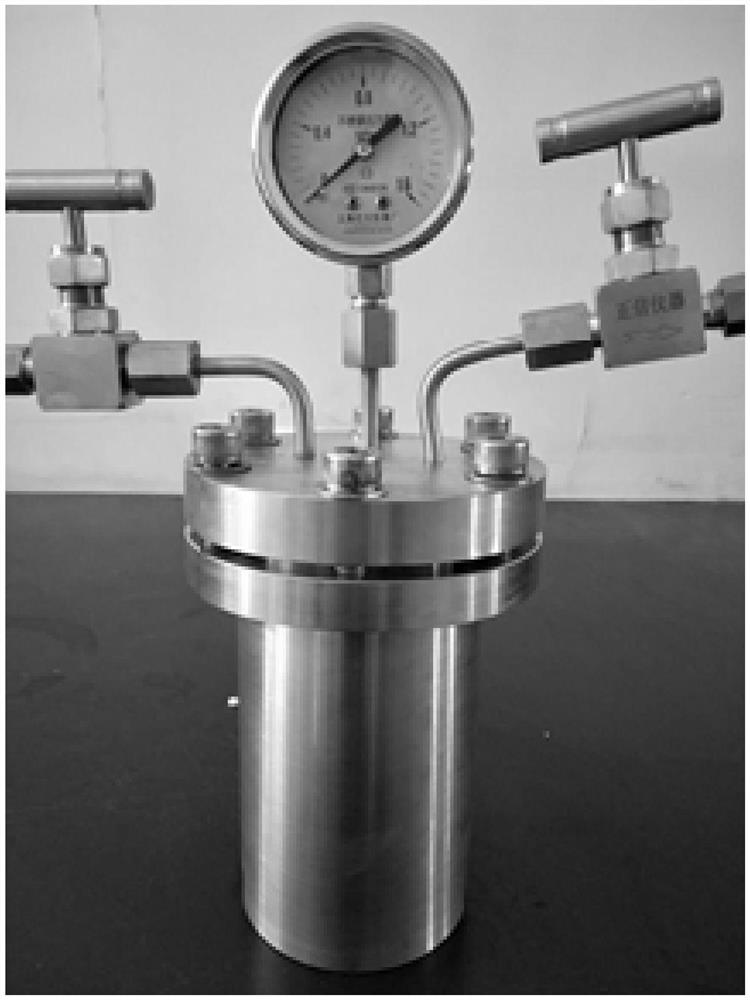
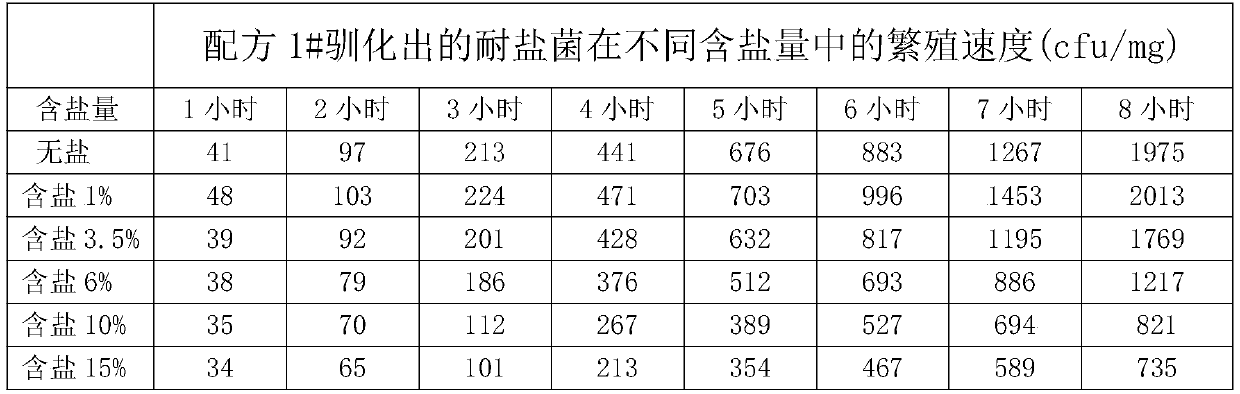
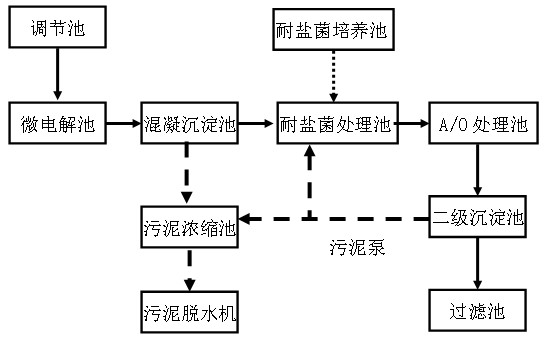
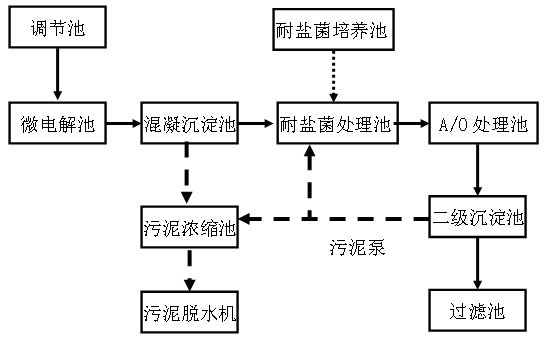
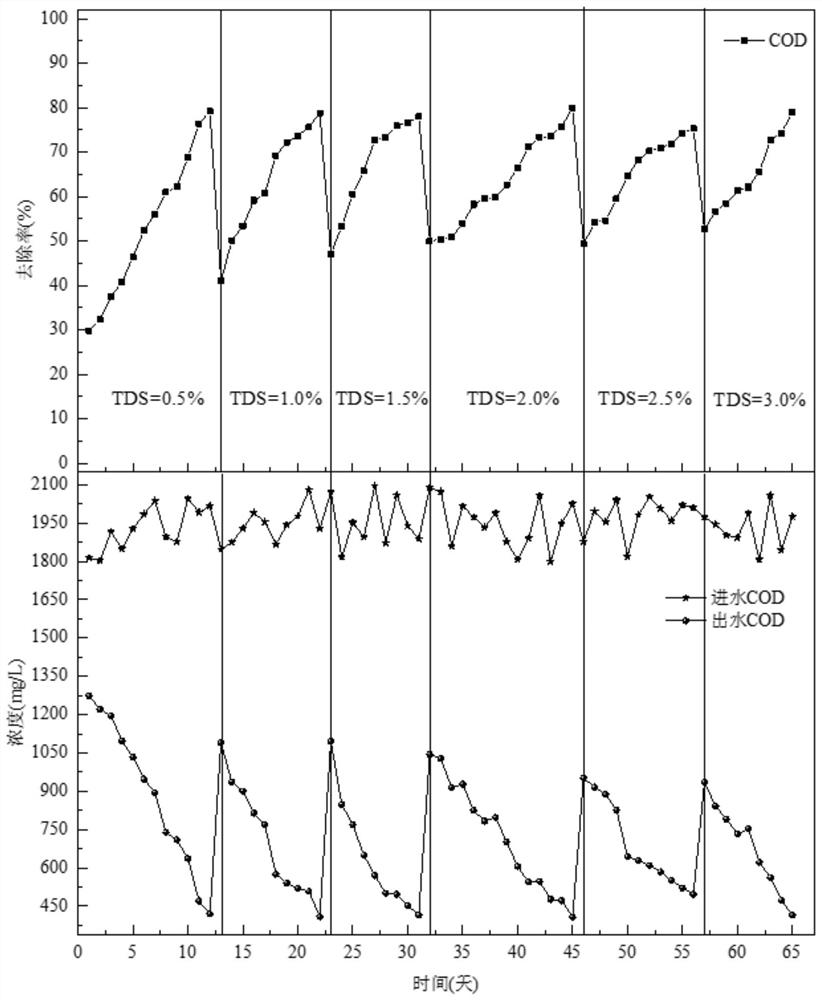
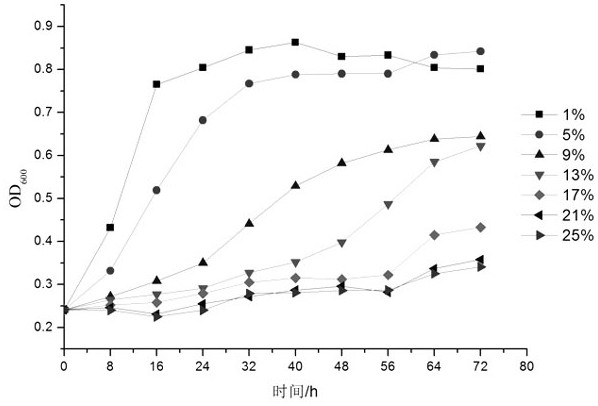
Patents
Literature
34 results about "Halotolerant bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Halotolerant pathogens are an important cause of food-borne illnesses because they survive and multiply in salty food. For example, the halotolerant bacteria S. aureus, Bacillus cereus, and V. cholerae produce dangerous enterotoxins and are major causes of food poisoning.
