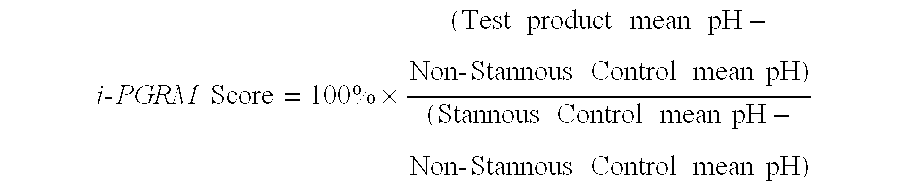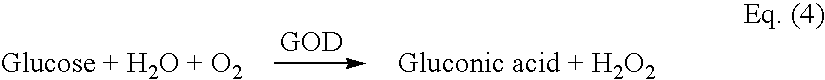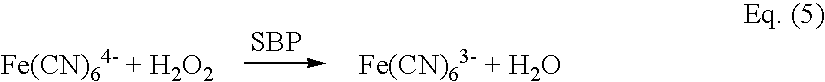Patents
Literature
294results about How to "Minimal effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
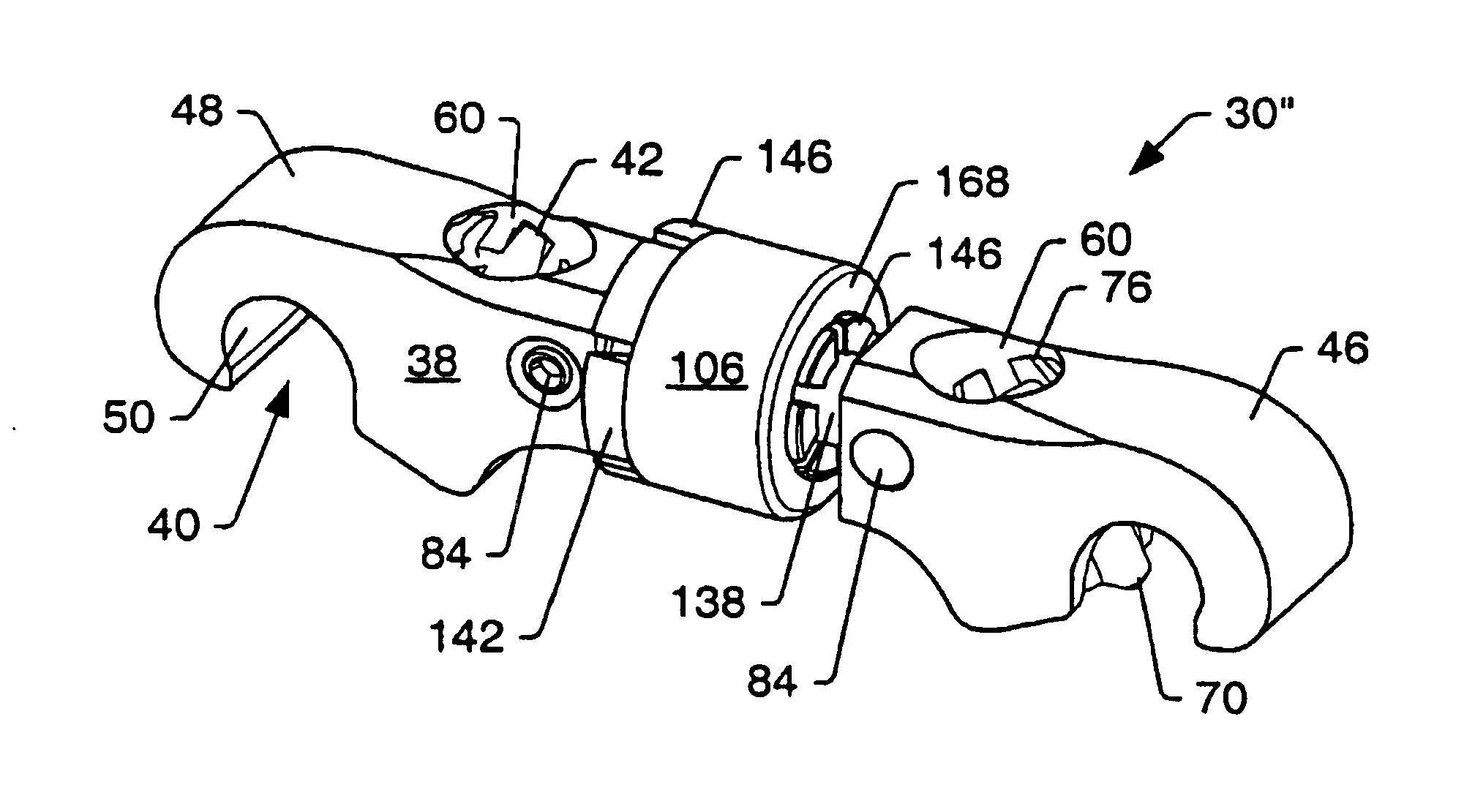
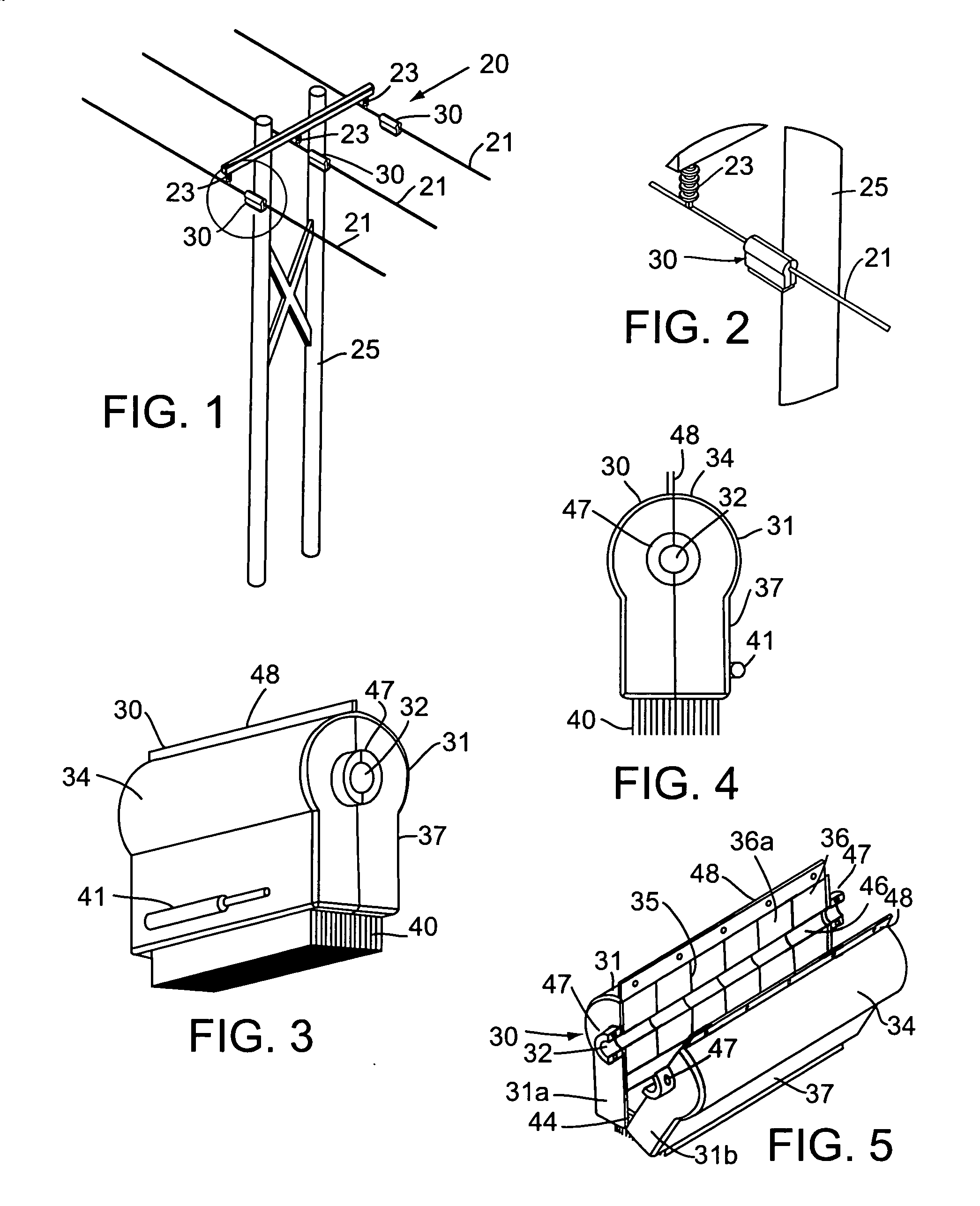
Adjustable transverse connector
InactiveUS6872208B1Easy to bendPrecise positioningInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsCamPlastic surgery
A transverse connector may be attached to rods of an orthopedic stabilization system. The rods of the stabilization system may be non-parallel and skewed in orientation relative to each other. The transverse connector may include two members that are joined together by a fastener. The transverse connector may be adjustable in three separate ways to allow the transverse connector to attach to the rods. The length of the transverse connector may be adjustable. The rod openings of the transverse connector may be partially rotatable about a longitudinal axis of the transverse connector. Also, a first member may be angled towards a second member so that the transverse connector can be attached to rods that are diverging. The transverse connector may include cam locks that securely attach the transverse connector to the rods. Rotating a cam locks may extend a rod engager into a rod opening. The rod engager may be a portion of the cam lock. The extension of the rod engager into a rod opening may push a rod against a body of the transverse connector to form a frictional engagement between the transverse connector, the rod, and the rod engager.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
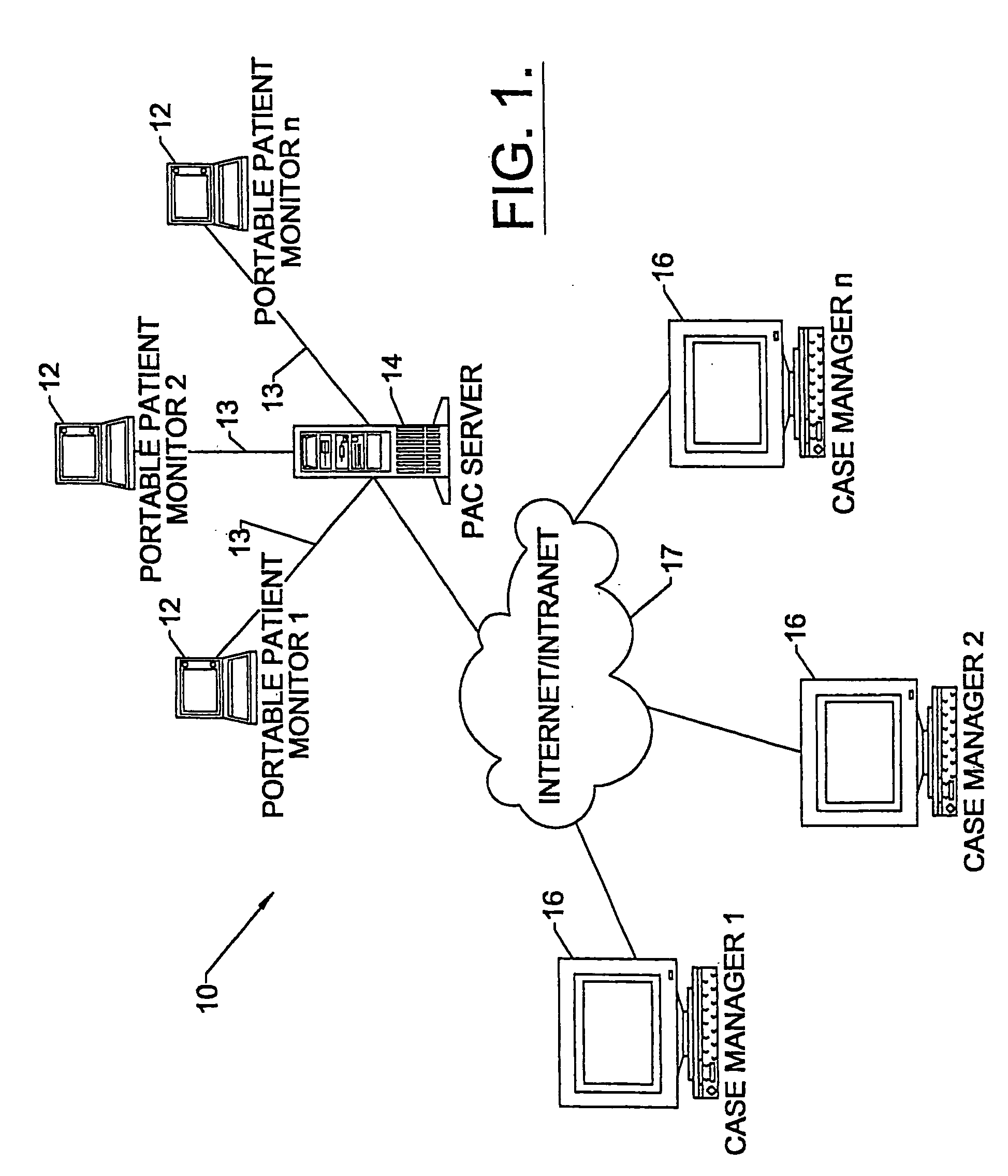
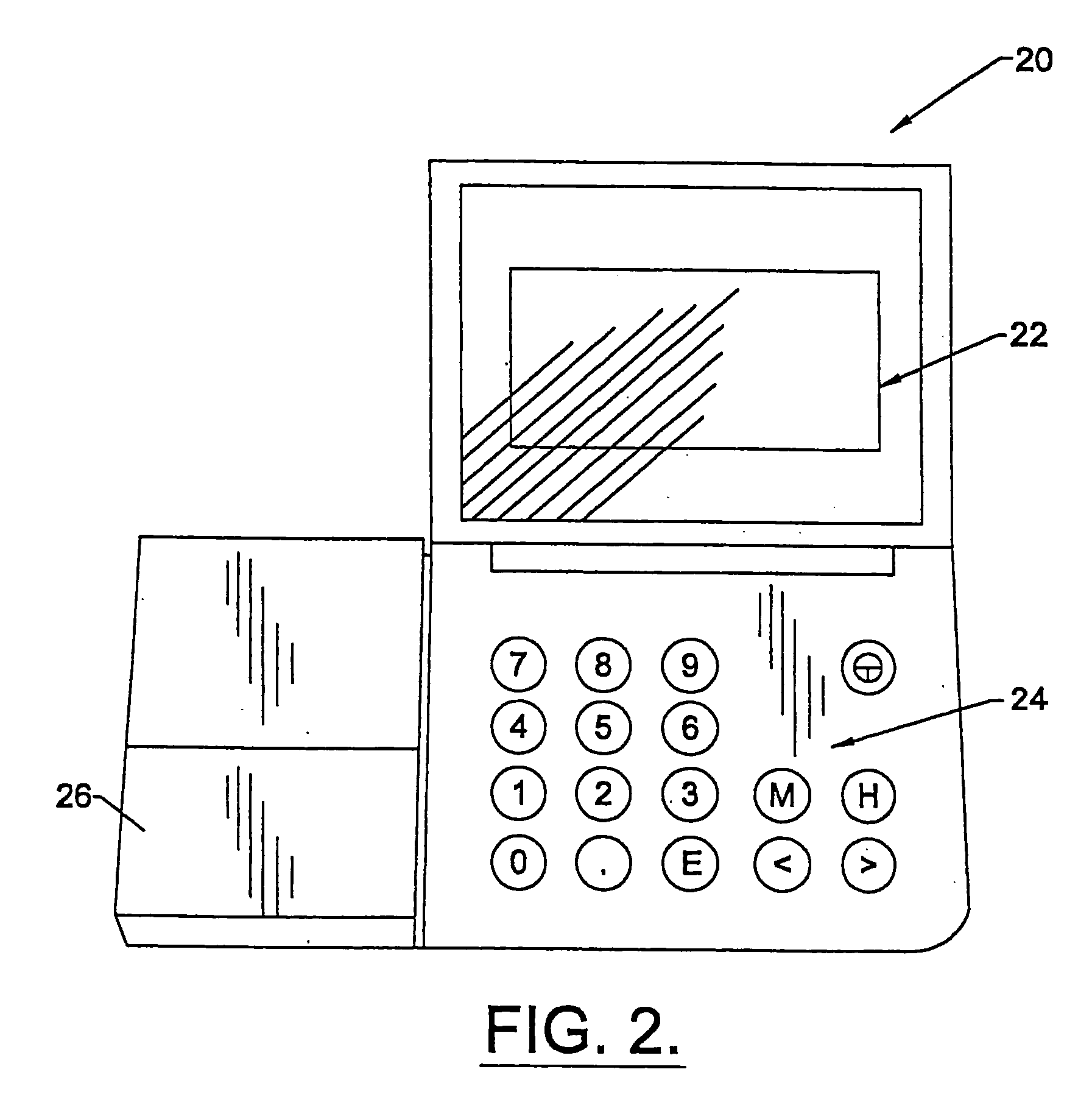
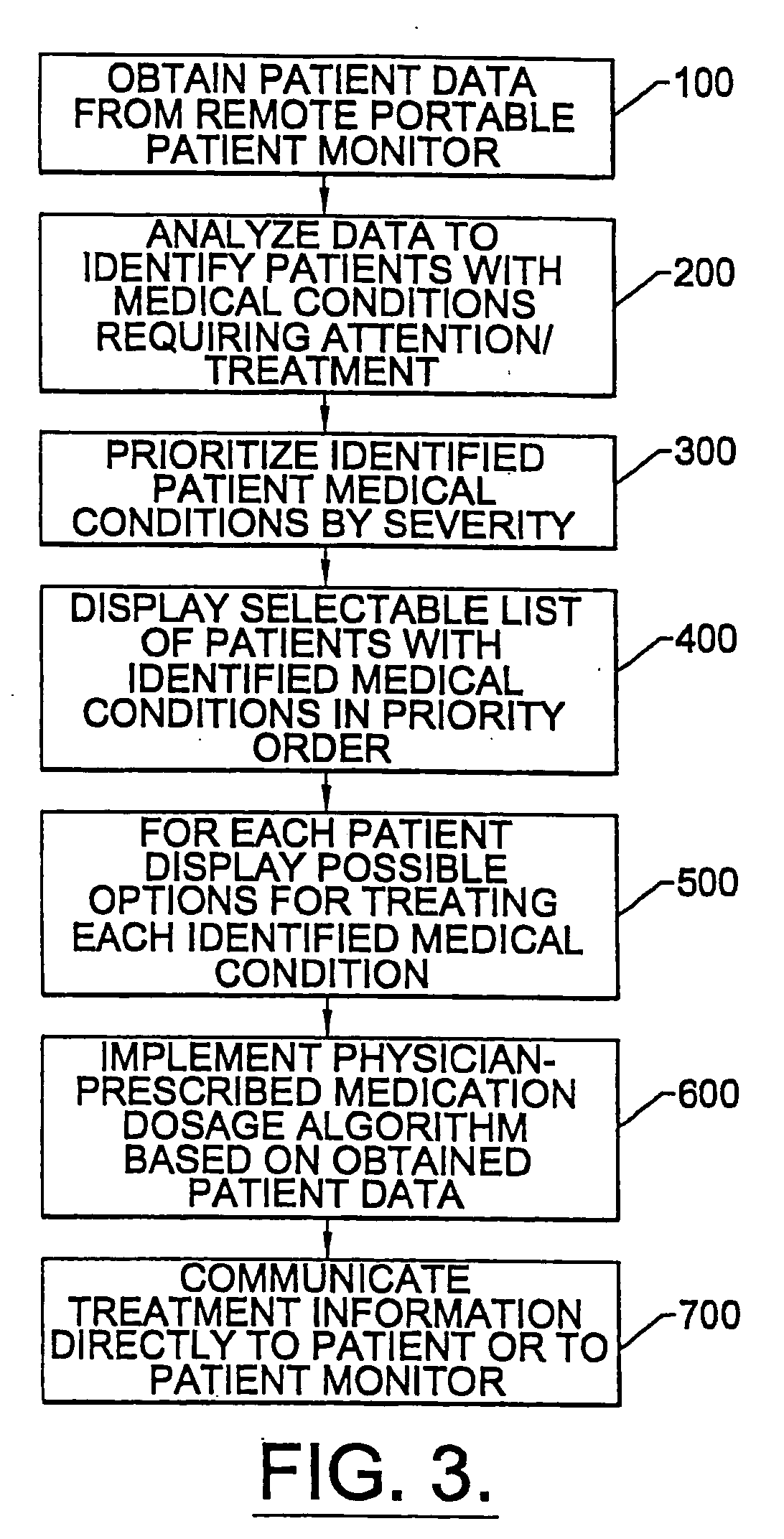
Apparatus and methods for monitoring and modifying anticoagulation therapy of remotely located patients
InactiveUS6980958B1Significant comprehensive benefitsCost-effectiveDrug and medicationsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionWarfarinRegimen
A patient apparatus is configured to receive and analyze information regarding patient compliance with anticoagulation medication and self-test coagulation regimens related to anticoagulation therapy. In addition, a patient apparatus is configured to receive data from a patient, including physiological data, pathophysiological data, biological data, psychological data, neuropsychological data, and / or behavioral data. Utilizing the received patient data, a patient apparatus can modify a warfarin regimen using an algorithm contained within the apparatus. The apparatus can communicate the modified warfarin regimen to the patient and to third parties, such as remotely located healthcare providers. In addition, the apparatus can prompt a patient when to perform a self-test and can prompt a patient to seek immediate medical attention, or to directly contact medical help, when so warranted.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CAPITAL AS AGENT
Stannous oral care compositions
InactiveUS20070025928A1Enhance therapeutic efficacyMinimal effectCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSurface-active agentsMagnesium
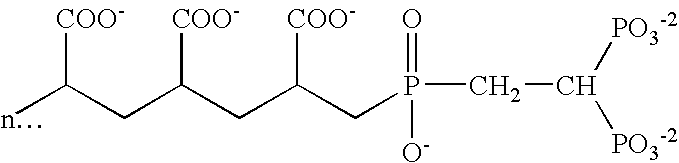
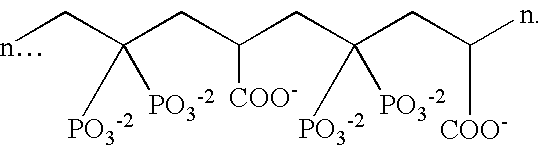
Disclosed are oral compositions comprising a stannous ion source, a polyvalent cation source and a mineral surface active agent, said compositions providing enhanced therapeutic efficacy derived from stannous fluoride and / or other stannous salt, including antimicrobial effects, control of breath malodor, control of dental plaque growth and metabolism, reduced gingivitis, decreased progression to periodontal disease, reductions in dentinal hypersensitivity and reduced coronal and root dental caries. The aforementioned benefits are provided along with significant improvements compared to conventional stannous containing compositions, including: 1) reduced levels of dental staining; 2) reduced astringency thereby improving aesthetic characteristics of the compositions; 3) reduction in dental calculus formation, and 4) enhanced stability, bioavailability and thus, efficacy of stannous. The mineral surface active agents are agents that are substantive to mineral surfaces such as teeth and have chelating activity for polyvalent cations including stannous (Sn+2), zinc (Zn+2), copper (Cu+2), aluminum (Al+2), iron (Fe+2, Fe+3), strontium (Sr+2), calcium (Ca+2), barium (Ba+2), magnesium (Mg+2), and manganese (Mn+2). Preferred mineral surface-active agents include polymers or copolymers containing phosphate, phosphonate, or carboxy groups. The compositions may also comprise a fluoride ion source and may be formulated as single phase or dual phase compositions.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBNE CO
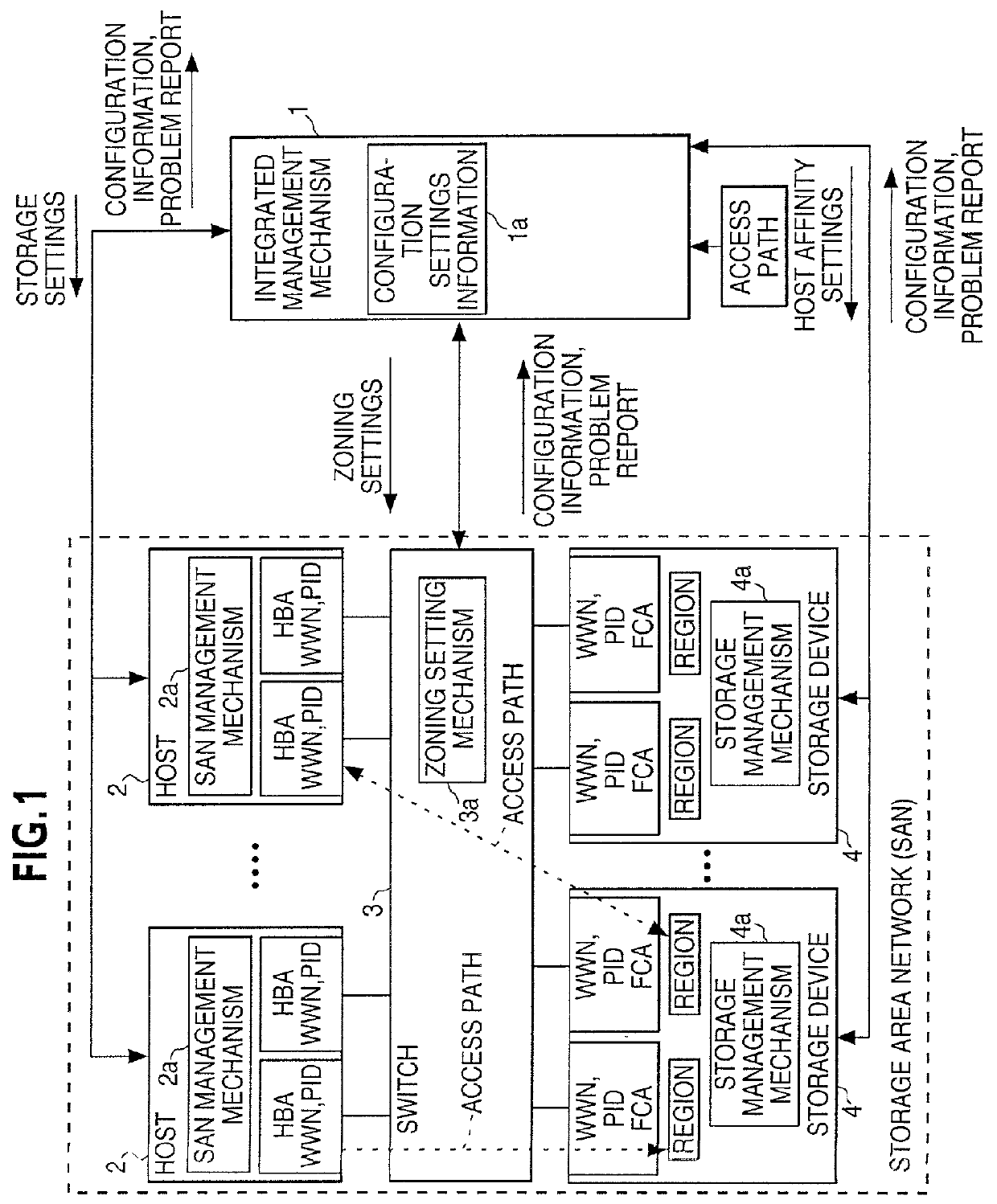
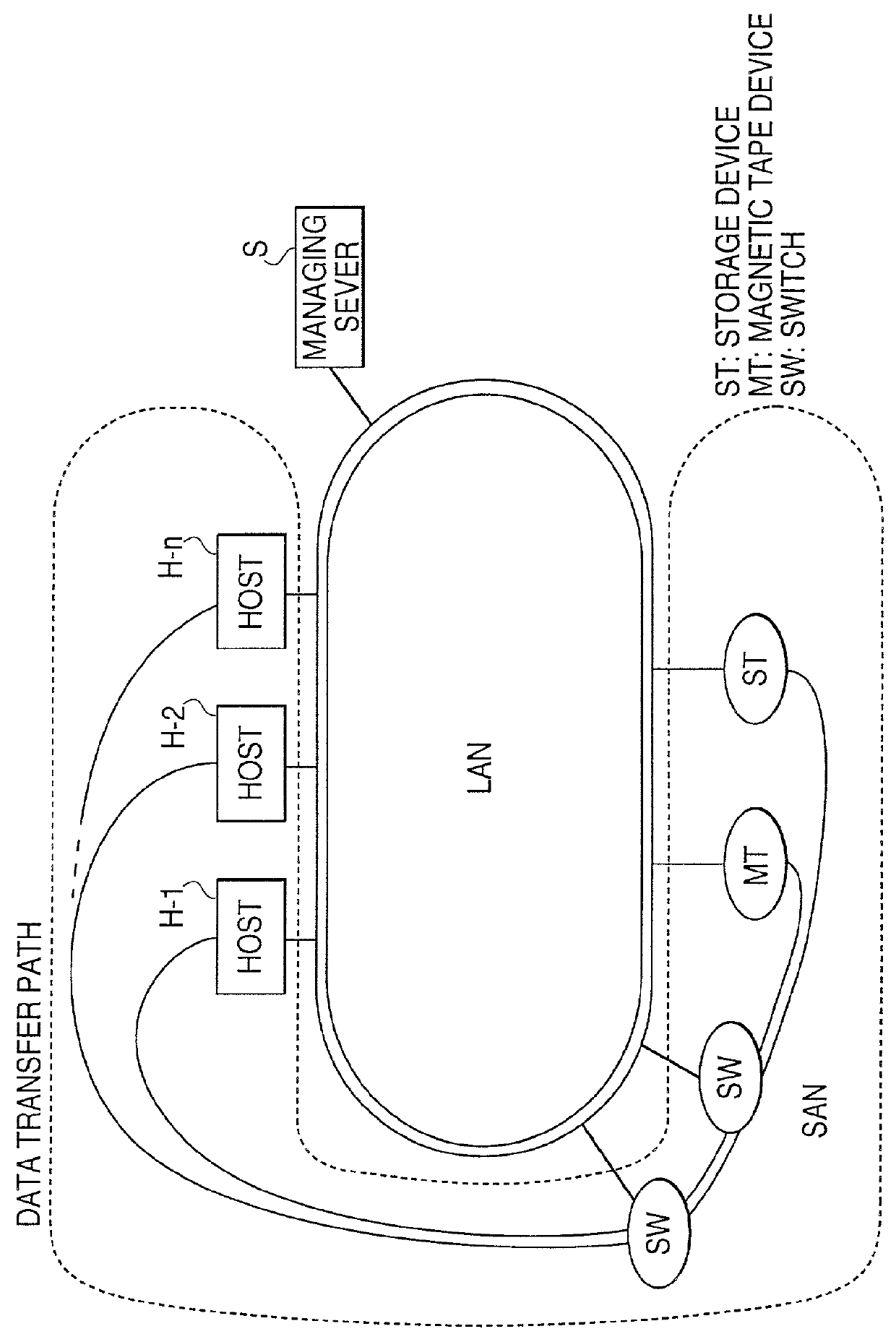
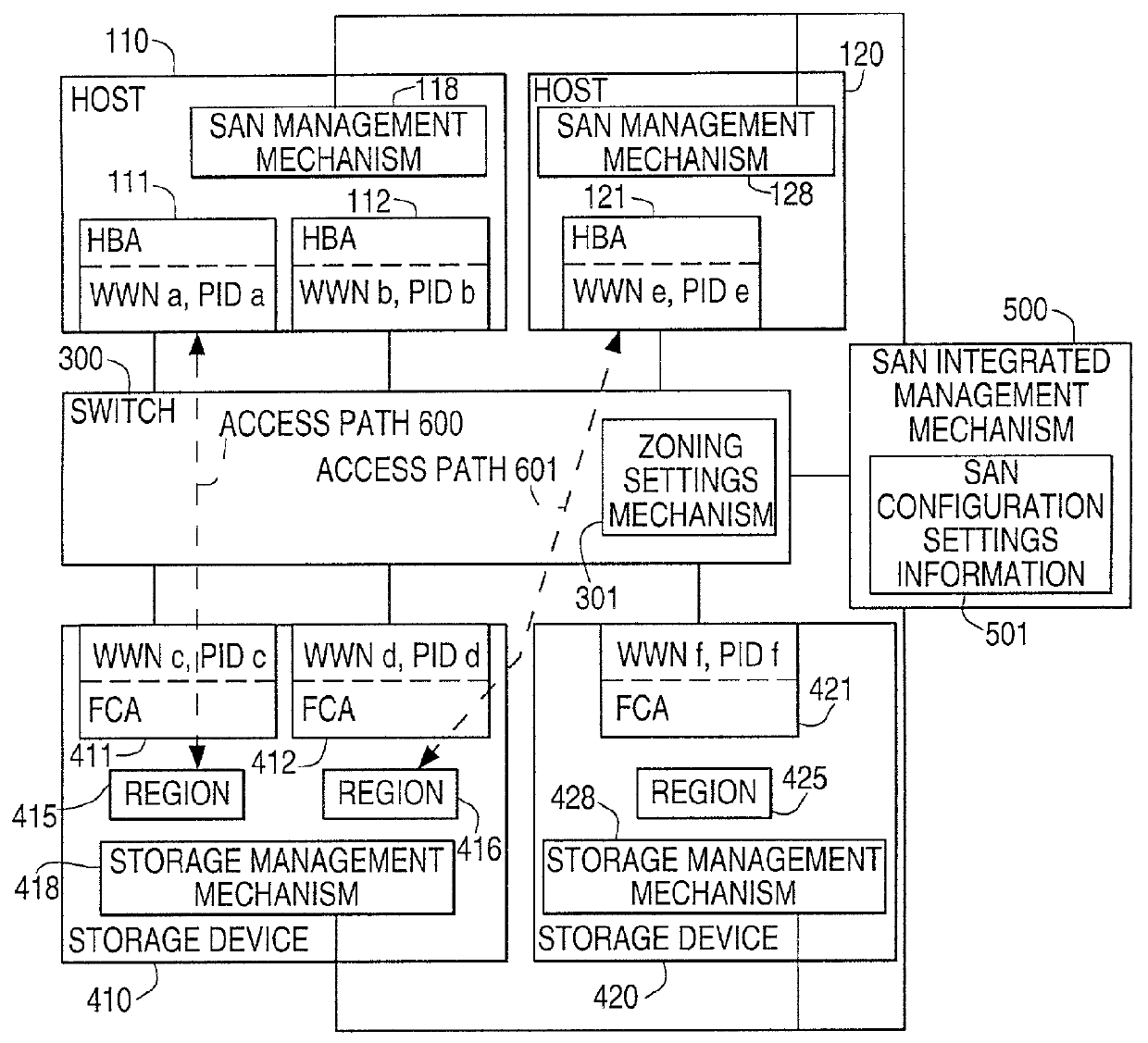
Storage area network management system, method, and computer-readable medium
InactiveUS20010054093A1Convenient to accommodateHighly reliable SAN systemMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksFiberStorage area network
An integrated management mechanism of a storage area network (SAN) integrates and manages a traditionally dispersed security system from a single source and automates security management in the SAN. The integrated management mechanism integrates and manages the SAN, and is configured so that access relationships of the host computers and the storage devices of the SAN are managed using the integrated management mechanism. An access path on the integrated management mechanism, including a region of the storage devices to which access is attempted from the host computer, the fiber channel adapters used when accessing that storage, and the host bus adapters (HBA) are configured. Based on the access path information configured, the integrated management mechanism establishes respective storage settings, zoning settings, and accessible region permissions for a SAN management mechanism of the host computer, a zoning settings mechanism of the switch, and a storage management mechanism of the storage device.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Biosensor and method
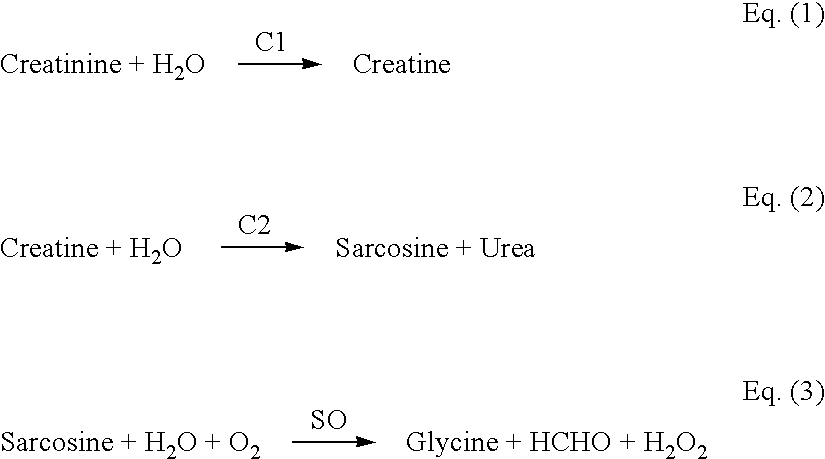
ActiveUS20040217019A1Keep for a long timeEasy to optimizeWeather/light/corrosion resistanceWave amplification devicesAnalytePeroxidase
An improved biosensor having at least a first working electrode and a first electrode material disposed on the first working electrode. The first electrode material is a mixture made by combining at least one enzyme where the at least one enzyme is a capable of reacting with the analyte to be measured, a redox mediator capable of reacting with a product of an enzymatic reaction or a series of enzymatic reactions involving the at least one enzyme, a peroxidase capable of catalyzing a reaction involving the redox mediator where the redox mediator is oxidized, a binder and a surfactant.
