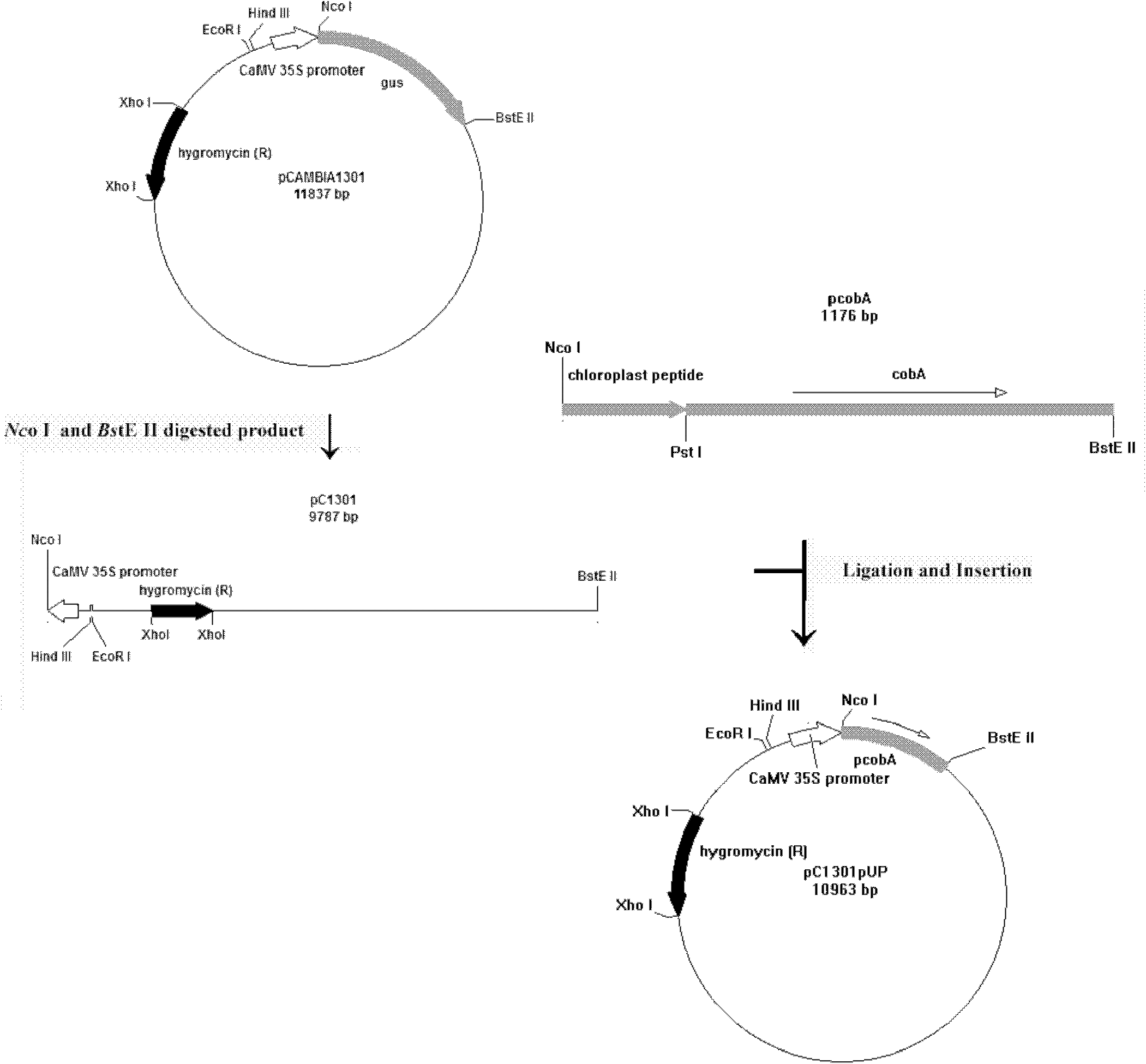
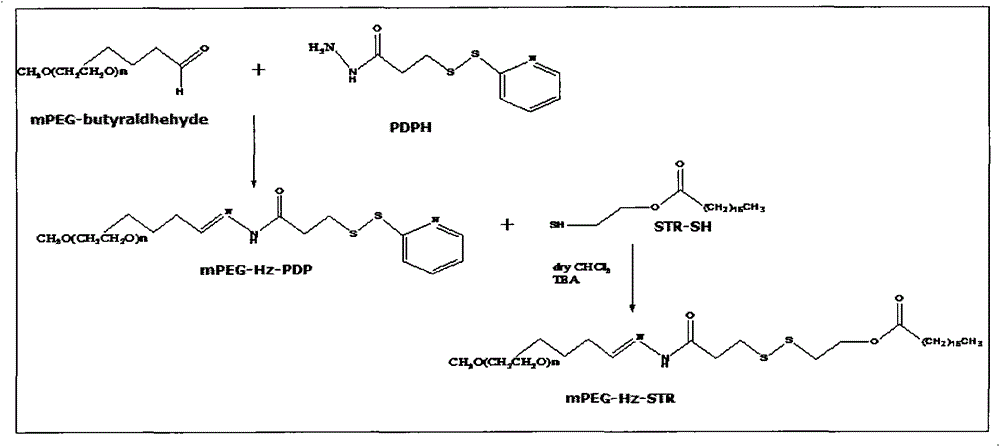
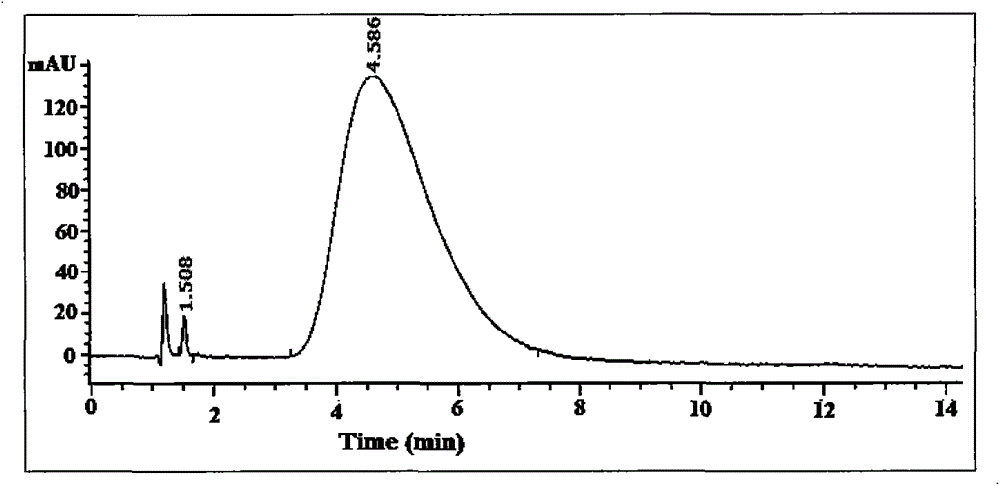
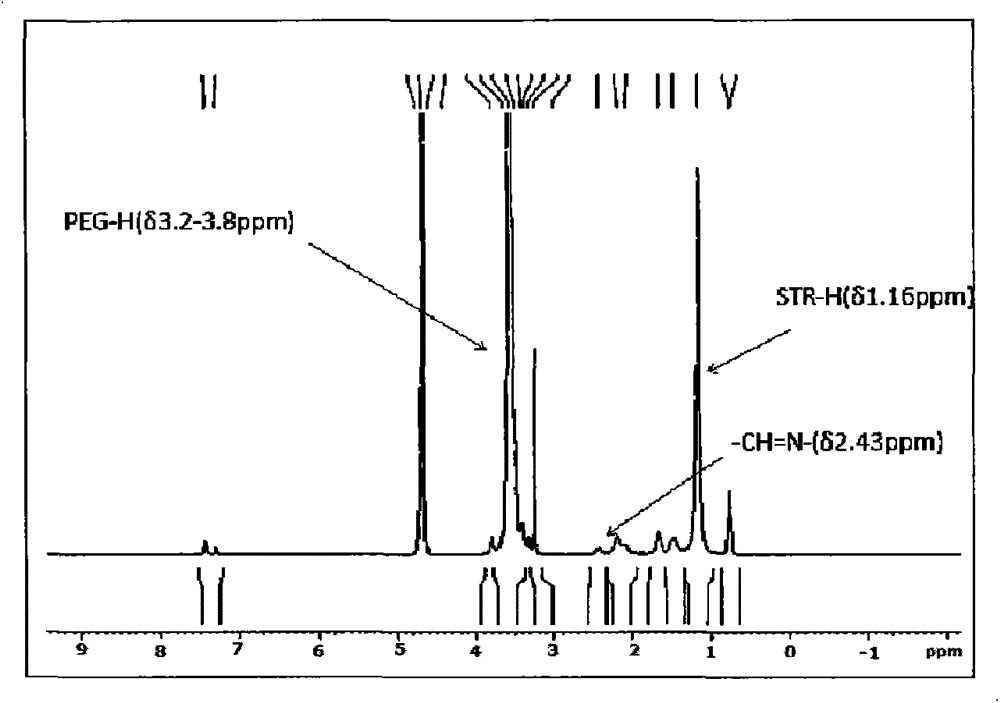
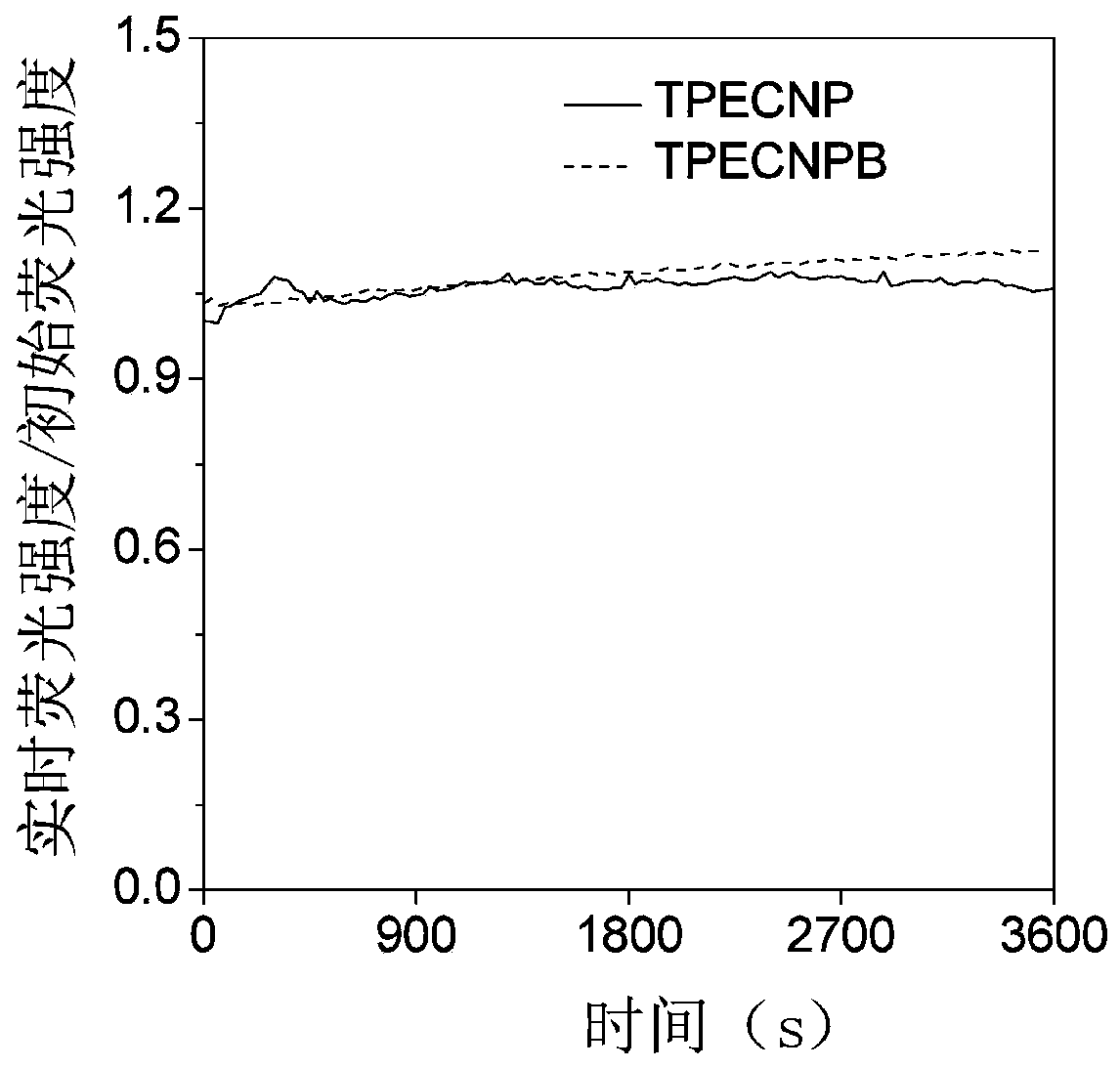
Patents
Literature
75 results about "Subcellular organelle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
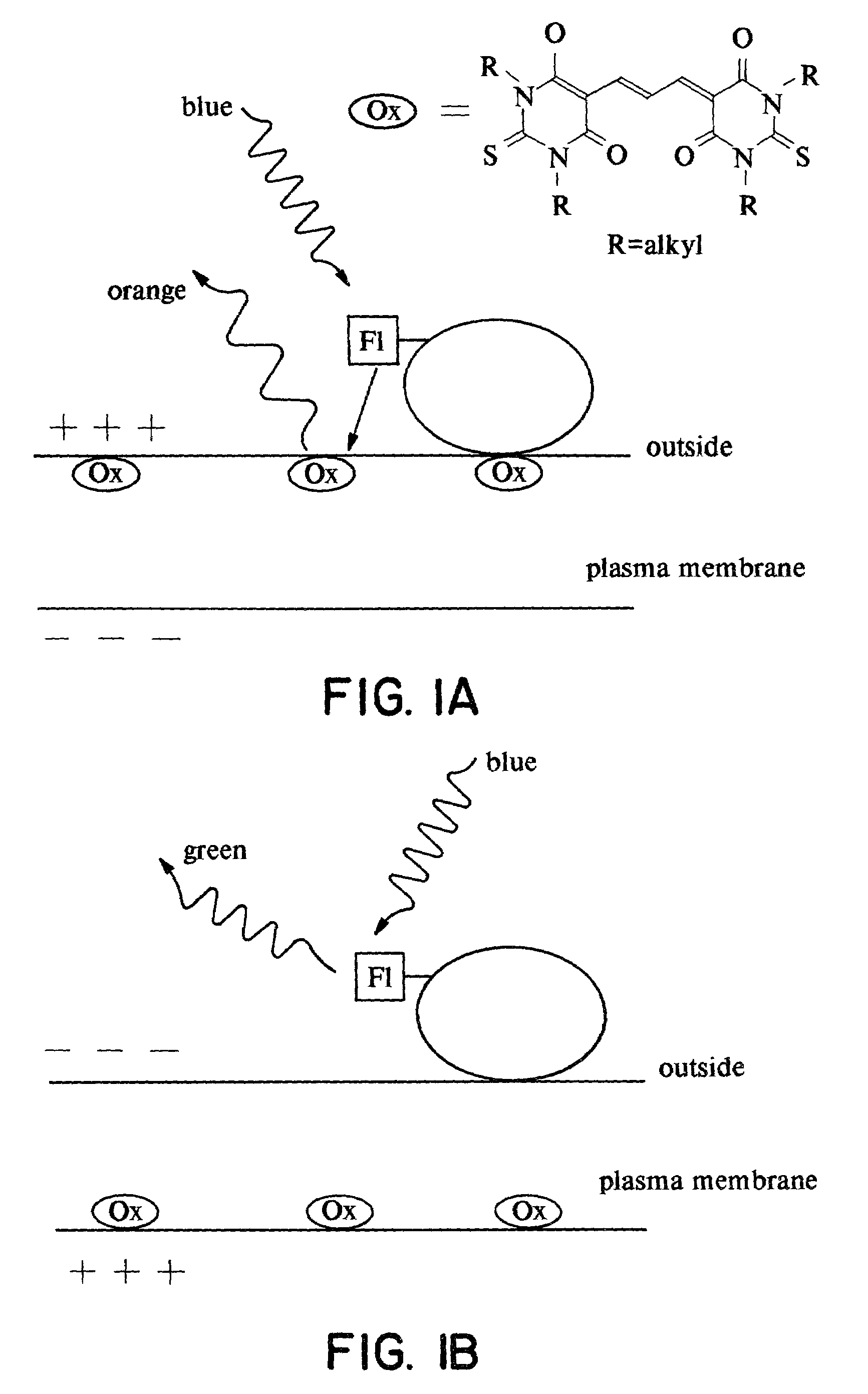
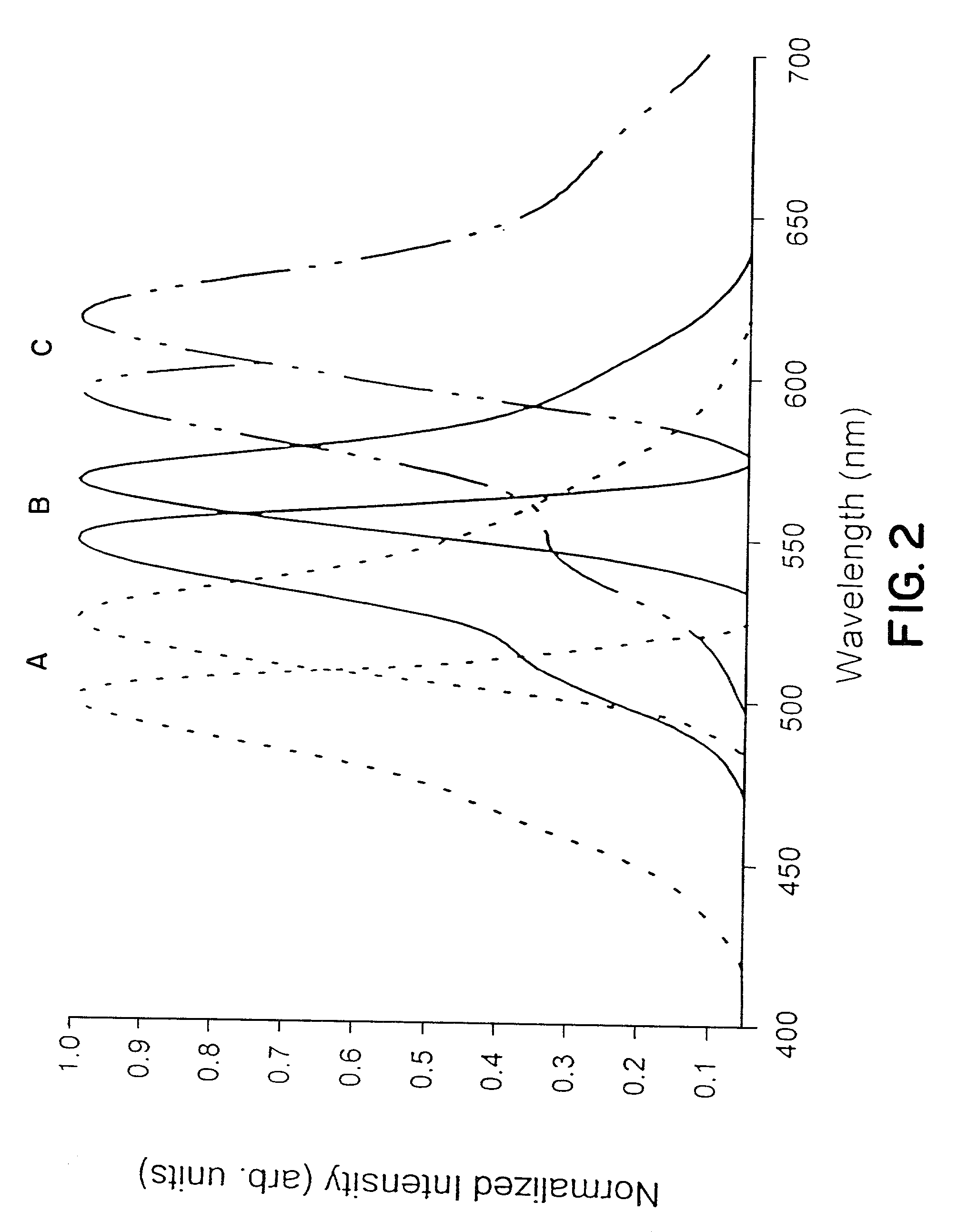
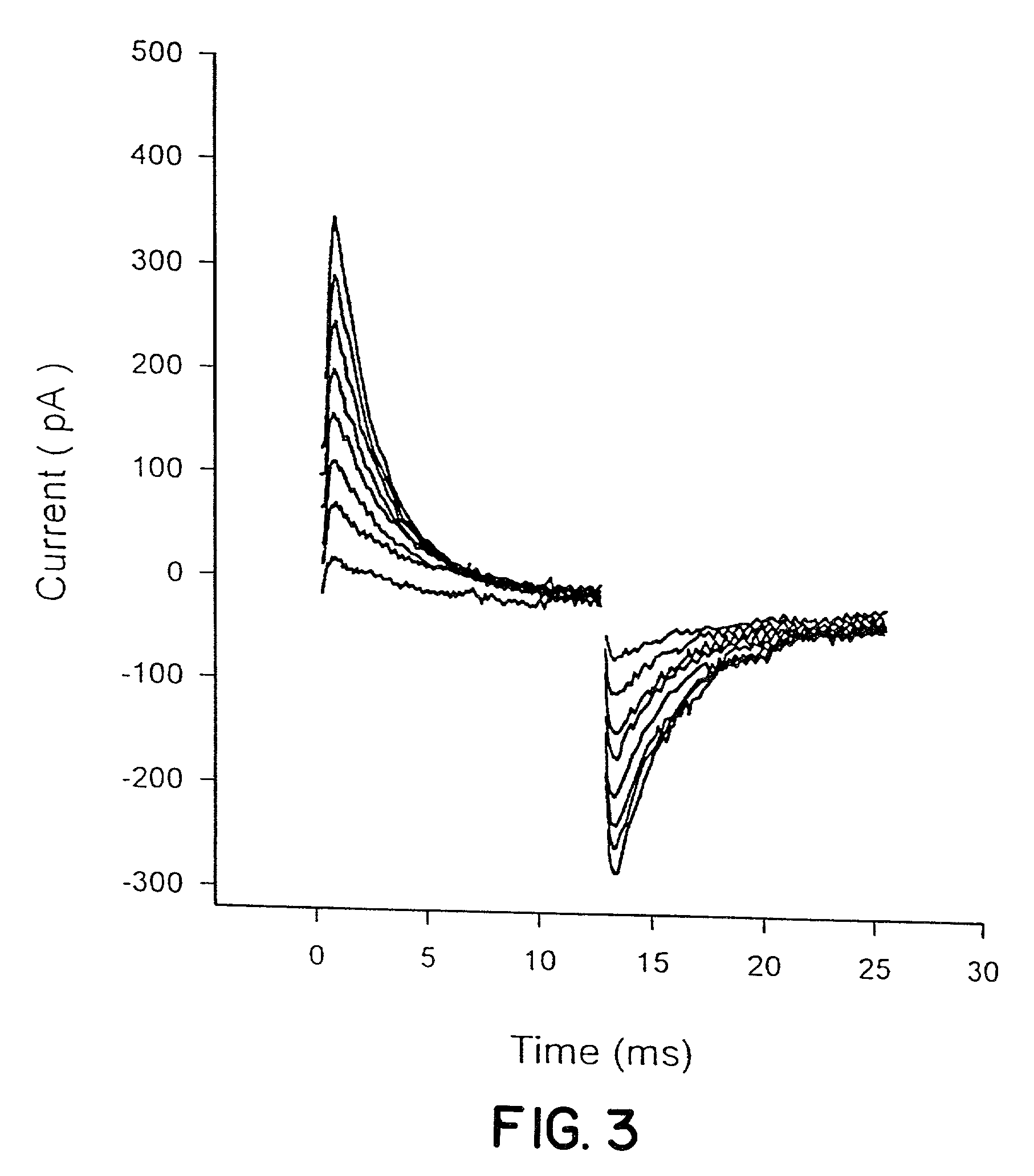
An organelle is a subcellular structure that has a specific function. The activities of cells depends on the activities of subcellular structures within the cell (subcellular structures include organelles, the plasma membrane).