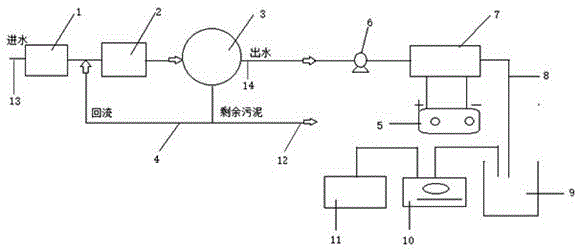
Method for treating or recycling waste water with high salt content and applications
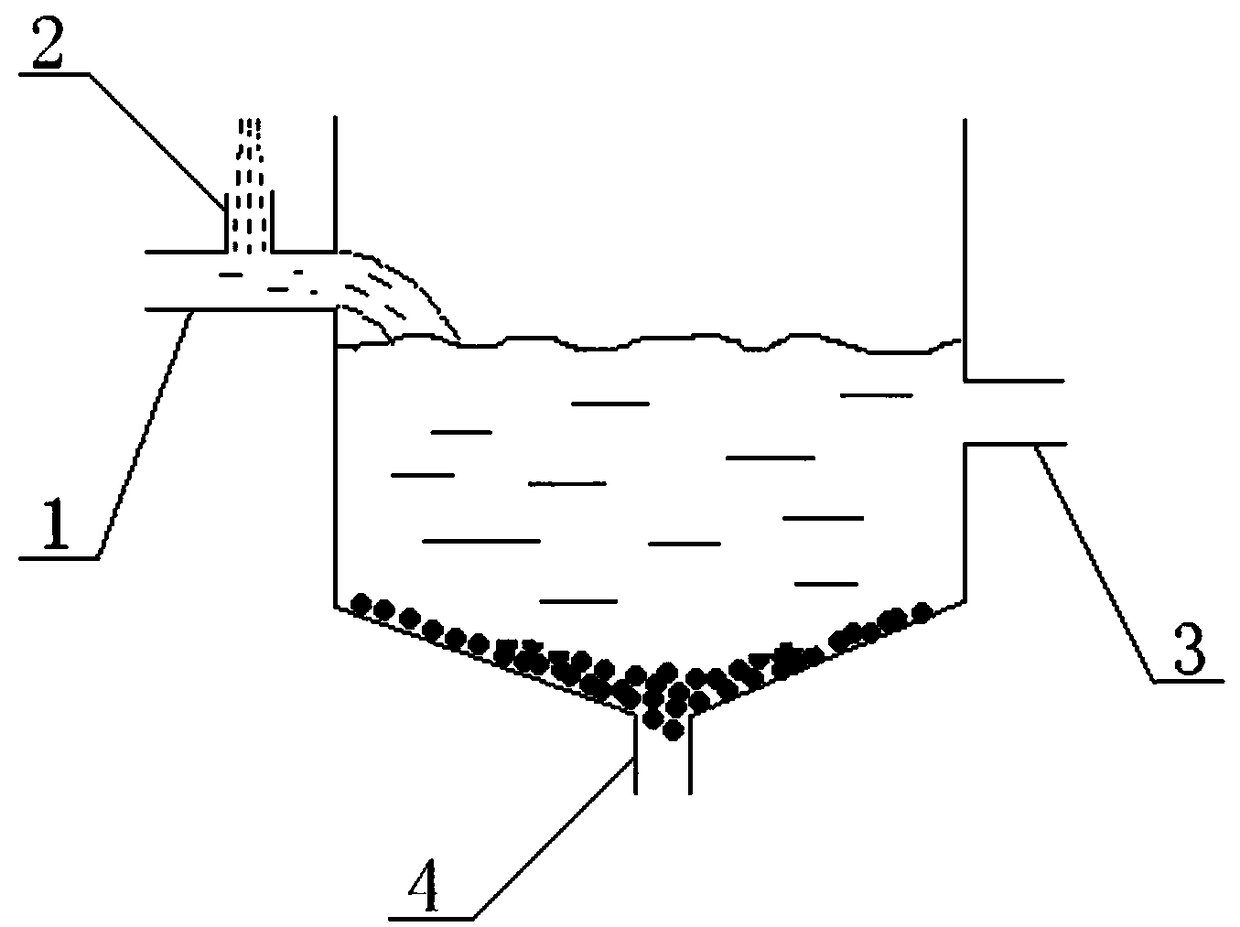
InactiveCN101723539AAchieve recyclingAchieving "Zero Emissions"Fatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisSalt resistanceSludge
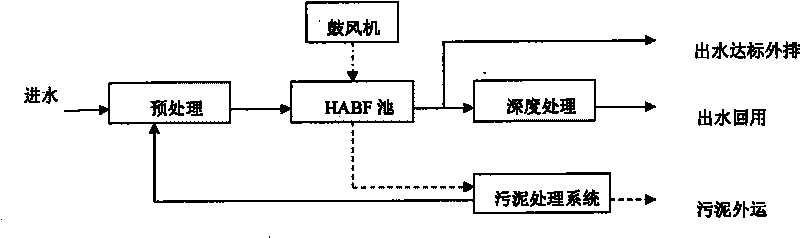
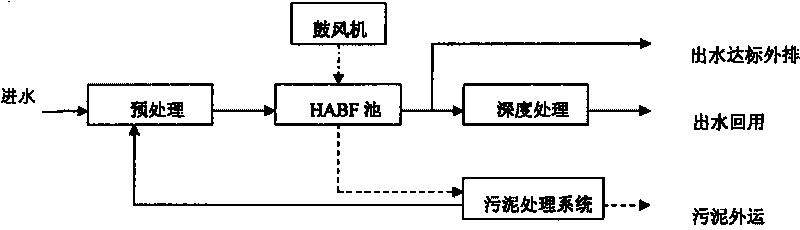
The invention provides a method for treating or recycling waste water with a high salt content and applications. The method adopts combination processes of pretreatment, a high-efficiency aeration biological filter and depth treatment; and the detail process is shown in the description. The method of invention has the advantages of rapid degradation speed of the high-efficiency aeration biological filter to the pollutants in waste water, high treatment efficiency, good salt resistance, strong anti-impact capacity, stable operation and less sludge generation amount, and being beneficial for enrichment of halotolerant bacteria; the high-efficiency aeration biological filter is taken as a pretreatment process of the membrane treatment, which can effectively prevent membrane surface from scaling, prevent the membrane from being polluted and plugged by colloidal substances, suspended solid grains, organic matters and microorganisms, prolongs reverse purging period, increases the service life of the membrane, keeps stable water generation amount of a membrane system, thus lowering the operation cost. The invention is not only suitable for standard discharge or recycling of concentrated solution before the membrane separation in a membrane separation process, bus also suitable for treatment and recycling of waste water with a high salt content, such as oil extraction waste water and the like, and transformation and upgrading of the existing engineering.
