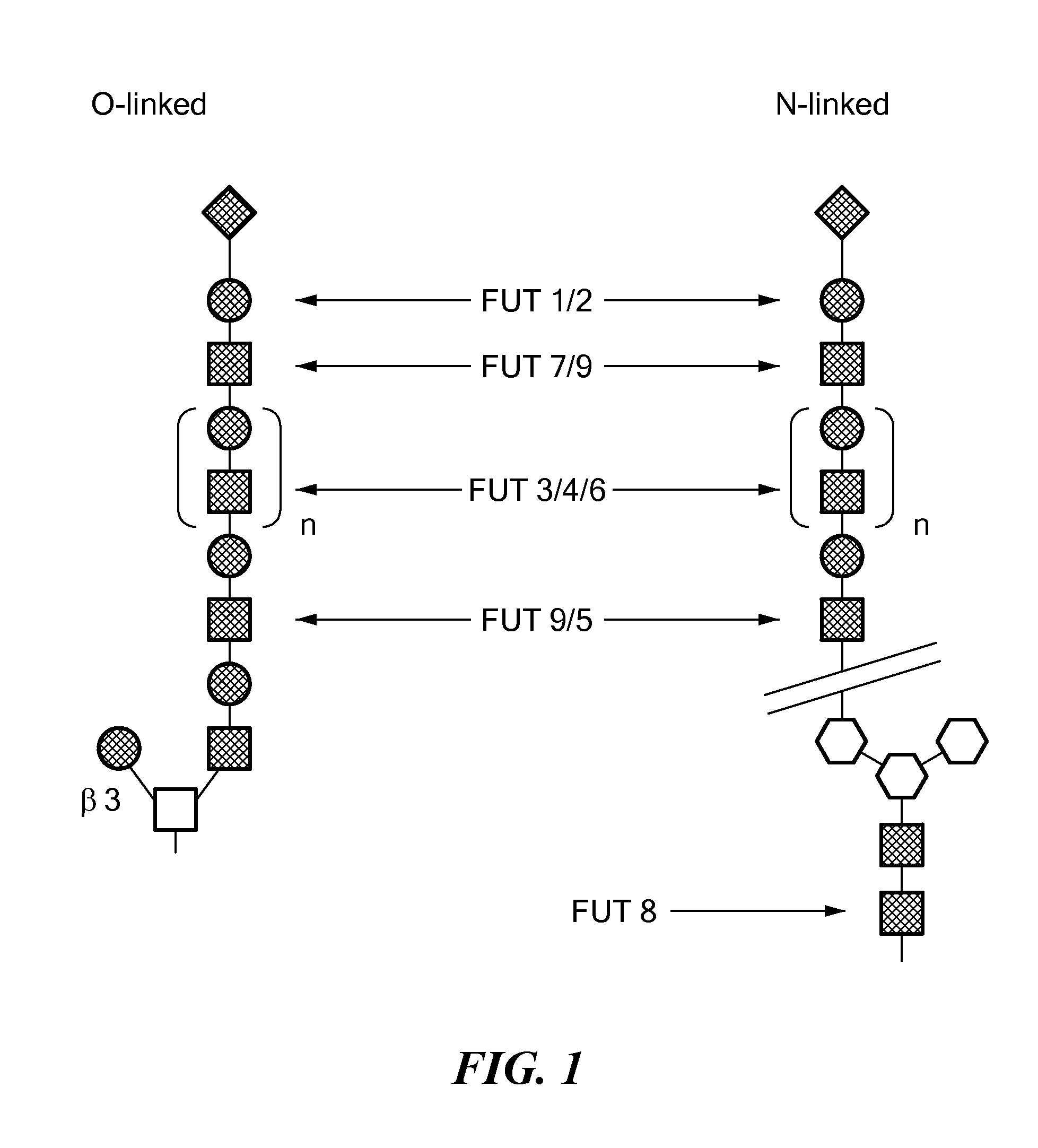
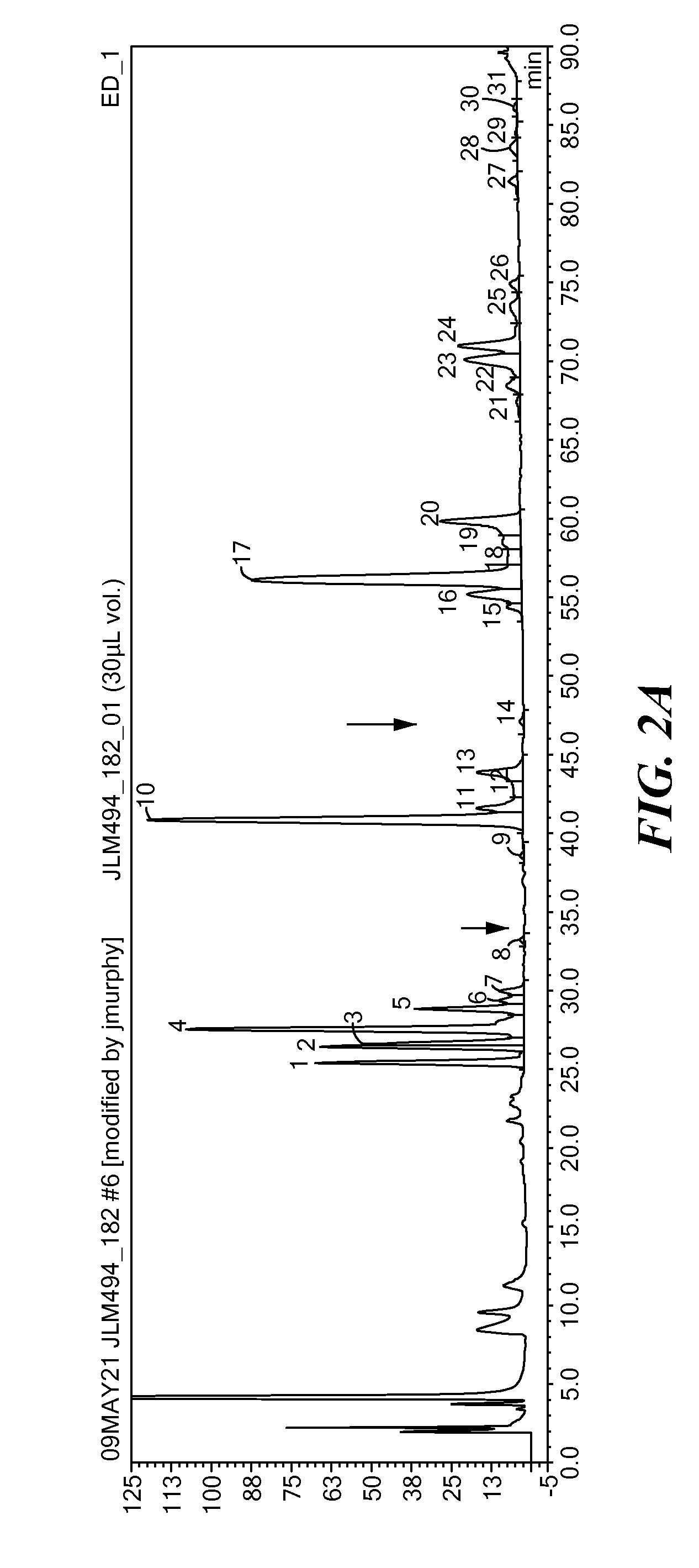
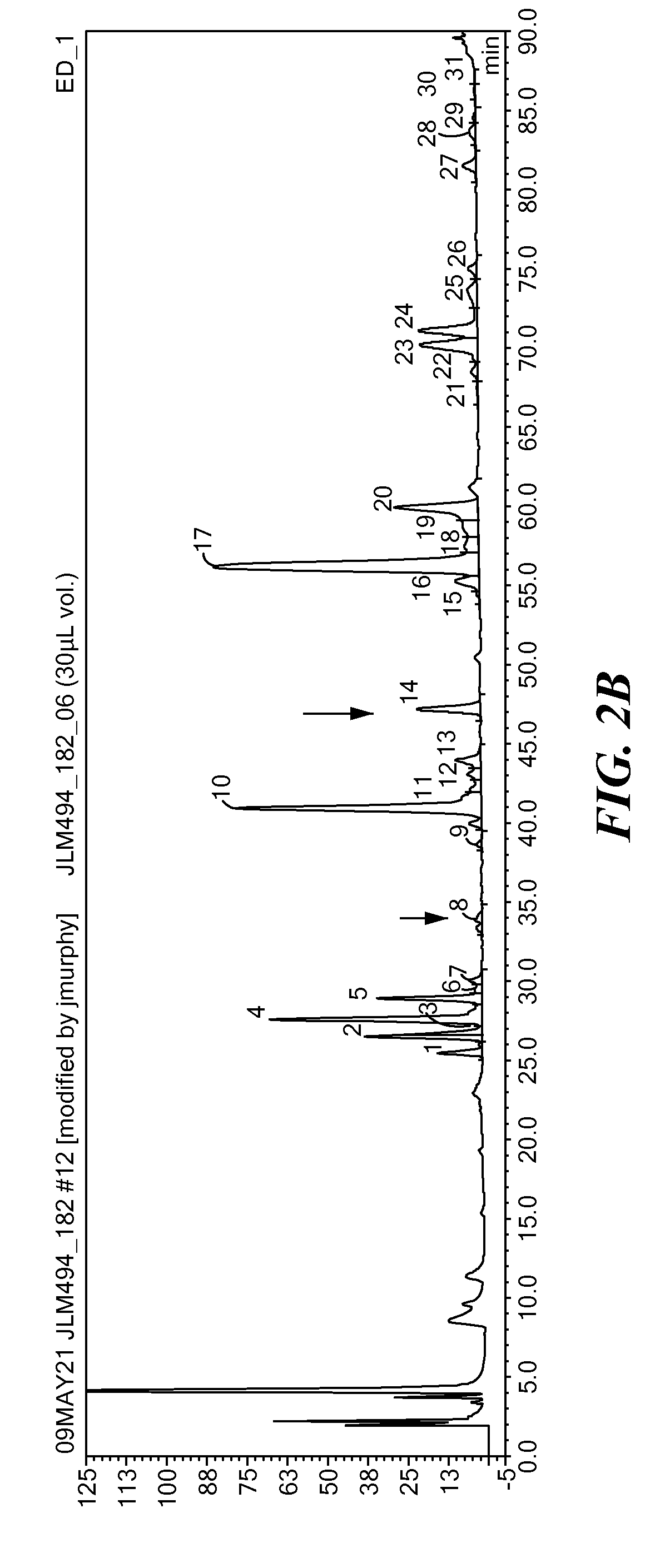
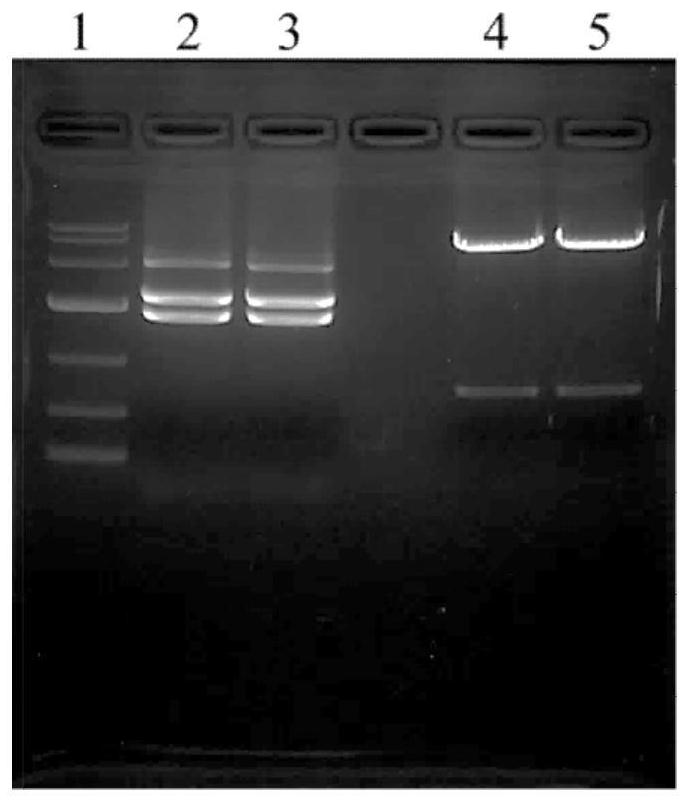
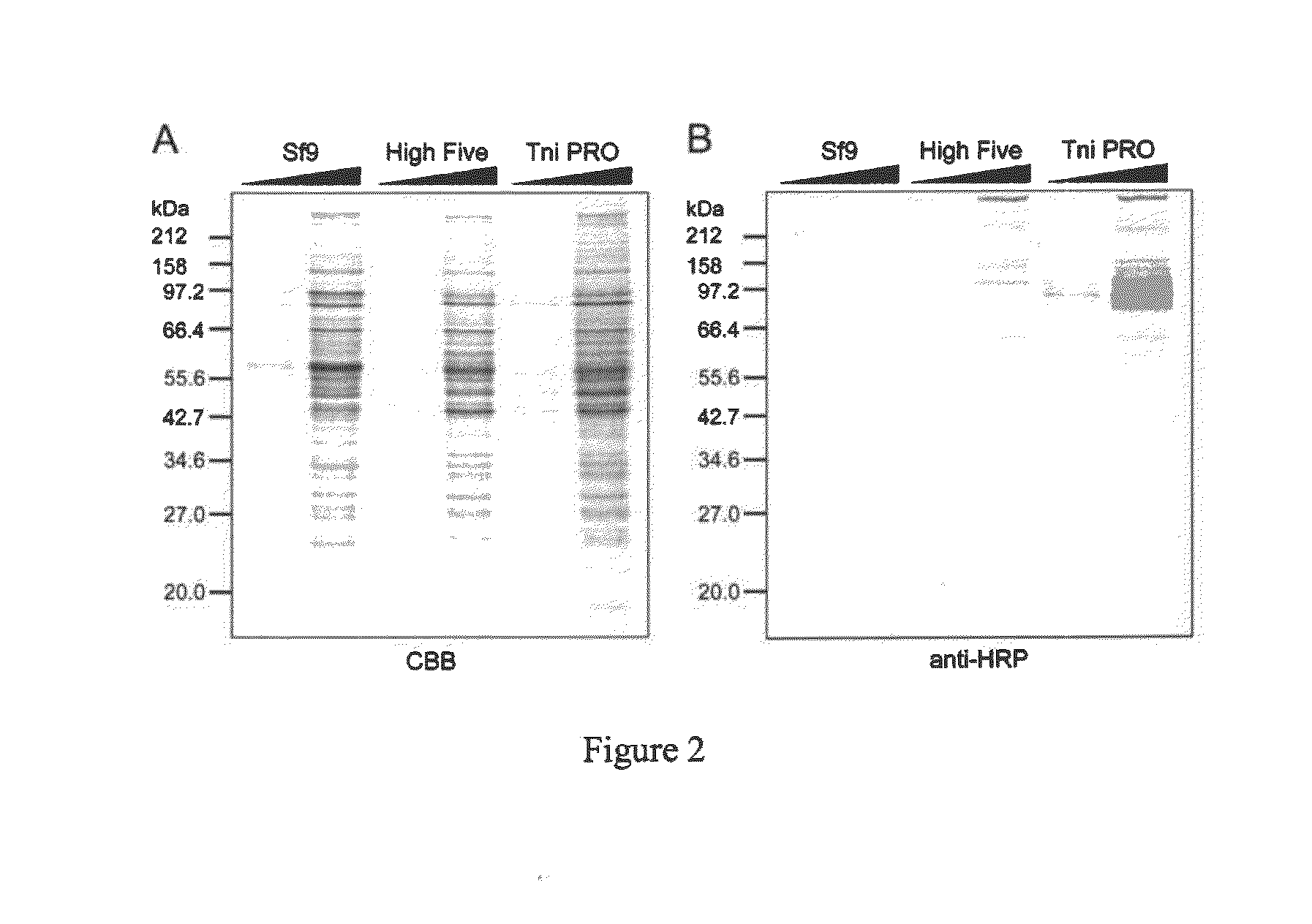
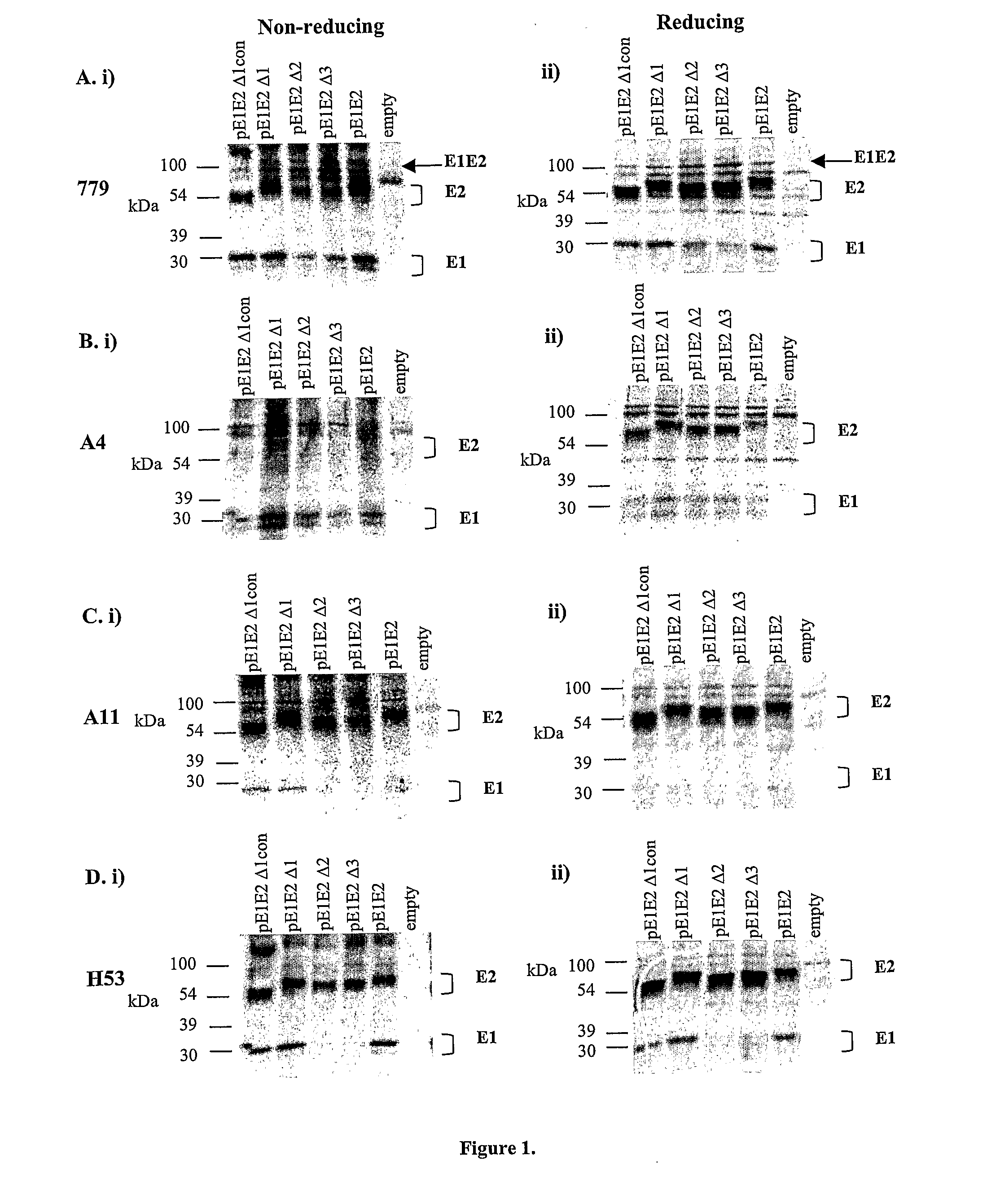
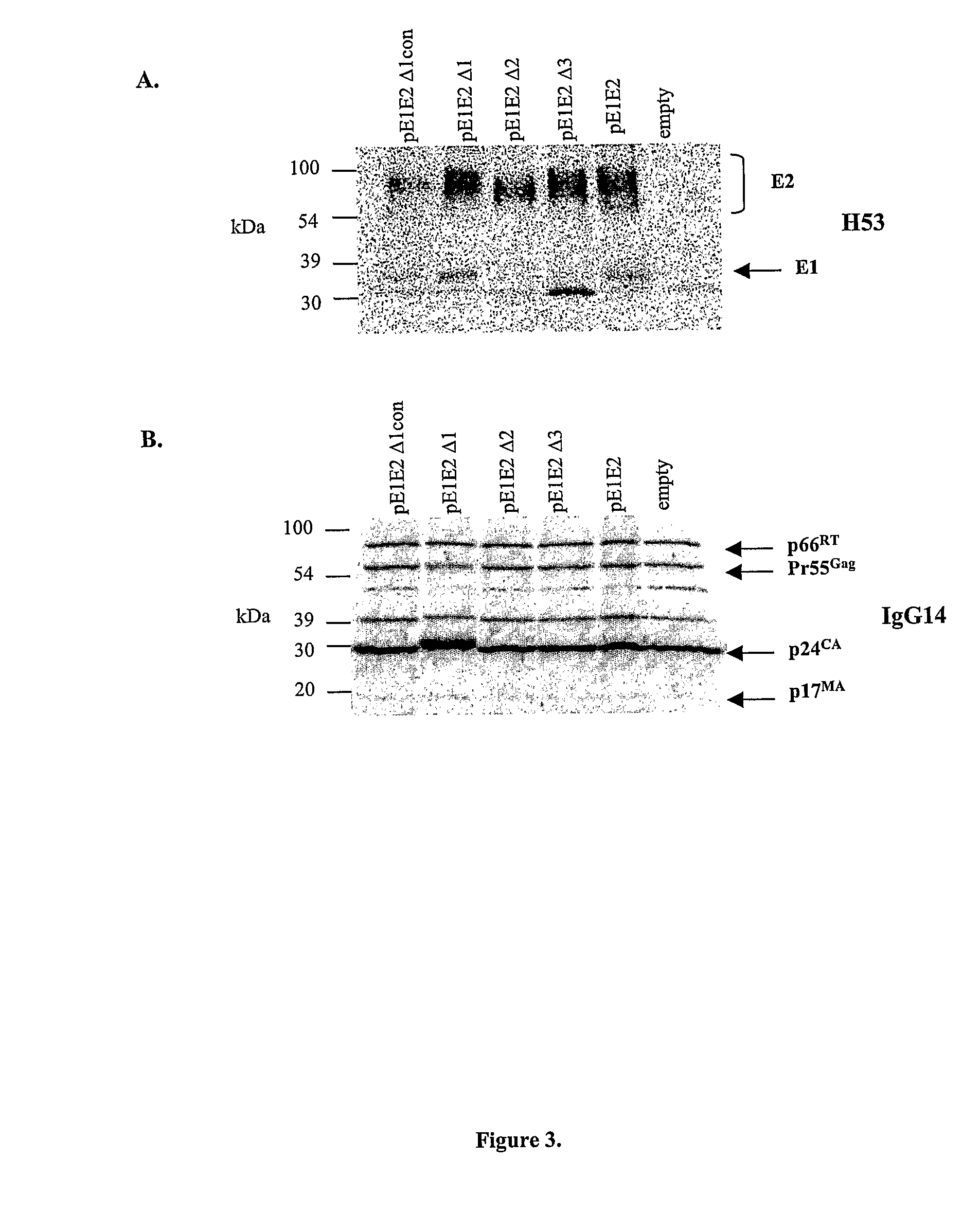
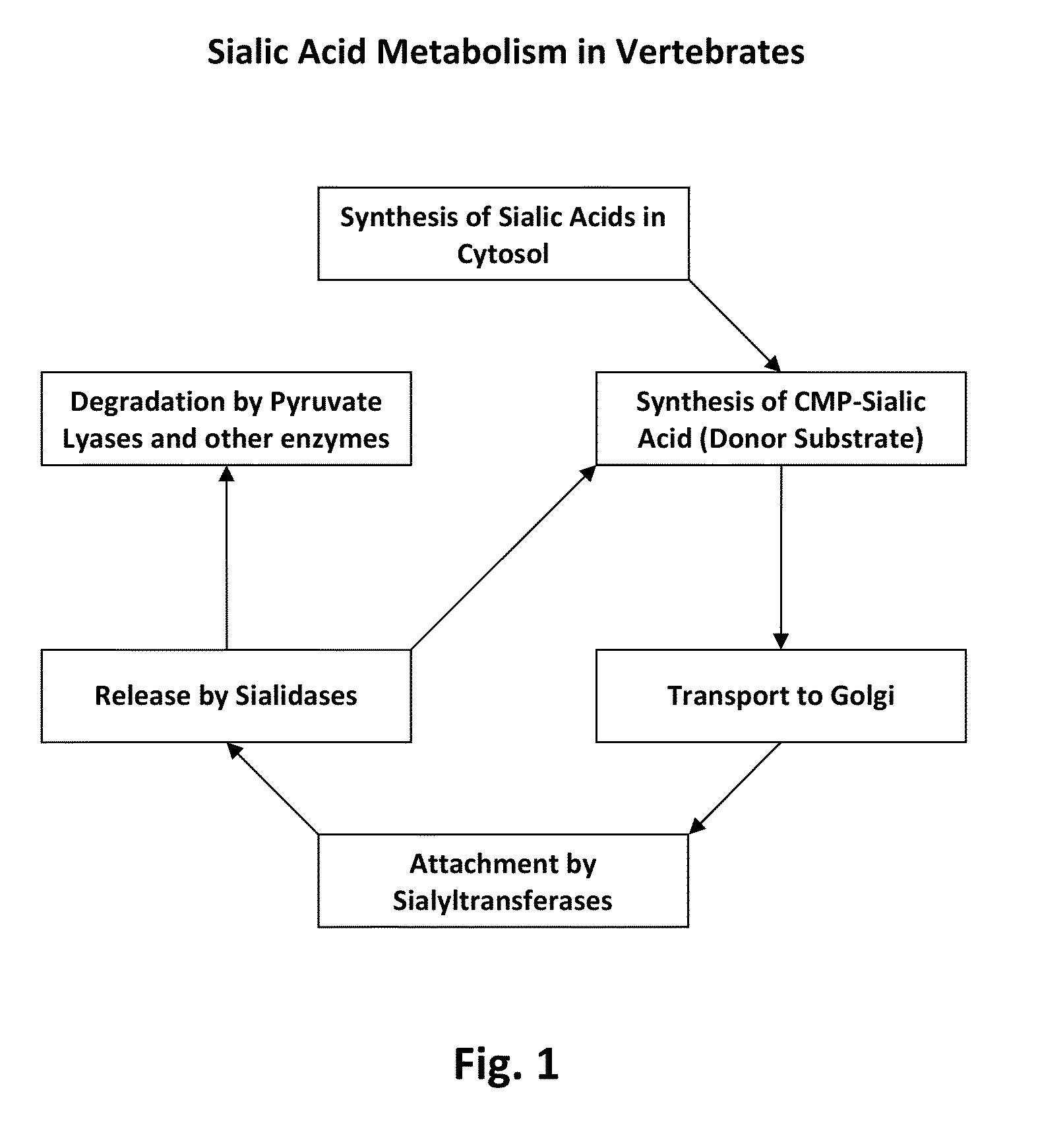
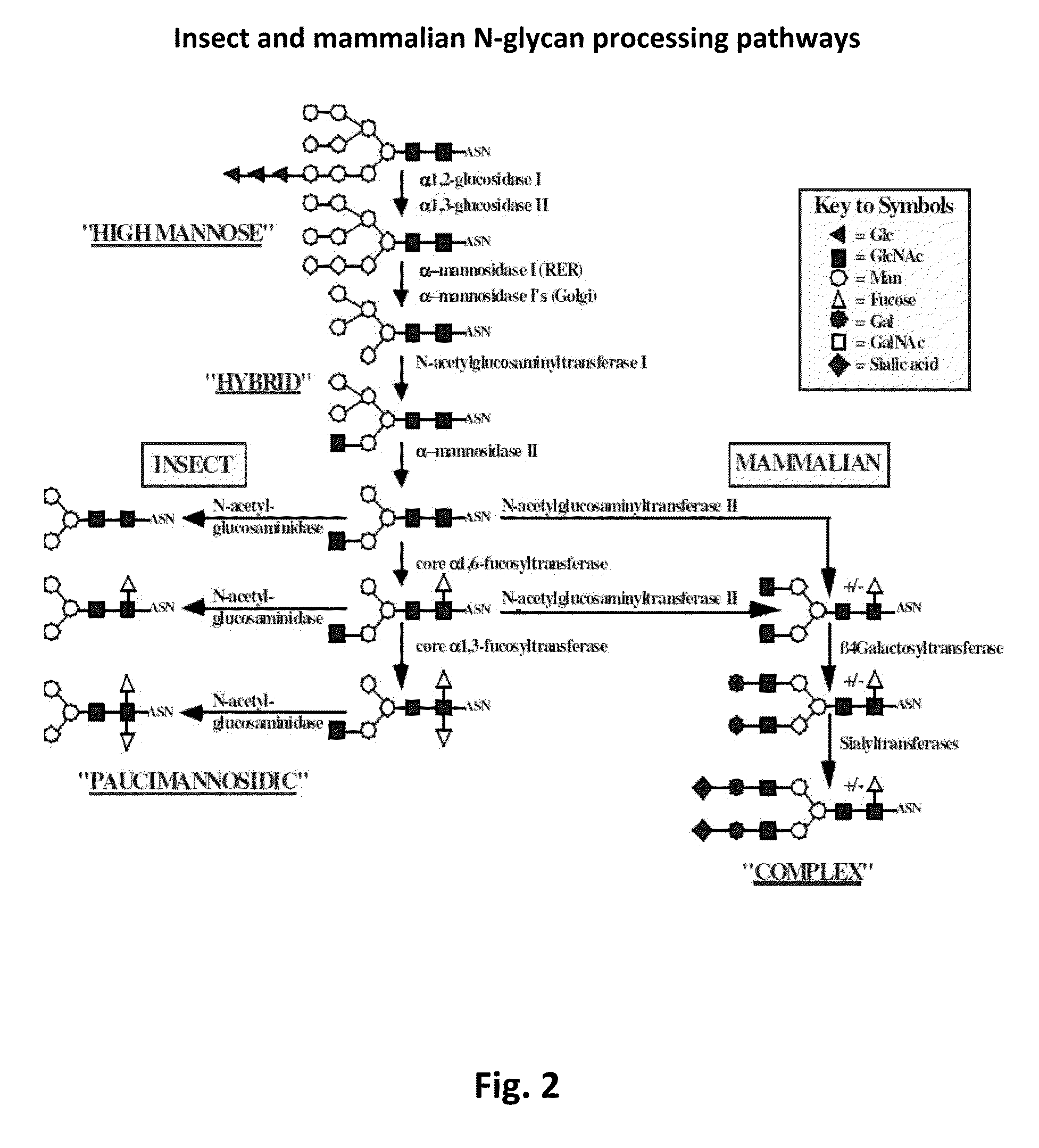
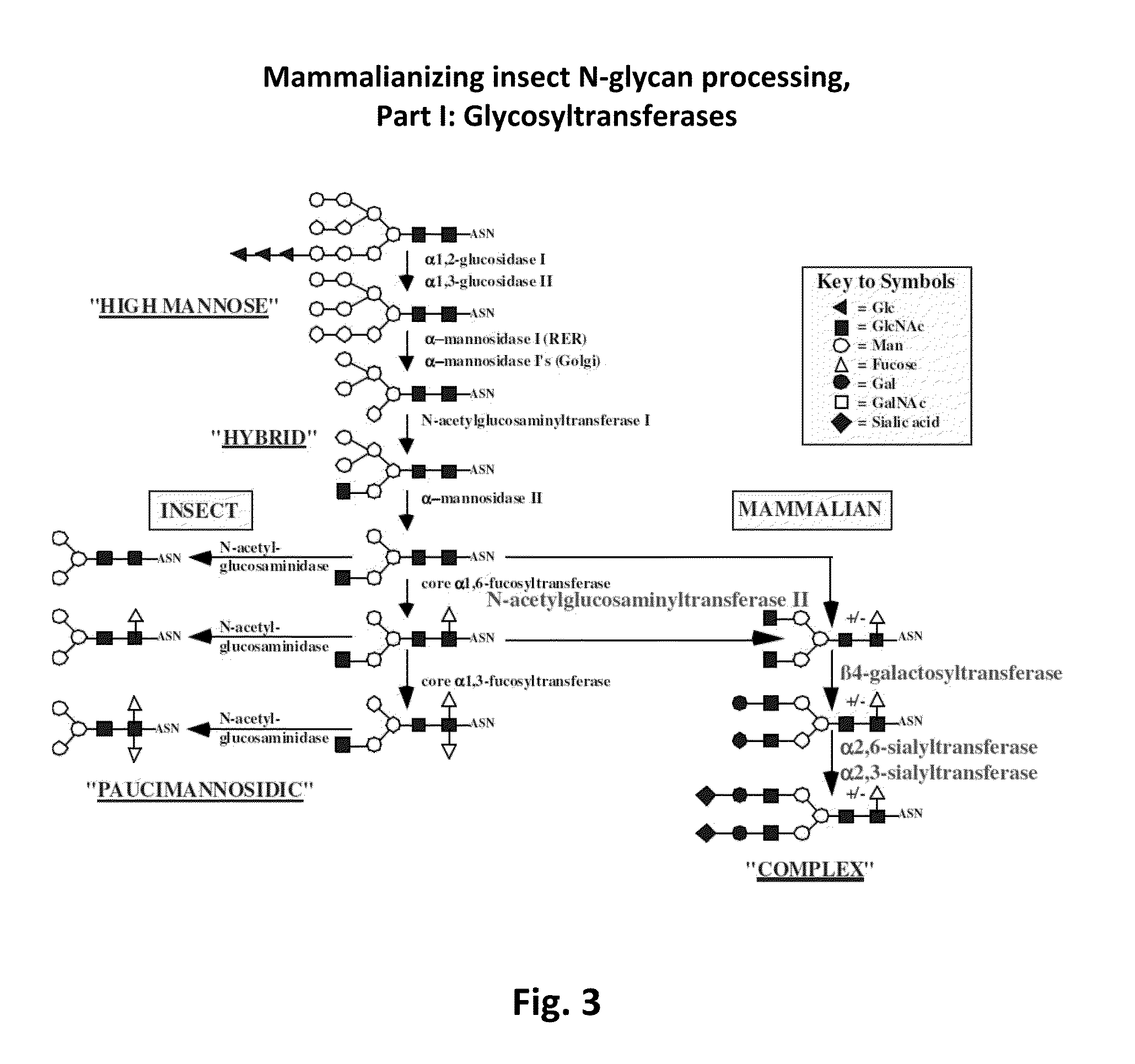
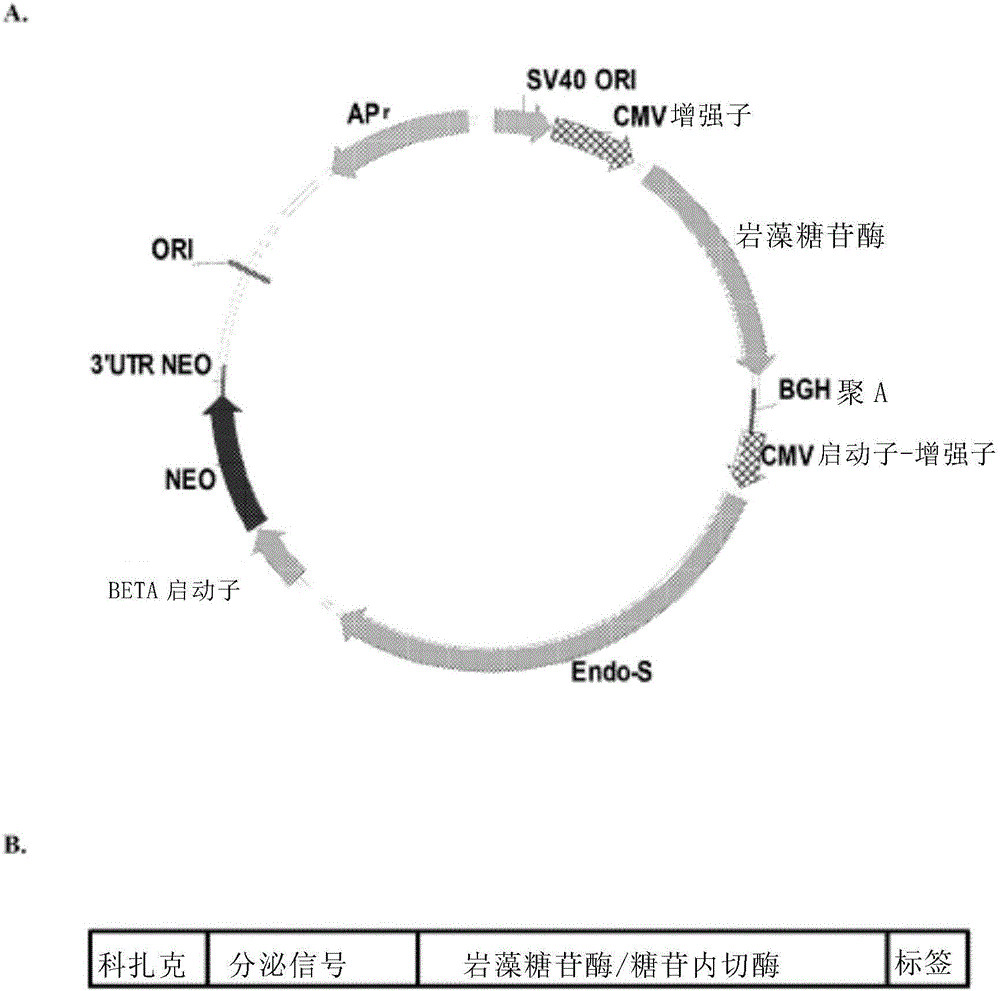
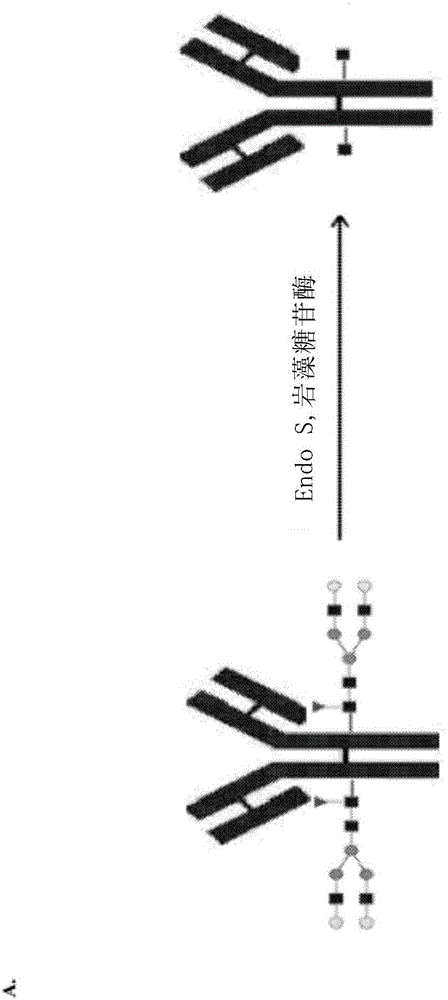
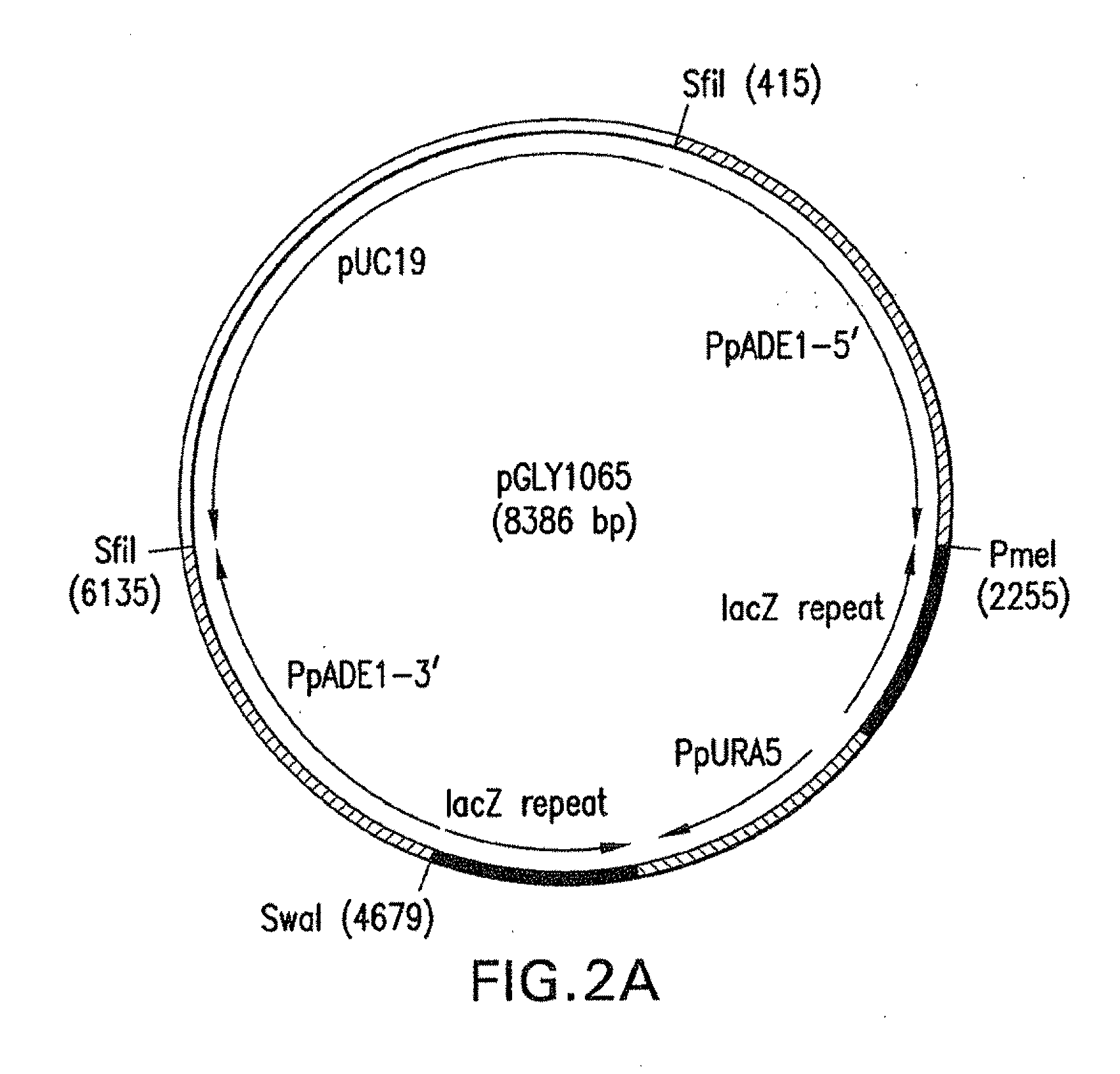
Patents
Literature
74 results about "Recombinant glycoprotein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminogly ycanases
PendingUS20060104968A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsSenses disorderNervous disorderHyaluronidaseRecombinant glycoprotein
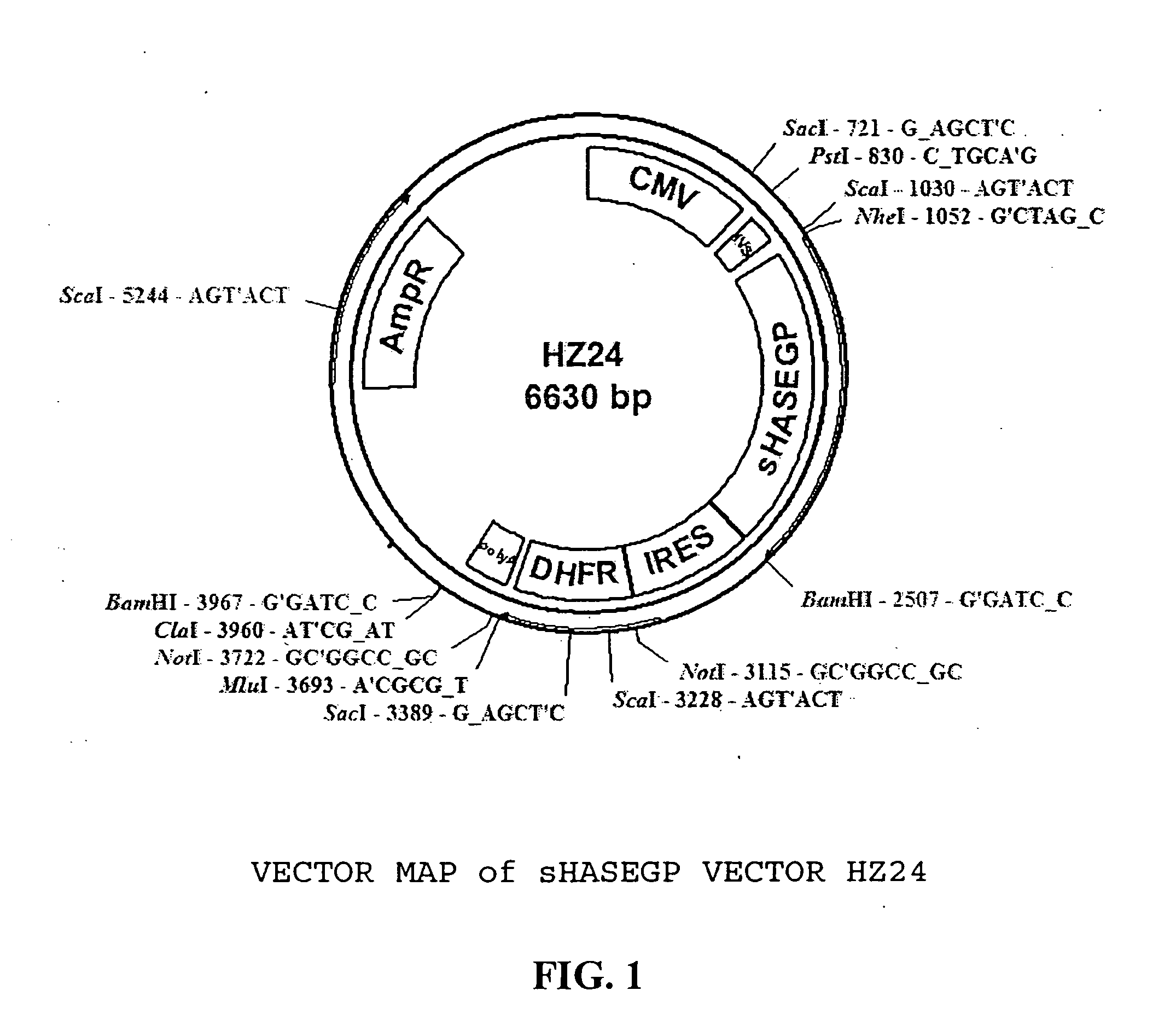
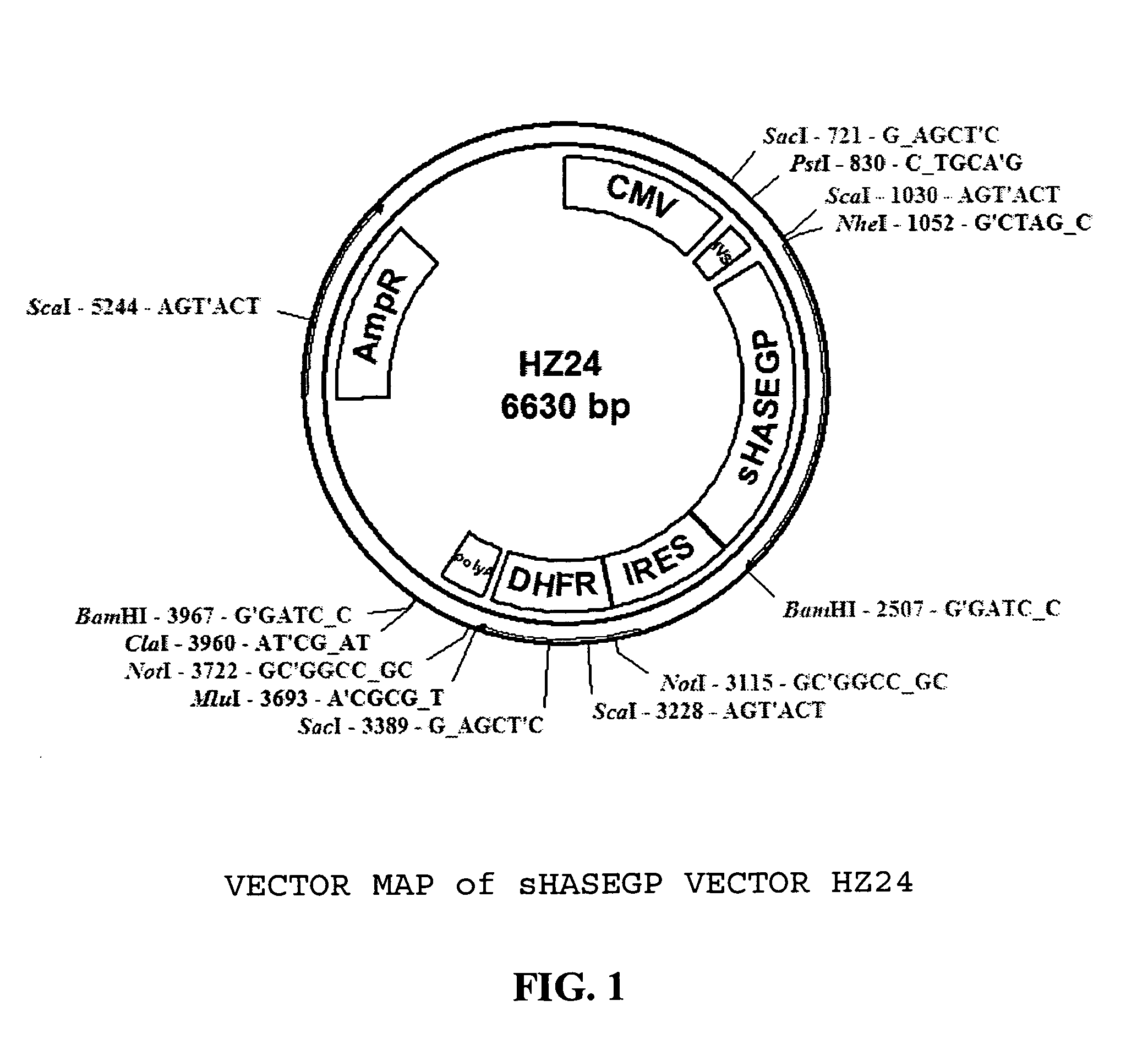
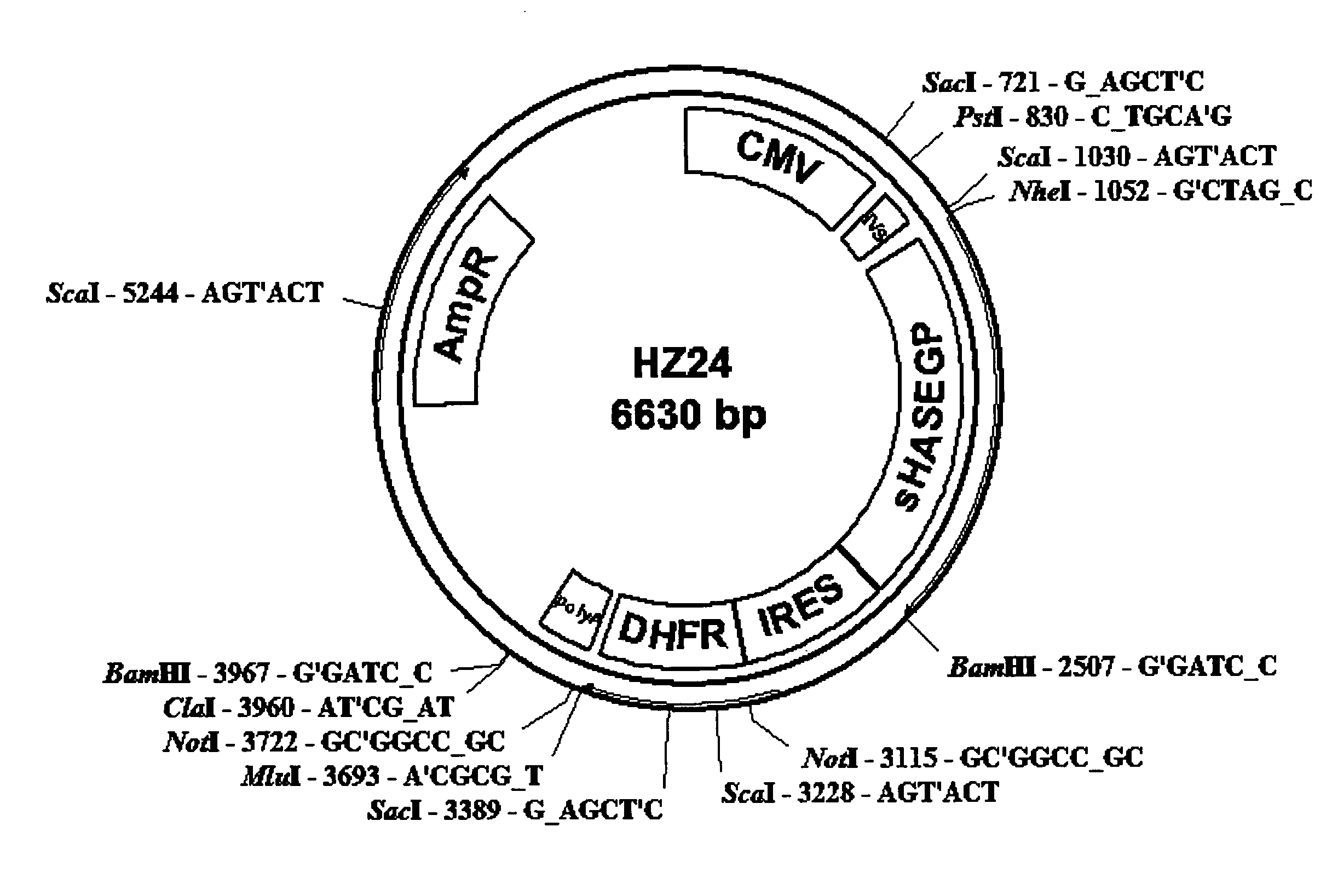
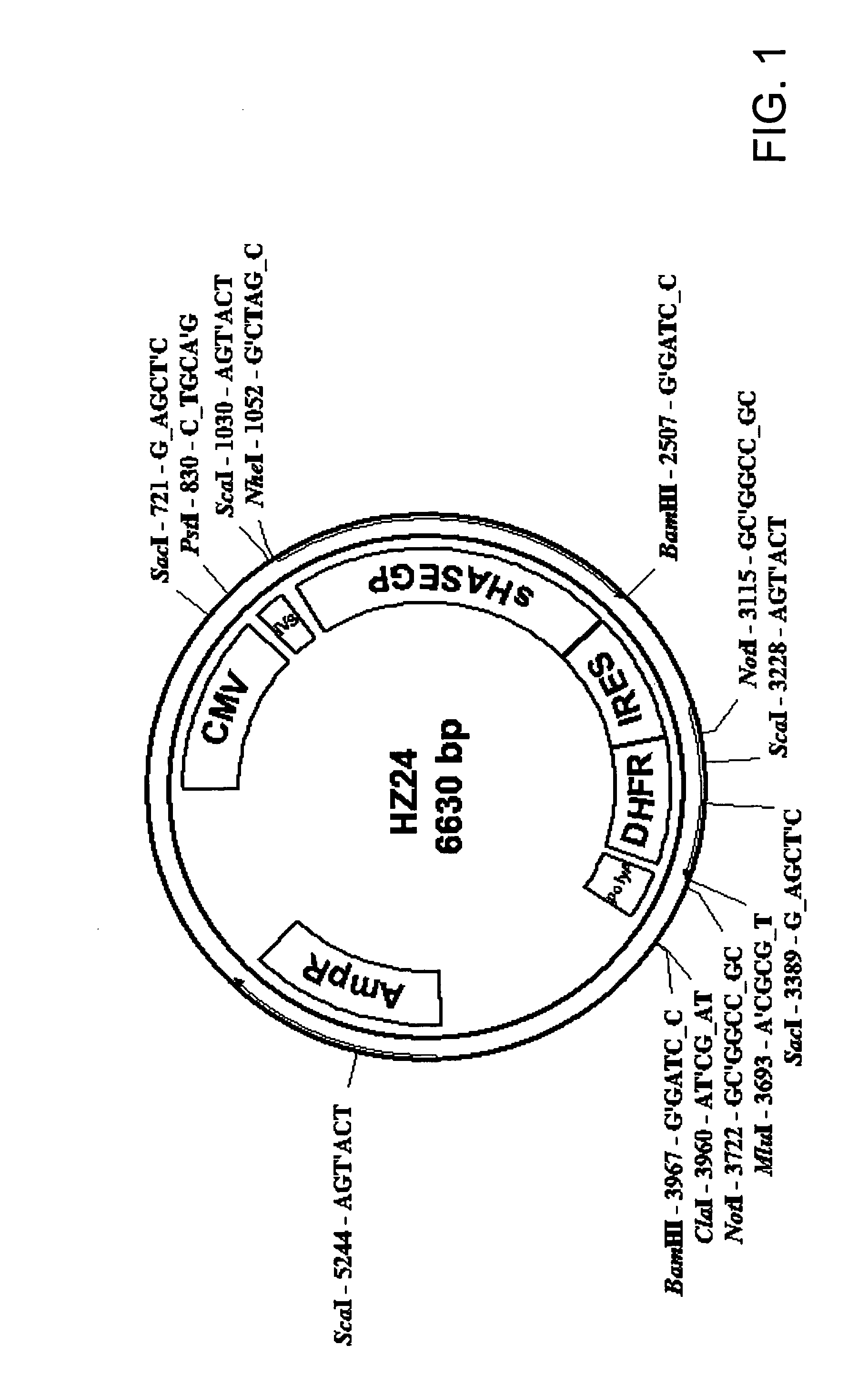
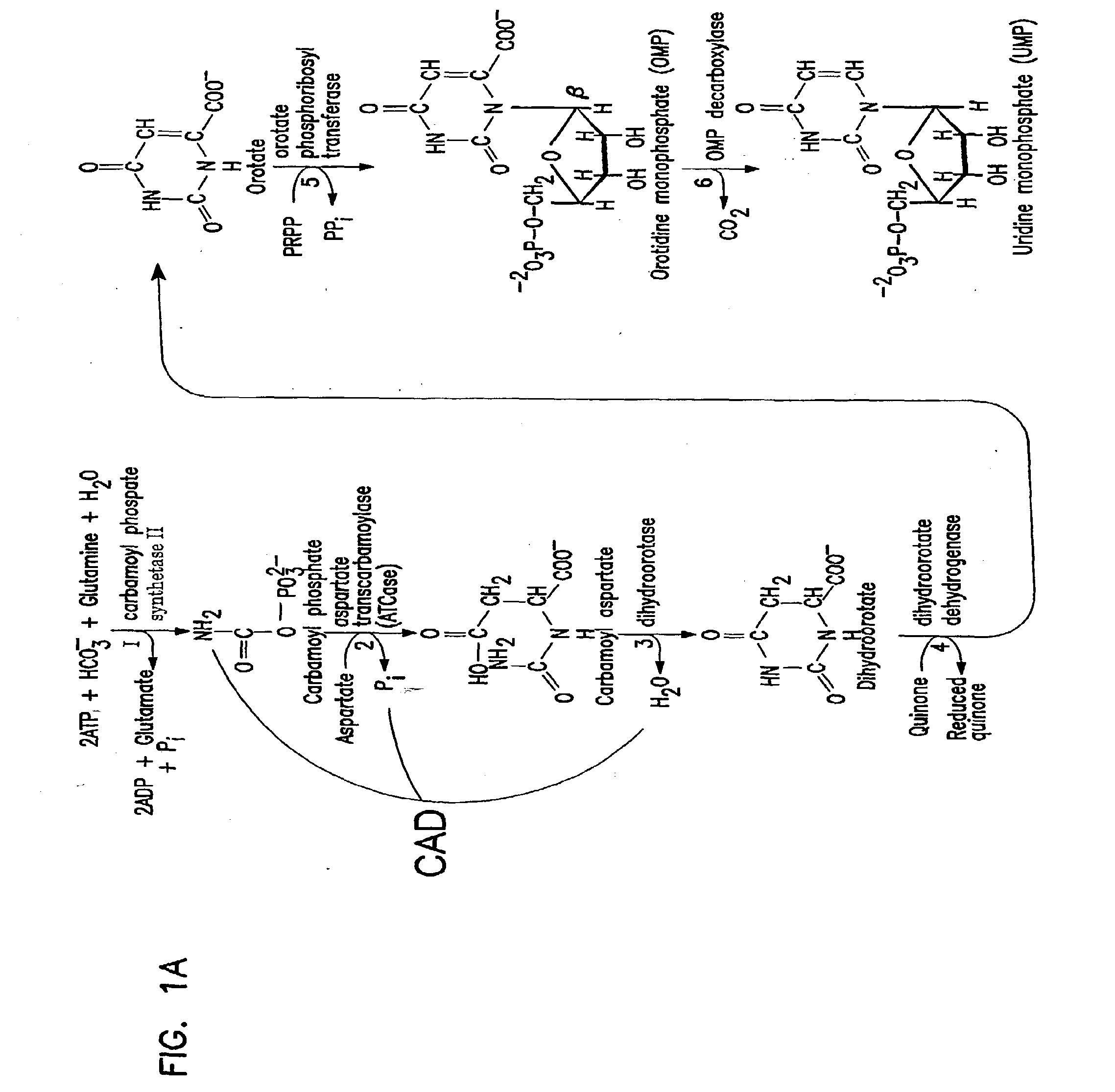