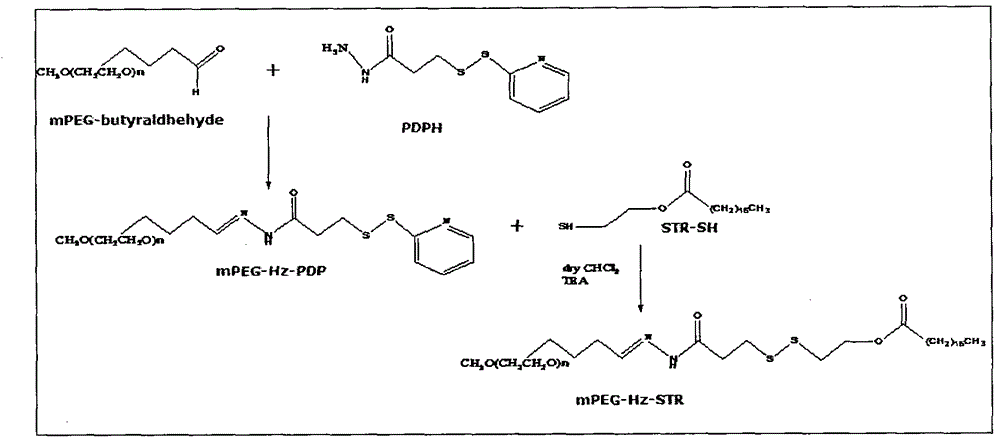
Chemical address tags
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to the fields of chemoinformatics, chemogenomics, drug discovery and development, and drug targeting. In particular, the present invention provides subcellular localization signals (e.g., chemical address tags) that influence (e.g., direct) subcellular and organelle level localization of associated compounds (e.g., drugs and small molecule therapeutics, radioactive species, dyes and imagining agents, proapoptotic agents, antibiotics, etc) in target cells and tissues. The compositions of the present invention modulate the pharmacological profiles of associated compounds by influencing the compound's accumulation, or exclusion, from subcellular loci such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, vesicles, granules, nuclei and nucleoli and other subcellular organelles and compartments. The present invention also provides methods for identifying chemical address tags, predicting their targeting characteristics, and for rational designing chemical libraries comprising chemical address tags.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Production of fc-fusion polypeptides in eukaryotic algae
InactiveUS20110151515A1Increase serum stabilityEfficient separation and purificationUnicellular algaeVaccinesHeterologousProtein regulation
Methods and compositions are disclosed to engineer plastids comprising heterologous genes encoding immuno-activating domains fused to an extracellular domain (ECD) of a receptor or surface glycoprotein, a growth factor or an enzyme and produced within a subcellular organelle, such as a chloroplast. The immuno-activating domains may include those regions of a protein capable of modulating the interaction between immune effector cells via proteins containing stereoselective binding domains and specific ligands, such as the Fc regions of antibodies. The present disclosure also demonstrates the utility of plants, including green algae, for the production of complex multi-domain fusion proteins as soluble bioactive therapeutic agents.
Owner:SAPPHIRE ENERGY
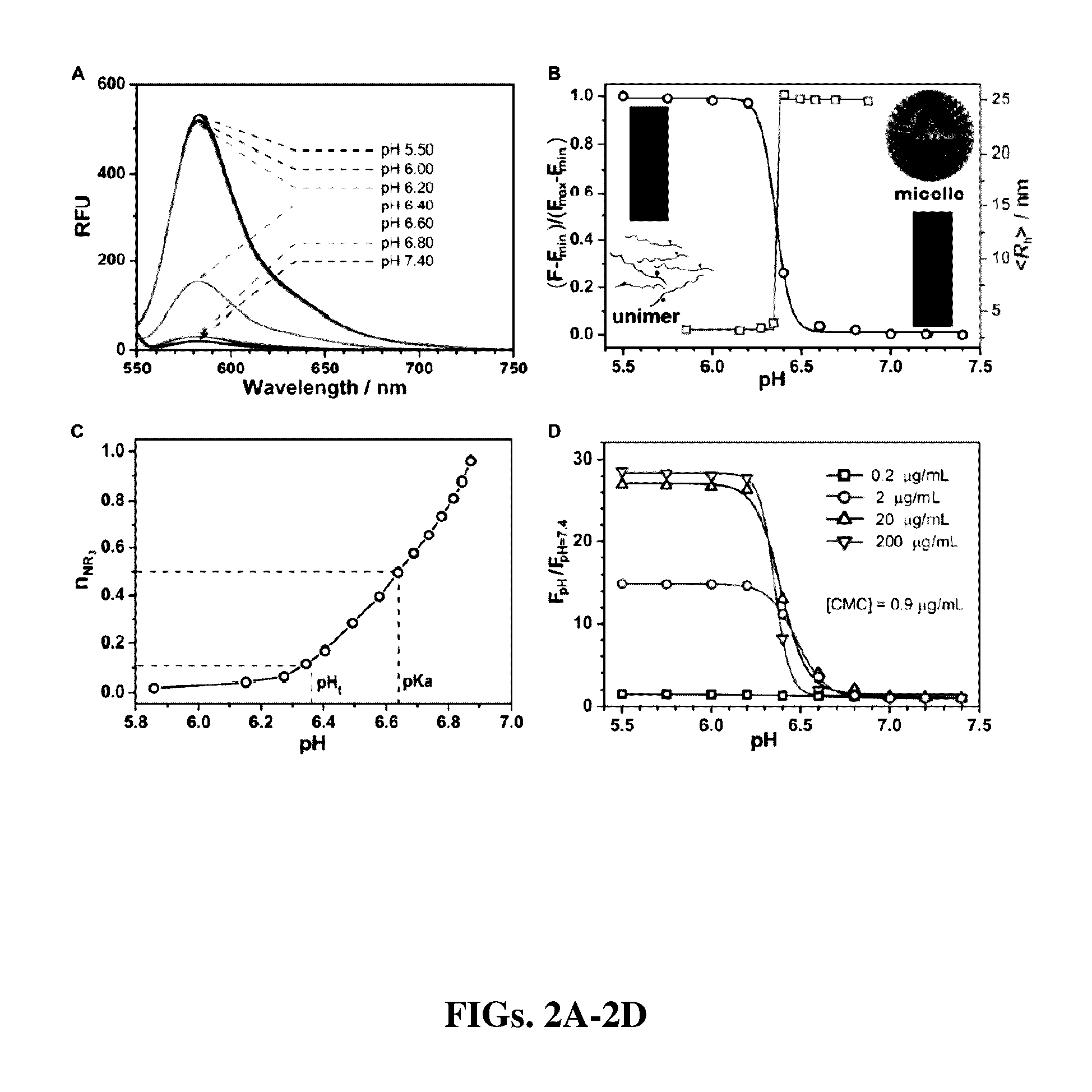
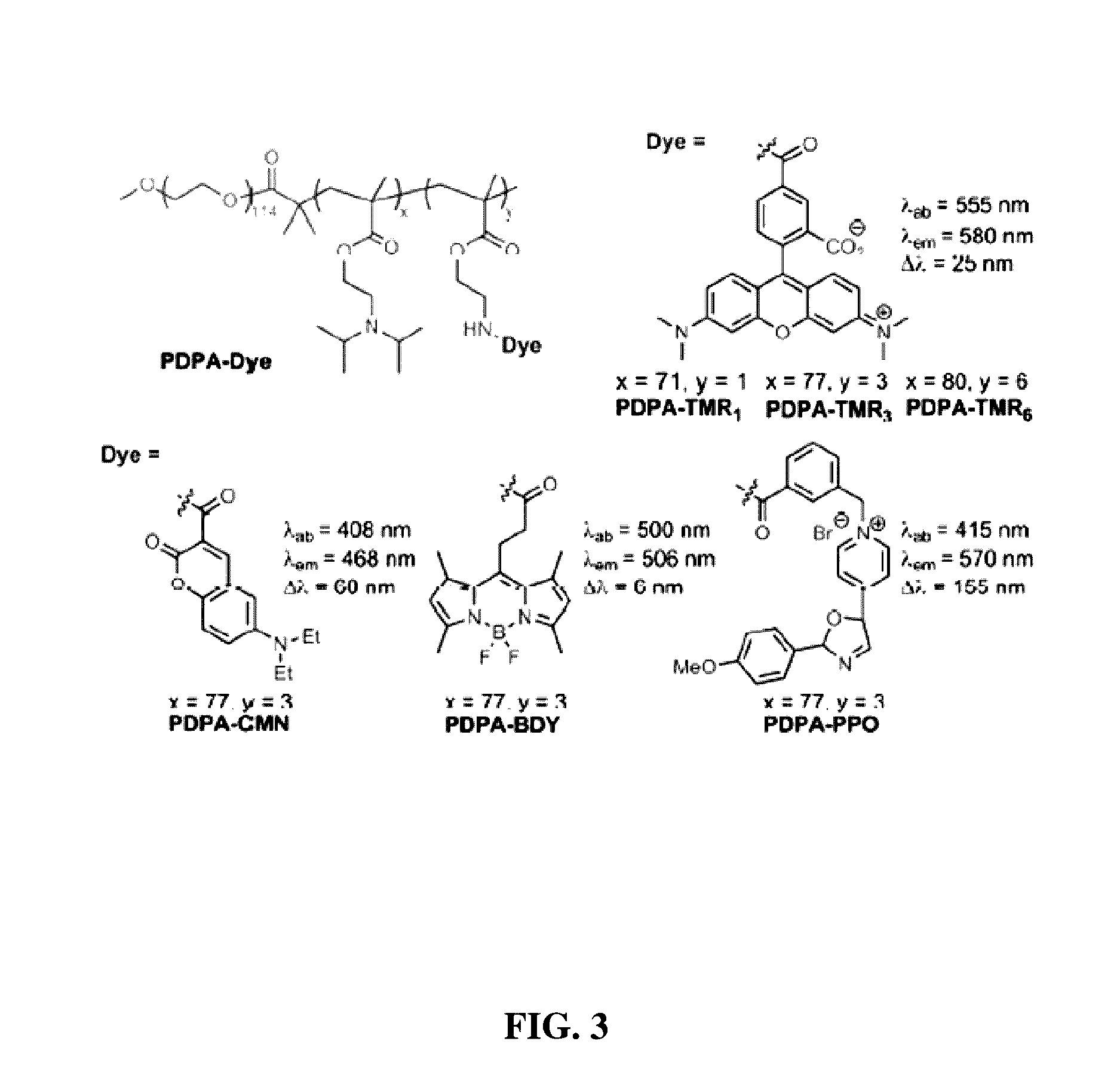