Owner:周兆宇
Method for solidifying sand by utilizing halotolerant bacteria
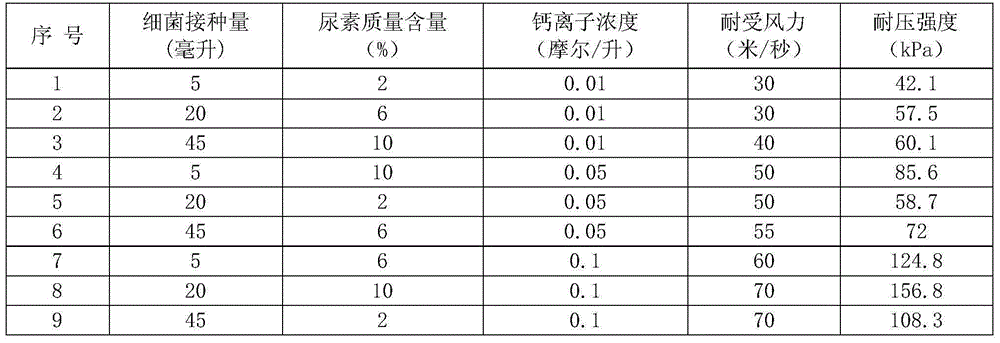
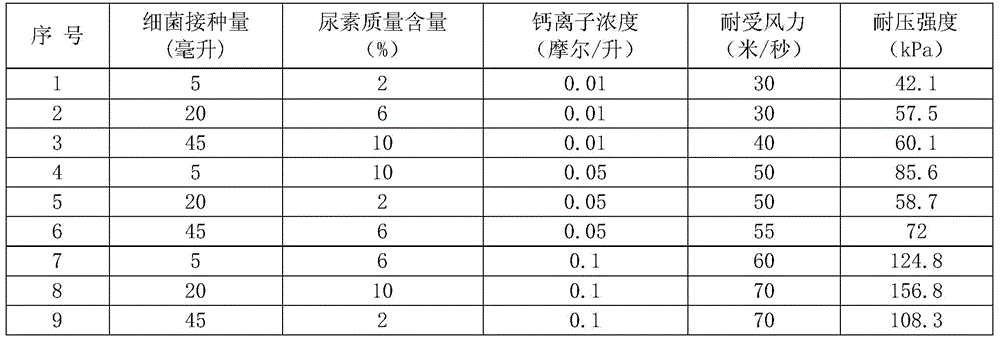
The invention relates to a method for solidifying sand by utilizing halotolerant bacteria. The method selects Sporosarcina pasteurii as bacteria, the strain comes from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC), and the collection number is ATCC 11859. The method comprises the following steps: putting the strain in a nutrient broth medium to obtain a bacterial solution after domestication and enrichment; putting the bacterial solution in desert underground brine containing urea, calcium ions and salinity, and culturing to obtain a bacterial solution with an induced solidification effect; spraying the bacterial solution on the surface of sand soil; putting the sand soil of which the surface is sprayed with the bacterial solution in the natural drying environment for culturing; and naturally air-drying, so that the bacteria can utilize the desert underground brine to cement and solidify sand grains on the surface of the sand soil through the solidification effect so as to prevent the sand soil on the surface layer from migrating under the wind effect. The method is environment-friendly, is low in cost, and can be widely used for solidifying mobile and semi-mobile dunes.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ECOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recycling treatment system and treatment method of high-salinity high-organic-matter chemical wastewater
