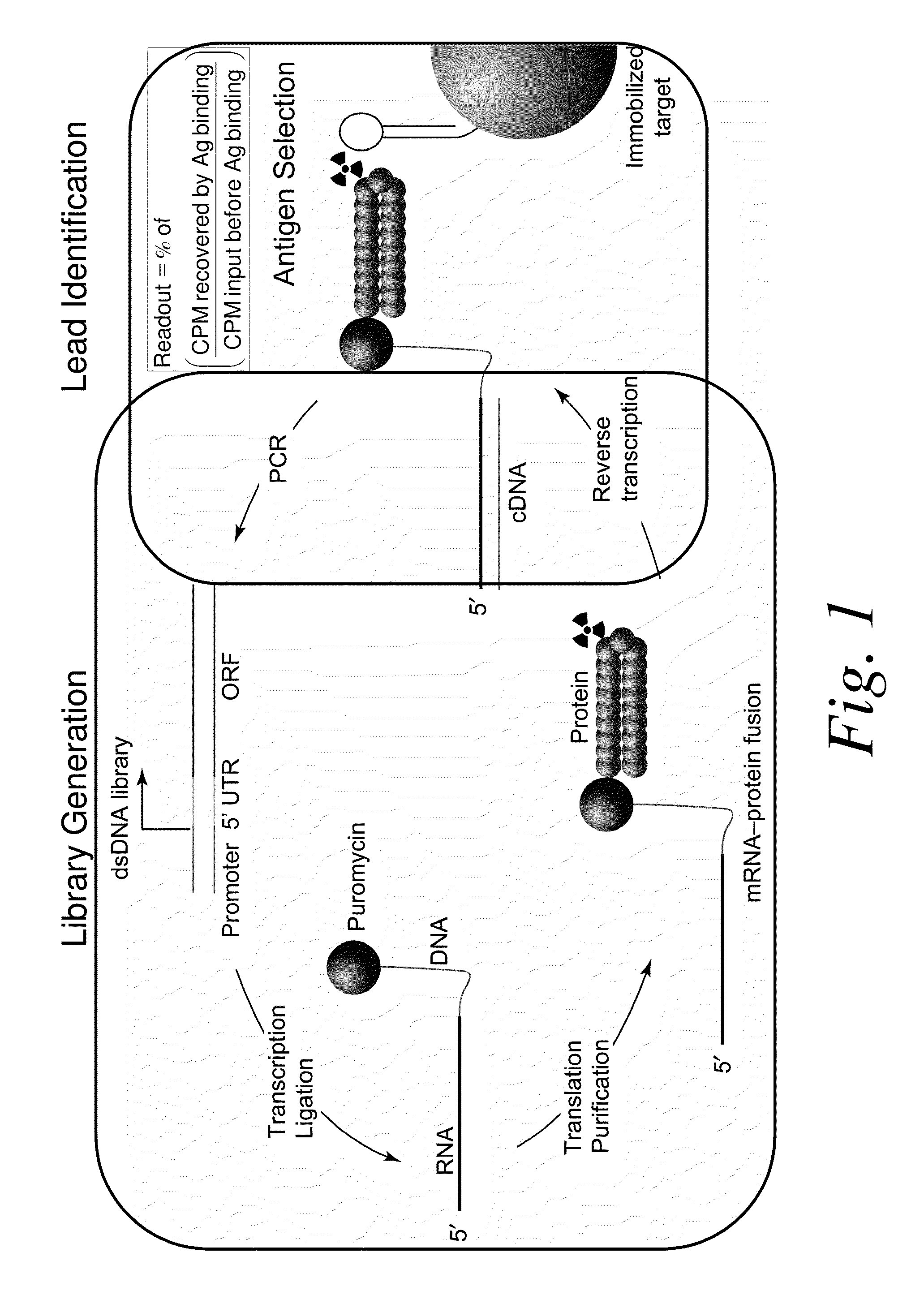
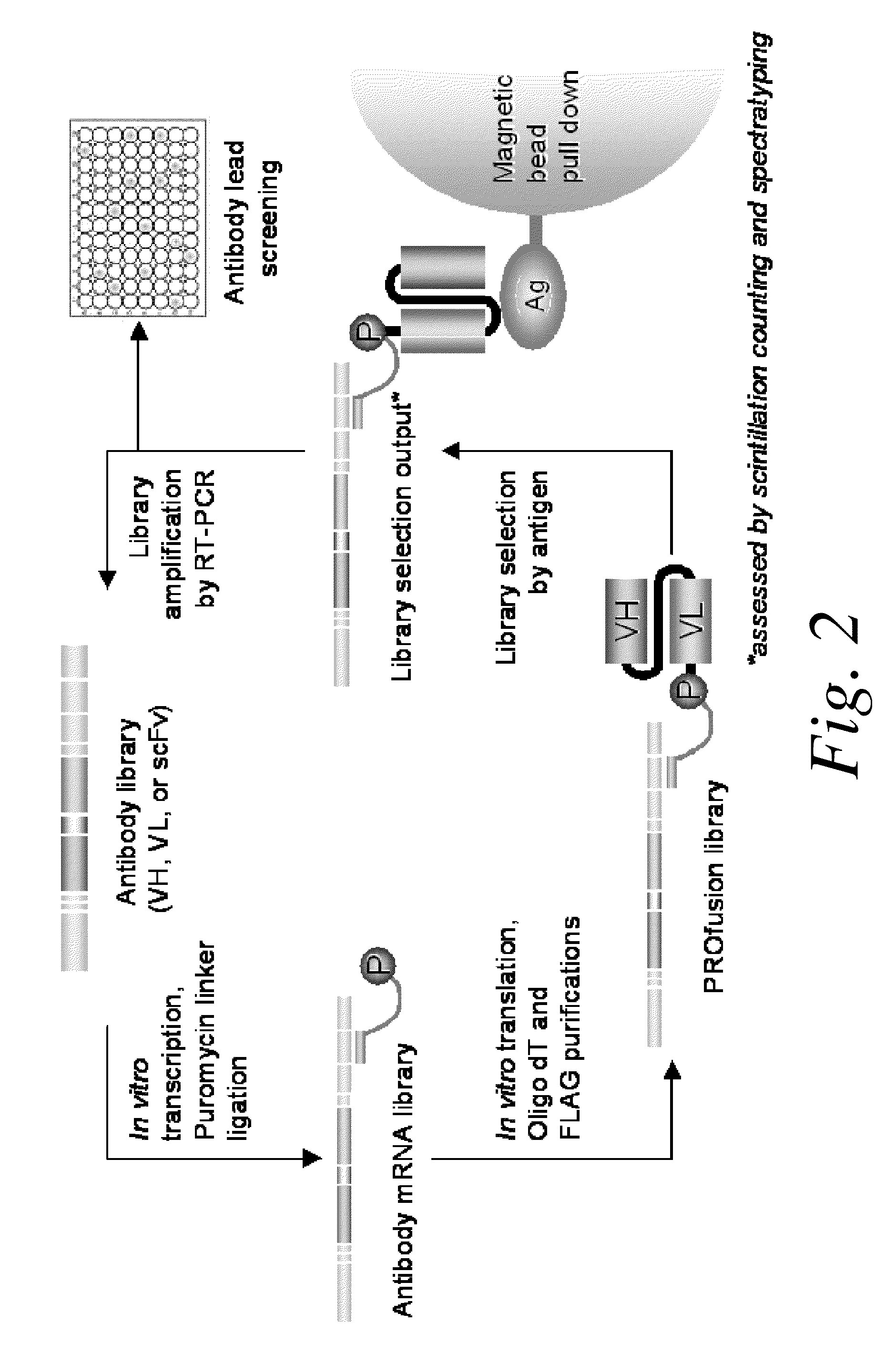
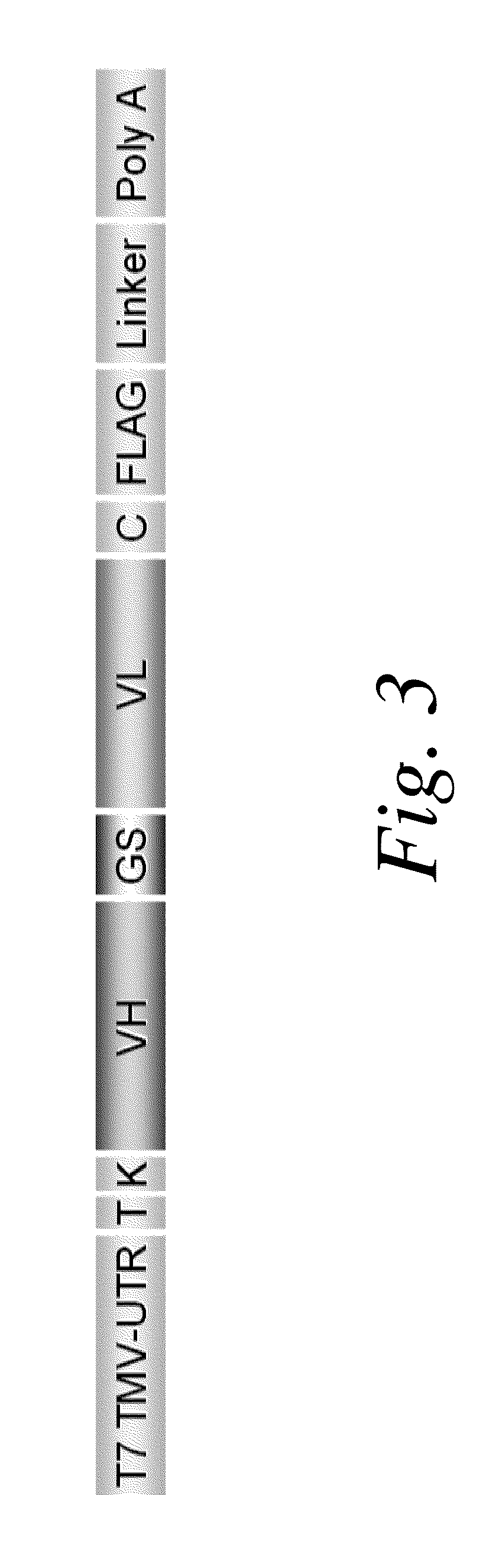
Methods of RNA Display
ActiveUS20100105569A1Solve problemsFunction increaseLibrary screeningDNA preparationExpression LibraryScFv Antibodies
The present invention features improved methods of in vitro RNA display to allow reliable expression and selection of scFv antibody molecules from expression libraries. The improved methods, in part, involve the use of mildly reducing conditions, which favor of scFv intra-chain disulphide bond and thus correct folding of the scFv antibody molecules. Although particularly suited to expression and selection of scFv antibody molecules, the methods of the invention are also expedient for in vitro RNA display of all classes of protein.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO +1
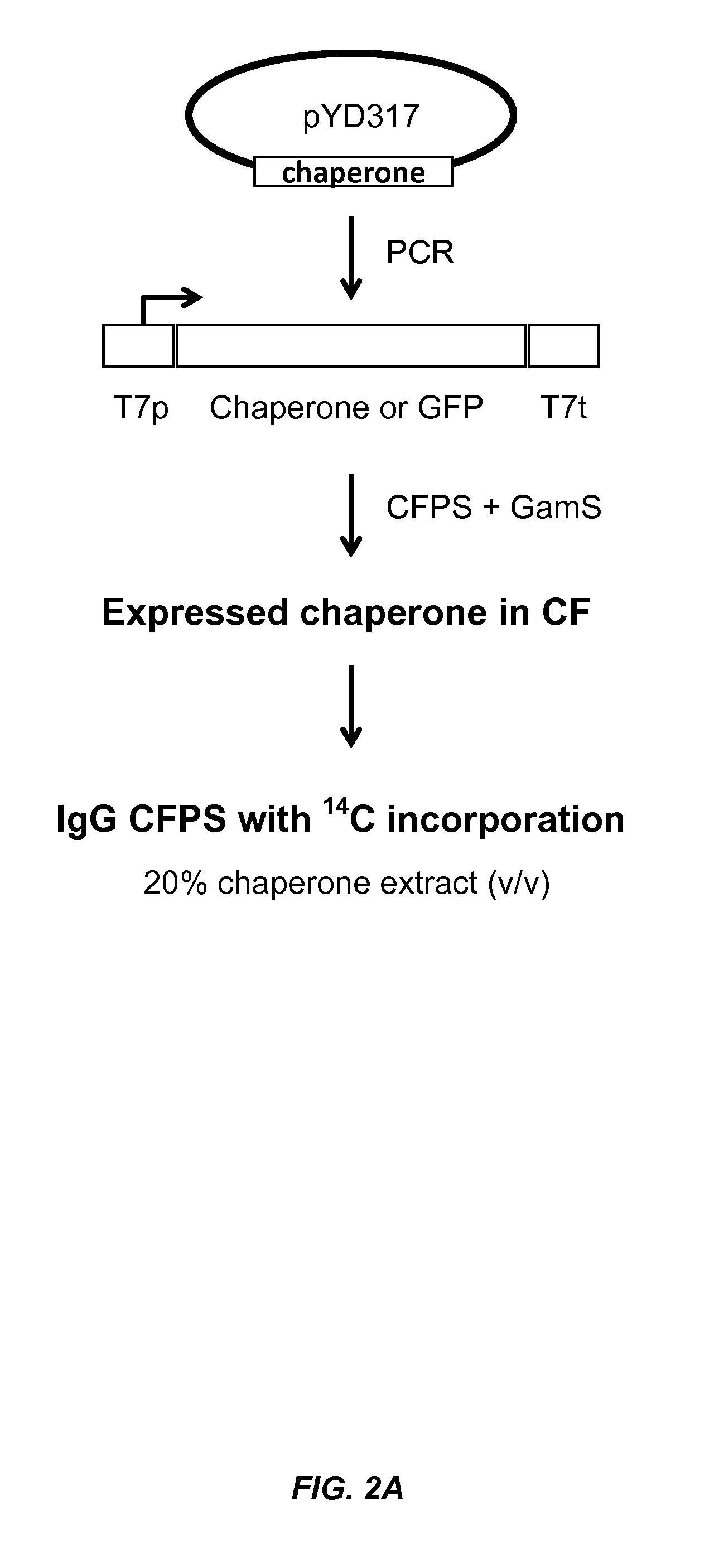
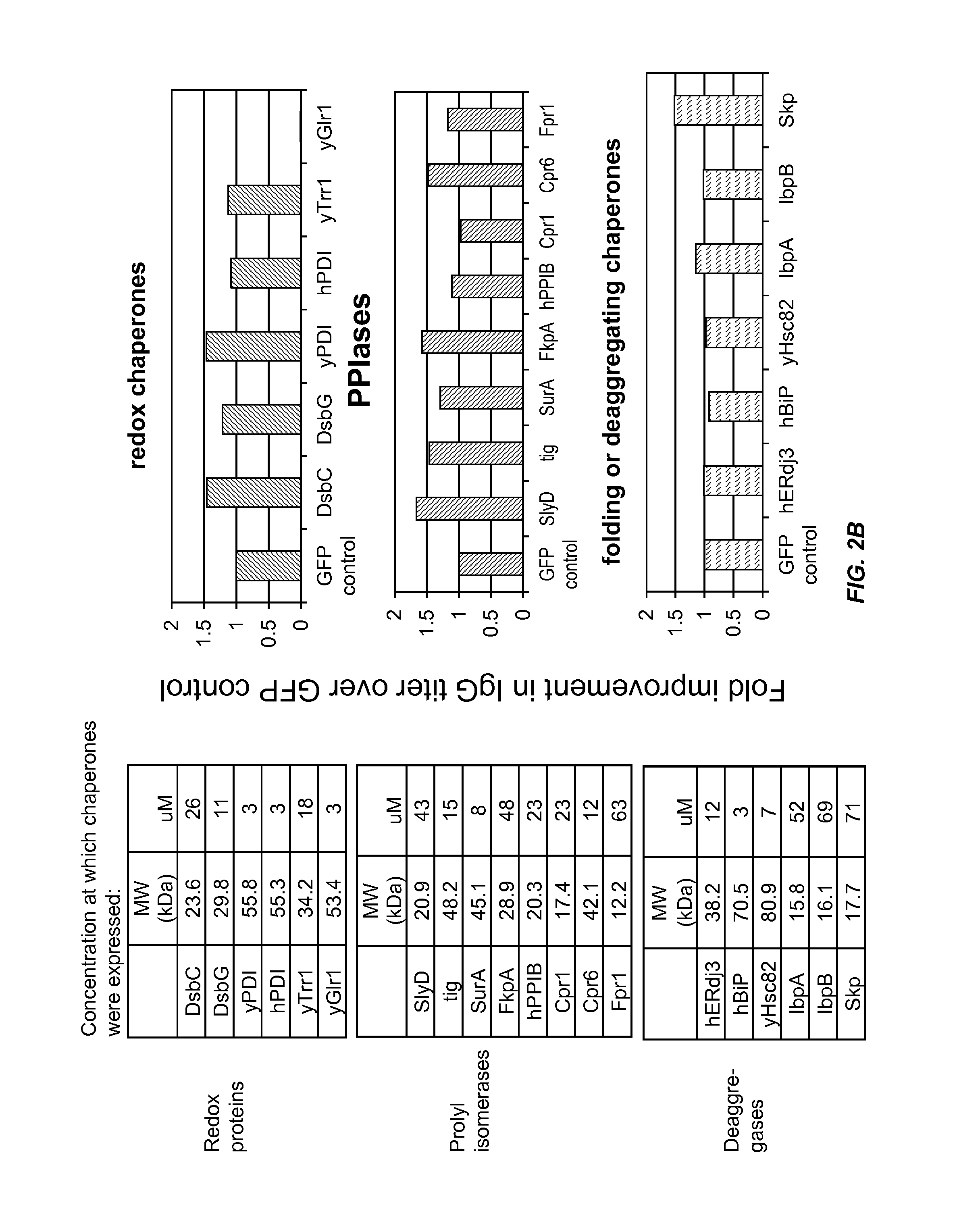
Expression of biologically active proteins in a bacterial cell-free synthesis system using bacterial cells transformed to exhibit elevated levels of chaperone expression
The present disclosure describes methods and systems for improving the expression of a properly folded, biologically active protein of interest in a cell free synthesis system. The methods and systems use a bacterial cell free extract having an active oxidative phosphorylation system, and include an exogenous protein chaperone. The exogenous protein chaperone can be expressed by the bacteria used to prepare the cell free extract. The exogenous protein chaperone can be a protein disulfide isomerase and / or a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. The inventors discovered that the combination of a protein disulfide isomerase and a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase produces a synergistic increase in the amount of properly folded, biologically active protein of interest.