Ratiometric pH fluorescent probe as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105693591AGet rid of preparationGet rid of the optimization processGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical structureFluorescence
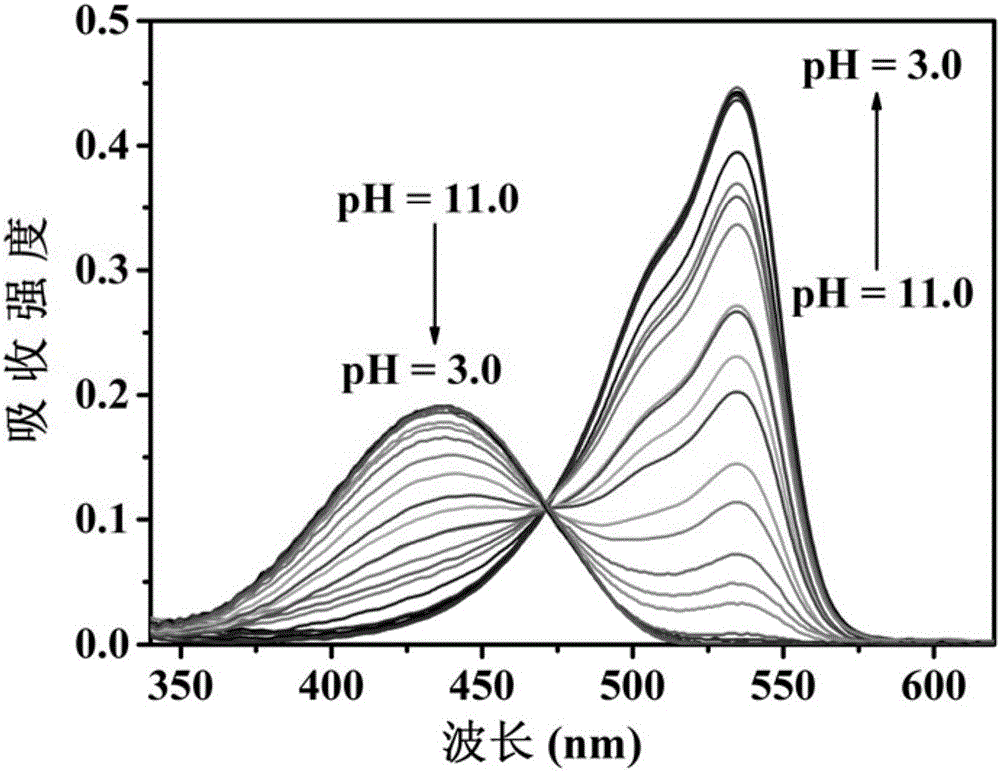
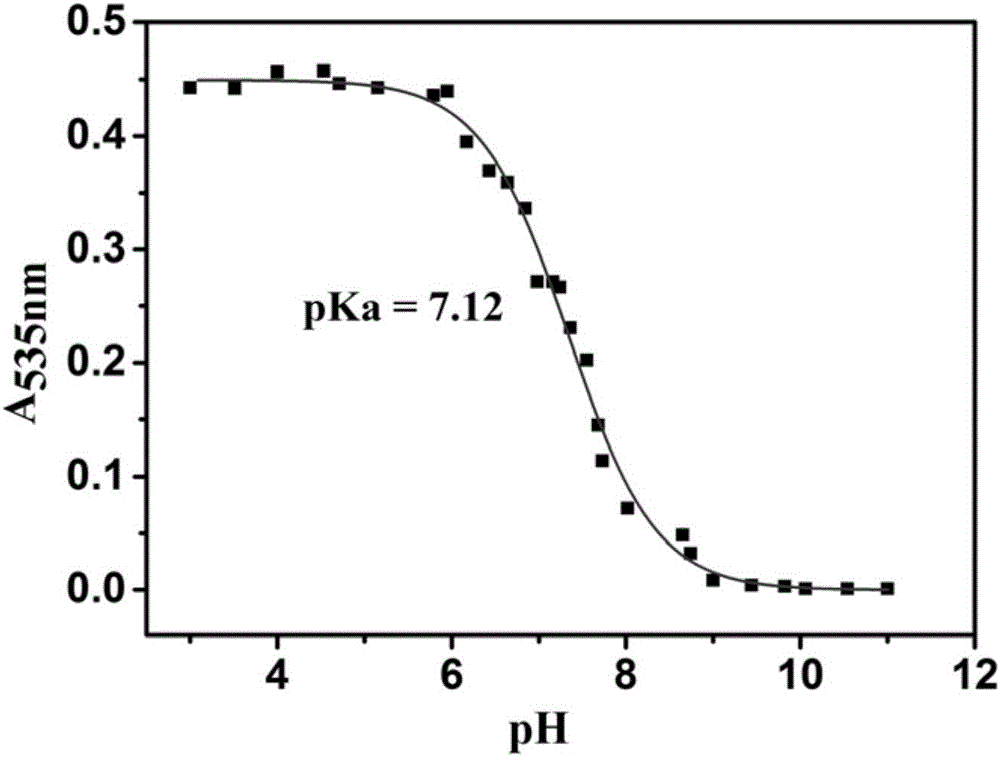
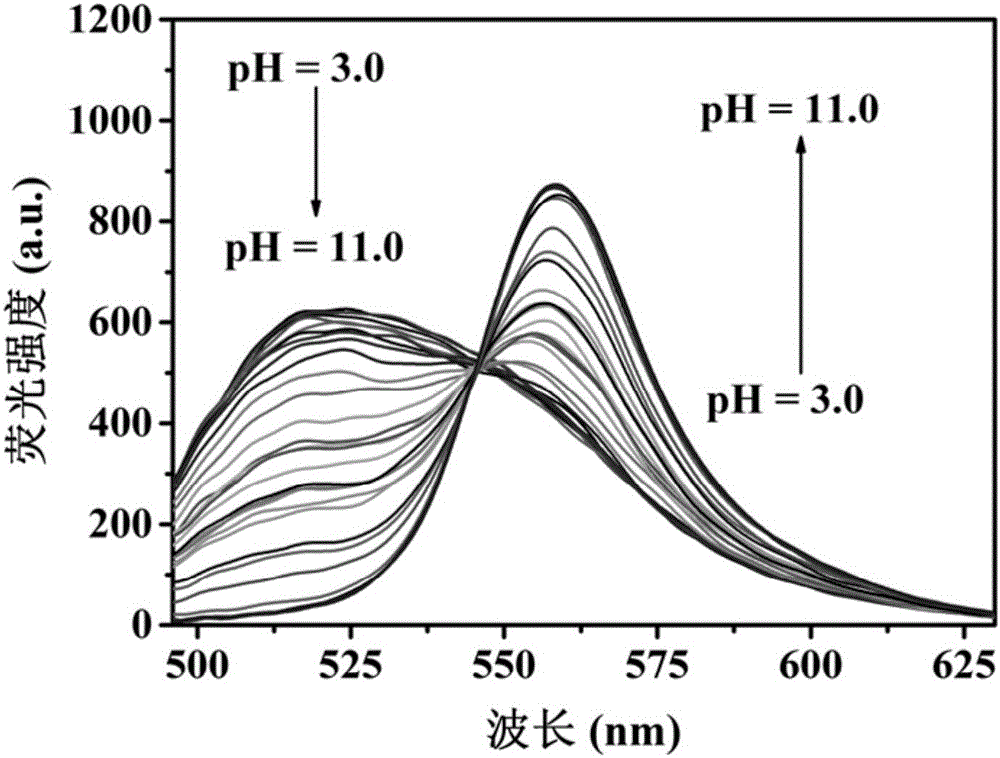
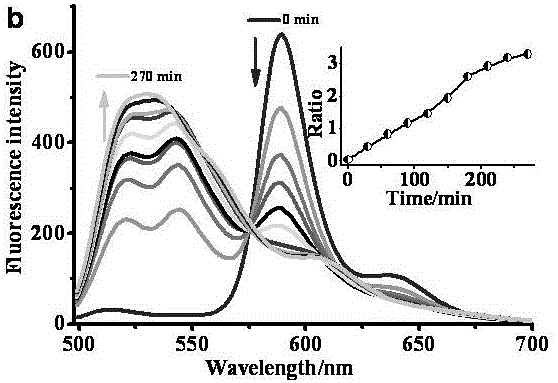
The invention relates to a ratiometric pH fluorescent probe as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The chemical structural formula of the fluorescent probe is shown as formula I in the specification, wherein R is -OH or a subcellular organelle positioning receptor, and the subcellular organelle positioning receptor comprises either of two components shown in the specification. Compared with the prior art, the ratiometric pH fluorescent probe has good light stability, high selectivity, wide pH value detection range and high sensitivity, the preparation method is simple, and the ratiometric pH fluorescent probe can be used for detecting the pH value of a chemical system or the pH value in living cells of creatures.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Detection of transmembrane potentials by optical methods
InactiveUS7173130B2Improve spatial resolutionCompound screeningMethine/polymethine dyesSubcellular organelleMembrane potential
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Novel high protein tortillas
InactiveUS20050095726A1Easy to adaptBetter meetingEgg immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansProtein-protein complexSubcellular organelle
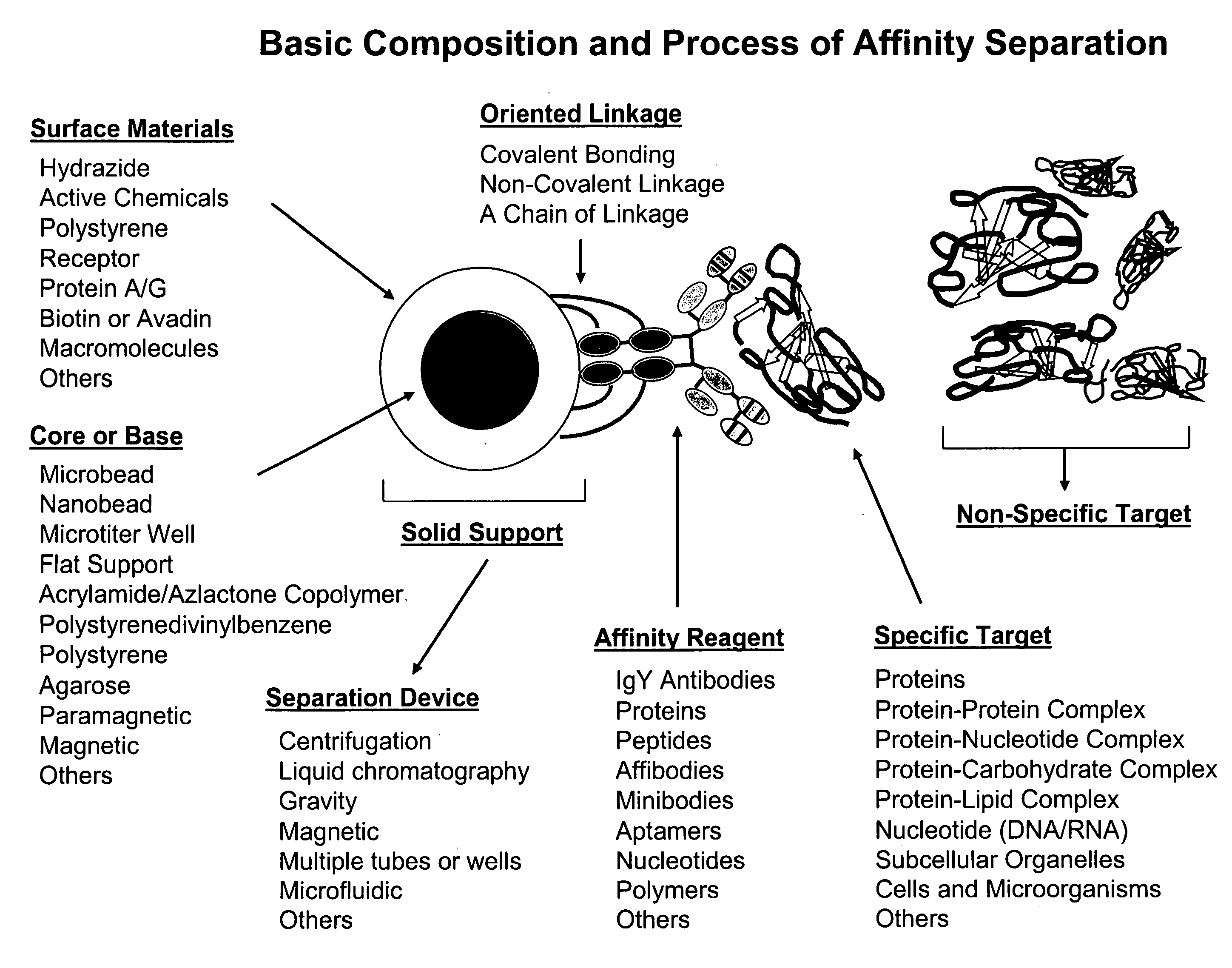
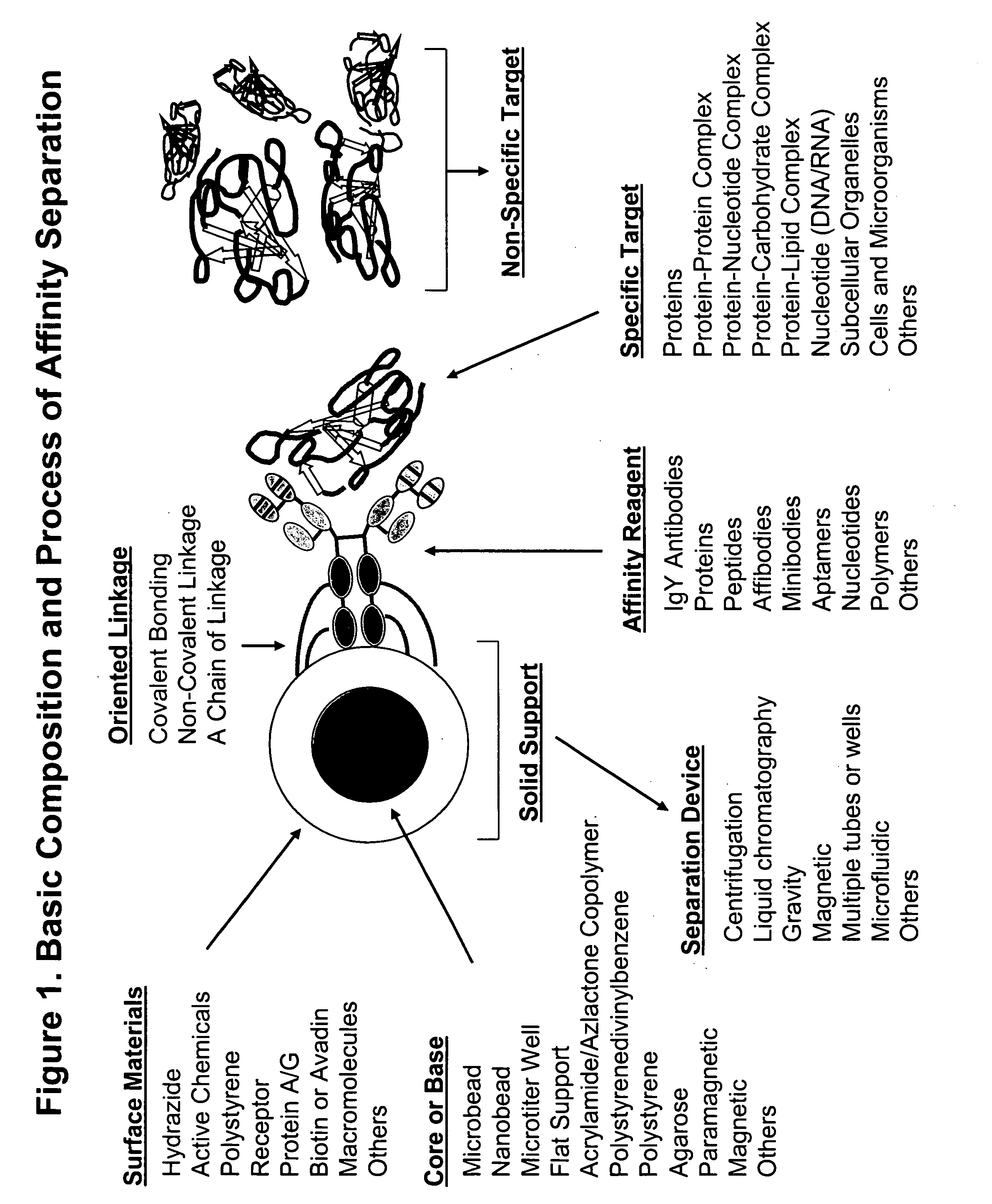
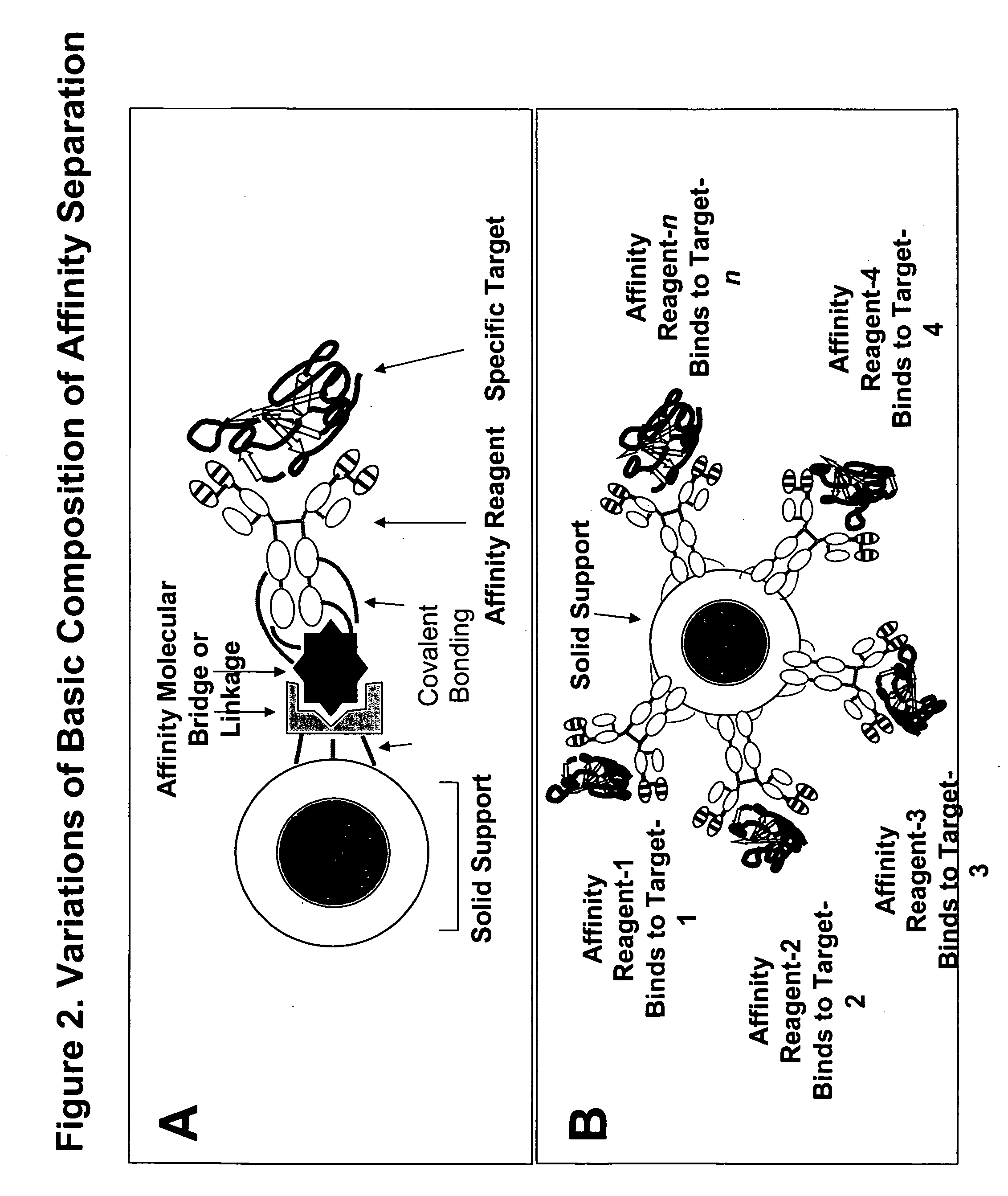
Affinity separation compositions and methods are disclosed for separating targets from complex mixtures. Affinity reagents are bound to a solid support oriented in a manner to facilitate the activity of the affinity reagents which are capable of binding specific targets by affinity recognition. Affinity reagents include IgY antibodies, proteins, peptides, nucleotides and polymers. Targets include proteins, protein-protein complexes, protein-nucleotide complexes, nucleotides, cells and subcellular organelles.
