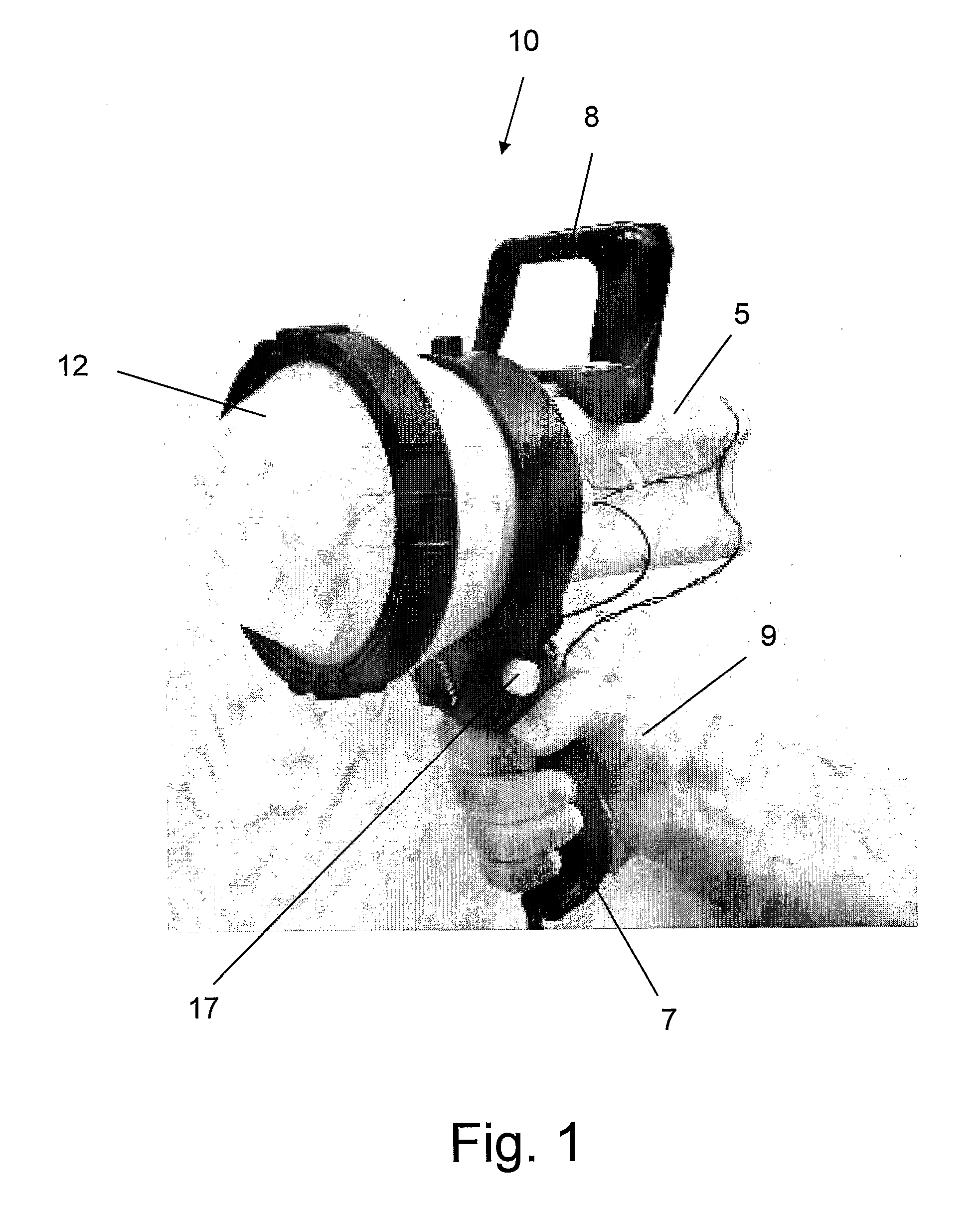Patents
Literature
199 results about "Distance to target" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
For most people it’s 20 yards. Once you find your 20-yard point, you can judge the distance from there to the target, or work in 20-yard increments until reaching the target.
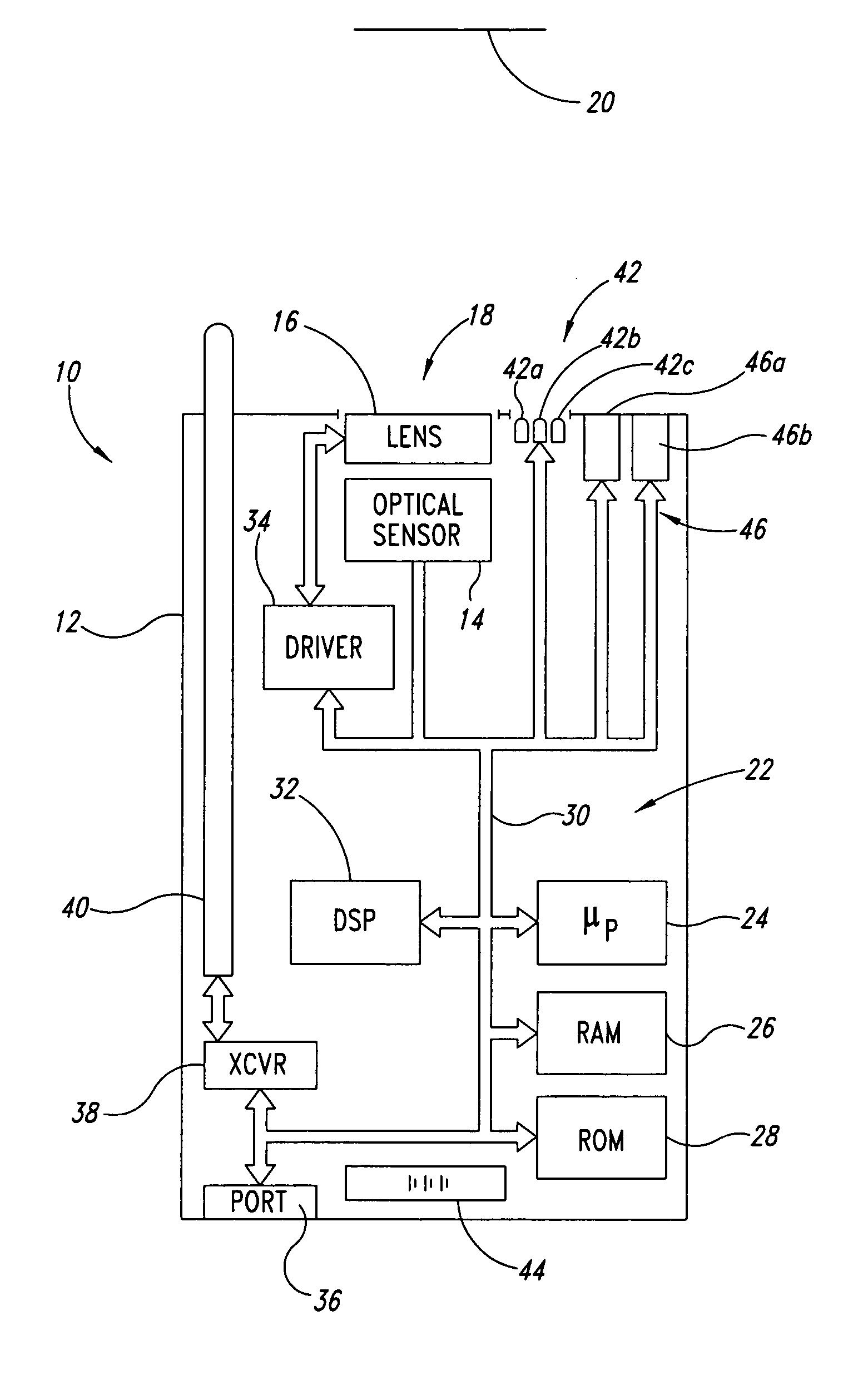
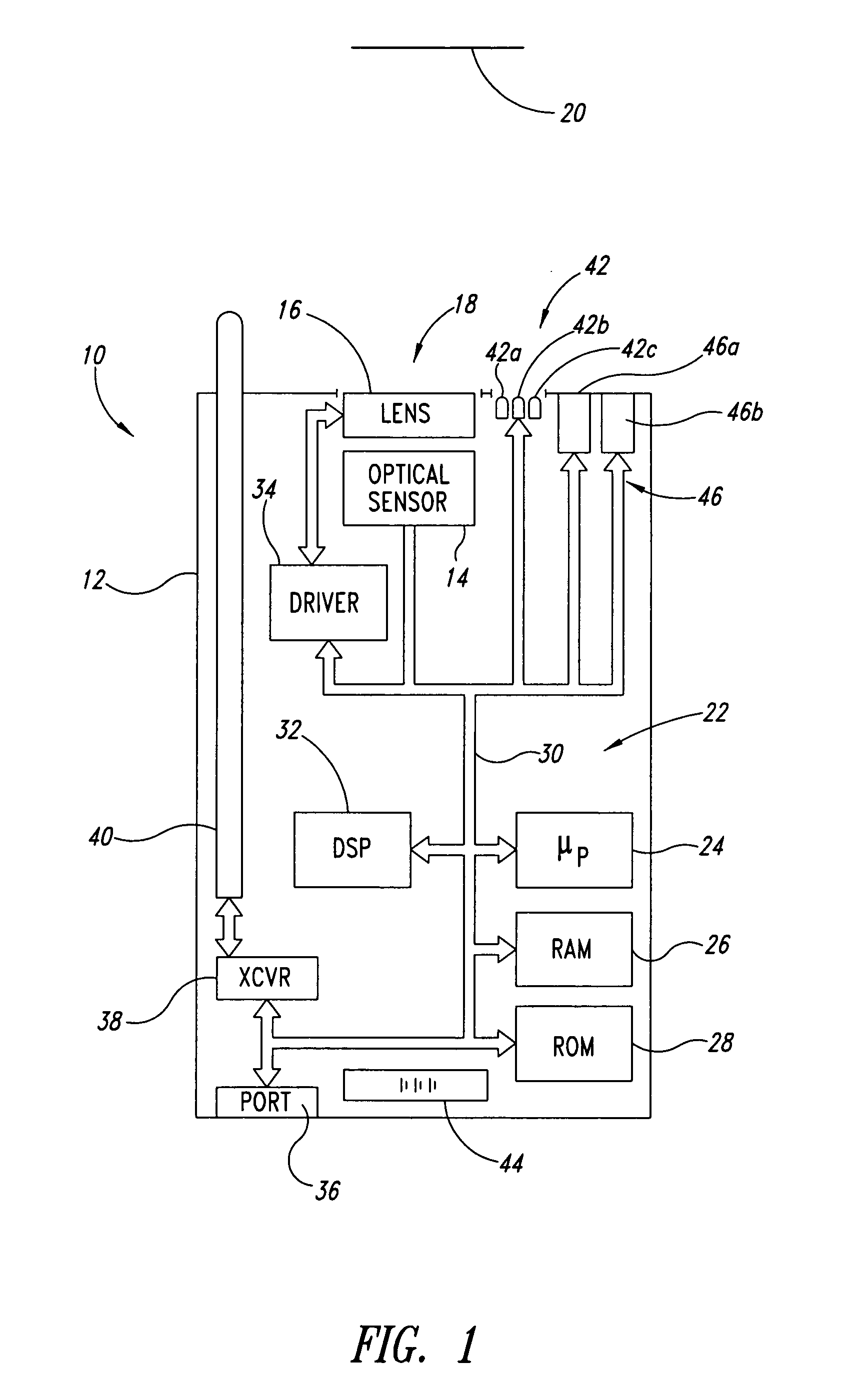
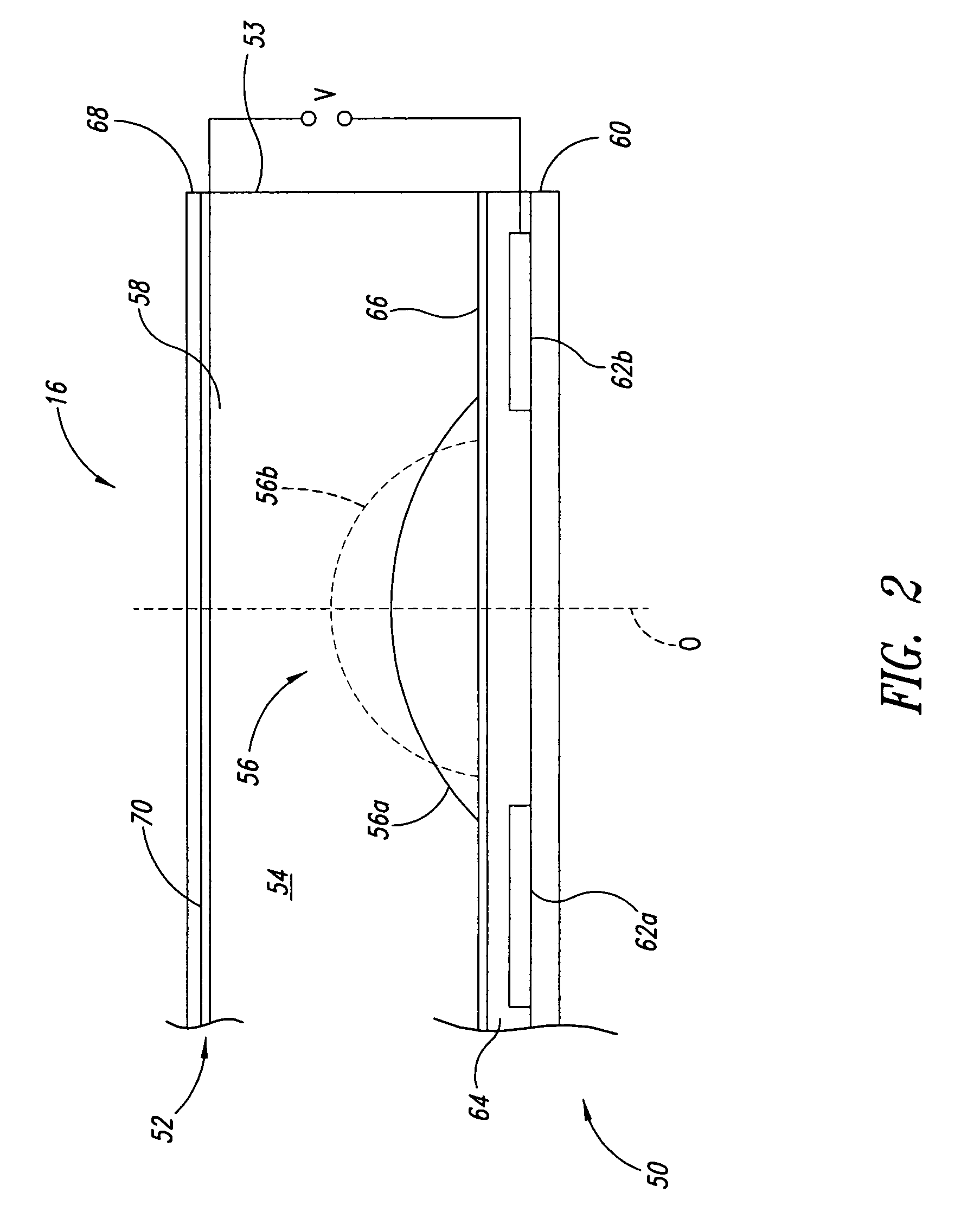
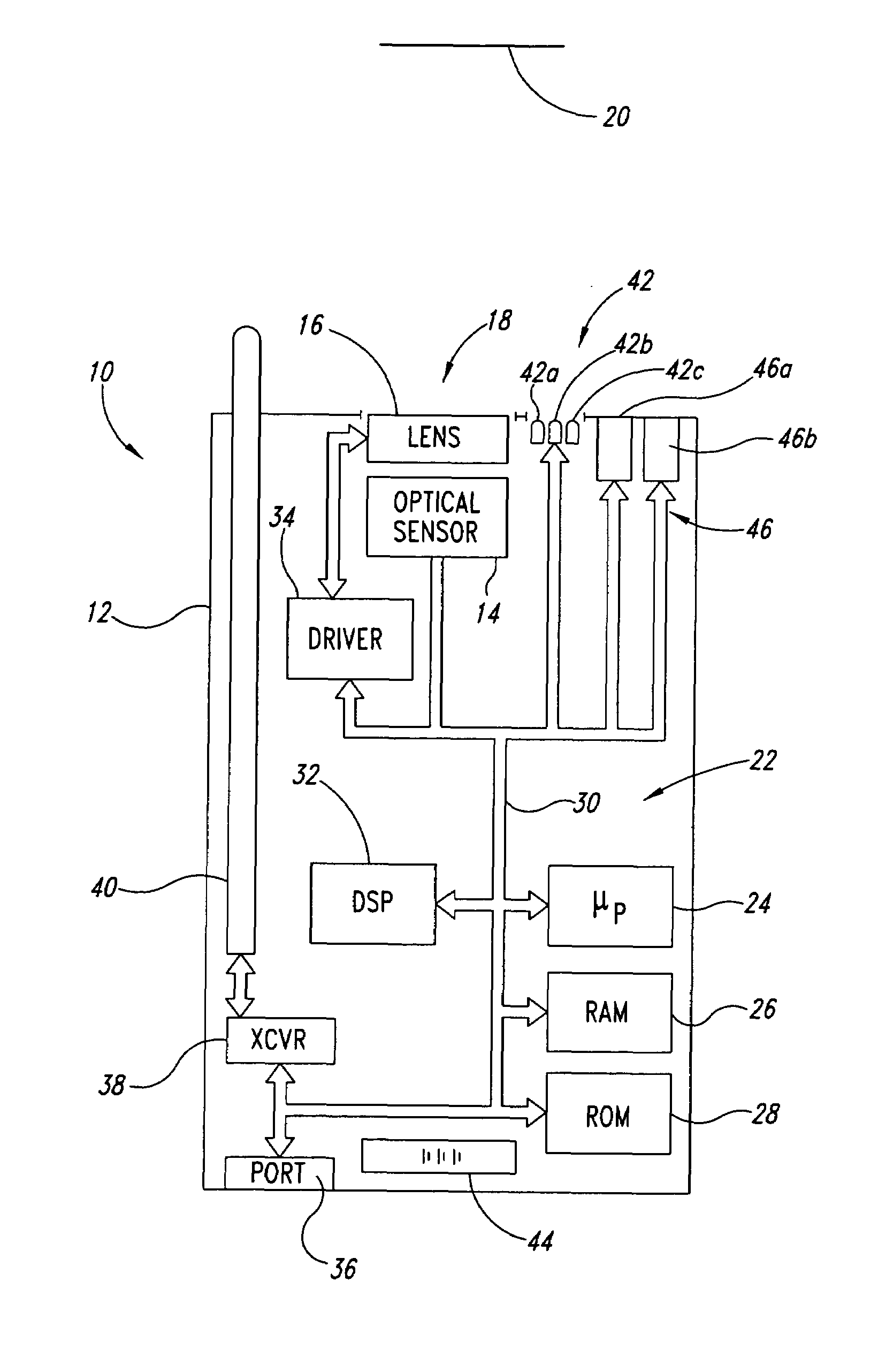
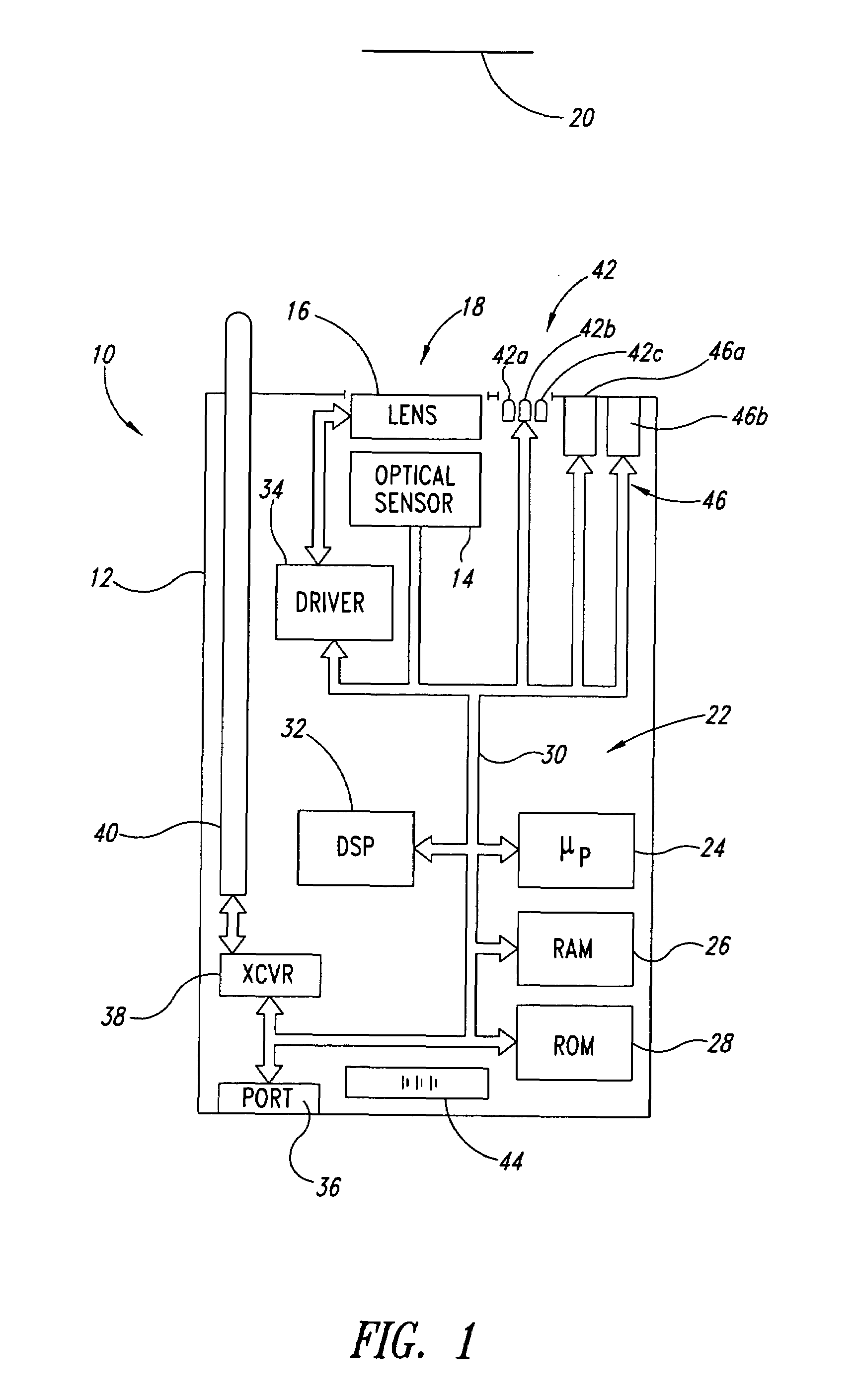
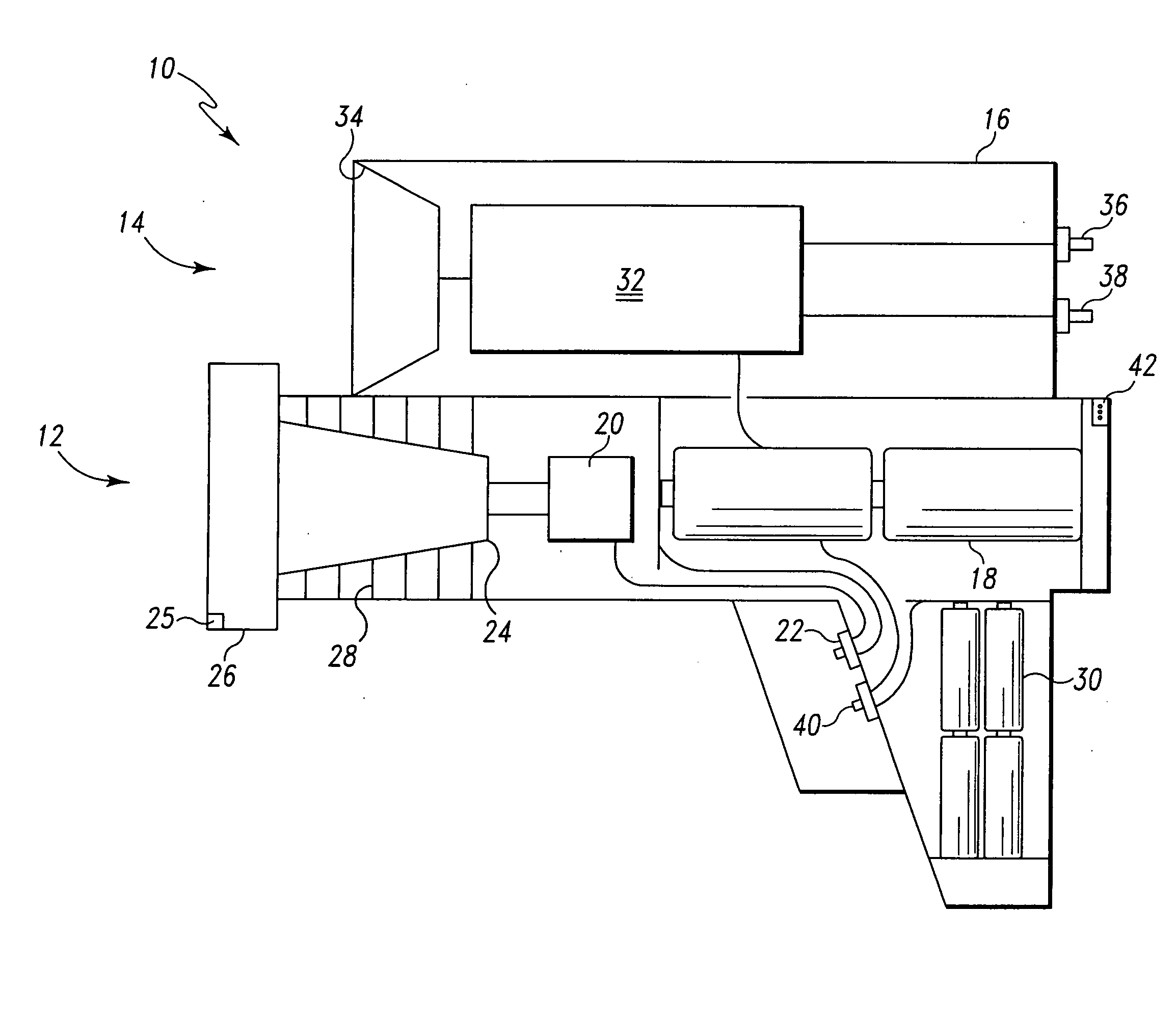
Autofocus barcode scanner and the like employing micro-fluidic lens
ActiveUS20050218231A1Wide spatial resolution rangeReduce and eliminate needProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementBarcodeAutofocus
A machine-readable symbol reader includes a microfluidic lens assembly providing responsive, reliable auto-focus functionality. A range finder may provide distance to a planar target (e.g., barcode symbol) information for use in auto-focusing, with or without localization. Illumination system, if included, is selectively controlled based on the distance to target and auto-focusing functionality to substantially reduce power consumption. The localization may color optical sensors.
