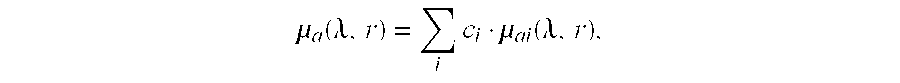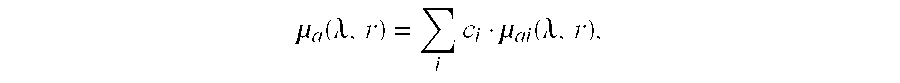Patents
Literature
56results about How to "For accurate visualization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
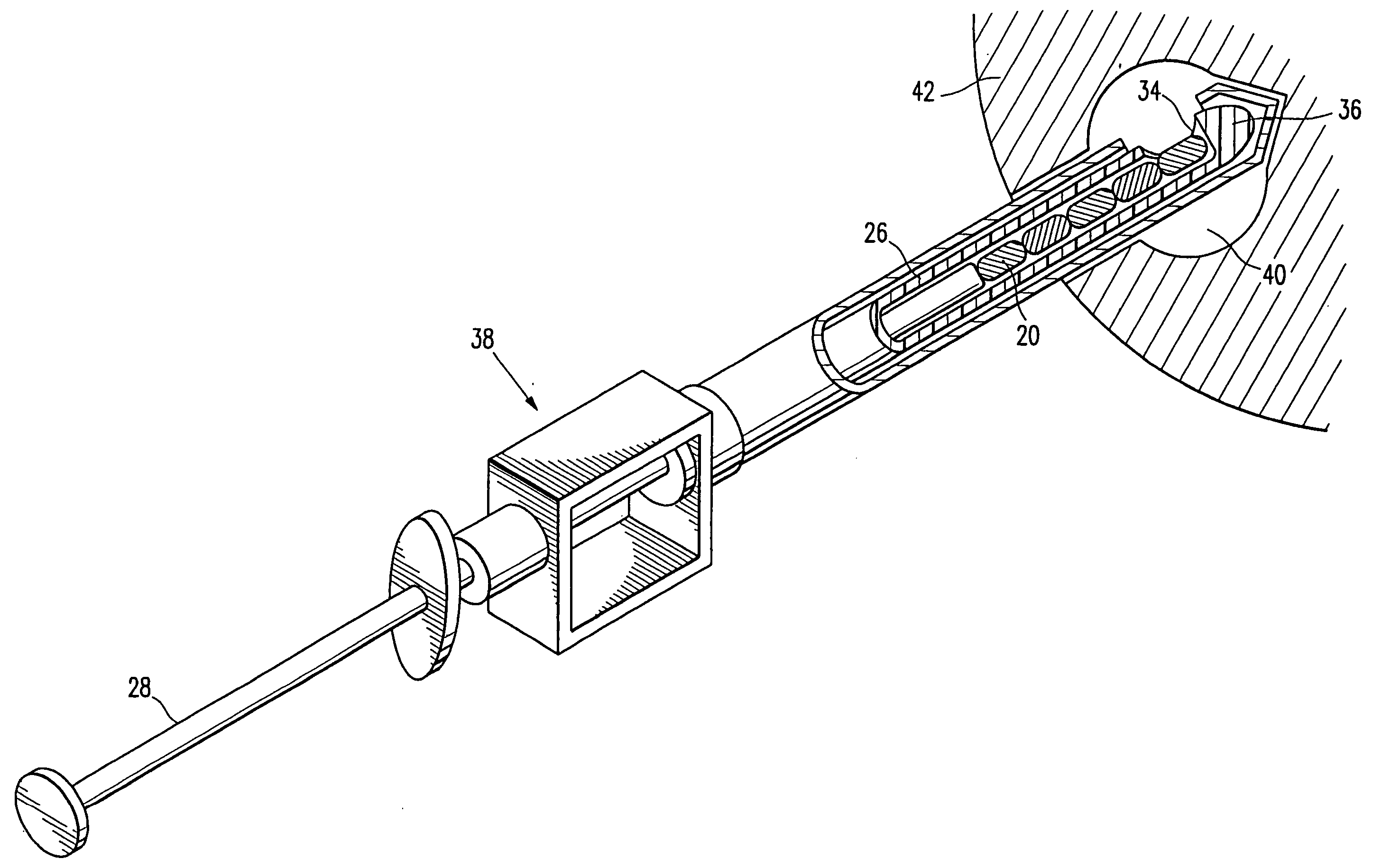
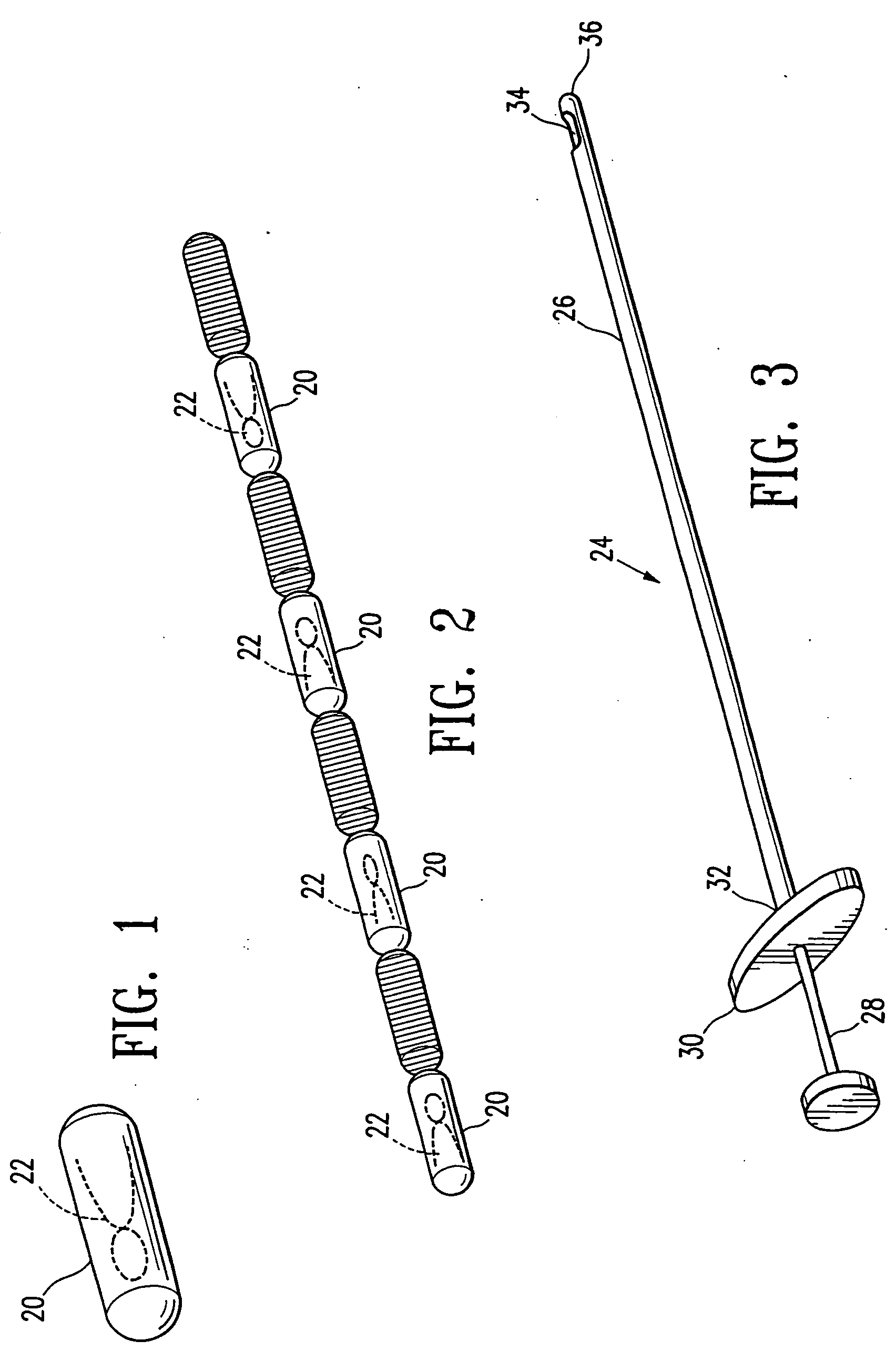
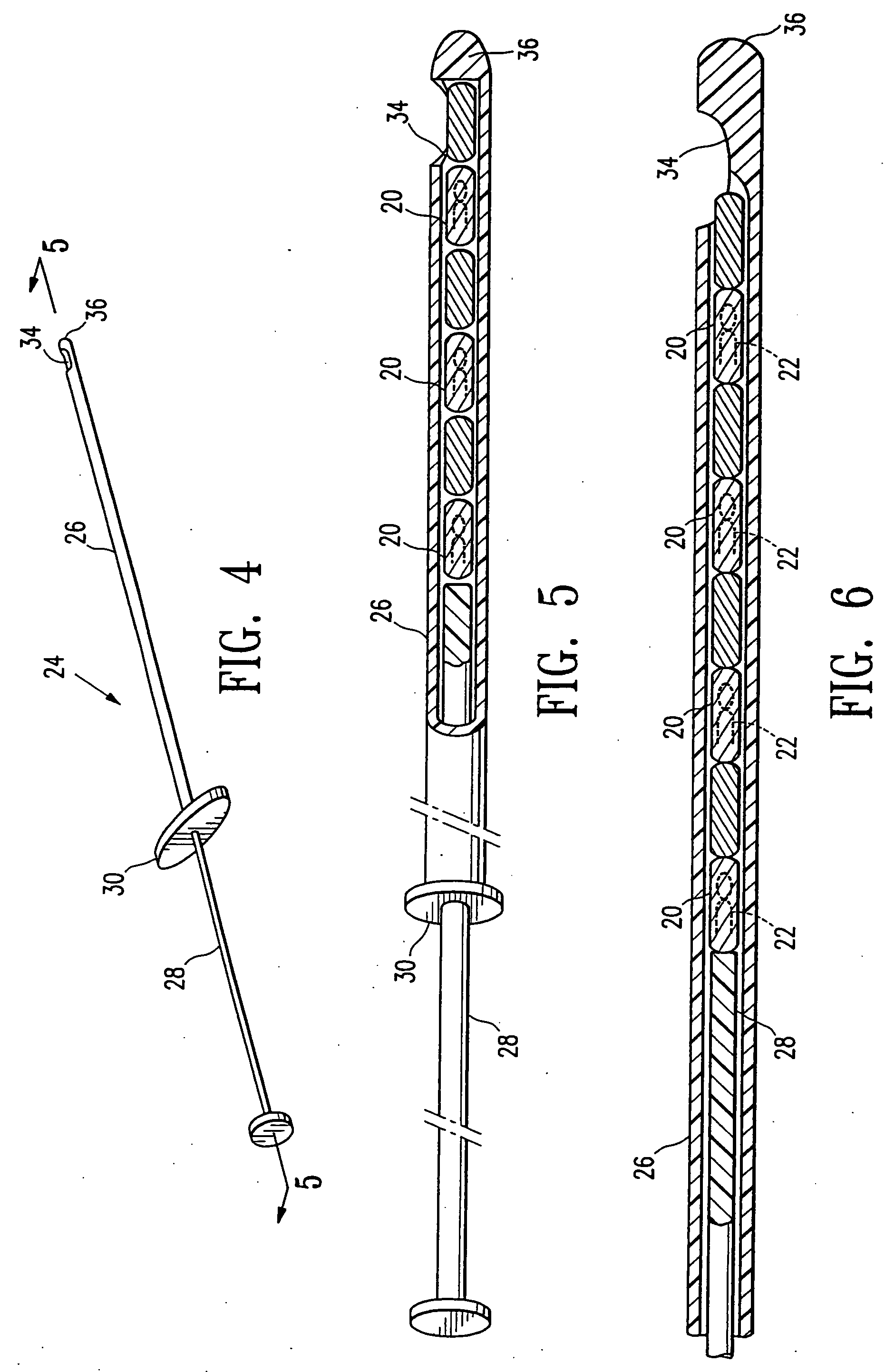
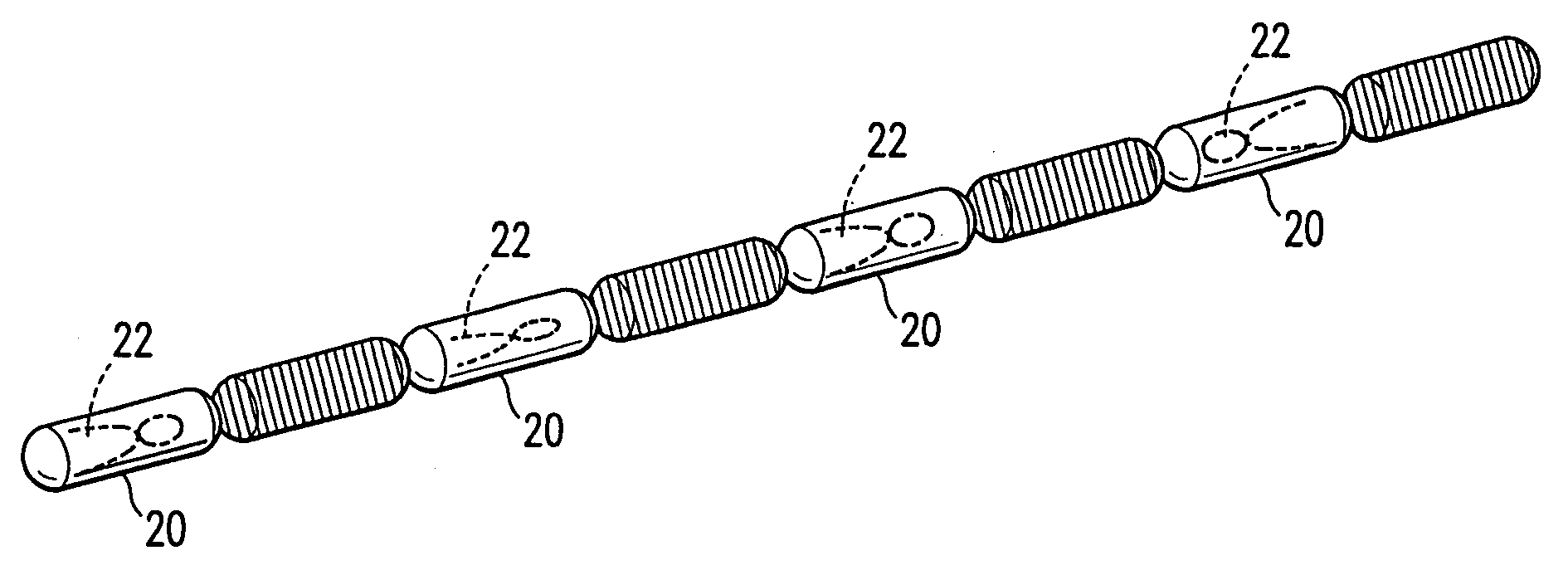
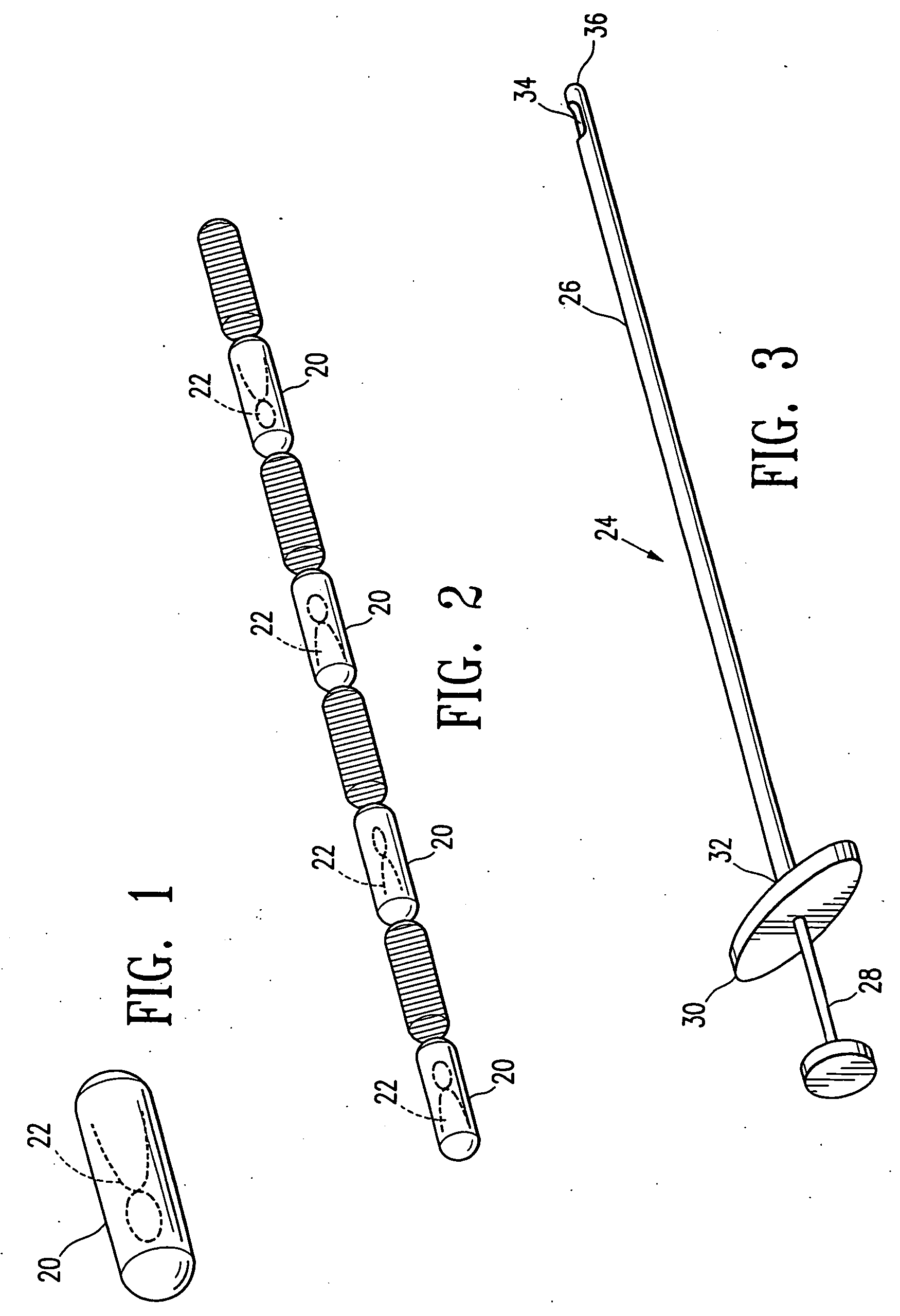
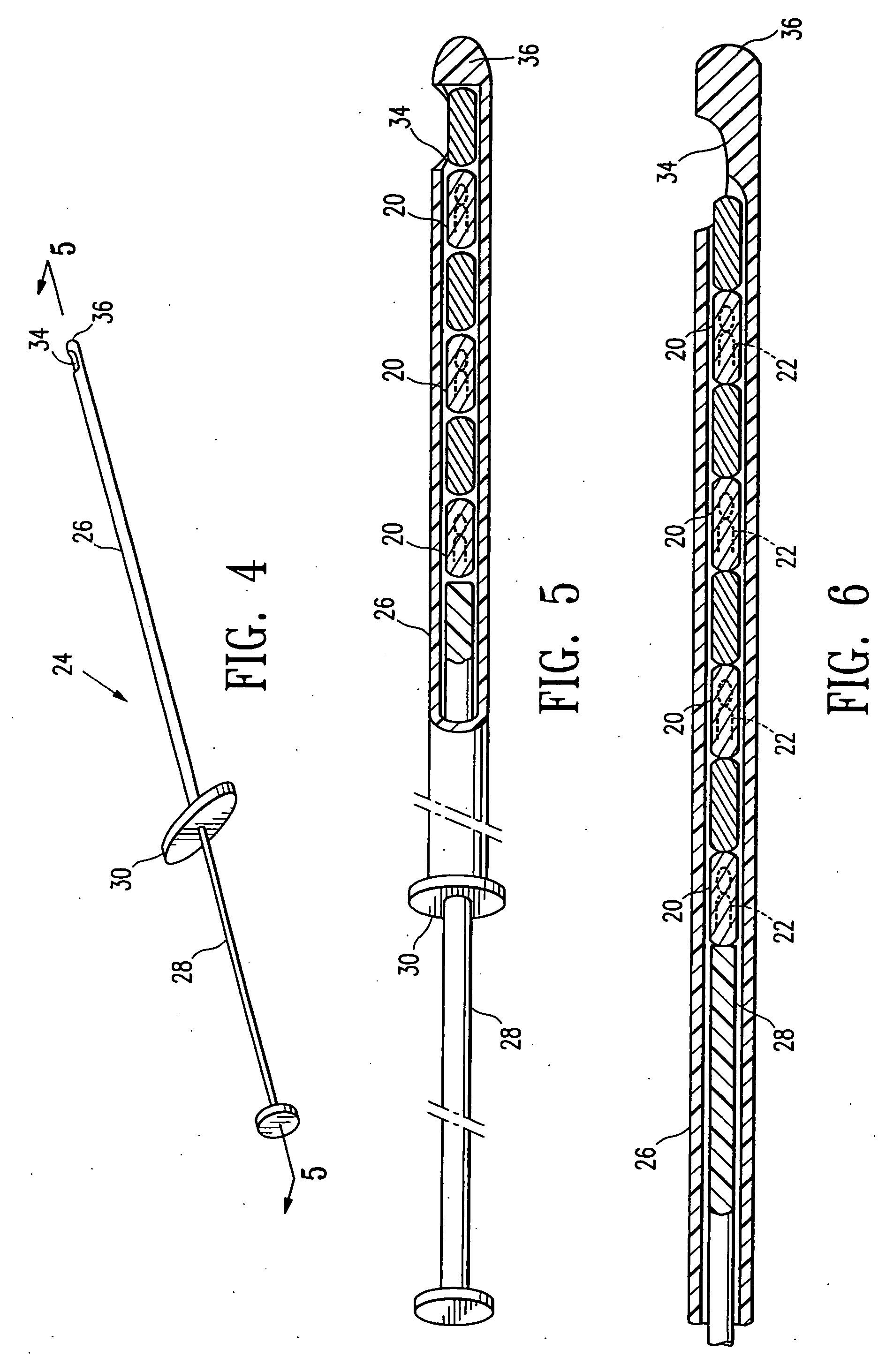
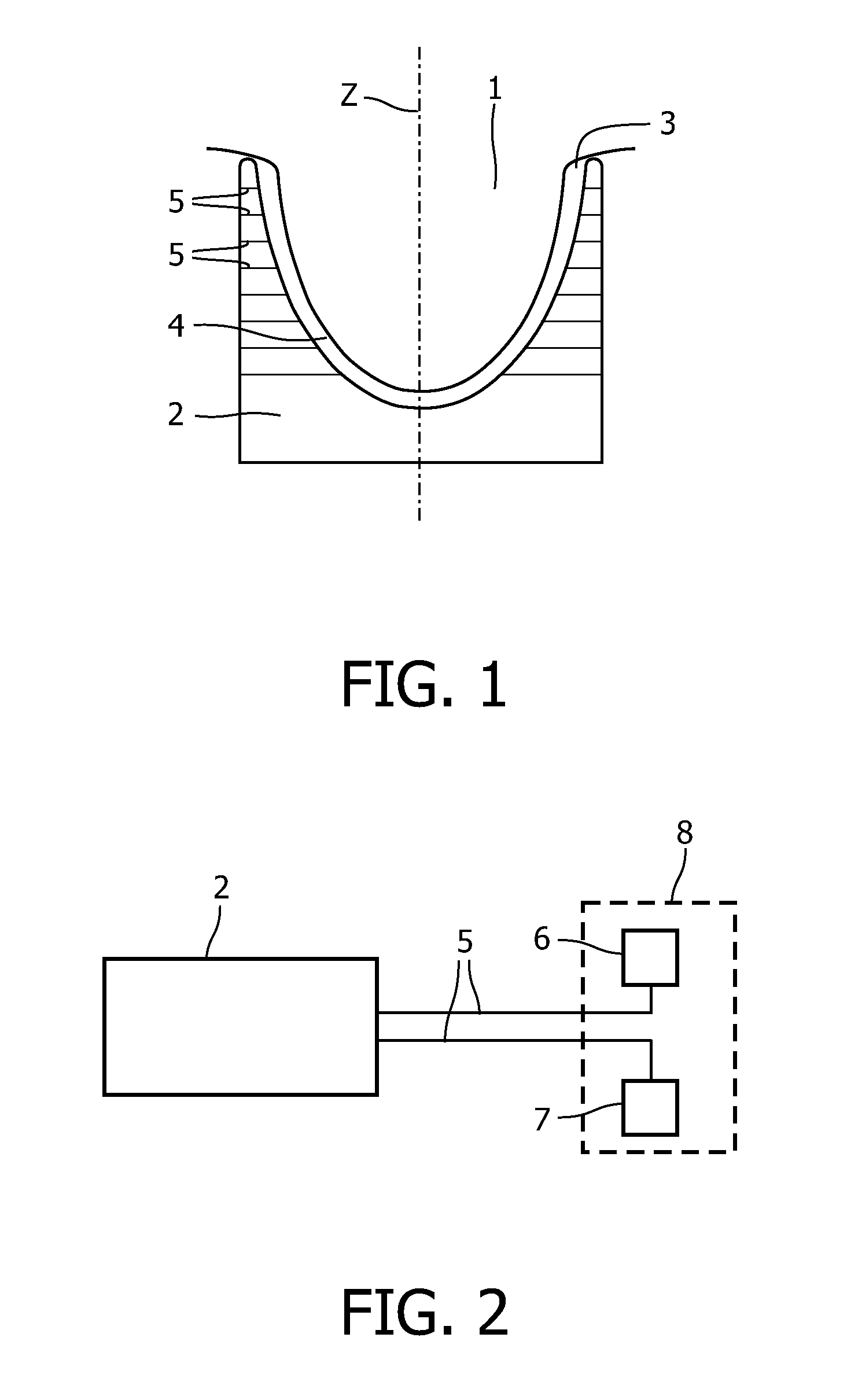
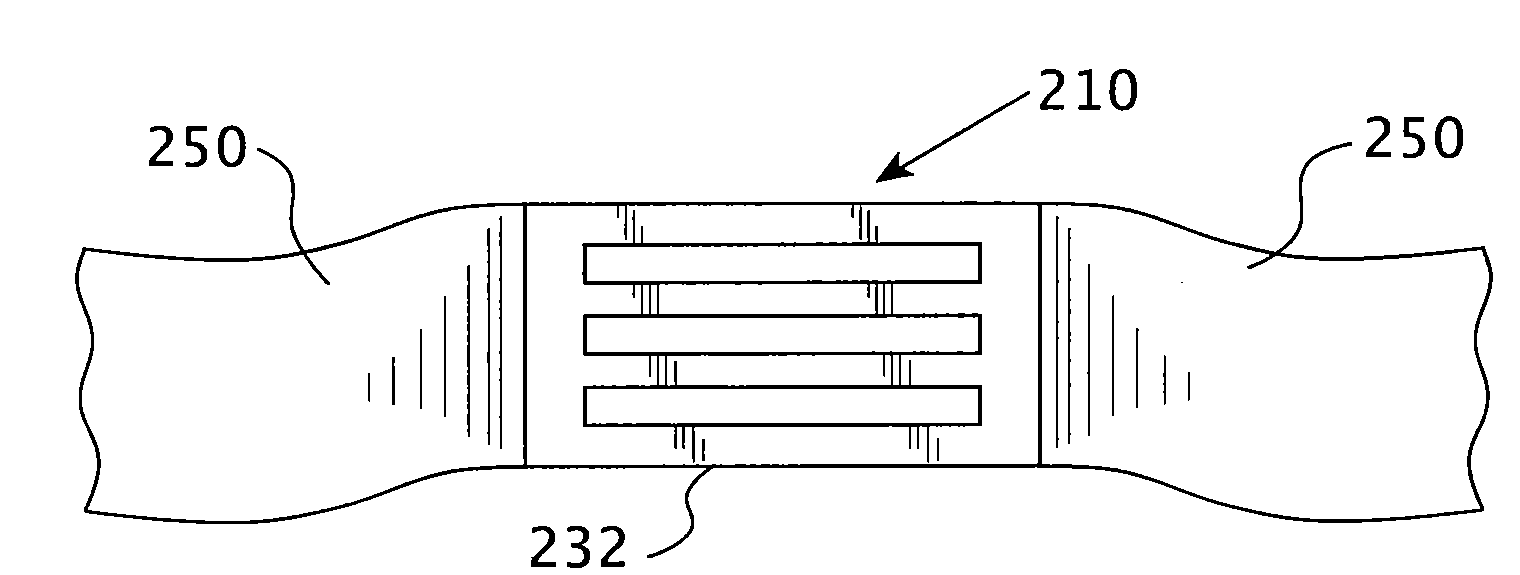
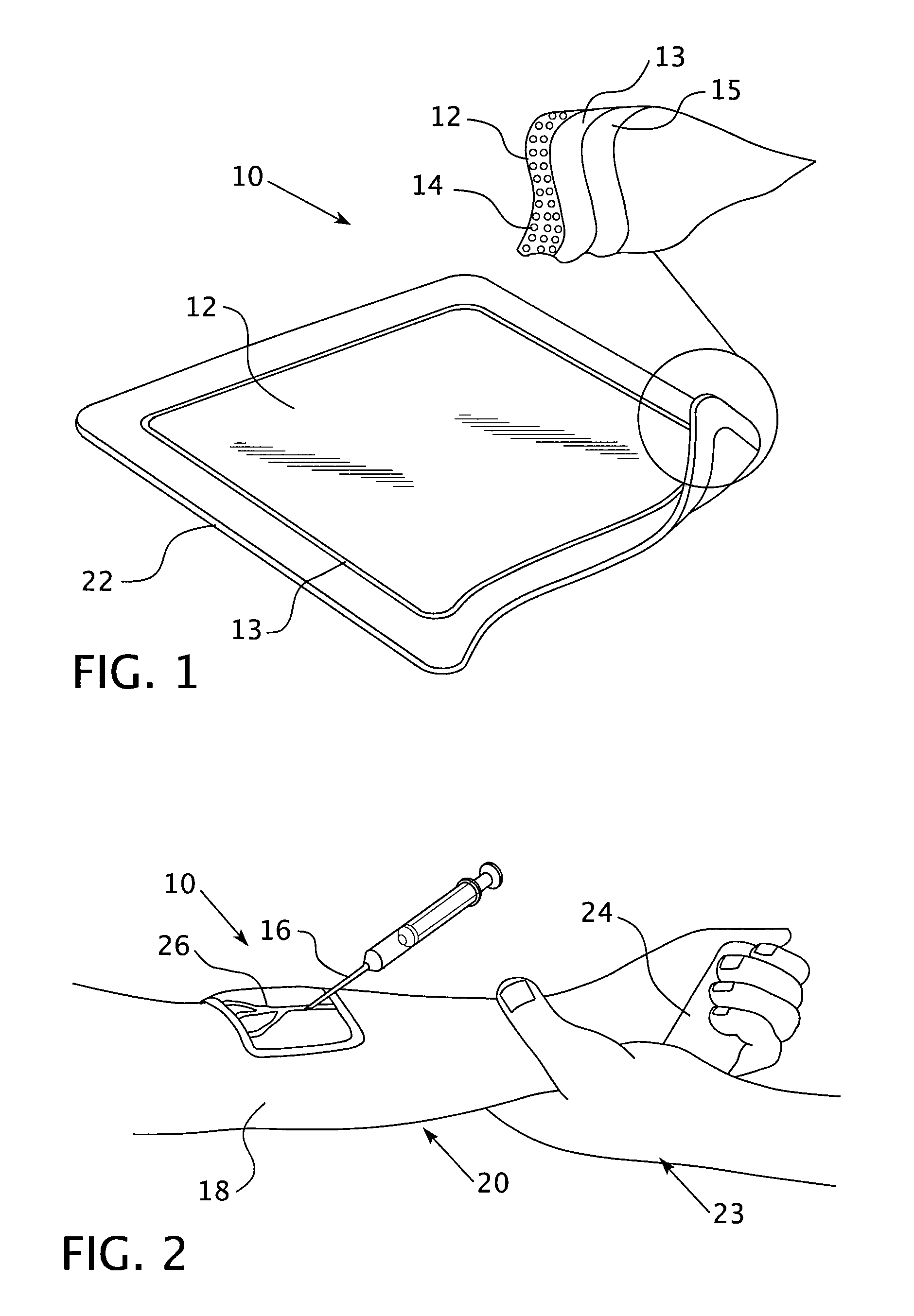
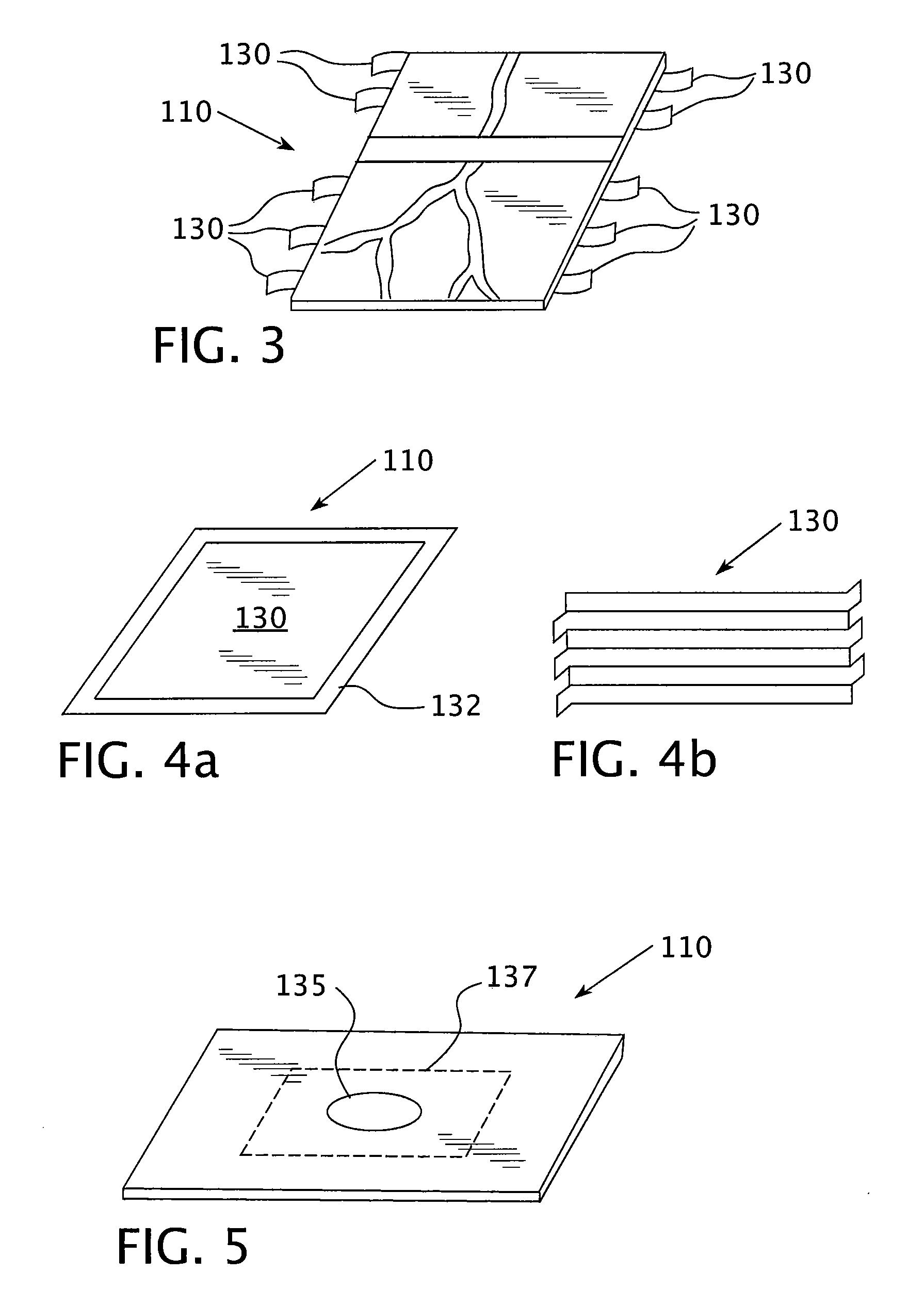
Imageable biopsy site marker
InactiveUS20060122503A1Accurately excise and remove a quantityMark accuratelyLuminescence/biological staining preparationOrgan movement/changes detectionRadiologyPiston
A biopsy site marker having at least one small marker body or pellet of bioresorbable material such as gelatin, collagen, polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid which has a radiopaque object, preferably with a non-biological configuration. The at least one bioresorbable body or pellet with a radiopaque object is deposited into the biopsy site, by an delivery device that includes an elongated tubular body with a piston slidable within the tubular body. One end of the tube is placed into the biopsy site. At least one but preferably several marker bodies or pellets are deposited sequentially into the biopsy site through the tube. At least the bioresorbable materials of the detectable markers remain present in sufficient quantity to permit detection and location of the biopsy site at a first time point (e.g., 2 weeks) after introduction but clear from the biopsy site or otherwise do not interfere with imaging of tissues adjacent the biopsy site at a second time point (e.g., 5-7 months) after introduction.