Owner:NOVA BIOMEDICAL
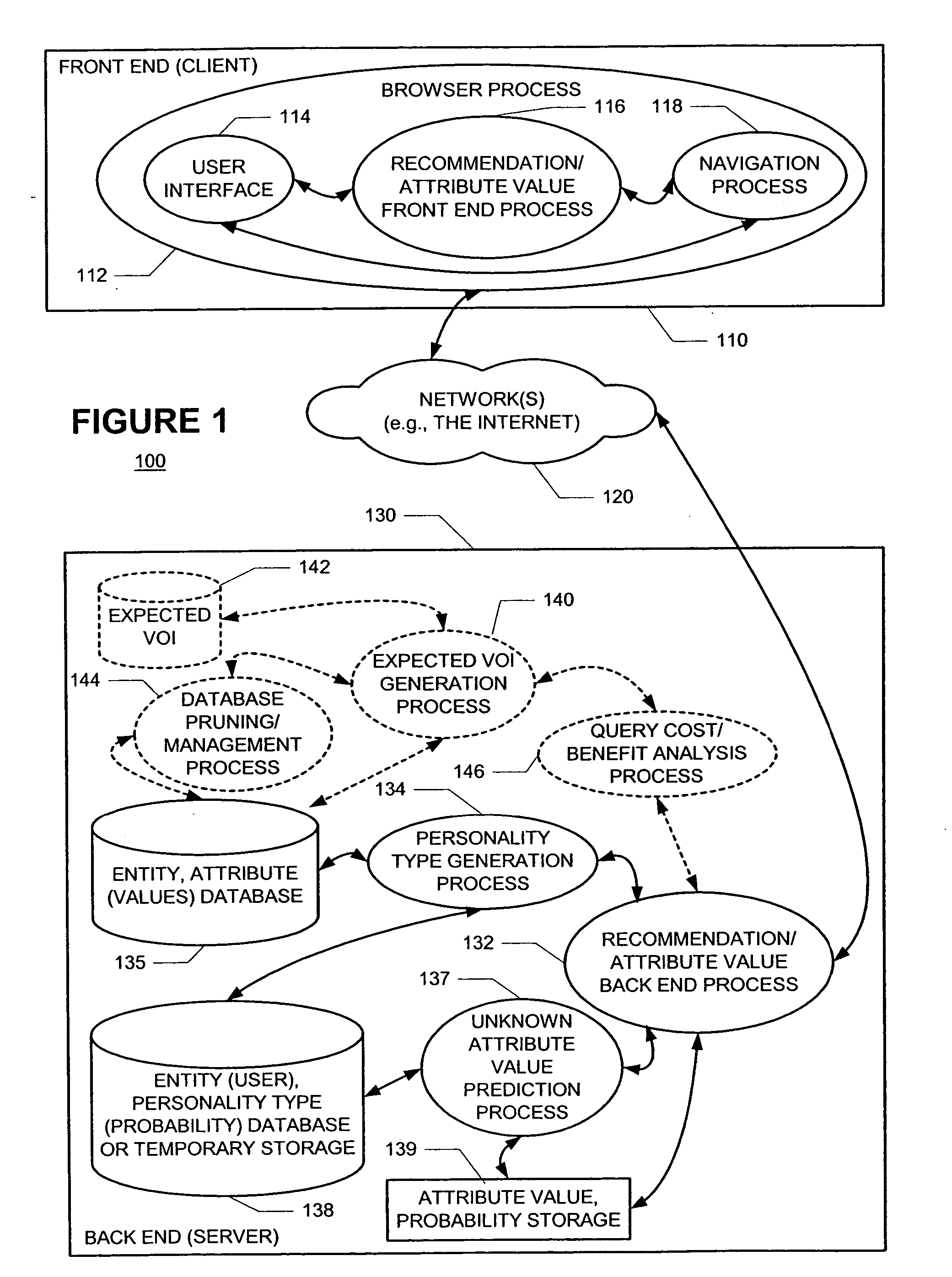
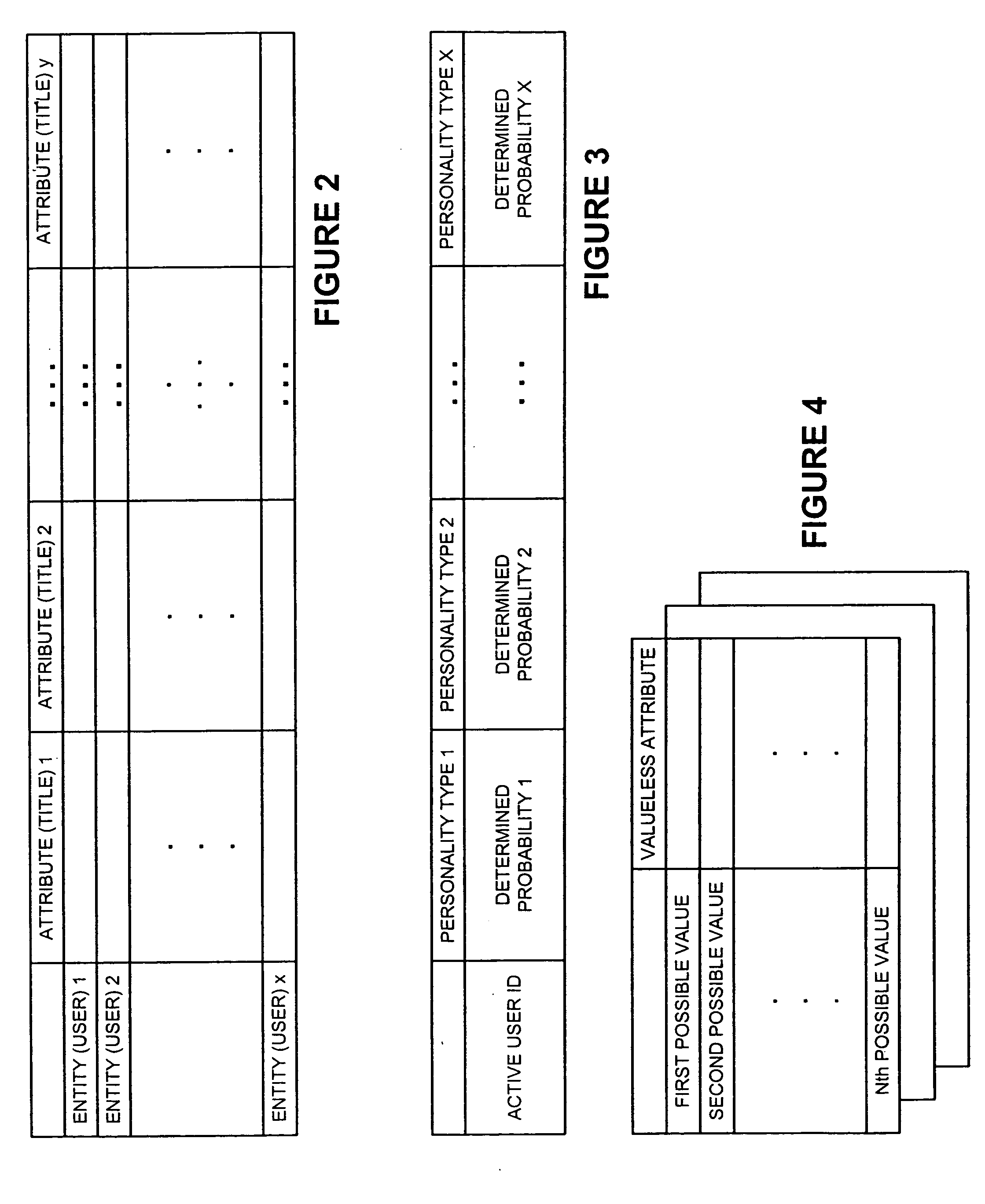
Methods and apparatus for predicting and selectively collecting preferences based on personality diagnosis
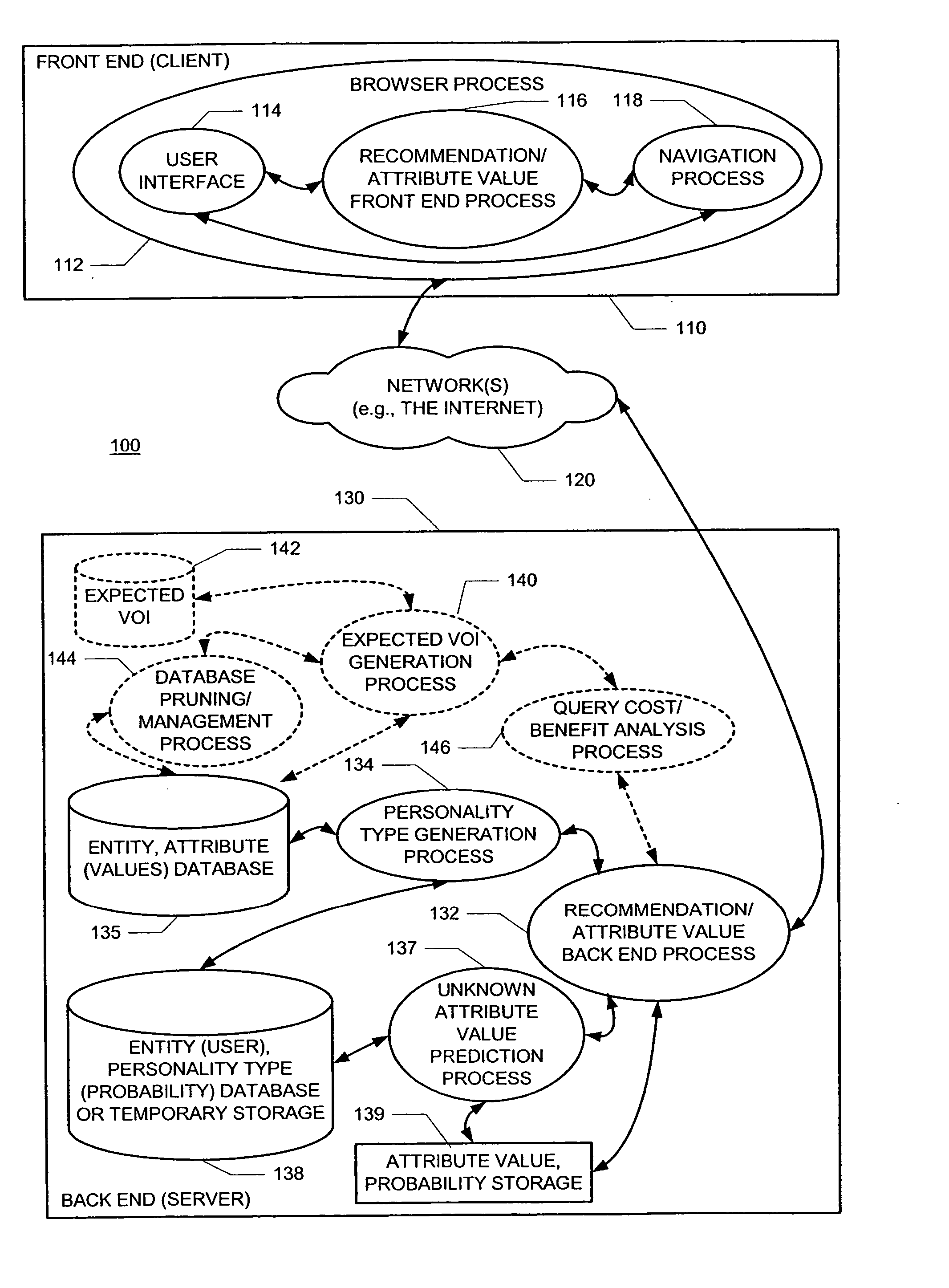
InactiveUS20040076936A1Minimal effectCumbersome processMarket predictionsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsProbabilistic semanticsValue of information
A new recommendation technique, referred to as "personality diagnosis", that can be seen as a hybrid between memory-based and model-based collaborative filtering techniques, is described. Using personality diagnosis, all data may be maintained throughout the processes, new data can be added incrementally, and predictions have meaningful probabilistic semantics. Each entity's (e.g., user's) reported attributes (e.g., item ratings or preferences) may be interpreted as a manifestation of their underlying personality type. Personality type may be encoded simply as a vector of the entity's (e.g., user's) "true" values (e.g., ratings) for attributes (e.g., items) in the database. It may be assumed that entities (e.g., users) report values (e.g., ratings) with a distributed (e.g., Gaussian) error. Given an active entity's (e.g., user's) known attribute values (e.g., item ratings), the probability that they have the same personality type as every other entity (e.g., user) may be determined. Then, the probability that they will have a given value (e.g., rating) for a valueless (e.g., unrated) attribute (e.g., item) may then be determined based on the entity's (e.g., user's) personality type. The probabilistic determinations may be used to determine expected value of information. Such an expected value of information could be used in at least two ways. First, an interactive recommender could use expected value of information to favorably order queries for attribute values (e.g., item ratings), thereby mollifying what could otherwise be a tedious and frustrating process. Second, expected value of information could be used to determine which entries of a database to prune or ignore-that is, which entries, which if removed, would have a minimal effect of the accuracy of recommendations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
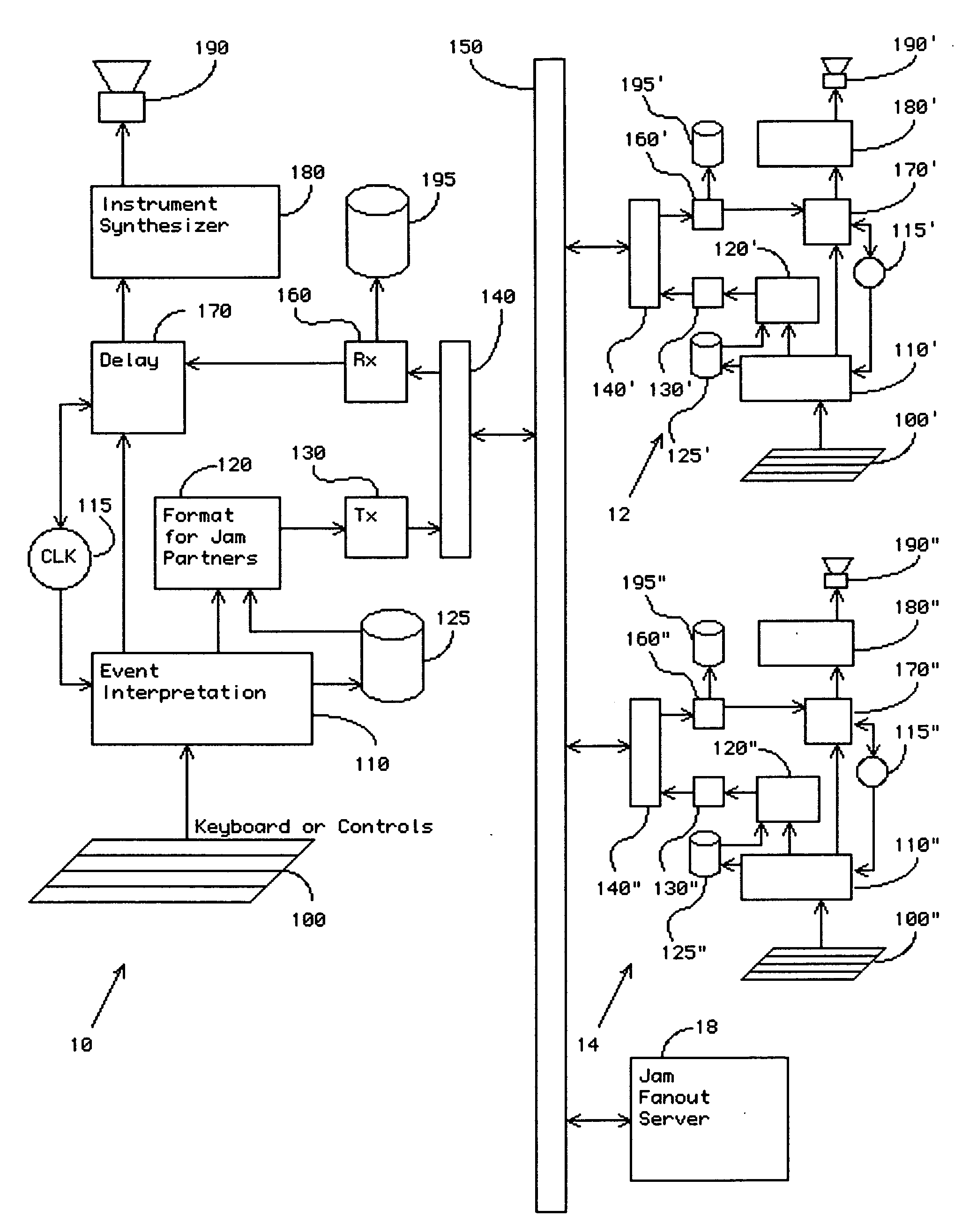
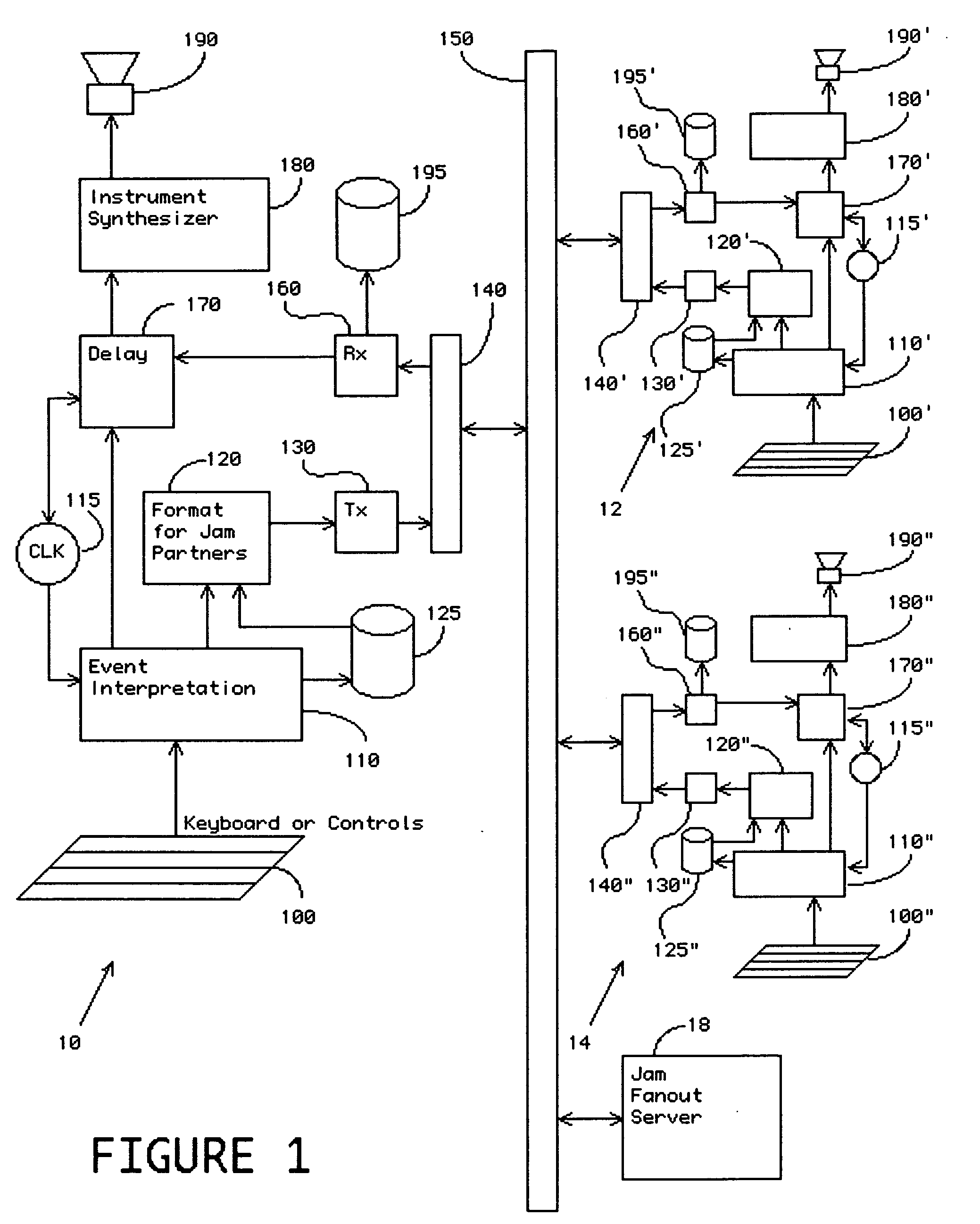
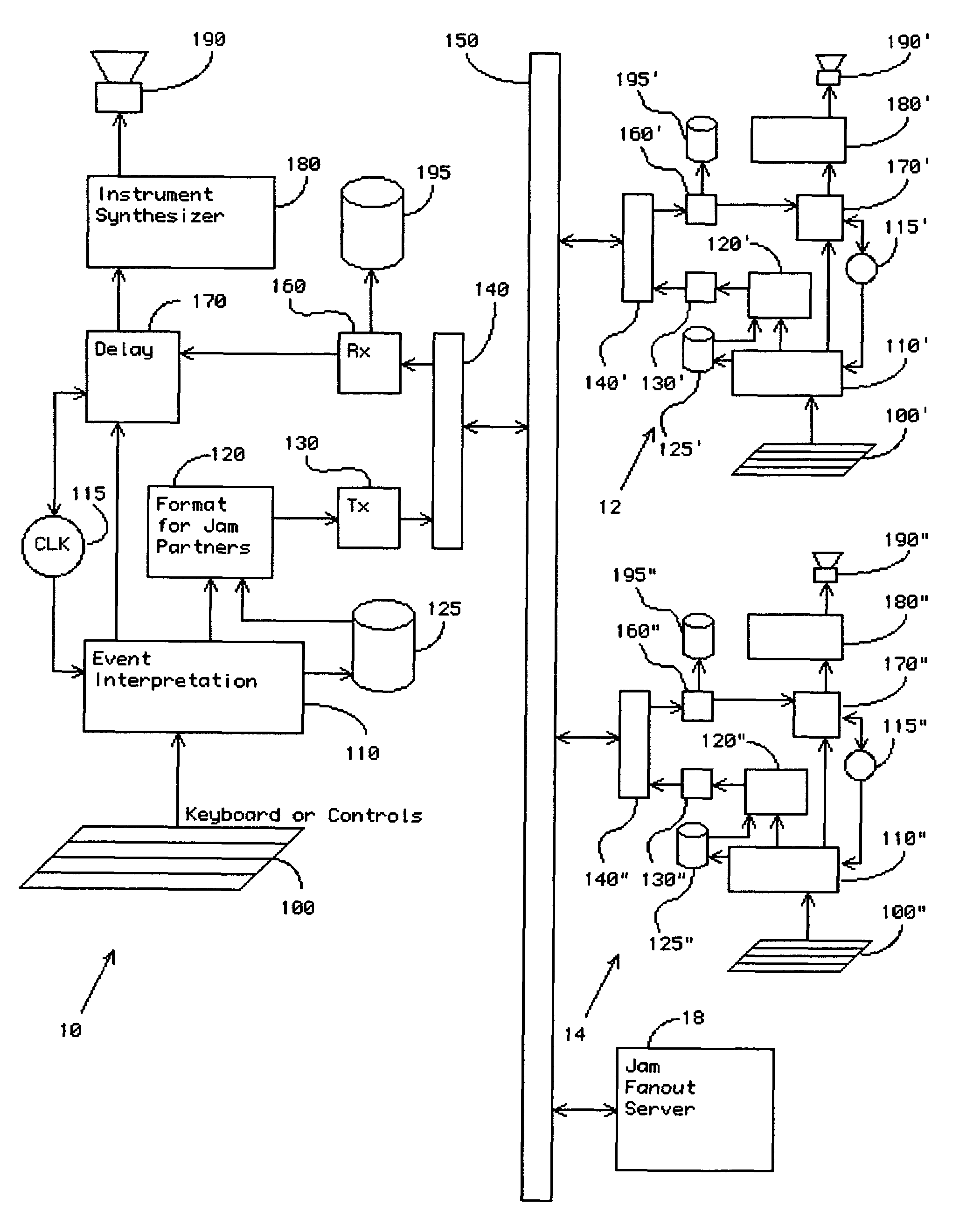
Method and apparatus for remote real time collaborative music performance and recording thereof
InactiveUS20070039449A1Bandwidth limitRemarkable effectGearworksMusical toysLatency (engineering)Improved method
An improved method and apparatus are disclosed to permit real time, distributed performance by multiple musicians at remote locations, and for recording that collaboration. The latency of the communication channel is transferred to the behavior of the local instrument so that a natural accommodation is made by the musician. This allows musical events that actually occur simultaneously at remote locations to be played together at each location, though not necessarily simultaneously at all locations. This allows locations having low latency connections to retain some of their advantage. Artifacts resulting from an unreliable communication channel, for instance dropouts and jitter, are eliminated in the recorded performance. Limitations of communications bandwidth are managed in real time, with full fidelity restored in the recording.