Owner:SUTRO BIOPHARMA
Immuno-conjugates and methods for producing them
ActiveUS20120171115A1Reducing and preventing residuePermit productionFungiBacteriaImmunoglobulin Heavy Chain Variable RegionDisulphide bonds
The present invention provides an isolated protein comprising an immunoglobulin variable region comprising at least two cysteine residues positioned within framework region (FR) 2 and / or at least two cysteine residues positioned within framework region (FR3), wherein if at least two of the cysteine residues in FR2 and / or FR3 are not conjugated to a compound then an intra-framework disulphide bond is capable of forming between the cysteine residues. Preferably the protein comprises an immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (VH) and an immunoglobulin light chain variable region (VL), wherein at least one of the variable regions comprises the two cysteine residues. The present invention also provides conjugates of the protein and another compound.
Owner:AVIPEP
Shell layer dropping type nanometer medicine carrier preparation based on amphiphilic block copolymer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101953804ALocal release implementationProlong blood circulation timePowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsOrganic solventDrug carrier
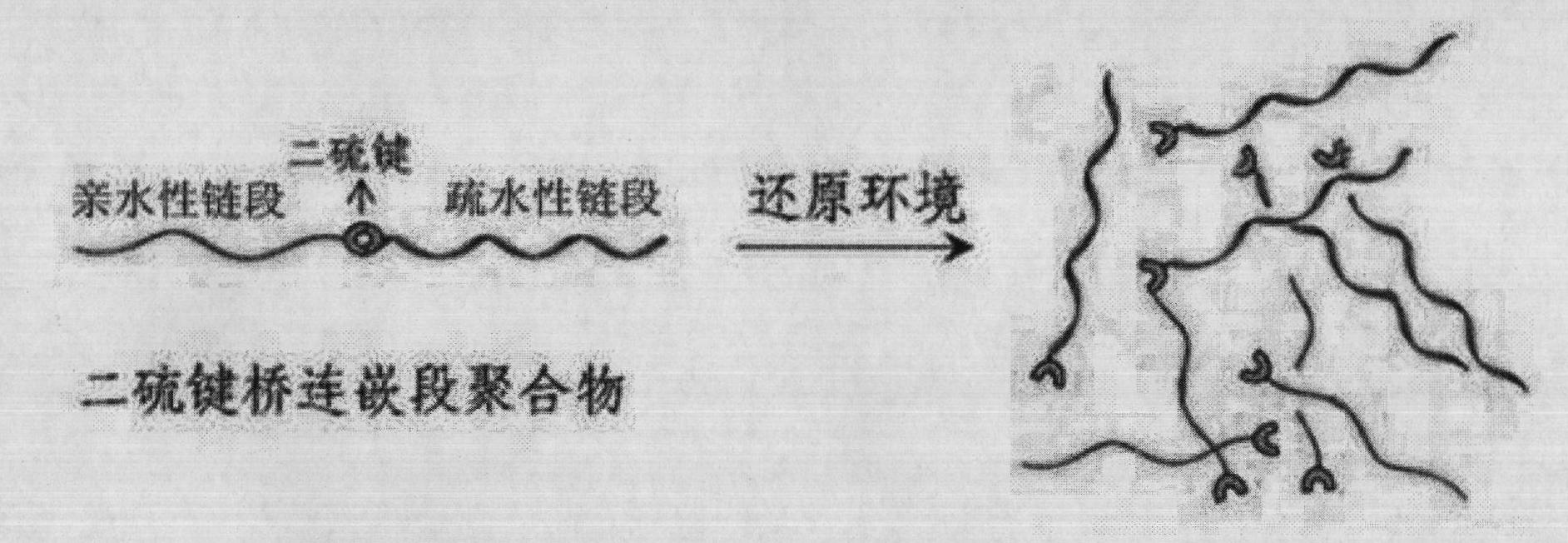
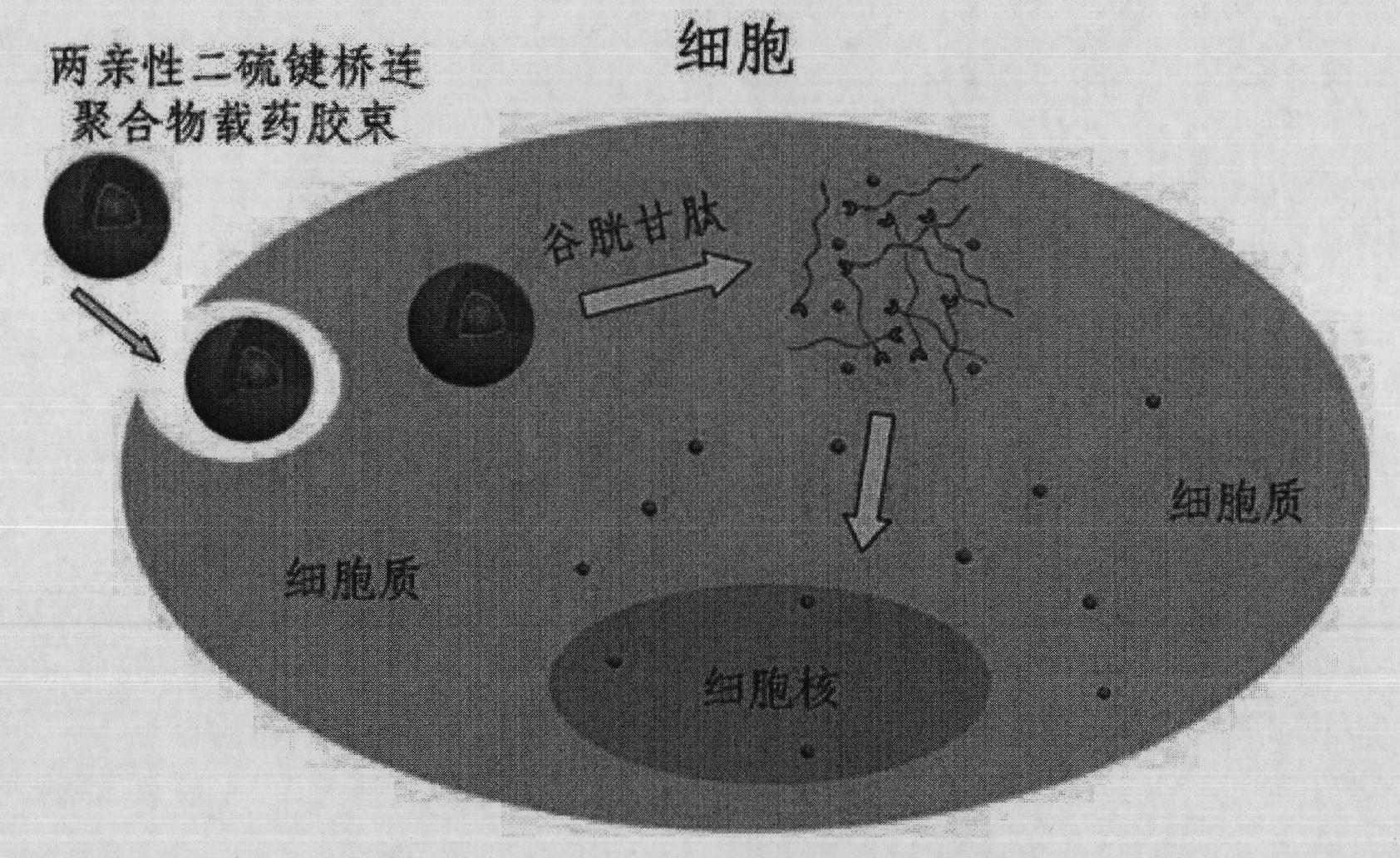
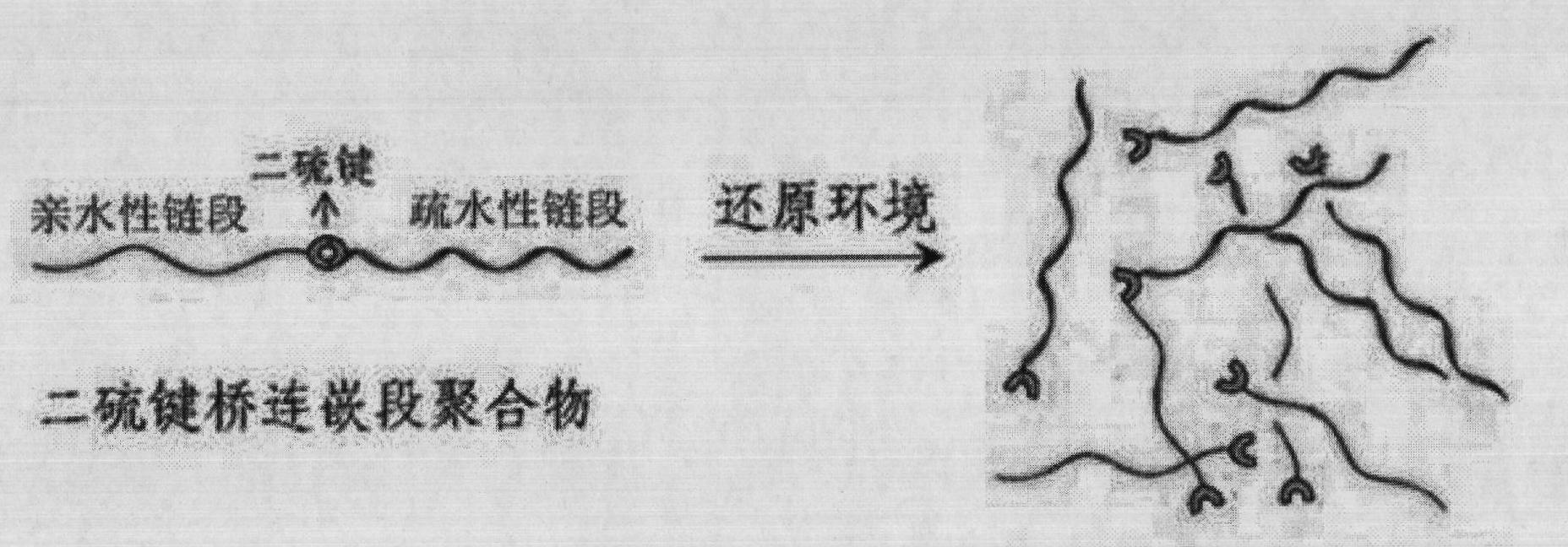
The invention discloses a shell layer dropping type nanometer medicine carrier preparation based on an amphiphilic block copolymer and a preparation method thereof. The preparation is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 1 to 20 parts by weight of active ingredient medicines, 10 to 200 parts by weight of amphiphilic block copolymers and 20 to 500 parts by weight of organic solvents. The nanometer medicine micelle carrier preparation is in a core-shell structure, the core of which is a hydrophobic chain segment used for wrapping active ingredients and the shell of which is an amphiphilic block copolymer hydrophilic chain segment, and a hydrophilic segment and a hydrophobic segment in the amphiphilic block copolymer are connected through a disulphide bond S-S. The medicine carrier preparation can be preserved easily and has the advantages of high stability, high medicine cladding ratio, large medicine loading capacity, low toxicity and high medicine bioavailability.
Owner:苏州同科生物科技有限公司
Trimer of HIV env gene expression product
InactiveUS6737067B1Peptide/protein ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsAdjuvantRecombinant glycoprotein
The invention concerns a purified recombinant glycoprotein having the following properties: a) an adherence capacity to CD4; b) an affinity with a anti-gp120 antibody capable of neutralizing in vitro HIV cell infection; c) an affinity with an anti-gp41 antibody; d) a timeric form free from inter-chain disulphide bonds. The invention also concerns a vaccine comprising said purified glycoprotein and an adjuvant. The invention further concerns a method for obtaining said glycoprotein, which consists in expressing, by means of genetic recombining techniques, a glycoprotein corresponding to the properties a), b) and c) mentioned above; purifying it, and subjecting it to steps involving at least a reducing agent, an ionic detergent and / or a neutral detergent in conditions leading to a glycoprotein having said properties.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTUER LTD
Fusion proteins having mutated immunoglobulin hinge region
ActiveUS8067548B2Inhibition formationExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesHinge regionImmunoglobulin Hinge Region
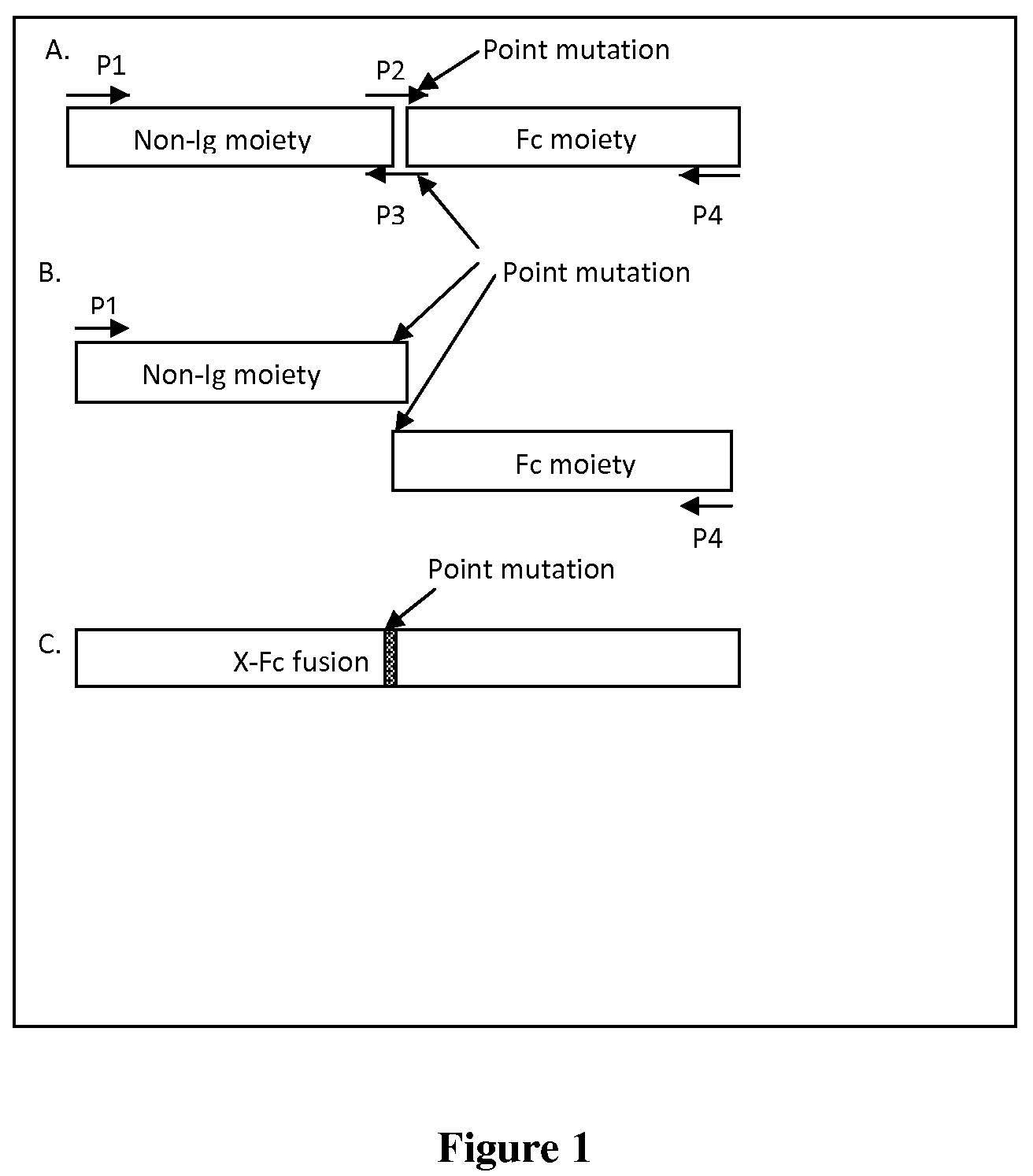
A fusion protein having a non-immunoglobulin polypeptide having a cysteine residue proximal to the C terminal thereof, and an immunoglobulin component with a mutated hinge region is provided. The mutation comprises a point mutated site corresponding in position to the position in a native hinge region of the cysteine residue located nearest the cysteine residue of the non-Ig component. The distance from the cysteine residue of the non-immunoglobulin polypeptide and any remaining cysteine residues of the mutated hinge region is sufficient to prevent the formation of a disulphide bond therebetween.