Owner:SENORX
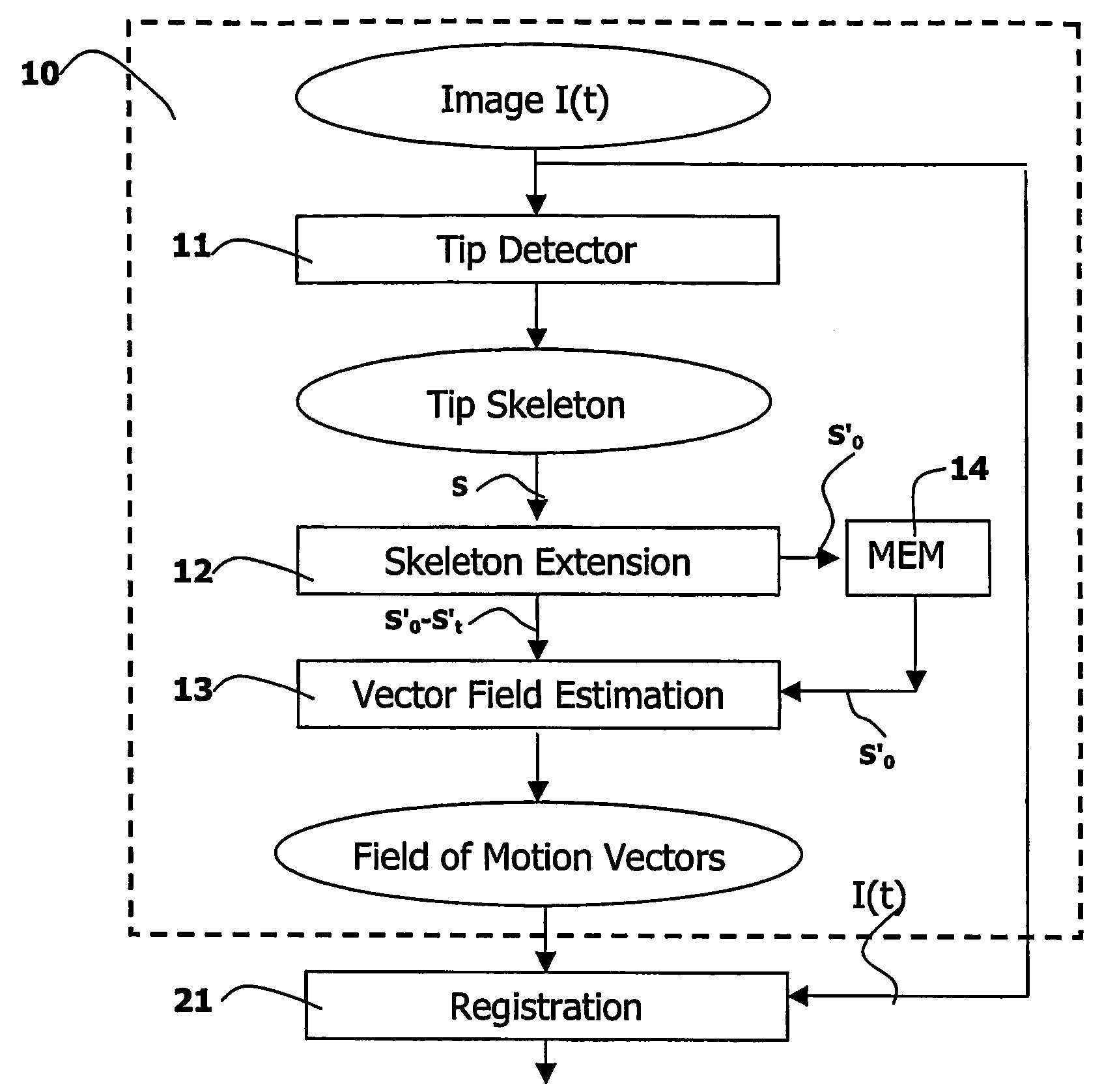
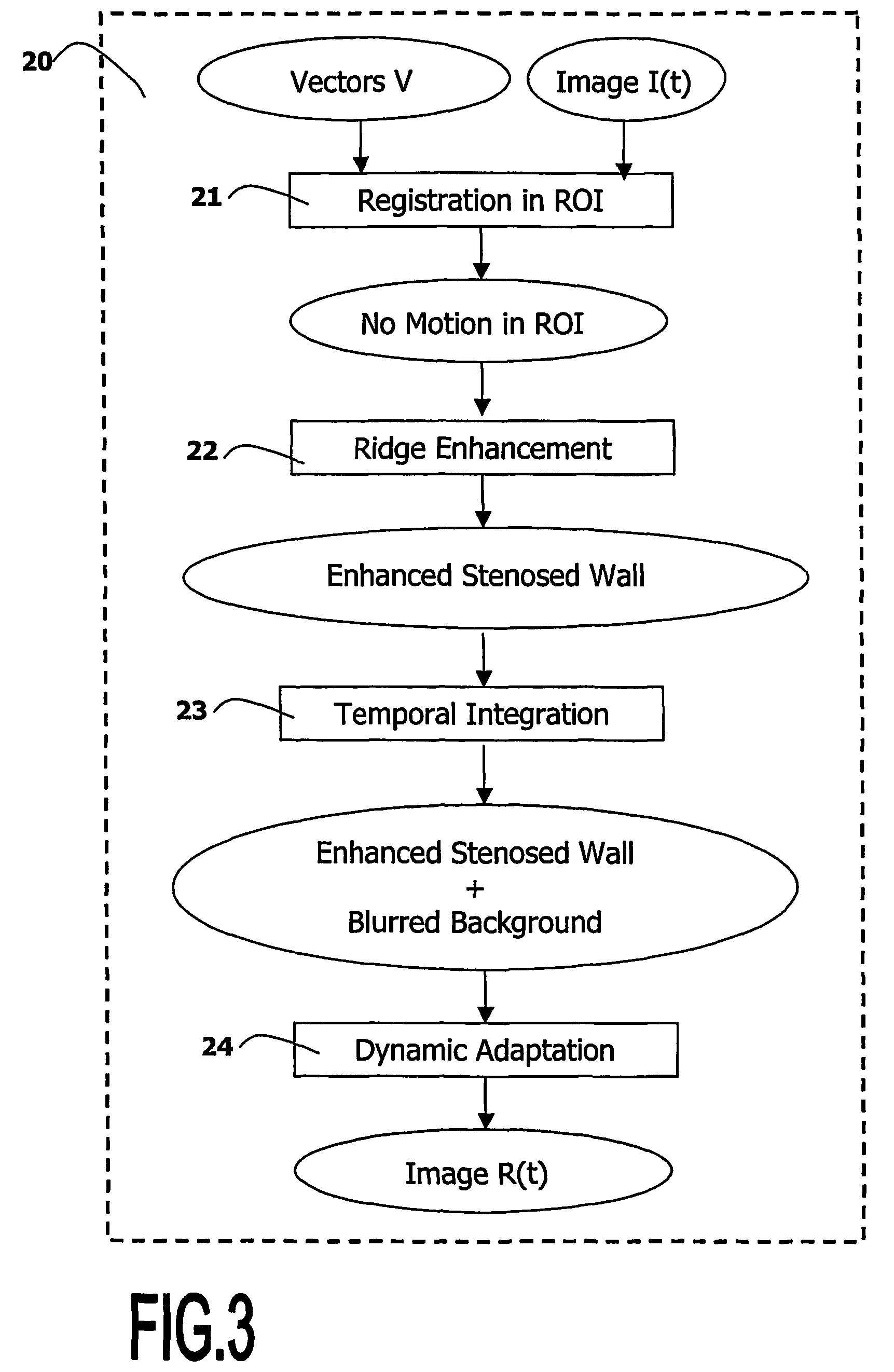
Medical viewing system and method for detecting boundary structures
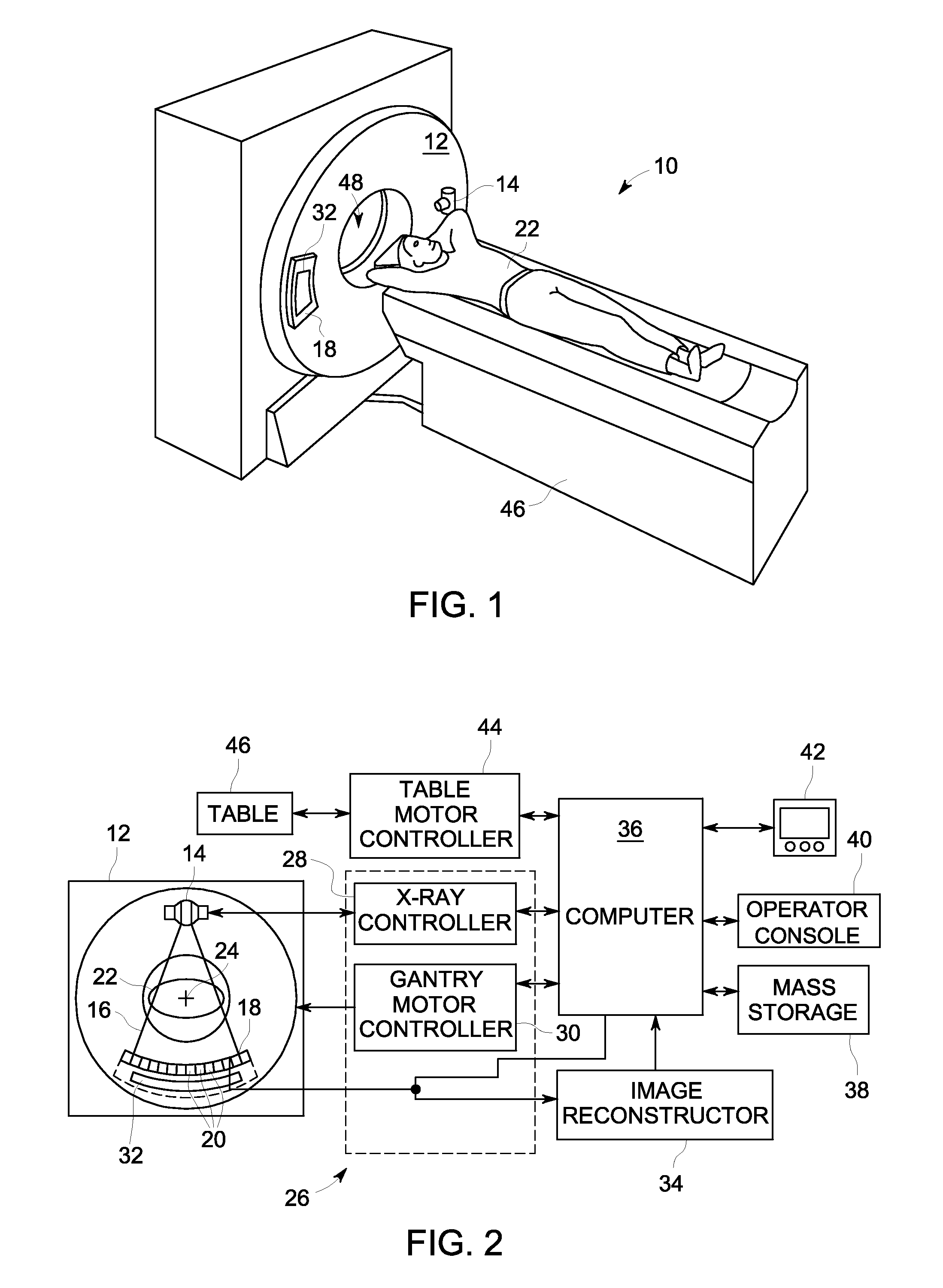
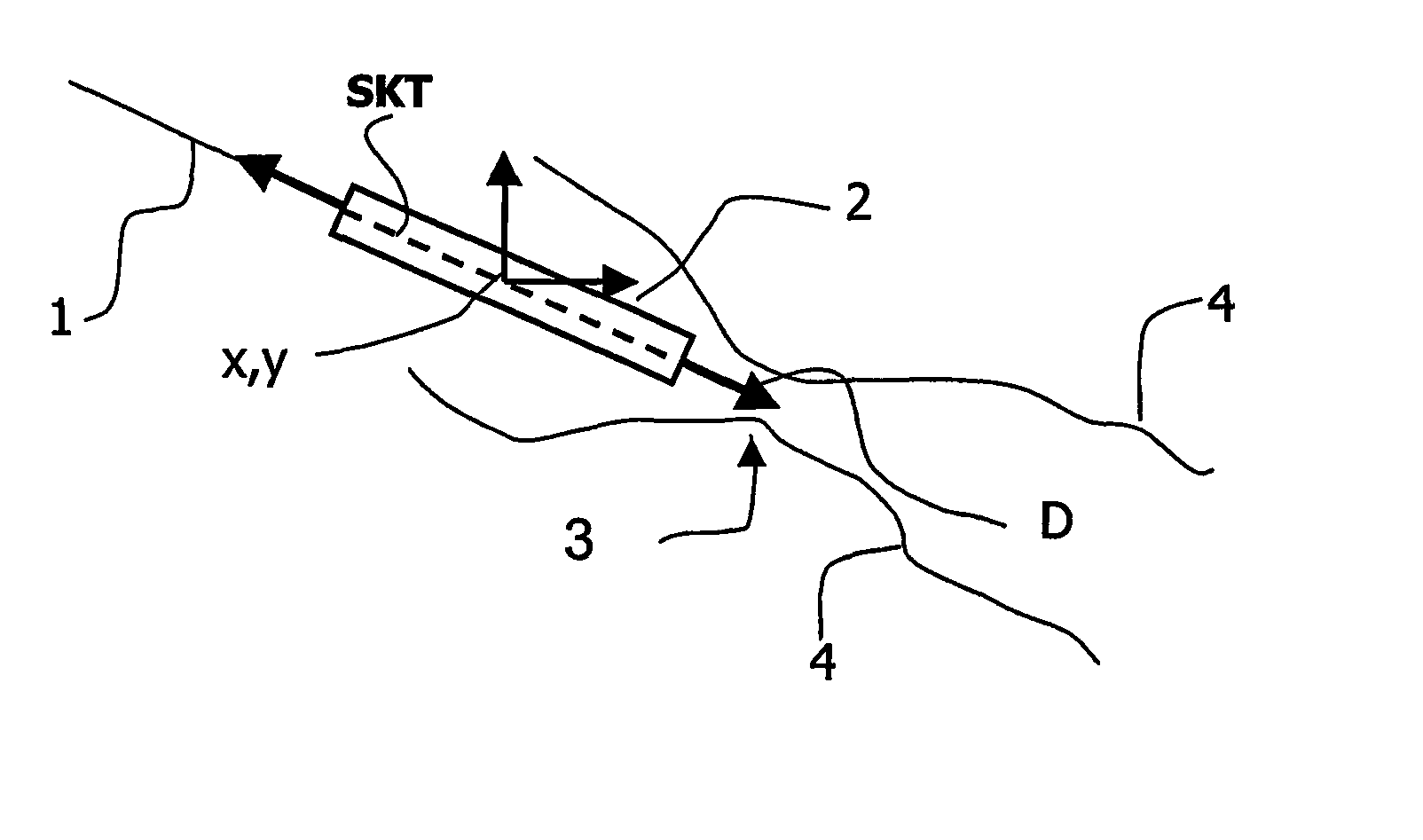
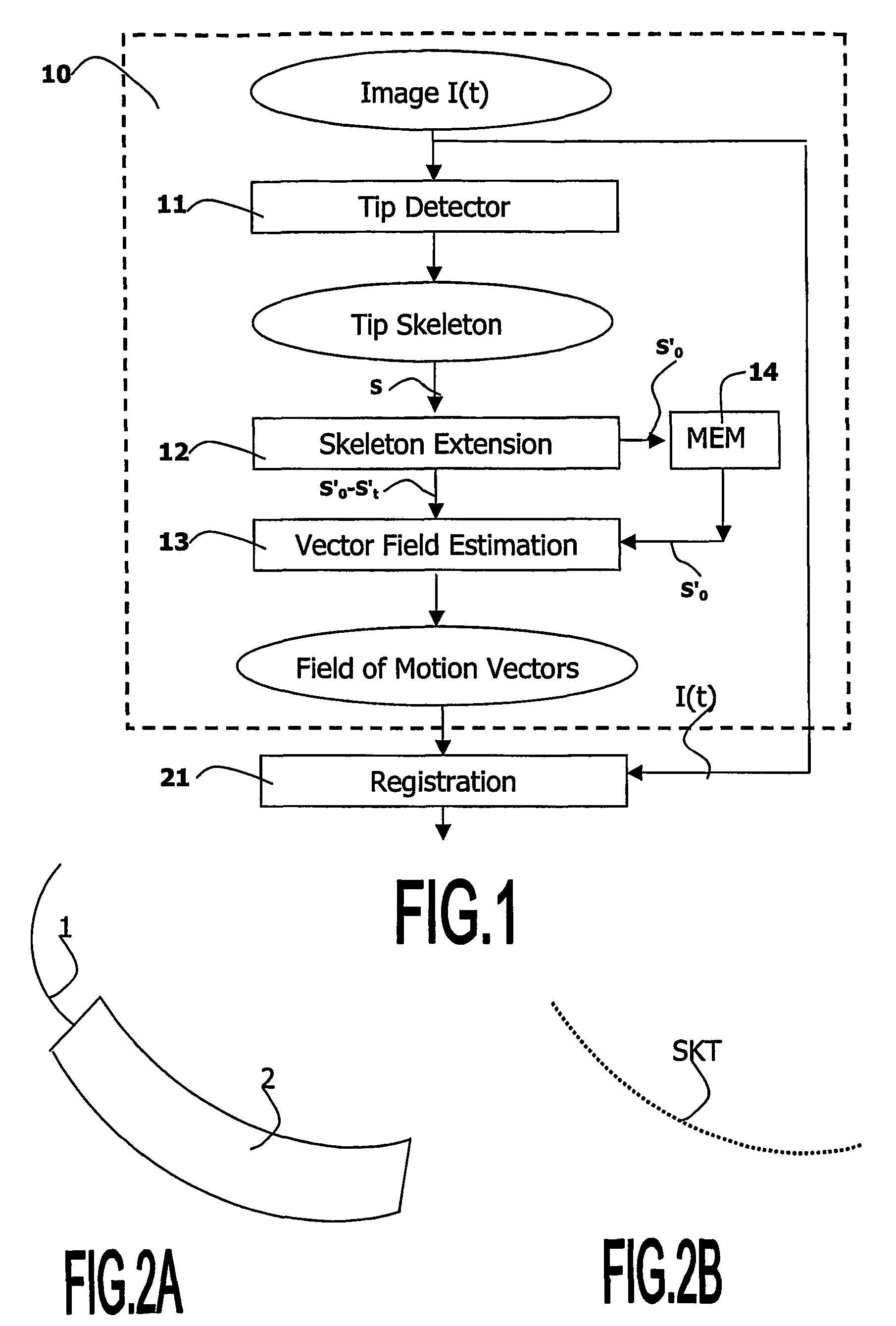
ActiveUS20060058643A1Increase awarenessFor accurate visualizationImage enhancementImage analysisDisplay processingBoundary structure
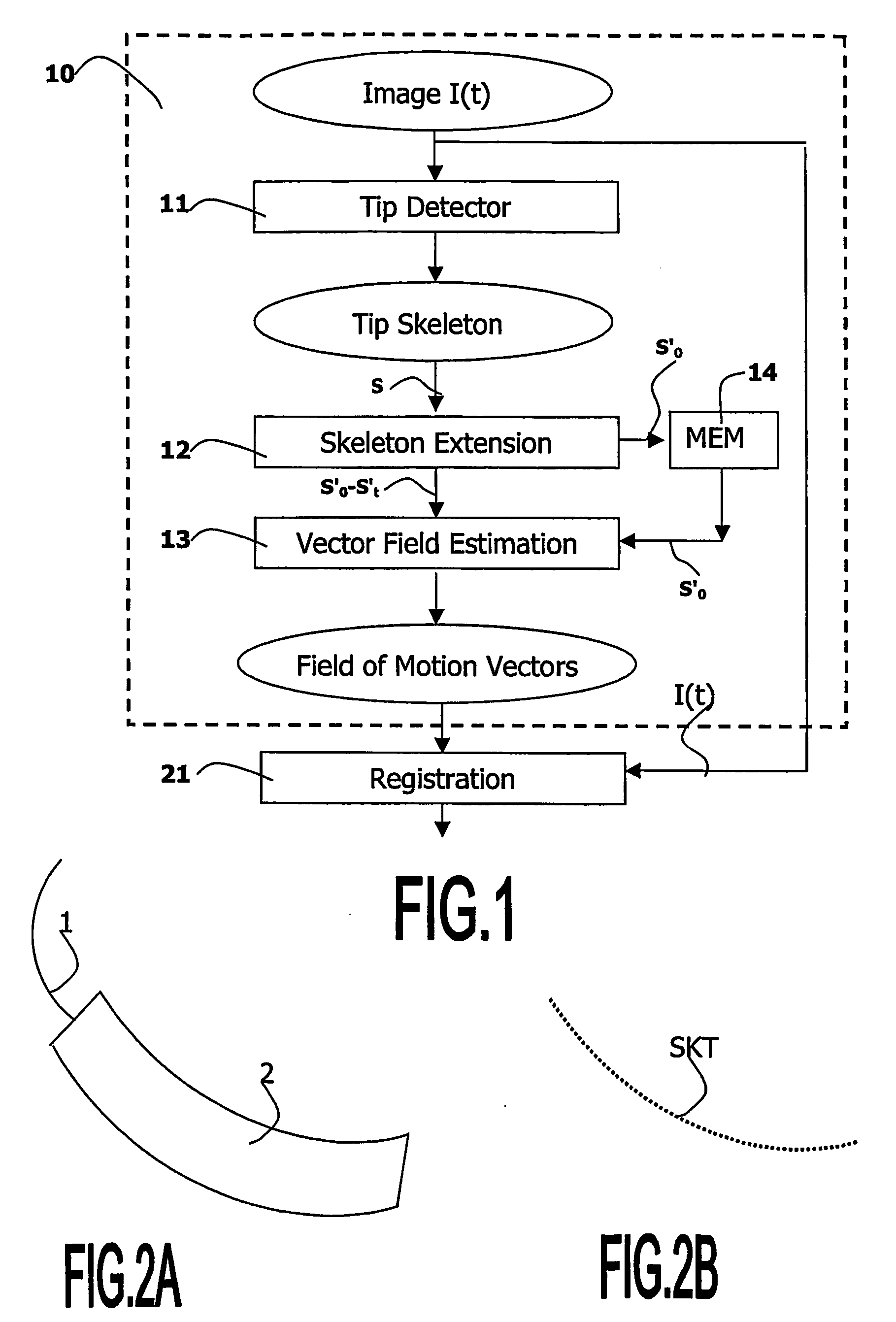
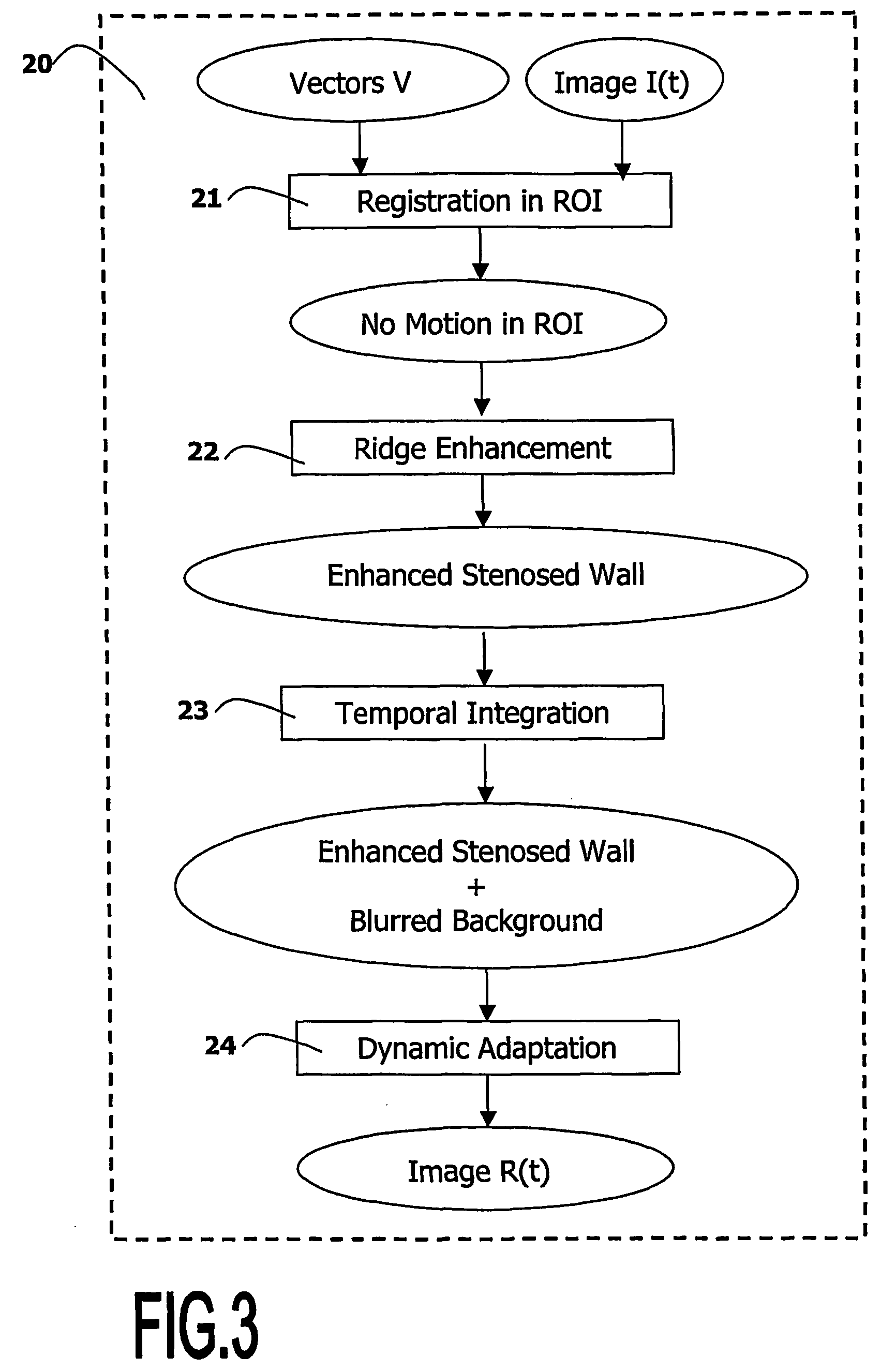
A medical viewing system for displaying a sequence of medical images that represents moving and / or positioning a guide-wire, in a blood vessel, which guide-wire has a guide-wire tip that is contrasted with respect to the guide wire, this system comprising acquisition means that acquires an original sequence of noisy images called live sequence and processing means for processing said live sequence of images in real time, the processing means comprising: first means (10) for automatically detecting the guide-wire tip, yielding skeleton information of the guide-wire tip and a field of motion vectors based on said skeleton information; second means (20) for automatically registering the guide-wire tip with respect to a reference based on the field of motion vectors and for enhancing the guide-wire and the vessel walls while blurring the background in the registered images; and comprising: Display means for displaying a live sequence of processed images.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method for blood vessel stenosis visualization and quantification using spectral ct analysis
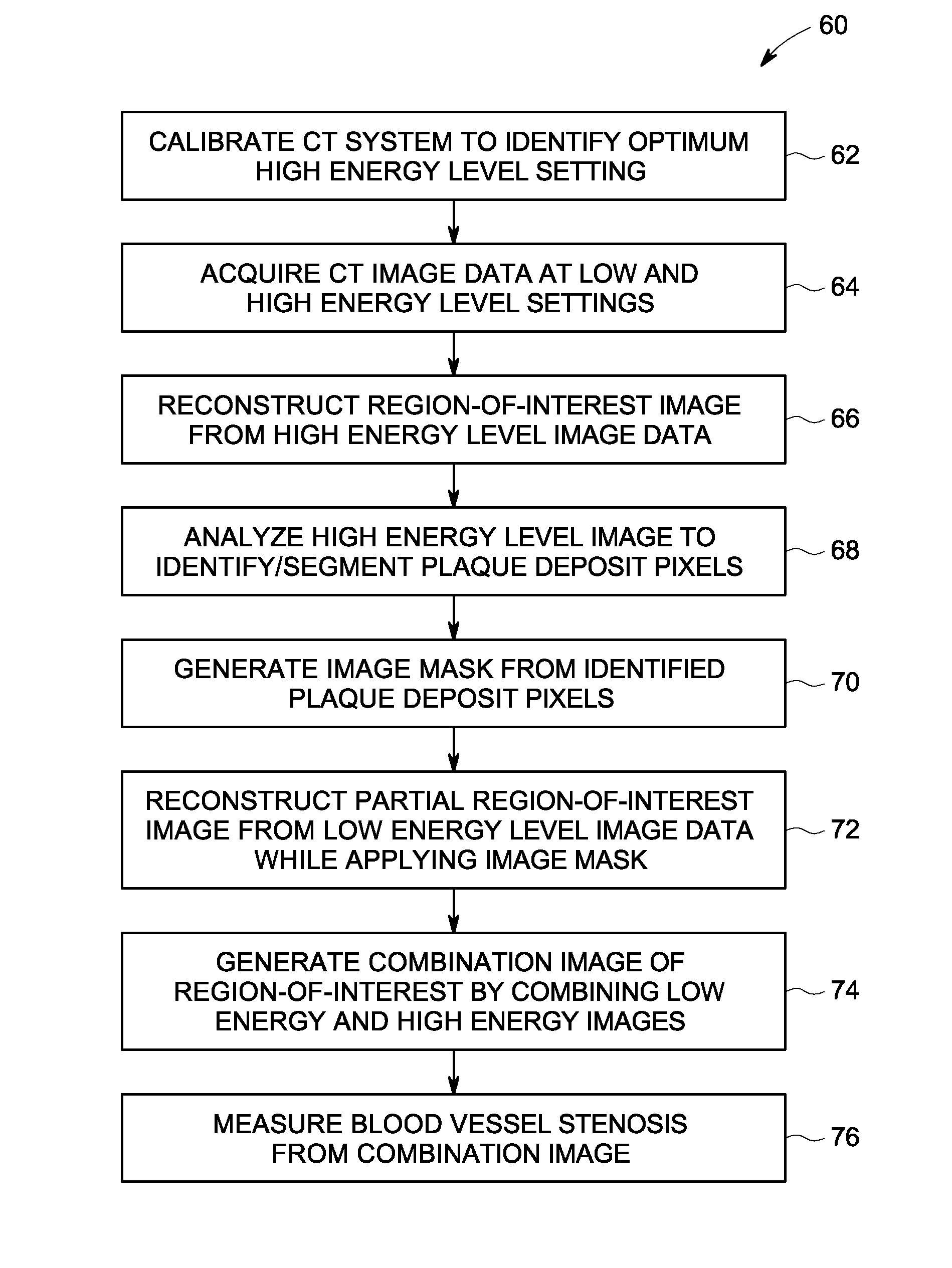
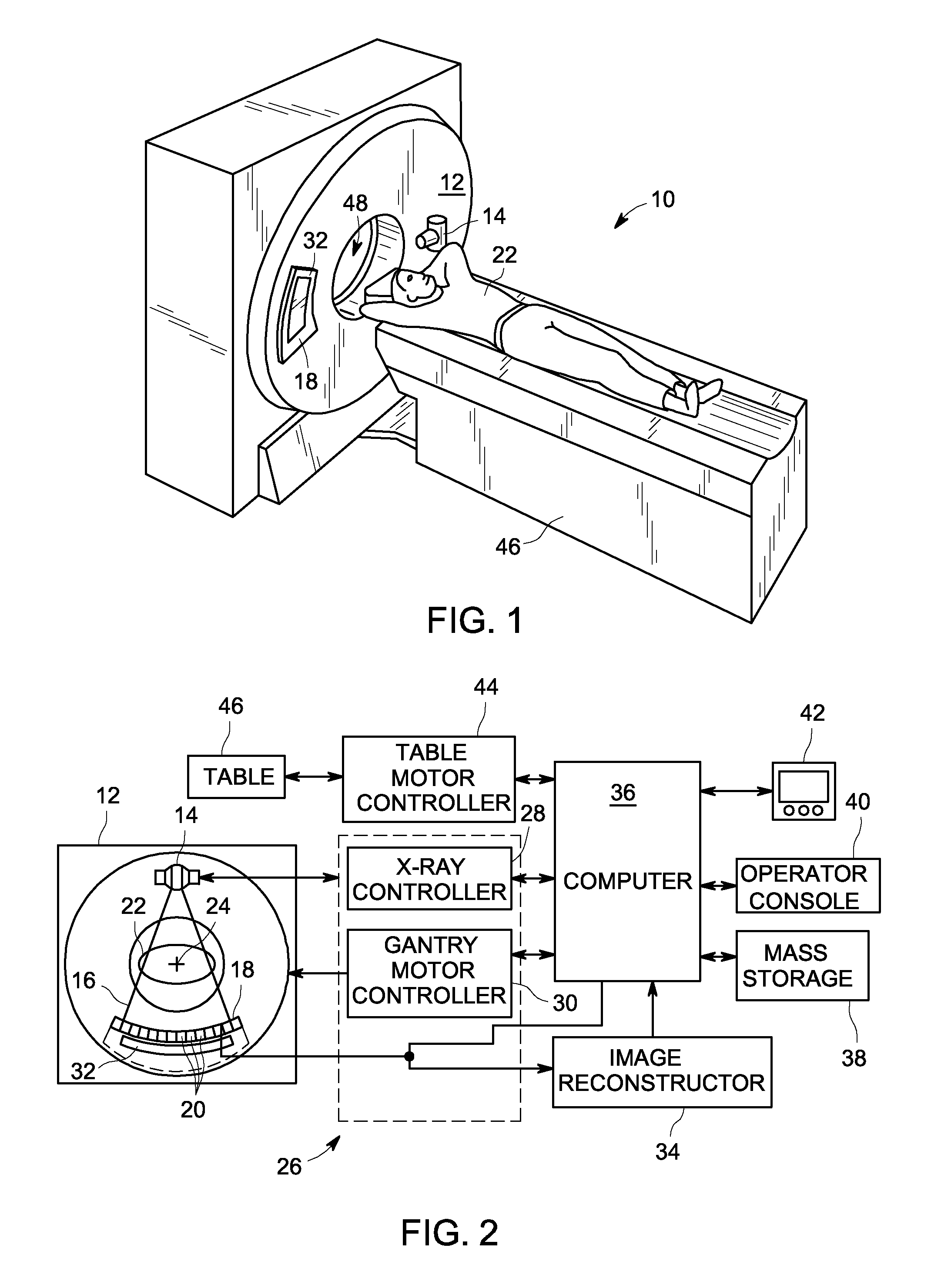
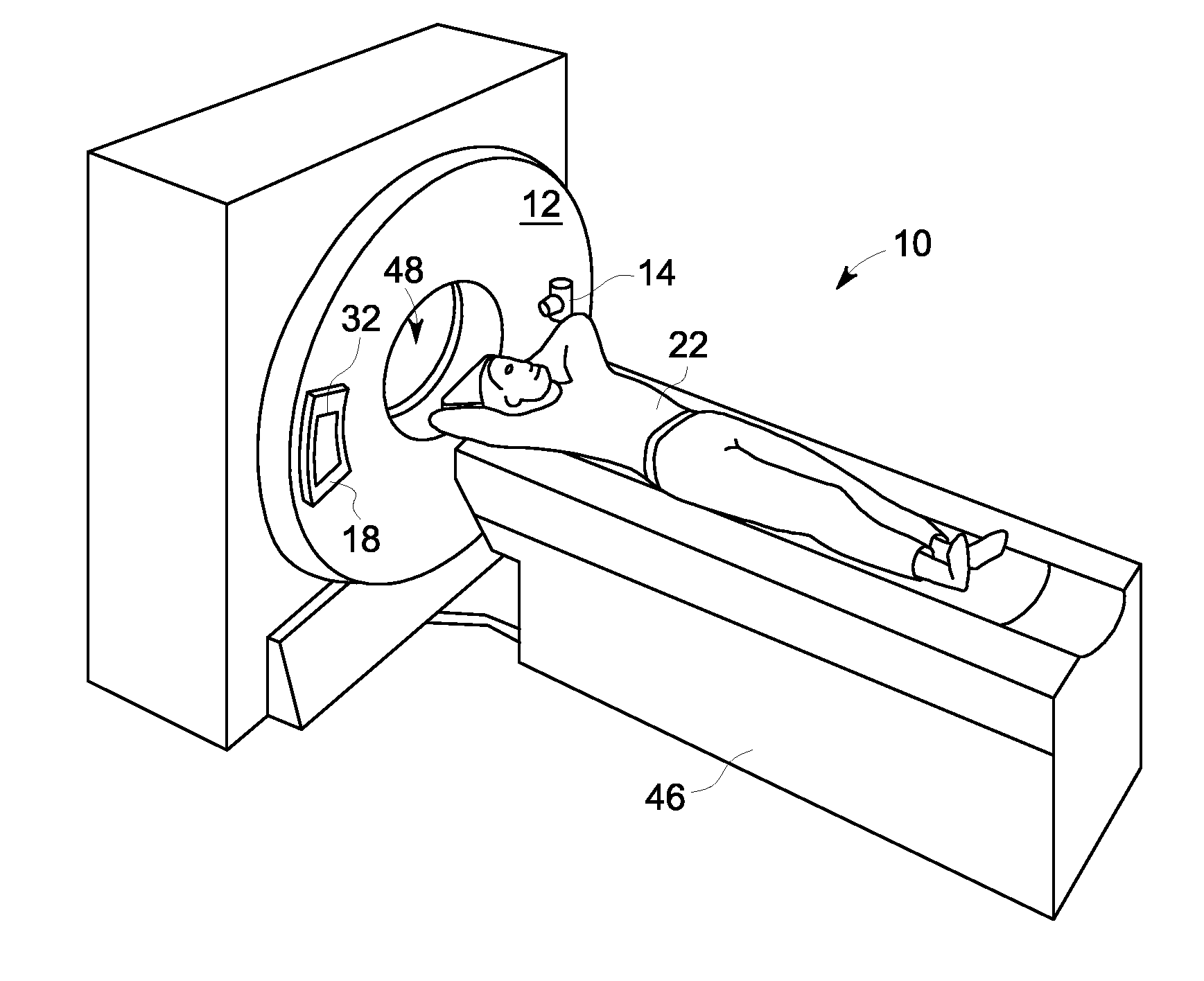
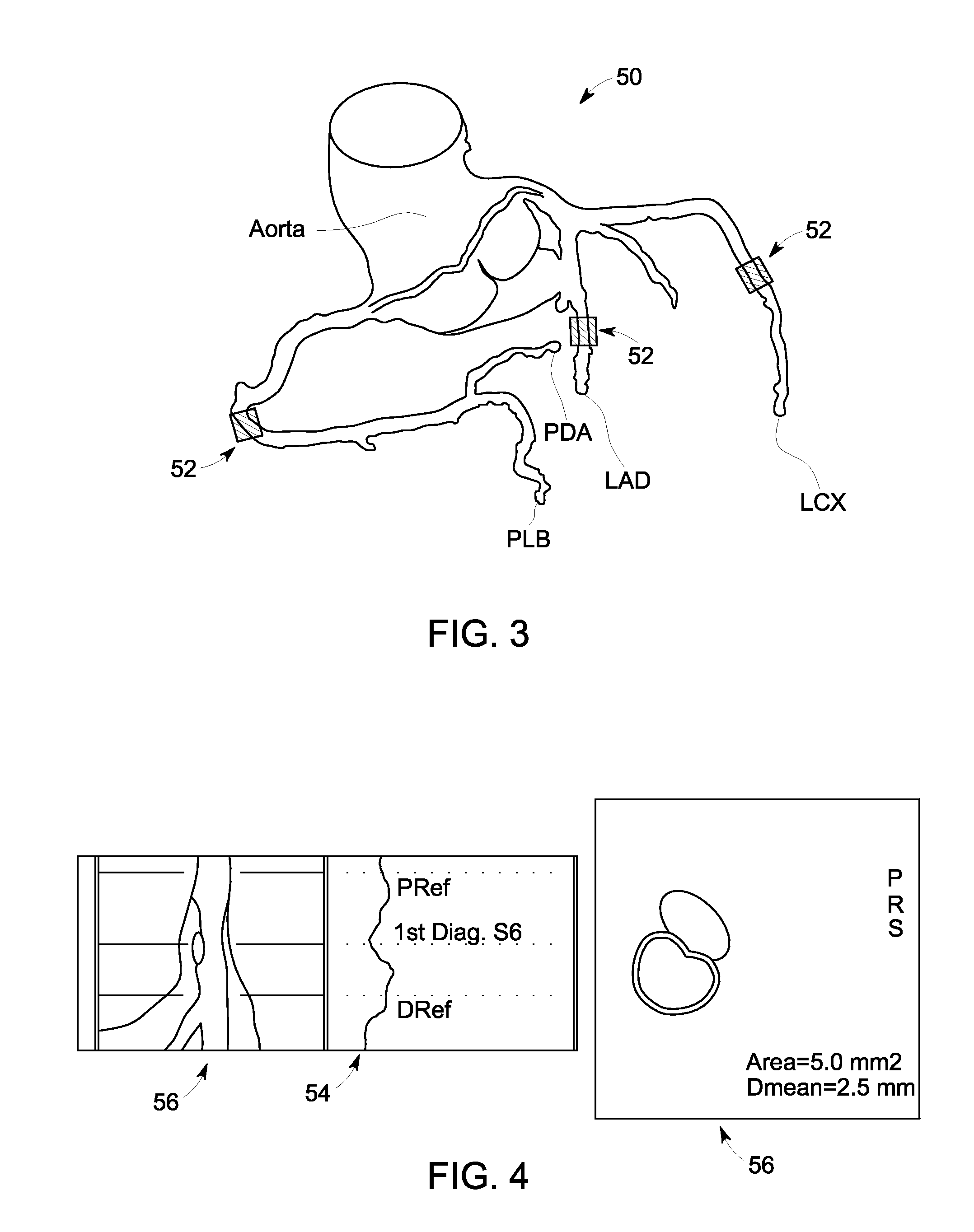
ActiveUS20120076377A1For accurate visualizationQuantitative precisionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayData acquisition
A system and method for dual energy CT spectral imaging that provides for accurate blood vessel stenosis visualization and quantification is disclosed. The CT system includes an x-ray source configured to project x-rays toward a region-of-interest of a patient that includes a blood vessel in a stenosed condition and having a plaque material therein. The CT system also includes an x-ray detector to receive x-rays emitted by the x-ray source and attenuated by the region-of-interest, a data acquisition system (DAS) operably connected to the x-ray detector, and a computer programmed to obtain a first set of CT image data for the region-of-interest at a first chromatic energy level, obtain a second set of CT image data for the region-of-interest at a second chromatic energy level that is higher than the first chromatic energy level, and identify plaque material in the region-of-interest by analyzing the second set of CT image data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system for distinctively displaying selected floor with sufficient details in a three-dimensional building model
ActiveUS8233008B2Fine granularitySufficient detailCathode-ray tube indicatorsSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsFloor level
A method, system and program product for distinctively displaying selected floors with sufficient details in a three-dimensional building model includes graphical metaphors that permit a selected or highlighted floor and their respective elements to be absolutely clear and distinct from the floors immediately above and below. The graphically displayed metaphors comprise “drawers”, “wireframe”, “expansion / compression”, “projected floor”, “sliding unselected floors”, “turning the pages”, “big map-small map”, and “fisheye” graphical configurations. Such graphically displayed metaphors can be utilized to highlight a selected floor, separate it from adjacent floors, and provide a graphical effect of depicting the floor's vertical position within a building.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Imageable biopsy site marker
InactiveUS20060084865A1Accurately exciseAccurate removalLuminescence/biological staining preparationOrgan movement/changes detectionRadiologyPiston
A biopsy site marker having at least one small marker body or pellet of bioresorbable material such as gelatin, collagen, polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid which has a radiopaque object, preferably with a non-biological configuration. The at least one bioresorbable body or pellet with a radiopaque object is deposited into the biopsy site, by an delivery device that includes an elongated tubular body with a piston slidable within the tubular body. One end of the tube is placed into the biopsy site. At least one but preferably several marker bodies or pellets are deposited sequentially into the biopsy site through the tube. At least the bioresorbable materials of the detectable markers remain present in sufficient quantity to permit detection and location of the biopsy site at a first time point (e.g., 2 weeks) after introduction but clear from the biopsy site or otherwise do not interfere with imaging of tissues adjacent the biopsy site at a second time point (e.g., 5-7 months) after introduction.
