Patents
Literature
599 results about "Encoding algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An encoding algorithm merely presents data in an alternative format. It does not in any way attempt to hide data, it merely expresses the same data in an alternative syntax. Base64 is such an encoding algorithm.
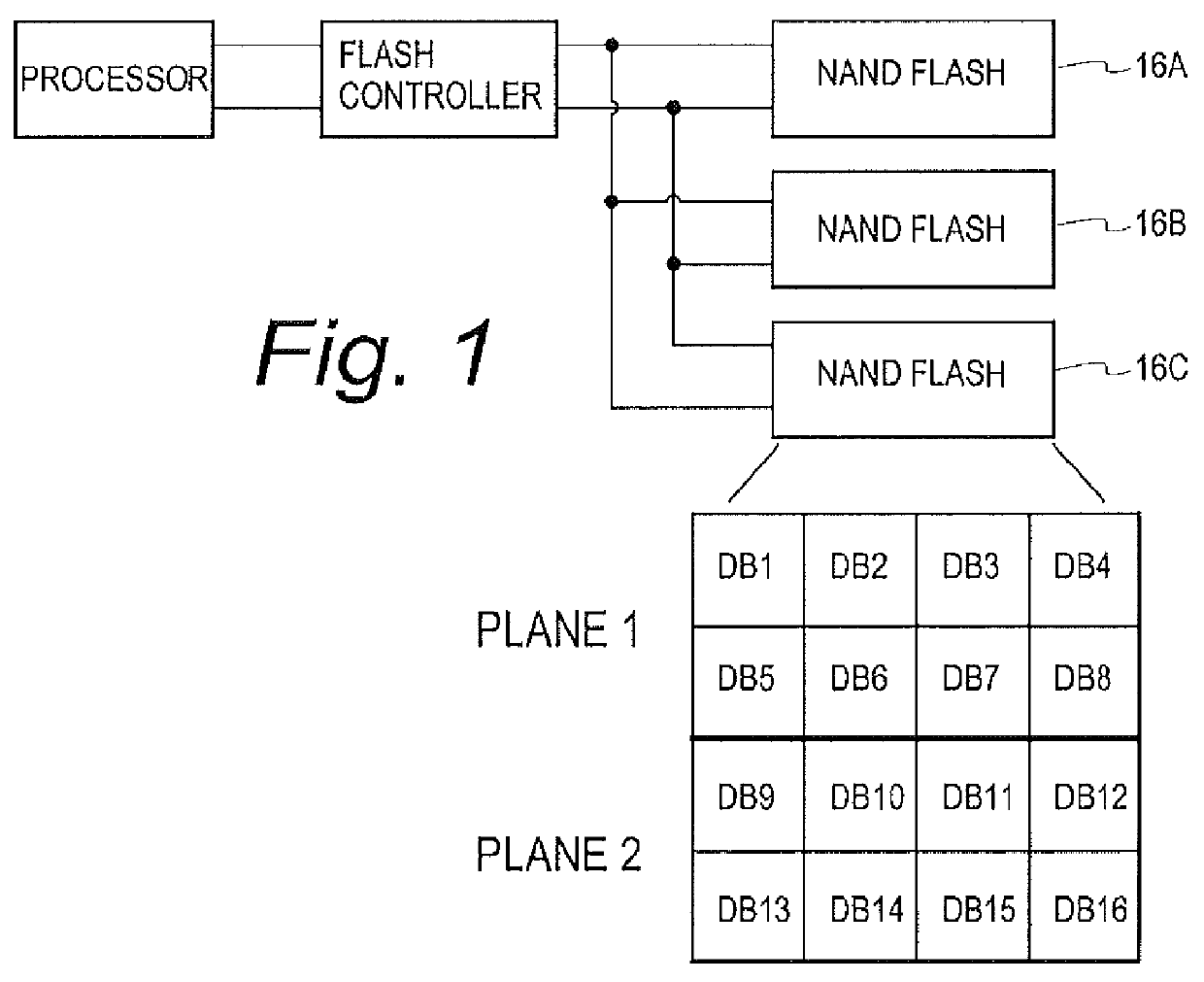
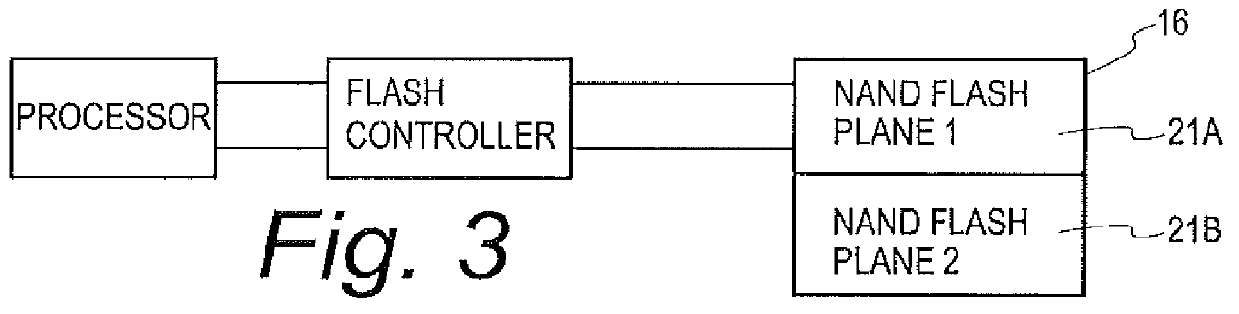
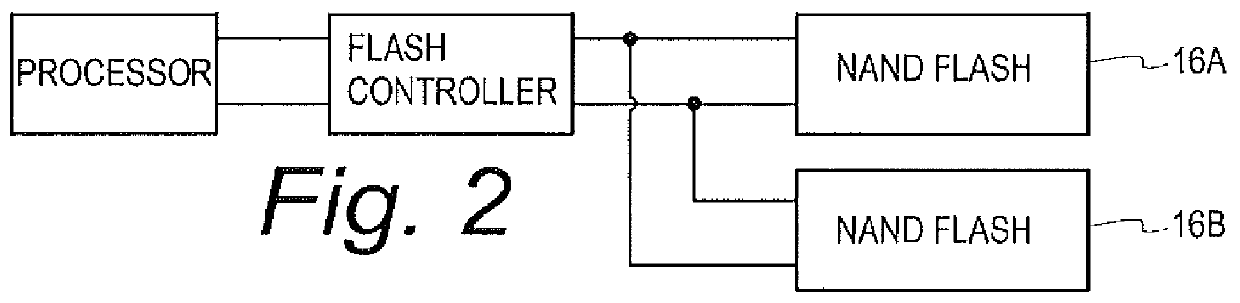
Mission critical NAND flash
InactiveUS20120226934A1Data storage is reliableAccurate contentMemory systemsRedundant hardware error correctionComputer hardwareComputer architecture
A flash controller reliably stores data in NAND FLASH by encoding data using an encoding algorithm, and storing that data across multiple pages of the memory. In one embodiment, true data is accepted by the controller, and the controller in turn creates coded data that is the bit-for-bit complement of the true data. The true data and the coded data are then written to the NAND FLASH on a page by page basis. A property of the coding techniques used is that, in at least some cases, detected errors can be corrected.
Owner:GREENTHREAD
Method and device for image and video transmission over low-bandwidth and high-latency transmission channels
InactiveUS20070183493A1Increase the compression ratioLow priorityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningVideo transmissionEncoding algorithm
The present invention provides a method for transmission of a images and / or video over bandwidth limited transmission channels having varying available bandwidth, which method comprises the use of a classification algorithm for decomposing the images and / or video to be transmitted into multiple spatial areas, each area having a specific image type; detecting the image type of each of those areas separately selecting for each of those areas an image and / or video encoding algorithm having a compression ratio. The classification algorithm prioritizes each of the areas, the classification algorithm increasing the compression ratio of the image and / or video encoding algorithm dedicated to spatial areas having lower priority in case of decreasing bandwidth.
Owner:BARCO NV
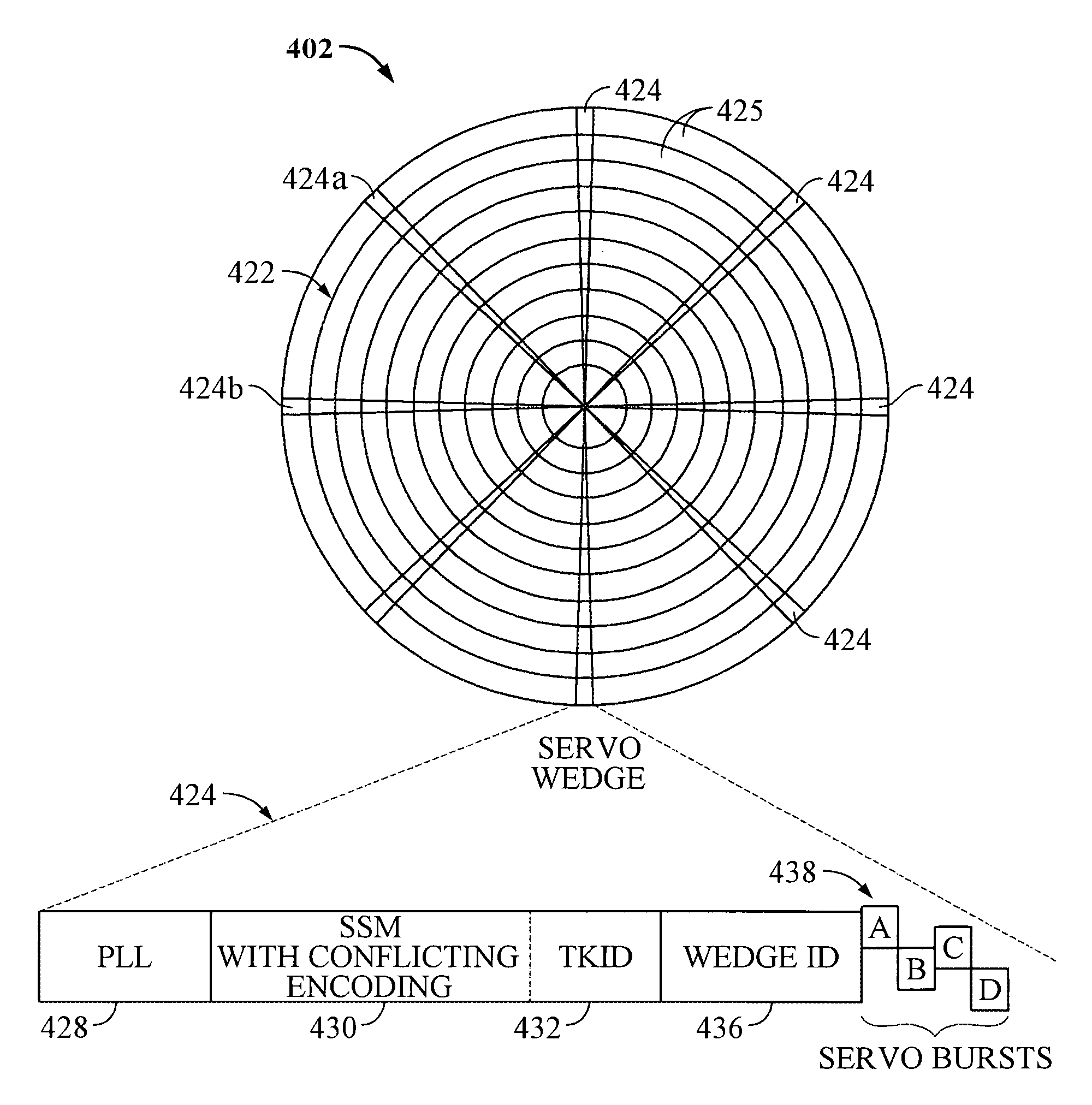
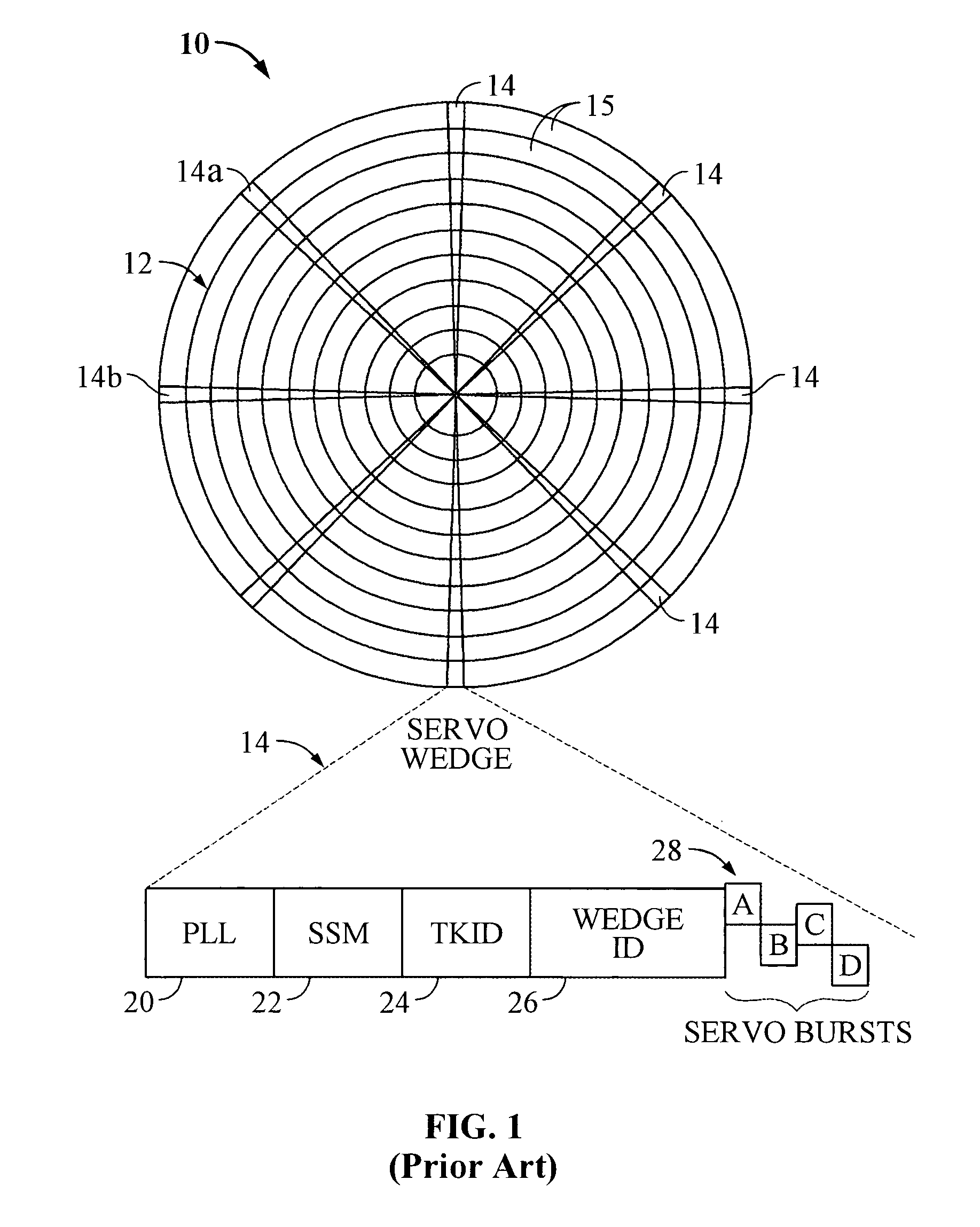
Servo synchronization based on a servo synch mark that conflicts with self-clocking encoding algorithms
InactiveUS6934104B1Disc-shaped record carriersRecord information storageEncoding algorithmComputer science
Disclosed is a rotatable media storage device (RMSD) that performs servo synchronization based on a servo synch mark (SSM) that conflicts with self-clocking encoding algorithms. The RMSD includes a disk having a plurality of tracks wherein each track comprises a plurality of data regions interspersed between servo wedges. The servo wedges comprise a servo synch mark field including a servo synch mark (SSM) and a track identification field including a track identifier (TKID). The TKID is encoded in accordance with a self-clocking encoding algorithm whereas the SSM is encoded in accordance with a second algorithm that conflicts with the self-clocking encoding algorithm of the TKID. Thus, the SSM is prevented from being decoded as a portion of the TKID.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
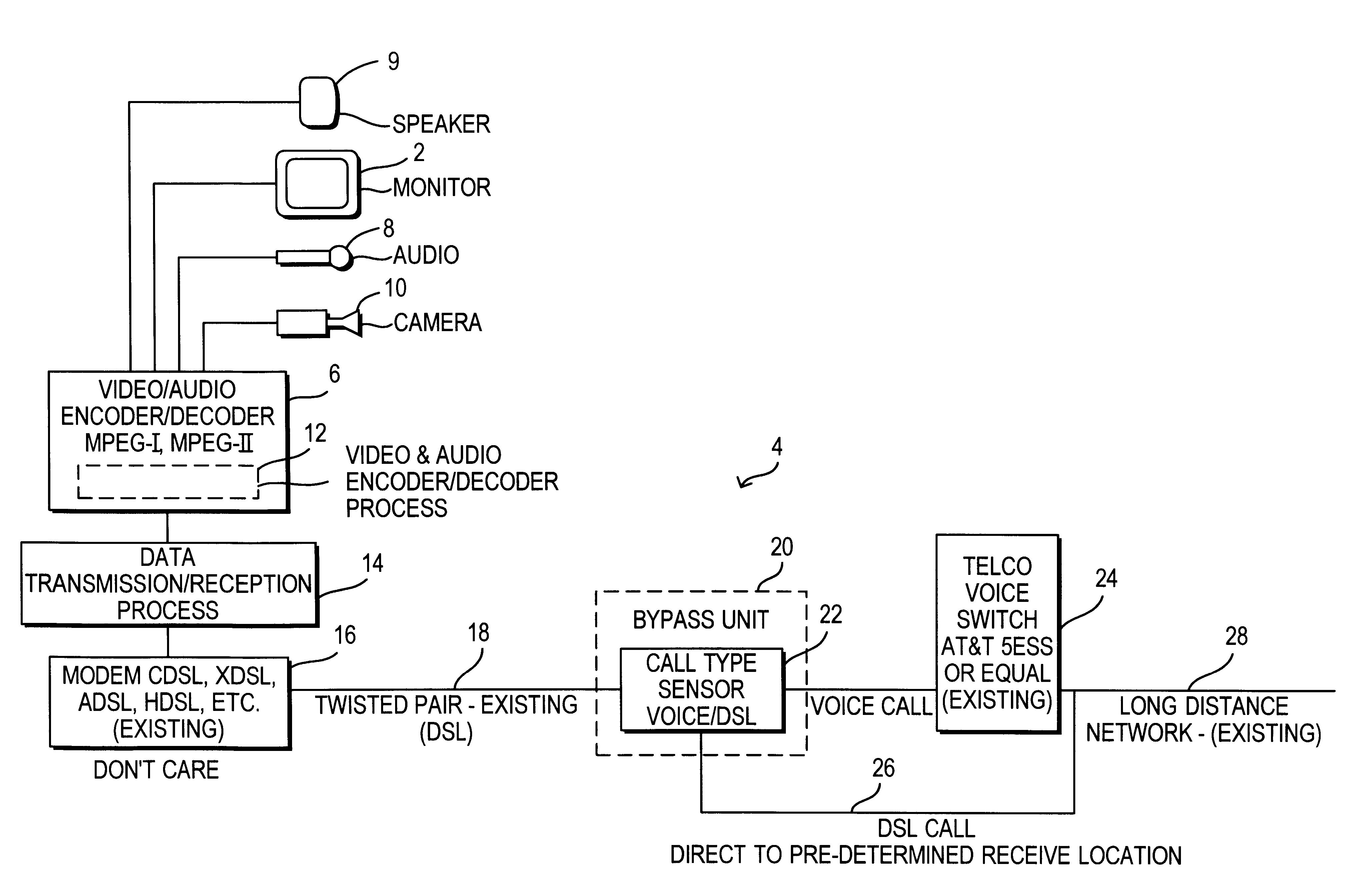
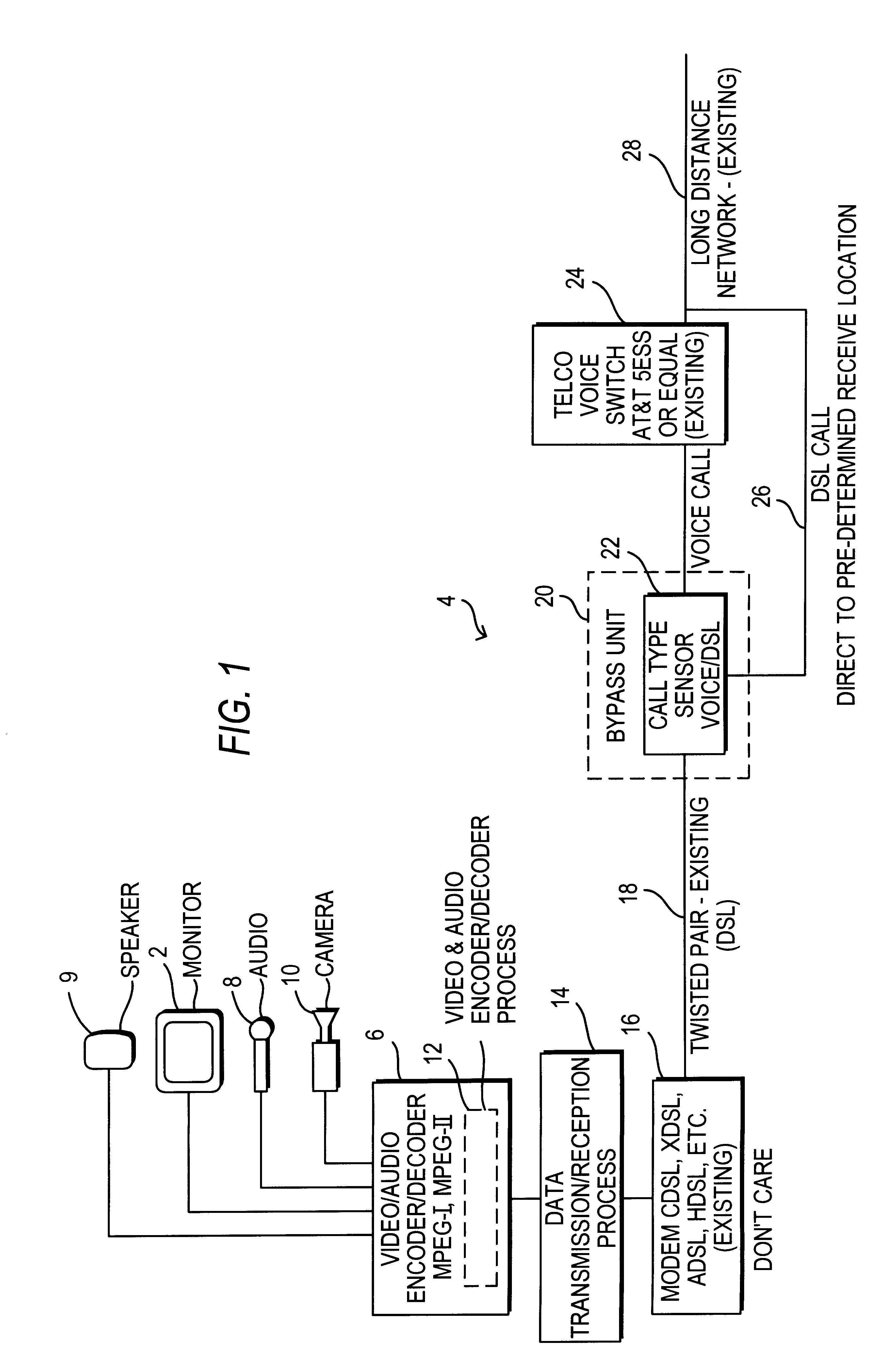
High speed video transmission over telephone lines
InactiveUS6181693B1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision conference systemsEncoding algorithmHigh speed video
A system for sending and receiving full motion, live, full duplex video of broadcast quality over existing telephone lines comprises apparatus for converting audio / video data recorded at a first location into a stream of packets, apparatus for reconverting the stream of packets into audio / video data to be presented at a second location, and apparatus for bypassing telephone company voice switches at central offices, thereby allowing the packets to travel directly from the local telephone lines to the long distance telephone network. The packets are created at the first location and are received at the second location and, in addition to encoded audio / video data, each packet contains a start flag, an end flag, and at least data specifying the encoding algorithm by which the encoded audio / video data was encoded.
Owner:HIGH SPEED VIDEO HLDG
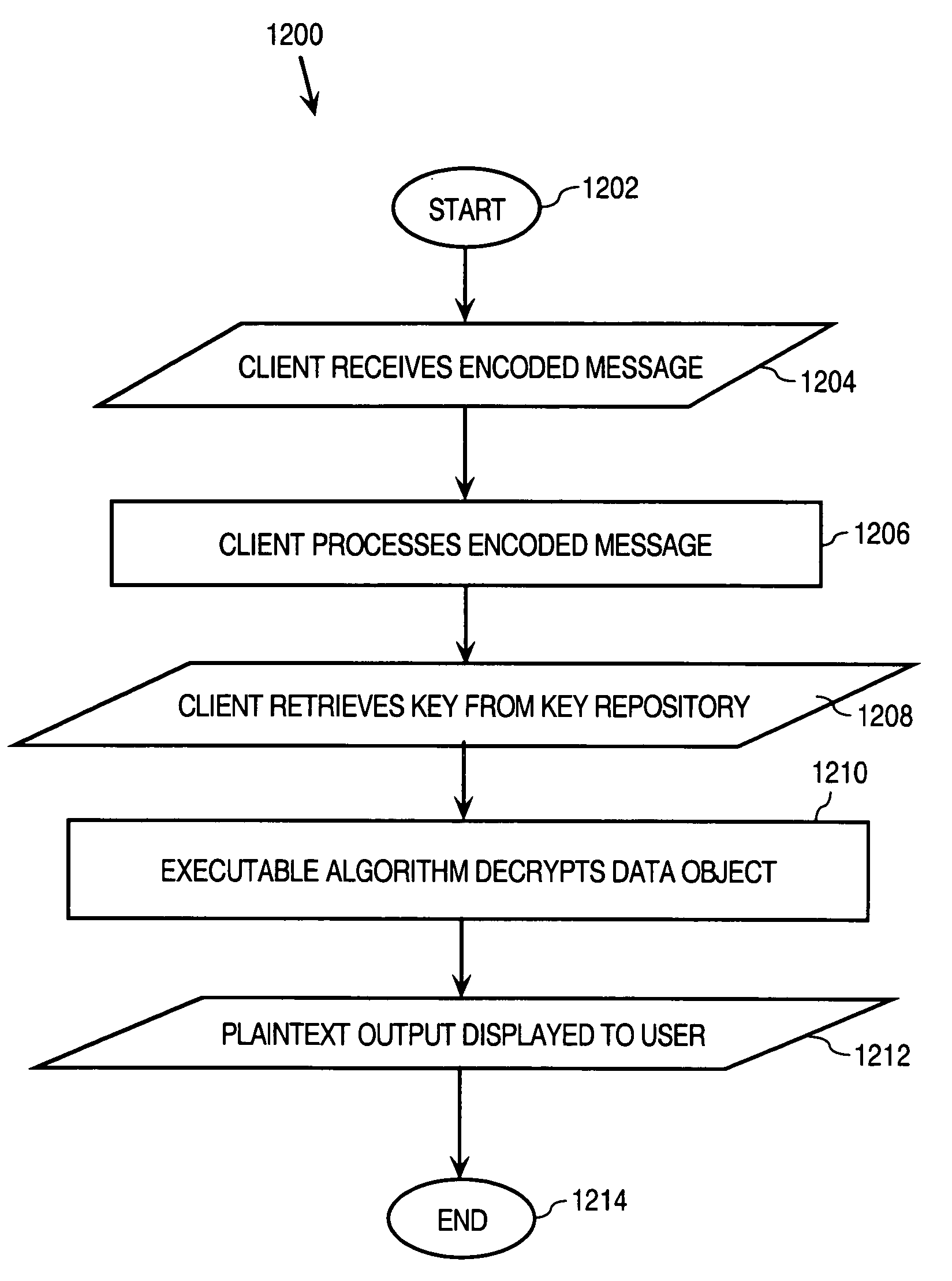
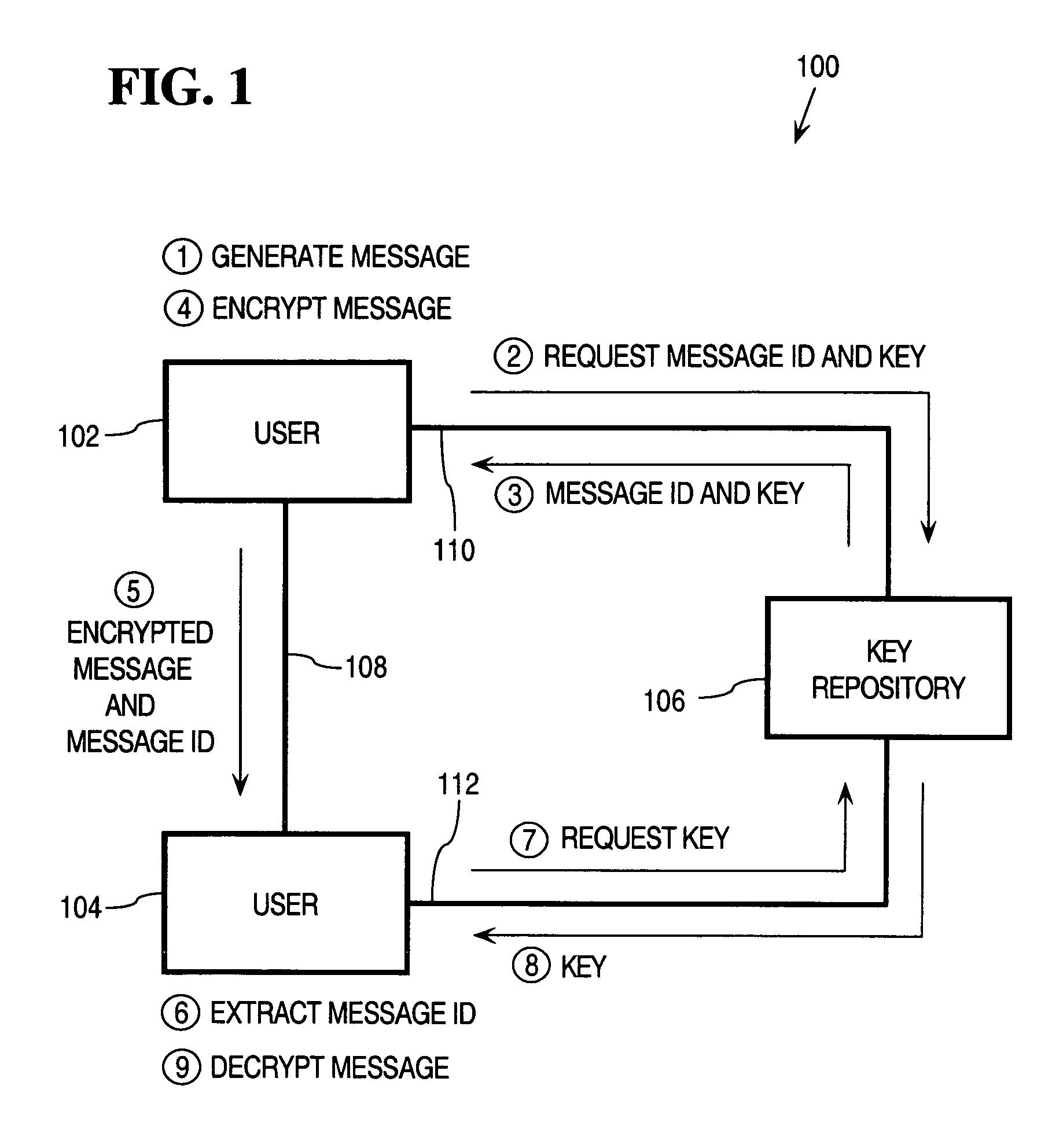
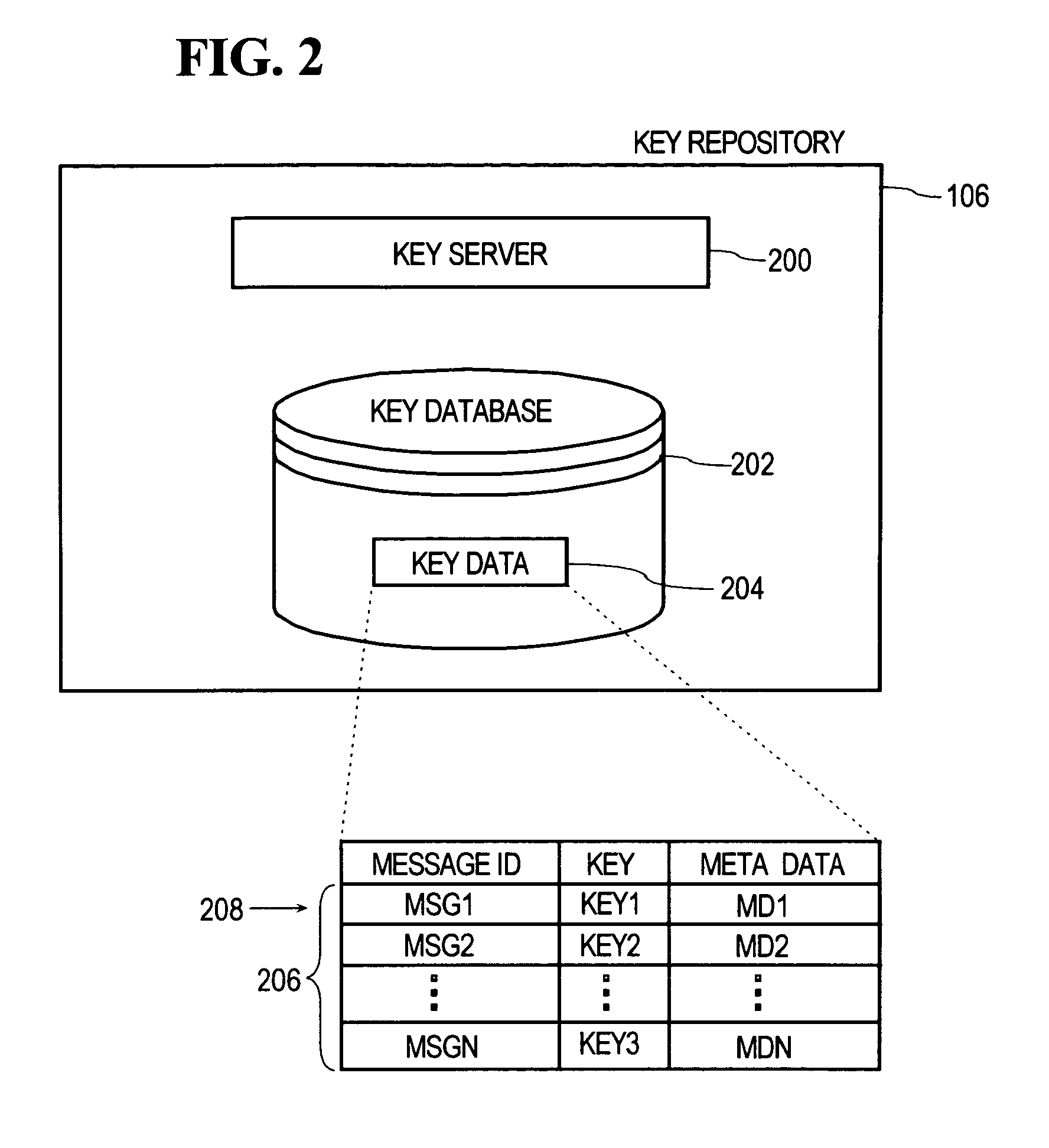
Dynamic encoding algorithms and inline message decryption
InactiveUS7096355B1Prevent copyingKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usagePlaintextThird party
In general, data exchanged between users is protected using any of various encoding approaches. An example of encoding is encryption, but any kind of encoding may be used. The data used to encrypt the data exchanged between the users, referred to as a “key”, is maintained only in a key repository. Users must obtain a key from the key repository to either encode or decode, encrypt or decrypt data, after which the user's copy of the key is destroyed or otherwise rendered inoperable. A key management policy is employed to control access to the keys maintained by the key repository. Encoding algorithms may be dynamically changed over time. Users may negotiate different algorithms to be used with specific users or messages. Thus, different algorithms may be used between different sets of users depending upon what the member users of those sets negotiate among themselves. The frequency at which algorithms are changed may also be separately negotiated between users. The frequency may vary depending, for example, upon the perceived risk of intrusion by unauthorized third parties, the content of the messages being transmitted, or both. According to an inline message decryption approach, an encoded message is provided to a user in a form that enables the user's client to process the encoded message using conventional client tools and obtain the cleartext message. This eliminates the need for a user's client to be aware of the particular encoding algorithm used to encode the message. Various embodiments of the inline message decryption approach include: a) in-situ decryption; b) remote decryption; and c) data uploading. An approach is also provided for exchanging data between nodes in a network using sets of associated URLs.
