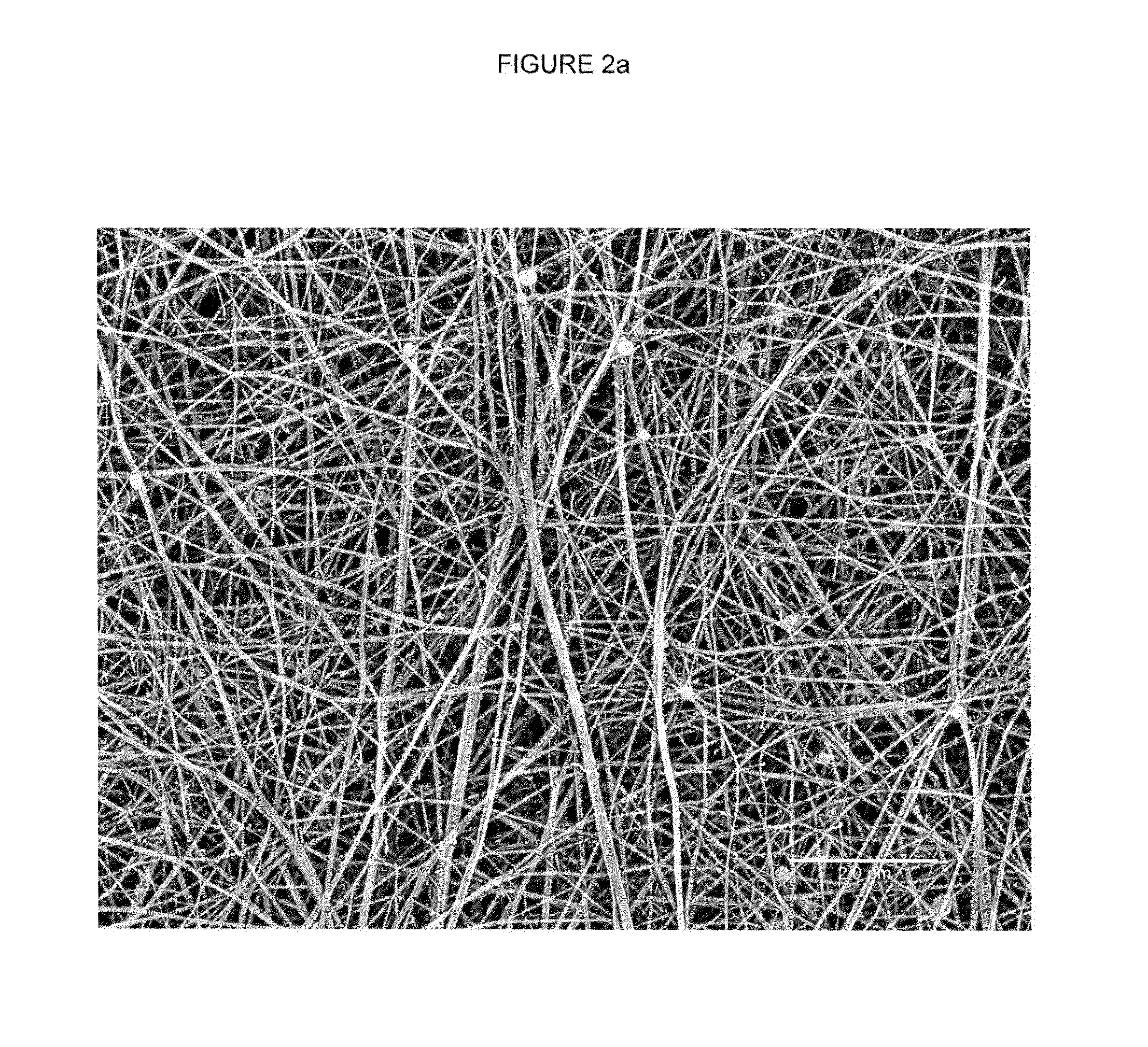
Patents
Literature
312 results about "Expanded polytetrafluoroethylene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gore-Tex was co-invented by Wilbert L. Gore and Gore's son, Robert W. Gore. In 1969, Bob Gore stretched heated rods of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and created expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE). His discovery of the right conditions for stretching PTFE was a happy accident, born partly of frustration.
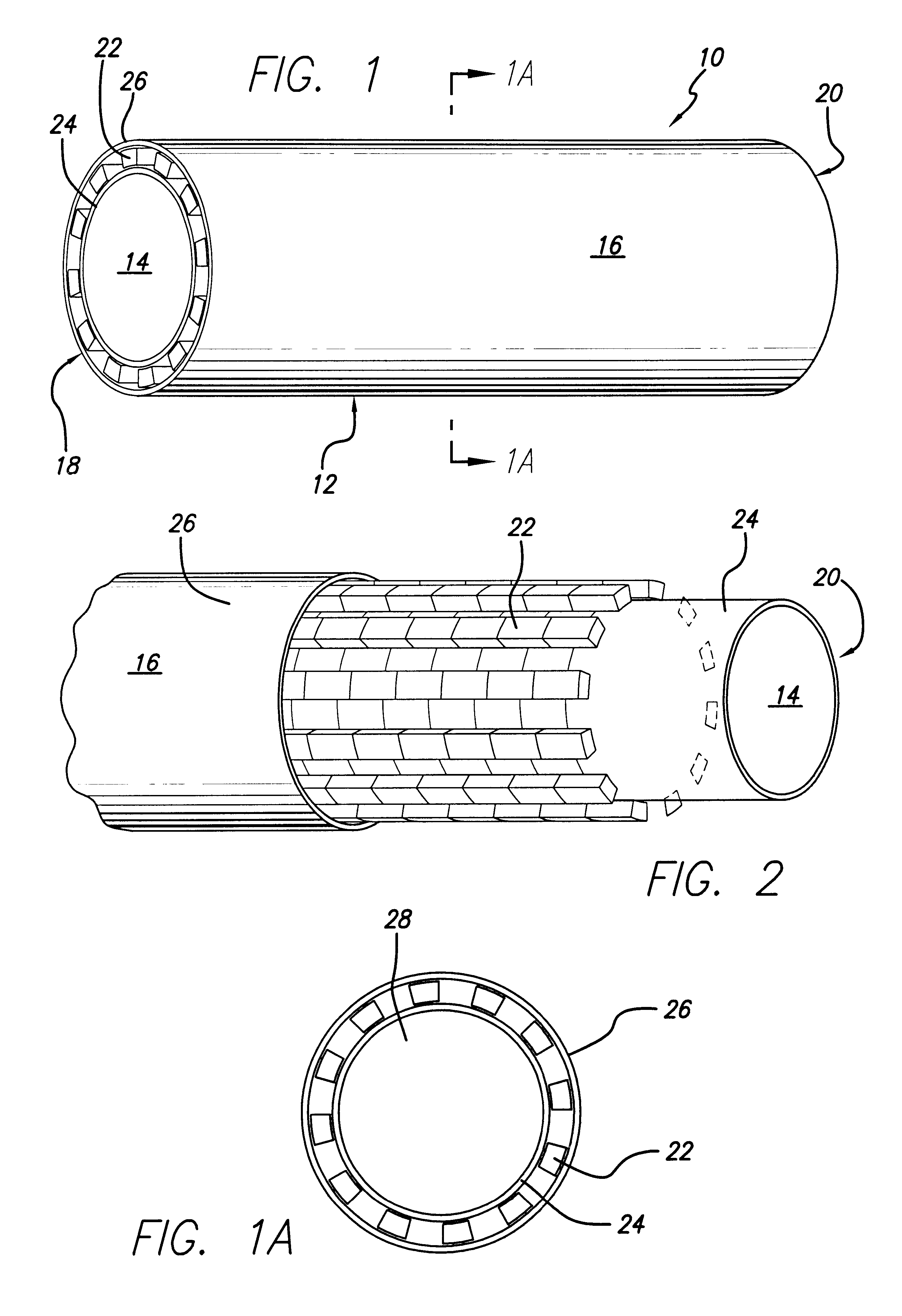
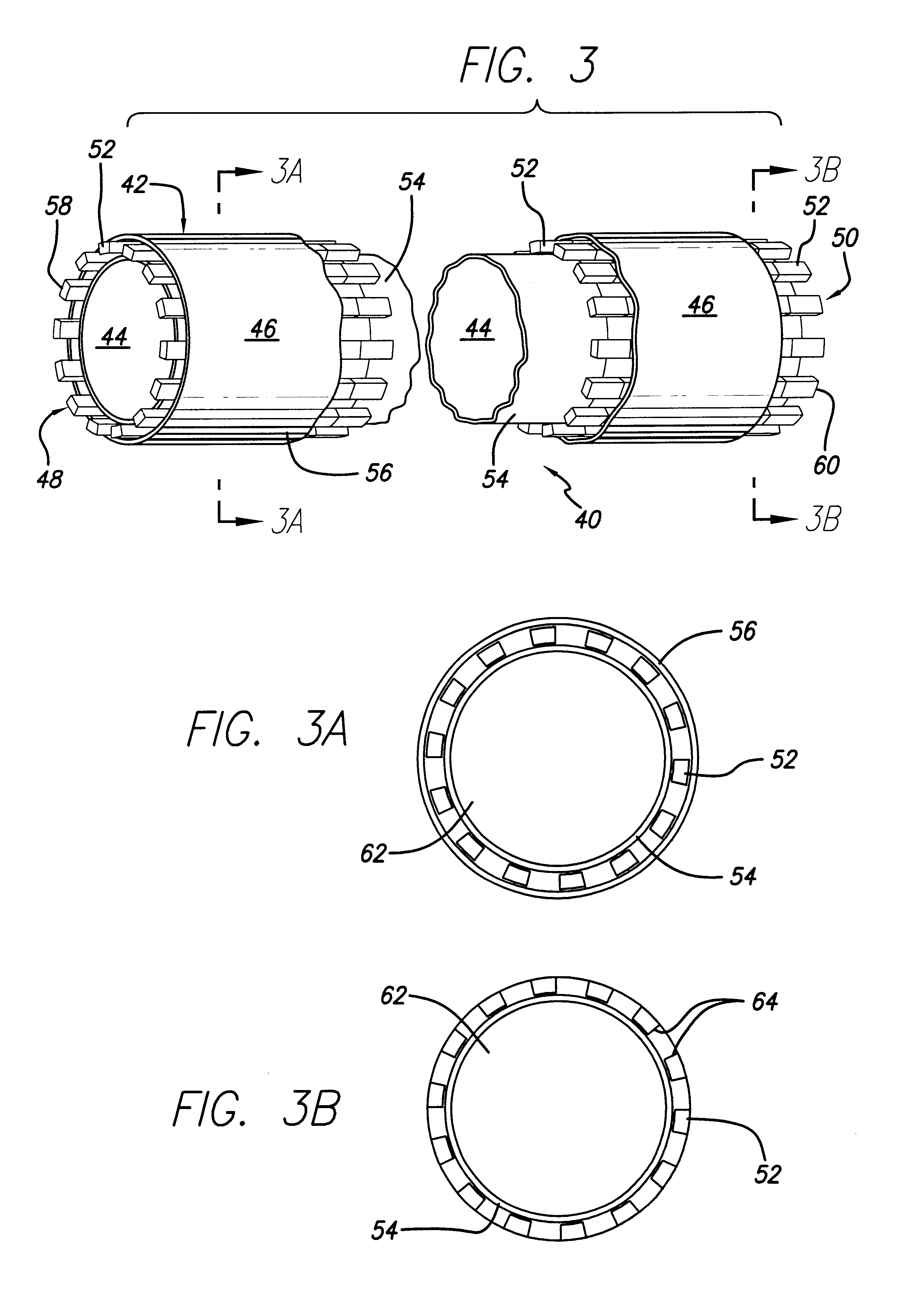
Surgical implant devices and systems including a sheath member
InactiveUS20050177156A1Easy to installImprove clinical outcomesSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisAnatomical structuresSpinal column
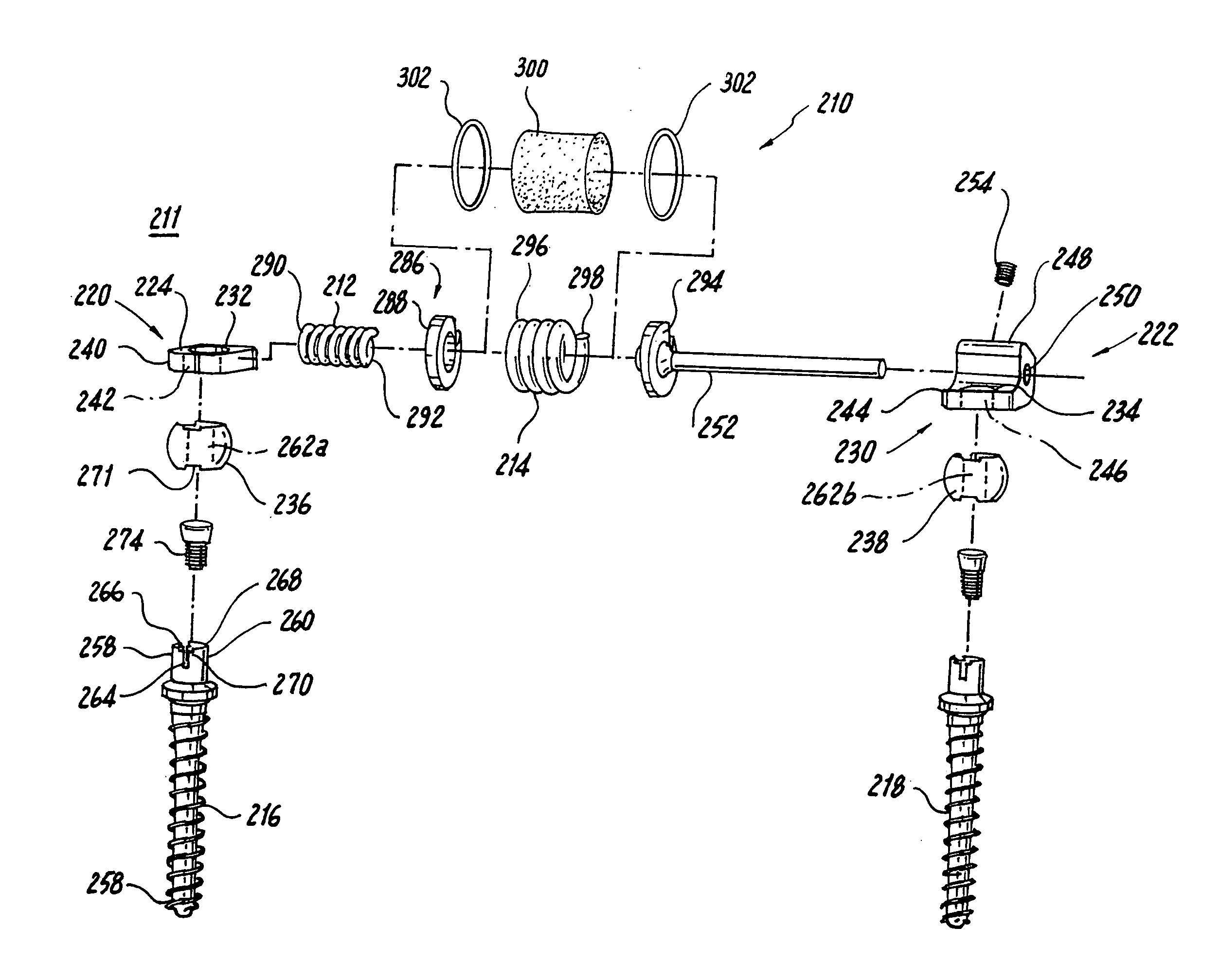
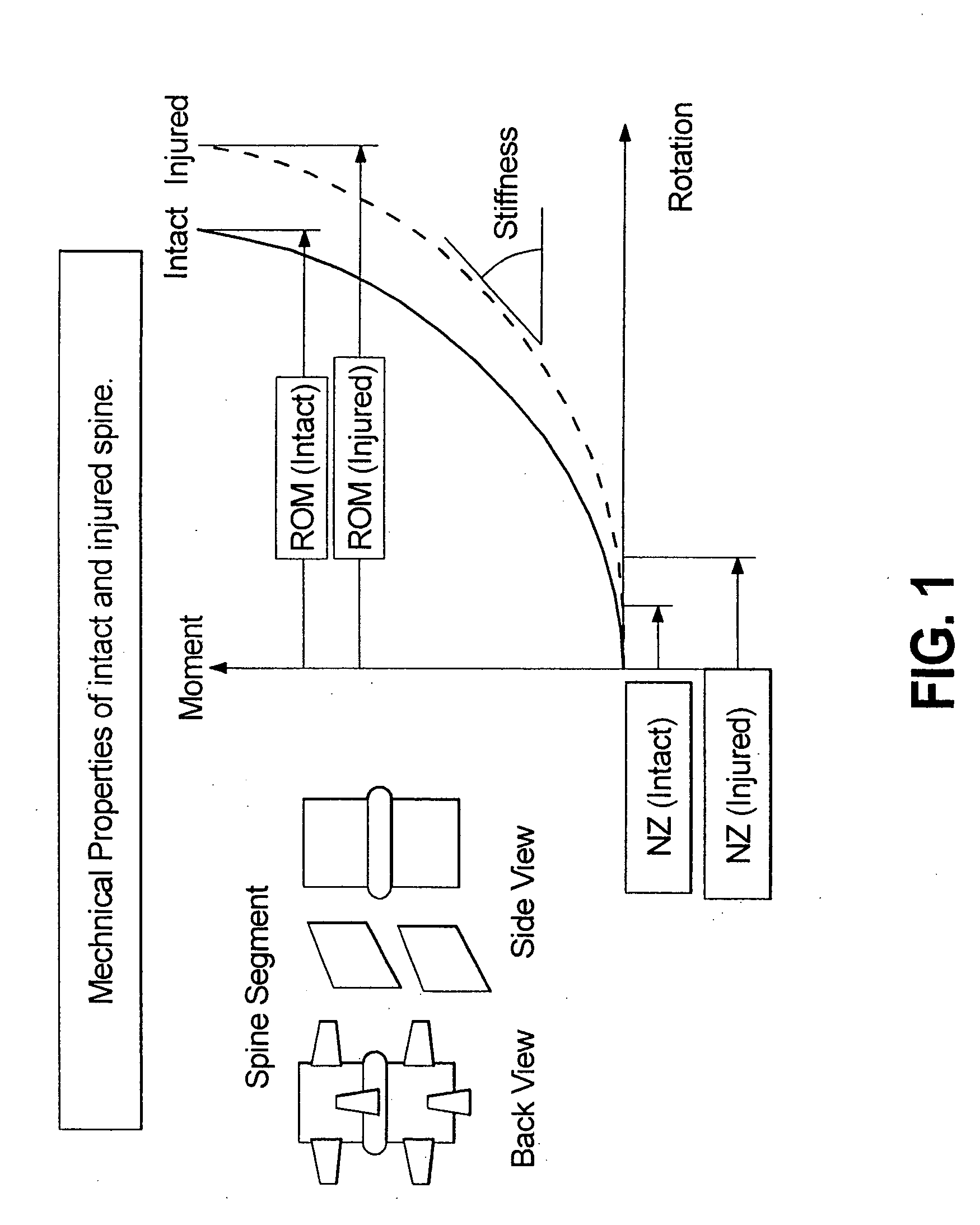
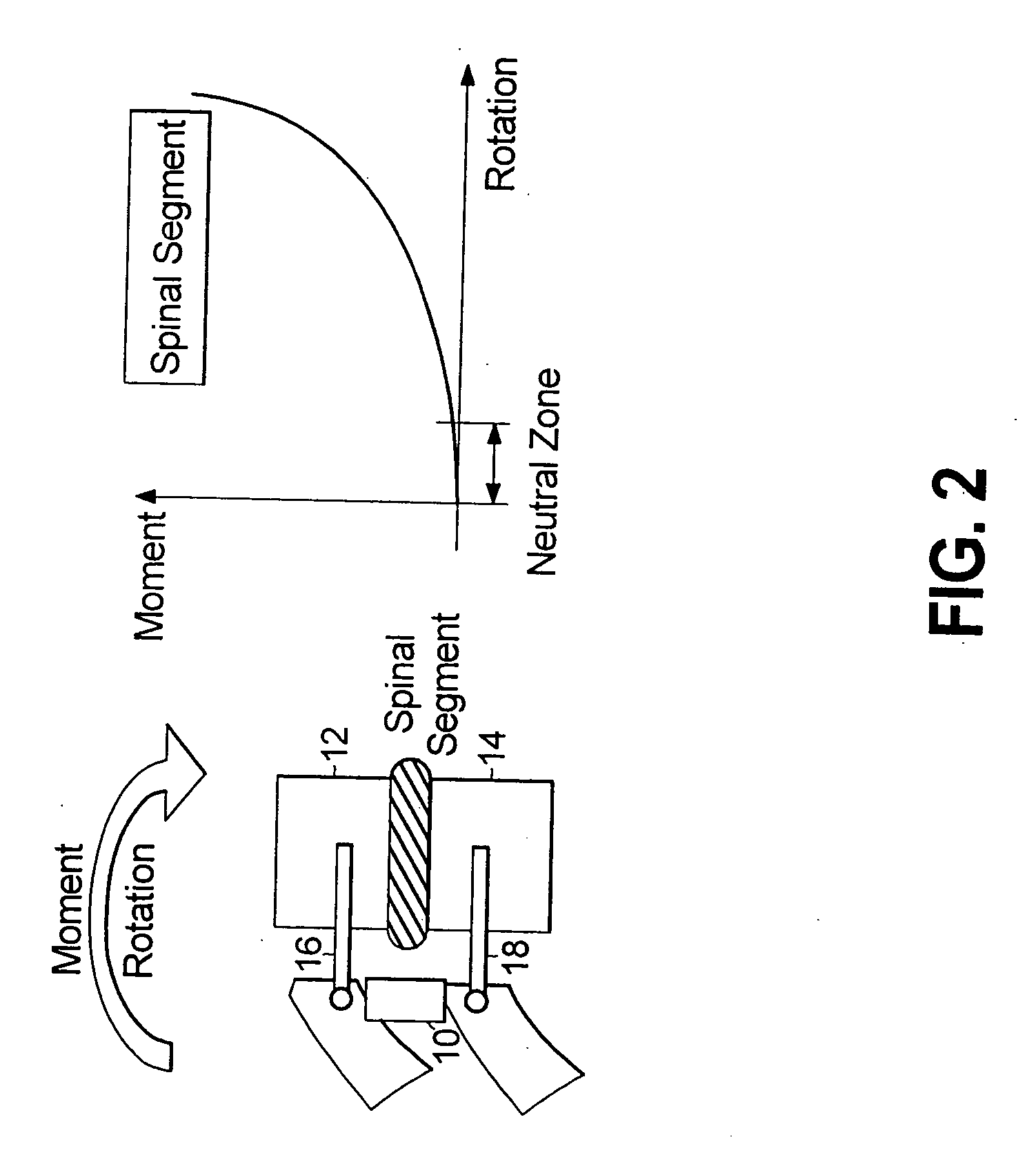
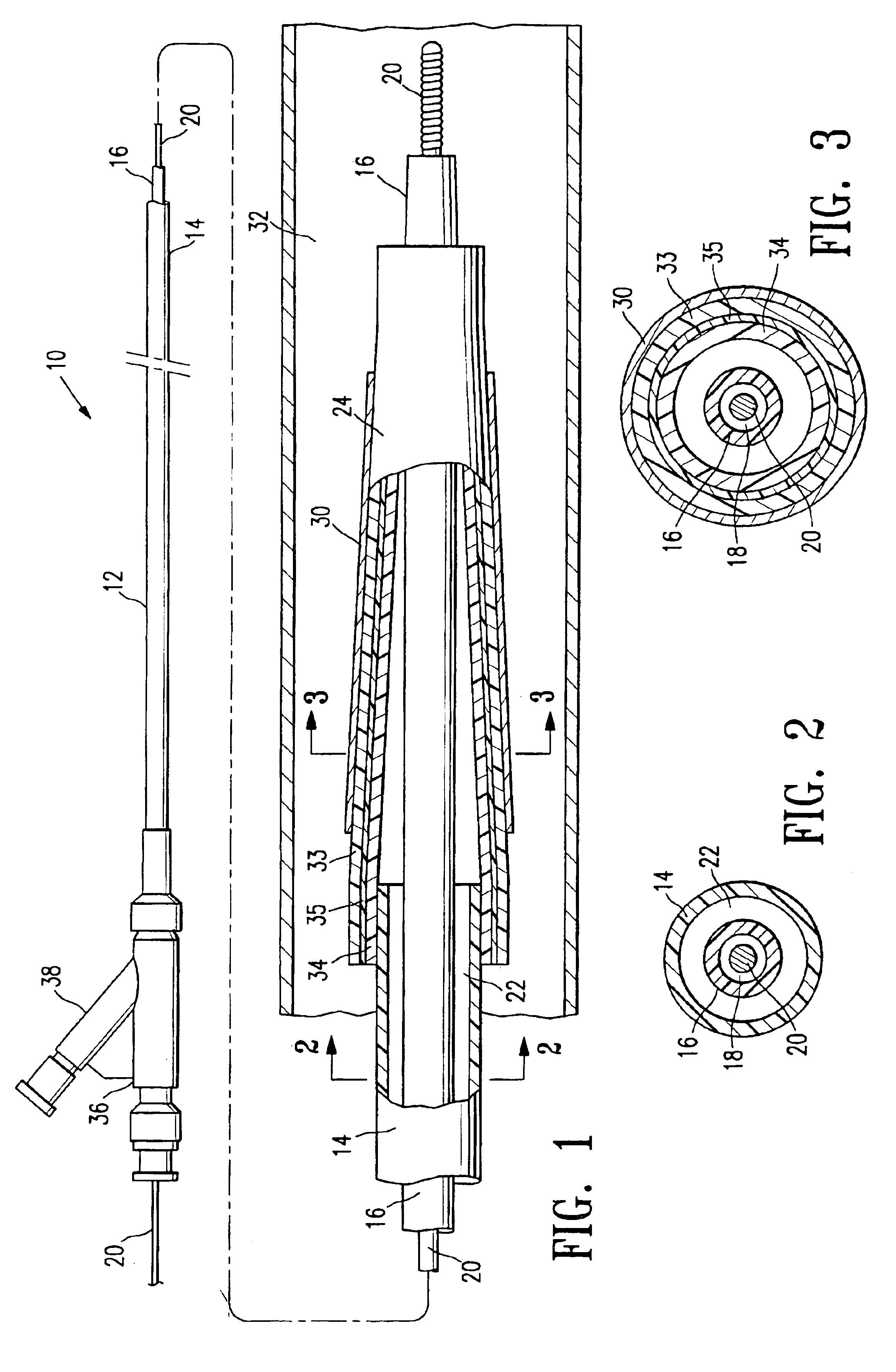
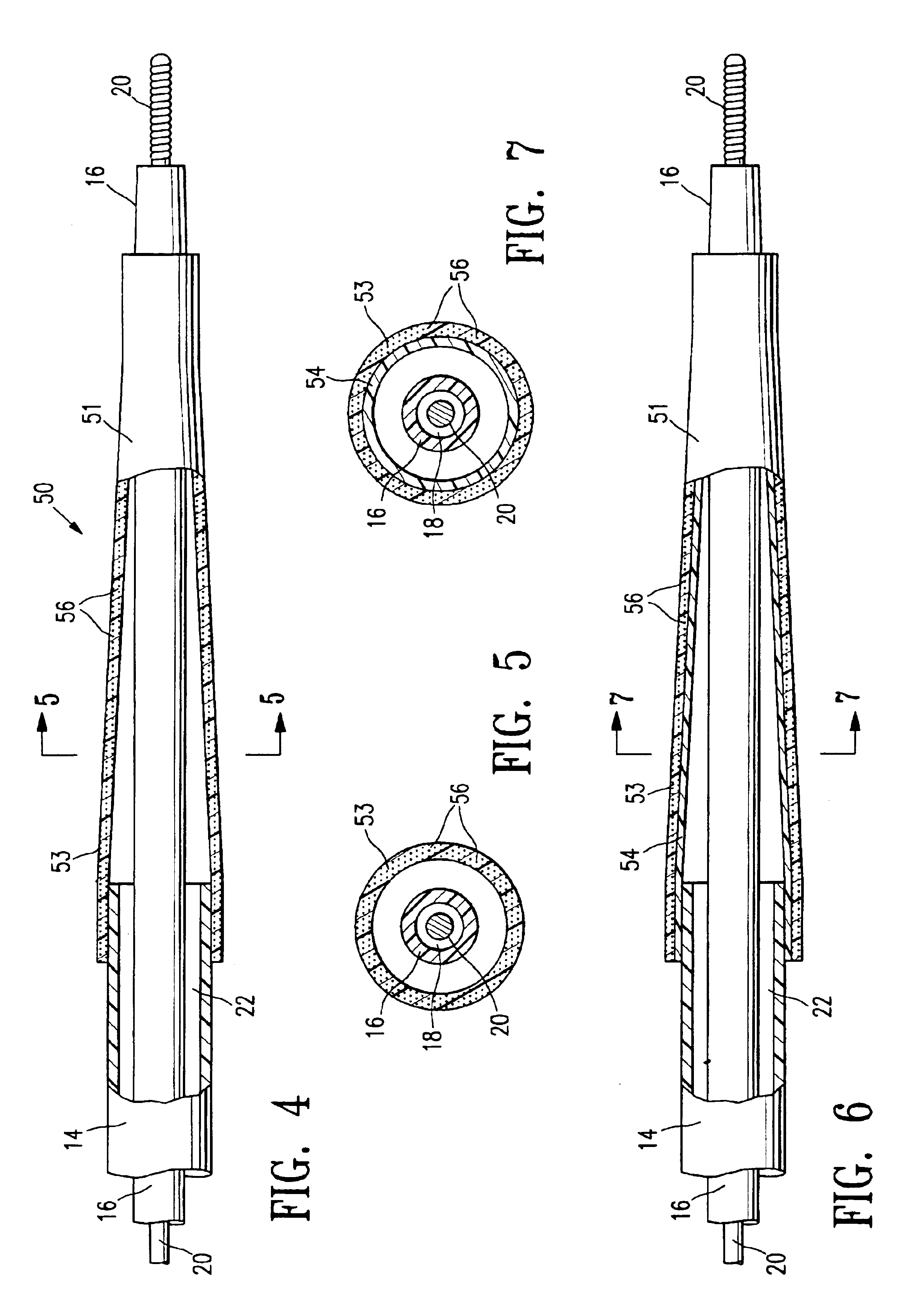
