Acid-sensitive liposome drug delivery system with internalization effect, and preparation method and applications thereof
A drug delivery system and liposome technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of small critical micelle concentration, failure to consider and improve the hydration layer hindrance of PEG, low modification rate of acid-sensitive conjugates, etc., to achieve easy large-scale Effects of production quality control, strong selectivity, strong acid sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
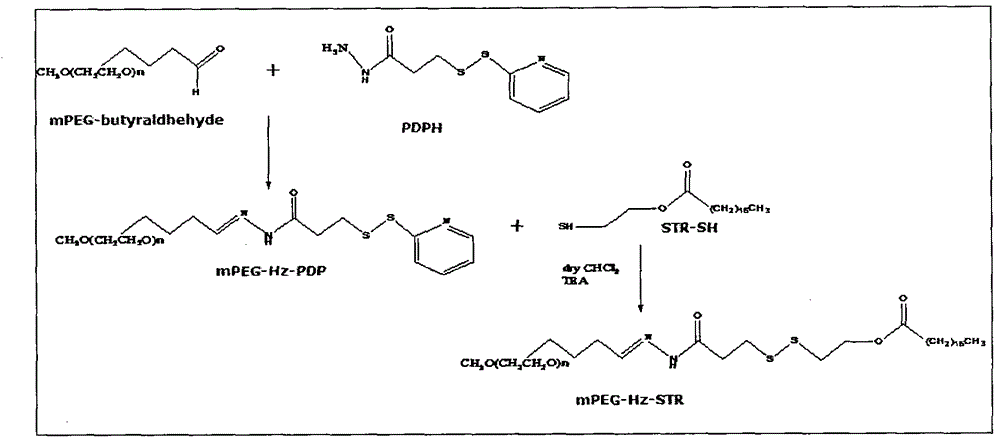
[0077] Synthesis and purification of embodiment 1 acid sensitive poly Z glycol-hydrazone bond-stearic acid conjugate
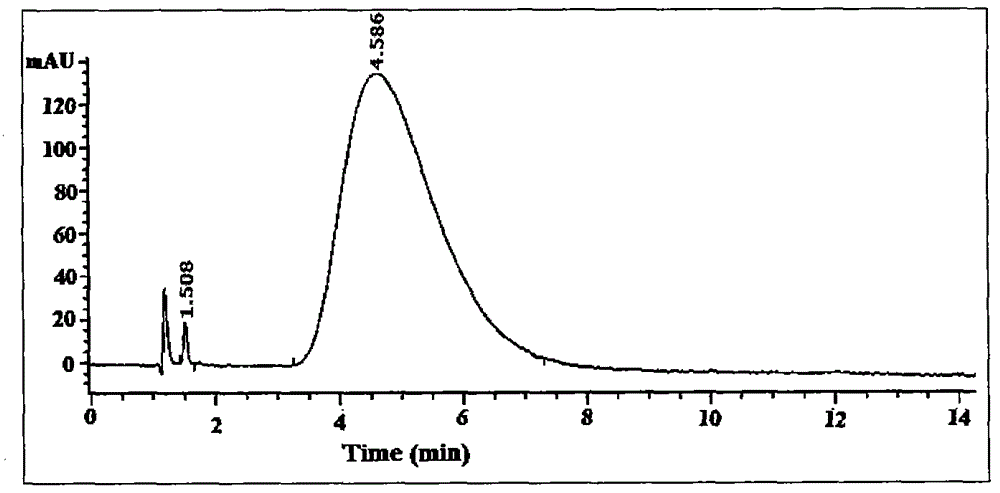
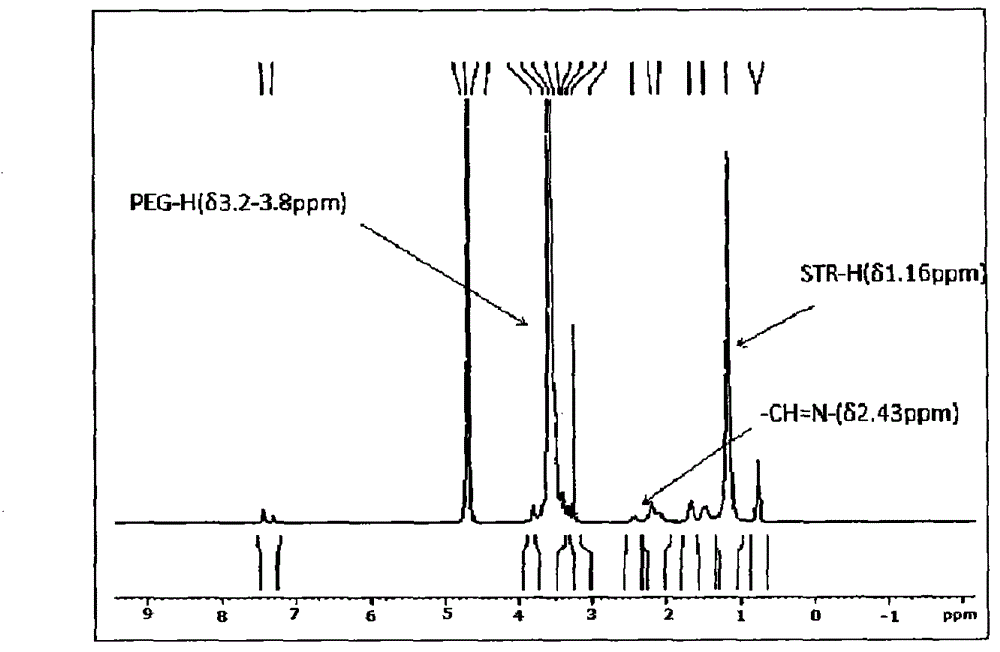
[0078] The synthetic route is shown in Figure 1. mPEG 2000 -CHO was dissolved in a chloroform solution containing a slight excess of PDPH, reacted at room temperature for 48 hours, and stirred under argon protection to synthesize mPEG 2000 -HZ-PDP. STR-SH was dissolved in anhydrous chloroform containing excess mPEG 2000 -HZ-PDP, add triethylamine, stir overnight at room temperature under the protection of argon. Chloroform was removed under reduced pressure, the conjugate was purified with Sepharose CL-4B, and freeze-dried to obtain a white powder. The Agilent HP1100 / ELSD method determines that the purity of the conjugate is 99% ( figure 2 ). 1NNMR spectrum ( image 3 ) proves the structure of the conjugate.
Embodiment 2
[0079] Example 2 Preparation of acid-sensitive liposome loaded fat-soluble drug coumarin with internalization