Owner:NOVAGEN HLDG CORP
Cysteine linked nanobody dimers
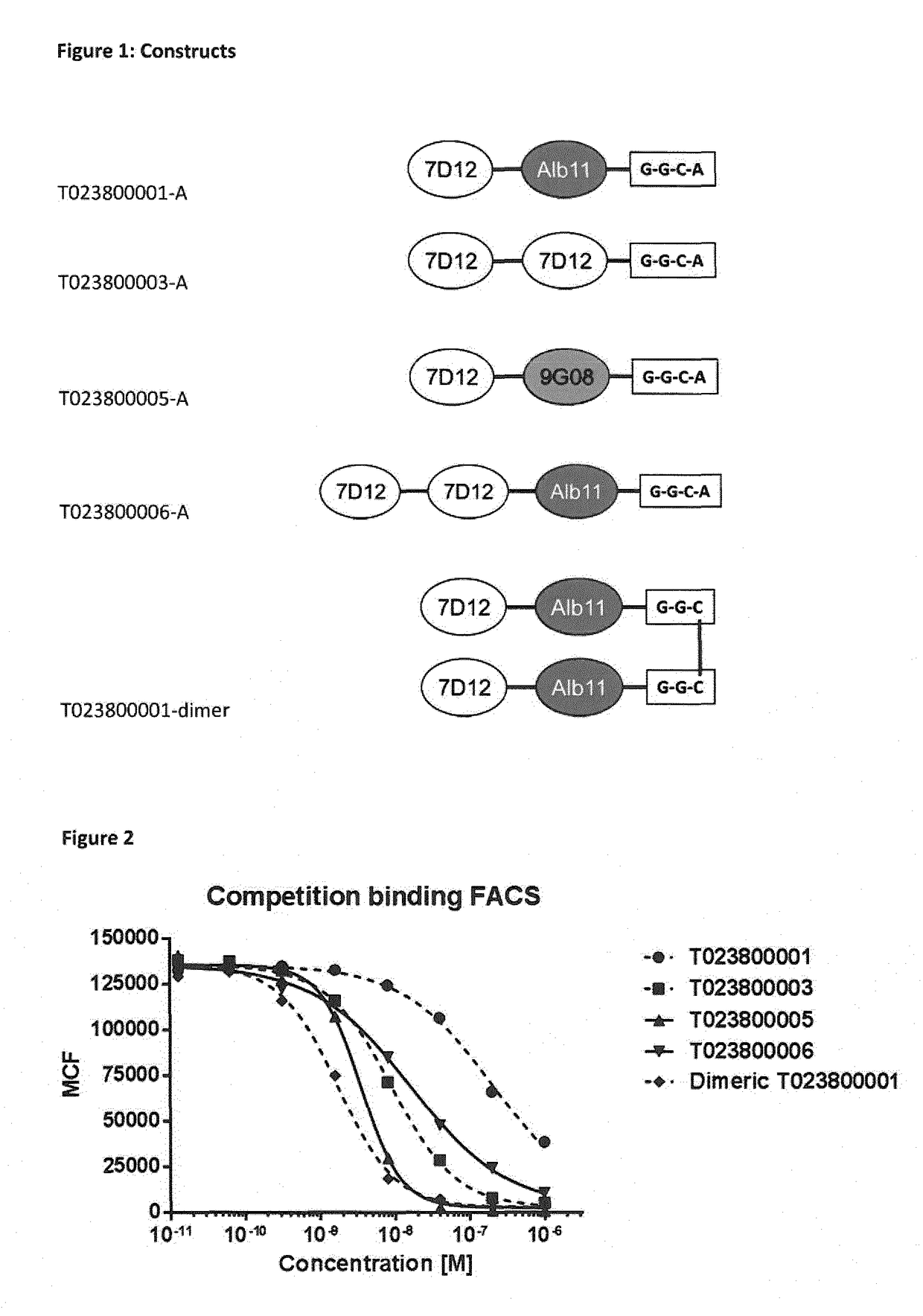
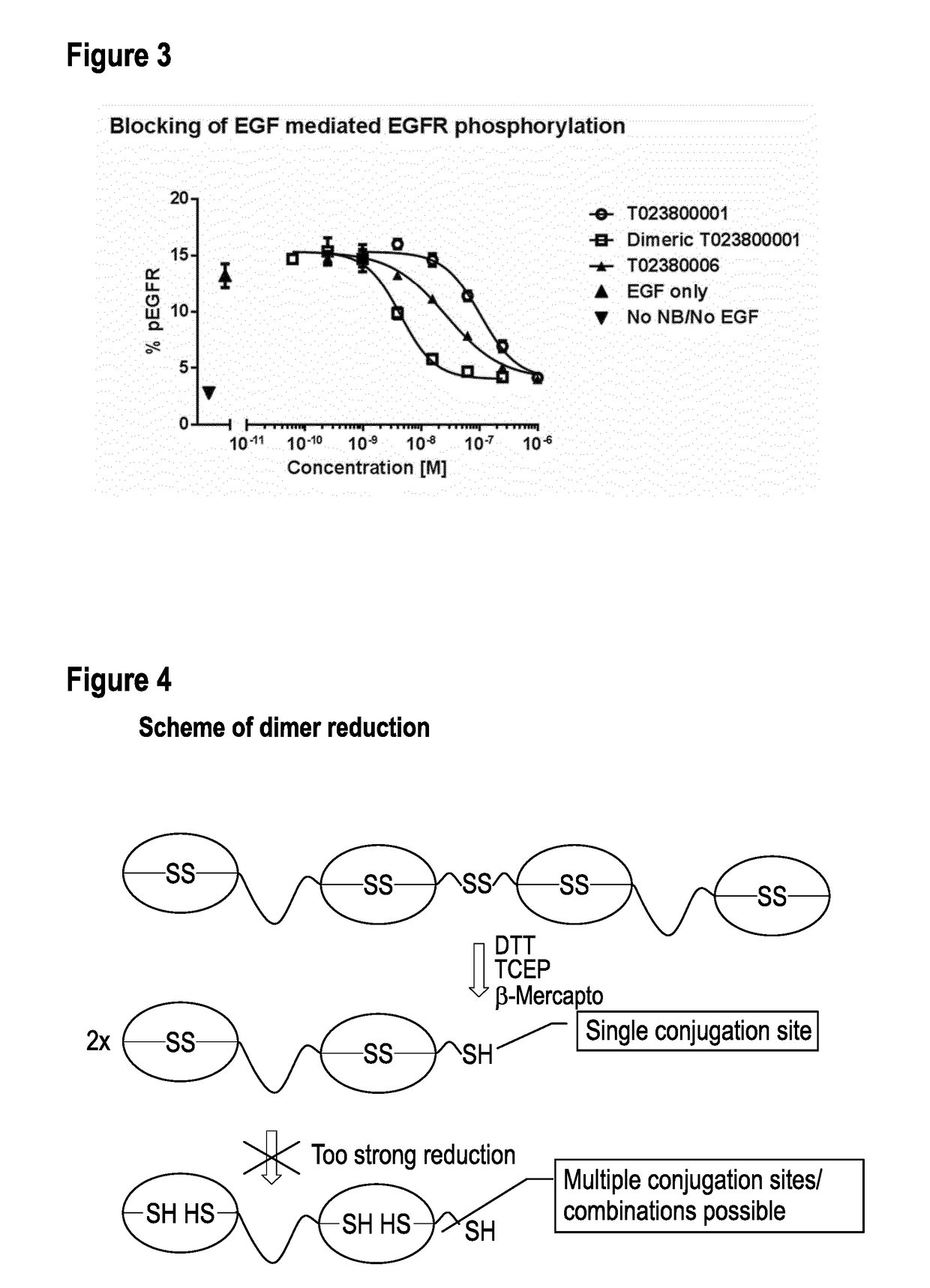
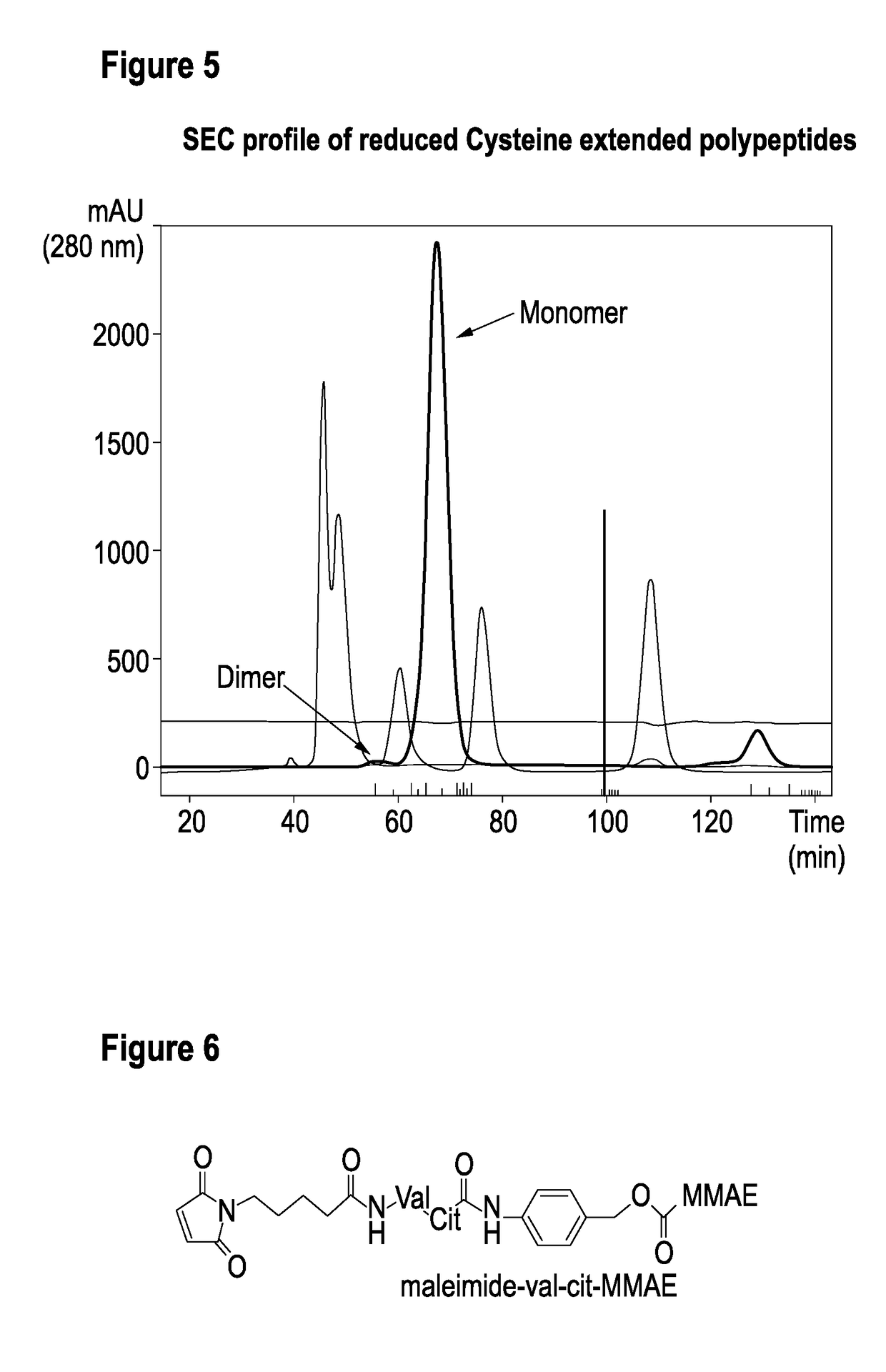
ActiveUS20170360955A1Intermolecular dimerization via disulfide bonds between two polypeptides is facilitatedImproved internalizationHybrid immunoglobulinsRadioactive preparation carriersC-terminusDisulphide bonds
The present invention relates to dimers comprising a first polypeptide and a second polypeptide, wherein each of said first and second polypeptide comprises at least one immunoglobulin single variable domain (1ISVD) and a C-terminal extension comprising a cysteine moiety (preferably at the C-terminus), wherein said first polypeptide and said second polypeptide are covalently linked via a disulfide bond between the cysteine moiety of said first polypeptide and the cysteine moiety of said second polypeptide, in which the dimer outperformed the benchmark constructs, e.g. cognate multivalent and multispecific constructs, in various assays. The present invention provides methods for making the dimers of the invention.
Owner:ABLYNX NV
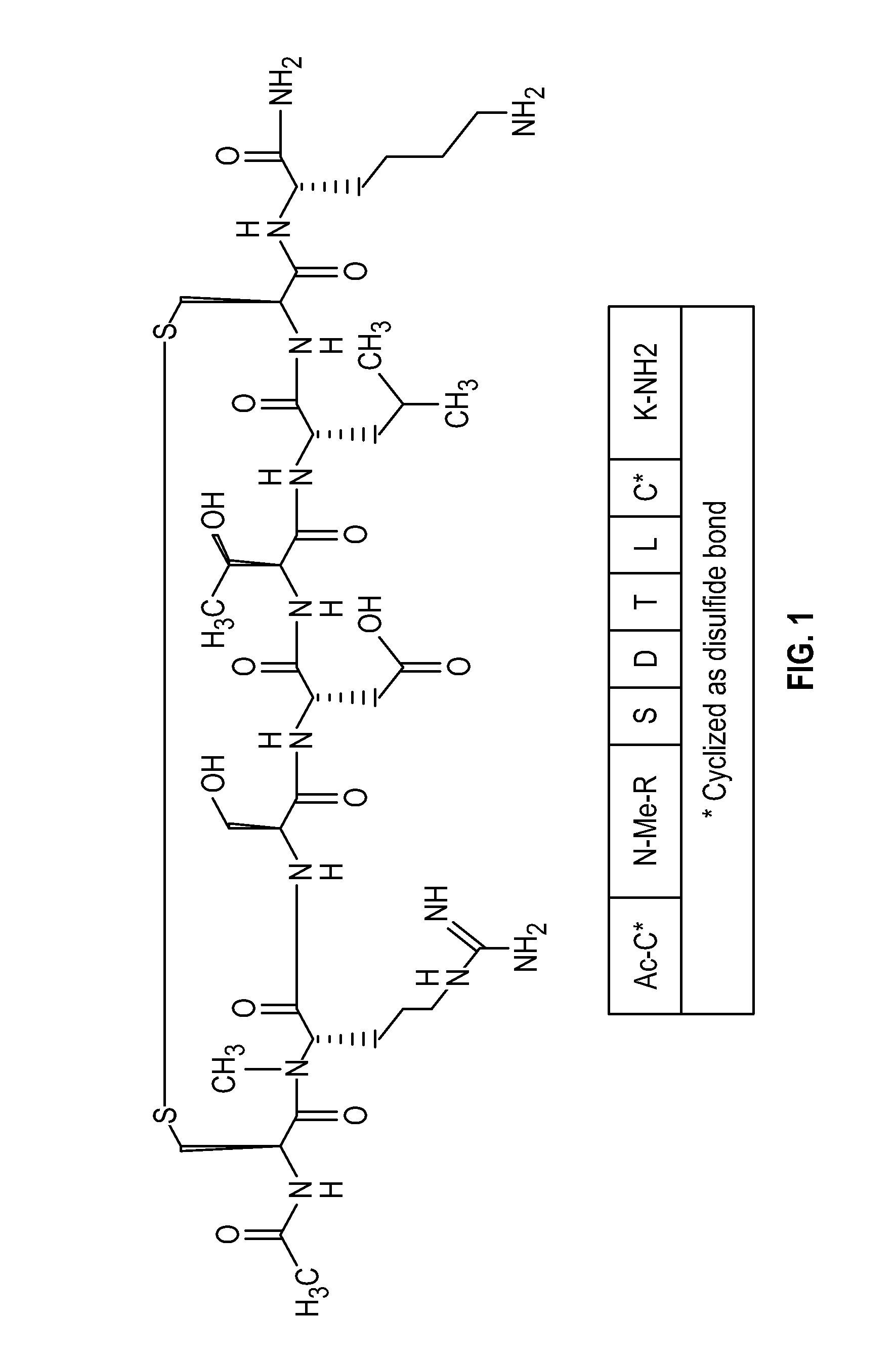
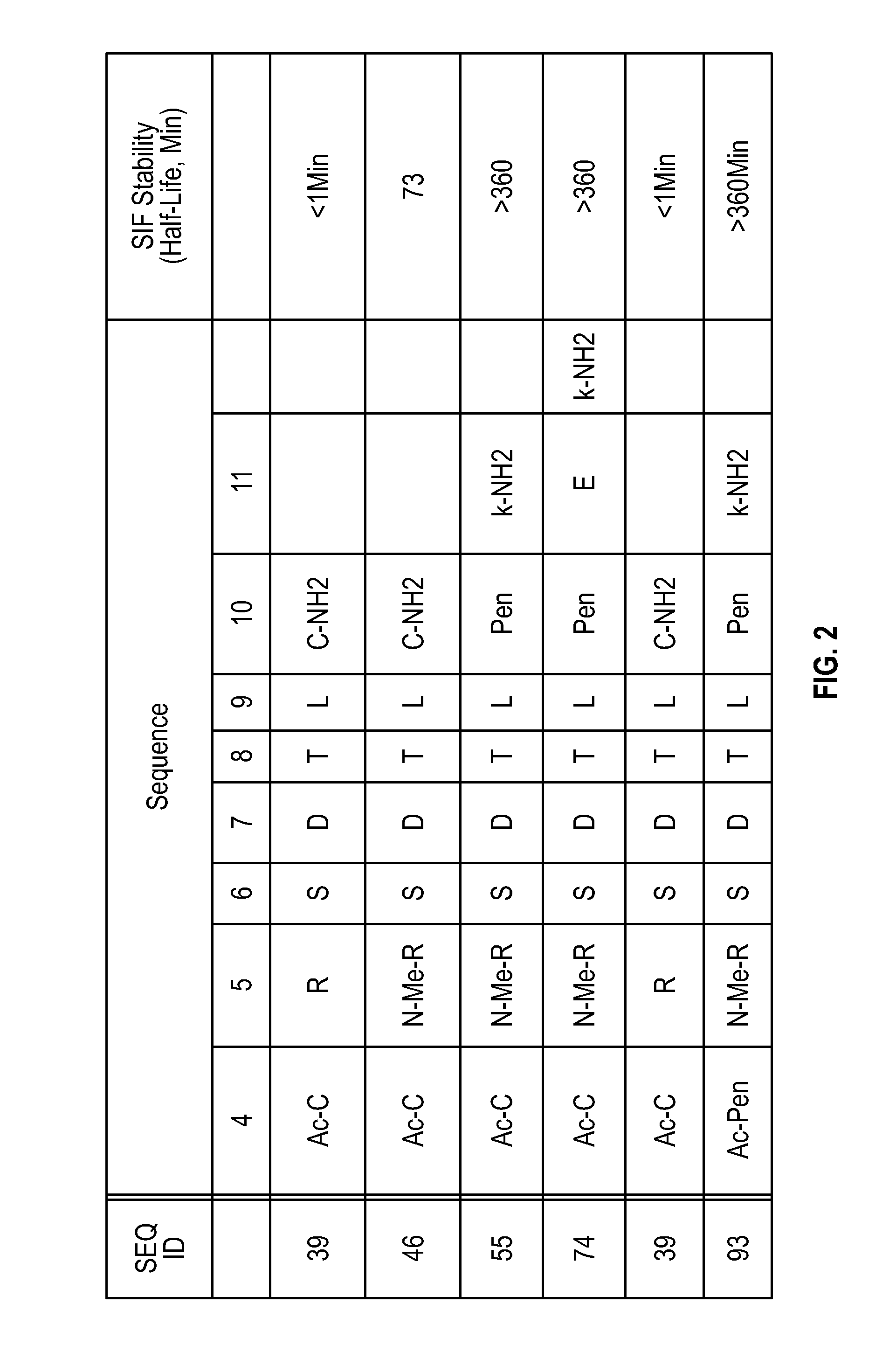
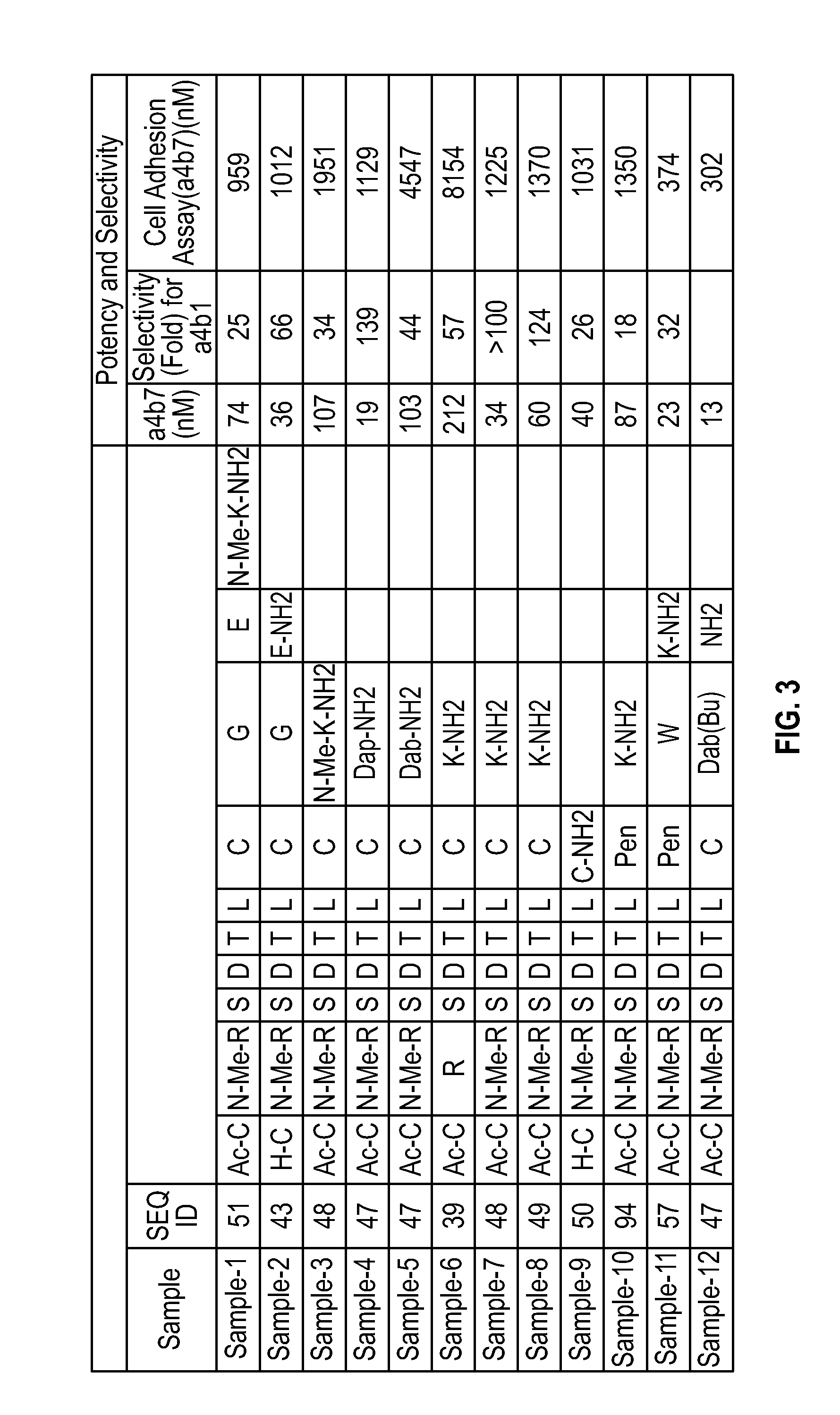
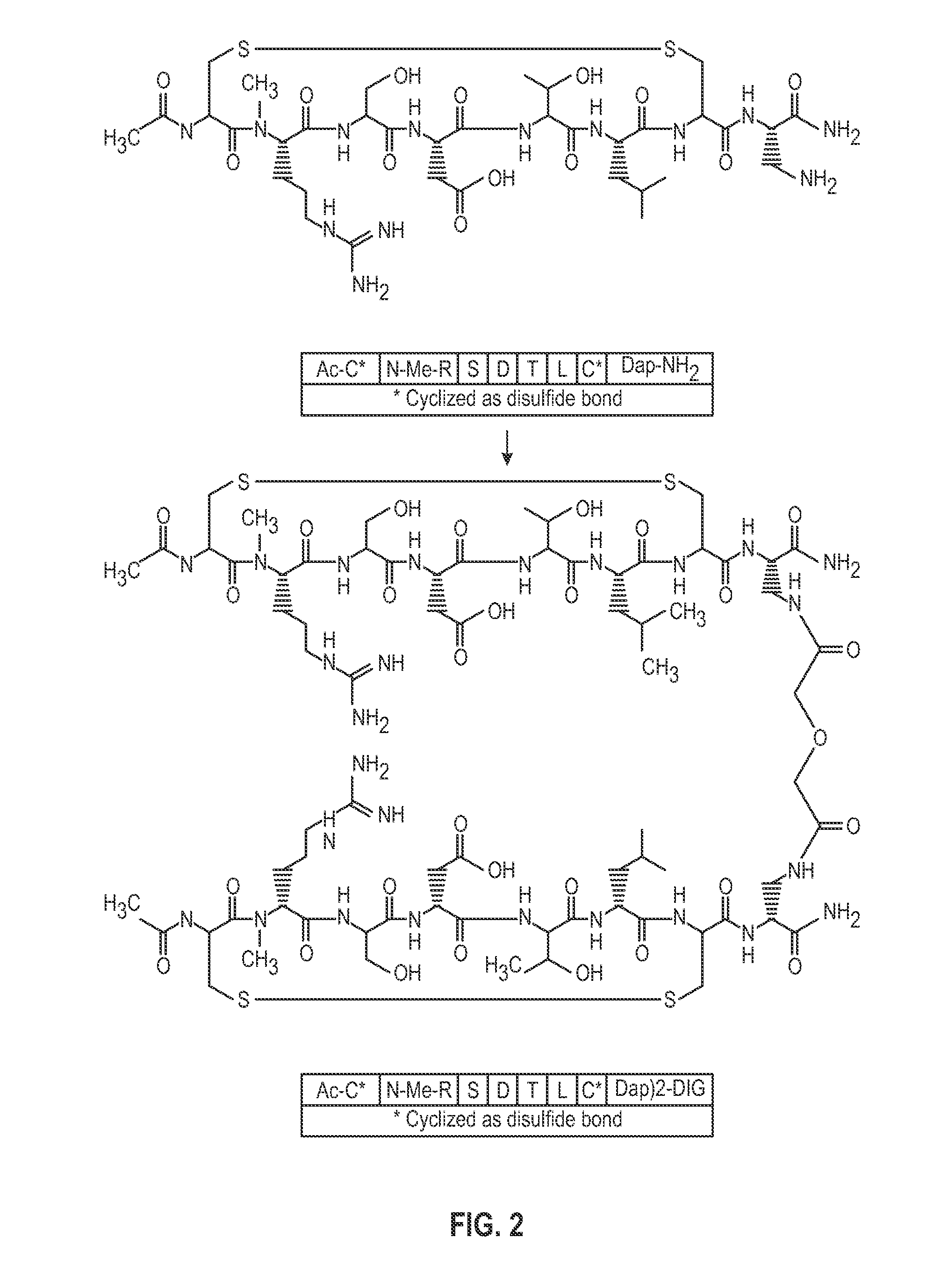
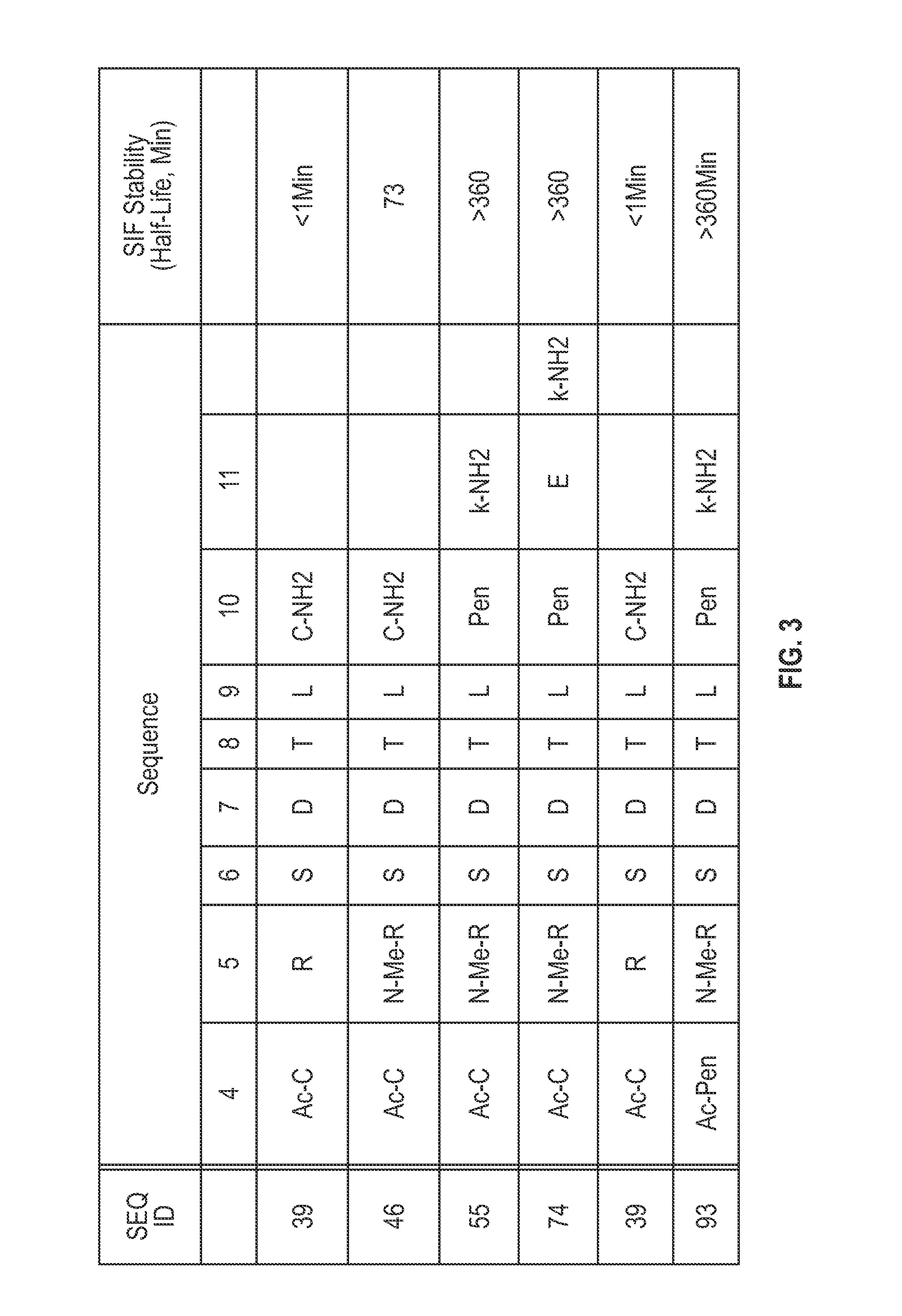
Novel a4b7 peptide antagonists
InactiveUS20140294902A1Strong specificityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticDisulphide bondsAntagonist
The invention relates to disulfide-rich peptide molecules which inhibit binding of α4β7 to the mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule (MAdCAM) in vivo, and show high selectivity against α4β1 binding.
Owner:PROTAGONIST THERAPEUTICS INC
Novel a4b7 peptide dimer antagonists
InactiveUS20140294901A1Strong specificityImprove stabilityAntipyreticAnalgesicsDimerDisulphide bonds
The invention relates to disulfide-rich dimer molecules which inhibit binding of α4β7 to the mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule (MAdCAM) in vivo, and show high selectivity against α4β1 binding.
Owner:PROTAGONIST THERAPEUTICS INC
Cloning, expression and application of eimeria tenella protein disulfide isomerase gene
InactiveCN101418309AGenetic material ingredientsRecombinant DNA-technologyEscherichia coliEmoia loyaltiensis