Owner:INTERMEC IP
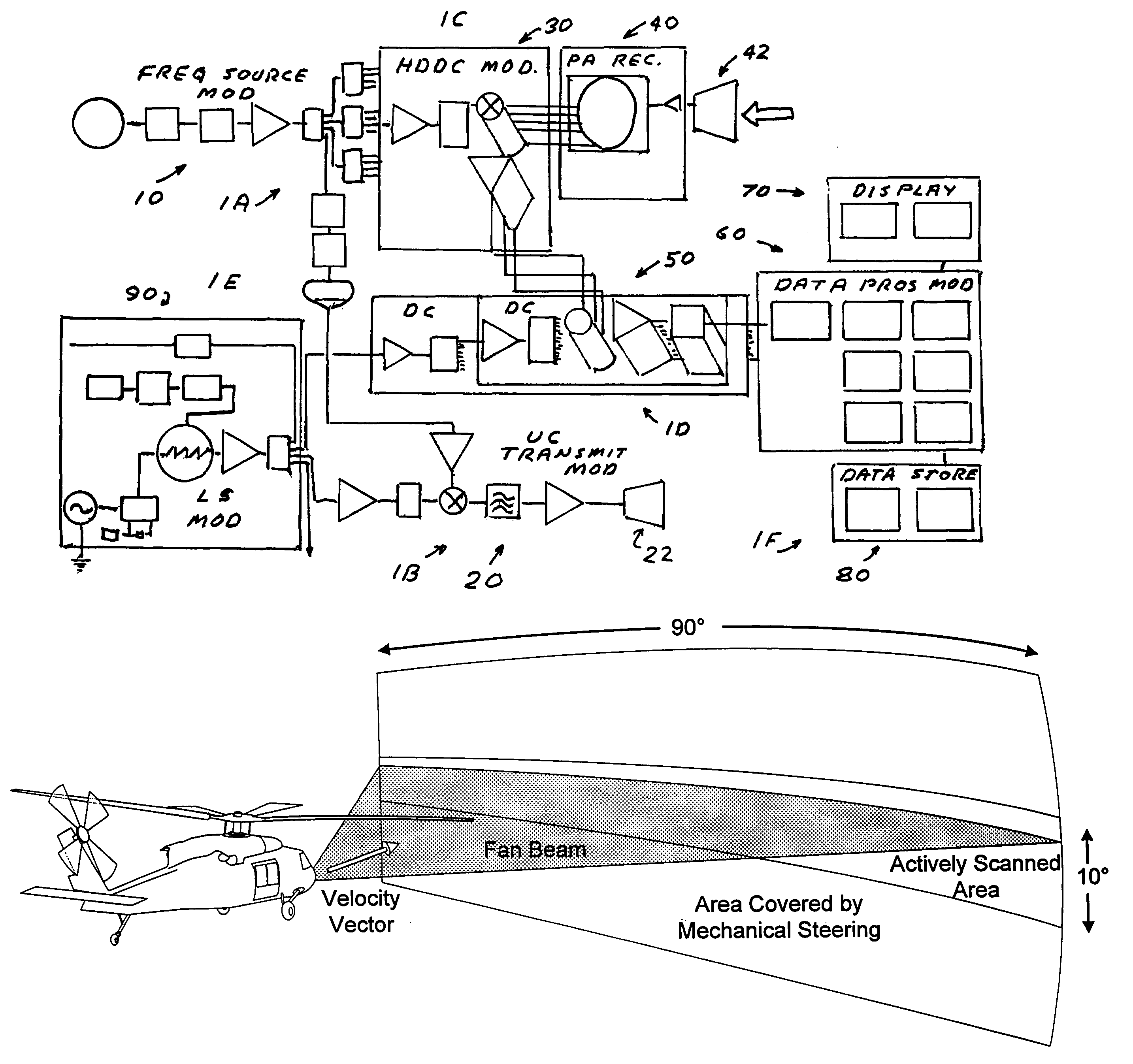
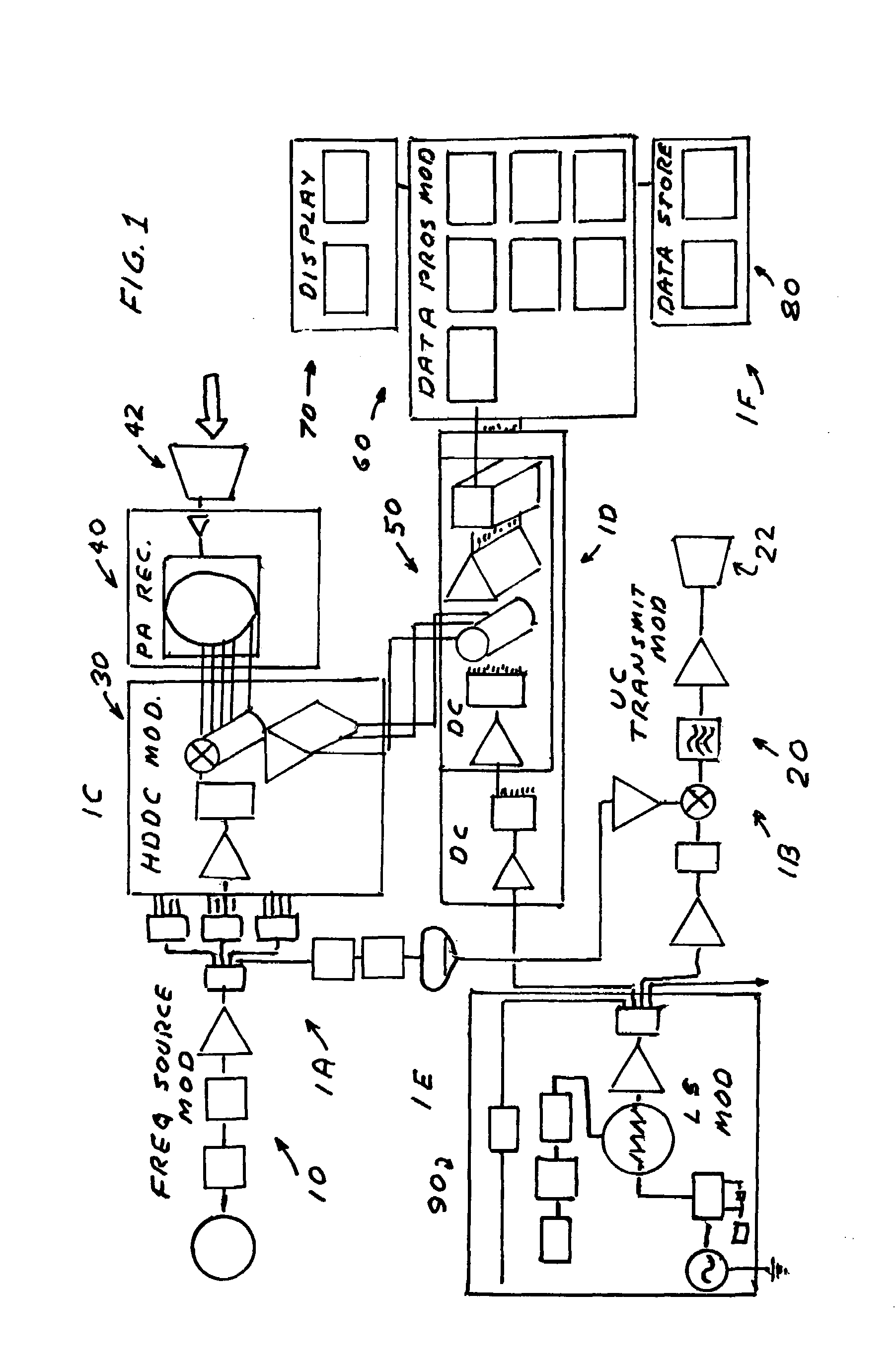
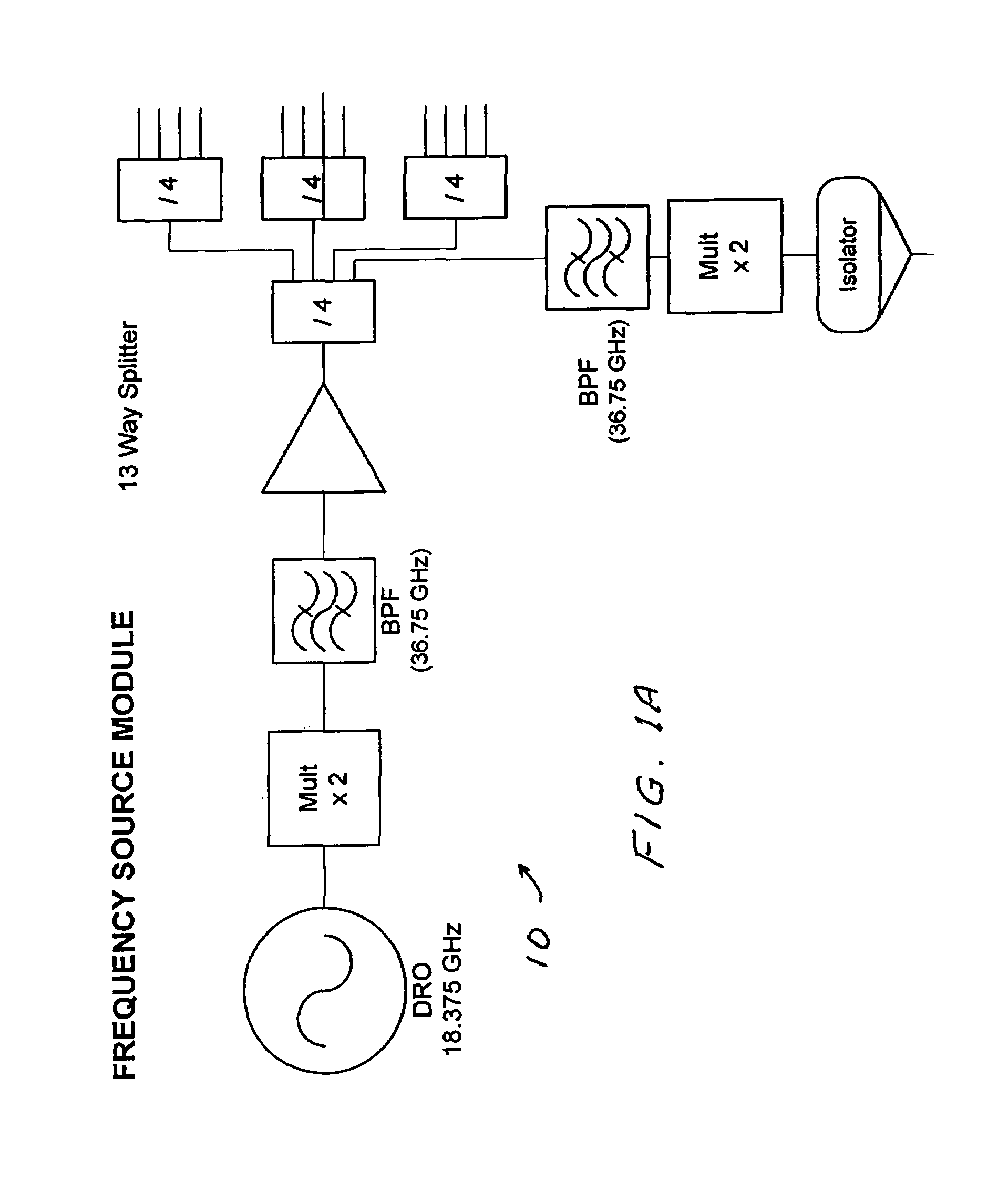
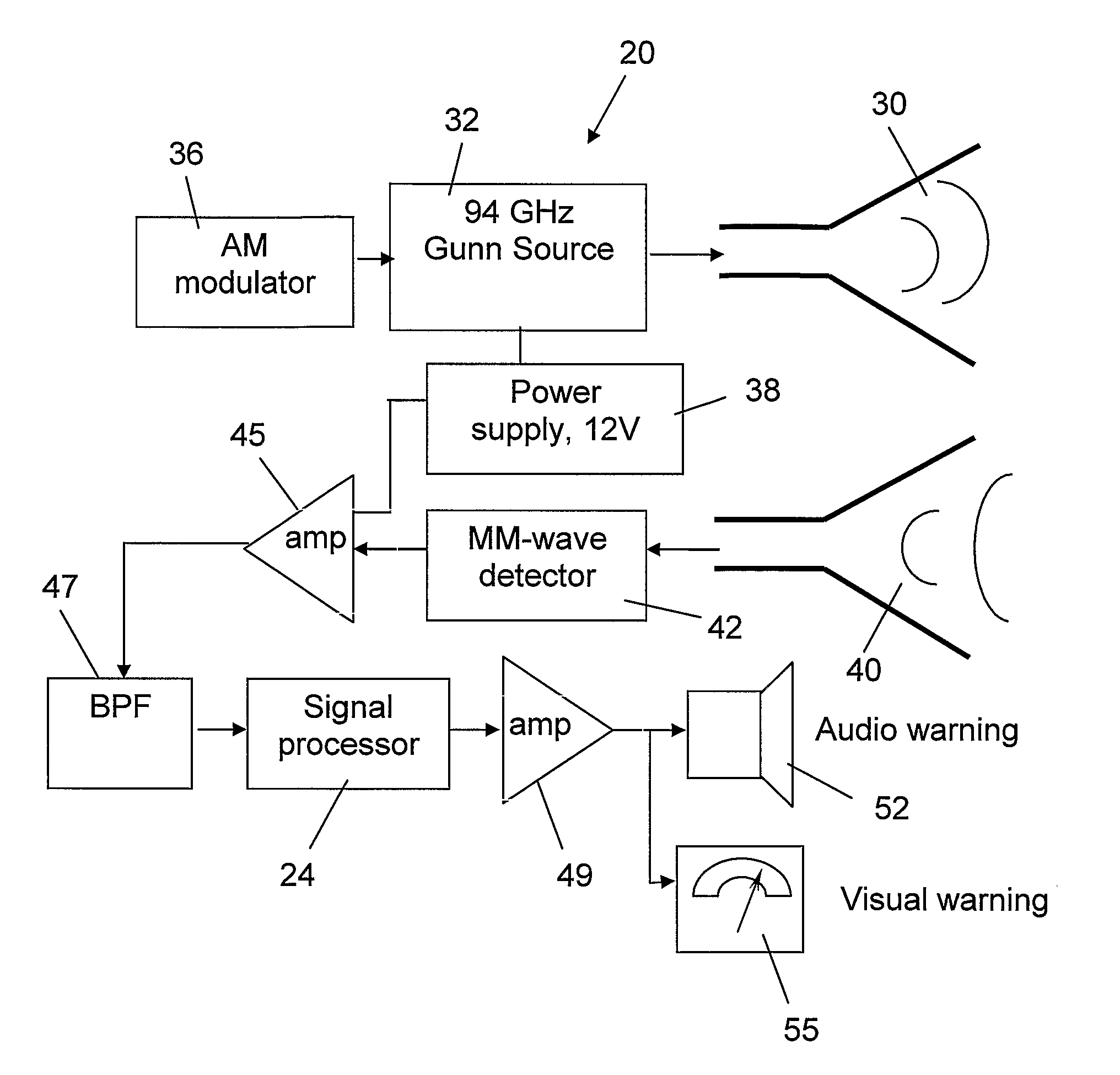
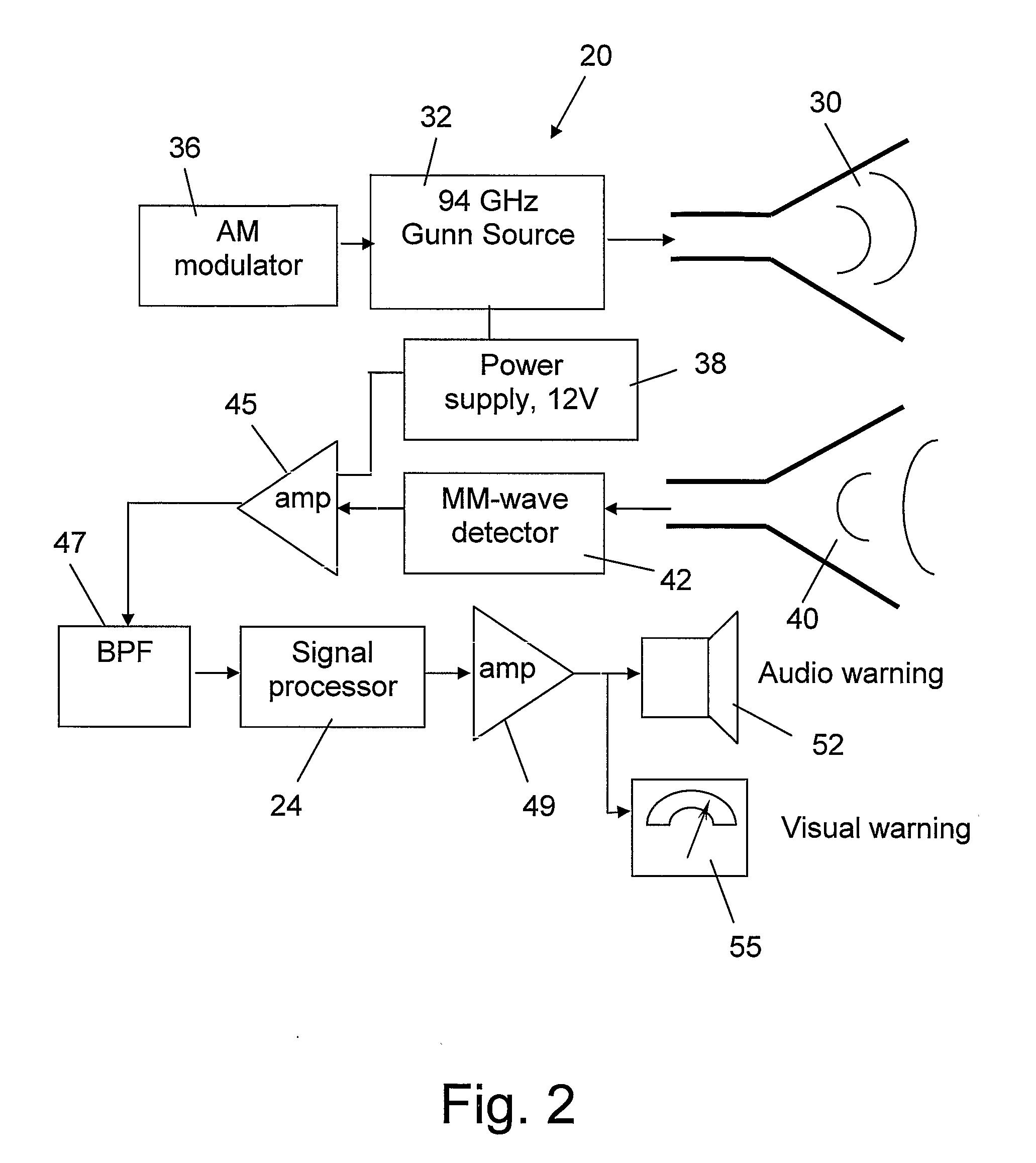
Imaging millimeter wave radar system
InactiveUS7019682B1Linear waveguide fed arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumDisplay device
An imaging millimeter wave radar system. The system includes a millimeter wave transmitter transmitting a frequency scanned millimeter beam that is narrow in the scanned direction and wide in a direction perpendicular to the scanned direction. The system includes a receive antenna and a Rotman type lens for forming a one-dimensional image in the perpendicular direction of targets in the antennas field of view based on millimeter wave radiation reflected from the targets. A computer creates a two dimensional image based on the scanning direction of the transmit beam of the transmit antenna and the one dimensional image from the receive antenna. Distance to the target is determined based on difference in frequency of the transmit signal and the receive signal. Thus, a three dimensional view of the systems field of view is determined by the system. This view can be displayed on a monitor using color to represent target distance. In a preferred embodiment the scanned direction is the vertical direction and the receive antenna forms a horizontal image from signals reflected from targets in the field of view. In this preferred embodiment the transmit antenna is a variable frequency millimeter wave single channel wave guide antenna operating in the 78 GHz to 81 Ghz spectral range to produce a scanning range of 10 degrees and a scanning rate of 60 Hz. The receive antenna is a multi-channel (176 channels) strip-line antenna also operating in the 78 GHz to 81 GHz spectral range, which with the Rotman lens, provides 192 horizontal pixel resolution.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Autofocus barcode scanner and the like employing micro-fluidic lens
ActiveUS7296749B2Wide spatial resolution rangeReduce and eliminate needProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementBarcodeDistance to target
A machine-readable symbol reader includes a microfluidic lens assembly providing responsive, reliable auto-focus functionality. A range finder may provide distance to a planar target (e.g., barcode symbol) information for use in auto-focusing, with or without localization. Illumination system, if included, is selectively controlled based on the distance to target and auto-focusing functionality to substantially reduce power consumption. The localization may color optical sensors.
Owner:INTERMEC IP
Weapon sight with ballistics information persistence
ActiveUS20060048432A1Facilitates weapon orientationSighting devicesDistance to targetComputer science
A device includes can be supported on a weapon, and has a range portion that specifies a range to a target, a sensor portion that provides sensor information representing an orientation of the device; and a sight that facilitates weapon orientation in preparation to fire the munition. The device has an electronic control portion responsive to sensor information from the sensor portion and a range from the range portion for calculating how to hit a target with a munition, and for causing the sight to present a visual indication of how to orient the weapon so that the munition will hit the target, the electronic control portion terminating the presentation of the visual indication by the sight in response to a lack of user activity for a selected time interval during the presentation of the visual indication.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Hand-held device and method for detecting concealed weapons and hidden objects
InactiveUS20090195435A1Improve uniformityGeological detection using milimetre wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWave detectionDisplay device