Owner:GENWAY BIOTECH
Microparticle-drug conjugates for biological targeting
InactiveUS20060008461A1Control releasePowder deliveryTripeptide ingredientsAntimicrobial drugMicroparticle
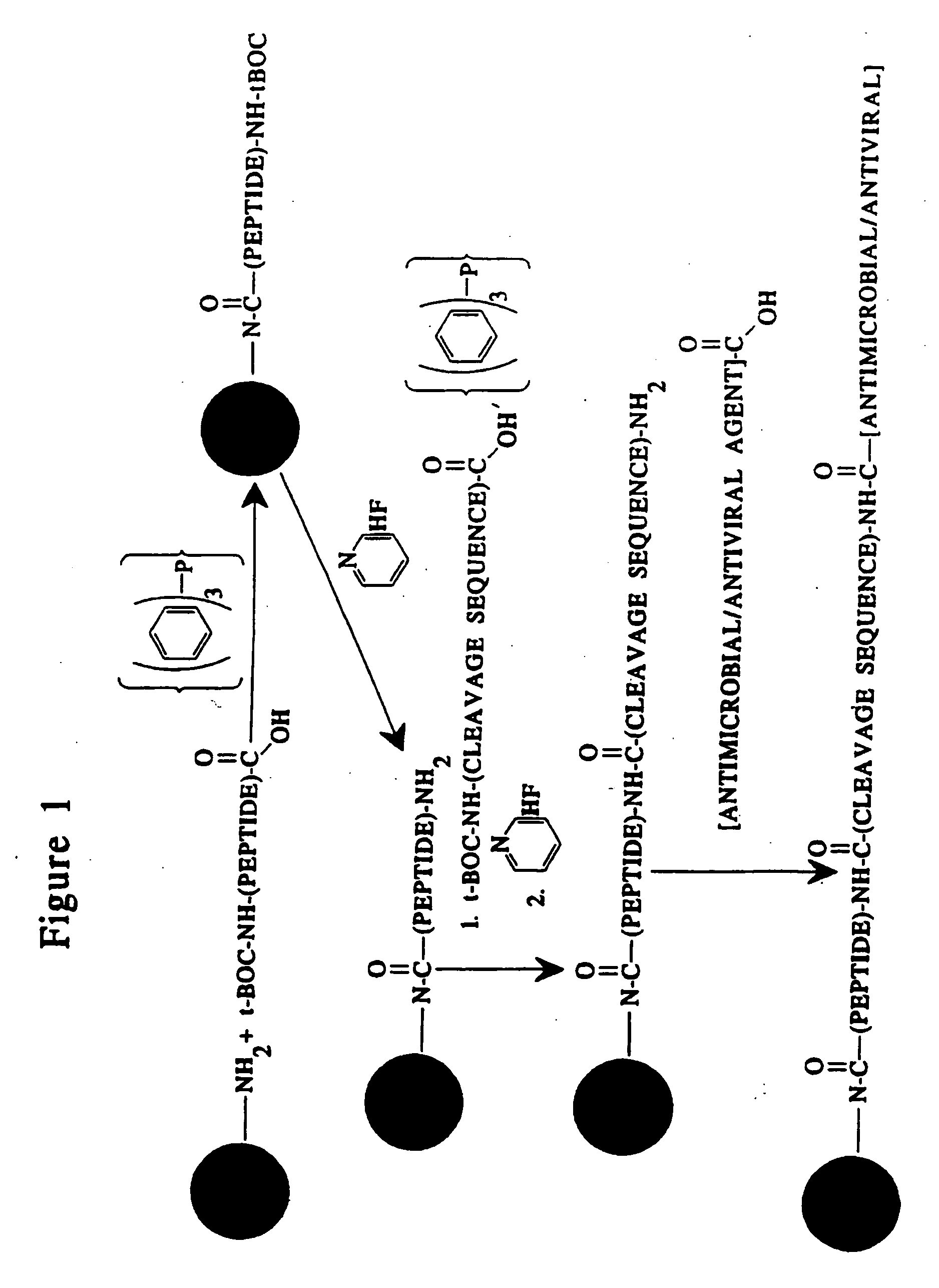
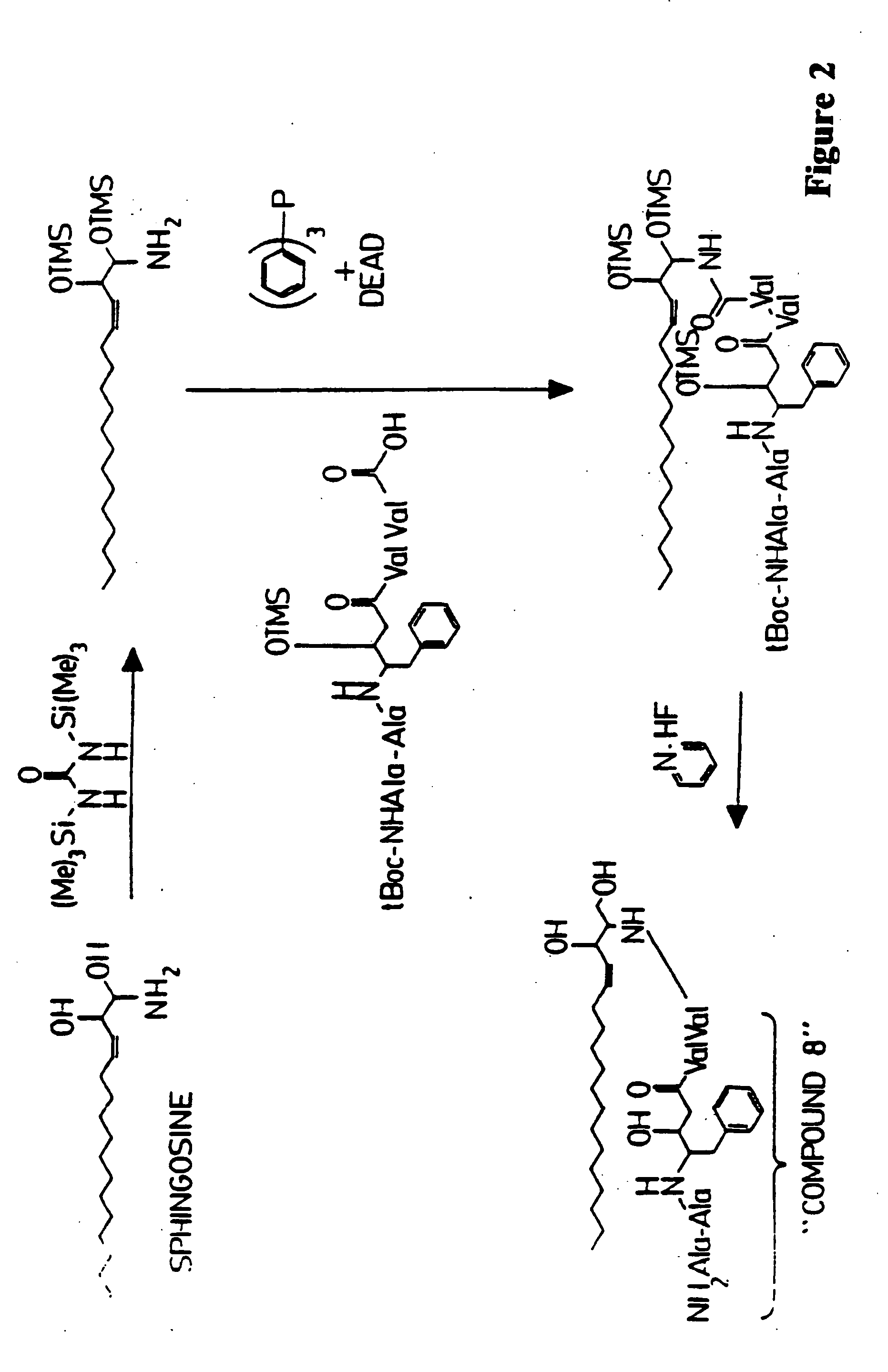
This invention provides novel methods and reagents for specifically delivering biologically active compounds to phagocytic mammalian cells. The invention also relates to specific uptake of such biologically active compounds by phagocytic cells and delivery of such compounds to specific sites intracellularly. The invention specifically relates to methods of facilitating the entry of antiviral and antimicrobial drugs and other agents into phagocytic cells and for targeting such compounds to specific organelles within the cell. The invention specifically provides compositions of matter and pharmaceutical embodiments of such compositions comprising conjugates of such antimicrobial drugs and agents covalently linked to particulate carriers generally termed microparticles. In particular embodiments, the antimicrobial drug is covalently linked to a microparticle via a cleavable linker moiety that is non-specifically cleaved in a phagocytic cell. In additional embodiments, the biologically-active compound is provided in an inactive, prodrug form that is activated by a chemical or enzymatic activity specific for cells infected by a microorganism, particularly a pathological or disease-causing microorganism. Thus, the invention provides cell targeting of drugs wherein the targeted drug is only activated in cells infected with a particular microorganism. Alternative embodiments of such specific drug delivery compositions also contain polar lipid carrier molecules effective in achieving intracellular organelle targeting in infected phagocytic mammalian cells. Particular embodiments of such conjugates comprise antimicrobial drugs covalently linked both to a microparticle via a cleavable linker molecule and to a polar lipid compound, to facilitate targeting of such drugs to particular subcellular organelles within the cell. Also provided are porous microparticles impregnated with antiviral and antimicrobial drugs and agents wherein the surface or outside extent of the microparticle is covered with a degradable coating that is degraded within a phagocytic mammalian cell. Also provided are nonporous microparticles coated with an antiviral or antimicrobial drug and further coated wherein the surface or outside extent of the microparticle is covered with a degradable coating that is degraded within a phagocytic mammalian cell. Methods of inhibiting, attenuating, arresting, combating and overcoming microbial infection of phagocytic mammalian cells in vivo and in vitro are also provided.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
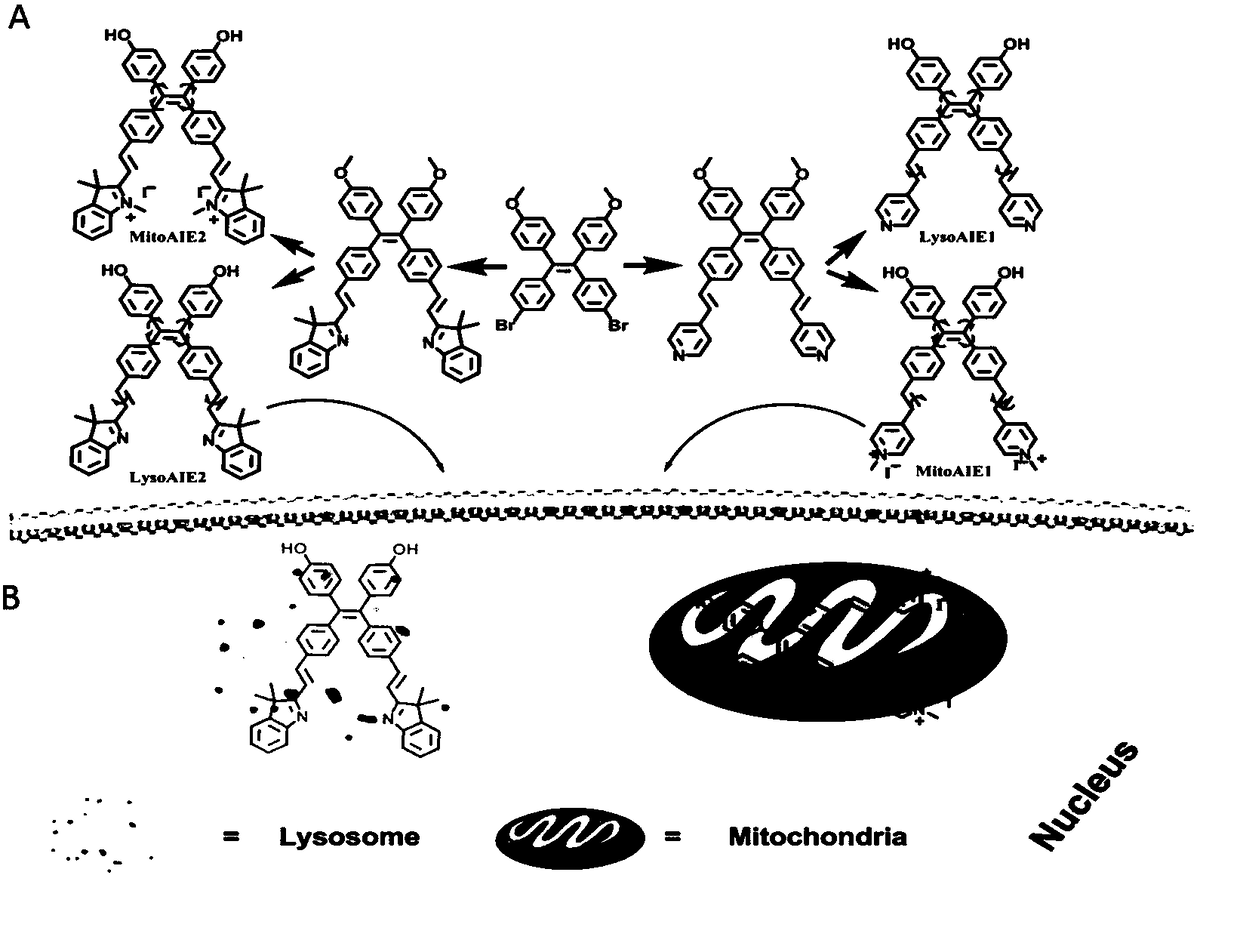
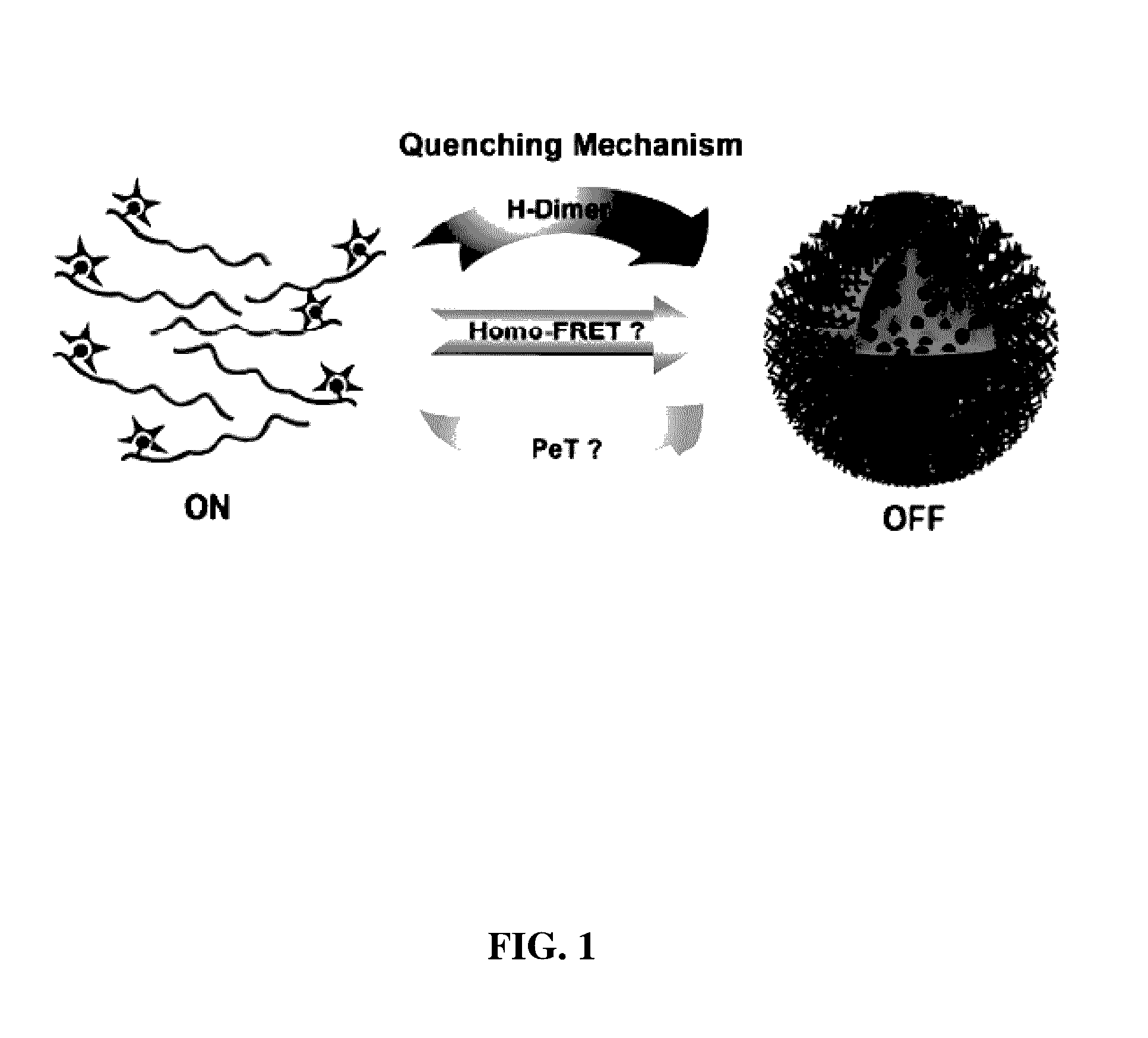
MULTICOLORED pH-ACTIVATABLE FLUORESCENCE NANOPLATFORM
ActiveUS20130330278A1Improved labelingSharp contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceLysosome
The present invention relates to pH-tunable, highly activatable multicolored fluorescent nanoplatforms and methods of using the nanoplatforms in a variety of applications including, but not limited to, investigating fundamental cell physiological processes such as pH regulation in endocytic vesicles, endosome / lysosome maturation, and effect of pH on receptor cycling and trafficking of subcellular organelles.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Plants tolerant of environmental stress conditions, methods of generating same and novel polynucleotide sequence utilized thereby
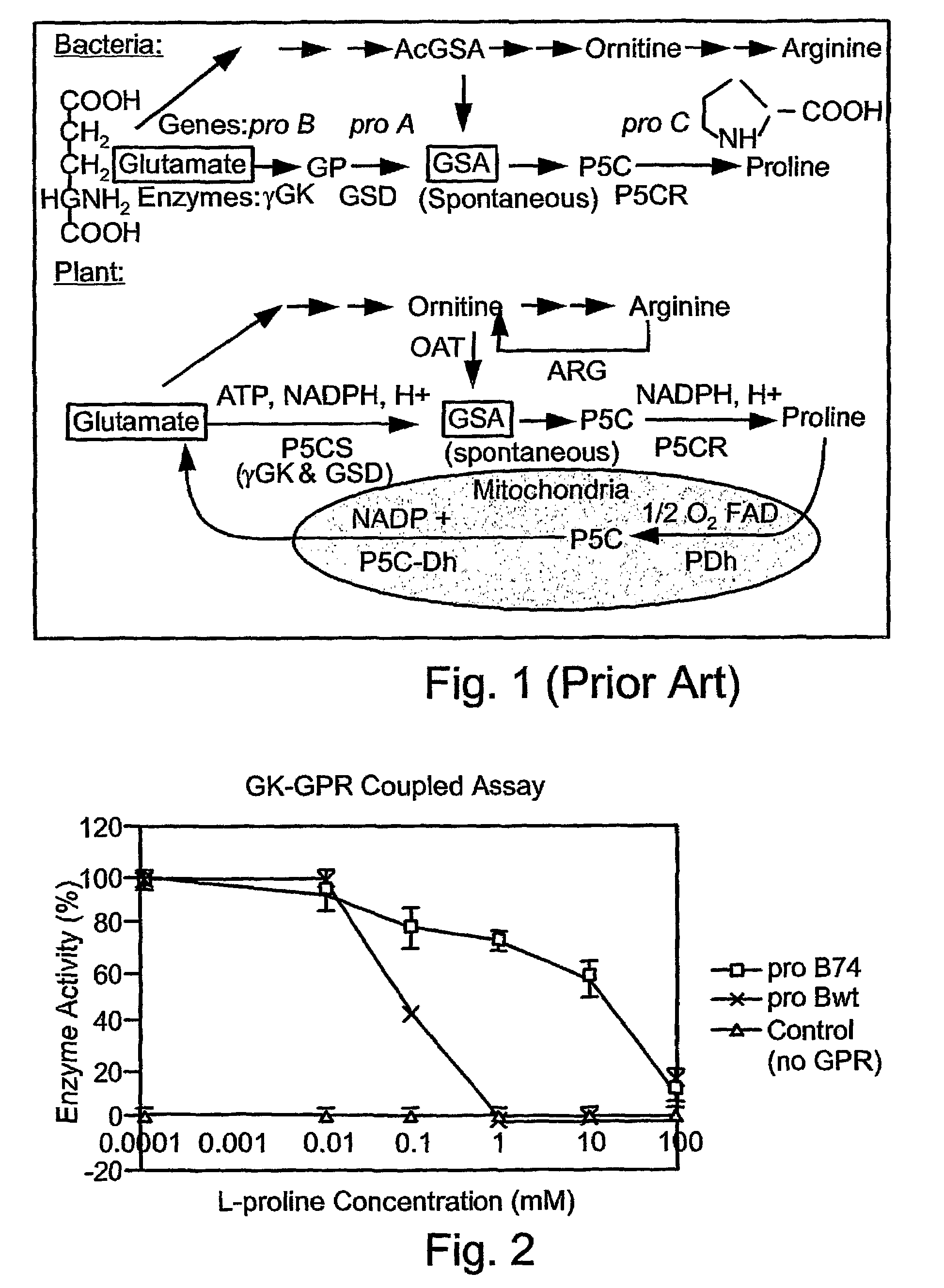
A method of generating a plant tolerant of environmental stress conditions, the method comprising the step of expressing within the plant exogenous polynucleotides encoding enzymes capable of catalyzing proline production, wherein the exogenous polynucleotides are expressed in a manner so as to allow accumulation of the enzymes within a subcellular organelle of the plant. The invention further describes novel polynucleotides and nucleic acid constructs useful in implementing the methods and a transgenic plant resultant therefrom.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
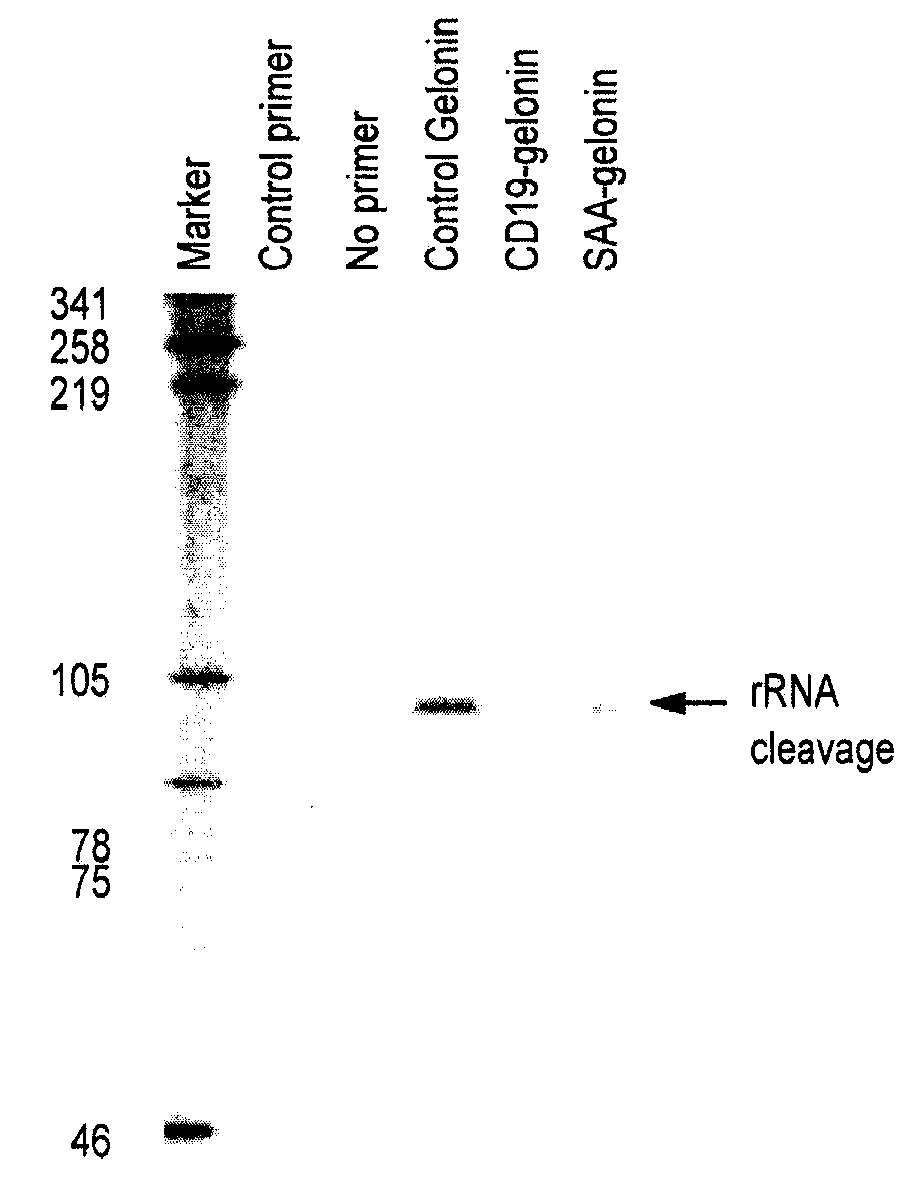
Production of cytotoxic antibody-toxin fusion in eukaryotic algae
InactiveUS20090148904A1Prevent proliferationSugar derivativesUnicellular algaeHeterologousCytotoxic antibody
Methods and compositions are disclosed to engineer chloroplast comprising heterologous genes encoding target binding domain fused to a eukaryotic toxin and produced within a subcellular organelle, such as a chloroplast. The present disclosure demonstrates that when chloroplasts are used, toxins normally refractive to production in eukaryotic cells may be used to produce recombinant fusion proteins with binding domains that are soluble, properly folded and post-translationally modified, where the multifunctional activity of the fusion protein is intact. The binding domains may include those from antibodies, receptors, hormones, cytokines, chemokines, and interferons. The present disclosure also demonstrates the utility of plants, including green algae, for the production of complex multi-domain proteins as soluble bioactive therapeutic agents.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Application of cell nucleus targeting chitosan-fatty acid graft as medicine carrier micelle