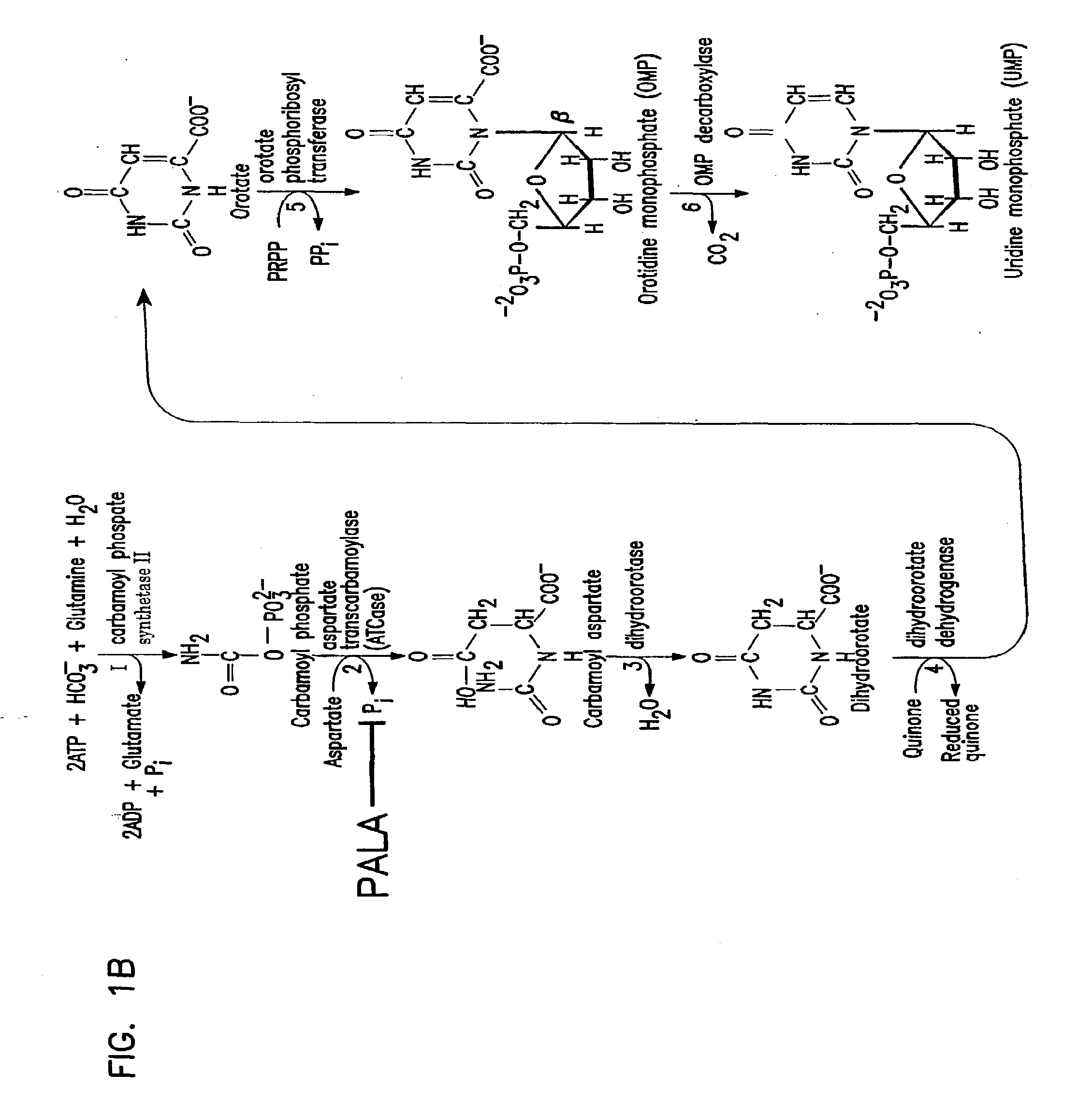
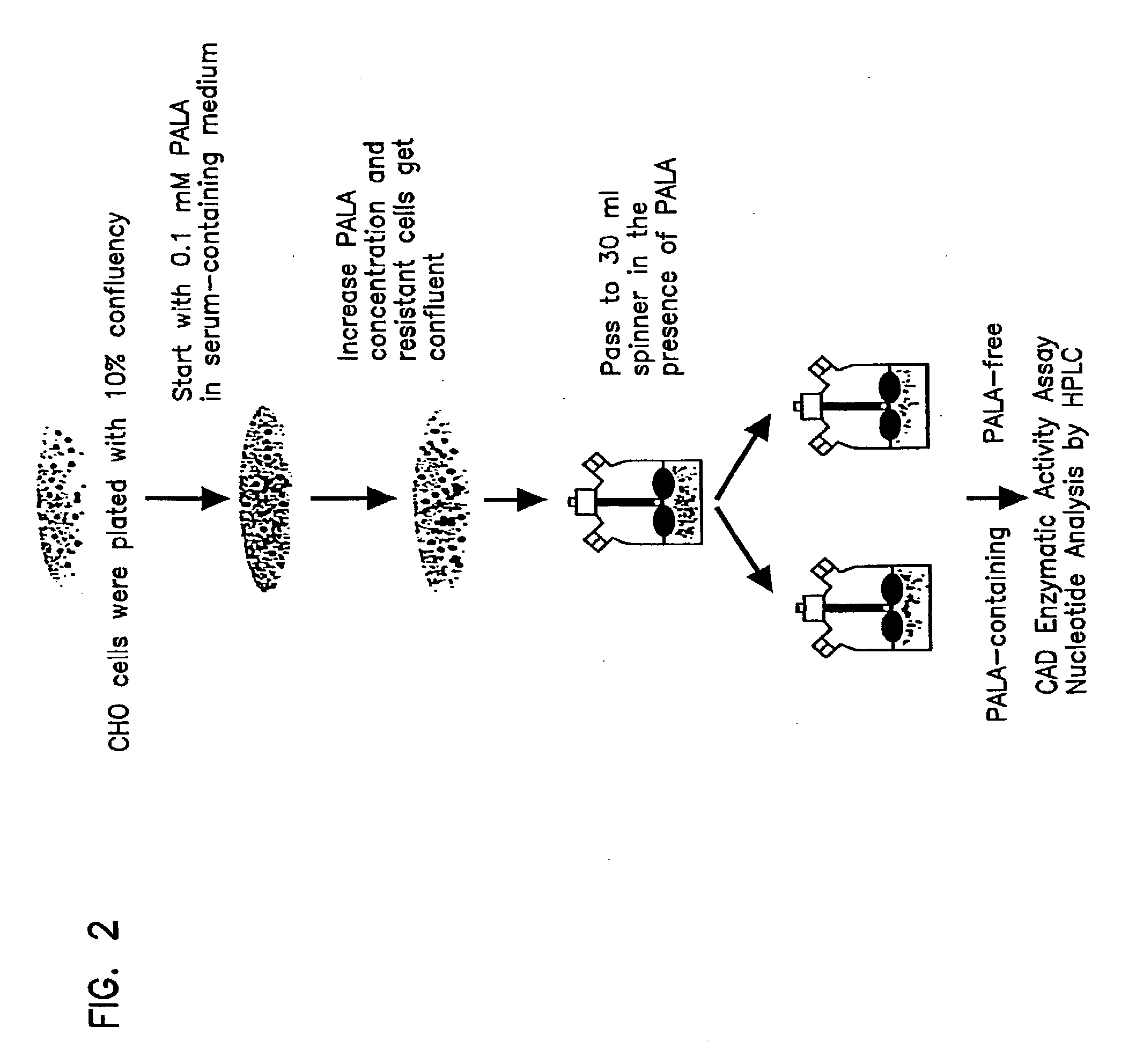
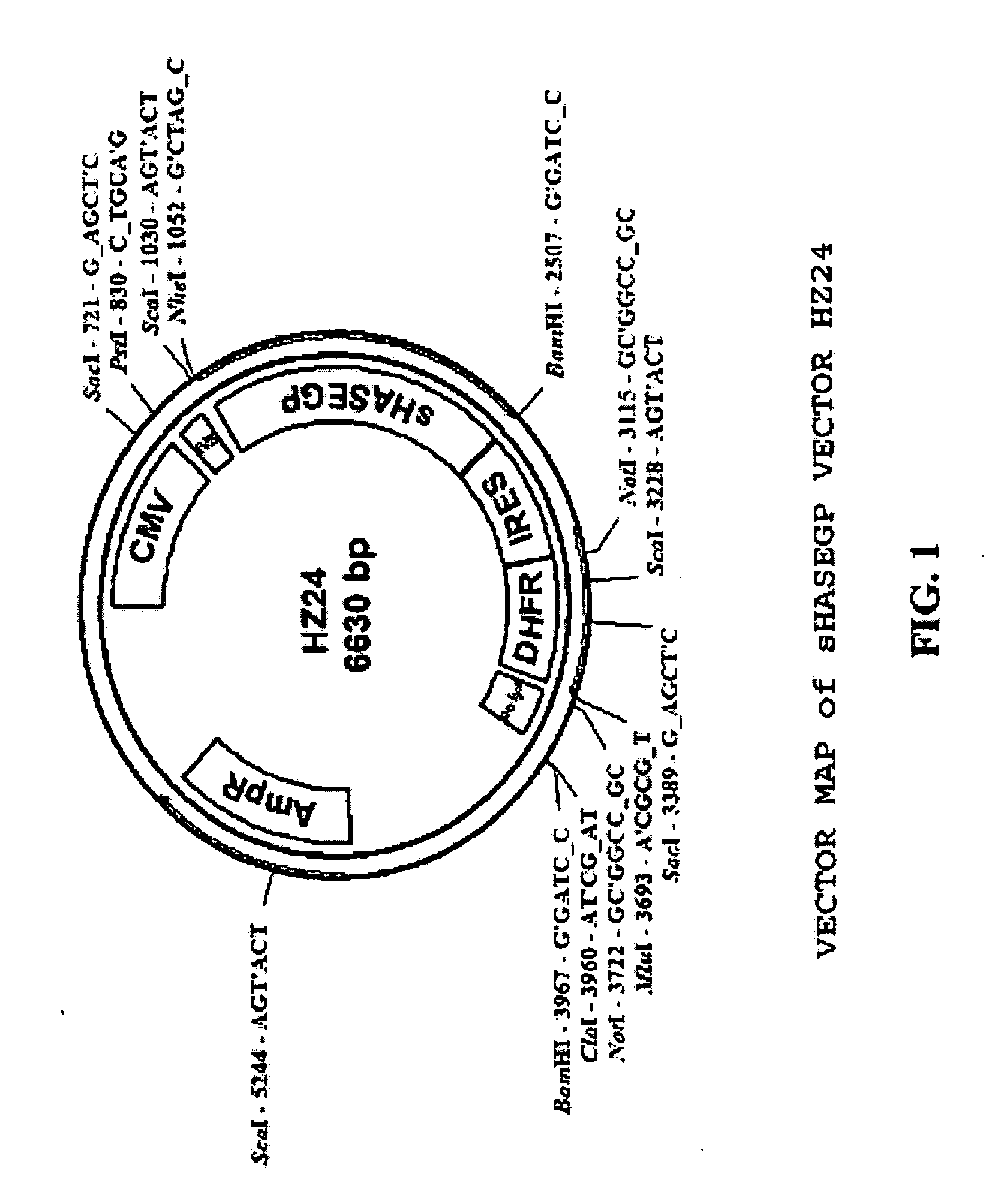
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20050260186A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Soluble hyaluronidase glycoprotein (sHASEGP), process for preparing the same, uses and pharmaceutical compositions comprising thereof
ActiveUS20090181013A1Reduce deliveryImprove usabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGP's), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
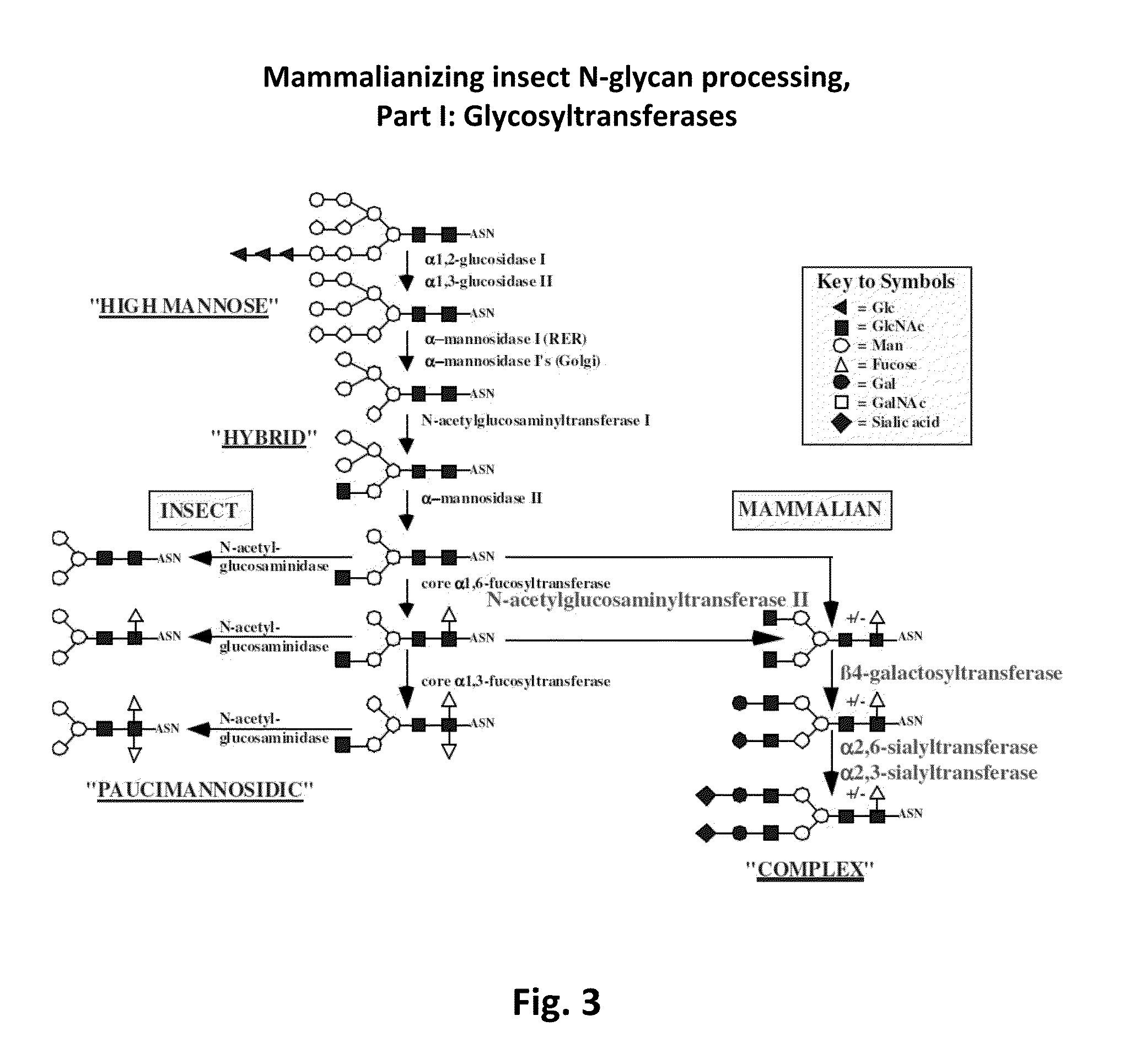
Galactosylation of Recombinant Glycoproteins
InactiveUS20070111284A1Enhanced intracellular CAD activityEasy to optimizeFungiBacteriaGlycoproteinRecombinant glycoprotein
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Human chondroitinase glycoprotein (chasegp), process for preparing the same, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising thereof
ActiveUS20070148156A1Increase enzyme activityOptimize allocationBacteriaSugar derivativesChondroitinase activityChondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycans
The invention relates to the discovery of a novel Chondroitinase Glycoproteins (CHASEGP's), methods of manufacture, and potential uses in conditions where removal of chondroitin sulfates may be of therapeutic benefit. Chondroitinase Glycoproteins require both a substantial portion of the catalytic domain of the CHASEGP polypeptide and asparagine-linked glycosylation for optimal chondroitinase activity. The invention also includes carboxy-terminal deletion variants of CHASEGP that result in secreted variants of the protein to facilitate manufacture of a recombinant CHASEGP. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant CHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity. CHASEGP is useful for the degradation of glycosaminoglycans and chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans under clinical conditions where their removal is of therapeutic value.