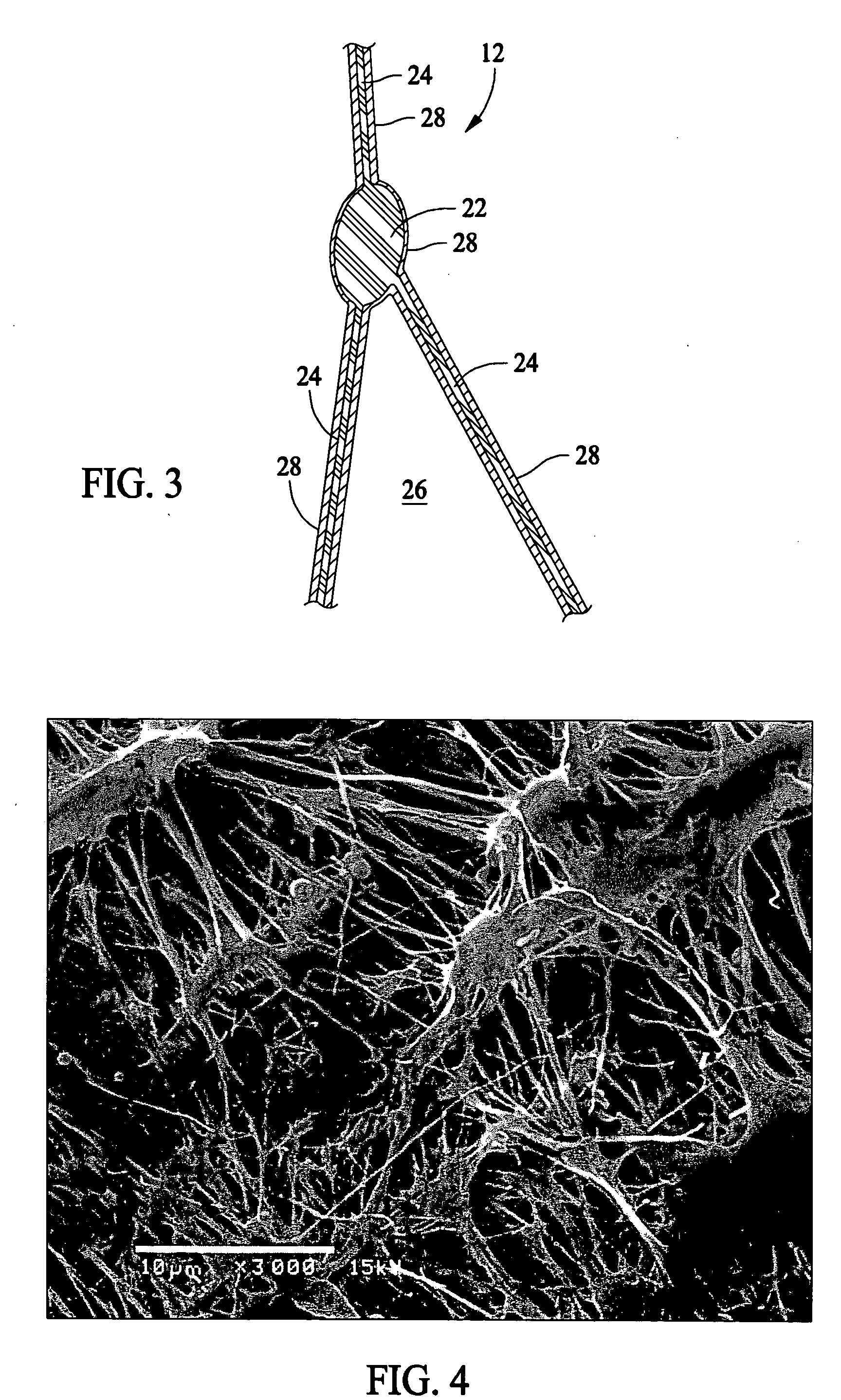
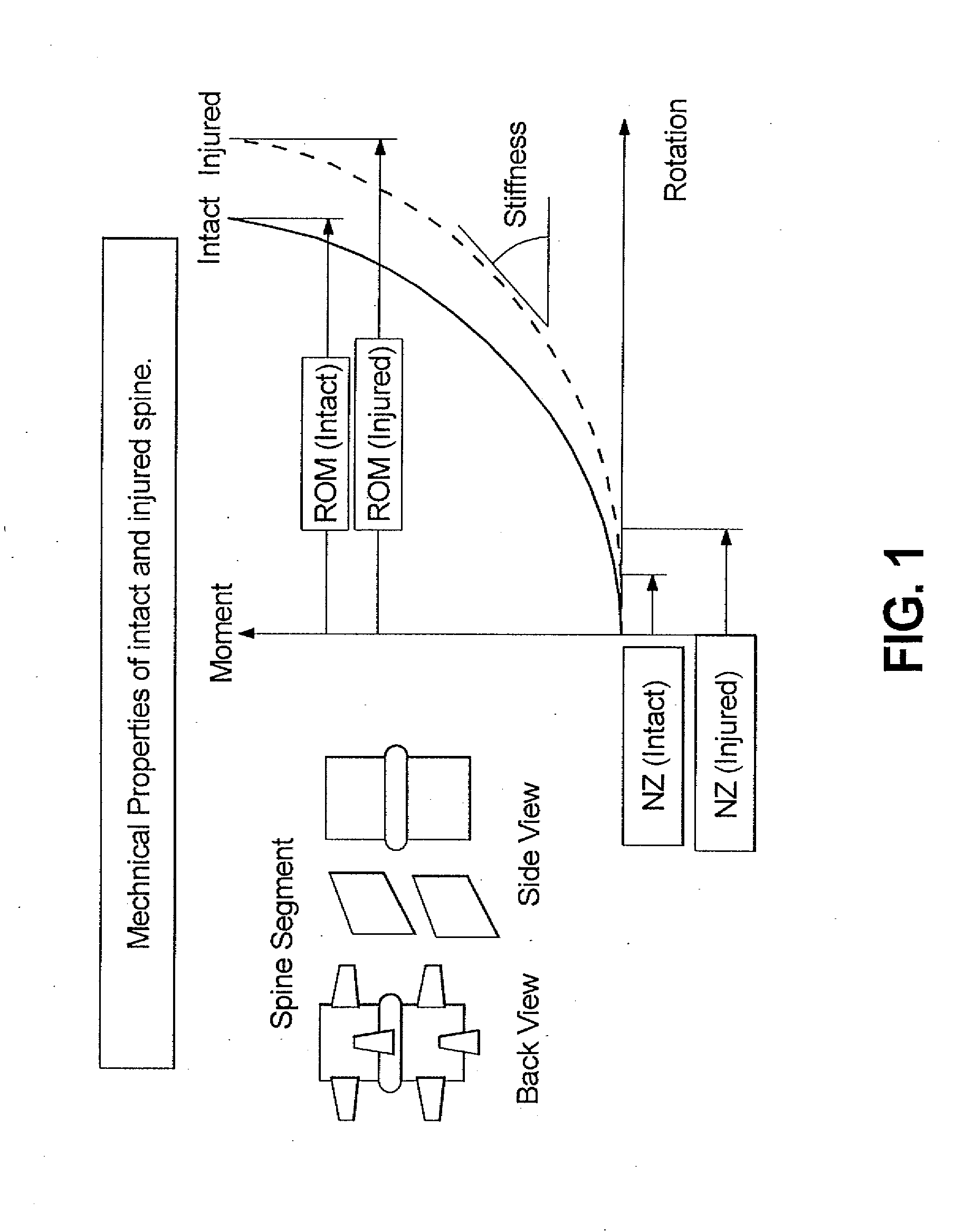
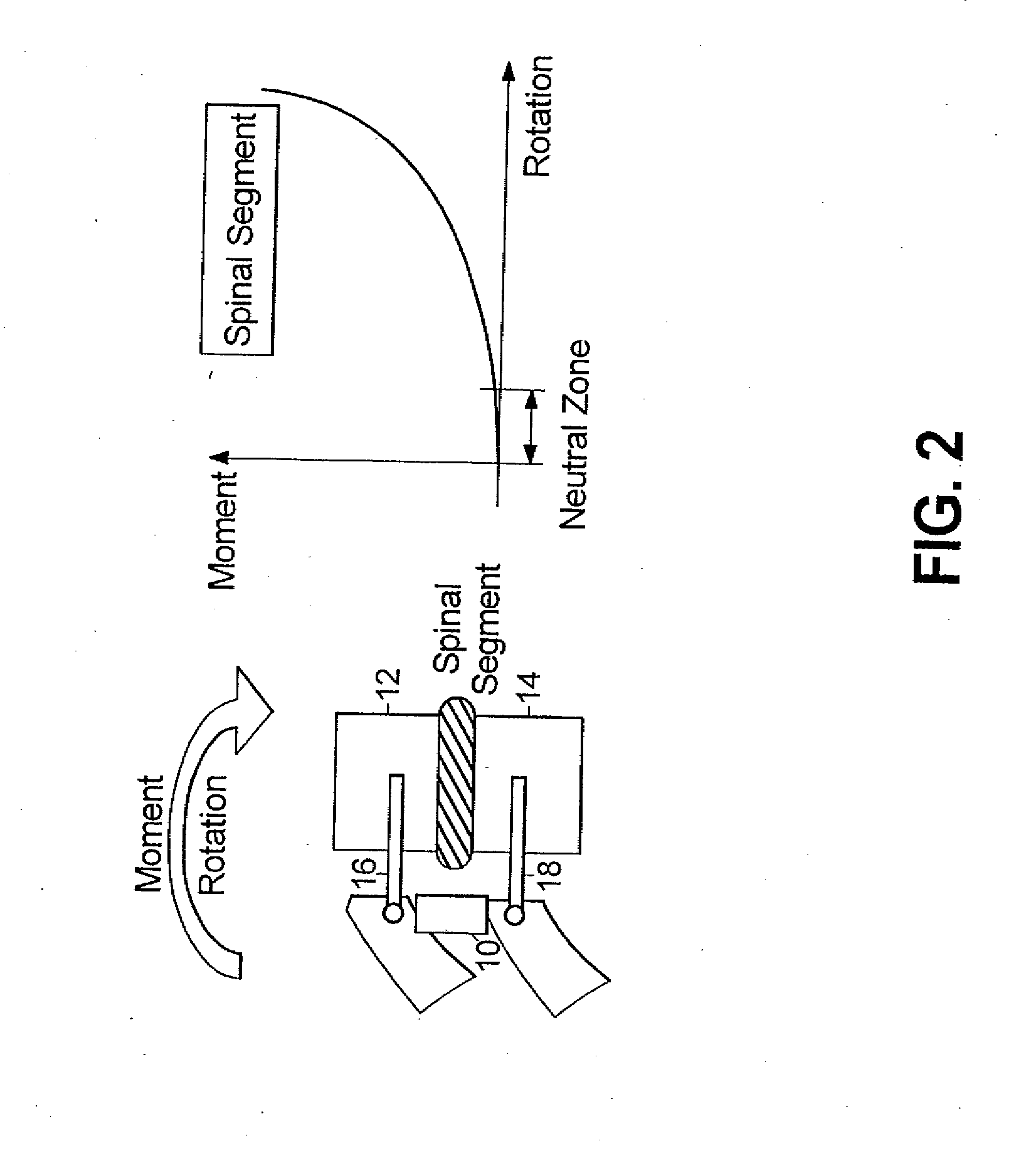
A surgical implant is provided that includes first and second abutment surfaces between which are positioned a force imparting mechanism. A sheath is positioned between the first and second abutment surfaces, and surrounds the force imparting mechanism. The sheath is fabricated from a material that accommodates relative movement of the abutment members, while exhibiting substantially inert behavior relative to surrounding anatomical structures. The sheath is generally fabricated from expanded polytetrafluoroethylene, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, a copolymer of polycarbonate and a urethane, or a blend of a polycarbonate and a urethane. The force imparting member may include one or more springs, e.g., a pair of nested springs. The surgical implant may be a dynamic spine stabilizing member that is advantageously incorporated into a spine stabilization system to offer clinically efficacious results.