InactiveCN101066461ALow carrier toxicityLow toxicityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsLysosomeCell membrane
The present invention is application of medicine carrying chitosan-fatty acid grafting micelle in preparing targeting antitumor medicine carrier, especially antitumor medicine carrier targeting to lung cancer cell nucleus, cervical carcinoma cell nucleus and mammary cancer cell nucleus. The chitosan-fatty acid grafting micelle of the present invention has grafting carrier with low toxicity, and may be ingested fast by cell nucleus to target to cell nucleus and to raise the curative effect of antitumor medicine by up to 80 times. It has cell nucleus targeting function of permeating cell membrane fast with less destruction by intracellular lysosome. The grafting micelle with hydrophobic kernel can envelop hydrophobic antitumor medicine targeting cell nucleus to form medicine carrying grafting micelle. The present invention provides nanometer subcellular organelle administration for high efficiency low toxicity tumor treatment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
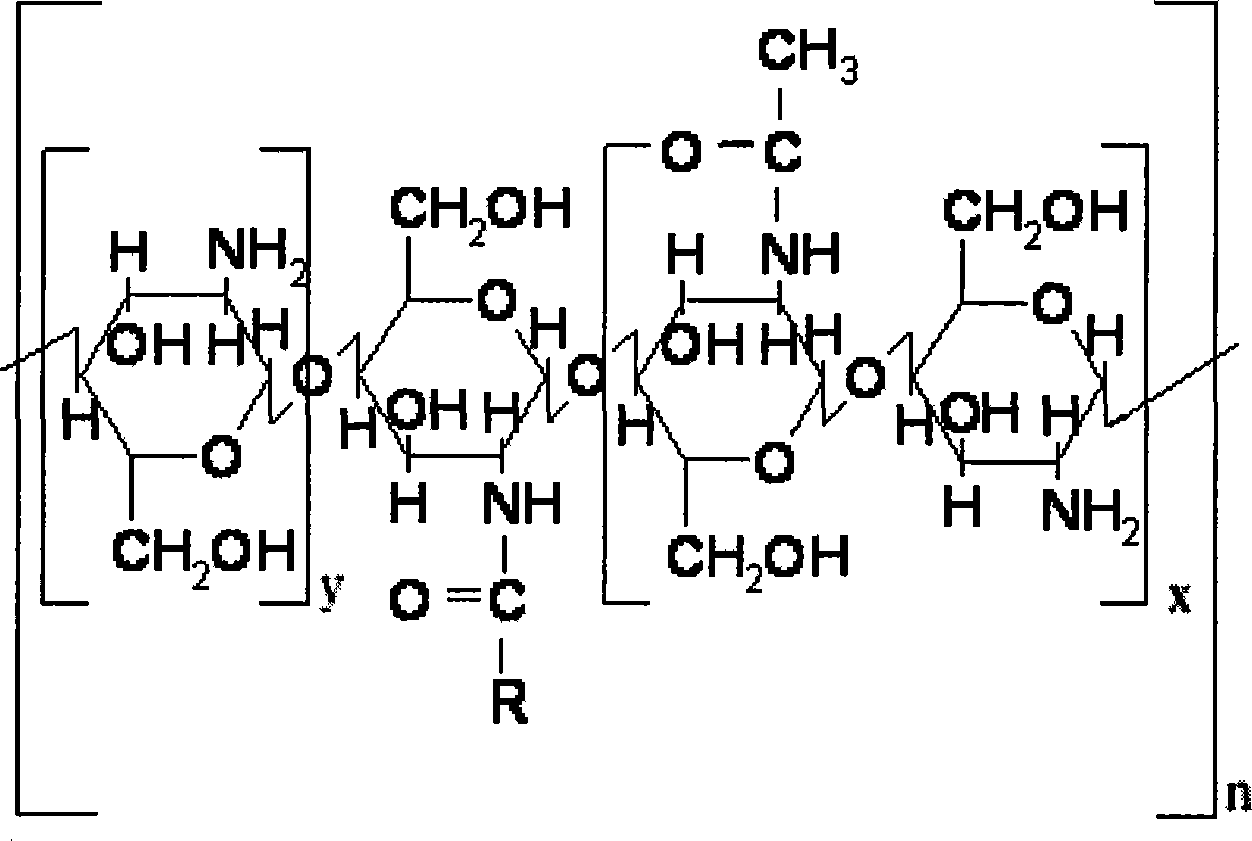
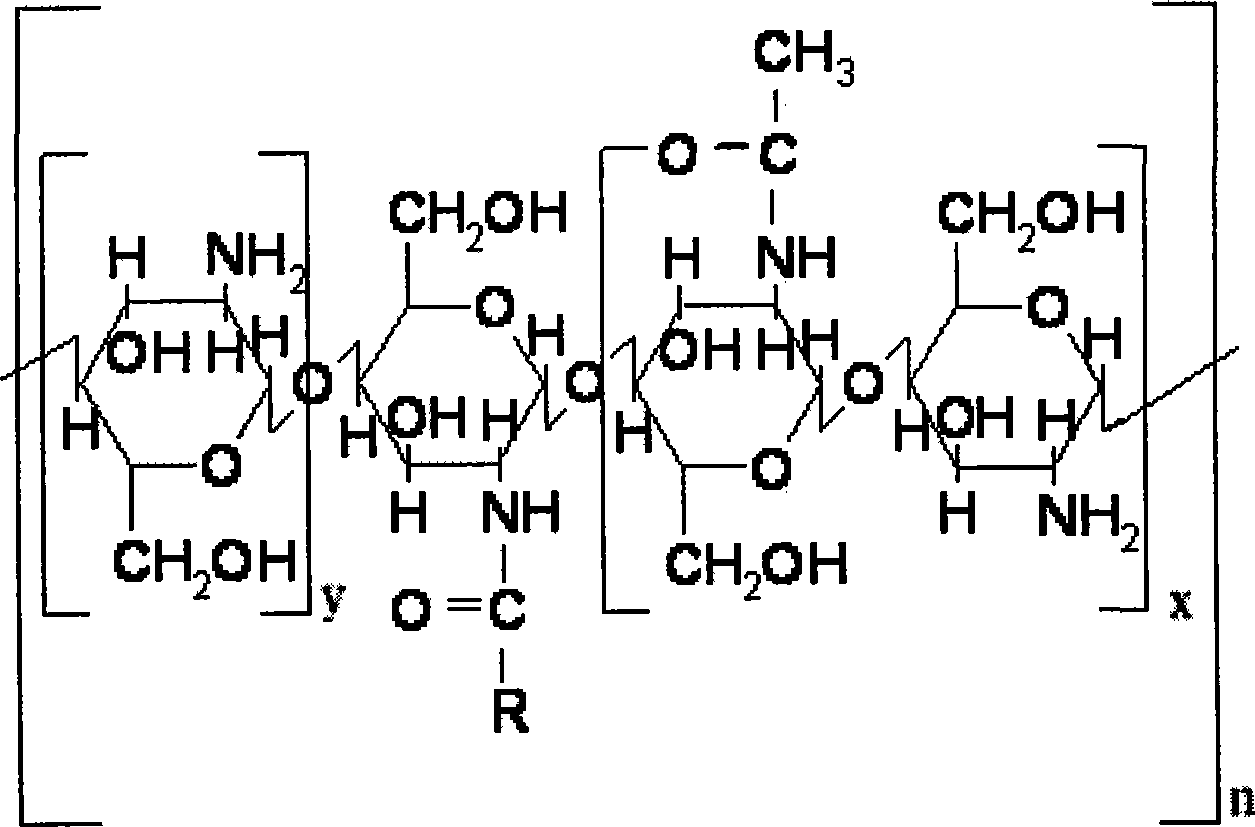
Subcellular organelle target directional Chitosan oligosaccharide-aliphatic acid grafting matter and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101081876AReflect the function of transportFast intakePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFermentationSubcellular organelleFatty acid
The present invention provides chitosan-fatty acid grafting in the structure as shown, and the chitosan has molecular weight of 1-100 kDa, deacetylating degree of 70-100 % and partial free amino radicals substituted by alkyl radical in the substitution degree of 1-90 %. Through one improved alkylating modification process, degraded chitosan or low molecular weight chitosan is alkylation modified to form the chitosan-fatty acid grafting in special structure. The chitosan-fatty acid grafting may form micelle capable of being used as particle carrier for subcellular organelle in relevant research and preparing target medicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Fluorescent probe for monitoring lipid peroxidation processes in different subcellular organelles
ActiveCN105001856AStable in natureEasy to storeGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFluoProbesPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for monitoring lipid peroxidation processes in different subcellular organelles, and belongs to the field of fine chemical engineering. The fluorescent probe is prepared through the steps of: enabling fluorine boron pyrrole derivatives to react with cinnamic aldehyde, wherein piperidine is used as a catalyst, and a 4 angstrom molecular sieve is used as a dehydrating agent; and performing quaternization on the obtained reactant so as to obtain molecules of the fluorescent probe. The probe contains active groups such as triphenylphosphine cations, morpholine and quaternary ammonium salt cations, the probe has a single-minded subcellular organelle targeting property because of the different active groups, and the probe can be optionally positioned on subcellular organelles such as mitochondria, lysosomes and cell membranes. The probe has zero toxin and zero side effects and is suitable for monitoring the lipid peroxidation processes in the subcellular organelles in different physiological processes through a fluorescent microscope or flow type cell analyzing technology. The probe is stable in solid condition nature and easy to store for a long time, an intuitional succinct detecting reagent with low cost is provided for inquiring processes relevant to the lipid peroxidation in cells, and microcosmic structural information is provided for detection by a subcellular organelle targeting property function.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
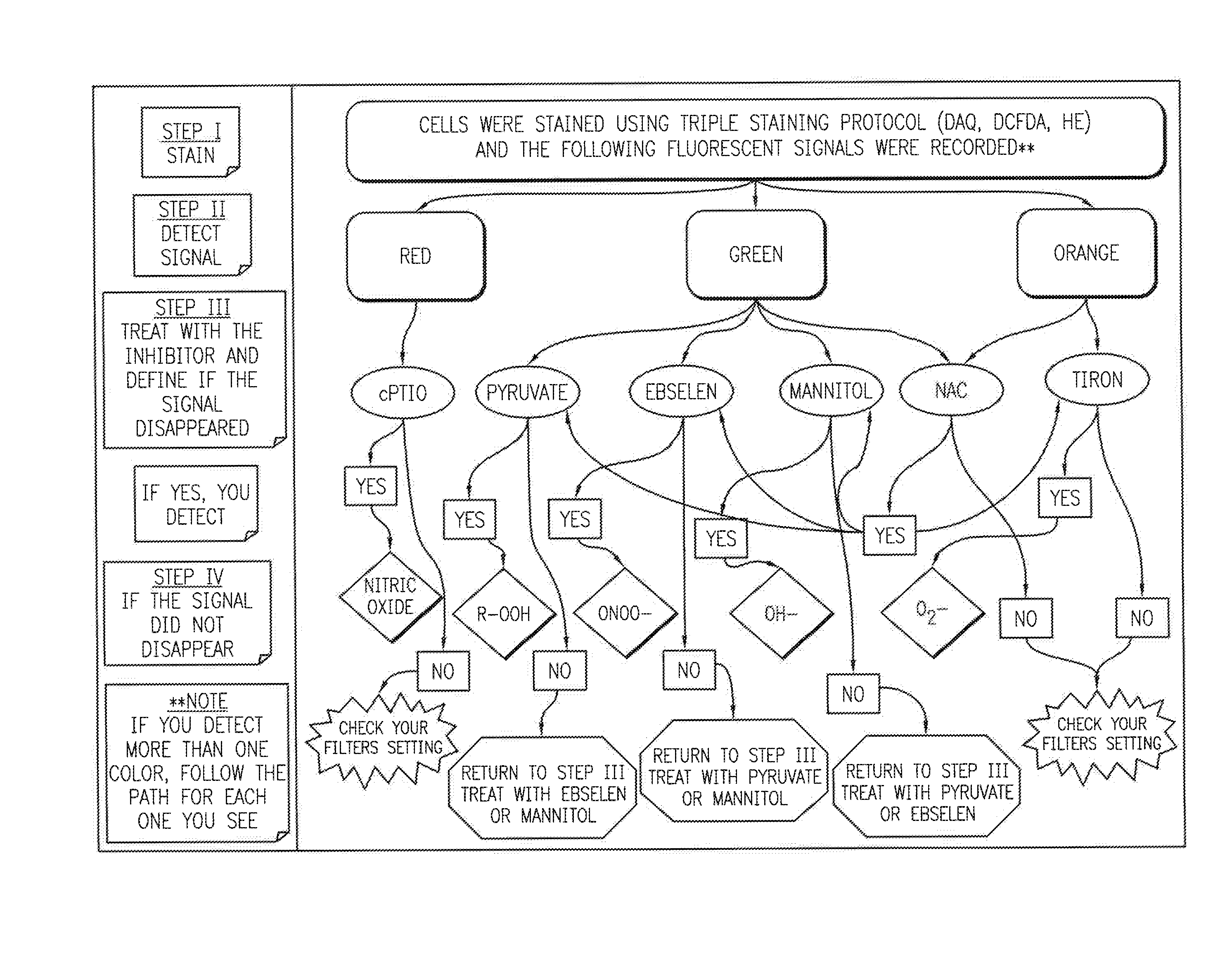
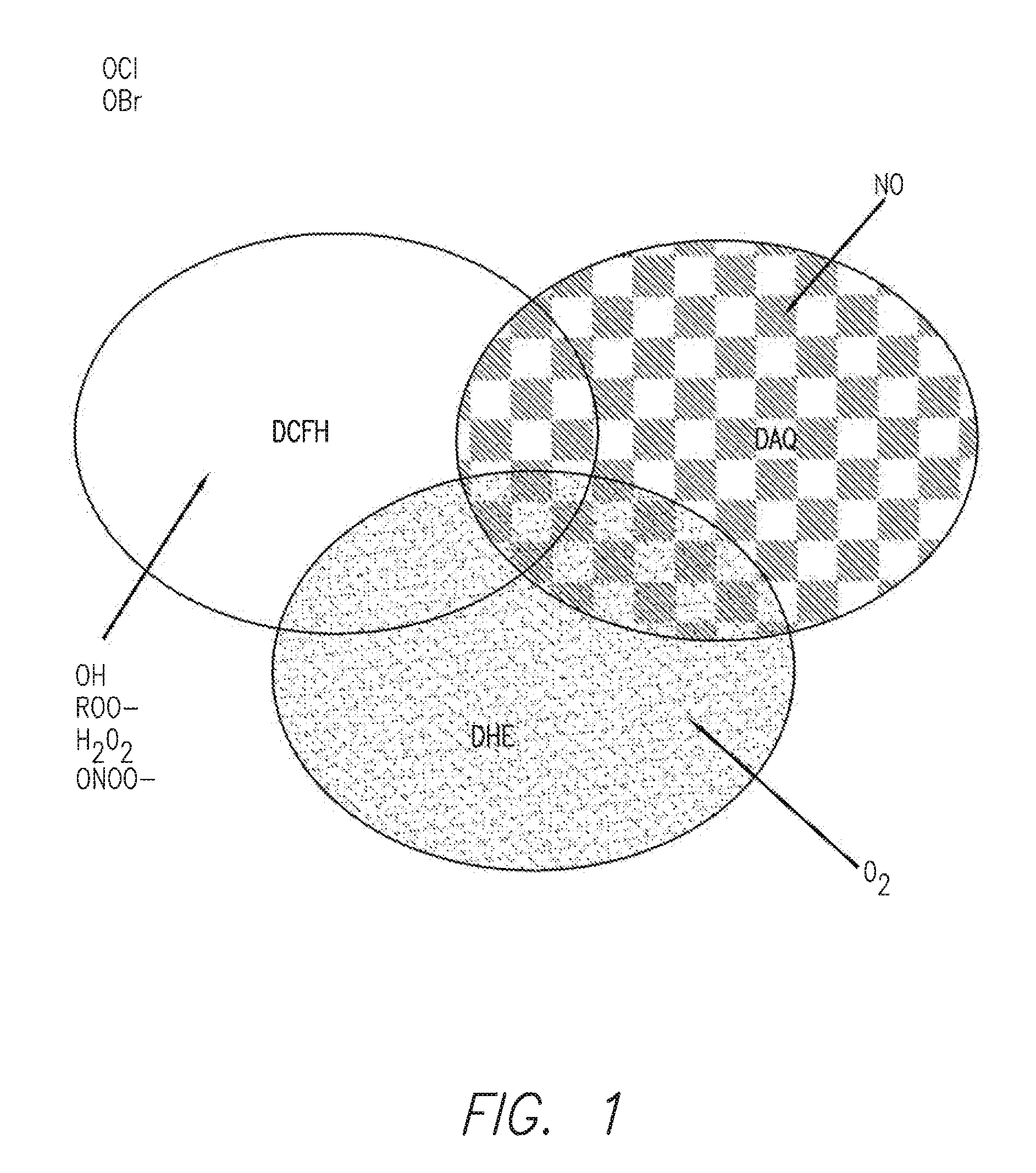
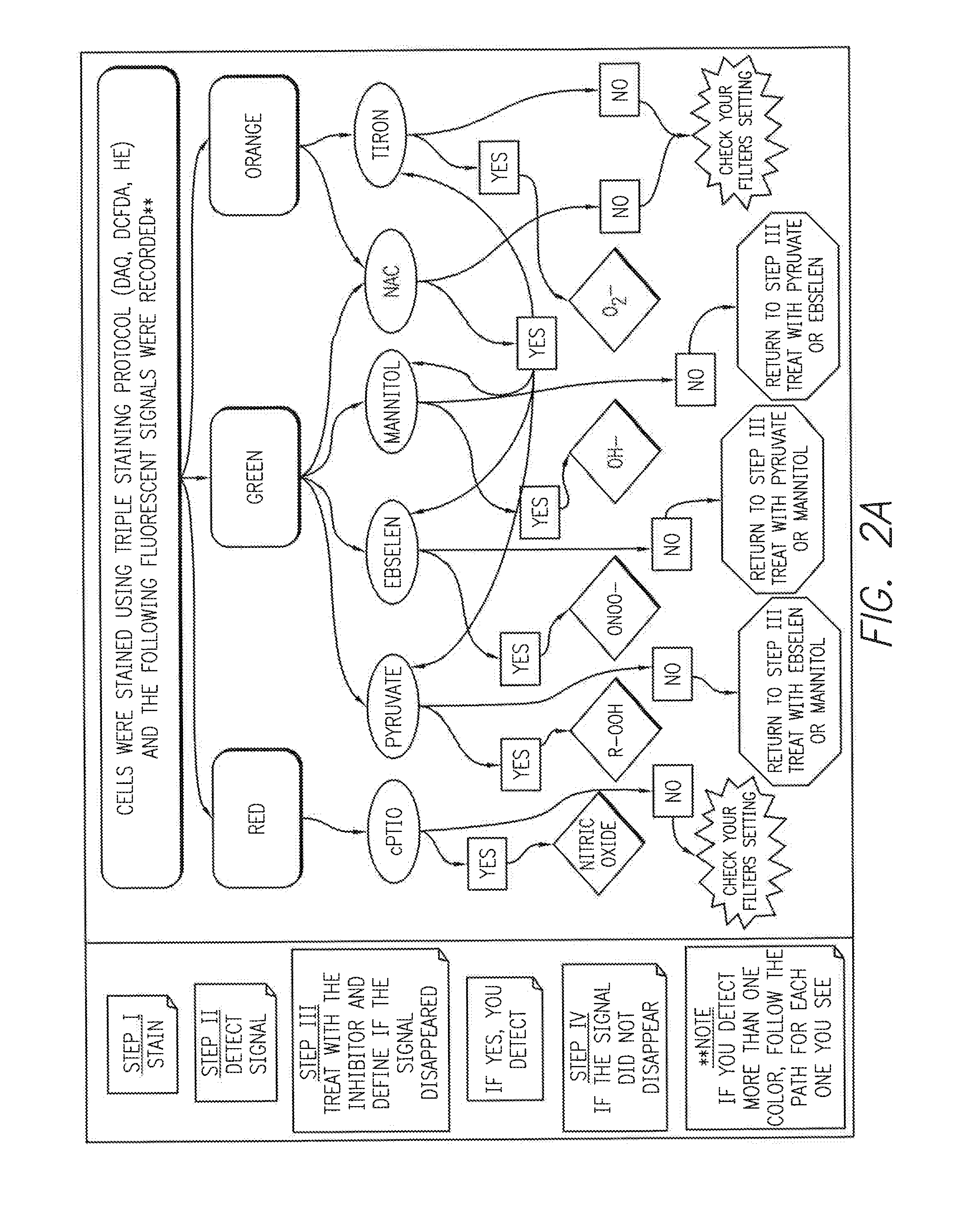
Profiling reactive oxygen, nitrogen and halogen species
InactiveUS20150192564A1Microbiological testing/measurementIndividual particle analysisHalogenFluorescence
This invention provides methods, kits and systems which permit simultaneous profiling of multiple reactive oxygen species (ROS), reactive nitrogen species (RNS) and / or reactive halogen species (RHS) including reactive chlorine species (RCS) and / or reactive bromine species (RBS) through multiplexed fluorescence detection of three or more indicator probes in live cells or subcellular organelles.