Owner:SENORX
Eyeglass lens with multiple optical zones having varying optical properties for enhanced visualization of different scenes in outdoor recreational activities
A lens for eyeglasses is provided with two or more optical zones on the lens body having different optical properties that enhance visualization of different scenes, including target objects within the scenes, that are associated with a specific recreational activity such as tennis, skiing, golf, hunting, or fishing. A first optical zone in an upper portion of the lens can be provided with pre-defined focus distance, transmission percentage, and / or transmission spectrum parameters for enhanced visualization of distant scenes associated with the specific recreational activity. A second optical zone in a lower or outer portion of the lens can be provided with different pre-defined focus distance, transmission percentage, and / or transmission spectrum parameters for enhanced visualization of close-in scenes associated with the specific recreational activity.
Owner:PEAKVISION SPORTS LLC
Method and system for distinctively displaying selected floor with sufficient details in a three-dimensional building model
ActiveUS20080177510A1Simple designAccelerate buildingCathode-ray tube indicatorsSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsFloor level
A method, system and program product for distinctively displaying selected floors with sufficient details in a three-dimensional building model includes graphical metaphors that permit a selected or highlighted floor and their respective elements to be absolutely clear and distinct from the floors immediately above and below. The graphically displayed metaphors comprise “drawers”, “wireframe”, “expansion / compression”, “projected floor”, “sliding unselected floors”, “turning the pages”, “big map-small map”, and “fisheye” graphical configurations. Such graphically displayed metaphors can be utilized to highlight a selected floor, separate it from adjacent floors, and provide a graphical effect of depicting the floor's vertical position within a building.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
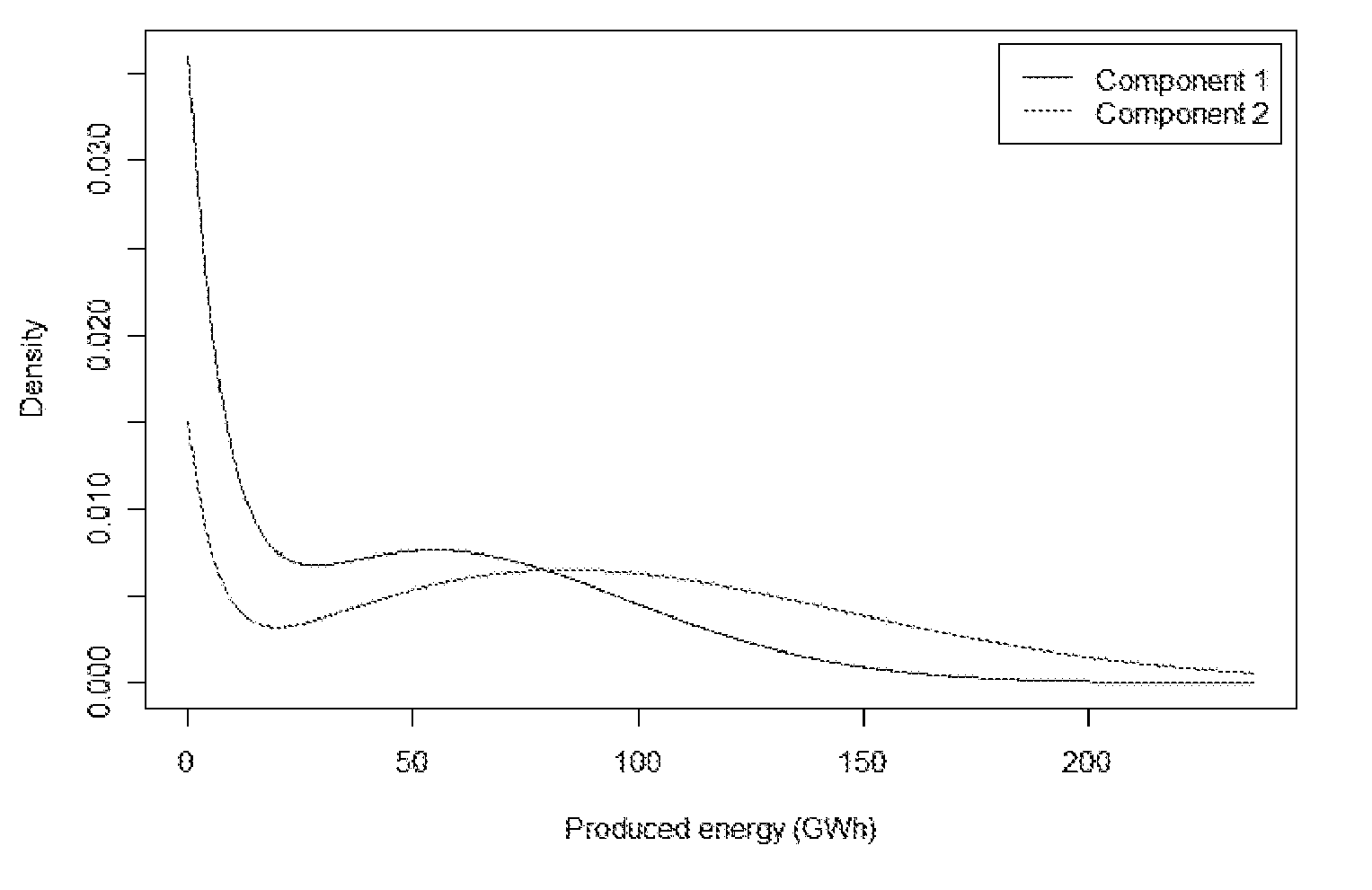
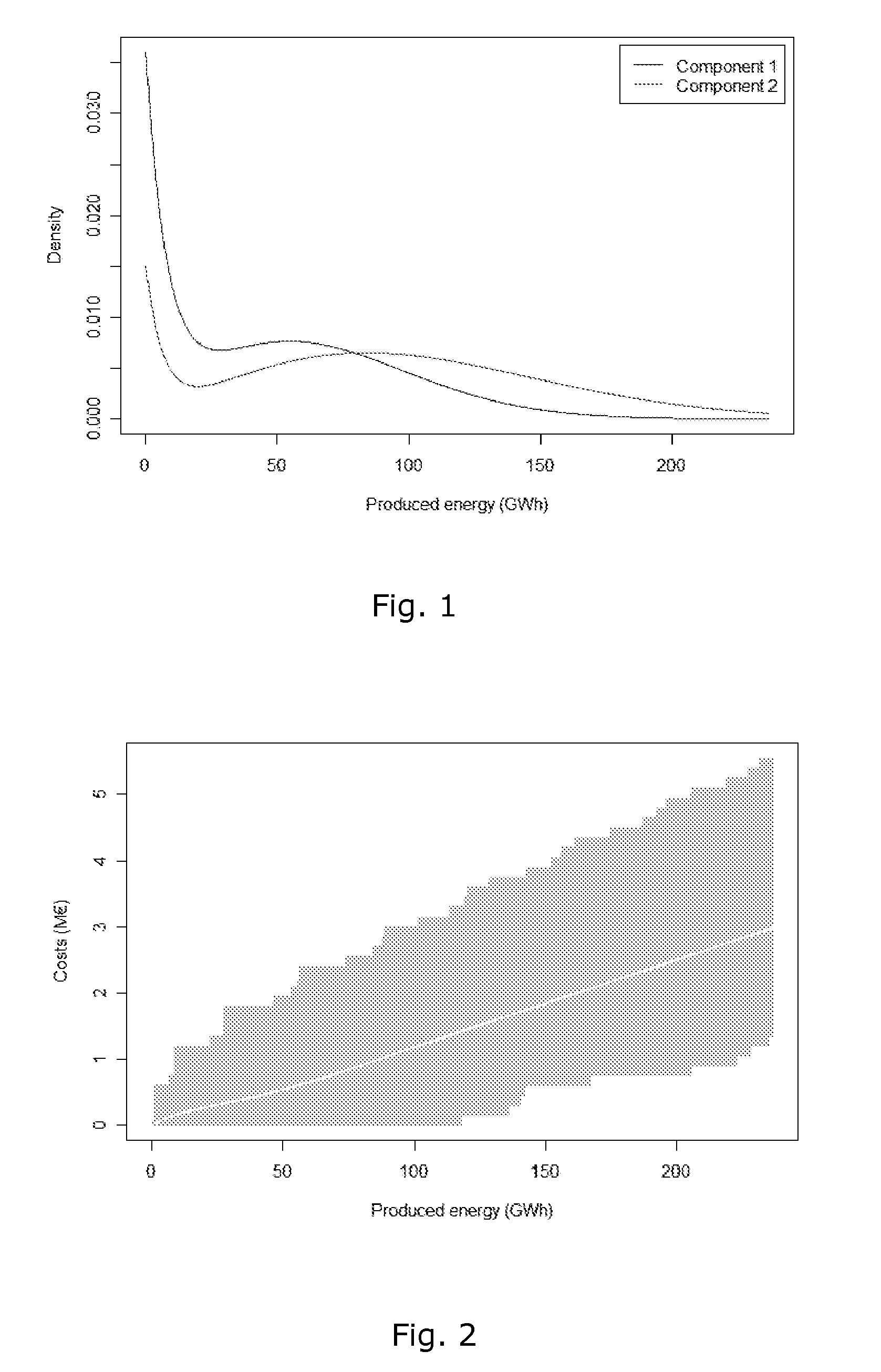
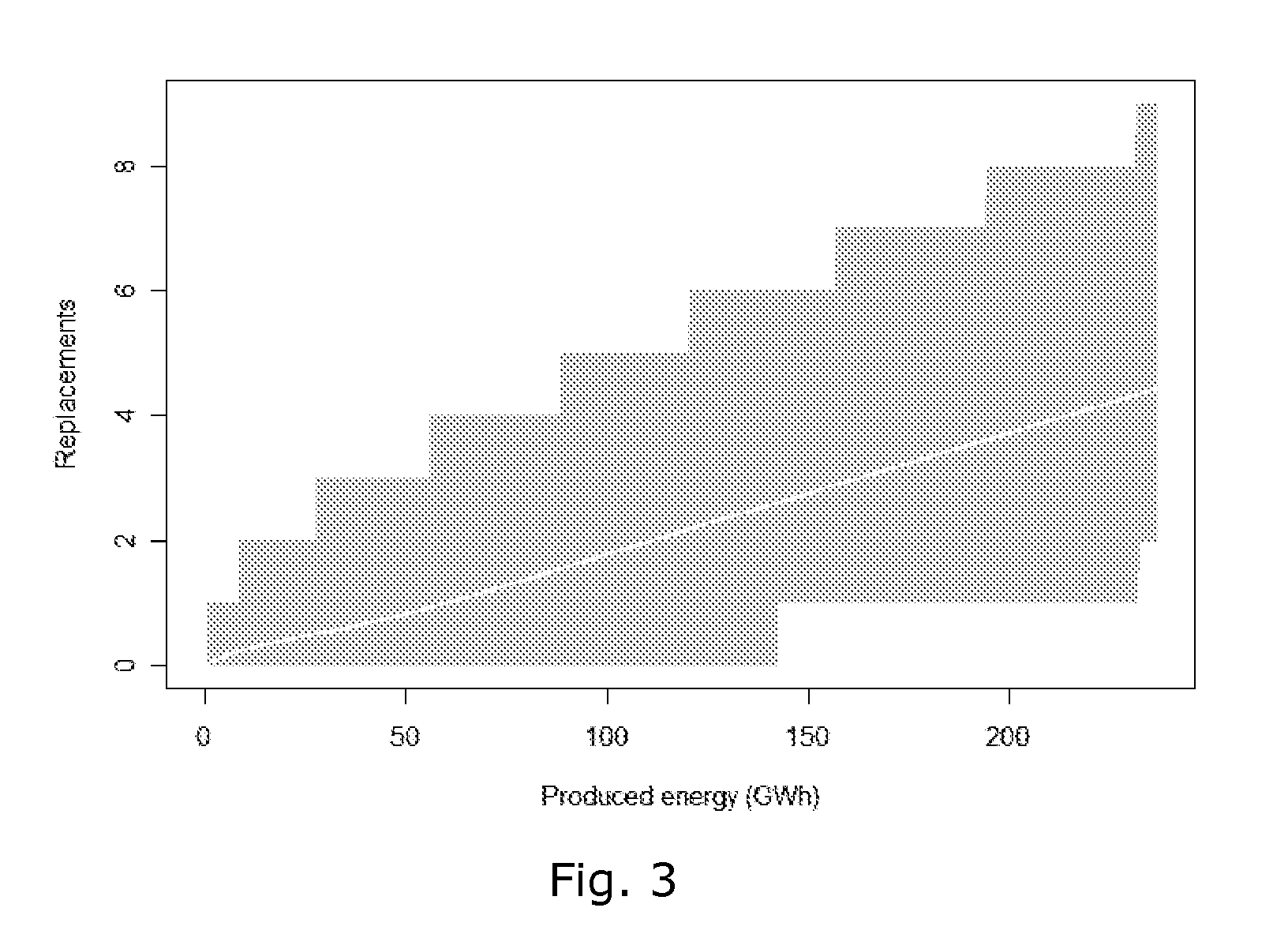
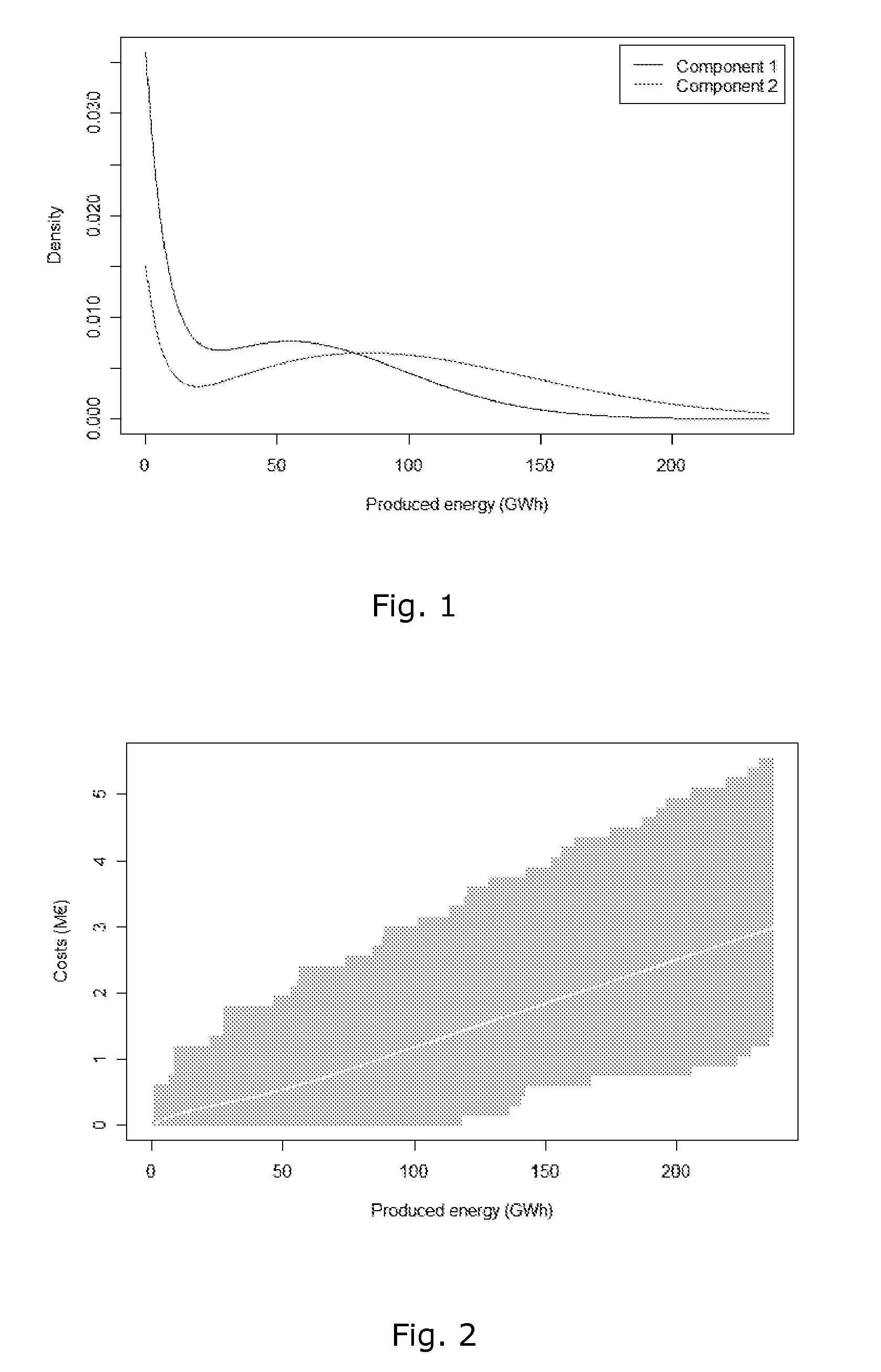
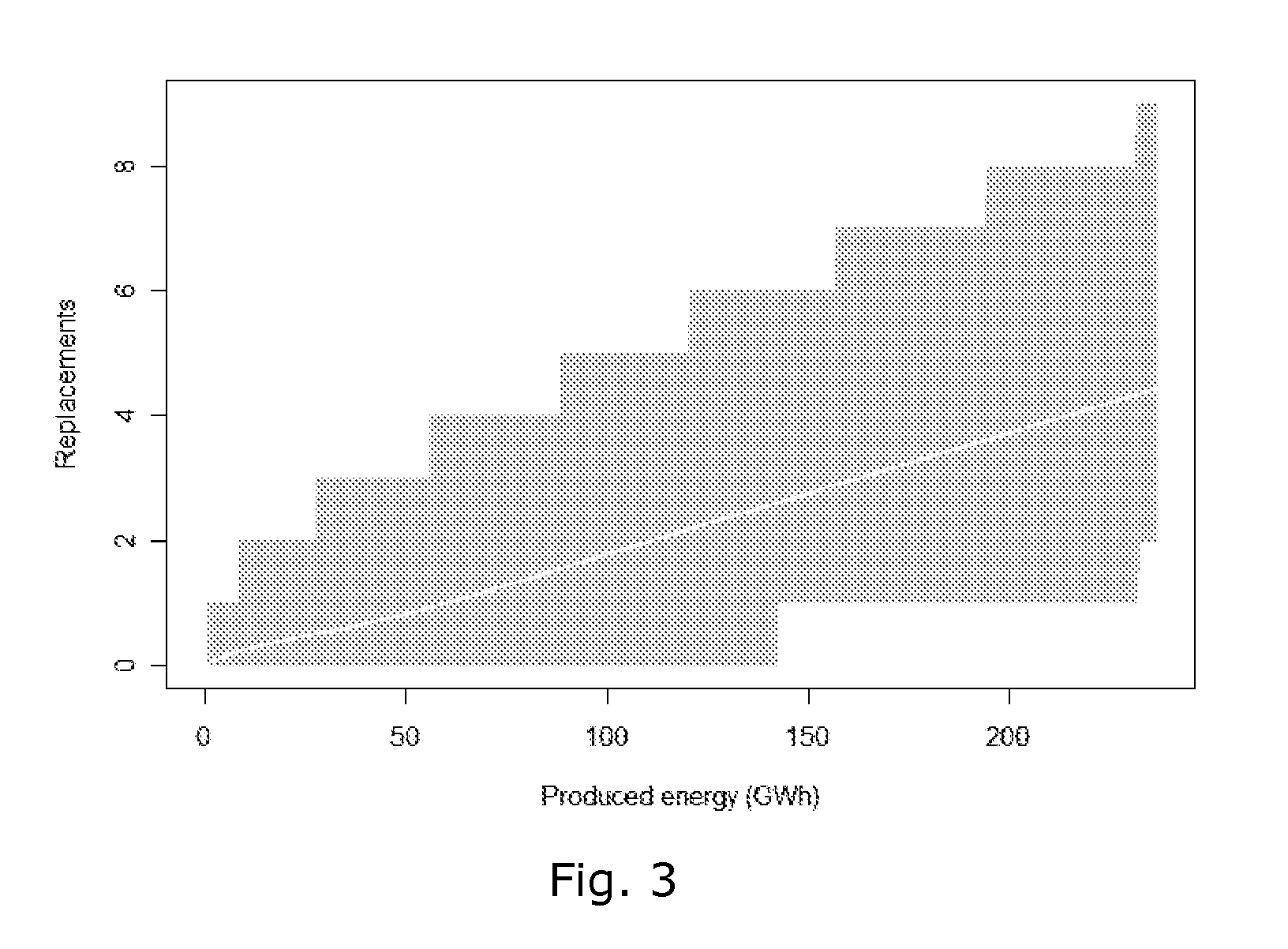
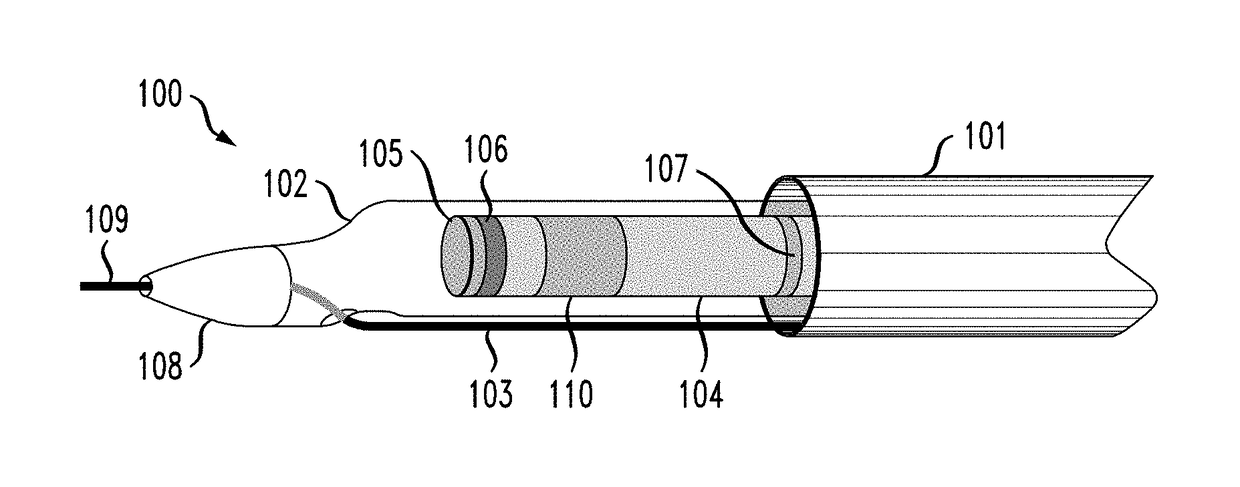
Wind Turbine Siting and Maintenance Prediction
ActiveUS20100312594A1Expensive computationsFor accurate visualizationOptimise machine performanceMachines/enginesEngineeringTurbine
A computer-implemented method for determining a site for a wind turbine within a confined geographical target region on the basis of an estimate of a maintenance parameter comprises determining a wind climate at the target region, the wind climate including e.g. average wind speed, pre-dominant wind directions, or turbulence intensities. A function expressing the maintenance parameter of the wind turbine as a function of the flow characteristics is defined, and the function is applied to the geographical position to compute an estimated value of the maintenance parameter at that position. Meteorological measurements may be used to obtain the flow characteristics. Wind measurements performed at one location may be numerically extrapolated by numerical methods, e.g. by CFD, to other locations. The maintenance parameter may be expressed as a maintenance risk, number of component replacements, or as a maintenance cost per energy unit. Three-dimensional visualization of wind turbines, e.g. in GoogleEarth™ is further provided by the invention.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Methods for mapping data into lower dimensions
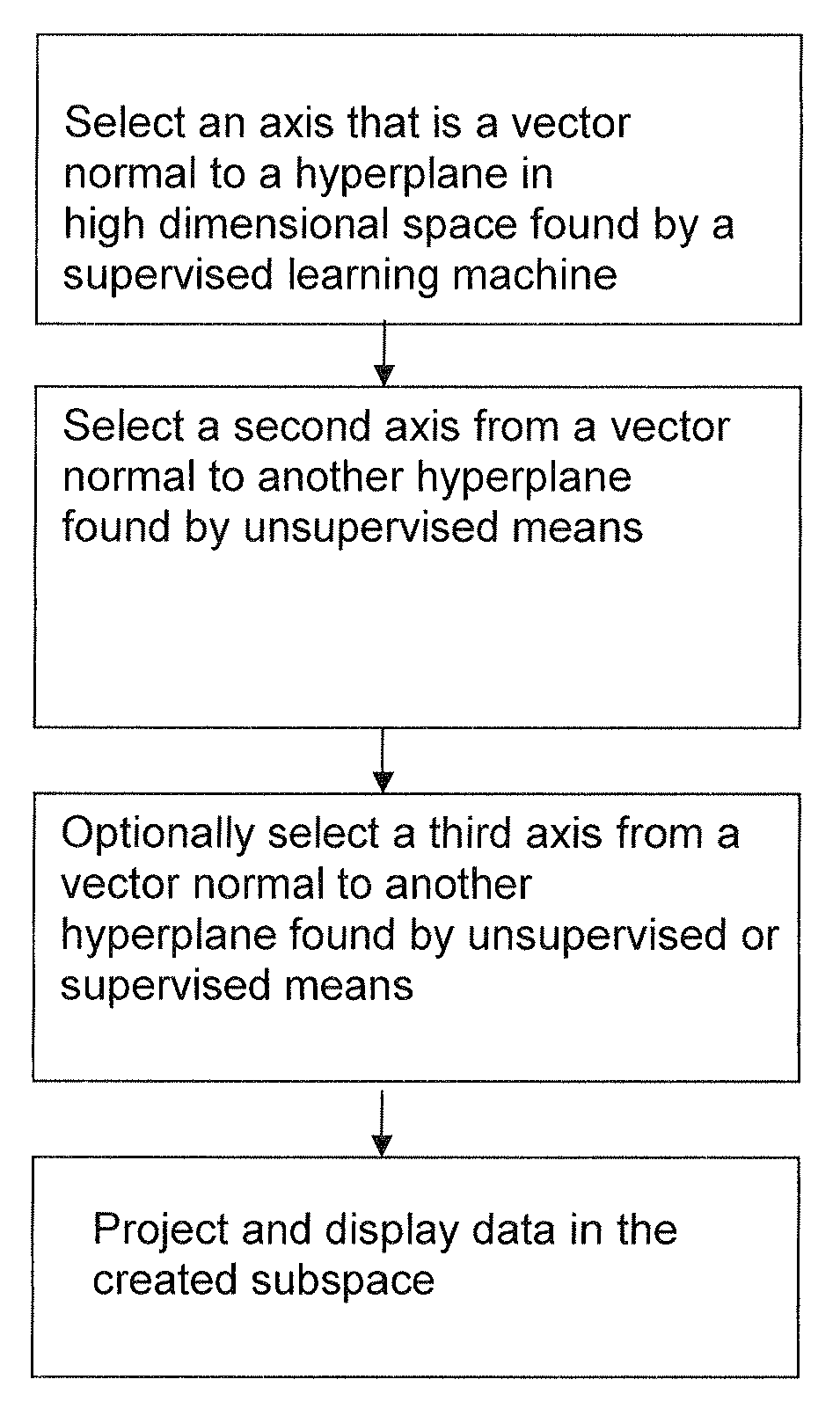
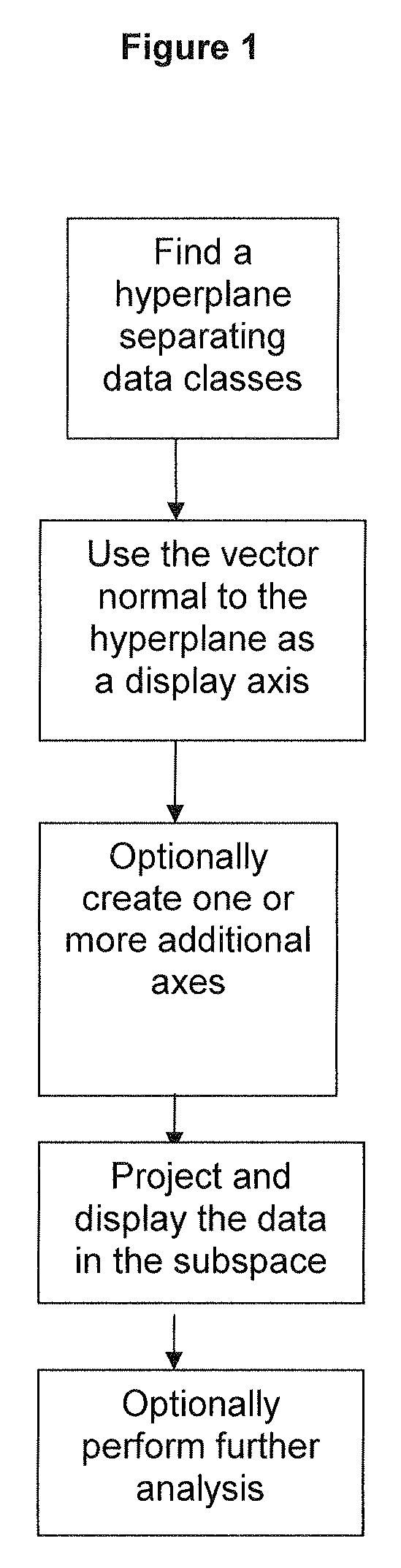
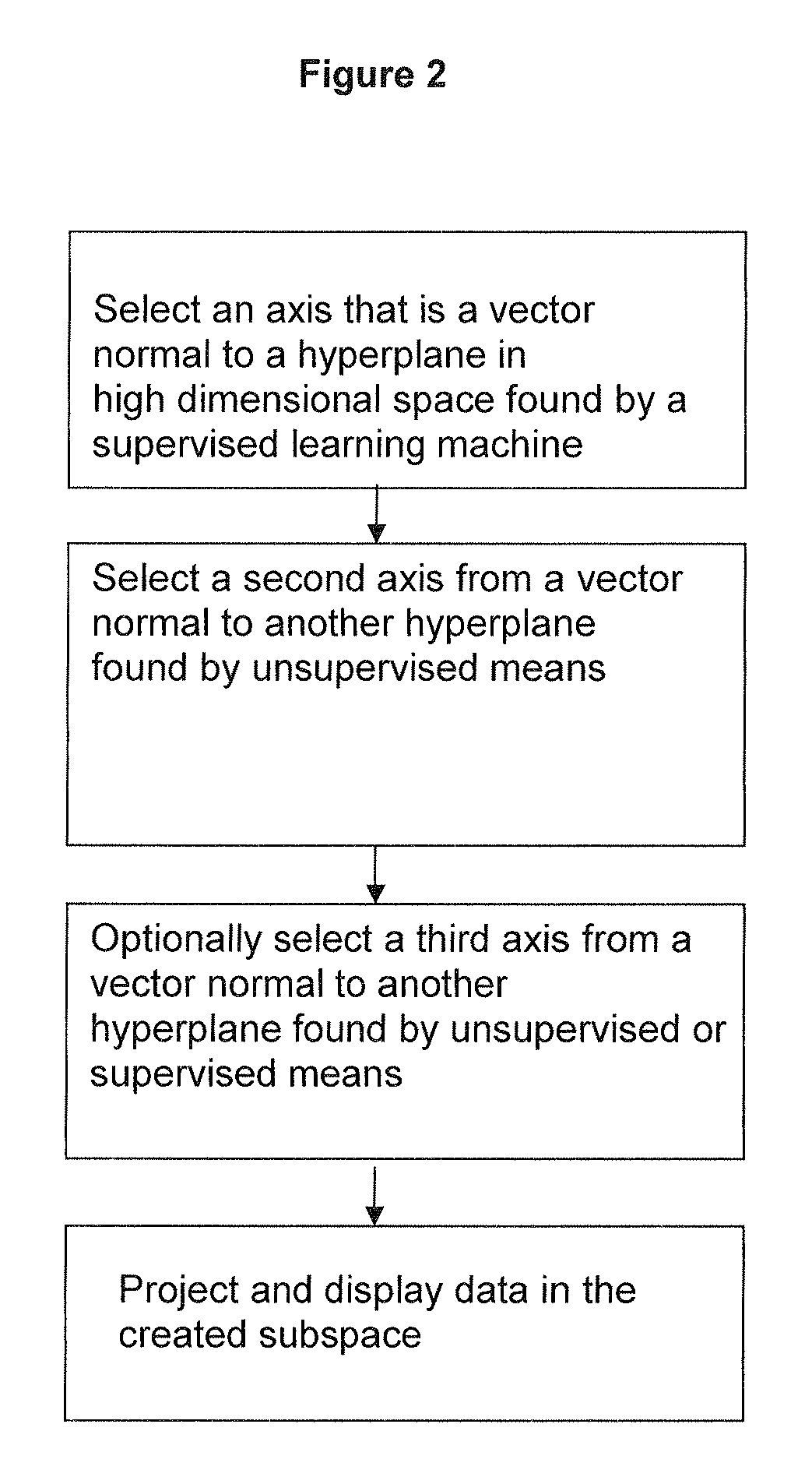
ActiveUS8812274B2Easy to useLighten the computational burdenKernel methodsDigital computer detailsAnalysis dataSupervised learning
Methods and systems for creating ensembles of hypersurfaces in high-dimensional feature spaces, and to machines and systems relating thereto. More specifically, exemplary aspects of the invention relate to methods and systems for generating supervised hypersurfaces based on user domain expertise, machine learning techniques, or other supervised learning techniques. These supervised hypersurfaces may optionally be combined with unsupervised hypersurfaces derived from unsupervised learning techniques. Lower-dimensional subspaces may be determined by the methods and systems for creating ensembles of hypersurfaces in high-dimensional feature spaces. Data may then be projected onto the lower-dimensional subspaces for use, e.g., in further data discovery, visualization for display, or database access. Also provided are tools, systems, devices, and software implementing the methods, and computers embodying the methods and / or running the software, where the methods, software, and computers utilize various aspects of the present invention relating to analyzing data.