Owner:EJAMMING
System and Method for Conducting a Fantasy Sports Competition
InactiveUS20080287198A1Increase valueAdverse effectApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesInformation sharingEngineering
The present invention embodiments pertain to conducting fantasy sports or other competitions, where users select or draft an entirely new team of professional players each week (or at other suitable time interval). The competition types (including playoffs) include fee based and free. Each fee based competition has a pre-determined entry fee, and prizes are awarded to the winner of that competition each week. The free competitions similarly include weekly prizes and further provide for a grand prize. Within each of the free and fee based types of competitions, users may compete in a “private” competition or a randomly composed “open” competition. Users within the free and fee based competitions may accumulate points that qualify for redemption to obtain prizes. These points are accumulated based upon the statistical performance of the drafted players for each team. The present invention embodiments further provide mechanisms for information sharing and interaction between users.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method and apparatus for remote real time collaborative music performance and recording thereof
InactiveUS7518051B2Promote collaborationConvenient recordingGearworksMusical toysLatency (engineering)Real time management
An improved method and apparatus are disclosed to permit real time, distributed performance by multiple musicians at remote locations, and for recording that collaboration. The latency of the communication channel is transferred to the behavior of the local instrument so that a natural accommodation is made by the musician. This allows musical events that actually occur simultaneously at remote locations to be played together at each location, though not necessarily simultaneously at all locations. This allows locations having low latency connections to retain some of their advantage. Artifacts resulting from an unreliable communication channel, for instance dropouts and jitter, are eliminated in the recorded performance. Limitations of communications bandwidth are managed in real time, with full fidelity restored in the recording.
Owner:EJAMMING
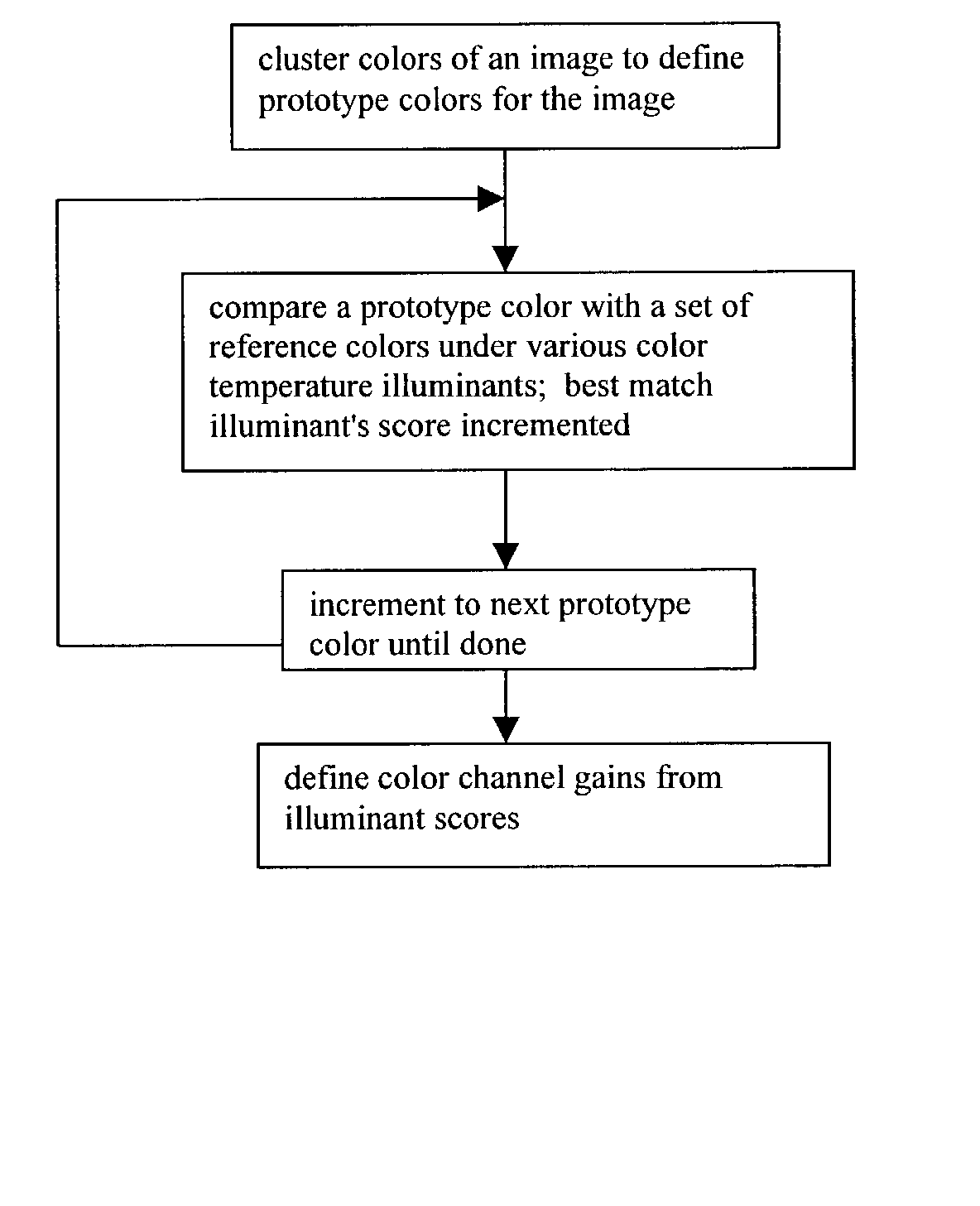
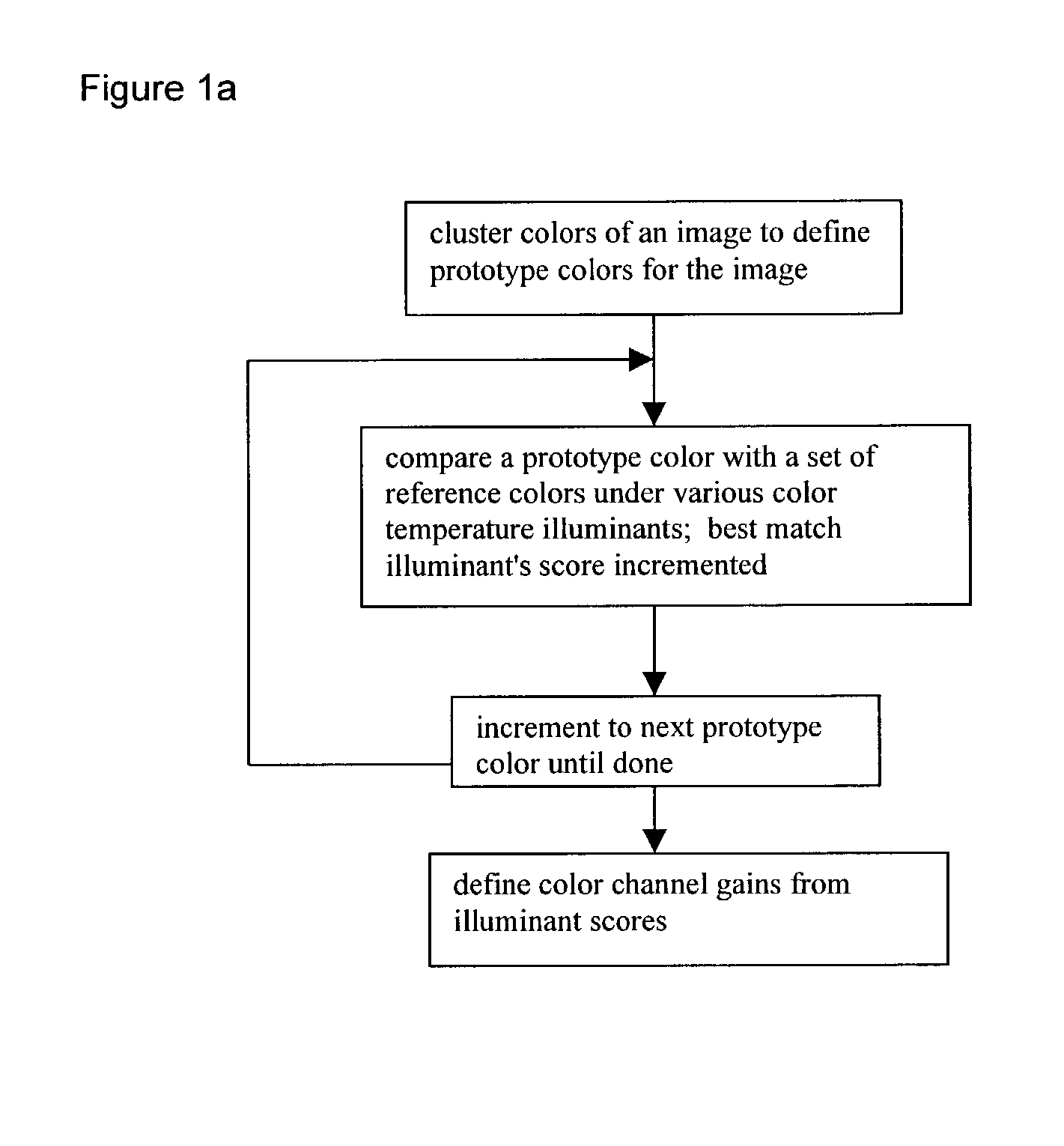
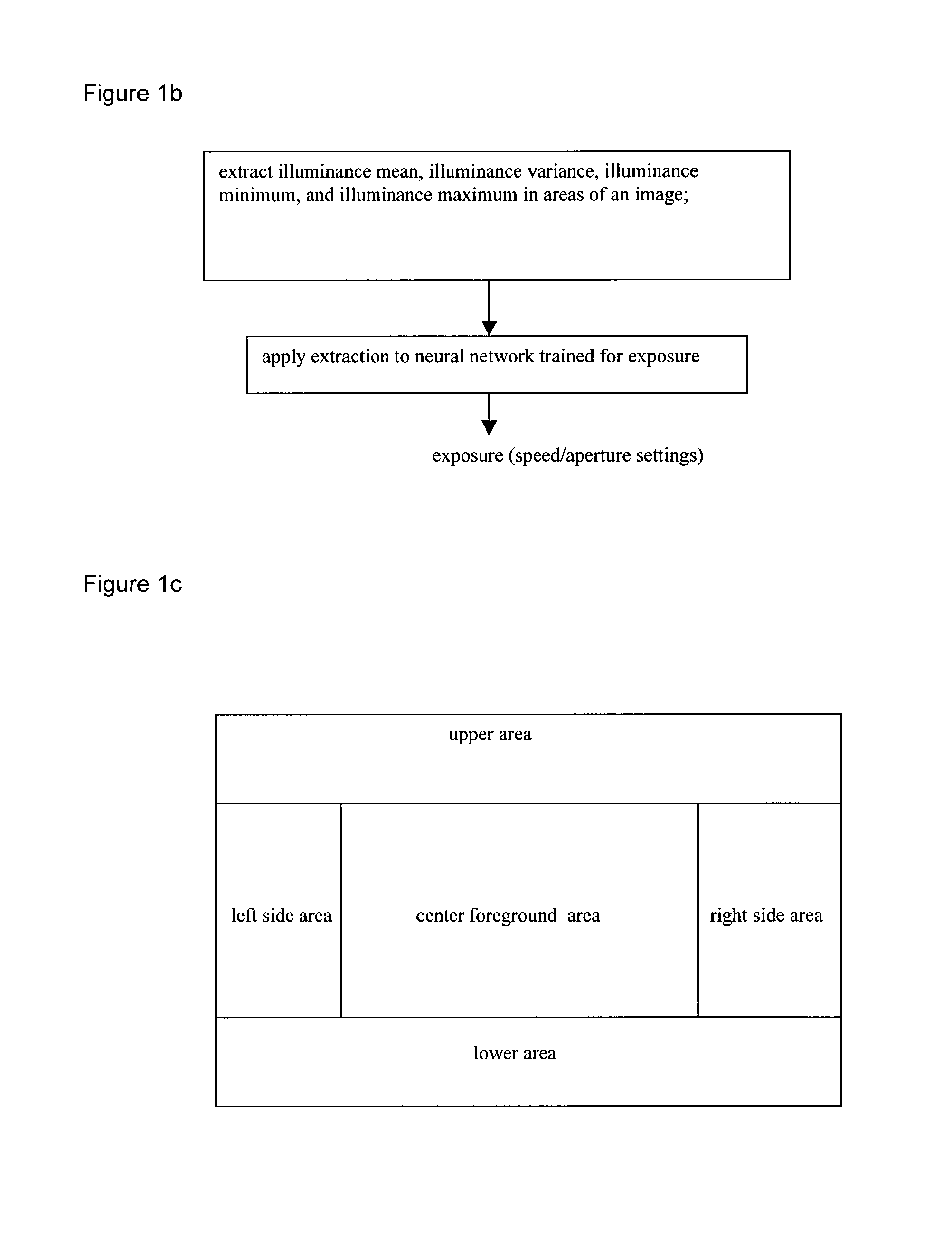
Automatic white balancing via illuminant scoring autoexposure by neural network mapping
ActiveUS20030052978A1Easy to useHigh scoreTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsIlluminanceComputer science
Automatic white balancing and / or autoexposure as useful in a digital camera extracts color channel gains from comparisons of image colors with reference colors under various color temperature illuminants and / or extracts exposure settings from illuminance mean, illuminance variance, illuminance minimum, and illuminance maximum in areas of an image with a trained neural network.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
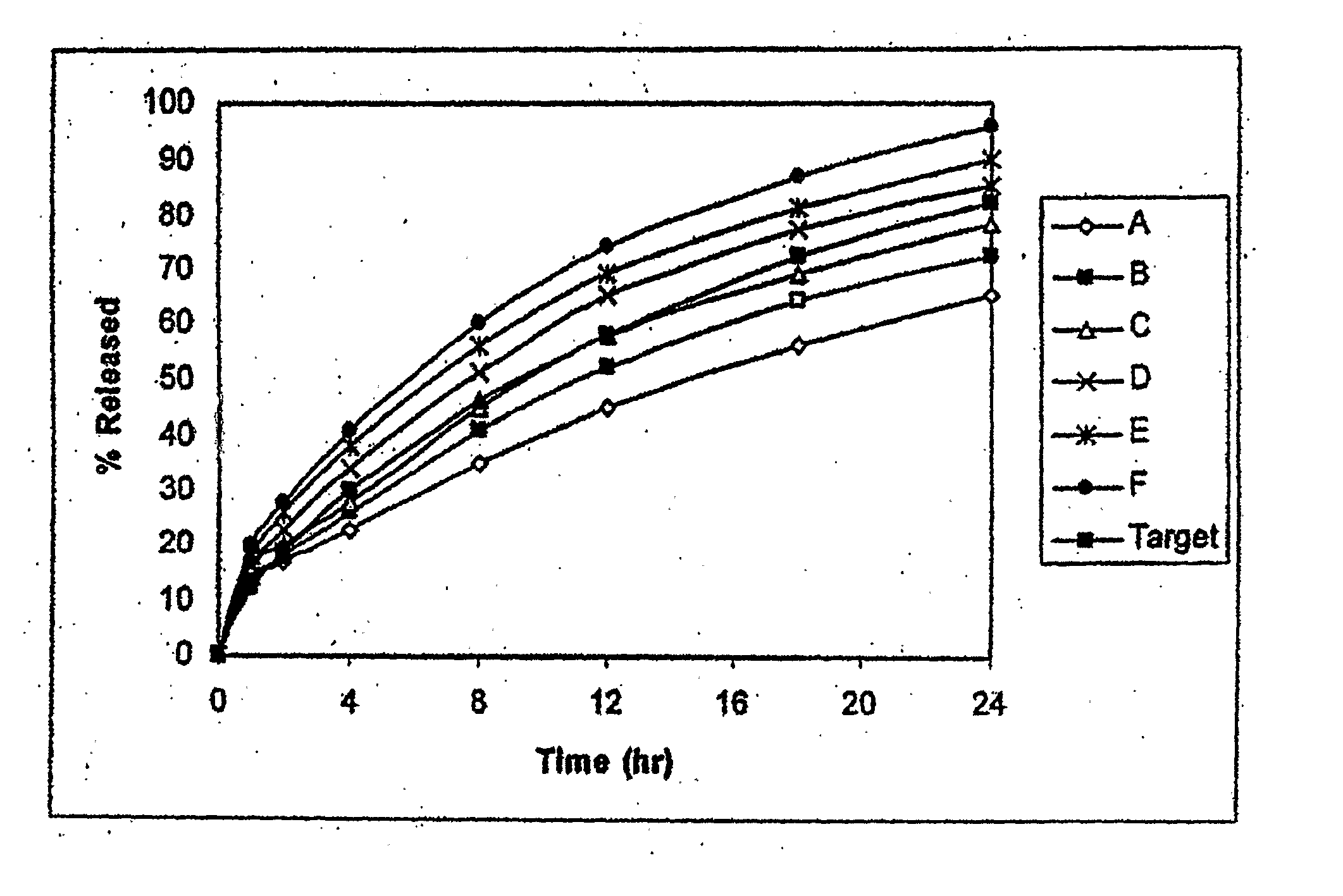
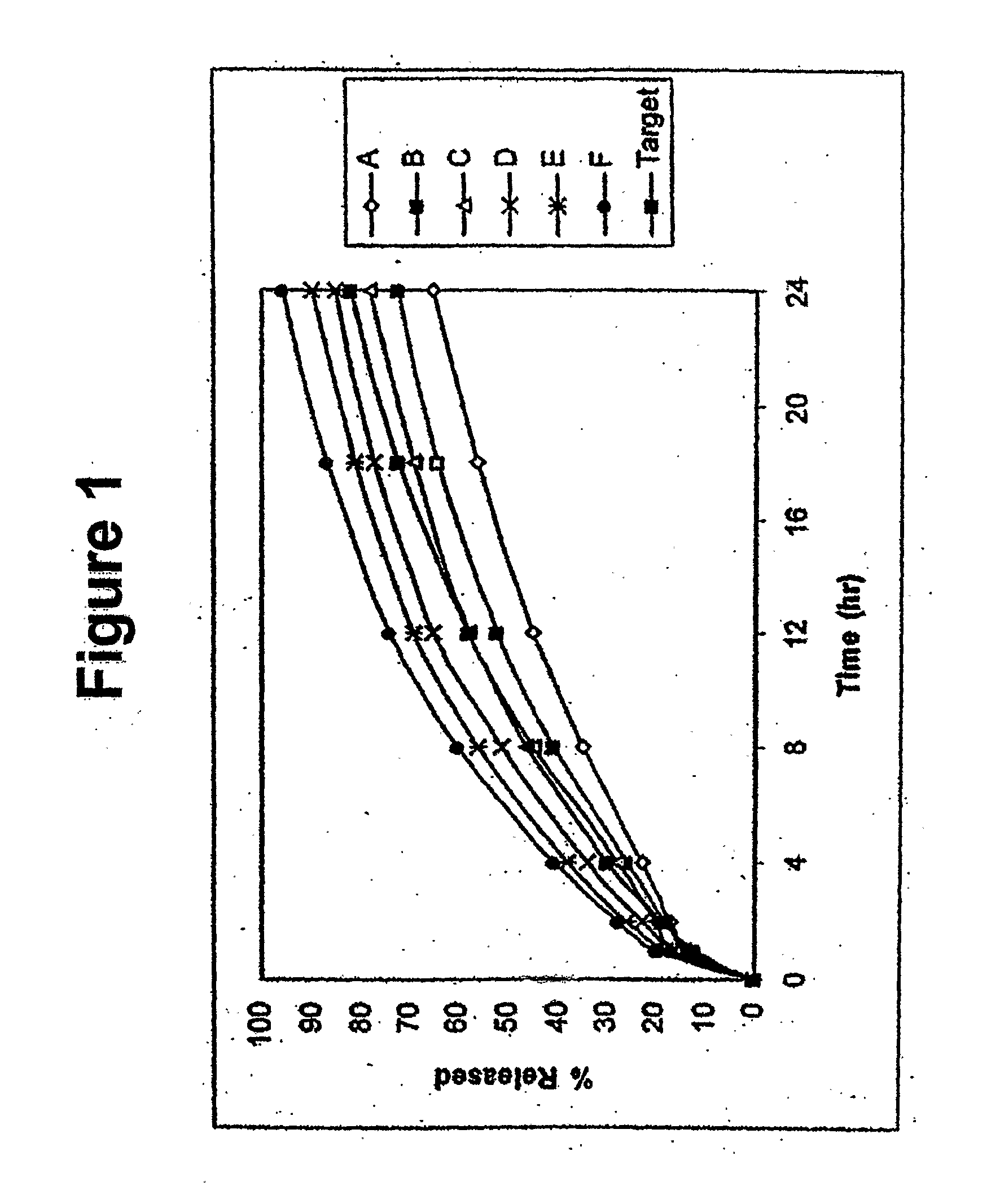
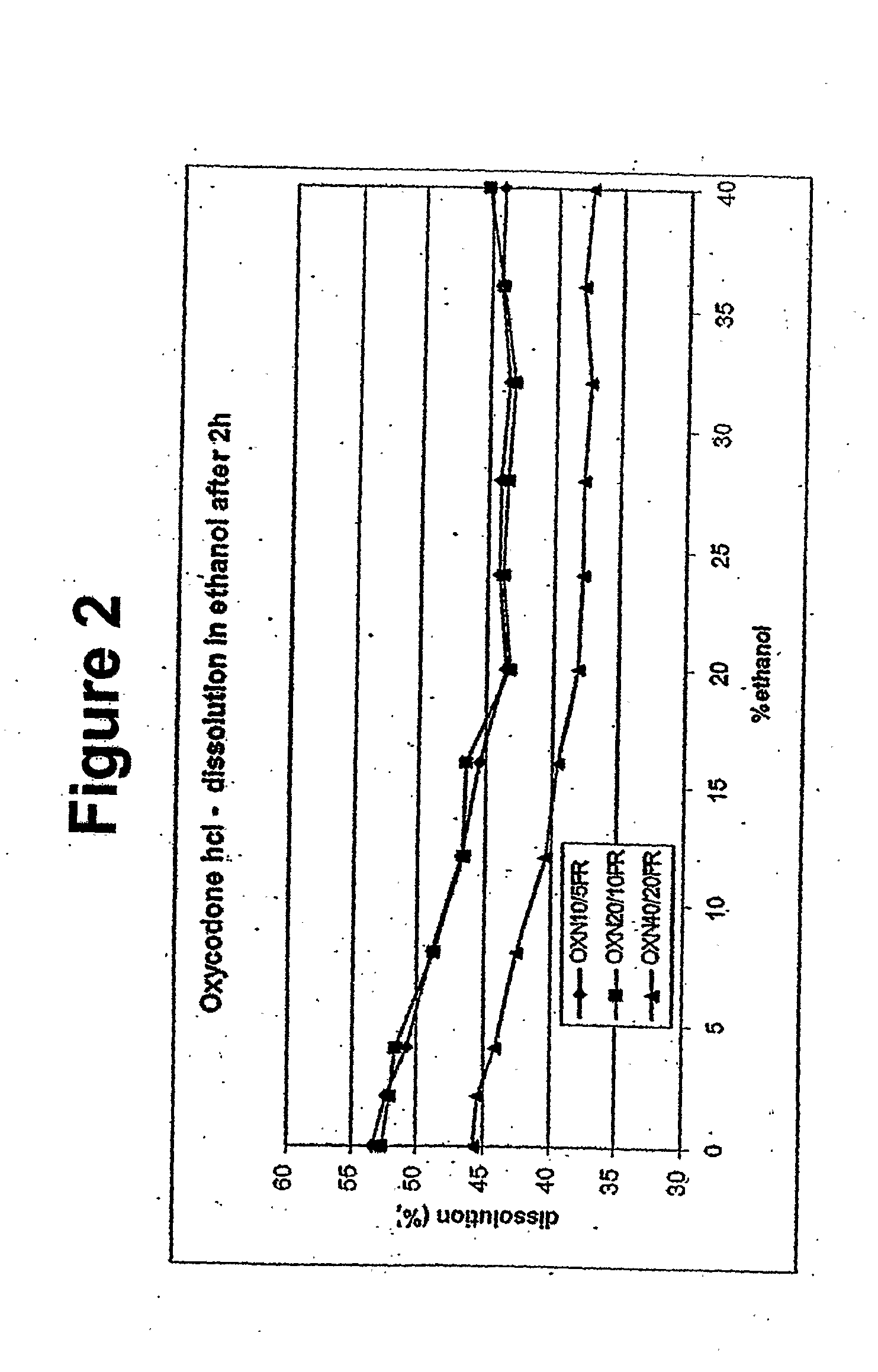
Alcohol Resistant Dosage Forms
Disclosed in certain embodiments is a controlled release dosage form comprising a matrix comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of an opioid analgesic in a controlled release material; wherein less than 25% of the opioid salt is released after 1 hour of in-vitro dissolution of the dosage form in 900 ml of Simulated Gastric Fluid with 20% ethanol using a USP Apparatus I (basket) apparatus at 100 rpm at 37 degrees C.°.