Owner:RACHIOTEK
Encapsulated stent
InactiveUS6383214B1Reduce thrombosisEasy to separateStentsBlood vesselsStent graftingPolytetrafluoroethylene
An encapsulated stent having a stent or structural support layer sandwiched between two biocompatible flexible layers. One preferred embodiment has a stent cover which includes a tubular shaped stent that is concentrically retained between two tubular shaped grafts comprised of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene. Another preferred embodiment has a stent graft which includes at least one stent sandwiched between the ends of two tubular shaped grafts wherein at least a portion of the grafts are unsupported by the stent. Still another embodiment includes an articulating stented graft which includes a plurality of stents spaced apart from one another at a predetermined distance wherein each stent is contained between two elongated biocompatible tubular members. The graft / stent / graft assemblies all have inseparable layers.
Owner:BARD PERIPHERAL VASCULAR
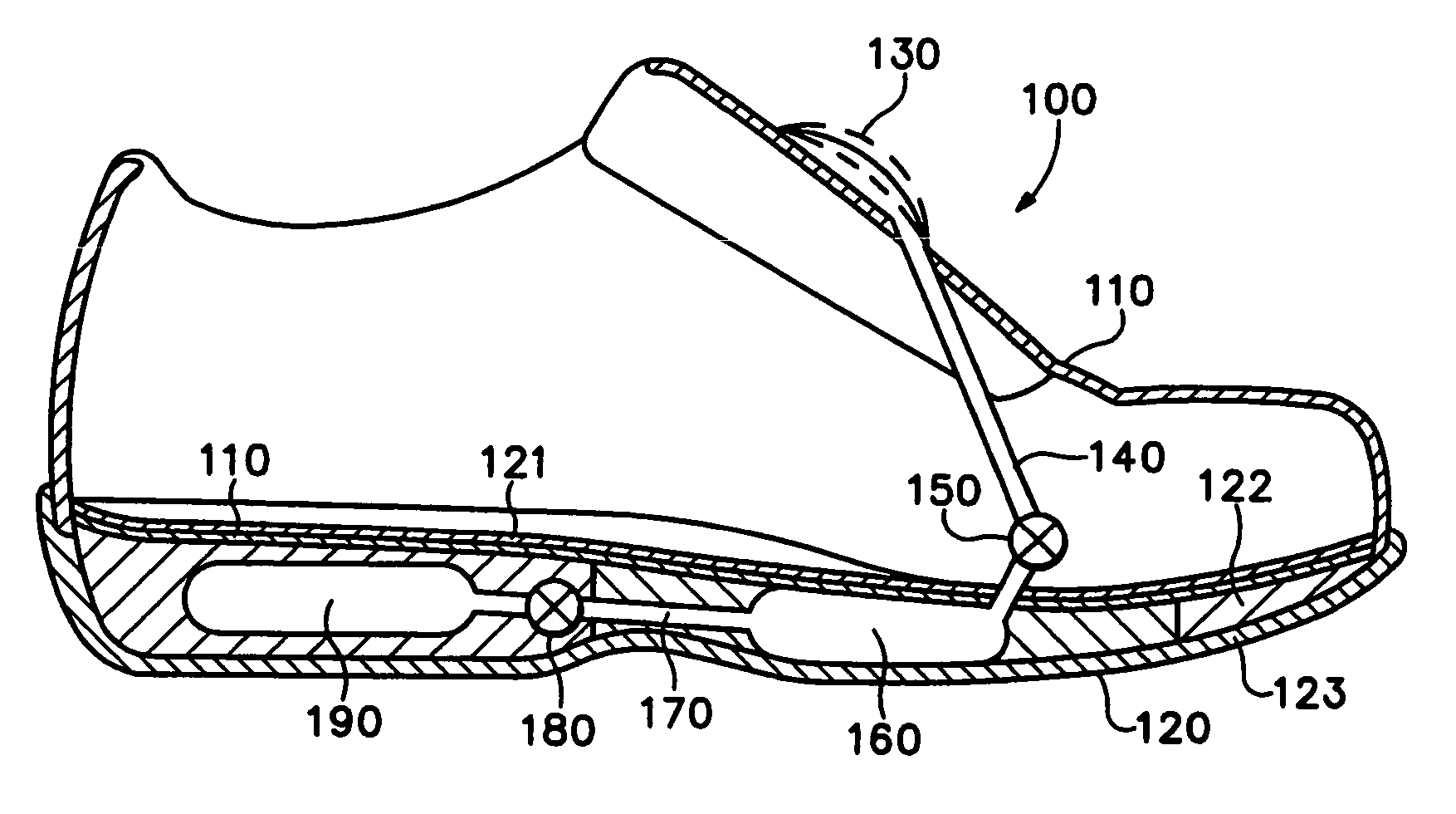
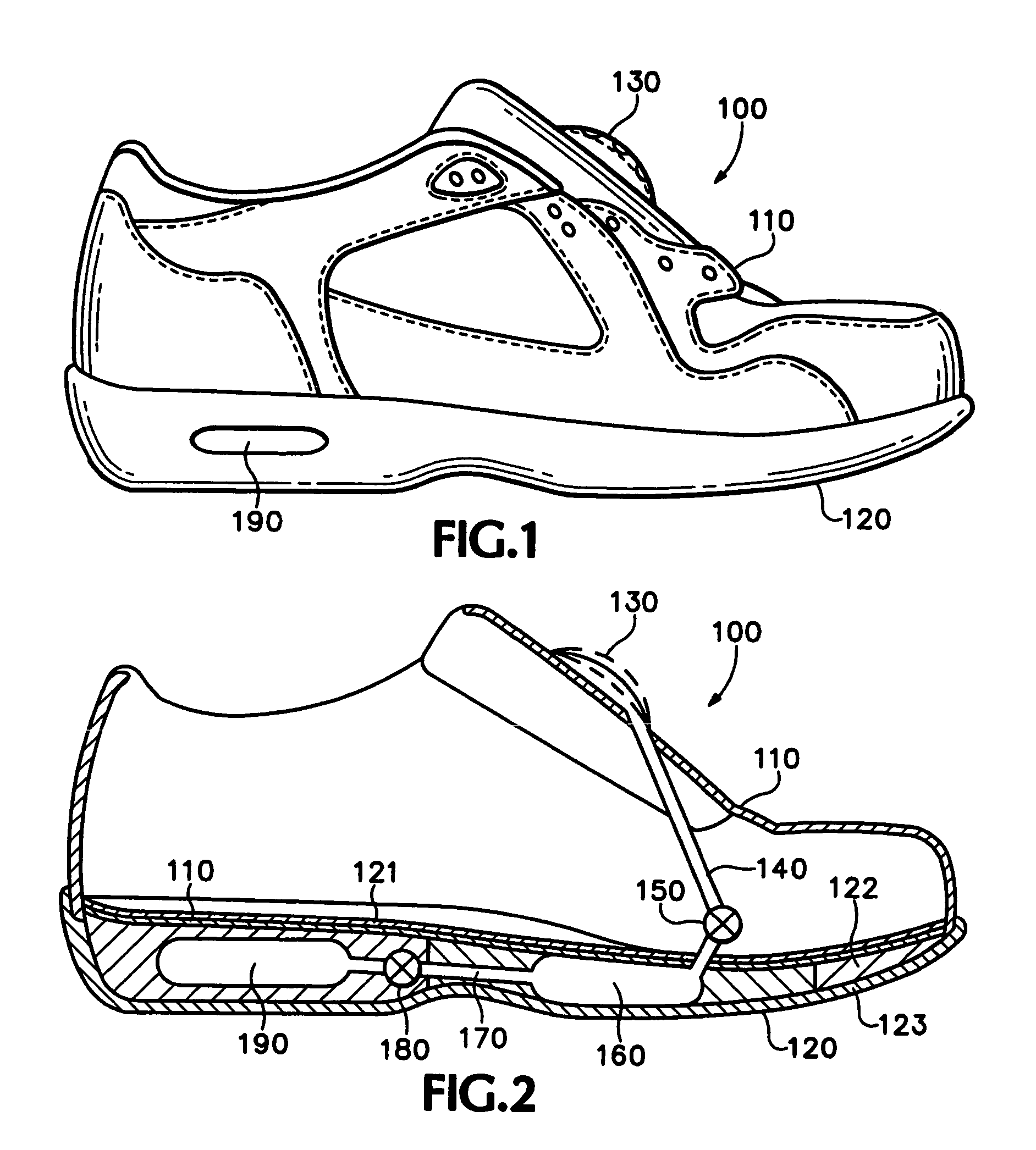
Footwear with bladder filter
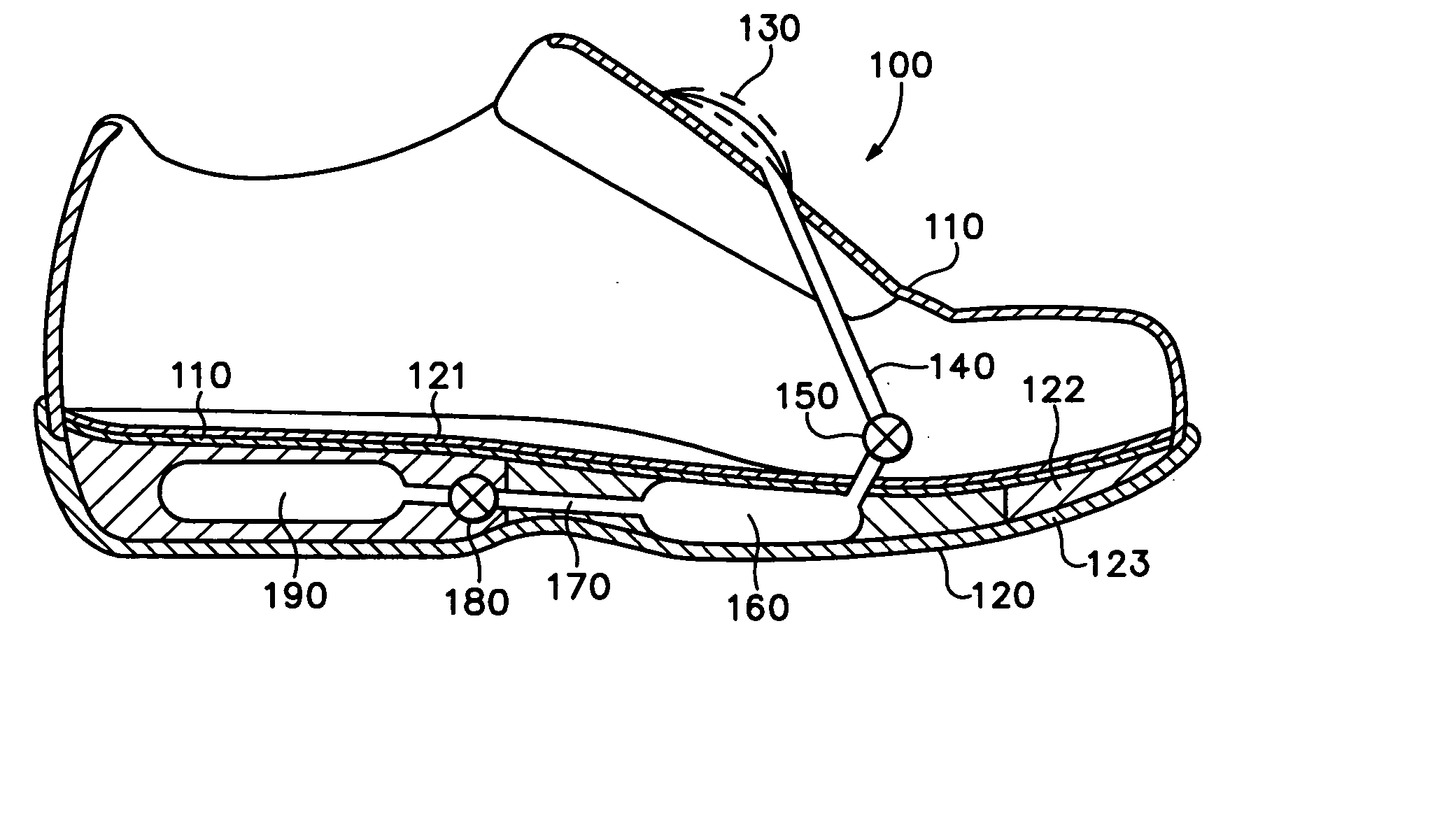
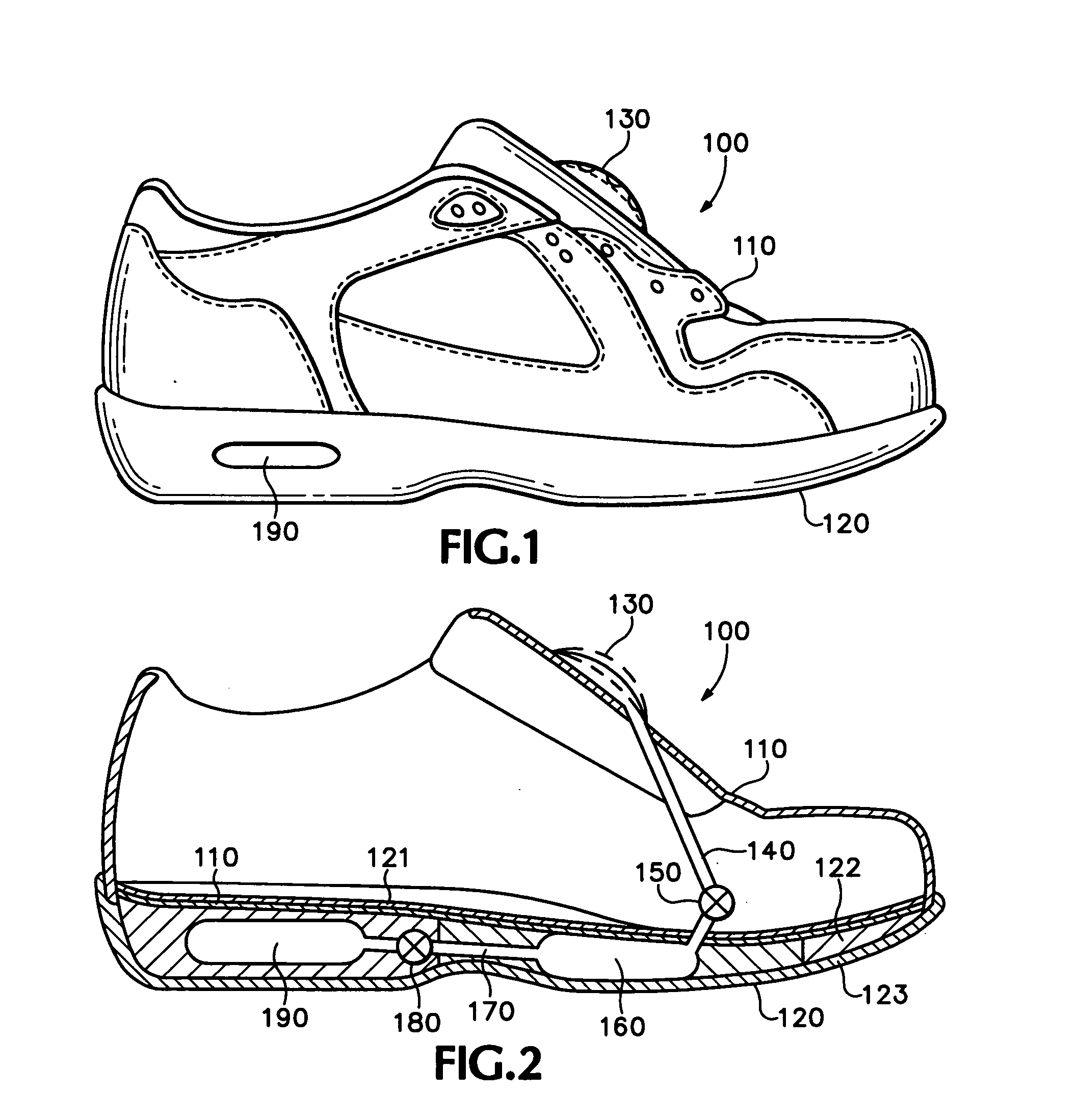
An article of athletic footwear having an air-filled bladder disposed in a sole structure is disclosed. The air-filled bladder is in fluid communication with ambient air through a filter that permits ambient air to enter the bladder but restricts liquids and particulates from entering the bladder. In operation, the filter and bladder may be portions of a bladder system that absorb shock when the footwear contacts a playing surface. Alternatively, the filter and bladder may be portions of a bladder system that ventilates the interior of the footwear. The filter may be formed of a material such as expanded polytetrafluoroethylene that is attached to a carrier.
Owner:NIKE INC
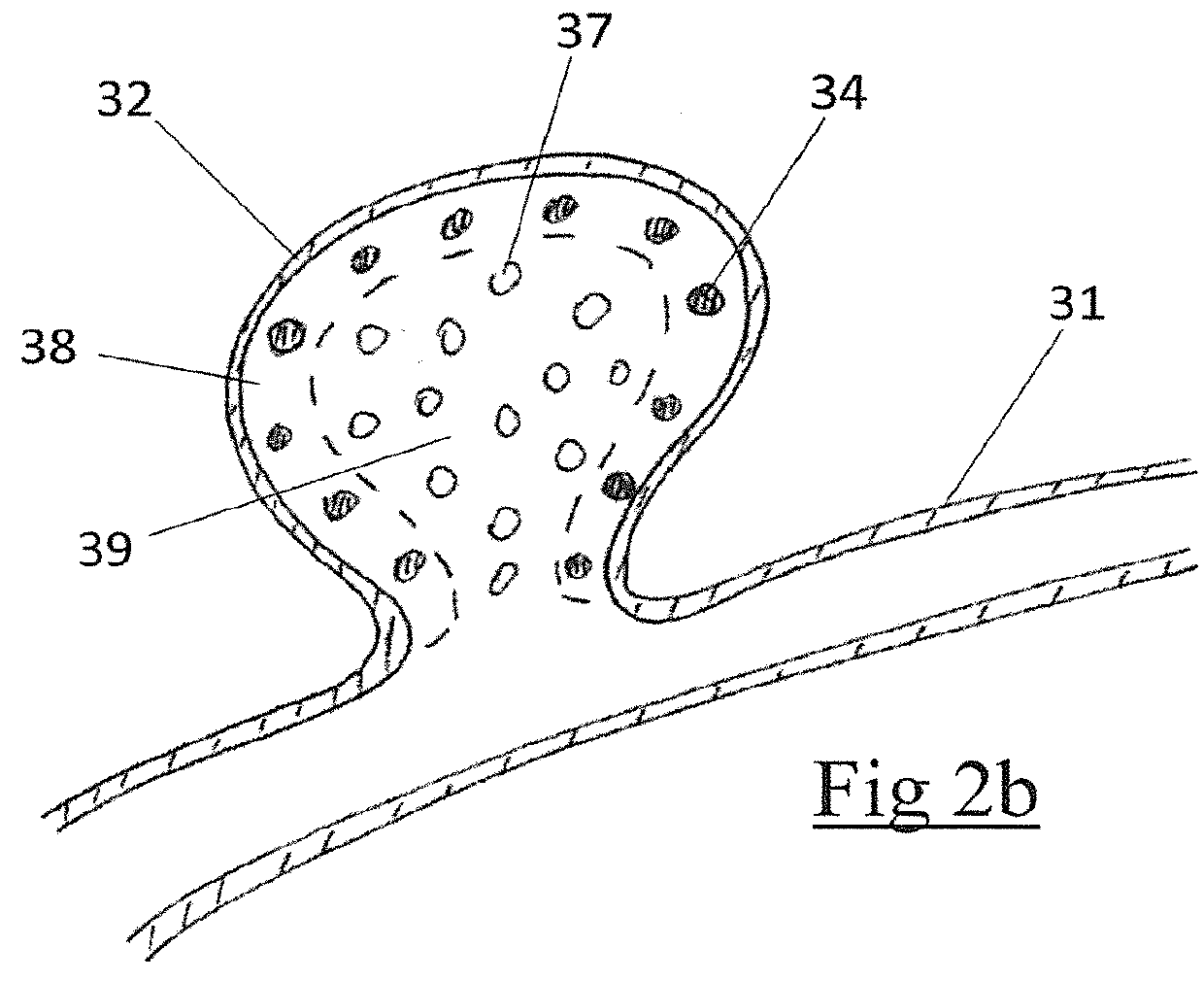
Encapsulation device and methods of use
An encapsulation device having an expandable, porous body with a cavity, the body having a sealed end and a sealable end, where the body is configured to receive one or more fluids through a port in the sealable end, the body is configured to expand to conform to a shape of a target, and where the sealable end may be sealed to prevent leakage into the body, and a method if using the encapsulation device, is disclosed. The body may comprise porous membrane including expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE), polyester fiberfill, metal / polymer mesh, and perforated or porous polymer / metal. The target may include a location within the human body. The port in the sealable end is configured to receive a first fluid into the cavity to expand the body to conform to the shape of the target, and the port is further configured to receive a second fluid into the cavity which displaces the first fluid by diffusing the first fluid through the pores in the body and which cures (such as, by an ultraviolet light source) to secure the body to the target. Optionally, the introduction of the second fluid may be unnecessary when the first fluid includes the desired filler material for the encapsulation device.