Owner:VIRKAR HEMANT V
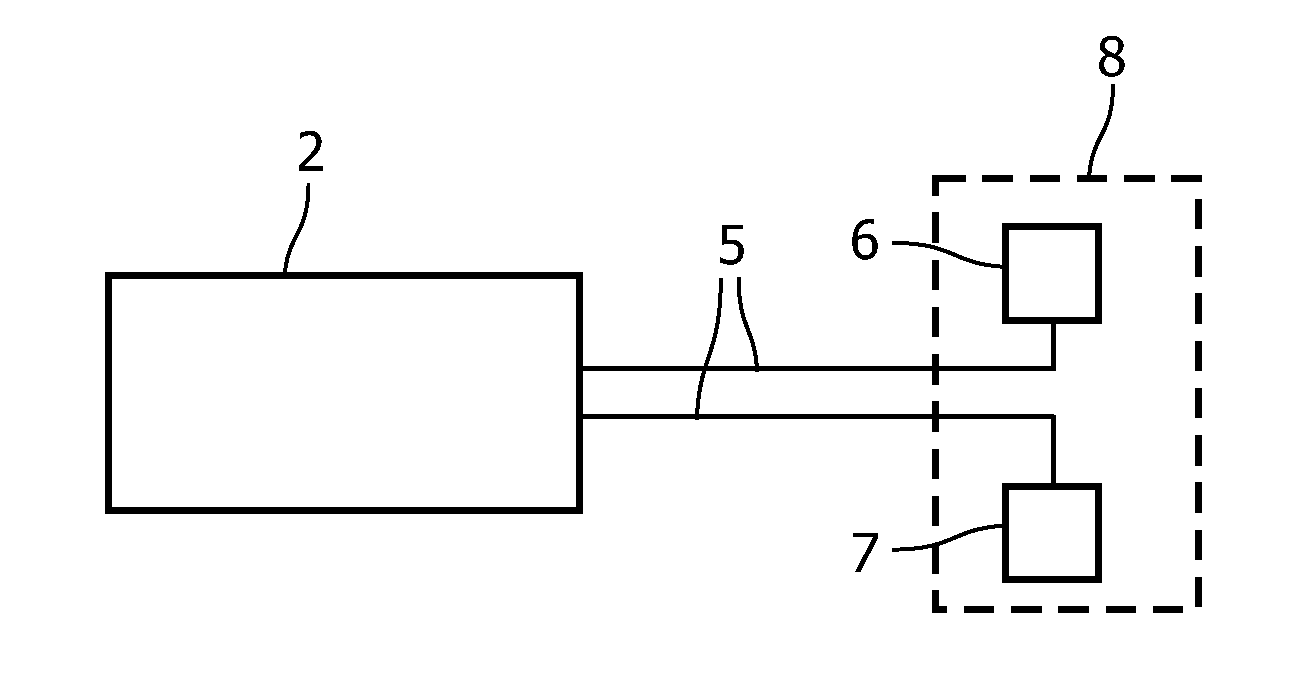
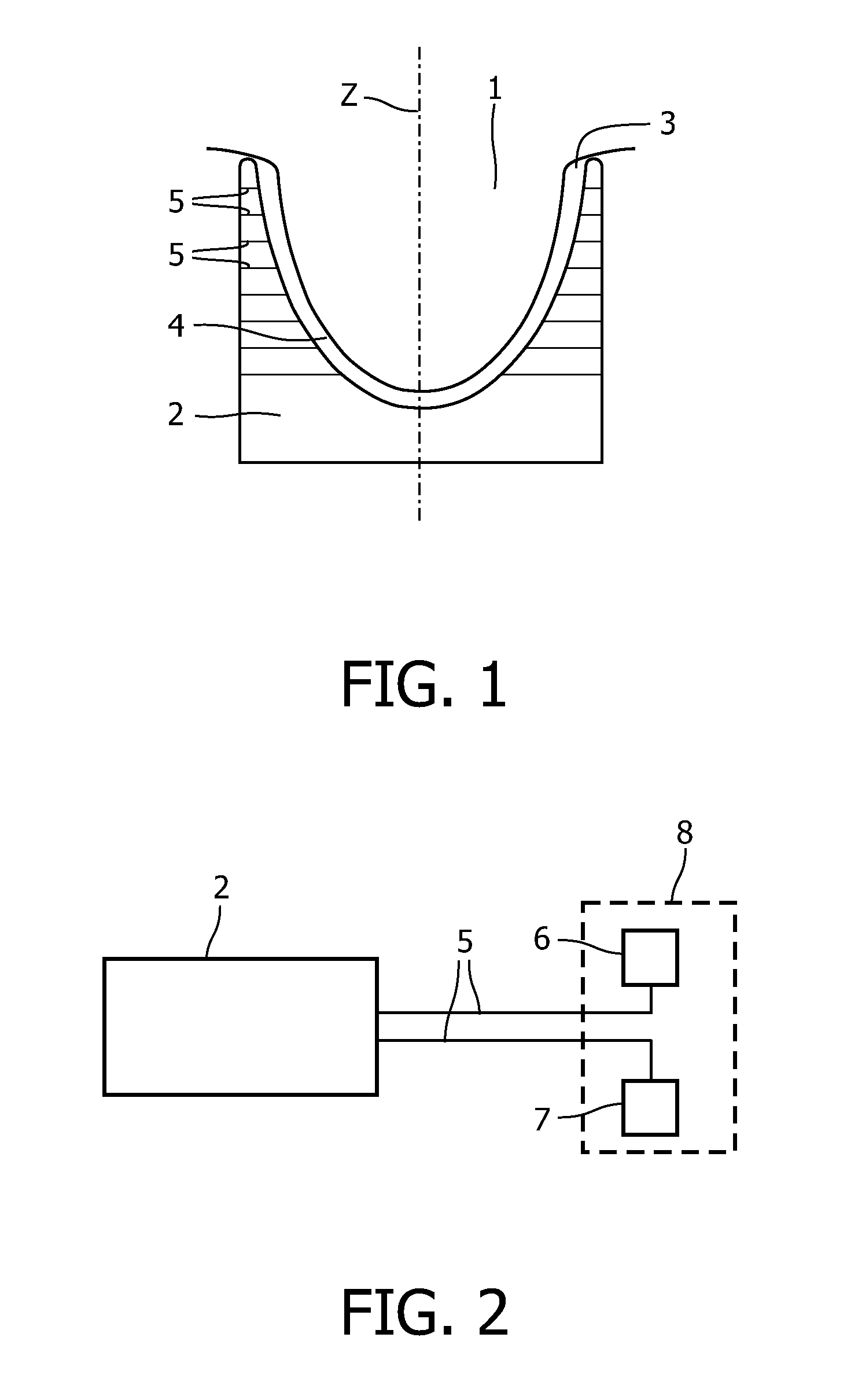
Method for reconstructing a fluorescent image of the interior of a turbid medium and device for imaging the interior of a turbid medium
InactiveUS8520921B2Accurately determineHigh precisionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPhotometryUltrasound attenuationFluorescence
A method for reconstructing a fluorescence image of the interior of a turbid medium is provided. The method comprises the step: accommodating a turbid medium (1) to which a fluorescent contrast agent has been administered in a measurement volume (4). The fluorescent contrast agent is capable of emitting light in a first range of wavelengths upon irradiation with light. The method further comprises: performing attenuation measurements at a plurality of different wavelengths (λi, . . . , λk) by subsequently irradiating the turbid medium (1) with light from a plurality of different source positions and detecting light emanating from the turbid medium (1) in a plurality of detection positions for each source position; reconstructing absorption properties (μa(r, λ) as a function of the position in the interior of the turbid medium (1) for the plurality of different wavelengths from the attenuation measurements; calculating absorption properties as a function of the position in the interior of the turbid medium (1) for wavelengths of the first range of wavelengths; performing a fluorescence measurement by subsequently irradiating the turbid medium (1) with light causing the fluorescent contrast agent to emit light in the first range of wavelengths from the plurality of source positions and detecting the light emanating from the fluorescent contrast agent in the plurality of detection positions for each source position; and reconstructing a fluorescence image of the spatial distribution of the fluorescent contrast agent in the interior of the turbid medium (1) from the fluorescence measurement using the calculated absorption properties.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
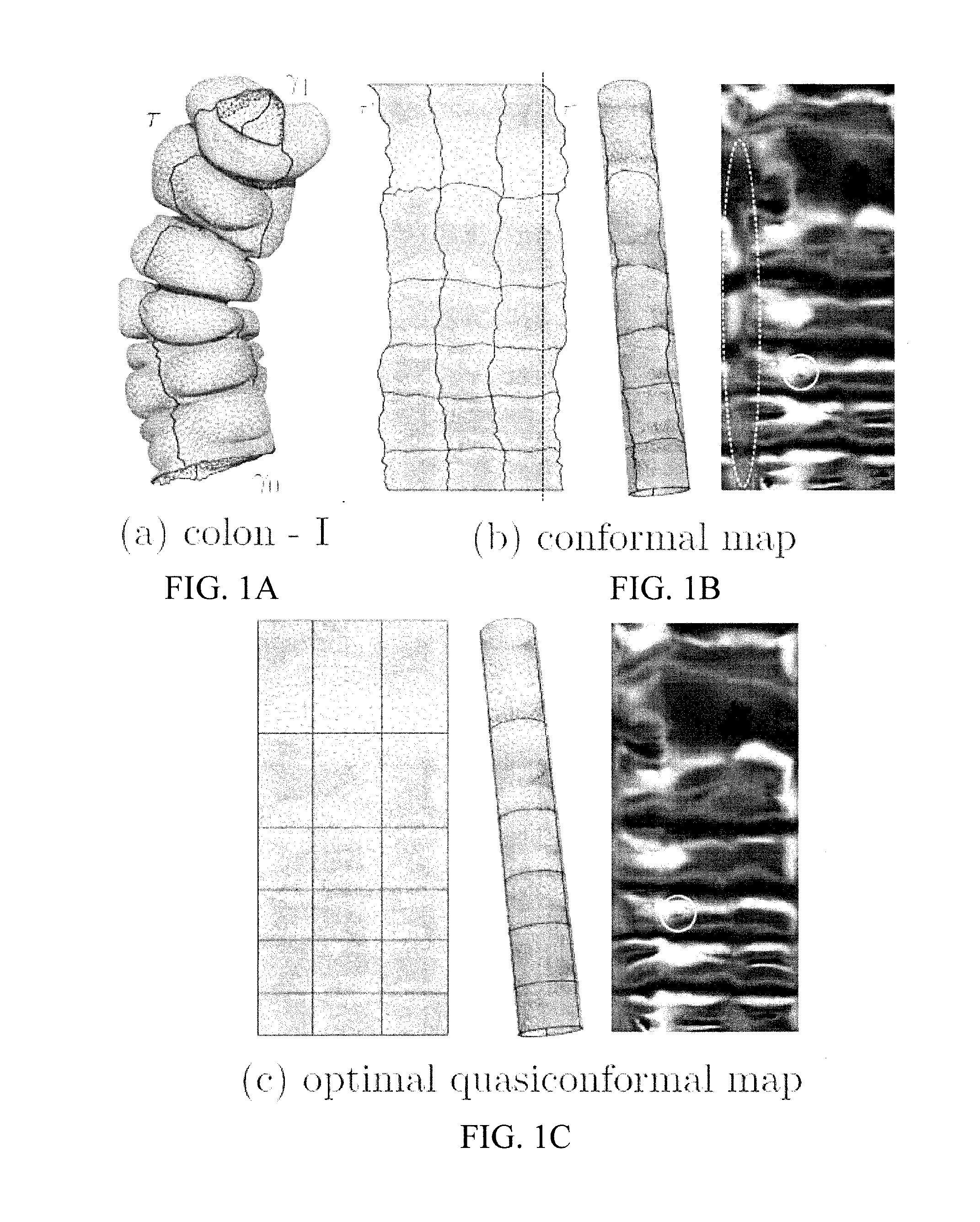
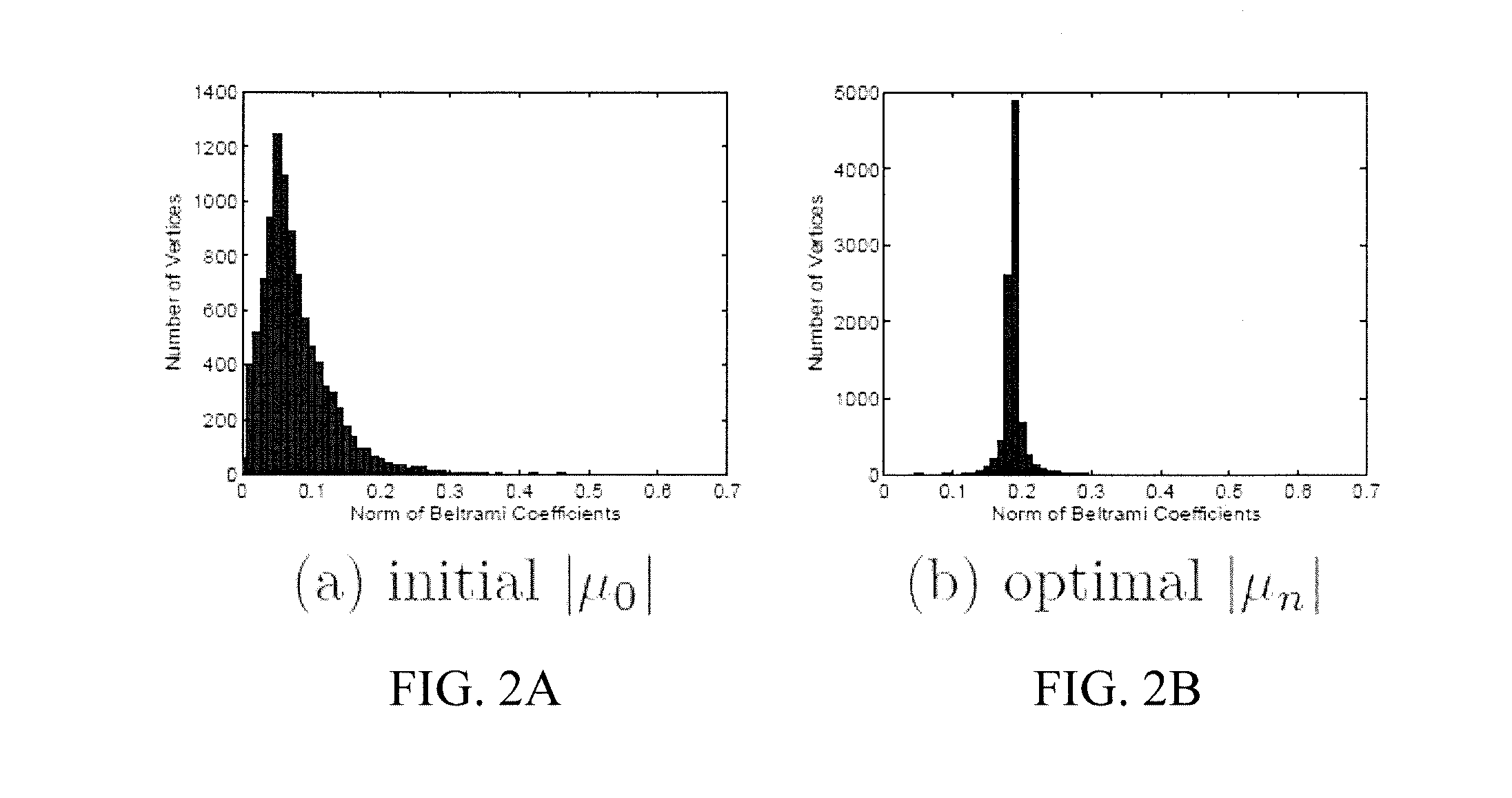
Systems and methods for shape analysis using landmark-driven quasiconformal mapping
ActiveUS20160350979A1Efficient flatteningTime complexityImage enhancementImage analysisDistortionLandmark
Methods, systems, and computer-readable media that can perform novel and effective flattening of an image are provided. The flattening can be based on quasiconformal mapping. Such mapping can be used to straighten the main landmark curves with least conformality (angle) distortion. This technique can be referred to as quasiconformal straightening (QCS), and it can provide a canonical and straightforward view of convoluted surfaces. The computation can be based on the holomorphic 1-form method with landmark straightening constraints and quasiconformal optimization.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
System and method for blood vessel stenosis visualization and quantification using spectral CT analysis
ActiveUS8494244B2For accurate visualizationQuantitative precisionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingData acquisitionX-ray
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for blood vessel stenosis visualization and navigation
InactiveUS20130066197A1Precise NavigationFor accurate visualizationImage enhancementImage analysis3d imageX-ray
A system and method for blood vessel stenosis visualization and navigation is disclosed. The CT system includes a rotatable gantry having an opening to receive a patient, an x-ray source positioned on the rotatable gantry to project x-rays toward a region-of-interest (ROI) of the patient that includes a plurality of blood vessels, an x-ray detector positioned on the rotatable gantry to receive x-rays emitted by the x-ray source and attenuated by the ROI, and a DAS operably connected to the x-ray detector. The CT system also includes a computer programmed to obtain CT image data for the ROI, reconstruct a 3D image of the plurality of blood vessels from the CT image data, automatically detect pathologies in the plurality of blood vessels, and identify the pathologies in the plurality of blood vessels on the 3D image, with a severity of the pathology being indicated on the 3D image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Medical viewing system and method for detecting boundary structures
InactiveUS7991453B2Increase awarenessFor accurate visualizationImage enhancementImage analysisMotion vectorGuide wires