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
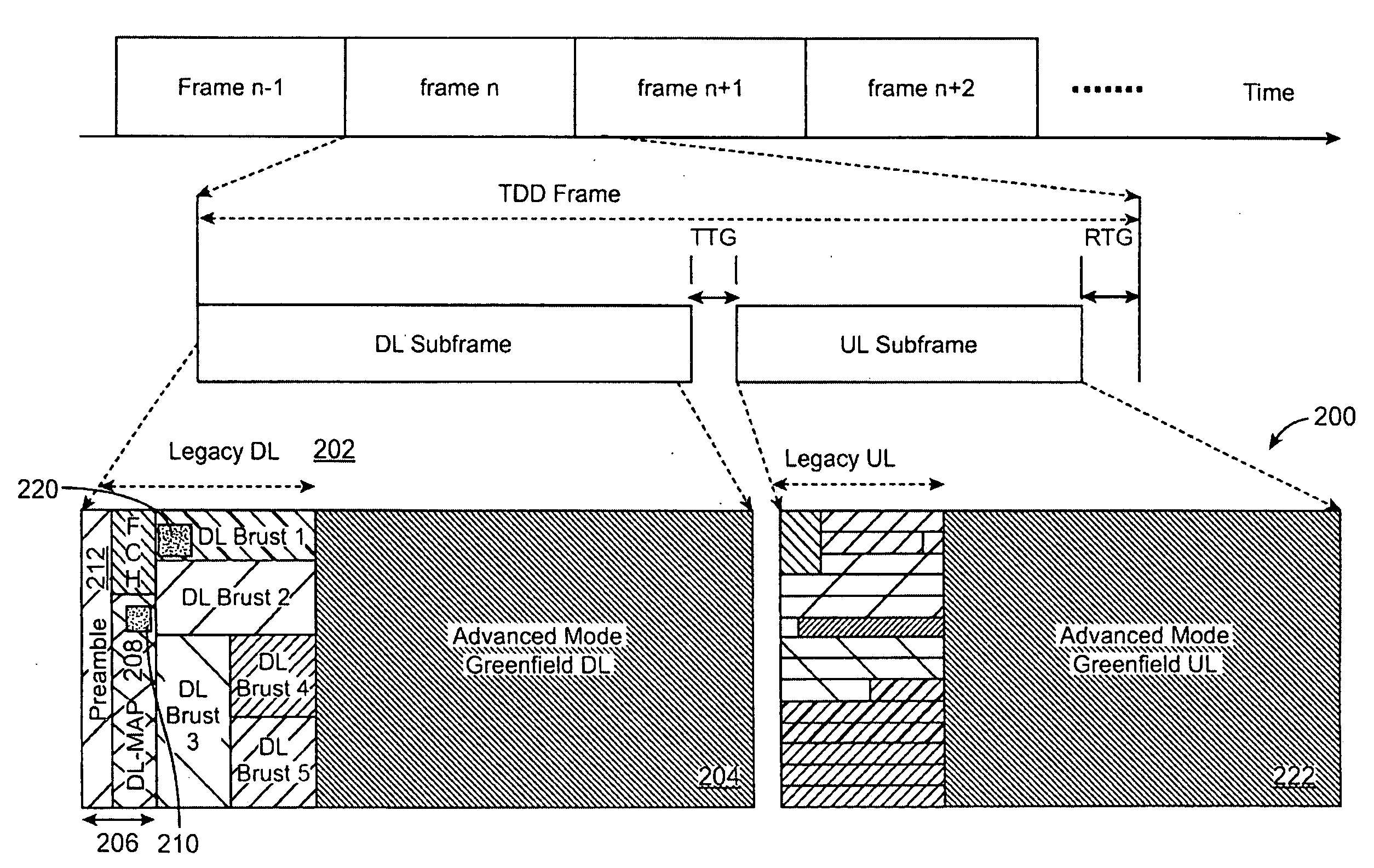
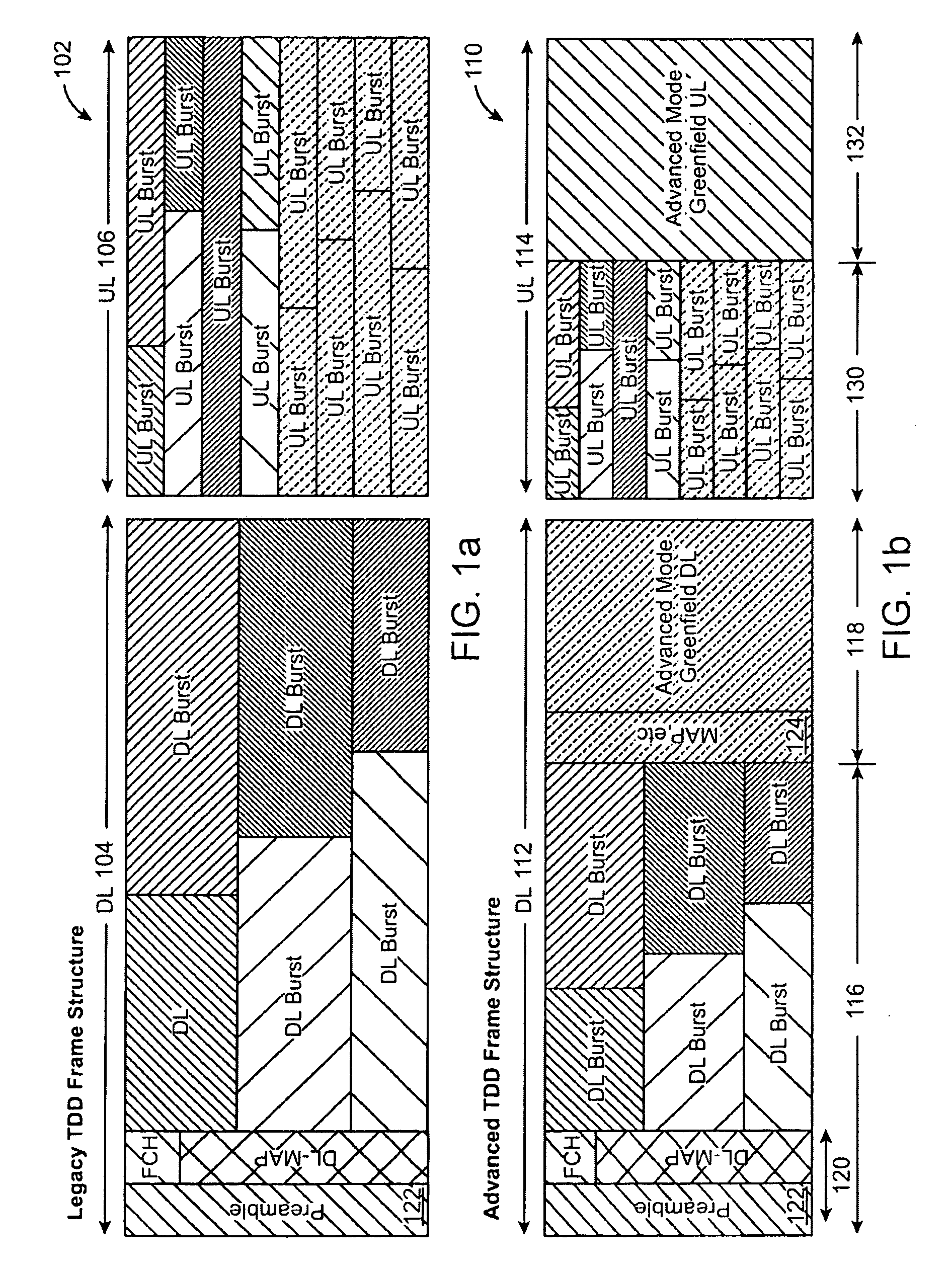
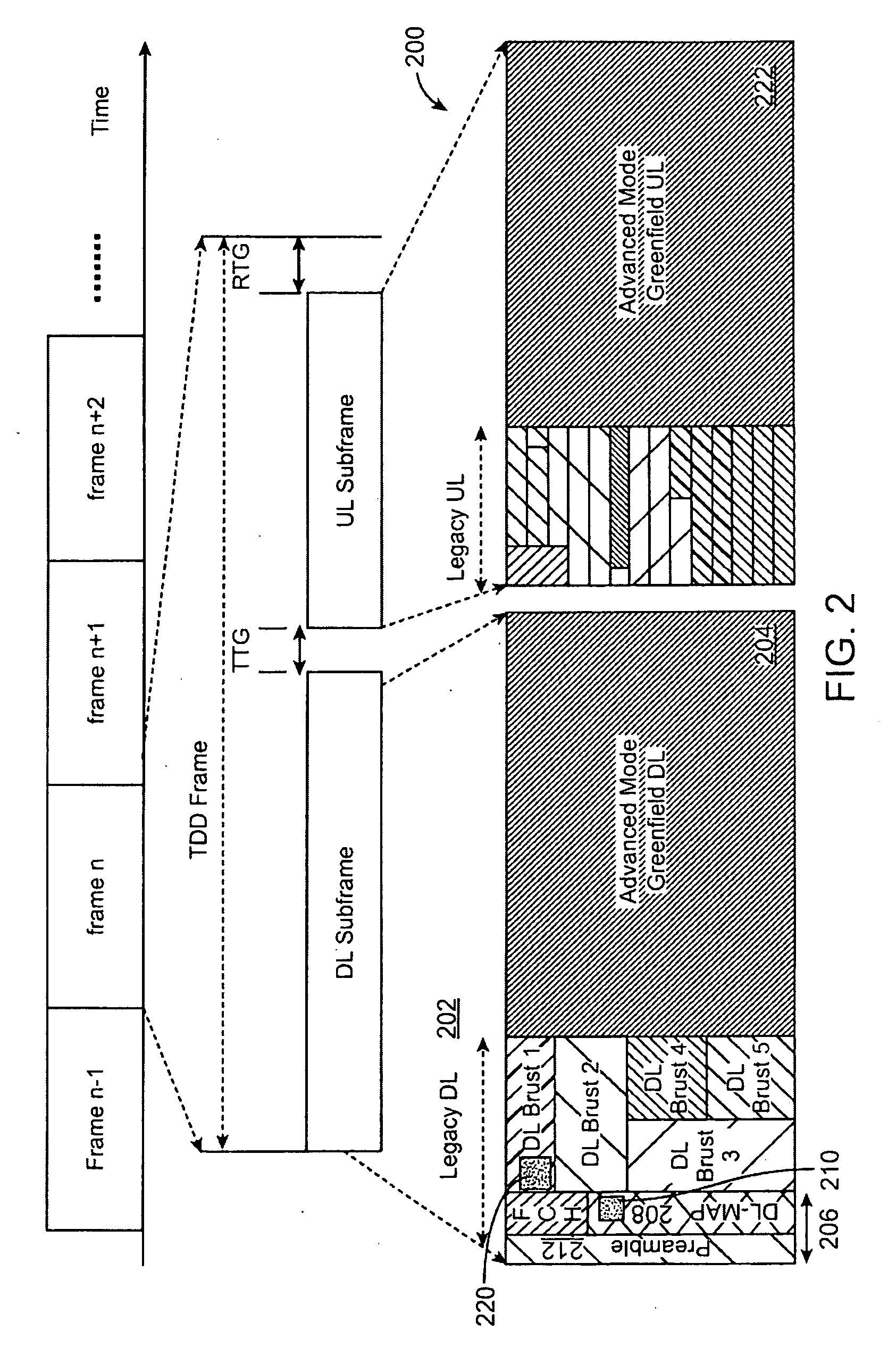
Advanced technology frame structure with backward compatibility
InactiveUS20090116427A1Minimal effectTransmission path divisionTime-division multiplexCommunications systemBackward compatibility
An advanced technology frame structure is described herein. The advanced technology frame structure can enhance a first technology frame structure in dimensions of time, frequency, or a combination of time and frequency. A second technology frame structure time division multiplexes second technology subframes with the first technology downlink and uplink subframes. The first technology downlink subframe can be divided into a first technology downlink subframe and one or more second technology downlink subframes. Similarly, the first technology uplink subframe can be divided into a first uplink subframe and one or more second technology uplink subframes. These principles can be expanded upon and can be applied in many communication systems.
Owner:MONUMENT BANK OF INTPROP LLC
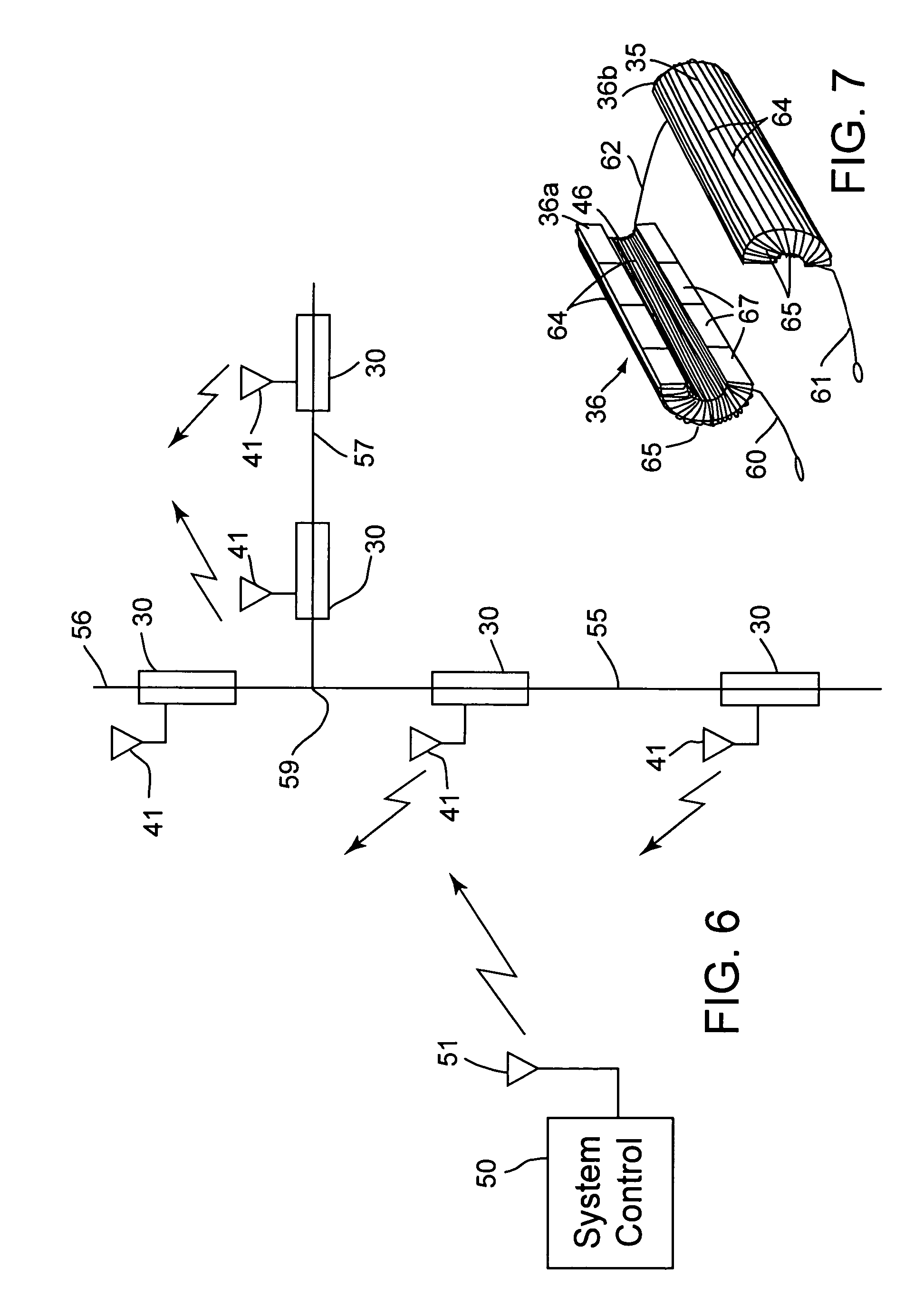
Distributed floating series active impedances for power transmission systems
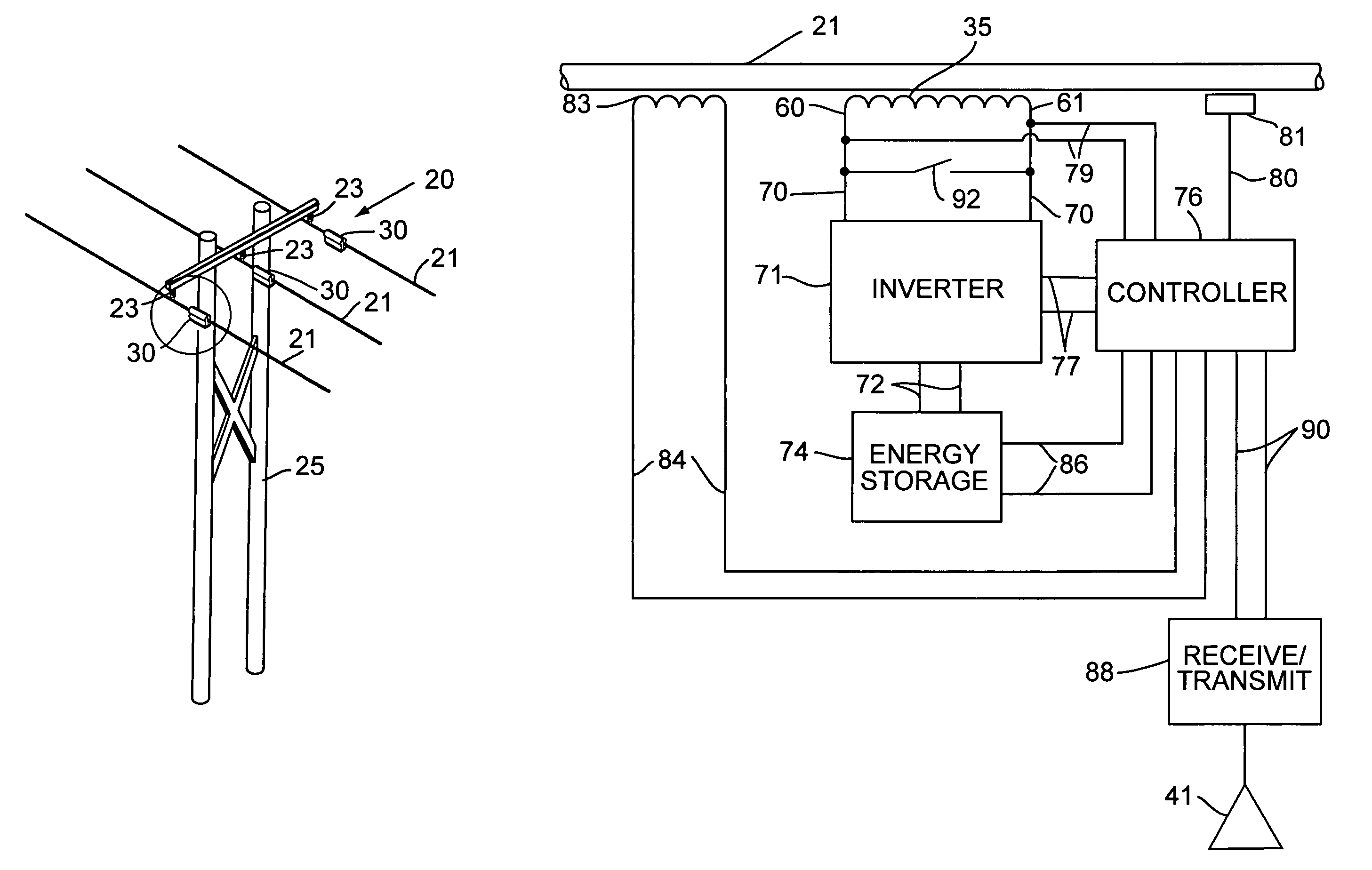
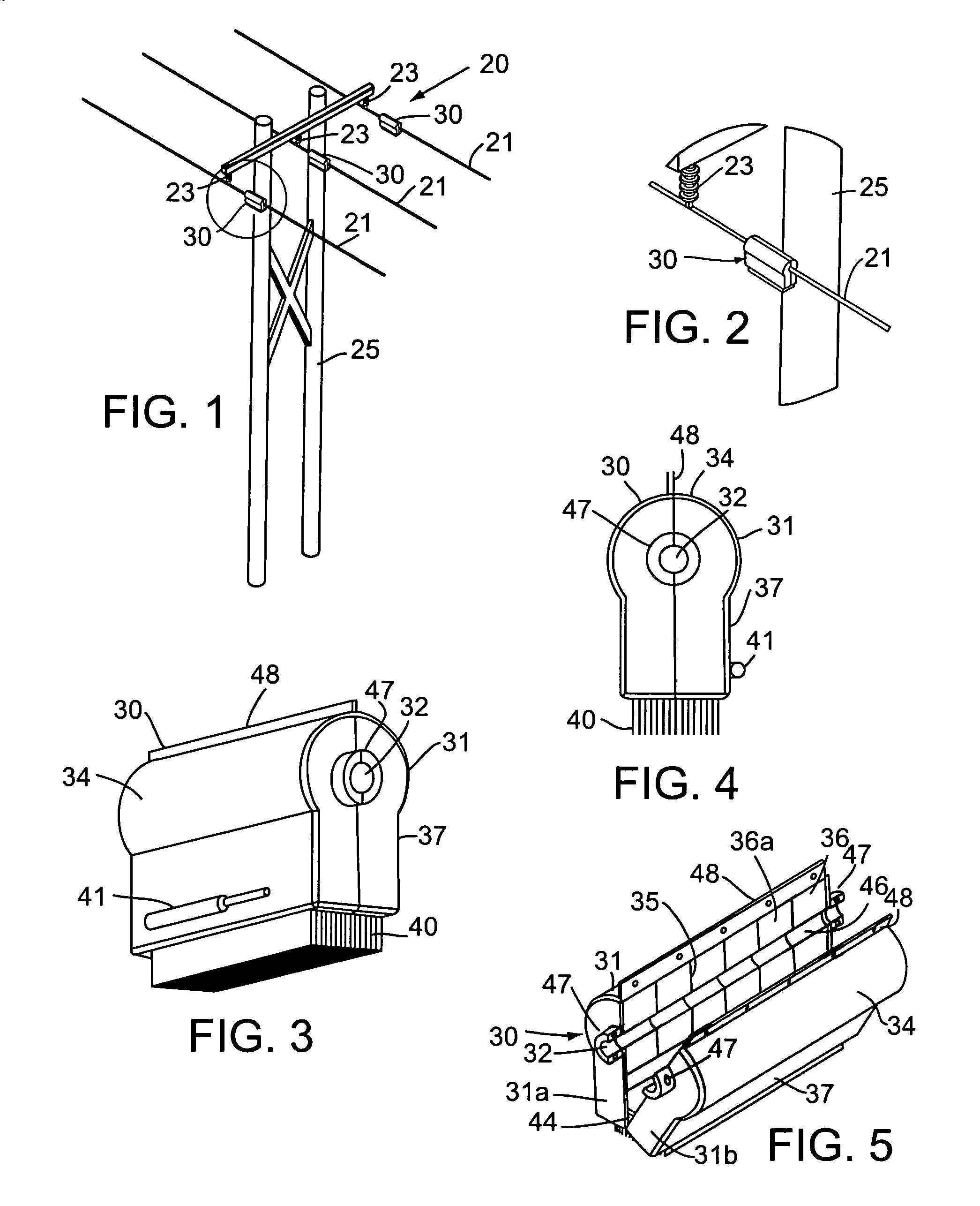
ActiveUS20050073200A1Reduce congestionGuaranteed normal transmissionFlexible AC transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionElectric power system
Floating electrically isolated active impedance modules are formed to attach to power transmission lines without breaking the lines such that the power line forms a secondary of the main transformer of the module. Each module includes an electrical energy storage device and a switching circuit, such as a single phase inverter, connected to the storage device and to the main transformer primary winding. The inverter can be controlled to couple a selected voltage to the transmission line through the main transformer primary winding which can provide effective positive impedance, negative impedance, or a voltage at or near phase quadrature with the line current. Many active impedance modules may be distributed over a power system grid to allow control of the impedance of the power lines in the grid and to steer power through the grid, with each module electrically isolated from ground and from other phase lines of the transmission system.