Owner:ENZO LIFE SCI INC
A plant transformation vector and its construction method and application
InactiveCN102286524AHigh expressionOvercoming the problem of preferenceVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsChloroplastMethyltransferase
The invention provides a plant transformation vector, and a construction method and application thereof. In the vector, a red fluorescent protein UPMT (uroporphyrinogen III methyltransferase) and a resistance screening alad gene are used as a reporter gene and a selected marker for plant transfection. The red fluorescent protein UPMT and the resistance screening alad gene have similar functions, are superior to antibiotic and a green fluorescent protein fusion marker for example, and can be used for screening and subcellular organelle positioning in rice chloroplast transformation. Thus, the two genes used as screening markers of a transgenic plant can indicate the positioning of the cytologic and tissue specificity of a target gene, and can also promote the photosynthesis efficiency of plants and the accumulation of nutrient substances. The invention has potential and broad application backgrounds in the transgenic plant research and marketing process, and is hopefully developed into a dominant selected marker system in plant transformation.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Difunctional tumor targeted liposome drug-delivery system and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN105012956AAcid sensitivityHigh selectivityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTumor targetArginine
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutic preparations in medical technology and discloses a difunctional tumor targeted liposome drug-delivery system and a preparation method and an application thereof. By directly coupling a cell-penetrating peptide rich in arginine residues and liposome surface long-chain organic acid and with the combination of a polyethylene glycol-hydrazone bond-long-chain organic acid conjugate, a tumor targeted liposome loading a fat soluble drug and a water-soluble anthraquinone slightly alkaline drug is prepared by a thin-film rehydration method, wherein the cell-penetrating peptide is polyarginine short peptide, preferably nonaarginine; molecular weight of polyethylene glycol is 500 Da-5000 Da, preferably 2000 Da; optimal cell-penetrating peptide density is 2-8% (preferably 4%) of density of phospholipid; and density of the polyethylene glycol-hydrazone bond-long-chain organic acid conjugate is 5-20% (preferably 8%) of density of phospholipid. The system provided by the invention solves the problem that existing liposome cellular internalization is difficult, and provides possibility for antitumor drug targeting subcellular organelle. The drug-delivery system basically is nontoxic, has a simple preparation technology and is easy for industrial application.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
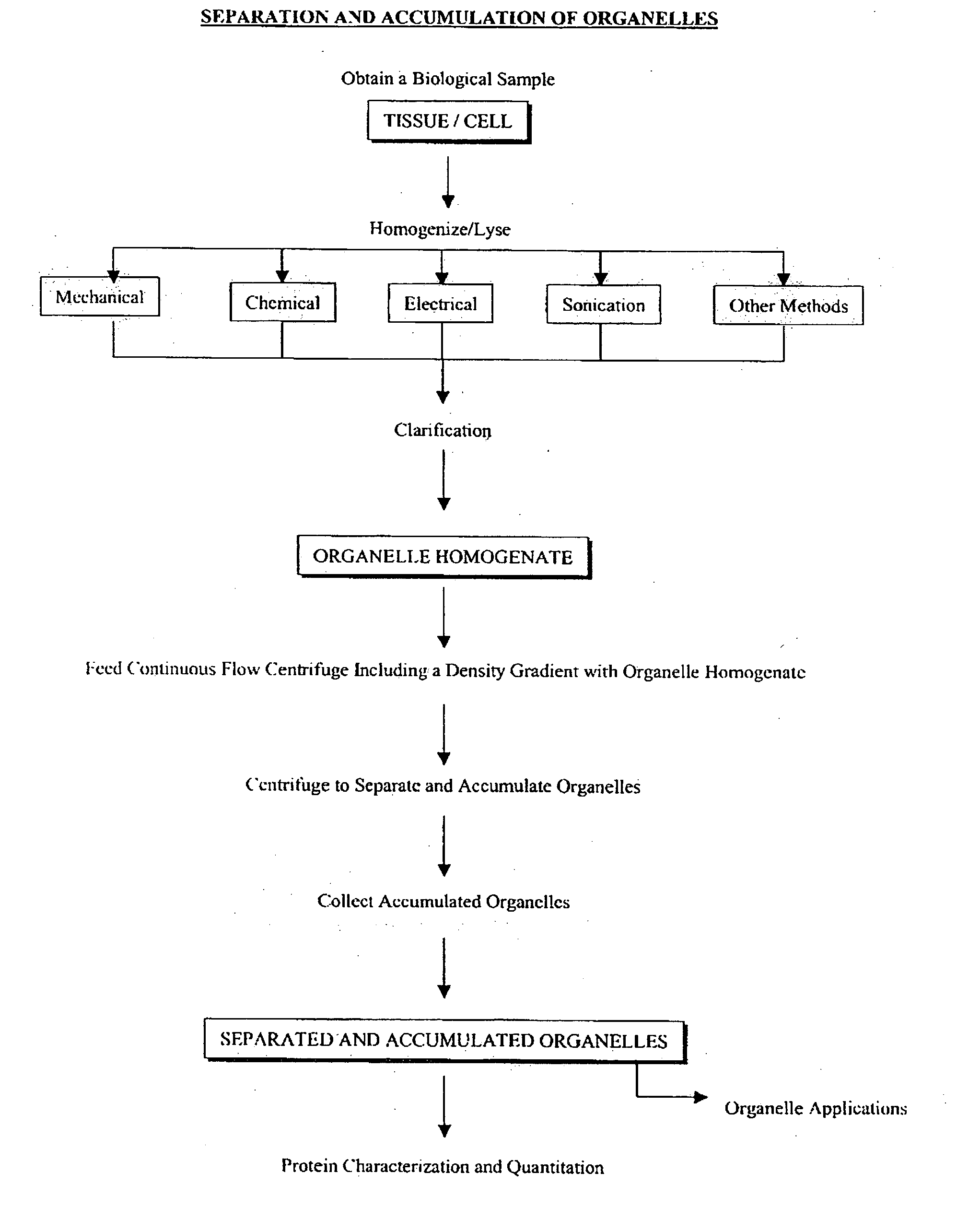
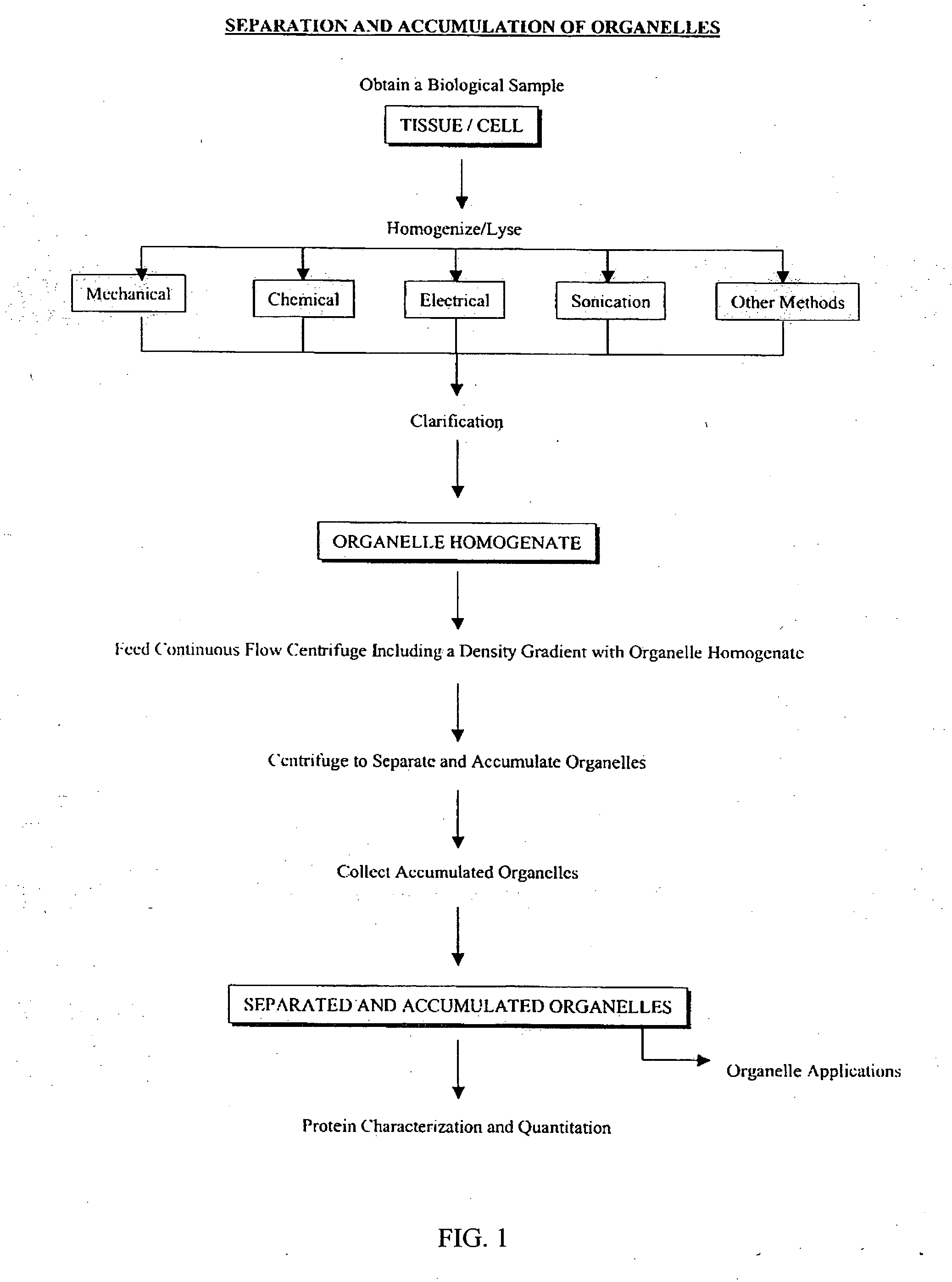
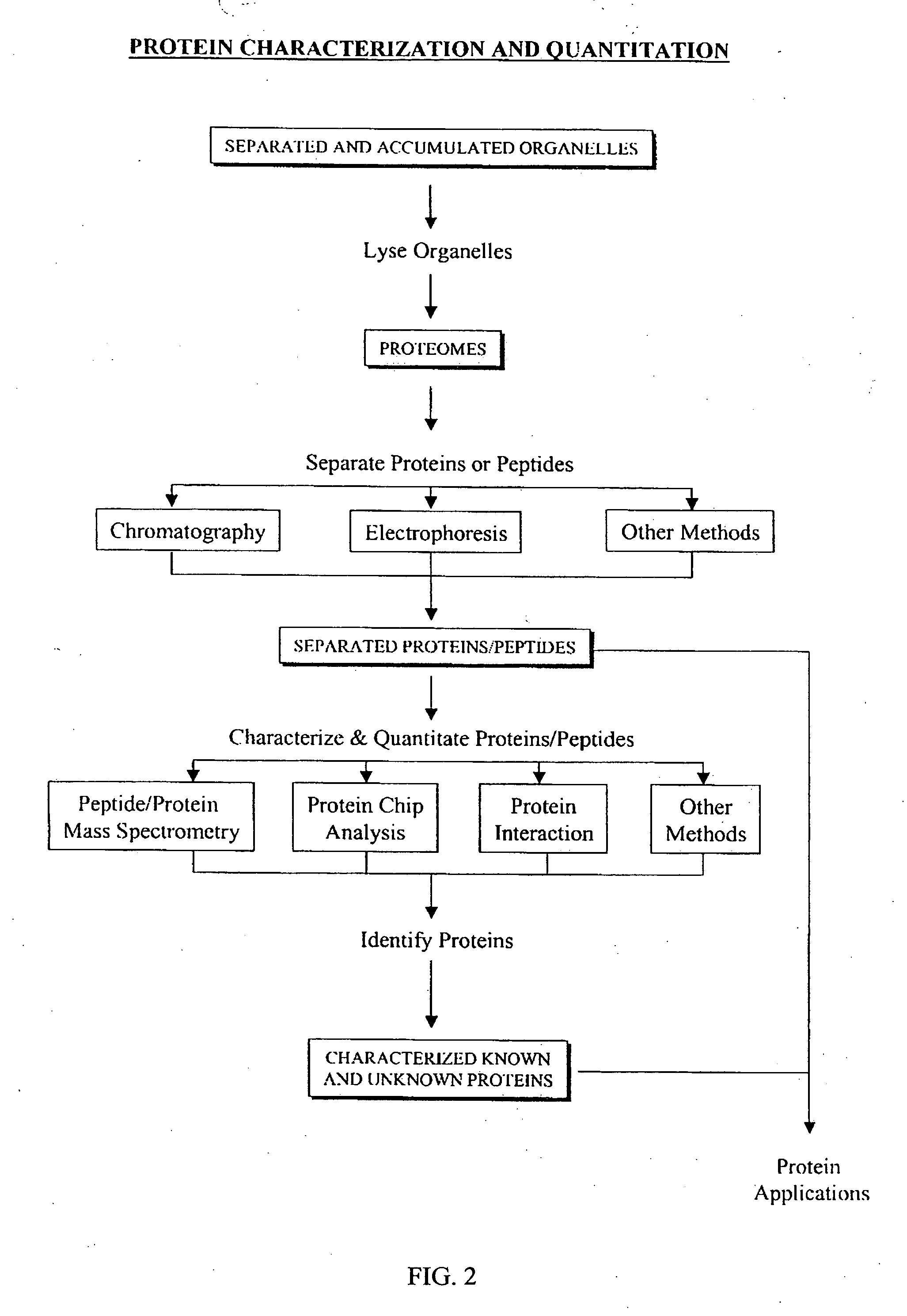
Separation and accumulation of subcellular components, and proteins derived therefrom
InactiveUS20060266715A1Sufficient yieldAvoid insufficient purityWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationMicrobiological testing/measurementFractionationContinuous flow
The present invention provides for proteome fractionation through the separation and accumulation of subcellar organelles from a biological sample such that the subcellular organelles are highly enriched, substantially pure, and whose structural integrity and functions are well-preserved. The methods of the invention provide a manner by which to reduce the complexity of the proteome and facilitate the detection and isolation of difficult-to-study proteins, such as low-abundance proteins. The methods of the present invention for pre-fractioning proteomes of biological samples by parallel separation and isolation of subcellular organelles from the biological samples using continuous-flow ultracentrifugation are also easily and effectively scalable through adjustment to ultracentrifugation parameters, such as, for example, rotor speed, rotor size, rotor geometry.