Owner:CHECK POINT SOFTWARE TECH INC
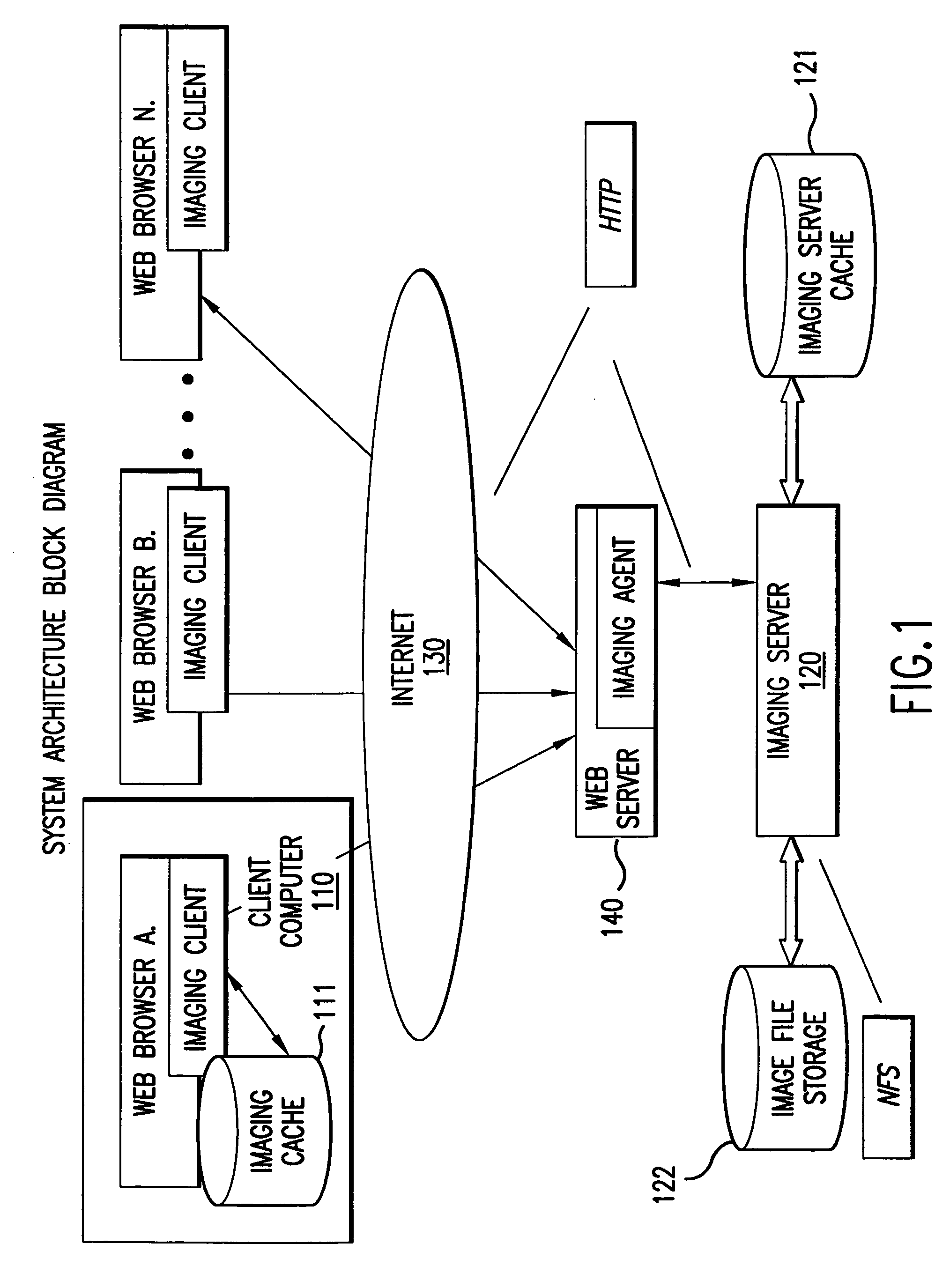
System and method for the lossless progressive streaming of images over a communication network
InactiveUS7024046B2Avoids computationally intensive taskEliminate needPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesNetworked Transport of RTCM via Internet ProtocolImage server
Owner:IDX INVESTMENT CORP
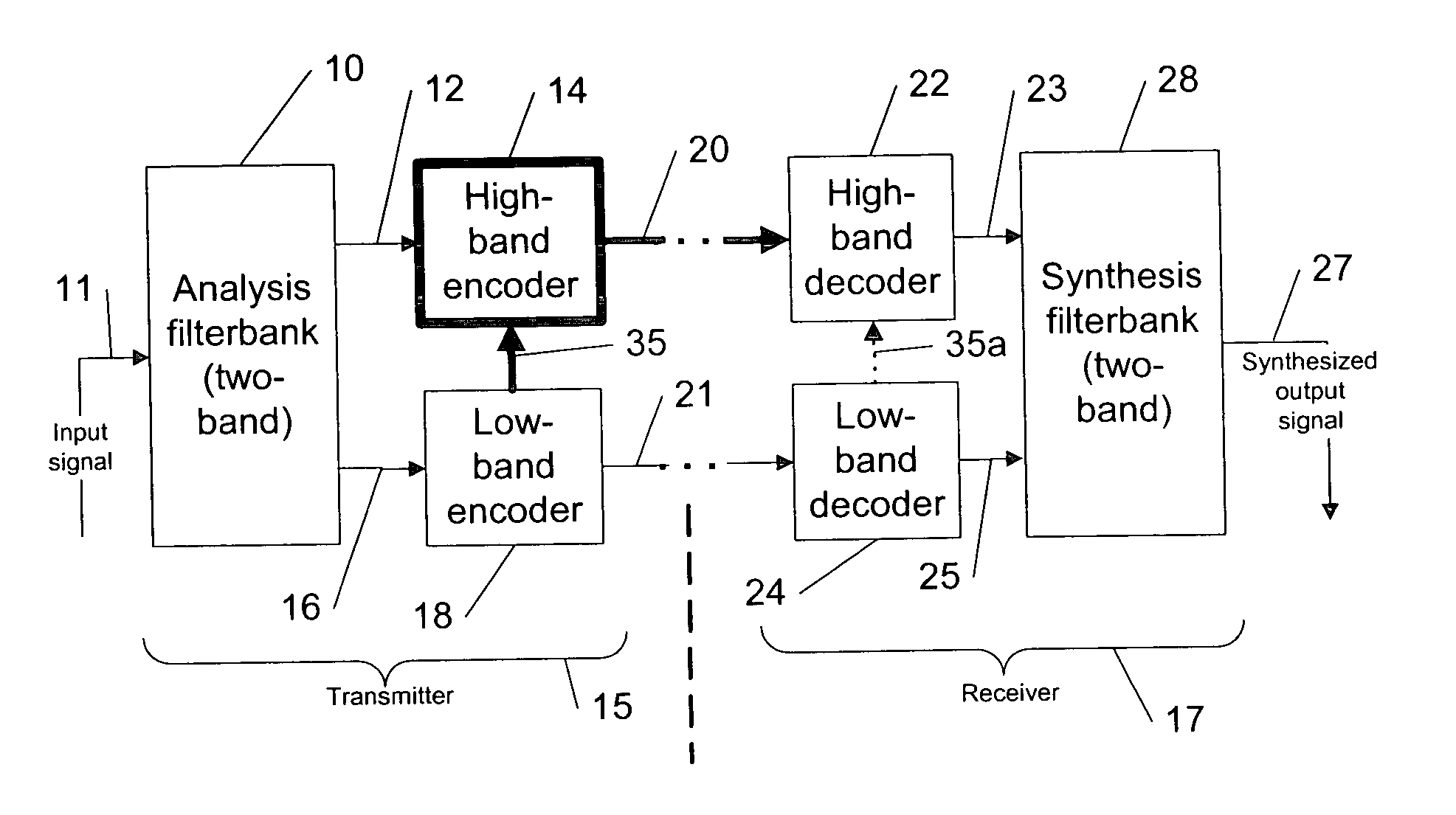
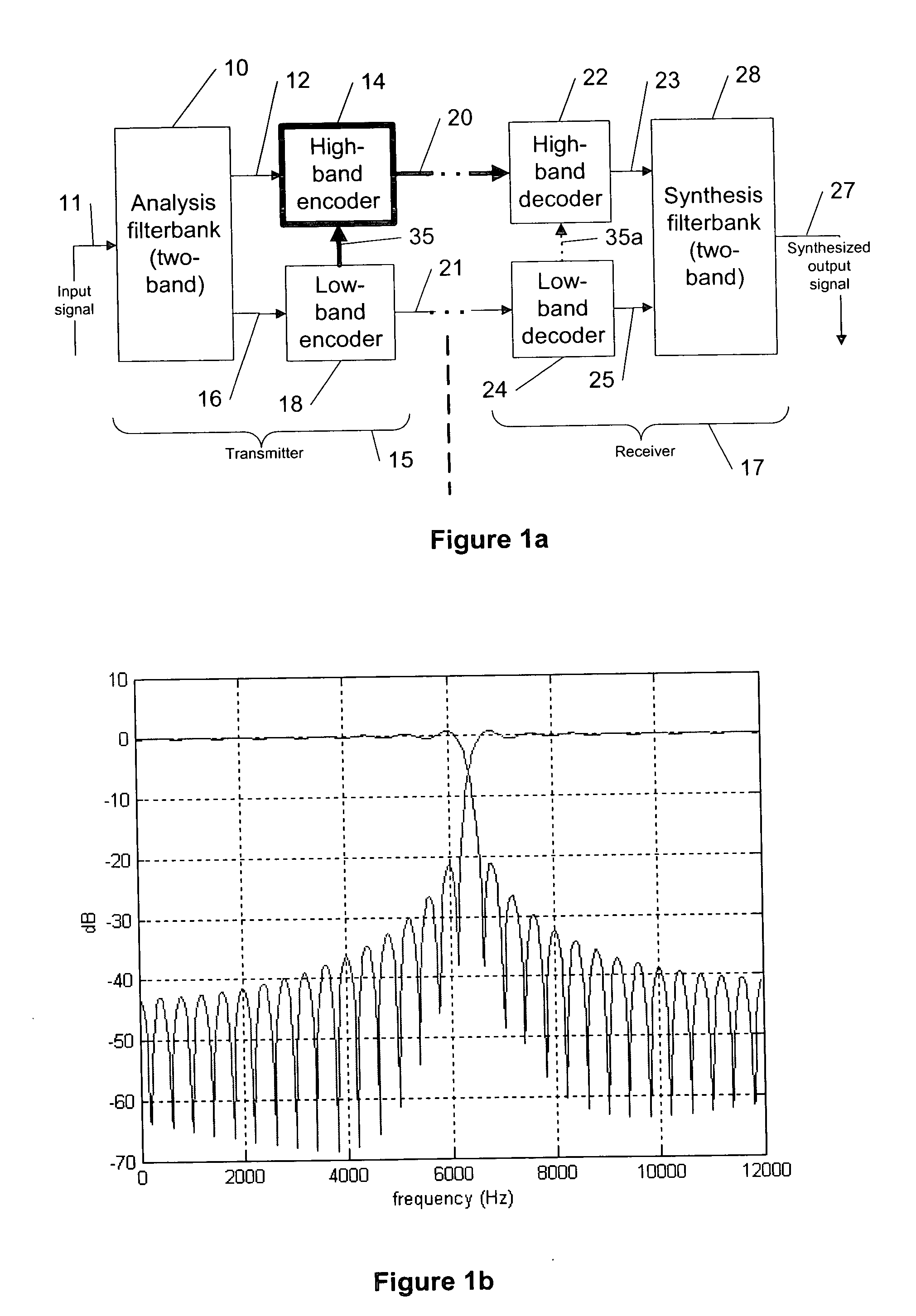
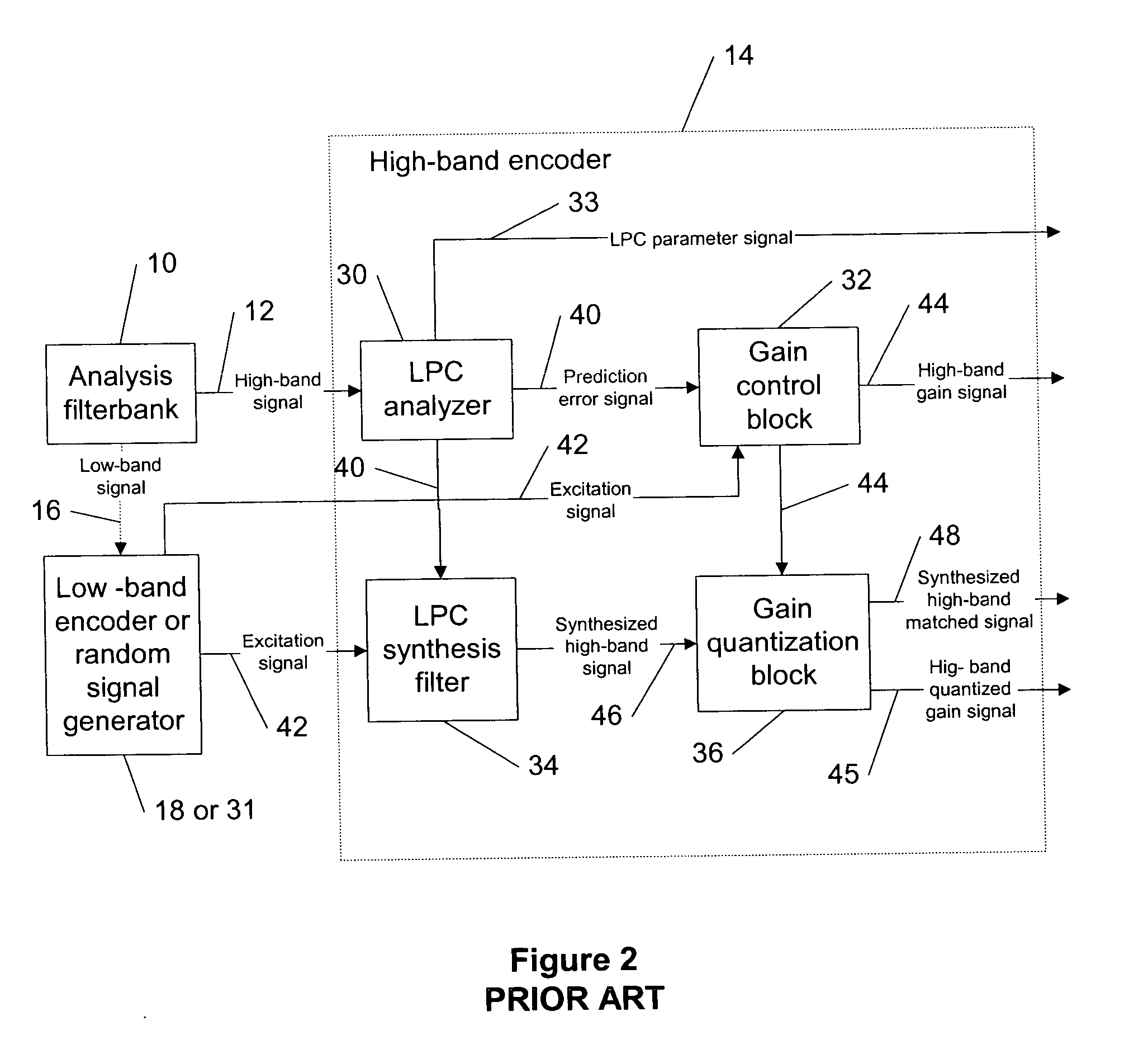
Apparatus and a Method for Decoding an Encoded Audio Signal
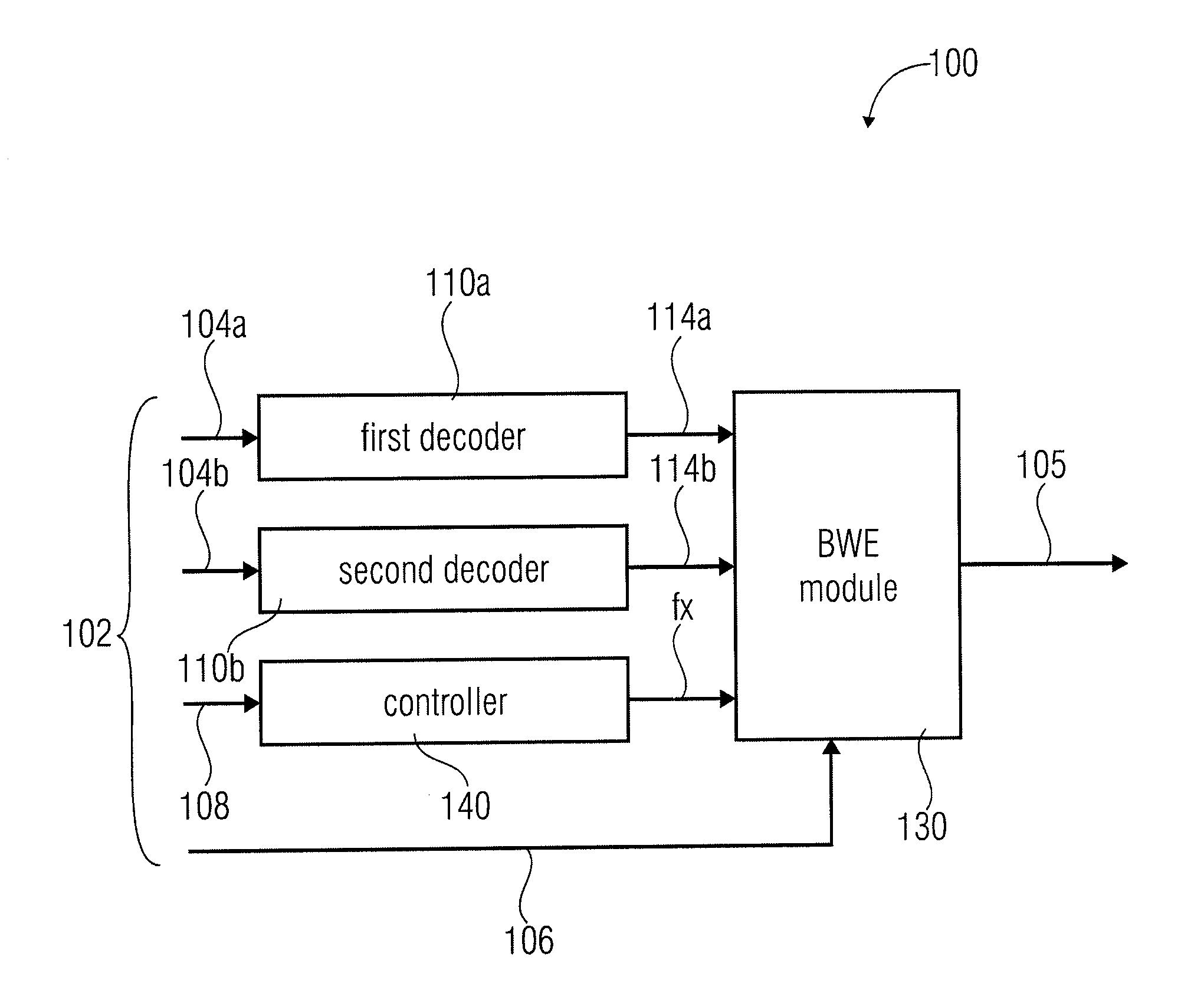
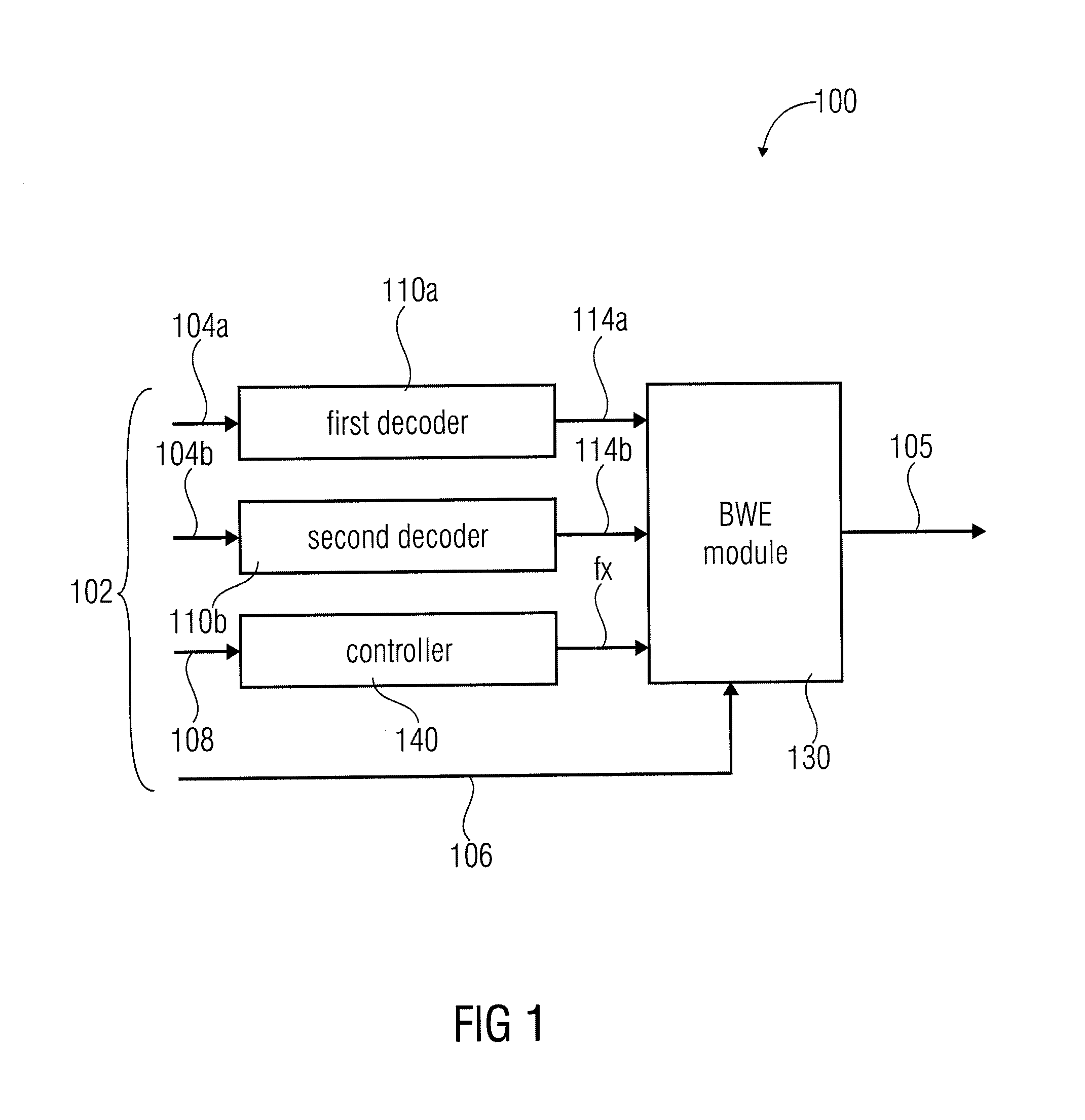
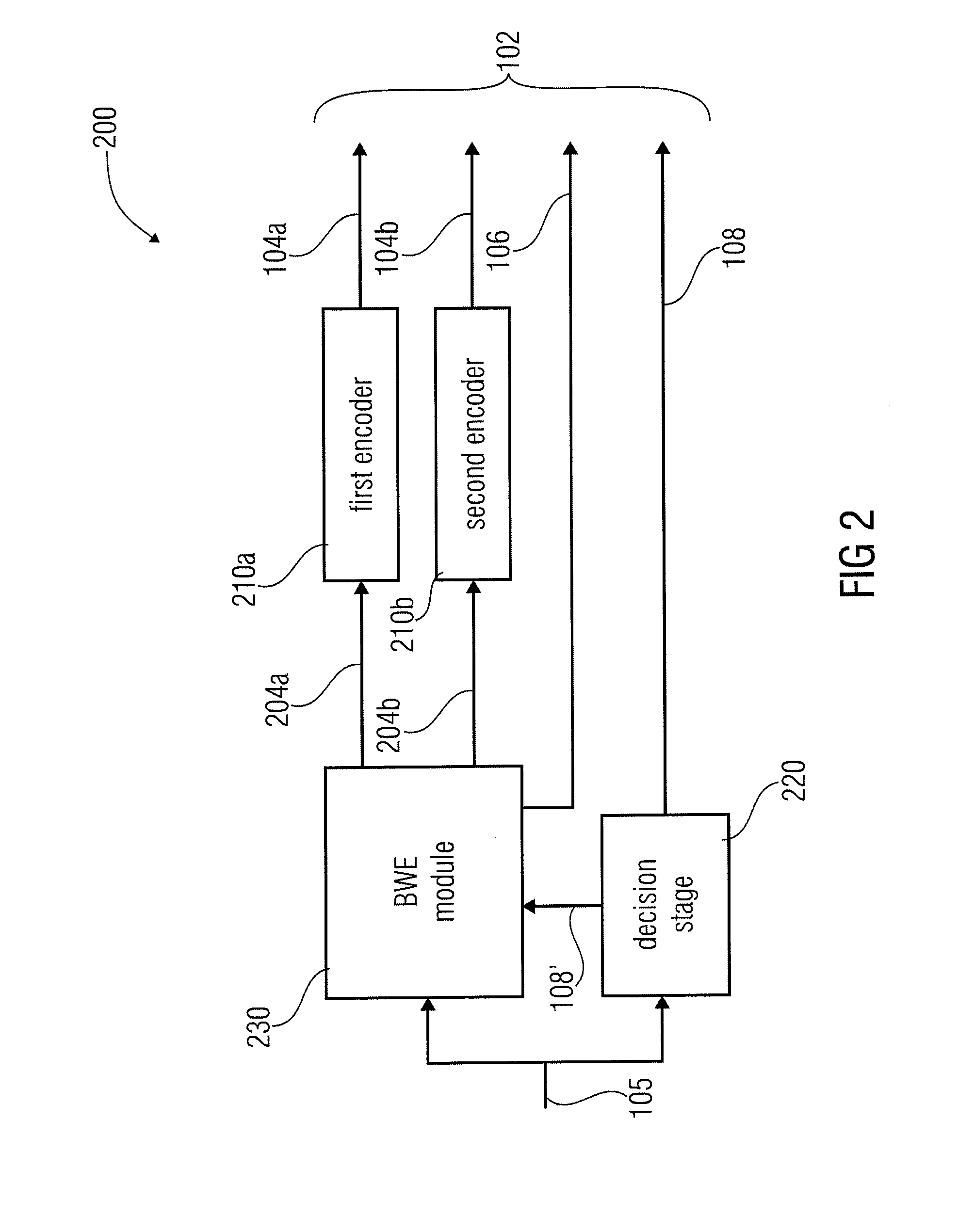
ActiveUS20110202353A1Improve perceived qualityHigh resolutionSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsBandwidth extensionEncoding algorithm
An apparatus for decoding an encoded audio signal having first and second portions encoded in accordance with first and second encoding algorithms, respectively, BWE parameters for the first and second portions and a coding mode information indicating a first or a second decoding algorithm, includes first and second decoders, a BWE module and a controller. The decoders decode portions in accordance with decoding algorithms for time portions of the encoded signal to obtain decoded signals. The BWE module has a controllable crossover frequency and is configured for performing a bandwidth extension algorithm using the first decoded signal and the BWE parameters for the first portion, and for performing a bandwidth extension algorithm using the second decoded signal and the bandwidth extension parameter for the second portion. The controller controls the crossover frequency for the BWE module in accordance with the coding mode information.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
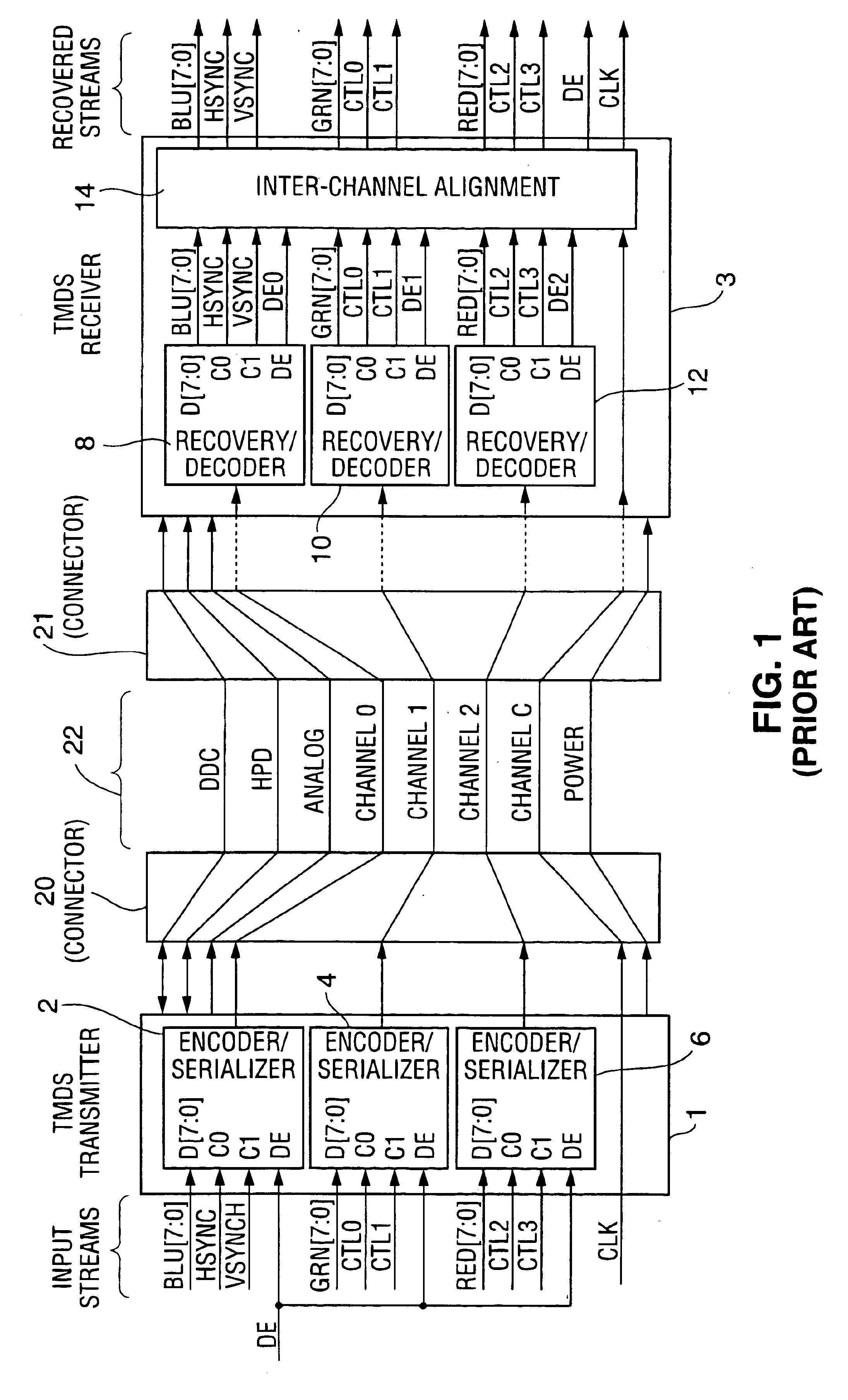
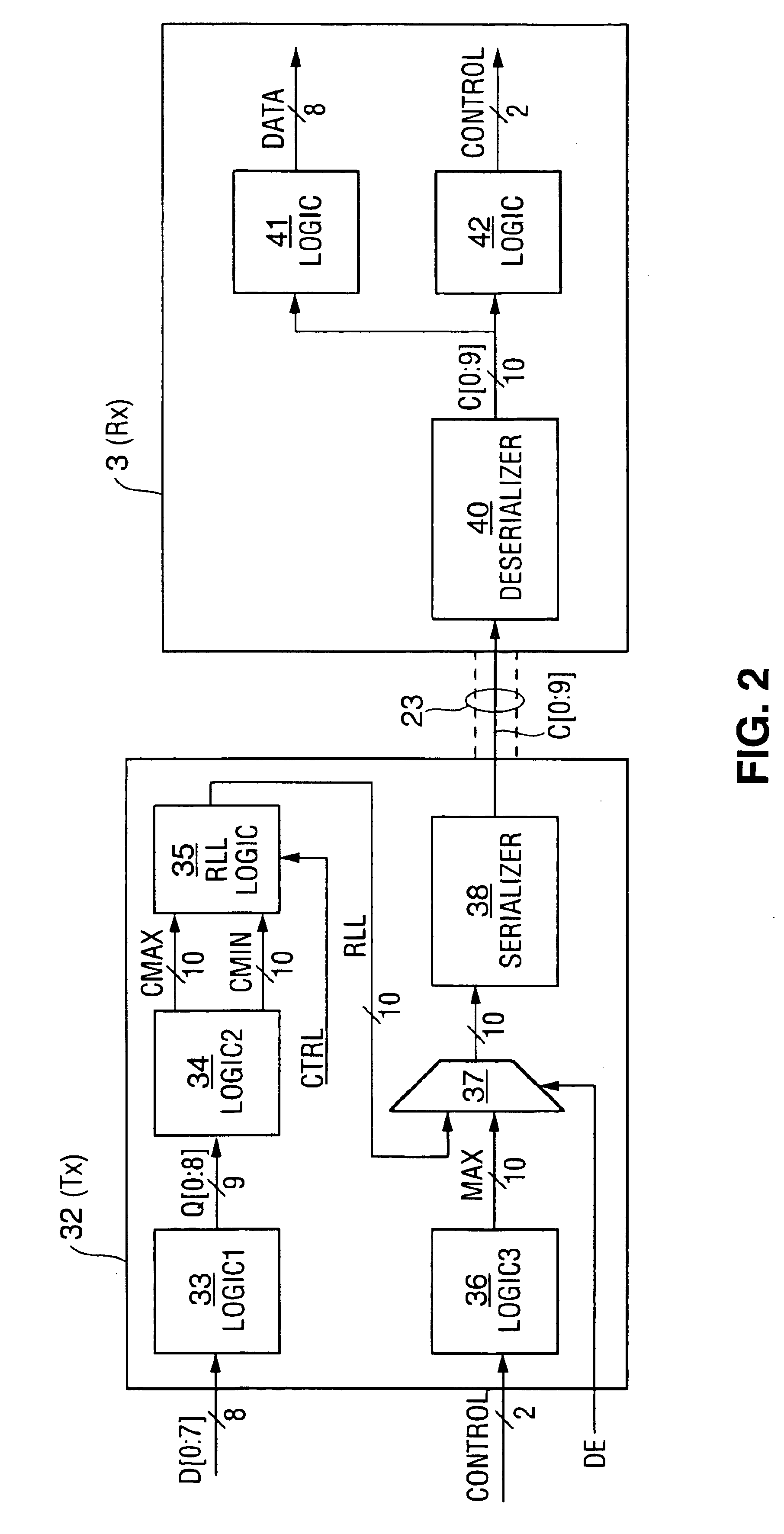
Method and apparatus for run length limited TMDS-like encoding of data
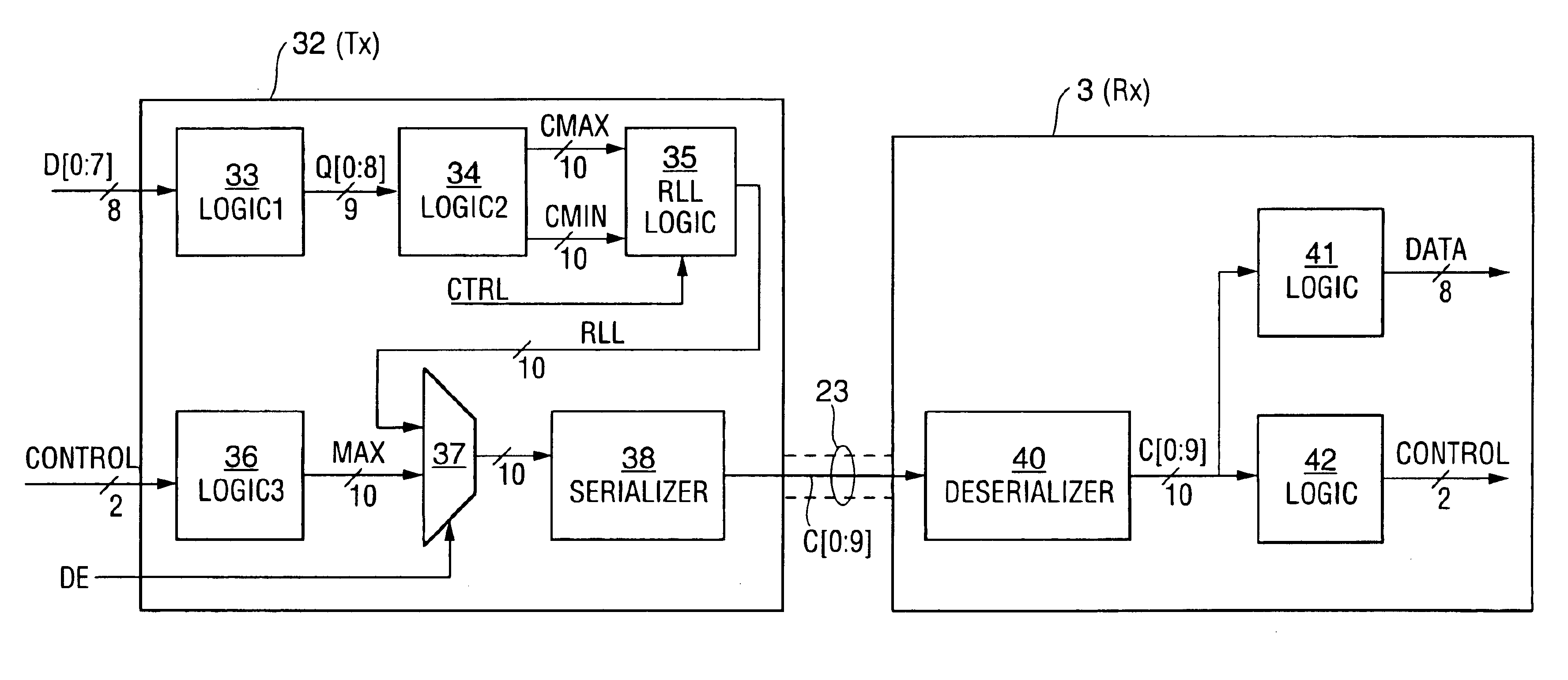
ActiveUS6897793B1Long run lengthReduce in quantityIndividual digits conversionComputer hardwareEncoding algorithm
A serial data transmission system in which a transmitter encodes data in accordance with a TMDS-like encoding algorithm and transmits the TMDS-like encoded data over a serial link to a receiver. The encoded data are transmitted as a run length limited (“RLL”) code word sequence, including transition-minimized code words. In some embodiments, the RLL code word sequence includes only Min words, including both DC balancing Min words and DC unbalancing Min words. In other embodiments, the RLL code word sequence includes both transition-maximized code words and transition-minimized code words. Other aspects of the invention are circuitry and methods for TMDS-like encoding of data for transmission as an RLL code word sequence.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