Owner:HALOZYME
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20100196423A1Reduce sensitivityGreater serum half-livesAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidaseNuclear chemistry
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated form of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Recombinant glycoproteins related to feline thyrotropin
Amino acid sequences of feline thyrotropin and polynucleotide sequences encoding feline thyrotropin are provided, as well as methods of making and using said sequences.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Trimer of HIV env gene expression product
InactiveUS6737067B1Peptide/protein ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsAdjuvantRecombinant glycoprotein
The invention concerns a purified recombinant glycoprotein having the following properties: a) an adherence capacity to CD4; b) an affinity with a anti-gp120 antibody capable of neutralizing in vitro HIV cell infection; c) an affinity with an anti-gp41 antibody; d) a timeric form free from inter-chain disulphide bonds. The invention also concerns a vaccine comprising said purified glycoprotein and an adjuvant. The invention further concerns a method for obtaining said glycoprotein, which consists in expressing, by means of genetic recombining techniques, a glycoprotein corresponding to the properties a), b) and c) mentioned above; purifying it, and subjecting it to steps involving at least a reducing agent, an ionic detergent and / or a neutral detergent in conditions leading to a glycoprotein having said properties.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTUER LTD
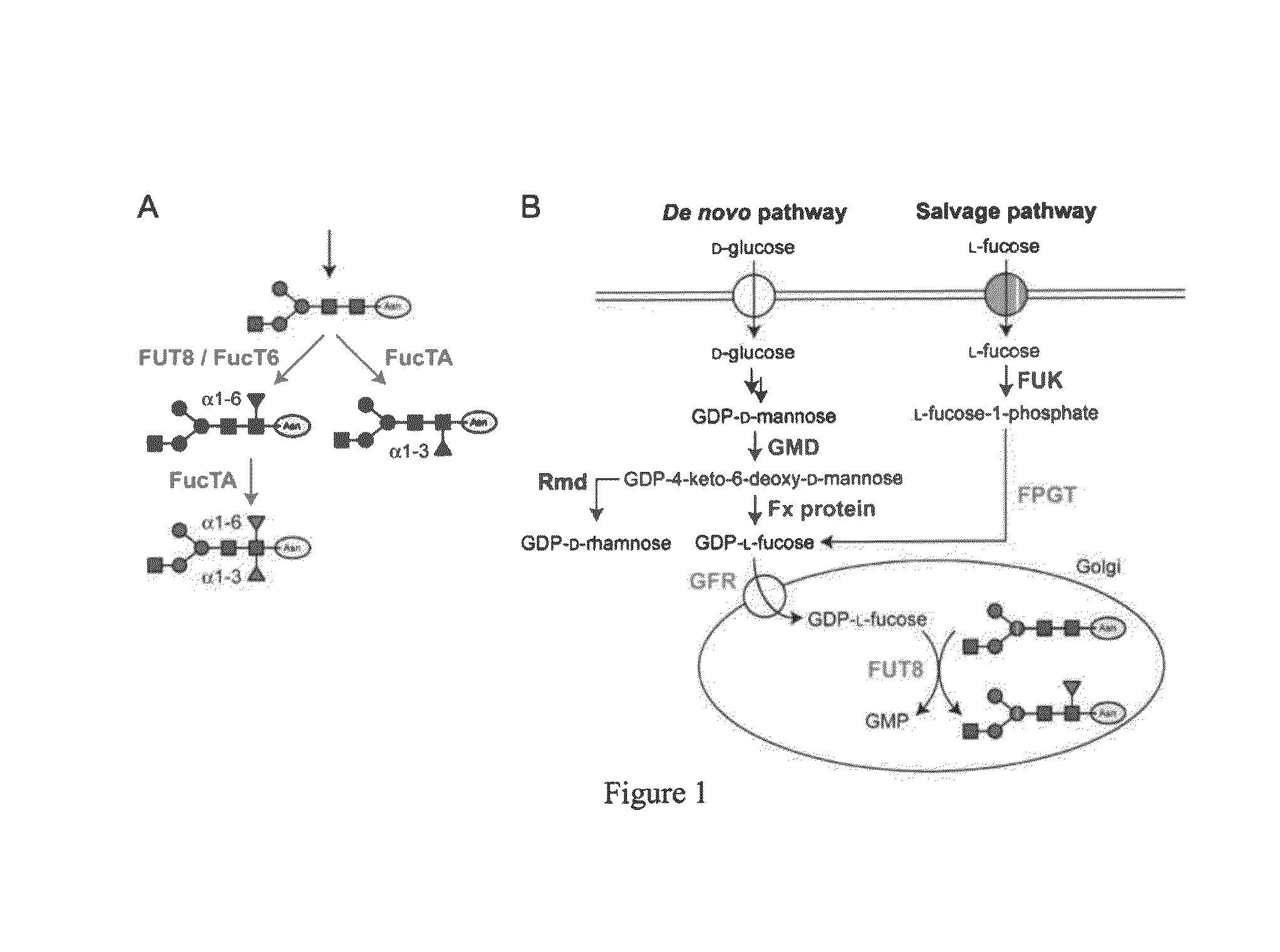
Antennary fucosylation in glycoproteins from cho cells
InactiveUS20110136682A1High and low levelHigh expressionOptical radiation measurementParticle separator tubesFucosylationRecombinant glycoprotein
Owner:MOMENTA PHARMA
Recombinant varicella zoster virus vaccine
ActiveCN112870344AHigh molecular weightImproving immunogenicityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsChickenpoxImmunogenicity
The invention discloses a recombinant varicella zoster virus vaccine, which comprises an amino acid sequence of a recombinant glycoprotein gE extracellular region of a live attenuated VZV strain (OKA strain) gene and a fusion protein formed by a human immunoglobulin Fc segment, and further comprises preparation and an application of the fusion protein, and a corresponding recombinant gene, an eukaryotic expression vector and the like. The fusion protein provided by the invention has good immunogenicity, and can induce generation of a high-level serum neutralizing antibody.
Owner:BEIJING LUZHU BIOTECH +1
Vectors and yeast strains for protein production: ca2+ atpase overexpression
InactiveUS20110143396A1Stabilize cytoplasmic mRNAImprove translation efficiencyFungiImmunoglobulinsHeterologousATPase
Lower eukaryote host cells in which an endogenous or heterologous Ca2+ ATPase is overexpressed are described. Also described are lower eukaryote host cells in which a calreticulin and / or ERp57 protein are overexpressed. These host cells are useful for producing recombinant glycoproteins that have reduced O-glycosylation.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Insect cell line for production of recombinant glycoproteins with sulfated complex n-glycans
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
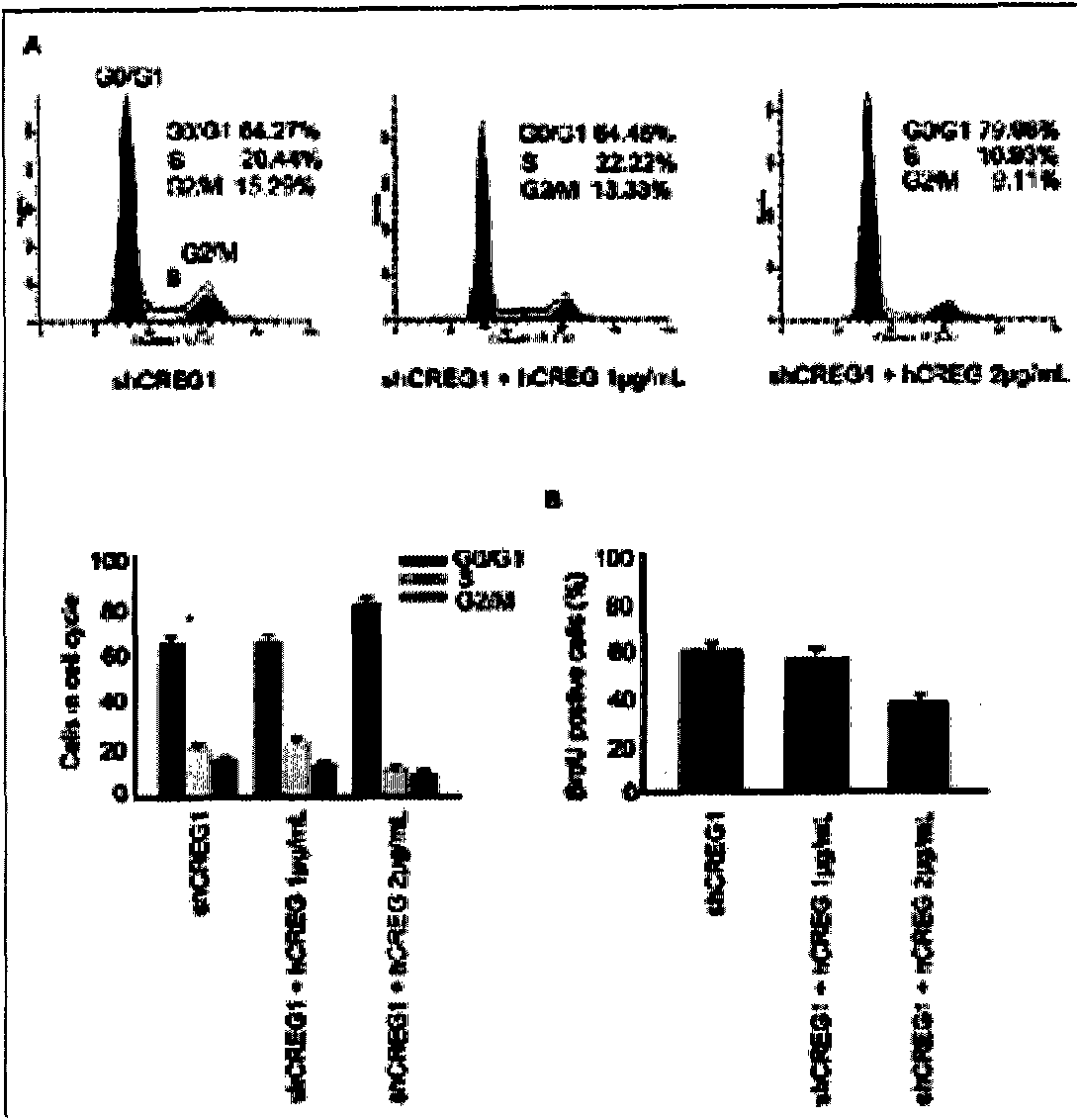
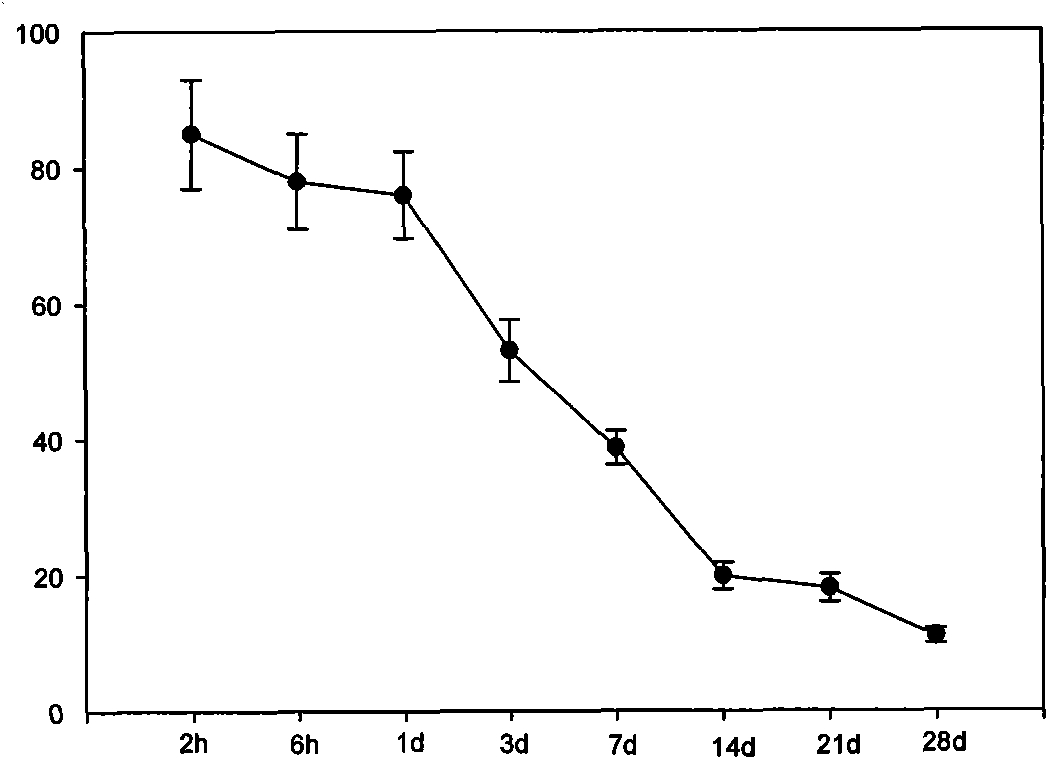
Coronary stent containing recombinant human cellular repressor of E1 A-stimulated genes (hCREG) glycoprotein and preparation method for coronary stent
InactiveCN102309781APrevent blood clotsPromotes re-endothelializationCoatingsProsthesisHuman bodyMedical equipment
The invention provides a coronary stent containing a recombinant human cellular repressor of E1 A-stimulated genes (hCREG) glycoprotein. The surface of the coronary stent is uniformly coated with the recombinant hCREG glycoprotein. After the coronary stent is implanted into a human body, the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells is restrained by the sustained release of hCREG glycoprotein components carried by the stent, the re-endothelialization of a vascular wall is promoted, and the damaged vascular wall is quickly cured, so that intraluminal thrombi caused by medical equipment are prevented, and the time used by a patient to take anti-thrombotic medicaments and blood platelet medicaments postoperatively is shortened.
Owner:LEPU MEDICAL TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
Method to Improve Glycosylation Profile and to Induce Maximal Cytotoxicity for Antibody