Owner:SOFT SWITCHING TECH
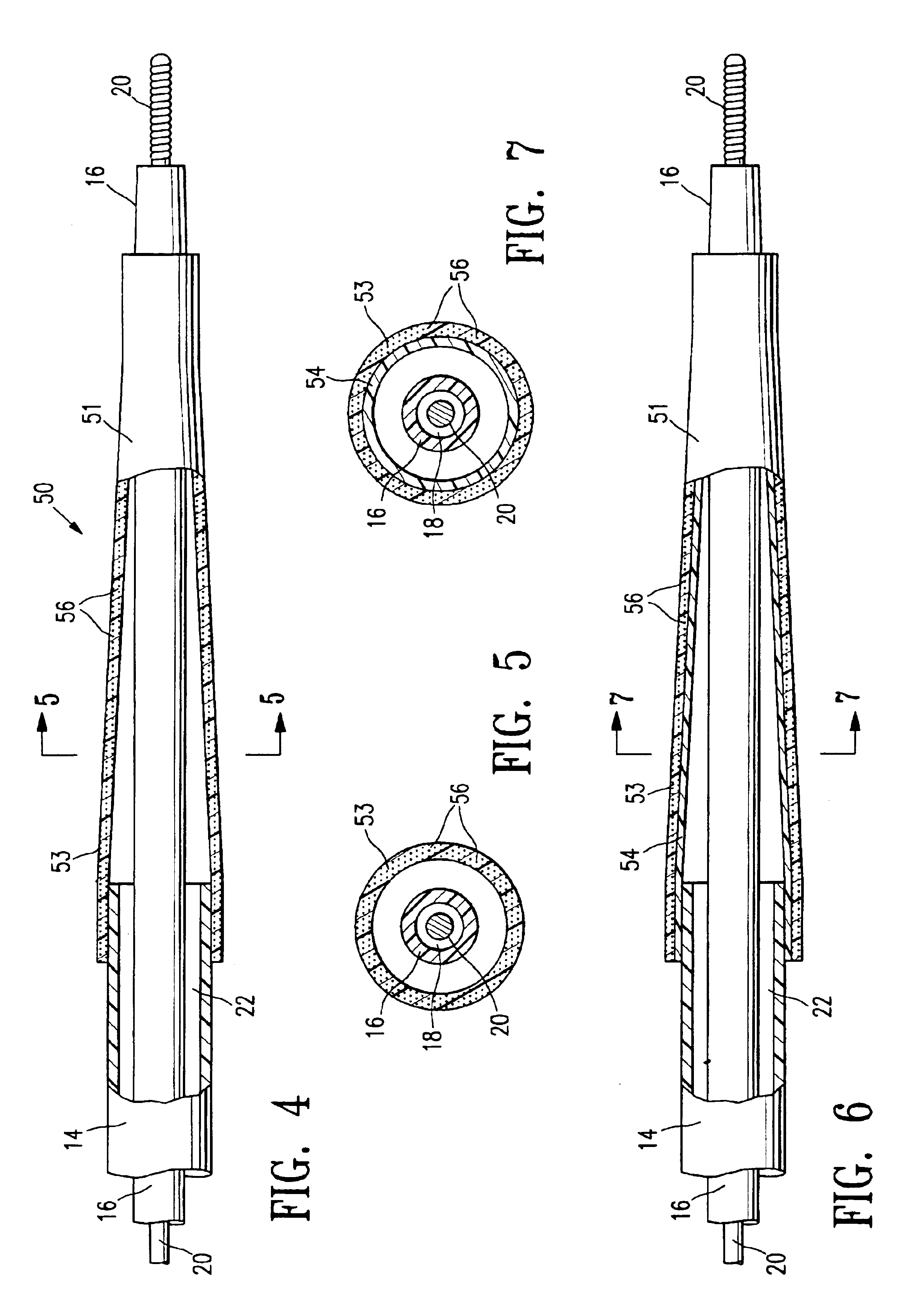
Catheter balloon formed of ePTFE and a diene polymer
InactiveUS6946173B2Improve performanceImprove adhesionEnvelopes/bags making machineryMouldsElastomerTetrafluoroethylene
A catheter balloon formed of a polymeric material such as expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) bonded to a second layer formed of a low tensile set polymer and / or impregnated with a low tensile set polymer. In a presently preferred embodiment, the low tensile set polymer is a silicone-polyurethane copolymer elastomer or a diene polymer elastomer. The low tensile set polymer has high strength, low modulus, high elongation, and low tensile set. The diene or silicone-polyurethane has a low tensile set, which facilitates deflation of the balloon to a low profile deflated configuration. One aspect of the invention provides improved attachment of the diene to the ePTFE. In one embodiment, the second layer is formed of a diene mixed with a bonding promoter such as a vulcanizing agent which is covalently bonded to the diene.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Apparatus and methods for monitoring and modifying anticoagulation therapy of remotely located patients
InactiveUS20050191716A1Maximizes therapeutic benefitRisk minimizationBiocideDrug and medicationsWarfarinRegimen
A patient apparatus is configured to receive and analyze information regarding patient compliance with anticoagulation medication and self-test coagulation regimens related to anticoagulation therapy. In addition, a patient apparatus is configured to receive data from a patient, including physiological data, pathophysiological data, biological data, psychological data, neuropsychological data, and / or behavioral data. Utilizing the received patient data, a patient apparatus can modify a warfarin regimen using an algorithm contained within the apparatus. The apparatus can communicate the modified warfarin regimen to the patient and to third parties, such as remotely located healthcare providers. In addition, the apparatus can prompt a patient when to perform a self-test and can prompt a patient to seek immediate medical attention, or to directly contact medical help, when so warranted.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CAPITAL AS AGENT
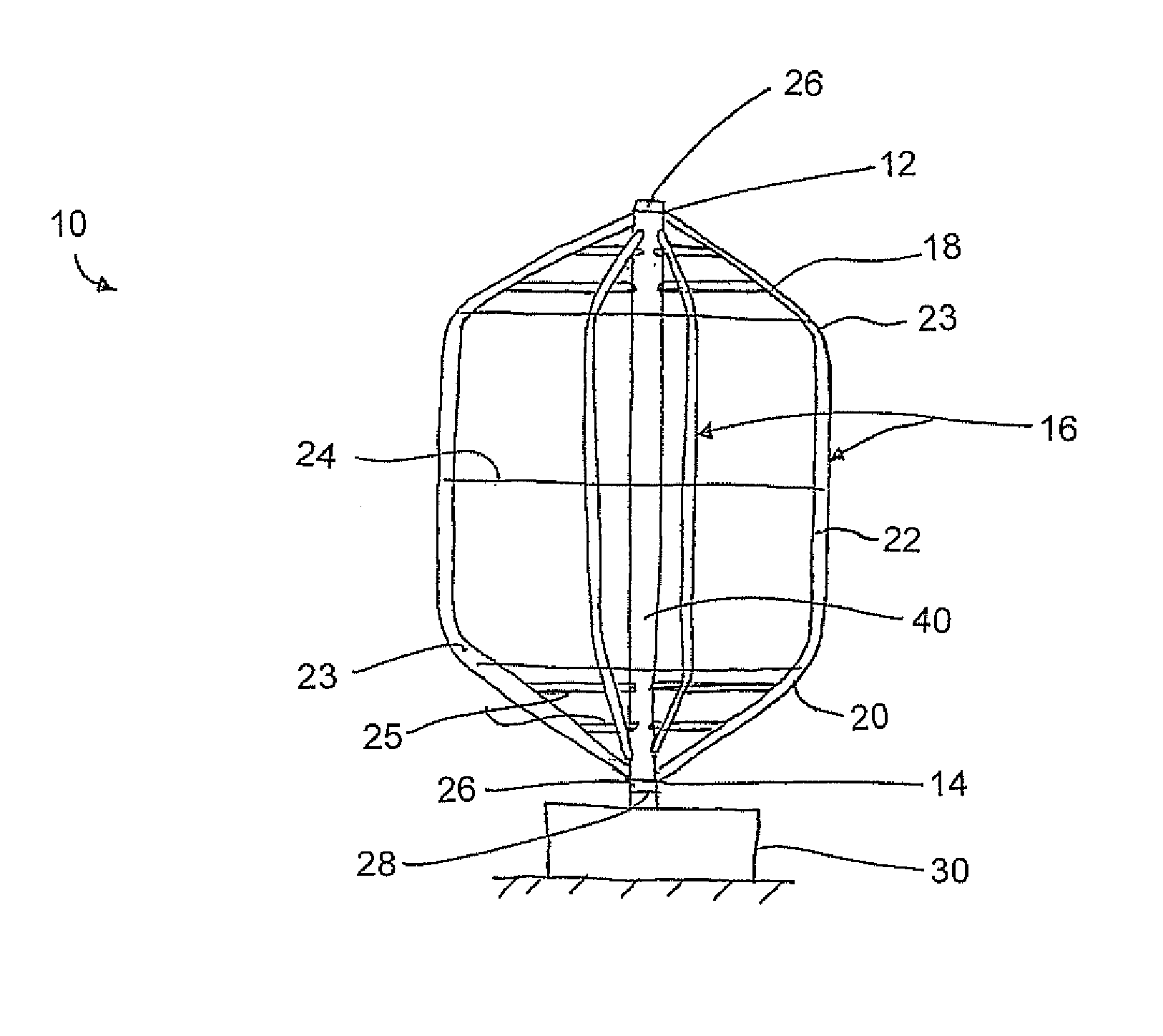
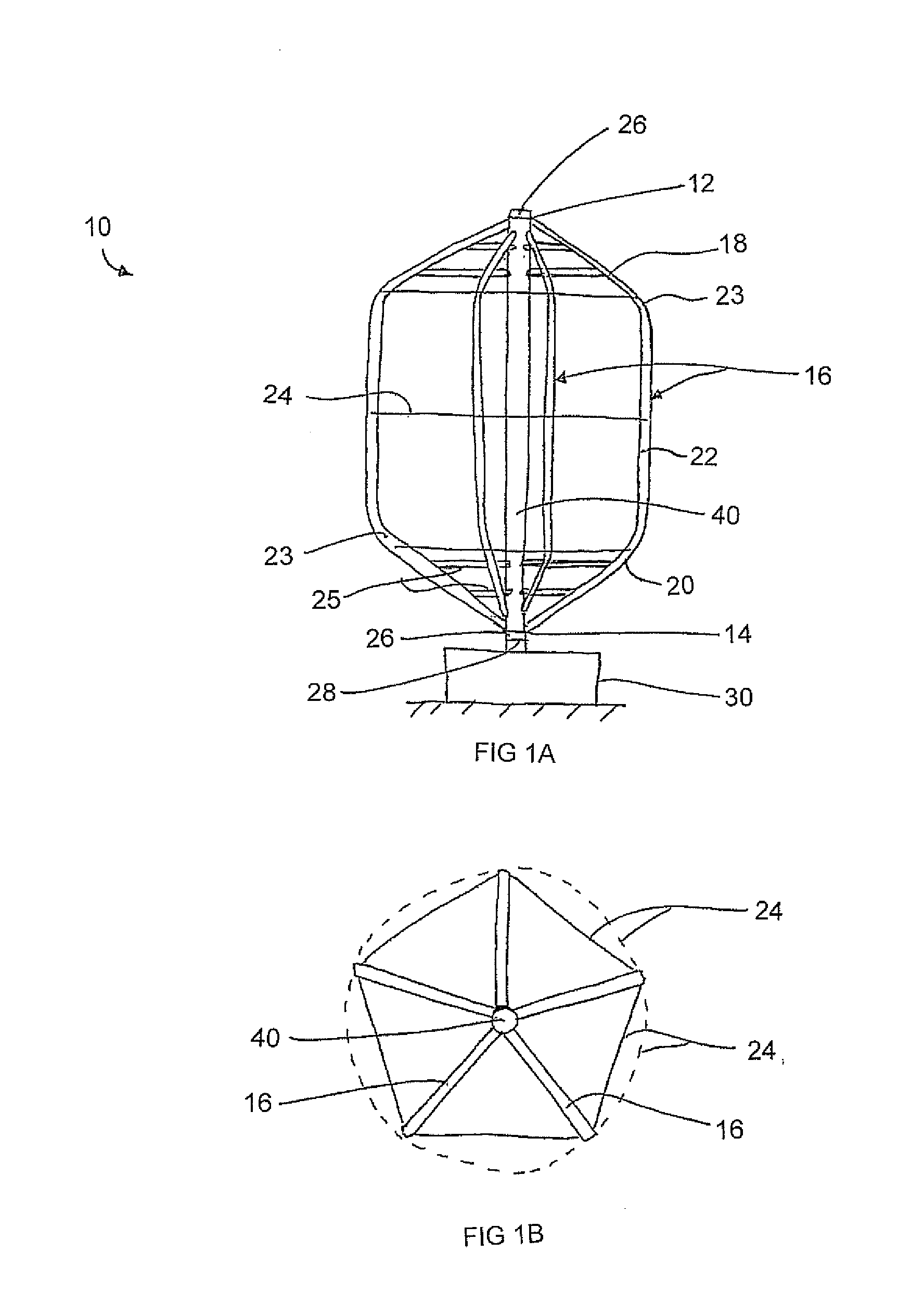
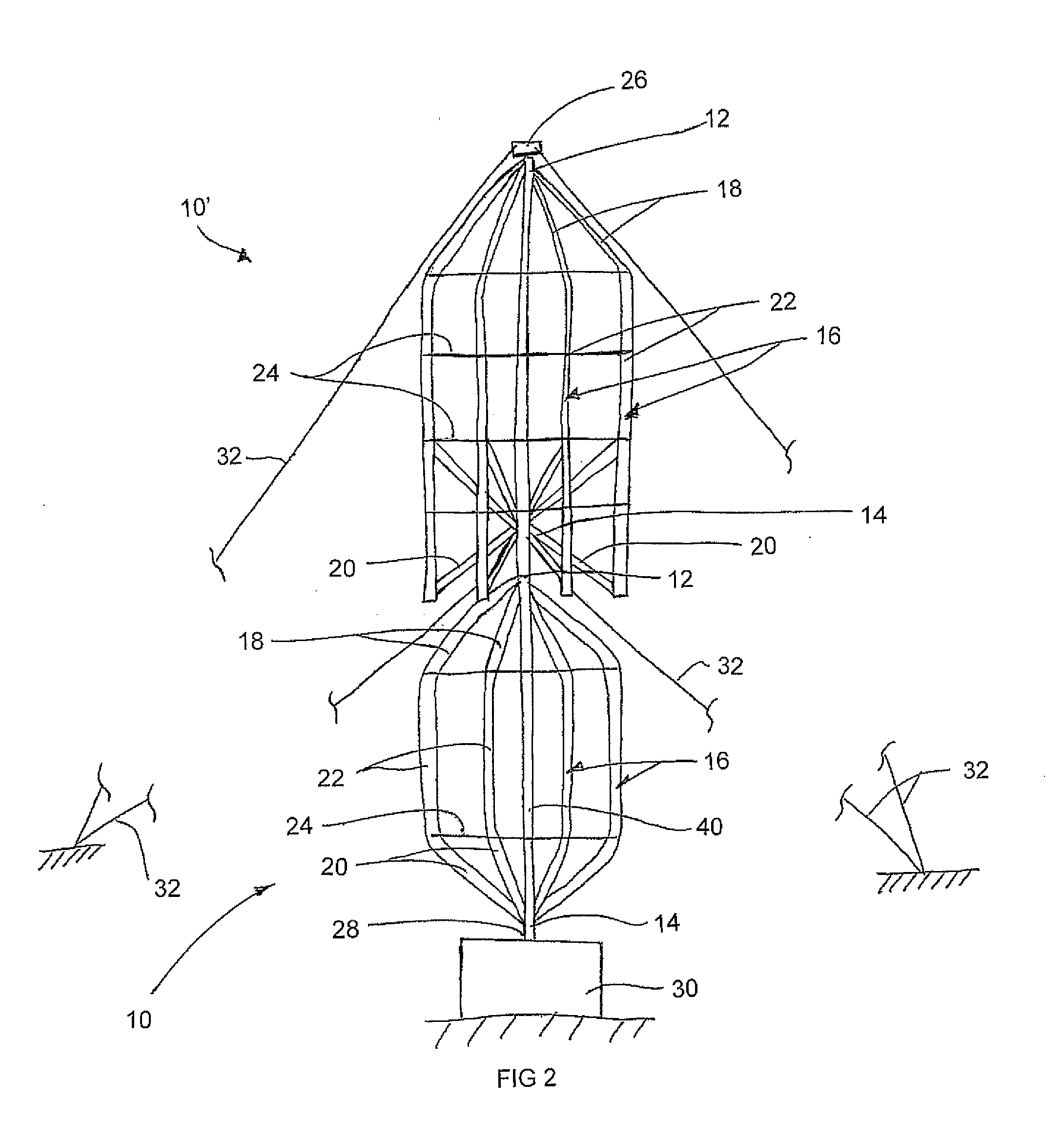
Modified Darrieus Vertical Axis Turbine
A lift-type turbine comprising at least three blades at circumferentially spaced positions is supported for rotation about a vertical axis. Each blade has an airfoil shape to generate a torque about the axis responsive to wind across the blades. A support comprising cables under tension is connected between adjacent ones of the blades to extend generally circumferentially about the turbine. Accordingly a minimum number of parts form the structure of the blades while minimizing the drag produced during rotation thereof due to the support members lying in a common circumferential path. The tension of the support members can support the blades in a pre-stressed condition to optimize the shape and performance thereof.
Owner:LUX
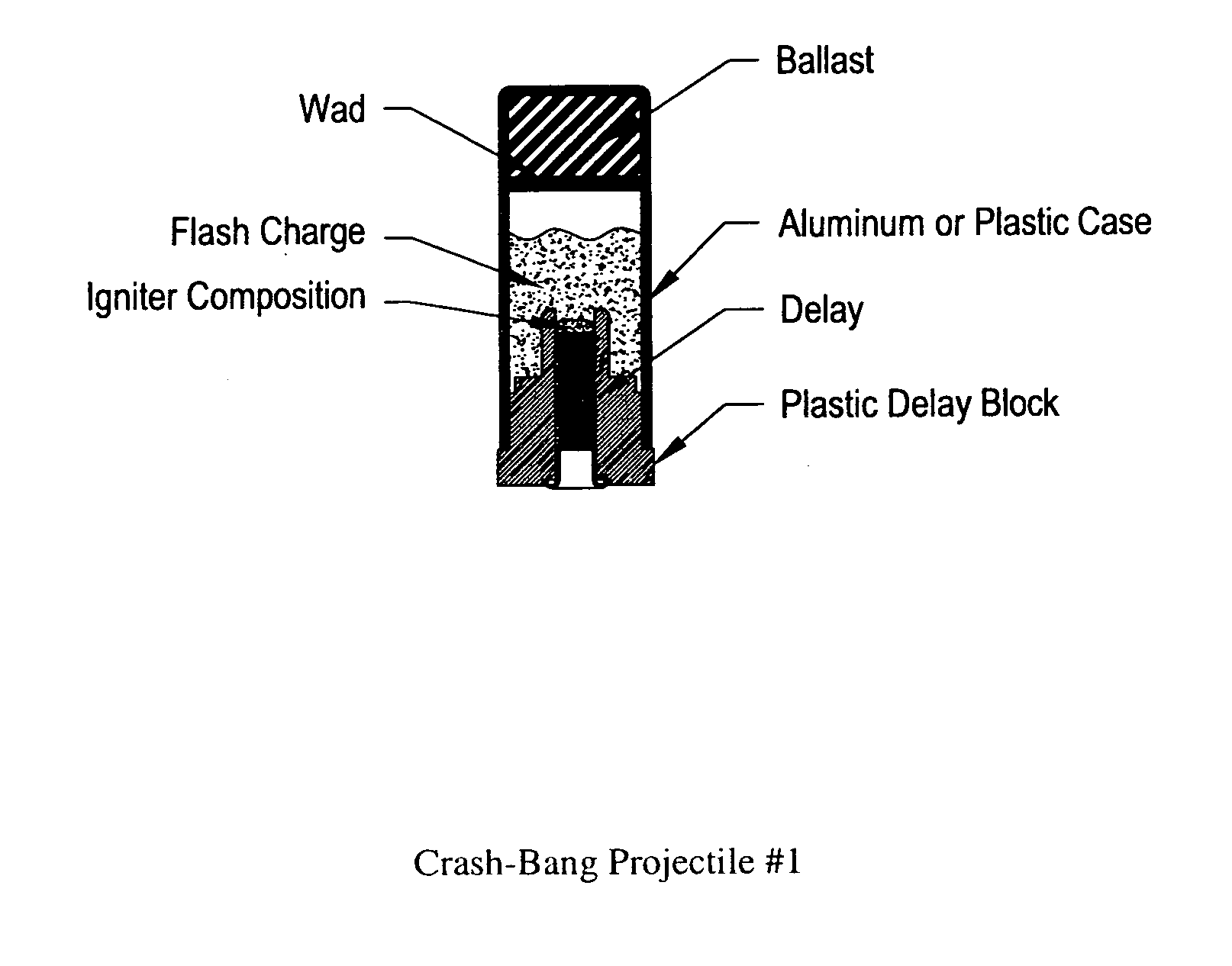
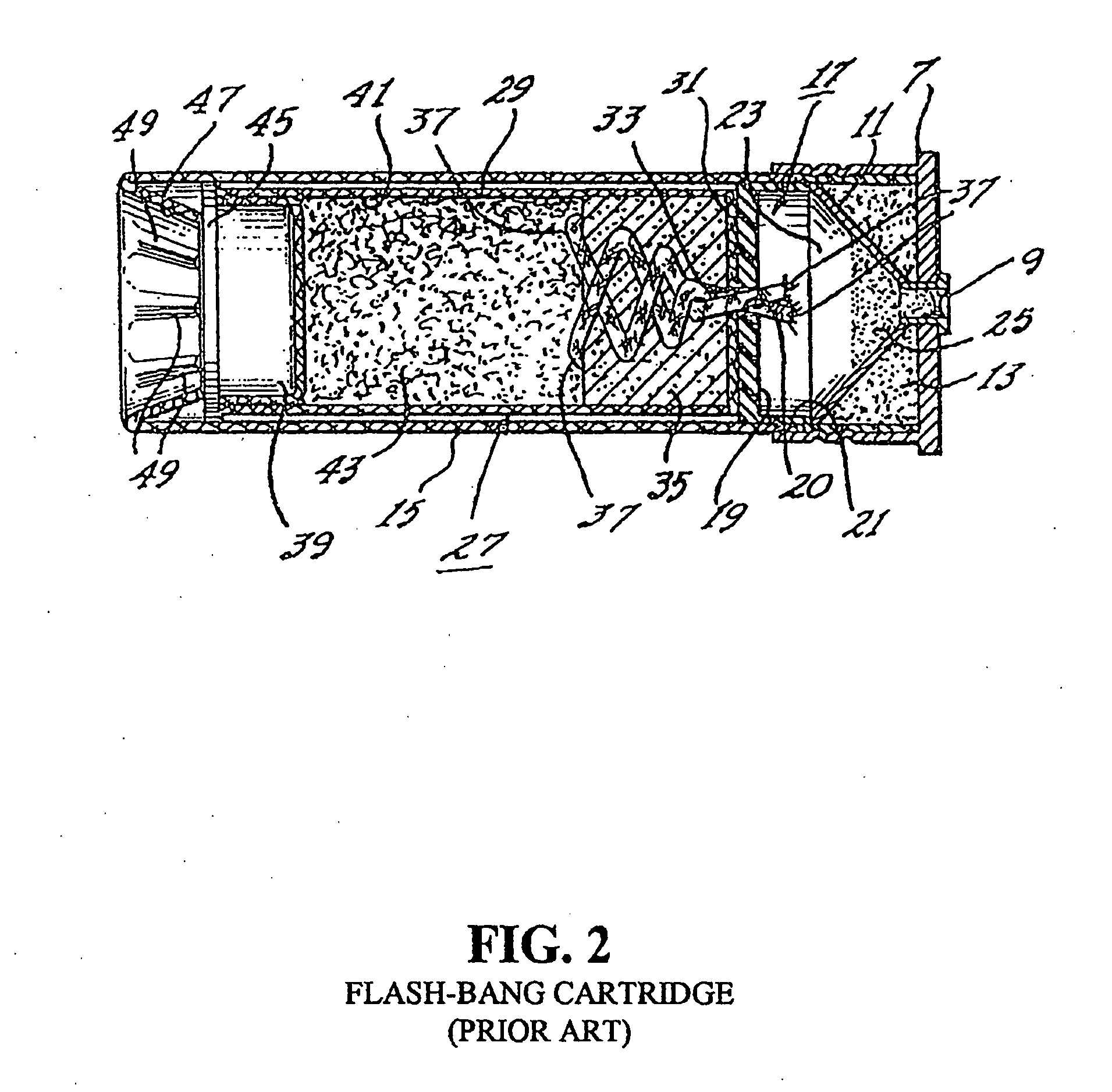
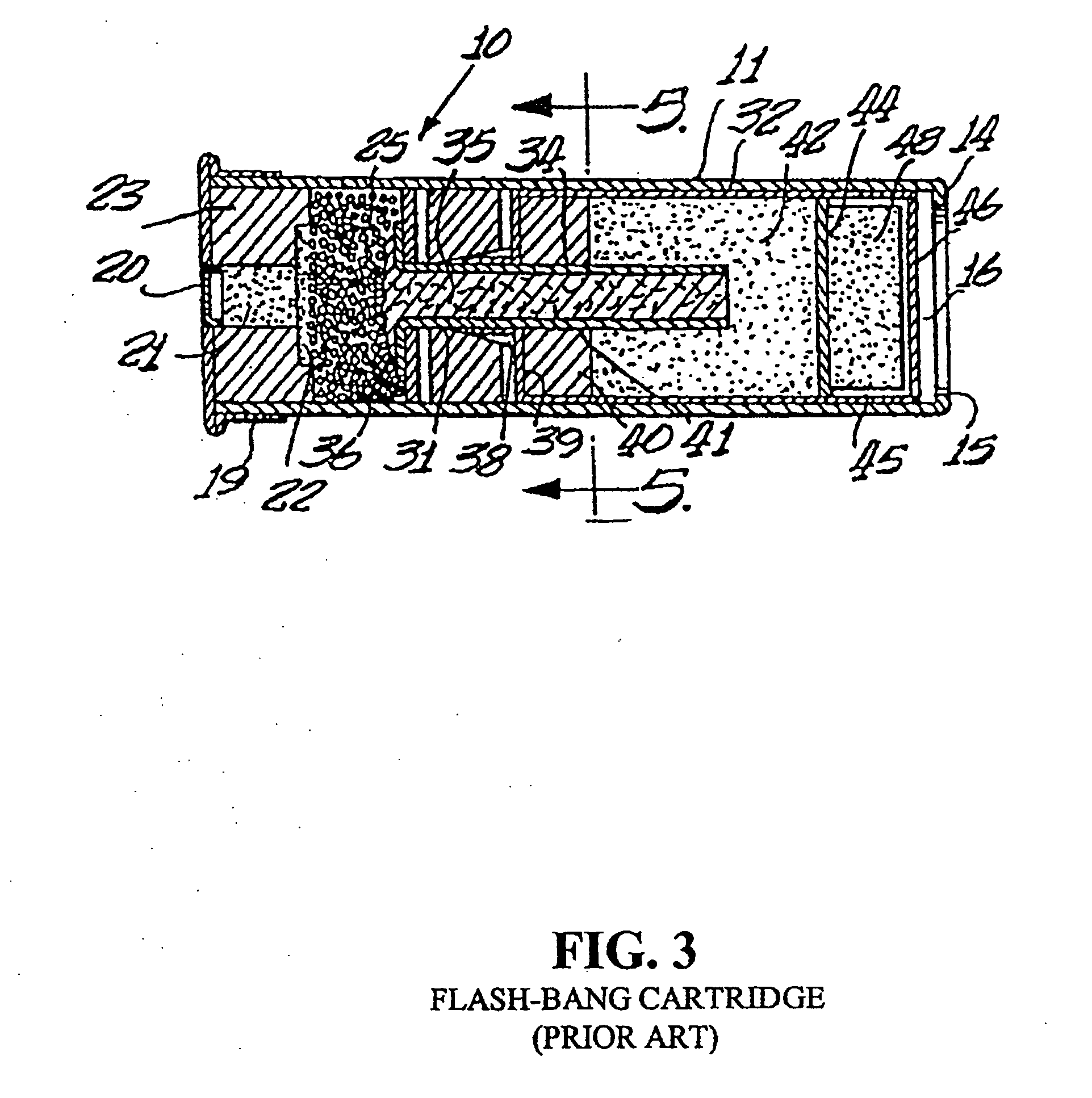
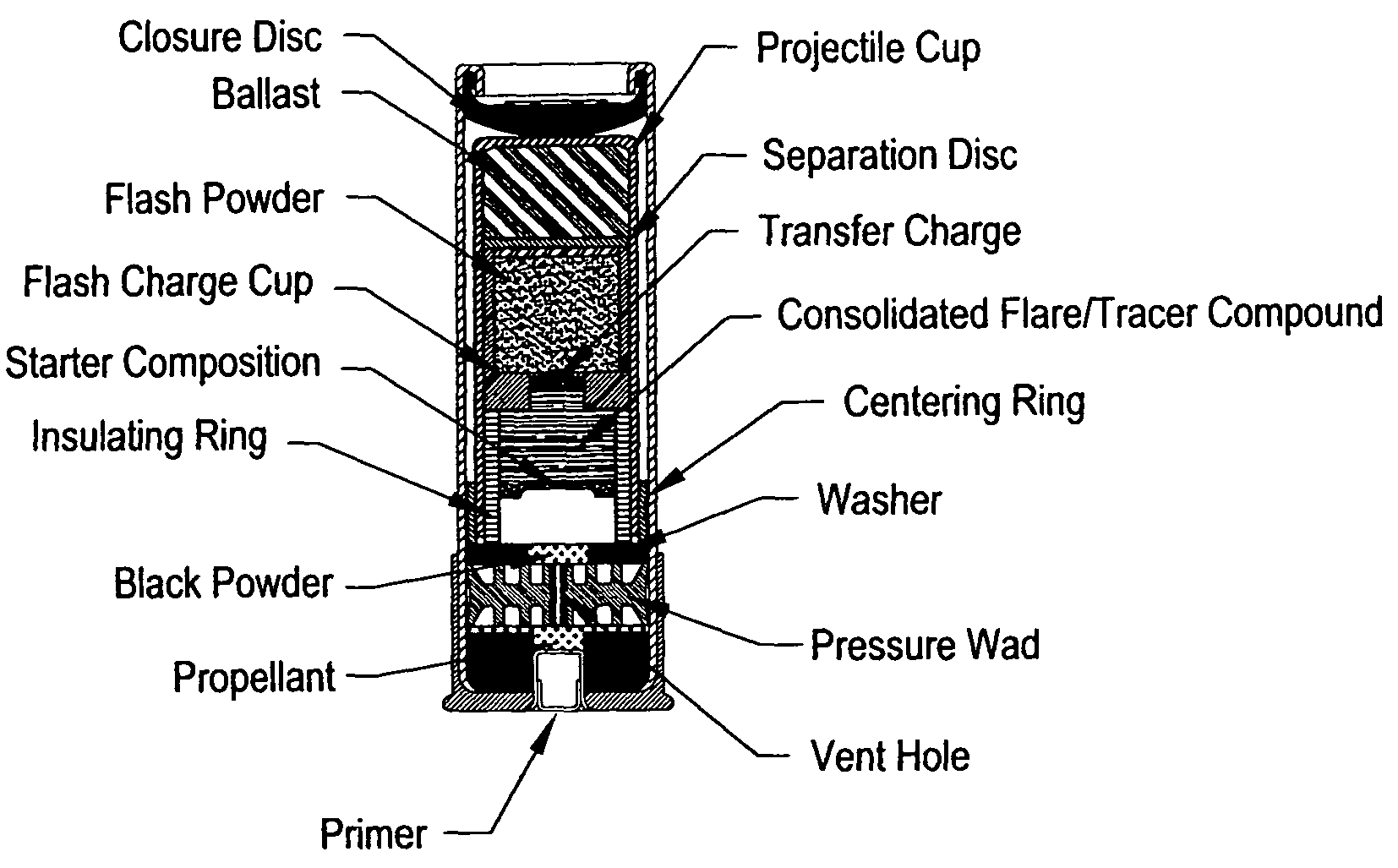
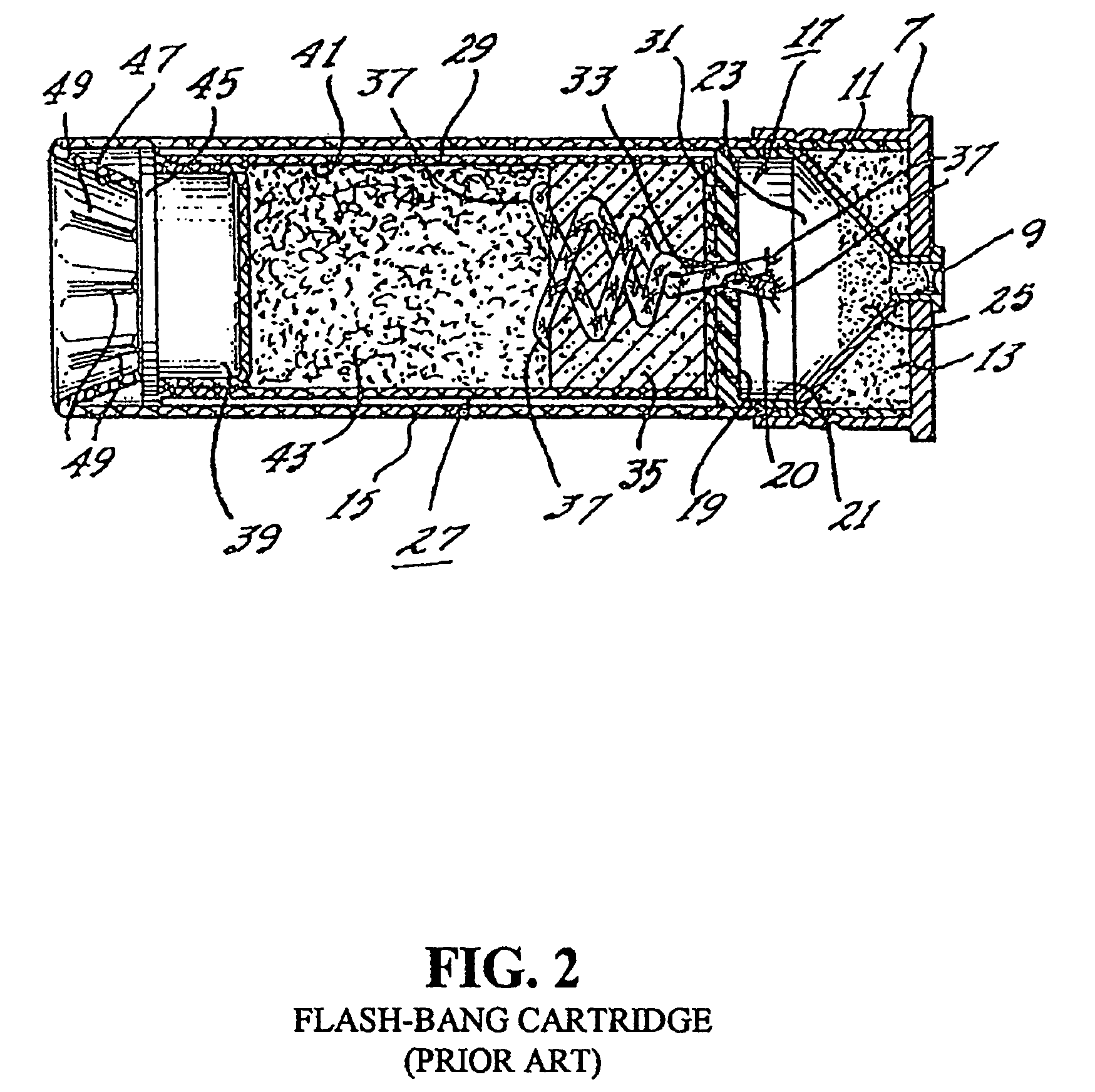
Flare-bang projectile
ActiveUS20100212533A1Improve stabilityImprove accuracyAmmunition projectilesFirework flares/torchesLeading edgeFlare
A flare-bang projectile is comprised of a weighty ballast in the front leading edge, a flash-bang charge, a transfer charge and a flare charge that is lit by a starter composition located at the rear of the flare charge. When the flare charge is ignited such that it burns during the flight of the projectile, an the projectile path is indicated to thereby provide warning signaling.
Owner:COMBINED SYST
Distributed floating series active impedances for power transmission systems
ActiveUS7105952B2Reduce congestionEfficient powerFlexible AC transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionTransformer
Floating electrically isolated active impedance modules are formed to attach to power transmission lines without breaking the lines such that the power line forms a secondary of the main transformer of the module. Each module includes an electrical energy storage device and a switching circuit, such as a single phase inverter, connected to the storage device and to the main transformer primary winding. The inverter can be controlled to couple a selected voltage to the transmission line through the main transformer primary winding which can provide effective positive impedance, negative impedance, or a voltage at or near phase quadrature with the line current. Many active impedance modules may be distributed over a power system grid to allow control of the impedance of the power lines in the grid and to steer power through the grid, with each module electrically isolated from ground and from other phase lines of the transmission system.