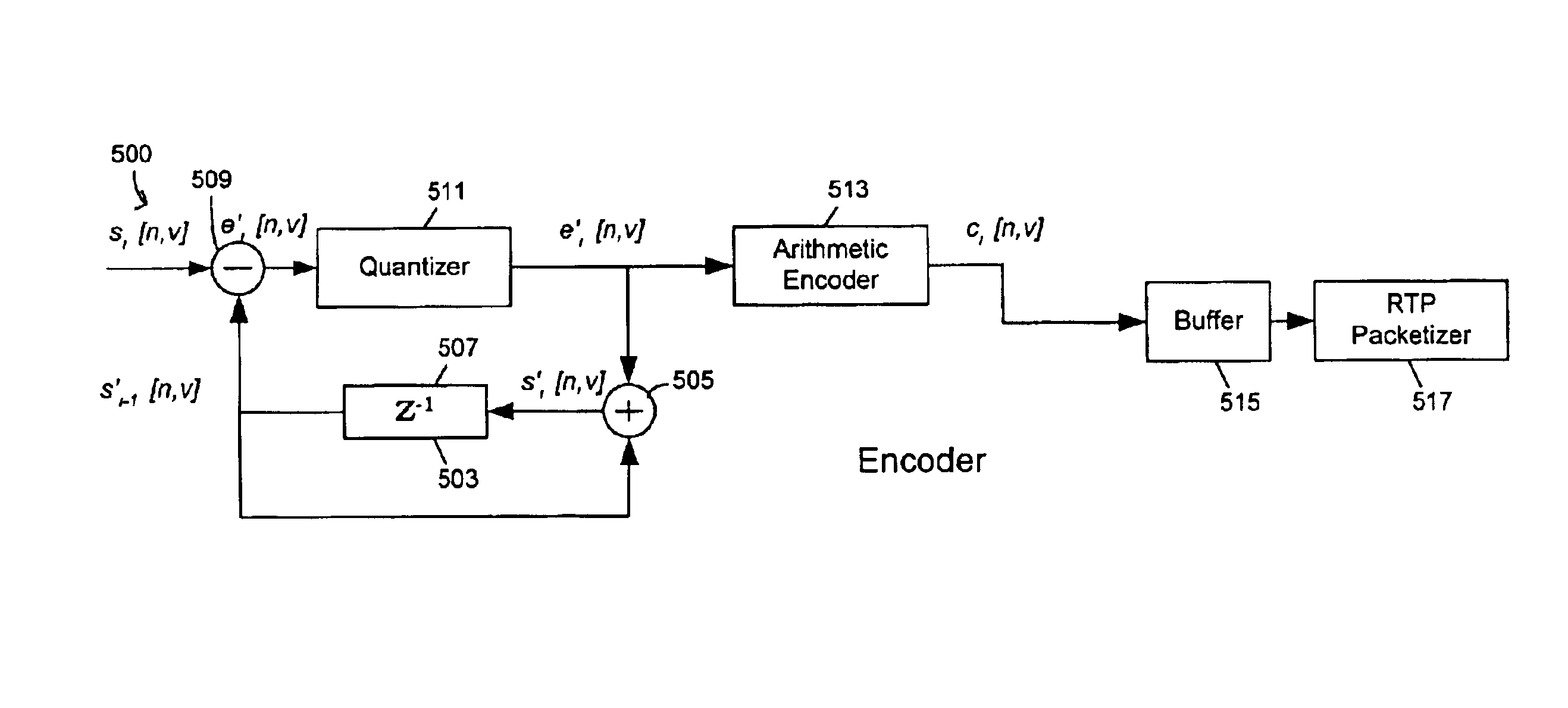
Coding of animated 3-D wireframe models for internet streaming applications: methods, systems and program products
A 3-D wireframe model expressed in terms of nodes and vertices receives a 3-D video or like signal representative of a scene expressed in terms of a reference model, I frames and P frames. A DPCM coder takes advantage of the temporal correlation of the displacement of each vertex along every axis in the 3-D space. The 3-D signal is a set of non-zero displacements of all vertices and all nodes (sl[n, v]) at time tl. The decoded set (animation frame) of the previous instance is used as the predicted value (si-l[n, v]). The prediction error el[n, v], i.e. the difference between the current displacement set and the predicted one, is computed and quantised (el[n, v]). Finally, the quantised samples are entropy coded (ci[n, v]) using an adaptive arithmetic coding algorithm to handle the unknown data statistics. The predictive scheme described above prevents quantization error accumulation. A DPCM decoder first decodes arithmetically the received samples (‘e’ [n, v]) and computers the decoded samples (si′ [n, v]).
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
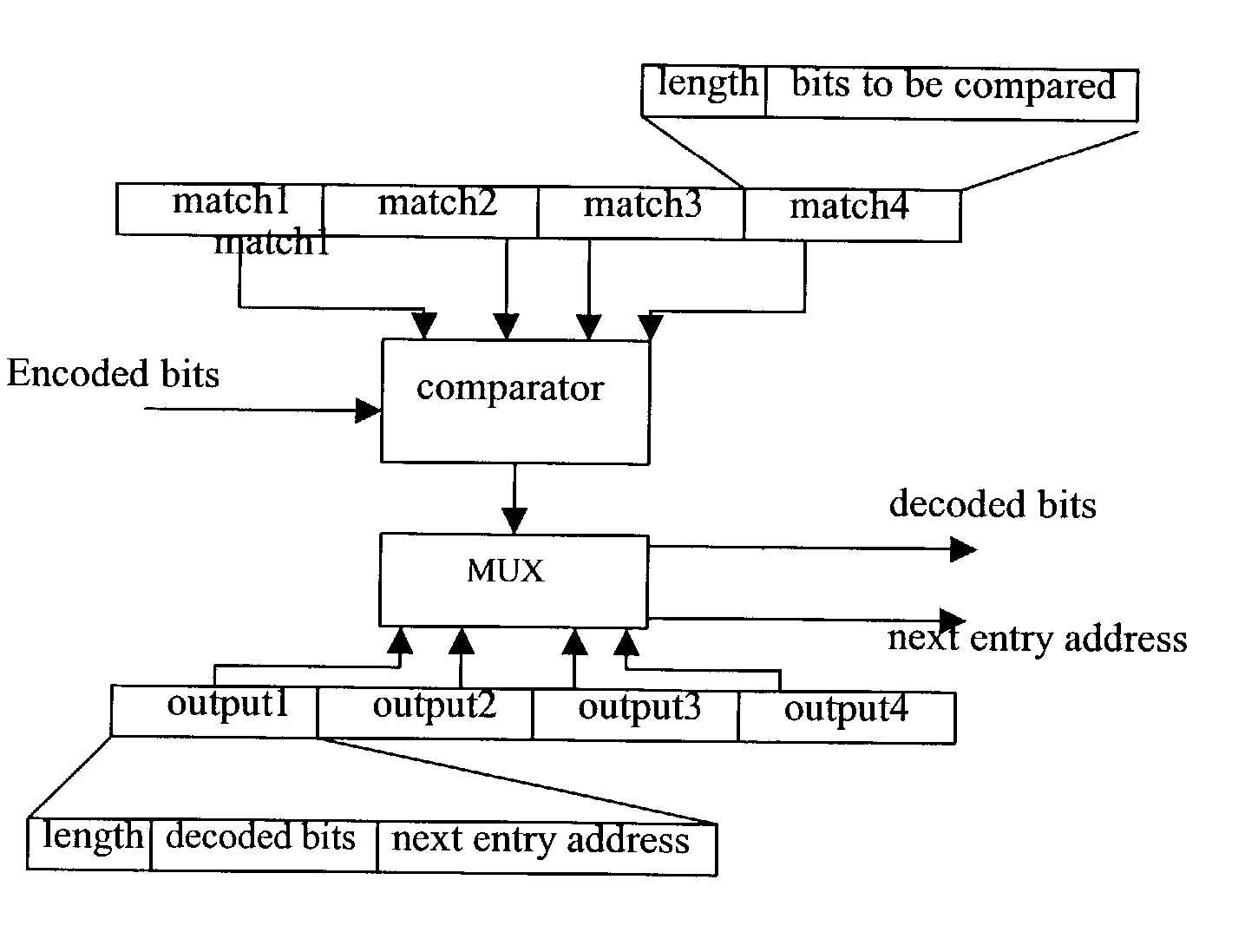
Code compression algorithms and architectures for embedded systems
InactiveUS7095343B2Increase the compression ratioSimple designCode conversionProbit modelAdaptive coding
Code compression techniques and decompression architectures for embedded systems are disclosed, providing good compression ratio while improving decompression time for VLIW instructions and reducing bus power consumption. The invention includes two fixed-to-variable (F2V) length code compression schemes based on a reduced arithmetic code compression algorithm combining arithmetic coding with probability models; a static probability model using static coding and semi-adaptive coding using a Markov model. Multi-bit decompression methods for the F2V techniques are presented, together with a parallel decompression scheme that tags and divides a compressed block into smaller sub-blocks. The Markov model provides better compression ratio, but the static model has a less complicated decompression unit design. The invention also includes two variable-to-fixed (V2F) length coding algorithms, one based on Tunstall coding and another on arithmetic coding. The V2F algorithms are also combined with a static model and a Markov model.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