InactiveUS20130217863A1Lower levelReduce the amount requiredImmunoglobulinsFermentationGlycanSialic acid
The present invention relates to the production of recombinant glycoproteins or antibodies that have an improved glycosylation profile and effector functions such as ADCC and / or CDC. The present invention is in particular related to the production of glycoproteins or antibodies having a valuable glycosylation profile, especially a low fucose level and / or a high oligomannose level and / or presence of sialic acid to the glycans.
Owner:INT DRUG DEV BIOTECH
Methods and Kits for Measuring Von Willebrand Factor
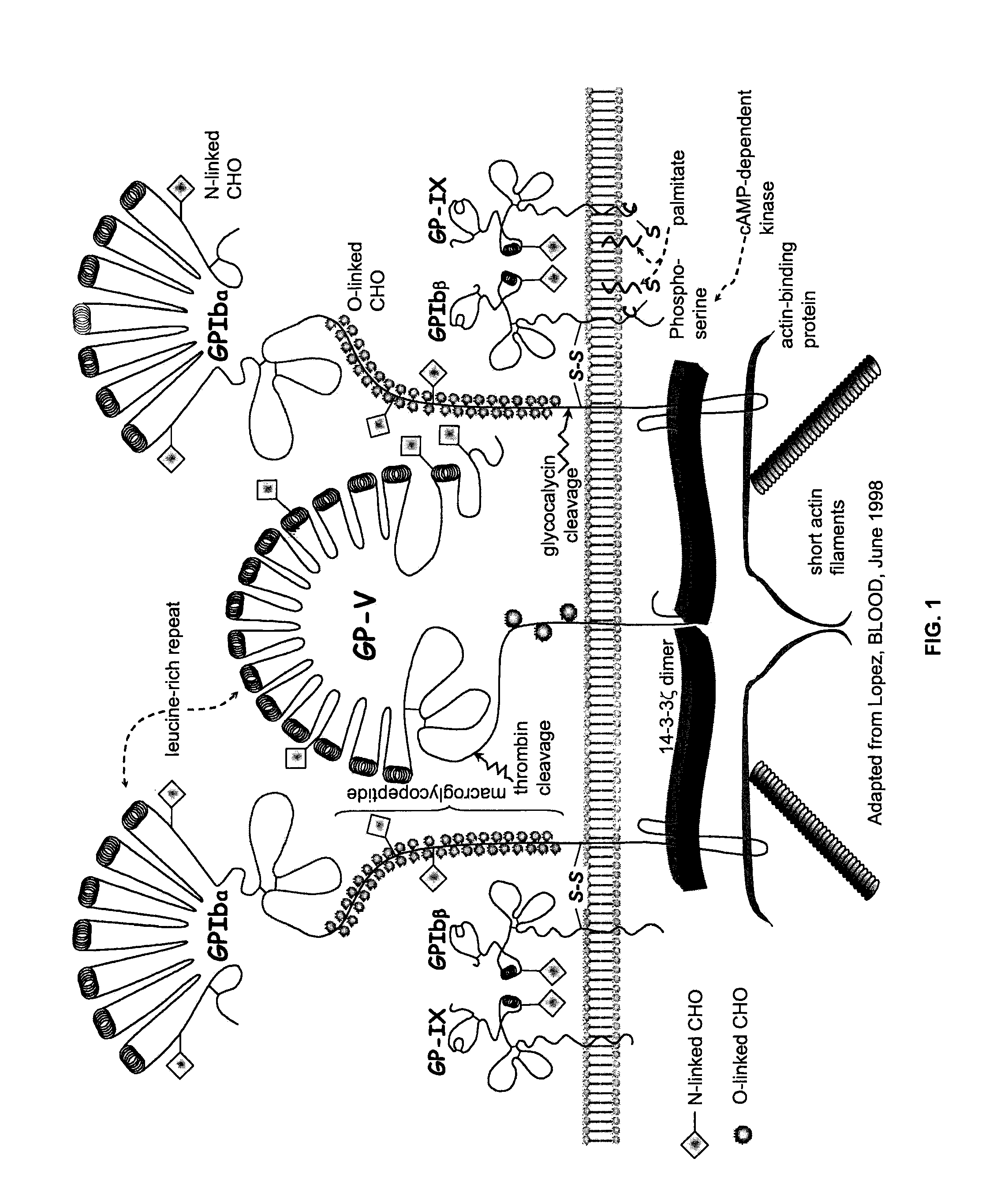
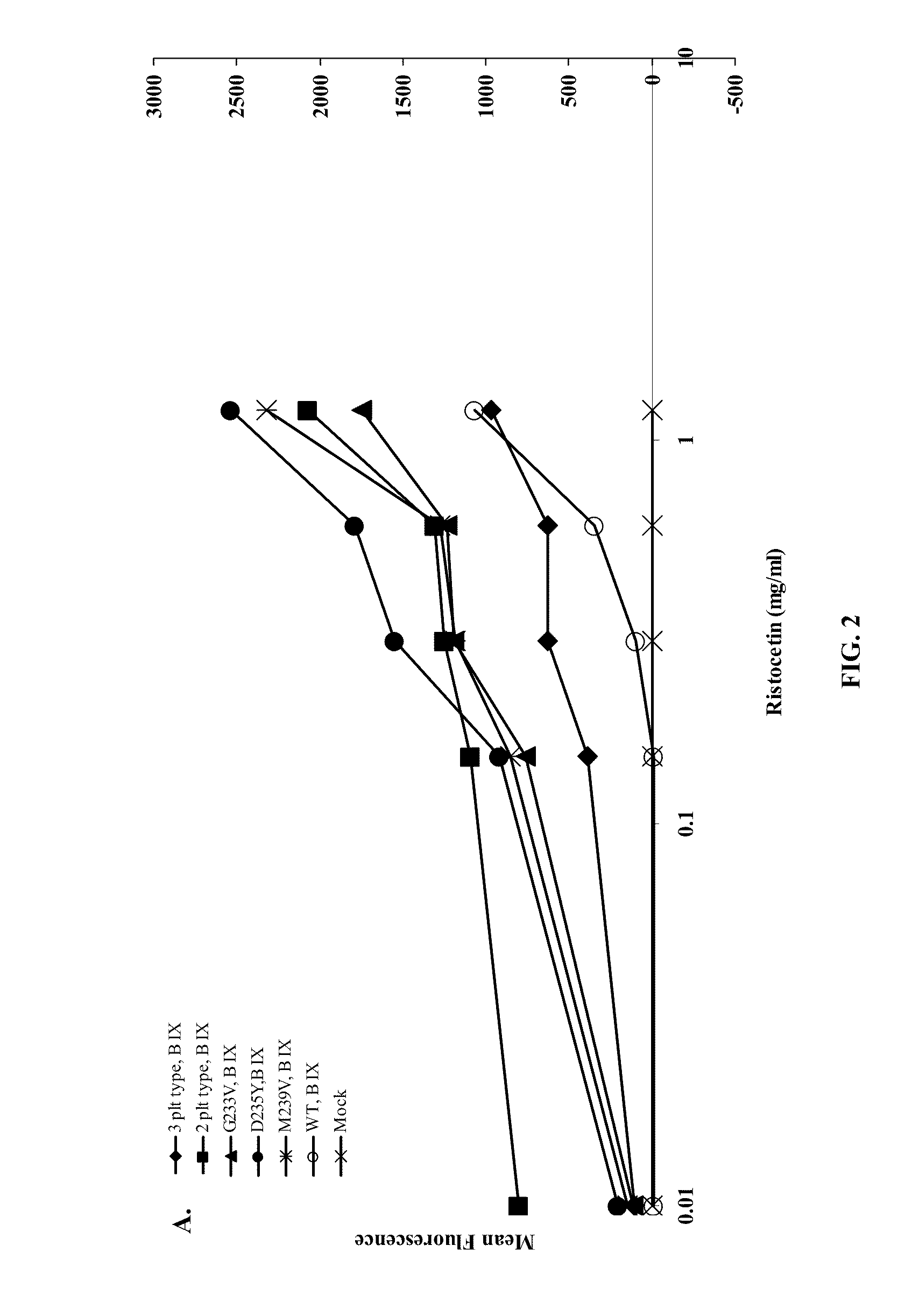
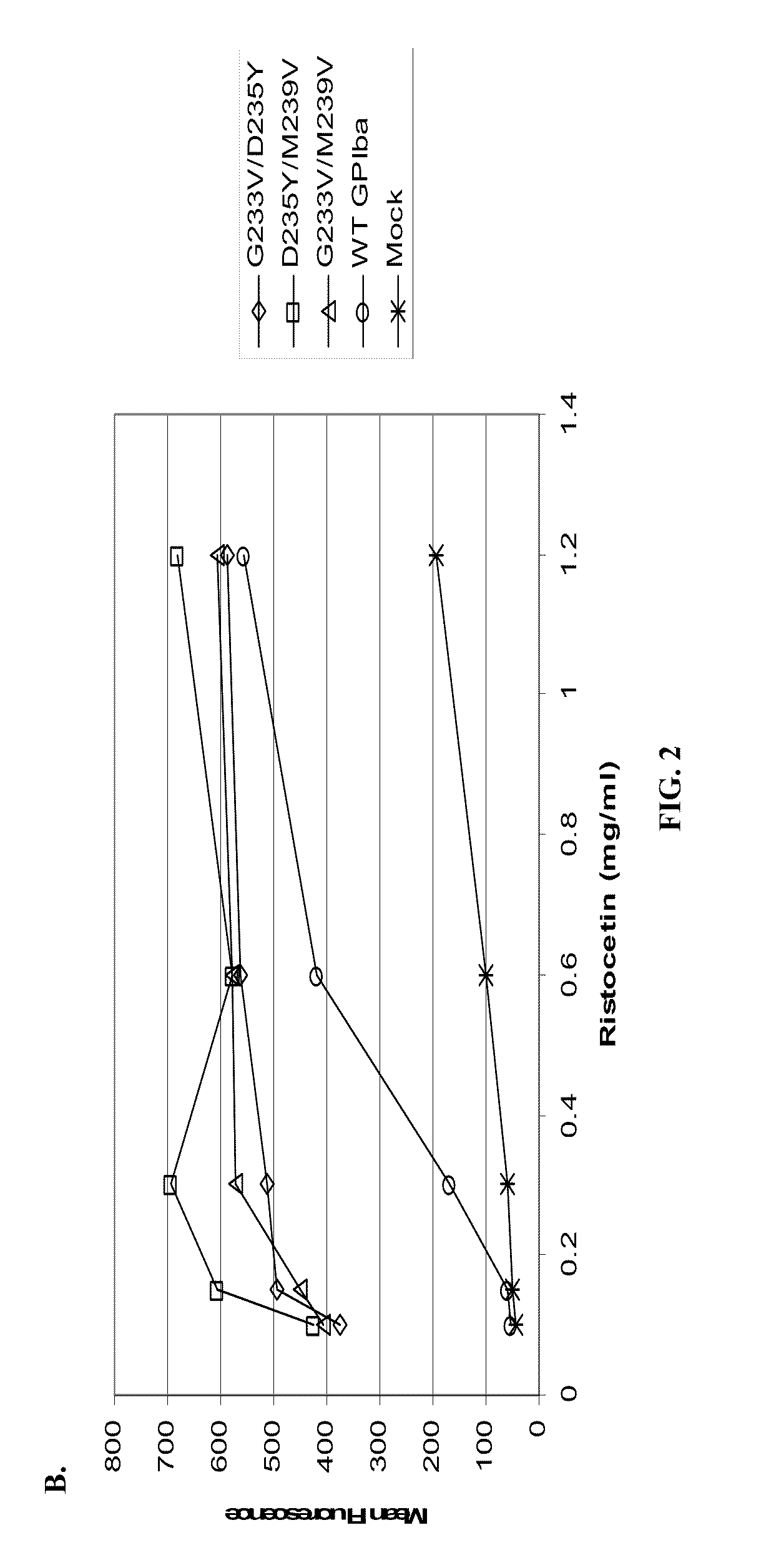
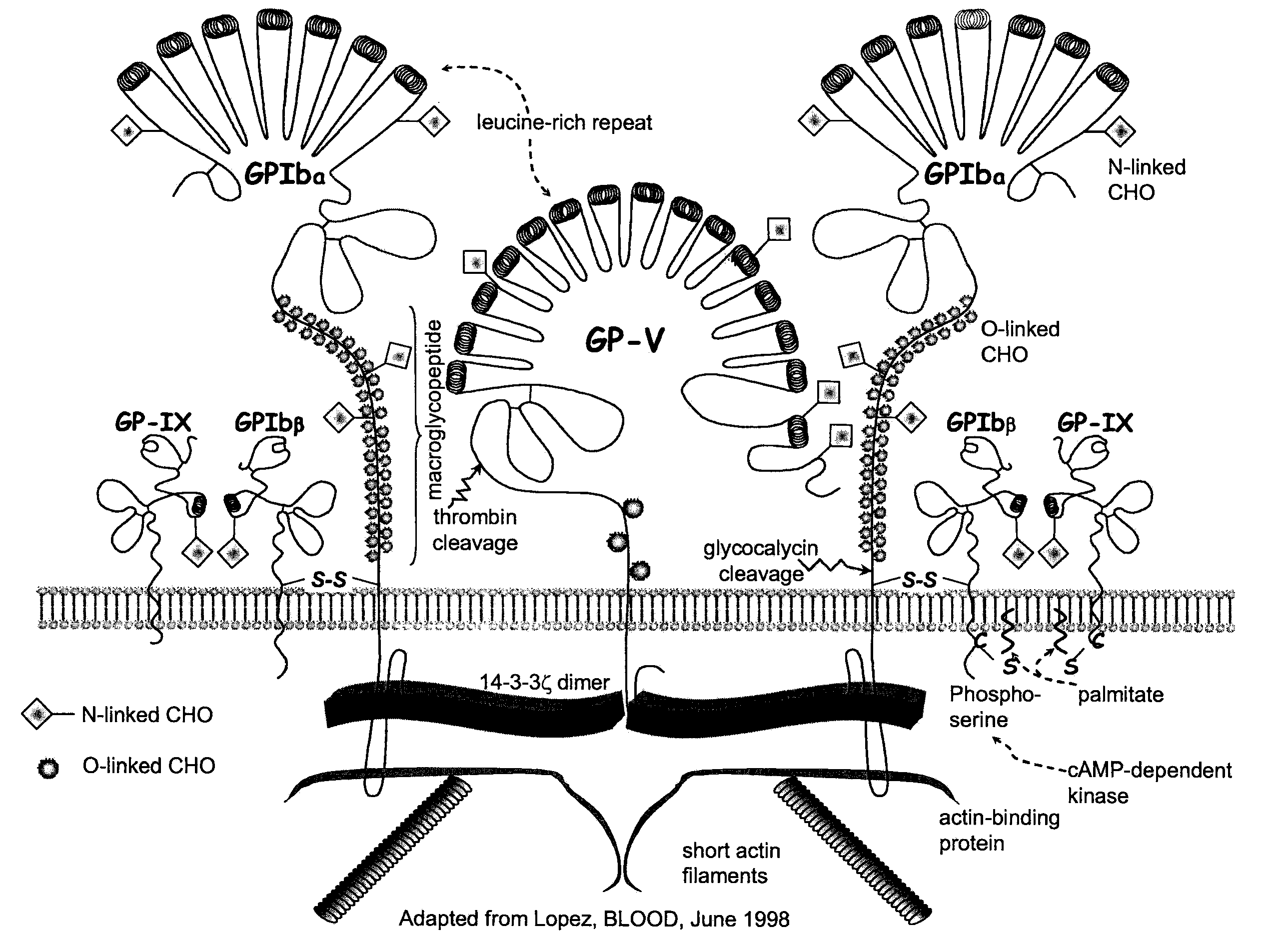
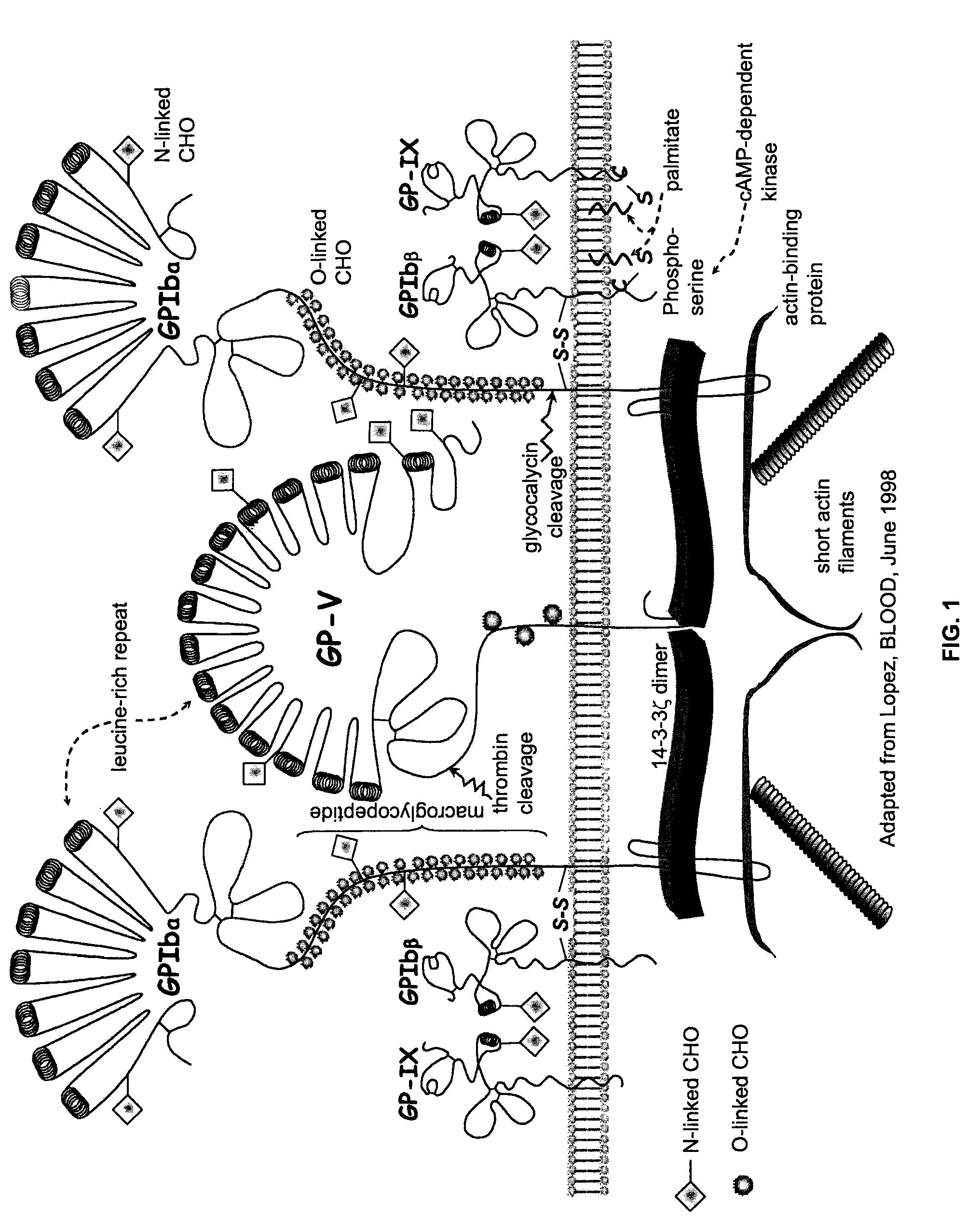
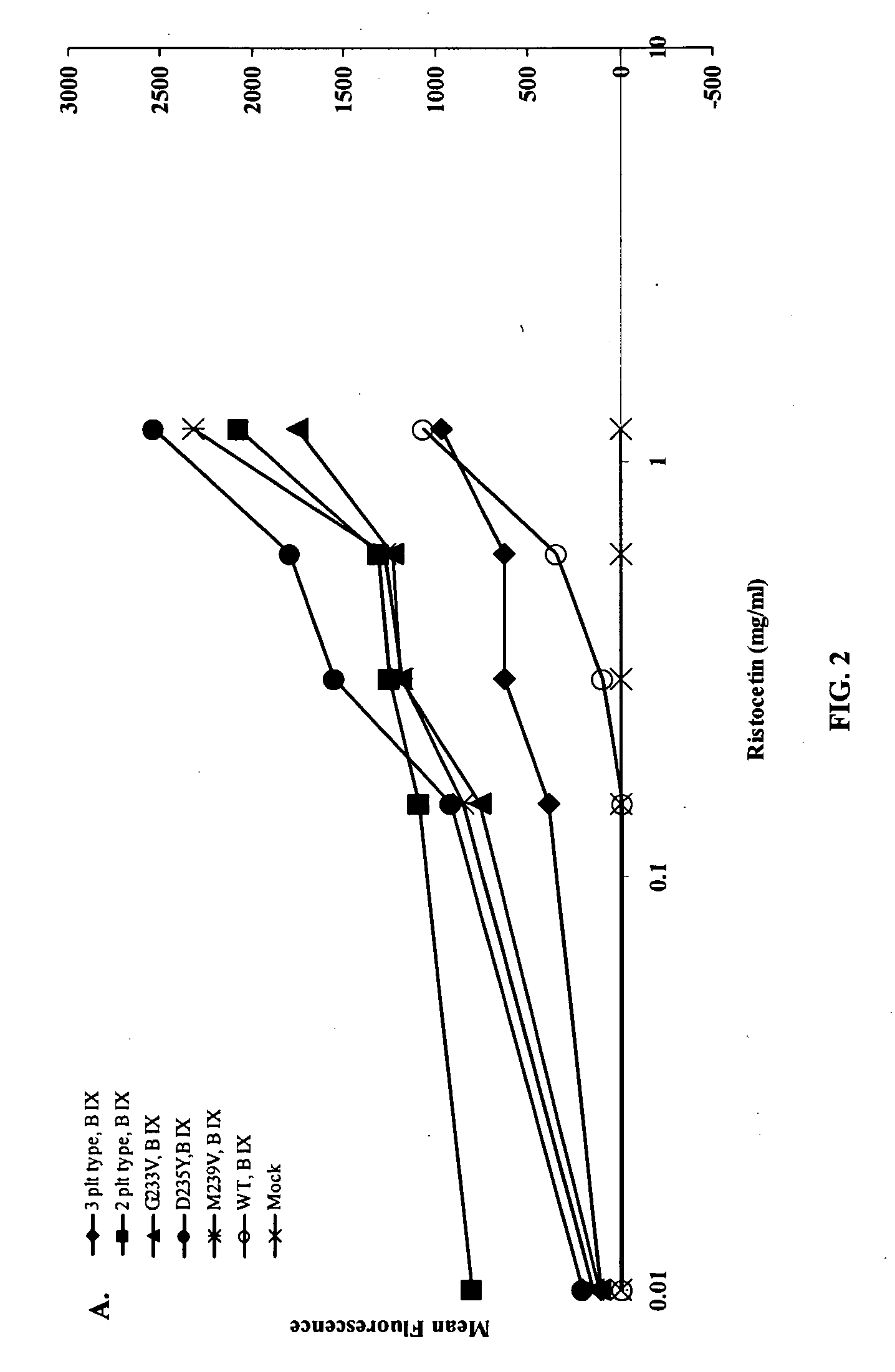
ActiveUS20120003670A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsFactor VIII vWFGlycoprotein i
Methods and kits for measuring levels of von Willebrand factor function in a sample without using a platelet aggregation agonist, such as ristocetin, comprising recombinant glycoprotein Ibα having at least two of a G233V, D235Y and M239V mutations and an agent to detect a complex between the recombinant glycoprotein Ibα and von Willebrand factor.
Owner:THE MEDICAL COLLEGE OF WISCONSIN INC +1
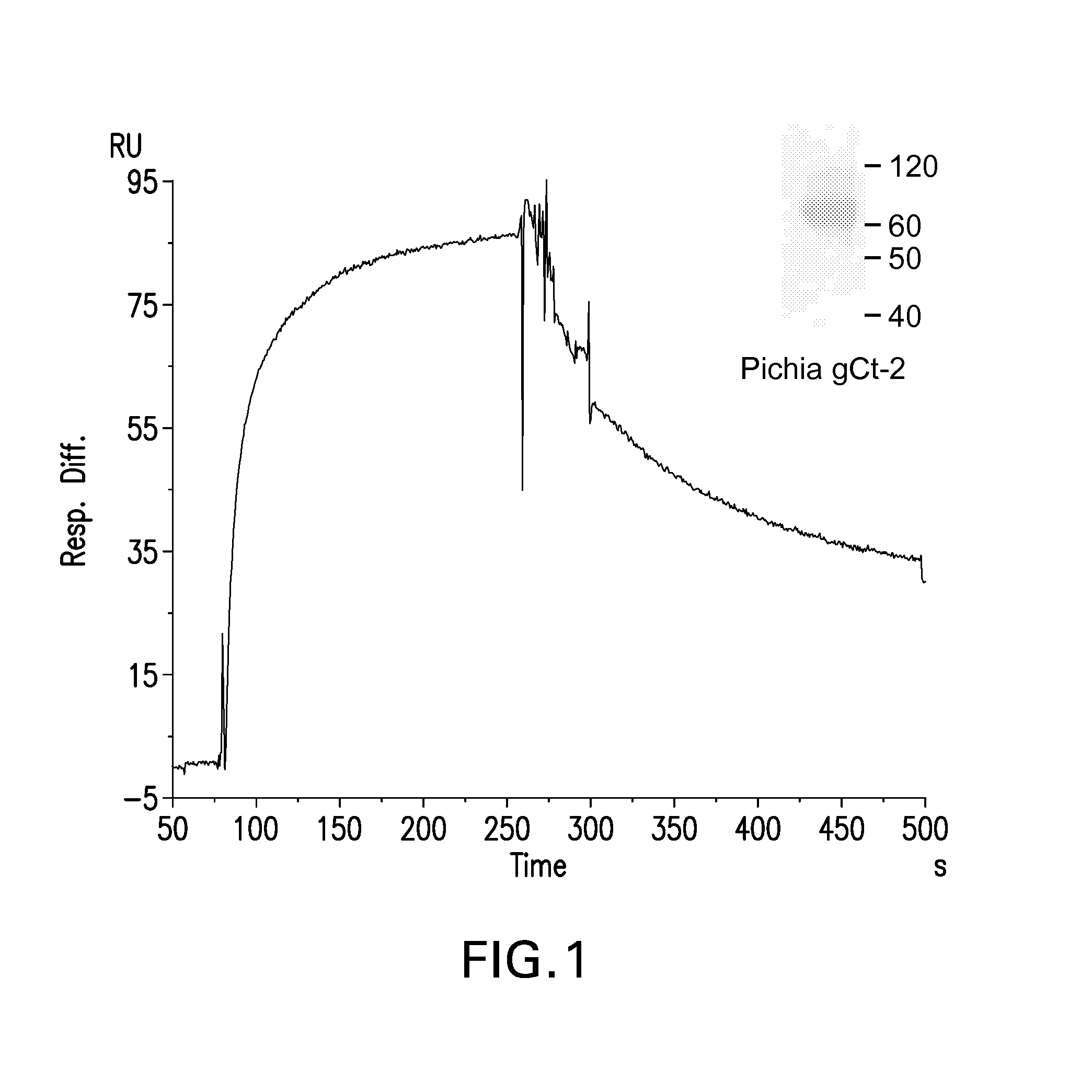
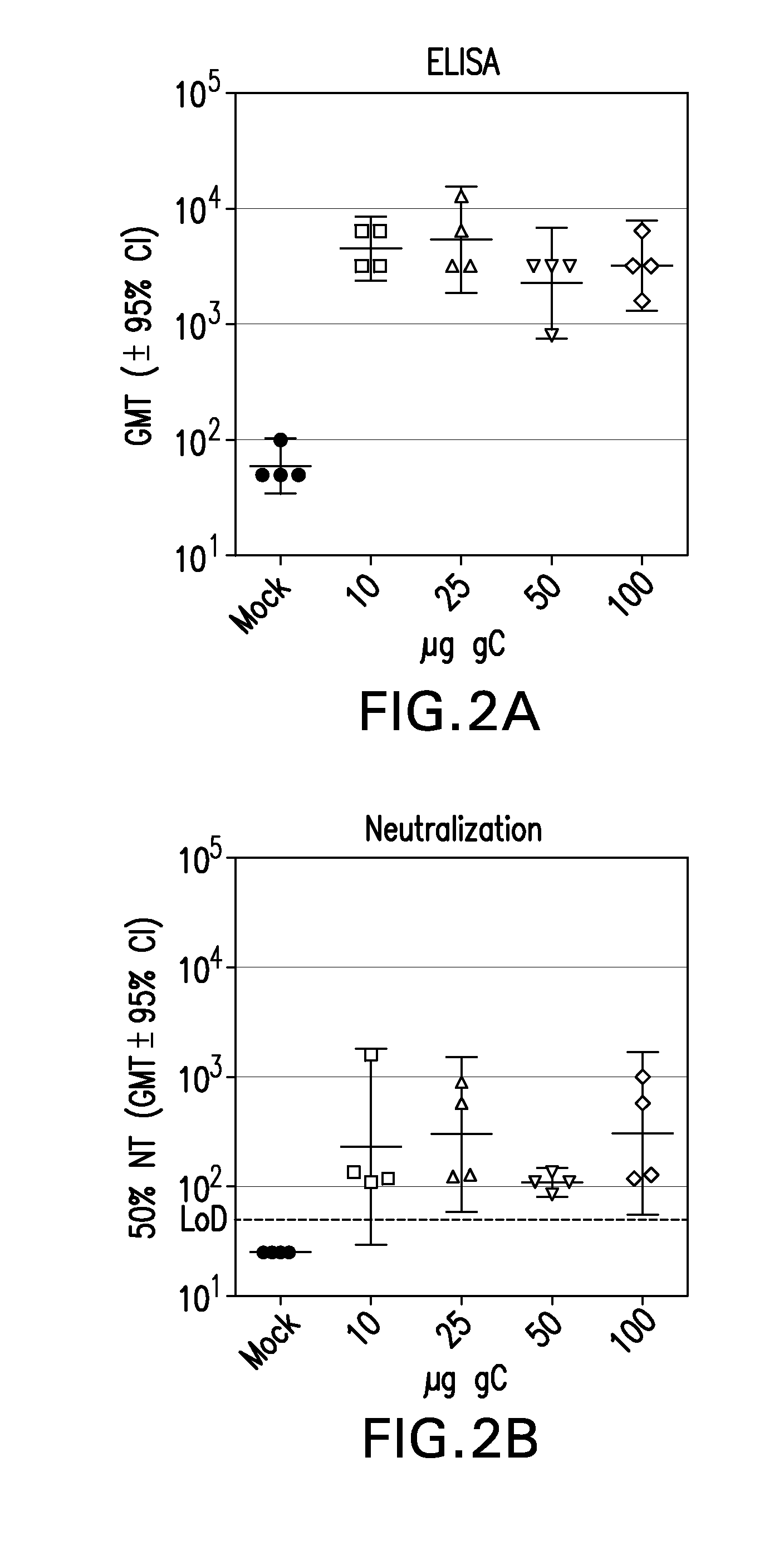
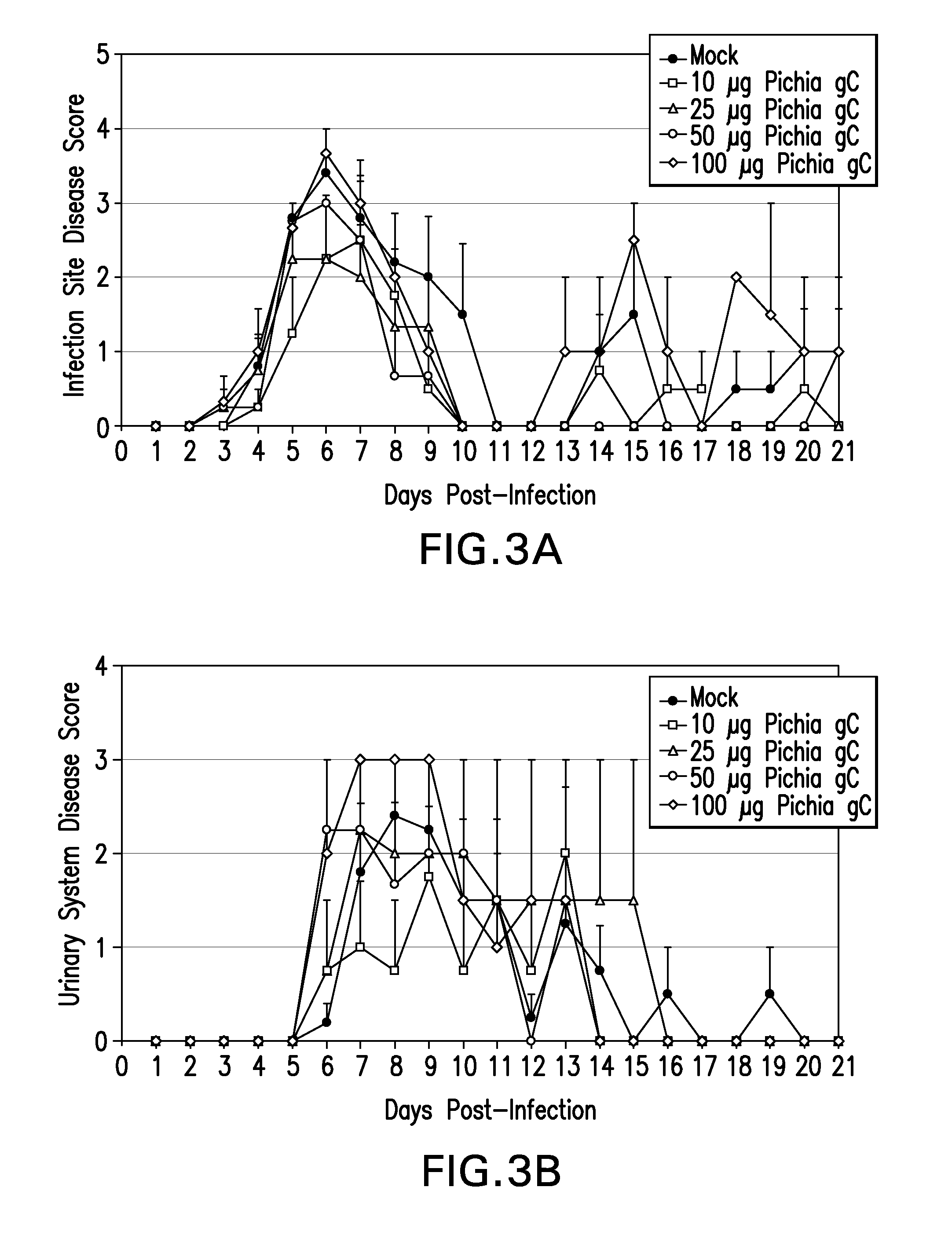
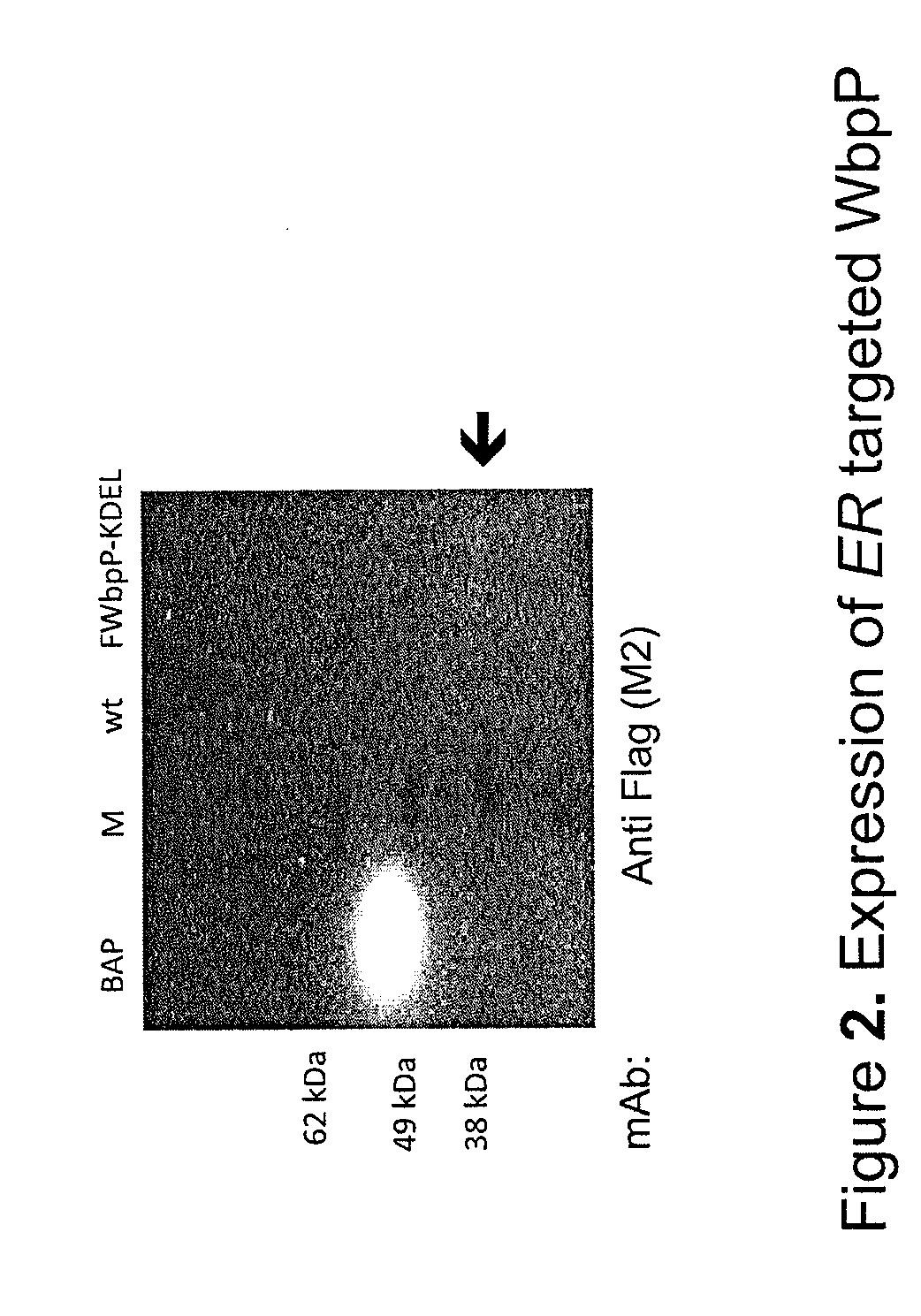
Recombinant ectodomain expression of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins in yeast
The present invention provides Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) gD, gC, gB and / or gE recombinant glycoproteins having a particular pre-selected N-linked glycosylation pattern as the predominant N-glycoform. The present invention also provides methods of producing these recombinant glycoproteins in yeast, preferably Pichia pastoris, which may be glycoengineered to provide particular glycosylation patterns. The present invention further provides vaccines comprising gD and gC, and optionally gB and / or gE, at least one of which has a particular pre-selected N-linked glycosylation pattern as the predominant N-glycoform. The recombinant glycoproteins are produced by a method which, in one embodiment, comprises transforming a yeast of the genus Pichia with an expression vector containing a DNA encoding an HSV glycoprotein, which is under regulation of a promoter functional in a yeast of the genus Pichia, culturing the yeast in a medium, and recovering the recombinant glycoprotein from the obtained culture. DNA encoding the recombinant glycoproteins is preferably codon-optimized to achieve optimal expression in Pichia.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Methods for glyco-engineering plant cells for controlled human o-glycosylation
This invention discloses the development of a novel platform for recombinant production of bioactive glycoproteins and cancer specific vaccines in plants. Plants and plant cell cultures have been humanized with respect to human mucin-type protein O-glycosylation. A panel of plant cell factories for production of recombinant glycoproteins with designed human O-glycosylation, including an improved cancer vaccine candidate, has been developed. The platform provides basis for i) production of an essentially unlimited array of O-glycosylated human glycoprotein therapeutics, such as human interferon α2B and podoplanin, and ii) for further engineering of additional cancer specific O-glycans on glycoproteins of therapeutical value. Currently, mammalian cells are required for human O-glycosylation, but plants offer a unique cell platform for engineering O-glycosylation since they do not perform human type O-glycosylation. Introduction of O-glycosylation into plant cells requires i) that wild-type plant cells do not modify the target peptide substrates and ii) that the appropriate enzymes and substrates are introduced into of plant cells such that O-glycosylation in the secretory pathway proceed and the glycosylated peptide substrates are preferentially exported to the exterior of the cell or accumulated in the cell. In this invention i) the integrity of transiently and stably expressed ‘mucin’ type target peptides in plants cells has been determined and ii) mucin-type O-glycosylation has been established in plants by transient and stable introduction of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa C4-epimerase, the human polypeptide GalNAc-transferases T2 and T4 (GalNAc-T2 and T4) and various human target peptides or proteins. In the present invention GalNAc-T2 and -T4 have been used to produce a Tn cancer glycoform of MUC1.