Owner:LOEWY ZVI
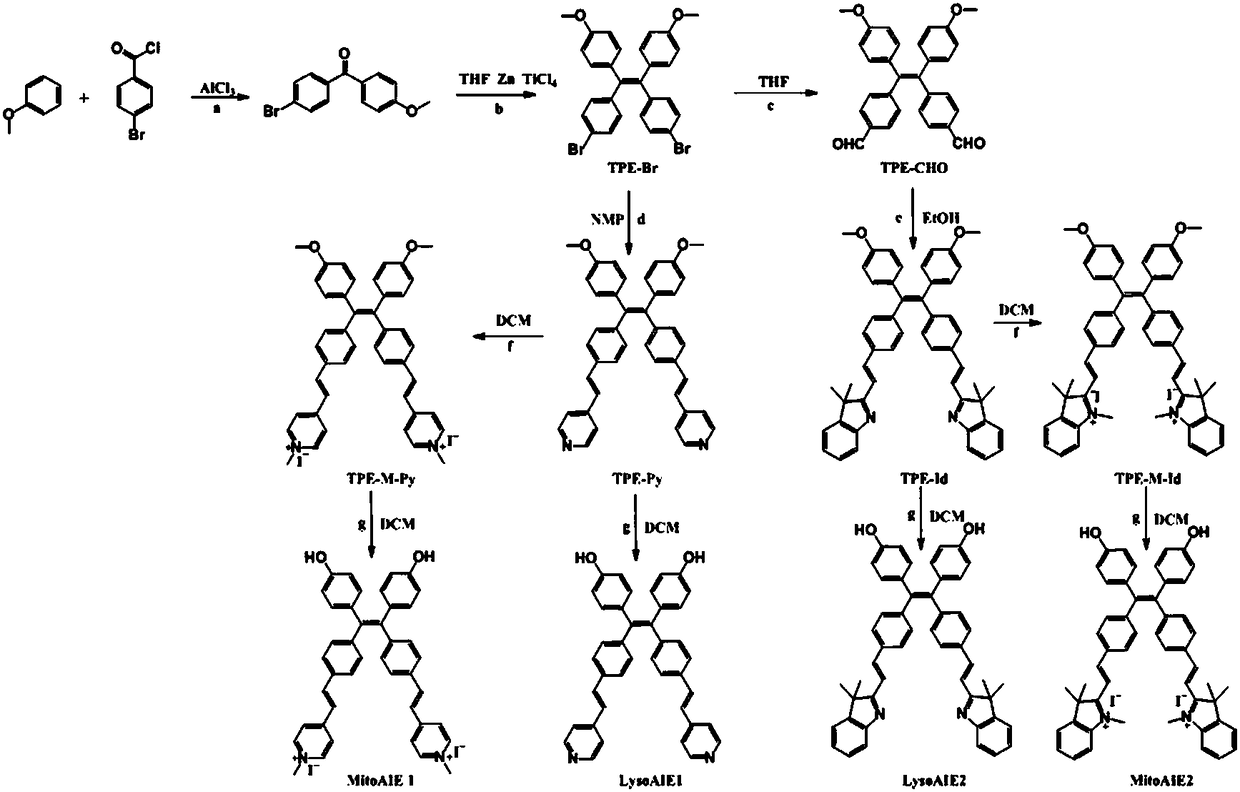
Tetraphenylethylene-based subcellular organelle viscosity probe, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108516950AImprove image contrastEasy to prepareOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolubilityLysosome
The invention provides a tetraphenylethylene-based subcellular organelle viscosity probe, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The subcellular organelle viscosity probe comprises a mitochondrial viscosity probe and a lysosomal viscosity probe. The preparation method mainly comprises the following steps (1) synthesis of a compound TPE-Br, (2) synthesis of a compound TPE-CHO, (3) synthesis of the mitochondrial viscosity probe, and (4) synthesis of the lysosomal viscosity probe. The synthesized viscosity probe can be used for detecting the viscosity of subcellular organelles. Thepreparation method of the tetraphenylethylene-based subcellular organelle viscosity probe is simple; the synthesized viscosity probe has good water solubility, and has no influences on the state of studied cells in the working concentration range; the viscosity probe has weak self-fluorescence background, so the imaging contrast of the subcellular organ viscosity monitoring is improved; and the viscosity probe is sensitive to the viscosity, has strong anti-interference, and has good targeting specificity to the subcellular organelles.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Hypoxia activation doxorubicin prodrug and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108395460AGood treatment effectGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthSide effect
The invention discloses a hypoxia activation doxorubicin prodrug and a preparation method thereof. The doxorubicin prodrug is synthesized by modification of an amino group located at a 3' position ofdoxorubicin by an azo bond having a hypoxia activation effect and a response functional group having a self-occluded structure. The doxorubicin prodrug provided by the invention can effectively realize selective activation under a hypoxic environment, and can regulate and control growth activity of tumor cells by regulating subcellular organelle distribution of the doxorubicin in normoxia and hypoxic environments, thereby reducing toxic and side effects of a drug on normal cells, improving targeting efficiency of the drug on tumor treatment, and providing more novel ideas for development of antitumor drugs; and the synthetic method for the hypoxia activation doxorubicin prodrugs provided by the invention is simple, raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, and the hypoxia activation doxorubicin prodrugs are convenient for industrialized production and clinical transformation.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Near-infrared fluorescent dye based on coumarin skeleton and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN110684370AHas red light emitting propertiesAvoid interferenceAntibacterial agentsPhotodynamic therapyAminocoumarinsStaining
The invention discloses a near-infrared fluorescent dye based on coumarin structure and a synthesis method thereof. The general structural formula of the fluorescent dye is shown in the description: wherein R represents C1 alkyl group, X- represents PF6- or R represents any one of C2-C12 alkyl groups, X- represents Br-. 4-(diethylamino) coumarin is subjected to Vilsmeier-Haack reaction to synthesize 4-(diethylamino) coumarin aldehyde, 4-(diethylamino) coumarin aldehyde reacts with cyanopyridine and halogenated alkanes with different carbon chain lengths in turn to obtain a series of fluorescent dyes. The fluorescent dye of the invention can specifically label suborganelles in living cells through regulation and control of ammonium salt side chains, and the fluorescent dye with R representing C3 alkyl group can realize rapid dyeing and washing-free in the labeling process; the maximum emission wavelength of fluorescent dye is in the red luminescence region, which can significantly eliminate the interference of self-fluorescence phenomenon in cell imaging. In addition, fluorescent dyes with R representing C9 and C12 alkyl groups have the property of producing singlet oxygen and havecertain application potential in photodynamic therapy of cells and bacteria.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
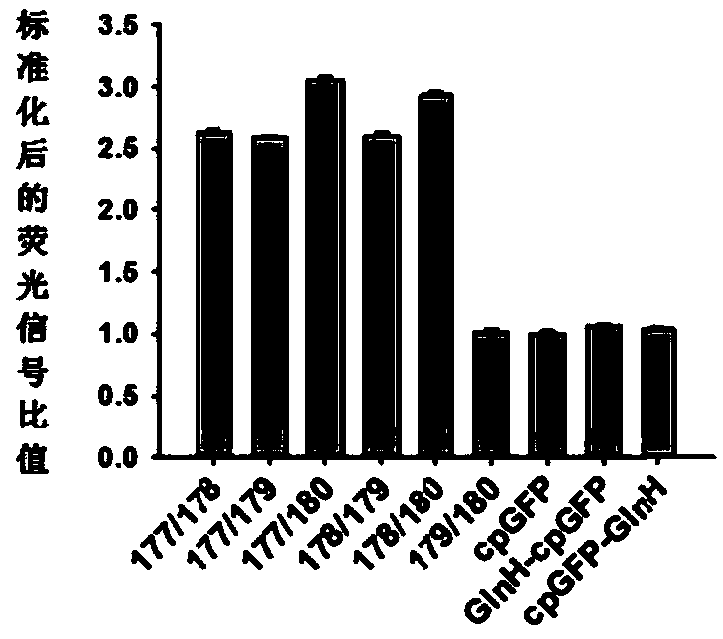
Glutamine optical probe and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109666075AMature and simpleLarge dynamic changes in fluorescenceBacteria peptidesFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceHigh flux
The invention relates to a glutamine optical probe and a preparation method and application thereof. On one hand, the optical probe comprises glutamine sensitive polypeptide or a functional variant thereof and optically active polypeptide or a functional variant thereof, wherein the optically active polypeptide or the functional variant thereof is located in the sequence of the glutamine sensitivepolypeptide or functional variant thereof. The invention also relates to the preparation method of the probe and the application of the probe in the detection of amino acids. The glutamine optical probe has relatively smaller molecular weight and is easy to mature, has large fluorescence dynamic change and good specificity and can be expressed in different subcellular organelles of cells, and theamino acids can be quantitatively detected inside and outside the cells with high flux.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Acid-sensitive liposome drug delivery system with internalization effect, and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104784118AHigh hemolytic concentrationMaximize the effectiveness of internalizationPowder deliveryLyophilised deliveryPolyethylene glycolPhospholipid
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutic preparation of medical technology, and discloses an acid-sensitive liposome drug delivery system with internalization effect, and a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method comprises following steps: direct coupling of a cell penetrating peptide rich in arginine residues with a liposome surface long chain organic acid is realized so as to obtain an acid-sensitive polyethylene glycol-hydrazone bond-long chain organic acid coupling compound; and the tumour targeted liposome loaded with lipid-soluble drugs and water-soluble anthraquinone alkalescent drugs is prepared via filming-rehydration; wherein the cell penetrating peptide is a poly arginine short peptide which is GGRRRRRRRRR preferably; molecular weight of polyethylene glycol ranges from 500 to 5000Da, and preferably 2000Da; optimized cell penetrating peptide density accounts for 2 to 8% of that of phosphatide, and preferably 4%; and density of the polyethylene glycol-hydrazone bond-long chain organic acid coupling compound accounts for 5 to 20% of that of phosphatide, and preferably 8%. The acid-sensitive liposome drug delivery system is capable of solving a problem that liposome cell internalization is difficult, and providing possibility for development of antitumor drug targeted subcellular organelle. The acid-sensitive liposome drug delivery system is nontoxic basically; preparation technology is simple; and the acid-sensitive liposome drug delivery system is convenient for industrialized application.
Owner:谢辉 +1
Database establishing method suitable for plant transposase accessible chromatin analysis
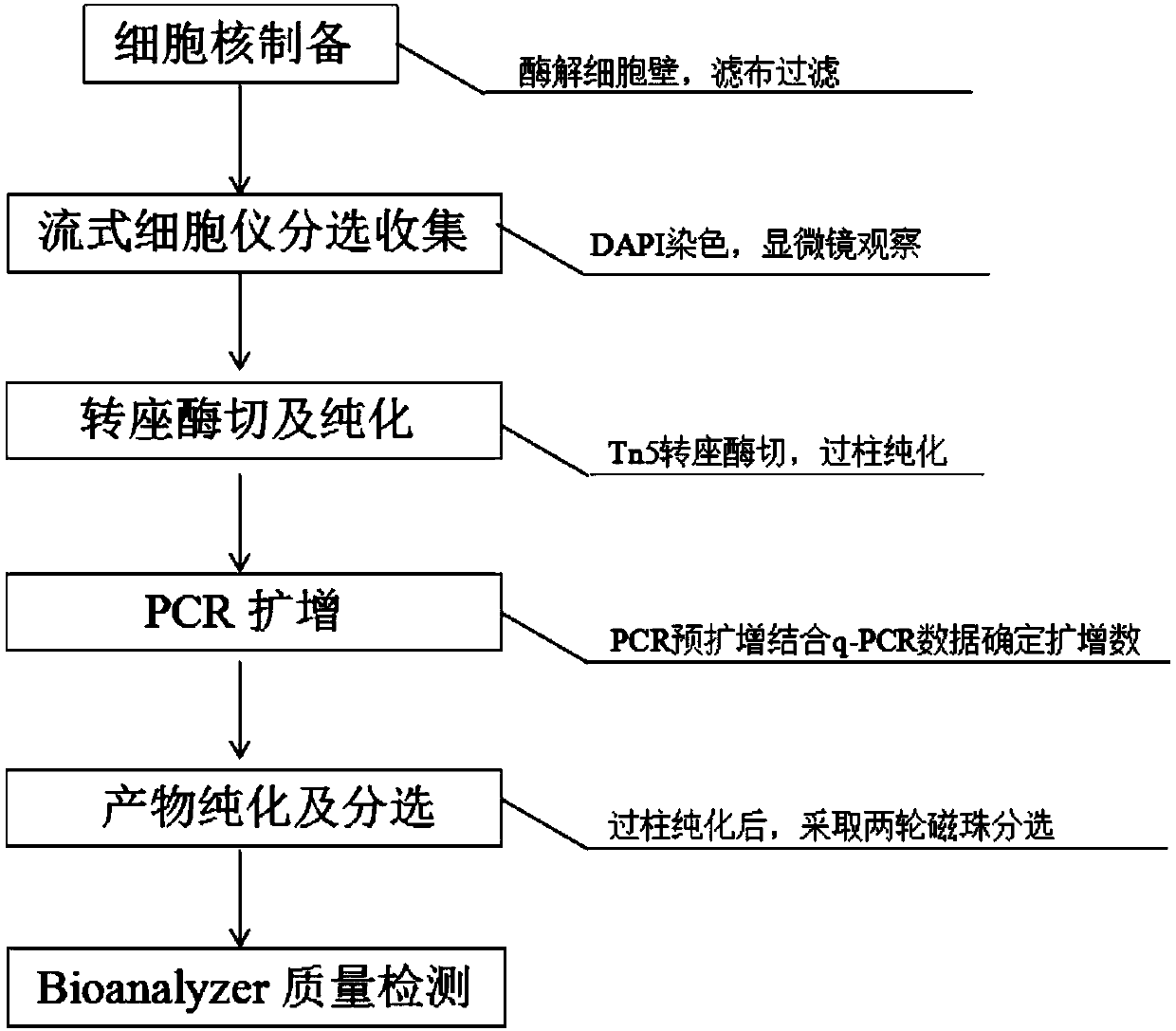
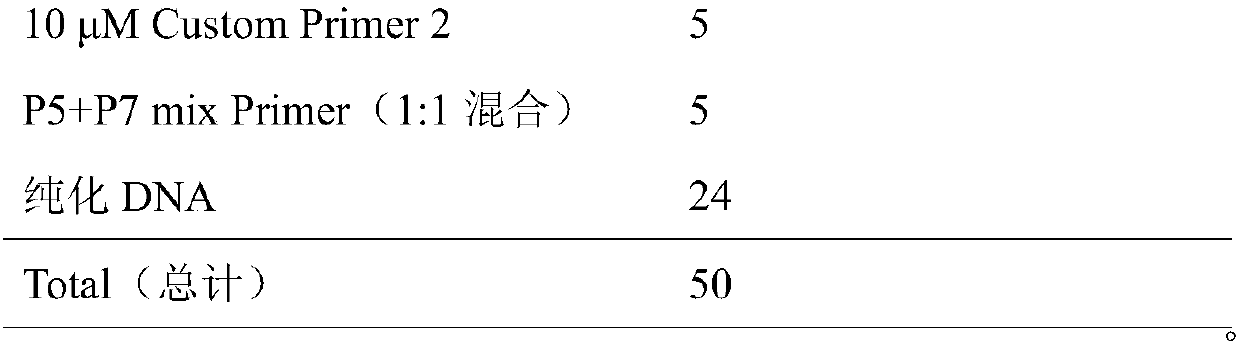
InactiveCN108130323AReduce distractionsQuality improvementLibrary creationDNA preparationCell wallDigestion
The invention discloses a database establishing method suitable for plant transposase accessible chromatin analysis. The database establishing method comprises following steps: firstly, plant tender tissue is subjected to pre-treatment, enzymatic hydrolysis is cell walls is carried out, filtering is carried out, DAPI dyeing is adopted to sort and collect nucleuses on a flow cytometer, the obtainednucleuses are filtered so as to reduce interference of cell walls and subcellular organelles on experiment data; Tn5 transposase digestion reaction and purification are carried out, qPCR is adopted to determine circulating number needed by database establishing; at last obtained single library is subjected to equimolar mixing. According to the database establishing method, the high quality on computer library is obtained via optimized two circles of magnetic cell sorting at a certain ratio, so that important experiment method reference is provided for study of scientific research personnel onplant tender tissue accessible transposase nucleus chromatin high flux sequencing.
Owner:奥明(杭州)基因科技有限公司
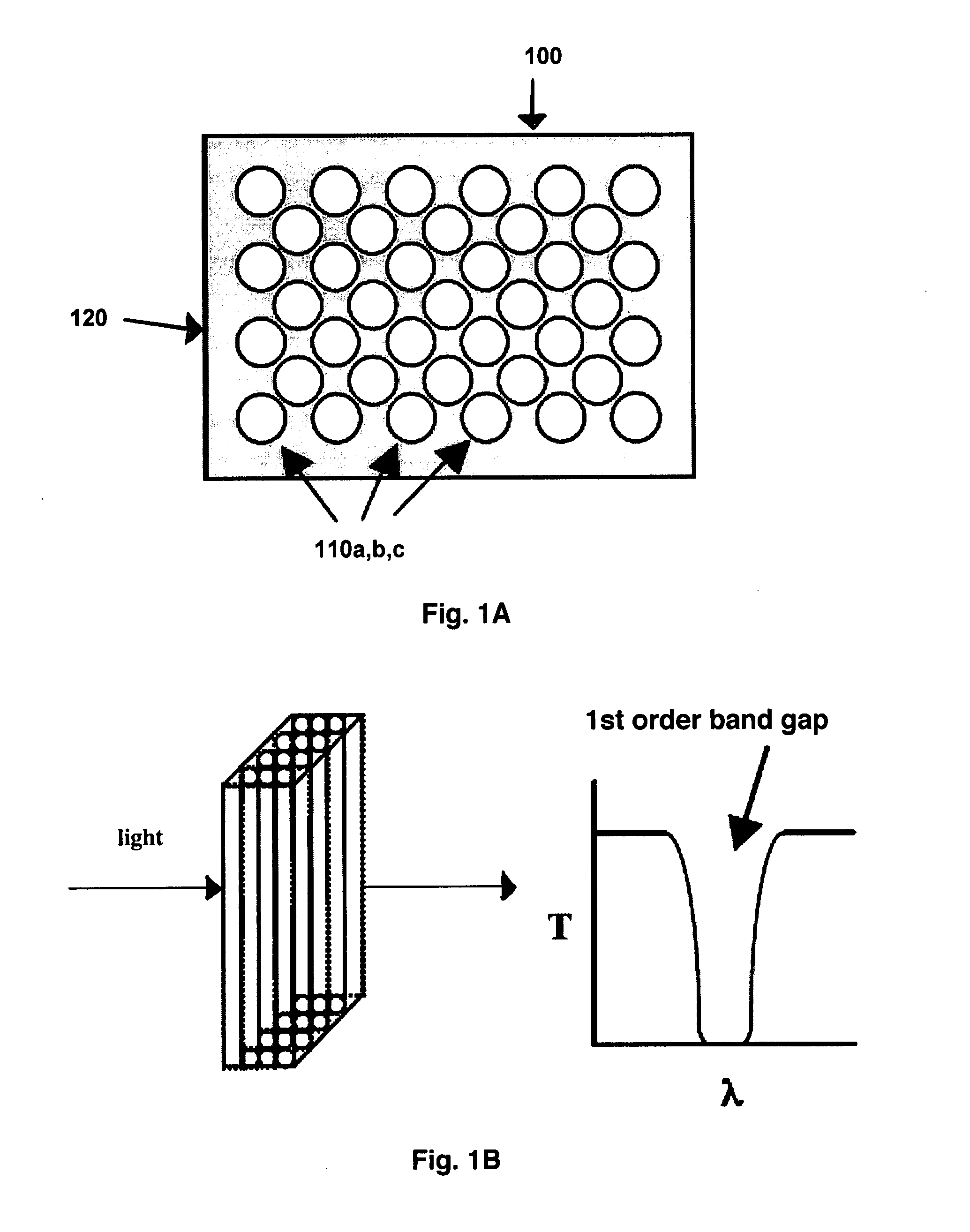
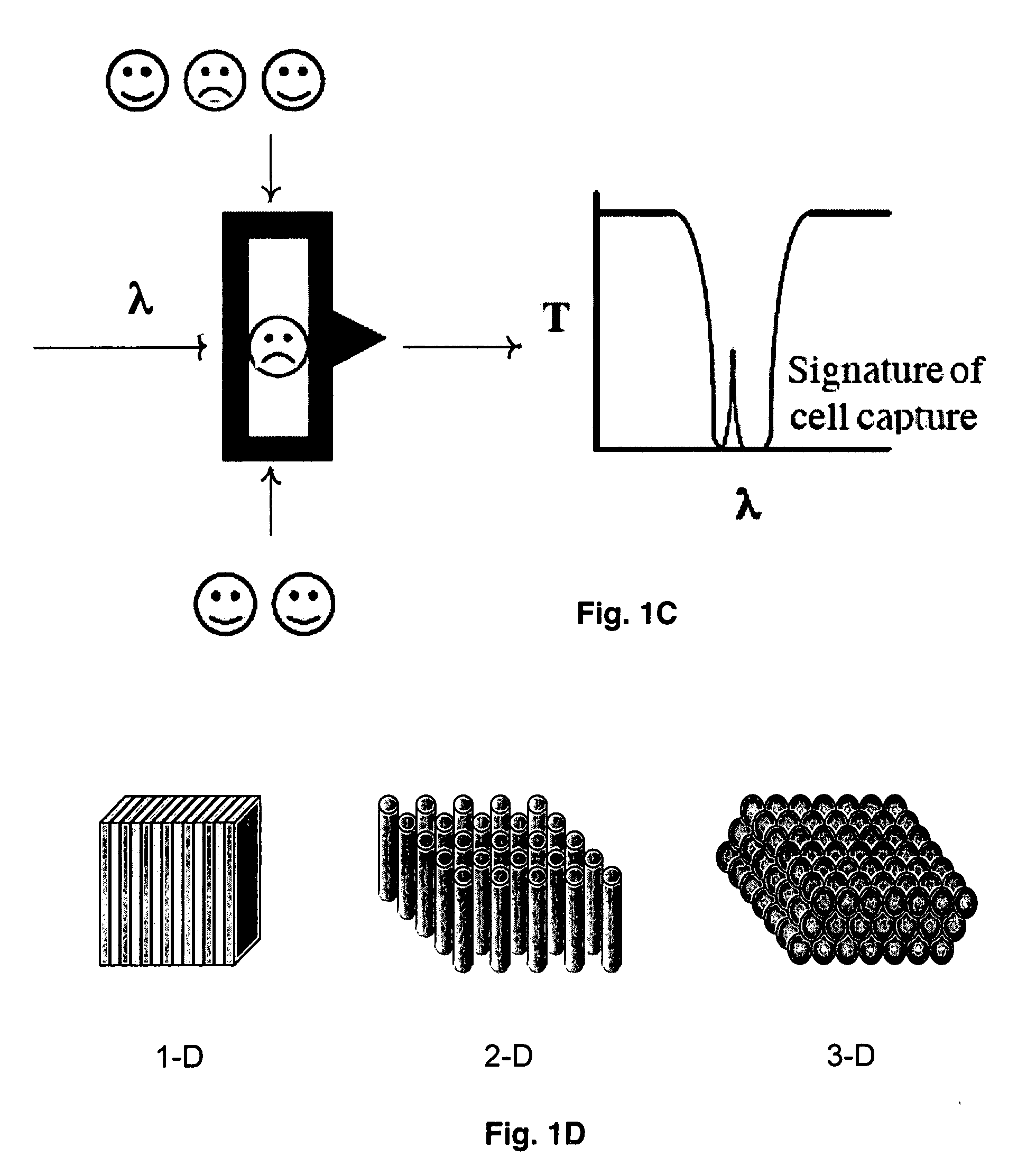
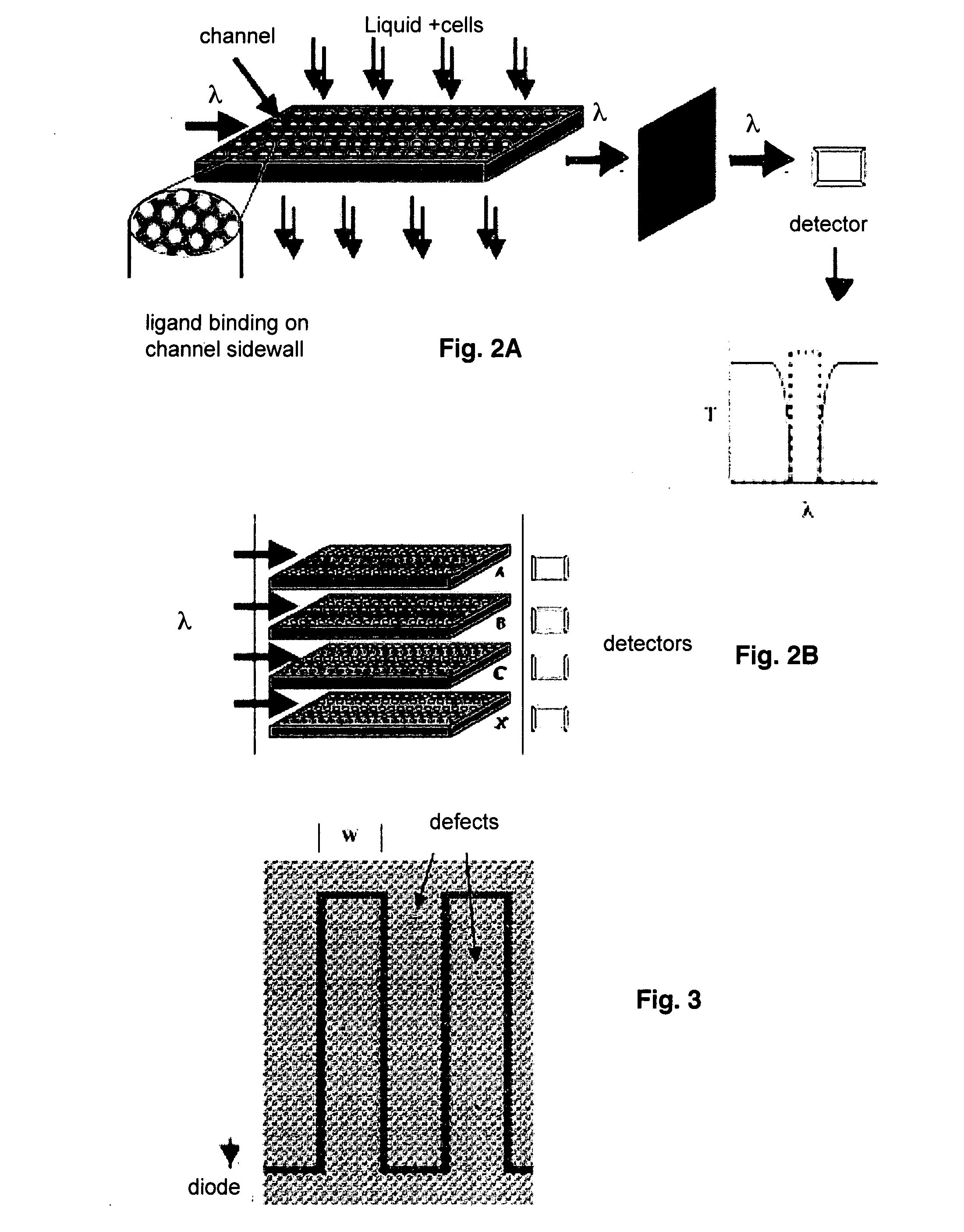
Real Time Detection of Molecules, Cells and Particles Using Photonic Bandgap Structures
InactiveUS20090305230A1Spread the wordHigh light transmittanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalytePhotonic bandgap
Provided herein is a photonic bandgap (PBG) detector effective to detect inorganic molecules, organic biomolecules or biopolymers, cells, subcellular organelles, and particles. The PBG detector utilizes photonic crystals having a binding agent attached to channel surfaces comprising the crystals to selectively bind a molecule, cell or particle of interest so that an increase in light transmission is detectably induced within the photonic bandgap upon binding. Also provided are methods of optically detectiing an analyte and of identifying the presence of a cell or a particle in a biological sample.