The invention discloses an E.tenella protein disulfide linkage isomerase gene EtPDI (Clone ID is BW1-E06,and the Genbank accession number of is EF552214). The gene is connected with a procaryon expression vector pGEX-4T-2; a procaryon expression recombination plasmid pGEX-4T-EtPDI is constructed and is expressed in a colibacillus system; and most of the expressed recombining protein exists in a soluble form. The recombining protein 4T-EtPDI is purified to carry out SPS-PAGE and is transferred to a PVDF film; and antiserum of E.tenella oocyst oral immunized chicken is used as first resistance and goat anti-chicken IgG is used as second resistance to carry out Western-blot analysis, thereby indicating that the gene has certain antigen. The gene is used for preparing an anti-chicken coccidiosis drug and an anti-chicken coccidiosis vaccine.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
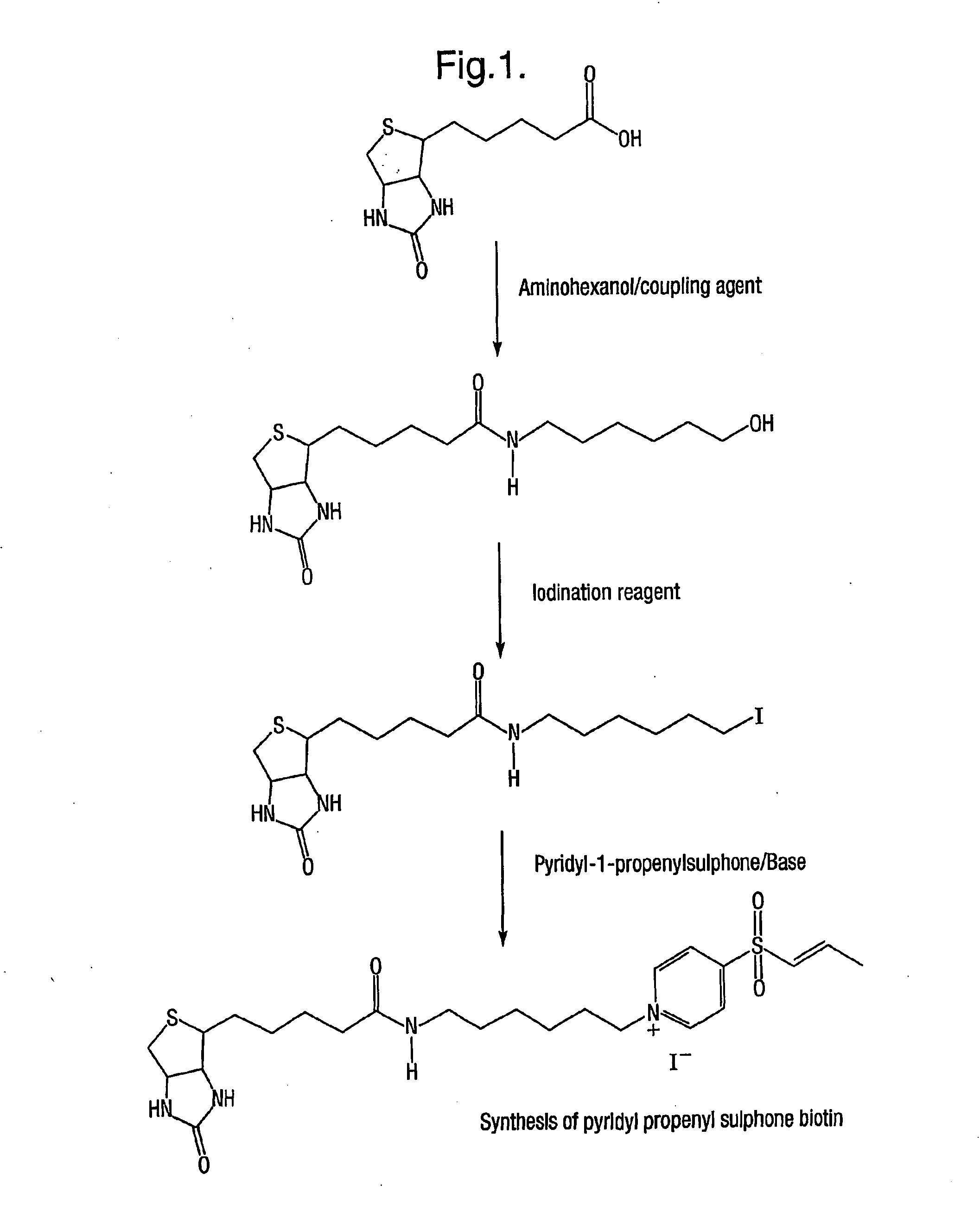
Conjugated biological molecules and their preparation
ActiveUS7939630B2Favourably alter pharmacokineticsExtended circulation timePeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsHydrogen atomMedicinal chemistry
Novel biologically active compounds of the general formula (I) in which one of X and X′ represents a polymer, and the other represents a hydrogen atom; each Q independently represents a linking group; W represents an electron-withdrawing moiety or a moiety preparable by reduction of an electron-withdrawing moiety; or, if X′ represents a polymer, X-Q-W— together may represent an electron withdrawing group; and in addition, if X represents a polymer, X′ and electron withdrawing group W together with the interjacent atoms may form a ring; each of Z1 and Z2 independently represents a group derived from a biological molecule, each of which is linked to A and B via a nucleophilic moiety; or Z1 and Z2 together represent a single group derived from a biological molecule which is linked to A and B via two nucleophilic moieties; A is a C1-5 alkylene or alkenylene chain; and B is a bond or a C1-4 alkylene or alkenylene chain; are formed by conjugating a suitable polymer to a suitable biologically active molecule via nucleophilic groups in said molecule, preferably via a disulphide bridge.