Owner:YANG ZHANG +7
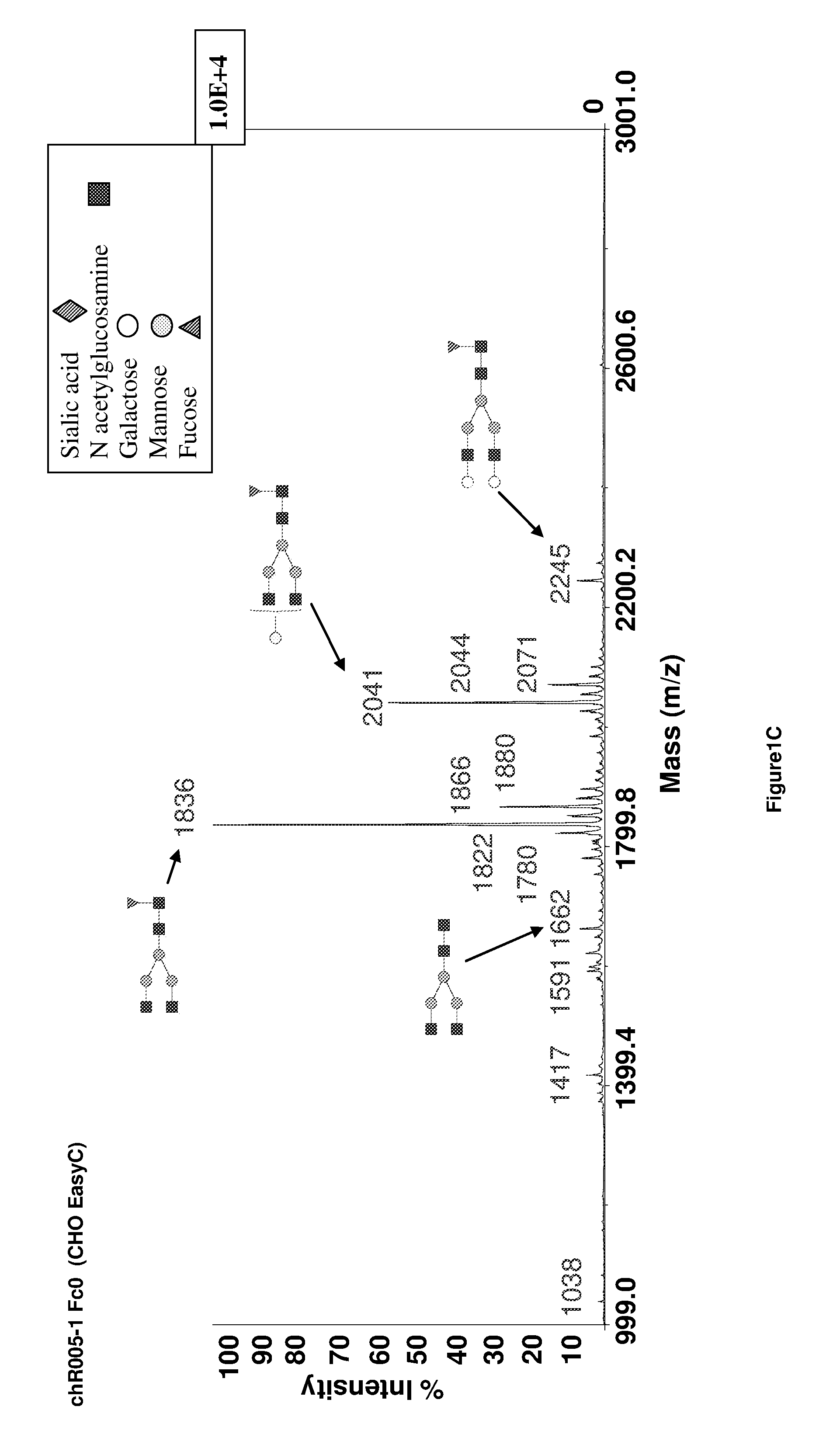
Method of Mapping Glycans of Glycoproteins in Serum Samples
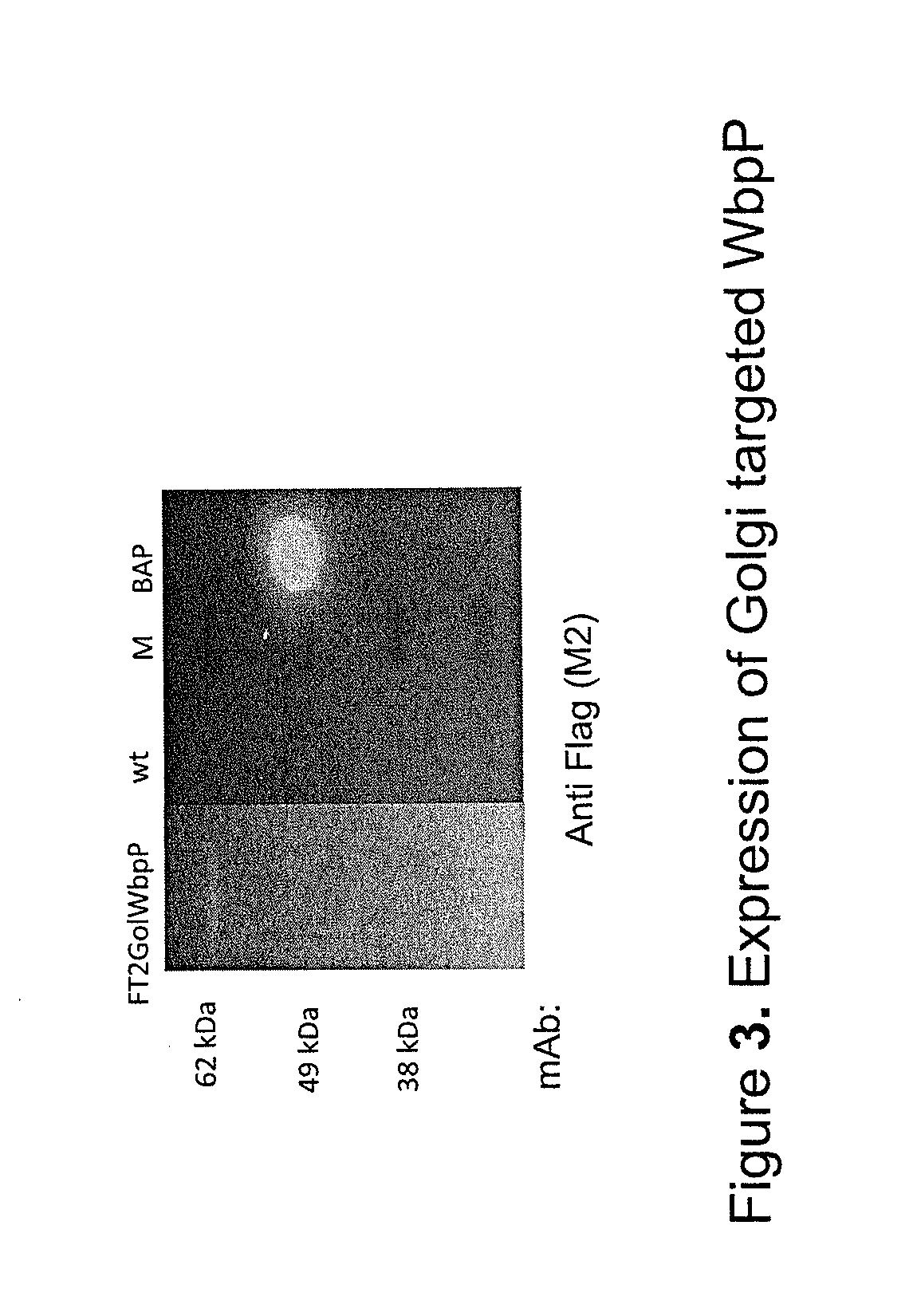
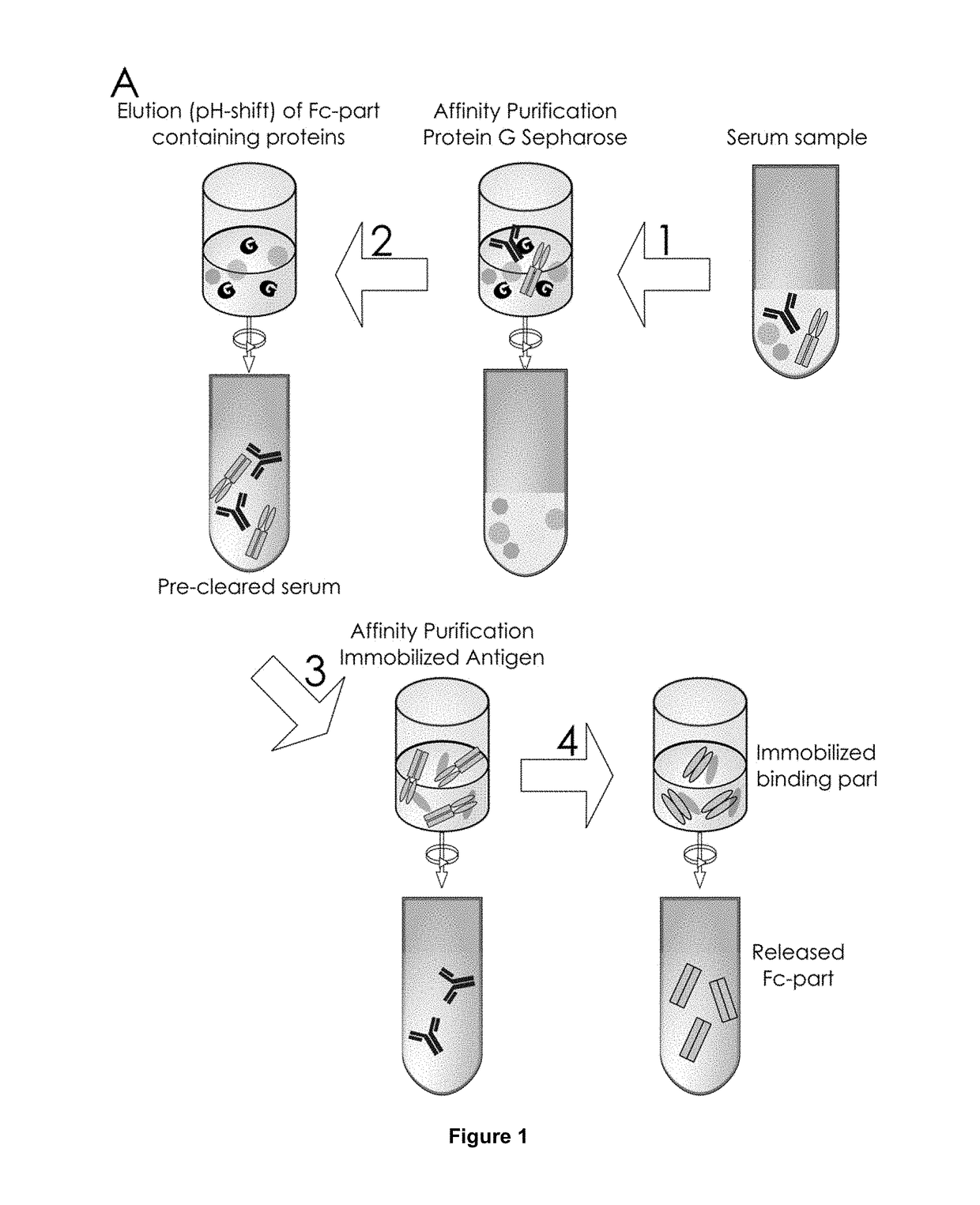
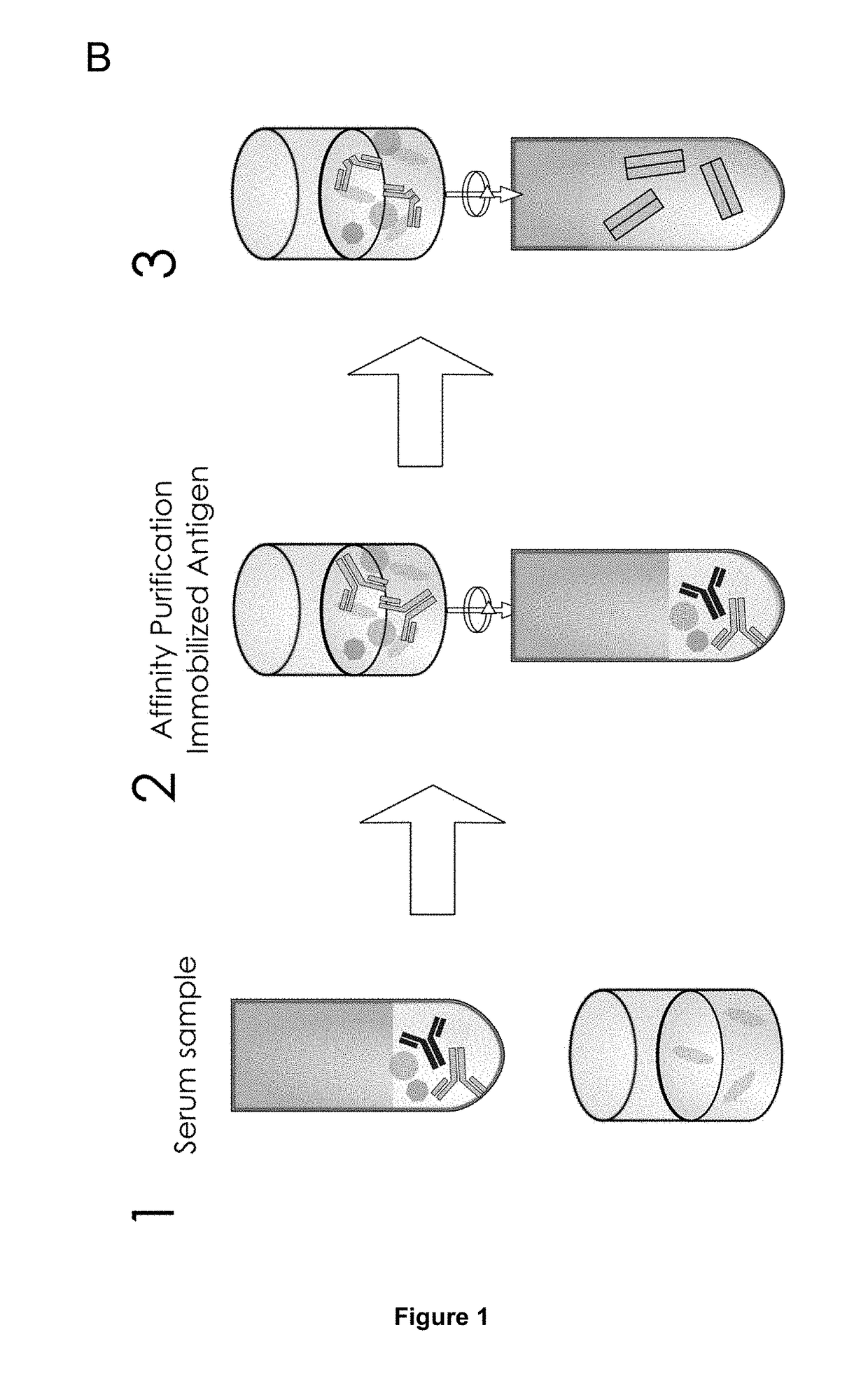
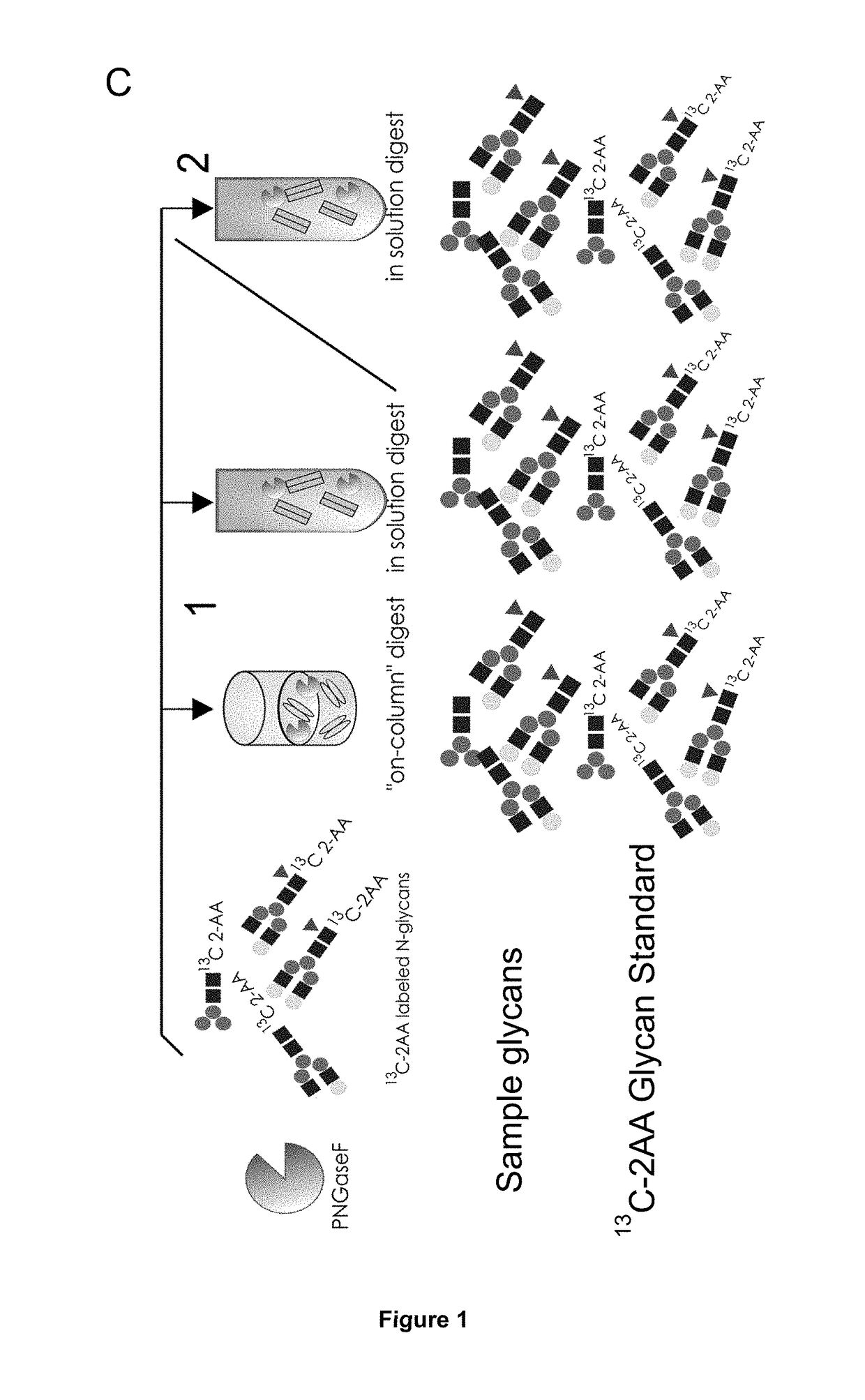
The present invention relates to a method for analyzing glycans of a recombinant glycoprotein in a liquid sample of a mammal. Specifically the method comprises a step of affinity purifying the recombinant glycoprotein from the sample, enzymatically releasing a glycan containing fragment from the immobilized glycoprotein, adding a reference standard containing isotopically labeled glycans, fluorescently label the glycans and analyzing the glycans using LC-MS. The present invention also relates to a method further comprising analyzing the glycans of the immobilized recombinant glycoprotein fragment, further comprising a pre-clearing step of the liquid sample, and releasing the glycans from the immobilized recombinant glycoprotein fragment. The methods allow for the use of a small sample volume and the possibility to operate with high throughput, such as in a 96-well plate sample preparation and are therefore suited to measure pharmacodynamics parameters of a recombinant glycoprotein in a mammal in clinical or pre-clinical studies.