Owner:DEBEER NICHOLAS
DEVICE AND METHOD FOR ENDOVASCULAR TREATMENT OF ANEURYSMS USING EMBOLIC ePTFE
InactiveUS20160066921A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismDilatorsEndovascular treatmentConnective tissue
An embolic occlusion device for the treatment of aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations comprises expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE). The ePTFE permits ingrowth of cells with connective tissue deposition to promote adherence of the aneurysm wall to the embolic device thereby preventing continued growth or re-growth of the aneurysm as well as blocking blood flow into an aneurysm. An occlusion device is also described which comprises an embolic element and a polymeric pre-formed component.
Owner:NEURAVI
Catheter balloon formed of ePTFE and a diene polymer
InactiveUS6946173B2Improve performanceImprove adhesionEnvelopes/bags making machineryMouldsElastomerTetrafluoroethylene
A catheter balloon formed of a polymeric material such as expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) bonded to a second layer formed of a low tensile set polymer and / or impregnated with a low tensile set polymer. In a presently preferred embodiment, the low tensile set polymer is a silicone-polyurethane copolymer elastomer or a diene polymer elastomer. The low tensile set polymer has high strength, low modulus, high elongation, and low tensile set. The diene or silicone-polyurethane has a low tensile set, which facilitates deflation of the balloon to a low profile deflated configuration. One aspect of the invention provides improved attachment of the diene to the ePTFE. In one embodiment, the second layer is formed of a diene mixed with a bonding promoter such as a vulcanizing agent which is covalently bonded to the diene.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
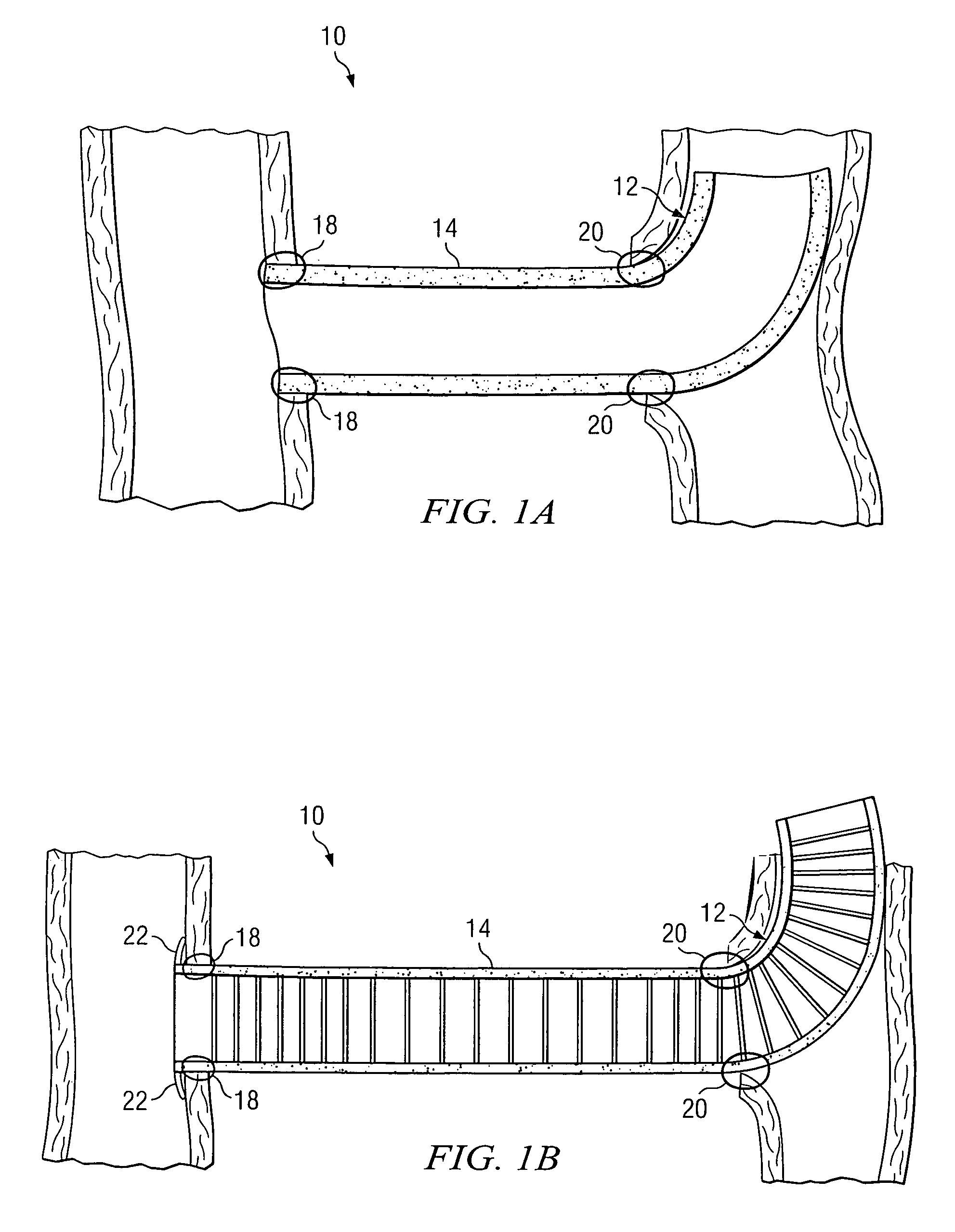
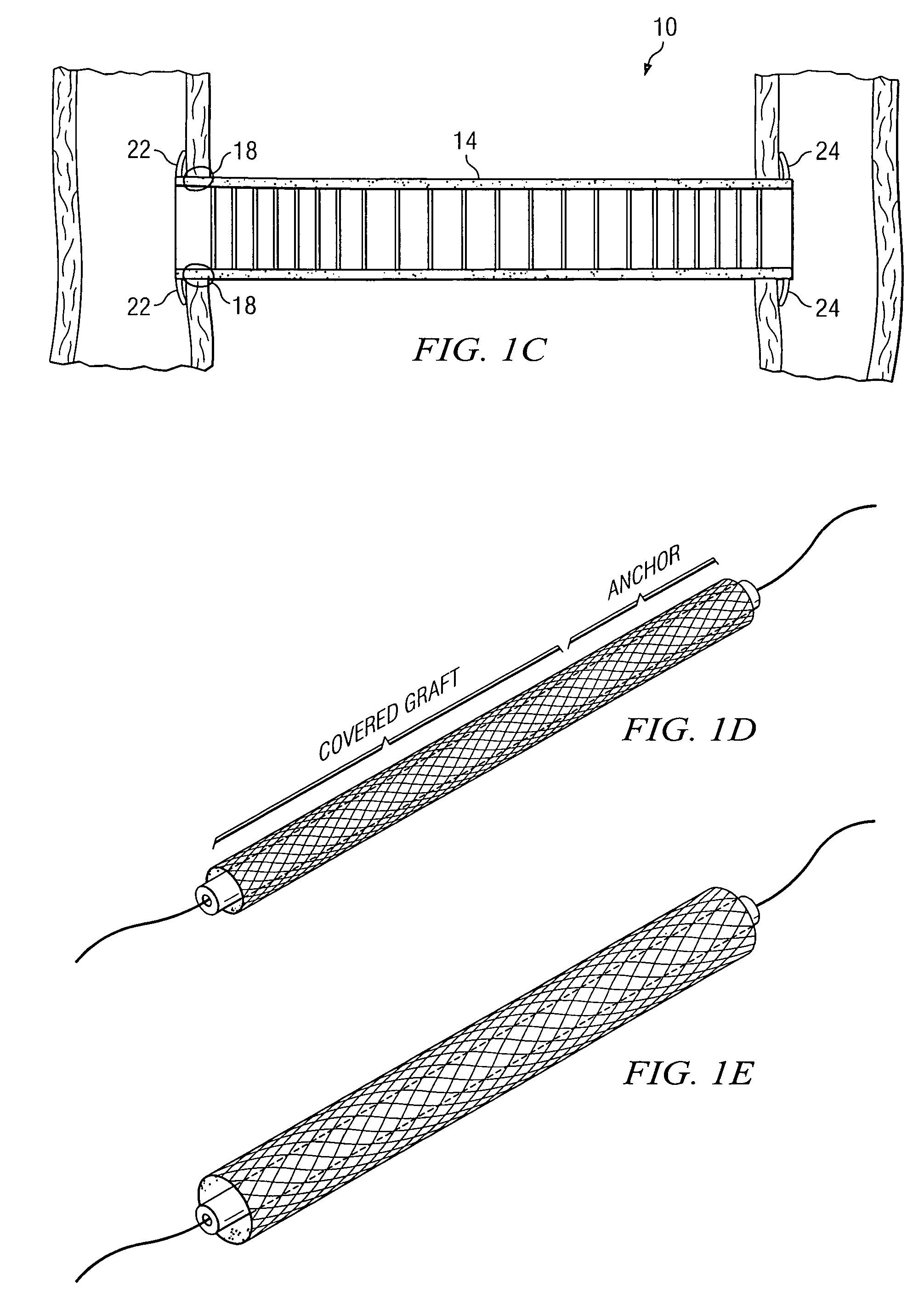
System and method for providing a graft in a vascular environment
InactiveUS20080009781A1Easy to moveMinimal stenosisStentsEar treatmentBiodegradable scaffoldCatheter
An apparatus is provided that includes a graft for coupling two vascular conduits within a patient. The graft includes: 1) an anchor system that forms an arc at one end of the conduits; and 2) a body element coupled to the anchor system. The anchor system comprises a biodegradable stent. In particular embodiments, portions of the graft are either self-expandable or balloon-expandable. In still other embodiments, anchor system includes NITINOL and the anchor system is substantially self-sealing at one end of the conduits. In one embodiment, the body element comprises polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (EPTFE). In yet other embodiments, the body element includes either a gelatinous or an elastomeric coating disposed on its surface.
Owner:GRAFTECH INT HLDG INC
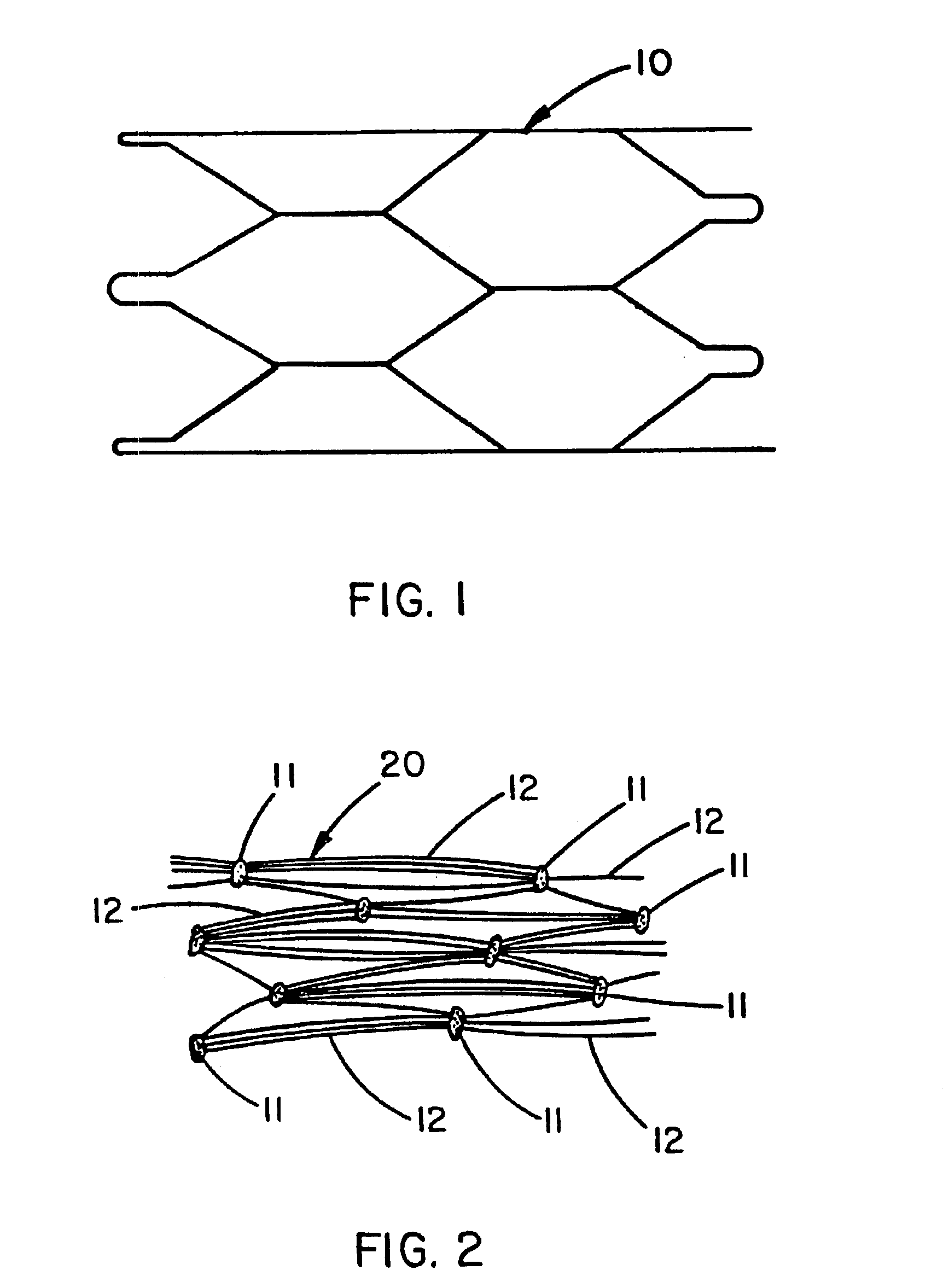
Lattice
ActiveUS20130131780A1Significant differencePulsatile complianceStentsLigamentsElastomerSurgical operation
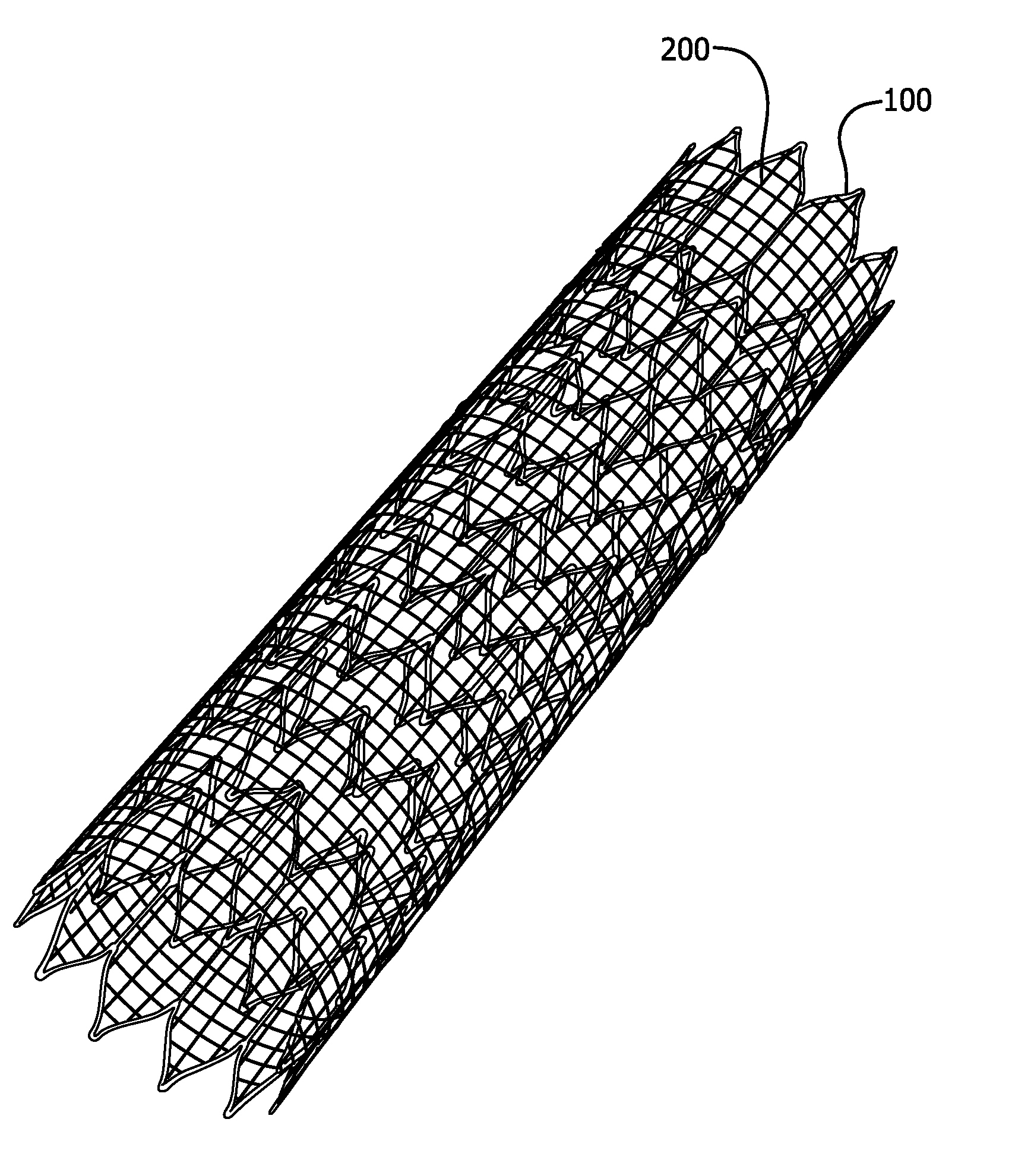
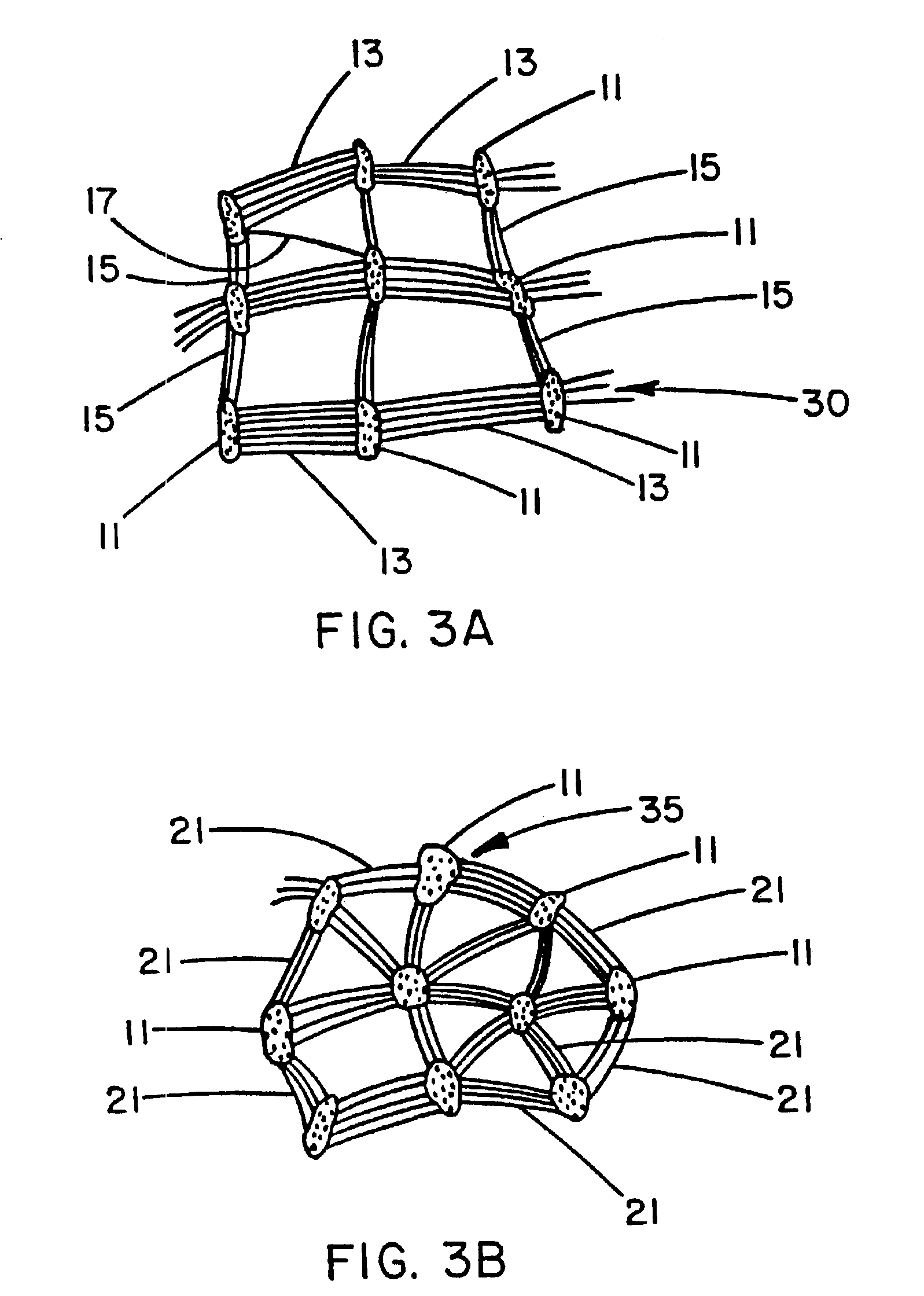
The invention relates to medical devices and methods of using them. The devices are prostheses which can be percutaneously deliverable with (or on) an endovascular catheter or via other surgical or other techniques and then expanded. The prostheses are configured to have a lattice resistant to dilation and creep, which is defined by a plurality of openings. The prosthesis may also optionally have a stent disposed proximal to the lattice. In exemplary embodiments, the fluoropolymer is expanded polytetrafluoroethylene. The composite materials exhibit high elongation while substantially retaining the strength properties of the fluoropolymer membrane. In at least one embodiment, the lattice is made of a composite material that includes a least one fluoropolymer membrane including serpentine fibrils and an elastomer. A lattice including a generally tubular member formed of a composite material including a least one fluoropolymer membrane containing serpentine fibrils and an elastomer is also provided.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Article of footwear incorporating a fluid system
An article of athletic footwear having an air-filled bladder disposed in a sole structure is disclosed. The air-filled bladder is in fluid communication with ambient air through a filter that permits ambient air to enter the bladder but restricts liquids and particulates from entering the bladder. In operation, the filter and bladder may be portions of a bladder system that absorb shock when the footwear contacts a playing surface. Alternatively, the filter and bladder may be portions of a bladder system that ventilates the interior of the footwear. The filter may be formed of a material such as expanded polytetrafluoroethylene that is attached to a carrier.