Owner:SOFT SWITCHING TECH
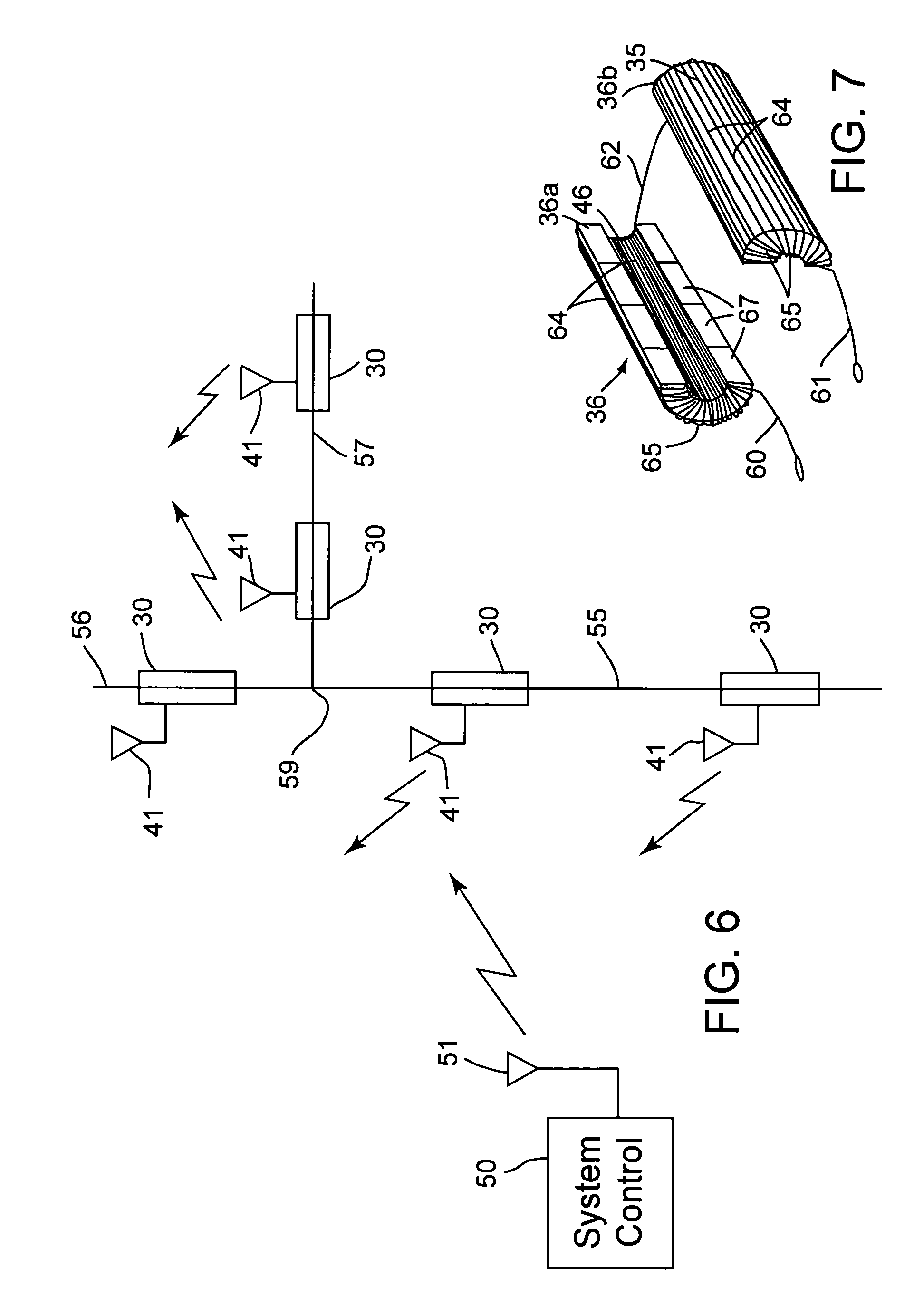
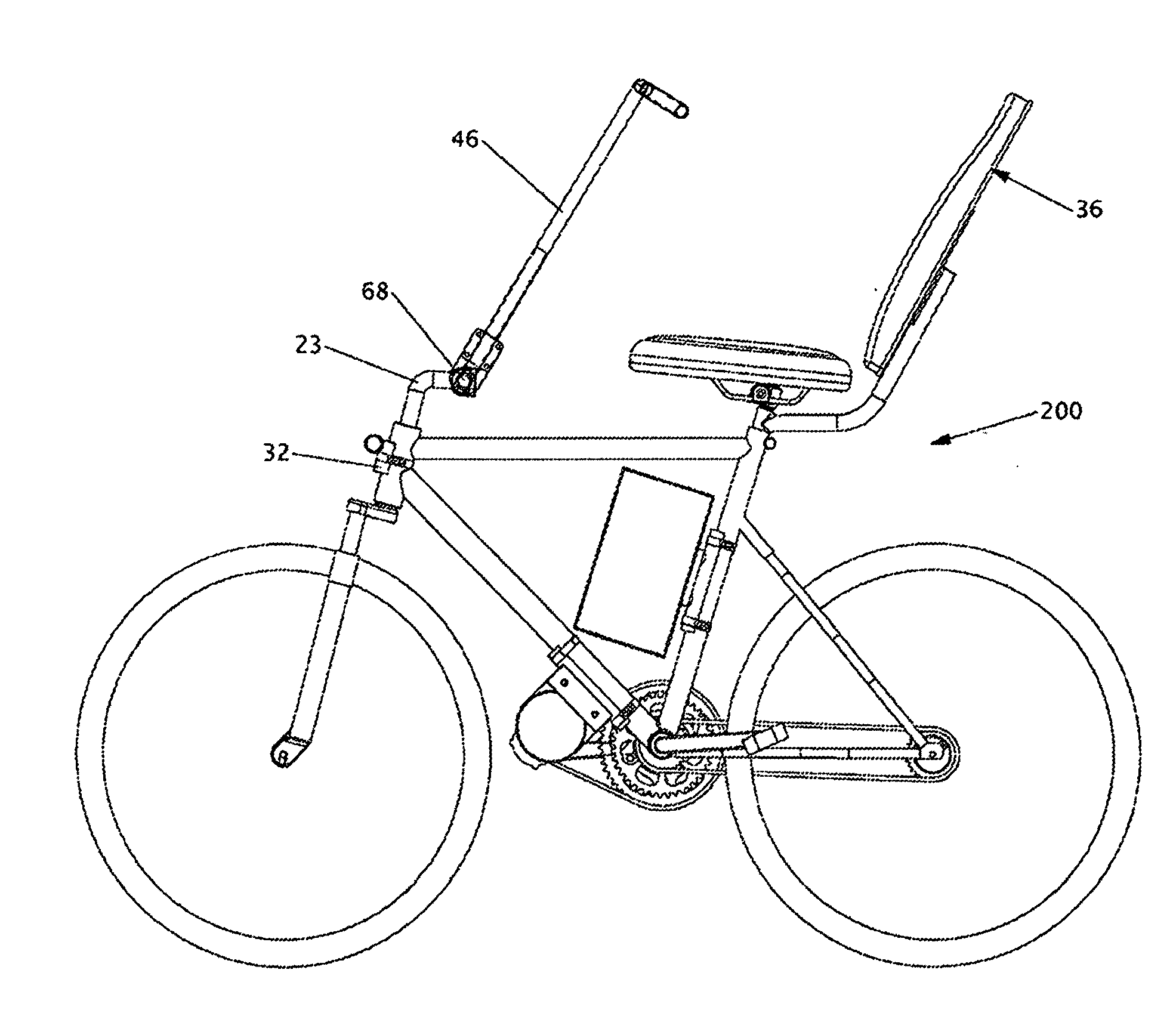
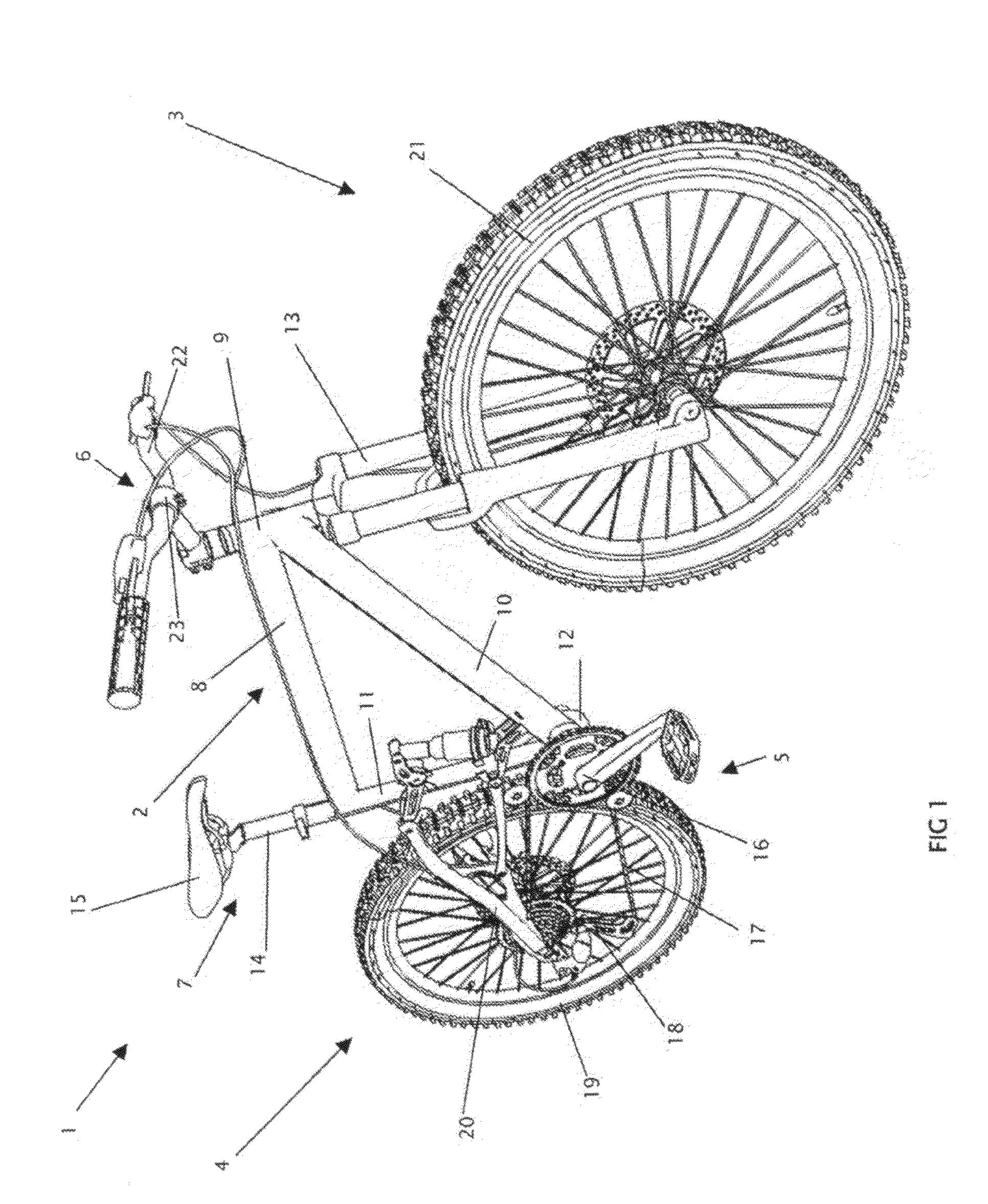
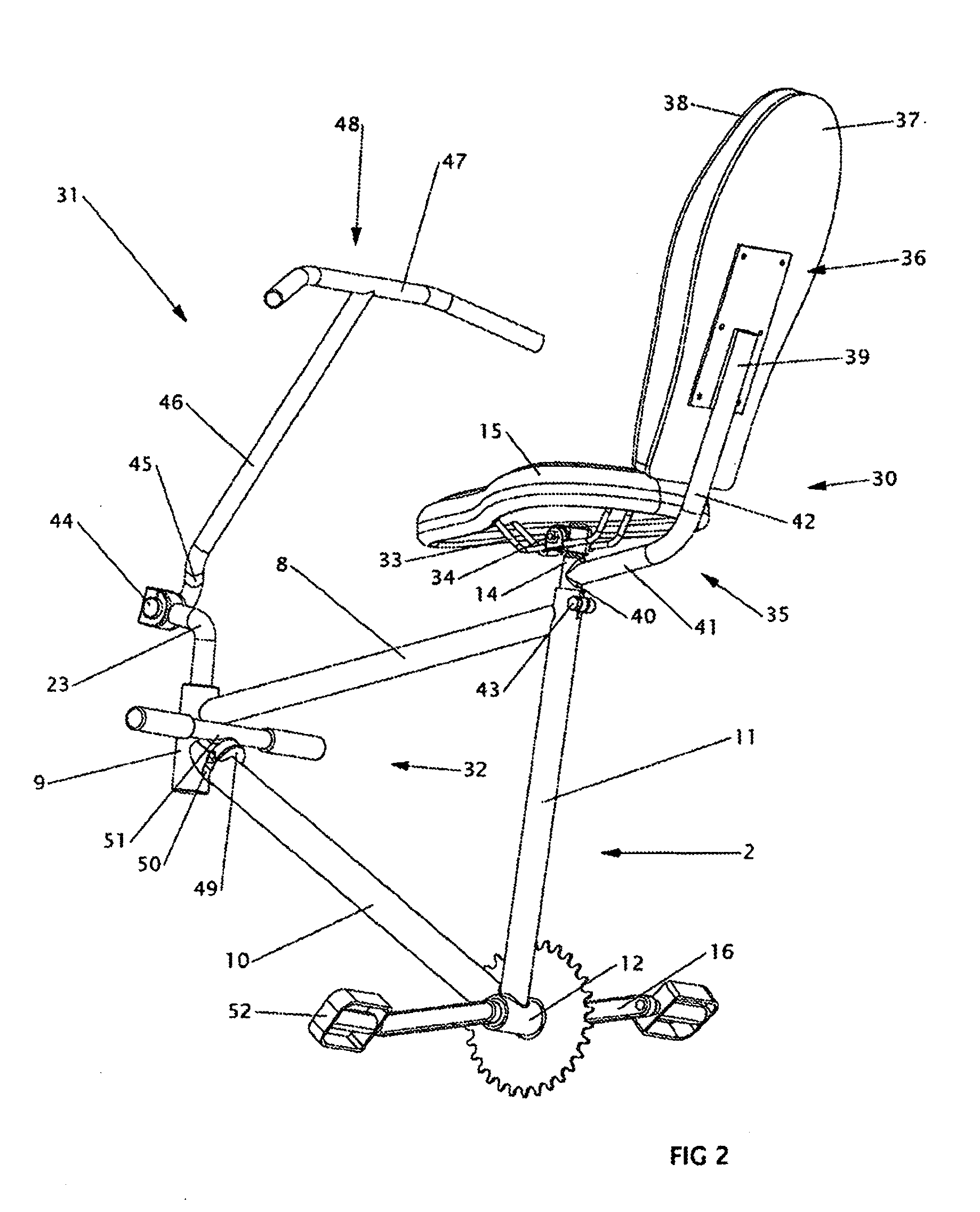
Dual-posture electric assist bicycle
InactiveUS20100206652A1Significant to useEfficient aerodynamicsWeather guardsFoot-restsRecumbent PositionVehicle frame
A dual-posture Electric Assist Bicycle (EAB) permits a rider to assume a rider-upright position while peddling or a rider-recumbent position while coasting with the electric assist propulsion system engaged. The rider can alternate between positions safely and while in motion. The dual-posture EAB comprises: a seat assembly, a footrest assembly and an extended handlebar assembly. The EAB's seat assembly includes an inclined backrest that is typically affixed to the EAB's seat post. Left and right footrests are affixed near the EAB's headtube. The extended handlebar typically includes means for quickly repositioning the controls while under way to optimize ergonomics for whichever seating posture is being used. In another example of the invention the frame of the bicycle is foldable into a dolly configuration for easy moving and storage. In yet another example of the invention the seat assembly, extended handlebar assembly, footrest assembly and an electric assist propulsion system are provided in kit form for converting a standard peddle bicycle into a dual-posture EAB. In still another example of the invention a trailer is provided with the EAB for towing additional batteries.
Owner:KIELLAND PETER
Partial weight bearing suspension walker
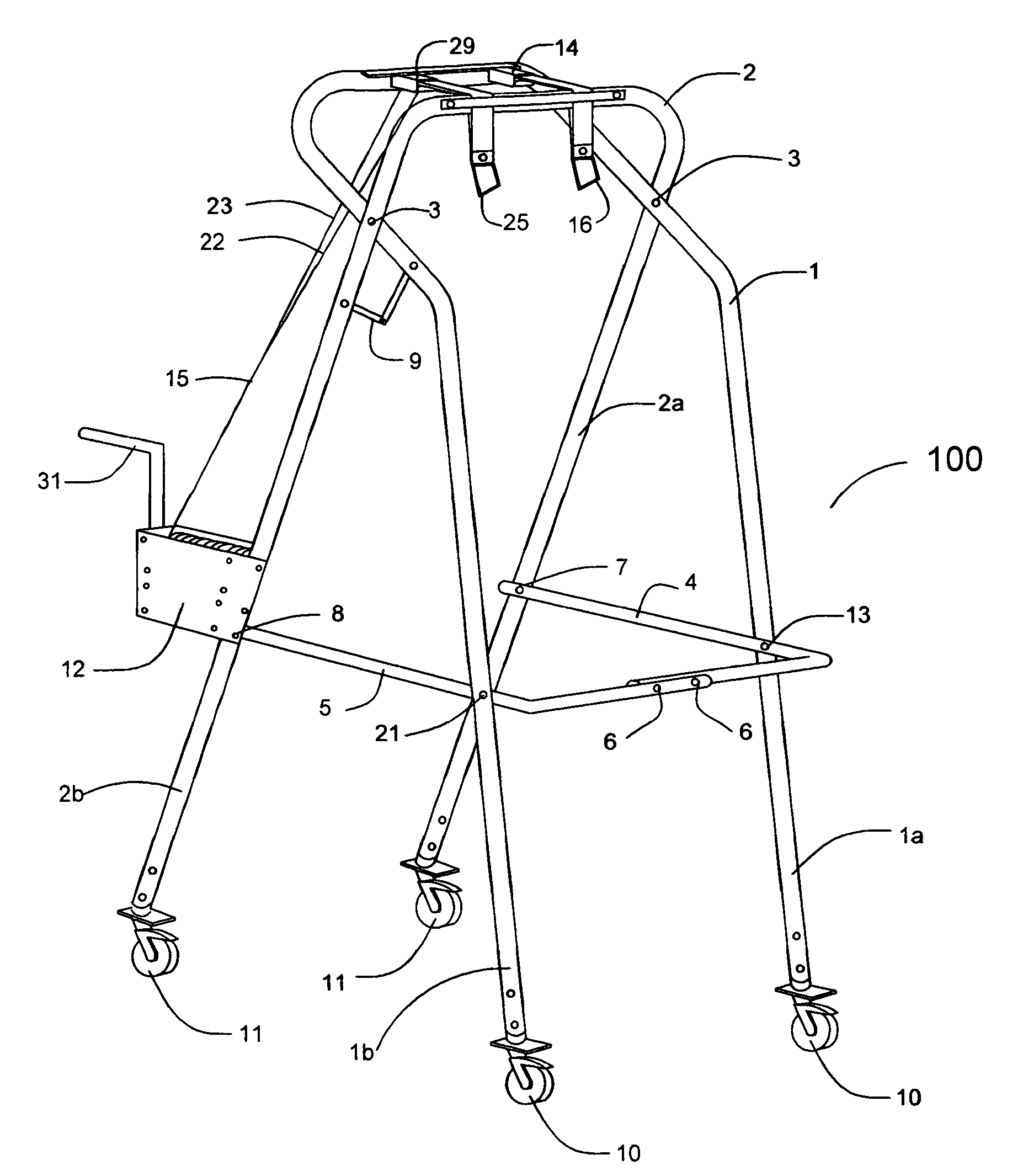
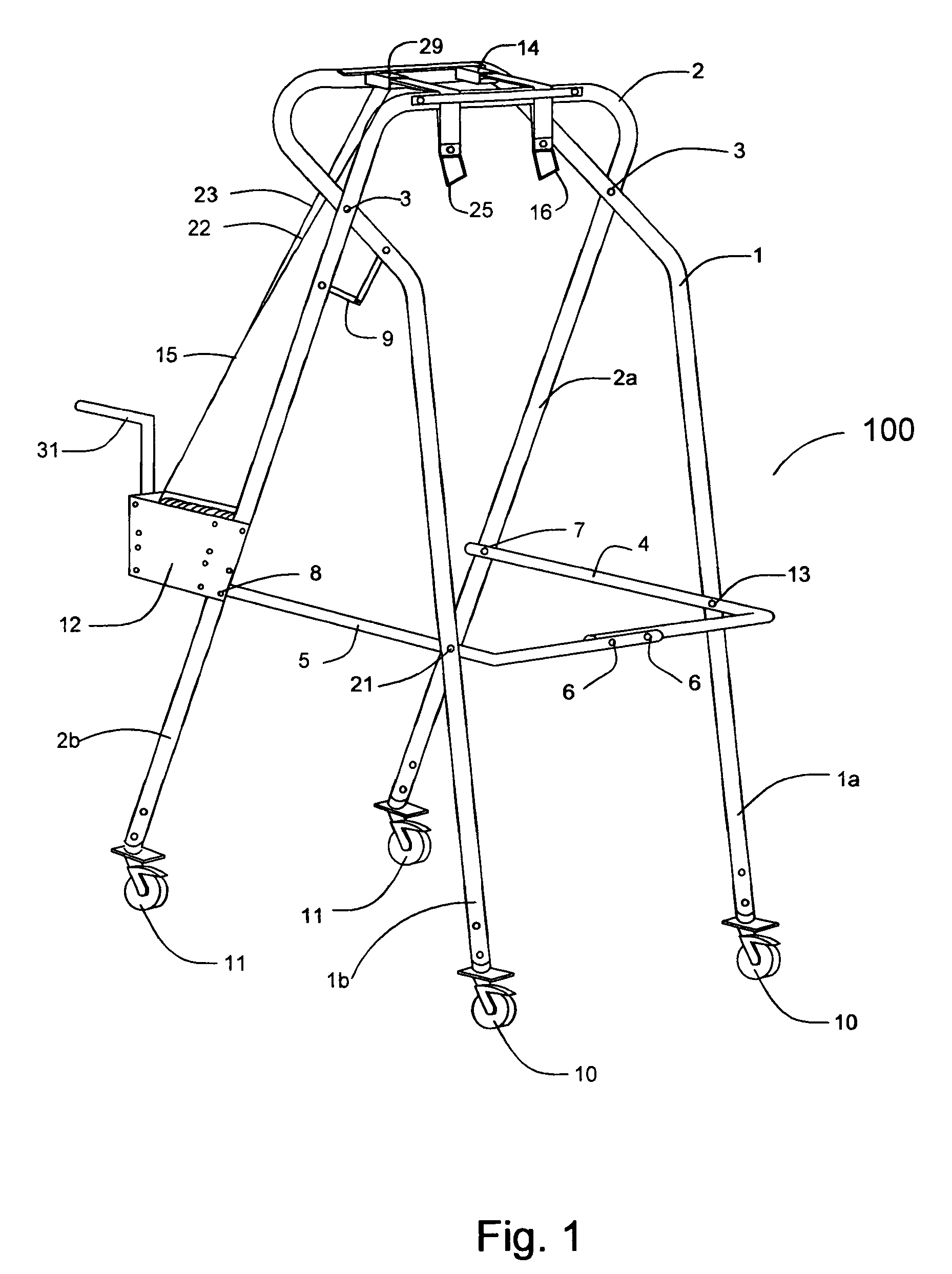
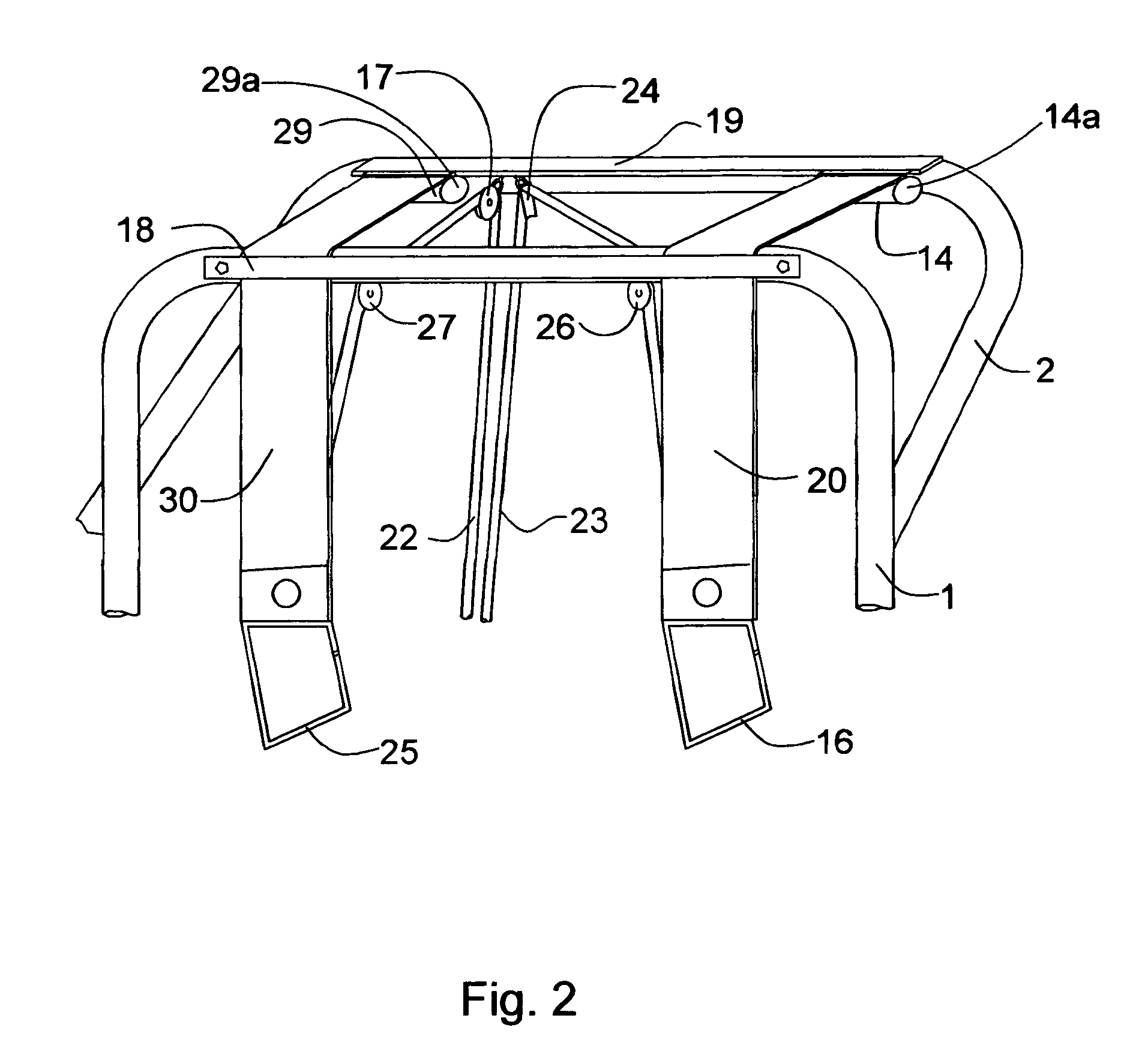
ActiveUS7294094B1Carry partial weightSmall sizeWalking aidsChildren furnitureWheelchairGait training
A lightweight, foldable device for the partial weight bearing during walking and gait training is provided. The lightweight, partial weight bearing suspension walker is made from two frames that are pivotally attached and can be folded at the pivot point for storage or transport. The apparatus can be adjusted to fit over wide treadmills or wheelchairs and through narrow doors. The apparatus includes two fail-safe lift and support devices to insure patient safety in case of unintentional release by the operator.
