EUV lpp source with improved dose control by tracking dose over specified window
a technology of euv radiation and dose control, which is applied in the direction of x-ray tubes, electric discharge tubes, x-ray apparatuses, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete extraction of power amplifier gain, further variations in euv pulse energy, and less stable plasma, so as to improve the control of a dose of euv radiation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
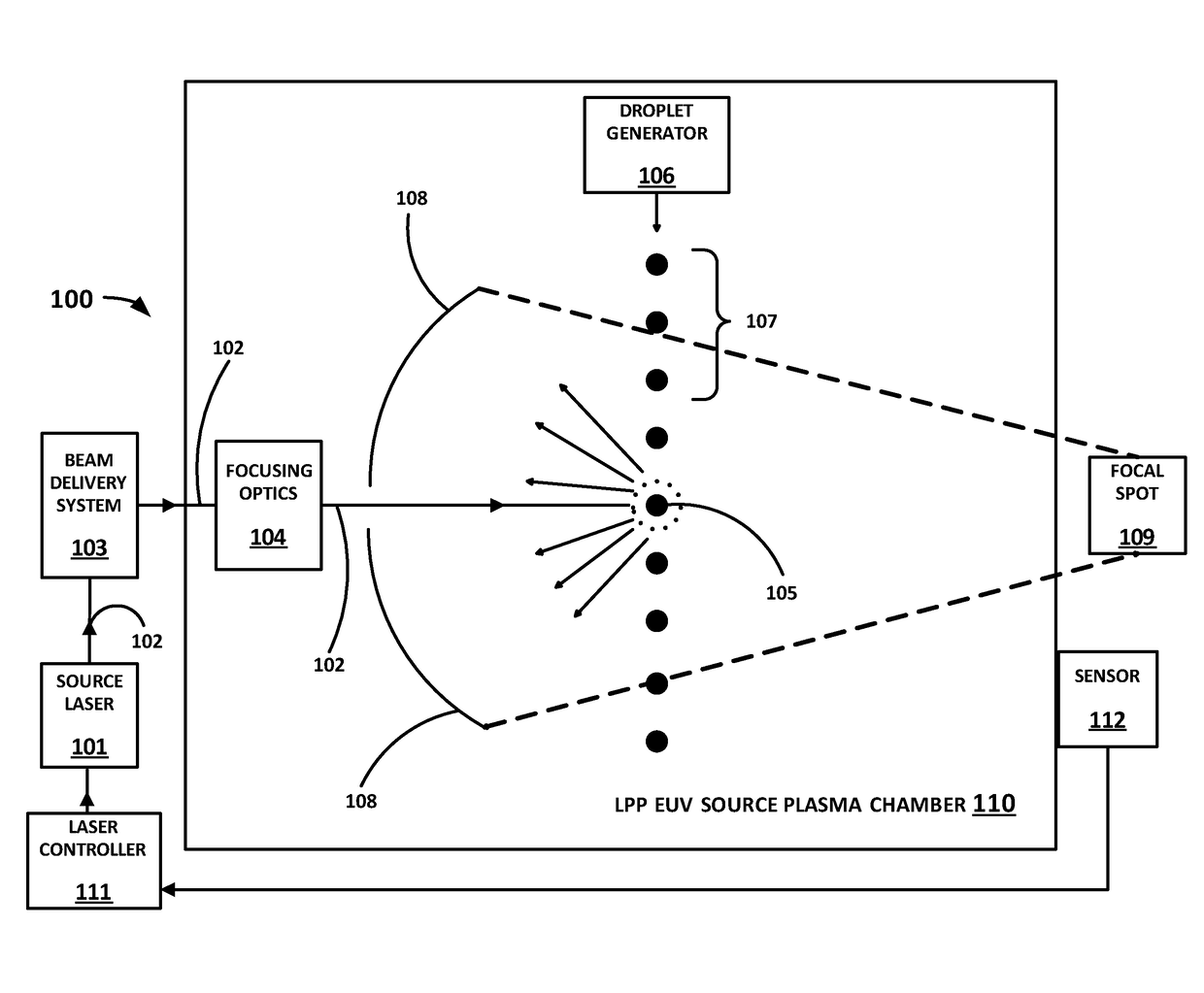
[0024]The present application describes a method and apparatus for improving the control of a dose of EUV radiation generated by a laser produced plasma (LPP) extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light source and applied to an item, such as a semiconductor wafer, being processed.