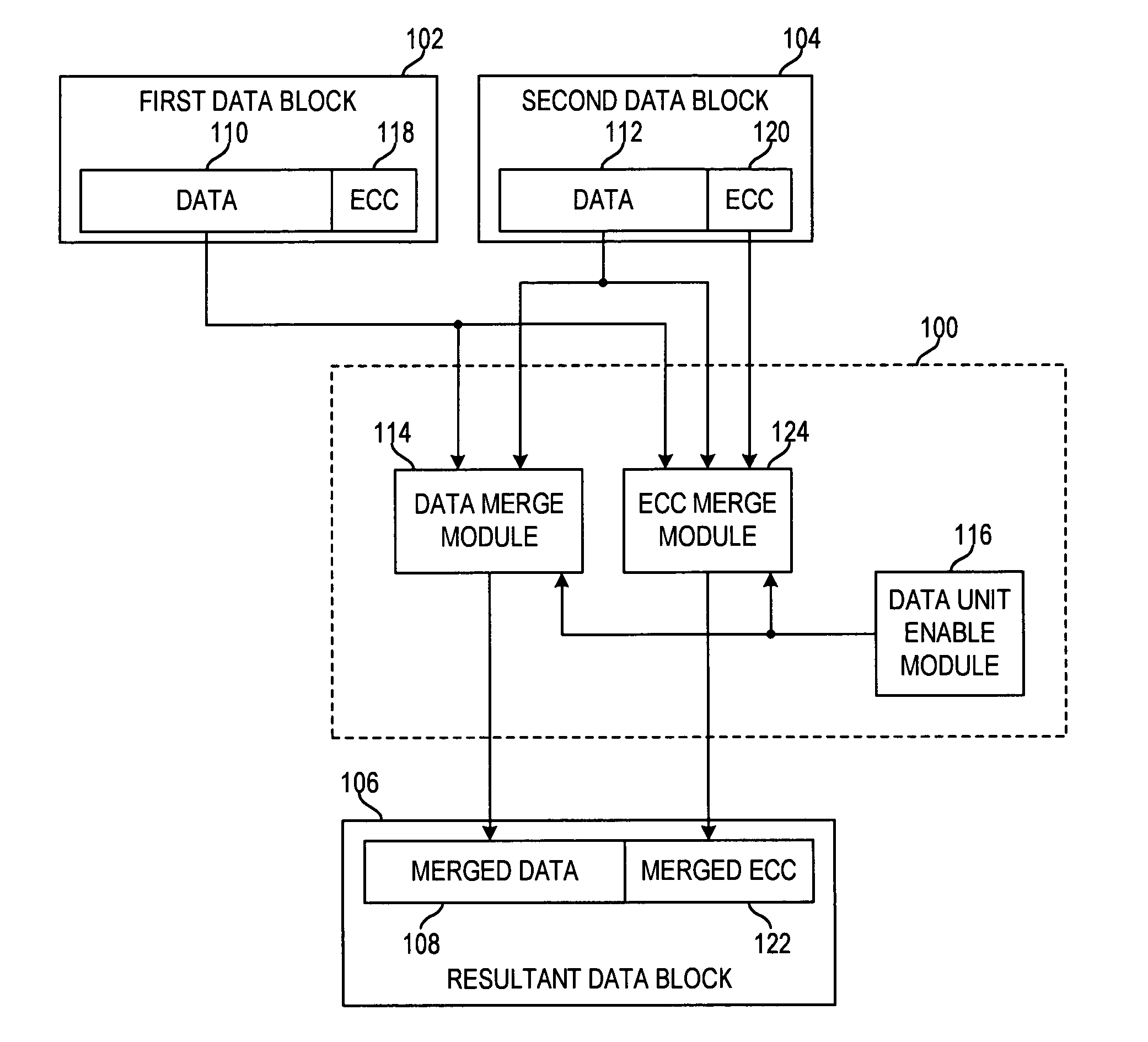
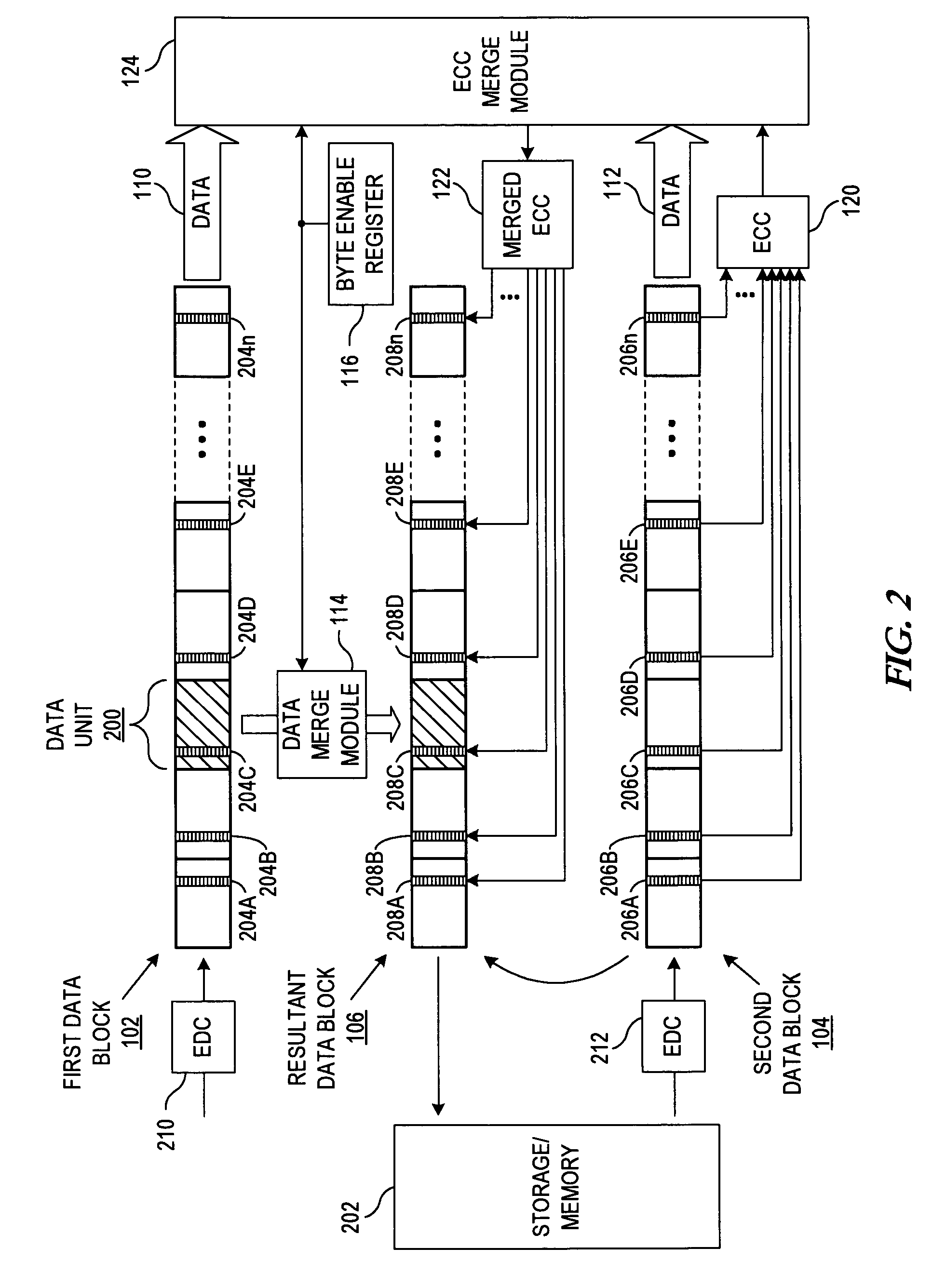
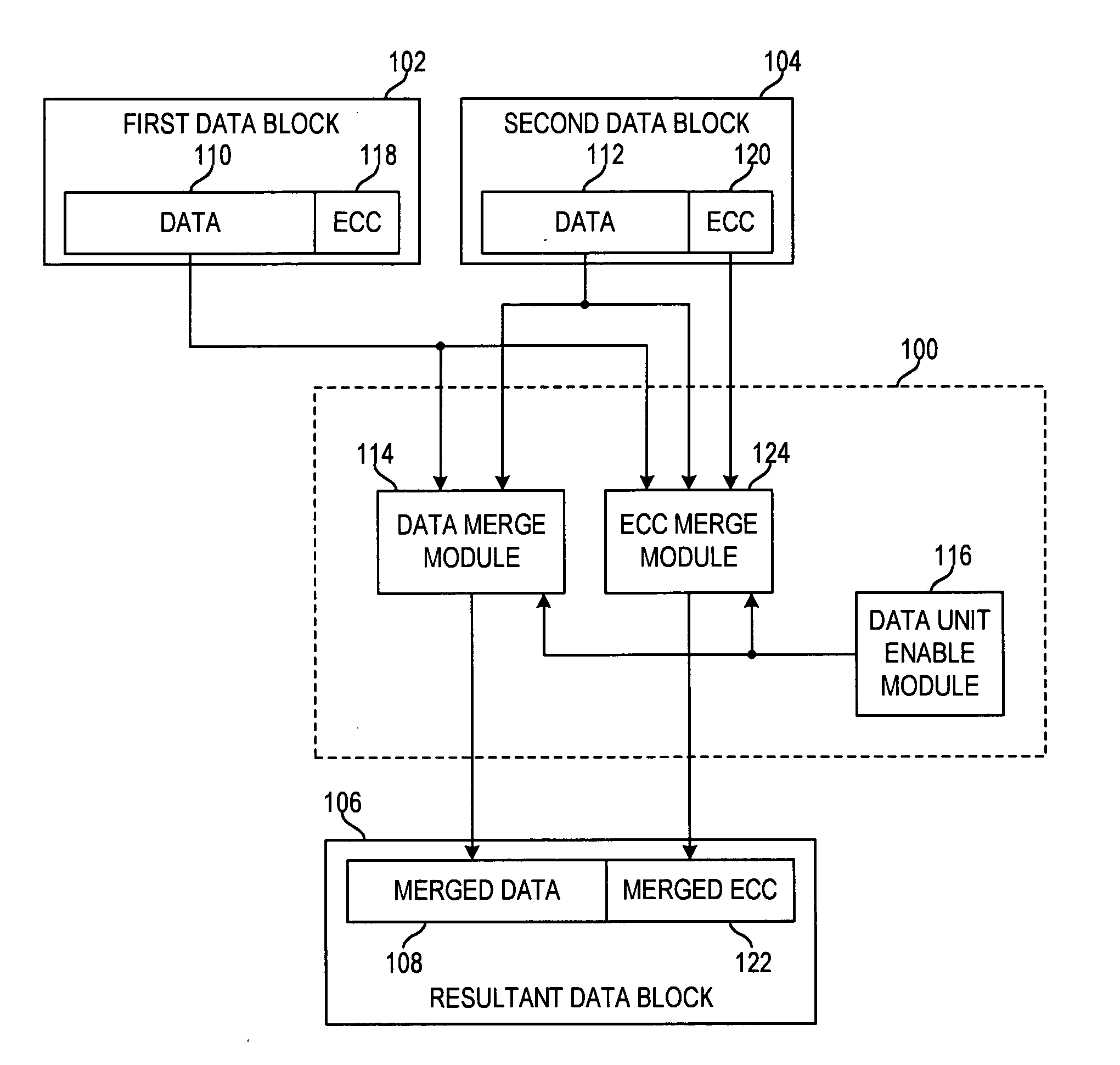
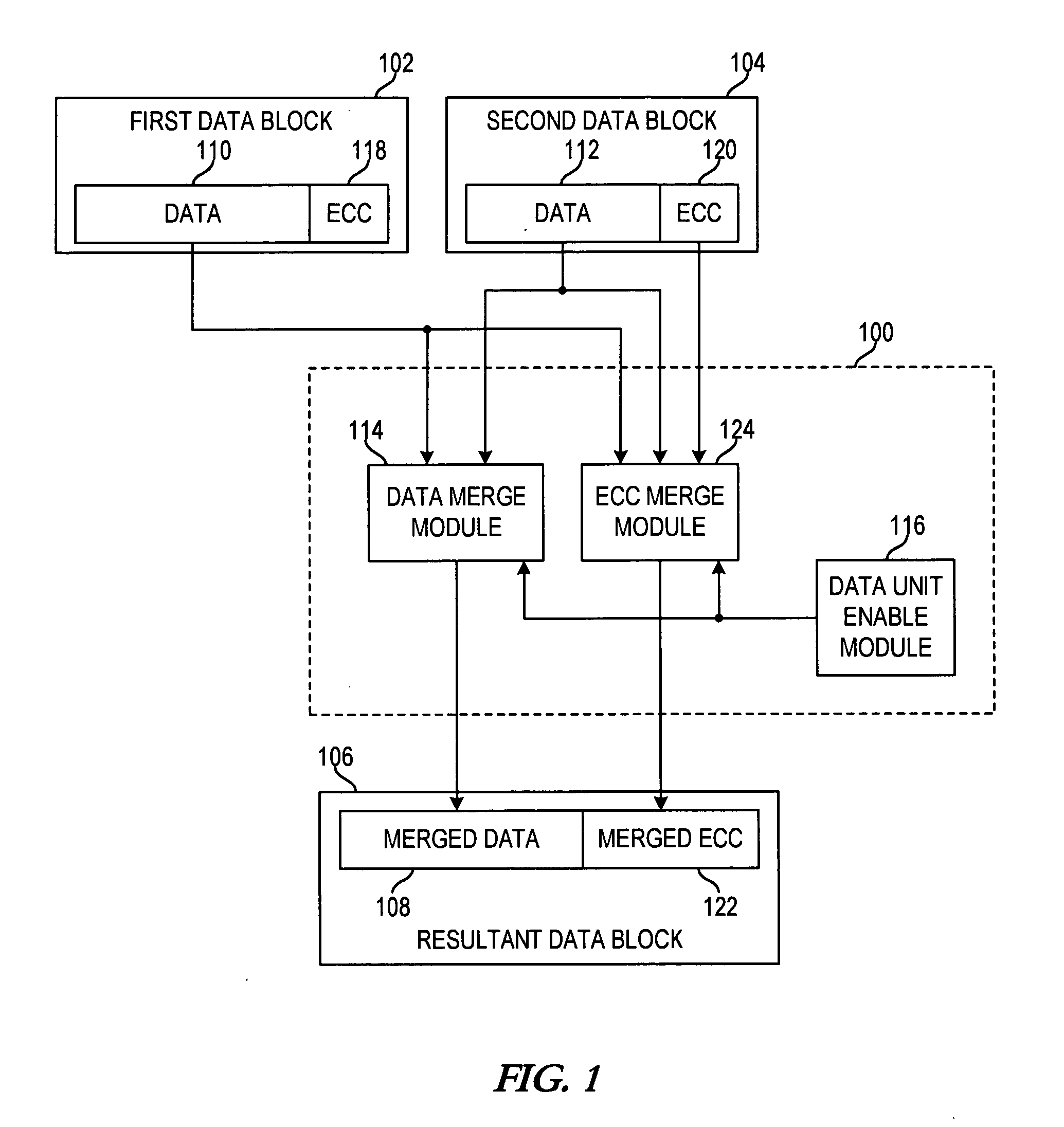
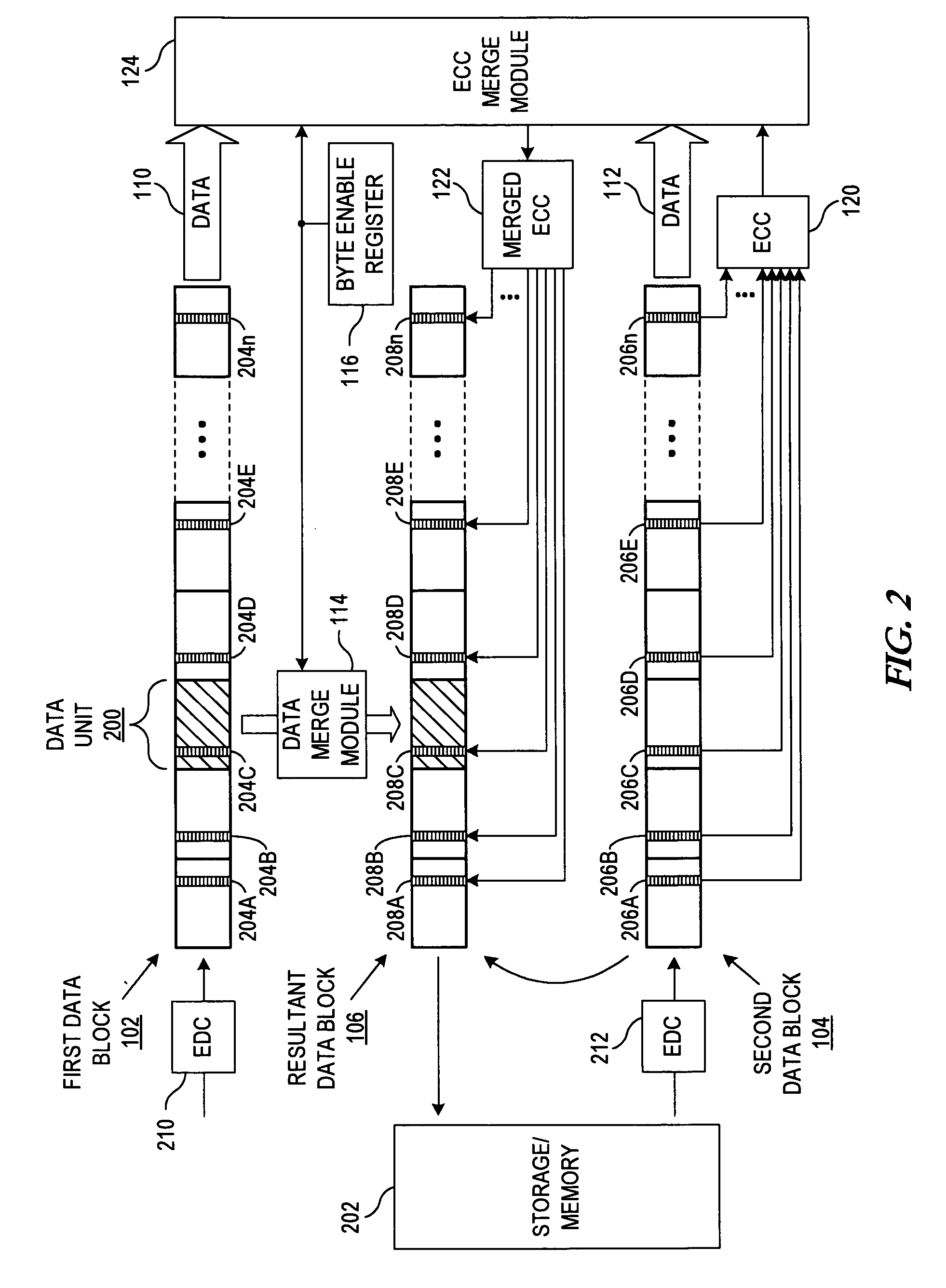
Apparatus and method for merging data blocks with error correction code protection
An apparatus and method for selectively deriving Error Correction Codes (ECCs) or other data integrity information for integration into merged data blocks. First data is merged into second data that is error-protected using an ECC generated by a coding algorithm. Bytes or other data units are identified in the first data to be merged into the second data. It is determined whether each of the check bits of the ECC will differ from its original state in response to merging the first and second data. The check bits of the ECC that have been determined to differ from their respective original states are modified to create a “merged ECC.” The resulting data block includes the merged data and the merged ECC.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
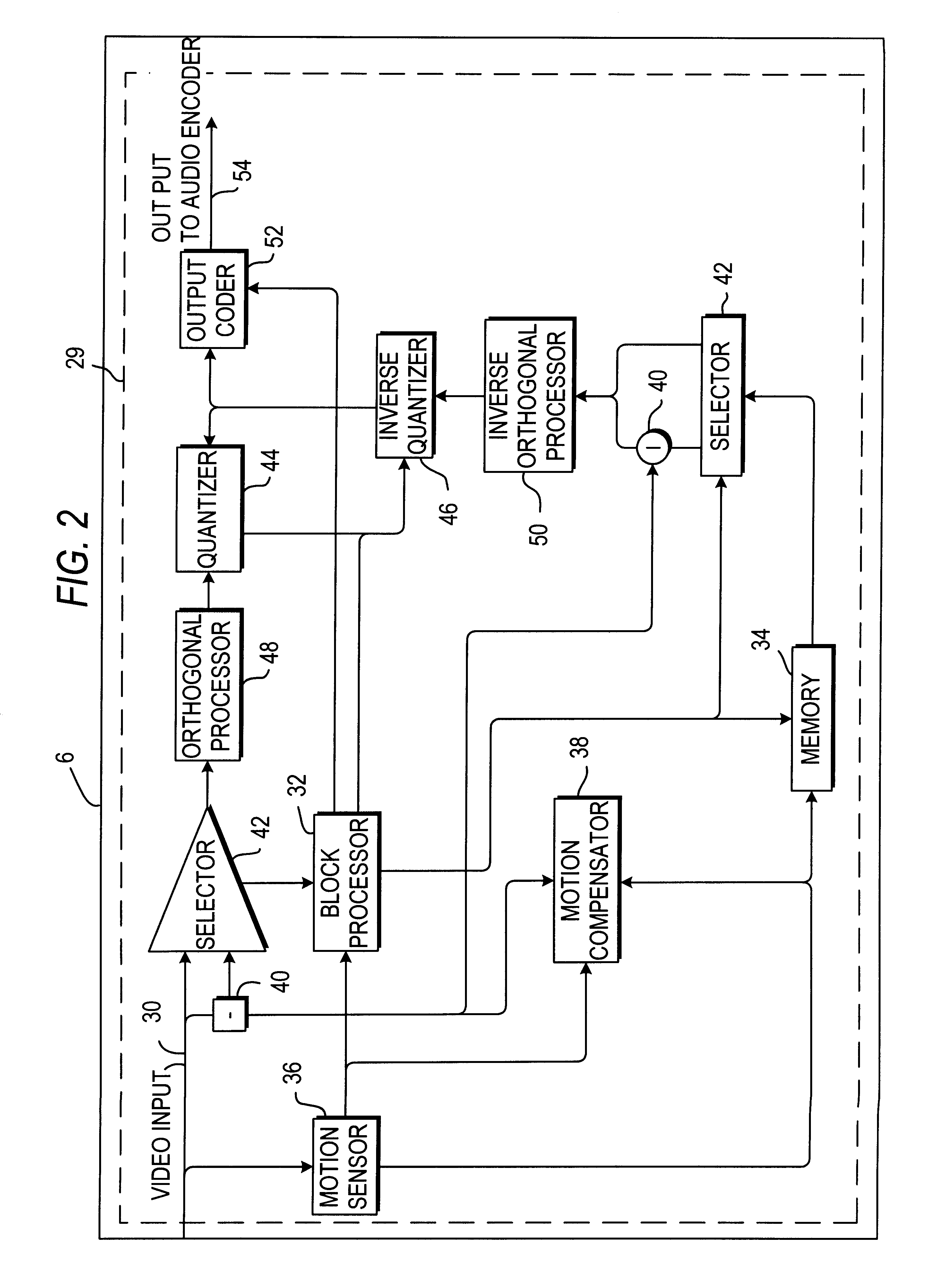
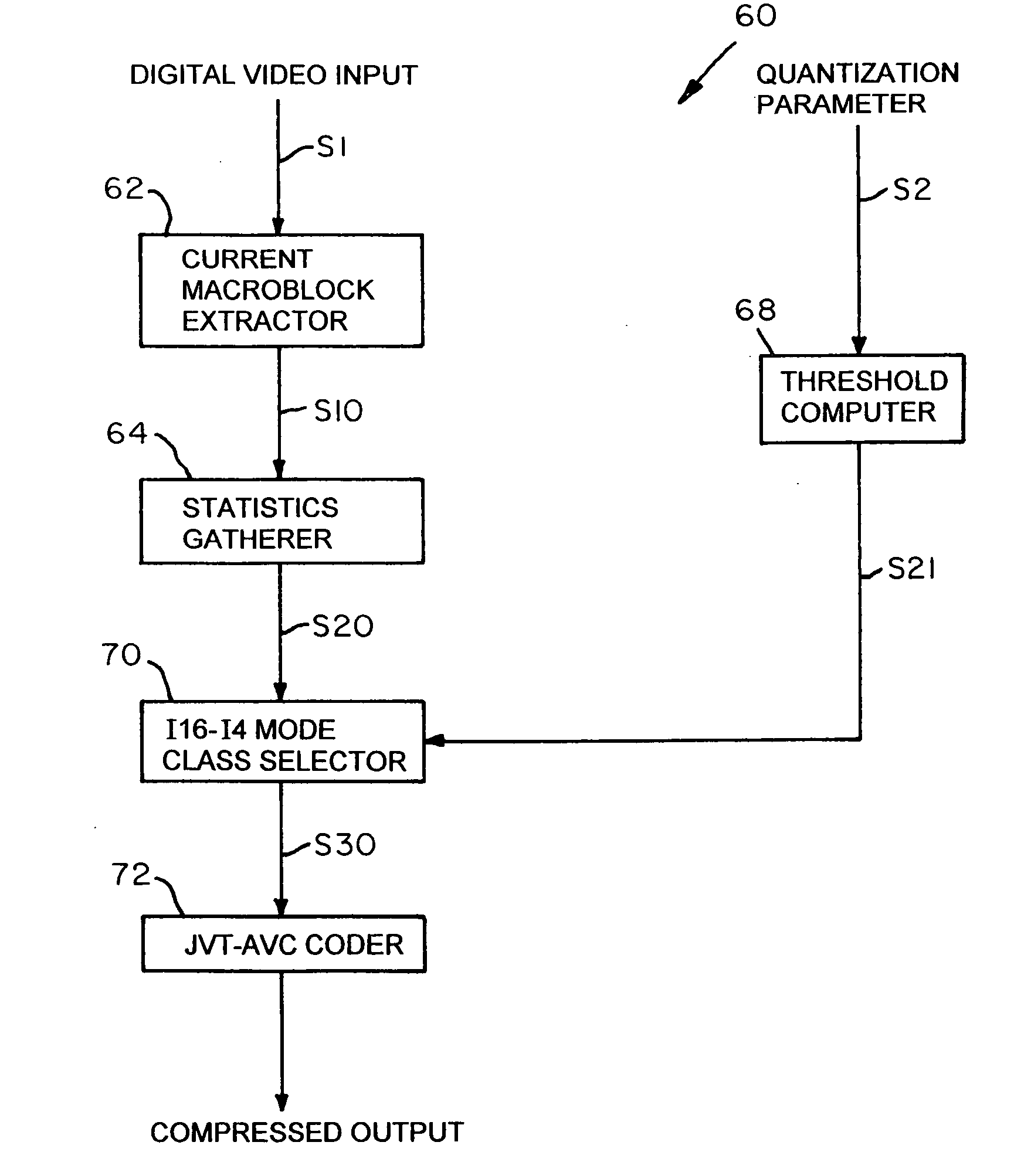
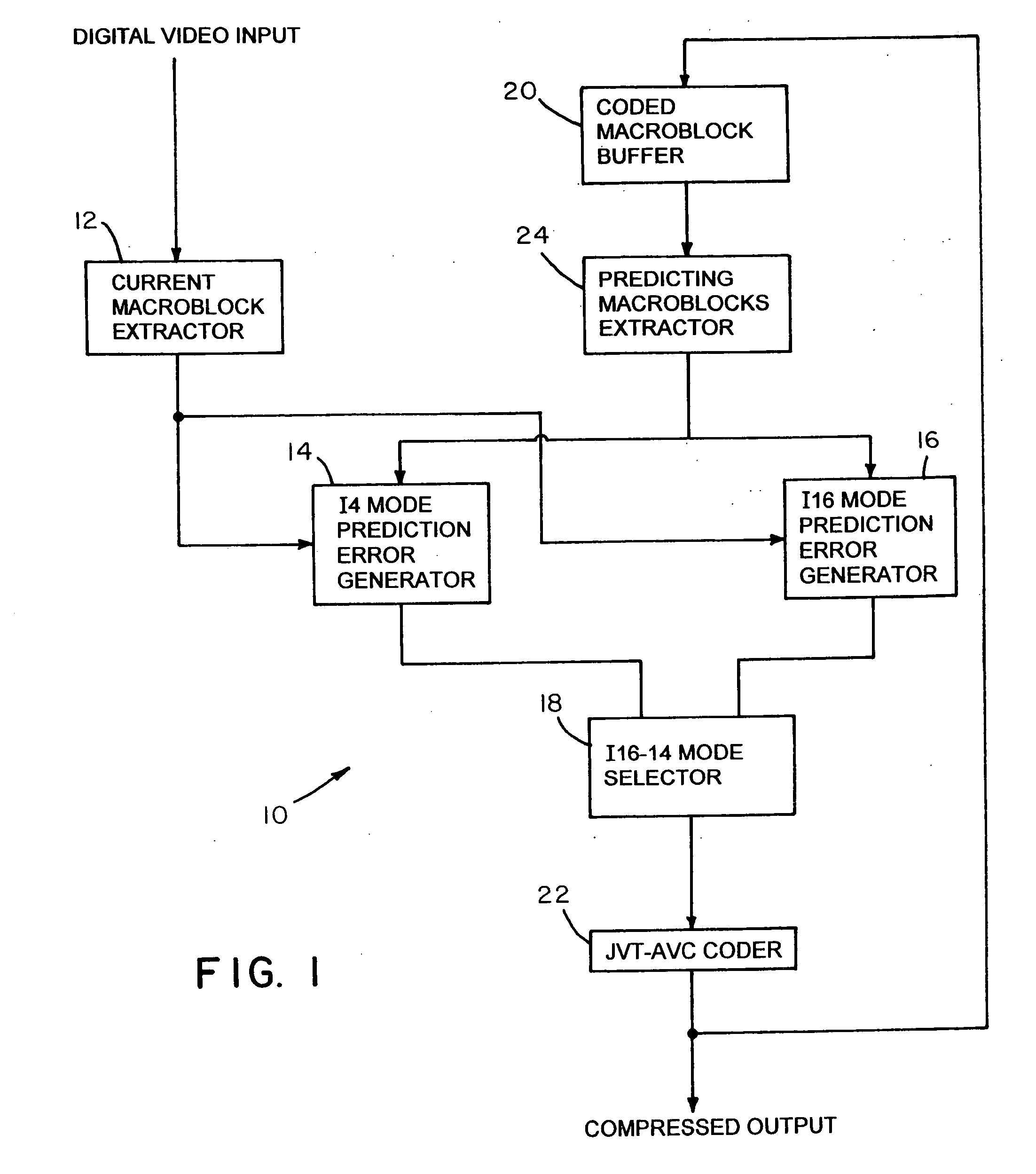
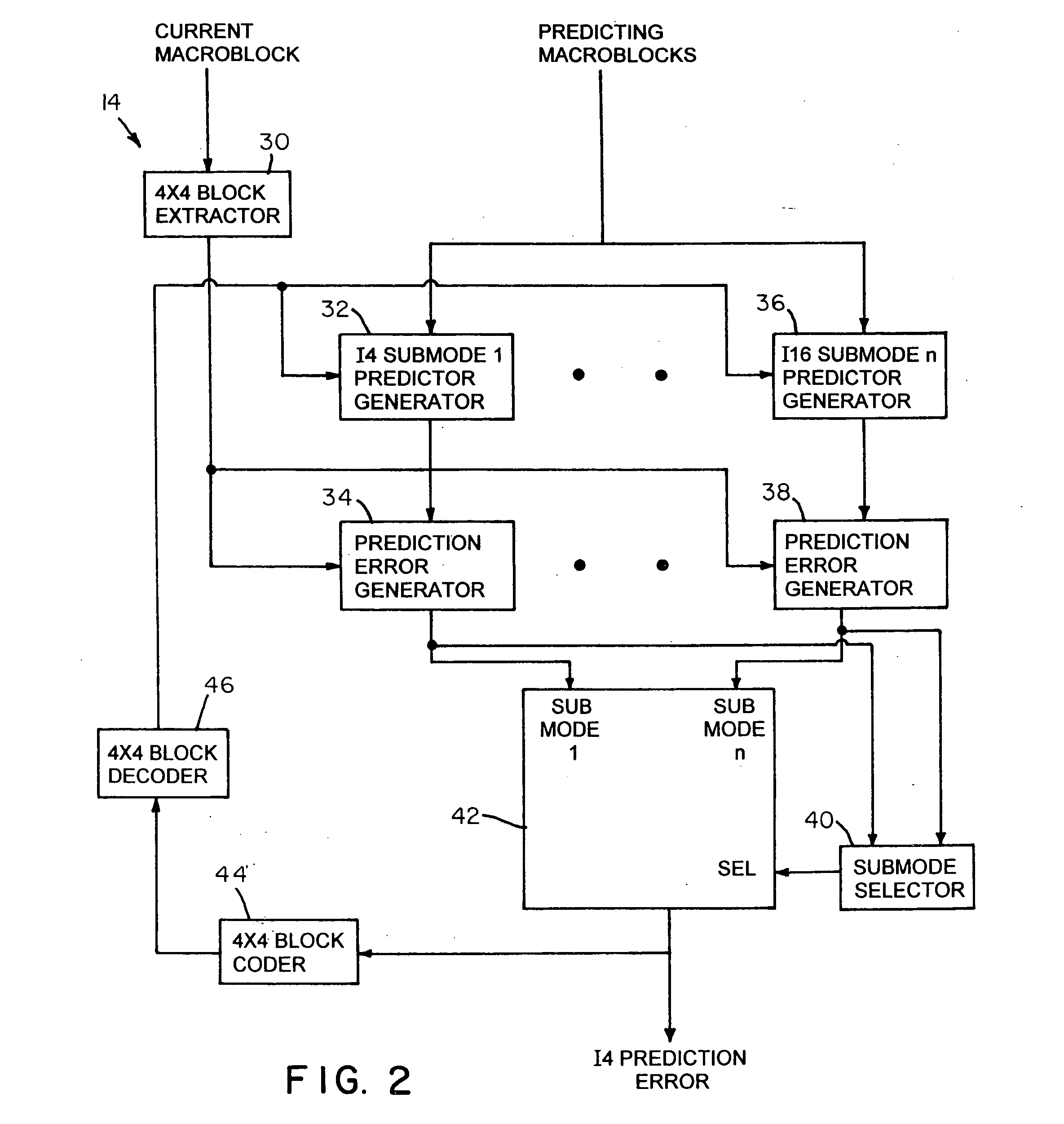
Method and apparatus to determine prediction modes to achieve fast video encoding
ActiveUS20050249277A1Reduce complexityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionHadamard transformEncoding algorithm
An improvement to a predictive video encoding method or apparatus that includes selecting a mode class within which to choose an encoding algorithm to encode individual blocks of video information. Rather than implementing each algorithm in each mode class to ascertain an acceptable compression, the improvement eliminates searching through a class of encoding modes based simply on heuristics. The method comprises obtaining statistical information related to previous blocks of encoded video information, determining a mode class within which to chose a particular encoding algorithm based on the statistical information (e.g., heuristics) gathered, choosing an algorithm within the selected mode class using conventional techniques, and encoding the video information according to the chosen algorithm. Statistical information may include quantization parameters, prior encoding decisions, intensity or frequency values, or Hadamard transform coefficients of previously encoded macroblocks. Encoding complexity in the coder is reduced since one class of encoding modes is eliminated.