Owner:HOWLE EDWARD SAMUEL
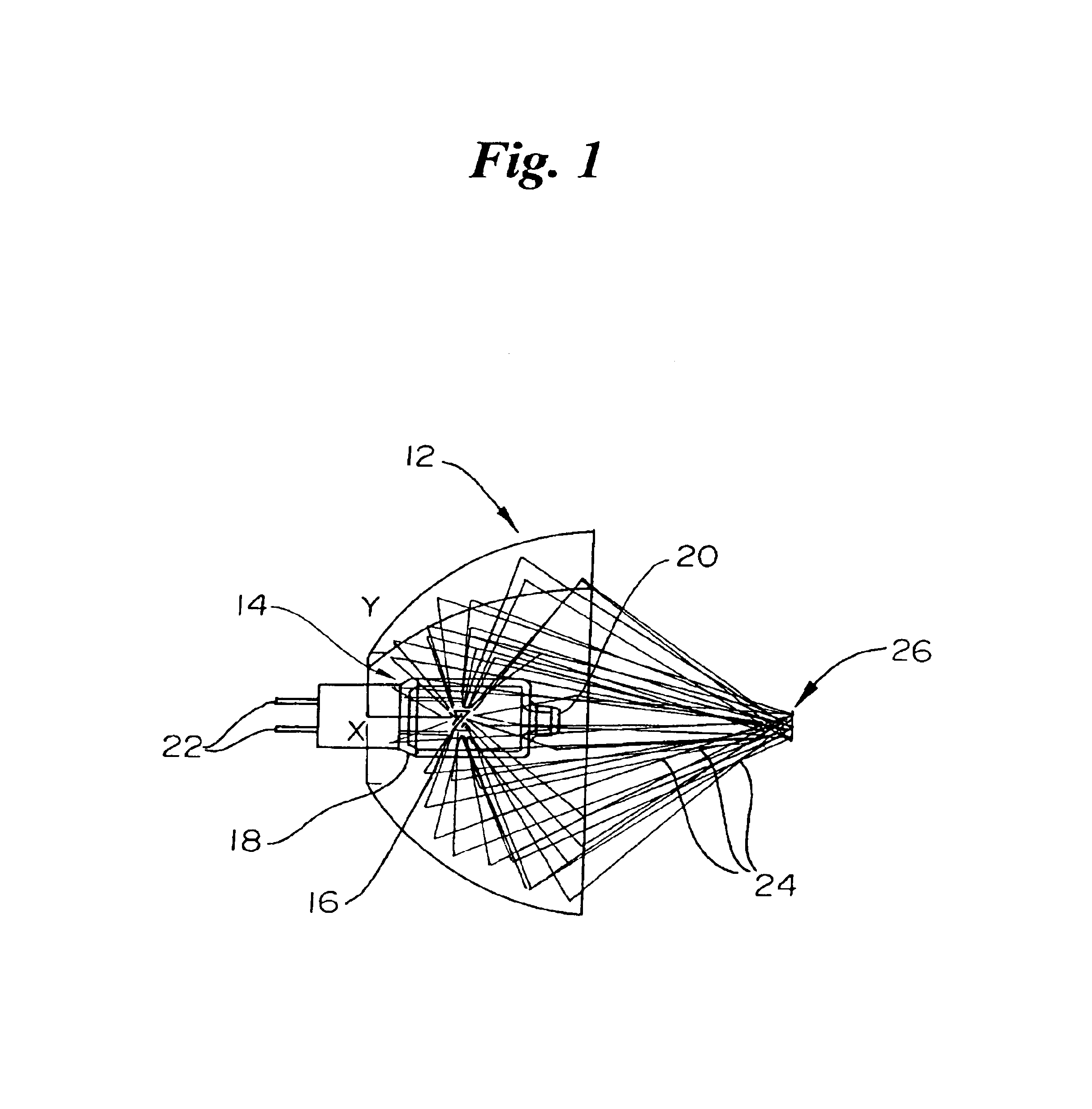
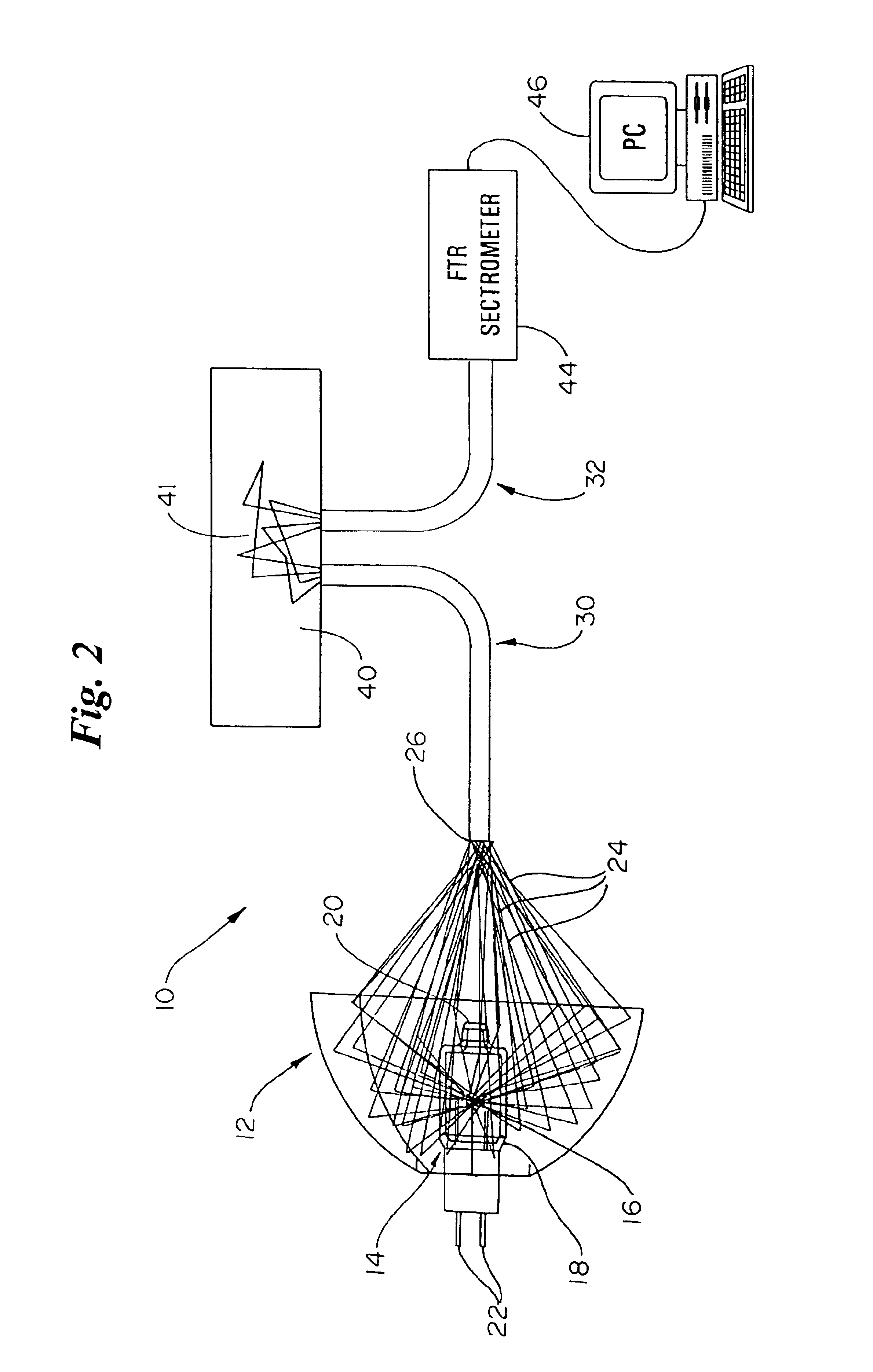
Illumination device and method for spectroscopic analysis
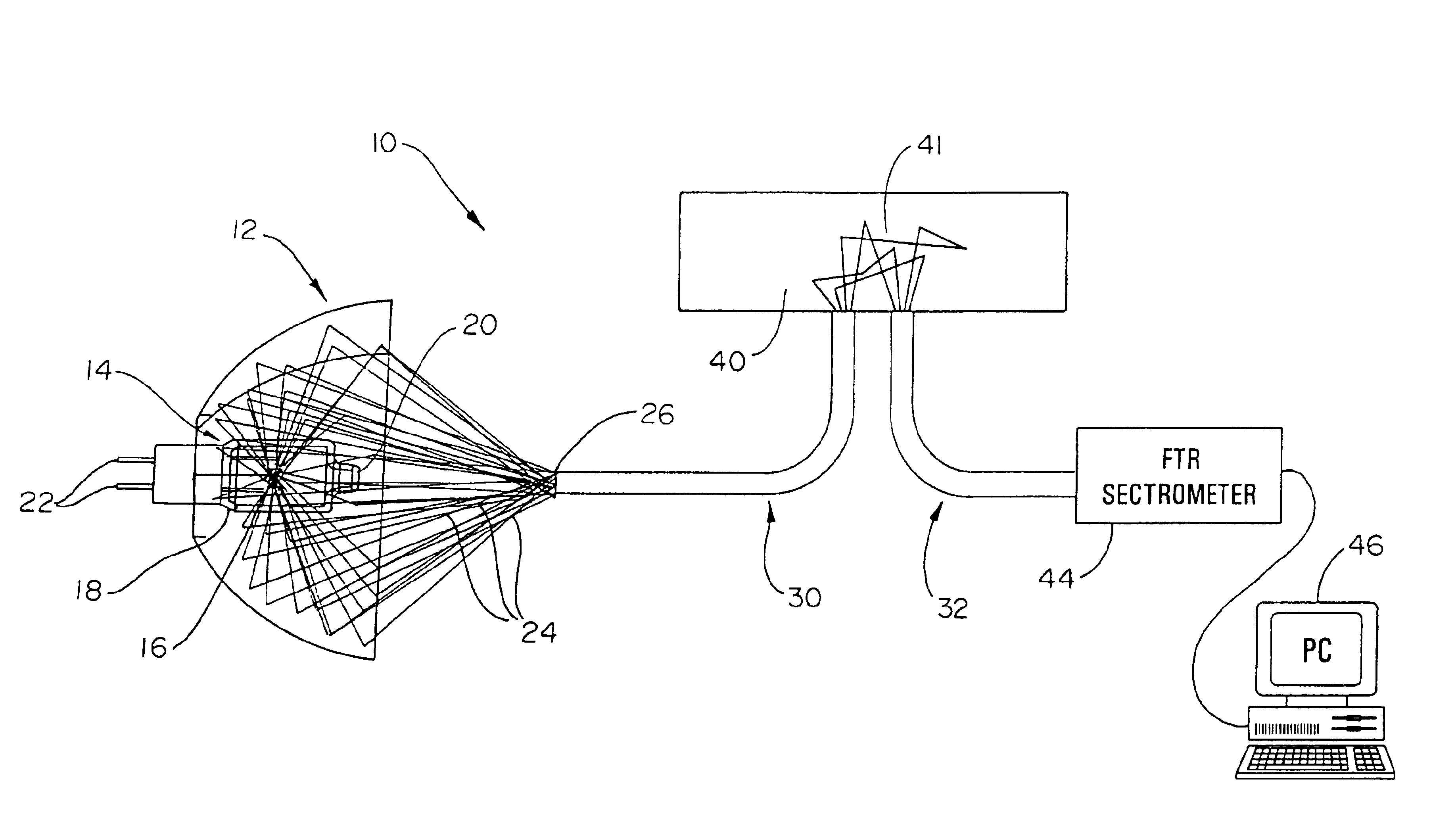
InactiveUS6862091B2Eliminate needMinimal effectRadiation pyrometryPolarisation spectroscopyBandpass filteringSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
An illumination subsystem for use in optical analysis which provides spatially and angularly homogenized radiation to the sample being analyzed. The system eliminates the illumination system as an interferent in the overall optical analysis. Thus, modest translations or rotations of the illumination source or changing the illumination source does not require recalibration of the instrument or prior modeling of illumination variability due to such changes. Illumination stability is achieved by incorporating a light pipe which both angularly and spatially homogenizes the light. Further, a series of filters and / or lenses are incorporated to provide bandpass filtering which eliminates unwanted wavelengths or bands of wavelengths from contacting the tissue and allows for a higher signal-to-noise ratio when the sample is tissue, while preventing thermal damage.
Owner:RIO GRANDE MEDICAL TECH
Apparatus and method for devices for imaging structures in or at one or more luminal organs
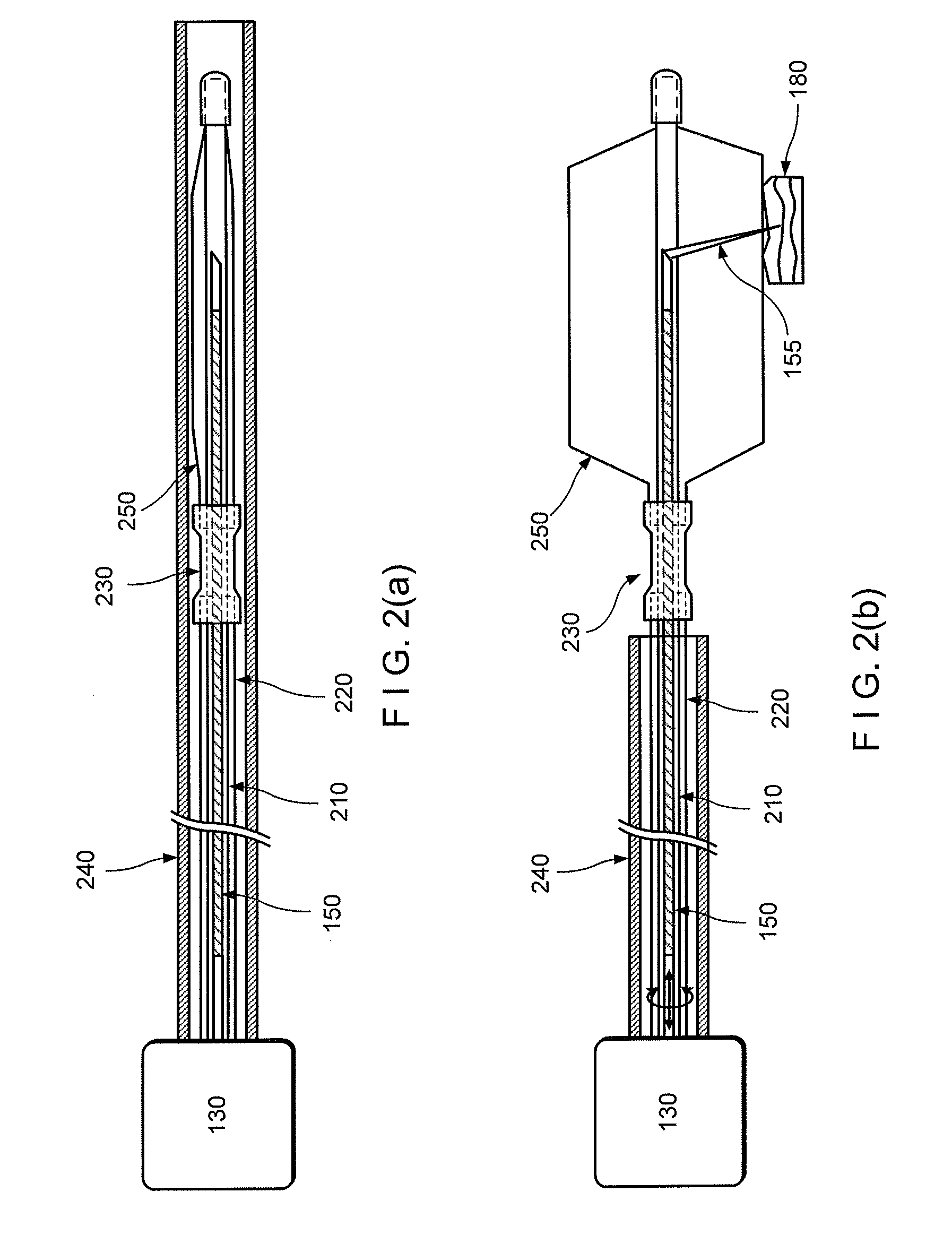
In accordance with exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure, device and method can be provided which can facilitate imaging of biological tissues, e.g., luminal organs in vivo, using optical techniques. The exemplary device can include different designs an features of one or more catheters, which can illuminate the tissues, and collect signals from the inside of the lumen. In another exemplary embodiment according to the present disclosure, a balloon-catheter can be provided with the flexible neck, which can absorb most of the bending. According to still another exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure, a balloon-catheter tethered capsule can be provided, and according a yet further exemplary embodiment, a structured balloon design can be provided with one or more protuberances, thus enabling imaging of the structures in close contact, e.g., without compressing of the tissue.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Centrifuge with aerodynamic rotor and bucket design
A rotor and specimen holder assembly for producing a relatively low power, low audible level, cool running centrifuge. The centrifuge rotor assembly is designed to enable a specimen holder to retract into the body of the rotor during centrifugation to produce aerodynamic features.
Owner:DRUCKER COMPANY INC THE
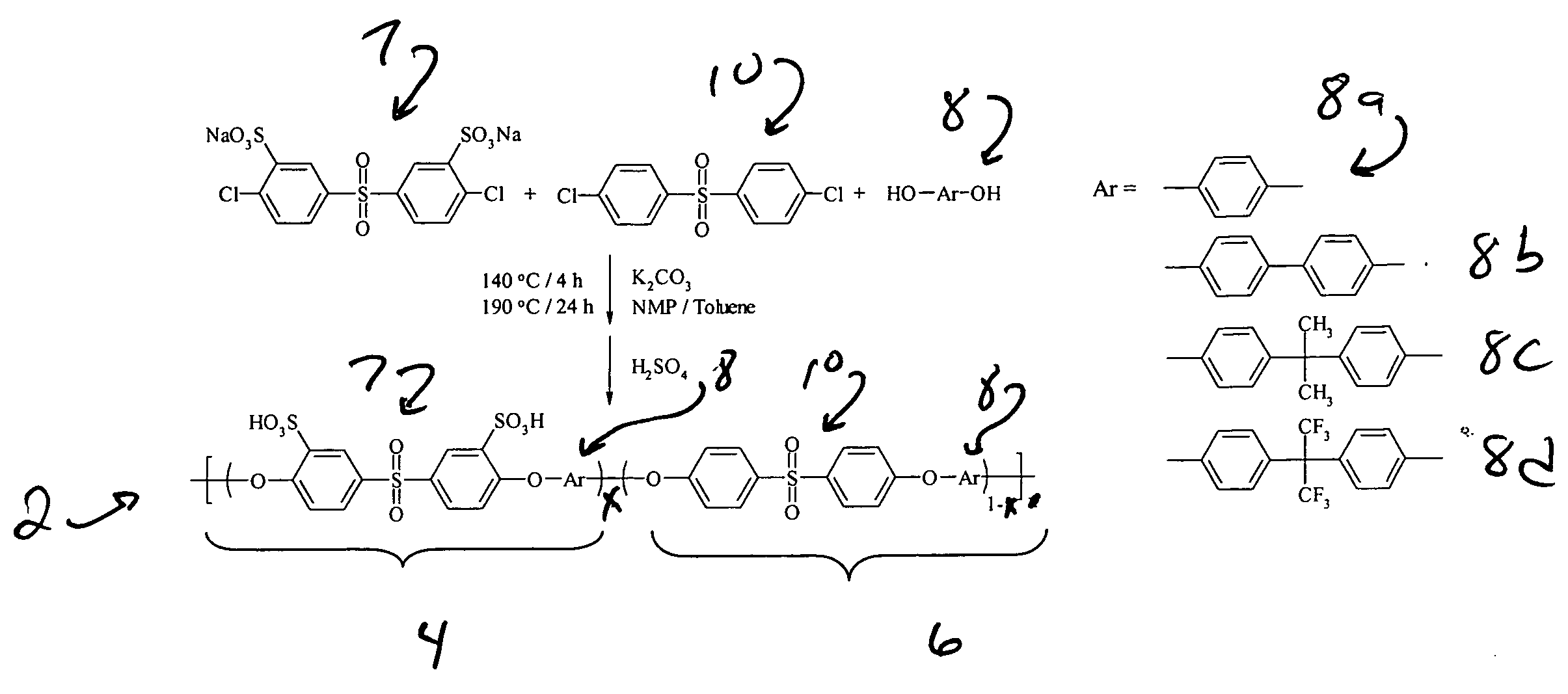
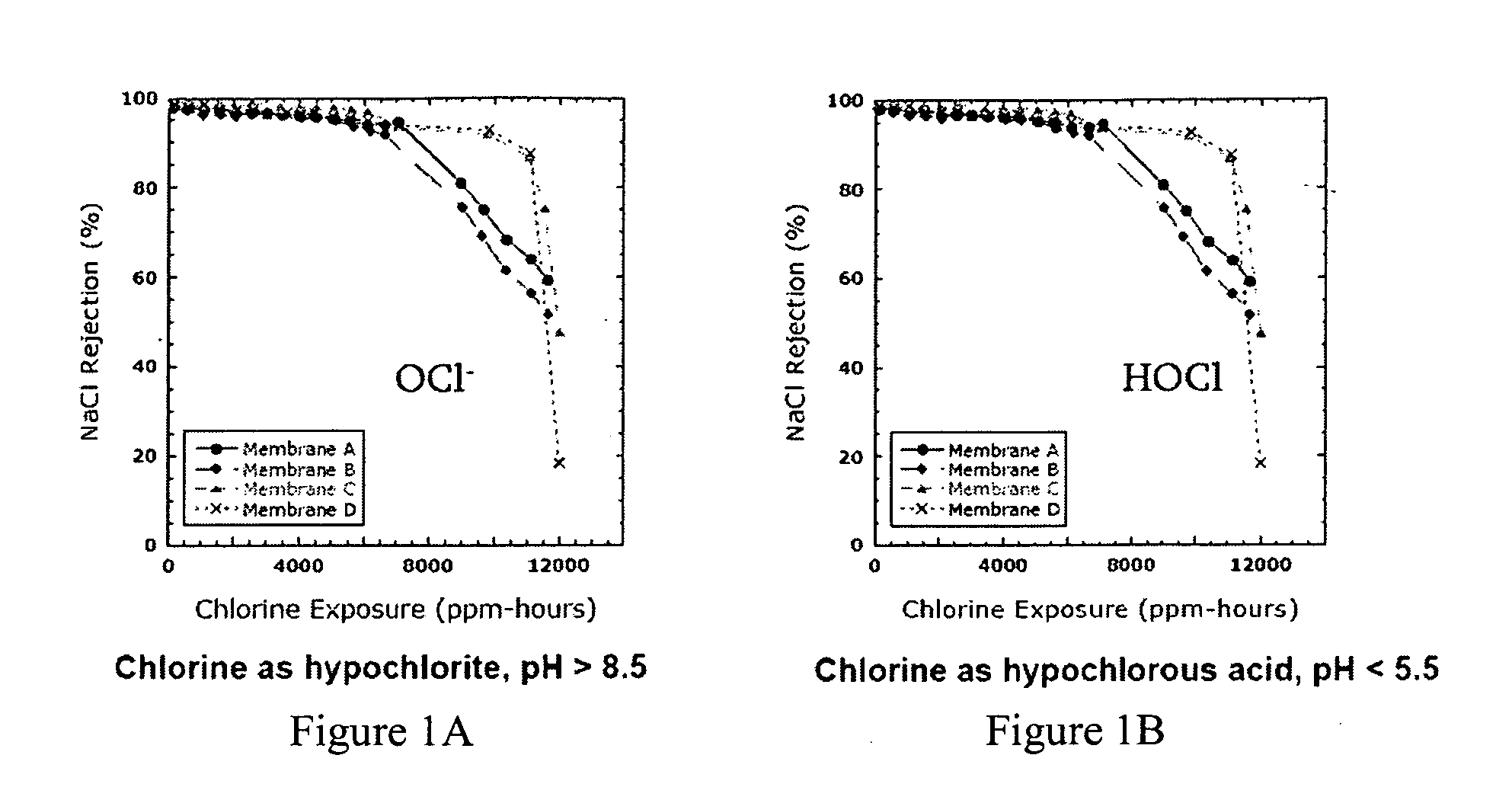
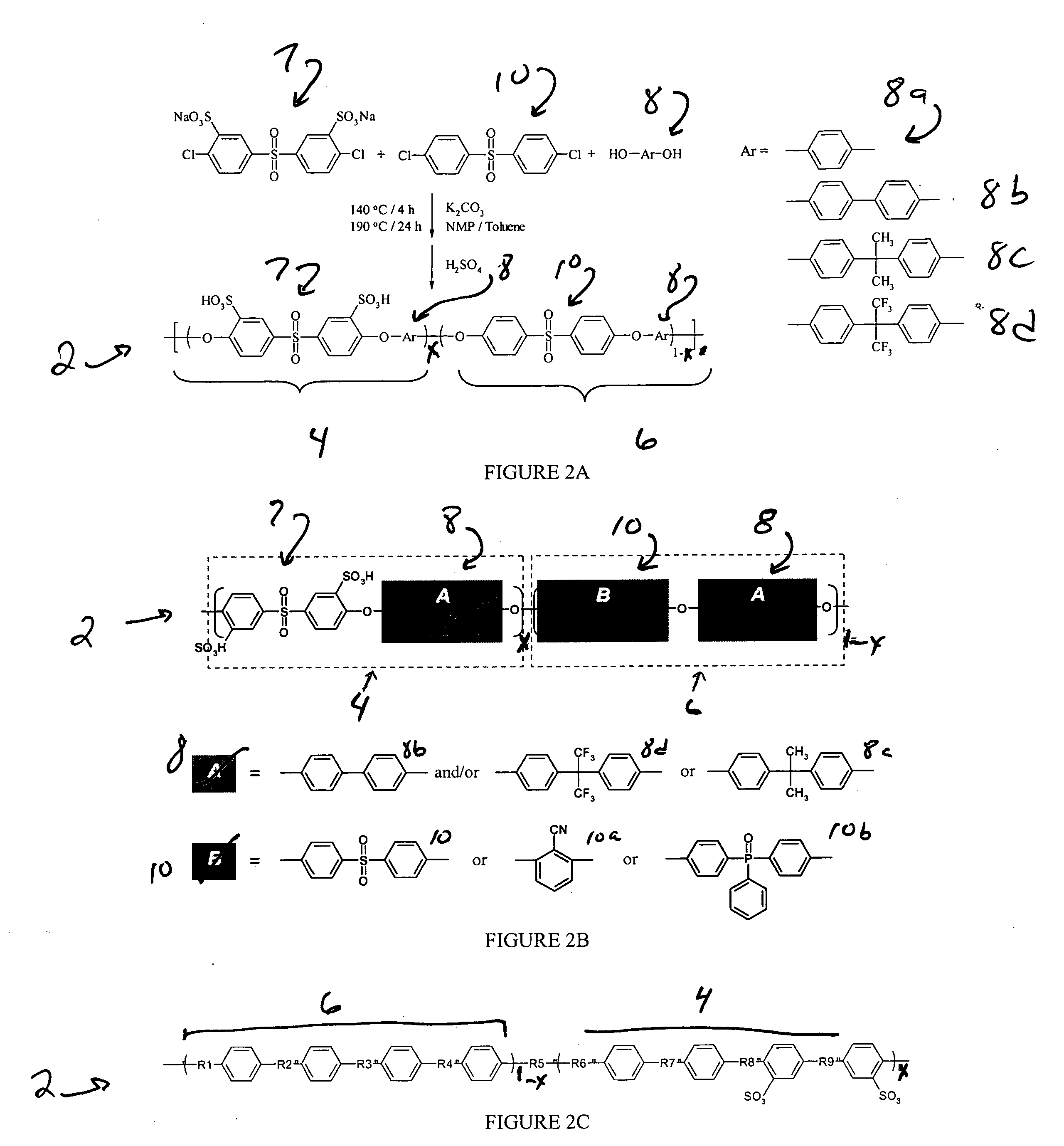
Chlorine resistant desalination membranes based on directly sulfonated poly(Arylene Ether Sulfone) copolymers
ActiveUS20070163951A1Improve pressure resistanceExemption stepsSemi-permeable membranesMembranesHydrophilic monomerSulfonate
The present invention provides a membrane, kit, and method of making a hydrophilic-hydrophobic random copolymer membrane. The hydrophilic-hydrophobic random copolymer membrane includes a hydrophilic-hydrophobic random copolymer. The hydrophilic-hydrophobic random copolymer includes one or more hydrophilic monomers having a sulfonated polyarylsulfone monomer and a second monomer and one or more hydrophobic monomers having a non-sulfonated third monomer and a fourth monomer. The sulfonated polyarylsulfone monomer introduces a sulfonate into the hydrophilic-hydrophobic random copolymer prior to polymerization.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
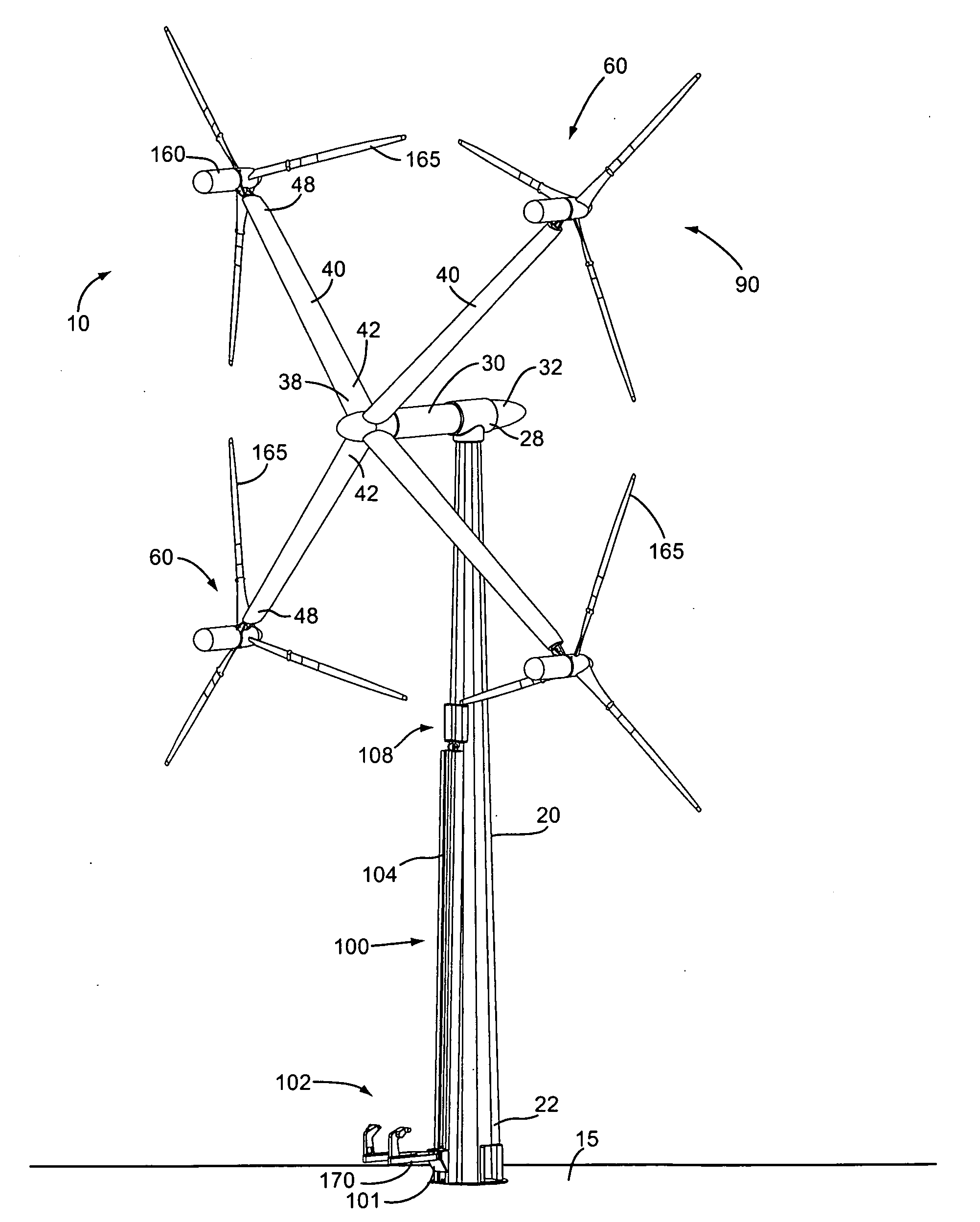
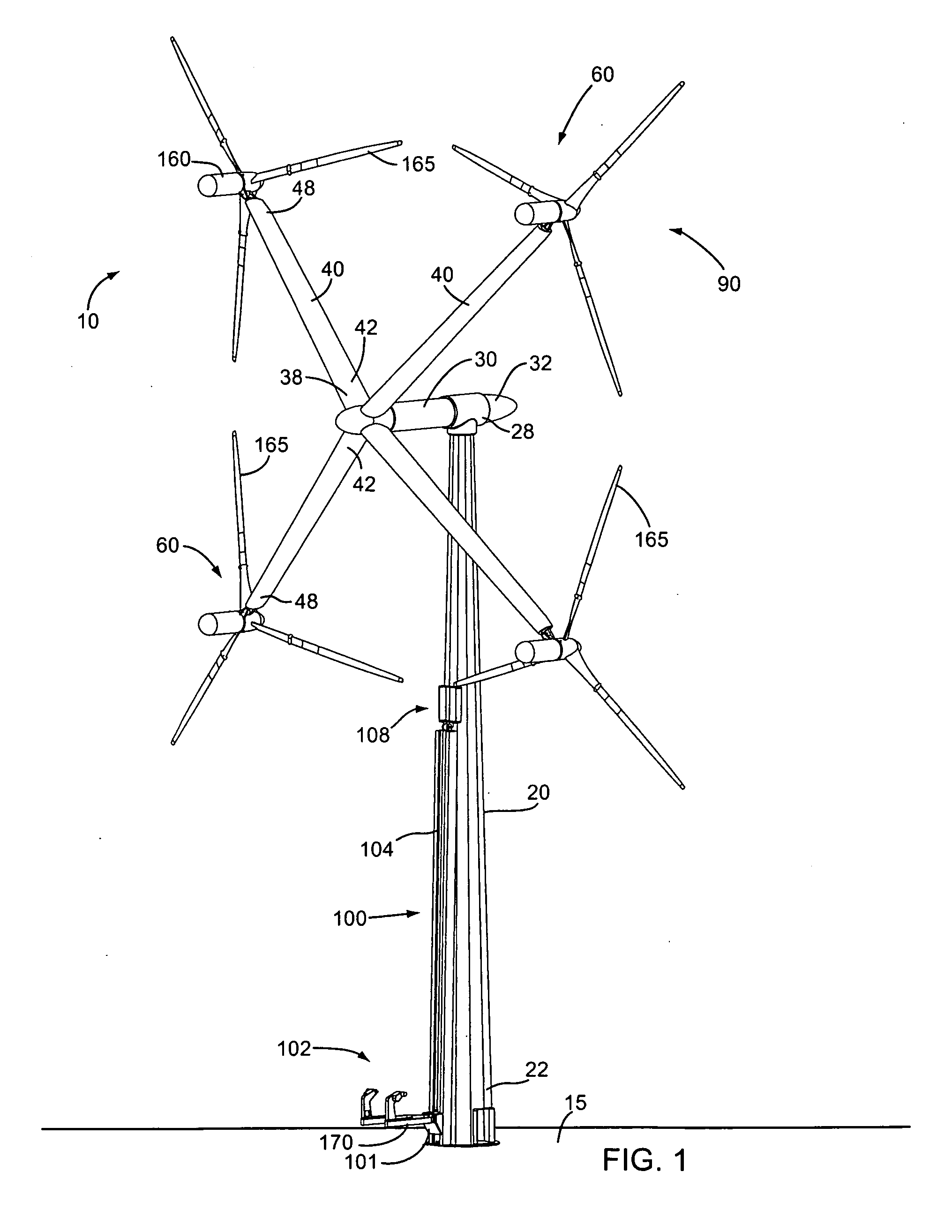
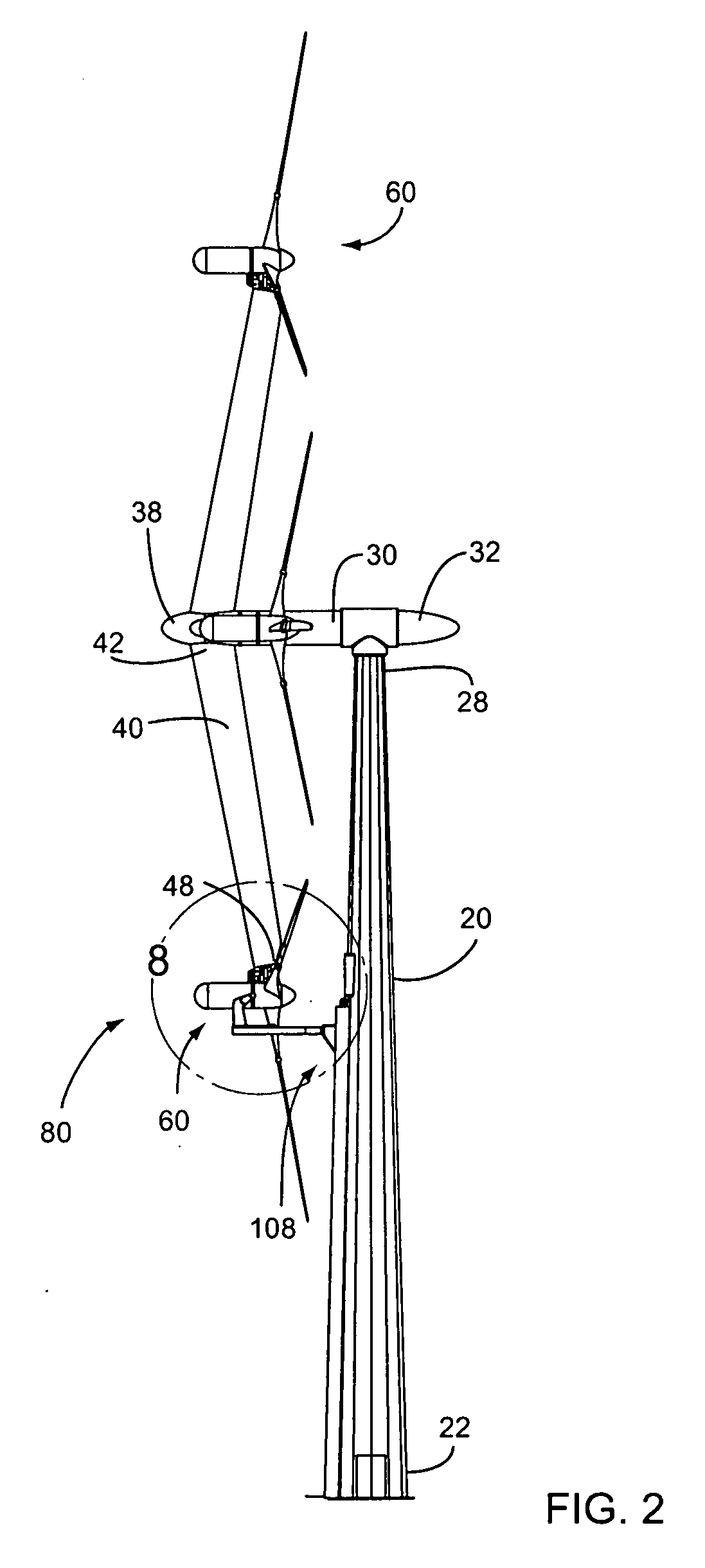
Wind turbine improvements
A wind turbine arrangement is disclosed that includes a substantially vertical tower mounted to a ground surface, a horizontally-extending hub rotatably fixed in a substantially horizontal plane to an upper end of the tower, at least one radial support arm rotatably fixed with a distal end of the hub, each support arm including a turbine mounting means at a distal end thereof, and at least one electricity-generating turbine selectively mountable with the turbine mounting means of the any of the support arms. An elevator means adapted to raise and lower each of the turbines between an upper loading position adjacent to a lower loading position of each support arm, and a lower loading position adjacent to the ground surface. In use, each support arm may be rotated to the loading position for receiving one of the turbines thereon. The support arm is then rotated about the hub into an operating position.