A medical viewing system for displaying a sequence of medical images that represents moving and / or positioning a guide-wire in a blood vessel, which guide-wire has a guide-wire tip that is contrasted with respect to the guide wire, this system comprising acquisition means that acquires an original sequence of noisy images called live sequence and processing means for processing said live sequence of images in real time, the processing means comprising: first means (10) for automatically detecting the guide-wire tip, yielding skeleton information of the guide-wire tip and a field of motion vectors based on said skeleton information; second means (20) for automatically registering the guide-wire tip with respect to a reference based on the field of motion vectors and for enhancing the guide-wire and the vessel walls while blurring the background in the registered images; and comprising: Display means for displaying a live sequence of processed images.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
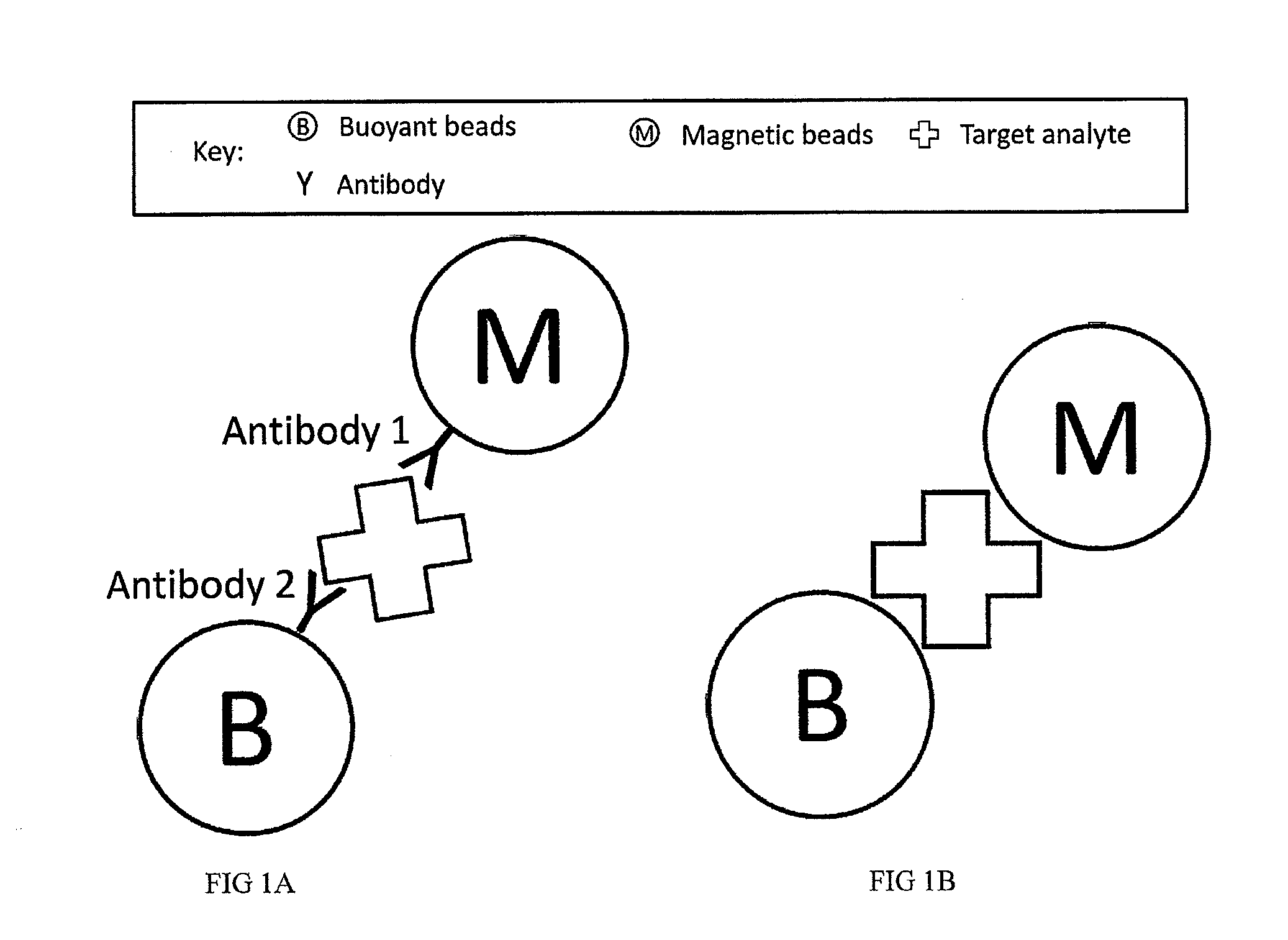
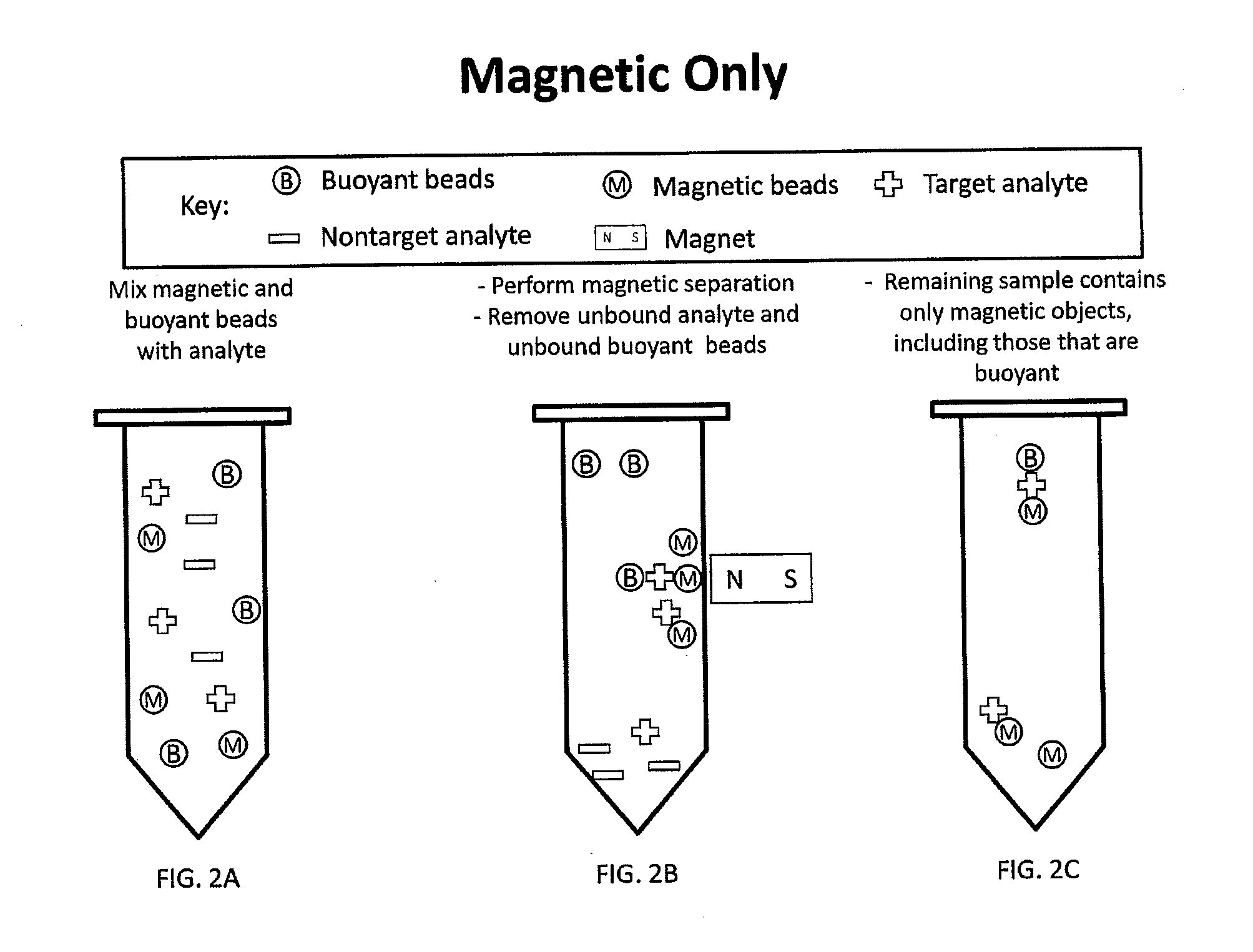
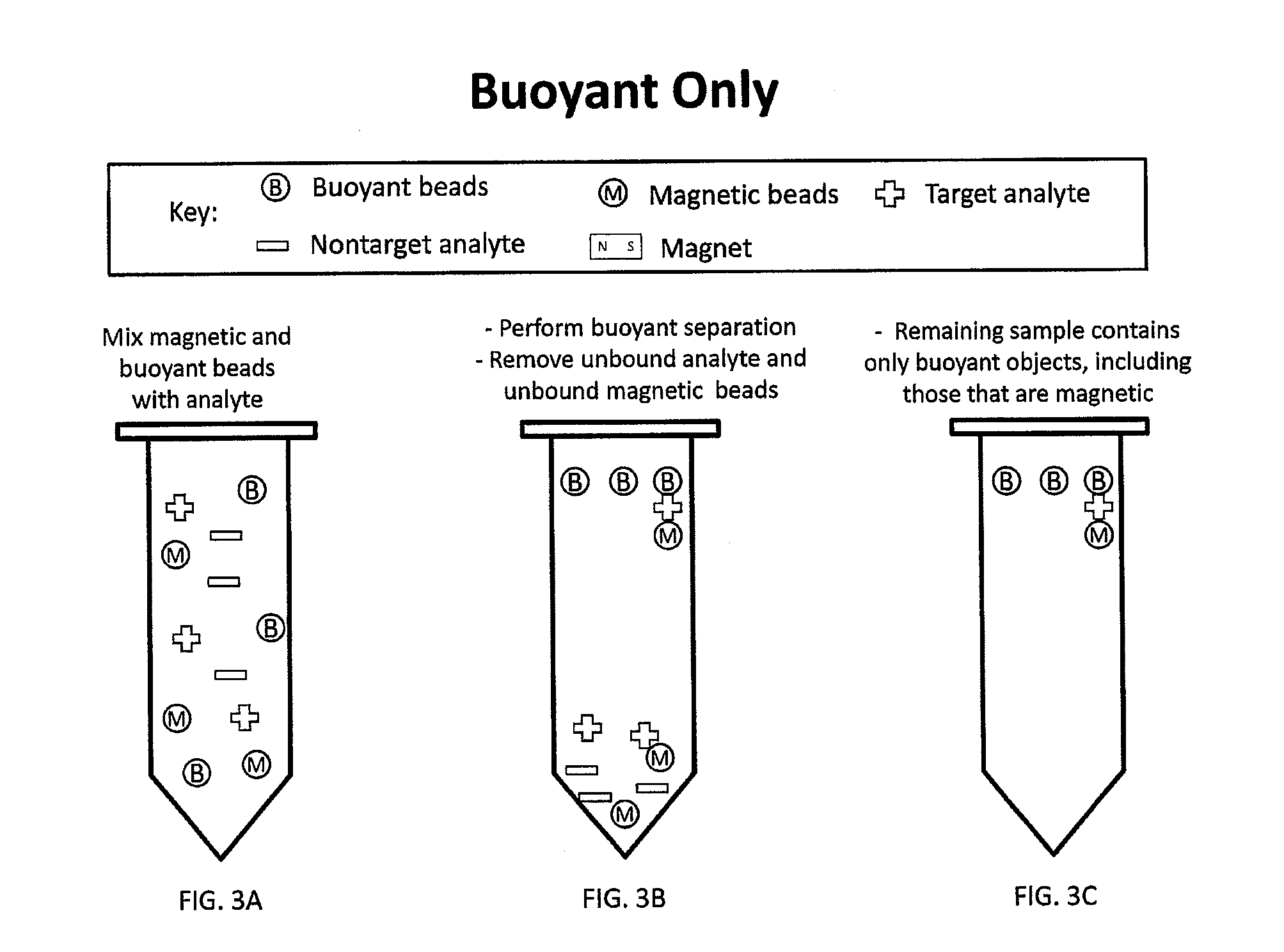
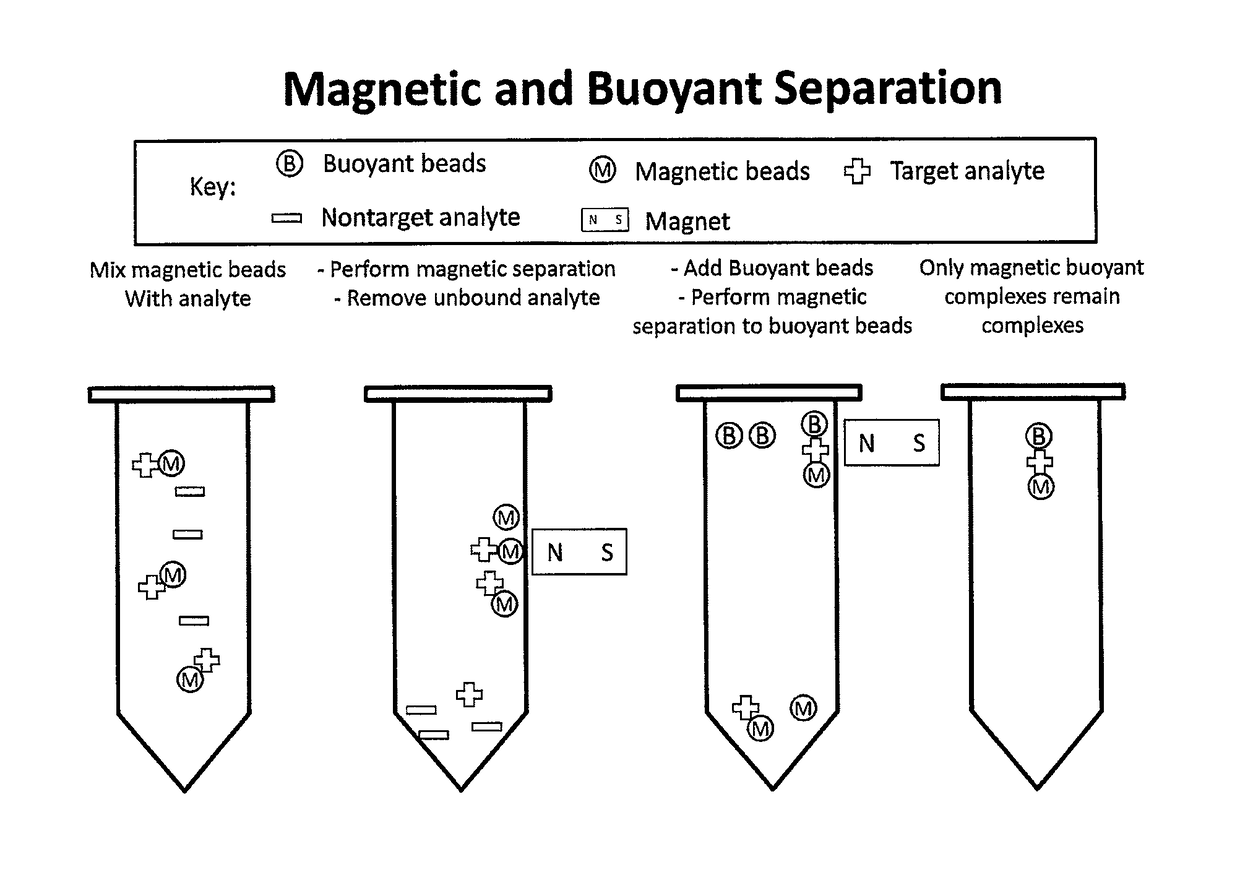
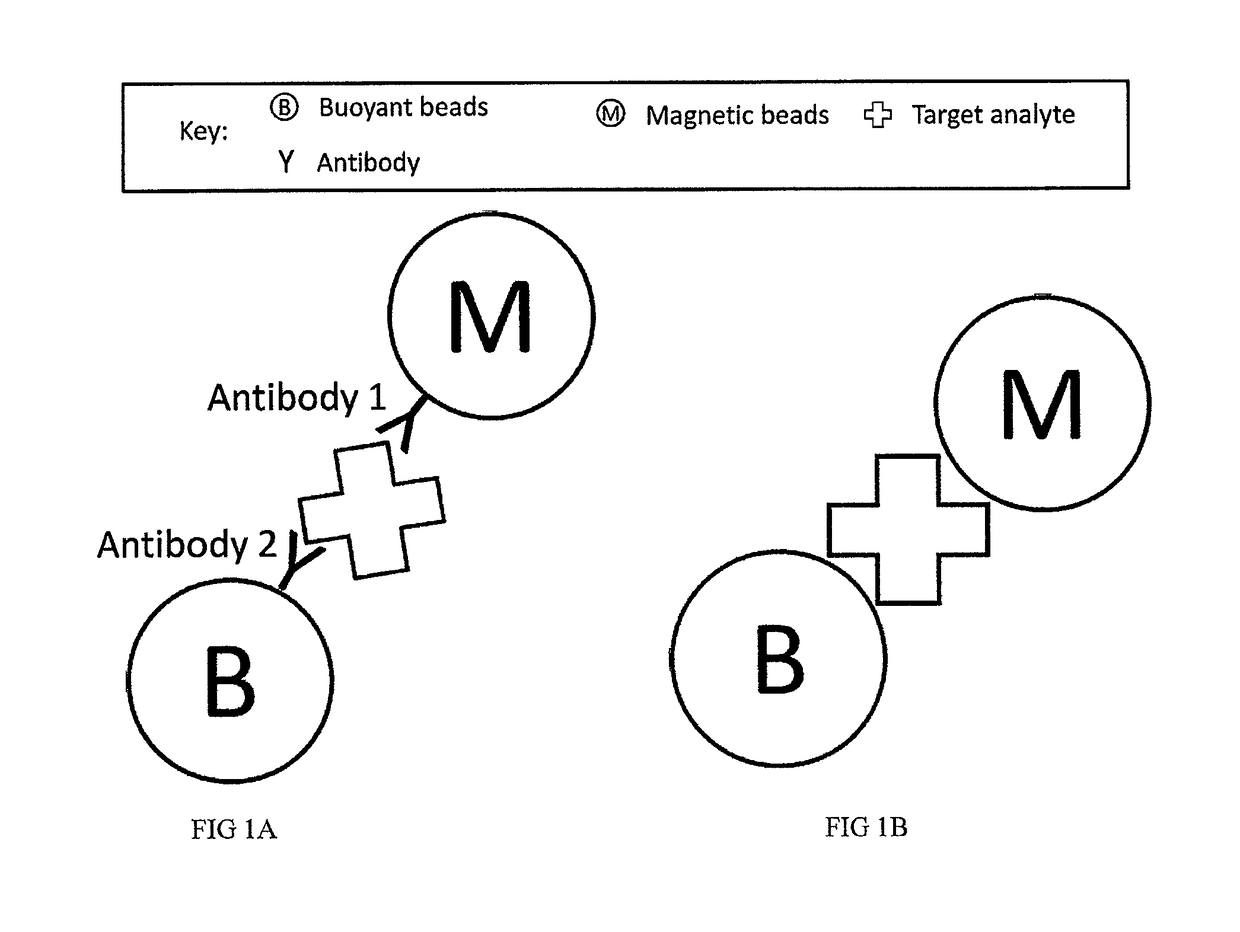
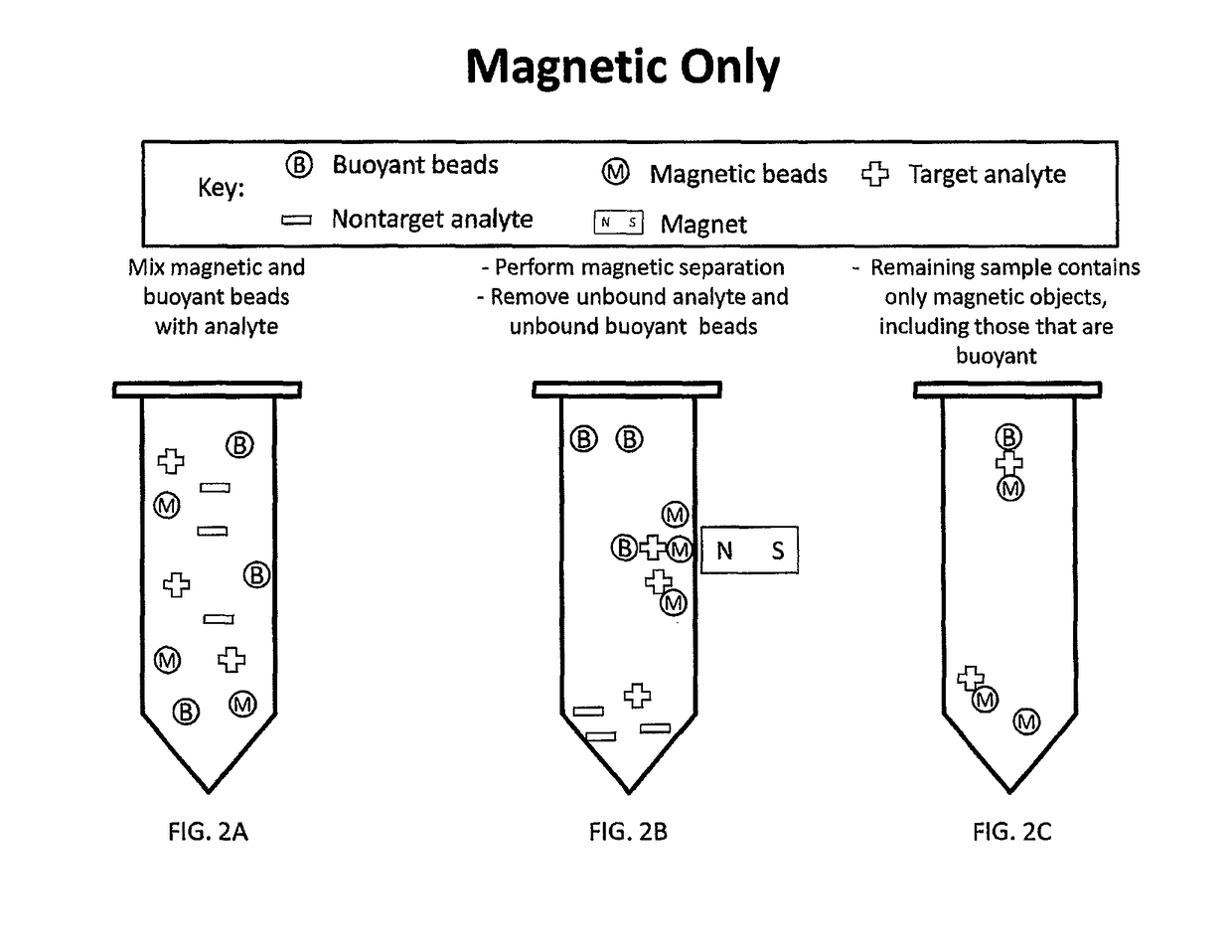
Multi-Mode Separation for Target Detection and Cell Growth Monitoring
ActiveUS20130337455A1Strong specificityEfficient removalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical physicsMagnetic bead
Sandwich separation is based on forming a sandwich complex with a magnetic bead, buoyant bead, and a target. Once a sandwich formation is created, the sandwich can be separated using its dual physical properties, namely magnetism and buoyancy. Sandwich separation is highly specific, allows for removal of the beads that do not have any attached target, and reduces the number of background beads. Sandwich separation can also be used to allow for target detection in raw specimen. Also, improvement of detection capability is accomplished by performing AMBR measurements on a solid interface, where the rotational period speeds up and allows for dramatically reduced time-to-result.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Thermochromic devices for vascular access procedures
InactiveUS20080146913A1Improved vein-locatingImproved vein-visualizationMedical devicesSensorsAdhesiveVenous structure
A device for locating a venous structure of a patient includes a frame having a bottom surface and a top surface, an adhesive disposed on the bottom surface of the frame to allow the frame to be removably attached to skin or a patient, and one or more sections removably attached to the top surface of the frame. The sections are formed of a liquid crystal material that is sensitive to human skin temperature ranges.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
Wind turbine siting and maintenance prediction
ActiveUS8495911B2Expensive computationsFor accurate visualizationOptimise machine performanceIndication/recording movementEngineeringTurbine
A computer-implemented method for determining a site for a wind turbine within a confined geographical target region on the basis of an estimate of a maintenance parameter comprises determining a wind climate at the target region, the wind climate including e.g. average wind speed, pre-dominant wind directions, or turbulence intensities. A function expressing the maintenance parameter of the wind turbine as a function of the flow characteristics is defined, and the function is applied to the geographical position to compute an estimated value of the maintenance parameter at that position. Meteorological measurements may be used to obtain the flow characteristics. Wind measurements performed at one location may be numerically extrapolated by numerical methods, e.g. by CFD, to other locations. The maintenance parameter may be expressed as a maintenance risk, number of component replacements, or as a maintenance cost per energy unit. Three-dimensional visualization of wind turbines, e.g. in GoogleEarth™ is further provided by the invention.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
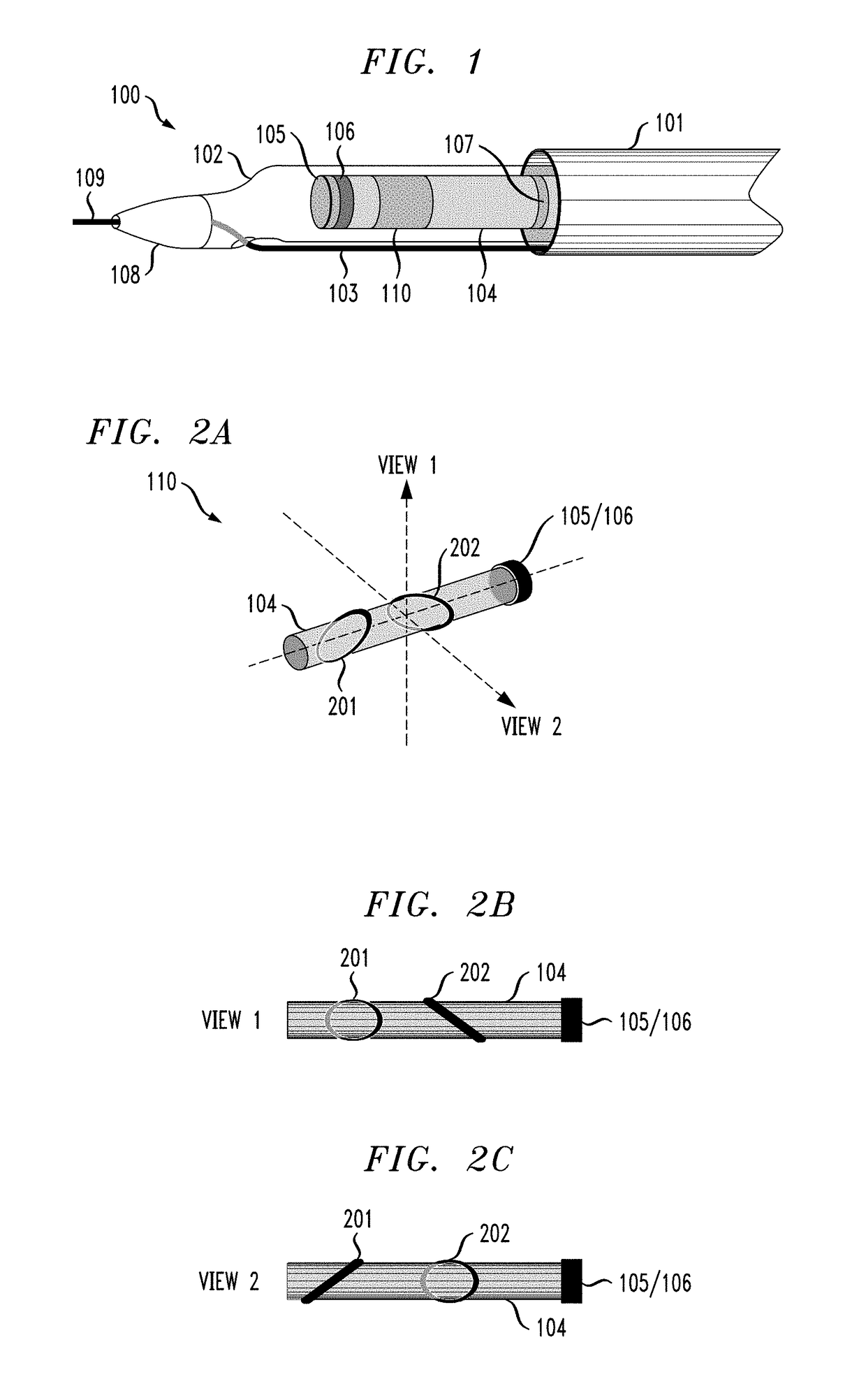
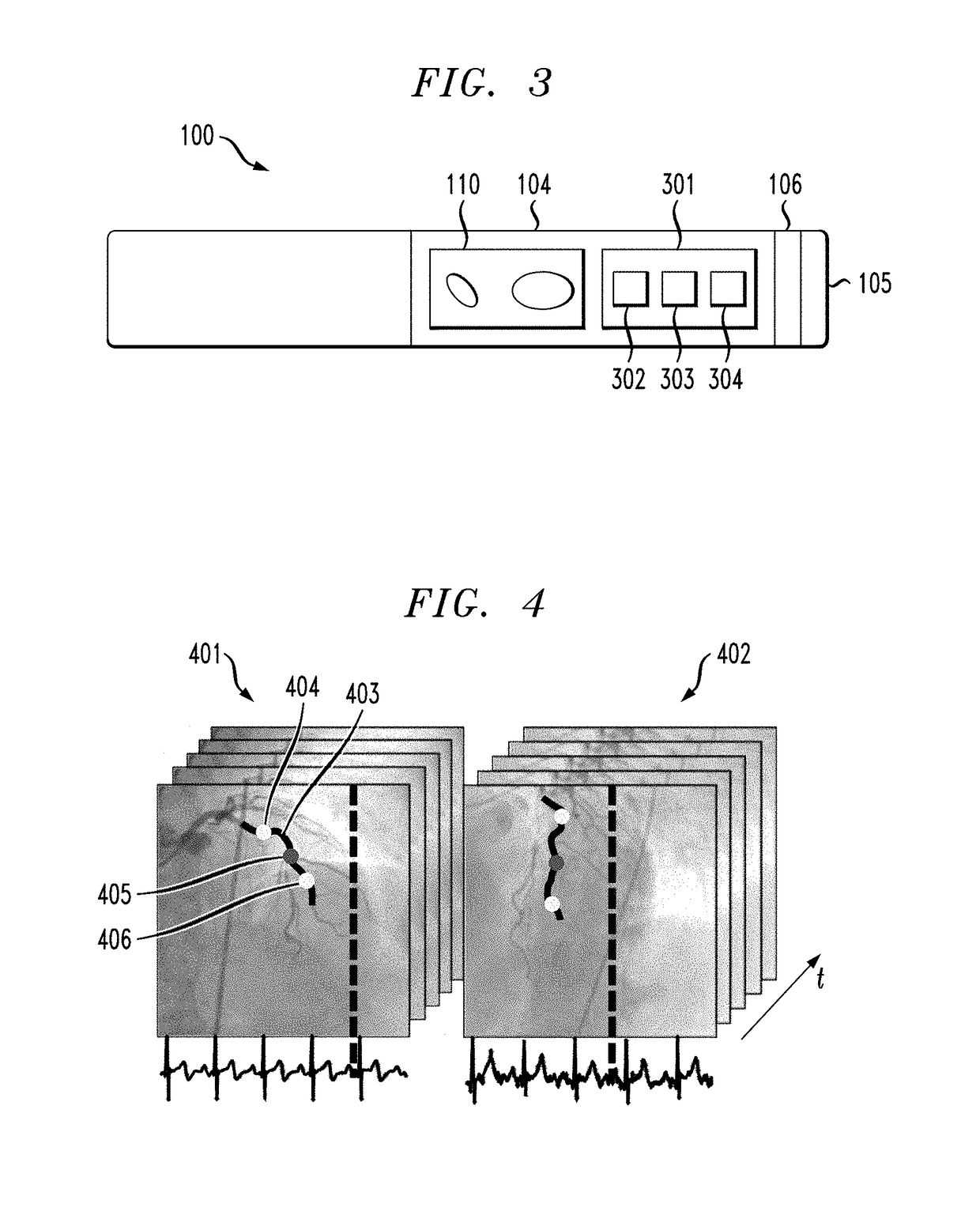
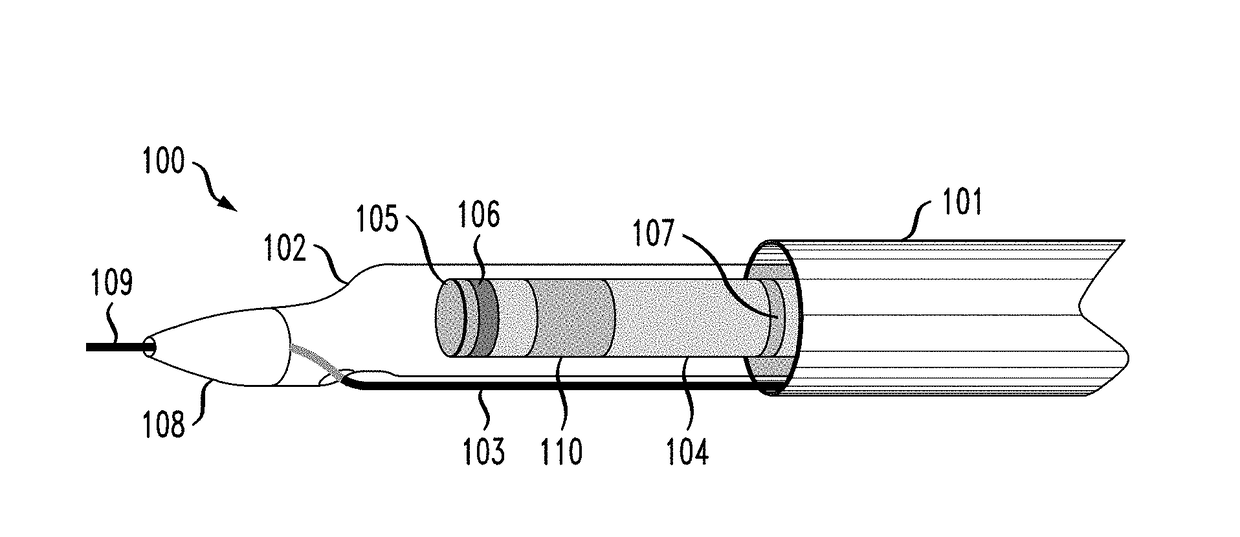
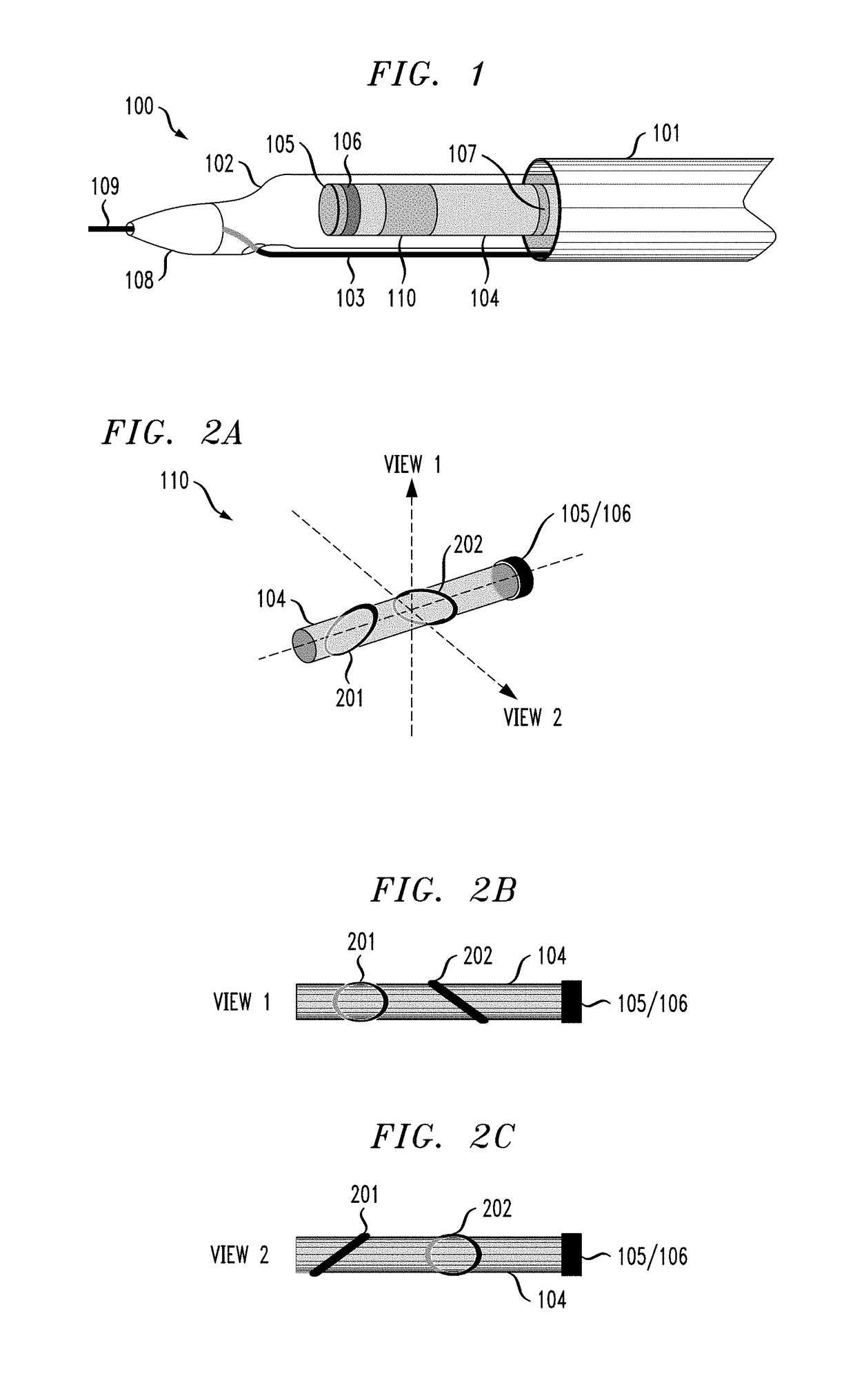
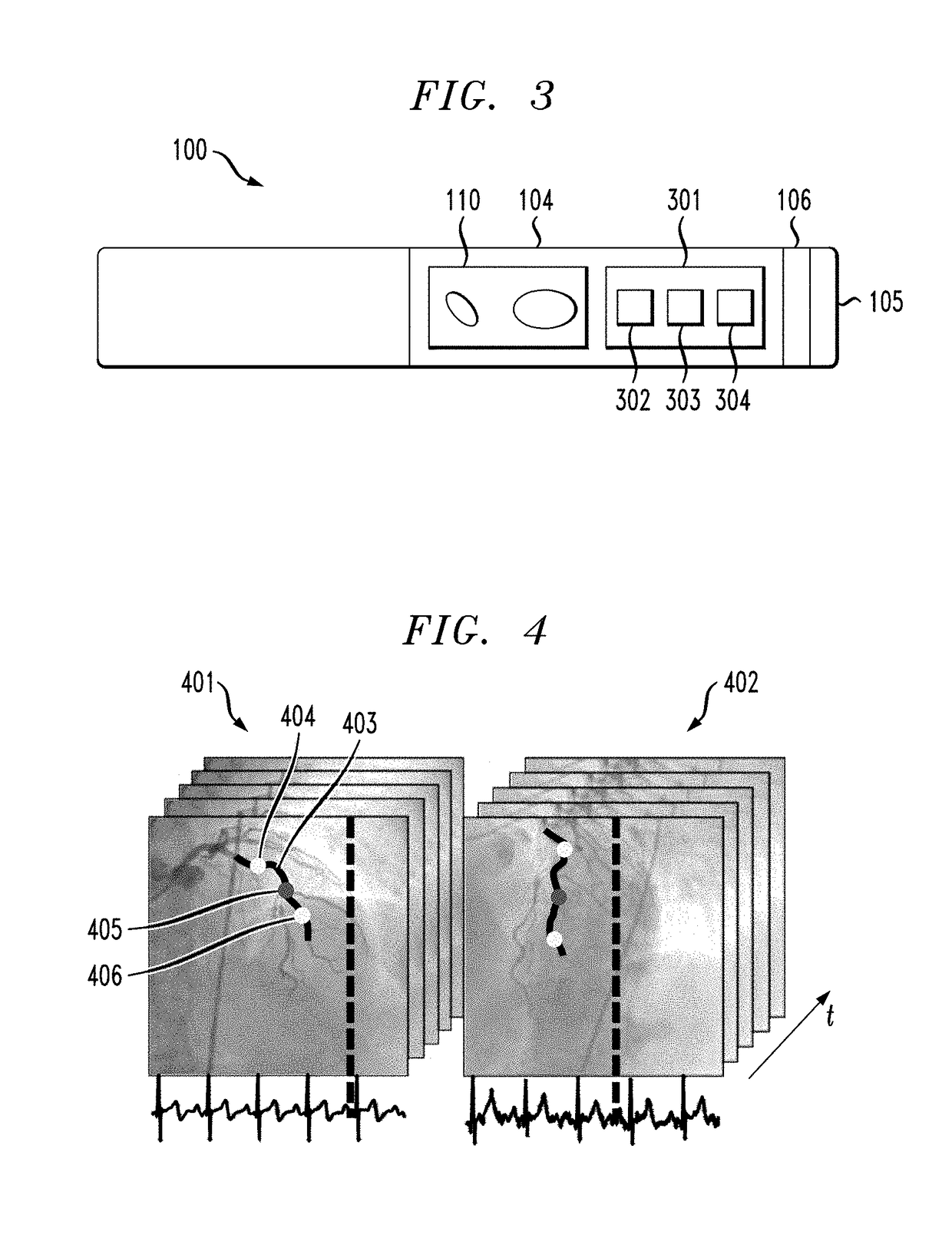
Intravascular catheter for modeling blood vessels
ActiveUS20180310992A1Accurate visualizationIncrease heightSurgical navigation systemsCatheterBlood vessel spasmIntravascular catheter
A method of generating a 4D model includes capturing imagery of a catheter and a vessel as the catheter is directed through the vessel to a location of interest, wherein the catheter is disposed on a guidewire, constructing a 3D time varying reference curve describing a trajectory of the guidewire, and constructing a time varying 3D model of the artery using the reference curve.