The present invention is an inexpensive, hand-held, and easy to operate millimeter-wave detection device that employs a non-imaging sensor which radiates a pulse of millimeter waves of a certain amplitude and frequency towards a target located at a distance from the detection device. The sensor receives pulses of millimeter waves that are reflected from the target and generates a voltage waveform that is characteristic mainly of the target material, while other parameters such as distance to the target are known. The processor of the detection device measures both the peak voltage and the rate of increase of the voltage until it reaches the maximum. Using an algorithm stored in a software module, the deviation between the rate of the voltage rise and the peak voltage is compared with values of similar parameters for a number of test targets made of different materials that were previously collected and stored in a calibration table in the memory of the device. A concealed object, e.g. a weapon, is positively identified when the measured voltage rise is found to be similar to one of the stored voltage rises. The circuitry of the detection device generates a visual and / or audio output to a display device which is indicative to the operator as to whether a concealed object is present and, if a match is found with the data in the calibration table, the nature of the concealed object is also displayed. In addition to the basic mode of operation described, various other operation modes can be employed with the detection device of the invention.
Owner:ARIEL UNIV RES & DEV
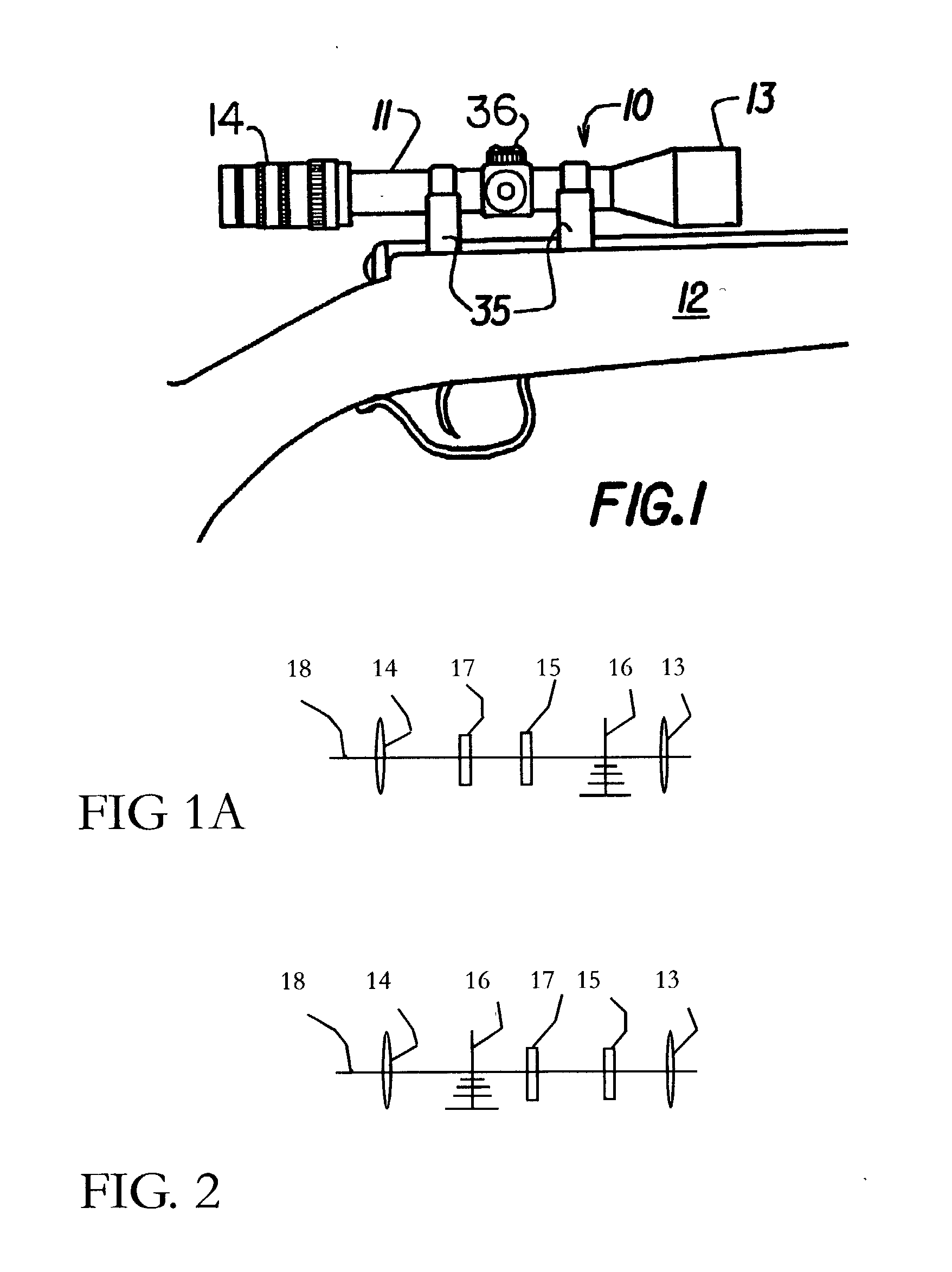
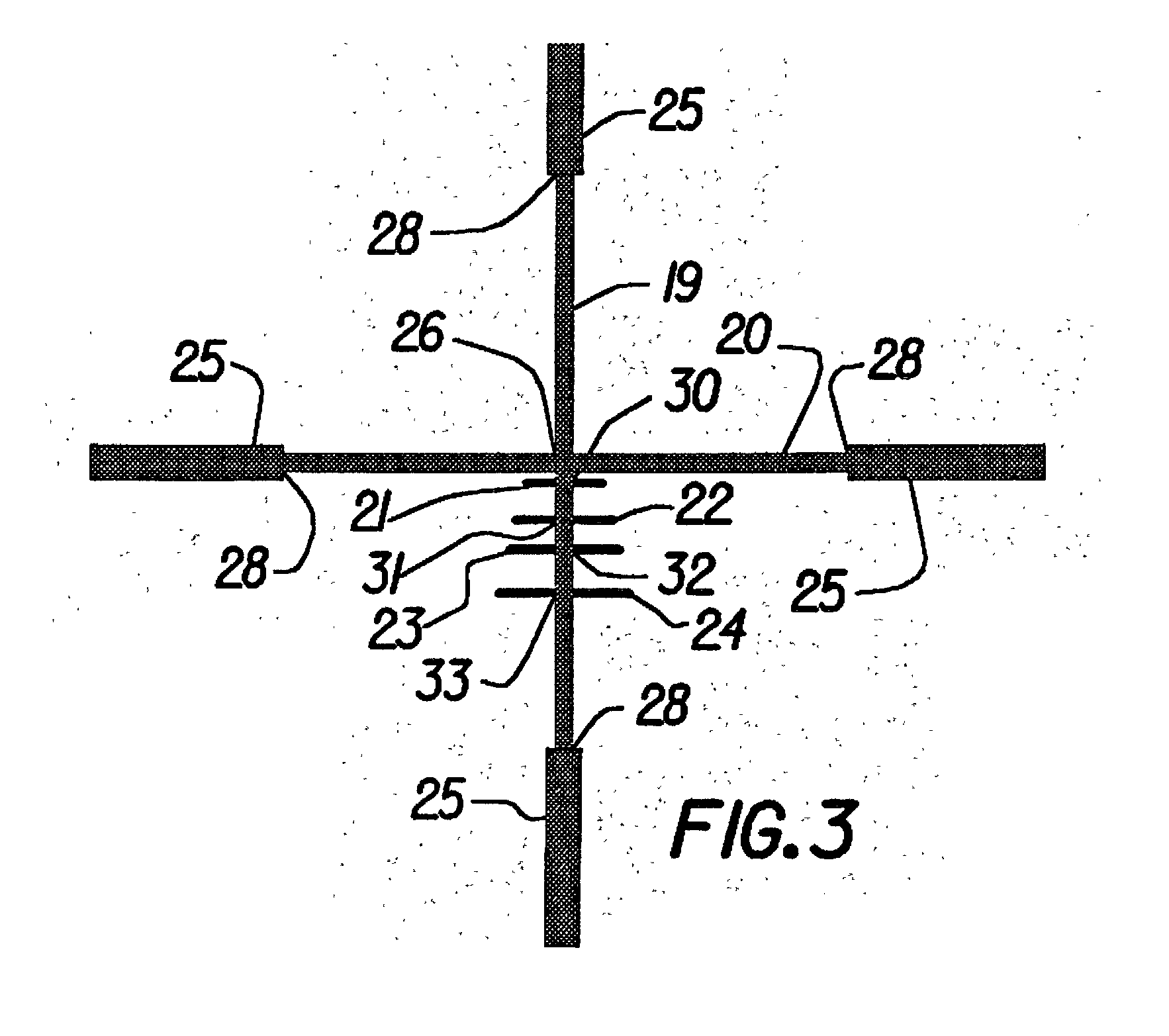
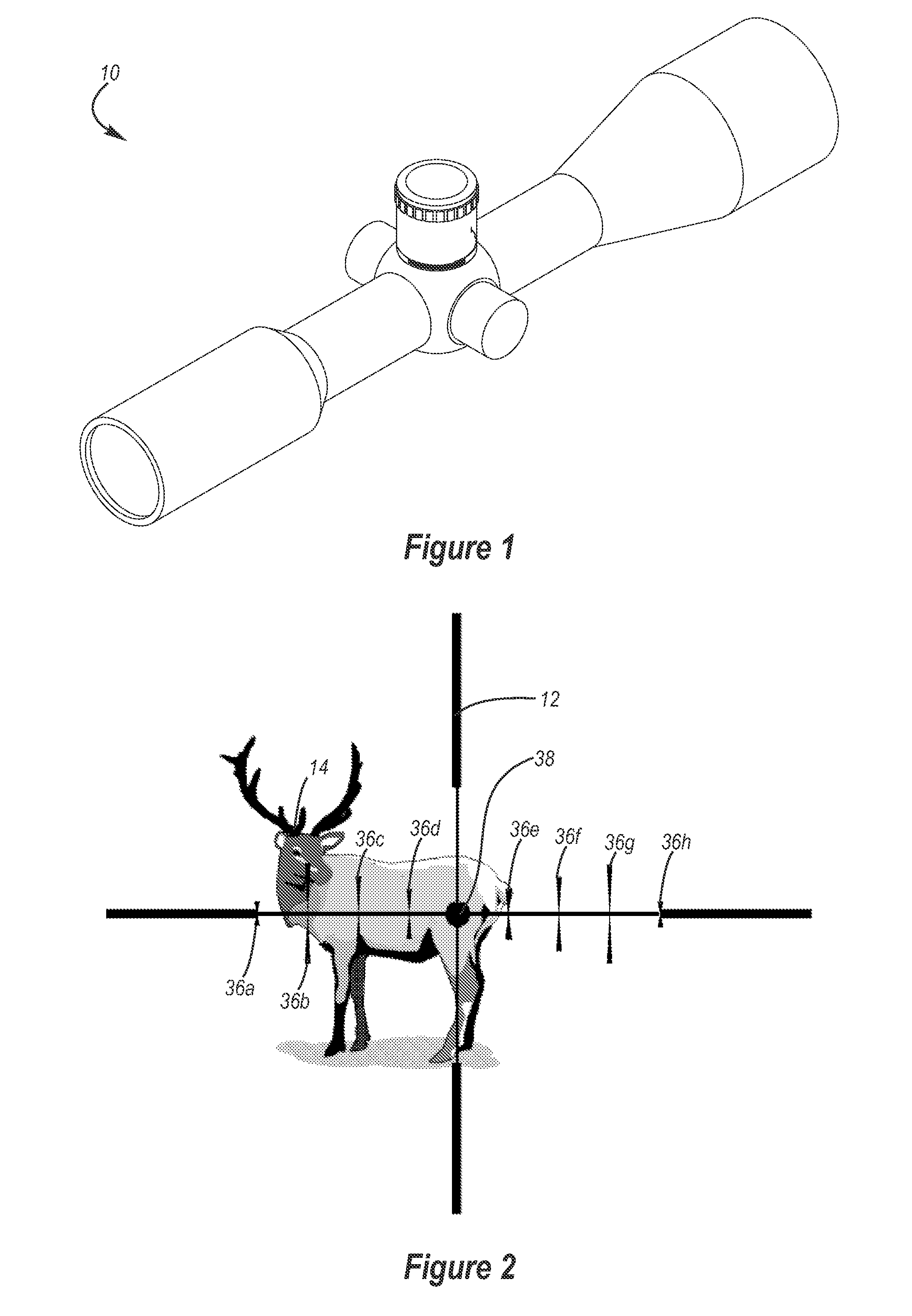
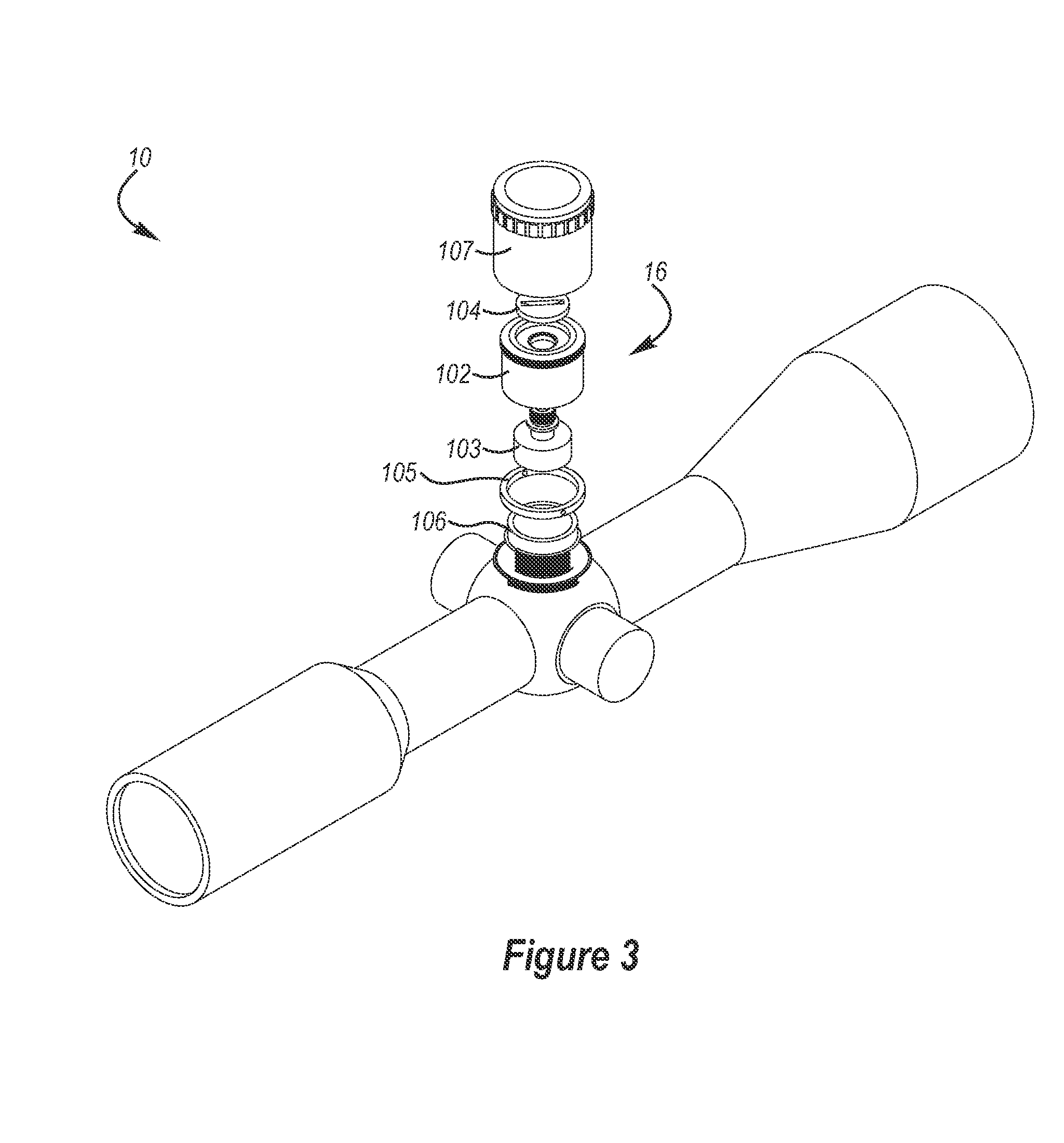
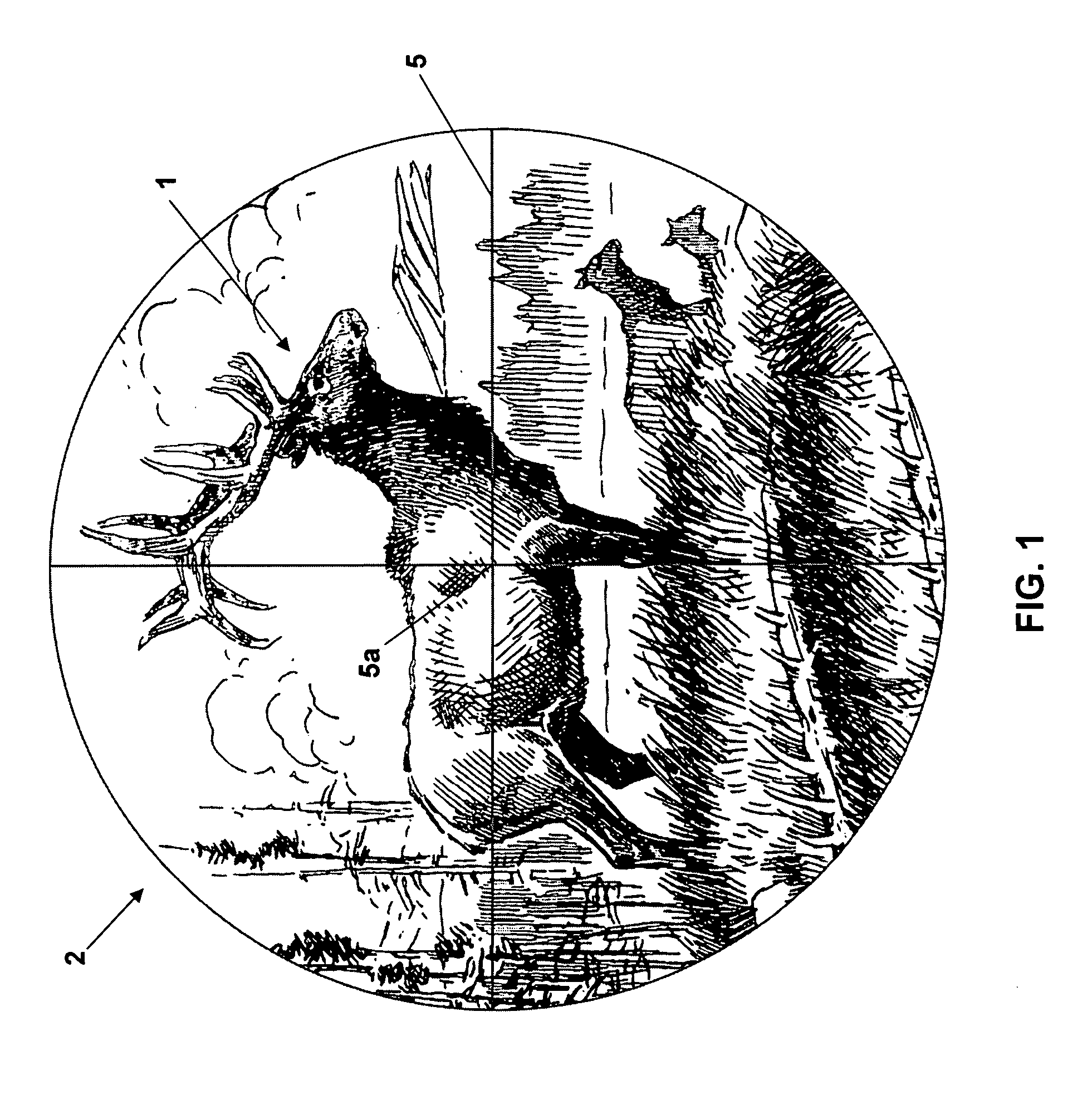
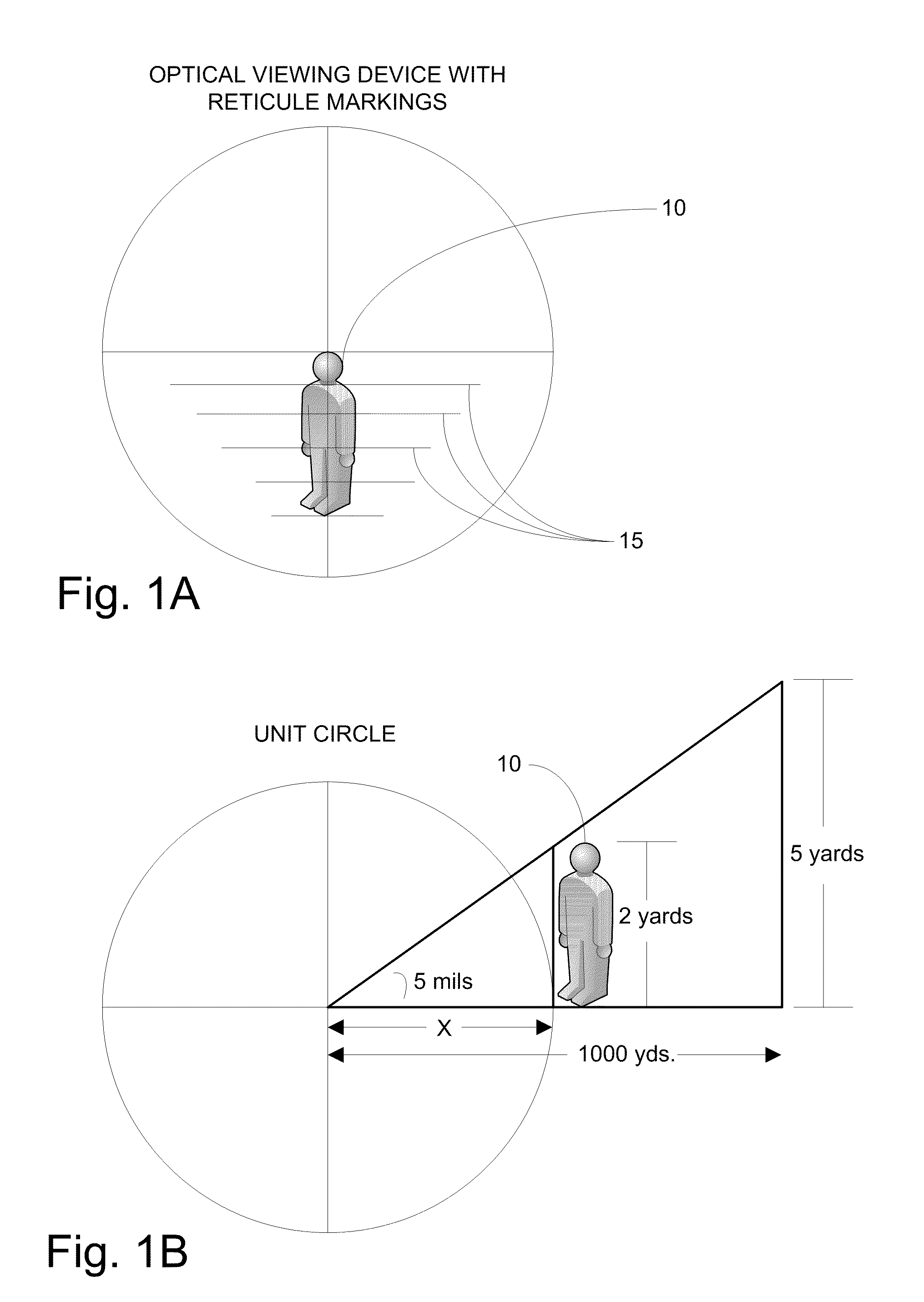
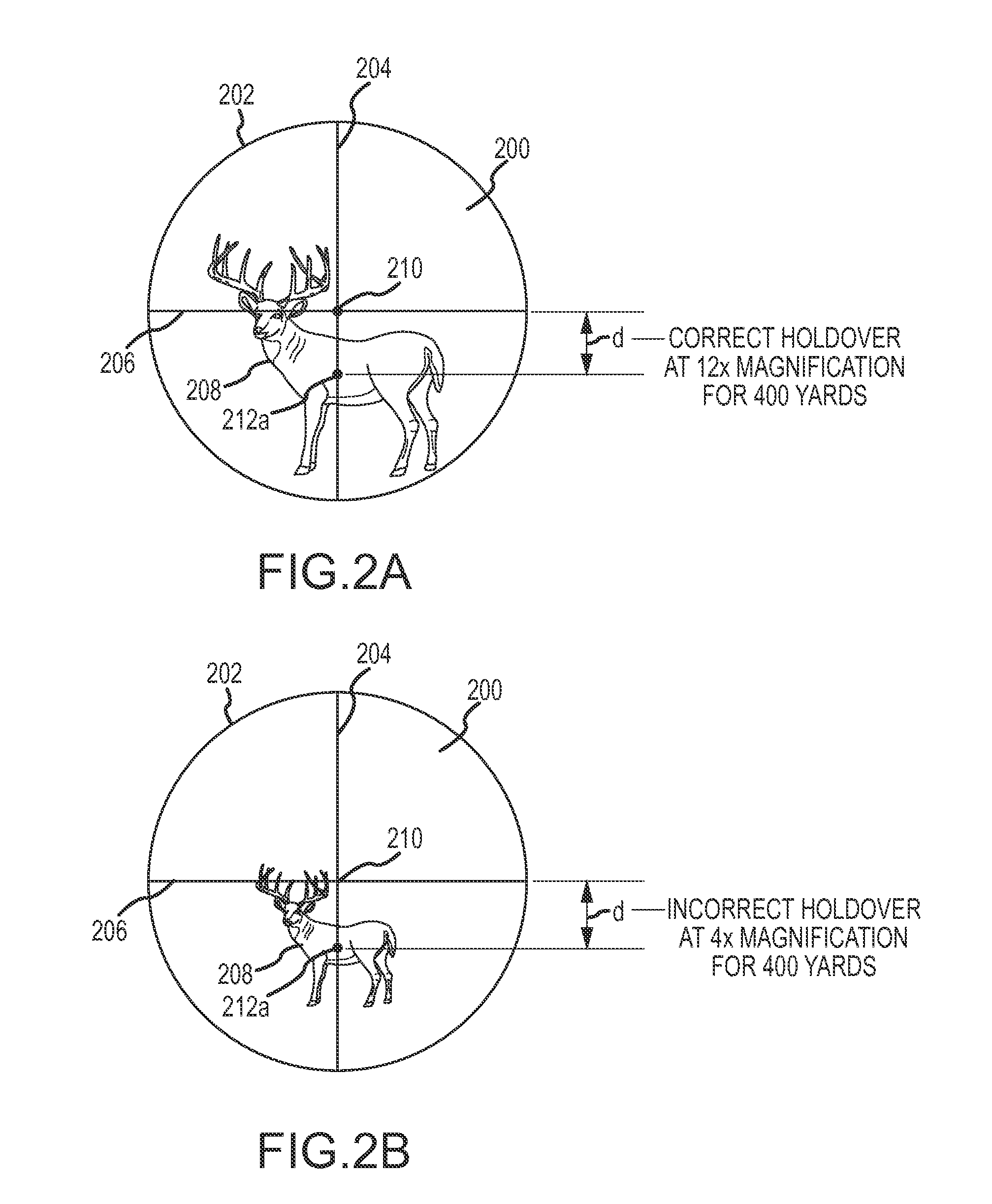
Reticle for telescopic gunsight and method for using cross reference to related application
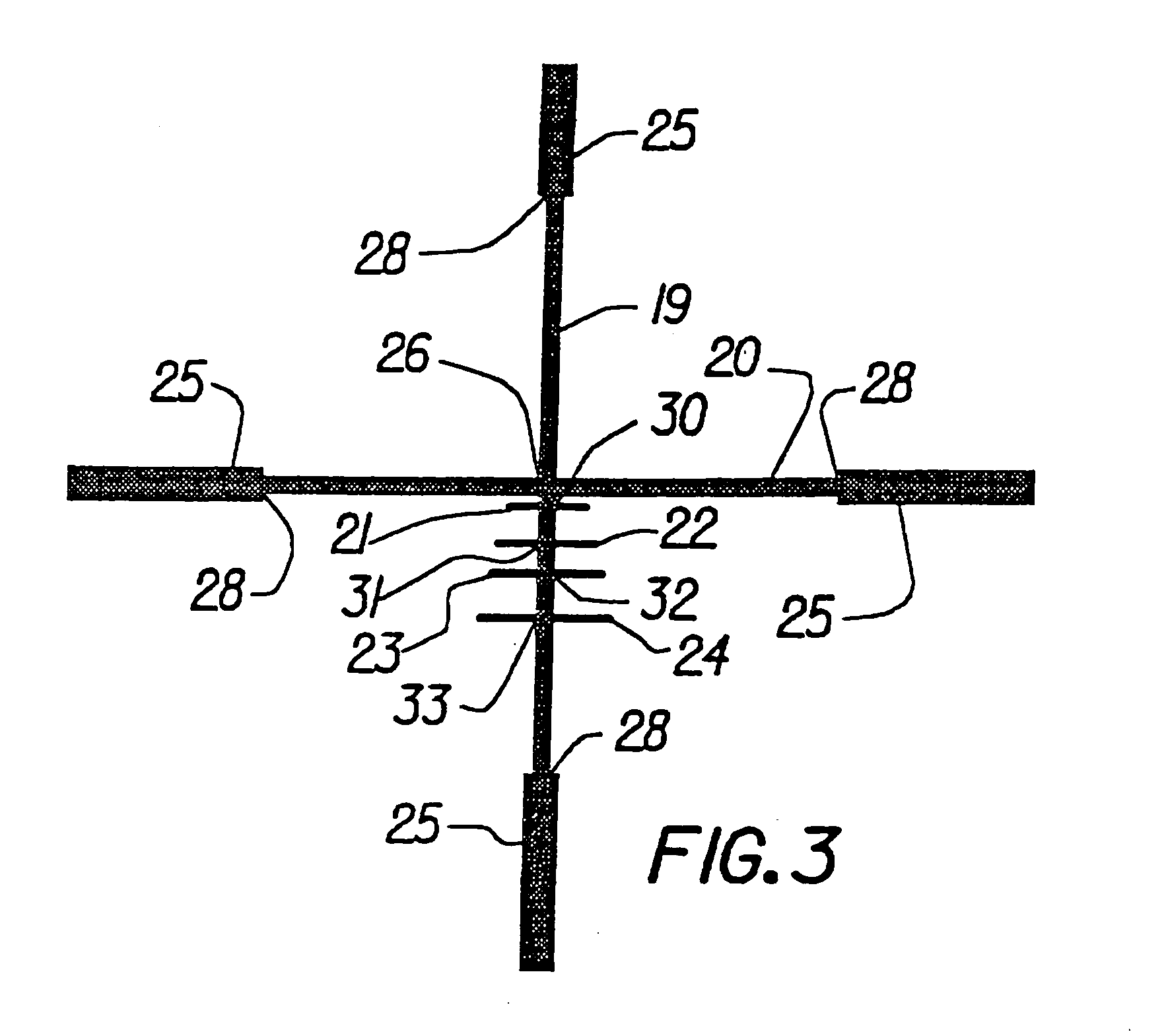
InactiveUS20050005495A1Promotes shooter confidenceEffect deterioratesSighting devicesTelescopesDistance to targetEngineering
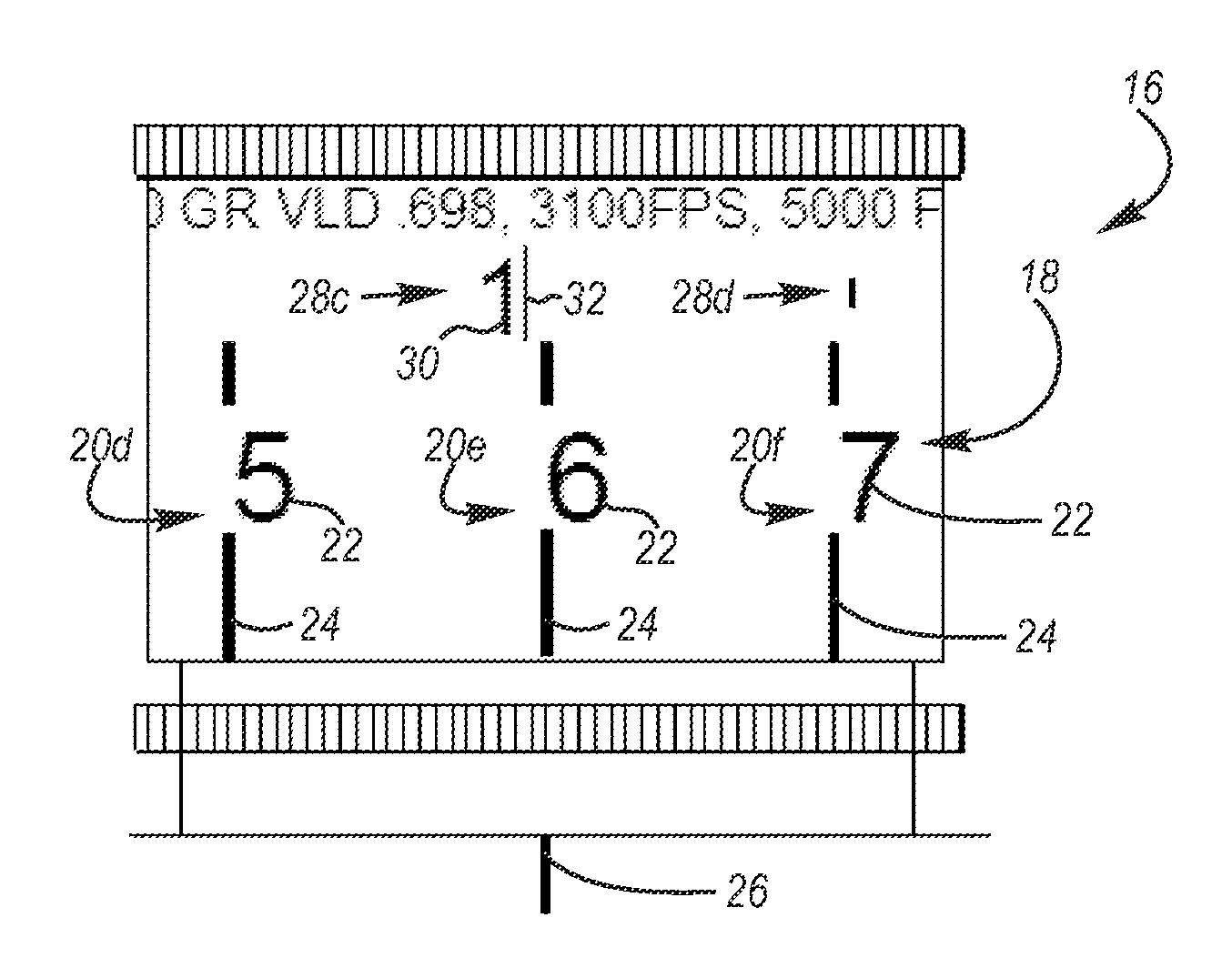
A gunsight reticle defines a system of dimensioned indicia spaced at specific separations to improve aiming accuracy of a gun. The indicia may include perpendicularly intersecting center vertical and center horizontal hairlines, and four (or more or less) horizontal range-marker lines disposed at specific angular separations below the horizontal hairline in bisected relationship with the center vertical hairline. Spacing of the range marker lines below the center horizontal hairline is proportional to bullet drop at selected ranges, depending upon ballistic characteristics of bullet used. Relative lengths of said range-marker bars on each side of the central vertical crosshair are proportional to a specific crosswind (say 10 mph) at target range reflected by respective range marker. The method involves employing this reticle to determine distance to target, and using distance thus determined to ascertain a precise aiming point on the reticle. These indicia also have other useful characteristics that allow the shooter to easily mentally calculate corrections for crosswind, moving targets and shooting at targets that are above or below the shooter at a significant angle.
Owner:SMITH THOMAS D III
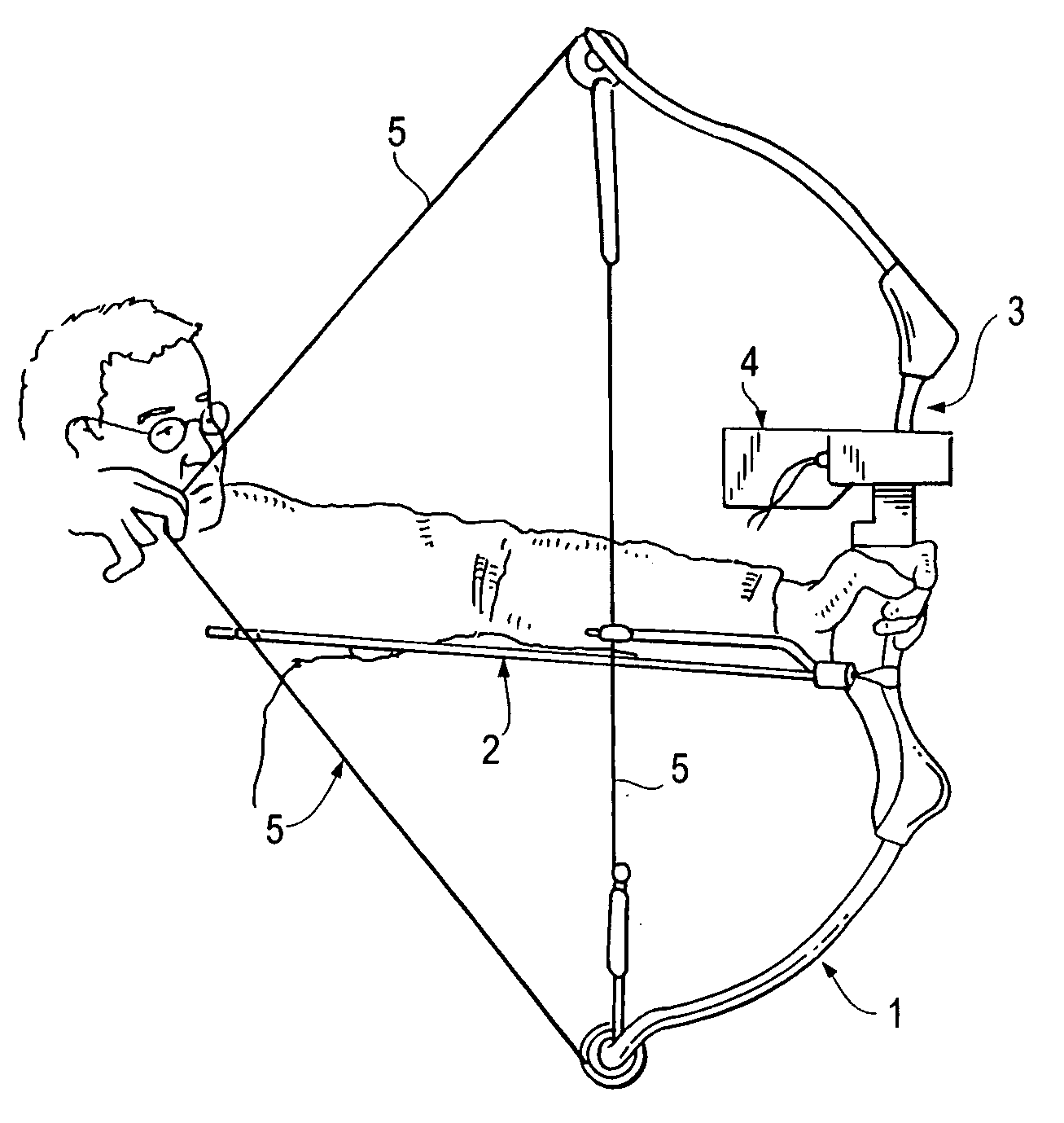
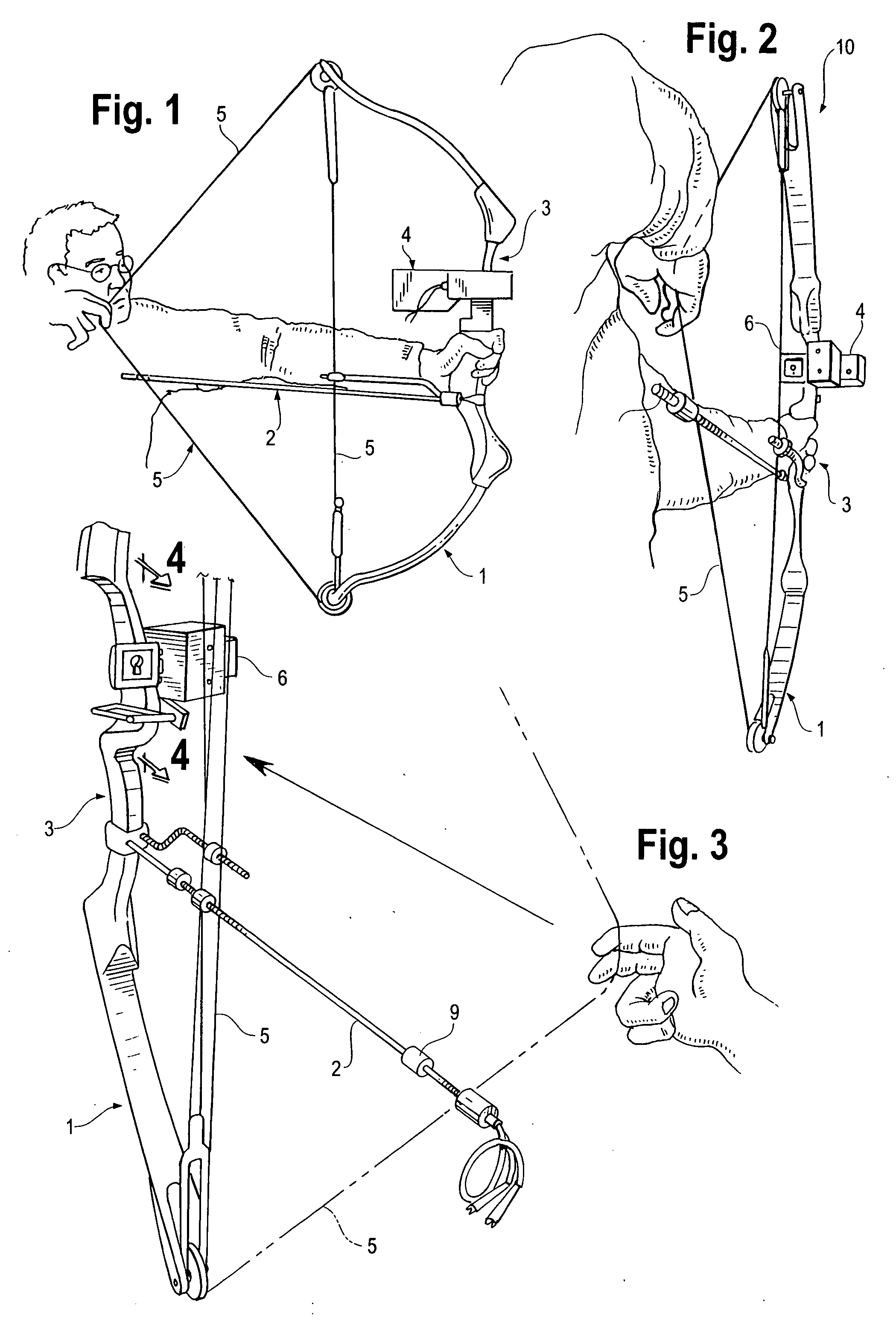
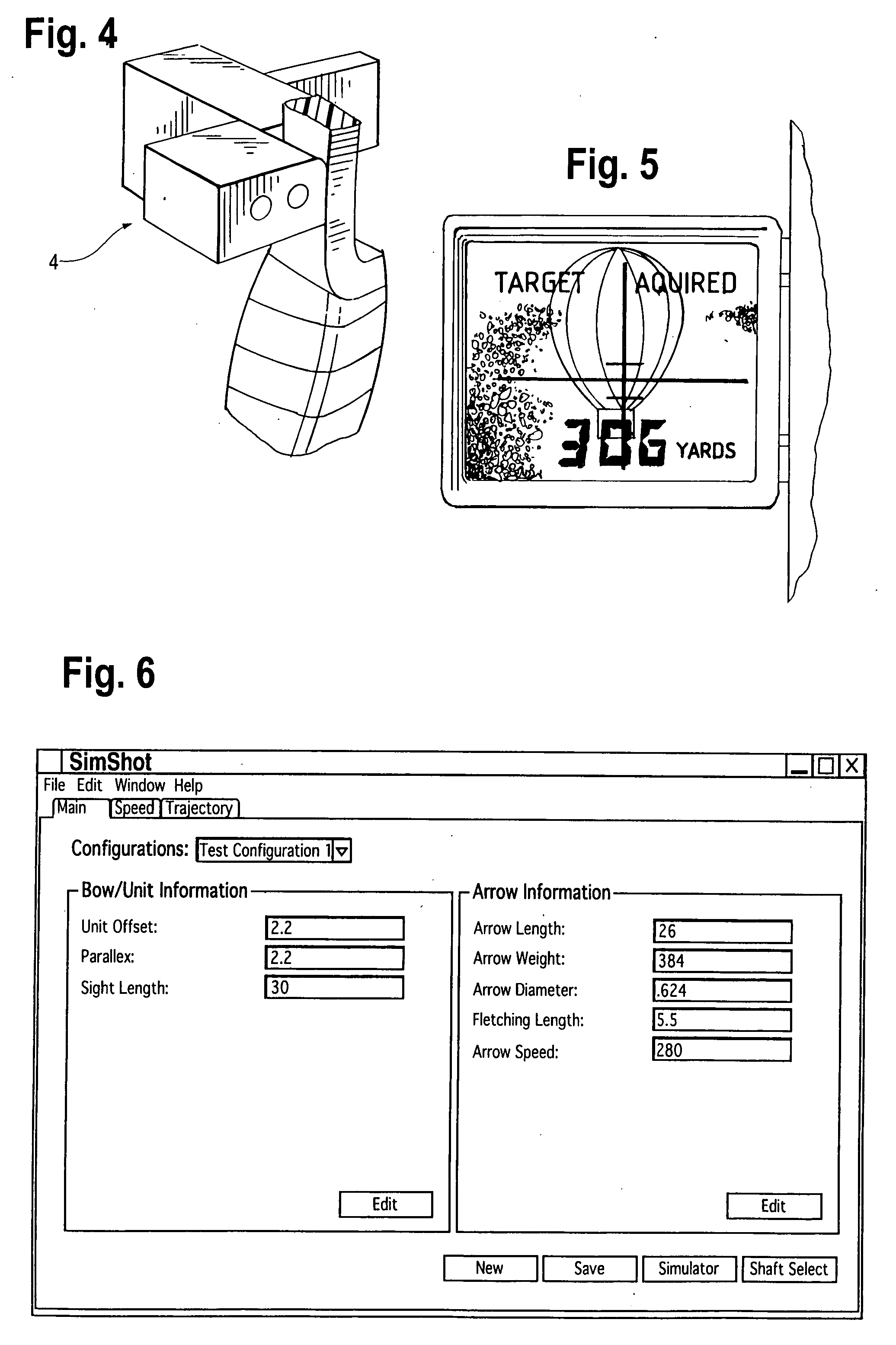
Simulated hunting apparatus and method for using same
InactiveUS20050123883A1Minimize and prevent rod flexMinimize and prevent and distortionBows/crossbowsSighting devicesDistance to targetData acquisition unit
A simulated hunting application for simulating the firing of a projectile such as an arrow or bullet, and displaying its flight path and that of its impact point on an intended target. In a preferred embodiment, the simulated hunting application includes a hunting instrument, such as an archery bow or gun, capable of launching a projectile such as an arrow or bullet; a data capture unit such as a video camera for capturing video data; a range finder for determining distance to target; a display screen for displaying images; trajectory calculating and video editing software programs; and a recording unit for storing the data captured by the data capture unit and data entered into the trajectory calculating software by the user. The flight path of the projectile, as well as its impact point with respect to the intended target, and interplay with background images, may be viewed by the hunter. Safe dry-firing of the hunting instrument may be provided using a momentum suppression rod which also forms part of the present invention. Interplay between the trajectory calculating software and an appropriate clinometer takes into account uphill or downhill shooting.