Owner:ABZENA UK LTD
Method of expressing proteins with disulfide bridges
InactiveUS20060246541A1High affinityFacilitate the proper folding of nascent recombinant CN disintegrin domainBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyADAMTS Proteins
This invention relates to methods of expressing eukaryotic proteins in prokaryotic hosts, particularly eukaryotic proteins that require formation of disulfide bridges for biological activity. Various approaches are used including fusion to thioredoxin, cytoplasmic expression of disulfide isomerases, deficiencies in thioredoxin and / or glutathione reductases, deficiencies in proteases, and the like. The method is applicable to express monomeric and dimeric forms of the eukaryotic protein with biological activity such as monomeric and dimeric forms of a disintegrin or a disintegrin domain. Included are the vectors, host cells expressing the proteins, the expressed proteins and methods of using the proteins.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Purified hepatitis C virus envelope proteins for diagnostic and therapeutic use
InactiveUS20040126395A1SsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsHcv treatmentDisulphide bonds
The present invention relates to a method for purifying recombinant HCV single or specific oligomeric envelope proteins selected from the group consisting of E1 and / or E2 and / or E1 / E2, characterized in that upon lysing the transformed host cells to isolate the recombinantly expressed protein a disulphide bond cleavage or reduction step is carried out with a disulphide bond cleavage agent. The present invention also relates to a composition isolated by such a method. The present invention also relates to the diagnostic and therapeutic application of these compositions. Furthermore, the invention relates to the use of HCV E1 protein and peptides for prognosing and monitoring the clinical effectiveness and / or clinical outcome of HCV treatment.
Owner:MAERTENS GEERT +2
Purified hepatitis C virus envelope proteins for diagnostic and therapeutic use
InactiveUS7101561B2Different reactivityEasy to prepareSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsHcv treatmentDisulphide bonds
The present invention relates to a method for purifying recombinant HCV single or specific oligomeric envelope proteins selected from the group consisting of E1 and / or E2 and / or E1 / E2, characterized in that upon lysing the transformed host cells to isolate the recombinantly expressed protein a disulphide bond cleavage or reduction step is carried out with a disulphide bond cleavage agent. The present invention also relates to a composition isolated by such a method. The present invention also relates to the diagnostic and therapeutic application of these compositions. Furthermore, the invention relates to the use of HCV E1 protein and peptides for prognosing and monitoring the clinical effectiveness and / or clinical outcome of HCV treatment.
Owner:GENIMMUNE NV
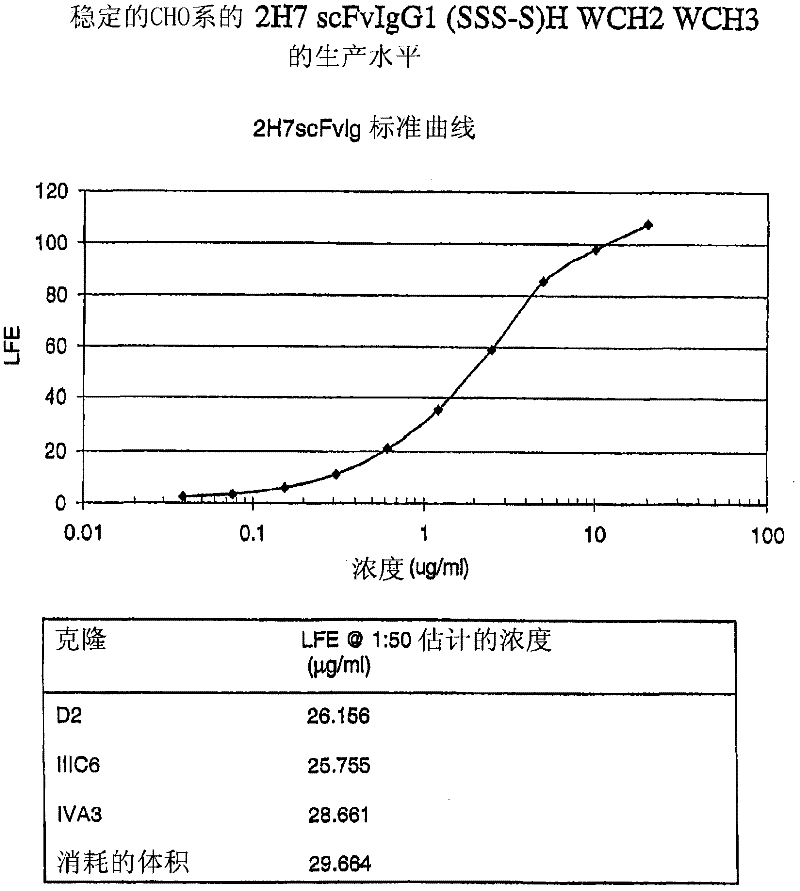
Homogeneous antibody populations
InactiveUS20130144041A1Efficient and economic productionEasy to eliminateNervous disorderAntipyreticMonoclonal antibodyHinge region
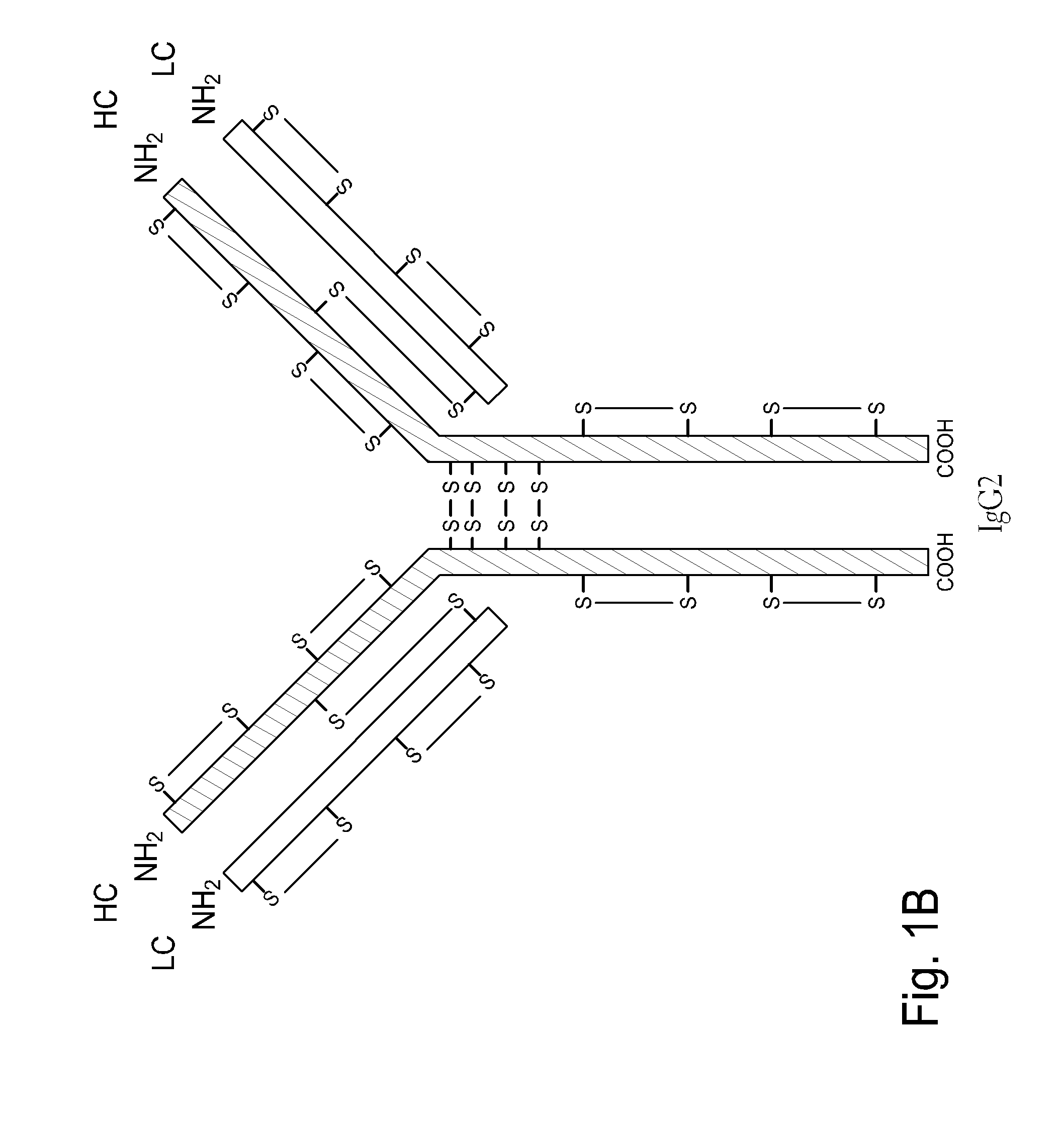
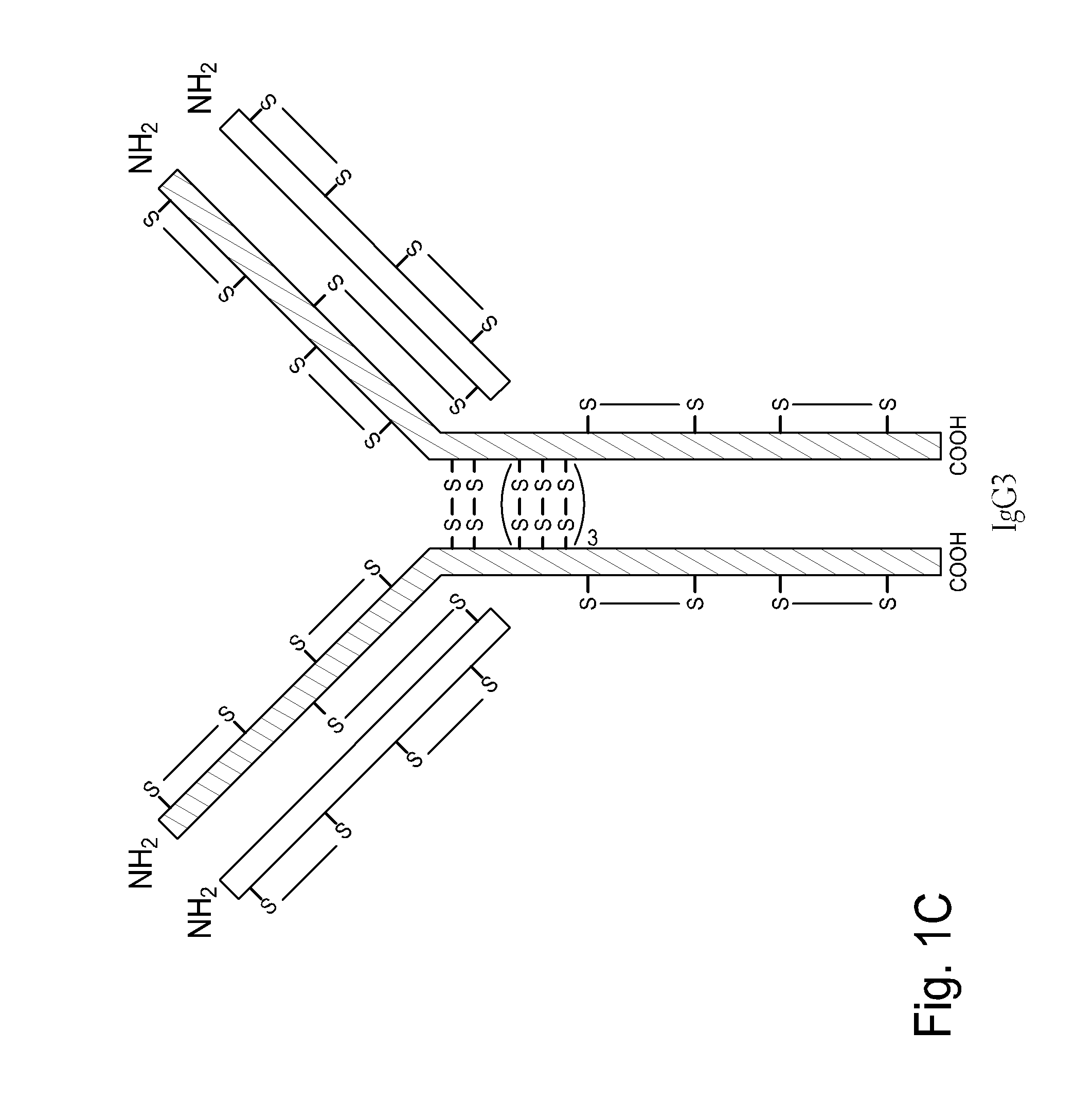
The present invention is generally directed to methods of producing an increase in the enrichment and / or recovery of preferred forms of monoclonal antibodies. More particularly, the invention relates to methods for eliminating disulfide heterogeneity in the hinge region of recombinant IgG2 antibody proteins.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Purified hepatitis C virus envelope proteins for diagnostic and therapeutic use
InactiveUS20030147918A1Reduce the possibilityHigh sensitivitySsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsHcv treatmentDisulphide bonds
The present invention relates to a method for purifying recombinant HCV single or specific oligomeric envelope proteins selected from the group consisting of E1 and / or E2 and / or E1 / E2, characterized in that upon lysing the transformed host cells to isolate the recombinantly expressed protein a disulphide bond cleavage or reduction step is carried out with a disulphide bond cleavage agent. The present invention also relates to a composition isolated by such a method. The present invention also relates to the diagnostic and therapeutic application of these compositions. Furthermore, the invention relates to the use of HCV E1 protein and peptides for prognosing and monitoring the clinical effectiveness and / or clinical outcome of HCV treatment
Owner:GENIMMUNE NV
Purified hepatitis C virus envelope proteins for diagnostic and therapeutic use
The present invention relates to a method for purifying recombinant HCV single or specific oligomeric envelope proteins selected from the group consisting of E1 and / or E1 / E2, characterized in that upon lysing the transformed host cells to isolate the recombinantly expressed protein a disulphide bond cleavage or reduction step is carried out with a disulphide bond cleavage agent. The present invention also relates to a composition isolated by such a method. The present invention also relates to the diagnostic and therapeutic application of these compositions. Furthermore, the invention relates to the use of HCV E1 protein and peptides for prognosing and monitoring the clinical effectiveness and / or clinical outcome of HCV treatment.