Owner:BEIJING PIANRUOJINGHONG TECH CO LTD
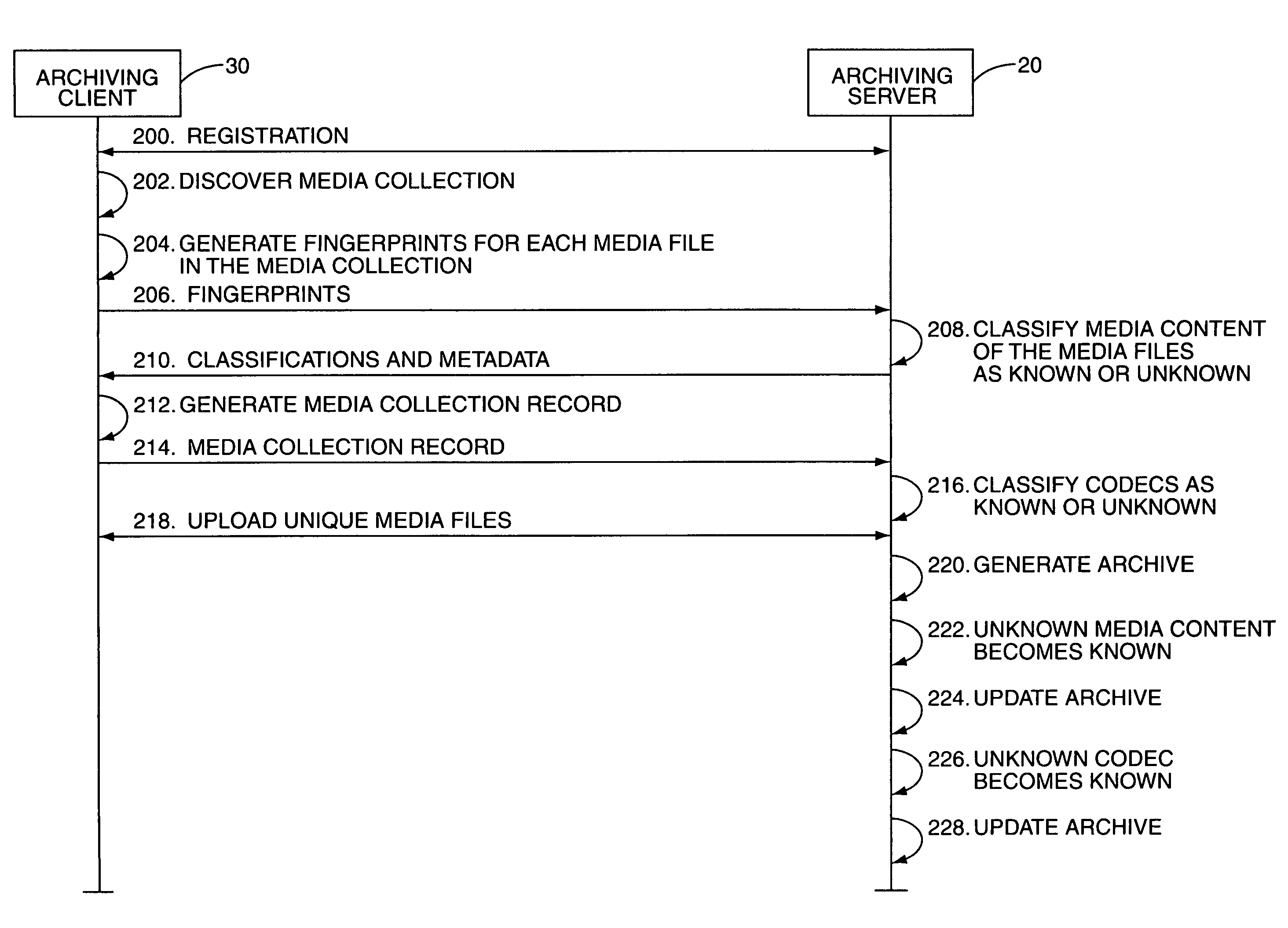
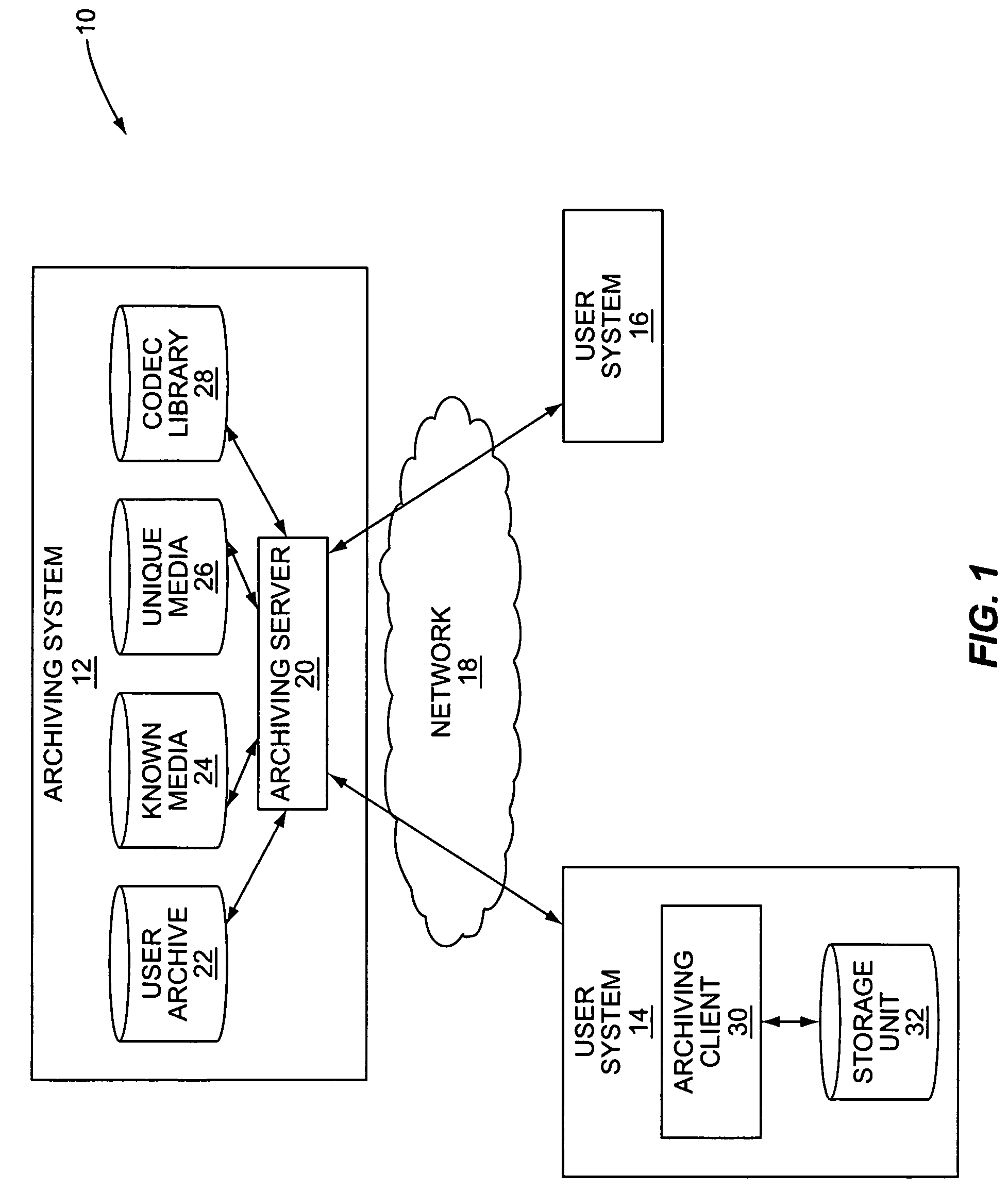
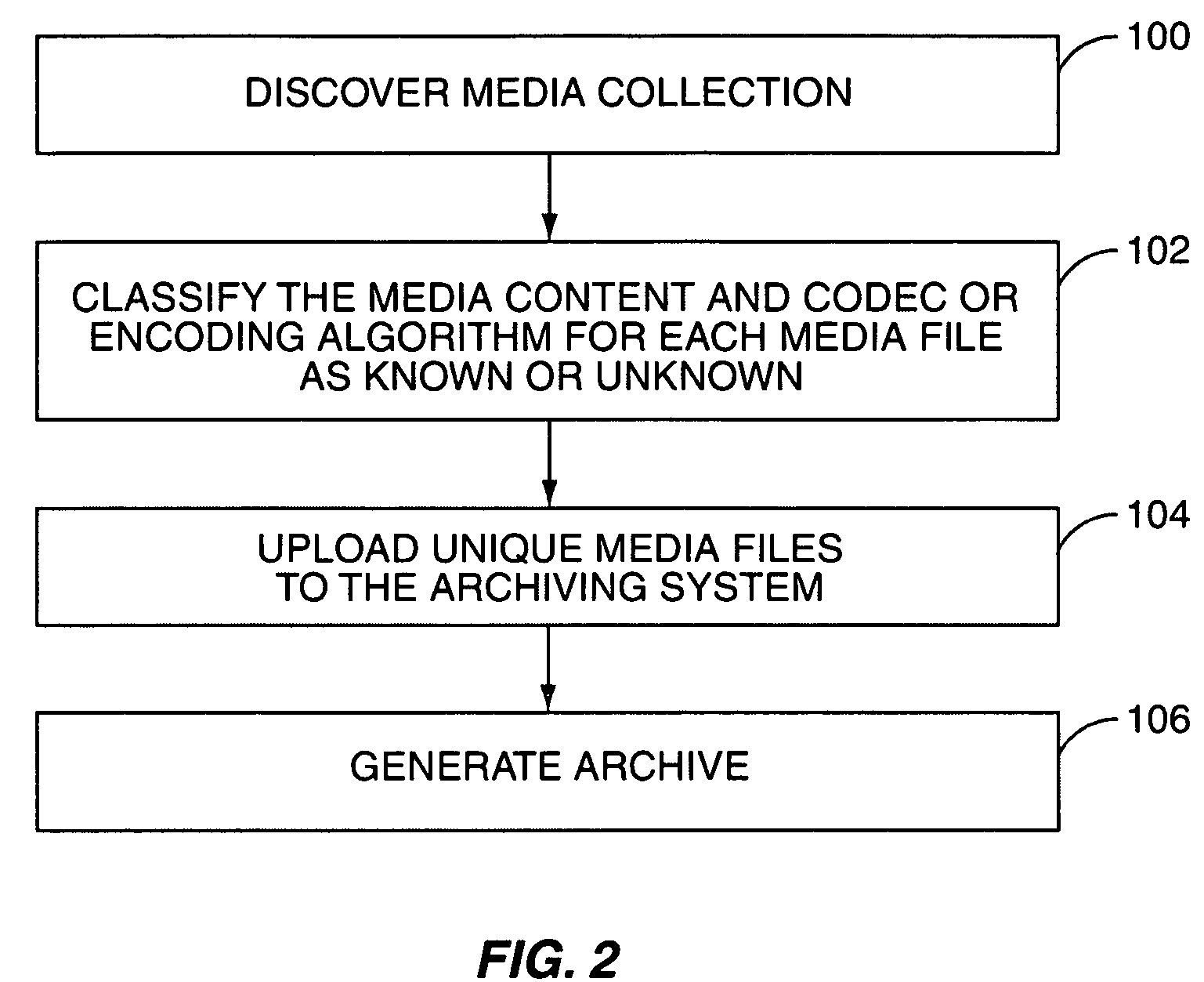
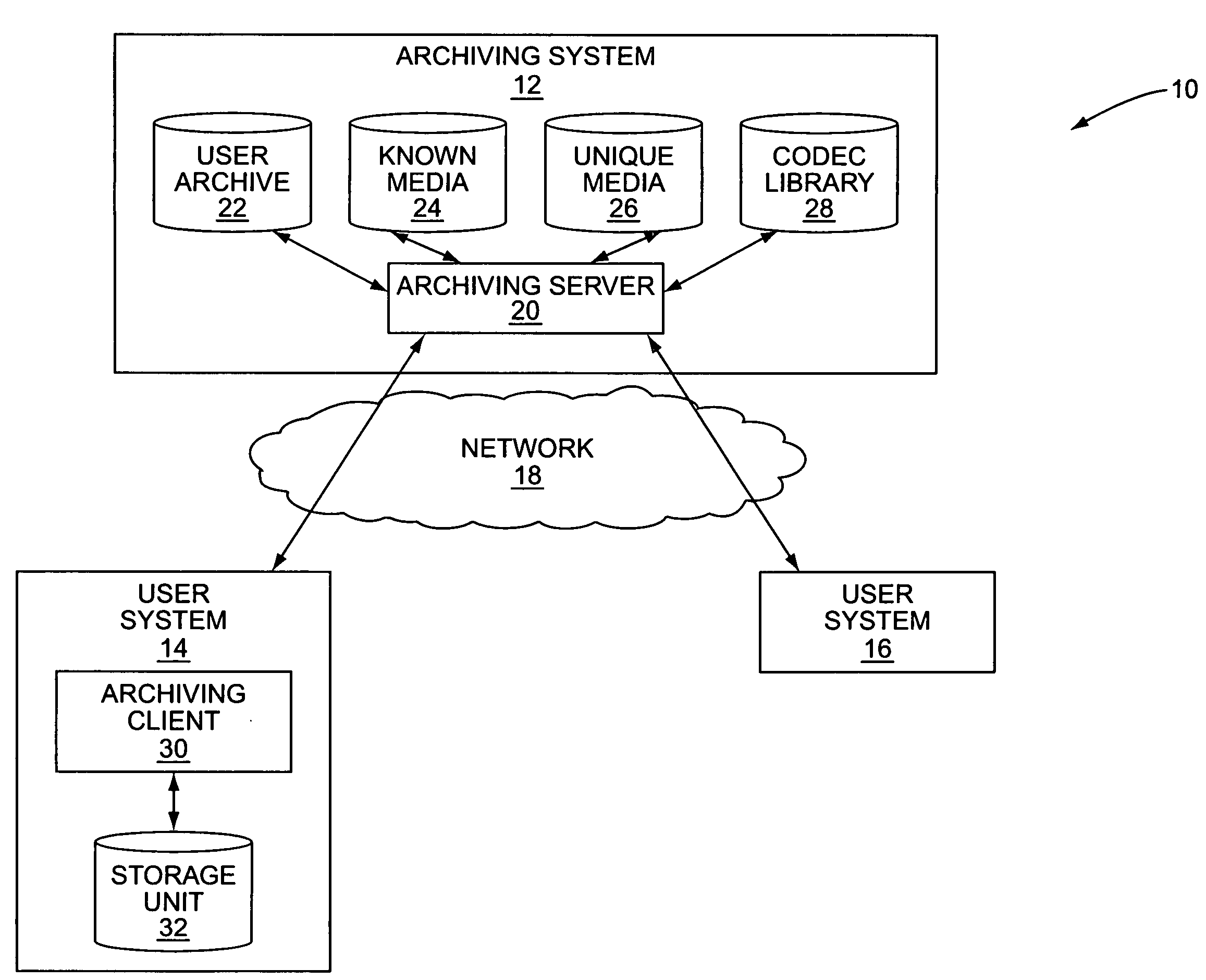
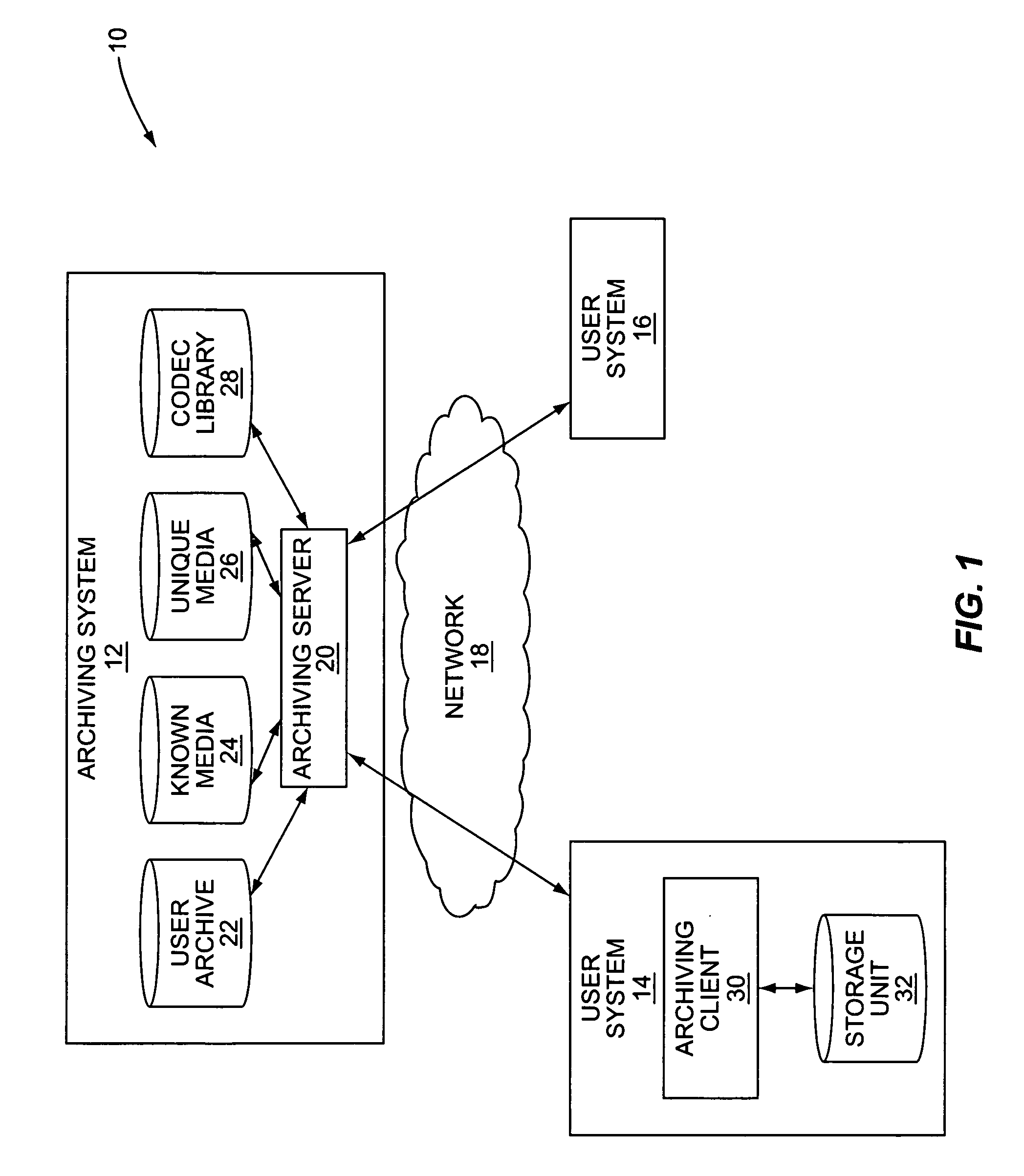
System and method for archiving a media collection
InactiveUS7765192B2Lower requirementMultimedia data indexingData processing applicationsComputer hardwareEncoding algorithm
Owner:CONCERT TECH
Encoder and decoder configuration for addressing latency of communications over a packet based network
InactiveUS20100226428A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareEncoding algorithm
An encoder for sending encoded video over a public packet-based communication network to a distribution server. The encoder comprises an encoder engine adapted for receiving video content and for encoding the received video content using a predefined encoding algorithm. The encoder also has a send buffer adapted for configuring the encoded content as an encoded video stream expressed as a plurality of packets for transmitting over the network, such that the send buffer has send buffer settings compatible with receive buffer settings associated with the distribution server, such that the distribution server is adapted for subsequent distribution of the encoded video stream over the network to a decoder having the algorithm for use in decoding of the encoded video stream, such that the socket configuration is between the send buffer of the encoder and the receive buffer of the distribution server.
Owner:TELEPHOTO TECH
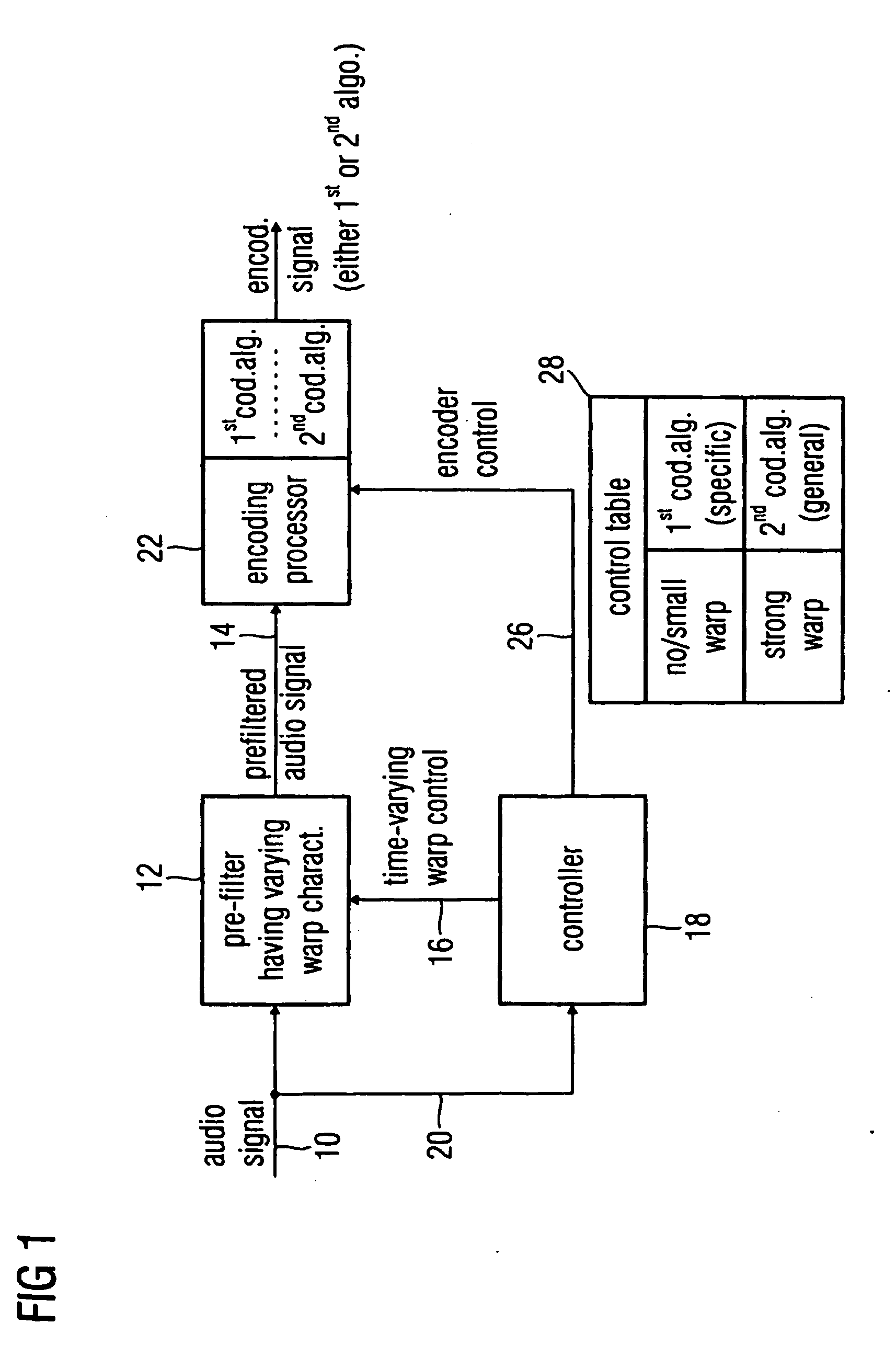
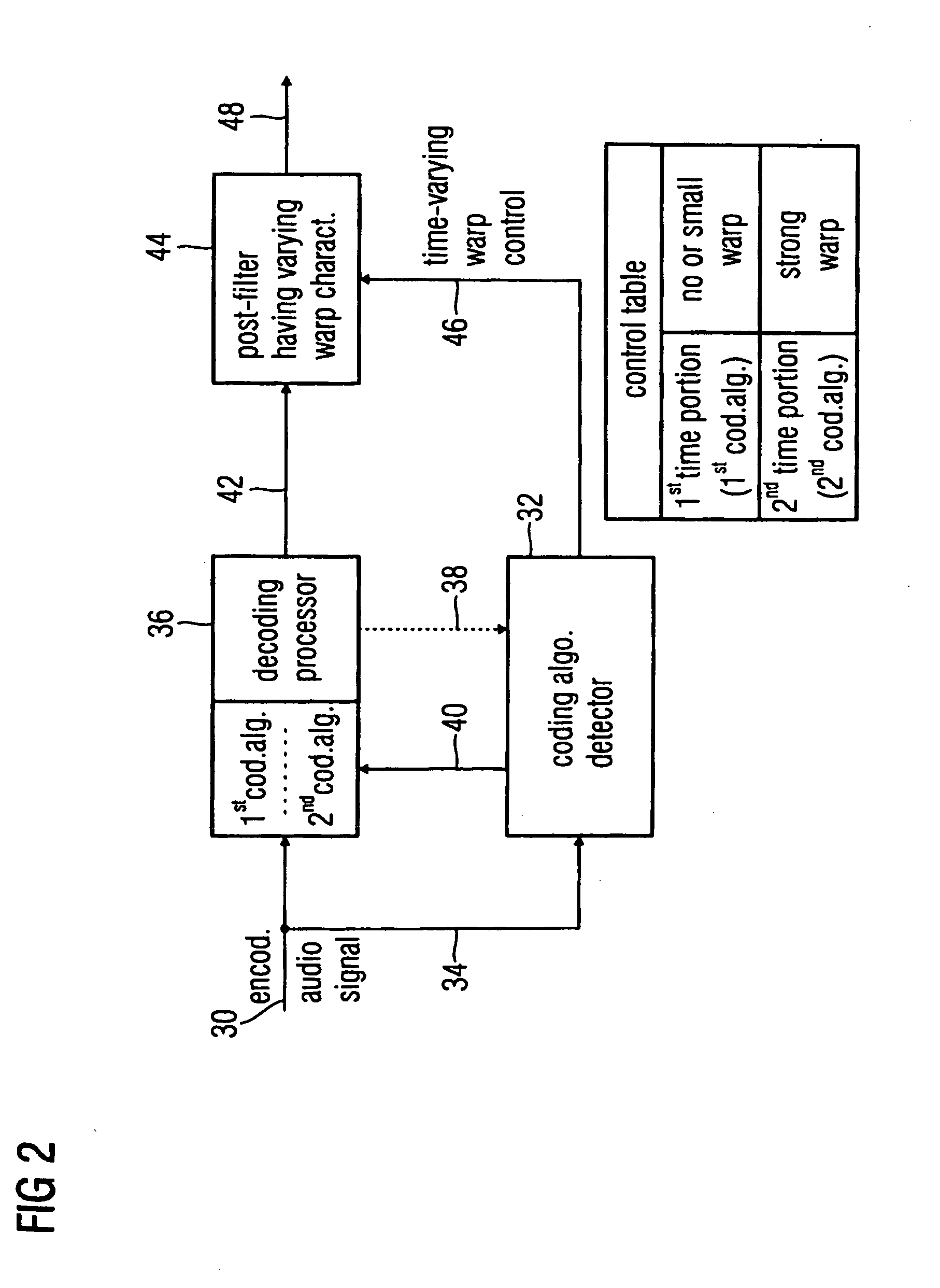
Audio encoder, audio decoder and audio processor having a dynamically variable warping characteristic
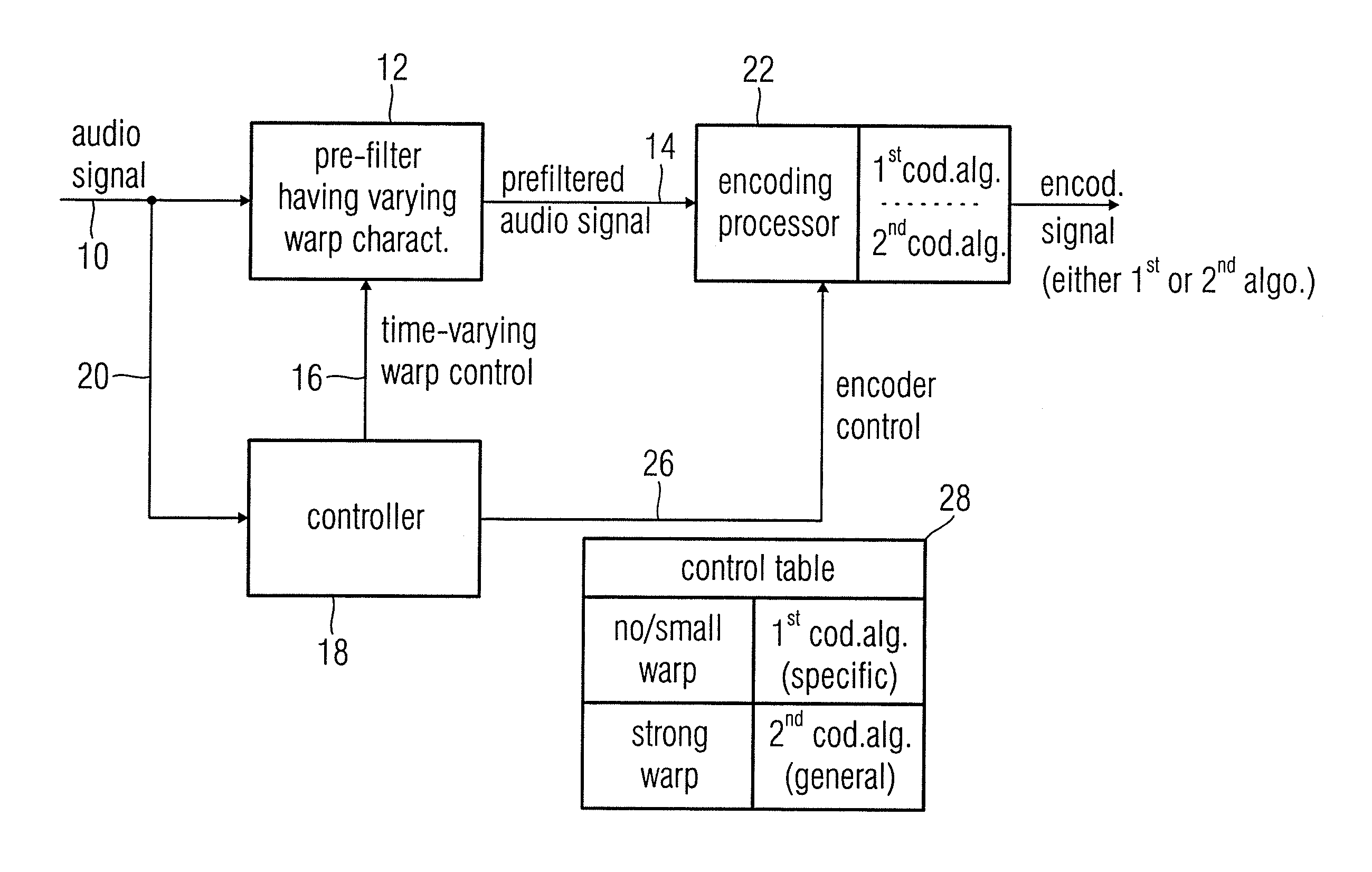
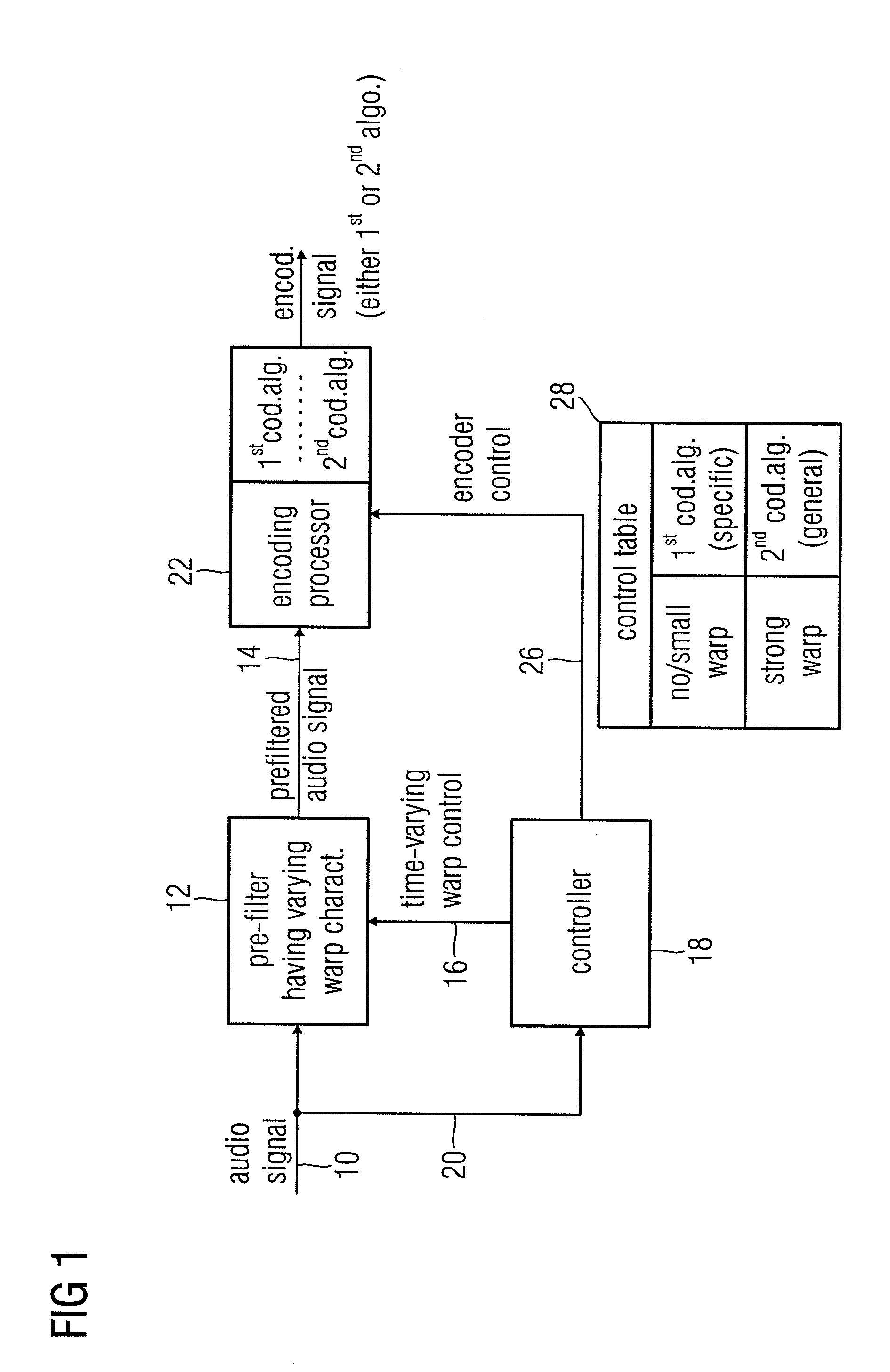
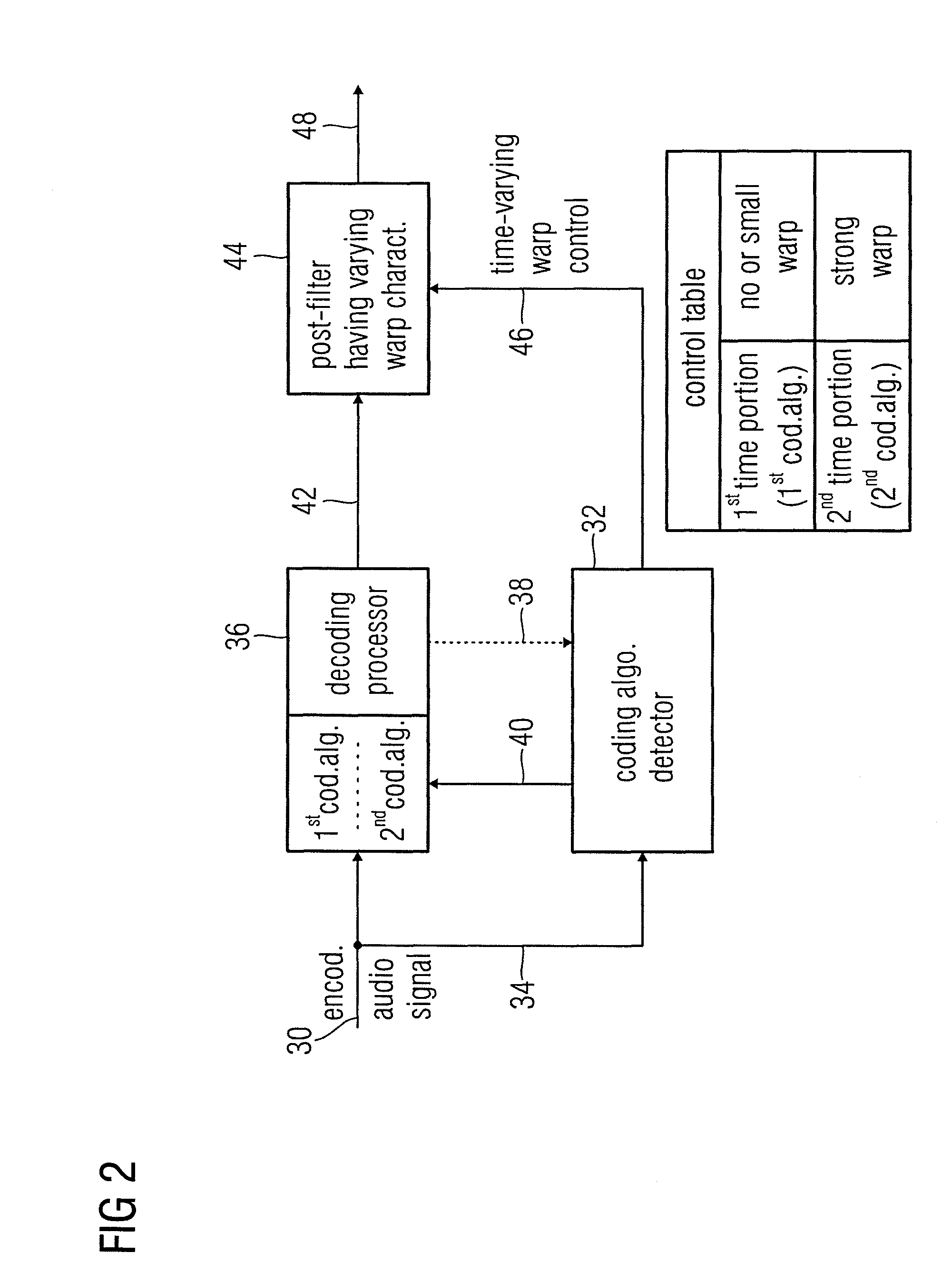
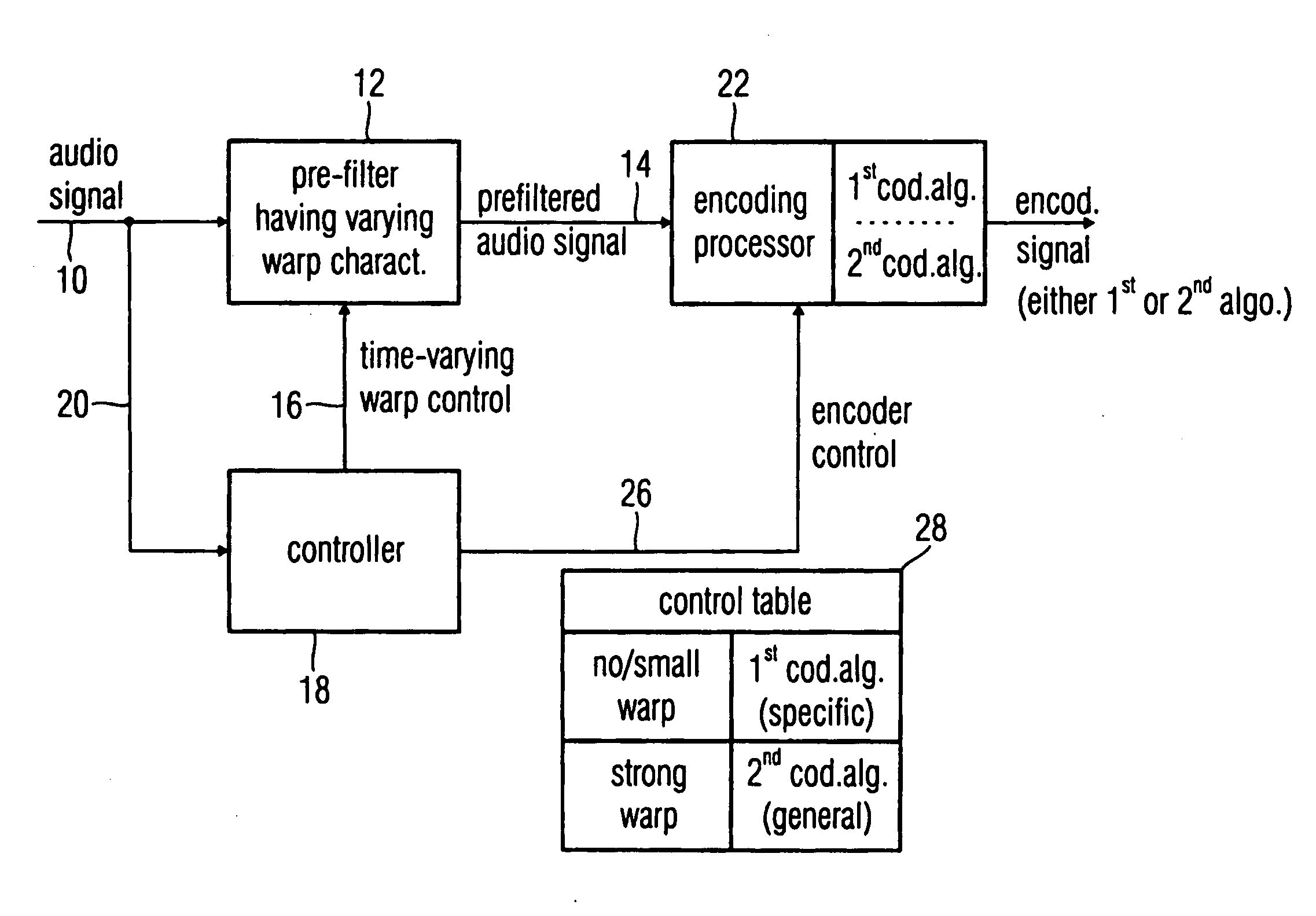
An audio encoder, an audio decoder or an audio processor includes a filter for generating a filtered audio signal, the filter having a variable warping characteristic, the characteristic being controllable in response to a time-varying control signal, the control signal indicating a small or no warping characteristic or a comparatively high warping characteristic. Furthermore, a controller is connected for providing the time-varying control signal, which depends on the audio signal. The filtered audio signal can be introduced to an encoding processor having different encoding algorithms, one of which is a coding algorithm adapted to a specific signal pattern. Alternatively, the filter is a post-filter receiving a decoded audio signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Audio encoder, audio decoder and audio processor having a dynamically variable warping characteristic
ActiveUS20100241433A1Quality improvementReduce bitrateSpeech analysisEncoding algorithmControl signal
An audio encoder, an audio decoder or an audio processor includes a filter (12) for generating a filtered audio signal, the filter having a variable warping characteristic, the characteristic being controllable in response to a time-varying control signal (16), the control signal indicating a small or no warping characteristic or a comparatively high warping characteristic. Furthermore, a controller (18) is connected for providing the time-varying control signal, which depends on the audio signal. The filtered audio signal can be introduced to an encoding processor (22) having different encoding algorithms, one of which is a coding algorithm adapted to a specific signal pattern. Alternatively, the filter is a post-filter receiving a decoded audio signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Pulmonary nodule detection device and method based on shape template matching and combining classifier
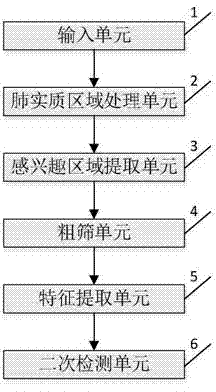
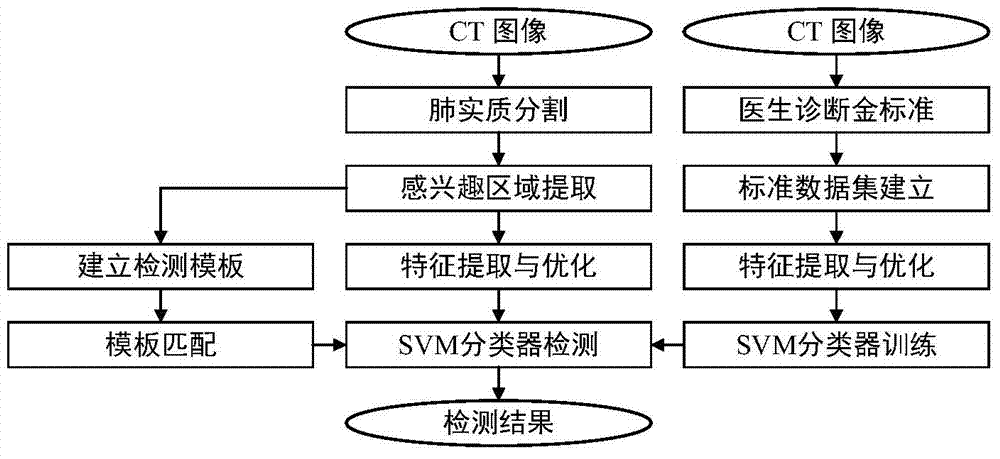
ActiveCN104751178AIncreased sensitivityEasy to detectImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPulmonary parenchymaPulmonary nodule
A pulmonary nodule detection device and method based on a shape template matching and combining classifier comprises an input unit, a pulmonary parenchyma region processing unit, a ROI (region of interest) extraction unit, a coarse screening unit, a feature extraction unit and a secondary detection unit. The input unit is used for inputting pulmonary CT sectional sequence images in format DICOM; the pulmonary parenchyma region processing unit is used for segmenting pulmonary parenchyma regions from the CT sectional sequence images, repairing the segmented pulmonary parenchyma regions by the boundary encoding algorithm and reconstructing the pulmonary parenchyma regions by the surface rendering algorithm after the three-dimensional observation and repairing; the ROI extraction unit is used for setting a gray level threshold and extracting the ROI according to the repaired pulmonary parenchyma regions; the coarse screening unit is used for performing coarse screening on the ROI by the pulmonary nodule morphological feature design template matching algorithm and acquiring selective pulmonary nodule regions; the feature extraction unit is used for extracting various feature parameters as sample sets for the post detection according to selective nodule gray levels and morphological features; the secondary detection unit is used for performing secondary detection on the selective nodule regions through a vector machine classifier and acquiring the final detection result.