Owner:GREENWARD TECH
Coatings for implantable medical devices
InactiveUS20060121089A1Improve hydrophobicityLong-term biocompatibilityBiocideSurgeryPropanolBiocompatibility
The present application teaches a coating having a biologically compatible compound conjugated to, or blended with, a polymer, wherein the polymer includes at least one olefin-derived unit and at least one unit derived from a vinyl alcohol, an allyl alcohol, or derivatives thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
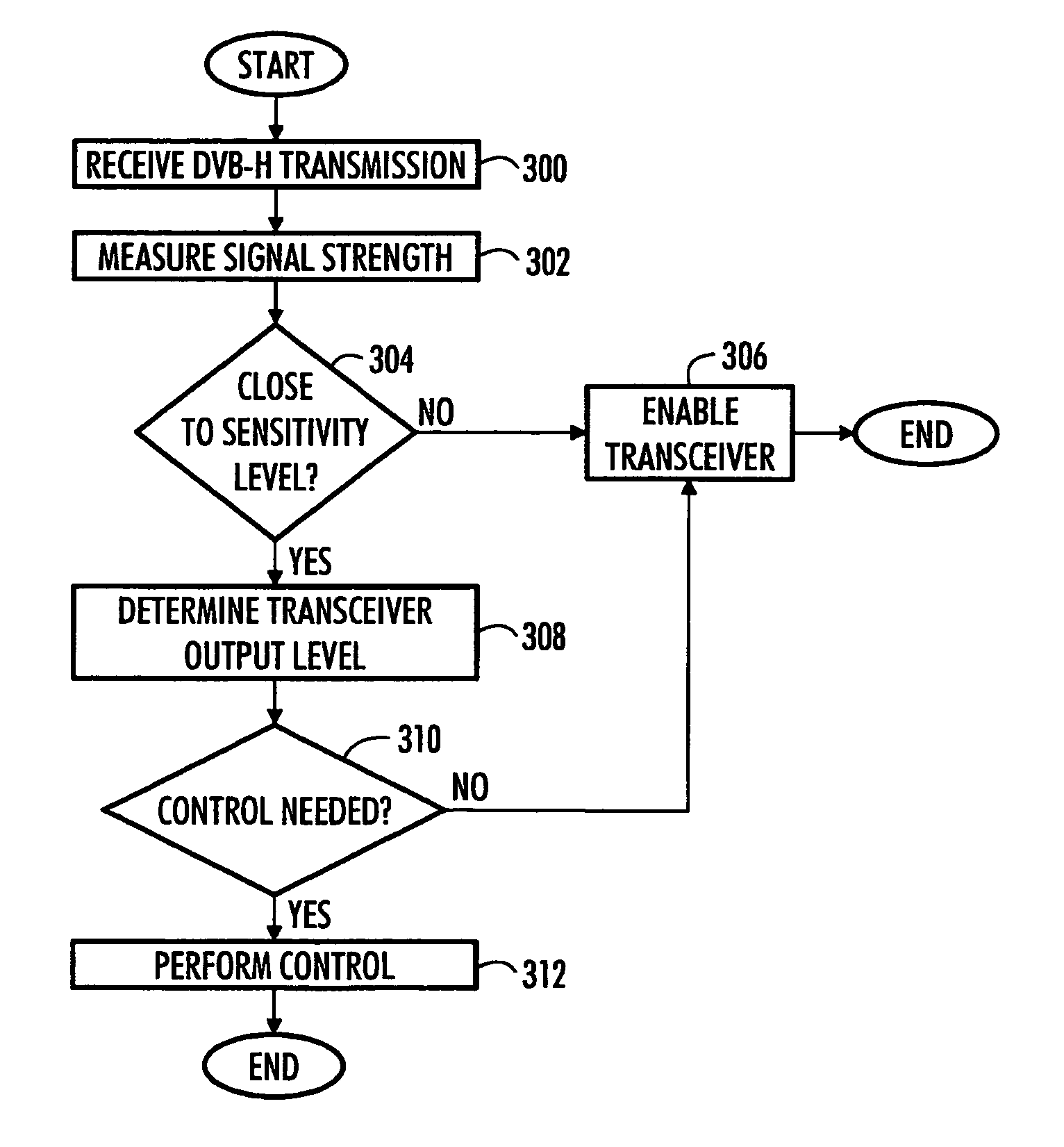
Operating multi-service receiver in non-interfering manner
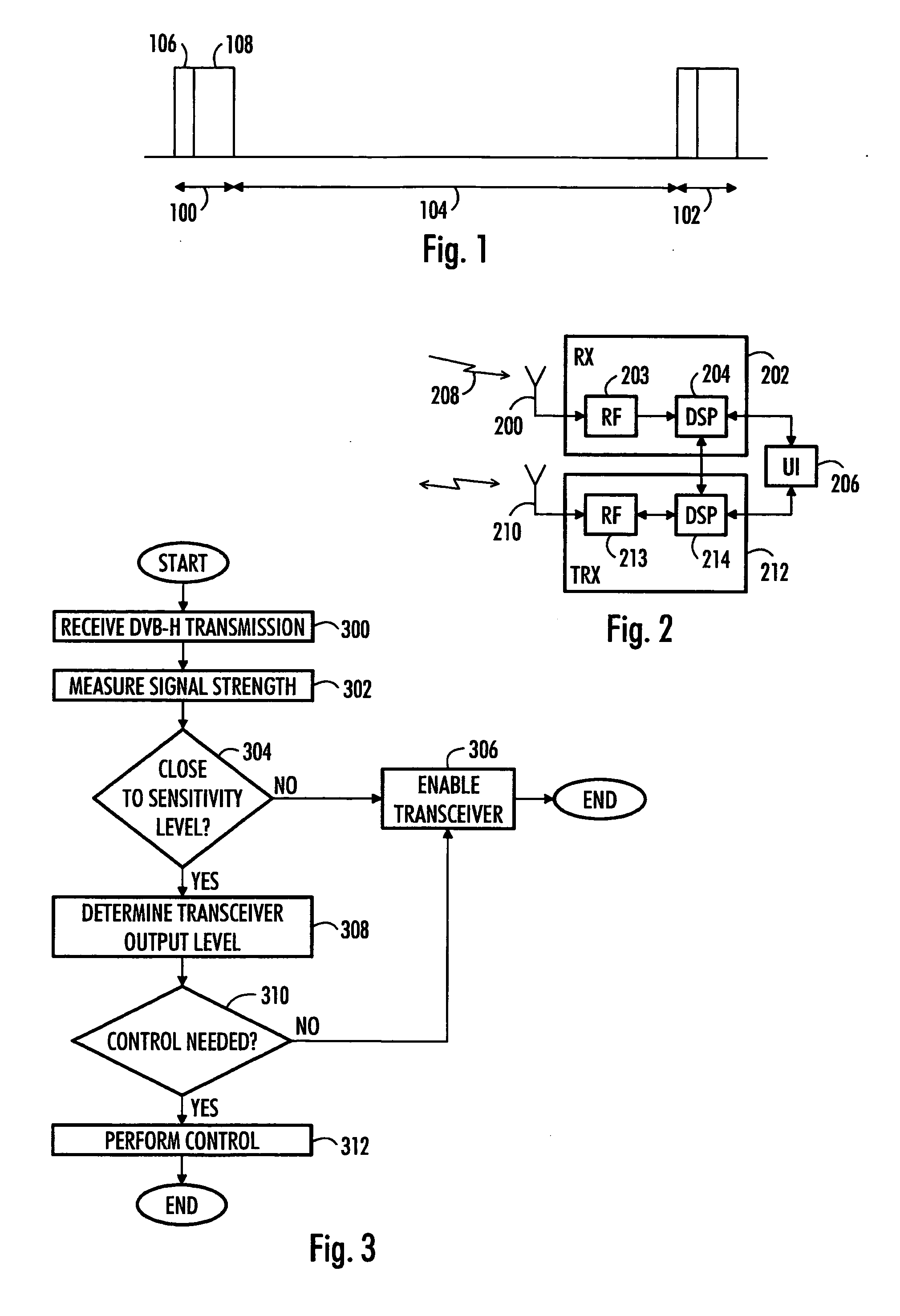
ActiveUS20070066228A1Minimal effectEffective protectionFrequency diversityTransmission monitoringTransceiverEngineering
A method for operating a receiver and a device are provided. The device comprises a first and a second antenna, a receiver operationally coupled to the first antenna and a transceiver operationally coupled to the second antenna. The receiver receives information in bursts on a first band of radio frequencies. A controller of the device measures signal strength of the information received with the receiver, compares the measured signal strength to a reference value and enables operation of the transceiver if the measured signal strength is above the reference value, and limits operation of the transceiver during reception of the bursts if the measured signal strength is below the reference value.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Flare-bang projectile
ActiveUS7908972B2Improve stabilityImprove accuracyAmmunition projectilesFirework flares/torchesLeading edgeFlare
A flare-bang projectile is comprised of a weighty ballast in the front leading edge, a flash-bang charge, a transfer charge and a flare charge that is lit by a starter composition located at the rear of the flare charge. When the flare charge is ignited such that it burns during the flight of the projectile, an the projectile path is indicated to thereby provide warning signaling.
Owner:COMBINED SYST
Moisture resistant microphone
InactiveUS20070003081A1Reduce condensationImprove long-term reliabilityCompletely in canal hearing aidsMicrophonesEngineeringAcoustic wave
Embodiments of the invention provide microphone assemblies which are resistant to moisture. One embodiment provides a microphone assembly comprising a housing, a diaphragm disposed in the housing and a backplate disposed in the housing. The housing includes a sound inlet port for the entry of sound waves. The backplate includes a surface and an electret portion having an embedded permanent charge. The diaphragm is configured to vibrate in response to sound waves entering the housing. The vibrations of the diaphragm interact with the electret portion to produce an electrical signal associated with the sound waves entering the housing. A hydrophobic coating can be applied to one or both of the backplate and diaphragm surfaces so as to reduce condensation and / or wetting of the backplate. This minimizes neutralization of an electric field of the backplate surface from condensation preserving the field and the function of the microphone in humid environments.
Owner:INSOUND MEDICAL INC
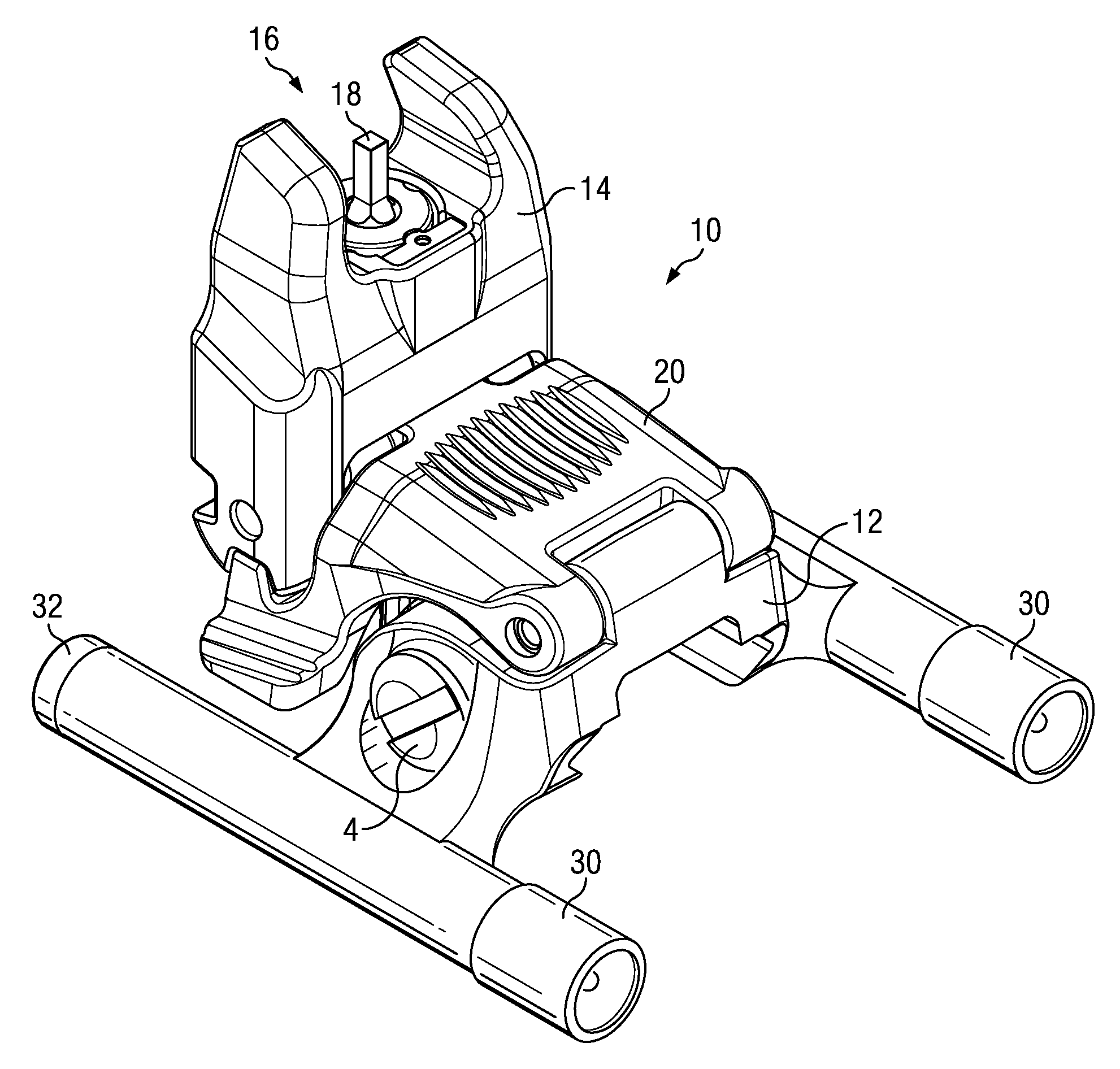
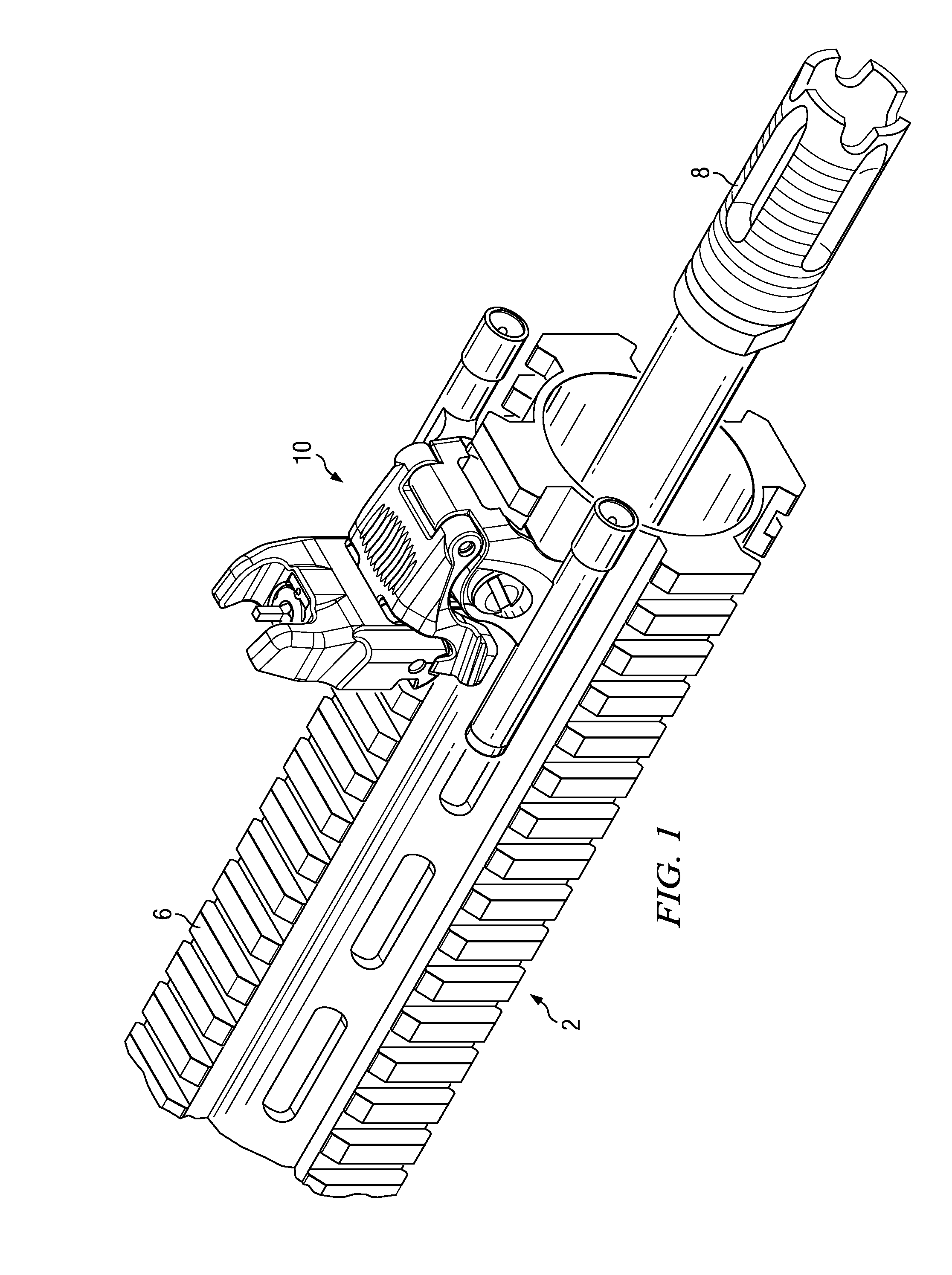
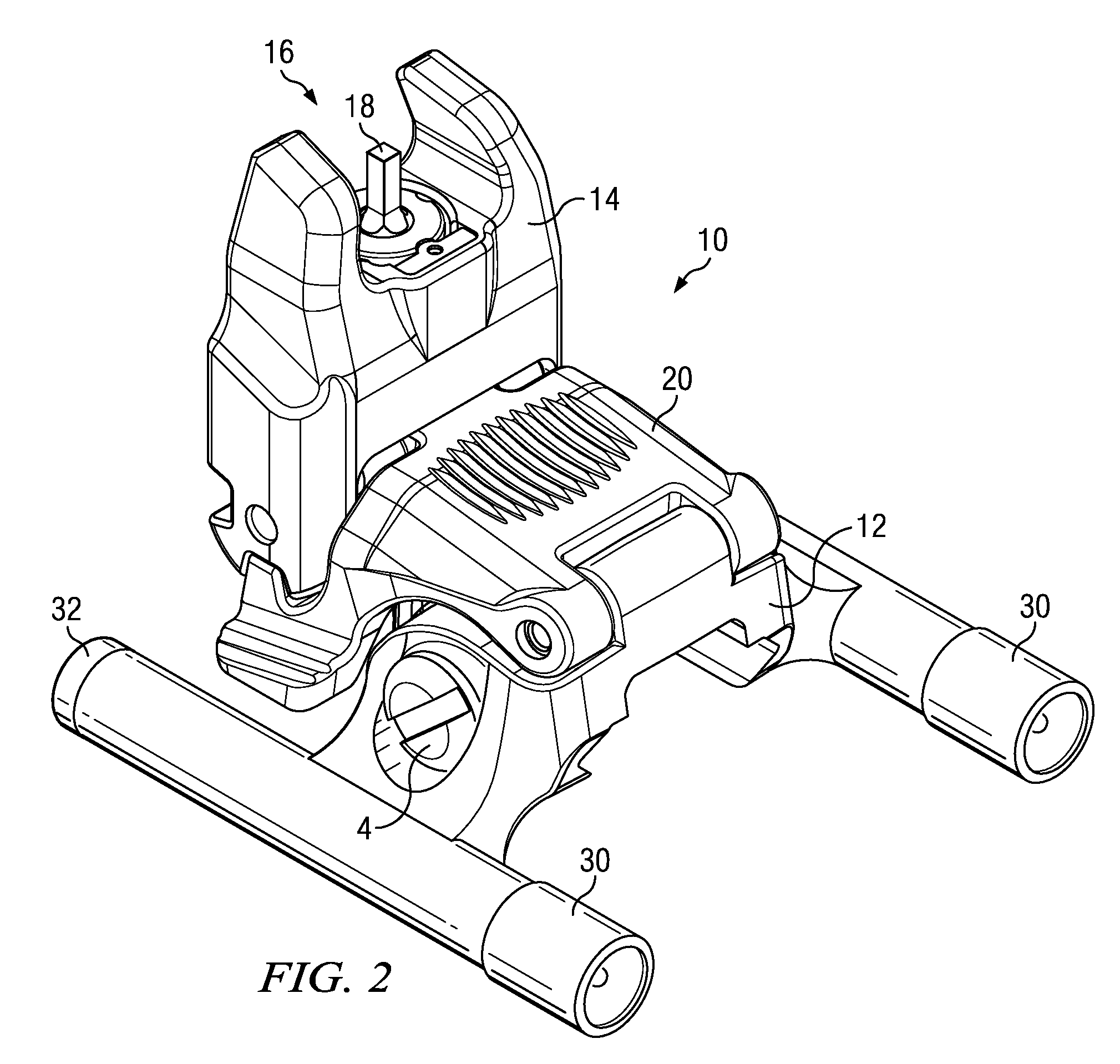
Forward mounted gun sight with illumination apparatus
The present invention is a rail mounted back-up sight with at least one, but preferred two, illumination apparatuses mounted thereon. The back-up sight features a sight housing that is configured to selectively alternate between a stowed and a spring-biased deployed position. Any type of illumination apparatus may be used, but the preferred apparatus is a flashlight, mounted upon wither side of a sight base. Either a front or a rear sight may be utilized as could different types of illumination apparatuses.
Owner:MAGPUL INDUSTRIES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com