Owner:IBM CORP
Intravascular catheter including markers
ActiveUS20180310830A1Accurate visualizationIncrease heightSurgeryInertial sensorsIntravascular catheterBlood vessel
A catheter including a monitoring body and a pair of markers disposed on the monitoring body, each marker of the pair of markers encircling the monitoring body, wherein the pair of markers are configured to indicate, through their appearance from a given point of view, an orientation of the monitoring body.
Owner:IBM CORP
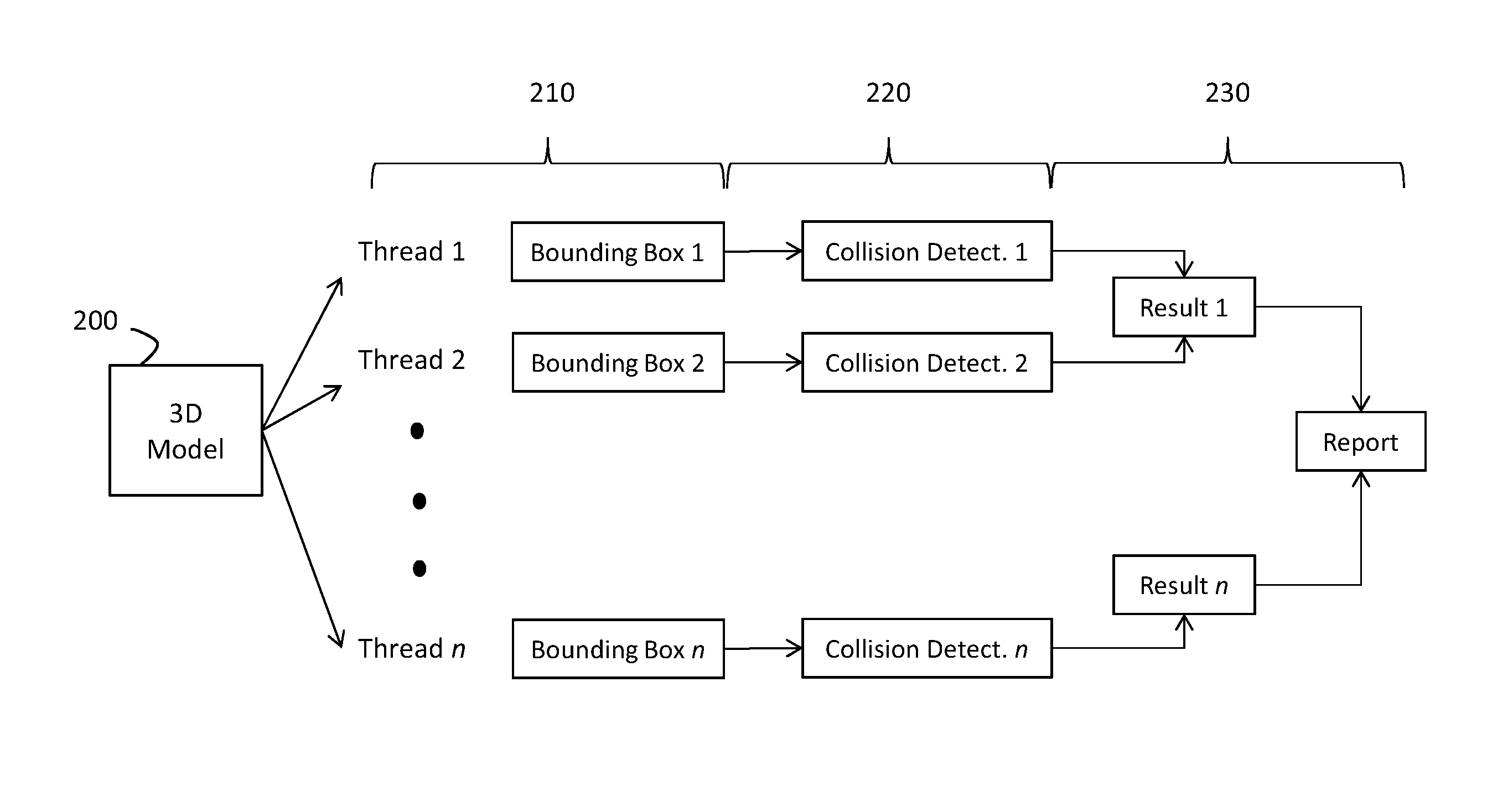
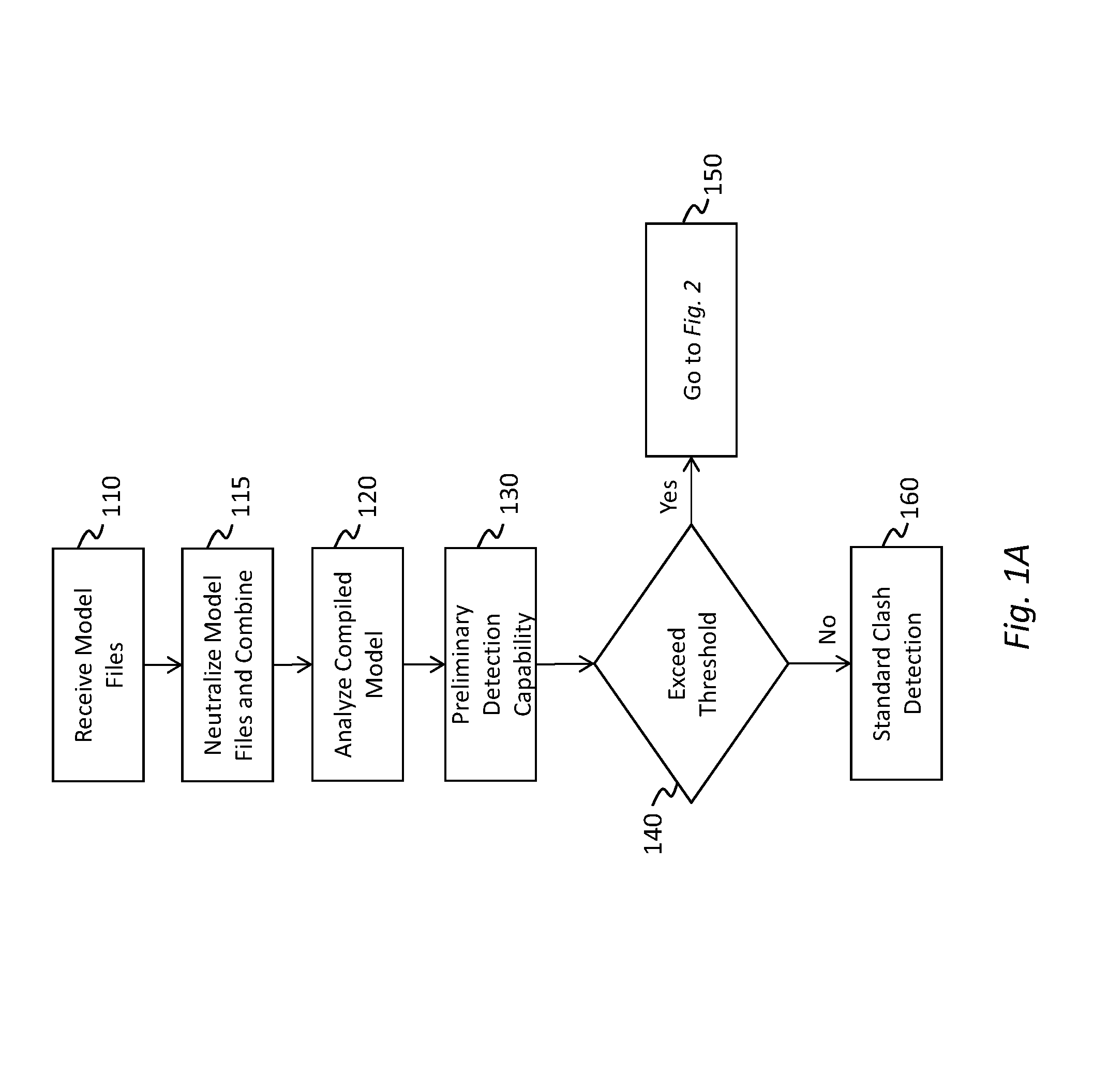
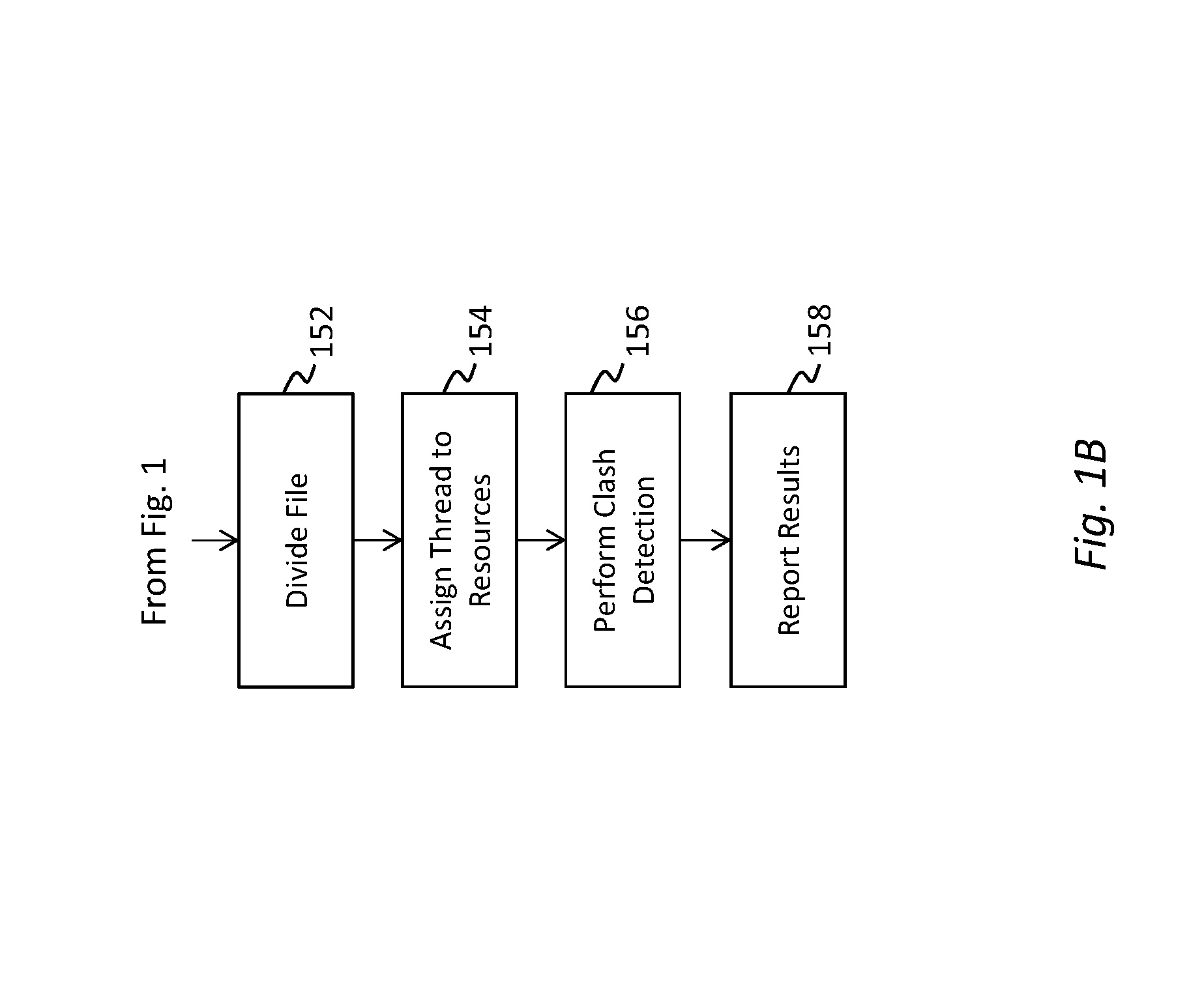
Method and apparatus for detecting interference in design environment
ActiveUS20140180641A1Accurately visualizedFor accurate visualizationCAD network environmentSpecial data processing applicationsRevision controlProcess rate
The disclosure provides a solution for clash detection in three-dimensional design by allowing multiple members to work on a centrally-located version of the model. The disclosure also provides massively-parallel processing of the design file which enables rapid processing and version control. The model can be maintained at one or more remote servers with significantly higher processing capability. Implementing clash detection on the remote server allows the system to take advantage of parallel processing. Complex 3D models can be identified and divided across multiple computational units to significantly increase processing speed.
Owner:GEHRY TECH
Multi-mode separation for target detection
ActiveUS9797817B2Strong specificityEfficient removalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic beadBuoyancy
Sandwich separation is based on forming a sandwich complex with a magnetic bead, buoyant bead, and a target. Once a sandwich formation is created, the sandwich can be separated using its dual physical properties, namely magnetism and buoyancy. Sandwich separation is highly specific, allows for removal of the beads that do not have any attached target, and reduces the number of background beads. Sandwich separation can also be used to allow for target detection in raw specimen. Also, improvement of detection capability is accomplished by performing AMBR measurements on a solid interface, where the rotational period speeds up and allows for dramatically reduced time-to-result.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
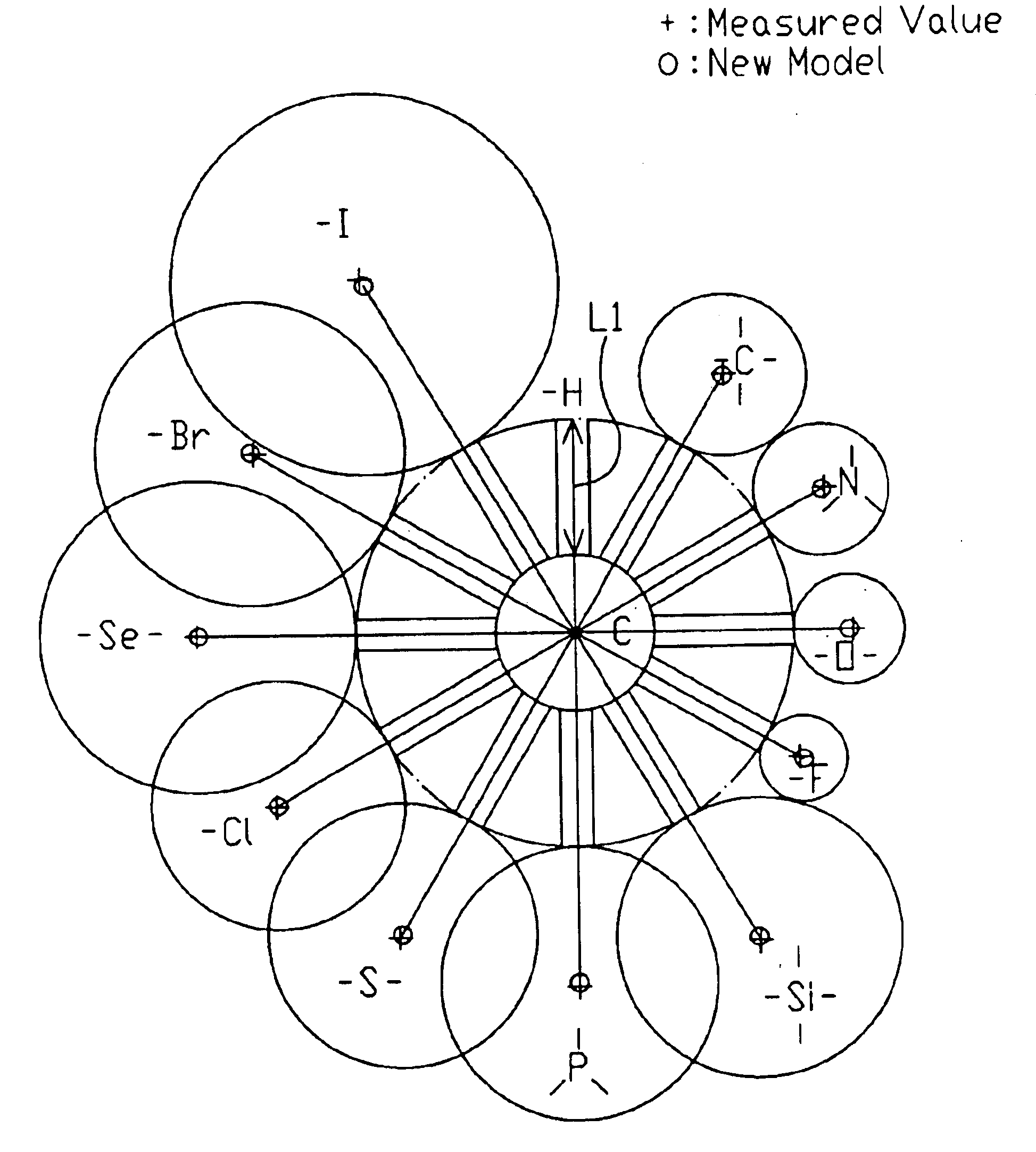
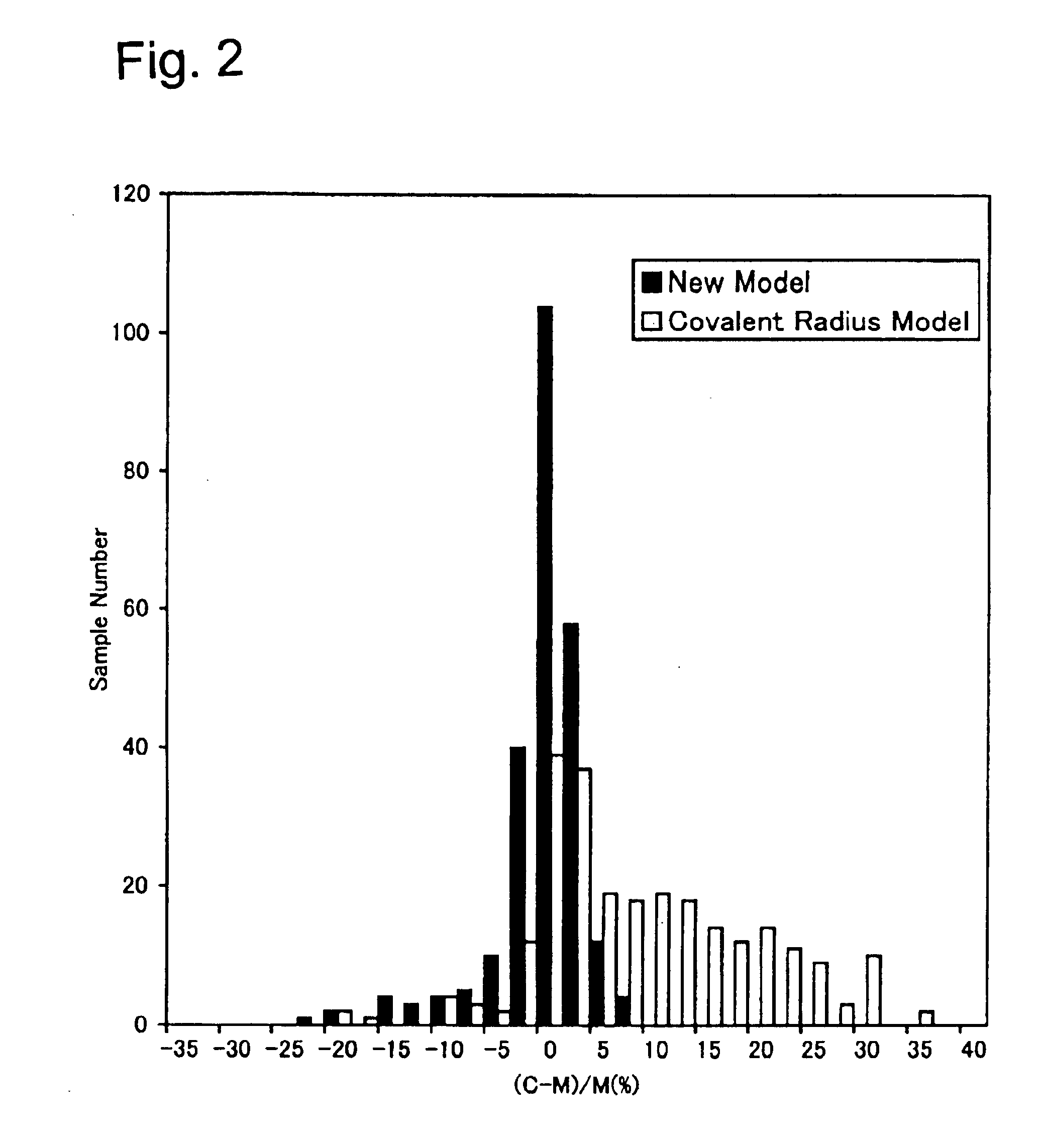
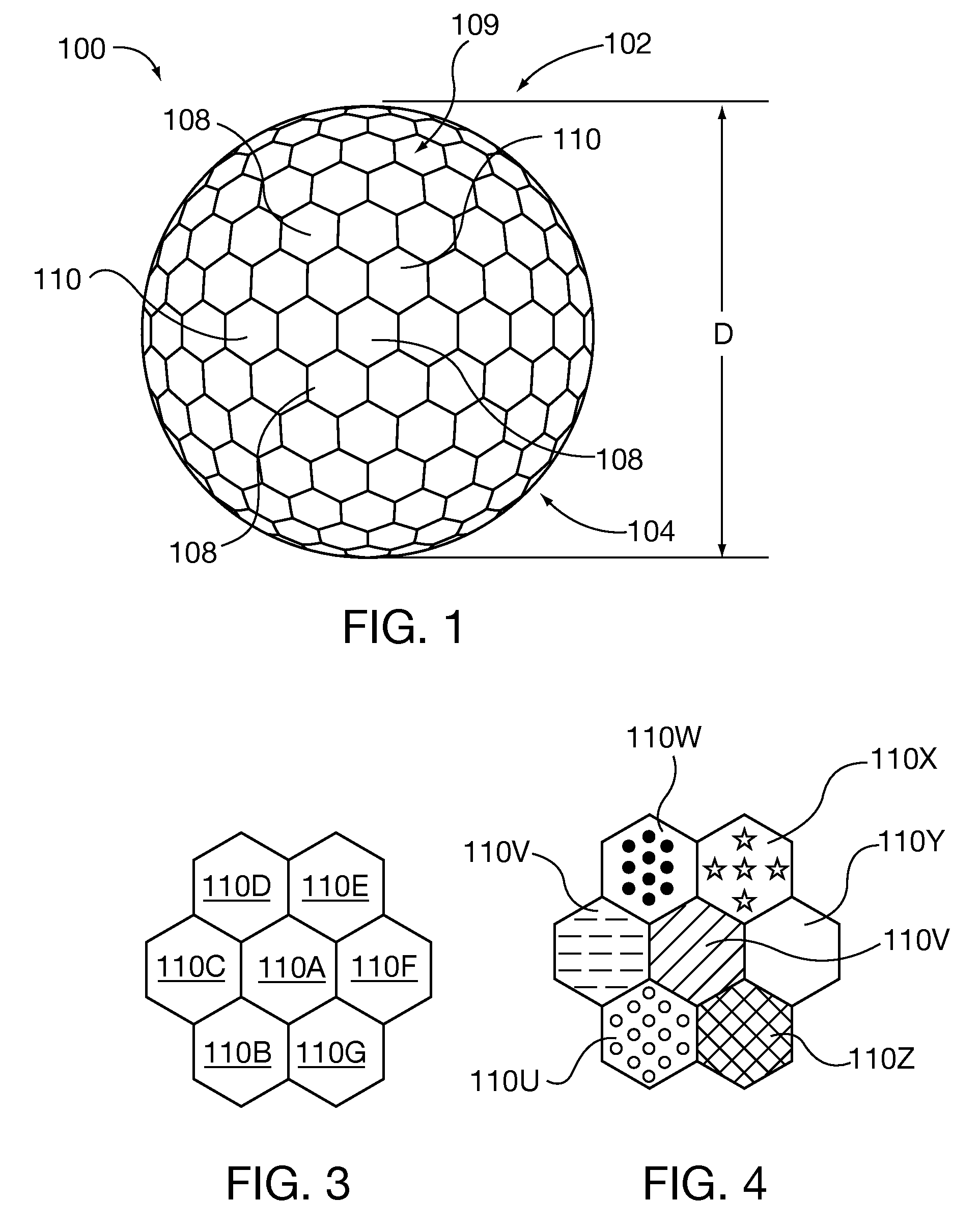
Molecular model representing molecular structure
InactiveUS6884079B2For accurate visualizationEducational modelsStructure analysisComputational chemistry
A molecular model for chemistry that shows a molecular structure by expressing the distance between the atoms obtained by molecular structure analysis as the total length from two atoms and one bond as well as accurately visualizing the molecular structure without using numeric values of the van der Waals radius or covalent bond radius. The molecular model is provided with a spherical body representing the atom and a bonding rod representing an inter-atomic bond. The molecular model is to establish a general solution with versatility by (a) differentiating the radiuses of the spherical atoms in the valence state rather than an element unit, and applying different radial lengths even within the same element, and (b) applying the bonding rod differentiated by the bonding state between the atoms.