Owner:KENNEN JOHN SCOTT +1
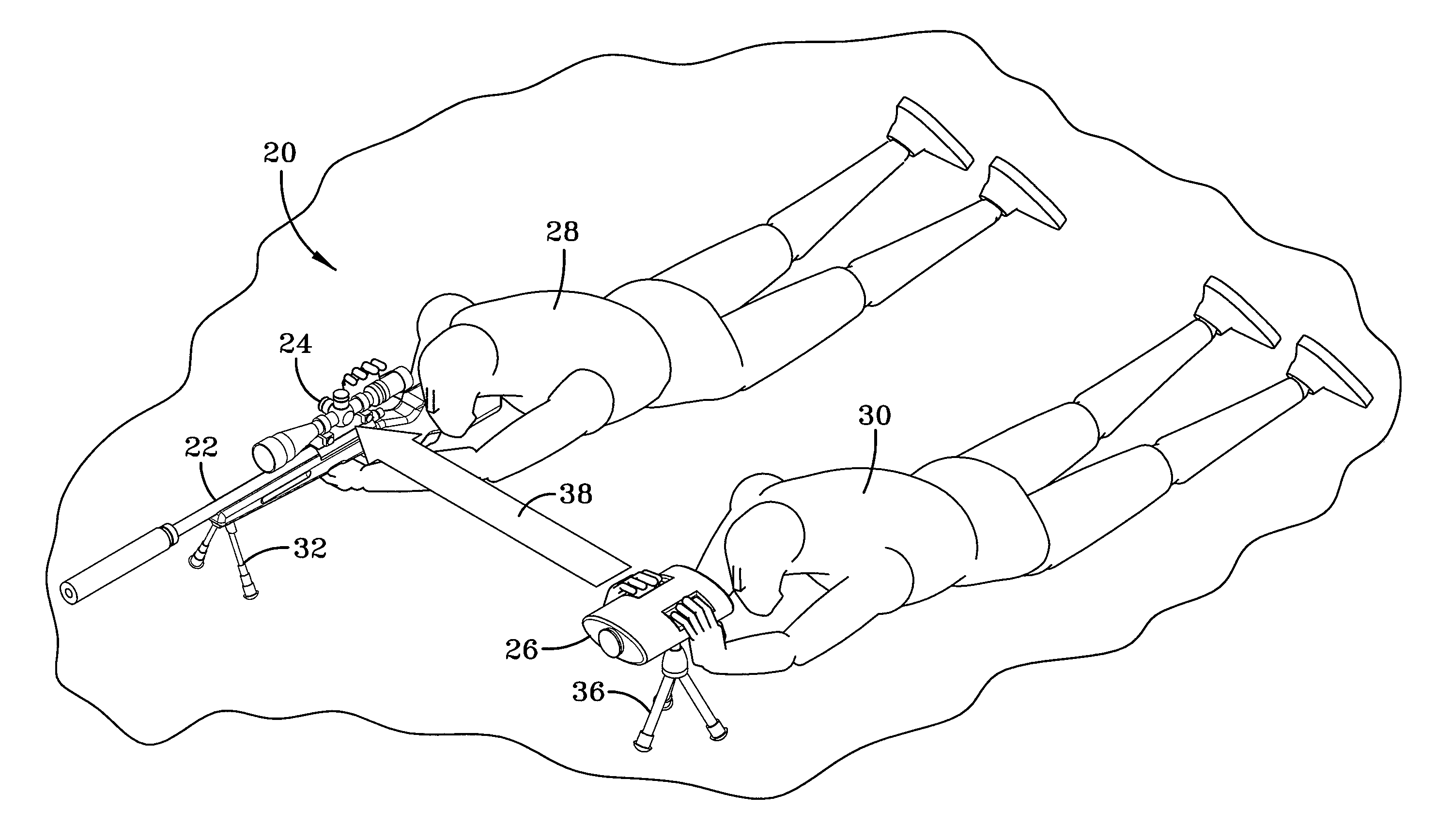
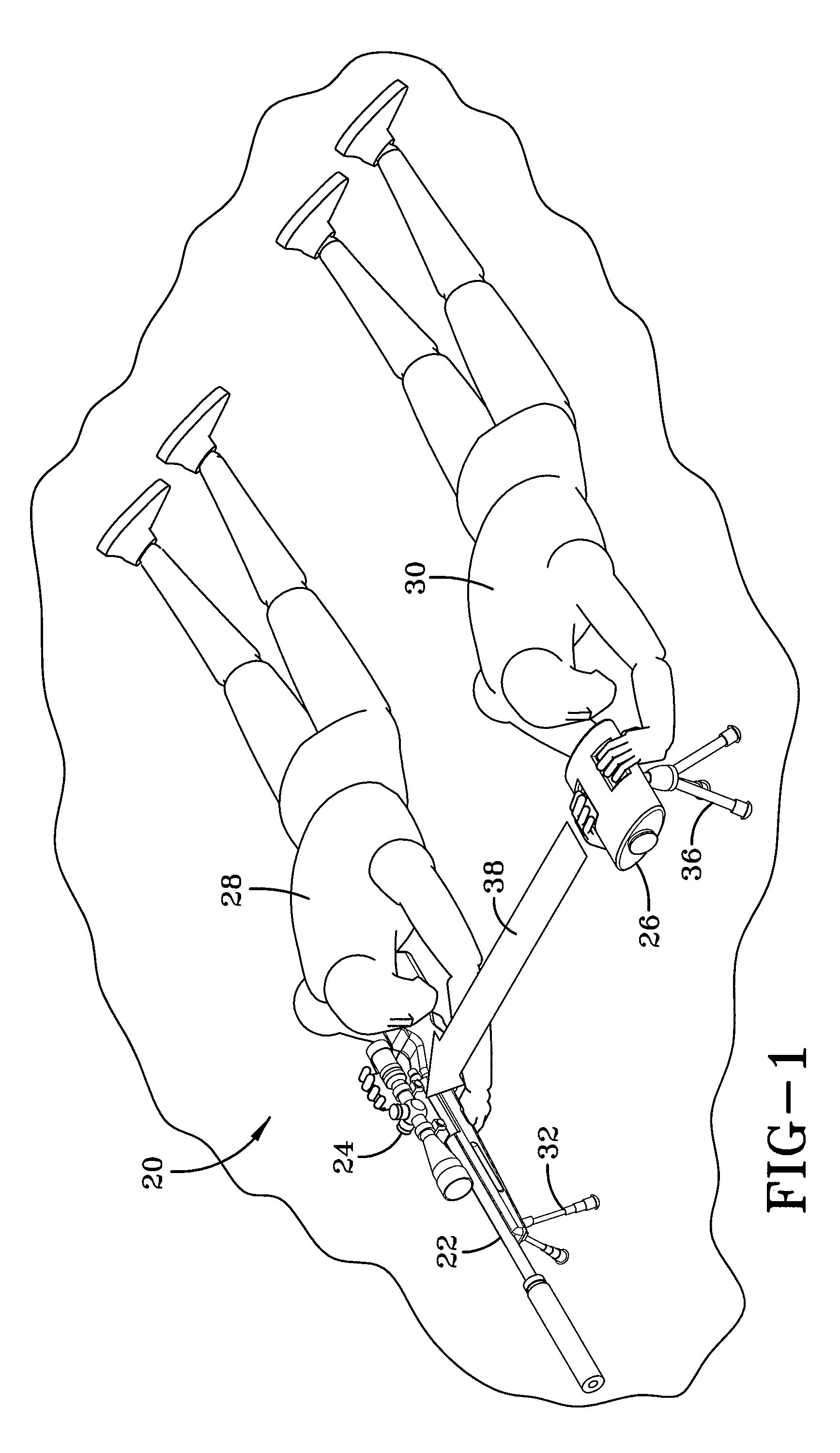
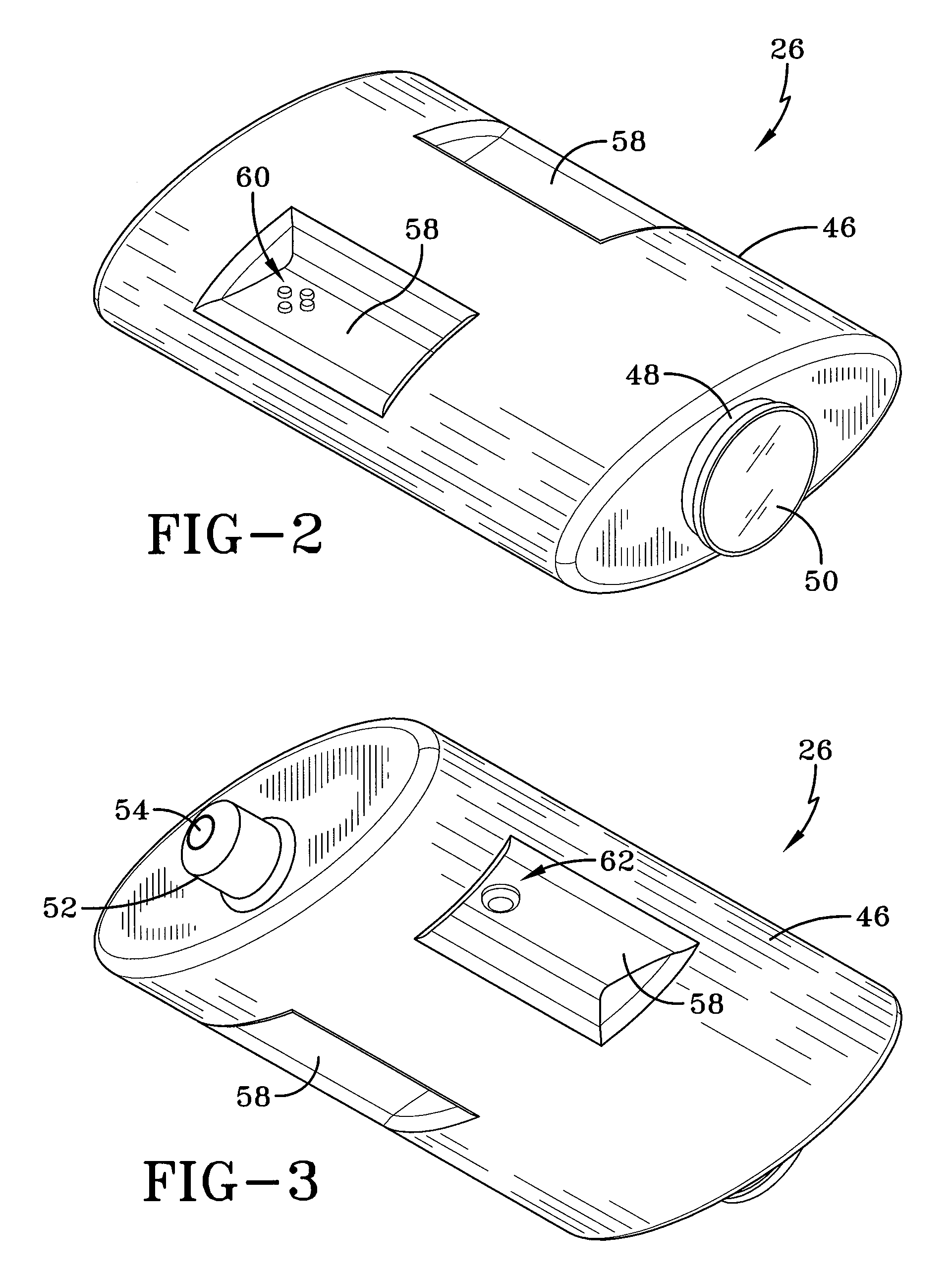
Assisted sighting system for snipers
InactiveUS20090320348A1Improve accuracyEasy to adjustOptical rangefindersSighting devicesDistance to targetFocal Plane Arrays
A spotter scope including an illuminator that generates a ranging signal is disclosed. The spotter scope further includes an imaging device with a focal plane array which detects backscatter radiation created by the ranging signal, and a controller which calculates a distance to a target. The controller also creates a wind profile between the spotter scope and the target based on scintillation statistics of backscatter detected by the focal plane array and provides corrective aiming instructions based on the wind profile.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Distance measuring method and distance measuring element for detecting the spatial dimension of a target
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
Ballistics systems and methods
ActiveUS8001714B2Quick selectionQuick identificationWave based measurement systemsComputer controlComputer moduleEngineering
A scope may include an adjustment dial, which may be moved among a plurality of positions to configure the scope to compensate for projectile drops. The adjustment dial may be labeled with dial-calibration data, which may include one or more distance indicators and / or one or more windage hold-off indicators. The scope may be attached to a gun and the dial-calibration data may be at least partially generated using ballistics performance data based on shots fired by the gun. The dial-calibration data may be at least partially generated using shooting conditions. An electronic device may include a derived distance calculation module, which may be configured to use a distance to a target and actual shooting conditions to calculate a derived distance. The derived distance may be used in connection with an adjustment dial labeled with dial-calibration data at least partially generated using shooting conditions different from the actual shooting conditions.
Owner:HUSKEMAW OPTICS
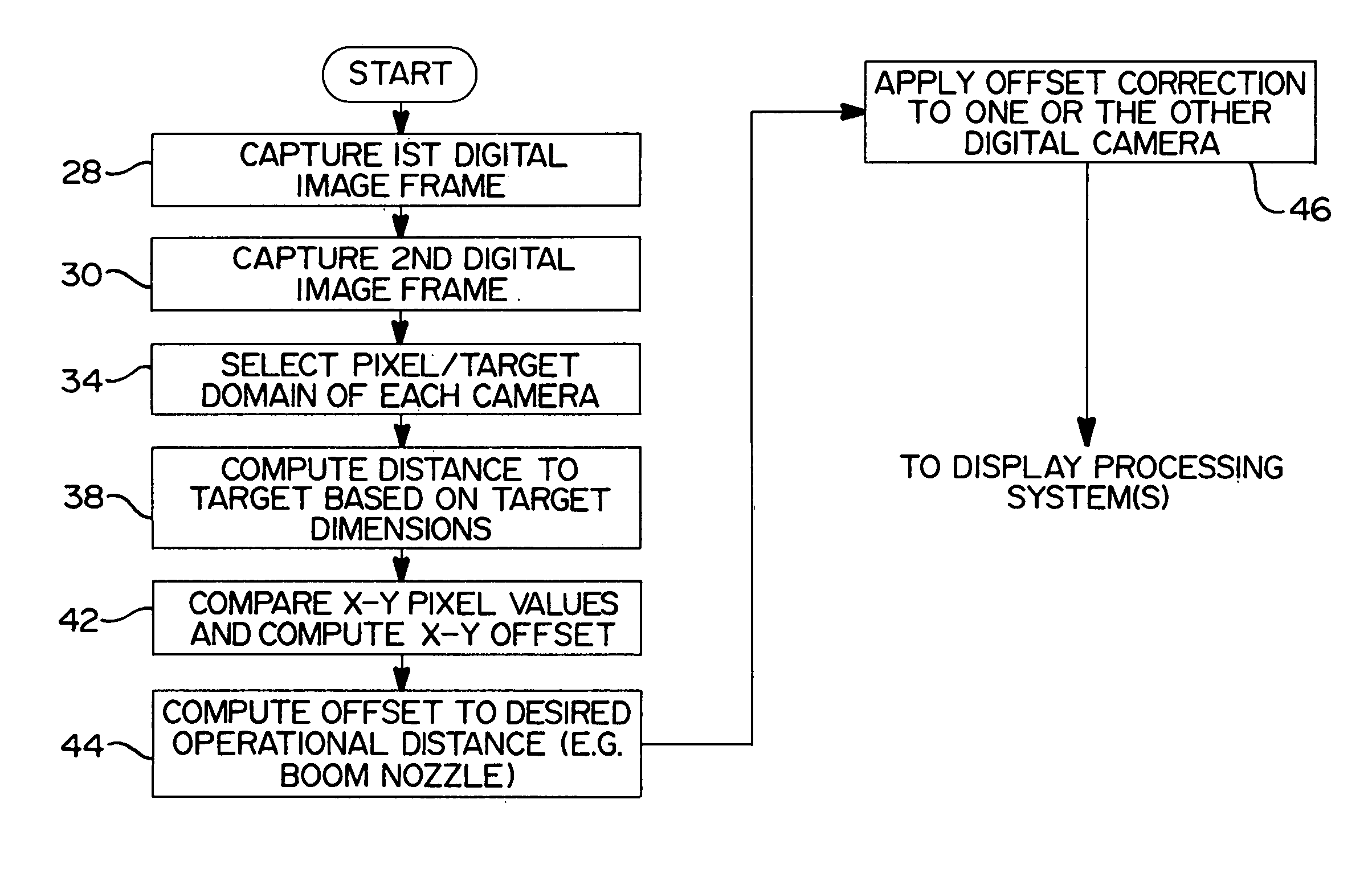
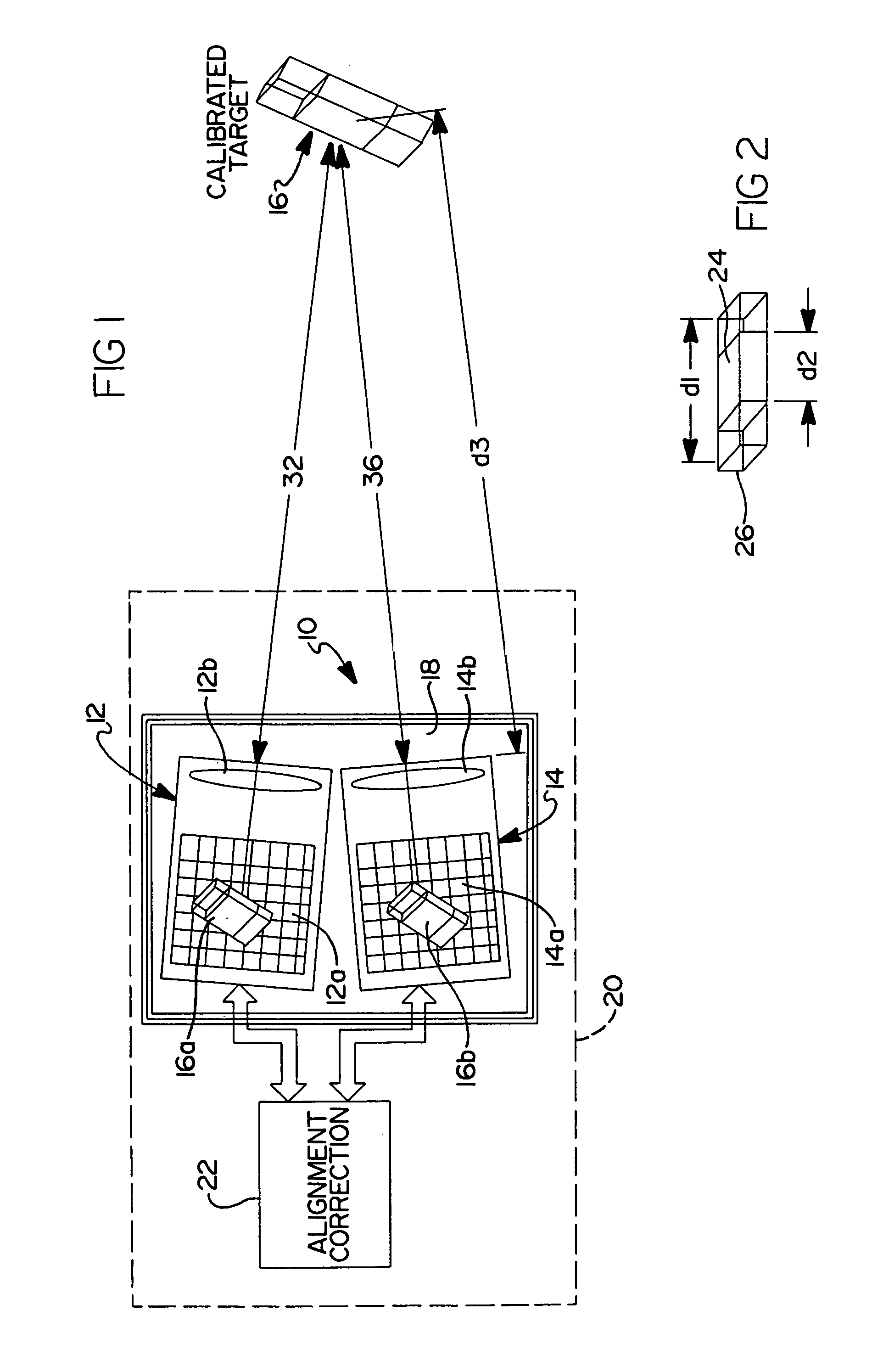
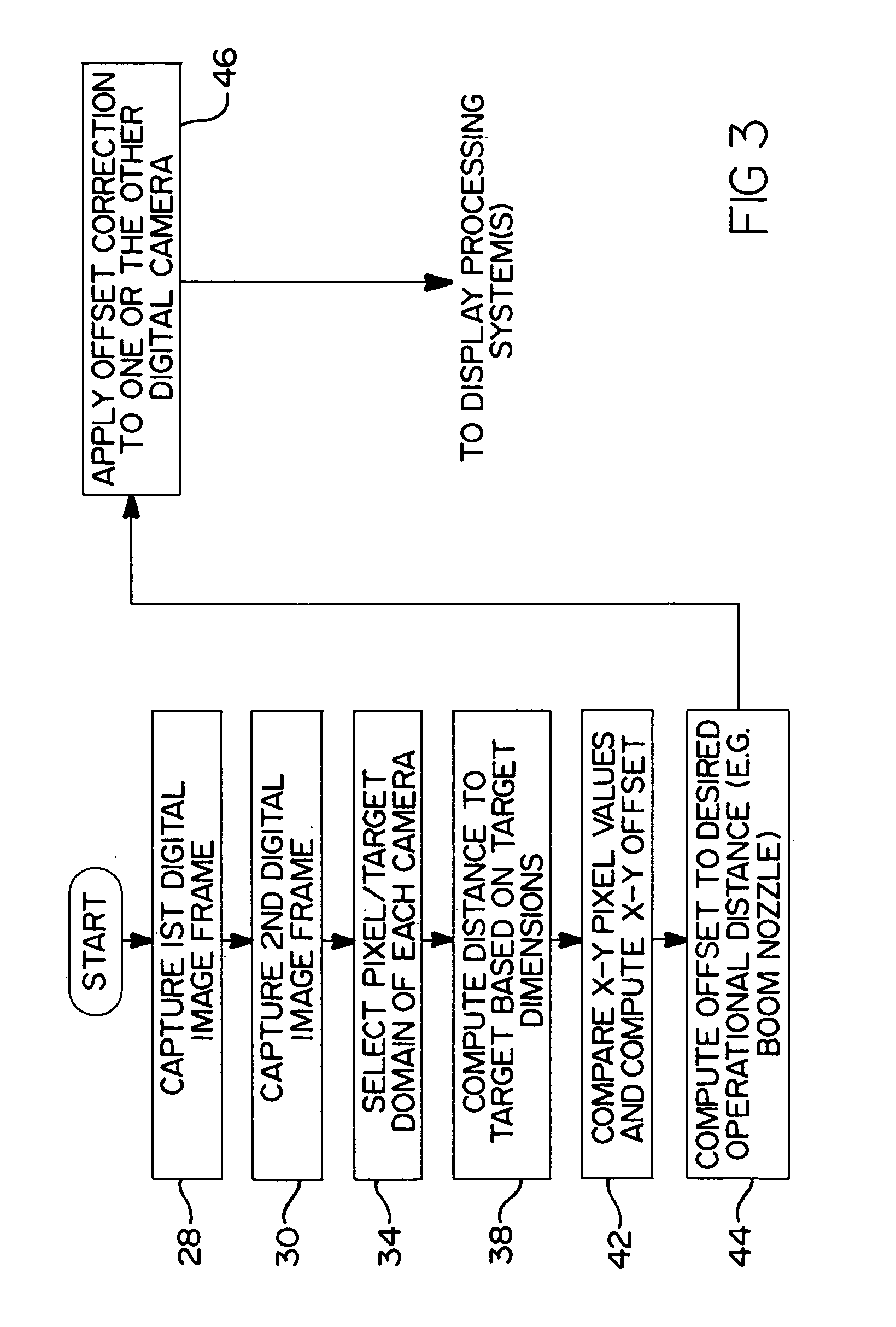
Method and apparatus for aligning a pair of digital cameras forming a three dimensional image to compensate for a physical misalignment of cameras
InactiveUS7209161B2Addressing slow performanceEliminate timeImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDistance to targetDigital camera back
An apparatus and method for detecting and correcting for physical misalignments of a pair of digital cameras creating a composite, three dimensional (3D) image of a target. The method involves using the distances from each of a pair of digital cameras to a target and determining correction offset values for one or the other of the images produced in the digital cameras to achieve pixel-to-pixel coincidence of the two images. The correction offset values are calculated and performed in real time and eliminate the need to physically remove a common platform on which the cameras are mounted from a mobile platform or other support structure, and to transport same to a laboratory environment for the needed calibration. Advantageously, the correction values are generated electronically and applied in real time as any misalignment between the cameras is sensed.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
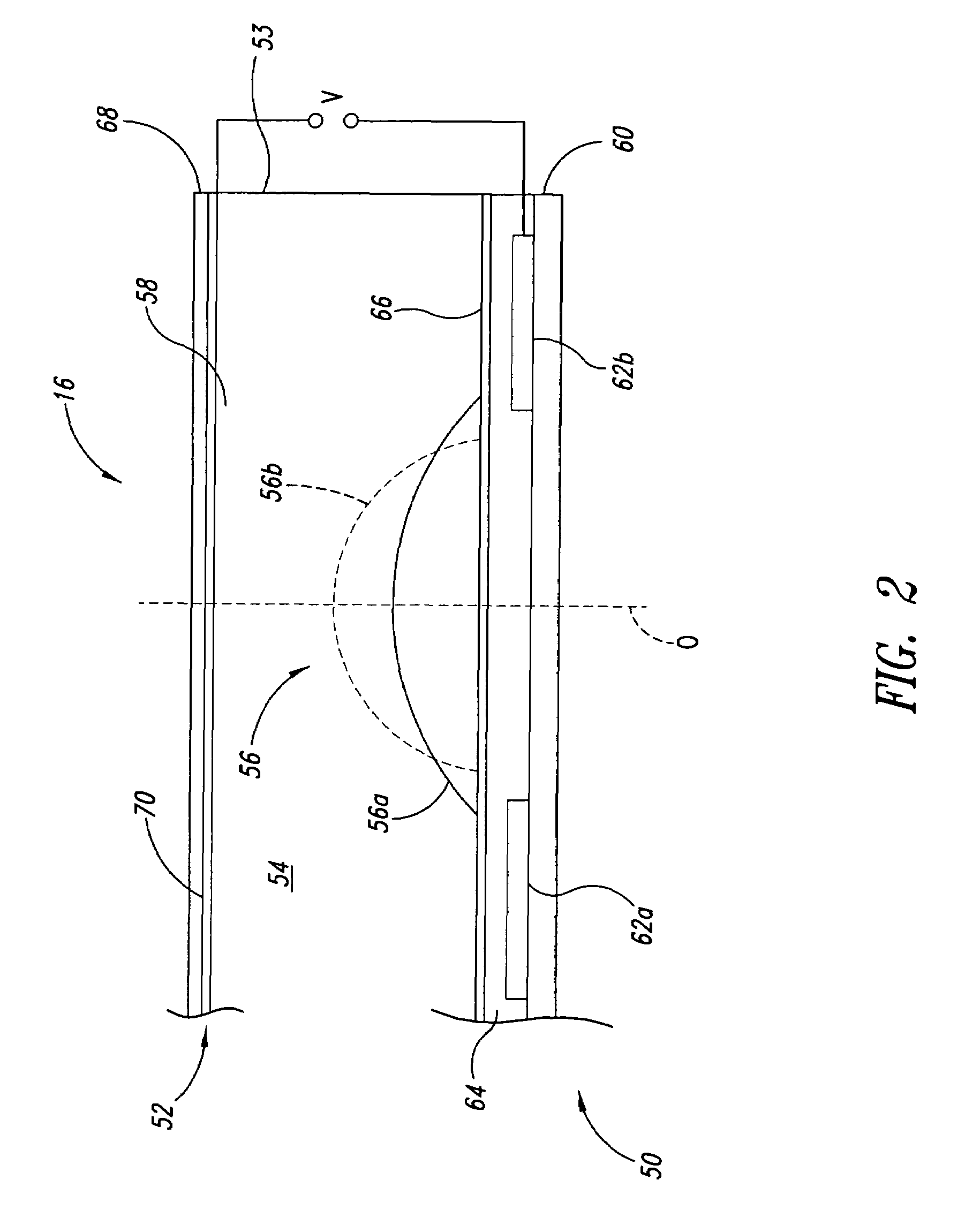
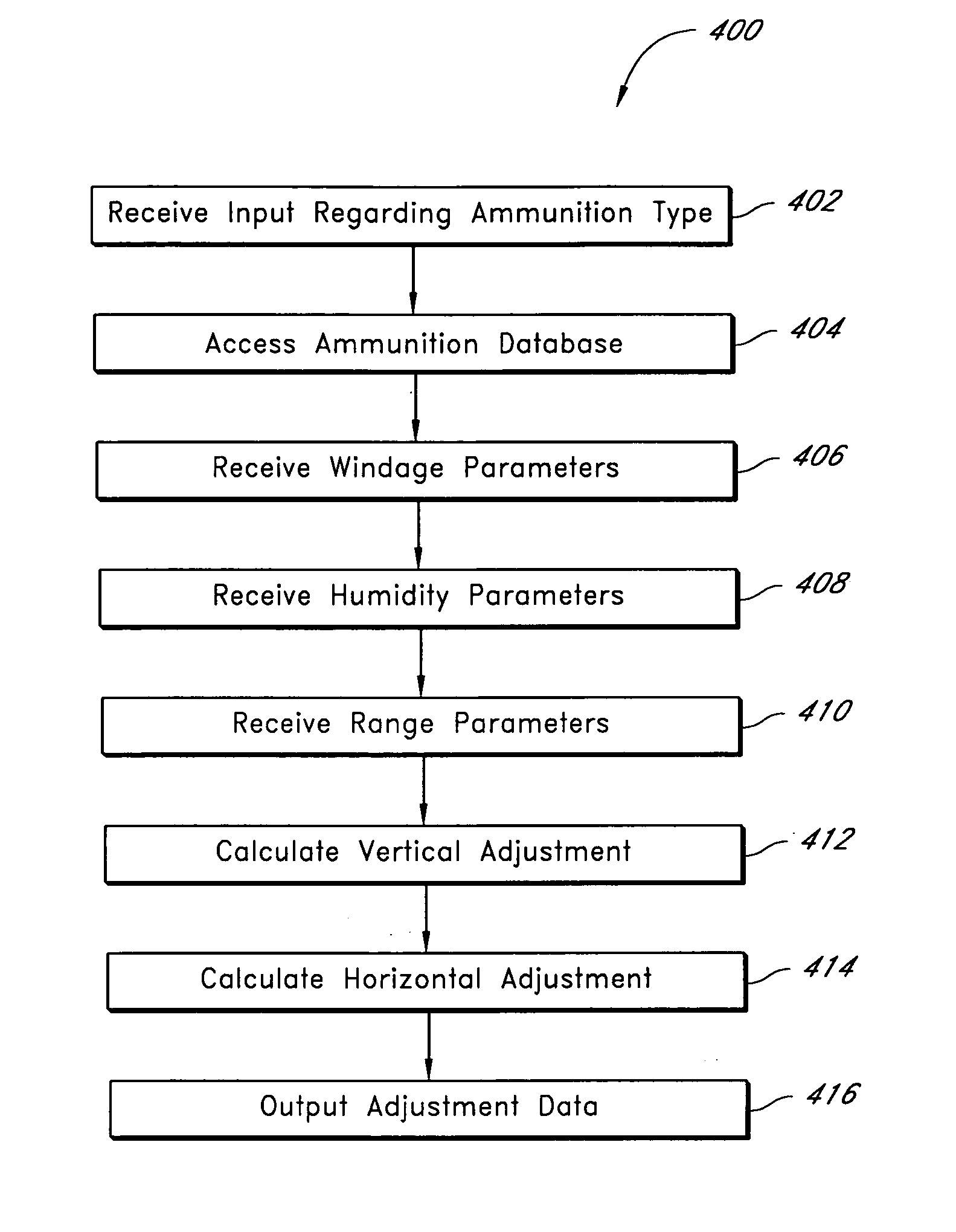
Systems and methods for adjusting a sighting device
Systems and methods usable to facilitate adjustments to a sighting device, such as a scope. In one example, an adjustment calculator associated with the scope receives data relating to a distance to a target and relating to at least one environmental variable, such as for example, wind and / or humidity, which may affect the trajectory of a projectile. The adjustment calculator processes the data and calculates a recommended scope adjustment. For instance, the adjustment calculator may output a number of adjustment “clicks” for a rifle scope in order to at least partially compensate for the distance and / or the environmental variable(s). In another example, the adjustment calculator receives data relating to properties of ammunition that may affect the trajectory of the ammunition.
Owner:MEADE INSTRUMENTS
Integrated dazzling laser and acoustic disruptor device
A method or device uses a dazzling laser light and an acoustic energy wave to non-lethally immobilize a person or animal. In some embodiments, the distance to the target is used to control the intensity of the dazzling laser light source striking the target subject and the acoustic energy output power.