Owner:NIKE INC
Lattice
The invention relates to medical devices and methods of using them. The devices are prostheses which can be percutaneously deliverable with (or on) an endovascular catheter or via other surgical or other techniques and then expanded. The prostheses are configured to have a lattice resistant to dilation and creep, which is defined by a plurality of openings. The prosthesis may also optionally have a stent disposed proximal to the lattice. In exemplary embodiments, the fluoropolymer is expanded polytetrafluoroethylene. The composite materials exhibit high elongation while substantially retaining the strength properties of the fluoropolymer membrane. In at least one embodiment, the lattice is made of a composite material that includes a least one fluoropolymer membrane including serpentine fibrils and an elastomer. A lattice including a generally tubular member formed of a composite material including a least one fluoropolymer membrane containing serpentine fibrils and an elastomer is also provided.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Articles including expanded polytetrafluoroethylene membranes with serpentine fibrils
InactiveUS20130183515A1High elongationSynthetic resin layered productsCeramic shaping apparatusElastomerFiber
Articles including expanded fluoropolymer membranes having serpentine fibrils are provided. The fluoropolymer membranes exhibit high elongation while substantially retaining the strength properties of the fluoropolymer membrane. The membrane may include a fluoropolymer and / or elastomer. Additionally, the article has an elongation in at least one direction of at least about 100% and a matrix tensile strength of at least about 50 MPa. The article may be formed by (1) expanding a dried, extruded fluoropolymer tape in at least one direction to produce an expanded fluoropolymer membrane and (2) retracting the expanded fluoropolymer membrane in at least one direction of expansion by applying heat or by adding a solvent. The application of a tensile force at least partially straightens the serpentine fibrils, thereby elongating the article. The expanded fluoropolymer membrane may include a microstructure of substantially only fibrils. The membranes may be imbibed with an elastomeric material to form a composite.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Articles Including Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Membranes with Serpentine Fibrils and Having a Discontinuous Fluoropolymer Layer Thereon
ActiveUS20130184807A1High elongationIncrease stiffnessDecorative surface effectsLighting elementsFiberTetrafluoroethylene
Articles comprising an expanded polytetrafluoroethylene membrane having serpentine fibrils and having a discontinuous coating of a fluoropolymer thereon are provided. The fluoropolymer may be located at least partially in the pores of the expanded fluoropolymer membrane. In exemplary embodiments, the fluoropolymer is fluorinated ethylene propylene. The application of a tensile force at least partially straightens the serpentine fibrils, thereby elongating the article. The expanded polytetrafluoroethylene membrane may include a microstructure of substantially only fibrils. The articles can be elongated to a predetermined point at which further elongation is inhibited by a dramatic increase in stiffness. In one embodiment, the articles are used to form a covered stent device that requires little force to distend in the radial direction to a first diameter but is highly resistant to further distension to a second diameter (stop point). A large increase in diameter can advantageously be achieved prior to reaching the stop point.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
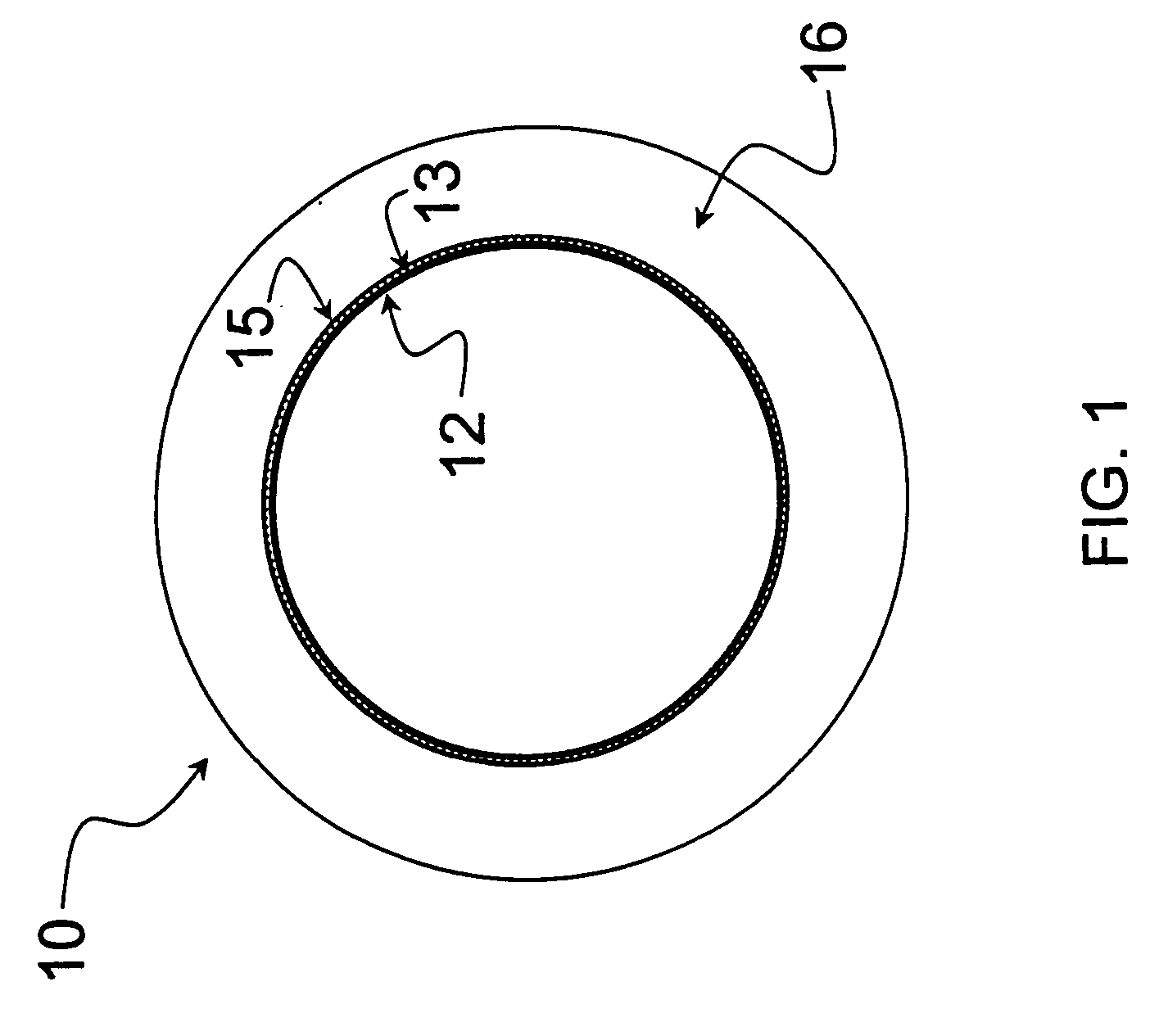
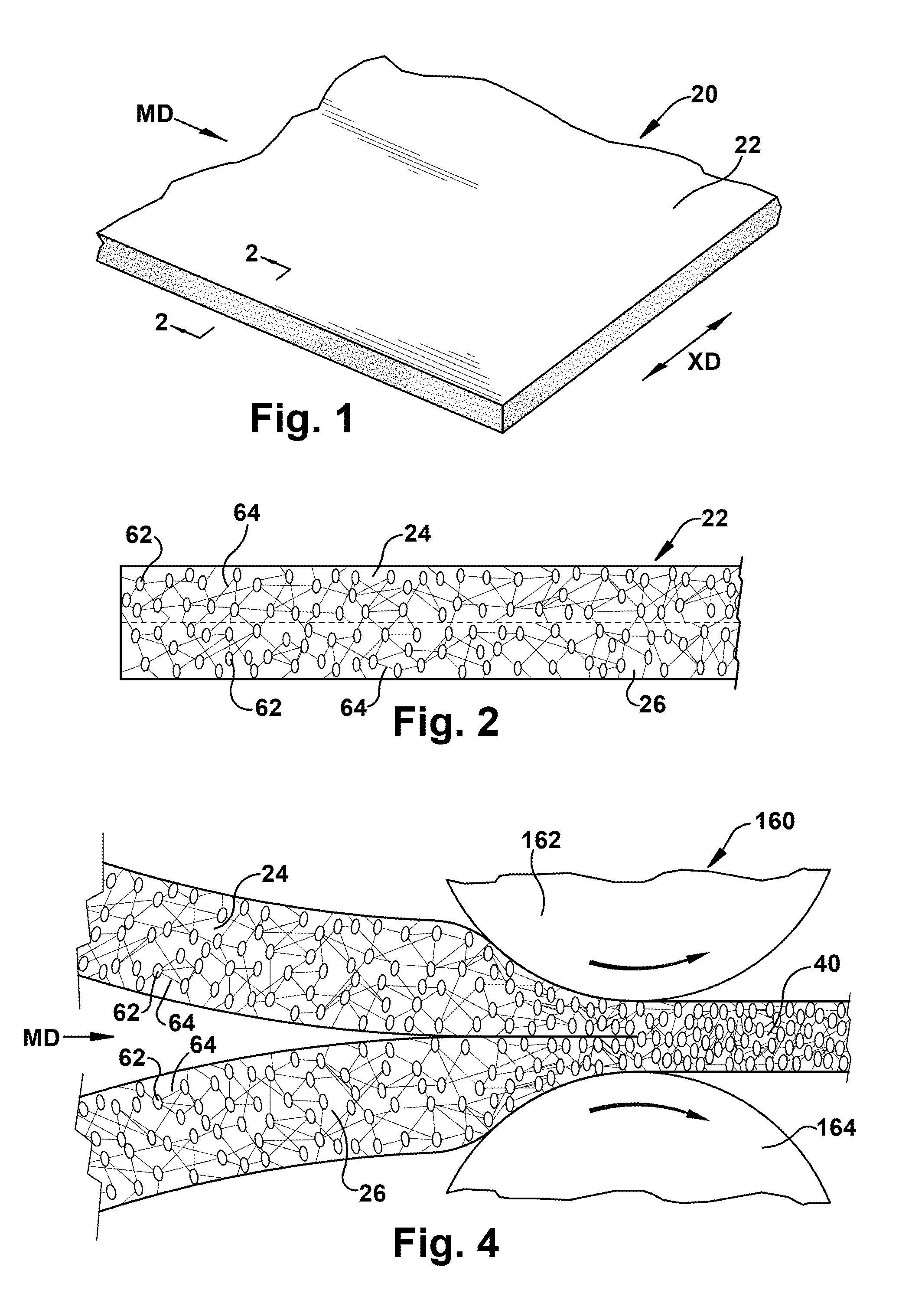
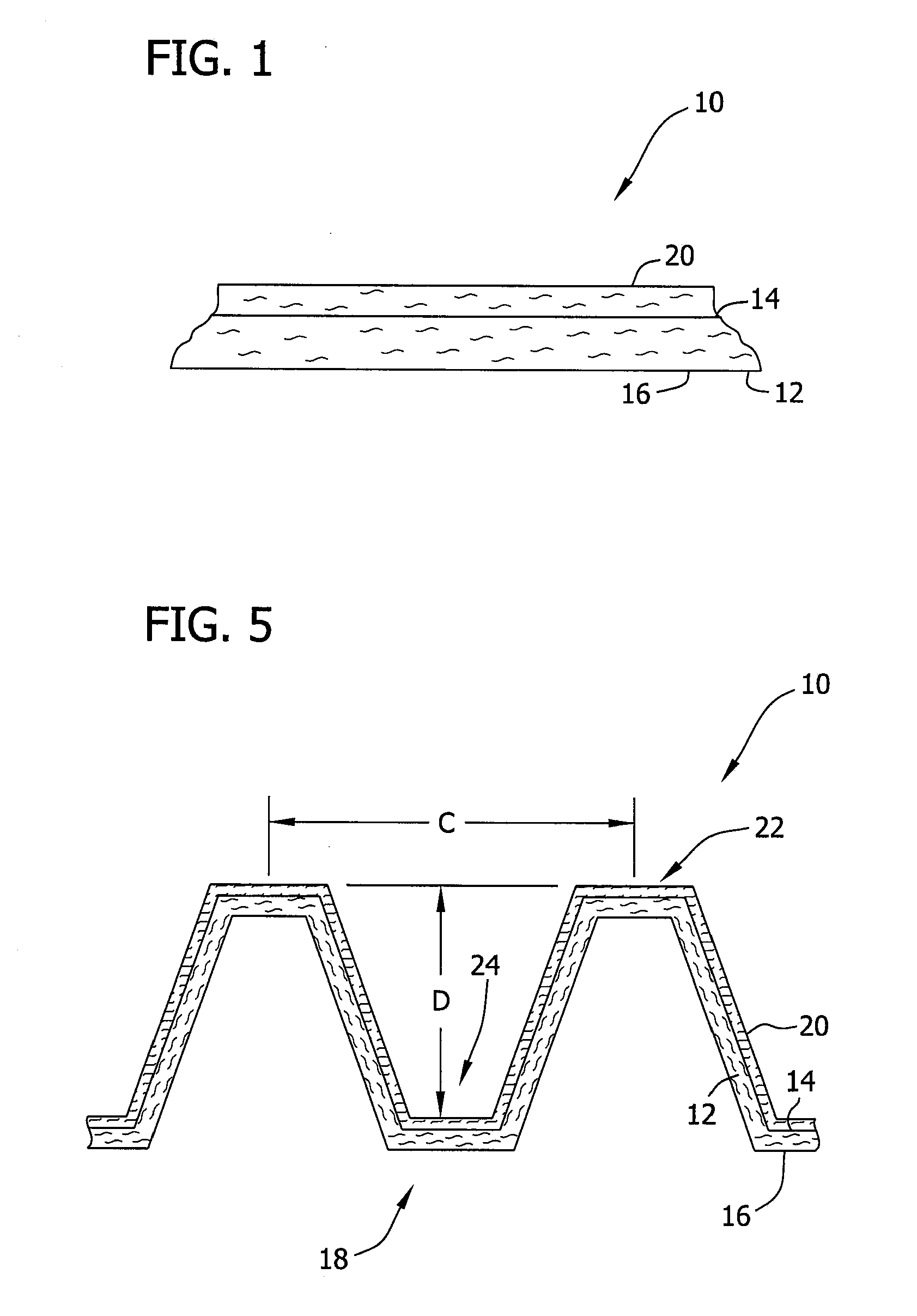
Expanded polytetrafluoroethylene vascular graft with coating
A vascular graft comprised of a tubular polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) sheet is provided. The ePTFE sheet has a substantially uniform coating of bioresorbable gel material, for example gelatin, on a surface thereof. The coating minimises bleeding through suture holes in the ePTFE sheet and provides an increase in longitudinal extensibility.
Owner:VASCUTEK
System and method for providing a graft in a vascular environment
InactiveUS7722665B2Eliminate and greatly reduce disadvantageEliminate and greatly reduce and problemStentsEar treatmentBiodegradable scaffoldCatheter
An apparatus is provided that includes a graft for coupling two vascular conduits within a patient. The graft includes: 1) an anchor system that forms an arc at one end of the conduits; and 2) a body element coupled to the anchor system. The anchor system comprises a biodegradable stent. In particular embodiments, portions of the graft are either self-expandable or balloon-expandable. In still other embodiments, anchor system includes NITINOL and the anchor system is substantially self-sealing at one end of the conduits. In one embodiment, the body element comprises polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (EPTFE). In yet other embodiments, the body element includes either a gelatinous or an elastomeric coating disposed on its surface.