ActiveCN106495396ARealize resourcesReduce SS contentWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesElectricityUltrafiltration
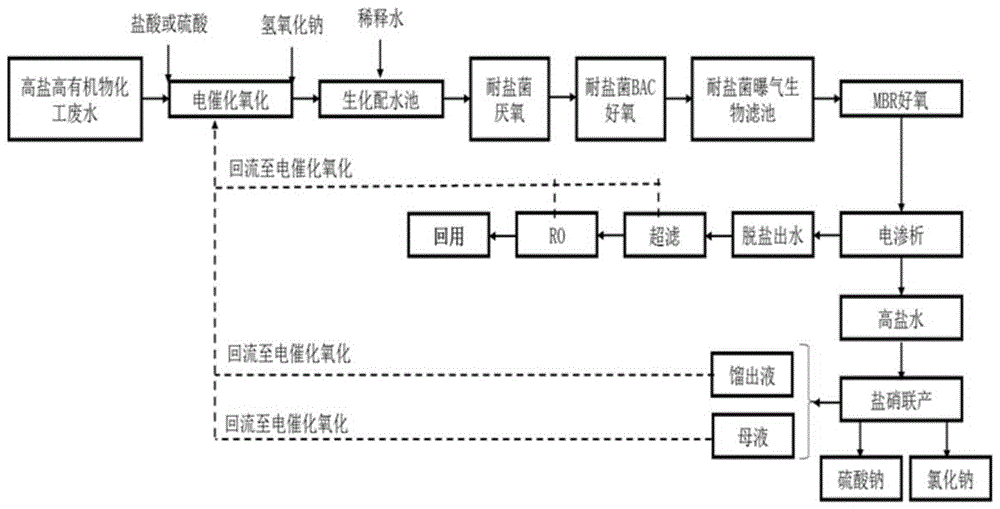
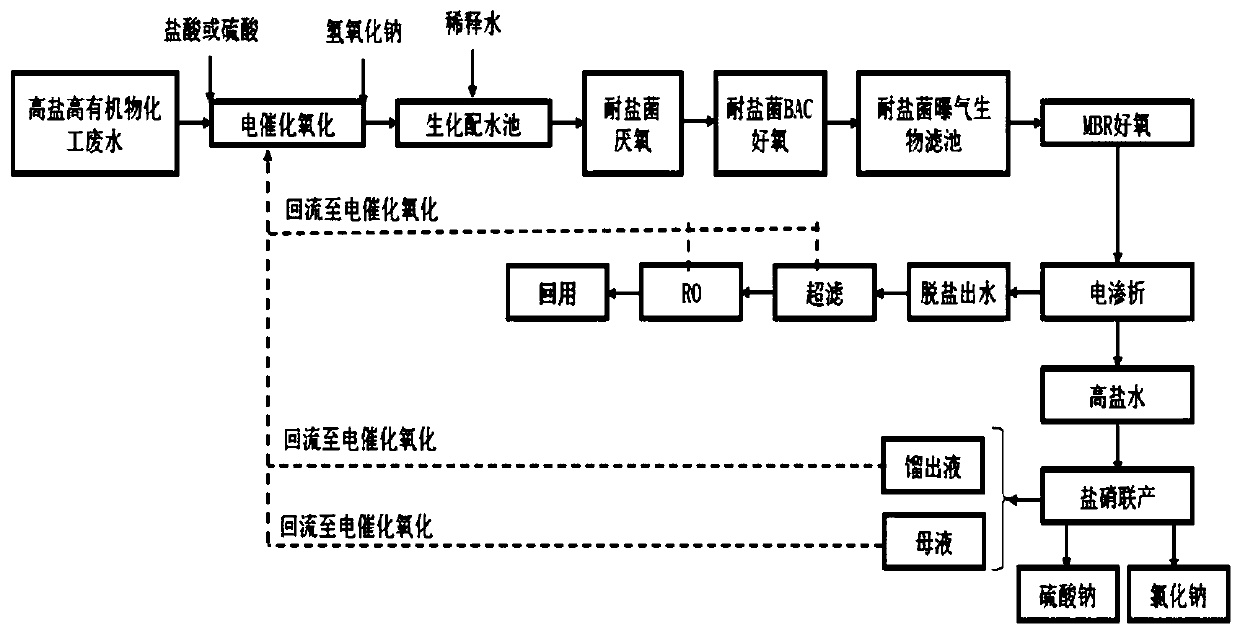
The invention discloses a recycling treatment system of high-salinity high-organic-matter chemical wastewater. The recycling treatment system comprises an electrocatalytic oxidation device, a halotolerant bacteria biochemical system, an MBR aerobic device, an electroosmosis unit, an ultrafilter and an RO unit, the halotolerant bacteria biochemical system comprises a halotolerant bacteria anaerobic device, a halotolerant bacteria aerobic device and a halotolerant biological aerated filter. The invention further discloses a treatment method of the high-salinity high-organic-matter chemical wastewater. By the recycling treatment system and the treatment method, the problem of recycling treatment of the high-salinity high-organic-matter chemical wastewater is solved effectively, recycling rate of water and salt is high, no wastewater is discharged basically, no solid waste is generated, generated water is high in quality, generated salt is high in purity, and water resources and salt in the high-salinity high-organic-matter chemical wastewater are recycled to greatest extent; zero discharging of wastewater in the process of enterprise production is realized, and the recycling treatment system and the treatment method have important environment benefit.