[0080] Soybean lecithin, cholesterol, stearic acid, and coumarin were dissolved in chloroform at a molar ratio of 2:1:0.08:0.02, and a thin film was formed on the wall of the bottle by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure. The drug-containing common liposome (CL) was formed after PBS hydration. Under magnetic stirring, EDCl was added, and S-NHS was added after about 1 min. The molar ratio of stearic acid, EDCl and S-NHS in the reaction was 1:40:100. After activation at room temperature for 15 minutes, adjust the pH to 12, add CPP equivalent to STP, stir at room temperature for 12 hours, then add 8% STR-HZ-PEG2000 and incubate for 12 hours. 10000g ultrafiltration (MW cut off=30000) for 20min to remove unreacted EDCl, S-NHS and CPP. See the preparation process Figure 4 The obtained acid-sensitive liposome loaded with coumarin has a particle diameter of 100-150...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Example 3 Preparation of acid-sensitive liposome loaded with doxorubicin with internalization
[0083]Film method: soybean lecithin, cholesterol and stearic acid are dissolved in chloroform at a molar ratio of 2:1:0.08, and a thin film is formed on the wall of the bottle by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure at 40°C. The aqueous solution (pH 4-5) containing citric acid is hydrated to form blank ordinary liposomes. Adjust the pH of the external aqueous phase to 7.5-8.0 with sodium carbonate buffer, add adriamycin hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, and incubate overnight in a water bath at 50° C. to obtain ordinary liposomes of adriamycin. Under magnetic stirring, EDCl was added, and S-NHS was added after about 1 min. The molar ratio of stearic acid, EDCl and S-NHS in the reaction was 1:40:100. After activation at room temperature for 15 minutes, adjust the pH to 12, add CPP equivalent to STR, stir at room temperature for 12 hours, then add 8% STR-HZ-PEG2000 and ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com