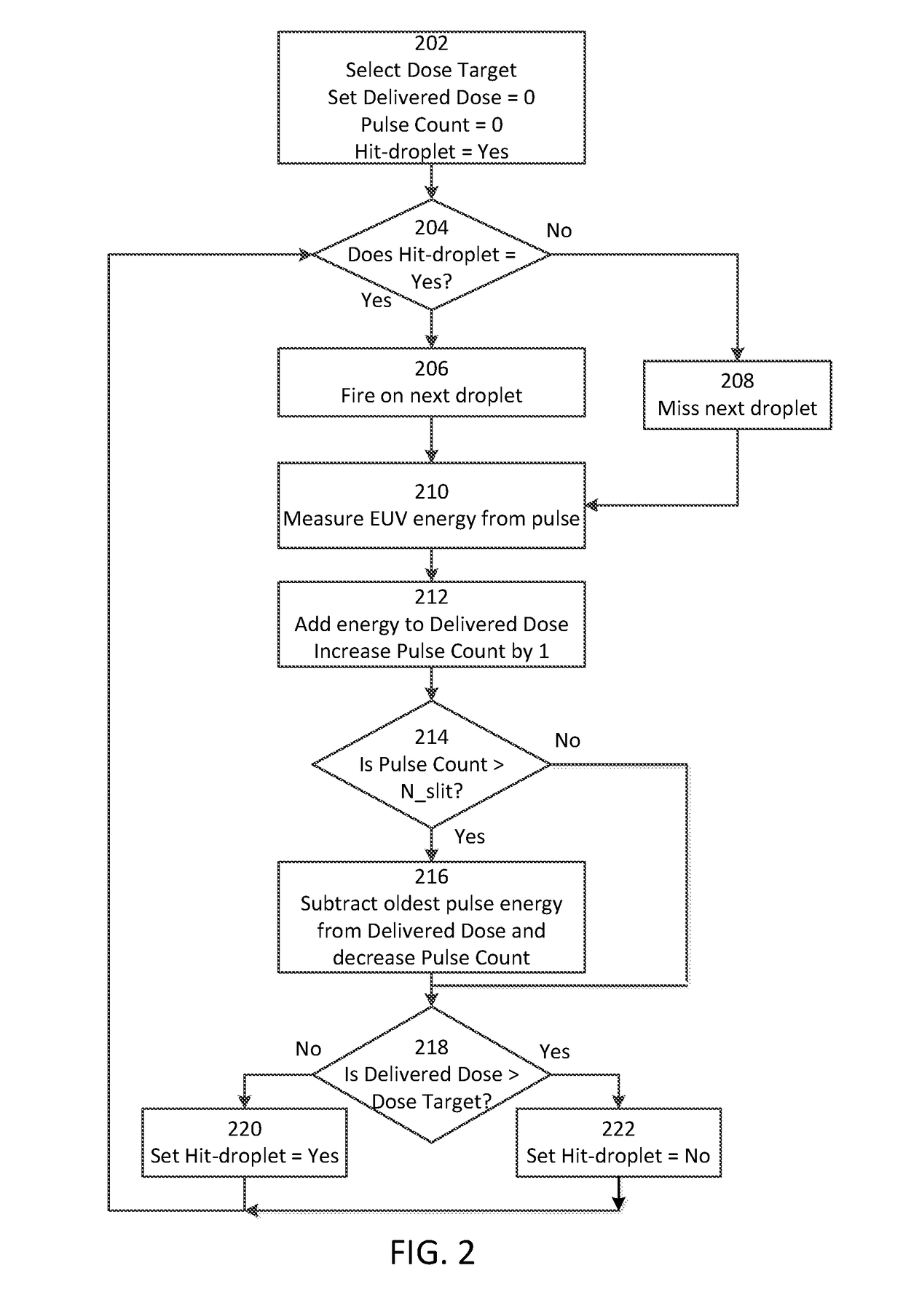
[0025]In one embodiment, a running total of the EUV energy generated over a number of laser pulses is measured. Once a certain predetermined number of pulses is exceeded, the energy from the oldest pulse within a moving window of the predetermined number of pulses is dropped from the running total, so that thereafter the running total is from the most recent predetermined number of pulses. If the running total of the EUV energy exceeds a target dose, the next pulse is caused to not hit a droplet; since the energy from the oldest pulse is dropped, in most cases this will reduce the running total of EUV energy slightly and cause it to be below the target dose.
[0026]Keeping a running total of the EUV energy generated over...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com