Owner:GRAFTECH INT HLDG INC
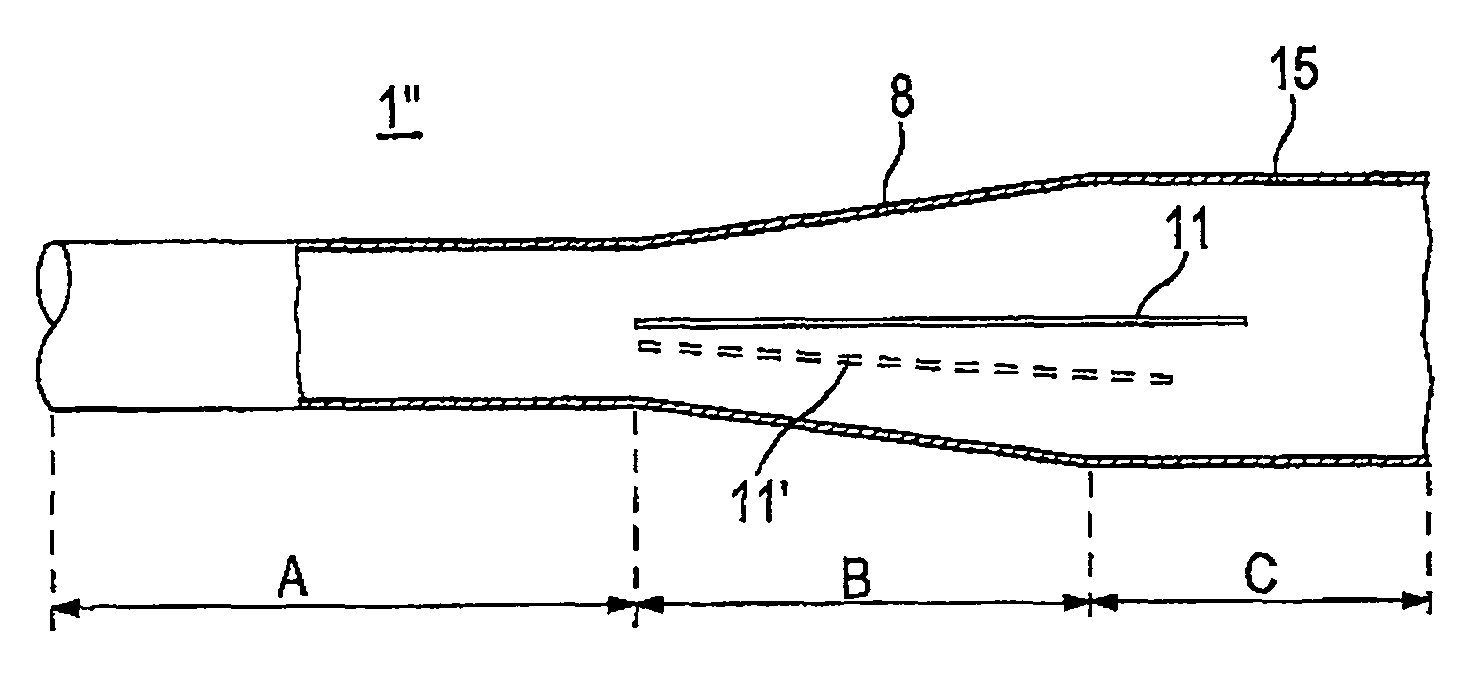
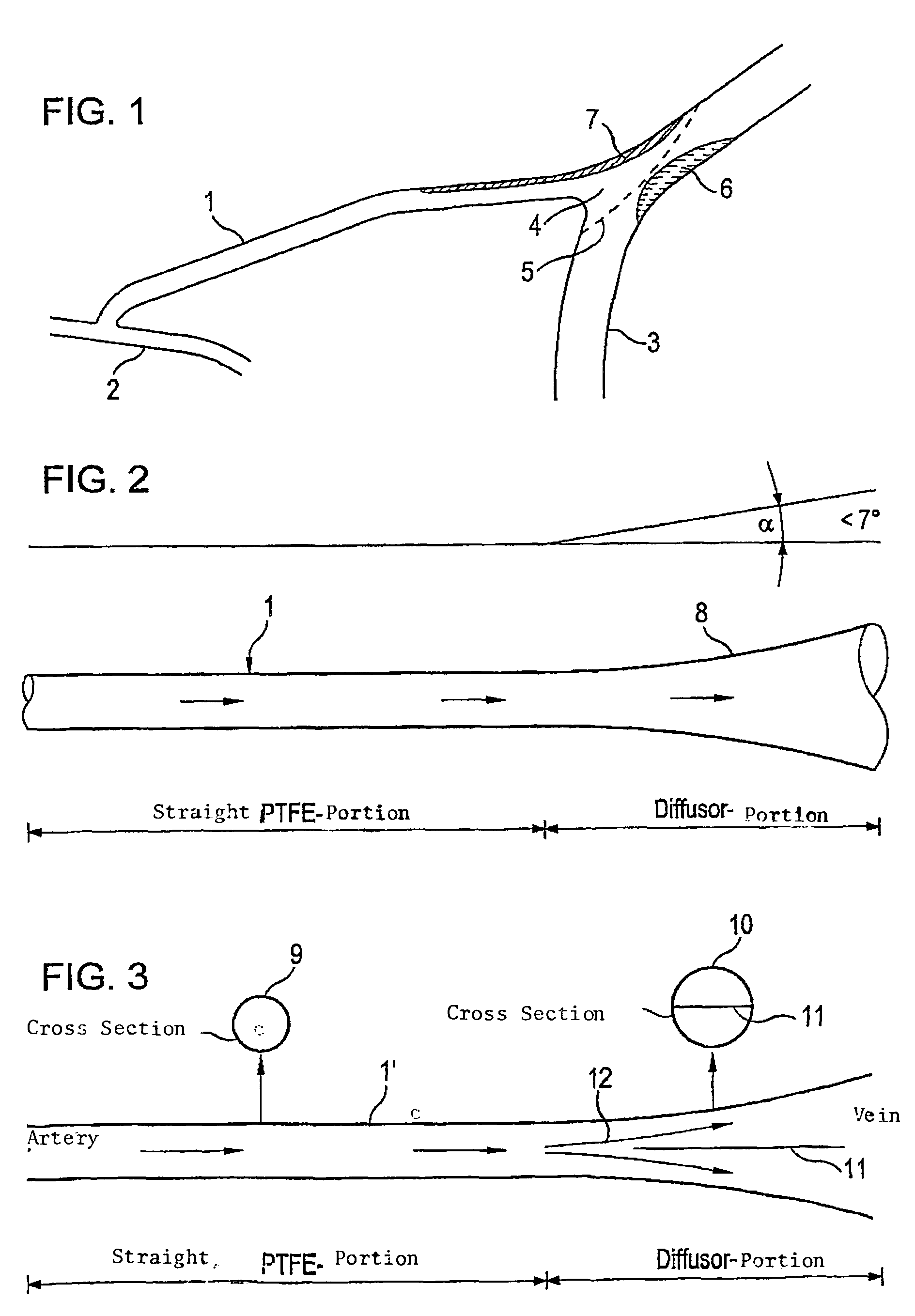
Tubular vascular transplant
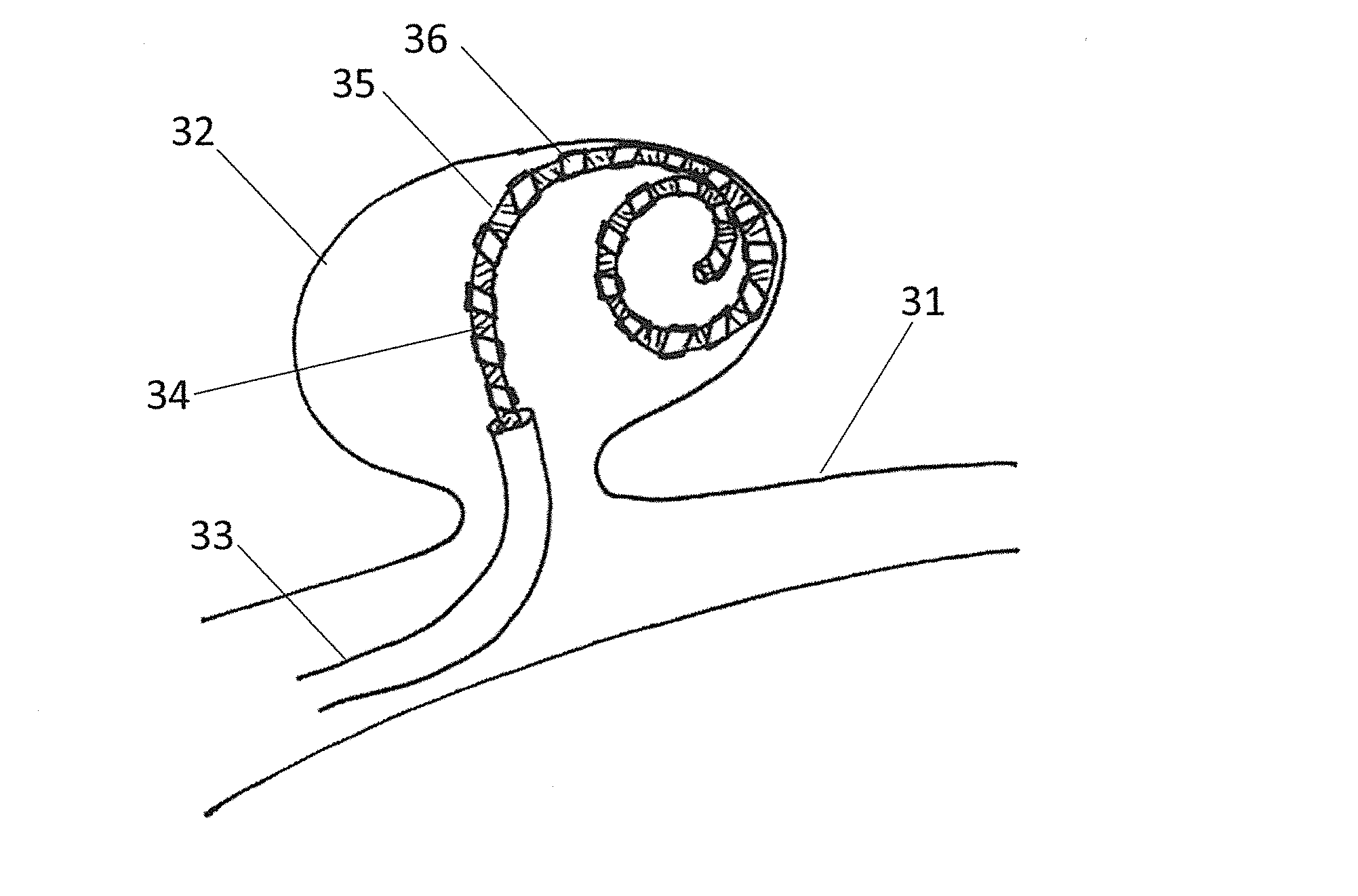
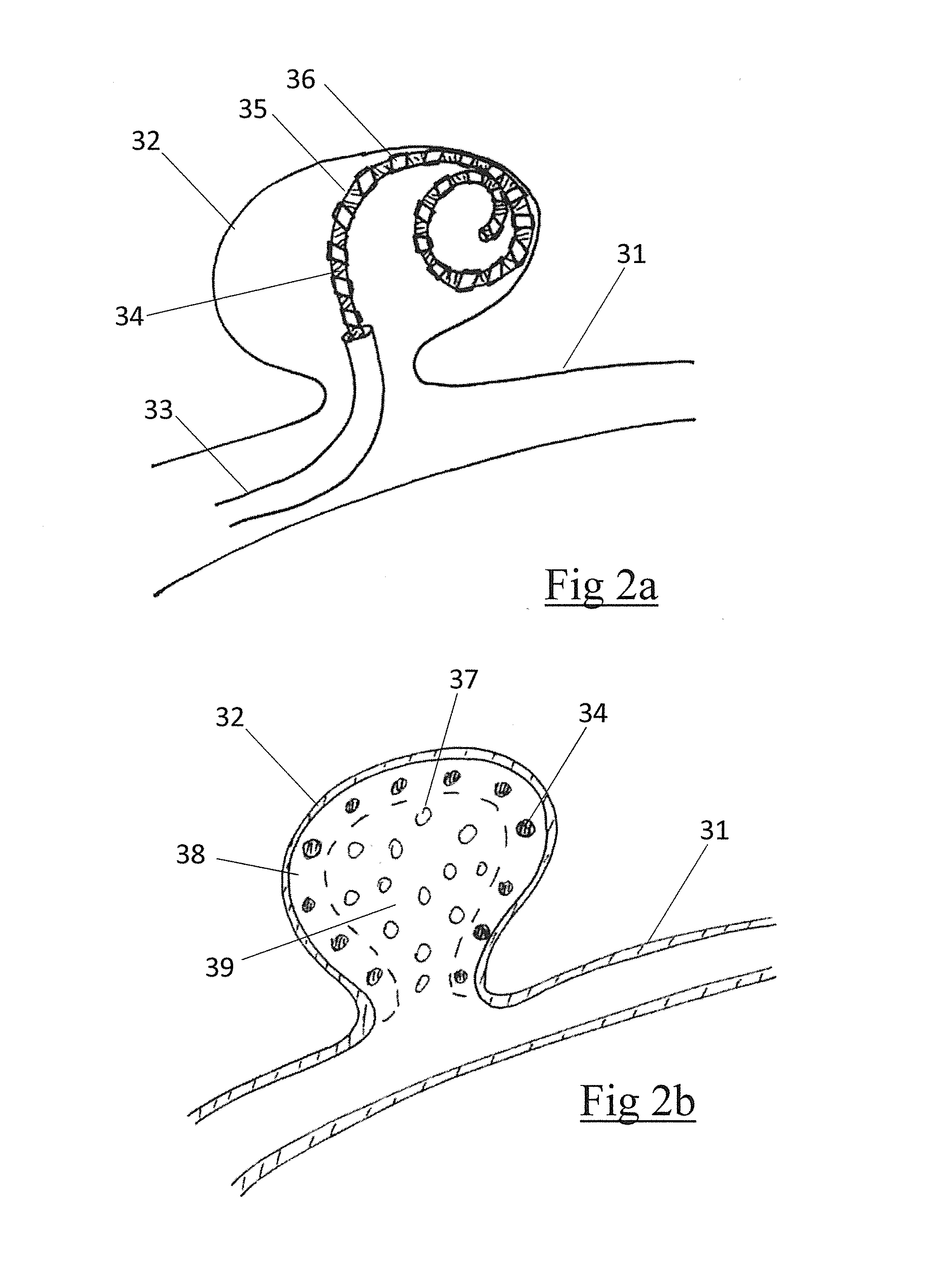
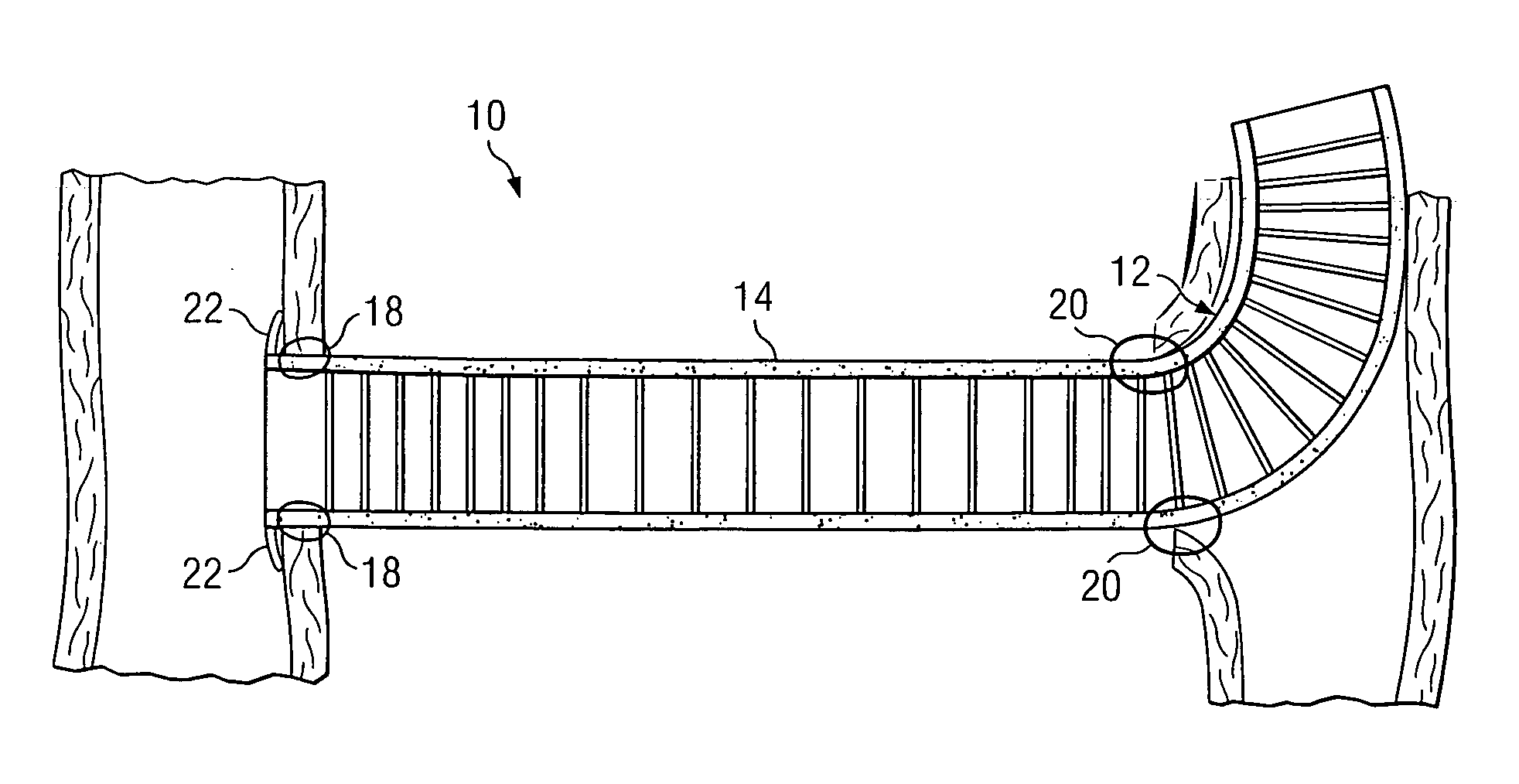
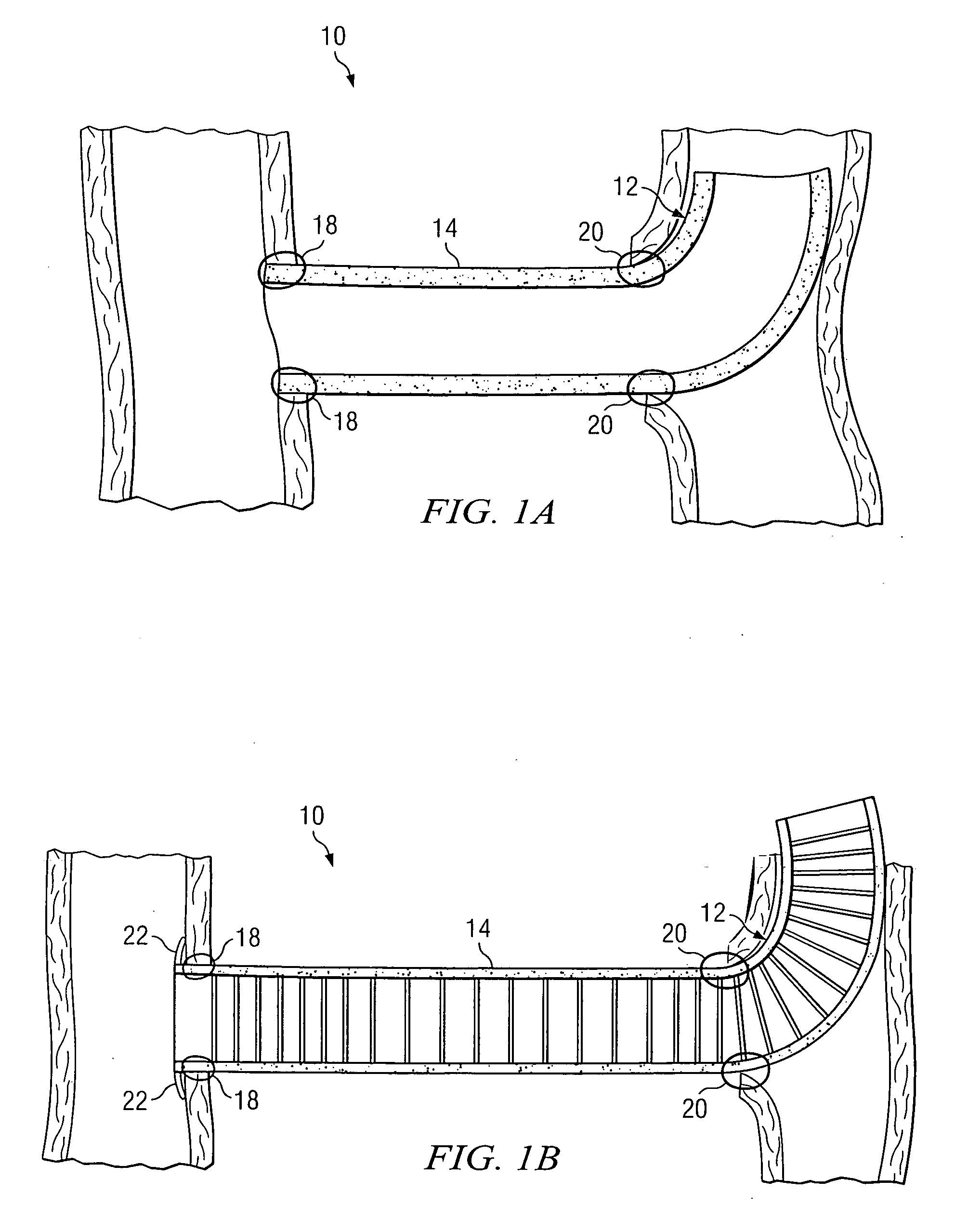
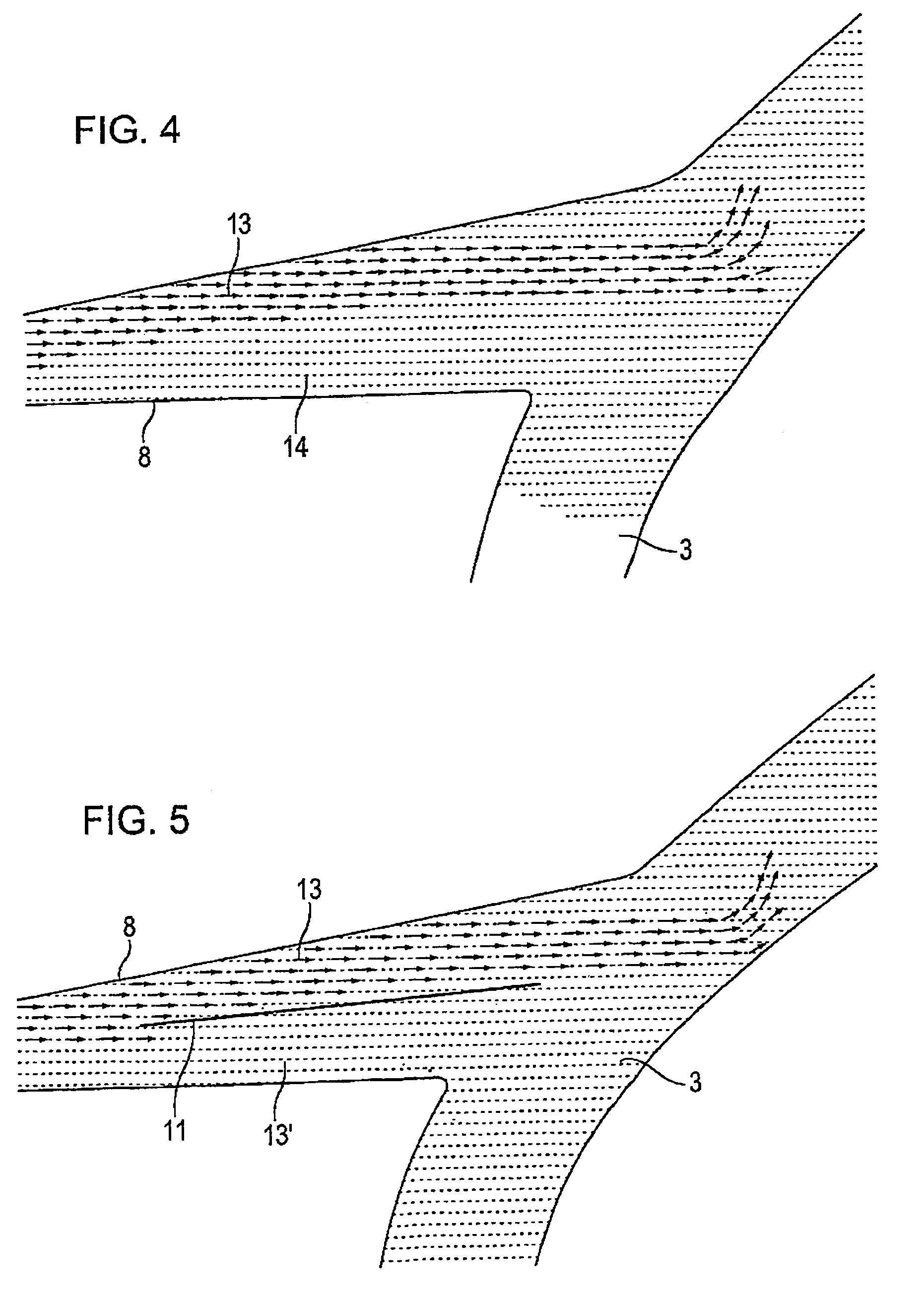
A tubular vascular transplant (1, 1′, 1″, 1′″) serves for connecting vessels in the human body. The transplant, in particular made of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE), can preferably be used for an arteriovenous shunt for carrying out a dialysis. The transplant is connected by its first, proximal end to a vessel, for example an artery (2), and by its distal end to another location of the same vessel or to a different vessel, for example a vein (3). The lumen of the transplant (1, 1′, 1″, and 1′″) widens in a steadily conical manner in the region of its distal end and forms a diffuser (8) there. The cone angle (a) of the wall of the diffuser (8) with respect to the central flow direction of the blood in the transplant (1′, 1″, 1′″) is preferably 6° to 7°. In the region of the diffuser (8), preferably at least one, preferably planar, dividing wall (11, 11′, 11a, and 11b) is provided, running in the central flow direction of the blood. This makes it possible to prevent the formation of an intimal hyperplasia and a pseudointima.