Owner:INNOGENETICS NV
Polypeptide synthesis method for octreotide acetate
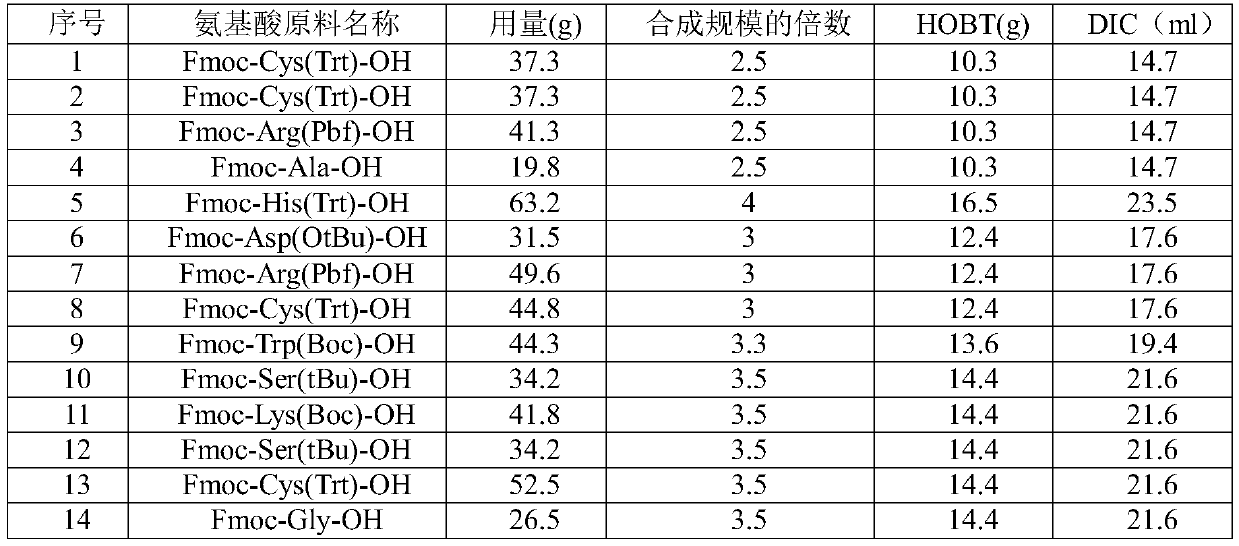
ActiveCN103351426AConvenient sourceReduce usagePeptide preparation methodsBulk chemical productionFluoroacetic acidAceric acid
The invention relates to a polypeptide synthesis method for octreotide acetate. The method comprises the following steps of: taking chloromethyl resin as a starting raw material, preparing a cesium salt from Boc-Thr(tBu)-OH, sequentially connecting amino acids with protecting groups according to a solid-phase synthesis method so as to obtain protected octapeptide resin, meanwhile, removing Boc protecting groups by sequentially using HCl / isopropyl alcohol, carrying out peptide connecting reaction in a manner of taking DIC and HOBT as condensing agents, carrying out reduction by using palladium carbon / hydrogen gas, meanwhile, cutting off peptide chains so as to obtain reduced octreotide, introducing air at the Ph of 7.8-9 so as to cyclize disulfide linkages, then, obtaining a crude octreotide product, and carrying out separation and purification through a C18 column, thereby preparing a fine octreotide acetate product. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that threoninol and Fmoc-threoninol are not adopted, the production cost is very low, the method has large-scale production capacity, the process is stable, the raw and auxiliary materials are convenient to obtain, the production cycle is short, the yield of connected peptide is high, the quality is stable, the use of highly-toxic reagents, such as hydrogen fluoride, trifluoroacetic acid and the like, is avoided, and the pollution caused by waste gas, waste water and waste residues is little.
Owner:SHANGHAI SOHO YIMING PHARMA
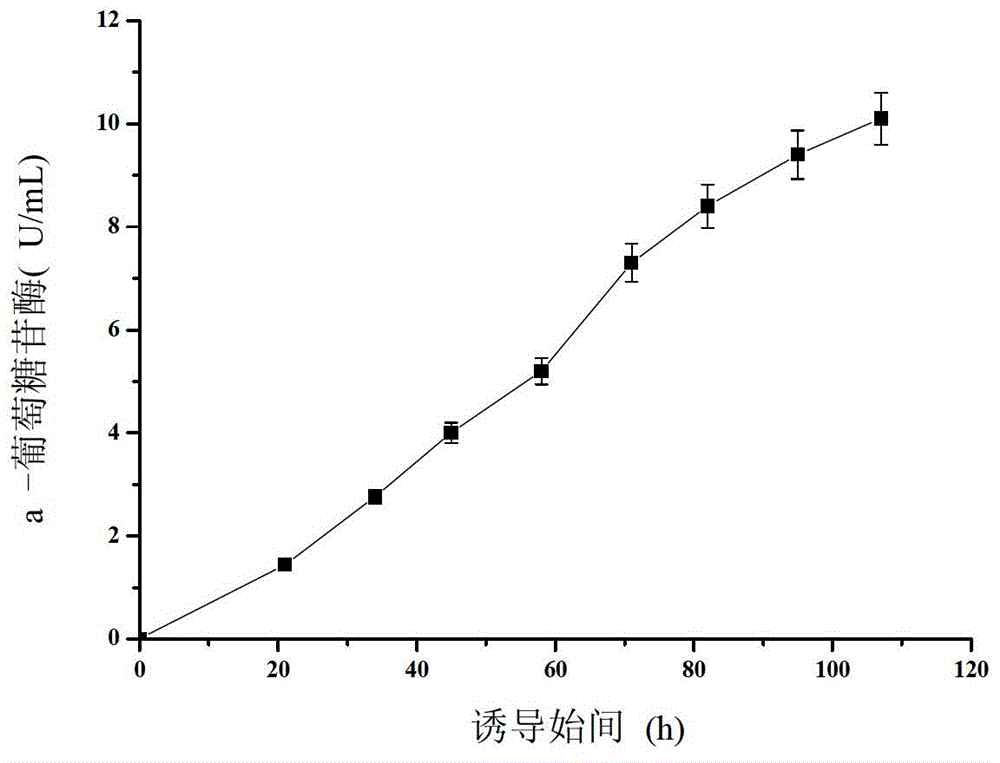
Aspergillus niger alpha-glucosidase gene and high-efficiency expression method thereof
The invention discloses an aspergillus niger alpha-glucosidase aglu<OP> and a high-efficiency expression method of the aspergillus niger alpha-glucosidase aglu<OP> in pichia pastoris. The nucleotide sequence of the optimized alpha-glucosidase gene is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The gene is constructed into a pichia pastoris expression vector, and the pichia pastoris expression vector and disulphide bond isomerase are transformed into the pichia pastoris for co-expression, and the enzyme activity of the alpha-glucosidase gene can be up to 10.1U / mL after induction is carried out for 110 hours in a 3L tank, and is 2.9 times of the enzyme cavity before optimization. The optimized alpha-glucosidase gene can be used for industrial production of the alpha-glucosidase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Immuno-conjugates and methods for producing them
ActiveUS20120164068A1Reducing and preventing residuePermit productionSenses disorderFungiCompound aImmunoglobulin Heavy Chain Variable Region
The present invention provides an isolated protein comprising an immunoglobulin variable region comprising at least two cysteine residues positioned within framework region 1 such that if at least two of the cysteine residues are not conjugated to another compound a disulphide bond forms between the cysteine residues. Preferably the protein comprises an immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region and an immunoglobulin light chain variable region, wherein at least one of the variable regions comprises the two cysteine residues. The present invention also provides a protein that binds to TAG72. The present invention also provides conjugates of the protein and another compound.
Owner:AVIPEP
Purified hepatitis C virus envelope proteins for diagnostic and therapeutic use
The present invention relates to a method for purifying recombinant HCV single or specific oligomeric envelope proteins selected from the group consisting of E1 and / or E1 / E2 characterized in that upon lysing the transformed host cells to isolate the recombinantly expressed protein a disulphide bond cleavage or reduction step is carried out with a disulphide bond cleavage agent. The present invention also relates to a composition isolated by such a method. The present invention also relates to the diagnostic and therapeutic application of these compositions. Furthermore, the invention relates to the use of HCV E1 protein and peptides for prognosing and monitoring the clinical effectiveness and / or clinical outcome of HCV treatment.
Owner:INNOGENETICS NV
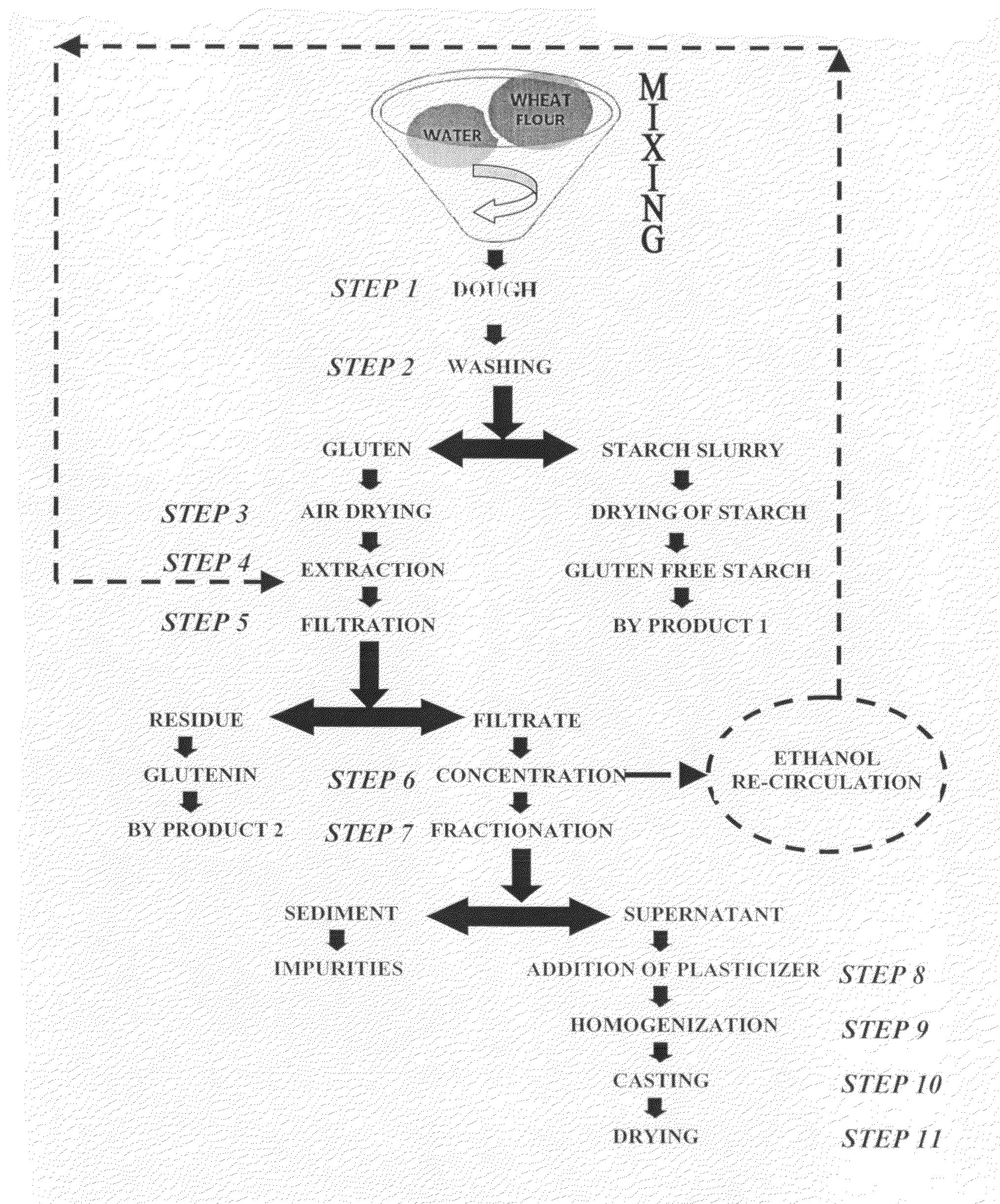
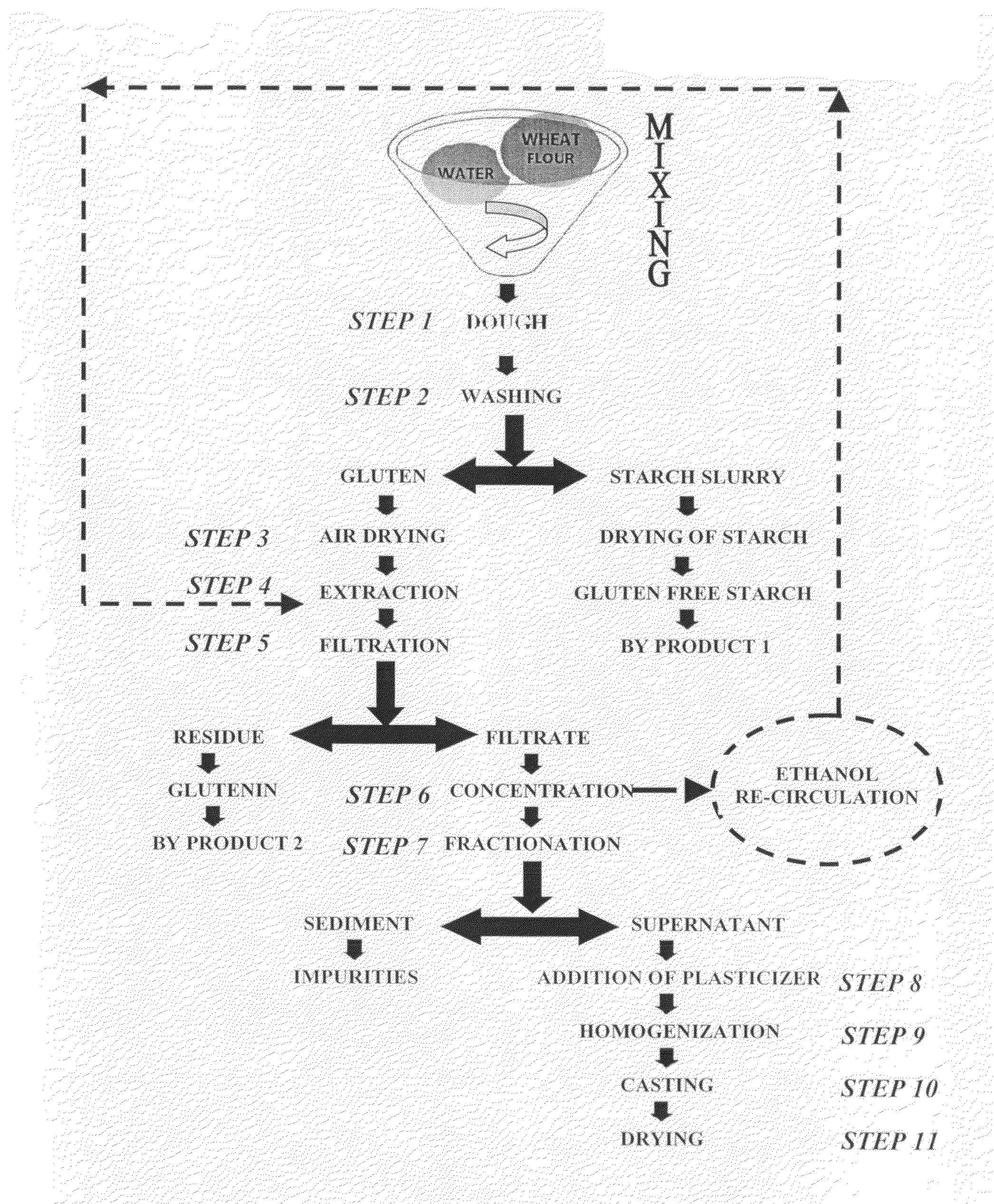
Method of fractionating gliadin from wheat gluten protein and fabrication of edible film therefrom
InactiveUS20090136641A1Excellent resistance to moisture and lipid and gas permeationImprove mechanical propertiesConfectionerySweetmeatsSolubilityGlycerol
A method for the development of biodegradable or edible film from wheat gluten protein has been revealed. For this purpose, a fraction of gliadin protein, on the basis of solubility, is recovered from ethanolic extract of wheat gluten protein to fabricate homogenous, transparent, heat sealable and water soluble edible films with novel functional and mechanical properties. To reduce film brittleness, glycerol was added in the formulation as a plasticizer. A three dimensional network of gliadin protein's fraction, water and plasticizer is formed by virtue of new hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions and disulphide bonds when such films are produced by casting technique followed by drying. This network provides resistance to moisture, lipid and gas permeation together with glossy sheen when coated on a variety of substrates.
Owner:AZAM MAHMOOD +3
Modification sequence of recombinant human mammilla tumor virus L1 capsid protein
InactiveCN101481407AStructural stability has no appreciable effectStructural Stability EffectsViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsAntigenHuman papillomavirus
The invention relates to the prevention and treatment field of human papillomavirus infection, in particular to an amino acid modification sequence of recombinant human papillomavirus (HPV) L1 capsid protein, a nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid modification sequence, and a carrier and a transformant containing the nucleotide sequence; and the invention further relates to application of an HPV L1 protein polymer consisting of the amino acid modification sequence to preparing vaccines, pharmaceutical compositions and diagnostic antigen or diagnostic antibodies. In the invention, an HPV L1 protein wild-type sequence is modified to prevent forming of a disulfide bond in the HPV L1 protein, the modification has no significant effect on the structural stability of the recombinant HPV L1 protein, but significantly improves the efficiency of purification process, and directly reduces the reagent consumption, thus effectively lowering the industrial production cost and having great economical benefit.
