Method for determining soybean phytophthora root rot resistant quantitative trait loci and use of the loci
A technology of quantitative genetics and Phytophthora sojae, which is applied in the fields of application, botany equipment and methods, and microbial measurement/inspection, can solve the problems of main QTL mining difficulties and achieve the effect of improving breeding efficiency and reducing waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
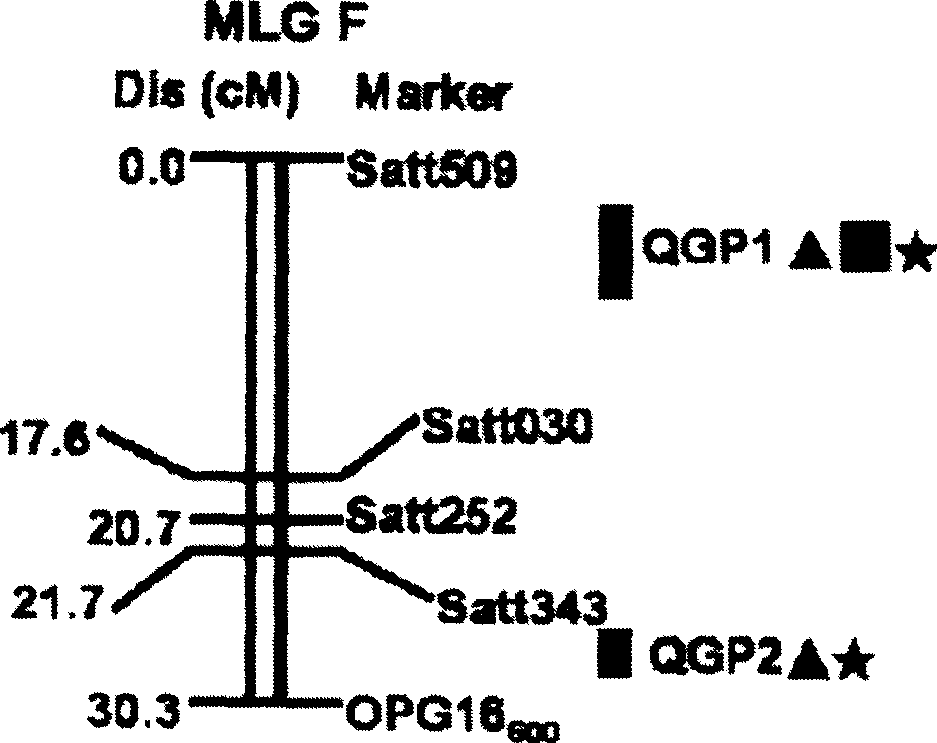
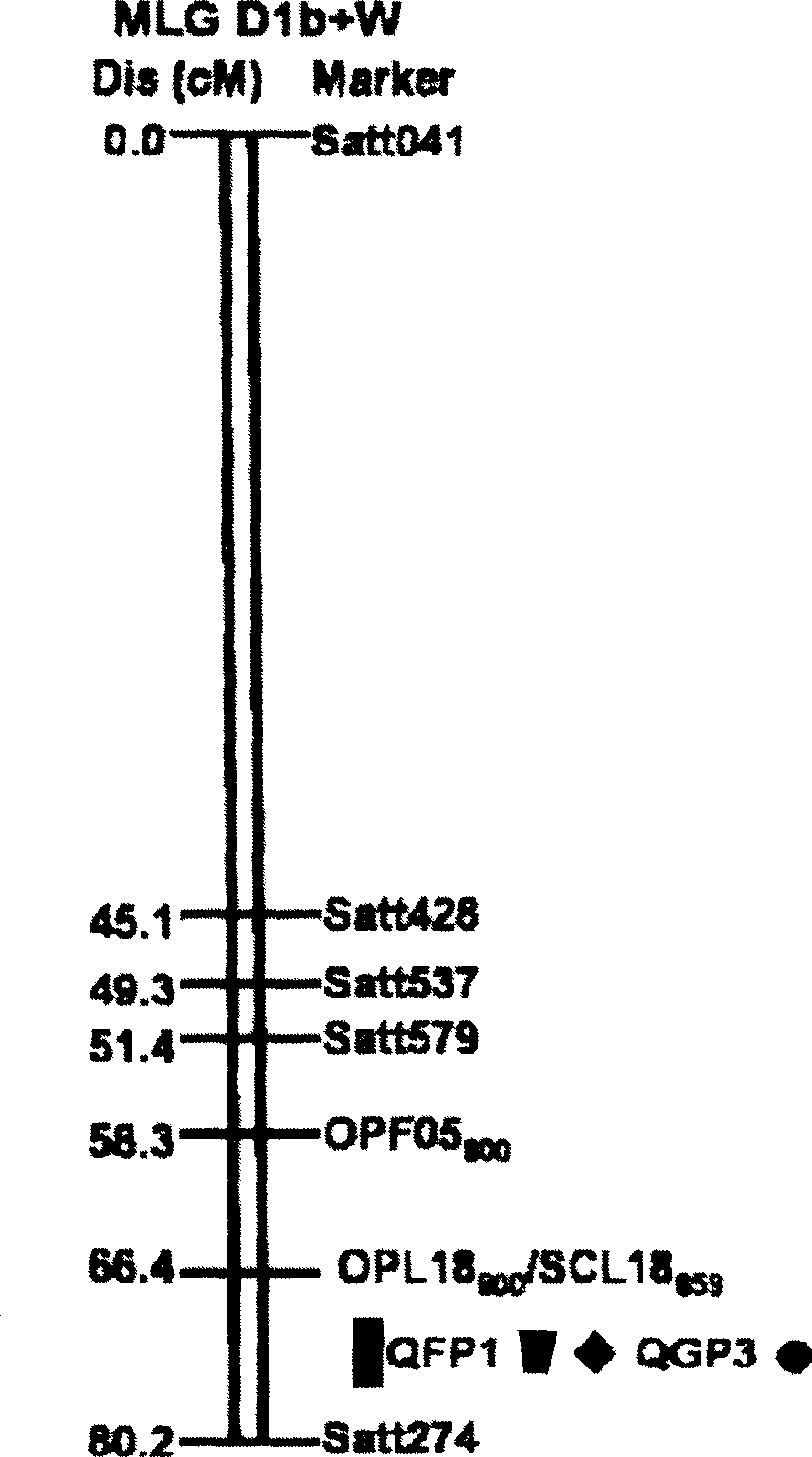
[0028] Identification of quantitative loci (QTL) associated with resistance to Phytophthora soybean root rot:
[0029] (1) Construction of Conrad recombinant inbred lines and identification of disease resistance:
[0030] The hybrid F 1 ; by Hybrid F 1 Generation self-pollination to obtain offspring, and F 6 Generation of recombinant inbred lines;
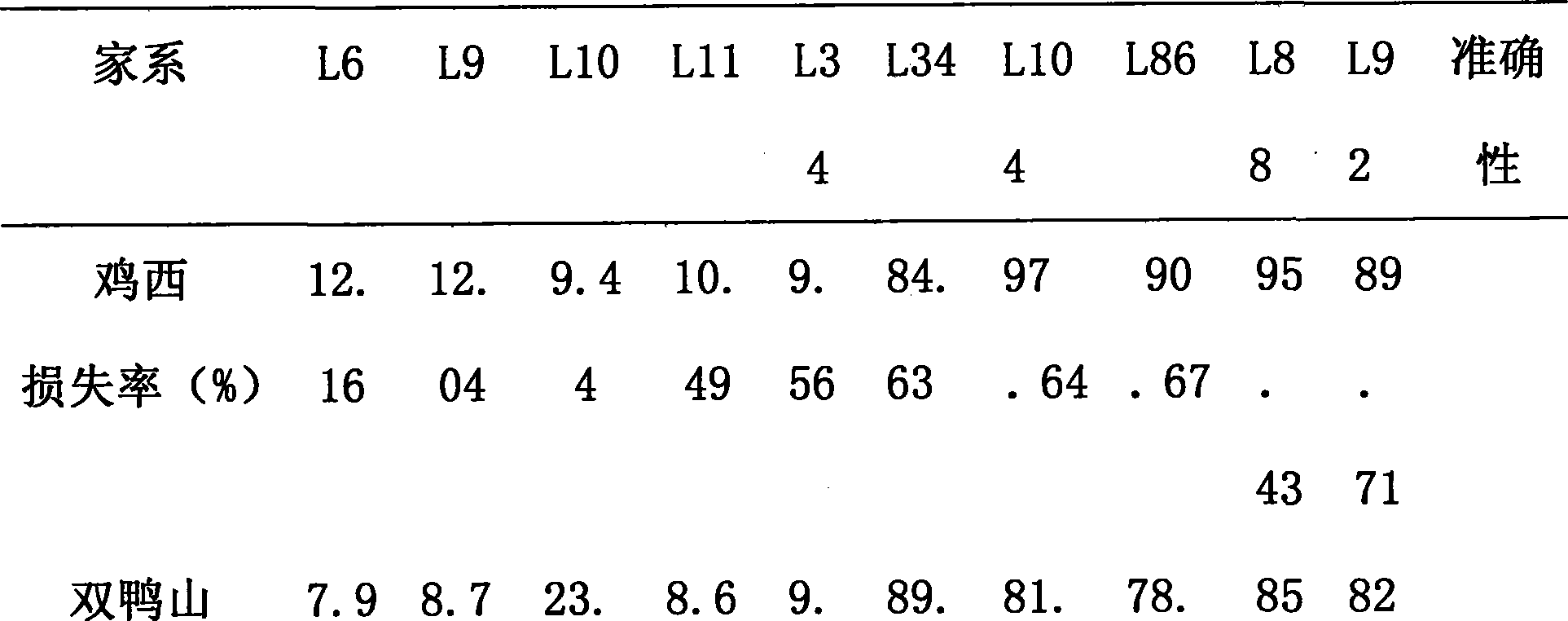
[0031] The mixed strains from Jixi, Shuangyashan, Jiansanjiang and North America in Heilongjiang Province, China were used for inoculation identification and disease loss rate statistics, with three repetitions.
[0032] (2) Genetic map construction and QTL analysis:
[0033] 39 random primers (RAPD), 89 simple repeat marker primers (SSR) and 1 pair of sequence characteristic application interval primers (SCAR) with amplified polymorphism between parents were selected for PCR amplification, and the bands were selected according to the population For the segregation situation in , the individual with the maternal type band is m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com