Owner:HEISE MICHAEL +1
Fluoroplastic composite elastomer
InactiveUS20060018777A1Improve bending resistanceLow costEnvelopes/bags making machineryFlexible member pumpsElastomerFiber
An improved fluoroplastic lined elastomeric tube that can maintain a stable flow rate while pumping aggressive chemicals in a peristaltic pump for an extended period of time and is fabricated in sizes ranging from 0.5 mm to 100 mm in inside diameter. The inner fluoroplastic liner comprises a composite of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene and a fluoroplastic polymer resulting in improved flex life over single component fluoroplastics. The inventive liner is bonded to either an unreinforced elastomer or a fiber reinforced elastomer for use in both low and high pressure peristaltic pump applications.
Owner:MAZTECH
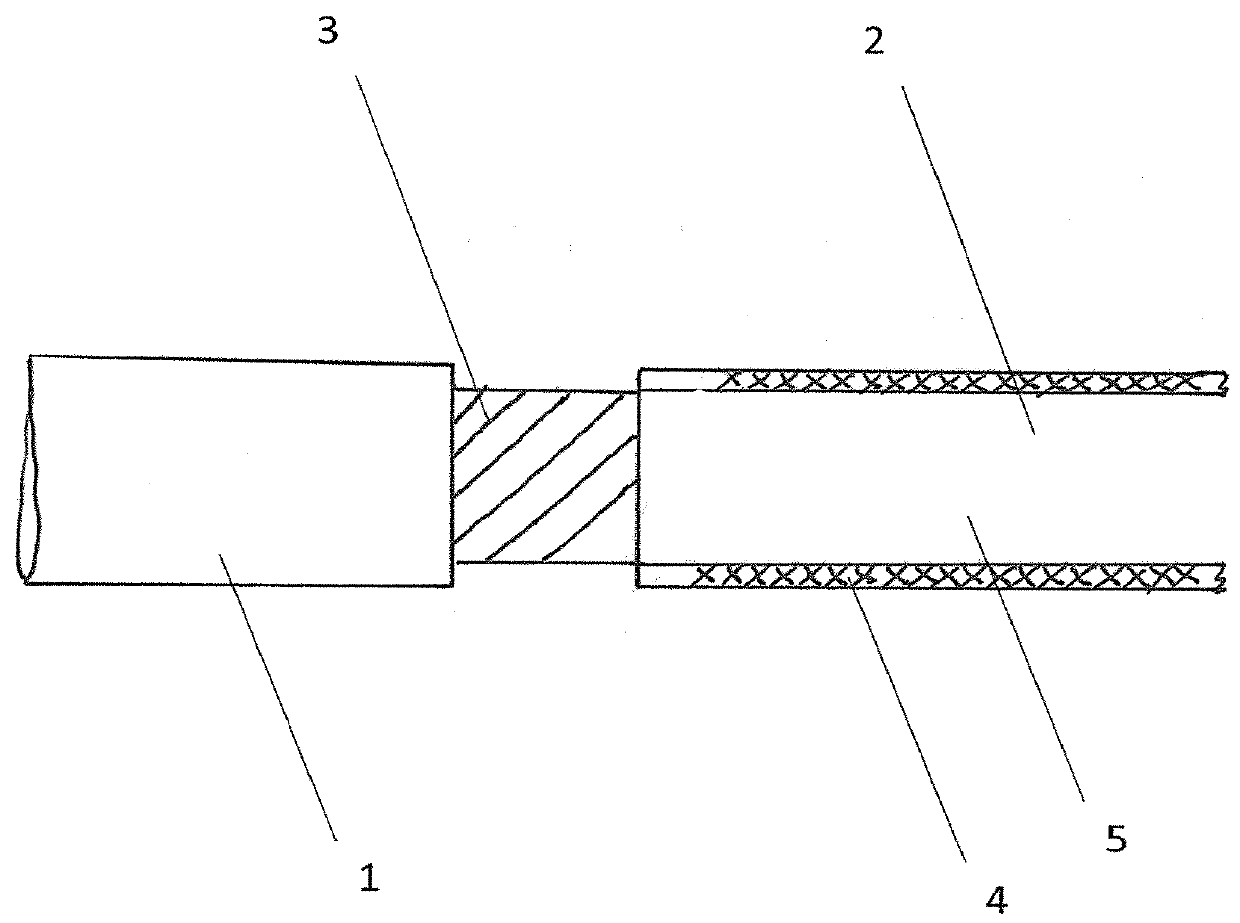
Endoscopic working channel and method of making same
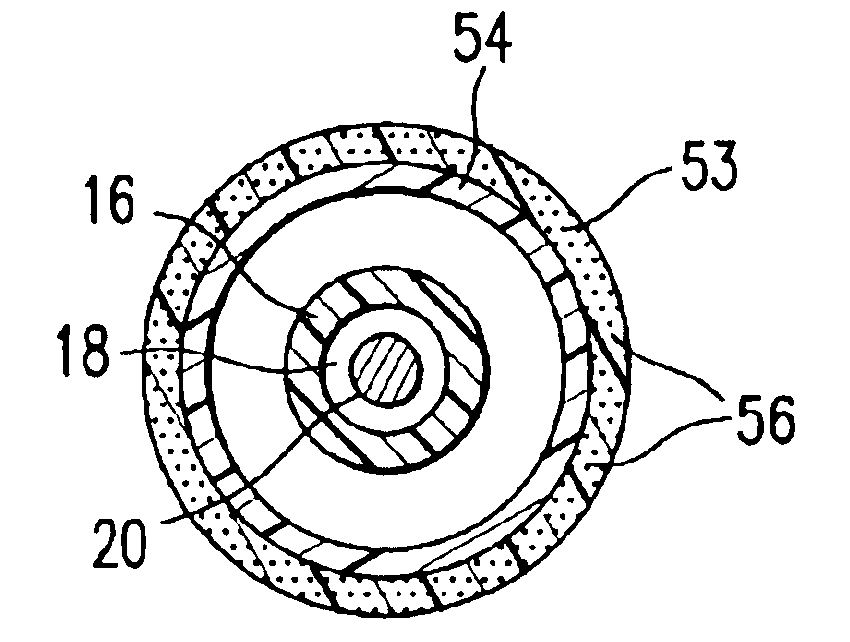
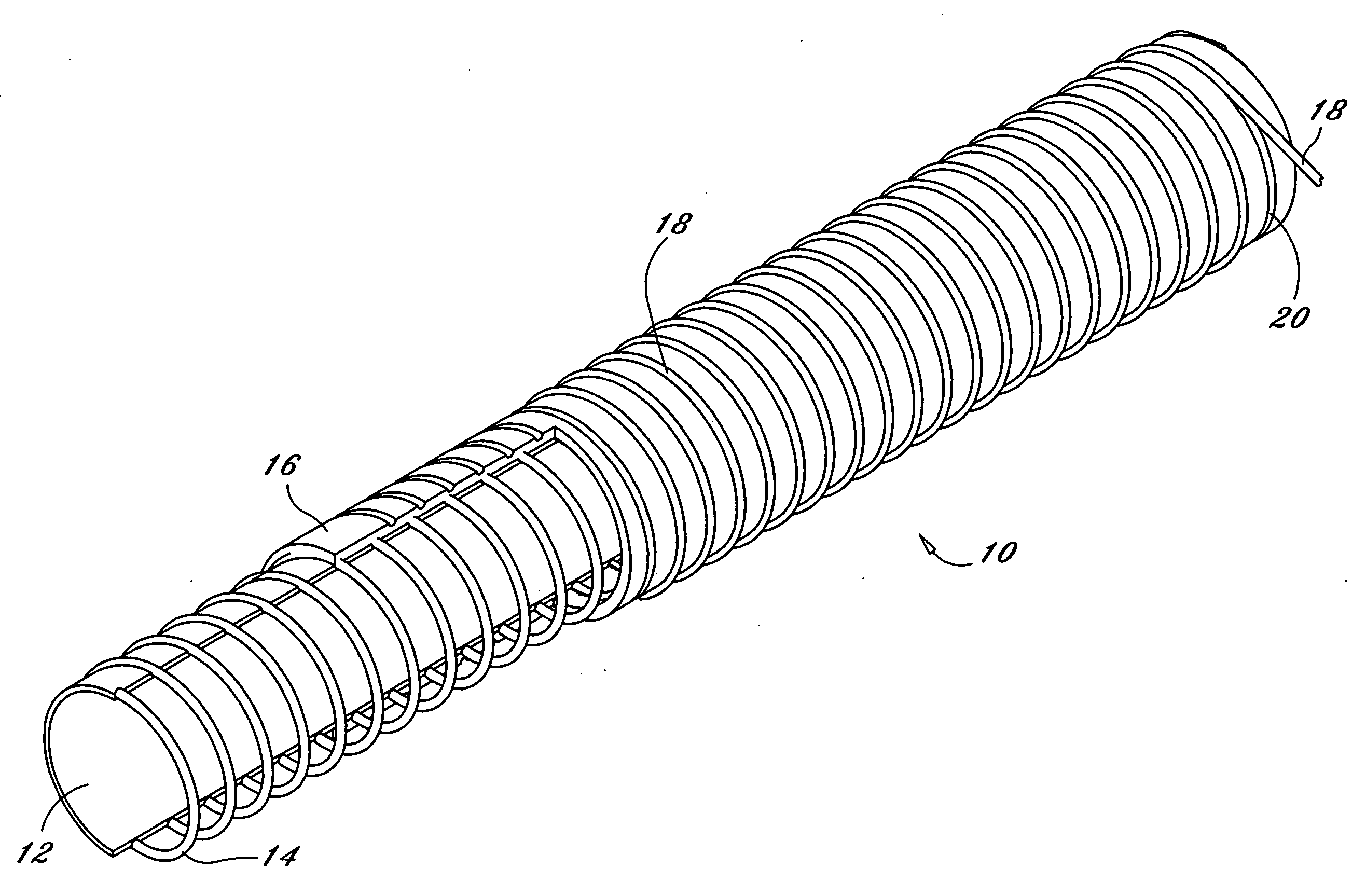
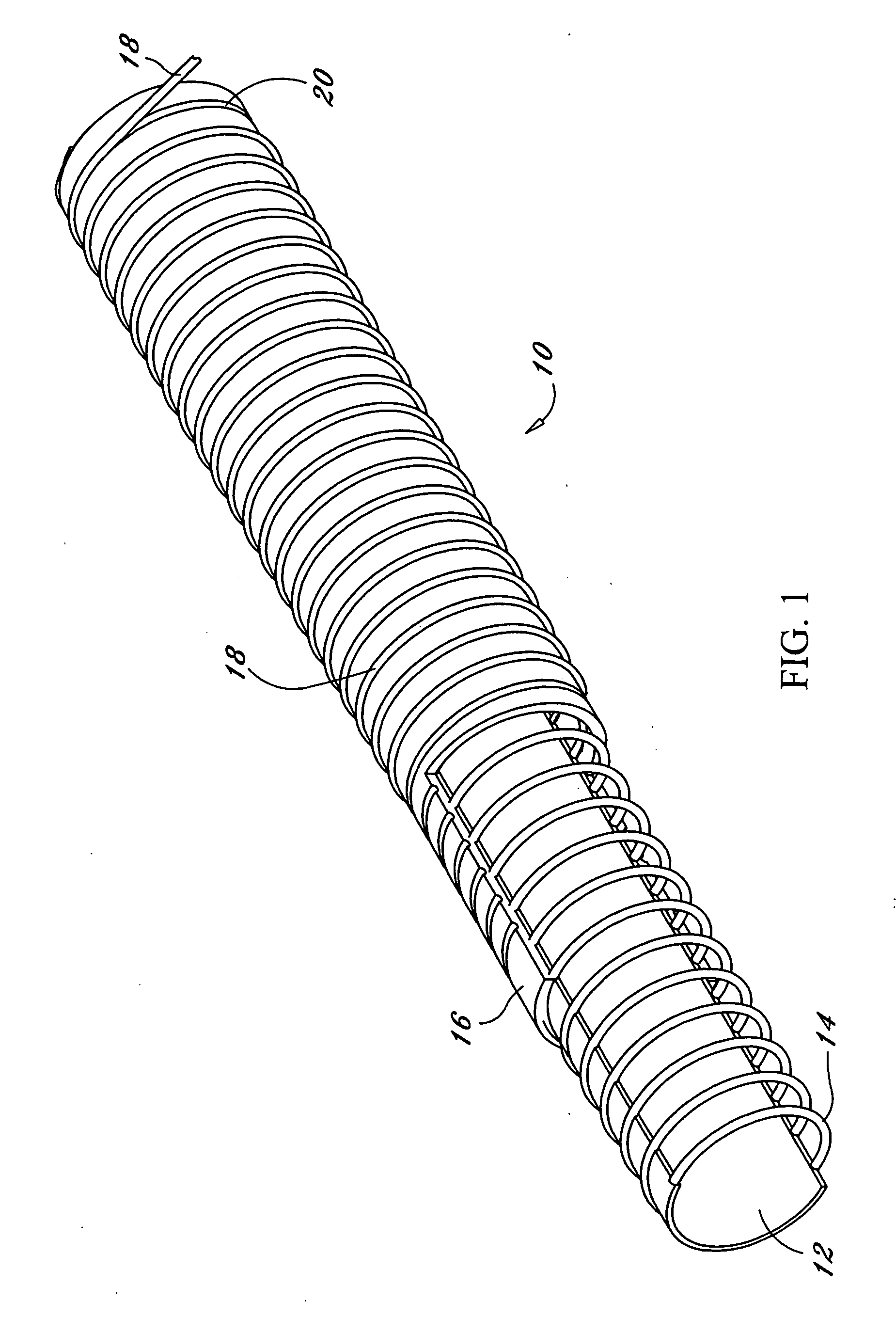
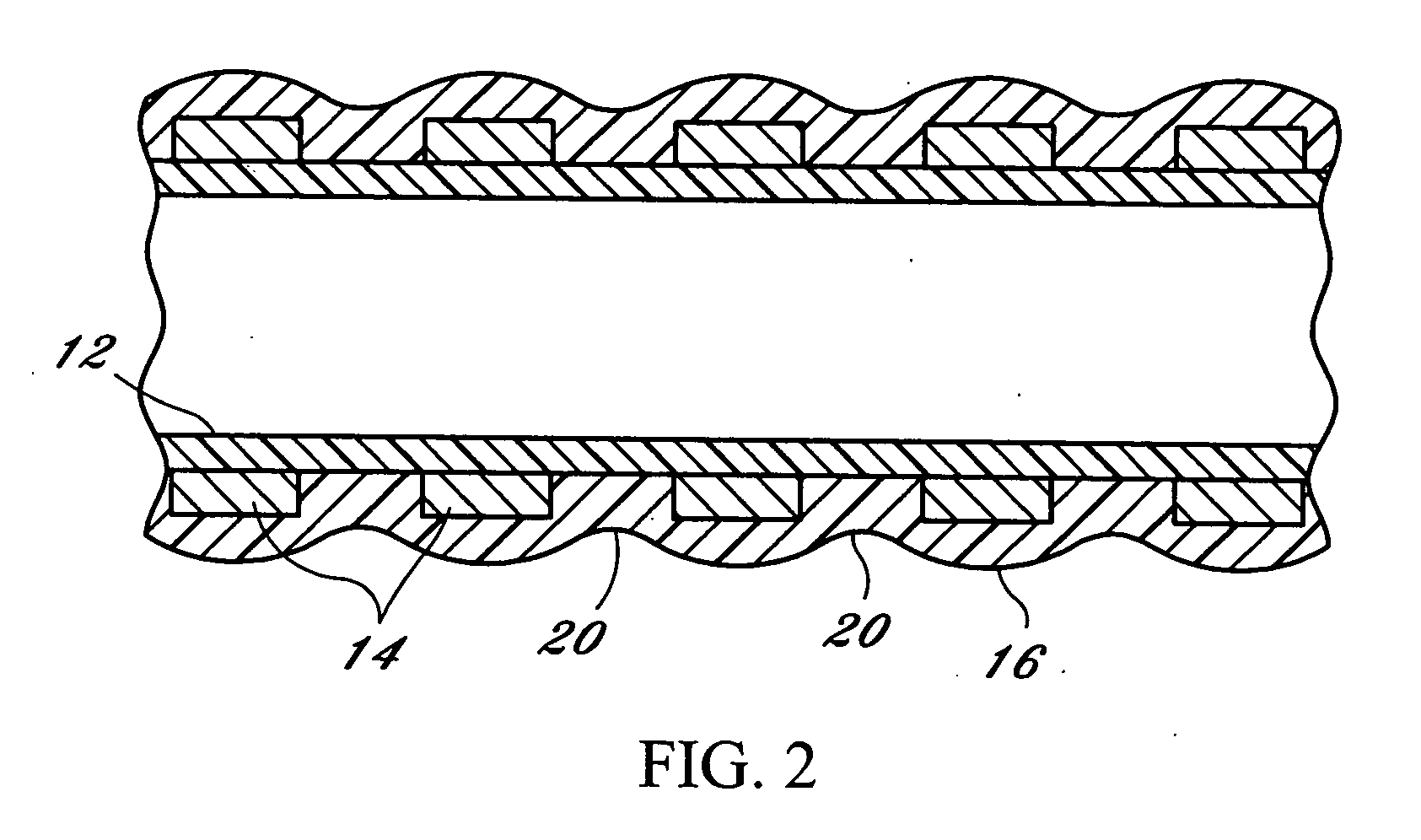
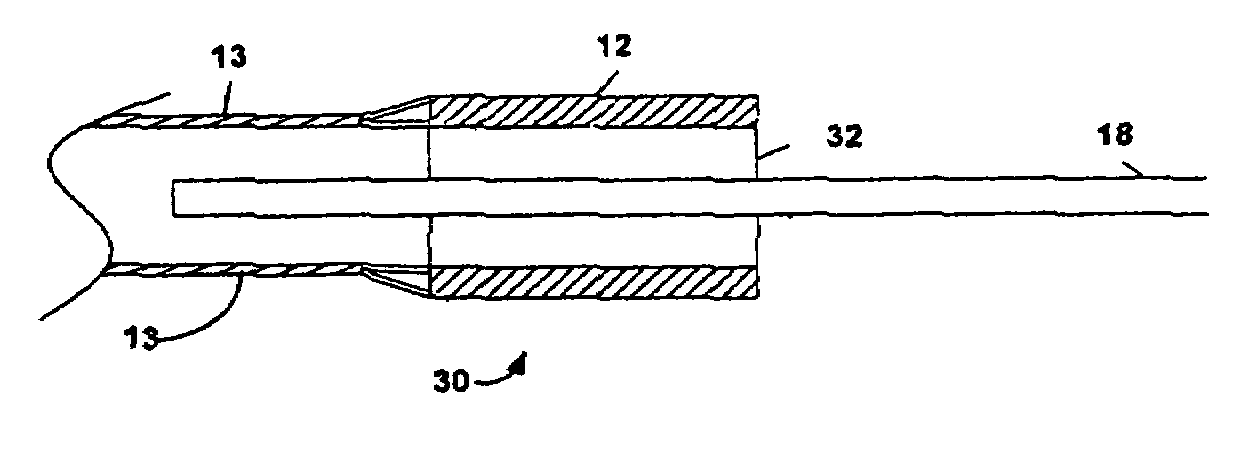
An endoscopic working channel is made of an inner polytetrafluoroethylene tube having a spiral wrap of wire over it with an outer expanded polytetrafluoroethylene tube bonded over the wire to the inner polytetrafluoroethylene tube.
