Distance measuring method and distance measuring element for detecting the spatial dimension of a target
A distance measuring method and a technology of a range finder, which are applied in the field of range finders and can solve problems such as parallel measurement of multiple sensors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
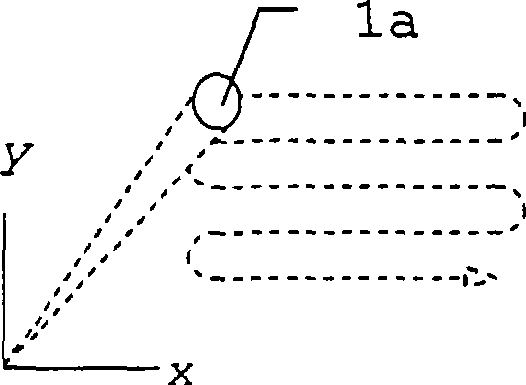
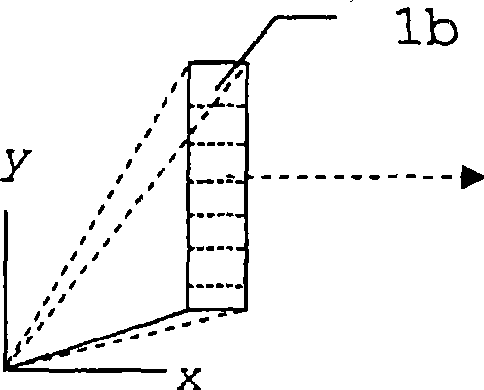
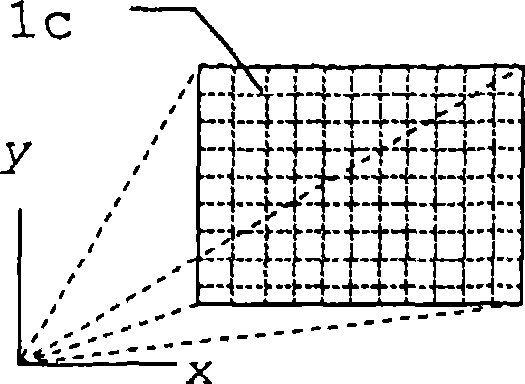
[0048] Figure 1a to Figure 1c A prior art method for determining the spatial dimension or shape of an object is explained. In order to scan the surface of an object, multiple light paths to many different points of the surface must be implemented.
[0049] like Figure 1a As shown, this can be achieved by a scanning movement of a single beam path with the aperture 1a, which in each case detects only a single point simultaneously. Objects are overwritten entirely sequentially. For this purpose, a light signal, generated for example by a laser, is directed onto the object via a scanning mechanism and is suitably shaped by the transmitter optics. A part of the light reflected by the object is received through the aperture 1a of the receiving optical system and guided to the optical sensor of the measuring system. Based on the signal transit time from the light source of the measurement system to the object and back to the sensor, the distance of each measured point can be der...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com