Owner:马润林 +1
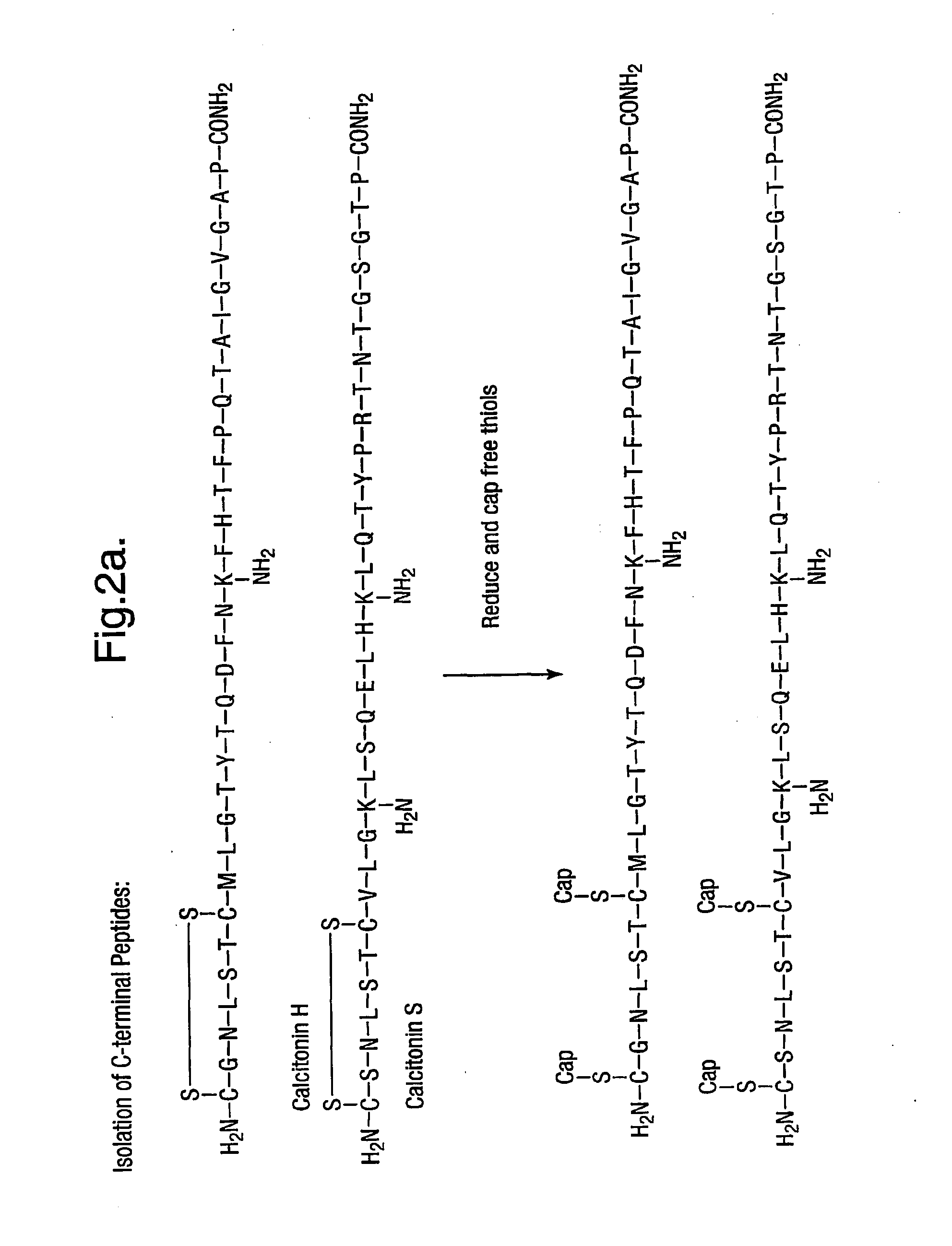
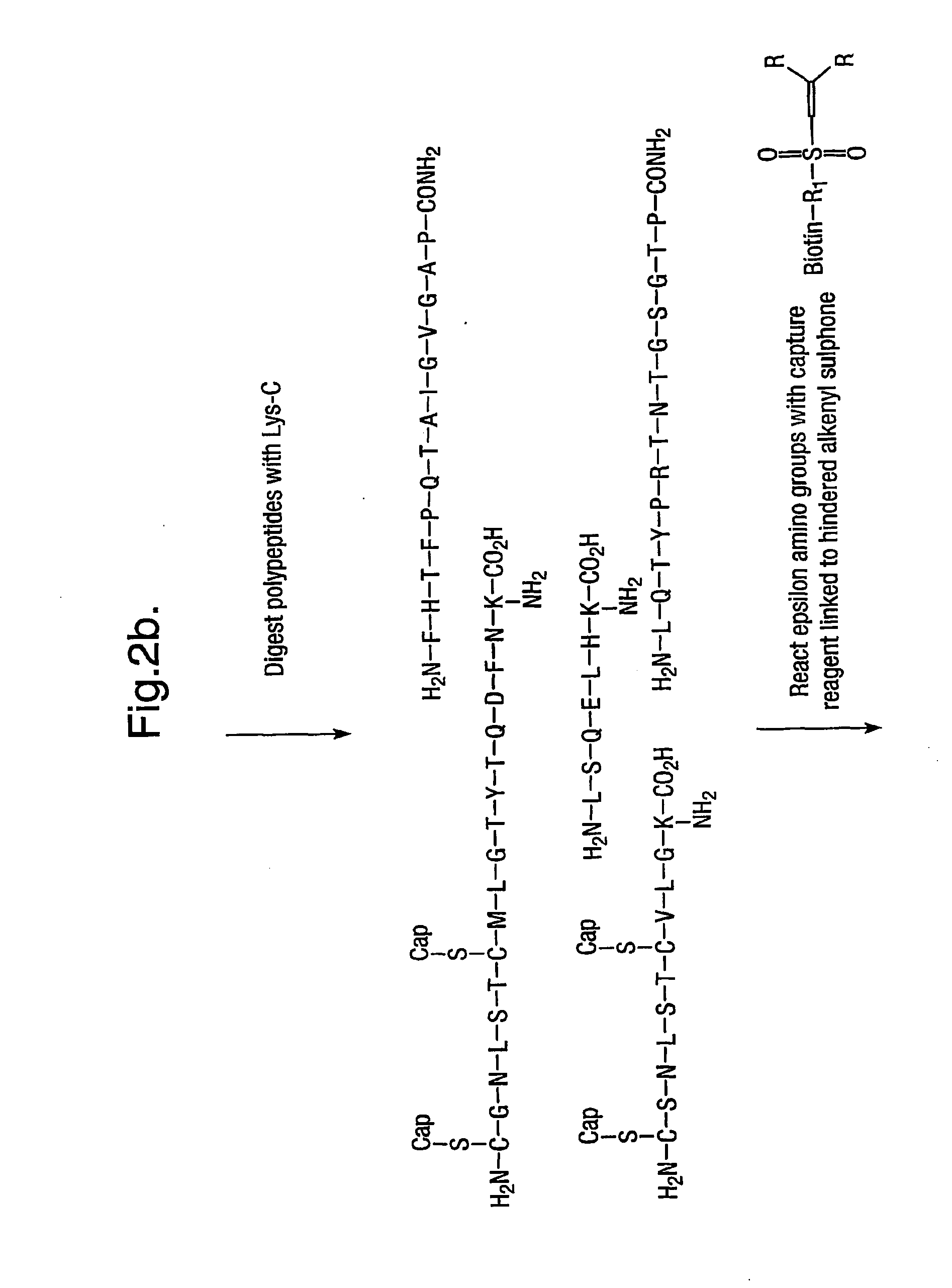
Characterising polypeptides
InactiveUS20050042713A1High selectivityImprove completenessPeptide/protein ingredientsComponent separationPeptide fragmentReactive agent
Provided is a method for characterising a polypeptide or a population of polypeptides, which method comprises the steps of: (a) optionally reducing disulphide linkages in the polypeptides, if they are present and capping free thiols in the polypeptides, if they are present; (b) contacting a sample comprising one or more polypeptides with a cleavage reagent which cleaves one or more polypeptides on the C-terminal side of a lysine residue to produce peptide fragments; (c) optionally deactivating the cleavage reagent; (d) contacting the sample with a lysine reactive agent to cap ε-amino groups; (e) removing those peptides having capped ε-amino groups; and (f) recovering the C-terminal peptides.
Owner:ELECTROPHORETICS LTD
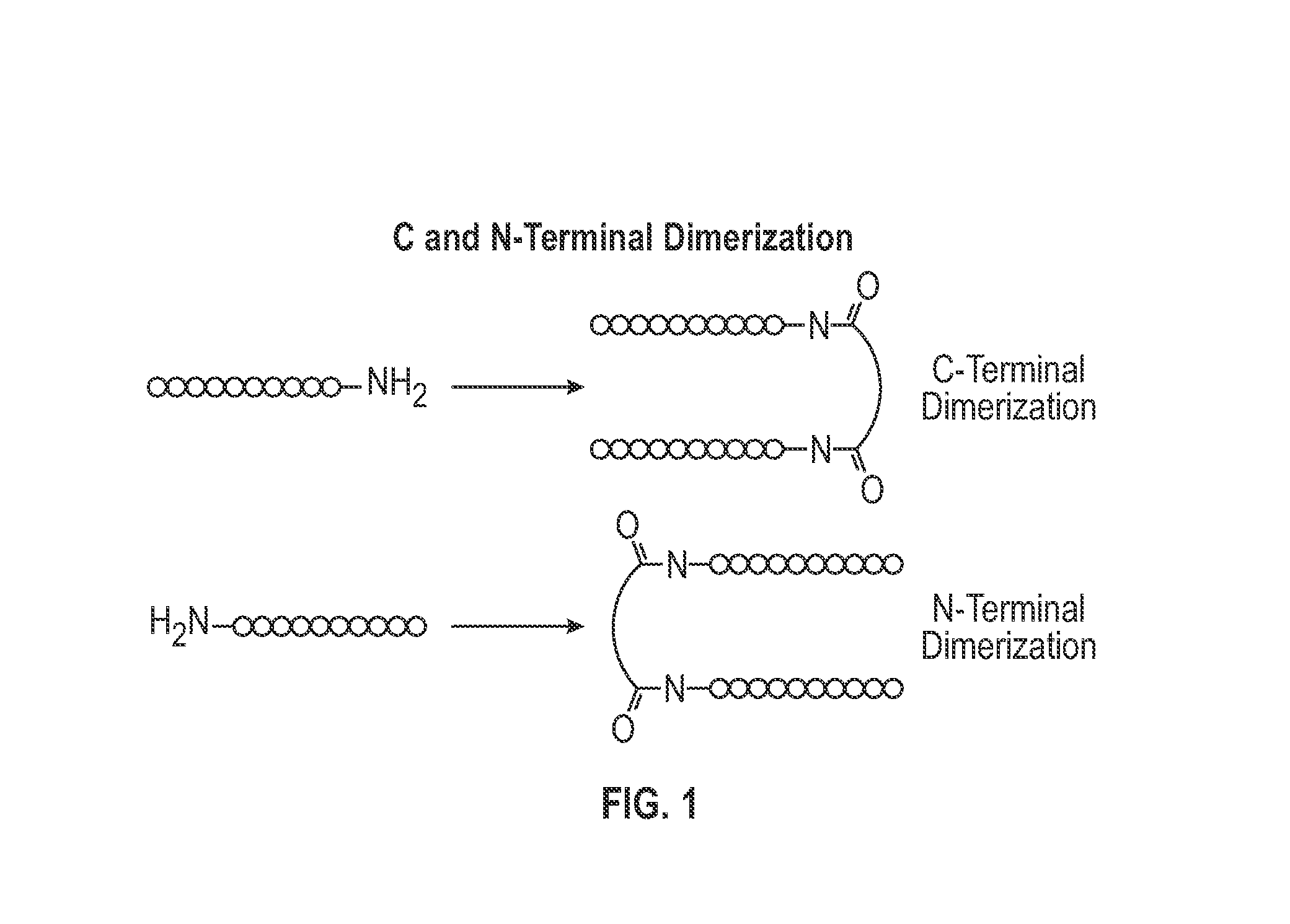
Covalently dimerized bivalent binding agents
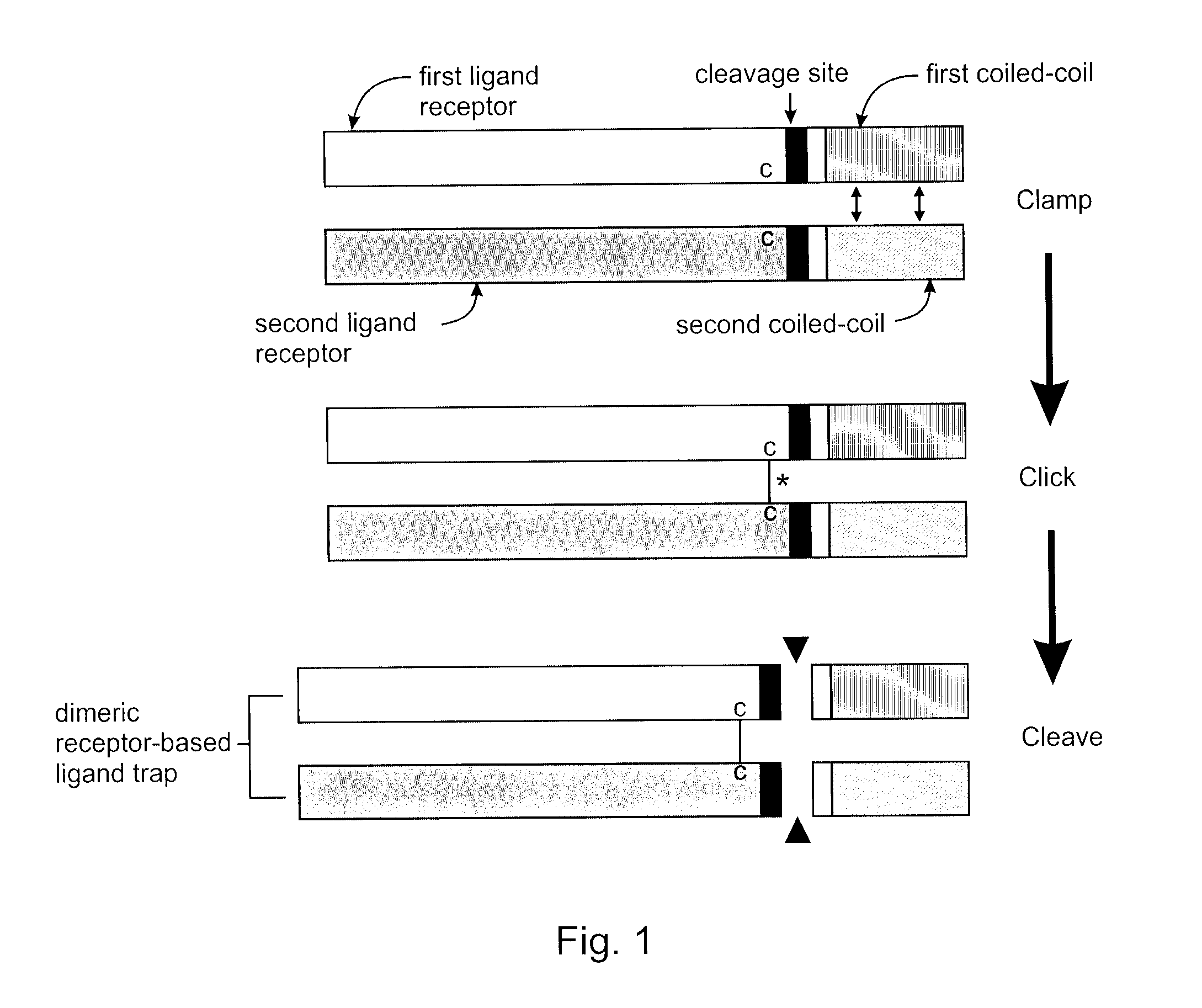
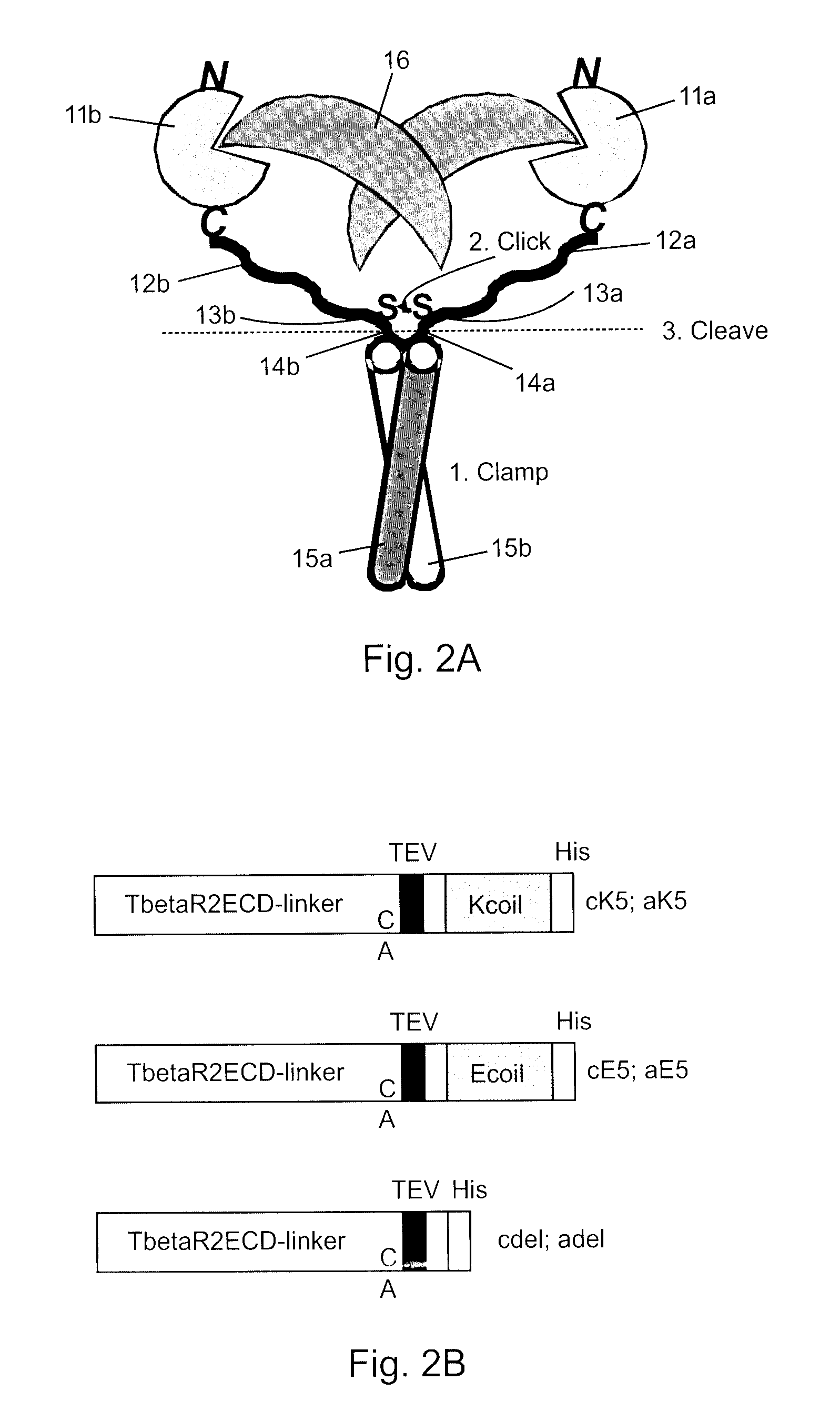
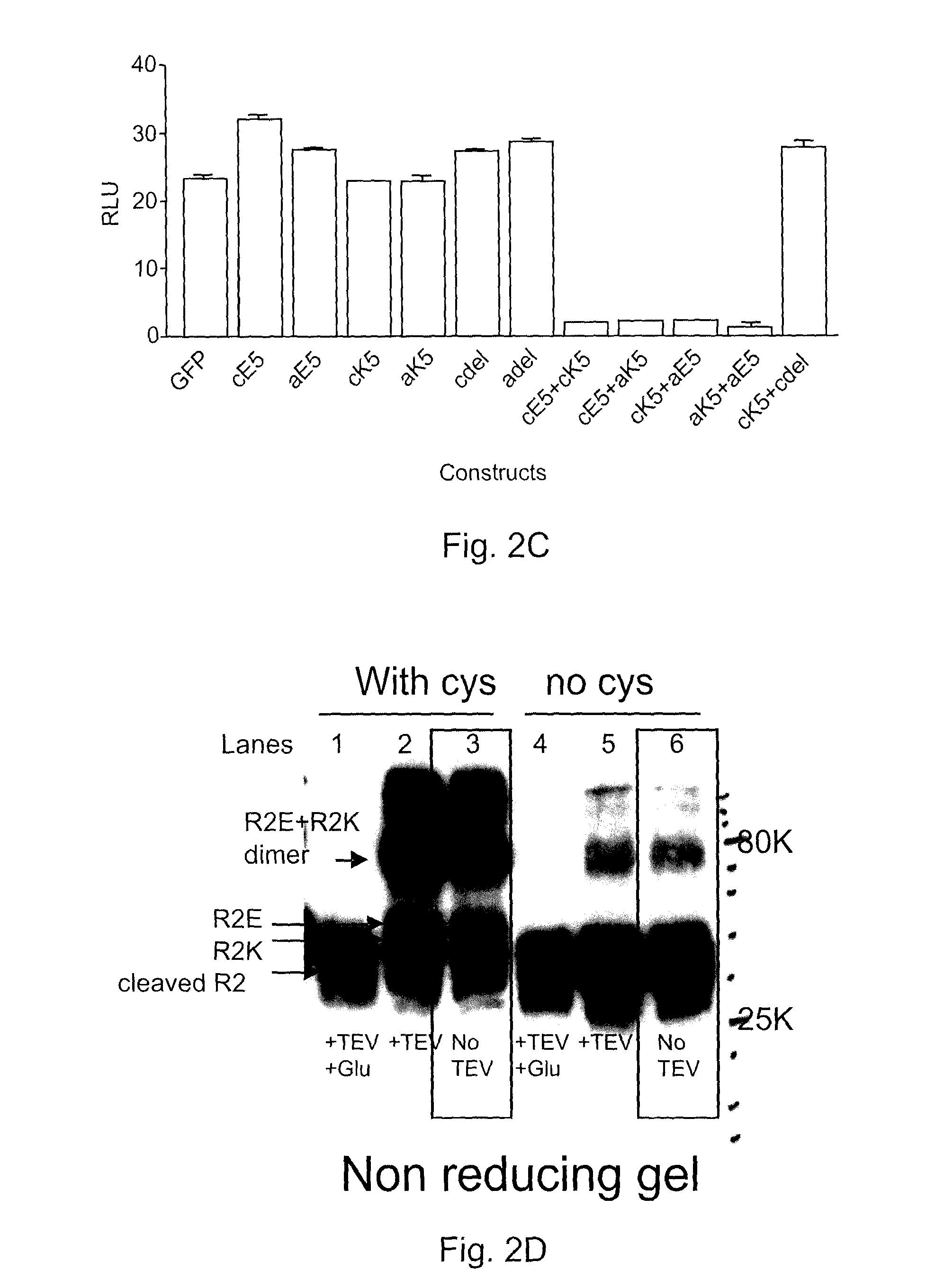
The present invention addresses limitations of prior art receptor-based traps through a methodology called the clamp / click / cleave (CCC) approach. Two fusion proteins each comprising a binding domain fused to a coiled-coil are non-covalently dimerized through the coiled-coil (clamp), and the dimer so formed is stabilized by a covalent disulphide bond (click) between cysteine residues located on the fusion proteins between the binding domains and coiled-coils. Once the disulphide bond has formed, the coiled-coils are subsequently removed (cleave) by cleaving the fusions proteins at cleavage sites located between the cysteine residues and the coiled-coils to provide the covalently dimerized bivalent binding agent of the present invention. Such binding agents are useful in the treatment and diagnosis of disease states characterized by production and / or overexpression of a ligand to which the binding domains bind. The invention is particularly useful for covalently dimerized receptor-based ligand traps where the binding domains are receptor ligand-binding domains, such as those of TGF-β receptors.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Large-scale preparation and purification method and application of mu-conopeptide
ActiveCN110894225AHigh synthesis efficiencyEasy to operateCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAmino acid synthesisCombinatorial chemistry