Owner:KANGDA INTERCONTINENTAL MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Method and Apparatus for Encoding and Decoding Multi-View Video Using Image Stitching
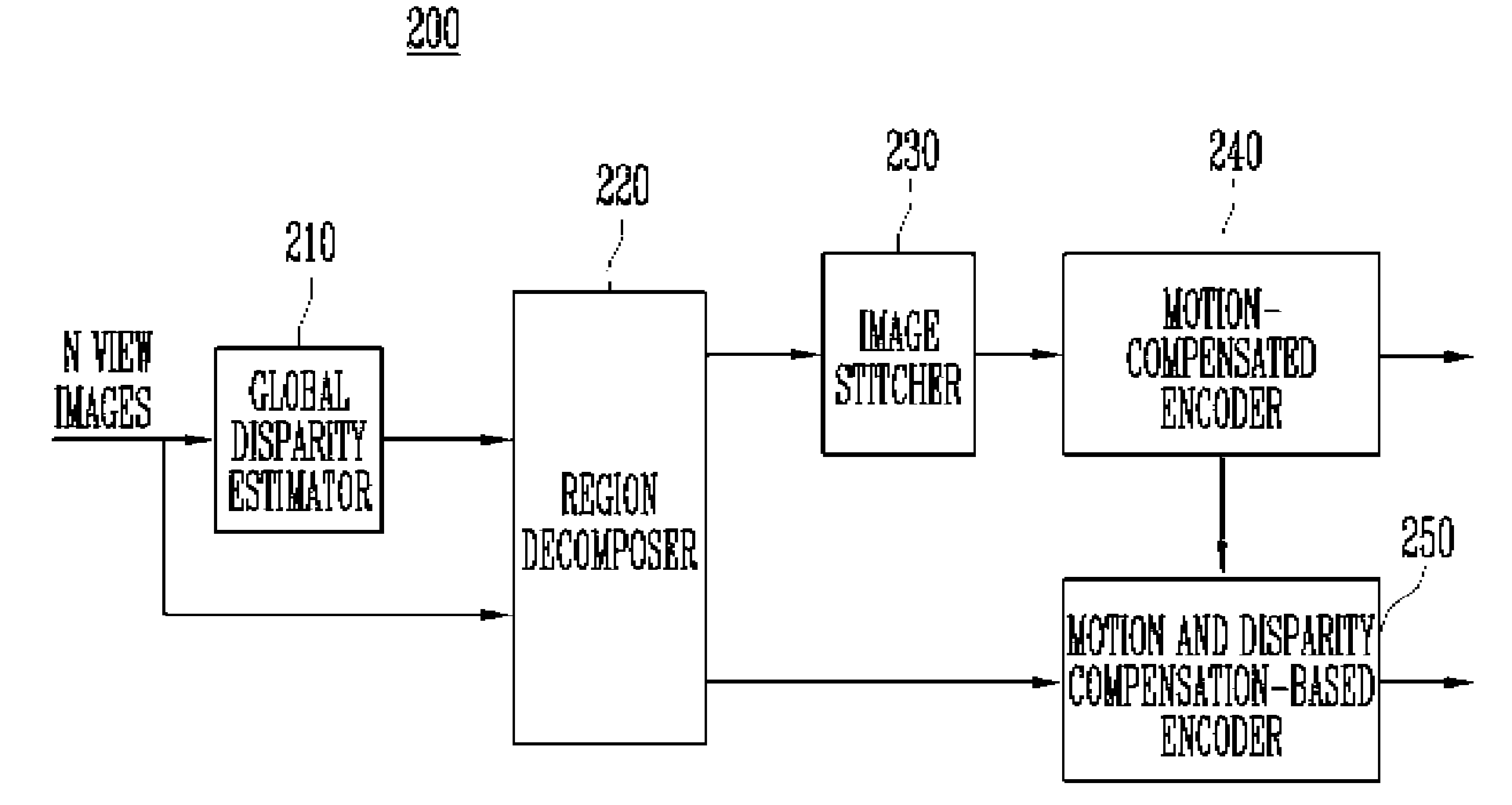
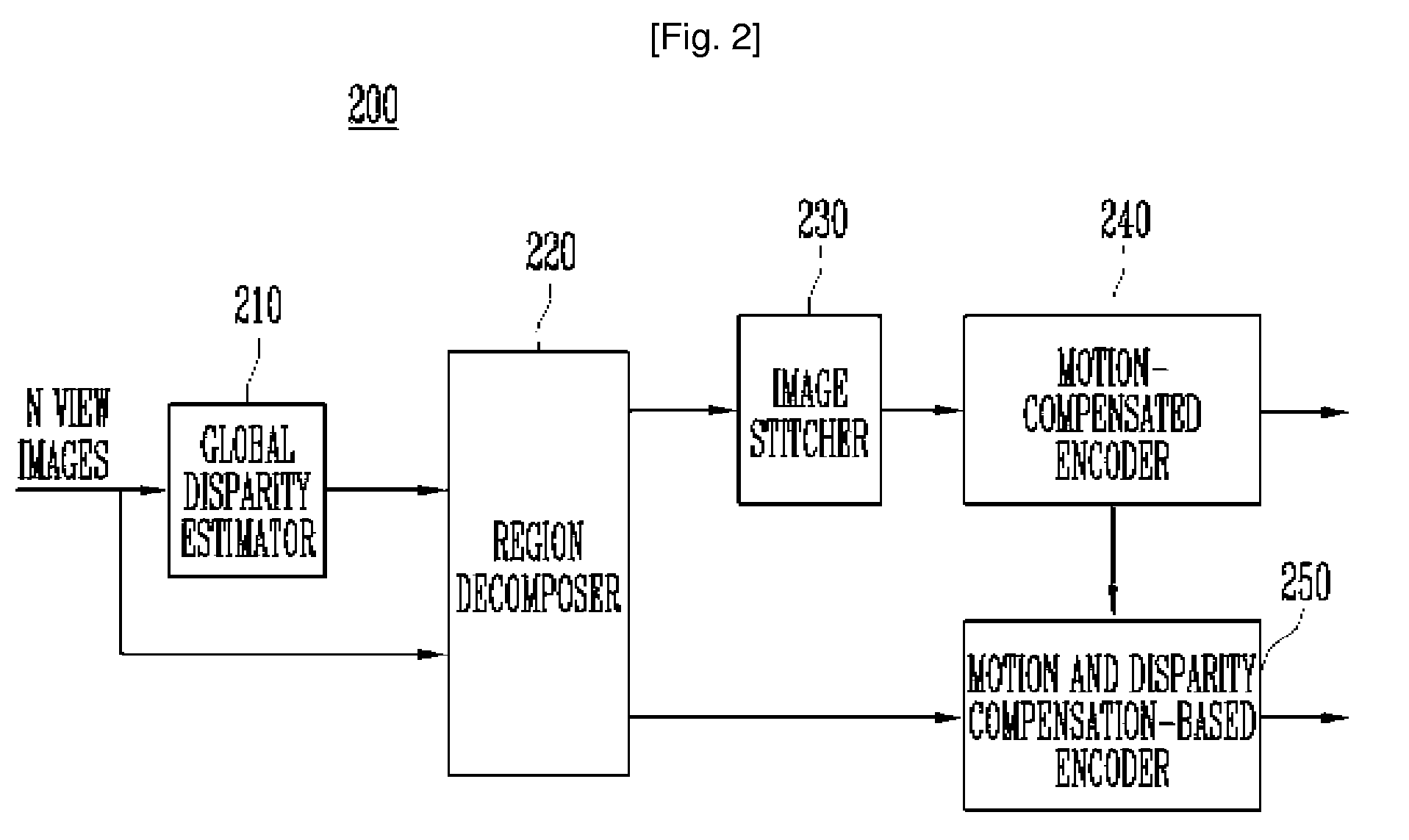
InactiveUS20080089405A1Increase the compression ratioImprove decoding efficiencyTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesParallaxImage estimation
Provided is a method and apparatus for encoding and decoding multi-view video data. The encoding method includes: decomposing each view image of the multi-view video into an overlapped region and a non-overlapped region, the overlapped region being overlapped with other view image and the non-overlapped region not being overlapped with other view image; generating a stitched image by combining the non-overlapped region of each view image and a middle view image; encoding the stitched image using a first encoding algorithm; and encoding the overlapped region of each view image, using a second encoding algorithm. Further, the decomposing step includes the steps of estimating disparity information for each view image, based on a predetermined view image; and decomposing each view image into said overlapped region and said non-overlapped region using the estimated disparity information.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
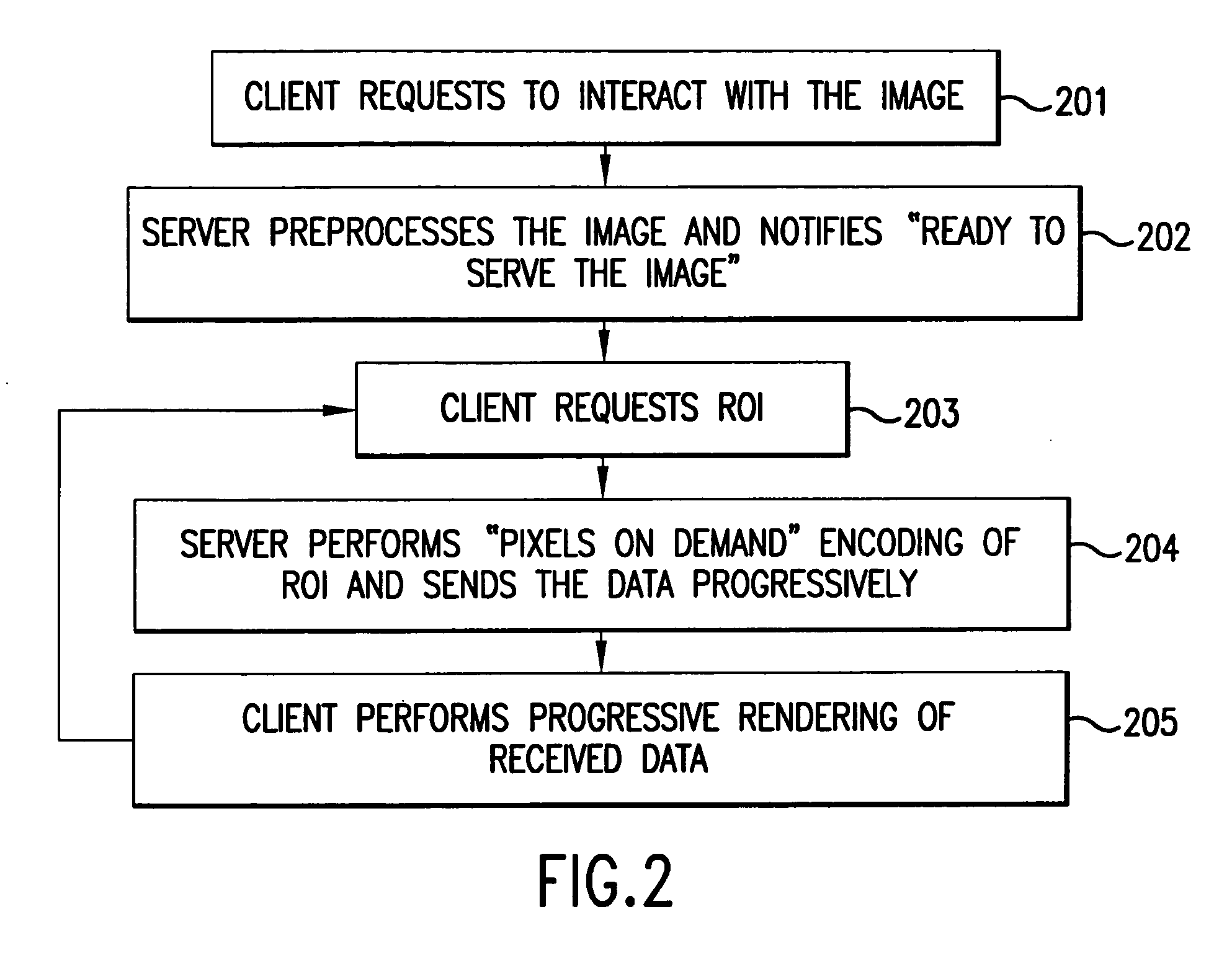
System and method for the lossless progressive streaming of images over a communication network
InactiveUS20050271283A1Avoids computationally intensive taskEliminate needPulse modulation television signal transmissionImage codingImage serverEncoding algorithm
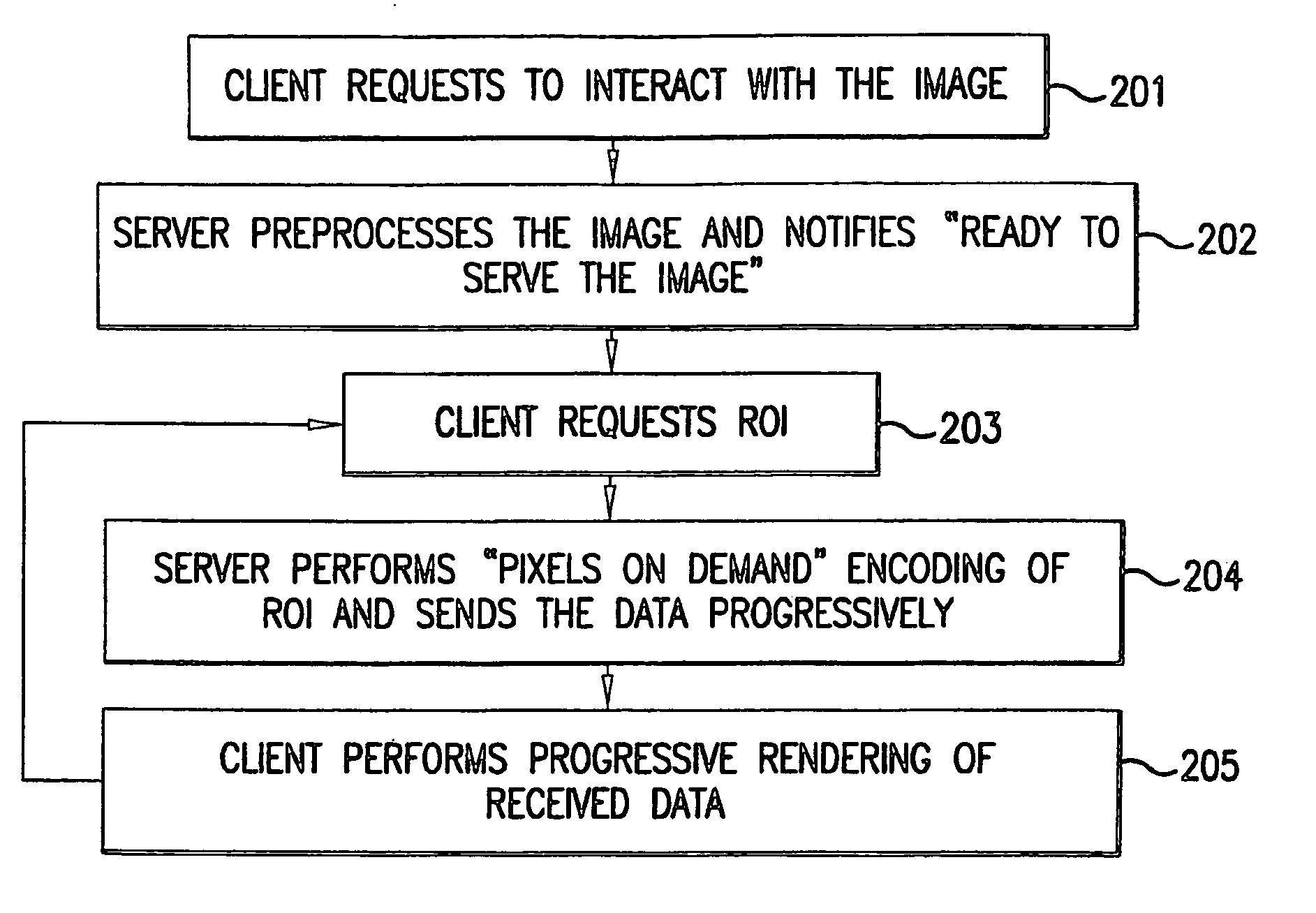
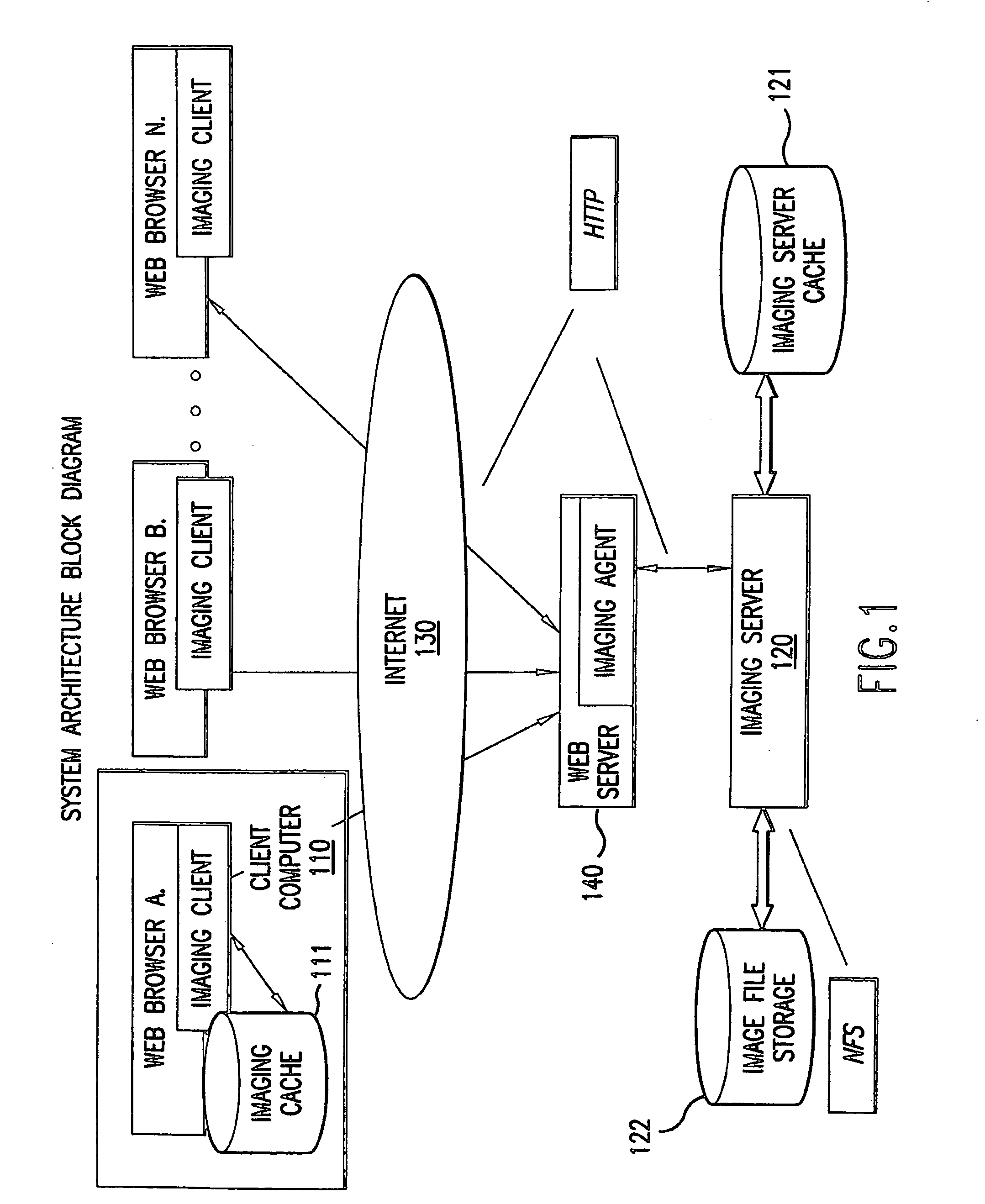
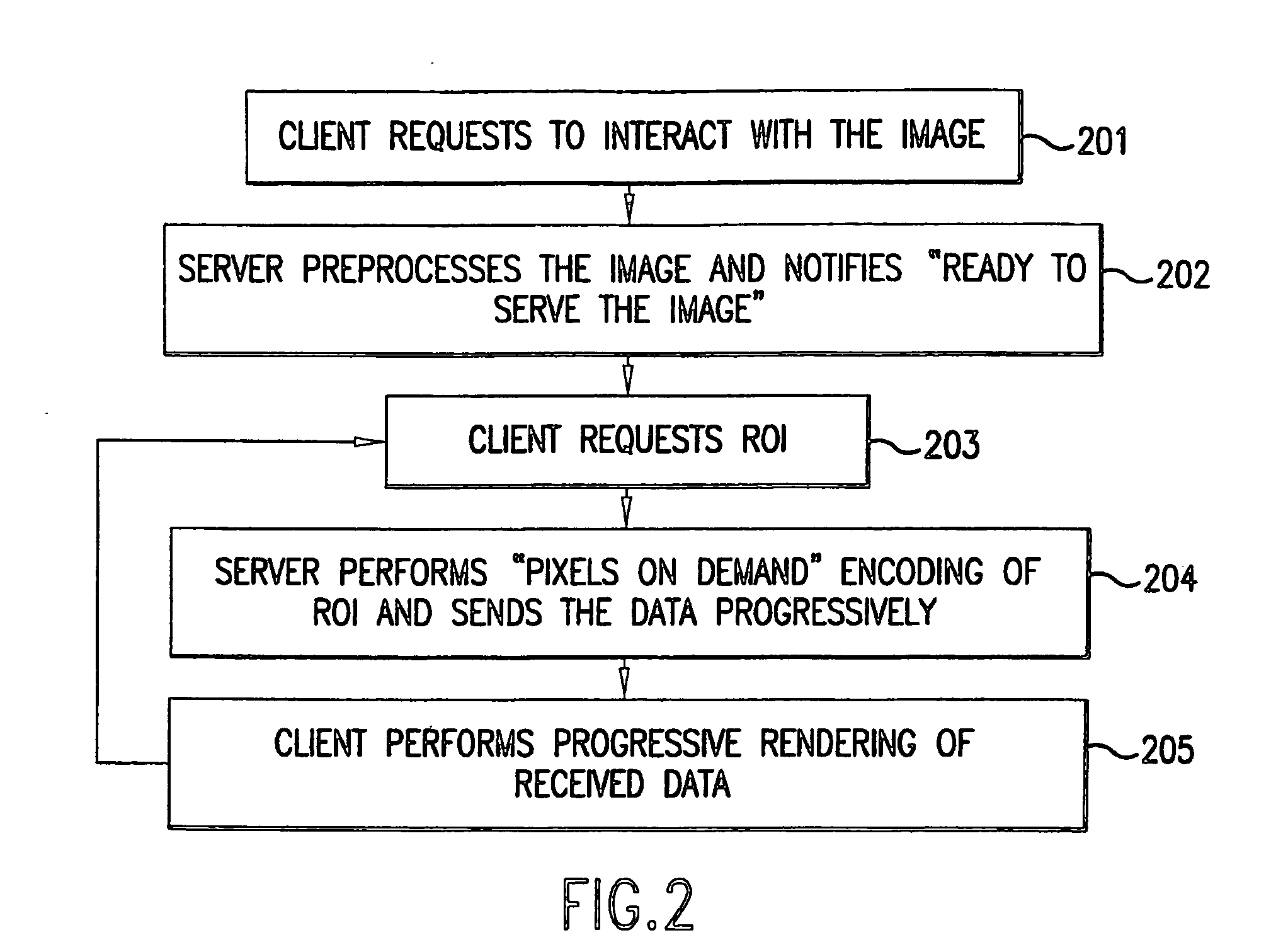
A lossless image streaming system for the transmission of images over a communication network. The system eliminates the necessity to store a compressed version of the original image, by losslessly streaming ROI data using the original stored image. The imaging system also avoids the computationally intensive task of compression of the full image. When a user wishes to interact with a remote image, the imaging client generates and sends a ROI request list to the imaging server. The request list can be ordered according to the particular progressive mode selected (e.g., progressive by quality, resolution or spatial order). The imaging server performs a fast preprocessing step in near real time after which it can respond to any ROI requests in near real time. When a ROI request arrives at the server, a progressive image encoding algorithm is performed, but not for the full image. Instead, the encoding algorithm is performed only for the ROI. Since the size of the ROI is bounded by the size and resolution of the viewing device at the client and not by the size of the image, only a small portion of the full progressive coding computation is performed for a local area of the original image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method to provide a software package and a provider station and a user station realizing the method and a basis software package
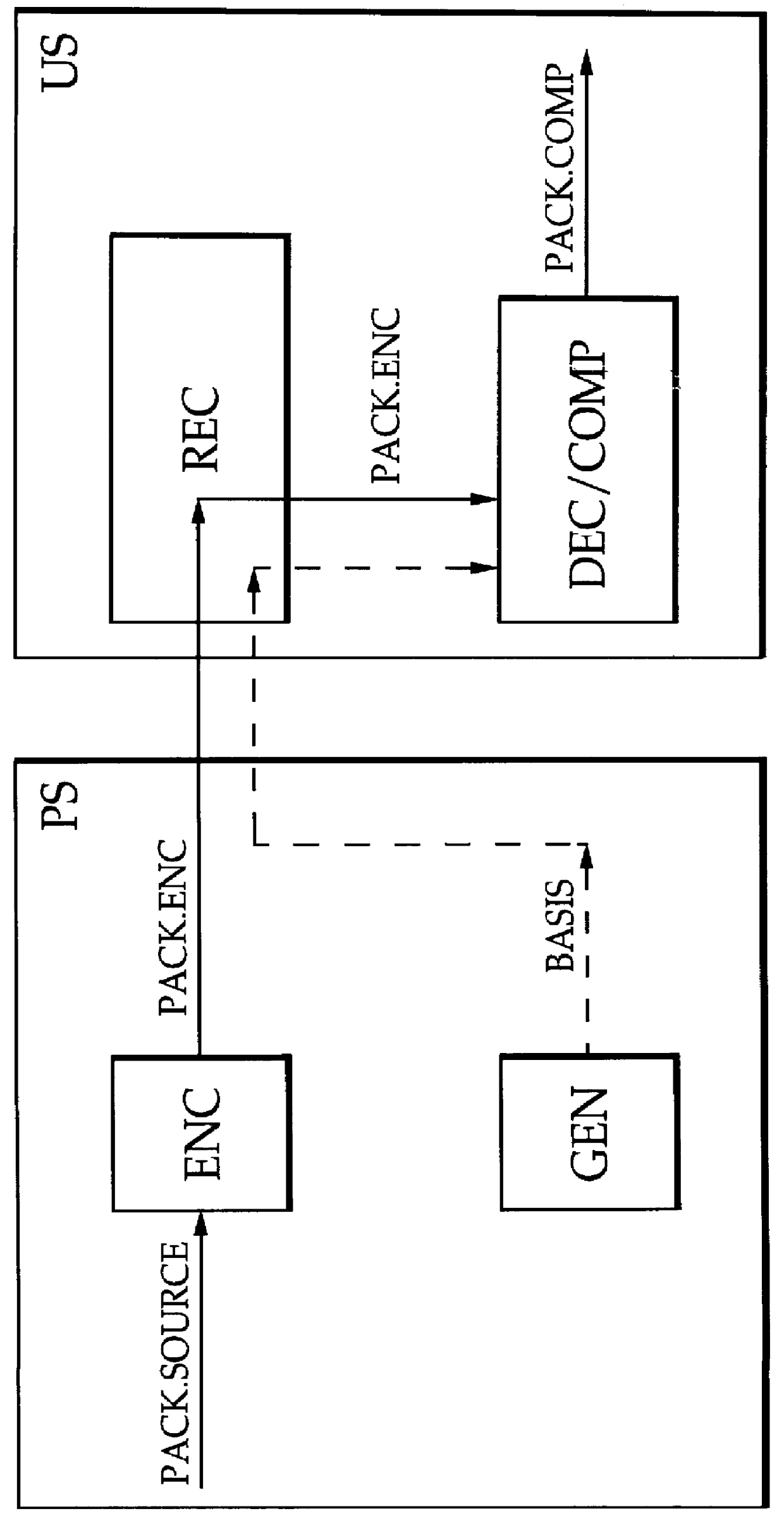
InactiveUS6063134ALess bulkyLower the volumeDigital data processing detailsInterprogram communicationEncoding algorithmSoftware engineering
The method is used to provide a software package for installation in a user station (US) without revealing the contents of the software package. The method includes the steps of encoding a readable source version (PACK.SOURCE) of the software package following a predefined encoding algorithm thereby generating an encoded software package (PACK.ENC) and delivering the encoded software package (PACK.ENC) from a provider station (PS) to the user station. In order to install the encoded software package (PACK.ENC) at the user station (US) the method further includes the step of providing, either together with the encoded software package (PACK.ENC) or separately, a basis software package (BASIS) for combined decoding and compiling of the encoded software package (PACK.ENC). The basis software package (BASIS) includes software to perform the combined decoding and compiling thereby generating a compiled software package (PACK.COMP).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Apparatus and method for merging data blocks with error correction code protection
ActiveUS20090313526A1Code conversionError correction/detection using block codesData integrityEncoding algorithm
An apparatus and method for selectively deriving Error Correction Codes (ECCs) or other data integrity information for integration into merged data blocks. First data is merged into second data that is error-protected using an ECC generated by a coding algorithm. Bytes or other data units are identified in the first data to be merged into the second data. It is determined whether each of the check bits of the ECC will differ from its original state in response to merging the first and second data. The check bits of the ECC that have been determined to differ from their respective original states are modified to create a “merged ECC.” The resulting data block includes the merged data and the merged ECC.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
Data compression over communications links which are exposed to occasional errors
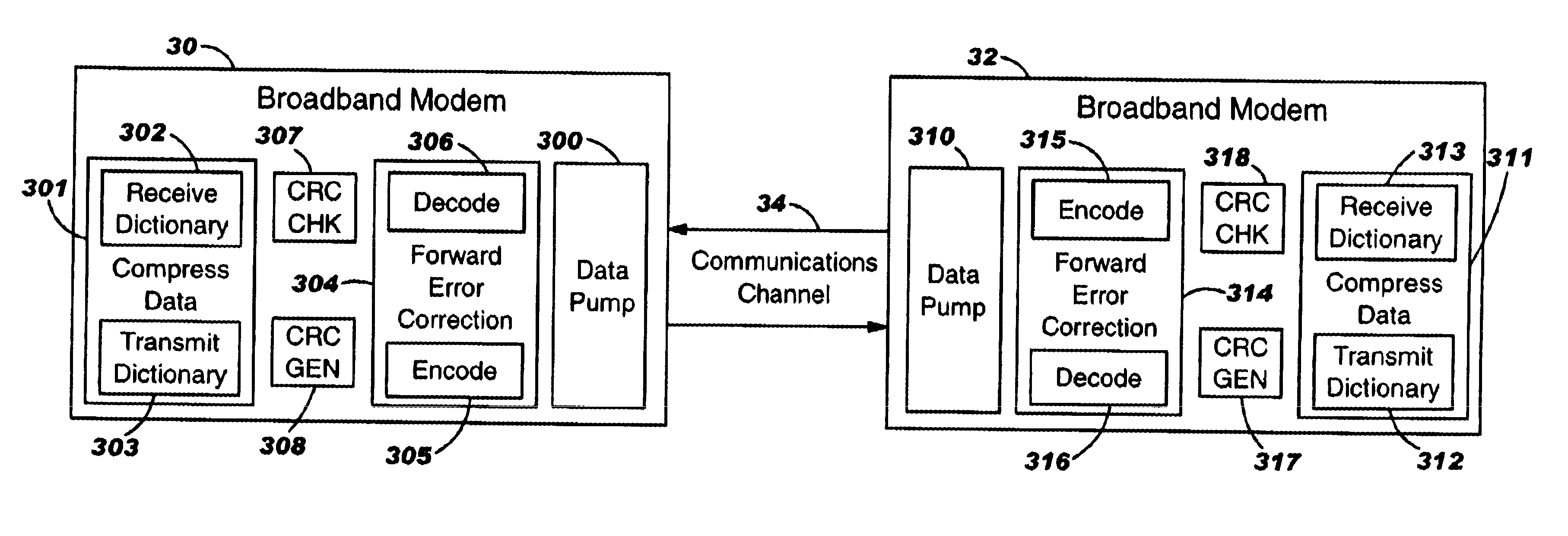
InactiveUS6643815B1Flexible systemAvoid timeoutError preventionError detection/correctionData compressionTransceiver
Re-synchronization of sets of transmit and receive state variables in a communication system is achieved when an error is detected, without disrupting the connection. Each of first and second transceivers, connected by a communications channel, have a common set of transmit and receive state variables supporting a data encoding algorithm function. The transmitter of one of the first and second transceivers fist encodes data to be transmitted and updates the transmit state variables according to the data encoding algorithm and the receiver of the receiving transceiver validates whether or not each data block has been received correctly. During the process of decoding the data, the receive state variables are updated according to the same algorithm used to update the transmit state variables, thereby keeping the two sets of state variables in synchronism with each other. When an error is detected, re-synchronization occurs by switching to transparent mode in the direction of communication in which the error occurred and resetting the corresponding transmit and receive sets of state variables.