Owner:BITAR PETE
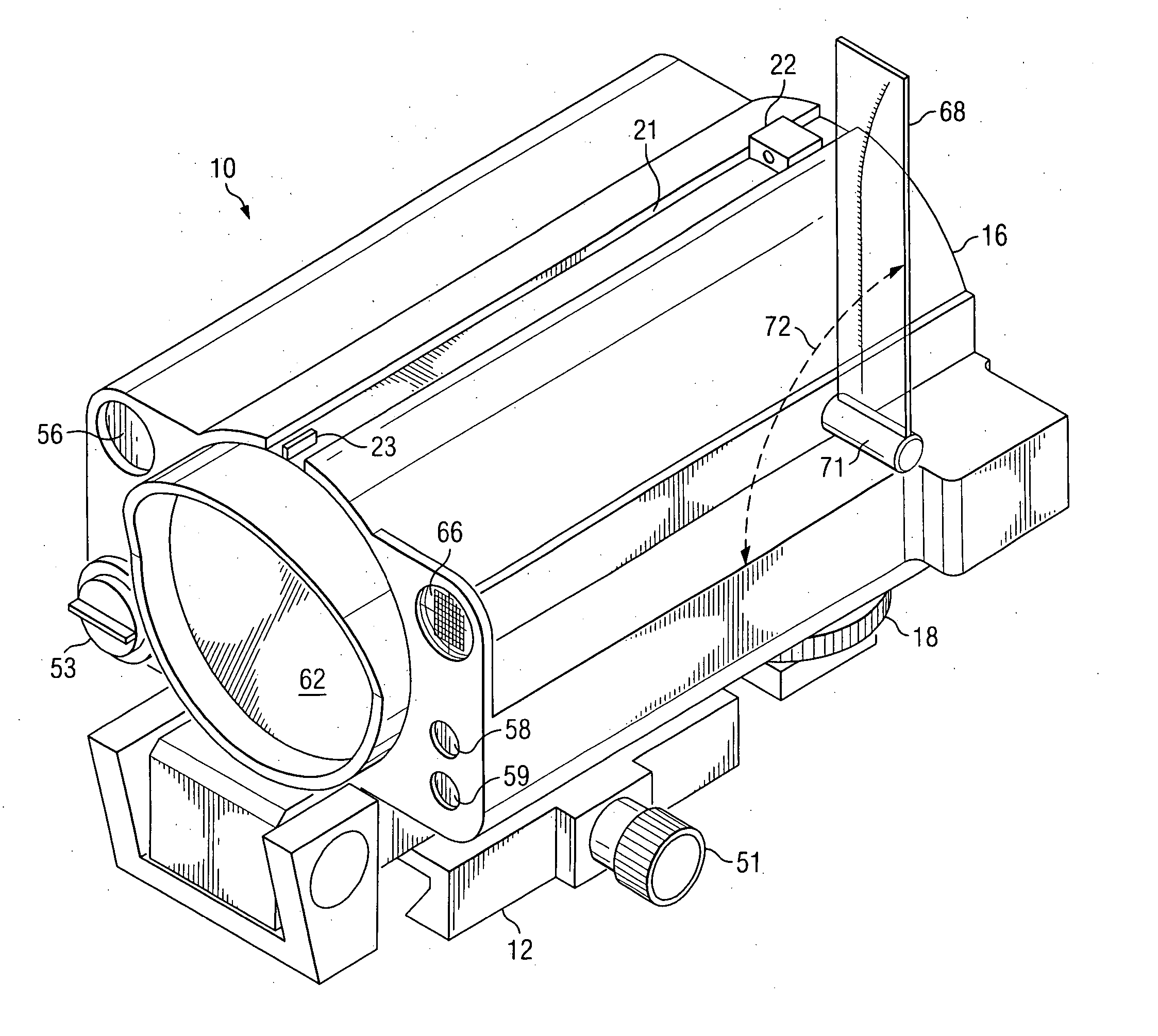
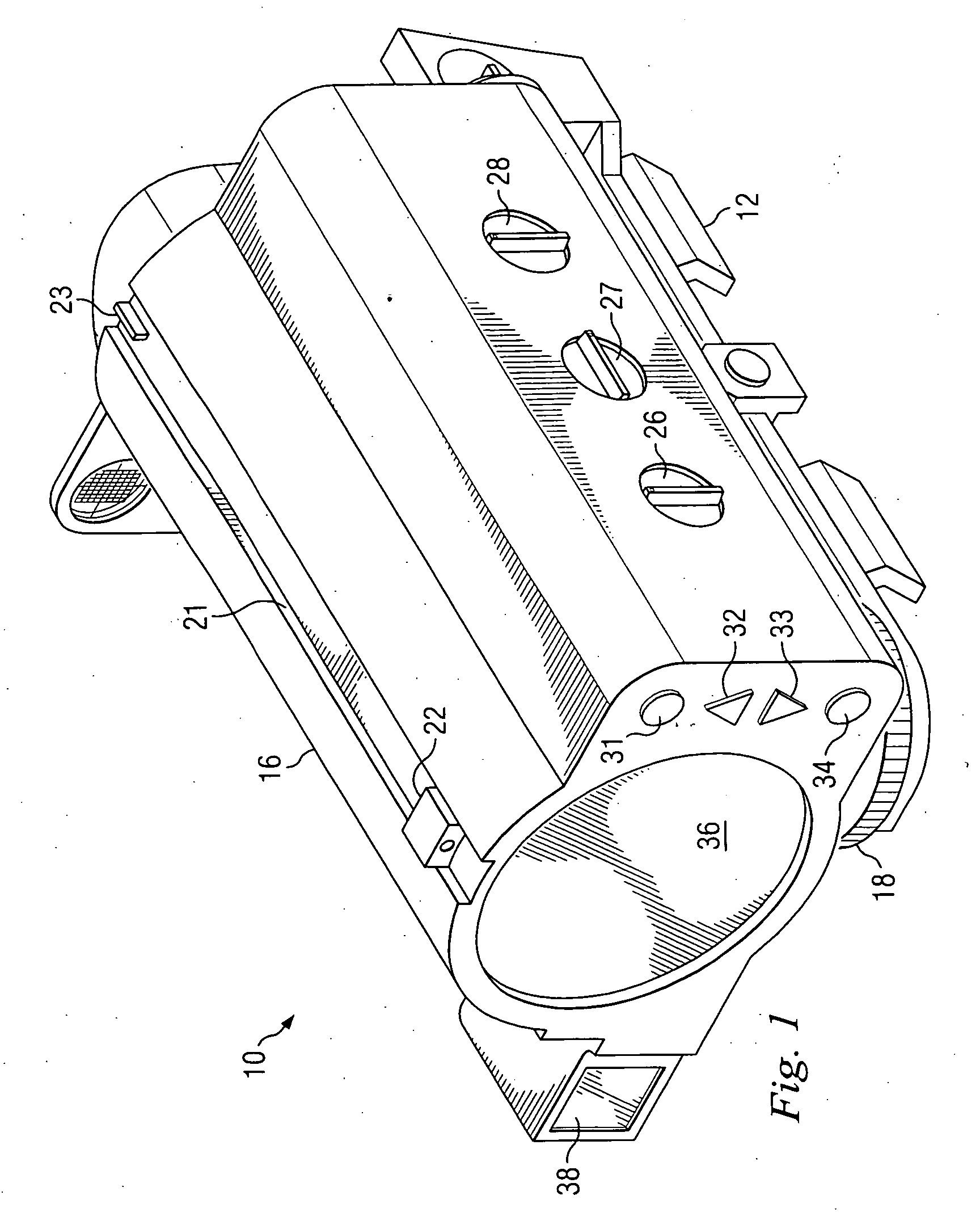
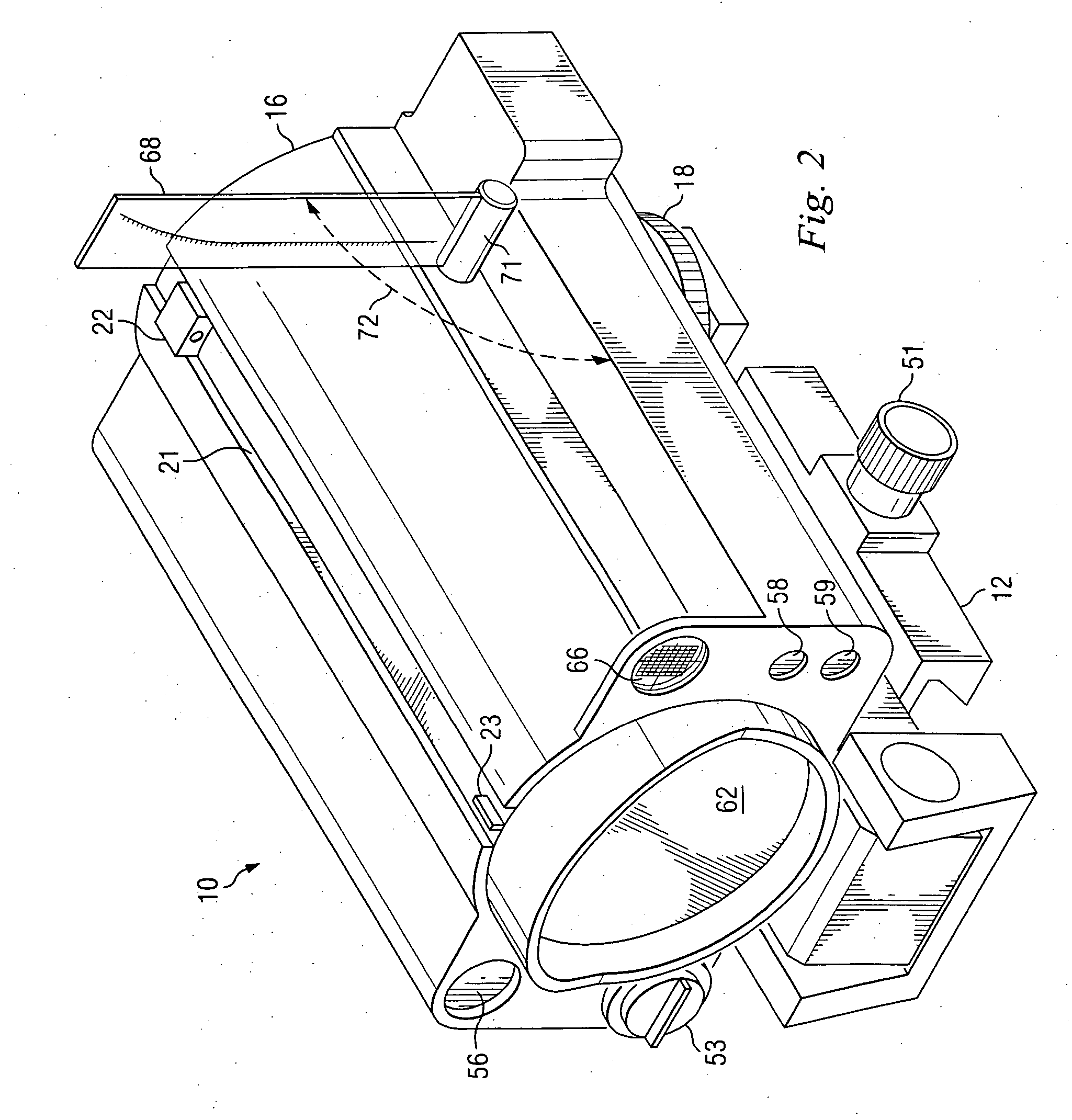
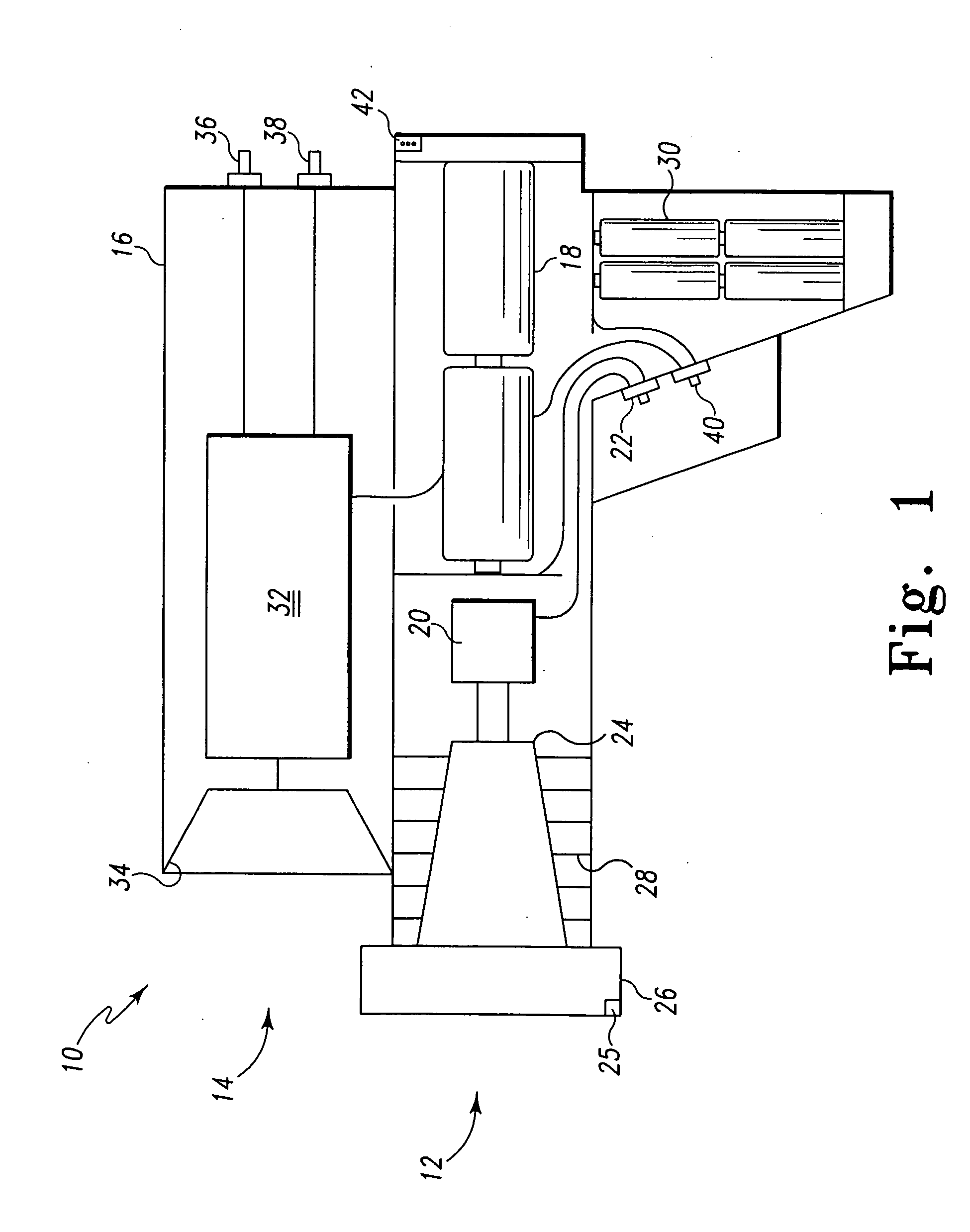
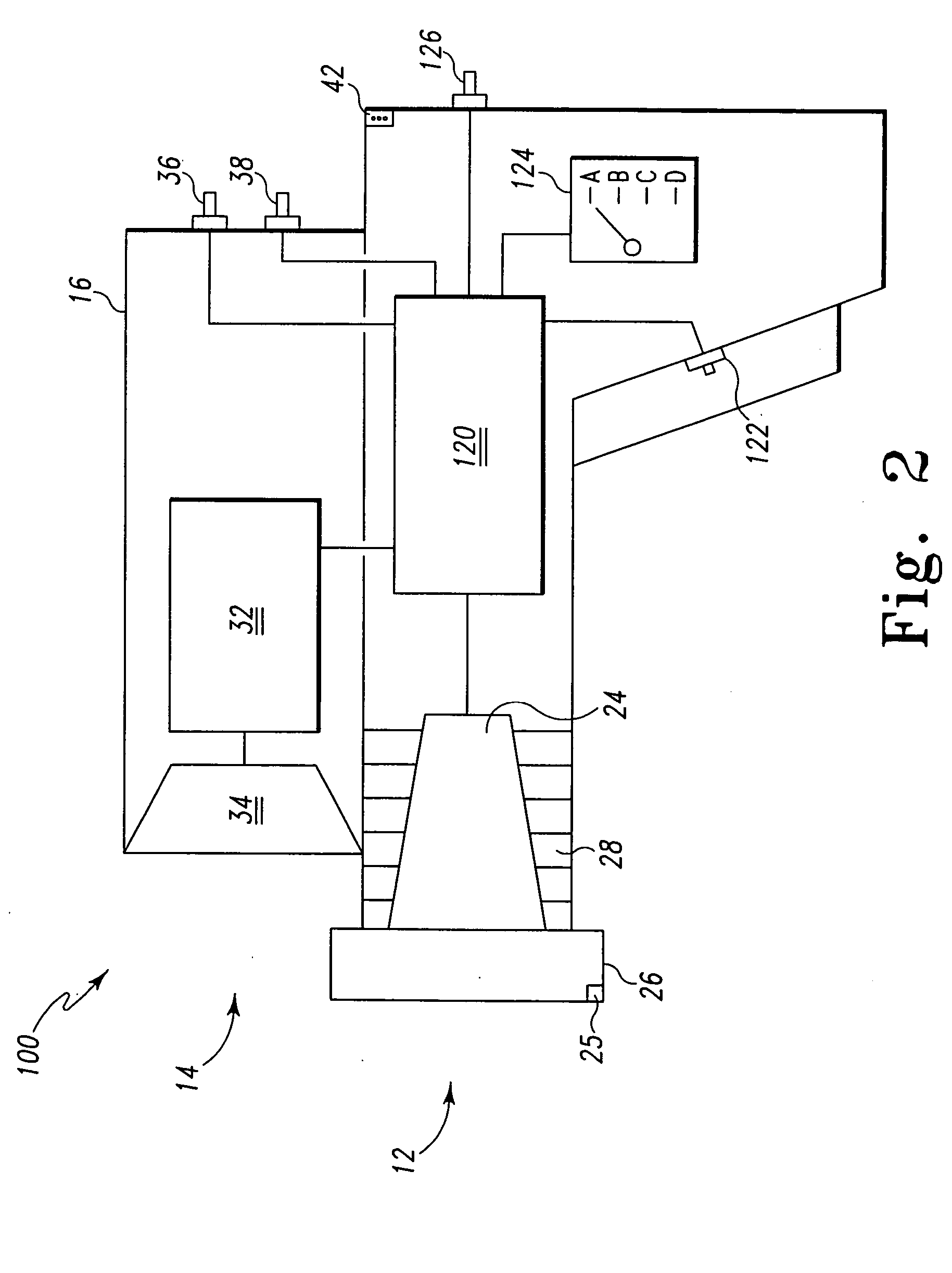
Weapon sight
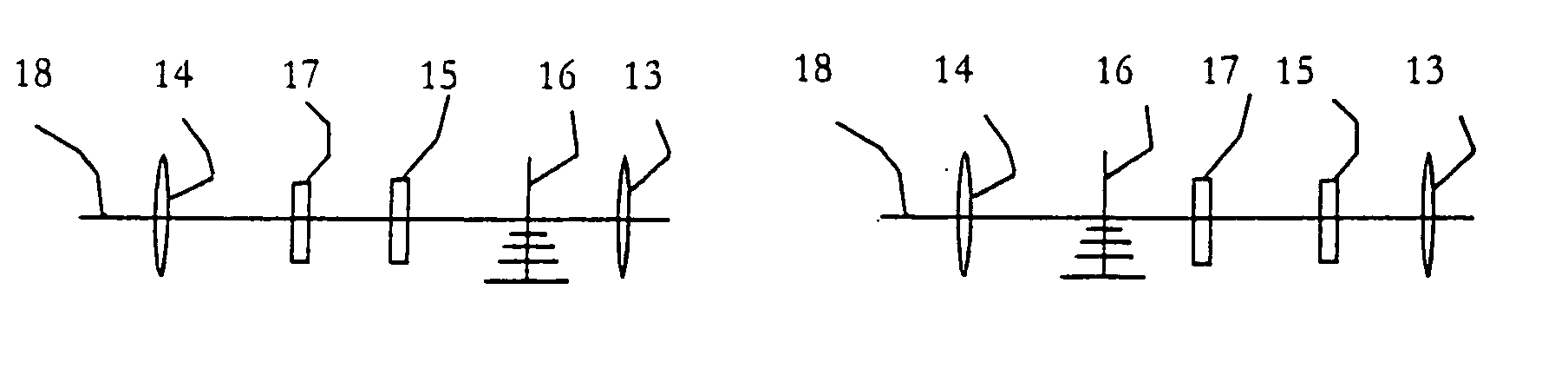
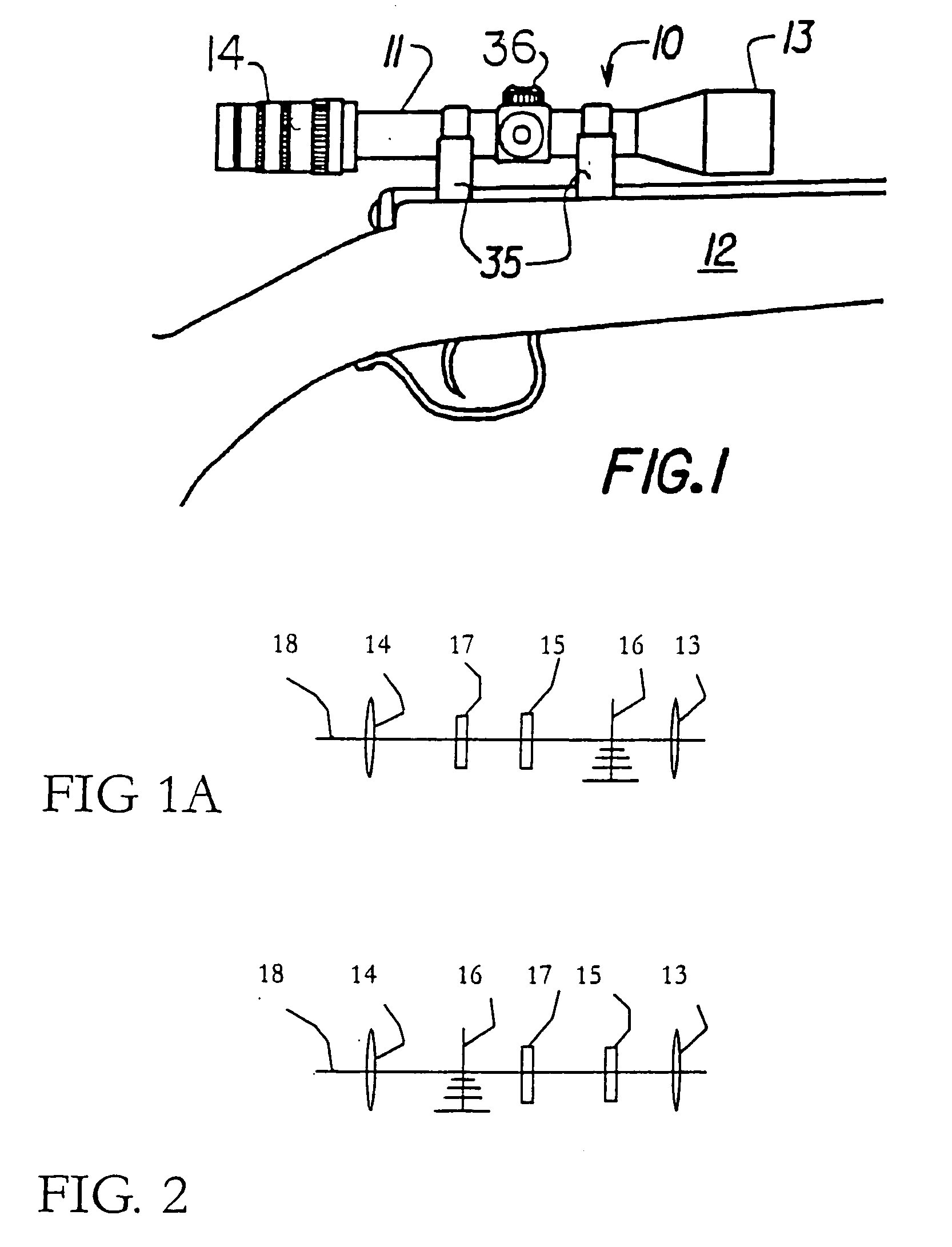
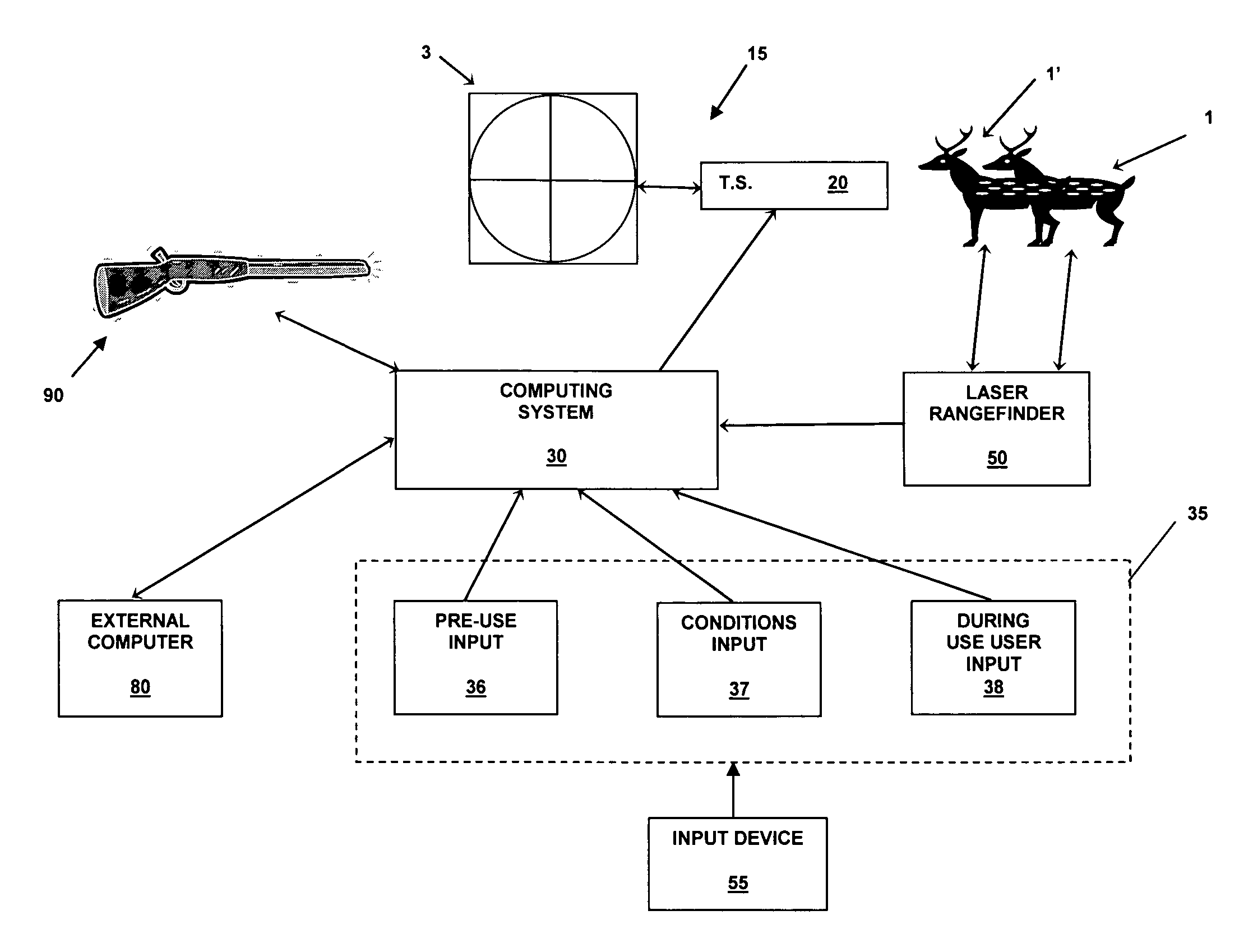
InactiveUS20070137090A1Accurate shooting experienceSighting devicesAiming meansEngineeringDistance to target
The invention includes a sighting system for use with a firearm that has a telescopic sight, a laser rangefinder for providing the distance to the target, device(s) for receiving various inputs, a computing system that calculates the point of aim of the firearm's projectile based upon the input(s) and the calculated distance to the target, and a display means that provides an image of the computed point of aim within the telescopic sight's field of view. A method and weapon that employs the sighting system is disclosed.
Owner:CONESCU PAUL
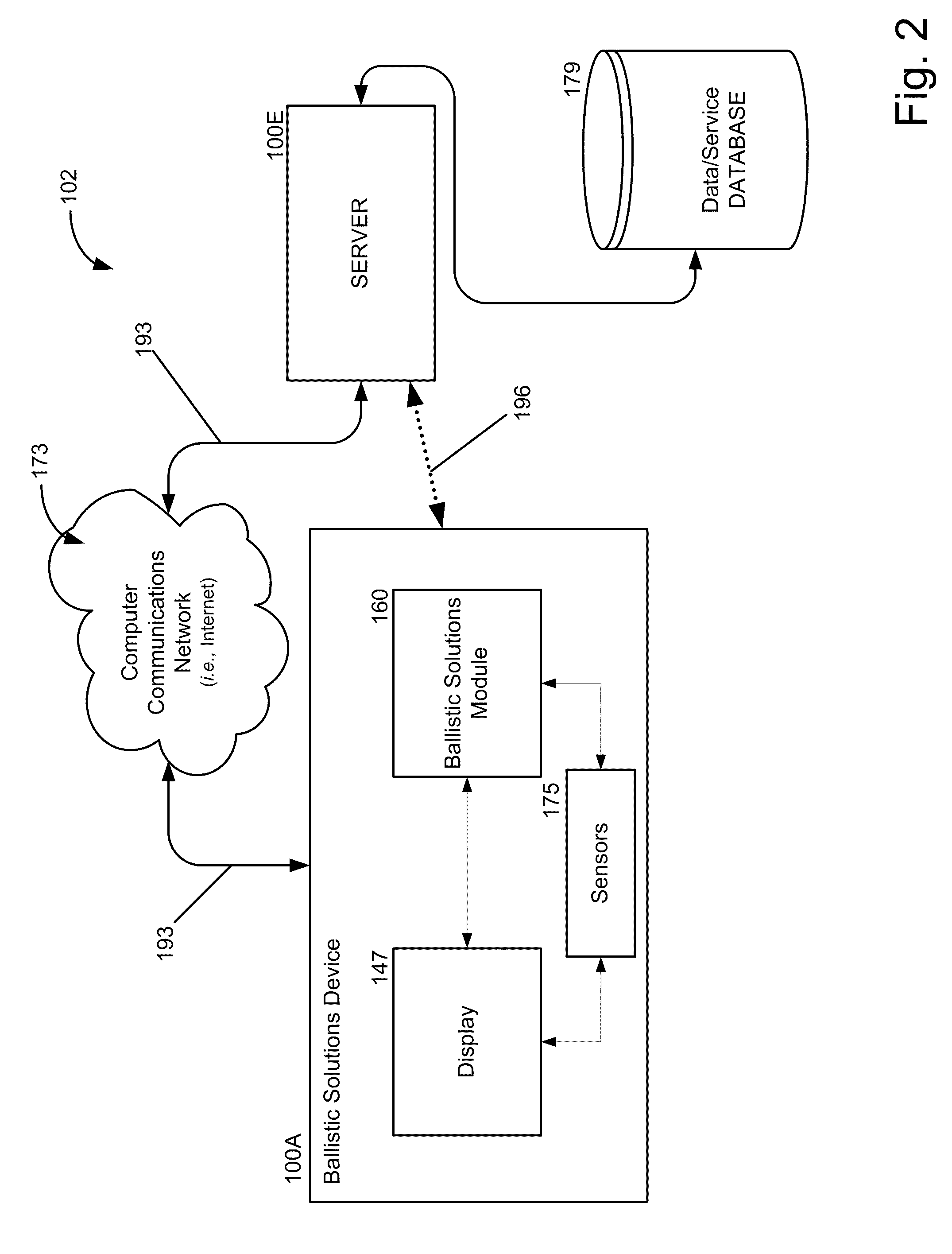
System and Method for Ballistic Solutions
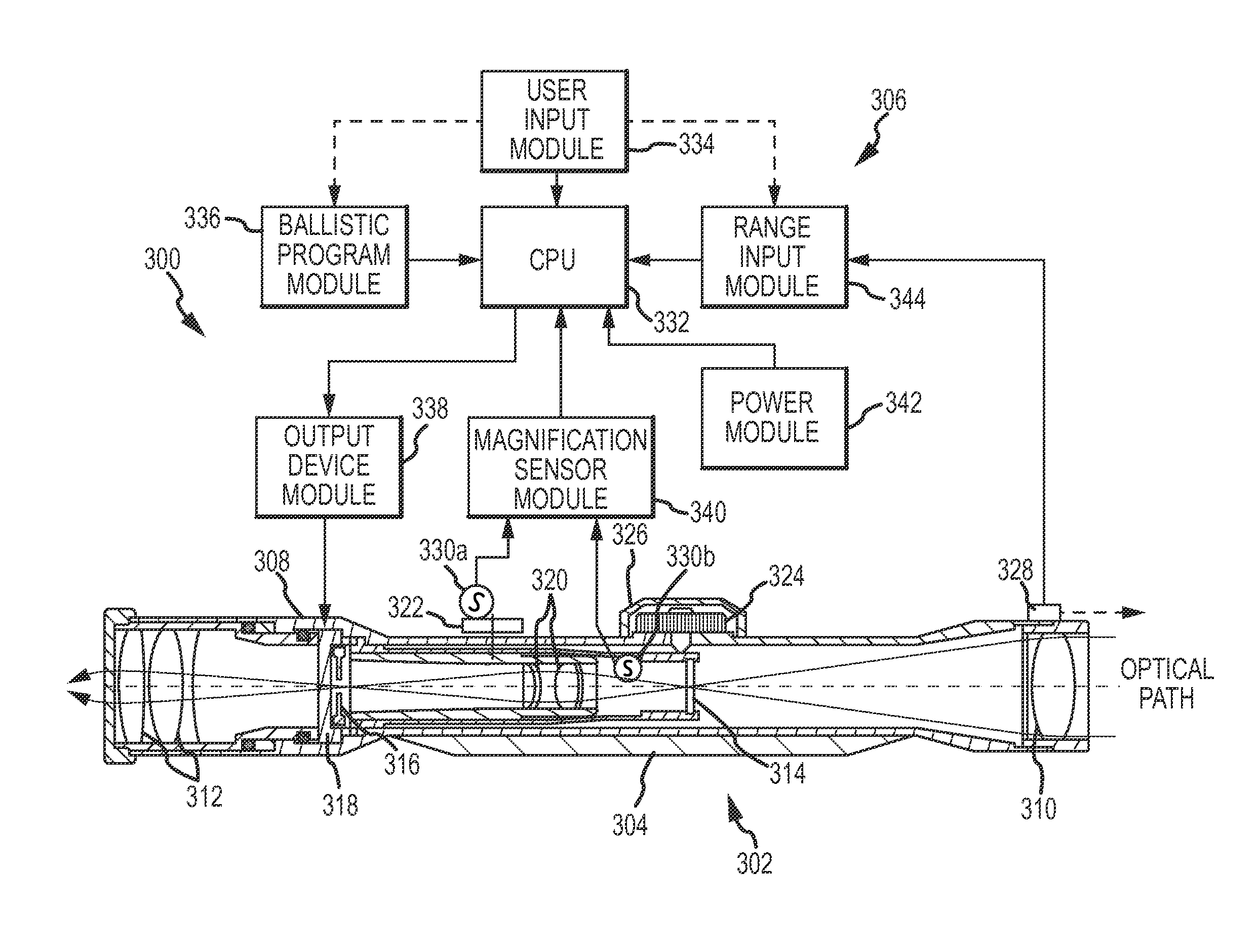
ActiveUS20110168777A1Good estimateIncrease investmentAngle measurementWeapon control systemsDistance to targetMagnification
Disclosed embodiments, as well as features and aspects thereof, are directed towards providing a system, device and method for calculating comprehensive ballistic solutions, or portions thereof, via a varying magnification optical range determining and ballistic trajectory calculating apparatus referred to as a ballistic solutions device. Advantageously, embodiments of a ballistic solutions device may drastically reduce marksman error in milling targets by employing a measurement component configured to measure angular movement of a projectile launching device, such as a rifle, thus delivering consistently accurate distance to target estimations. Additionally, embodiments of a ballistic solutions device may also comprise features and aspects that enable a user to leverage available real-time field data such that error associated with the measurement of those variables is minimized prior to calculating and rendering a comprehensive ballistic solution derived from stored DOPE.