Owner:BEATTIE KENNETH L +1
Multicolored pH-activatable fluorescence nanoplatform
ActiveUS9511152B2Improved labelingSharp contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryLysosomeFluorescence
The present invention relates to pH-tunable, highly activatable multicolored fluorescent nanoplatforms and methods of using the nanoplatforms in a variety of applications including, but not limited to, investigating fundamental cell physiological processes such as pH regulation in endocytic vesicles, endosome / lysosome maturation, and effect of pH on receptor cycling and trafficking of subcellular organelles.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Amino acid optical probe, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110003344AMature and simpleLarge dynamic changes in fluorescenceBacteria peptidesFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh fluxFluorescence
The invention relates to an amino acid optical probe, and a preparation method and an application thereof. On one hand, the invention relates to an optical probe comprising an amino acid sensitive polypeptide or a functional variant thereof and an optical active polypeptide or a functional variant thereof, wherein the optical active polypeptide or the functional variant thereof is located in a sequence of the amino acid sensitive polypeptide or the functional variant thereof. The invention also relates to the preparation method of the probe and an application of the probe in detection of aminoacids. The amino acid optical probe provided by the invention has relatively small molecular weight, has the advantages of easy maturation, large fluorescence dynamic change and good specificity, canbe expressed in different subcellular organelles of cells, and can detect amino acids inside and outside cells in high flux and quantitatively.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
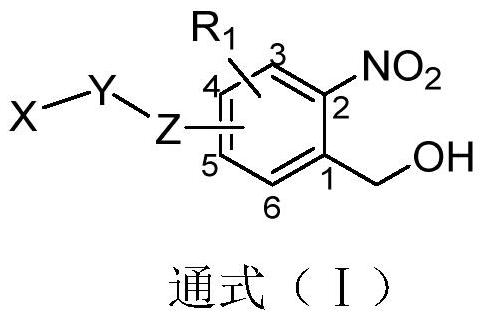
Photo-induced cell covalent labeled fluorescent molecules as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a photoinduced cell covalent labeled fluorescent molecule, and a preparation method and application thereof, in particular to a compound as shown in the following formula (I), or a tautomer, an enantiomer, an enantiomer, a diastereomer, a racemate, a precursor compound, an isotope compound and various forms of salts or hydrates thereof. The compounds can be used for preparing light-induced covalent labeled fluorescent probes and are used for positioning and imaging subcellular organelles in cell biology. The light-induced covalent labeled fluorescent probe has important application potential and outstanding practical value in cell biology research, proteomics research and dynamic change research of biomacromolecules.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cyanine compound and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103382189AImprove accuracyEliminate distractionsMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic chemistryCyanineFluorescence ratio
The invention discloses a cyanine compound and a preparation method and an application thereof. The compound has a structure as shown in the general formula I. The probe is especially sensitive to environmental viscosity and can be used in detection of fluids and biotic environmental viscosity. The probe can be positioned at different subcellular organelles and can monitor viscosity changes in subcellular organelles in living cells by a bimodal detection means of fluorescence ratio and fluorescence lifetime.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
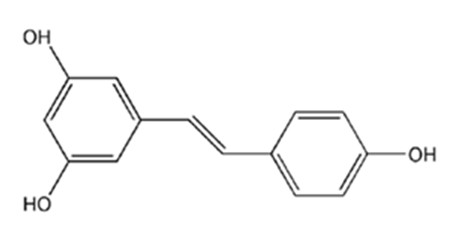
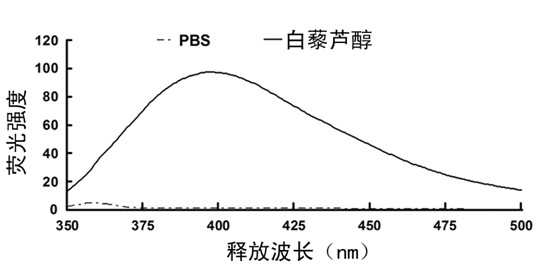
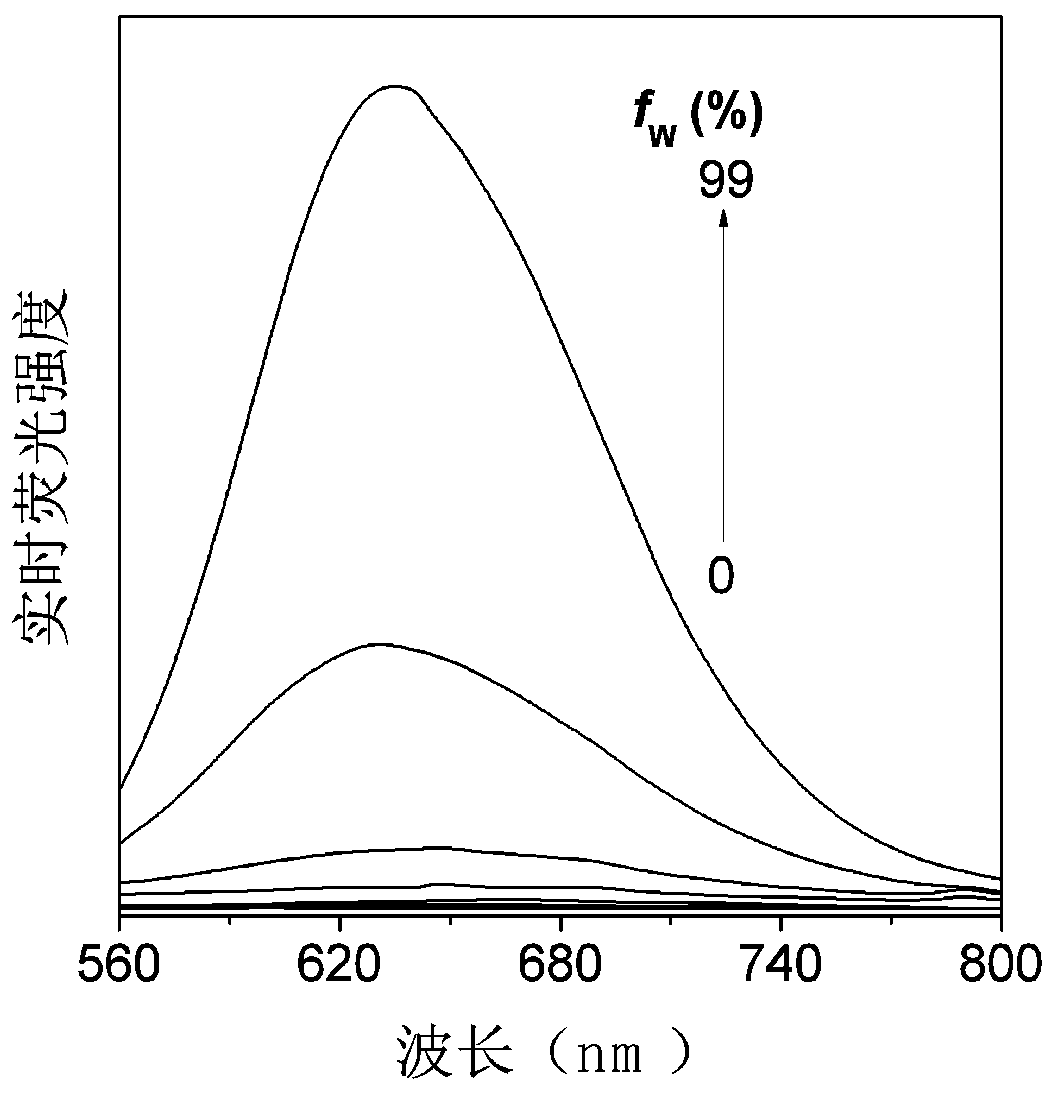
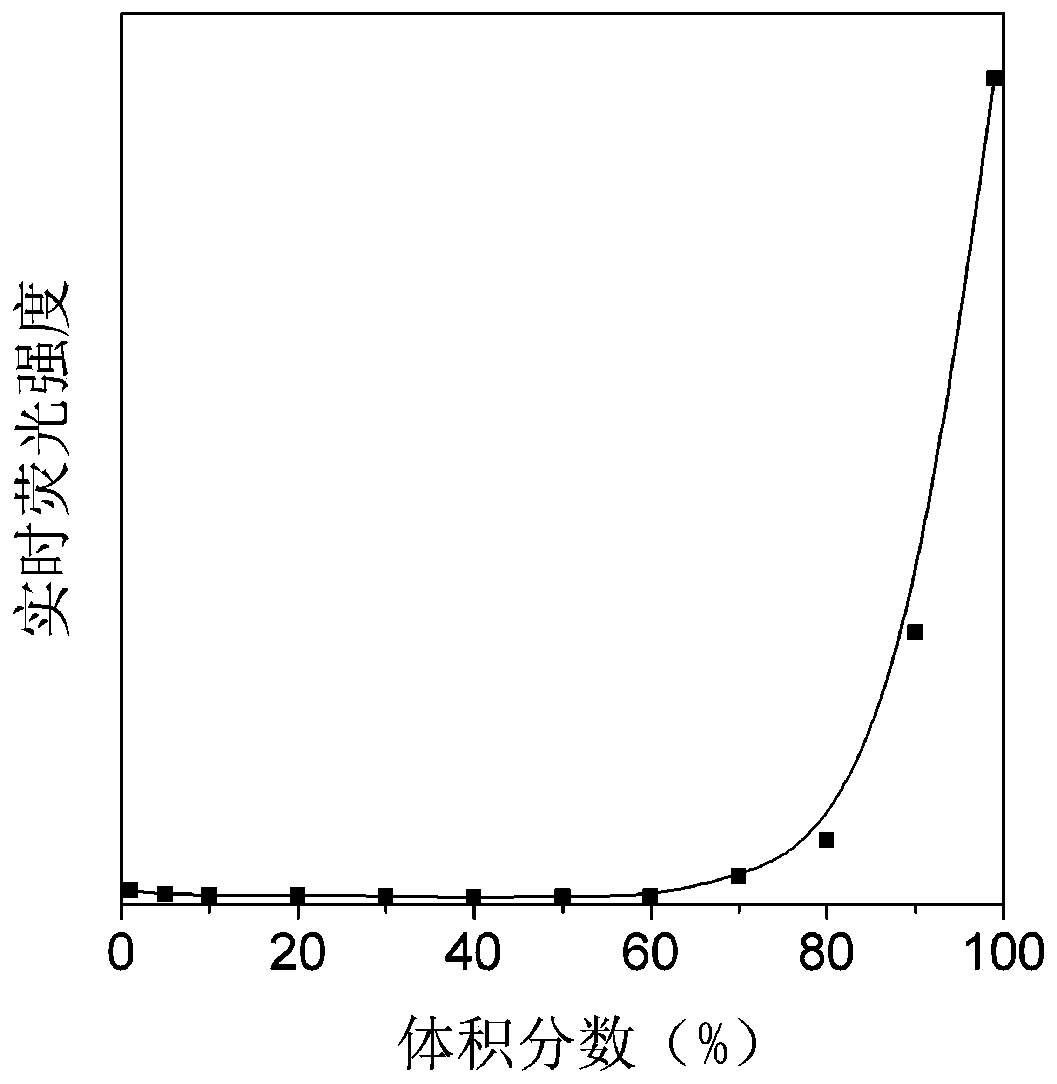
Method for detecting location of resveratrol in target cells
The invention discloses a method for detecting the location of resveratrol in target cells. Specifically, the method comprises the following steps of: firstly pretreating the target cells with resveratrol based on the autofluorescence property of resveratrol; then treating the target cells by using a specifically fluorescently-labeled subcellular organelle probe; and finally determining the distribution of resveratrol in the subcellular organelle of the target cells according to the overlap state of the autofluorescence of resveratrol and the fluorescence of the subcellular organelle probe in the cells. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for detecting the distribution of resveratrol in target cells, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Fluorescent probe with functions of detecting hydrogen peroxide and performing photodynamic killing on cancer cell activity as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110642882AImprove photostabilityStrong resistance to photobleachingPhotodynamic therapyGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFluoProbesCancer cell
The invention provides a fluorescent probe with functions of detecting hydrogen peroxide and performing photodynamic killing on cancer cell activity as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of a biochemical material. The fluorescent probe with the functions of detecting hydrogen peroxide and performing photodynamic killing on cancer cell activityhas aggregation induced luminescence characteristic, can specifically respond to the hydrogen peroxide, generates a substance with stronger fluorescence, can be applied to detection on the hydrogen peroxide in cells, and can selectively position subcellular organelle lipid droplets in the cells; the product obtained through action between the fluorescent probe and the hydrogen peroxide has large stokes displacement, so self-absorption can be avoided and background interference can be reduced; the fluorescent probe as well as the product obtained through the action between the fluorescent probeand the hydrogen peroxide have high light stability and photobleaching resistance, and are suitable for long-time tracing of the hydrogen peroxide in living cells or living bodies; meanwhile, the product obtained through the action between the fluorescent probe and the hydrogen peroxide has active oxygen generation capacity, can be applied to photodynamic killing of the cancer cells and can construct a diagnosis and treatment reagent integrating diagnosis and treatment functions.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of magnetic nanoparticles, magnetic energy conversion method and application
PendingCN109498806AReduce usageNo need to consider thermal stability issuesEnergy modified materialsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsThermal energyDisease
The invention discloses a preparation method of magnetic nanoparticles. After the magnetic nanoparticles prepared by the preparation method are distributed at specific positions of a living body, magnetic energy can be converted into mechanical energy and / or thermal energy under the action of a magnetic field, thereby stimulating a specific nerve center region or damage a cell structure in the living body, then realizing stimulation of a corresponding nerve center, causing the change in behaviors of the living body or achieving the effect of a malignant tumor by causing damage to cytomembranesand subcellular organelles. By adopting the preparation method, the usage amount of materials is reduced remarkably, the thermal stability of the materials does not need to be considered, a good control effect can be achieved for the active or passive physiological behaviors of numerous living bodies, and good pre-judgment and treatment effects can be achieved for neurogenic diseases. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a magnetic core containing magnetic metal oxide and coating with a polymer layer. The invention further discloses a magnetic energy conversion method and application of the magnetic nanoparticles prepared by the preparation method.
Owner:CIXI INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com