The invention discloses a large-scale preparation and purification method and application of mu- conopeptide. The large-scale preparation and purification method of the mu-conopeptide comprises the steps of preparation of linear peptide amino resin, cracking, linear peptide folding and crude peptide purification. Amino resin with the substitution degree of 0.6-0.8 is adopted, and the synthesis efficiency is improved; the amino acid is sequentially coupled through solid-phase synthesis to synthesize protected 22-peptide amino resin, and cracking and concentration are carried out; three pairs ofdisulfide bonds are formed by one-step folding through air oxidation, no extra oxidizing agent needs to be added in the folding process, and the method is simple to operate, low in cost and suitablefor industrial mass production; crude peptide is prepared and purified through HPLC, and the mu- conopeptide with the purity larger than 97% is obtained. The invention further provides the applicationof the mu- conopeptide in preparing wrinkle-removing cosmetics. An effect of injecting botulinum toxin can be achieved through simple smearing, and side effects such as pain and facial paralysis caused by botulinum toxin injection can be avoided.
Owner:珠海市维琪科技有限公司
Binding constructs and methods for use thereof
The invention relates to novel binding domain-immunoglobulin fusion proteins that feature a binding domain for a cognate structure such as an antigen, a counterreceptor or the like, a wild-type IgG, IGA or IgE hinge-acting region, i.e., IgE CH2, region polypeptide or a mutant IgGI hinge region polypeptide having either zero, one or two cysteine residues, and immunoglobulin CH2 and CH3 domains, and that are capable of ADCC and / or CDC while occurring predominantly as polypeptides that are compromised in their ability to form disulfide-linked multimers. The fusion proteins can be recombinantly produced at high expression levels. Also provided are related compositions and methods, including cell surface forms of the fusion proteins and immunotherapeutic applications of the fusion proteins and of polynucleotides encoding such fusion proteins.
Owner:EMERGENT PRODUCTS DEVELOPMENT SEATTLE LLC
Compounds and compounds for use in methods for treating diseases or conditions mediated by protein disulfide isomerase
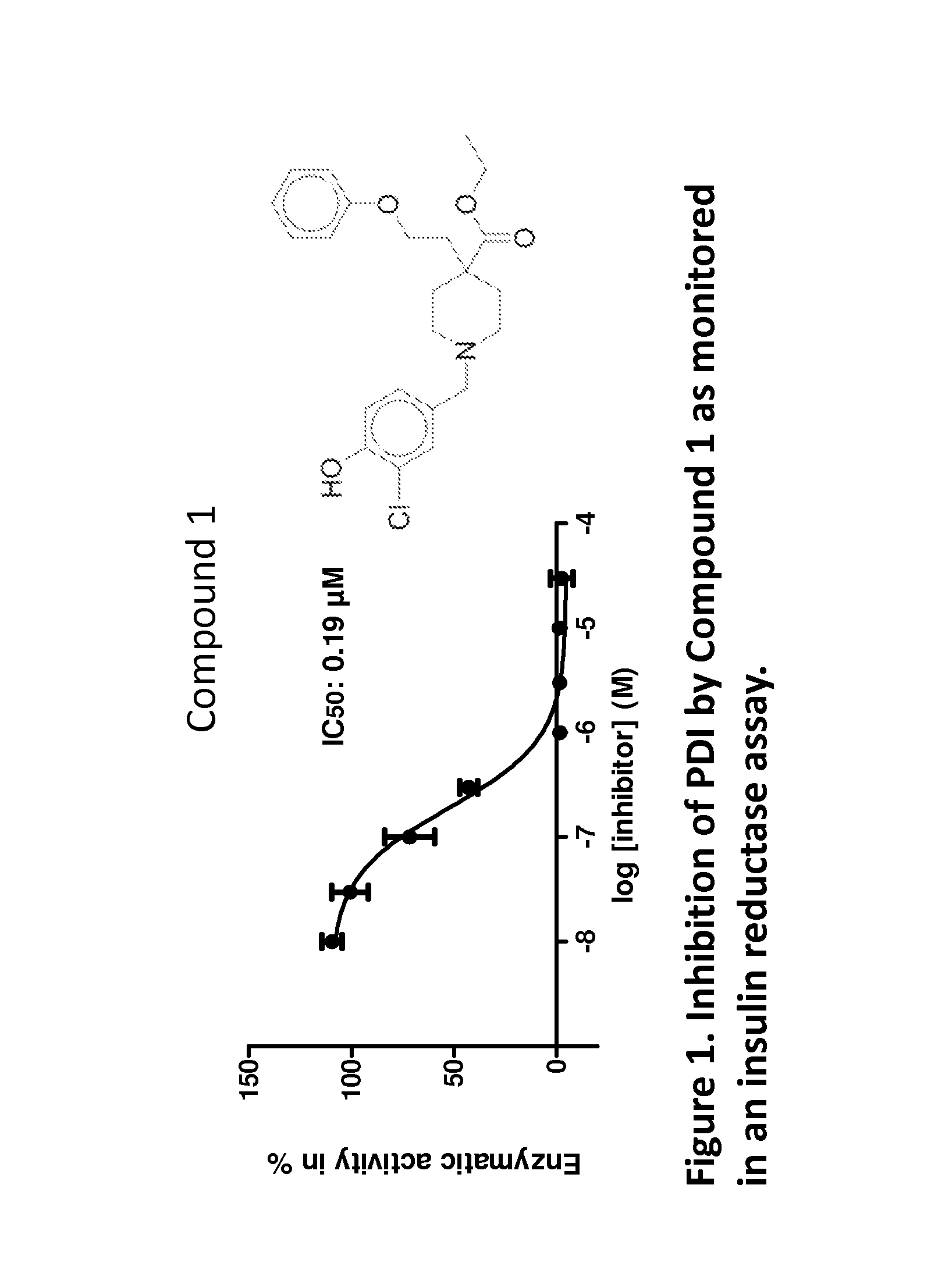
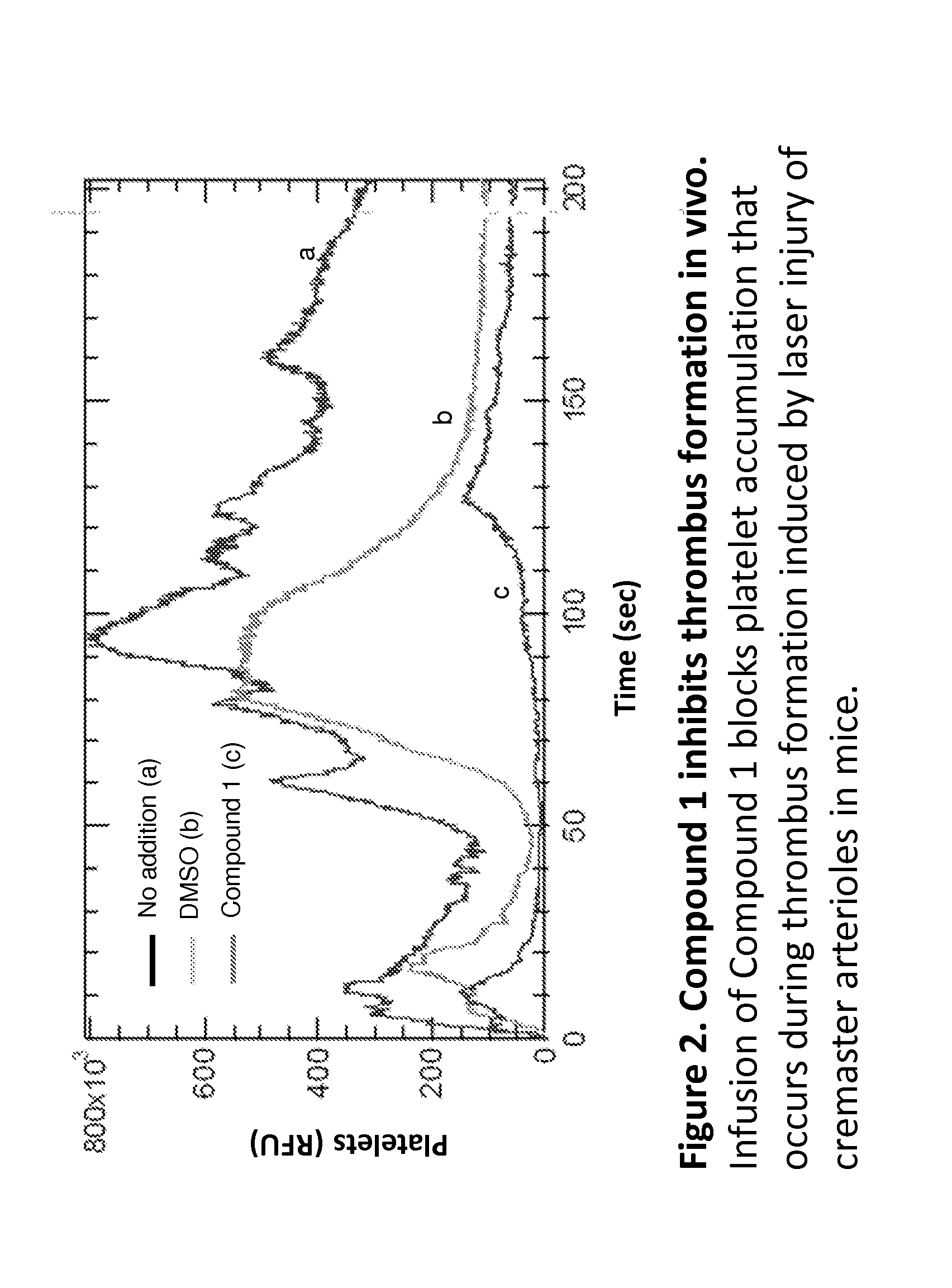
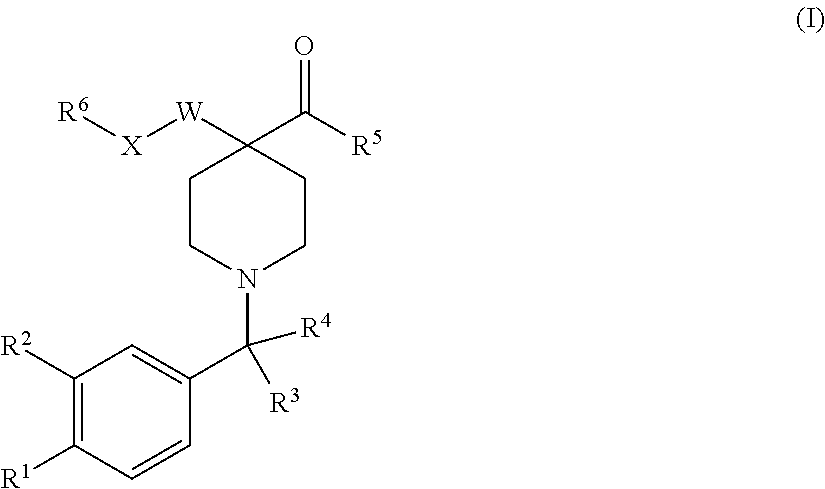
The invention provides compounds of formula (I) that inhibit PDI, for use in methods to treat or prevent a disease or condition in a subject that would benefit by inhibition of PDI. Formula (I)
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com