Owner:HEXAL AG
Vectors and yeast strains for protein production
InactiveUS20100311122A1High expressionReduce the amount of solutionFungiNucleic acid vectorATPaseMannosyltransferase
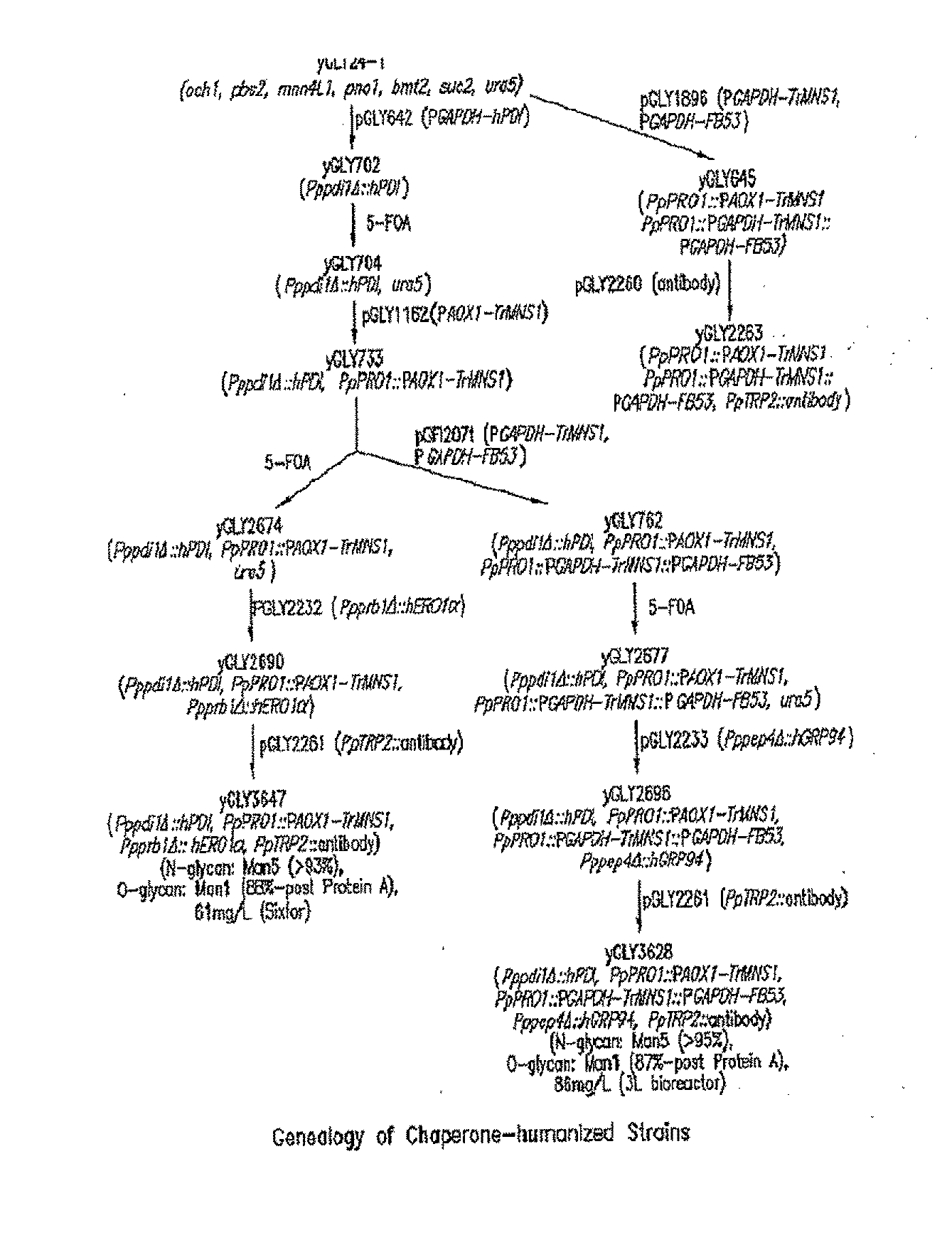
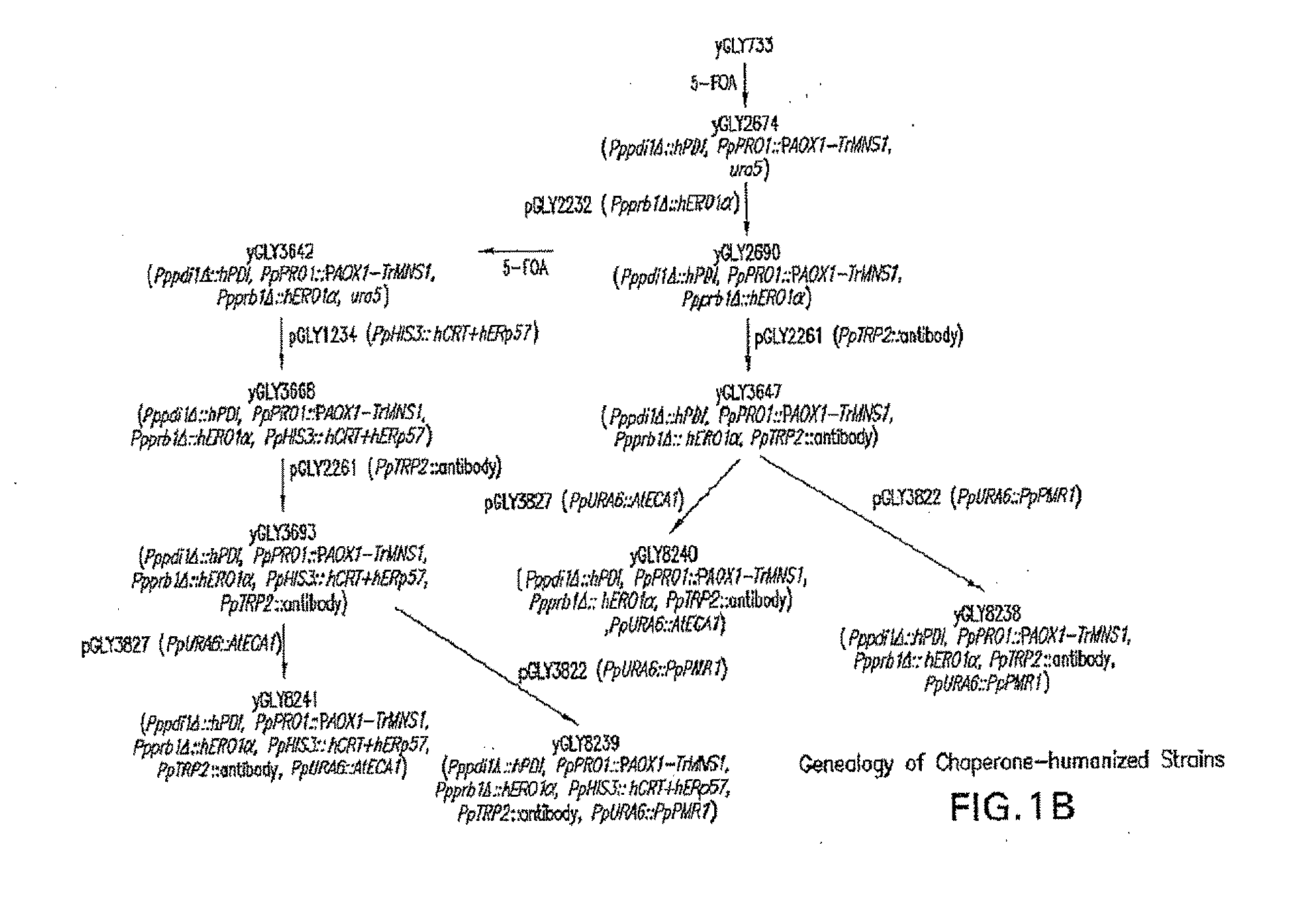
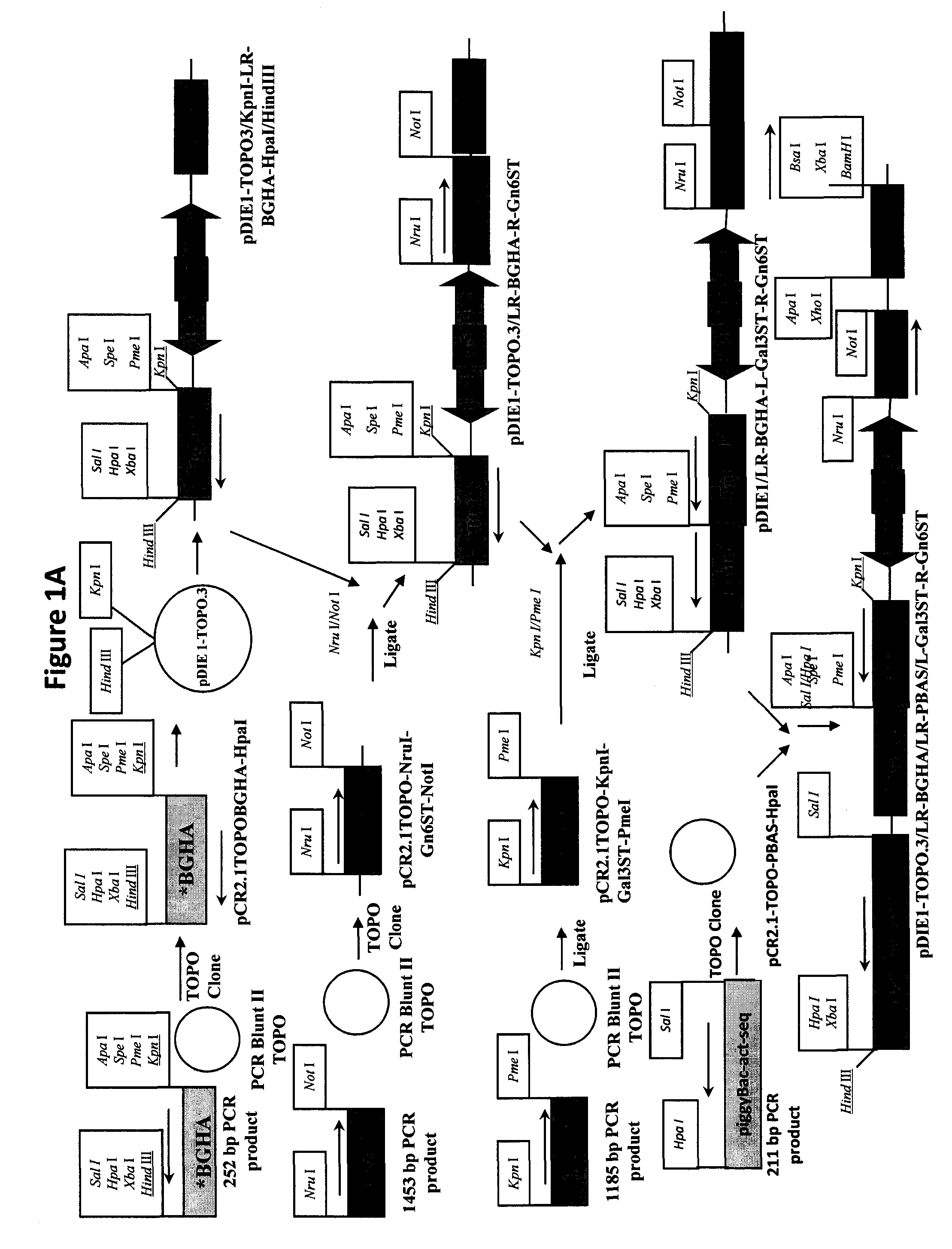
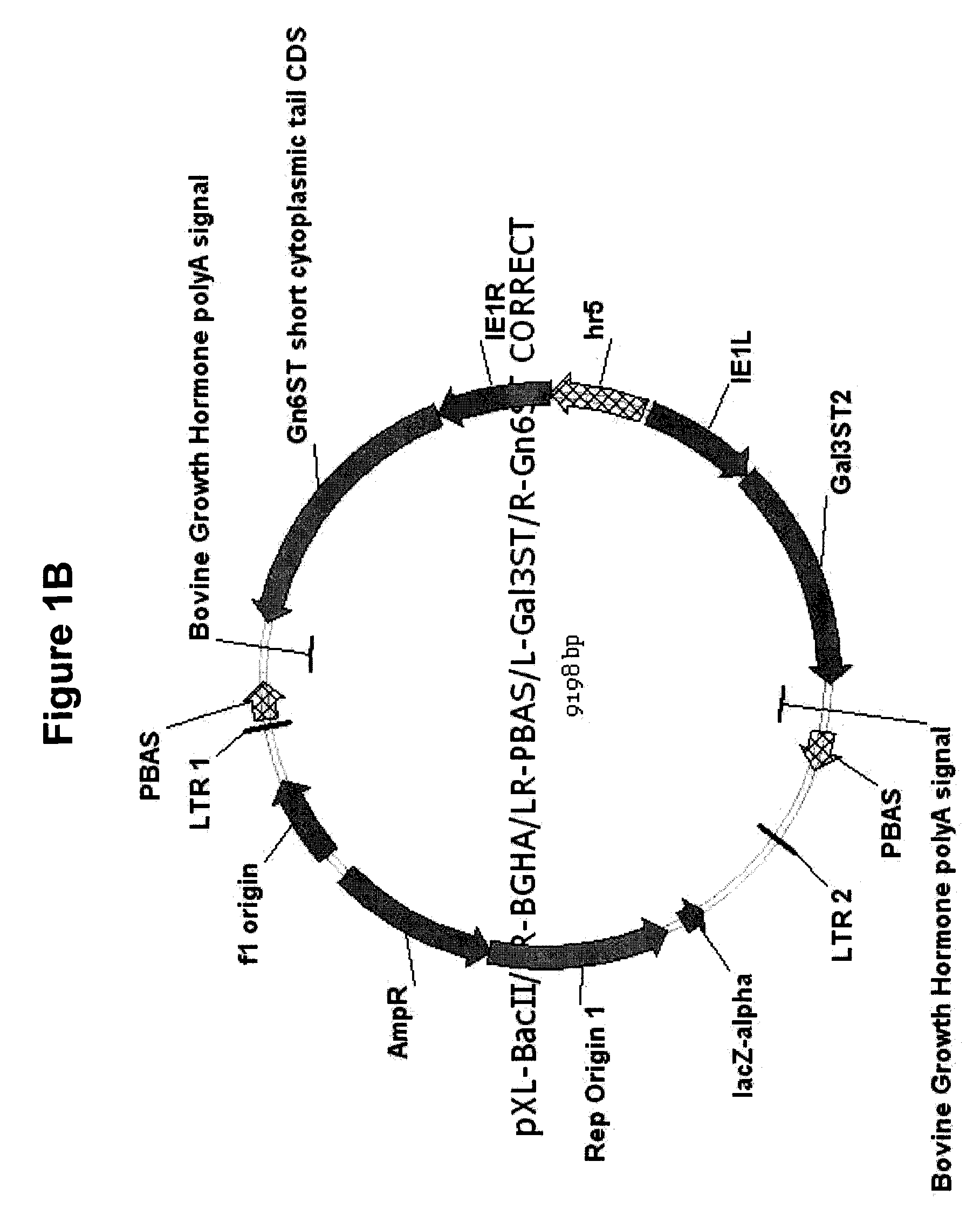
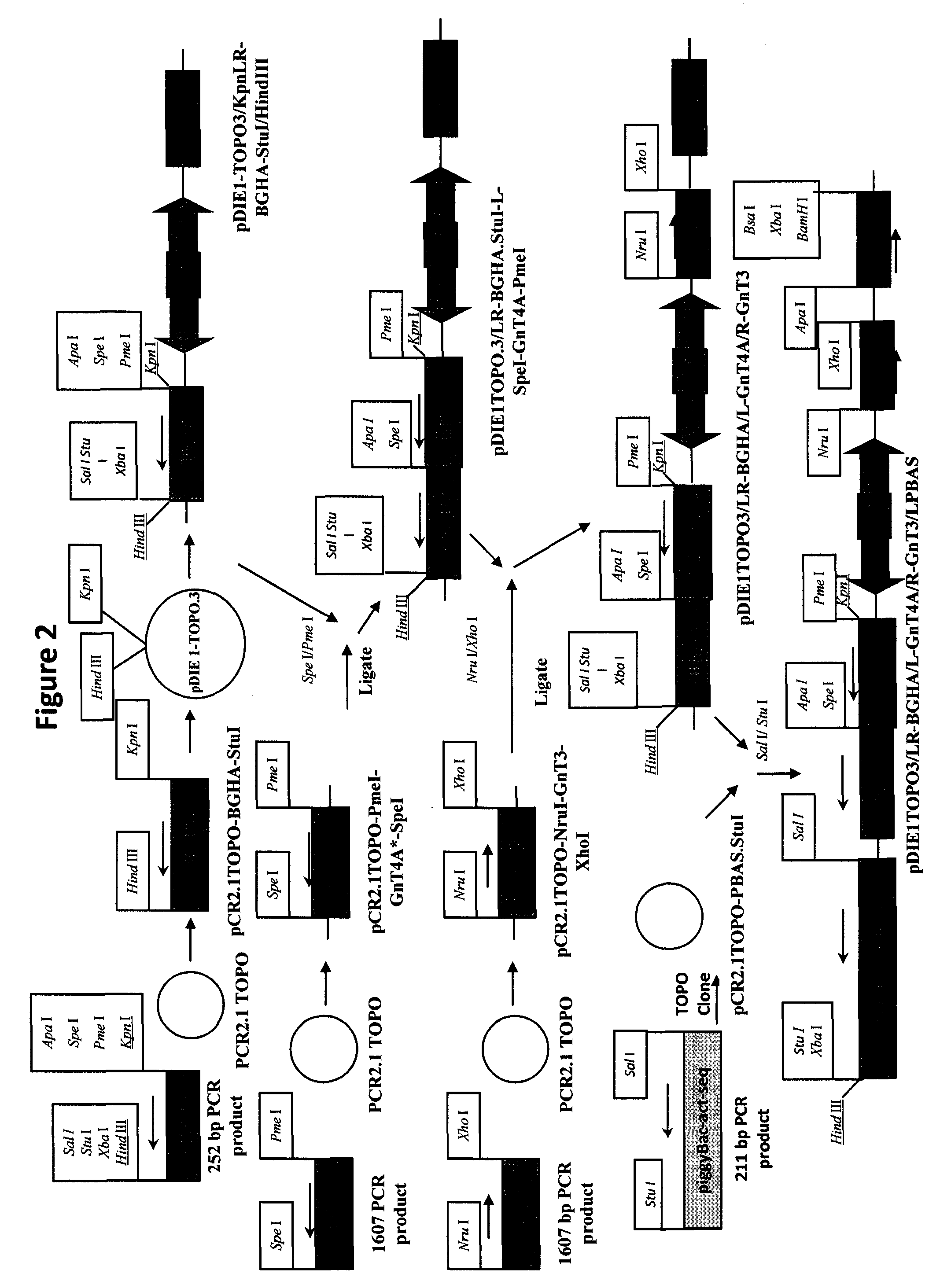
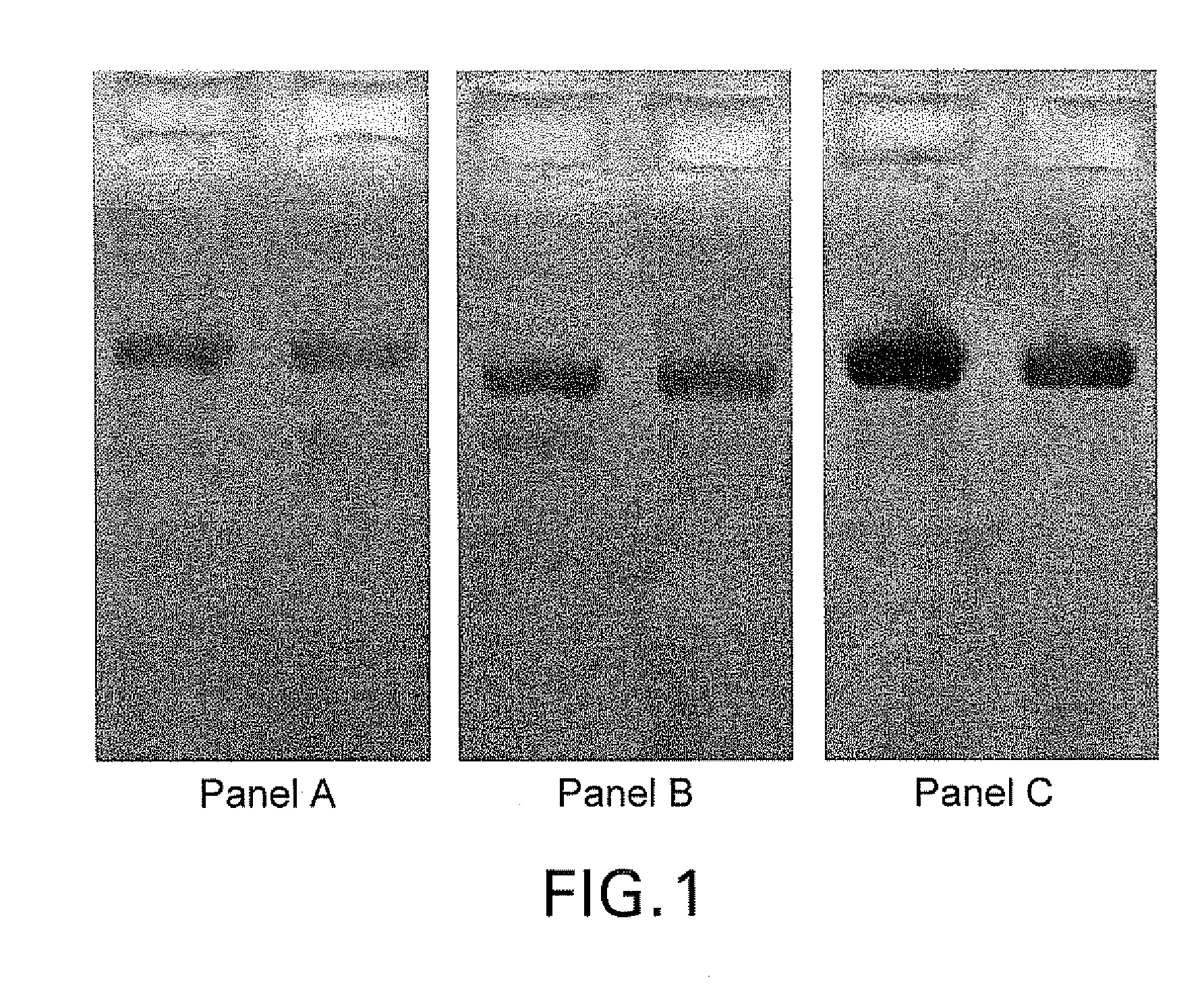
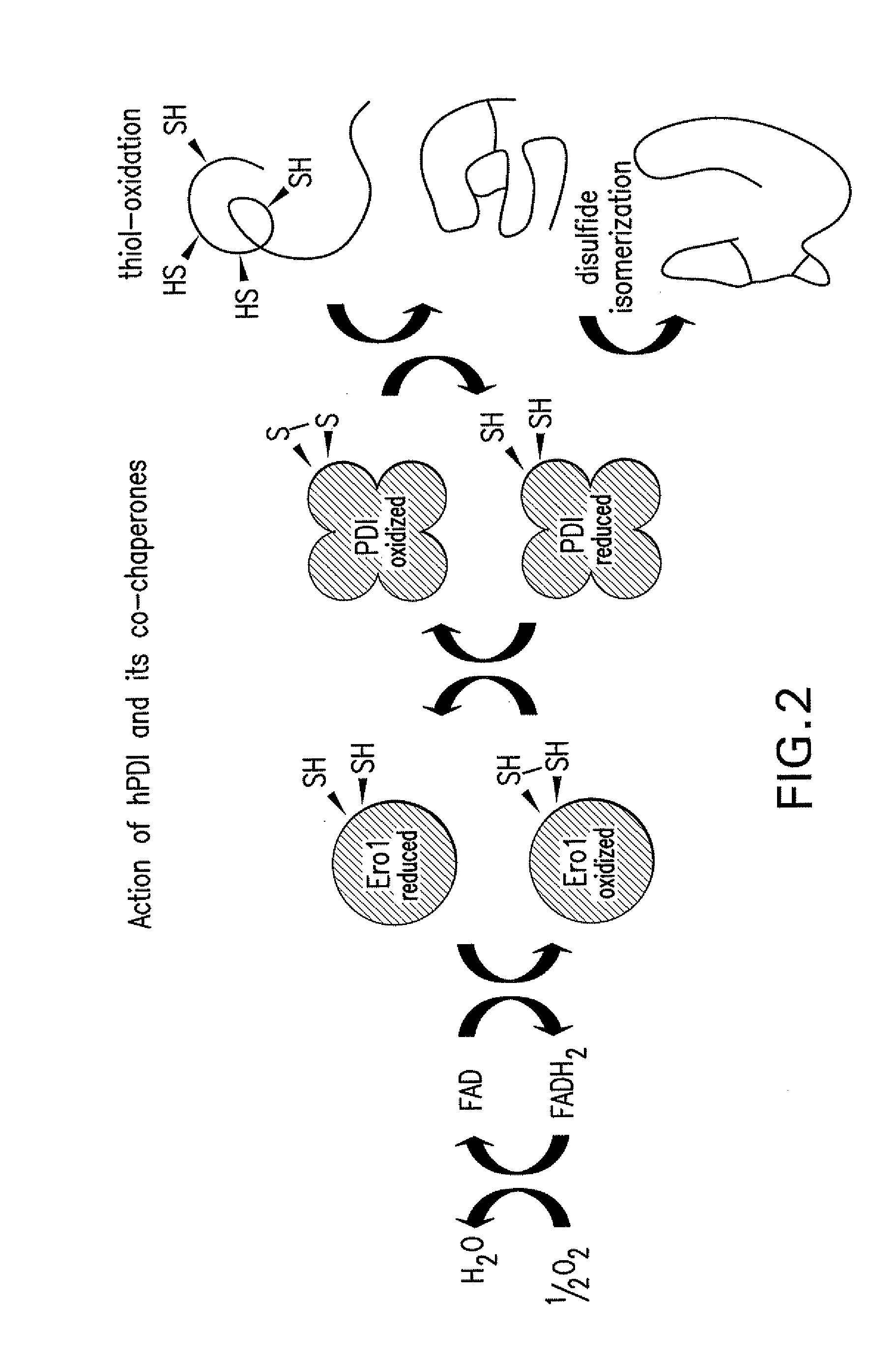
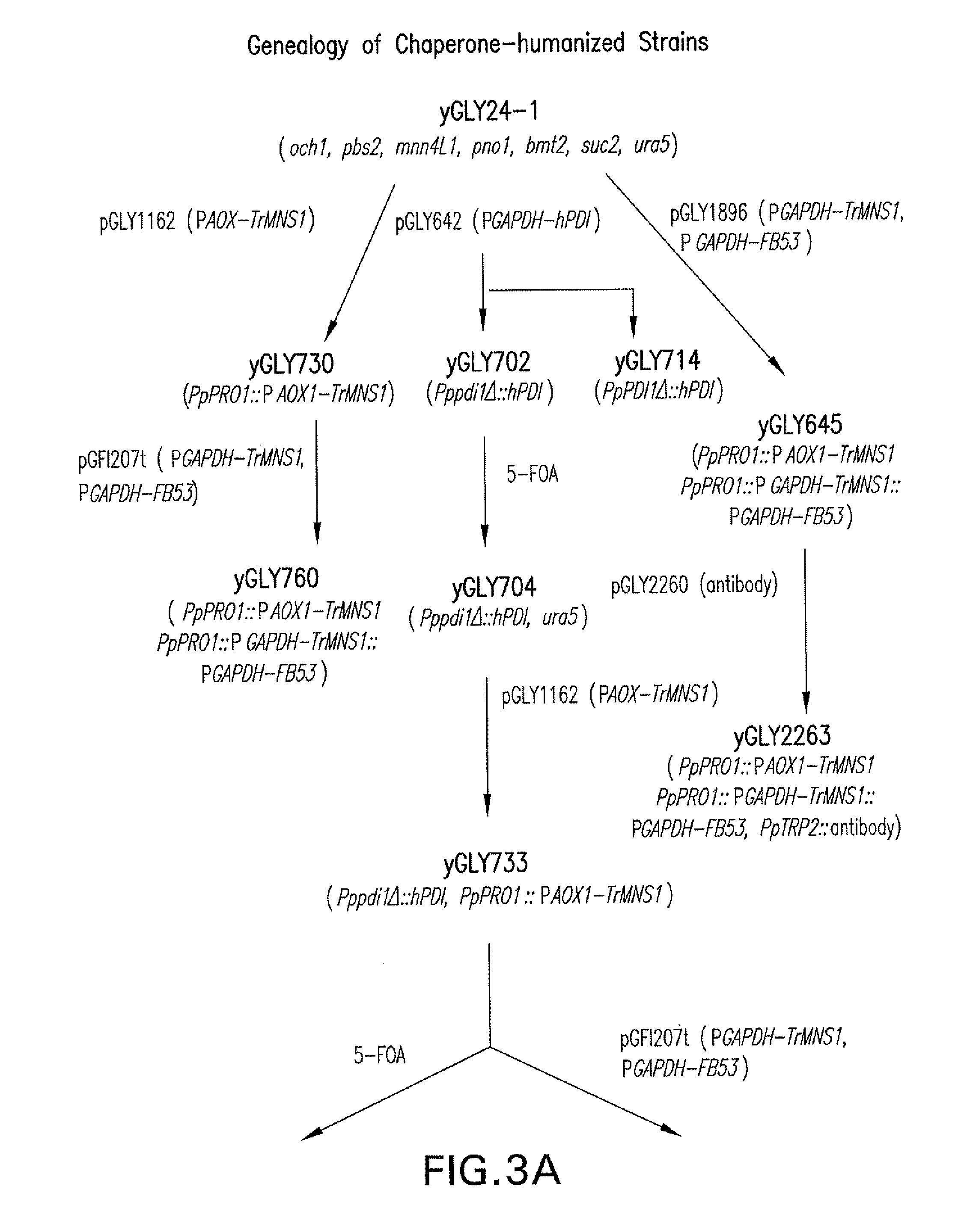
Lower eukaryote host cells in which the function of at least one endogenous gene encoding a chaperone protein, such as a Protein Disulphide Isomerase (PDI), has been reduced or eliminated and at least one mammalian homolog of the chaperone protein is expressed are described. In particular aspects, the host cells further include a deletion or disruption of one or more O-protein mannosyltransferase genes, and / or overexpression of an endogenous or exogenous Ca2+ ATPase. These host cells are useful for producing recombinant glycoproteins in large amounts and for producing recombinant glycoproteins that have reduced O-glycosylation.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Methods and kits for measuring von willebrand factor
ActiveUS20090142779A1Improve adhesionPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementFactor VIII vWFRistocetin
Methods and kits for measuring levels of von Willebrand factor function in a sample without using a platelet aggregation agonist, such as ristocetin, comprising recombinant glycoprotein Ibα having at least two of a G233V, D235Y and M239V mutations and an agent to detect a complex between the recombinant glycoprotein Ibα and von Willebrand factor.