Owner:TALON
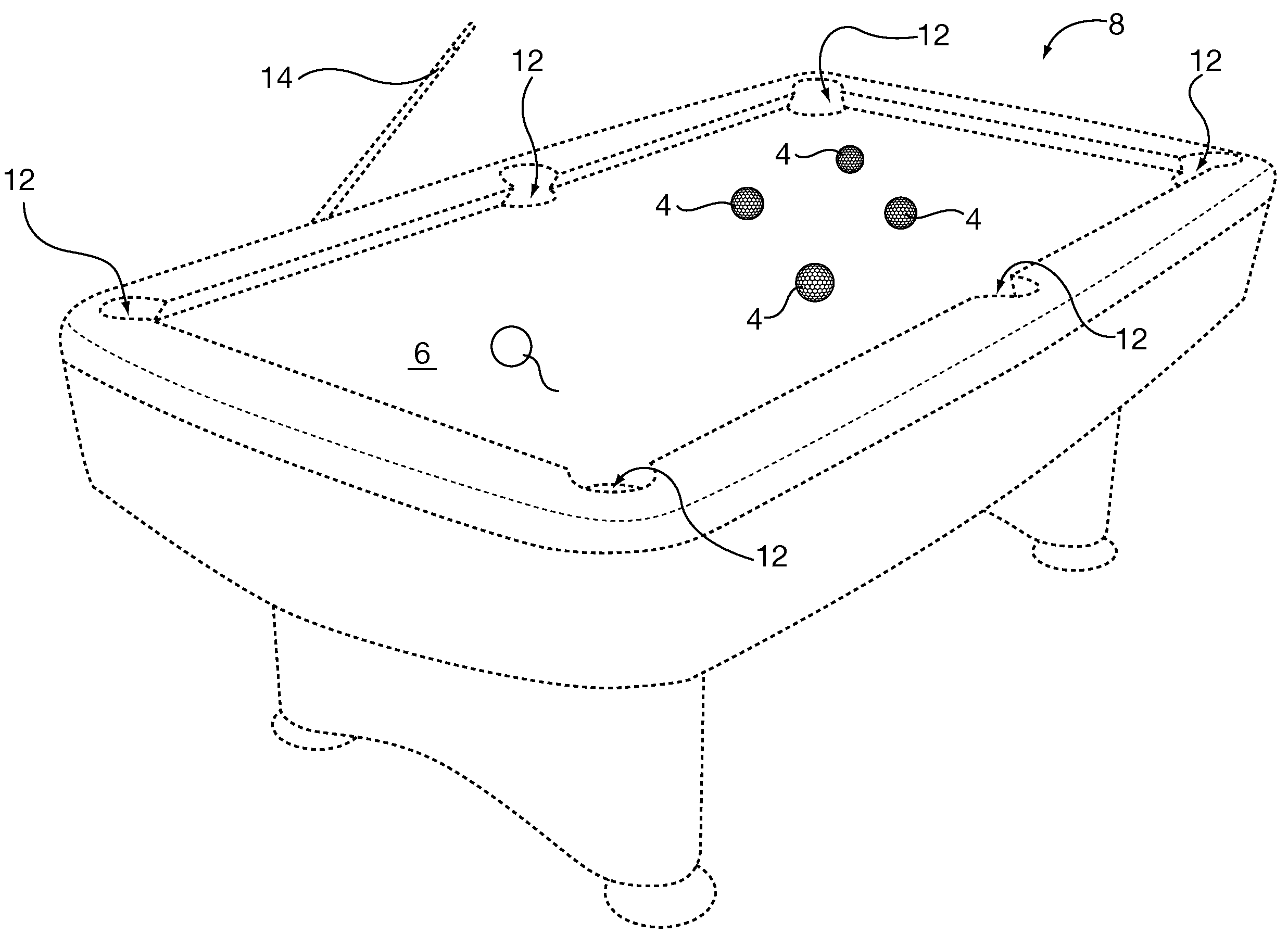
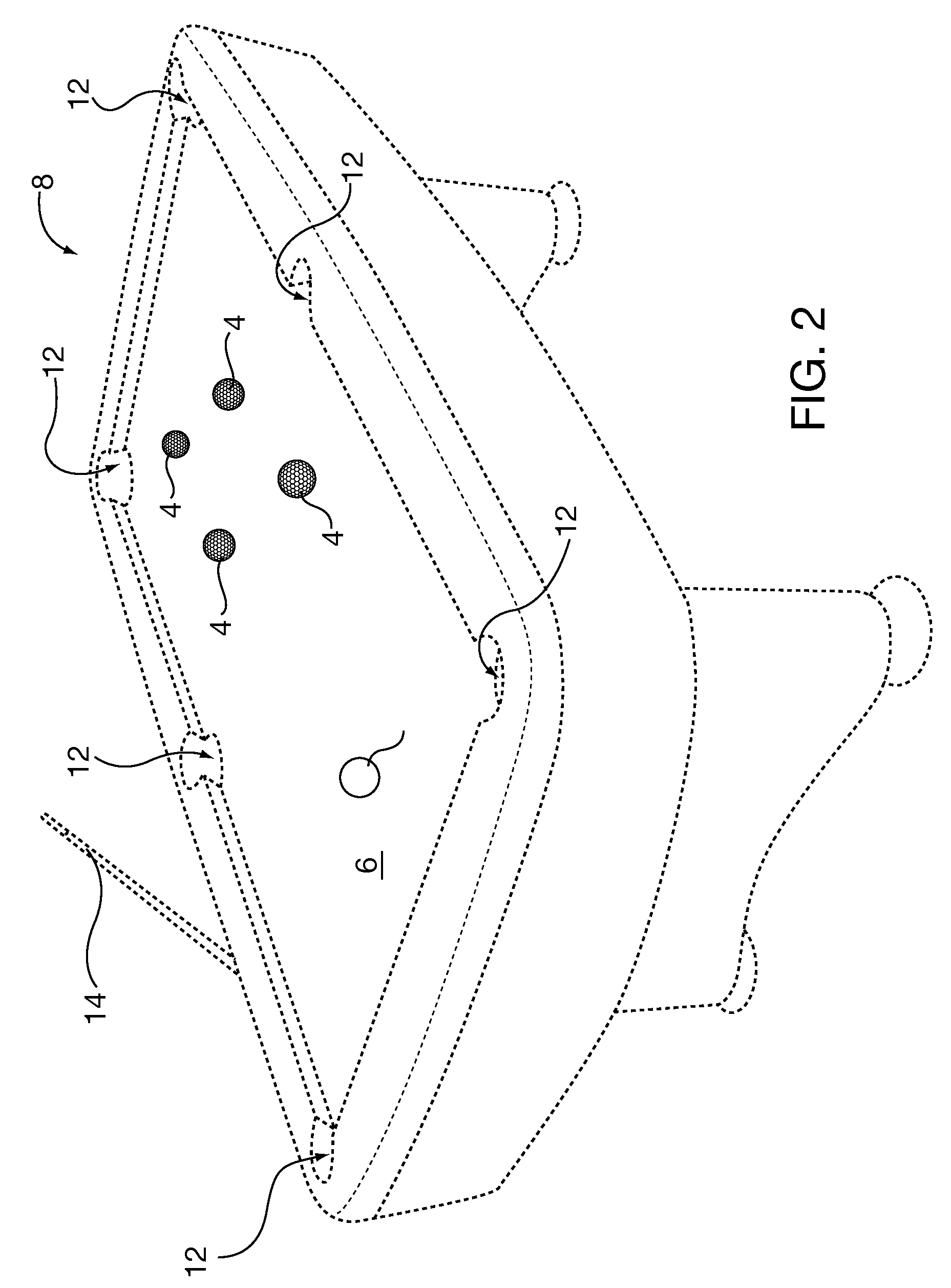
Training balls for pool and the like
ActiveUS20090264212A1Improve skillsFor accurate visualizationIndoor gamesSolid ballsShape displayEngineering
A training ball for pool type games. The training ball may comprise an array of visually coded bounded shapes disposed on the spherical exterior surface, wherein each one visually coded bounded shape has a characteristic visual coding such as color, and a diametrically opposed corresponding visually coded bounded shape having substantially identical characteristic visual coding, and wherein the array covers substantially all of the spherical exterior surface of the solid sphere. All of the visually coded bounded shapes display characteristic visual coding which is easily visually discernible from each adjacent one of the visually coded bounded shapes. In an associated method of play or practice, a player may visually hypothesize a straight line passing through the center of the training ball using the opposed similar visually coded bounded shapes, mentally set up a shot, and then execute that shot.
Owner:HERBERT WILLIAM S
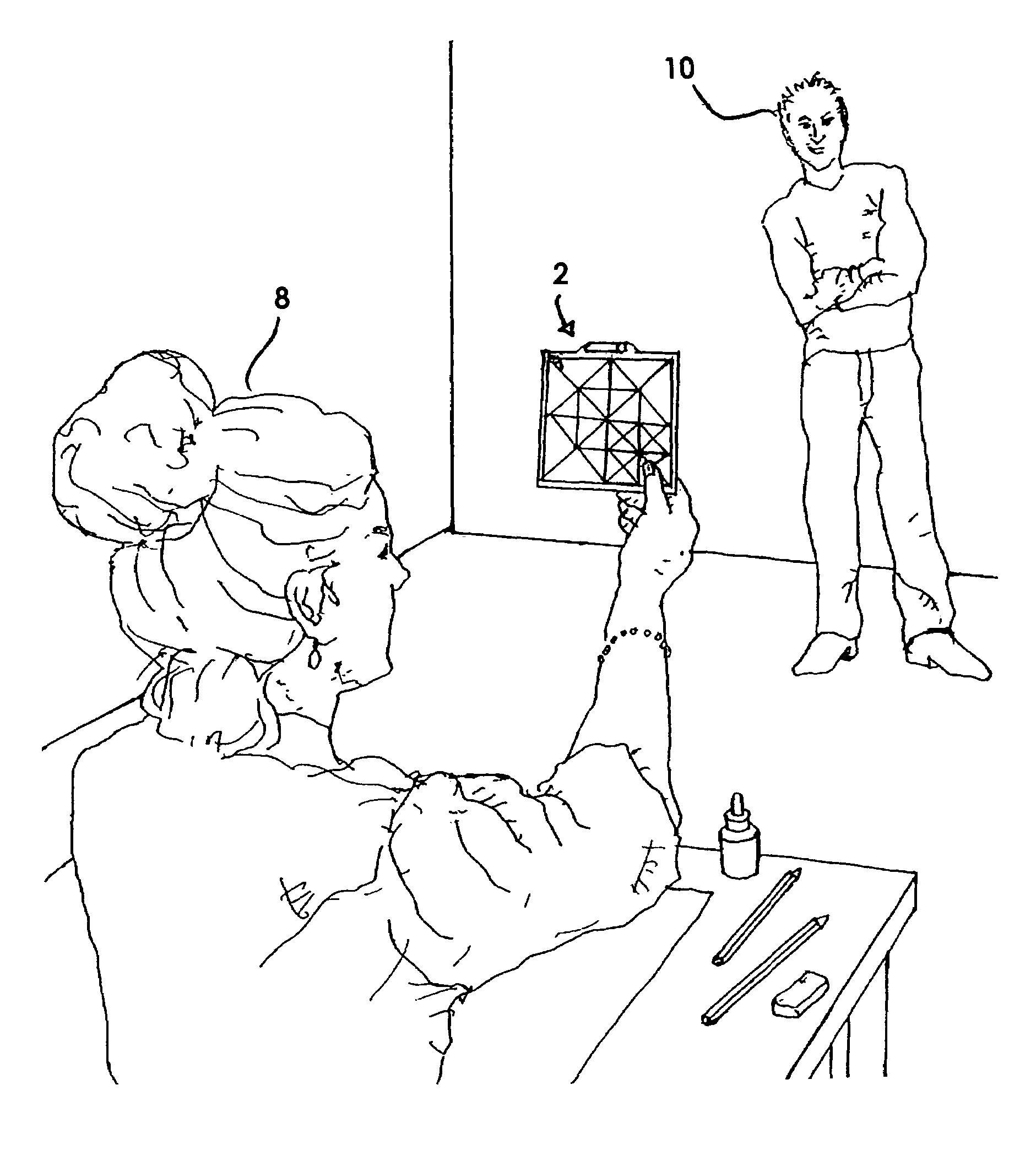
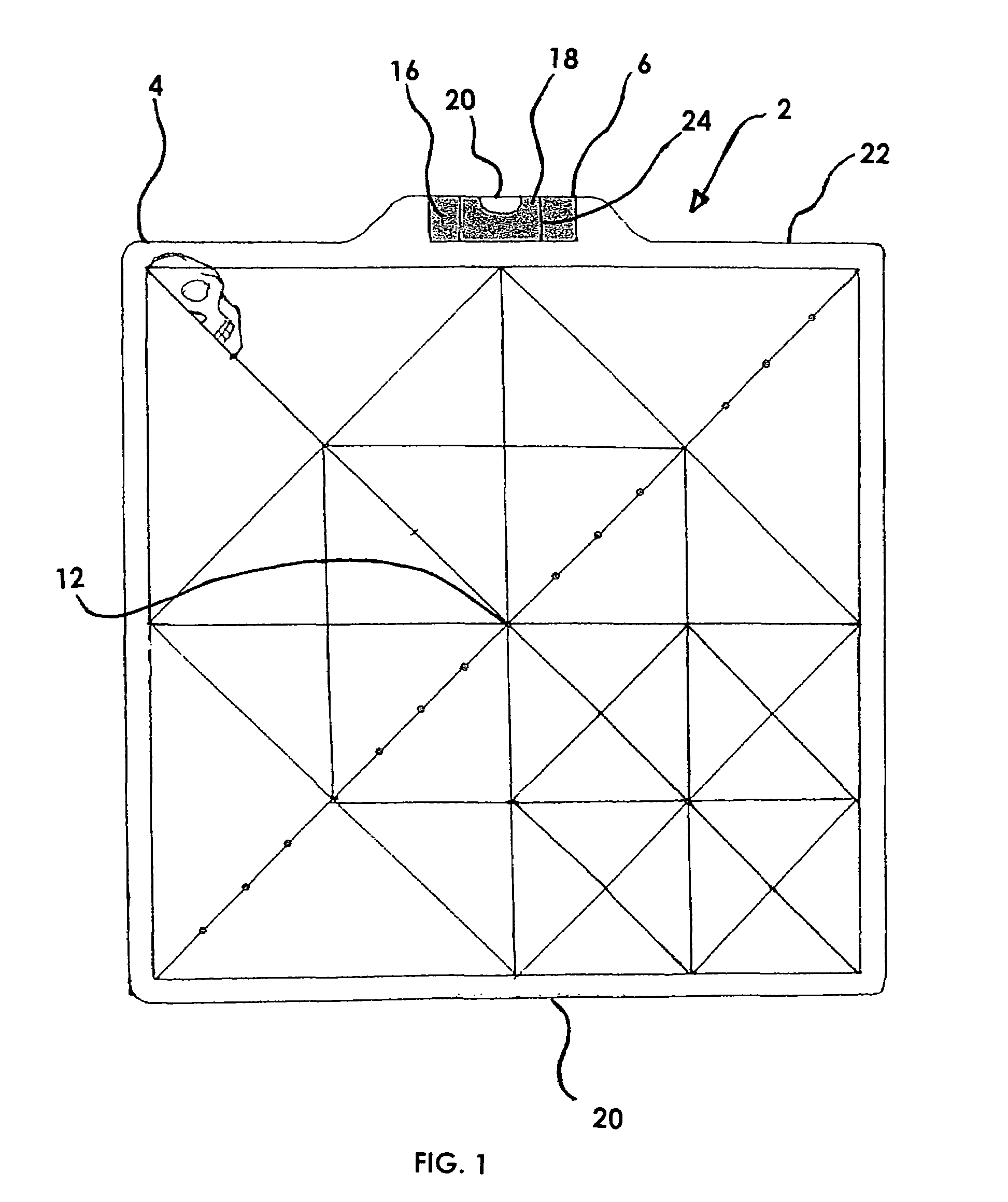
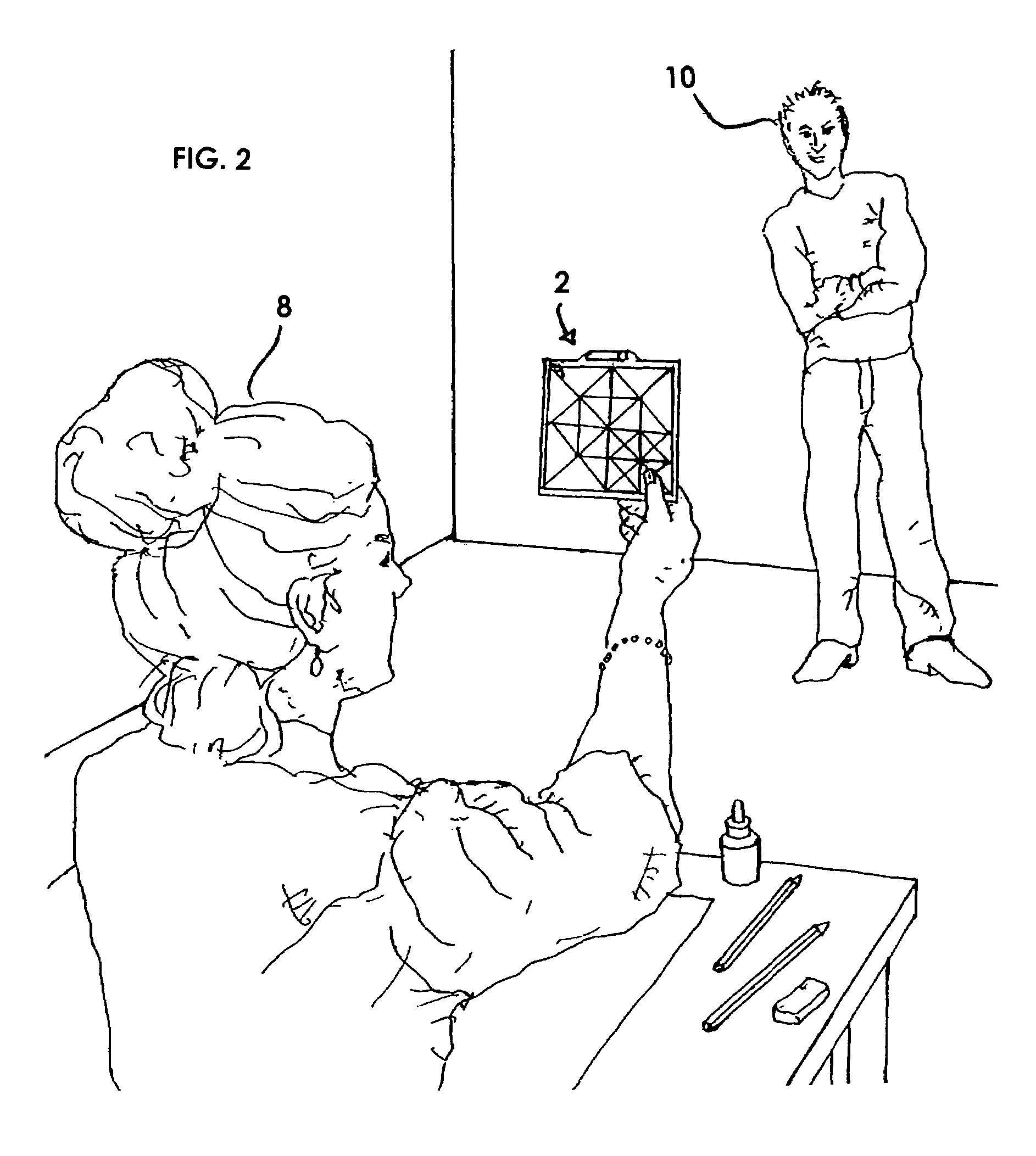
Artists's grid viewing device and method of use
InactiveUS7481654B1For accurate visualizationSmall sizeTeaching apparatusPhysical realityComputer science
The present invention is a handheld artist's aid designed to allow a freehand artist to establish horizontal fidelity, proportionality, subject scale, subject placement and angular relationships of a three-dimensional subject that is to become a two-dimensional work. It incorporates a visual leveling device in addition to a series of reference grids imposed there on. It is not designed as a copying or reproduction tool, but rather as an artist's aid that allows the artist freedom of expression yet frames the work within the physical reality of the structure. It is designed with multiple sized grids such that its use, can be enabled within the arms length of any artist.
Owner:MATEO LOUIS YLIZARDE
Instruments and methods for imaging collagen structure in vivo
ActiveUS20210052212A1Low variabilityStreamlined procedureImage enhancementMedical imagingSkin treatmentsRadiology
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS +1
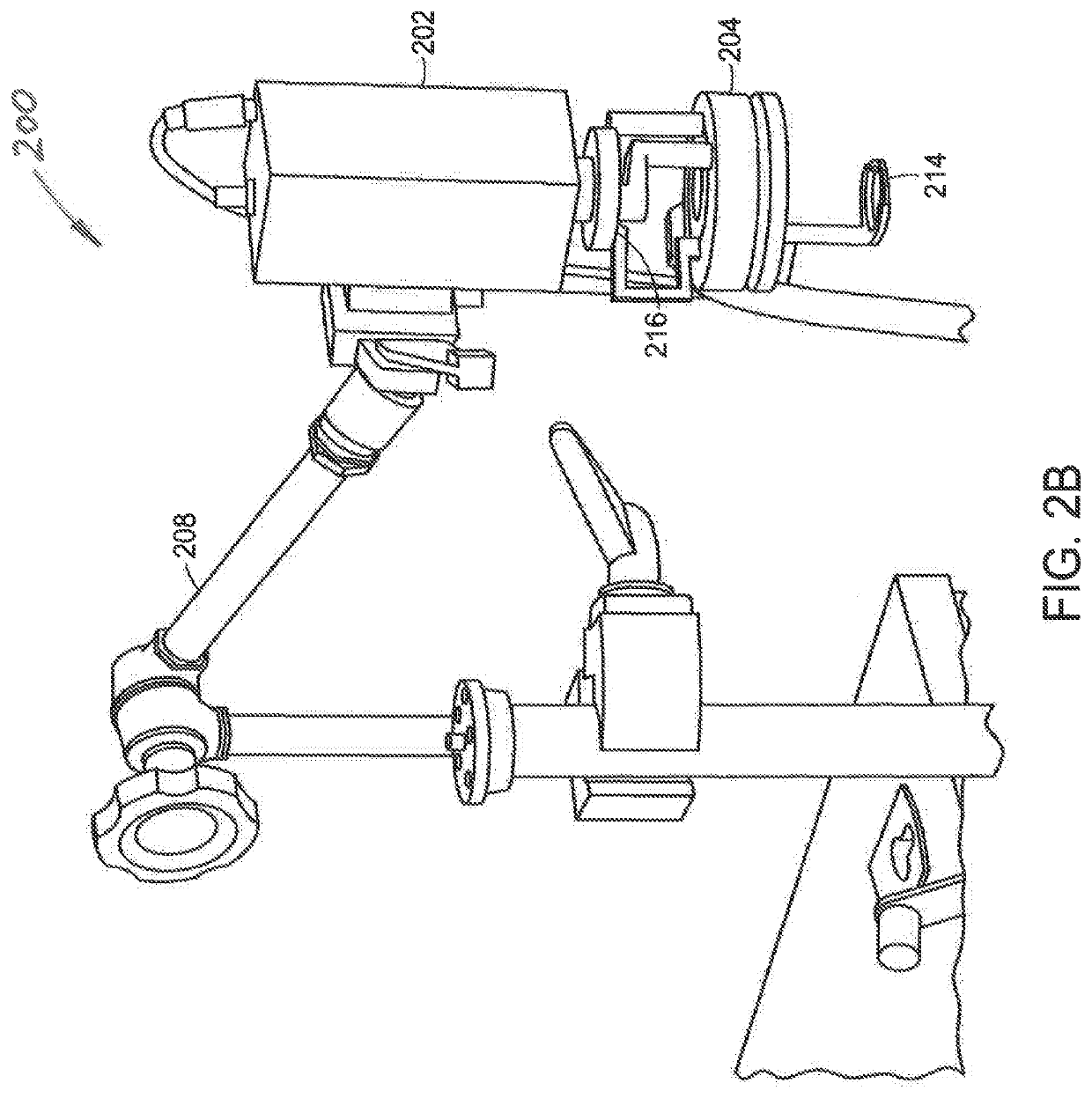
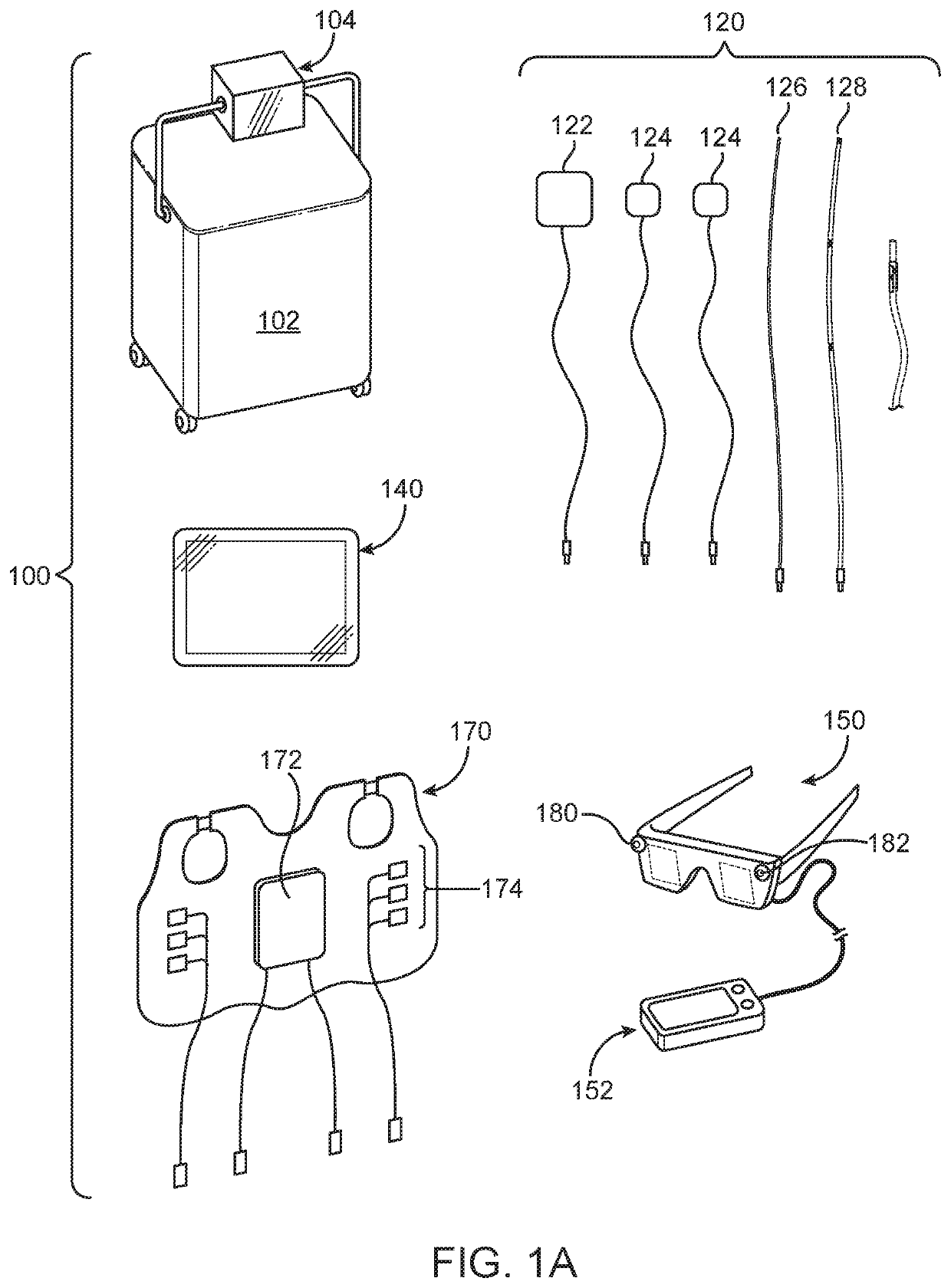
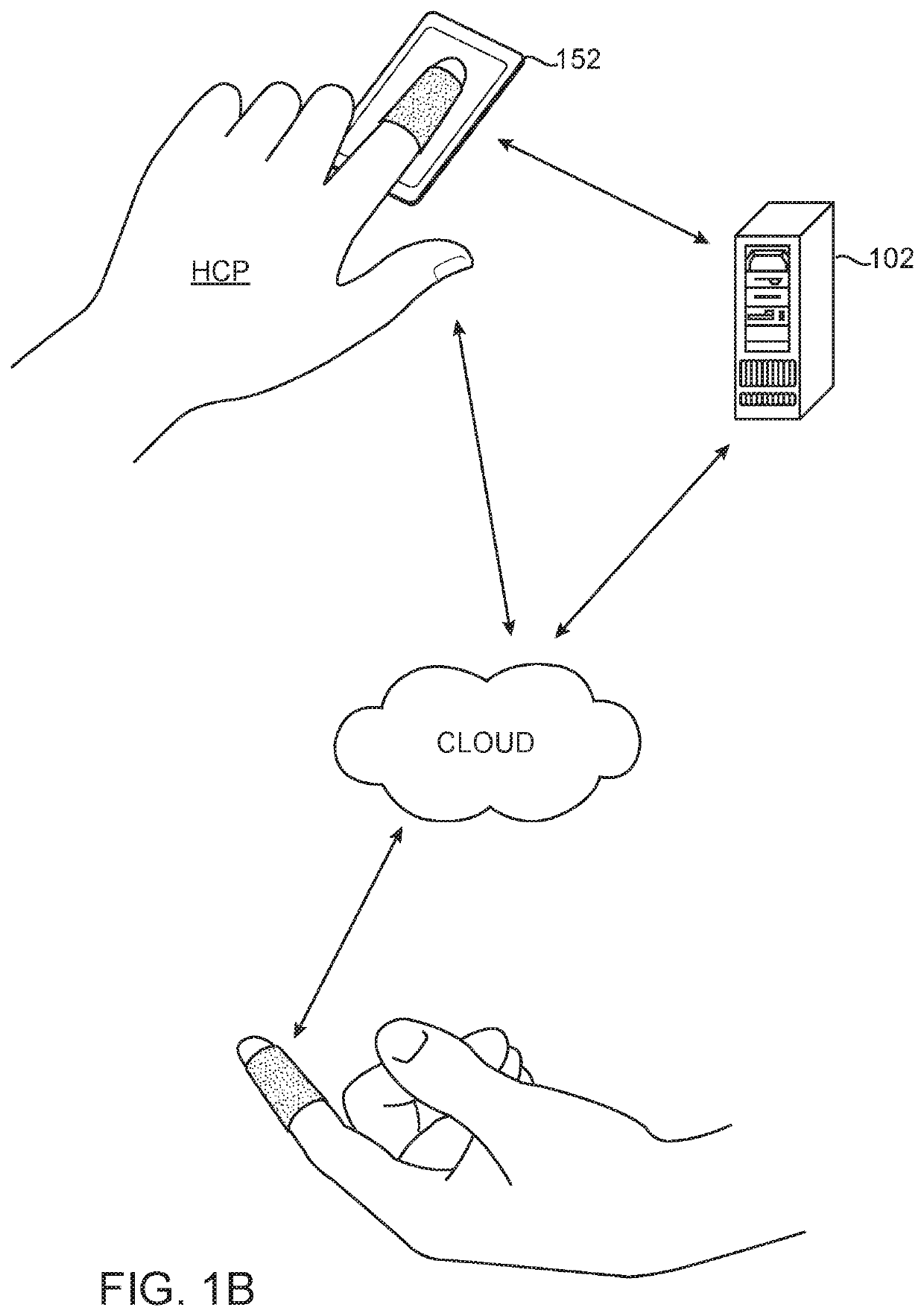
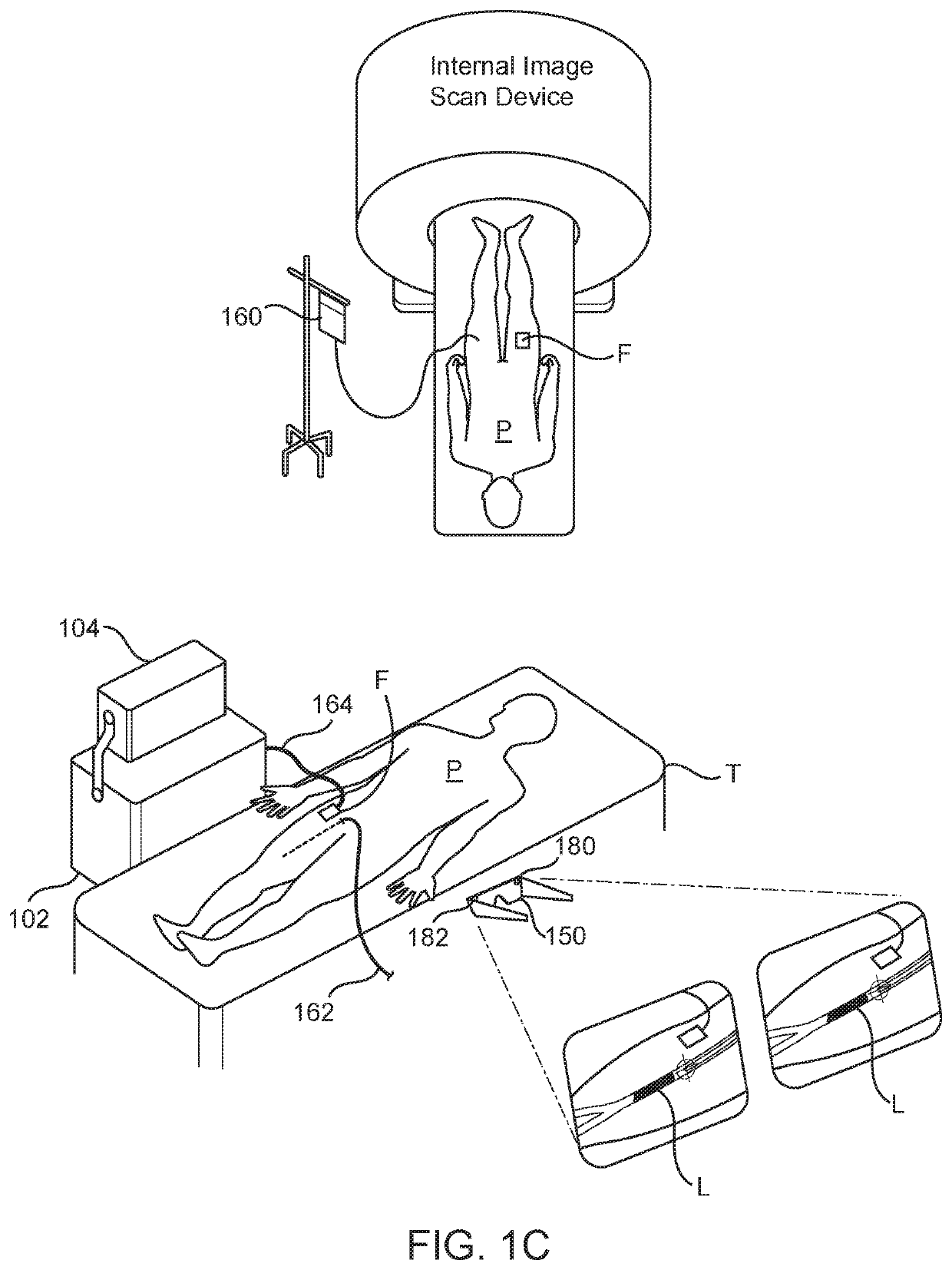
Enhanced reality medical guidance systems and methods of use
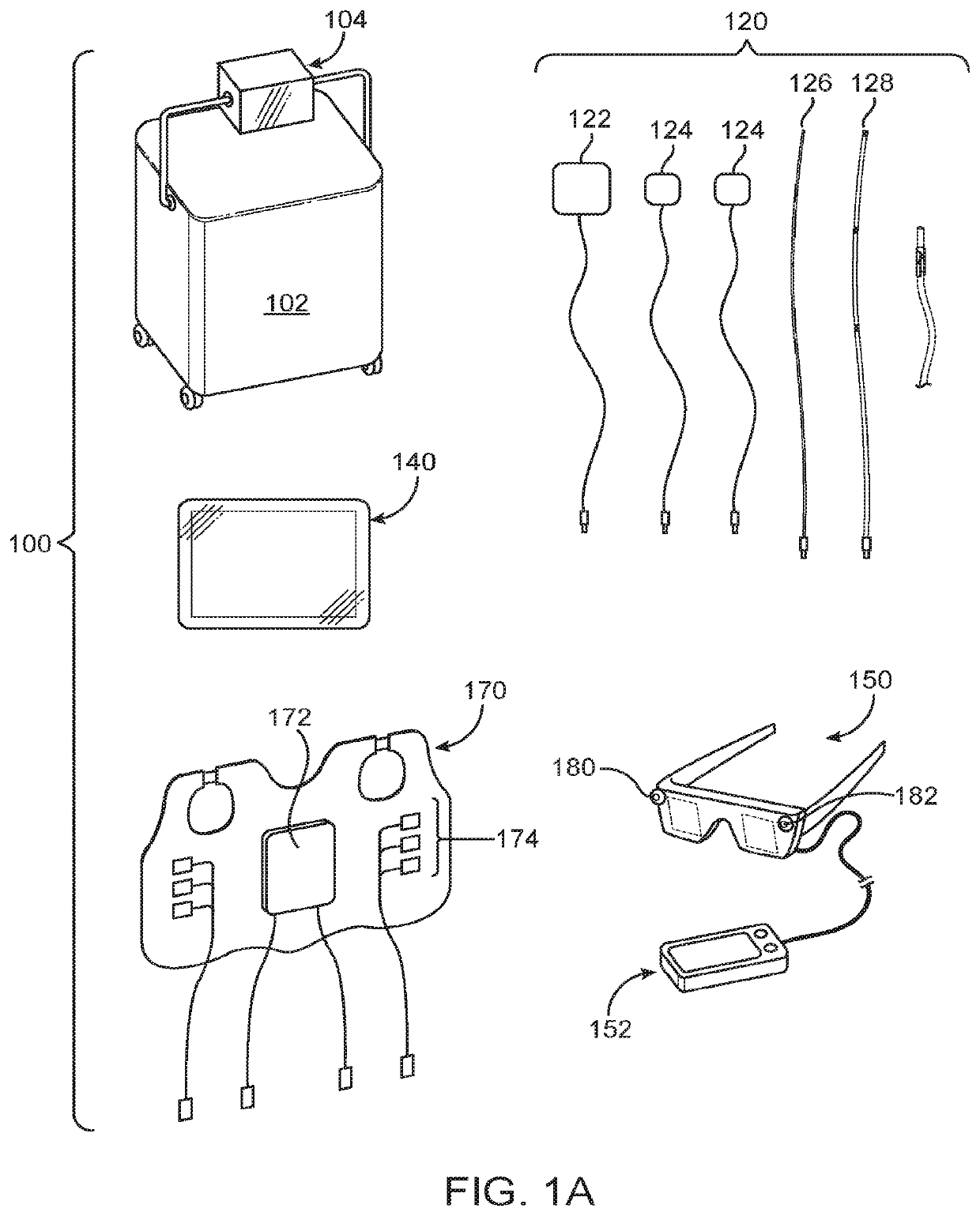
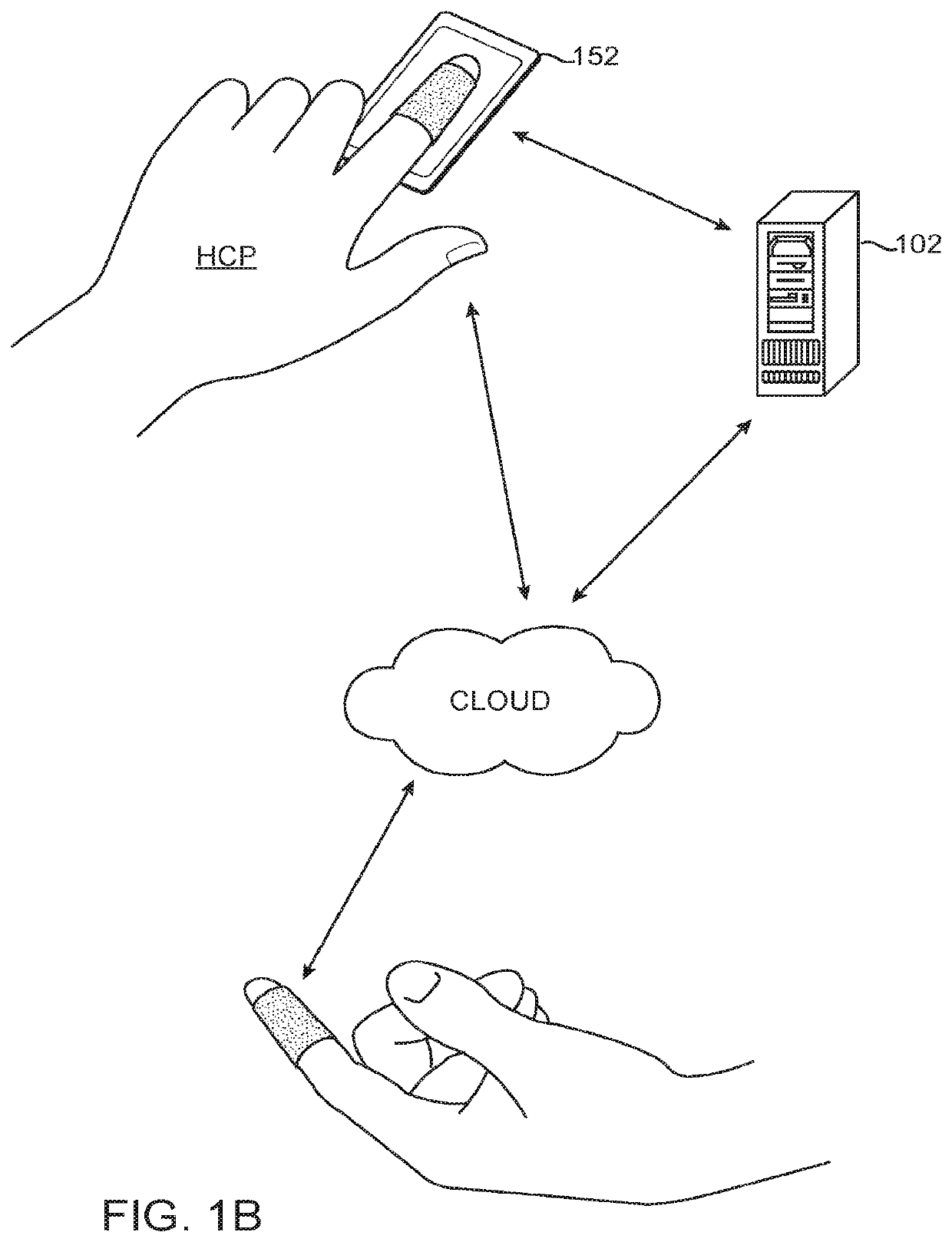
InactiveUS20200197098A1Facilitate cognitionEnhanced RealityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInput/output for user-computer interactionInterventional treatmentReoperative surgery
Apparatus, system and methods are described for providing a health care provider (HCP) with an enhanced reality perceptual experience for surgical, interventional, therapeutic, and diagnostic use. The apparatus, system and methods make use of a combination of sensors and audio visual data to cross-correlate information, and present the correlated information to the HCP on to one or more platforms for use during a diagnostic, interventional, therapeutic, or surgical procedure.
Owner:WORTHEEMED INC
Preparation method of T1 strengthened nuclear magnetic resonance nanometer contrast agent
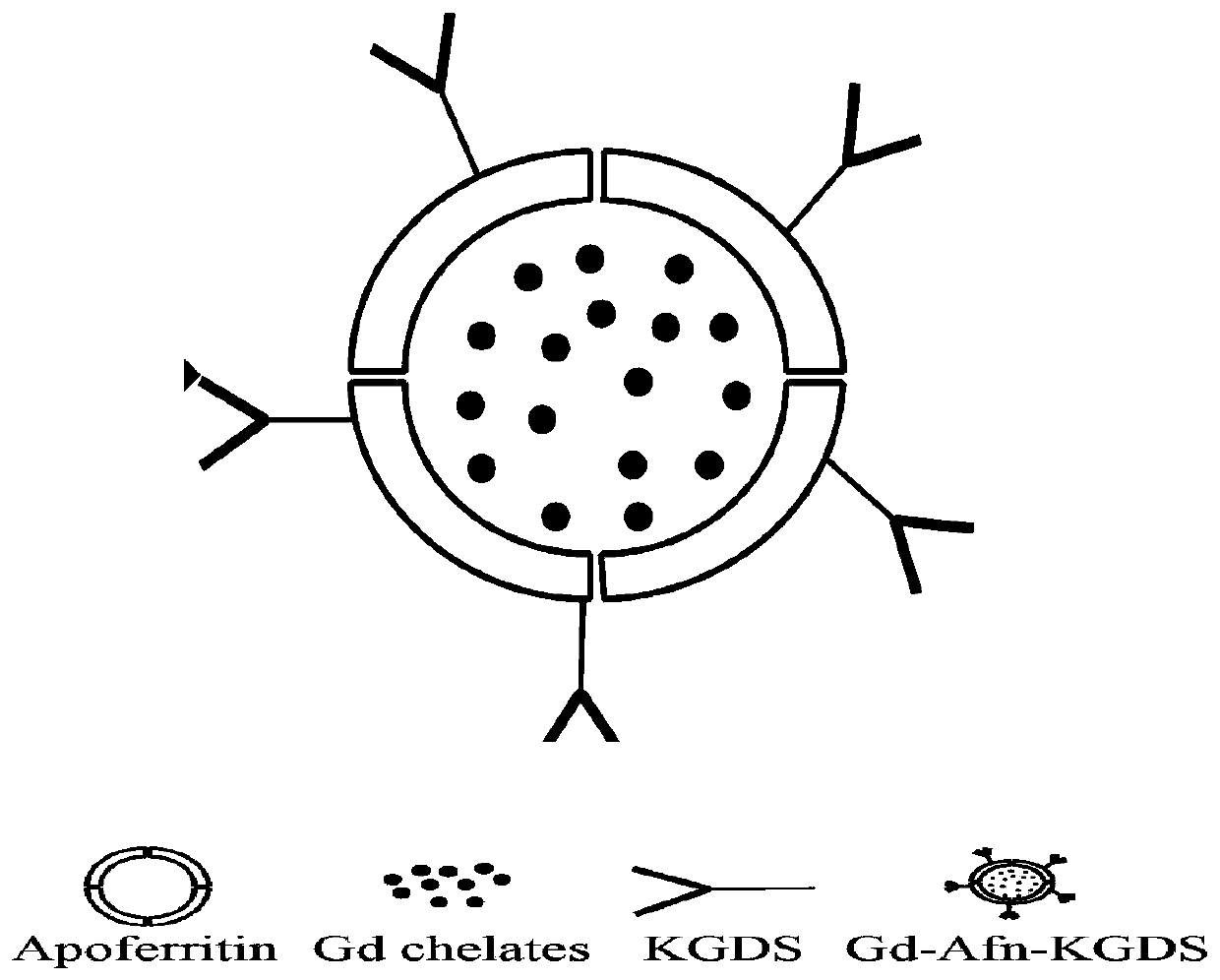
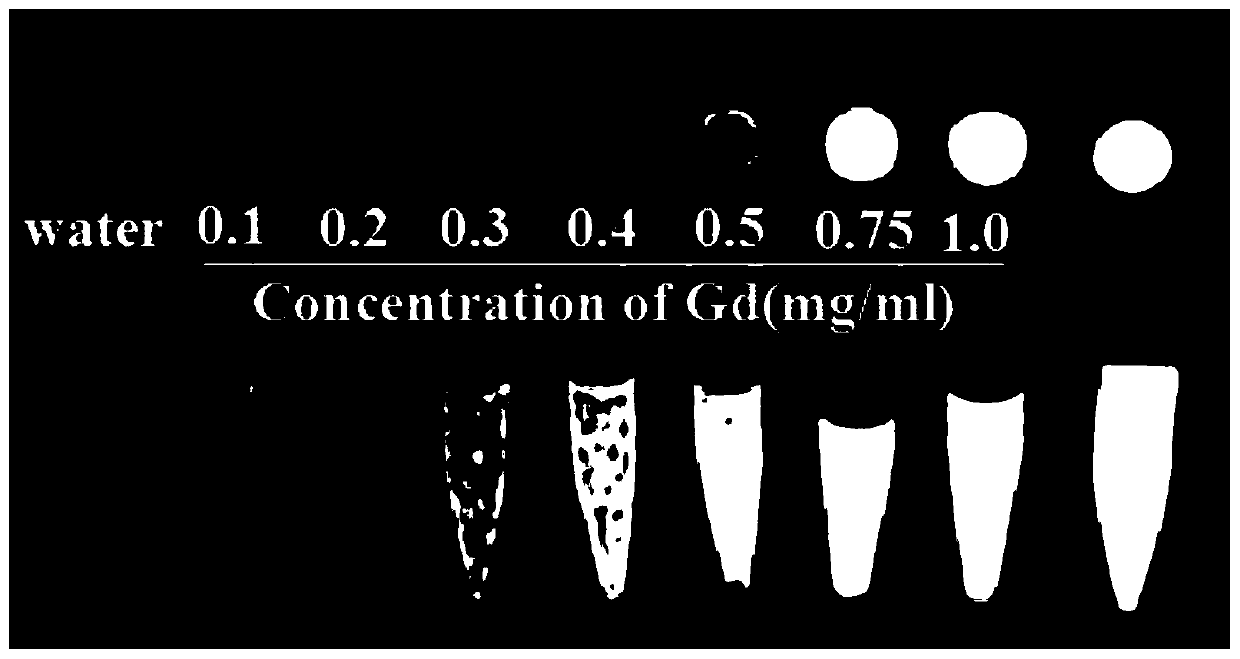
InactiveCN110639031AFor accurate visualizationActive targetingEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsDOTAContrast medium
The invention discloses a T1 strengthened nanometer magnetic contrast agent having the function of activating targeting properties of blood platelets and a preparation method of the T1 strengthened nanometer magnetic contrast agent belonging to the field of nuclear magnetic resonance contrast agents. The characteristics of "dissociation-self-assembly" and surface modificability of an apoferritin nanometer cage under different pH environment are utilized, paramagnetic Gd-DOTA is loaded into the apoferritin nanometer cage, ligand-KGDS tetrapeptide specifically targeting and activating the bloodplatelets is coupled to the surface of Gd-loaded apoferritin, and