Owner:BAY LAURENCE ANDREW
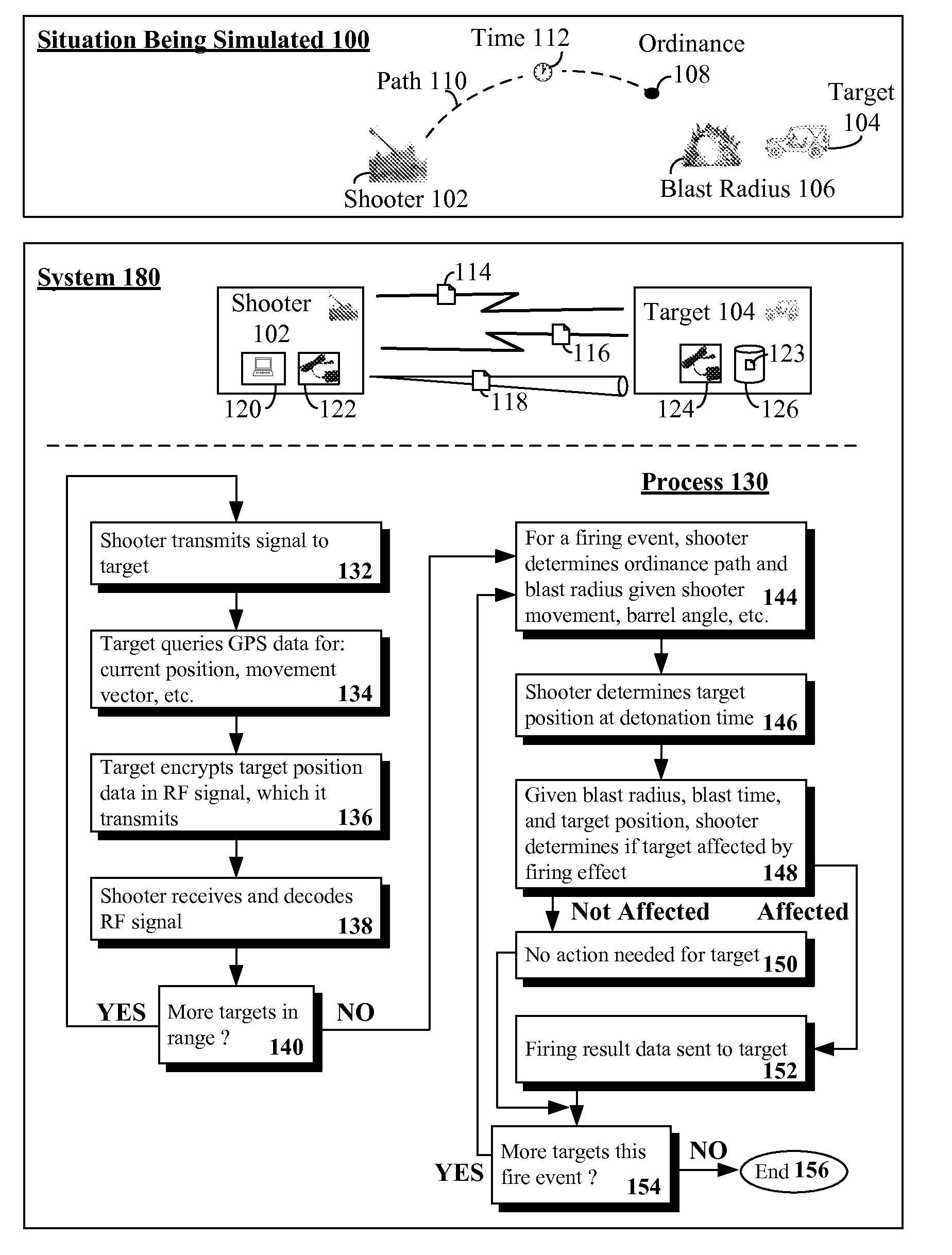
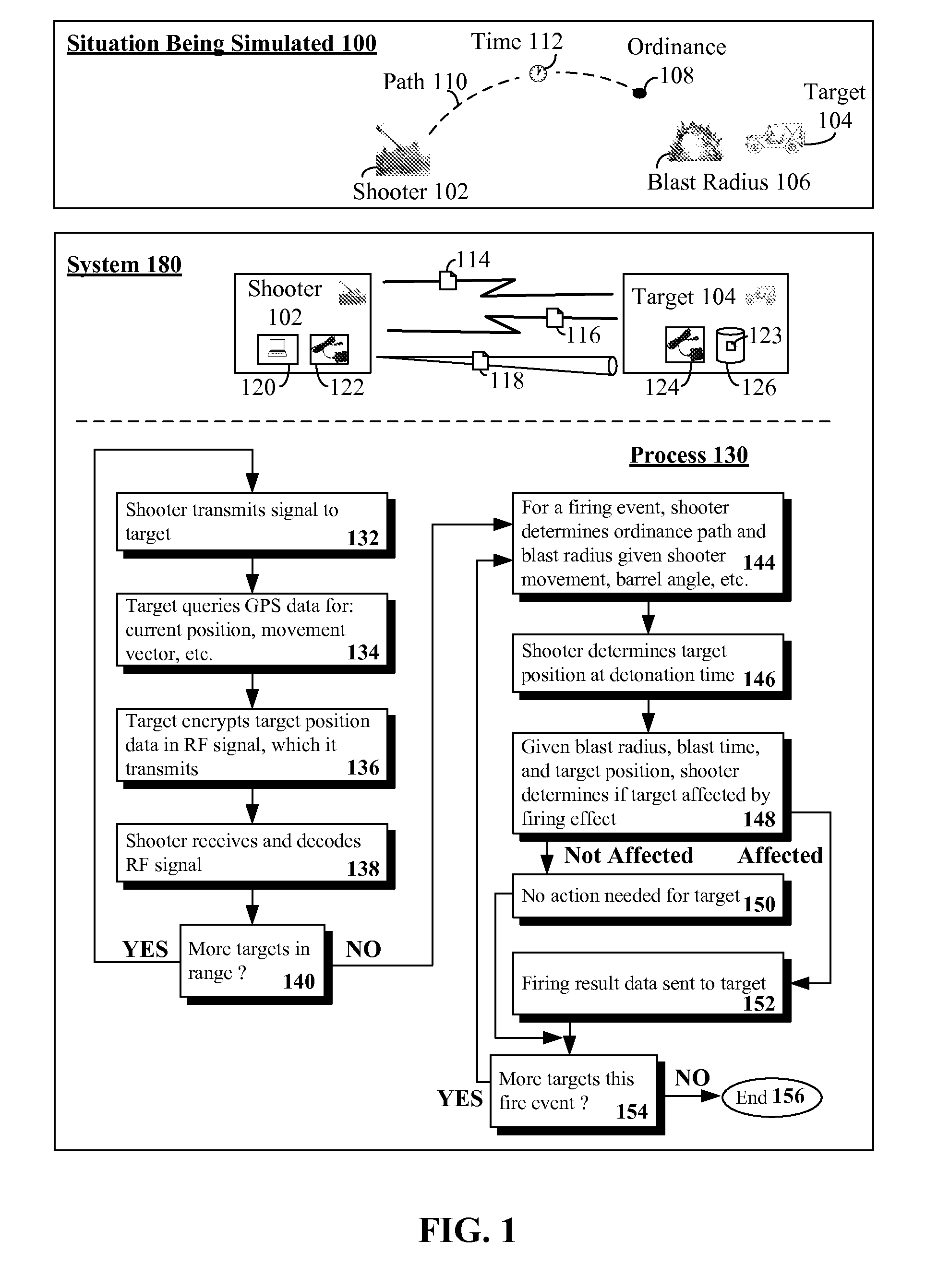
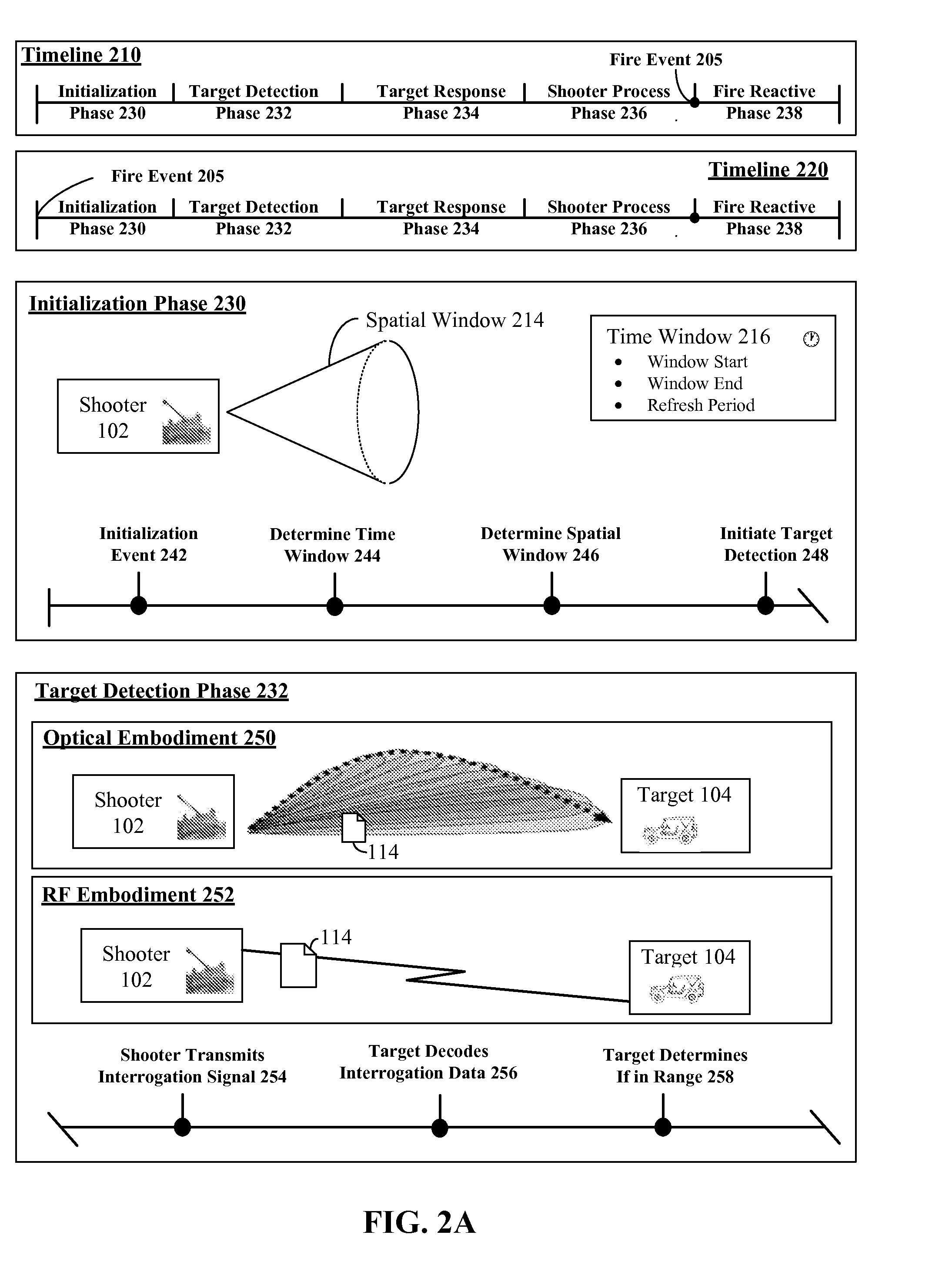
Trajectory simulation system utilizing dynamic target feedback that provides target position and movement data
A target in a physical environment can be interrogated. Feedback can be received from the target that is encoded within a radio frequency signal. The feedback can include position and movement data of the target. Adjustments can be calculated for a simulated kinetic projectile traveling to the target. The adjustments can account for target movement, kinetic projectile travel time, and travel path to the target. A distance from a point of origin of the simulated kinetic projectile to the target and movement of the target relative to the point of origin can be determined utilizing the feedback. A result signal can be conveyed that includes result data. The result data can include all information necessary for the target to react to the simulated kinetic projectile.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Multitone Radar with Range Determination and Method of Use
ActiveUS20160282457A1Large system bandwidthRelatively large bandwidthRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFast Fourier transformRadar systems
Method for determining distance to target using a multitone nonlinear radar system comprising providing a transmitter that transmits a signal comprising at least two predetermined frequency components; receiving transmitted signal upon reflection from target; determining the phase relationships of the frequency components when signal strikes target; determining distance the signal has travelled to target based upon the phase relationship of the frequency signal components at the time of reflection from target; computing the distance to target. A system comprising a transmitter subsystem that transmits radar signal comprising at least two frequency components; a receiver subsystem configured to receive a return signal comprising intermodulation and harmonic products; at least one processor configured to extract frequency samples from the return signal within a frequency range, apply a window function to the extracted frequency samples and perform an inverse fast Fourier transform on the resulting function to create a range profile.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Fire-control system
ActiveUS20120159833A1Increase awarenessReduce consumptionSighting devicesAiming meansFire-control systemDirect observation
A fire-control system comprising -a housing, -a light channel, through which a user may directly observe a target and receive visually displayed information simultaneously, said light channel comprising partially reflective optics a light source, for visualization of a reticle to the user via the partially reflective optics, -means for receiving a measure of the distance to the target a processor, for determining the adequate position of the reticle, based on the distance to the target, and for controlling the light source to emit light so that the reticle is visualized at the adequate position, wherein the light source is an array capable of selectively emitting light in well defined locations on its surface.
Owner:AIMPOINT AB
Stride analyzer and trainer
An analyzer and practice aid primarily for determining a ball pitcher's or hitter's stride angle and stride length. The analyzer is comprised of a ground or floor mat with a grid imprinted on it, the grid havings a reference point from which reference lines extend forwardly and outwardly at predetermined angles toward a target, such as the home plate. The grid also includes lines that intersect the reference lines for easy measurement of the distance from the reference point toward the target. The mat may also include means behind the reference point for mounting an adjustable pitching rubber. The analyzer can also be used for batting practice and in training for improvement in other sports such as golf for determining a proper stance.
Owner:FOSTER JEANNA M
Golf putt-line variance determining system
InactiveUS6890273B1Successful at achieveEasy to adjustBall sportsGolfing accessoriesData setOffset distance
An offset measurement system, for aiding a golfer when putting upon a putting green having varying slope between a golf ball, resting upon the green, and a hole having a hole center. A target having a target line is positioned at the hole with the target line aligned with a direct putt line that connects the hole center and ball. A measurement device is used to acquire multiple measurement data sets having the slope of the putting green at a position along the direct putt line and a distance to the target at that position. The measurement device calculates and displays a recommended offset distance from the measurement data sets that is used by the golfer to redirect the putt at the hole by the recommended offset distance from the direct putt line.
Owner:PEREZ BASILIO
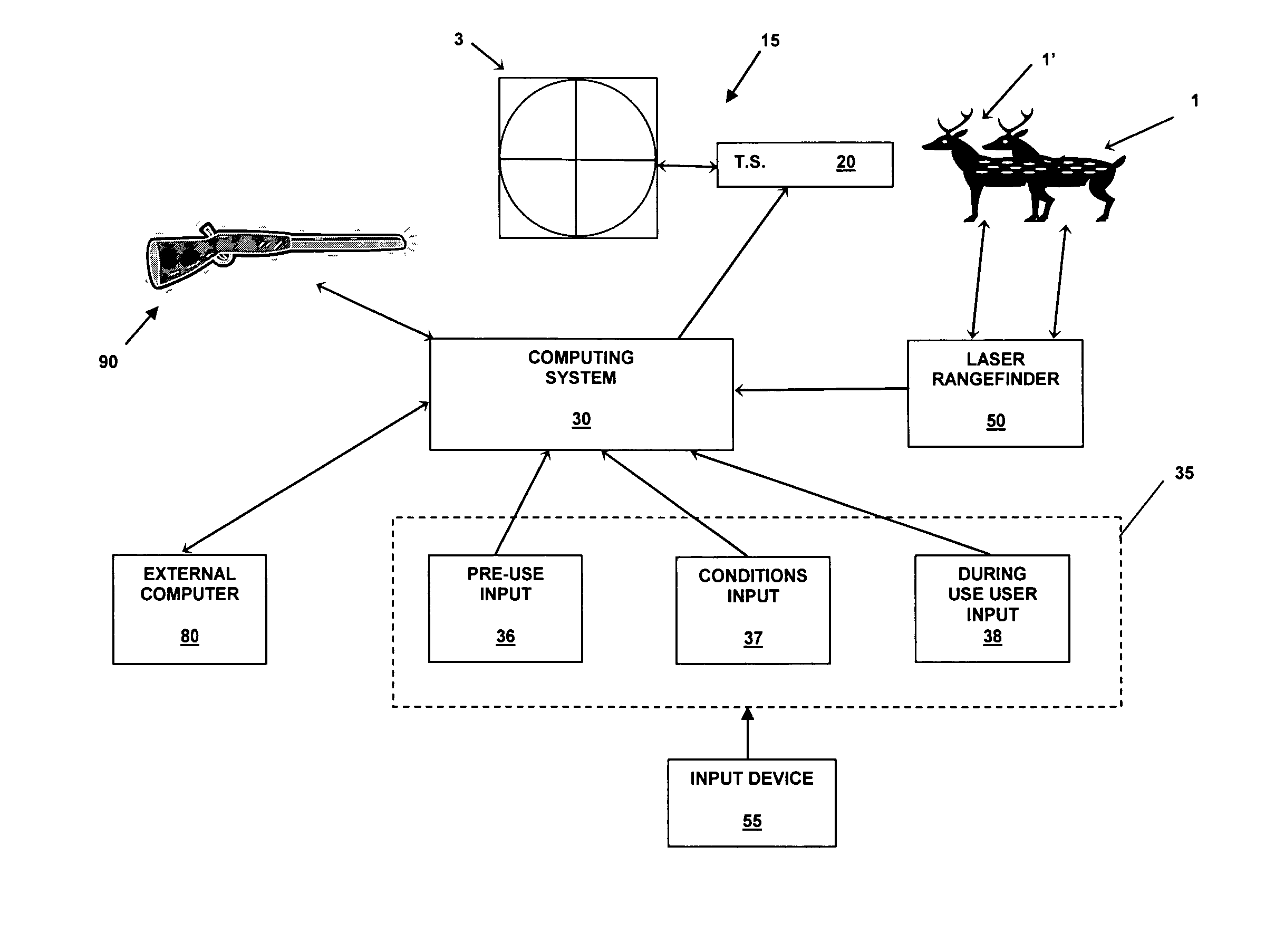
Method, device, and computer program for determining a range to a target
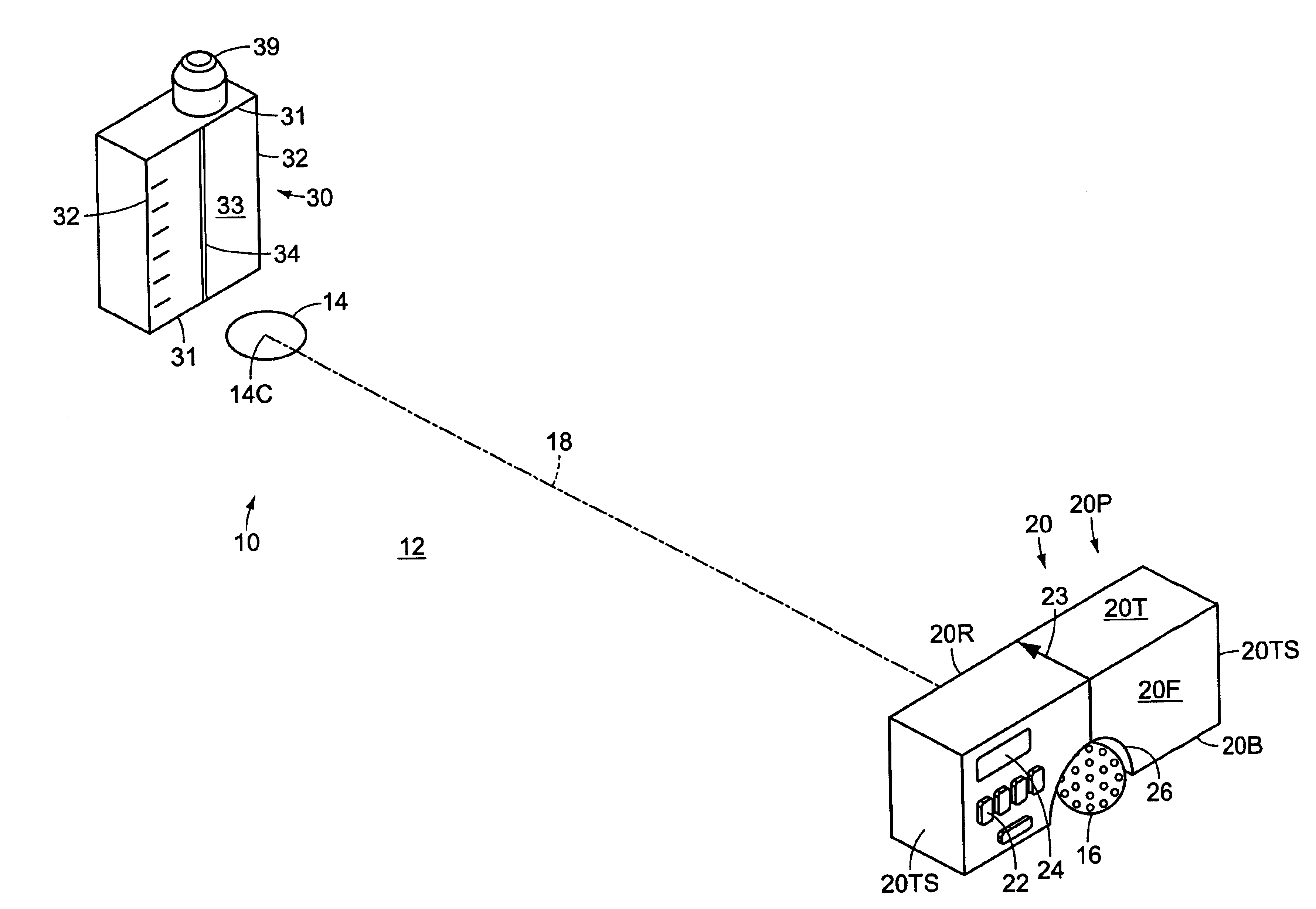
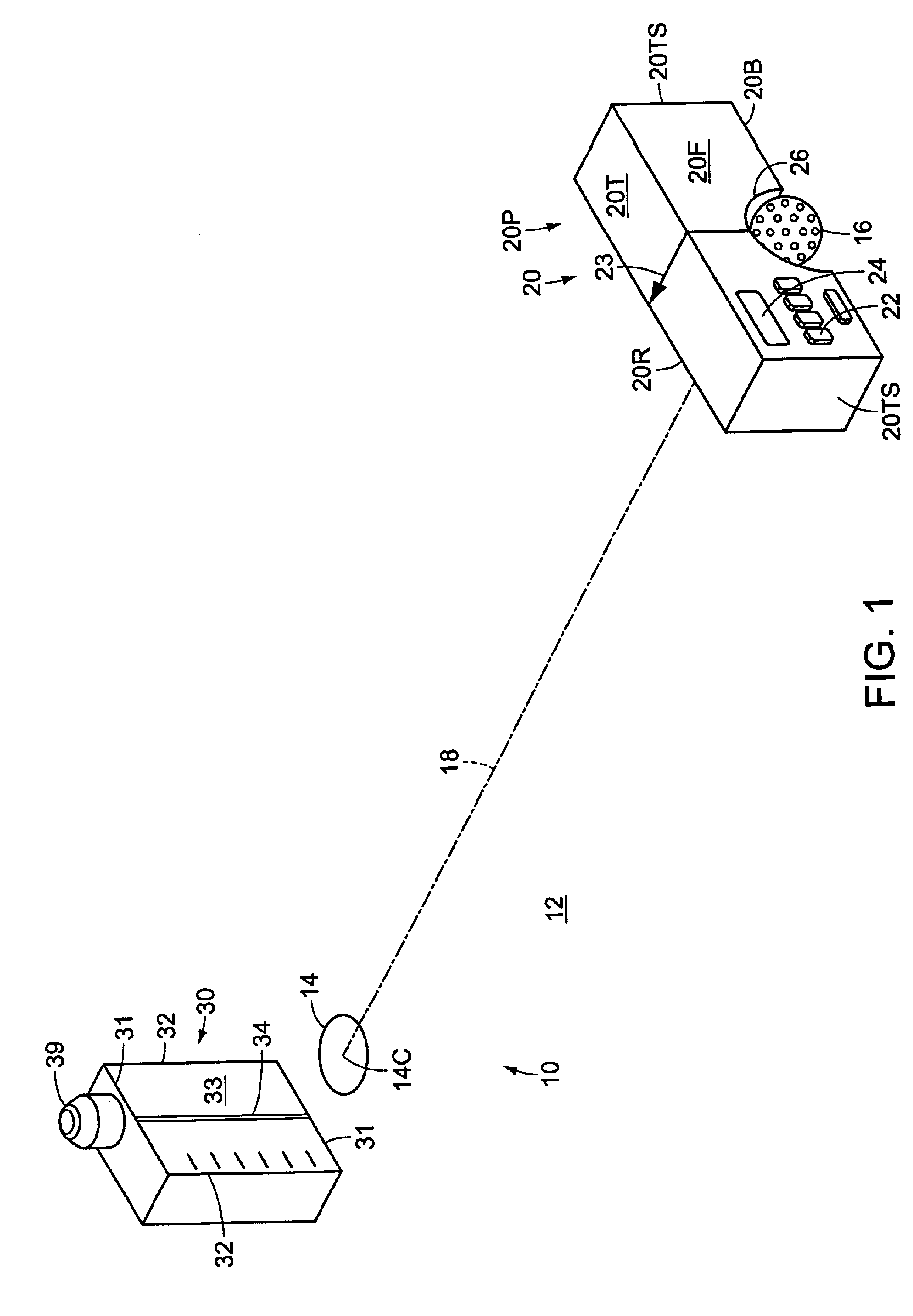
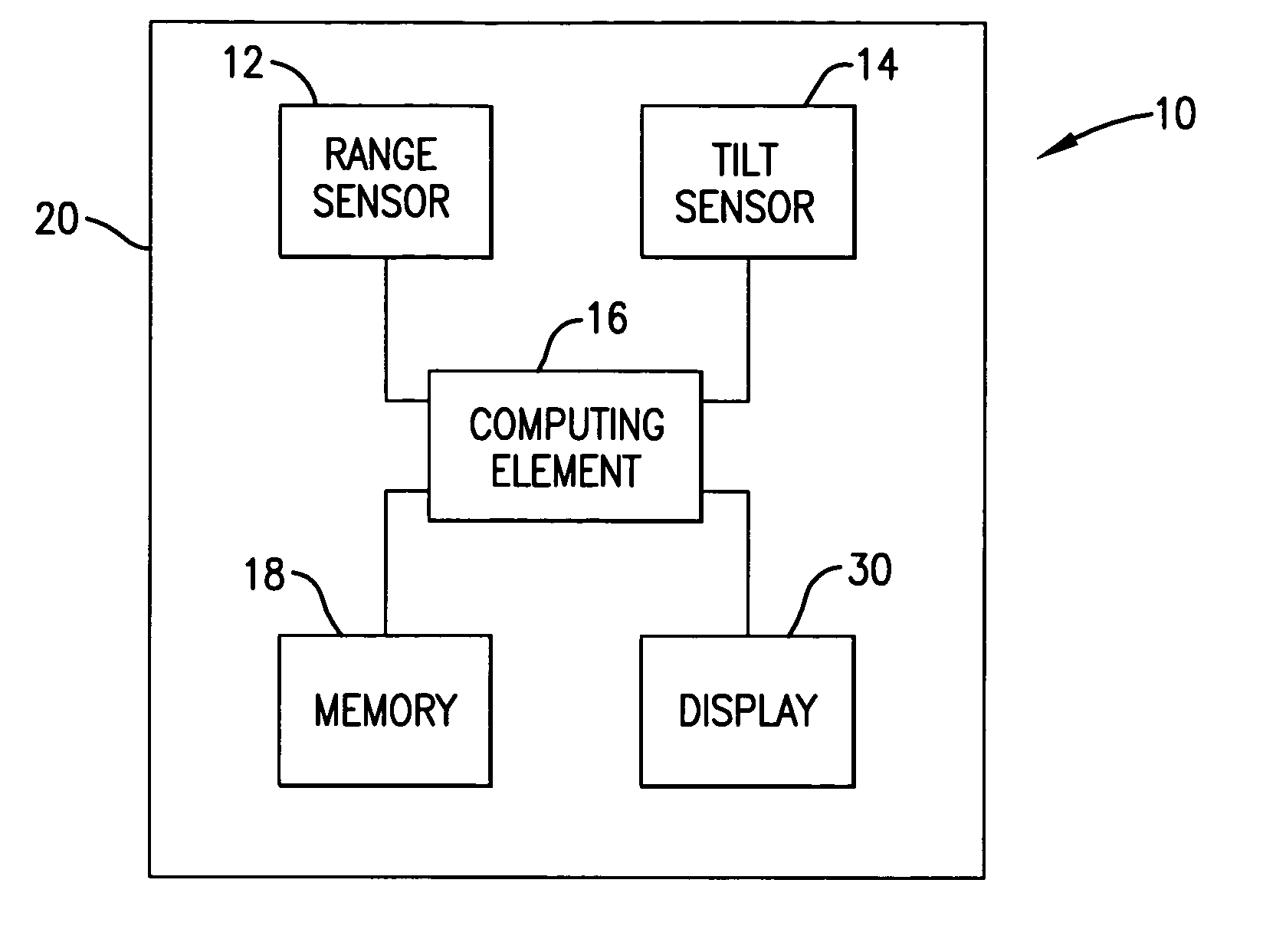
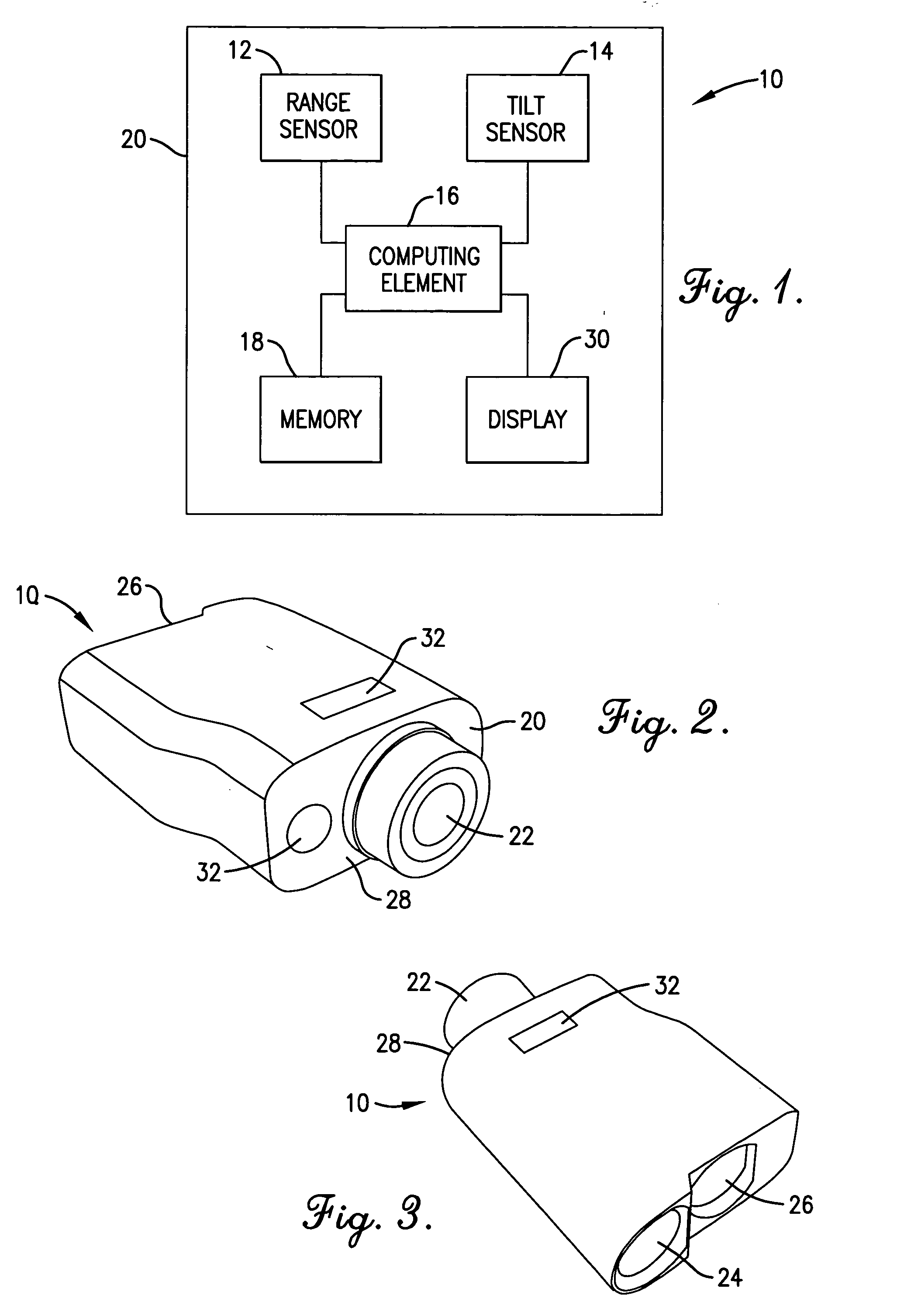
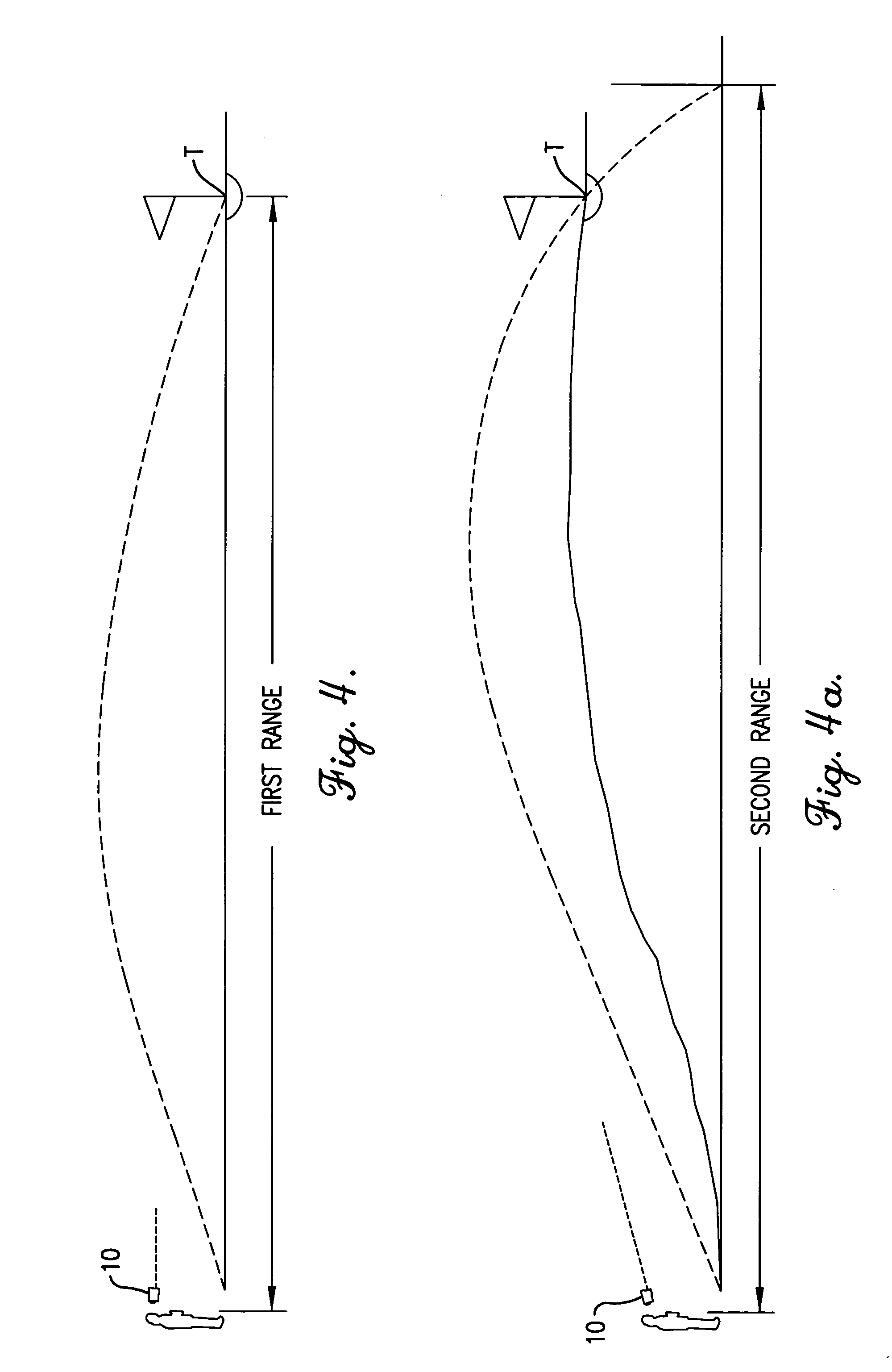
A method, device, and computer program for determining range to a target is disclosed. Specifically, the invention provides a method, device and computer program for determining a second range to a target based on a first range to the target and an angle to the target such that the parabolic trajectory of a projectile is accounted for in determining the second range. The device generally includes a range sensor for determining a first range to a target, a tilt sensor for determining an angle to the target, and a computing element for determining a second range to the target based on the first range and the determined angle.