Owner:THE MEDICAL COLLEGE OF WISCONSIN INC +1
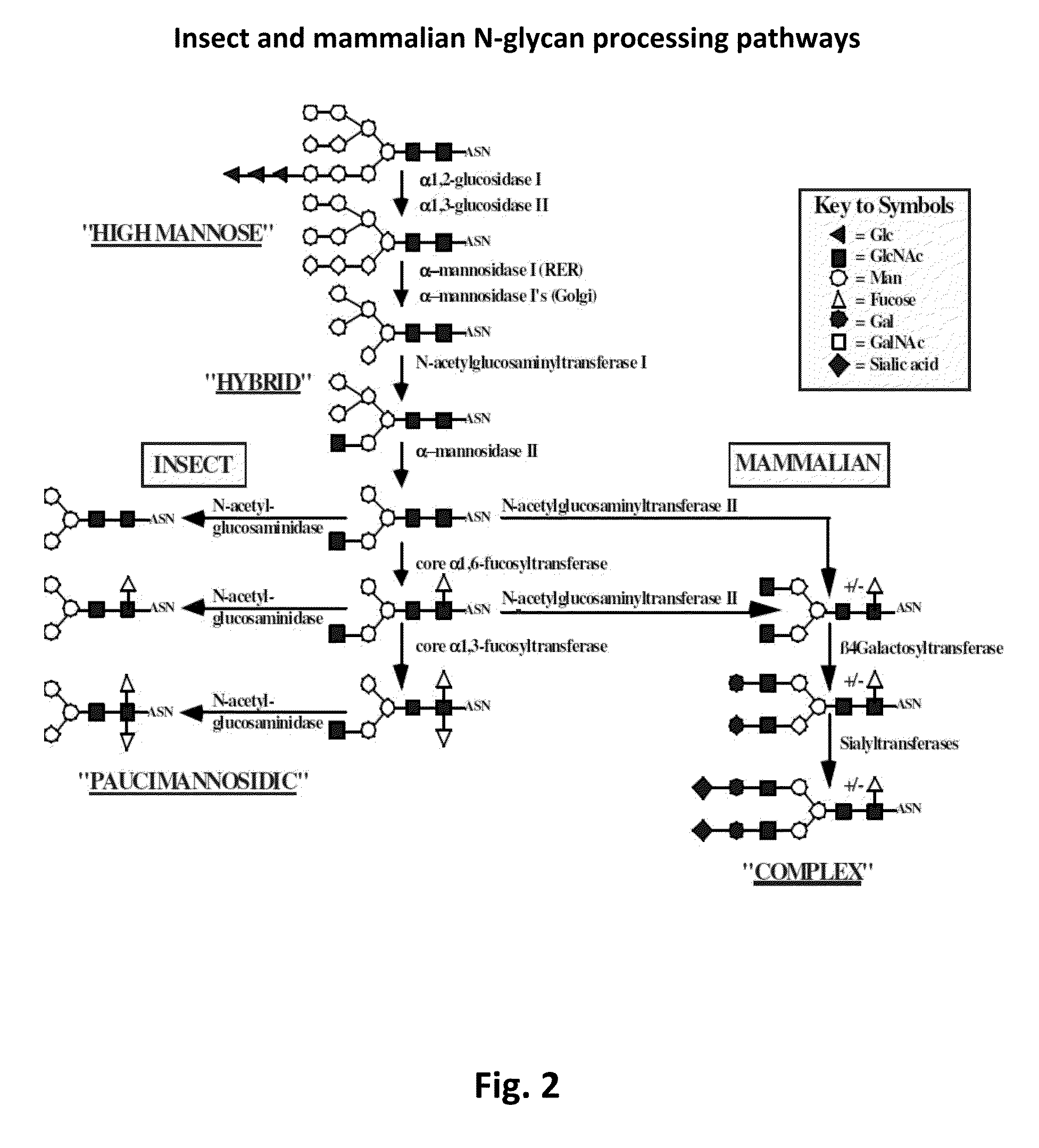
Compositions and methods for reducing fucosylation of glycoproteins in insect cells and methods of use thereof for production of recombinant glycoproteins
InactiveUS20150093782A1Enhanced inhibitory effectStabilizing inhibitionAnimal cellsPeptide/protein ingredientsFucosylationGlycoprotein
Compositions for reducing fucosylation of glycoproteins in insect cells are provided. Also disclosed are methods of use of such compositions for the production of recombinant humanized proteins.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Recombinant hcv e2 glycoprotein
ActiveUS20110014209A1SsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGlycoprotein iBinding domain
The invention provides modified hepatitis C virus (HCV) E2 glycoproteins comprising the HCV-E2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) including the HVR1, HVR2 and igVR variable regions wherein in at least one of said variable regions at least a part of the variable region is replaced with a flexible linker sequence. The invention also provides vaccine compositions comprising the modified glycoproteins as well as methods of use thereof.
Owner:THE MACFARLANE BURNET INST FOR MEDICAL RES & PUBLIC HEALTH LTD
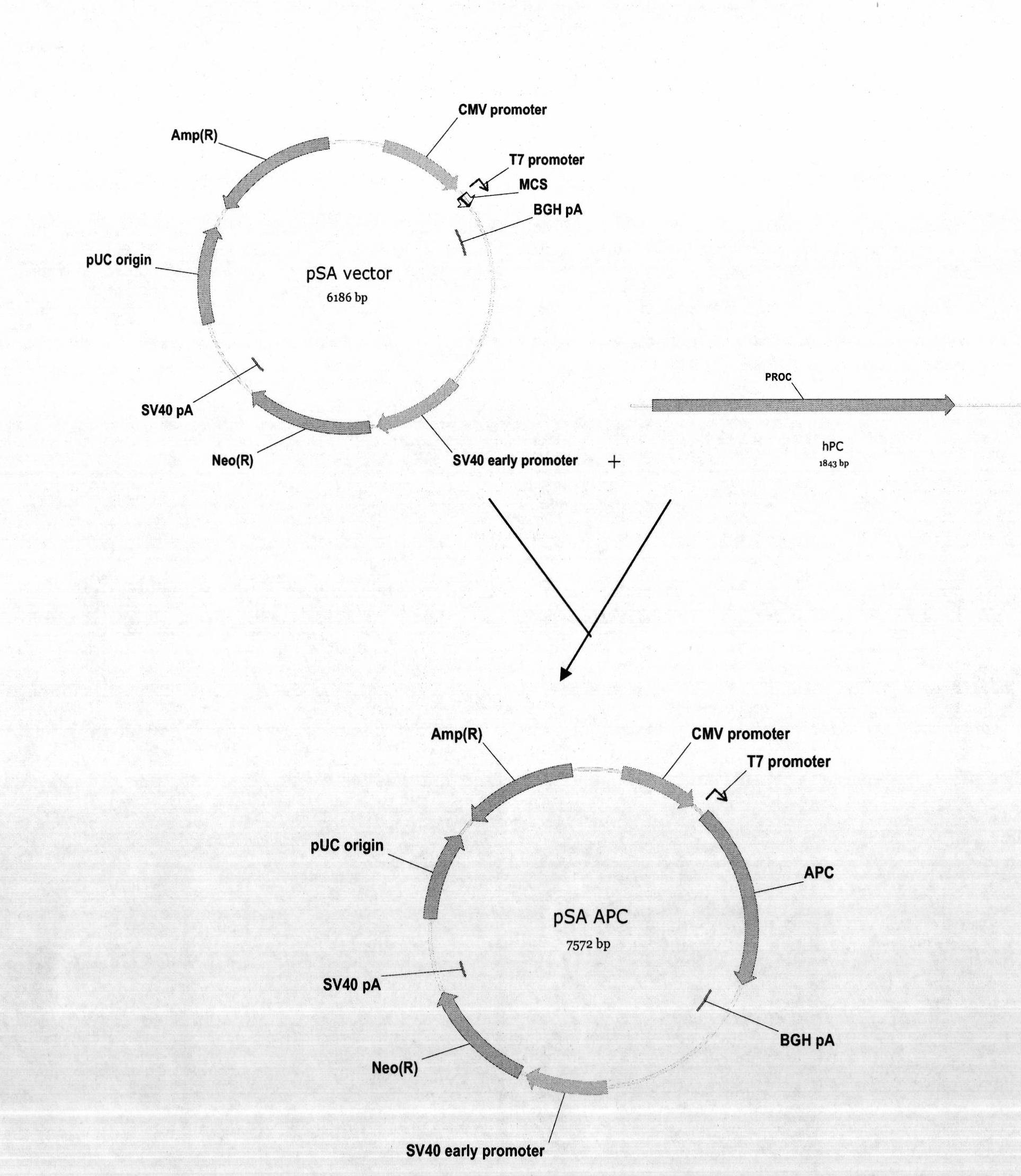
Vector system pSA for high-level expression of recombinant glycoprotein in eukaryotic cells
InactiveCN101906435AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHigh level expressionBiology
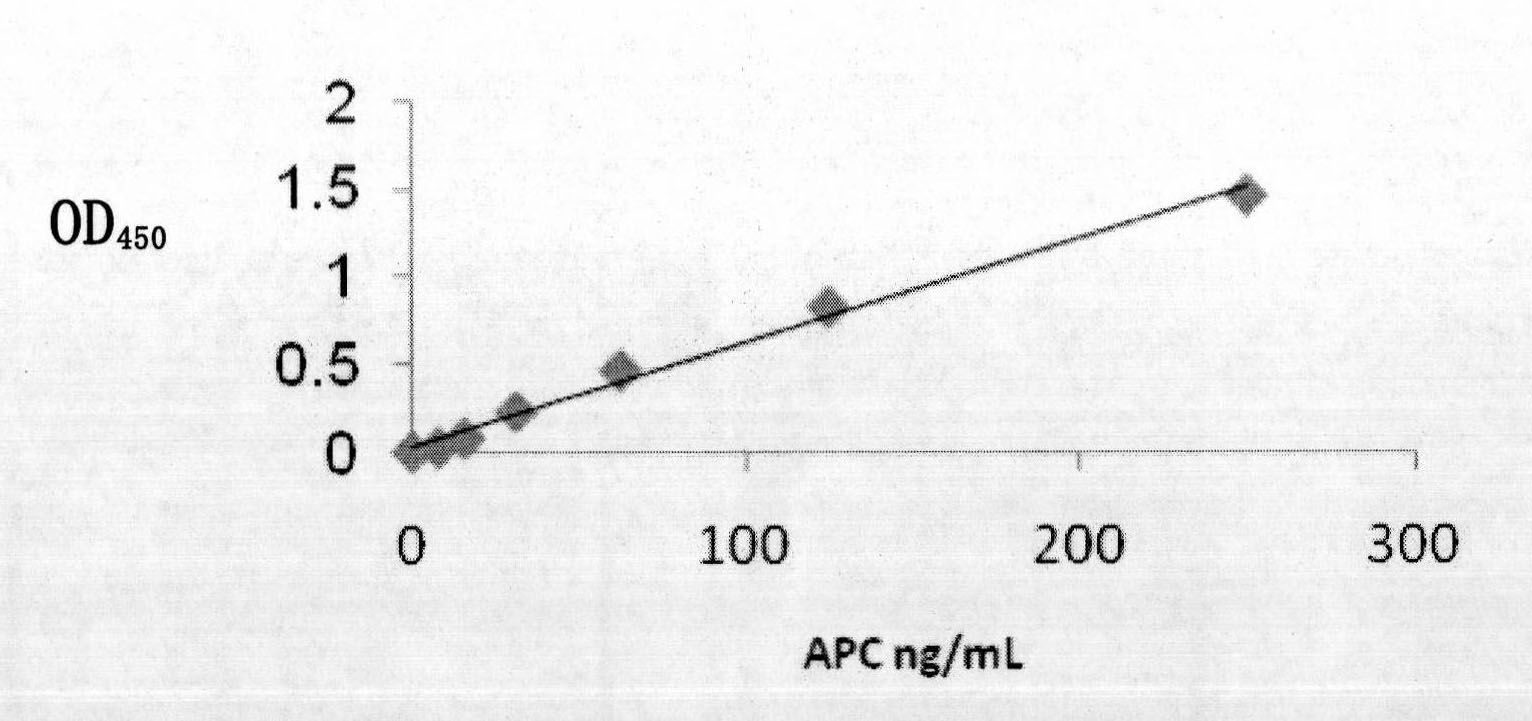
The invention provides a vector system pSA for high-level expression of a recombinant glycoprotein in eukaryotic cells, in particular an expression vector for expressing a foreign protein in animal cells. The vector system pSA comprises an expression cassette for expressing the foreign protein. The expression cassette is provided with the following elements sequentially from 5' to 3': (a) a first promoter, (b) a multiple cloning site and an optional coding sequence of the foreign protein, (c) a first polyA sequence; (d) a second promoter, (e) a selectable marker gene and (f) a second polyA signal sequence. The expression vector of the invention is particularly suitable to efficiently express a human activated protein C.
Owner:SUZHOU ZELGEN BIOPHARML
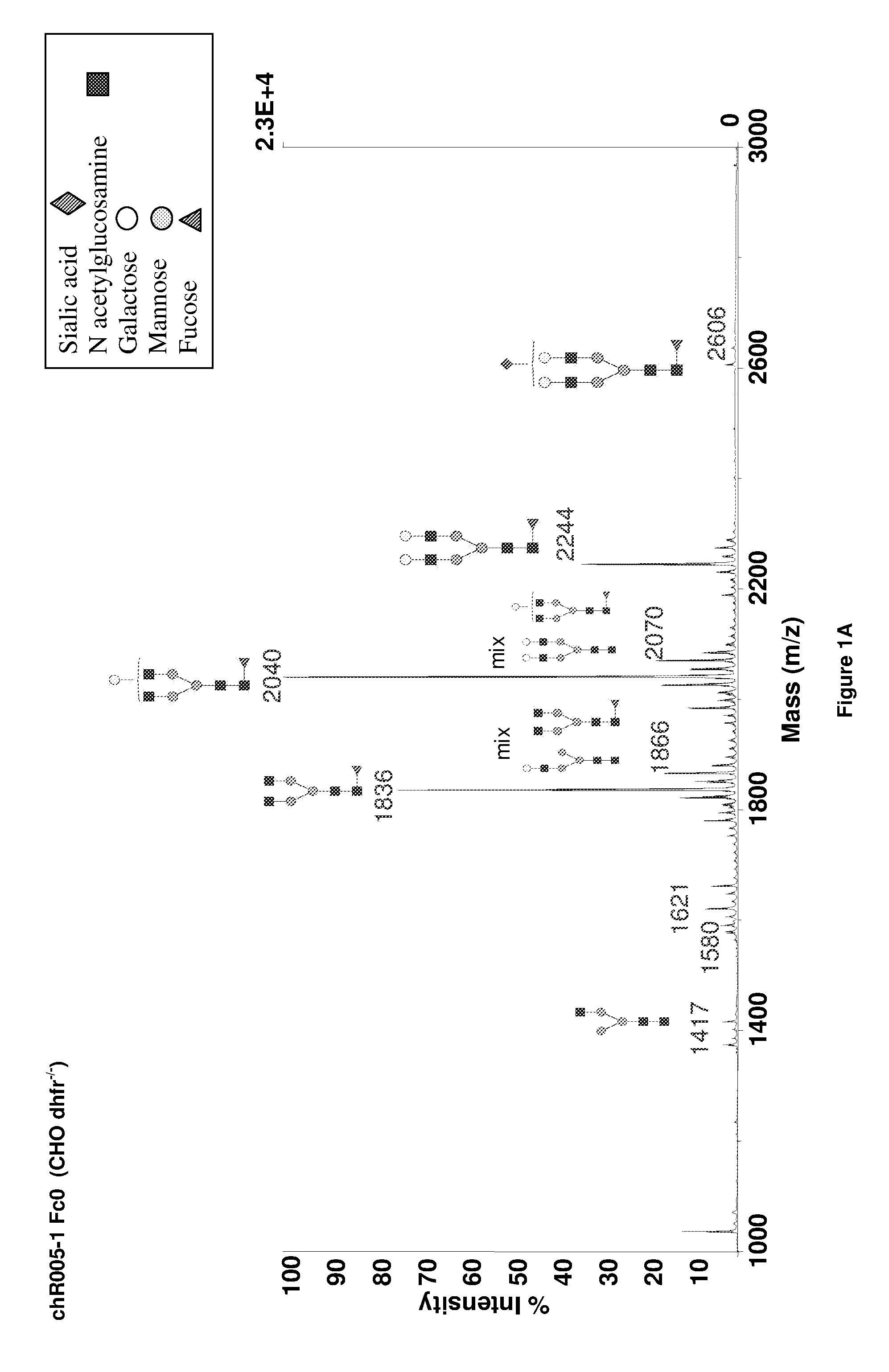
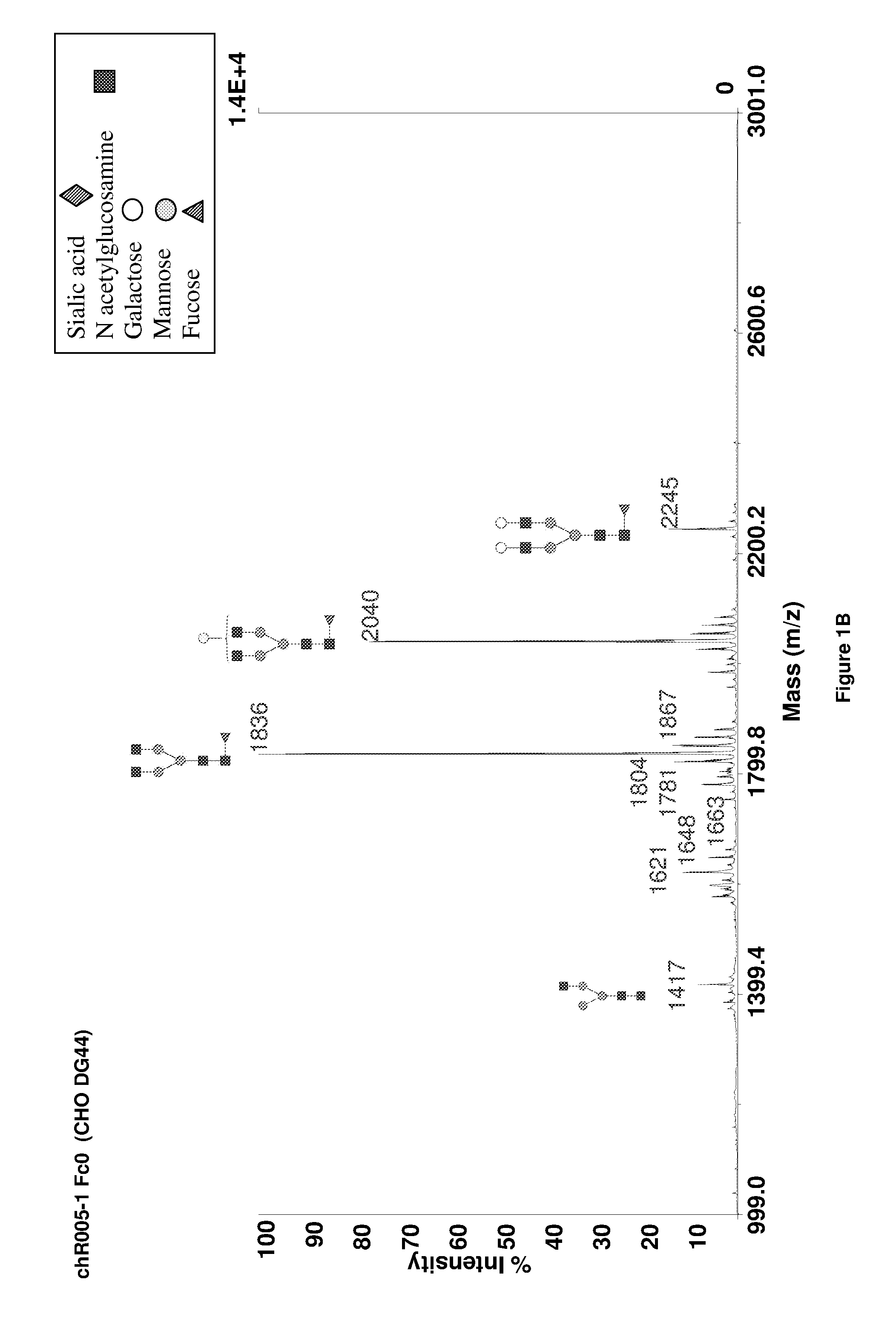
Method for preparing recombinant glycoproteins with high sialic acid content
ActiveCN102482674AIncreased sialic acid contentThrombopoietinCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsArginineTert-leucine
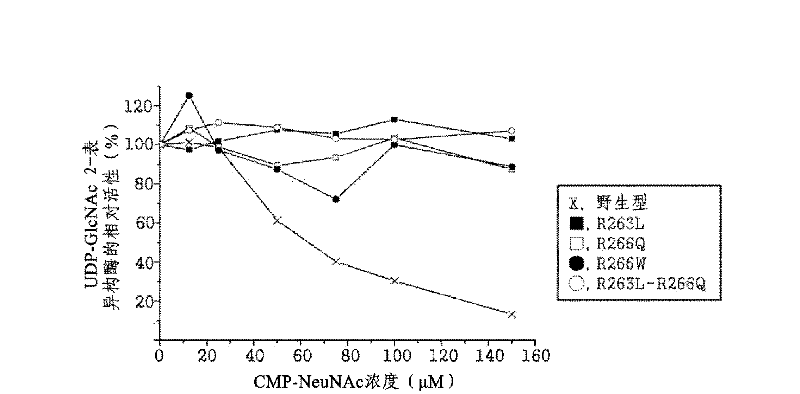
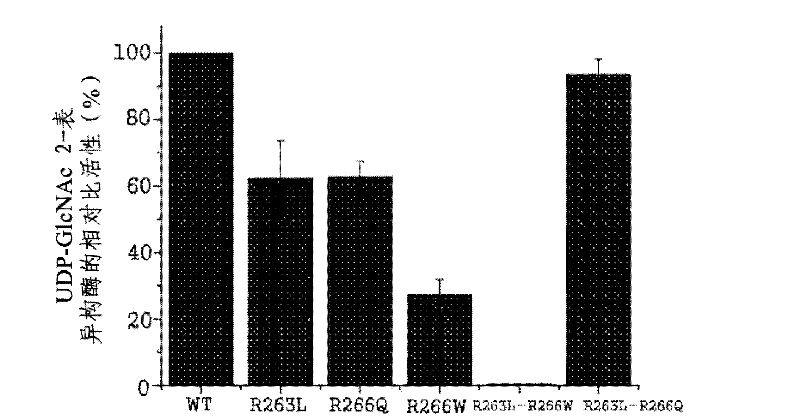
The present disclosure relates to a method for preparing recombinant glycoproteins with high sialic acid content. More specifically, for UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase / ManNAc kinase (GNE / MNK) enzyme where point mutation was induced by substituting arginine at position 263 by leucine only or by further substituting arginine at position 266 by glutamine, epimerase activity is constantly maintained, and overexpressed cells thereof experience an increase in intracellular cytidine monophosphate (CMP)-sialic acid content, irrespective of CMP-sialic acid concentration.,Particularly, since in an glycoprotein(such as, erythropoietin and thrombopoietin)-producing host cell where point mutationinduced GNE / MNK, human alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase and a CMP-sialic acid transporter gene are simultaneously overexpressed, intracellular content of CMP-sialic acid and sialic acid in glycoprotein increases in cells, overexpression in a host cell producing a sialylated recombinant glycoprotein the three genes above may be useful for preparing glycoprotein with increased sialic acid content.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Methods of using a bacterial GlcNAc-6-P 2'- epimerase to promote sialylation of glycoconjugates
The present invention relates to new methods to promote sialylation of glycoconjugates, including recombinant glycoproteins, in glycoconjugate production systems. The invention relates to methods to promote efficient glycoconjugate sialylation in recombinant expression systems, by providing simpler and more economical ways to produce large intracellular pools of sialic acid precursors. The invention is directed to nucleic acids, vectors, and cells harboring vectors comprising nucleic acids encoding enzymes involved in the synthesis of sialic acid precursors, and cells harboring these nucleic acids in combination with nucleic acids encoding glycosyltransferases, including sialyltransferases, to facilitate the production of humanized recombinant glycoproteins in bacterial, fungal, plant, and animal cell expression systems. The engineered cells can be used to produce glycosylated proteins in virally-infected, transiently-transformed, or stably-transformed host cells, including lepidopteran insects and cultured cell lines derived from Spodoptera frugiperda, Trichoplusia ni, and Bombyx mori that can be infected by baculovirus expression vectors.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Methods of Using a Bacterial GlcNAc-6-P 2'- Epimerase to Promote Sialylation of Glycoconjugates
The present invention relates to new methods to promote sialylation of glycoconjugates, including recombinant glycoproteins, in glycoconjugate production systems. The invention relates to methods to promote efficient glycoconjugate sialylation in recombinant expression systems, by providing simpler and more economical ways to produce large intracellular pools of sialic acid precursors. The invention is directed to nucleic acids, vectors, and cells harboring vectors comprising nucleic acids encoding enzymes involved in the synthesis of sialic acid precursors, and cells harboring these nucleic acids in combination with nucleic acids encoding glycosyltransferases, including sialyltransferases, to facilitate the production of humanized recombinant glycoproteins in bacterial, fungal, plant, and animal cell expression systems. The engineered cells can be used to produce glycosylated proteins in virally-infected, transiently-transformed, or stably-transformed host cells, including lepidopteran insects and cultured cell lines derived from Spodoptera frugiperda, Trichoplusia ni, and Bombyx mori that can be infected by baculovirus expression vectors.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Methods for producing recombinant glycoproteins with modified glycosylation
Genetically engineered host animal cells capable of producing glycoproteins having modified glycosylation patterns, e.g., defucosylation and / or monoglycosylation. Such host animal cells can be engineered to express fucosidase, endoglycosidase or both.
Owner:ONENESS BIOTECH
Yeast strains for protein production
ActiveUS20100279348A1Increase the number ofConvenient amountFungiSugar derivativesPichia pastorisYeast
Method and system for expression systems, based on ade1 and ade2 auxotrophic strains of yeast and fungi, including P. pastoris are disclosed. The expression systems are useful for increased cellular productivity of transformed cell lines and for production of recombinant glycoproteins at industrial scale.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Dna Sequence and Expressed Recombinant Glycoproteins Related to Feline Thyrotropin
Amino acid sequences of feline thyrotropin and polynucleotide sequences encoding feline thyrotropin are provided, as well as methods of making and using said sequences.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Efficient expression method and application of virus recombinant glycoprotein and eukaryotic cells thereof
ActiveCN109111507AHigh expressionSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsViral glycoproteinSecretory protein
The invention provides virus recombinant glycoprotein which is formed by replacing a signal peptide of target viral glycoprotein with a signal peptide of human or animal secretory protein. The invention also provides a method for efficiently expressing the recombinant glycoprotein by using eukaryotic cells. According to the virus recombinant glycoprotein and the method provided by the invention, the world technical problems of low expression and poor secretion of the virus recombinant glycoprotein in the eukaryotic cells are solved, a solid foundation is laid for developing vaccines and virusprotective antibody detection reagents and a good application prospect is realized.
Owner:北京派迪畅科技发展有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com