Macro method of coal-based graphene quantum dot
A graphene quantum dot, macro-quantity technology, applied in the macro-scale field of coal-based graphene quantum dots, can solve the problems of complex experimental process, difficult industrial mass production, and low yield, and achieve good water solubility and high yield , The effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
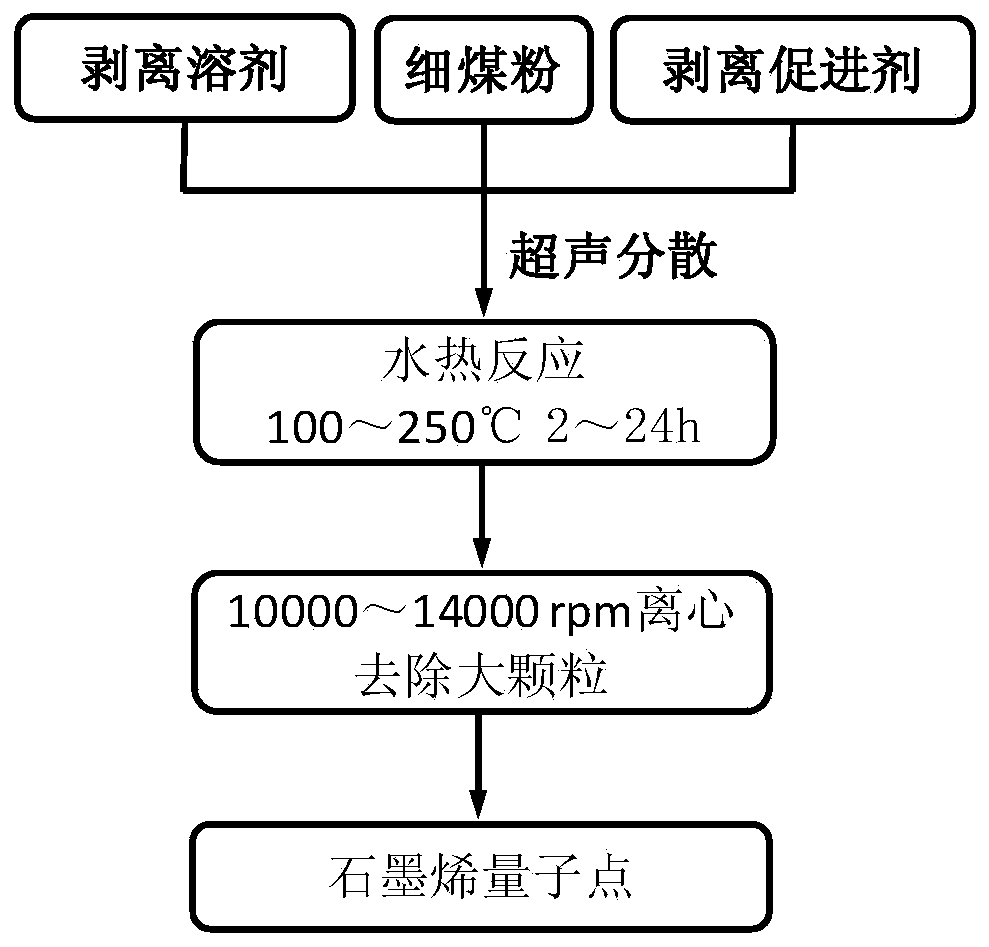
[0019] The present embodiment relates to a macroscopic method of coal-based graphene quantum dots, comprising the following steps:
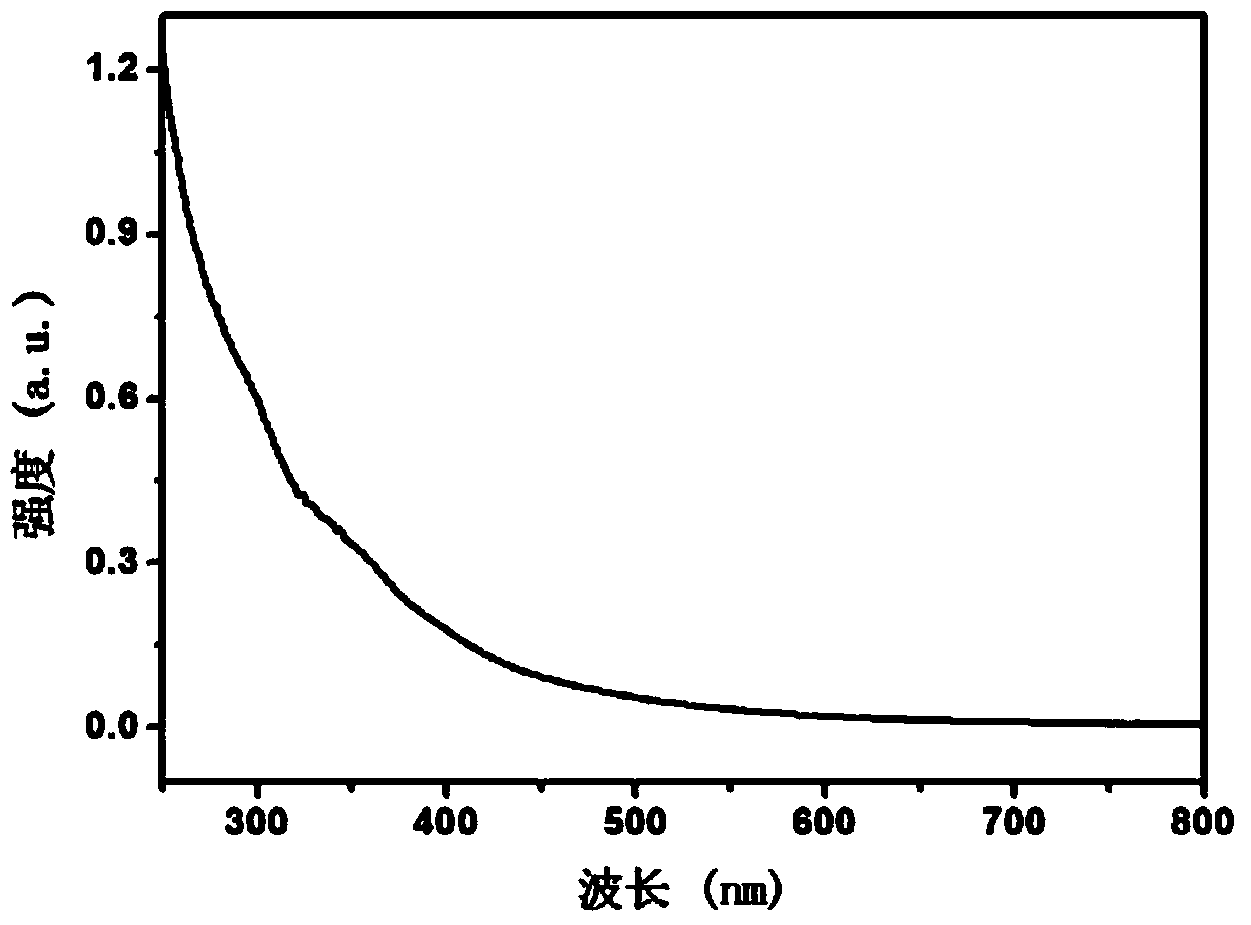
[0020] Such as figure 1 As shown, mix 0.1g of anthracite coal powder with a size of 200μm, 20ml of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone and 0.2g of trisodium citrate in a beaker and disperse in an ultrasonic pool for 30min (power 100W); then transfer the mixture into React in a 50ml hydrothermal reactor at 200°C for 8 hours under continuous magnetic stirring conditions, and after cooling, centrifuge at 14,000 rpm for 10 minutes to remove large particles to obtain water-soluble graphene quantum dots. Its UV-Vis absorption spectrum is as follows figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0022] The present embodiment relates to a macroscopic method of coal-based graphene quantum dots, comprising the following steps:
[0023] Such as figure 1 As shown, mix 0.2g of 100μm lignite powder, 60ml dimethyl sulfoxide and 0.6g sodium tartrate in a beaker and disperse in an ultrasonic pool for 30min (power 200W); then transfer the mixture into a 100ml hydrothermal reaction kettle React at 200°C for 10 h under continuous magnetic stirring conditions, and centrifuge at 13,000 rpm for 20 min after cooling to remove large particles to obtain water-soluble graphene quantum dots. Its UV-Vis absorption spectrum is as follows figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0025] The present embodiment relates to a macroscopic method of coal-based graphene quantum dots, comprising the following steps:
[0026] Such as figure 1 As shown, mix 0.1g of anthracite powder of 0.1μm size, 30ml of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone and 0.0g of trisodium citrate in a beaker and disperse in an ultrasonic pool for 10min (power 200W); then turn the mixture to Put it into a 50ml hydrothermal reaction kettle and react at 200°C for 2h under continuous magnetic stirring conditions. After cooling, centrifuge at 14000rpm for 2min to remove large particles to obtain water-soluble graphene quantum dots. Its UV-Vis absorption spectrum is as follows figure 2 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com