Owner:BUSHNELL
Magnification compensating sighting systems and methods
A method is used to determine an aiming point for a sighting system used by a shooter to shoot a target. The method includes receiving a range signal that corresponds to a distance from the shooter to the target. A first position signal is received from a magnification system sensor. A first magnification setting based at least in part on the first position signal is then determined. Thereafter, a first aiming point based at least in part on both of the range signal and the first magnification setting is determined.
Owner:BURRIS
Serial digital communication system and method
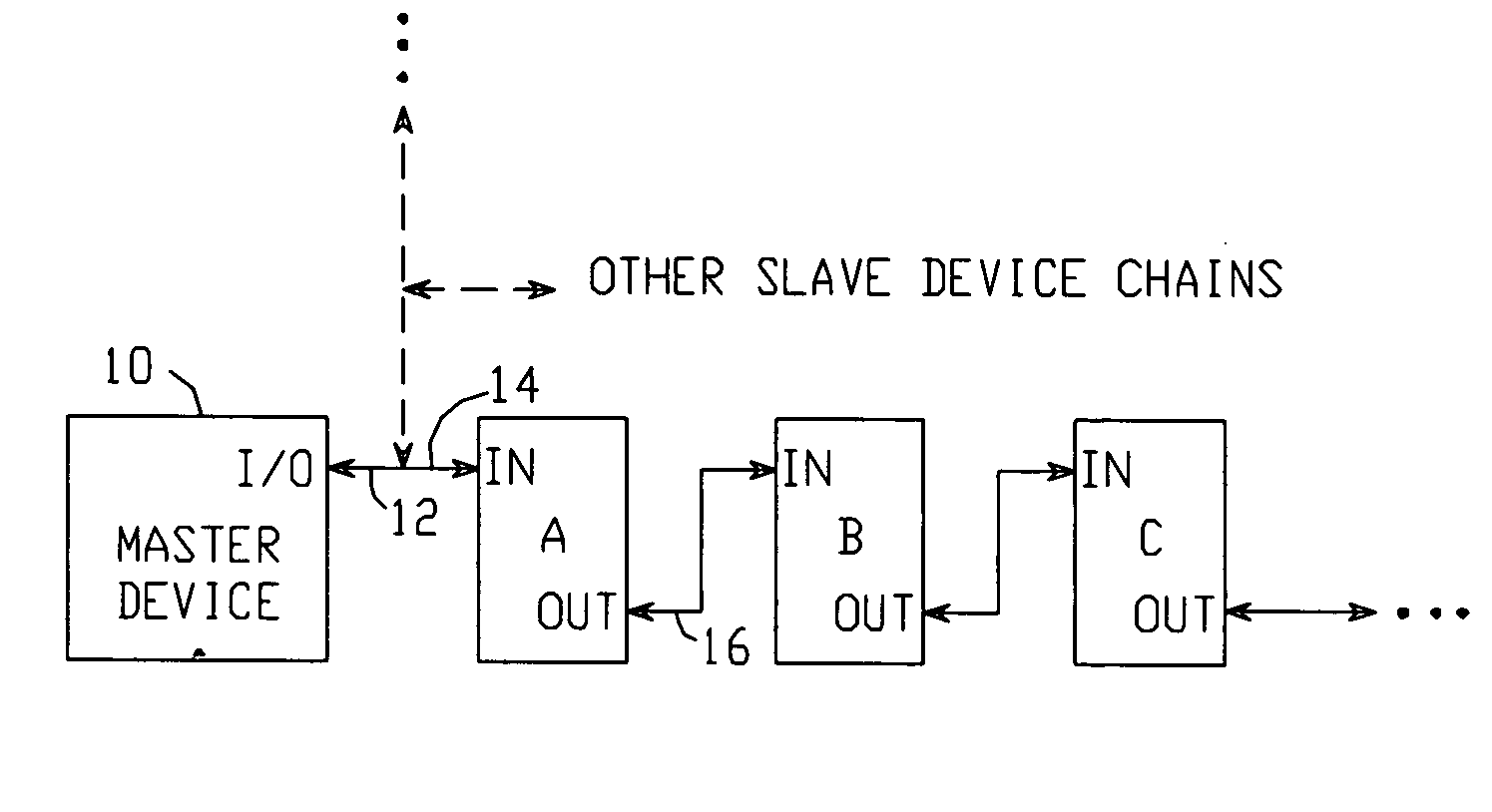
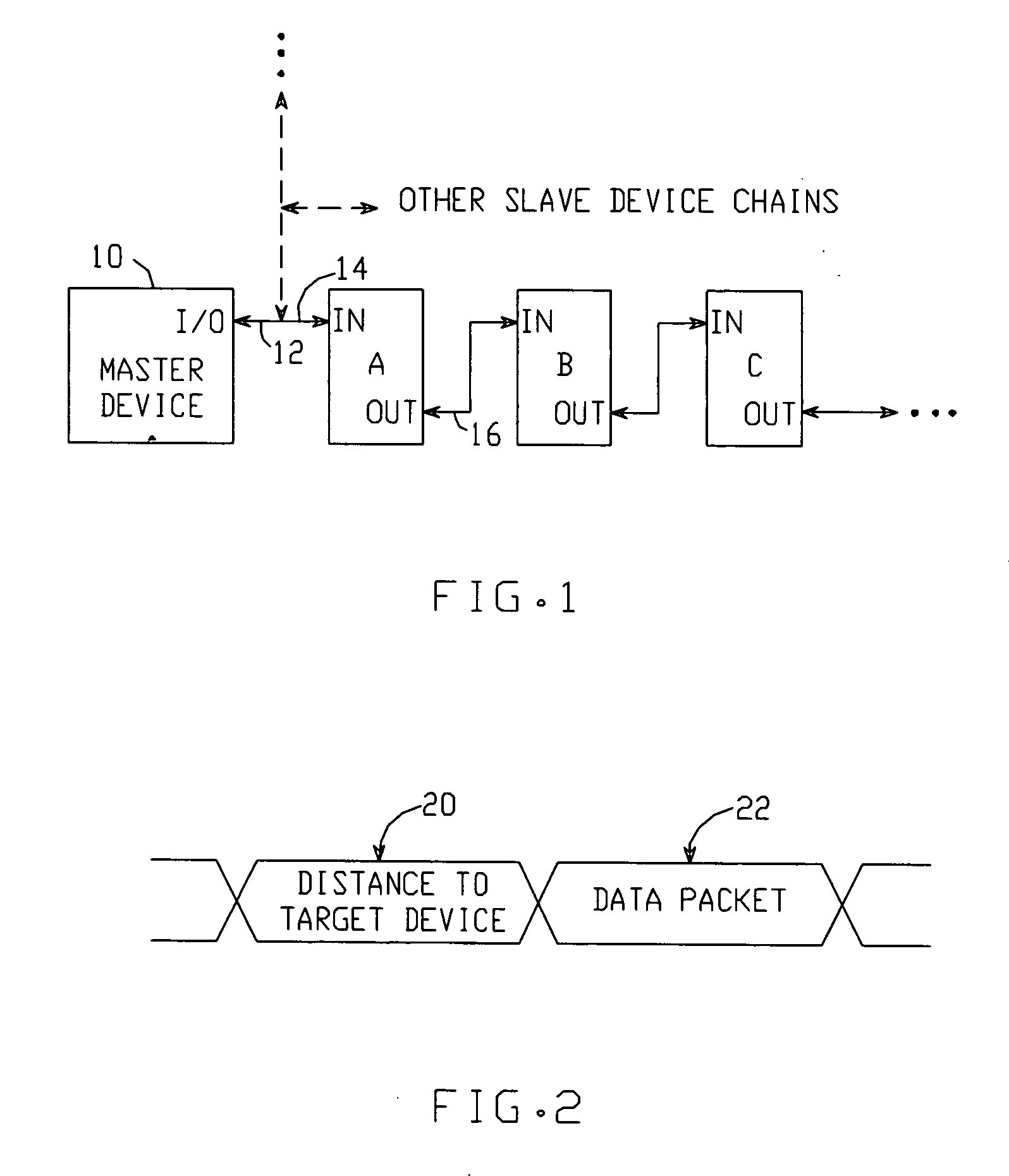
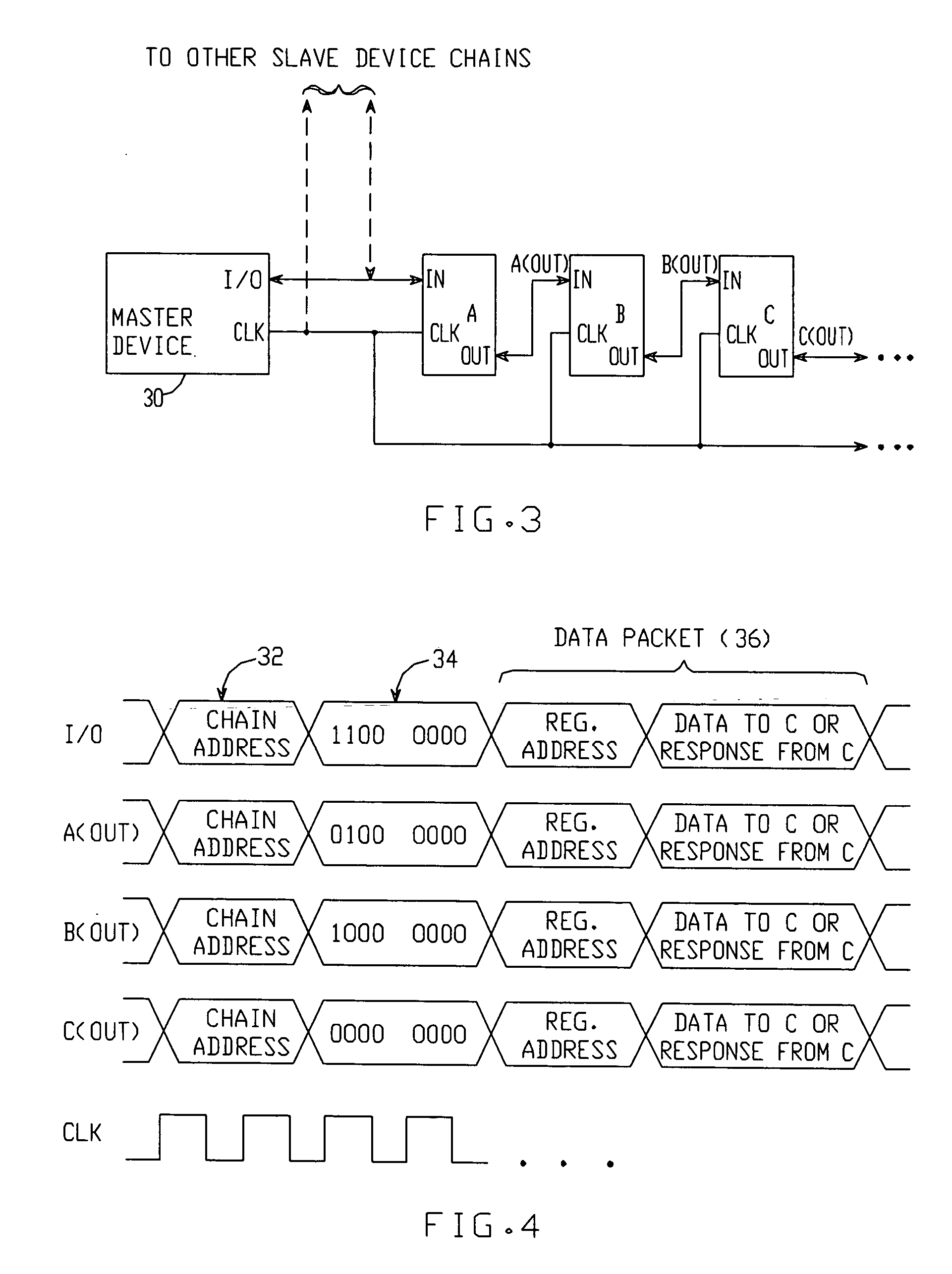
A communication system includes a master device which communicates with a chain of serially-connected slave devices. The master originates messages, each of which is intended for a particular ‘target’ slave device. Each message contains a ‘distance to target device’ value equal to the number of devices between the master and target, and a data packet containing data to be conveyed between the master and target. Each slave device determines if the ‘distance to target device’ value indicates that it is the target. If not, the slave device increments or decrements the value in real time, with no latency, and transmits the modified message to the next slave device until received by the target device. In one embodiment, the target device may place data in the data packet, and the slave devices are arranged to buffer the data back to the master device.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
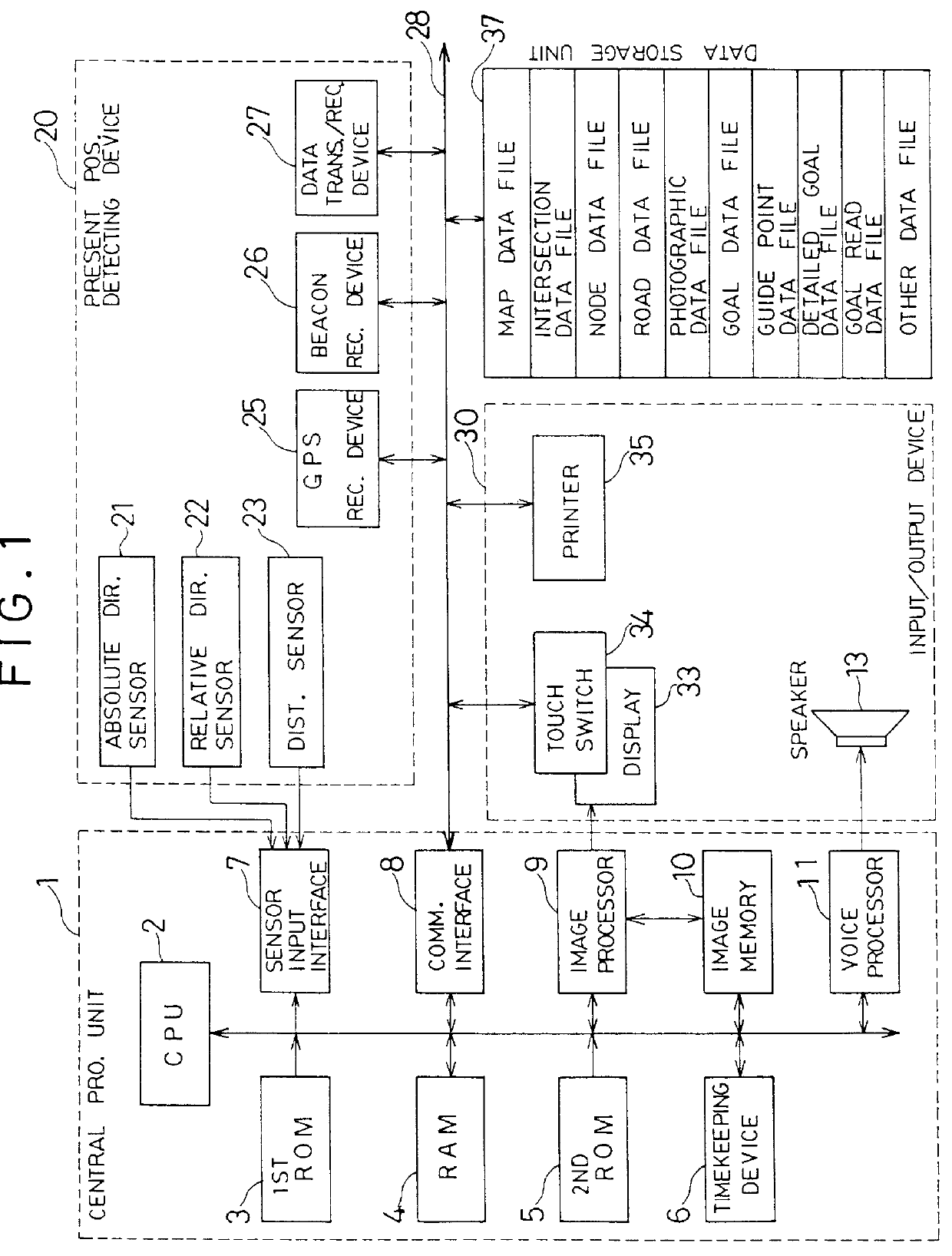
Navigation display device which indicates goal and route direction information
InactiveUS6070124AInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlDisplay deviceDistance to target
A goal direction mark and a distance to a goal are indicated when the car has approached the end point of route. When the car has deviated from the guide route to the goal or is running backwards on the guide route, there is indicated a mark to inform the direction of progress to the goal on the guide route. When the car has deviated from the guide route and the guide route is not indicated on the map picture, there is indicated the direction to the goal or the direction to the guide route itself. When the start point of route is remote from the present position at the start of the guidance, a mark is indicated to inform the direction to the start point of route. The driver is enabled to easily determine relying upon the indicated mark in which direction he should proceed. When the map picture is scrolled, there is informed the goal direction, route direction or the direction of progress to the goal on the route. The user therefore is enabled to easily know the direction to the goal.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
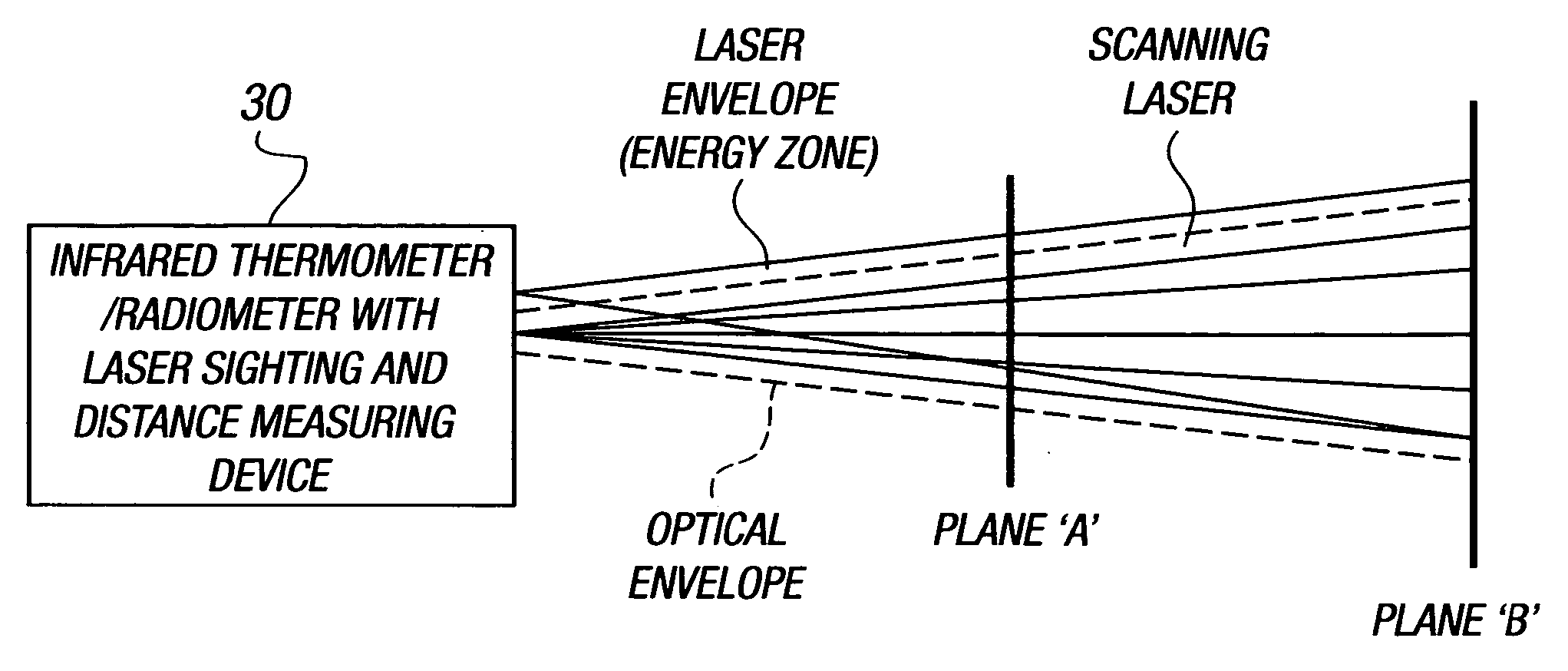
Infrared thermometers
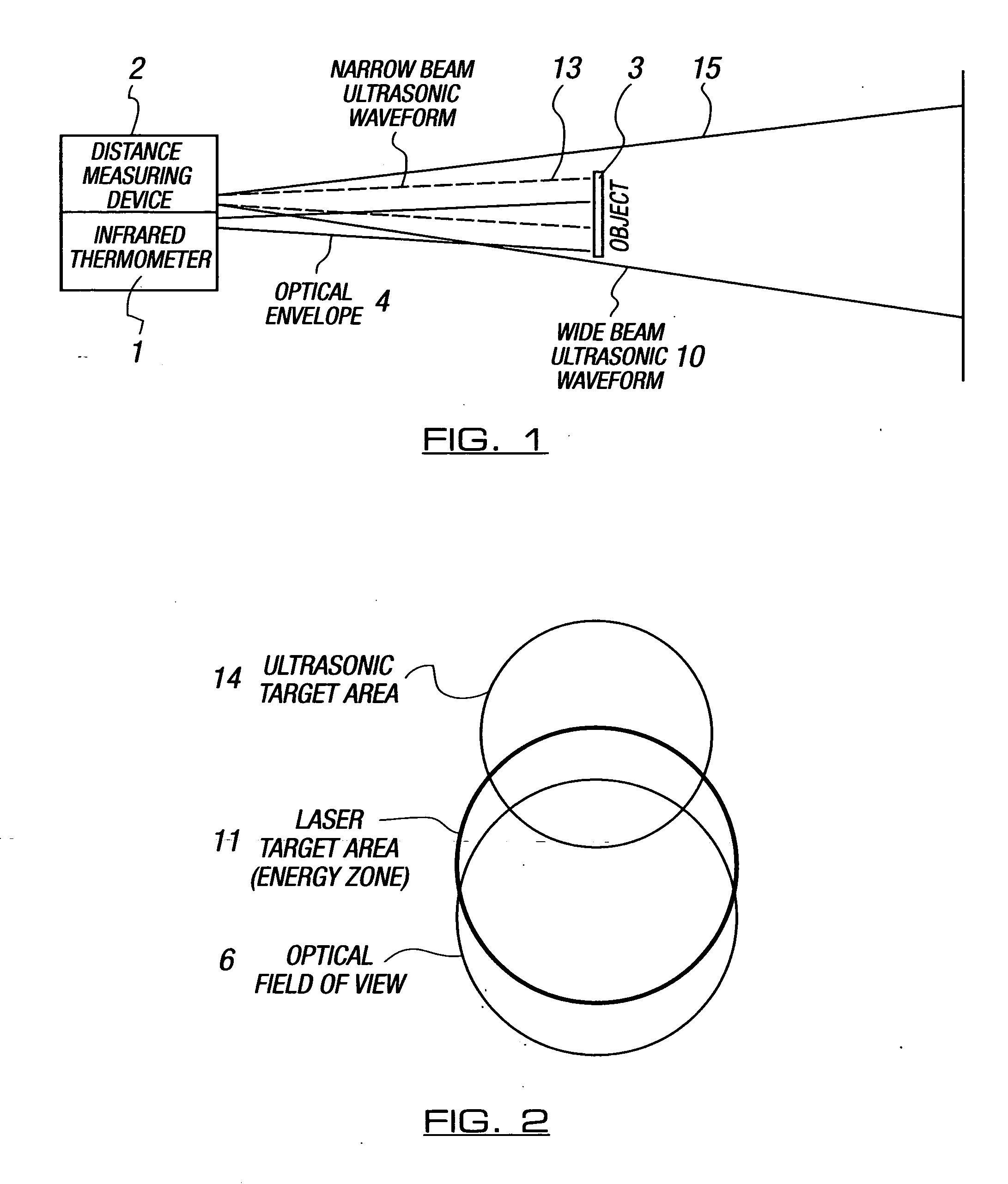
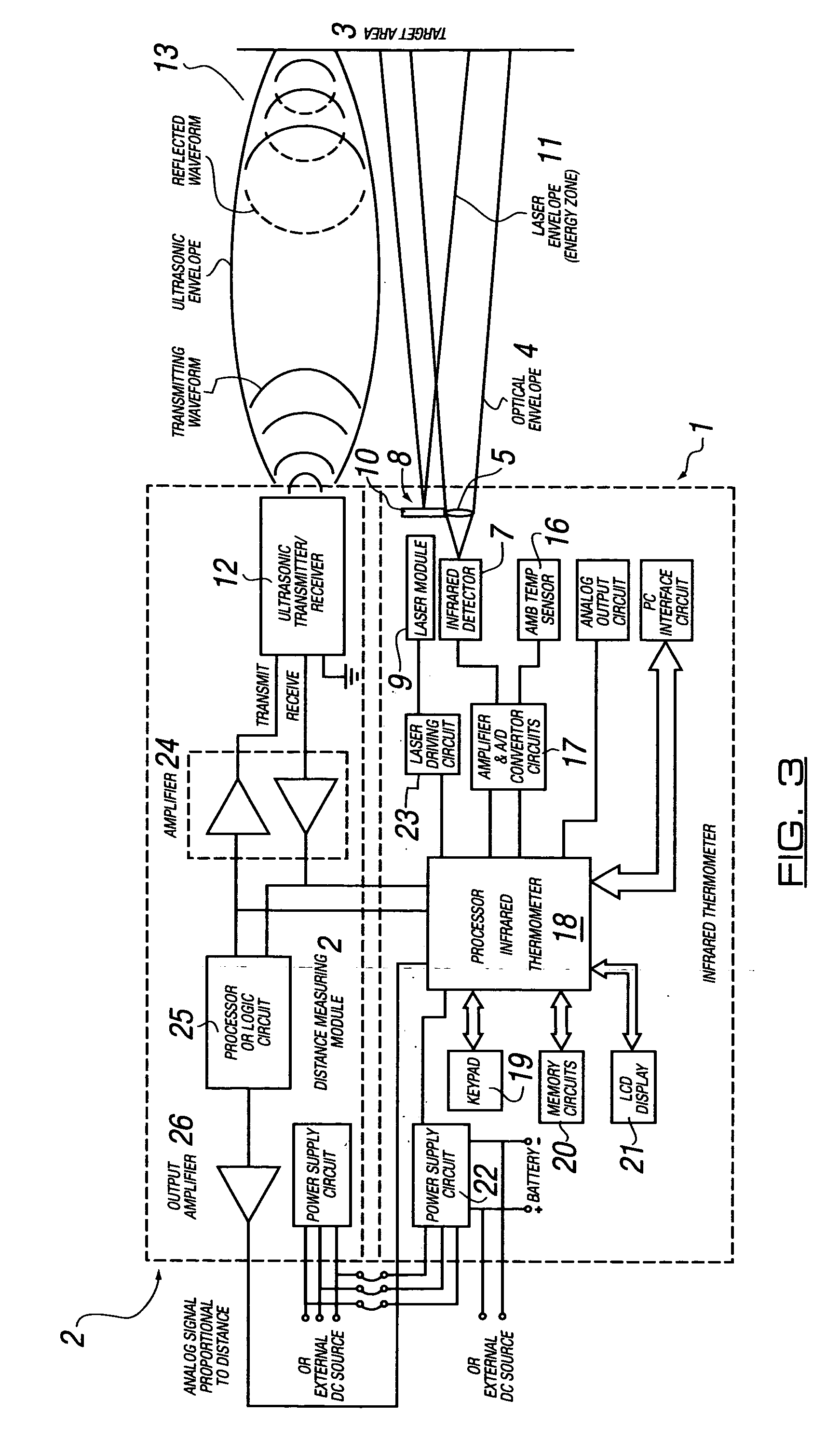
InactiveUS20050117624A1Accurate measurementMinimize power consumptionThermometer detailsRadiation pyrometryTarget surfaceLiquid-crystal display
The present invention is directed to a hand-held infrared thermometer or radiometer (1) for measuring, remotely, the temperature of a target surface (3). In one embodiment, the radiometer includes an infrared detector (7), associated optical system (7), and associated circuitry and an LCD display (21). Built into or mounted on the radiometer is a distance measuring device (2), the operation of which is controlled by the radiometer. The device (2) includes an ultrasonic transmitter / receiver (12) and associated circuitry for calculating, from a comparison of the transmitted and received pulses, the distance of the radiometer from the target surface. The distance-to-target is displayed on the LCD display (21).