Owner:INT POLYMER ENG
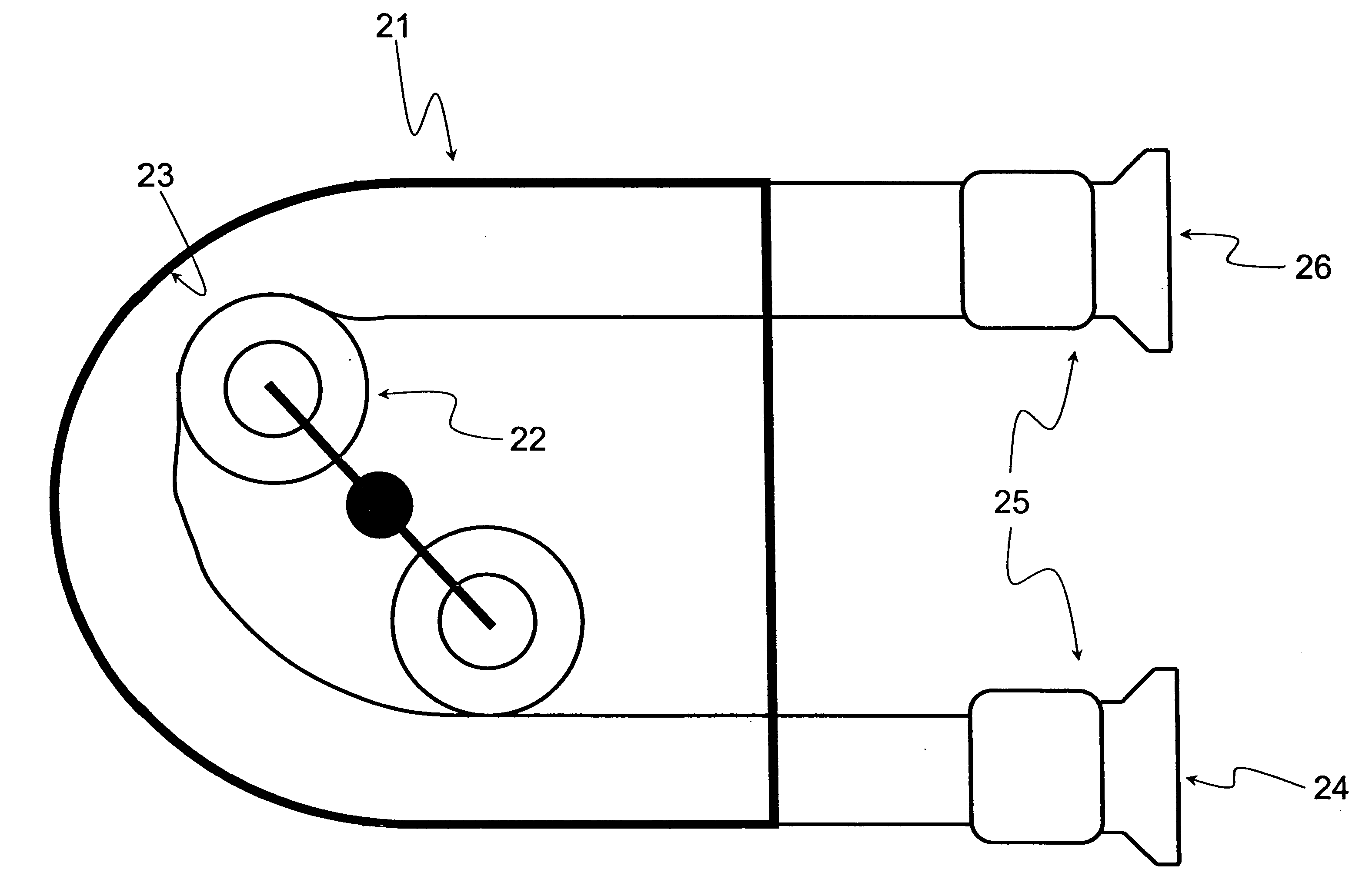
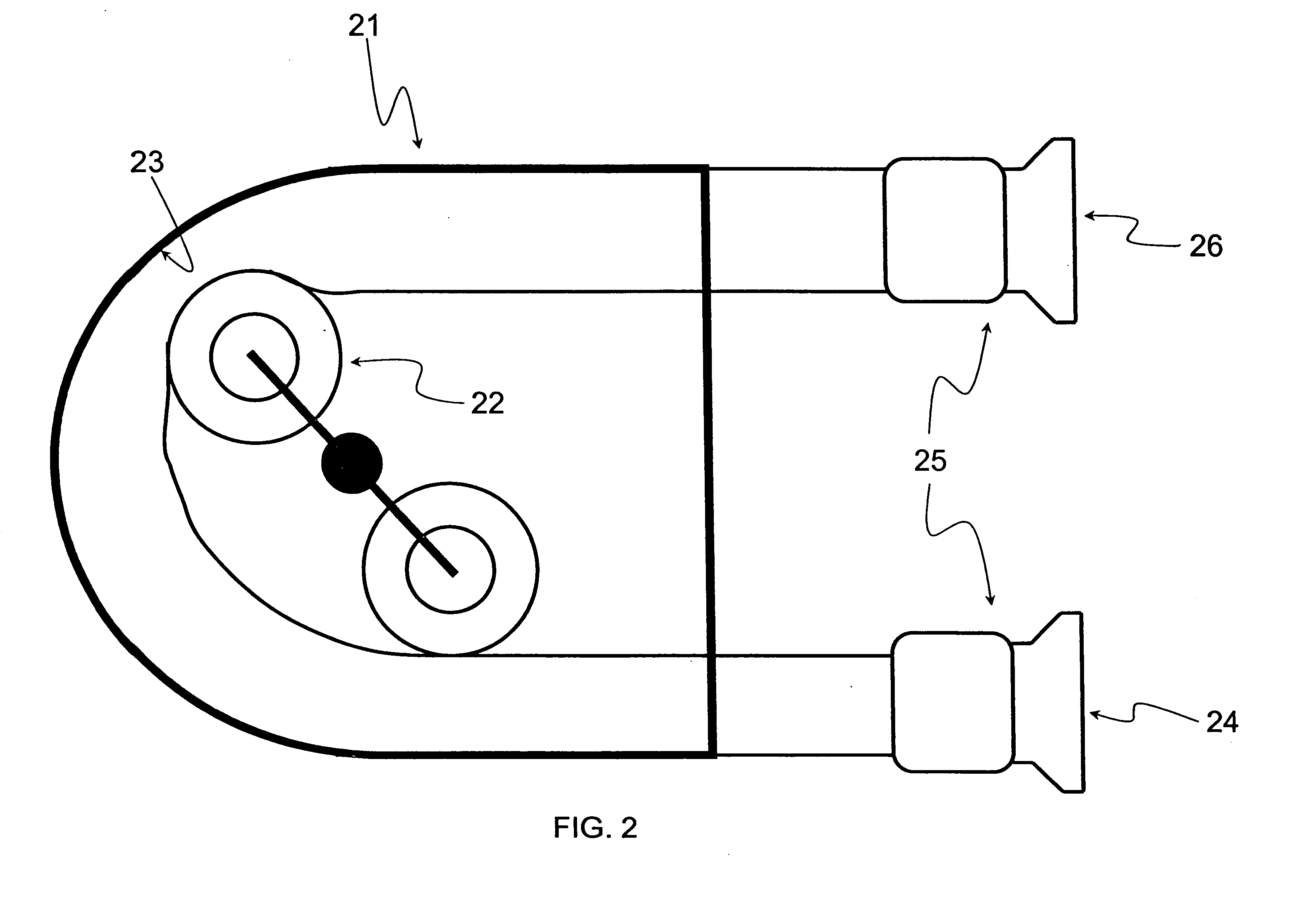
Ultrasonic transducer
ActiveUS7573182B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorEngineering
An ultrasonic transducer of the type containing a cylindrical piezoelectric active element mounted on a supporting tube is provided with a backing component made of an electrically and thermally insulating material forming a sleeve which extends between the piezoelectric element and the supporting tube. An insulating material is selected for the backing component which includes a substantial amount of entrained air. Preferably, the backing component is made of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (EPTFE).
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC +1
Fan cooling unit for cooling electronic components
InactiveUS20090139405A1Improve filtering effectEasy to chargeElectrostatic separationFiltration separationFiberEngineering
A fan cooling unit (10) for cooling electronic components, such as for an air-cooled telecommunications base station, comprises a protective covering for at least the air inlet opening (11) of a casing (8) in which the electronic components are housed. The protective covering (1) has a frame (2) into which a composite filter media (3) is mounted so as to create an air-tight fit. The composite filter media (3) comprises a membrane filtration layer (20) with a porous polymeric membrane, such as expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE), and at least one depth filtration layer (18) disposed on an upstream side of the membrane filtration layer (20). The depth filtration media layer comprises fibers having an electrostatic charge. The ePTFE membrane is preferably made from a blend of a PTFE homopolymer and a modified PTFE polymer.
Owner:SCHWARZ ROBERT +3
Balloon catheter having a balloon with a thickened wall portion
InactiveUS20060106337A1Increase wall thicknessHigh strengthStentsBalloon catheterHigh intensityBalloon catheter
A balloon catheter having a balloon with a thickened wall portion extending along at least a portion of the working length section of the balloon in a noninflated configuration. The balloon has a first layer formed of a first polymeric material and a second layer formed of a second, different polymeric material, the second layer having a wall thickness which is greater along the central working length section than the wall thickness of the second layer along a section proximal and / or a section distal to the central working length of the balloon. In a presently preferred embodiment, the first layer is formed of a porous material such as expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE), and the second layer of the balloon is formed of an elastomeric polymer. The balloon catheter has a highly flexible distal section and a relatively high strength, low profile balloon, due to the balloon configuration of the invention.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Fluoropolymer Fiber Composite Bundle
A fishing line having multiple UHMWPE fibers and (b) at least one fluoropolymer fiber comprising expanded polytetrafluoroethylene.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Method for preparing expanded polytetrafluoroethylene fiber for exhaust decomposition
InactiveCN1978717AReduce manufacturing costAvoid pollutionFilament/thread formingMonocomponent halogenated hydrocarbon artificial filamentFiberDecomposition
The invention discloses varicosity polytetrafluoroethylene fiber manufacturing method used in waste gas decomposition. It includes the following steps: mixing varicosity polytetrafluoroethylene resin, waste gas catalyst powder, with lubricant; sieving; ageing; compacting; spinning; degreasing; drawing; and hot forming. The produced fiber has multi-microcellular structure which can decompose the waste gas while passing, good quality, can be widely used in filtering material. Compared with the existing technique, the invention has the advantages of simple technology, low cost, no pollution etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Porous membrane
InactiveUS20110268959A1Improve stabilityHigh strengthSemi-permeable membranesMembranesPorous membraneEntry pressure
A membrane including a sheet of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene. The sheet is porous and has a gas permeability of at least 0.2 CFM according to ASTM D737 testing. The gas permeability of the membrane changes by less than 30% when the membrane is exposed to a temperature of 180° C. for a time of one hour. The sheet also has an average Mullen Hydrostatic Entry pressure of at least 135 psi according to ASTM D751 testing. The average Mullen Hydrostatic Entry pressure is substantially unchanged after exposure to a temperature of 180° C. for a time of one hour. The membrane has a bubble point value that changes by less than 20% when the membrane is exposed to a temperature of 180° C. for a time of one hour.
Owner:BHA ALTAIR
DEVICE AND METHOD FOR ENDOVASCULAR TREATMENT OF ANEURYSMS USING EMBOLIC ePTFE
InactiveUS20180263632A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationEndovascular treatmentArteriovenous malformation
An embolic occlusion device for the treatment of aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations comprises expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE). The ePTFE permits ingrowth of cells with connective tissue deposition to promote adherence of the aneurysm wall to the embolic device thereby preventing continued growth or re-growth of the aneurysm as well as blocking blood flow into an aneurysm. An occlusion device is also described which comprises an embolic element and a polymeric pre-formed component.
Owner:SEIFERT PAUL STEVEN +2
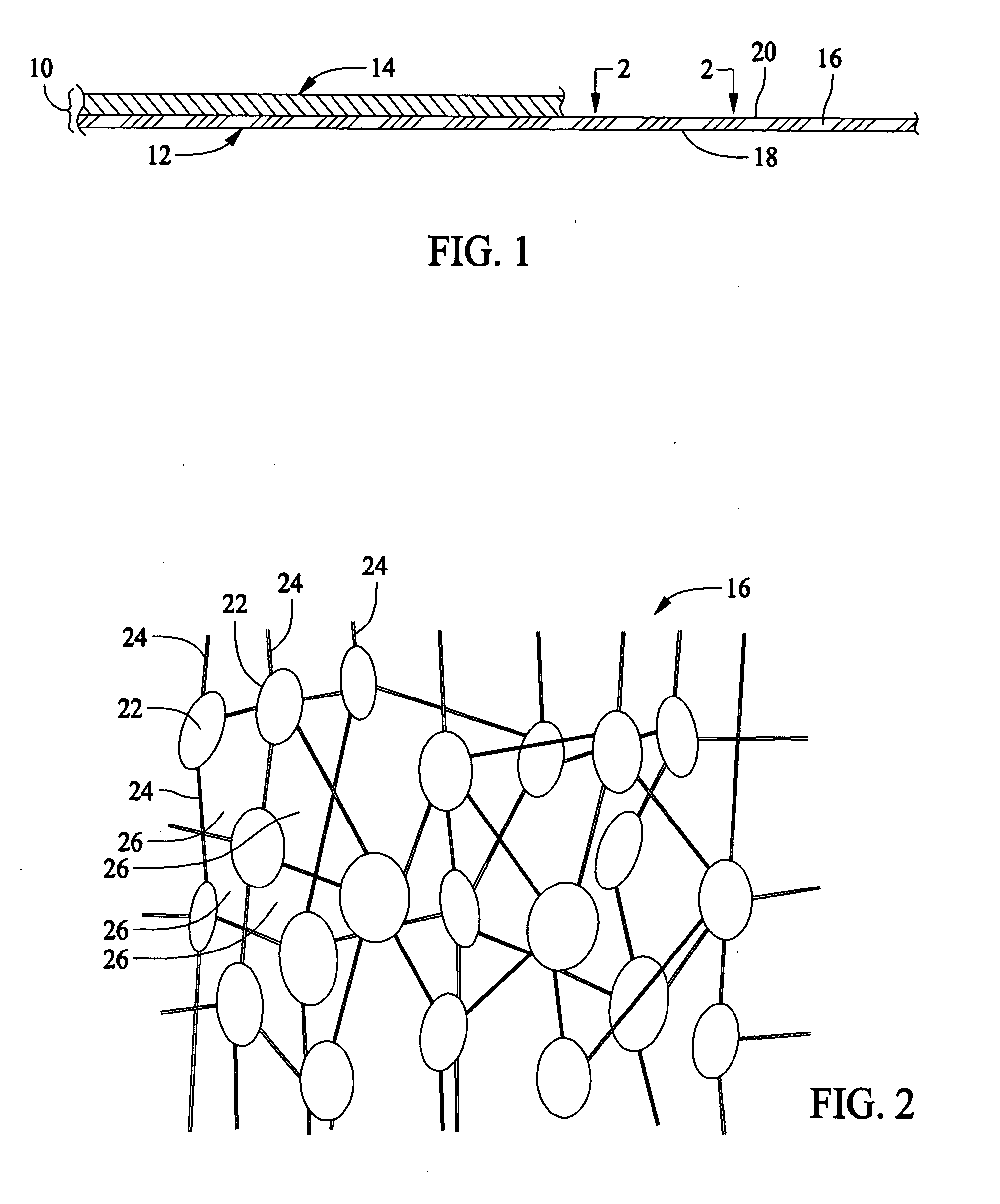
Durable membranes and methods for improving membrane durability
InactiveUS20080026190A1Increased durabilityGarment special featuresSemi-permeable membranesTetrafluoroethyleneThermoplastic elastomer
A durable membrane that includes a membrane that is moisture vapor transmissive and resistant to liquid penetration, and a non-continuous application of a thermoplastic elastomer on a side of the membrane. The membrane may be an expanded polytetrafluoroethylene membrane. The thermoplastic elastomer may be polyurethane. The non-continuous application of thermoplastic elastomer on a side of the membrane may include an application of thermoplastic elastomer that covers a portion of the surface area of the membrane and leaves the remainder uncovered.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High performance gas turbine inlet filter (HEPA) using membrane media
A composite filter media structure and an associated method of making are provided. The structure includes a base substrate that includes a nonwoven fabric substrate formed from a plurality of bicomponent synthetic fibers using a spunbond process. The composite filter media structure includes a surface layer deposited on one side of the base substrate where a thermal lamination process can be used to combine the base substrate and the surface layer. The surface layer is formed from a microporous expanded polytetrafluoroethylene membrane. In one aspect, the base substrate and the surface layer are configured to provide greater than 95% and equal to or less than 99.5% filtration efficiency measured in accordance with an EN 1822 test method. In another aspect, the filter media includes an embossing pattern or a plurality of corrugations formed using opposing rollers at a temperature of about 90° C. to about 140° C.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Method of making an intraluminal stent graft
A method of making an tubular intraluminal graft in the form of a tubular diametrically adjustable stent having a tubular covering of porous expanded polytetrafluoroethylene which is less than 0.10 mm thick. The covering may be on the exterior surface of the stent, or on the interior surface of the stent, or both. The covering may be affixed to the stent by an adhesive which is preferably fluorinated ethylene propylene.
Owner:GORE ENTERPRISE HLDG INC
Coating film with large moisture permeability
ActiveCN104029449AGood moisture absorption and moisture conductivityReliable performanceSynthetic resin layered productsGas-tight/water-tight arrangementsCelluloseMoisture absorption
The invention discloses a coating film with the large moisture permeability. The coating film comprises a basic film layer and a coating layer, wherein the basic film layer is an expanded polytetrafluoroethylene film layer; the coating layer coating the expanded polytetrafluoroethylene film layer is a polyurethane emulsion copolymerization coating layer containing superfine micro-powder of hemp stalk cores; a coating agent of the polyurethane emulsion copolymerization coating layer containing the superfine micro-powder of the hemp stalk cores is prepared by uniformly stirring the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 20-25% of polyurethane; 55-60% of a dimethylfomamide solvent; 2-5% of a hydrophilic group solvent and 18-25% of the superfine micro-powder of the hemp stalk cores. Through the manner, the coating film has good moisture absorbing and guide performances; the content of moisture permeable factor fibrin in the superfine micro-powder of the hemp stalk cores is large; micro-grooves and micropores exist in the coasting film, so that the moisture absorption area and the diffusion area are increased; the coating film has excellent performances such as ultraviolet resistance, water proofing, dust proofing, oil proofing, moisture permeability and corrosion resistance on oxide solutions.
Owner:PAN ASIAN MICROVENT TECH JIANGSU CORP
Composite article having hydrophilic properties and method of manufacture
A composite article includes a base material and a porous membrane laminated with the base material. The porous membrane has hydrophobic properties and includes at least one of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene, woven polytetrafluoroethylene, and non woven polytetrafluoroethylene. A coating layer is formed on at least a portion of the porous membrane. The coating layer has hydrophilic properties and includes at least one of an organofunctional siloxane and a polyether urethane polymer.
Owner:BHA ALTAIR
Method for stabilizing a spinal segment
ActiveUS20120253404A1The result is validEase of installation and in applicationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsAnatomical structuresSpinal column
A surgical implant is provided that includes first and second abutment surfaces between which are positioned a force imparting mechanism. A sheath is positioned between the first and second abutment surfaces, and surrounds the force imparting mechanism. The sheath is fabricated from a material that accommodates relative movement of the abutment members, while exhibiting substantially inert behavior relative to surrounding anatomical structures. The sheath is generally fabricated from expanded polytetrafluoroethylene, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, a copolymer of polycarbonate and a urethane, or a blend of a polycarbonate and a urethane. The force imparting member may include one or more springs, e.g., a pair of nested springs. The surgical implant may be a dynamic spine stabilizing member that is advantageously incorporated into a spine stabilization system to offer clinically efficacious results.
Owner:RACHIOTEK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com