therefore, nanometer particles which can actively target and activate the blood platelets and have nuclear magnetic resonance T1 weighted imaging strengthened contrast effects can be obtained. The particle diameter of the nanometer contrast agent is about 10nm, the nanometer contrast agent has favorable contrast effects, targeting properties for activating the blood platelets, and biocompatibility; precise visualization of thrombosis is hopefully realized through targeting and activating the blood platelets, and more comprehensive molecule information is provided for early prevention, diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:广州市番禺区中心医院
Enhanced reality medical guidance systems and methods of use
InactiveUS20220008141A1Facilitate cognitionEnhanced RealityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesInterventional treatmentReoperative surgery
Apparatus, system and methods are described for providing a health care provider (HCP) with an enhanced reality perceptual experience for surgical, interventional, therapeutic, and diagnostic use. The apparatus, system and methods make use of a combination of sensors and audio visual data to cross-correlate information, and present the correlated information to the HCP on to one or more platforms for use during a diagnostic, interventional, therapeutic, or surgical procedure.
Owner:PETAL SURGICAL INC
Method for reconstructing a fluorescent image of the interior of a turbid medium and device for imaging the interior of a turbid medium
InactiveUS20110026851A1Accurately determineSatisfactory accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPhotometryFluorescenceUltrasound attenuation
A method for reconstructing a fluorescence image of the interior of a turbid medium is provided. The method comprises the step: accommodating a turbid medium (1) to which a fluorescent contrast agent has been administered in a measurement volume (4). The fluorescent contrast agent is capable of emitting light in a first range of wavelengths upon irradiation with light. The method further comprises: performing attenuation measurements at a plurality of different wavelengths (λi, . . . λk) by subsequently irradiating the turbid medium (1) with light from a plurality of different source positions and detecting light emanating from the turbid medium (1) in a plurality of detection positions for each source position; reconstructing absorption properties (μa(r, λ)) as a function of the position in the interior of the turbid medium (1) for the plurality of different wavelengths from the attenuation measurements; calculating absorption properties as a function of the position in the interior of the turbid medium (1) for wavelengths of the first range of wavelengths; performing a fluorescence measurement by subsequently irradiating the turbid medium (1) with light causing the fluorescent contrast agent to emit light in the first range of wavelengths from the plurality of source positions and detecting the light emanating from the fluorescent contrast agent in the plurality of detection positions for each source position; and reconstructing a fluorescence image of the spatial distribution of the fluorescent contrast agent in the interior of the turbid medium (1) from the fluorescence measurement using the calculated absorption properties.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Portable Environment Sensing Device
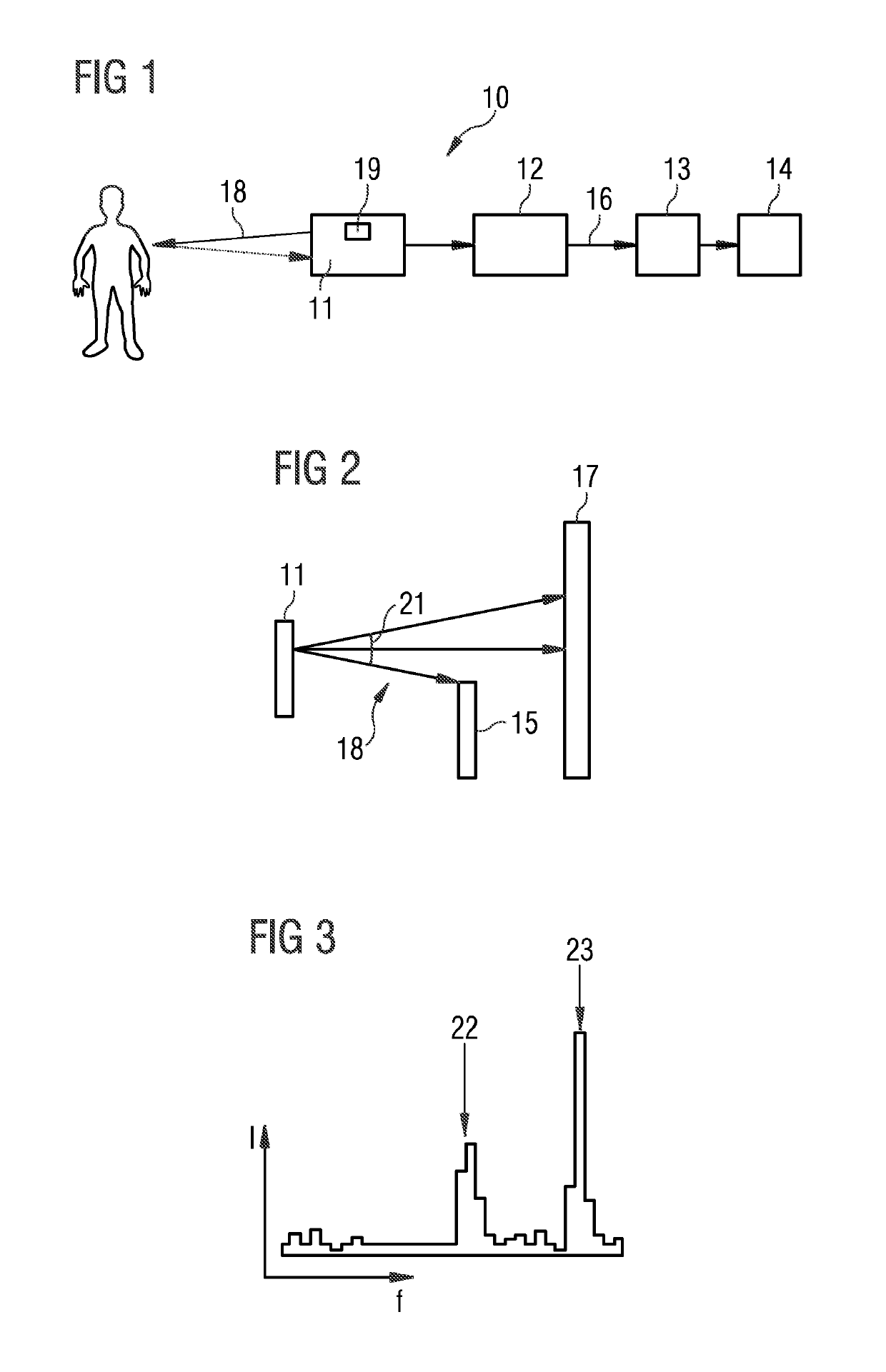
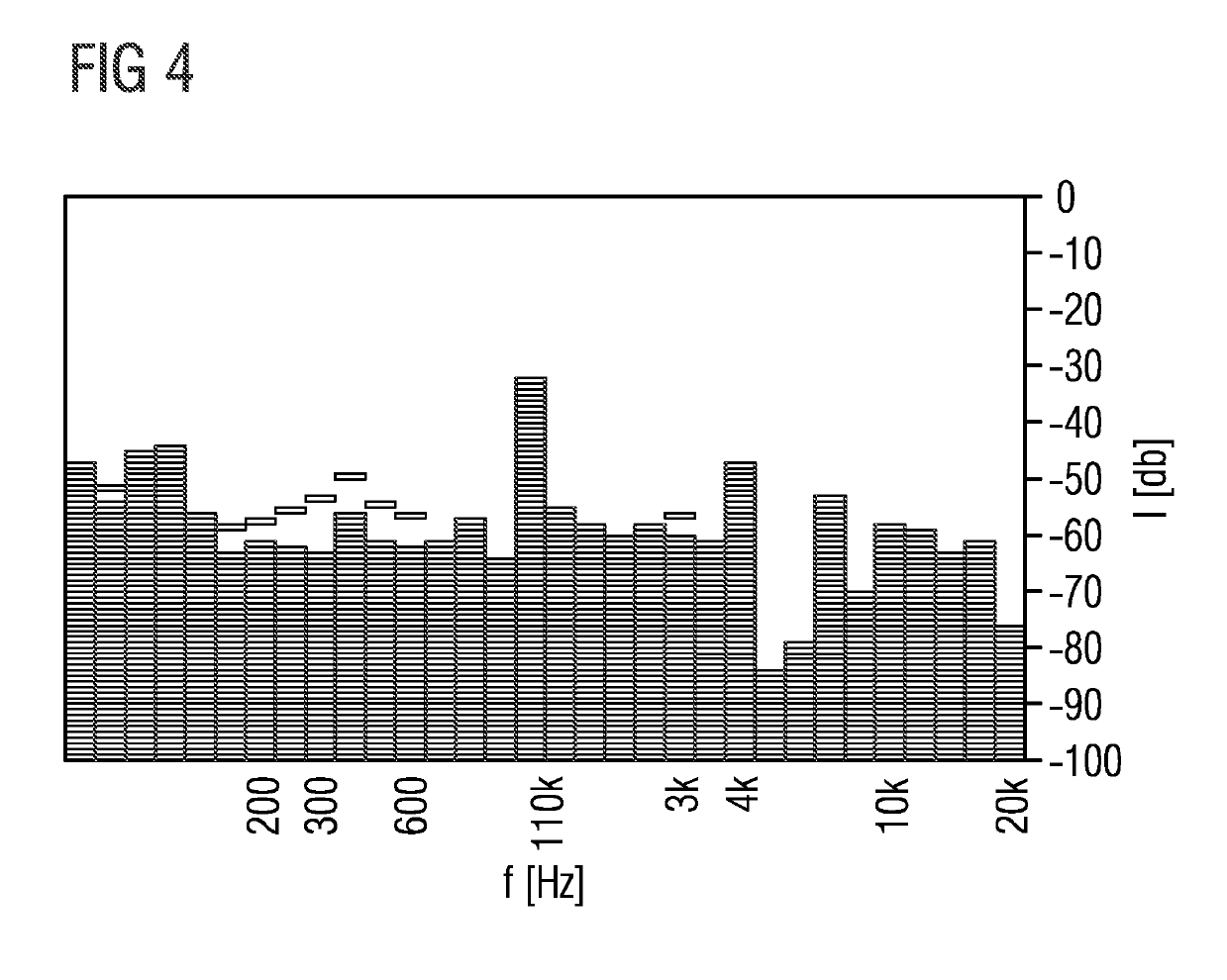
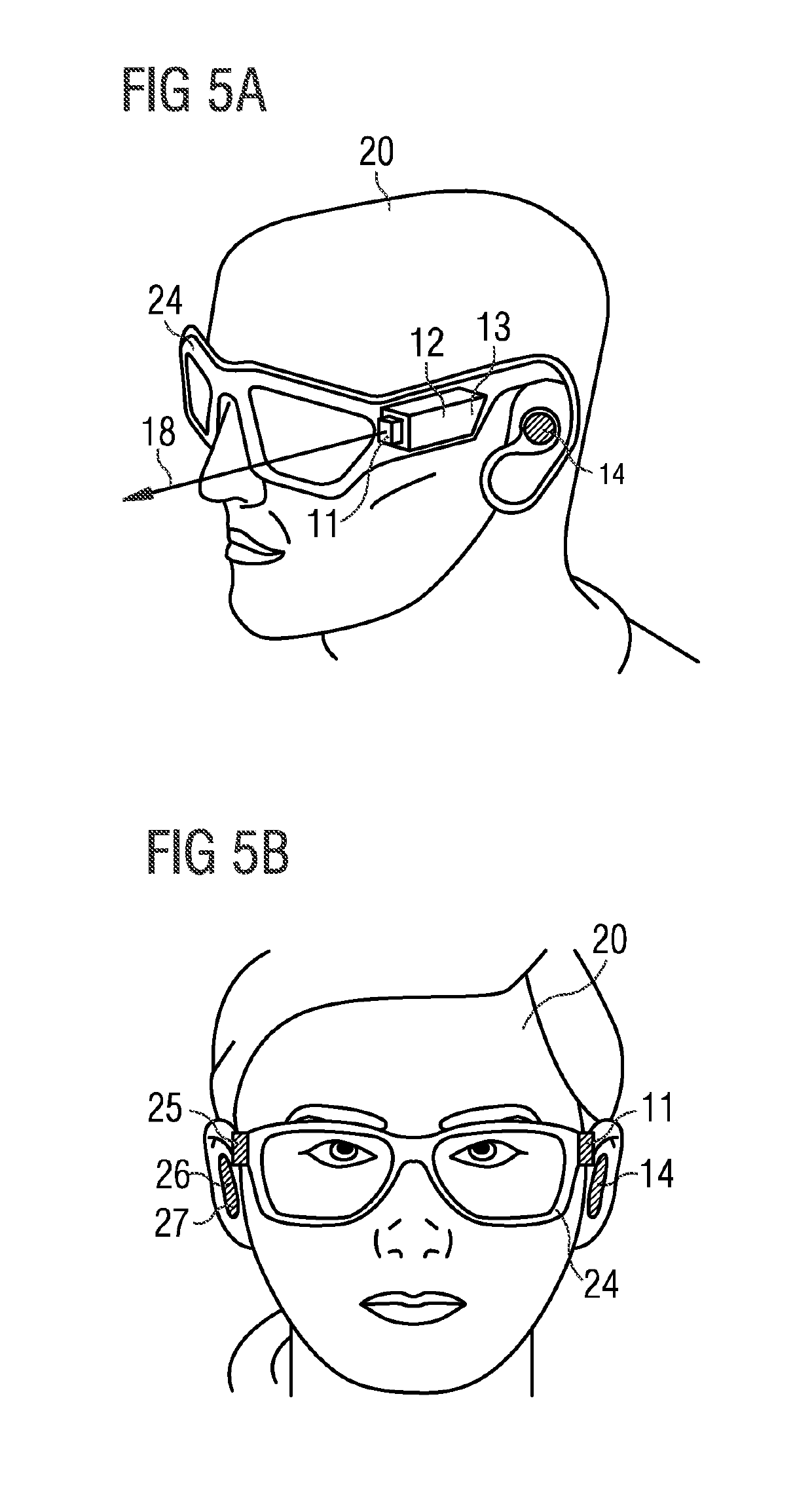
ActiveUS20190282432A1Guaranteed to move normallyInformation obtainedWalking aidsElectromagnetic wave reradiationTime of flight sensorField of view
A portable environment sensing device is described which comprises at least one time-of-flight sensor capable of detecting the distances from the time-of-flight sensor to at least two features within the field of view of the time-of-flight sensor simultaneously. The portable environment sensing device further comprises a processing unit capable of converting the at least two measured distances into at least two different distance signals, where each distance signal is correlated with the corresponding measured distance, and an output interface providing the at least two distance signals to a user simultaneously.
Owner:AMS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com