Owner:WHITE BOX
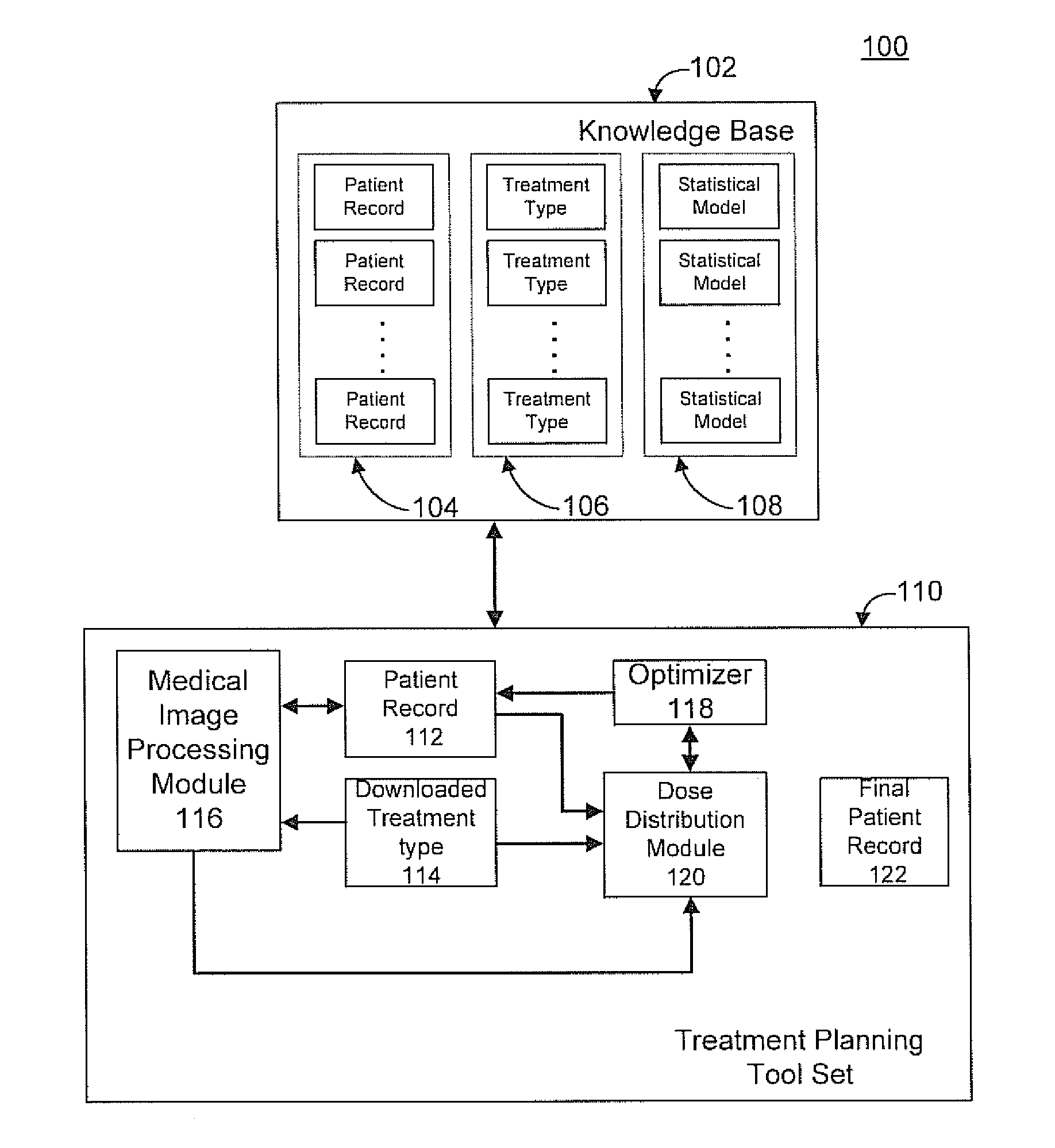
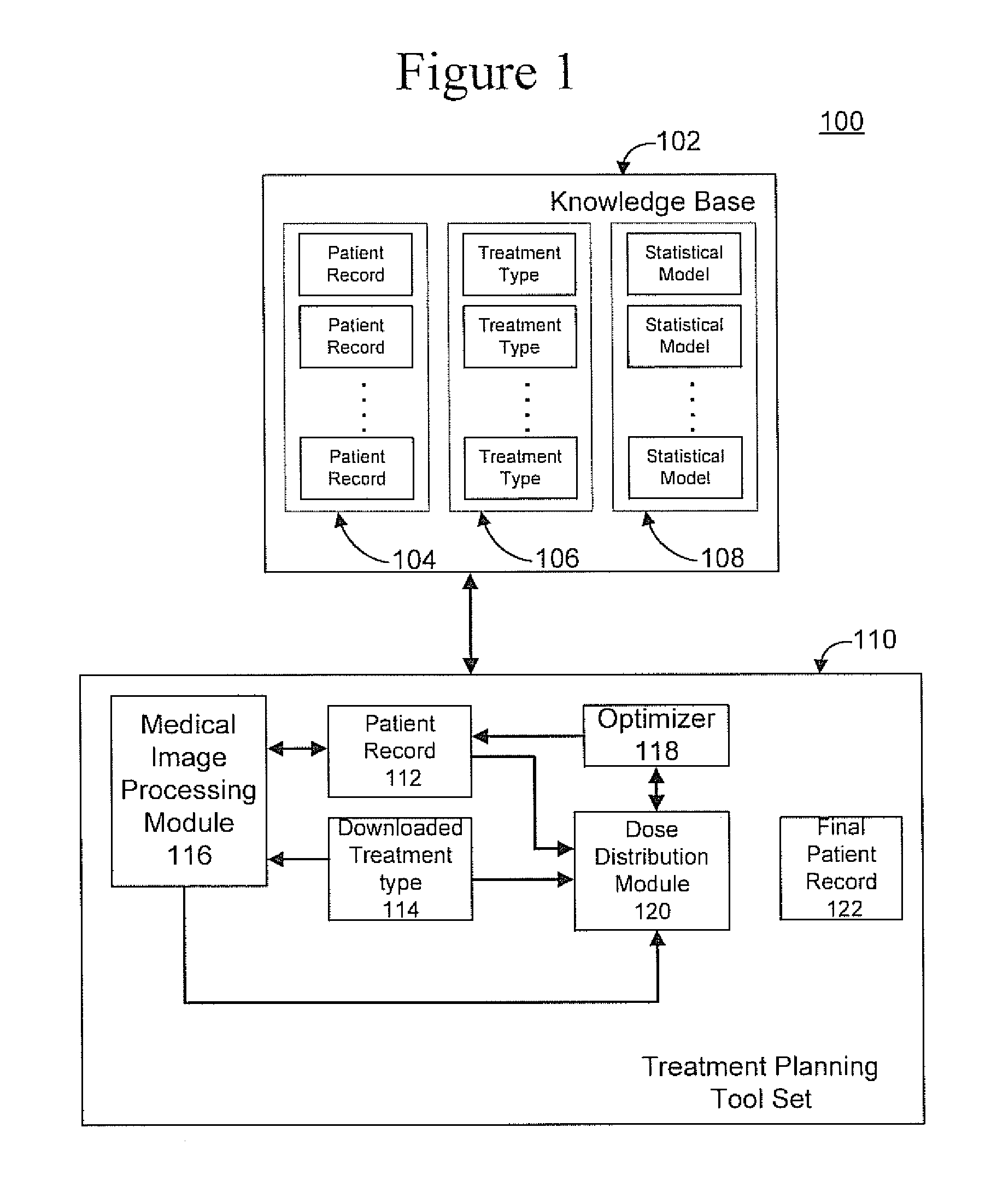
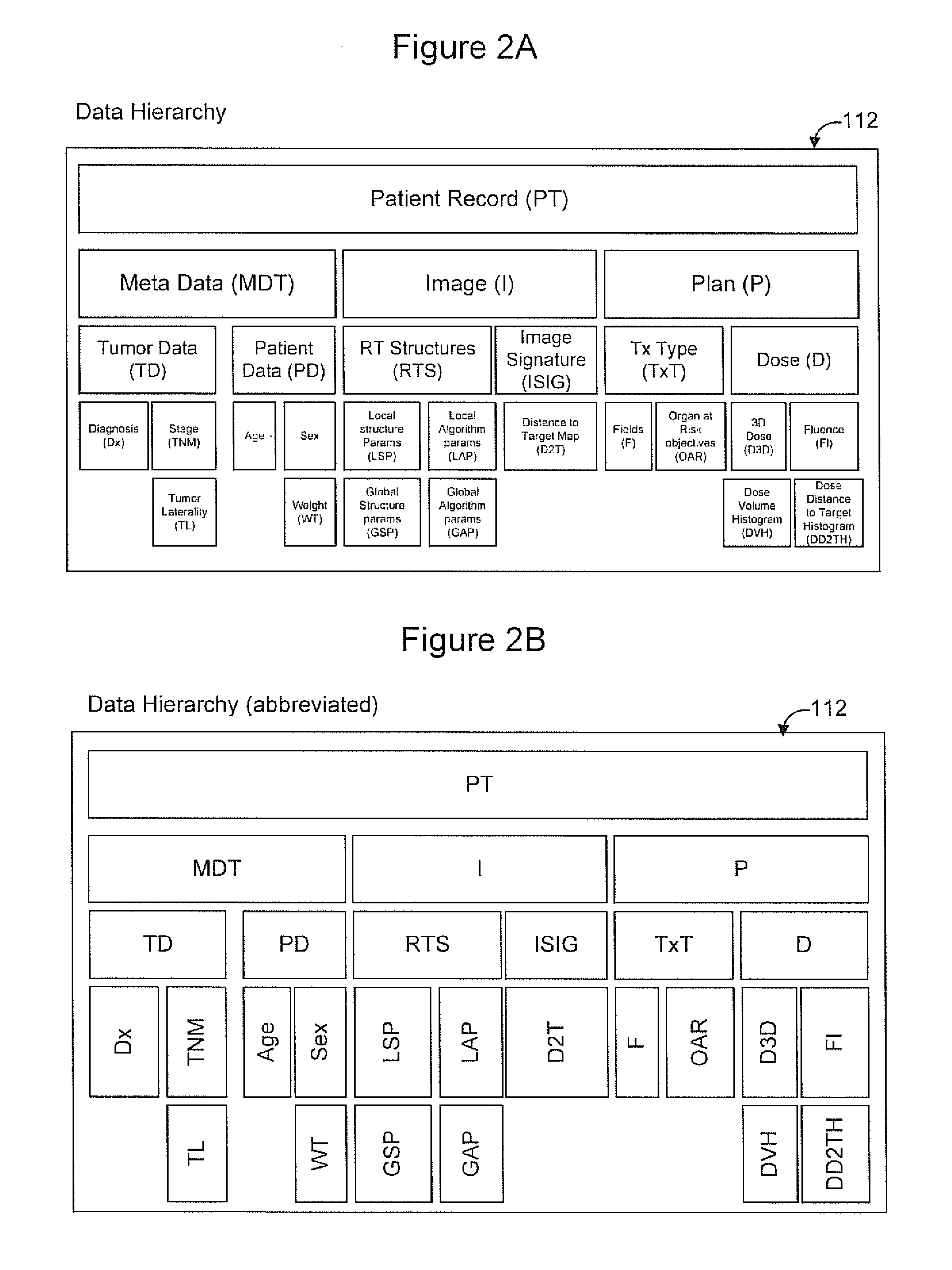
Radiation therapy treatment plan improvement through use of knowledge base
A radiation therapy dose distribution method starts with selecting a treatment type. Then an organ at risk (OAR) distance to target map is determined. The OAR distance to target map comprises distances to a target organ for portions of an OAR. The OAR distances are determined from at least one segmented patient organ image. A cohort average dose distance to target histogram is selected. A dose value to the portions of the OAR are assigned to form a first 3D dose distribution map. The dose values are from the selected cohort average dose distance to target histogram. A second 3D dose distribution map is determined based on a field arrangement determined by the treatment type and the first 3D dose distribution map. A dose distance to target histogram is calculated using the second 3D dose distribution map and the distance to target map.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
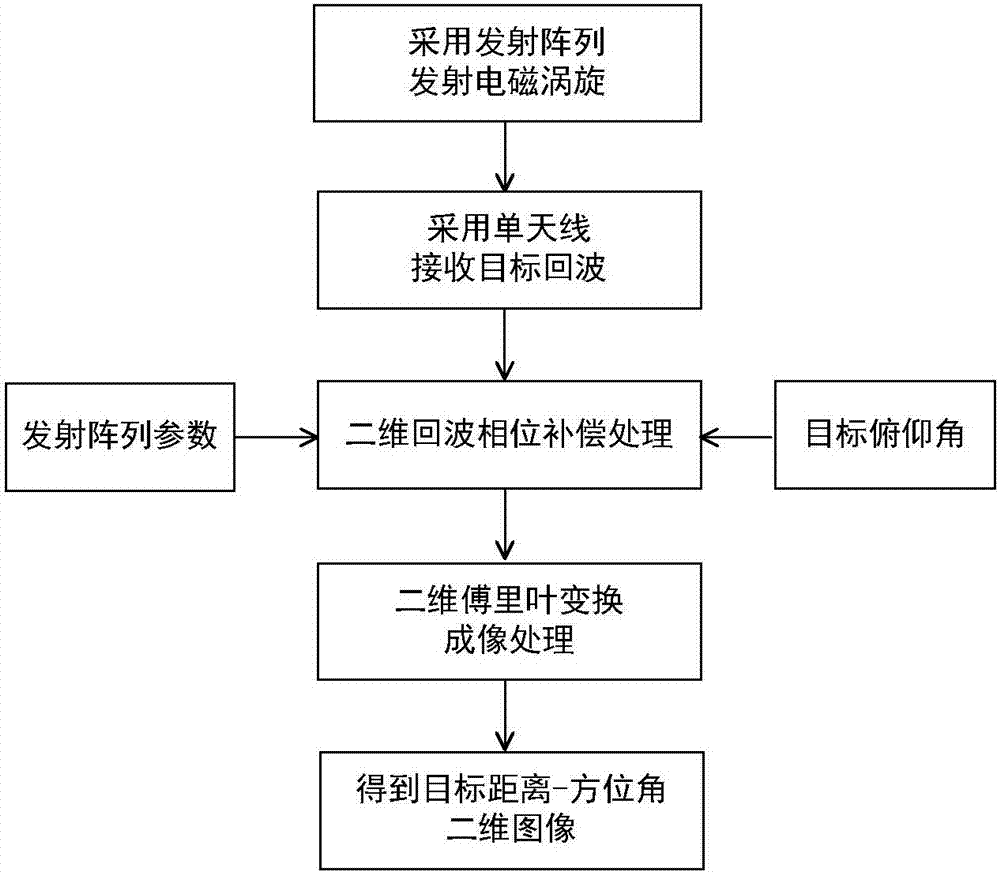
Electromagnetic vortex imaging method under single-antenna receiving condition
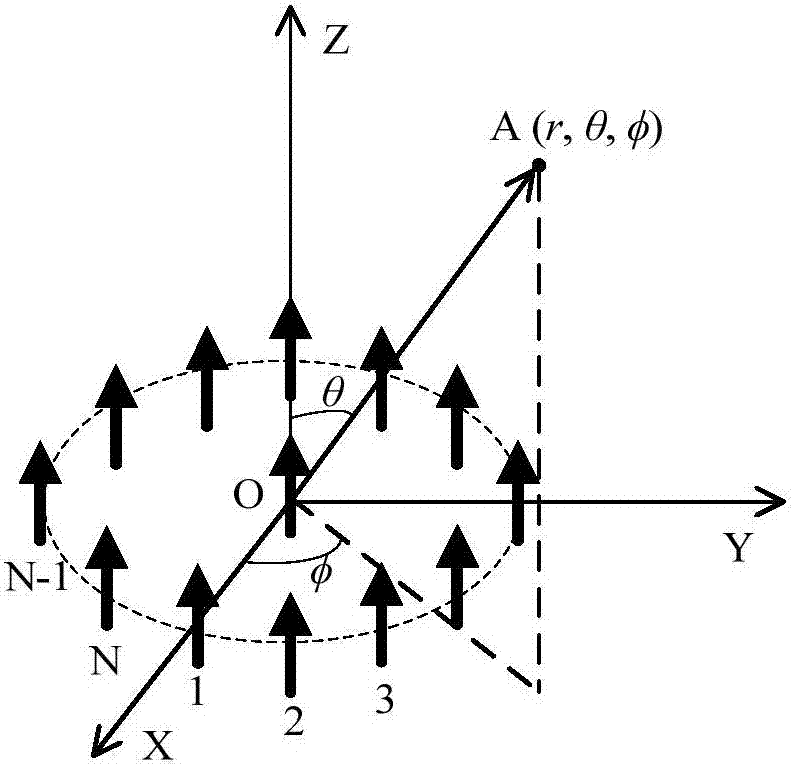
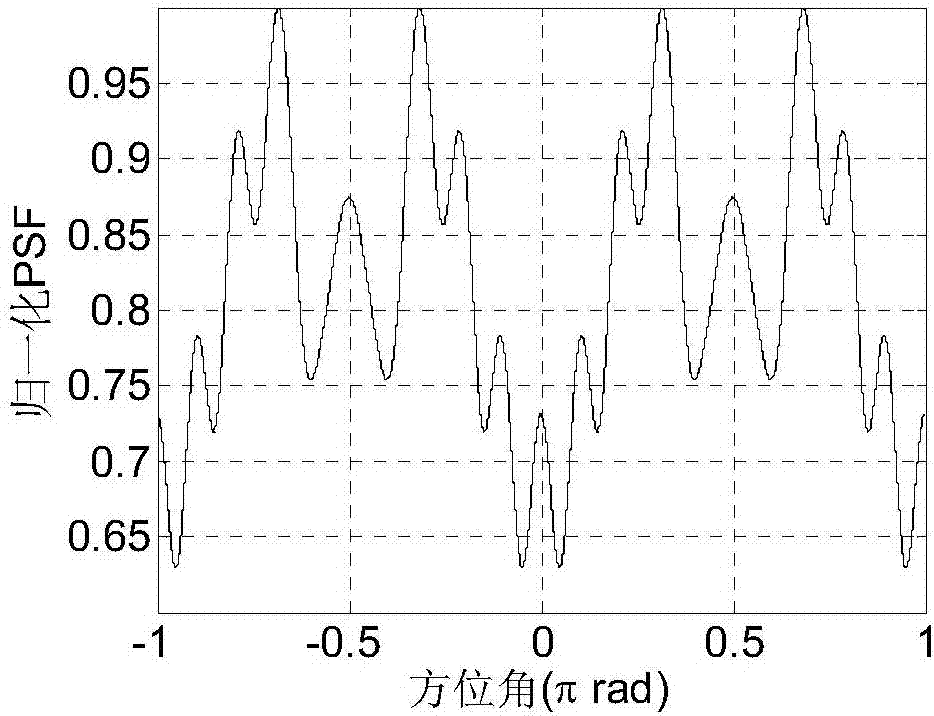
ActiveCN106886020AEasy to receiveNo synchronous reception requiredRadio wave reradiation/reflectionElevation angleMomentum
The invention provides an electromagnetic vortex imaging method under a single-antenna receiving condition. The technical scheme comprises the following steps: S1, N identical antennas are evenly distributed on a circumference to form a transmitting array; S2, electromagnetic vortexes of different frequencies and different orbital angular momentum modes are transmitted in turn using the transmitting array, and a single antenna in the center of the transmitting array receives each target echo, wherein the amplitude and phase information of the target echo received constitute frequency-orbital angular momentum mode two-dimensional echo data; S3, phase compensation is made for the received two-dimensional echo data according to the prior information of the parameters of the transmitting array and the elevation angle of a target to get preprocessed two-dimensional echo data; and S4, two-dimensional Fourier transform is carried out on the preprocessed two-dimensional echo data to get a distance-azimuth two-dimensional image of the target. The receiving process is simple. The method is easy to implement. Reference can be provided for the development of target recognition and new-system radar imaging technologies.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Reticle for telescopic gunsight and method for using
A gunsight reticle defines a system of dimensioned indicia spaced at specific separations to improve aiming accuracy of a gun. The indicia may include perpendicularly intersecting center vertical and center horizontal hairlines, and four (or more or less) horizontal range-marker lines disposed at specific angular separations below the horizontal hairline in bisected relationship with the center vertical hairline. Spacing of the range marker lines below the center horizontal hairline is proportional to bullet drop at selected ranges, depending upon ballistic characteristics of bullet used. Relative lengths of said range-marker bars on each side of the central vertical crosshair are proportional to a specific crosswind (say 10 mph) at target range reflected by respective range marker. The method involves employing this reticle to determine distance to target, and using distance thus determined to ascertain a precise aiming point on the reticle. These indicia also have other useful characteristics that allow the shooter to easily mentally calculate corrections for crosswind, moving targets and shooting at targets that are above or below the shooter at a significant angle.
Owner:SMITH THOMAS D III
Laser system architecture and method of using the same
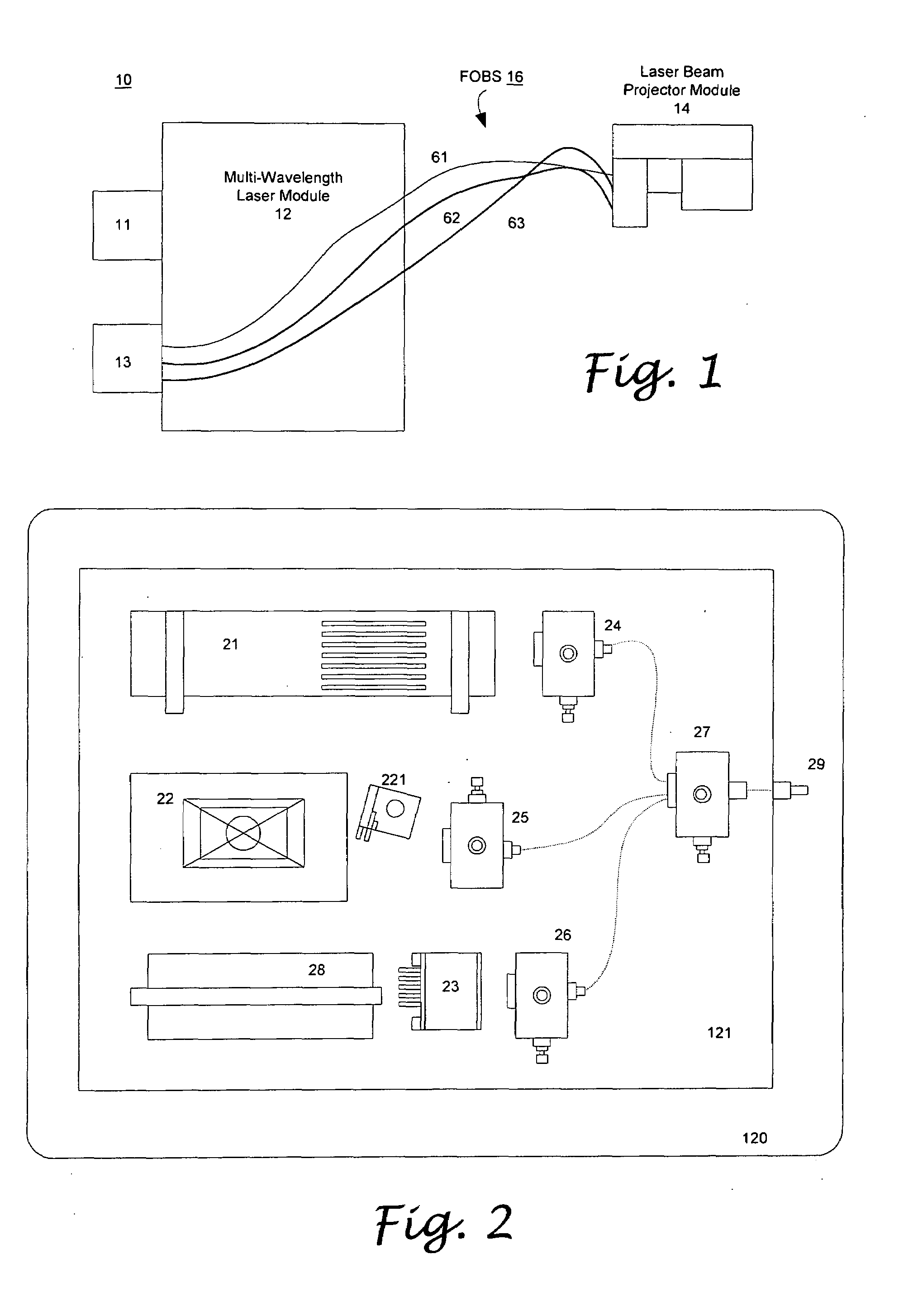
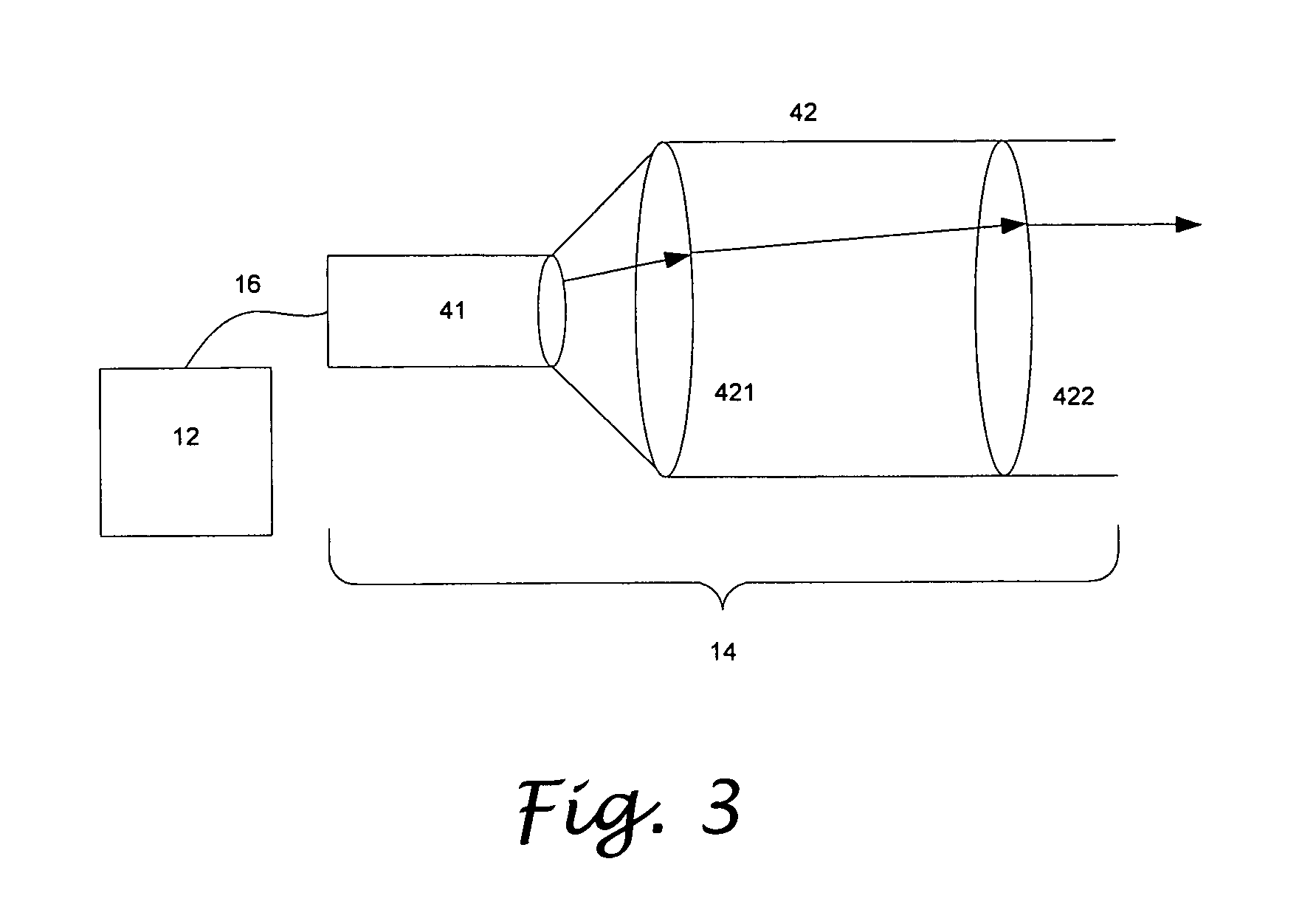
A color dazzle system to enhance area denial to personnel mission for law enforcement, homeland security, border patrol, and the military effectively by interrupting the ability of combatants to continue with their intended mission. The color dazzle system has a multi-wavelength laser module for generate desired color or wavelength ranges of light, a beam projector module for pointing the light towards the target to be dazzled, and a fiber optic beam delivery system for delivering the light to the beam projector module. By adjusting the power output according to the corresponding wavelength and the distance to the target, and quickly switching between the wavelengths of light, a dazzle effect can be obtained with an irradiance within a safety range for the eye.
Owner:HAUCK JAMES P +1
Weapon sight
InactiveUS7421816B2Accurate shooting experienceSighting devicesAiming meansEngineeringDistance to target
The invention includes a sighting system for use with a firearm that has a telescopic sight, a laser rangefinder for providing the distance to the target, device(s) for receiving various inputs, a computing system that calculates the point of aim of the firearm's projectile based upon the input(s) and the calculated distance to the target, and a display means that provides an image of the computed point of aim within the telescopic sight's field of view. A method and weapon that employs the sighting system is disclosed.
Owner:CONESCU PAUL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com