Owner:IBM CORP
Network architecture and methods for transparent on-line cross-sessional encoding and transport of network communications data
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
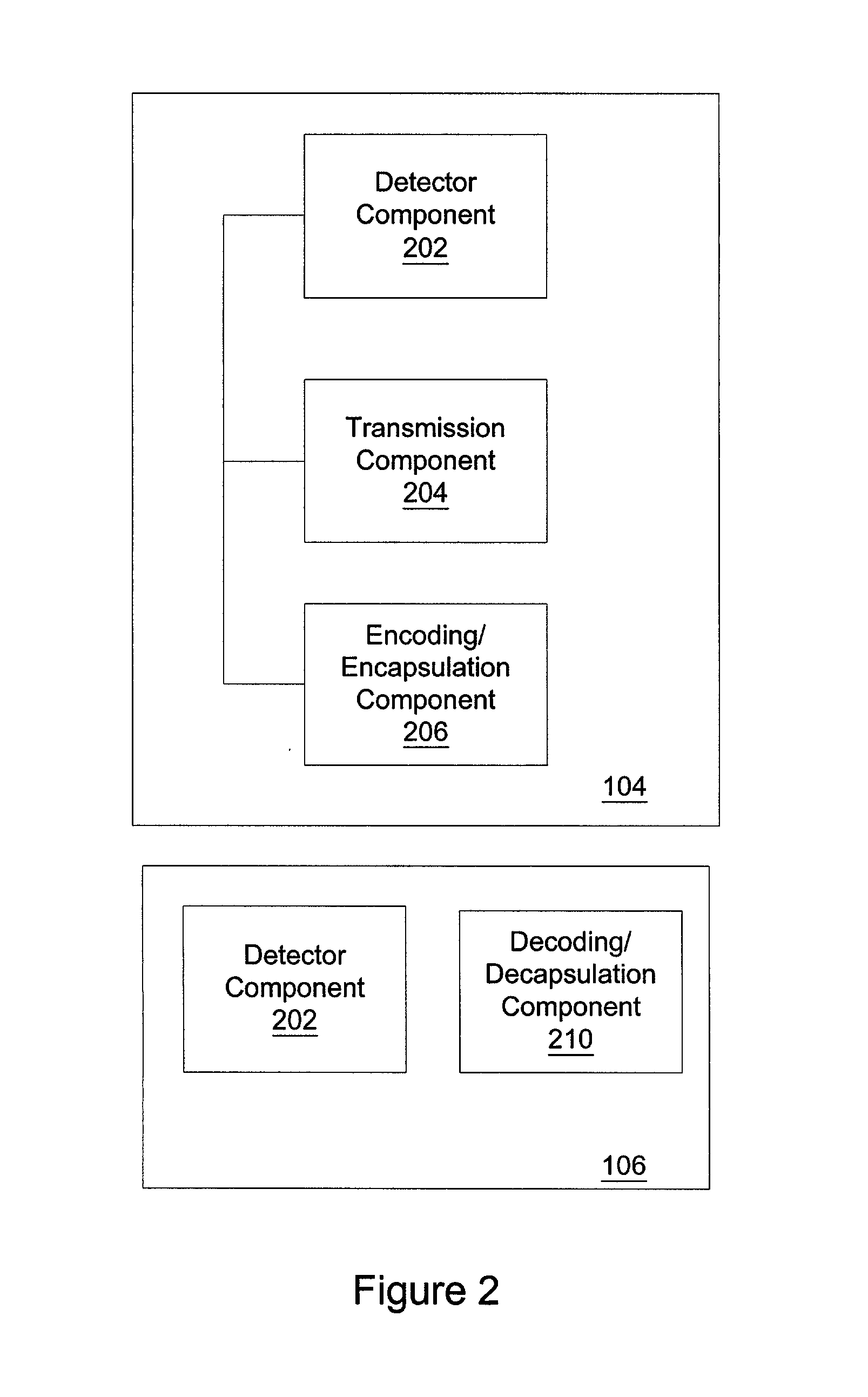
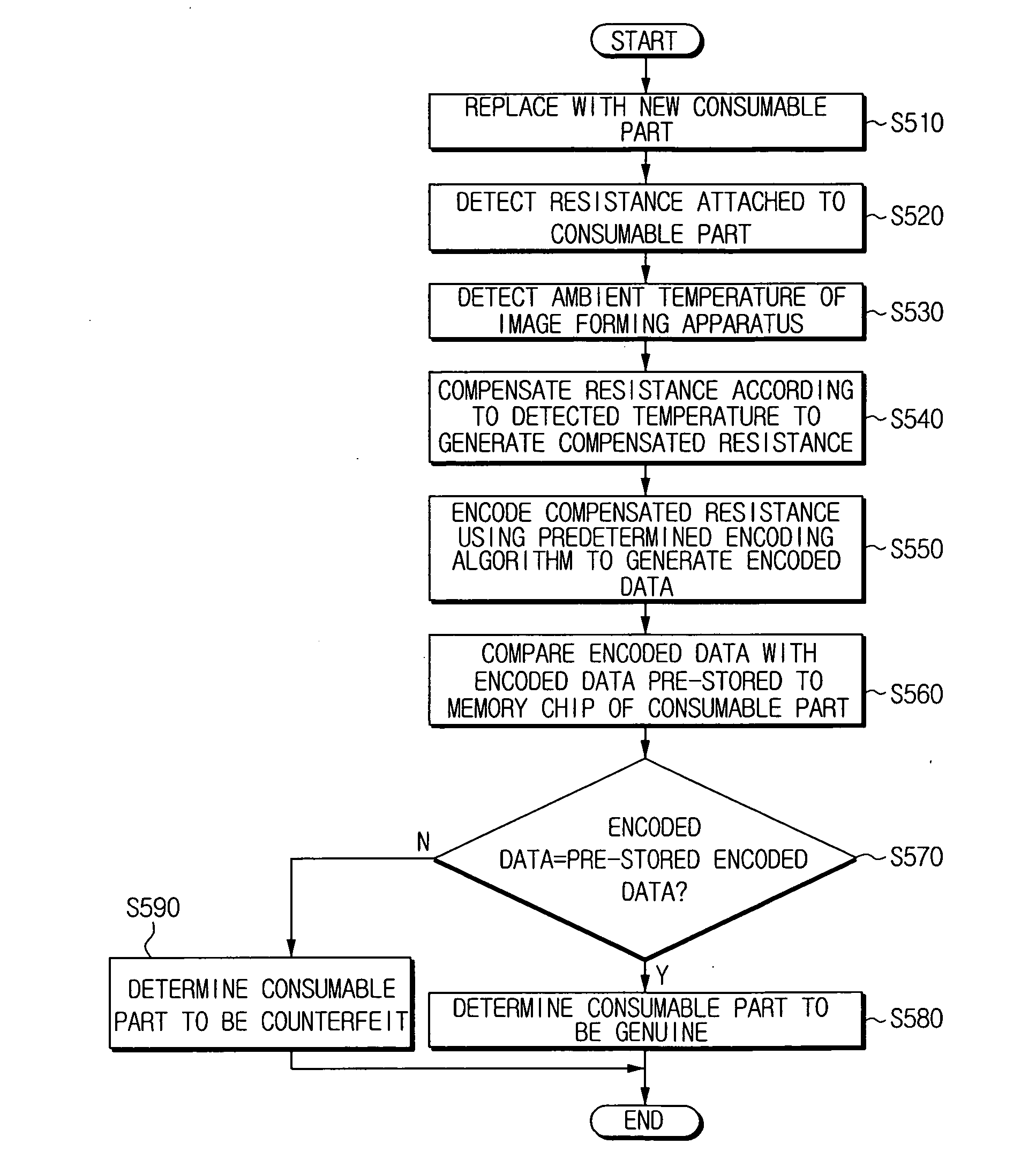
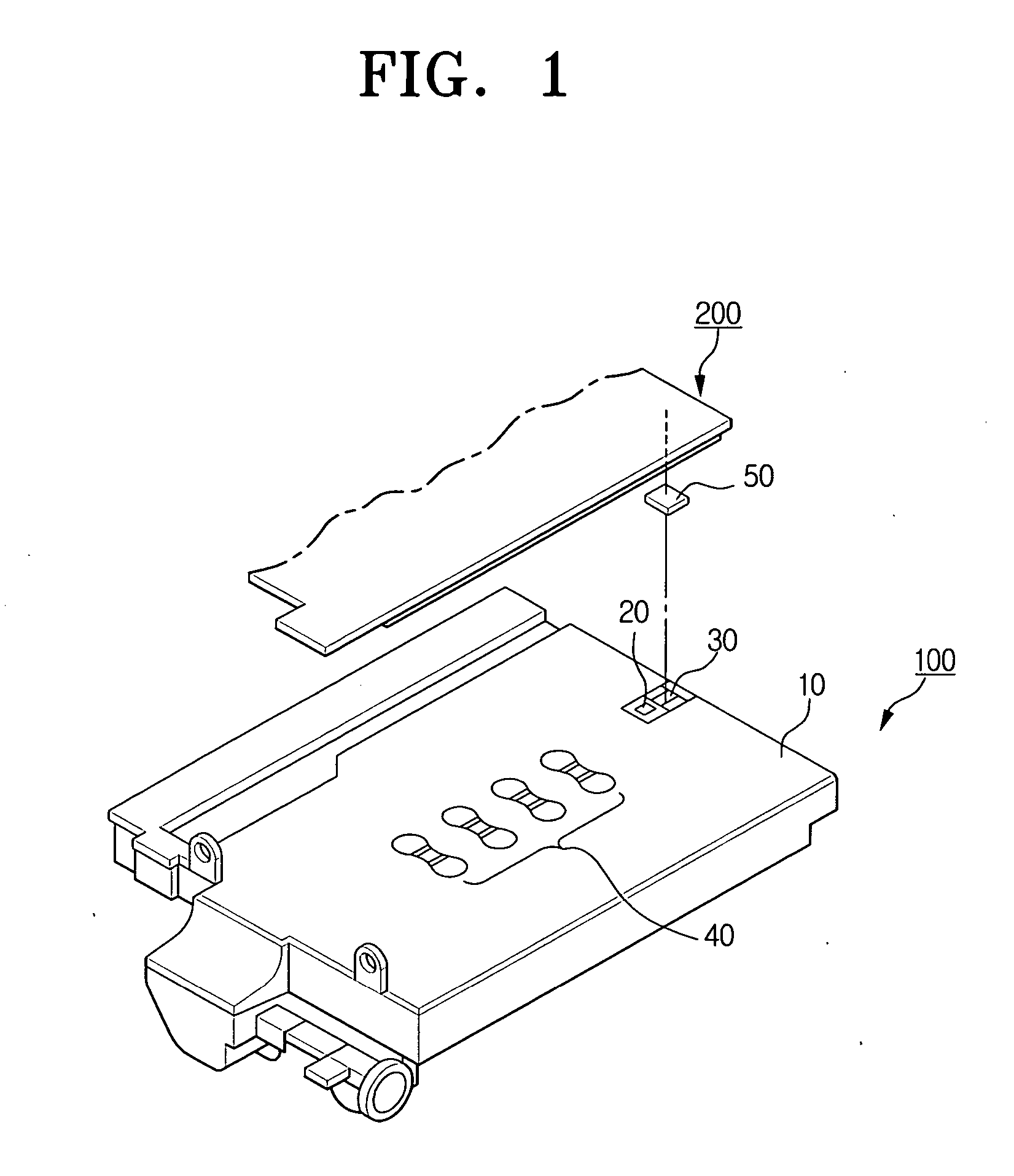
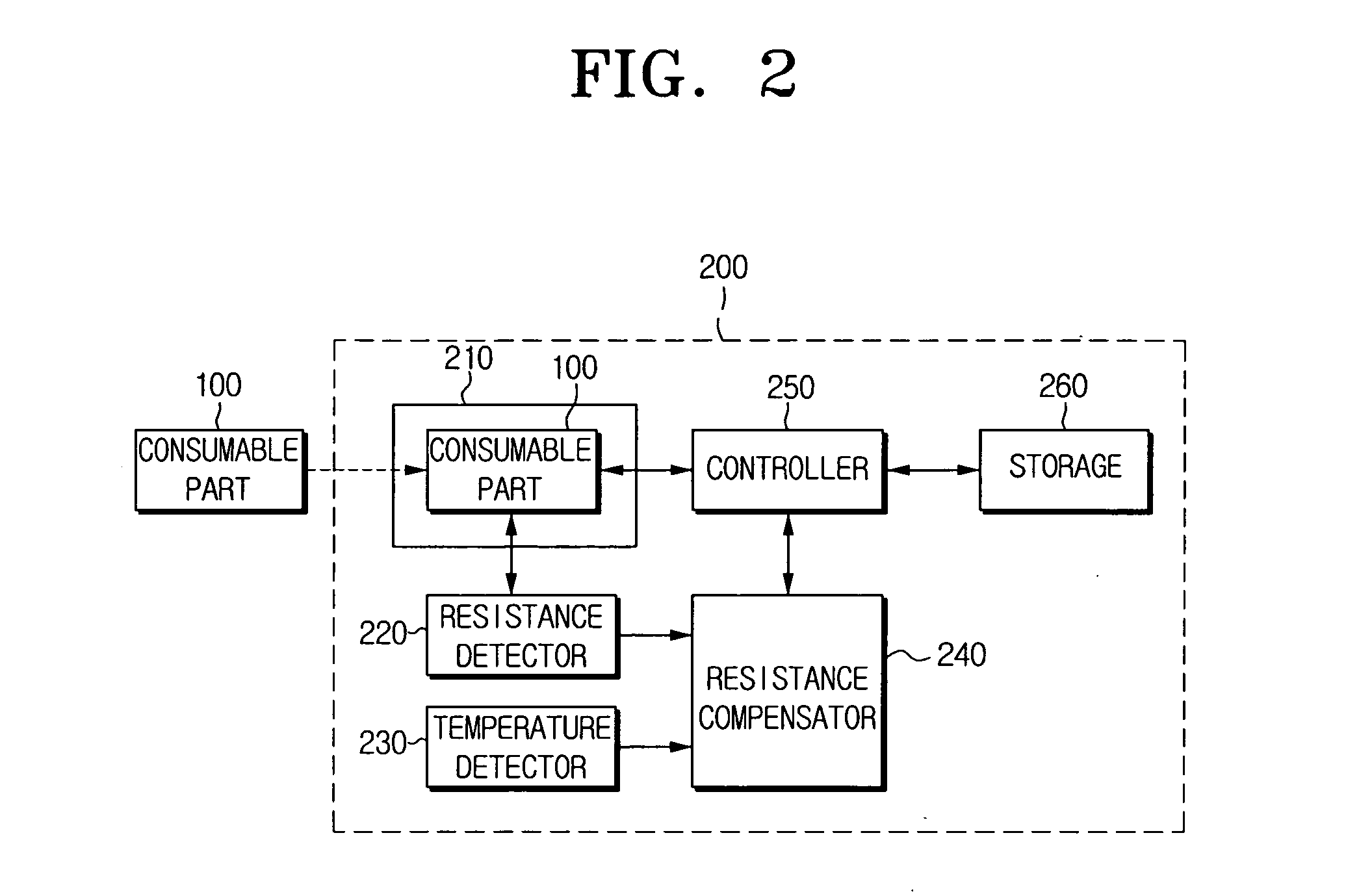
Method and apparatus for verifying genuineness of a consumable part
InactiveUS20060098993A1Quality improvementFacilitates discriminationDigital data processing detailsElectrographic process apparatusMemory chipEncoding algorithm
A method and apparatus are disclosed for verifying genuineness of consumable parts. The method for verifying genuineness of a consumable part comprises mounting a consumable part and detecting resistance value of a resistor coupled to the consumable part. The method generates encoded data by encoding the resistance value through an encoding algorithm, and compares the generated encoded data with pre-stored encoded data within a memory chip of the consumable part. When the generated encoded data is the same as the pre-stored data, it is determined that the consumable part is genuine. Accordingly, genuineness of the consumable part can be correctly determined.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
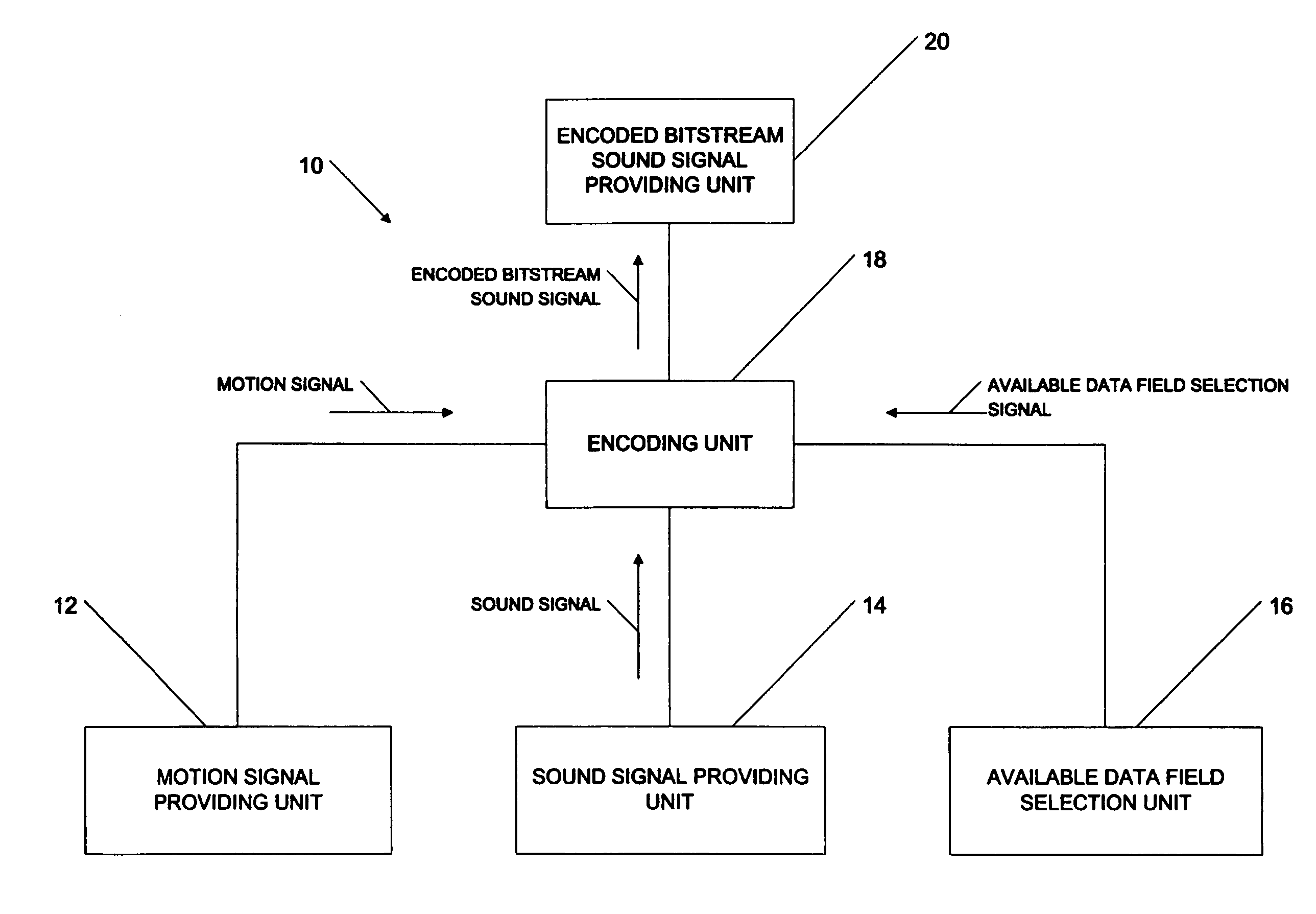
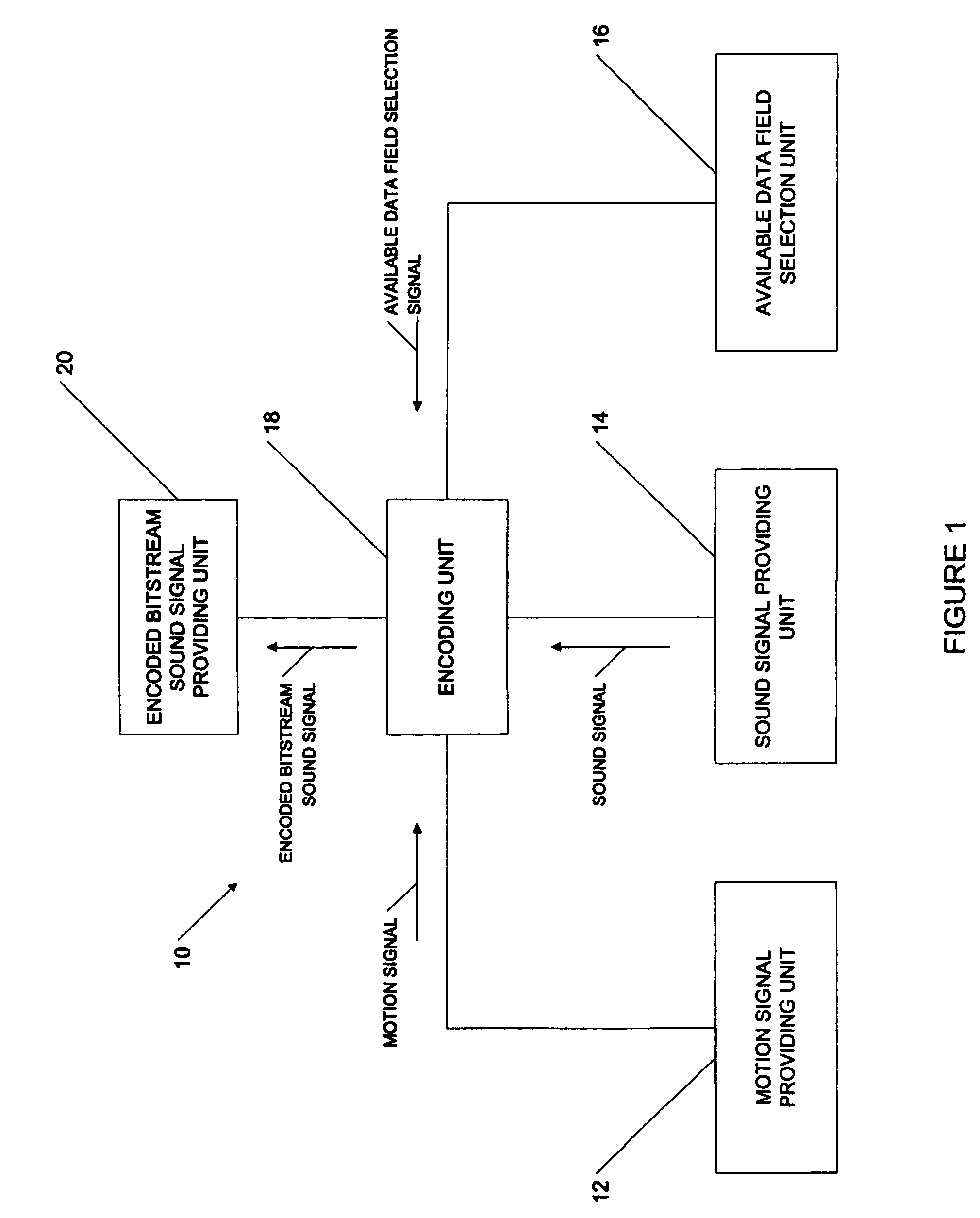
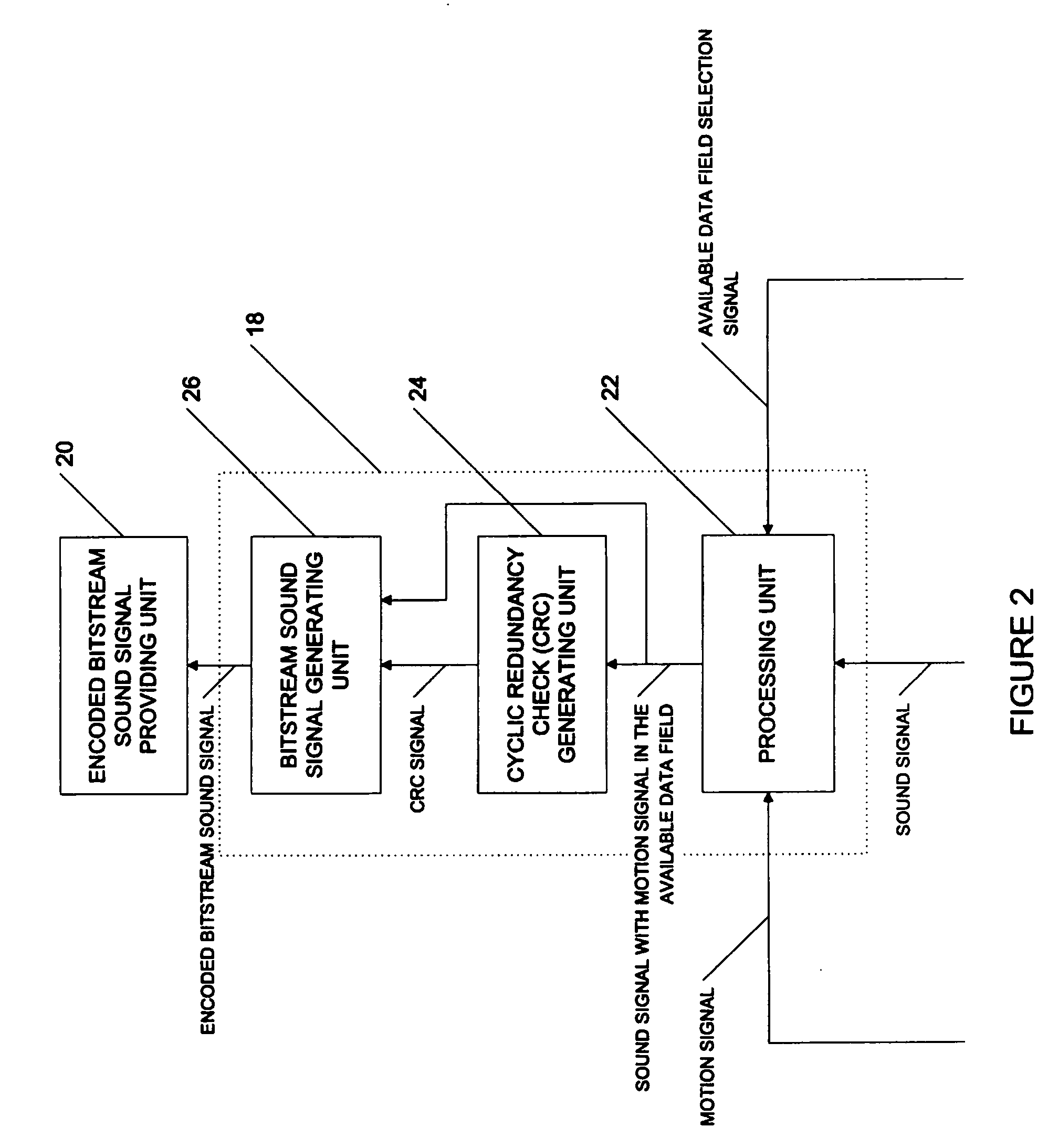
Method and apparatus for providing a motion signal with a sound signal using an existing sound signal encoding format
ActiveUS20060256972A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionEncoding algorithmData field
A method for providing a motion signal with a sound signal using an existing sound signal encoding format. The method comprises providing the motion signal, providing the sound signal, inserting the motion signal in an available data field provided in the existing encoding algorithm, encoding the sound signal with the inserted motion signal according to the existing encoding algorithm to generate an encoded bitstream sound signal and providing the encoded bitstream sound signal comprising the motion signal and the sound signal.
Owner:D-BOX TECHNOLOGIES
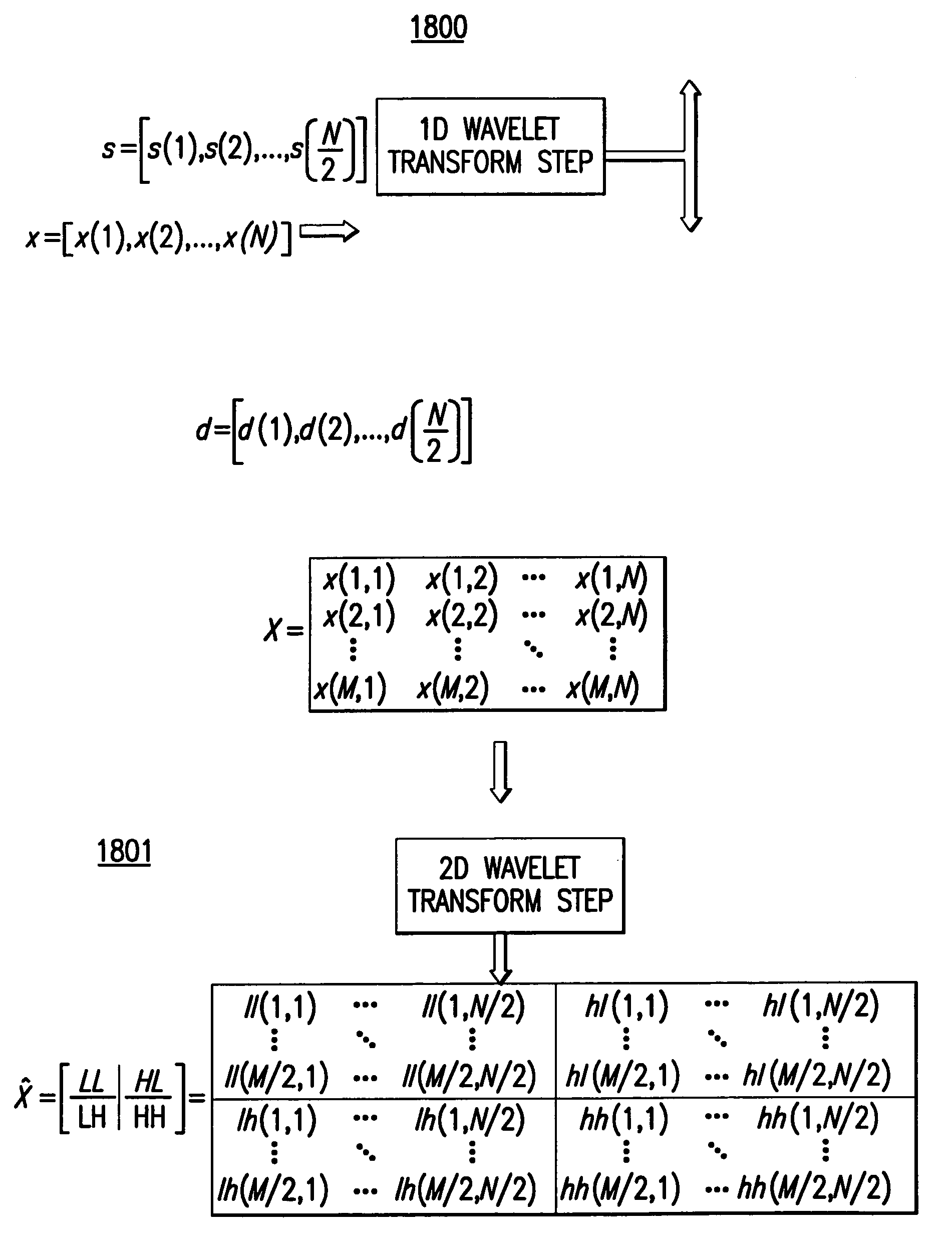
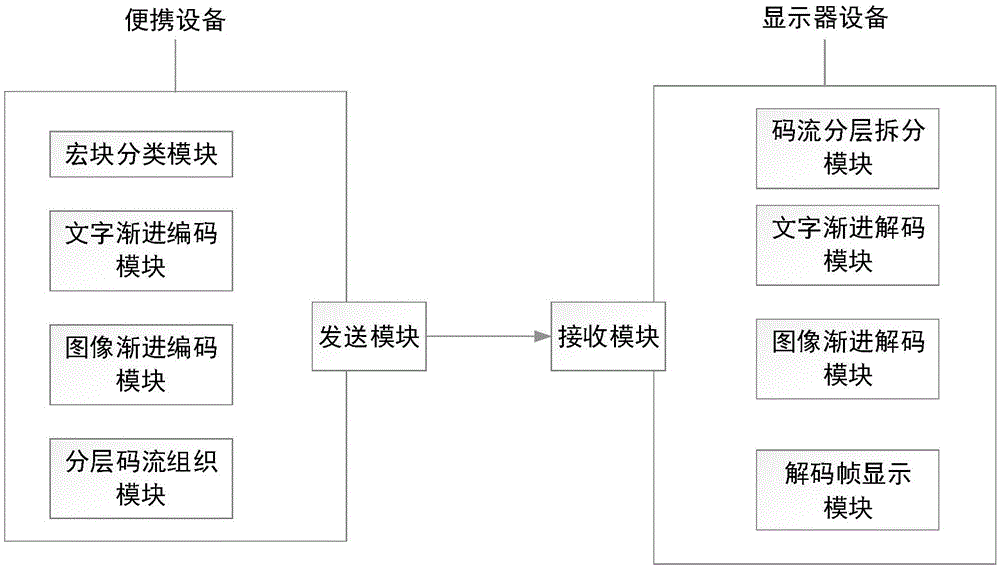
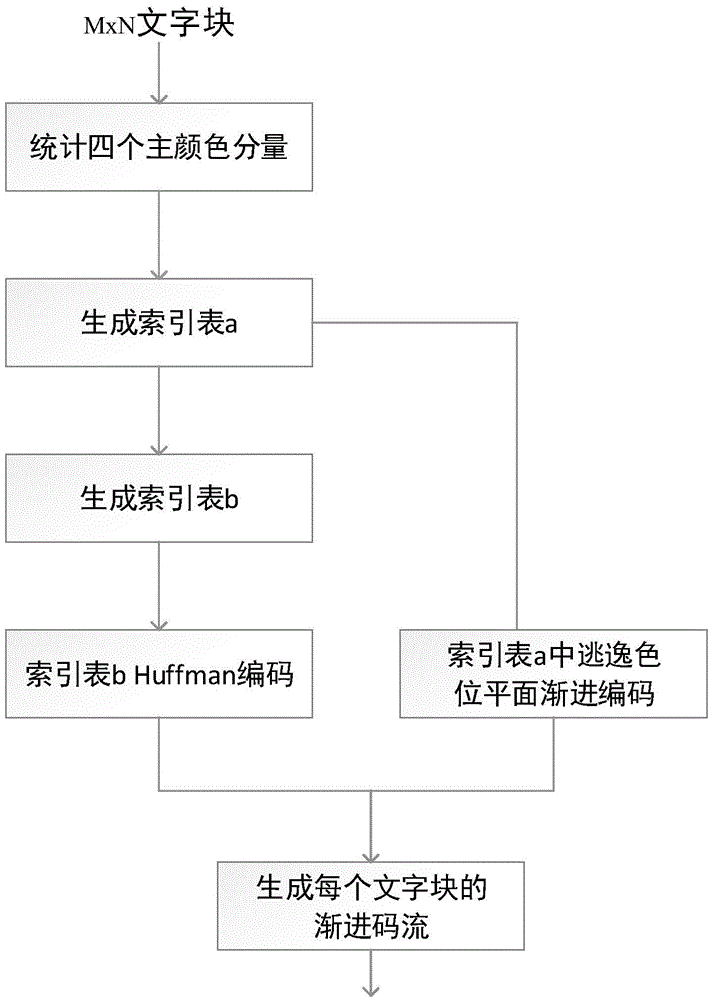
Screen video encoding and decoding method based on progressive character block compression and encoding and decoding device
ActiveCN105472392AImprove compatibilityWide adaptabilityDigital video signal modificationVideo encodingEncoding algorithm
The invention discloses a screen video encoding and decoding method based on progressive character block compression and an encoding and decoding device thereof. The screen video encoding and decoding method comprises the following steps: obtaining a frame in a screen video, and dividing the frame into M*N macro blocks; dividing each macro block into character blocks or image blocks according to the category; dividing each character block into a plurality of character compression code streams according to a main color and a non-main color; encoding the main color by an index table, and progressively encoding escape colors of the non-main color based on a bit plane; dividing each image block into a plurality of image encoding quality layers by using a progressive image encoding algorithm based on wavelet transform; transmitting the code streams to a receiving terminal according to different quality grades; and decoding and displaying the code stream of each quality layer by the receiving terminal. According to the screen video encoding and decoding method disclosed by the invention, in view of the limitation and defects of traditional character encoders, the progressive character encoding technology of a plurality of quality layers is realized, no support of special equipment is needed, and the screen video encoding and decoding method is applicable to all occasions needing to compress screen images containing characters.
Owner:XIAN WANXIANG ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Generating and interpreting secure and system dependent software license keys
ActiveUS7805616B1Reduce the possibilityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareSoftware license
A technique is provided for generating and interpreting secure and system dependent software license keys. According to one or more embodiments of the present invention, a device executing an encoding algorithm may generate a software license key by applying several layers of security. Illustratively, the device may initially define a license data representing a software license for the software. The device may also compute an authentication code based on a unique identification of hardware upon which the software is configured to operate. The license data and authentication code may be combined and encrypted into an encrypted result, which may be transformed into a software license key (e.g., human readable). Also, the device may apply a predetermined encryption technique (e.g., cipher) during the transformation as an additional layer of security. Conversely, a device configured to operate the software may execute a decoding algorithm to interpret the software license key similarly in reverse.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
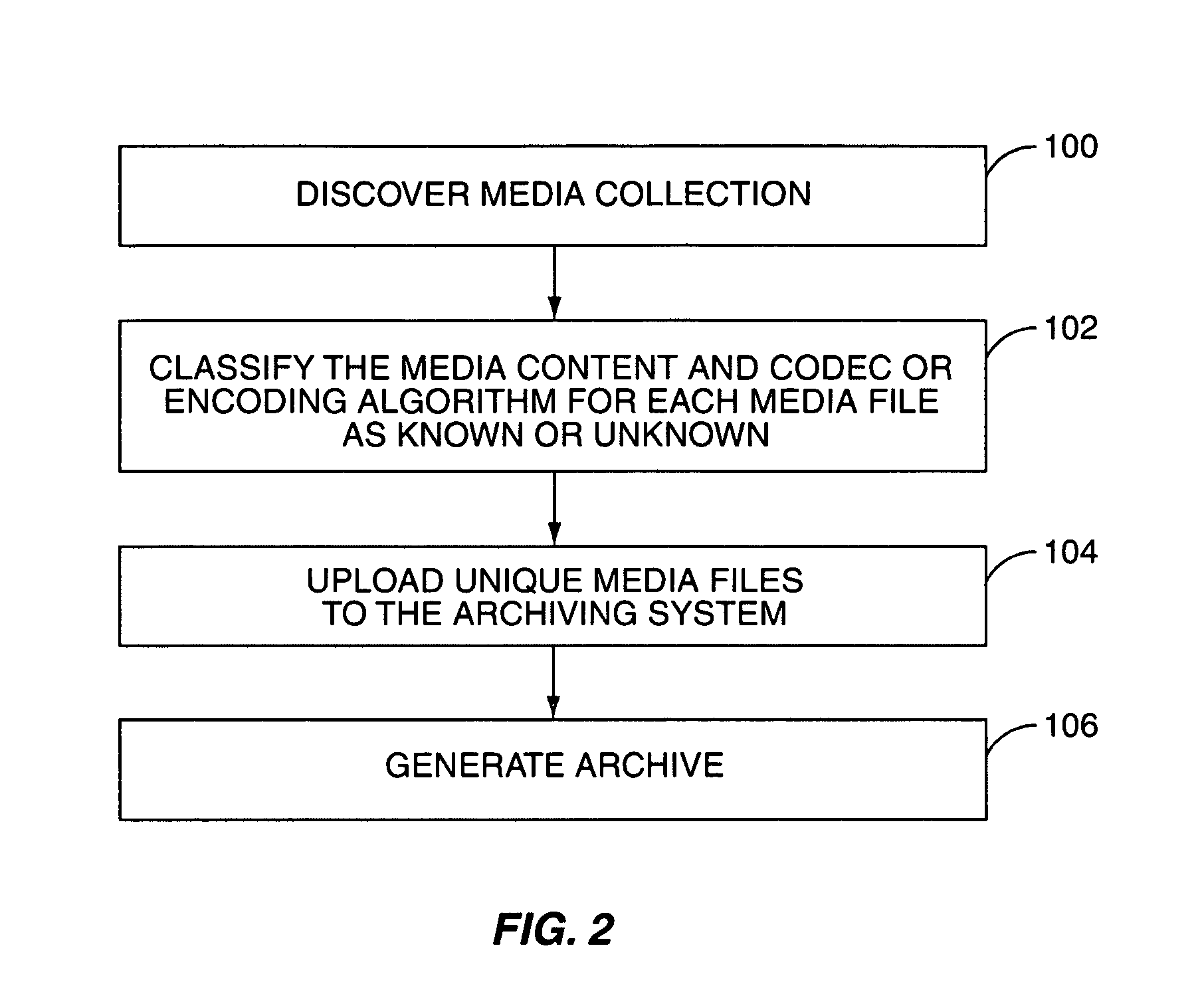
System and method for archiving a media collection
InactiveUS20090077084A1Reduce storageReduce transmission requirementsMultimedia data indexingData processing applicationsEncoding algorithmComputer hardware
A system and method for archiving a user's media collection are provided. In general, a central archiving system stores high-quality versions of a number of known media files and a number of known encoding algorithms. First, each media file in the user's media collection and an encoding algorithm used to encode each media file are classified as either known or unknown to the archiving server. For each known media file encoded with a known encoding algorithm, the archive includes information identifying the media file, information identifying the encoding algorithm for the media file, and optionally the one or more quality parameters such as bit rate, sampling frequency, and the like for the media file. For each unknown media file and / or media file encoded with an unknown CODEC or encoding algorithm, the archive includes the media file, which is uploaded and stored at the archiving system.
Owner:CONCERT TECH
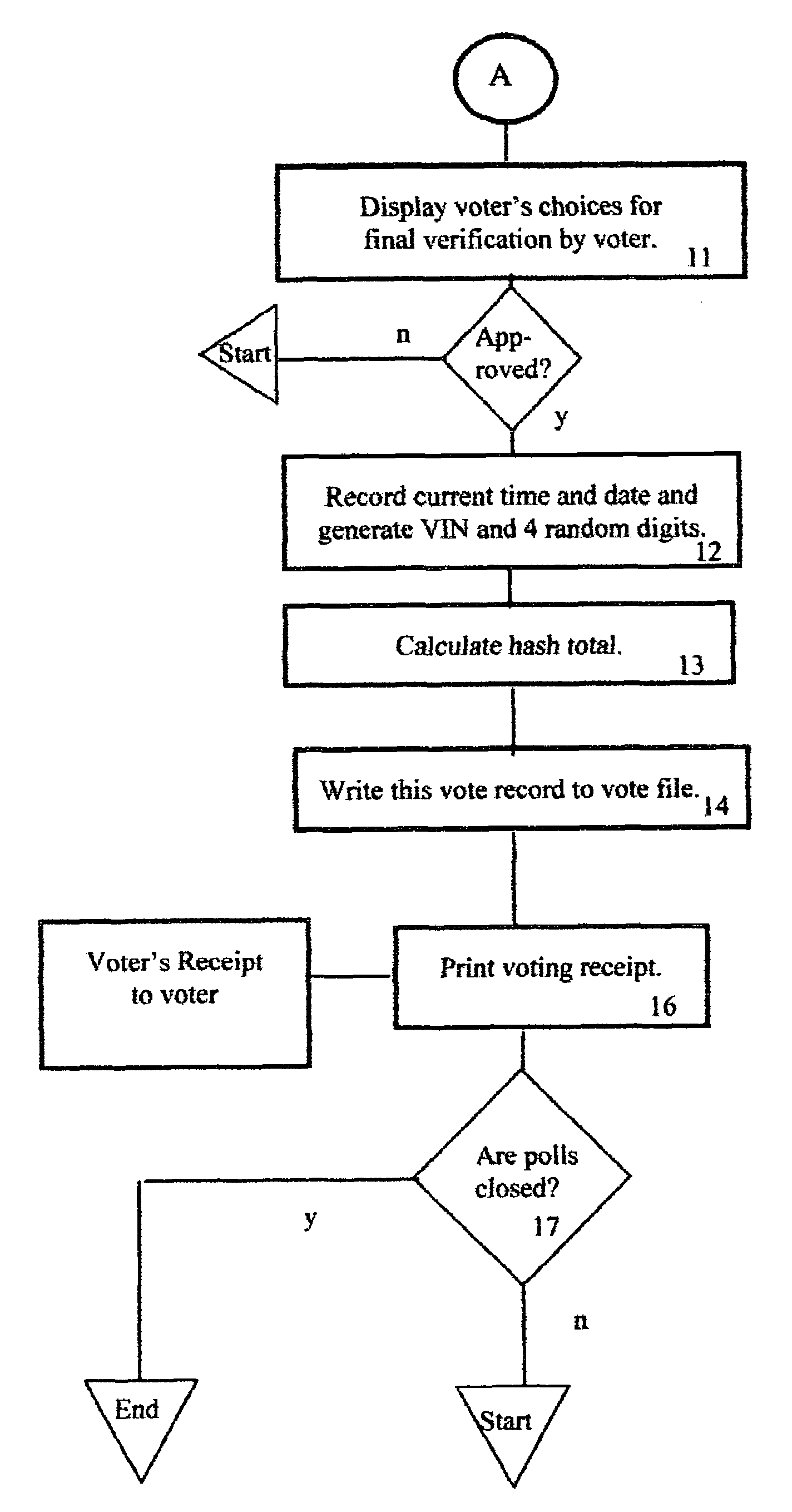
Method of accurately verifying election results without the need for a recount
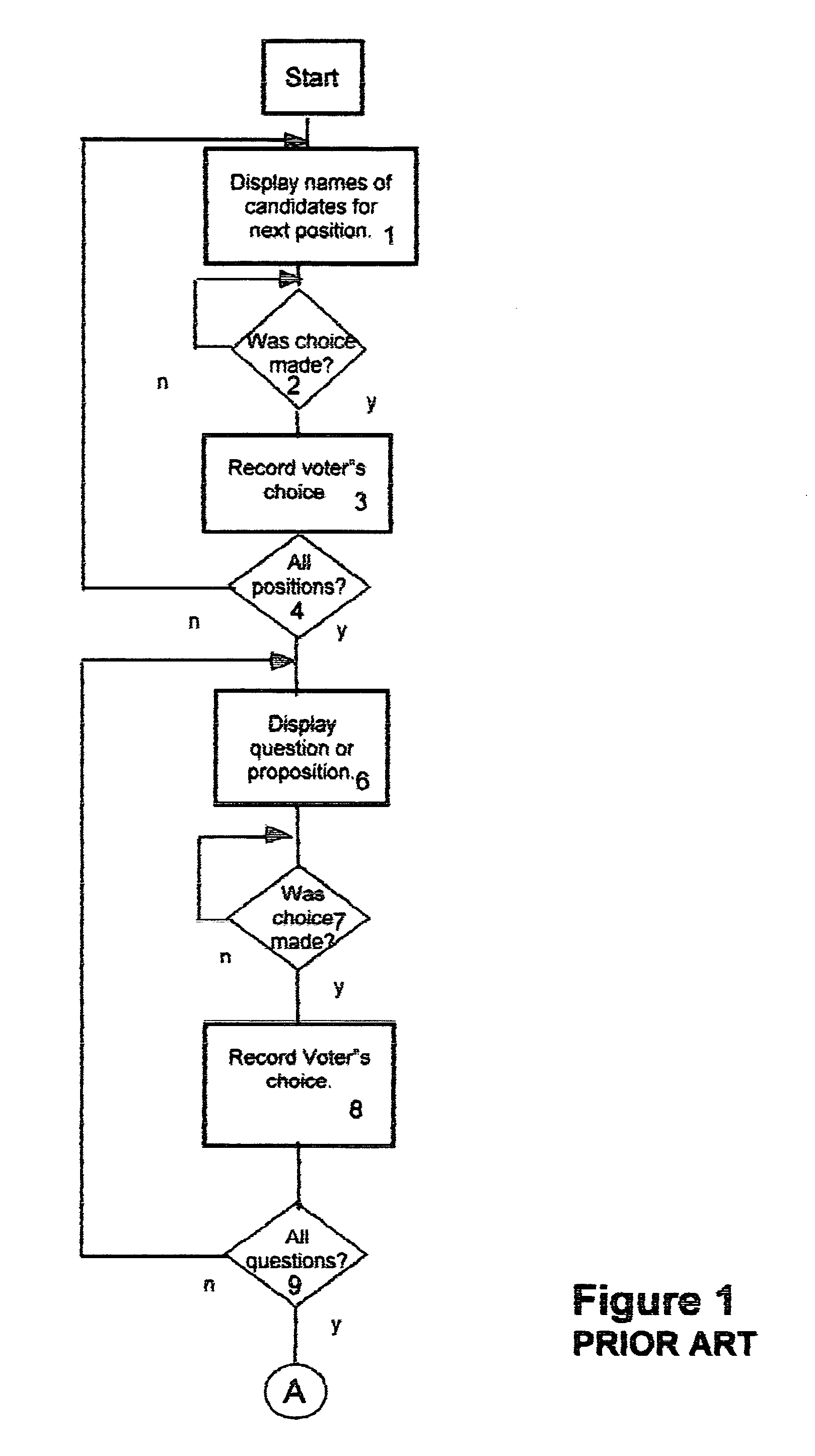
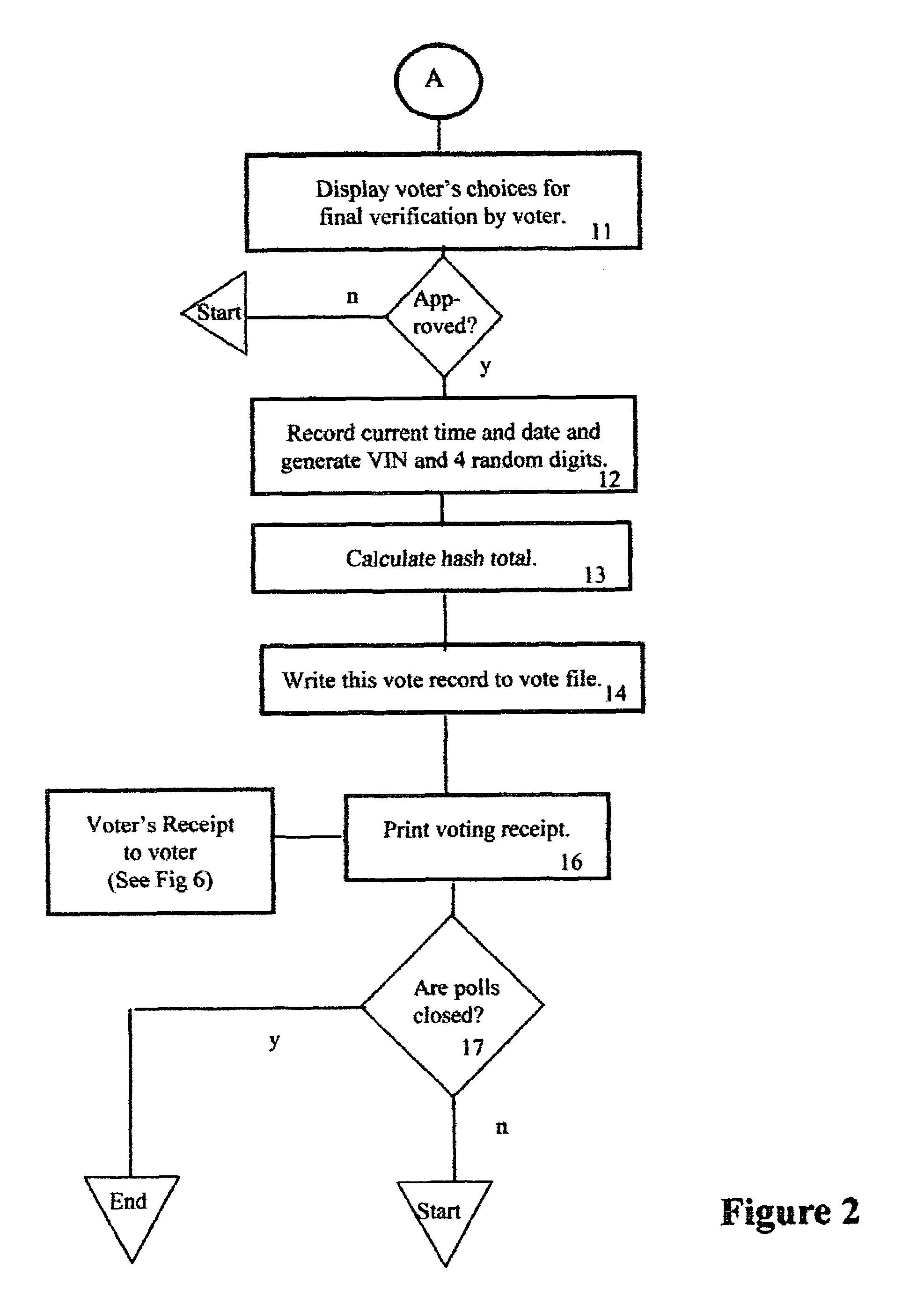
InactiveUS6971574B1Eliminate needSure easyVoting apparatusData processing applicationsComputer hardwareEncoding algorithm
Hash numbers are assigned to each individual ballot choice made by a particular voter and a hash total, establishing the voter's set of ballot choices, is recorded and a printed receipt is issued to the voter, bearing the voter's identification number, to assure him that his vote was correctly recorded along with his hash total. If the voter presents his receipt, to deny that he voted as shown on the receipt, an unfavorable comparison of the previously recorded hash total, with the hash total on the receipt, proves that the receipt was forged, and each such tampering attempt and voter ID is recorded. Recounts are unnecessary, unless the number of such recorded attempts at tampering exceed a predetermined number. A hacker attempt to change a recorded vote will fail because the hash totals of the altered ballot won't match the correct hash total because the hash encoding algorithm is secret.
Owner:HERSKOWITZ IRVING L
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com