Owner:JIANGSU LASON CHEM ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Biochemical treatment process for high salinity wastewater
ActiveCN104150608AQuantity maximizationEfficient degradationBiological water/sewage treatmentStart timeTotal investment
The invention discloses a biochemical treatment process for high salinity wastewater. In order to solve the problem of treating high salinity wastewater with relatively low operating cost and total investment, the biochemical treatment process for high salinity wastewater comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining halotolerant bacteria and attaching the halotolerant bacteria on filler in a reactor; 2) preparing simulated wastewater; 3) acclimatizing the halotolerant bacteria, wherein the simulated wastewater is mixed with the high salinity wastewater in different proportions to prepare various acclimatizing wastewater, and in the starting process of the reactor, the halotolerant bacteria are acclimatized by virtue of the various acclimatizing wastewater according to a sequence of the content of the simulated wastewater in the acclimatizing wastewater from high to low, so that the starting time of the reactor is shortened; 4) directly treating the high salinity wastewater by virtue of the acclimatized halotolerant bacteria. By virtue of acclimation and culture combined with a biological multiplying technology, the halotolerant bacteria are maximized in quantity, specialized in flora and efficient in degrading capability, so that organic pollutants in water are effectively degraded.
Owner:深圳永清水务有限责任公司
Halotolerant bacteria culture medium nutrient, preparation method, domestication method and application thereof
InactiveCN107603939AMeet processing needsImprove purification effectFungiBacteriaVitamin d 3Vitamin C
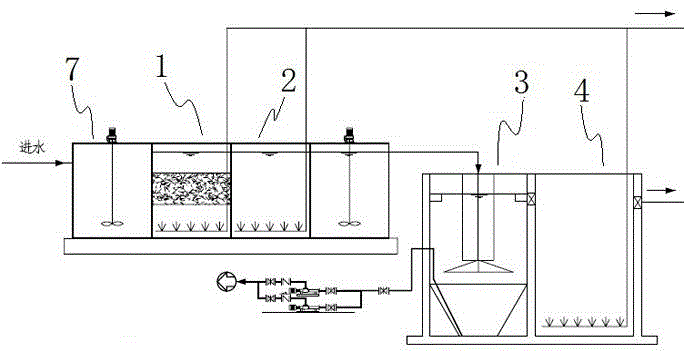
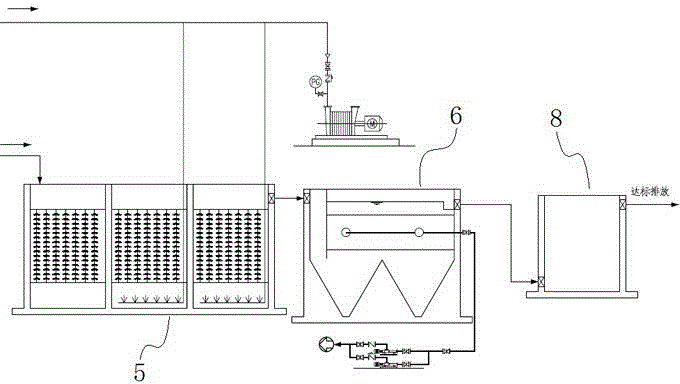
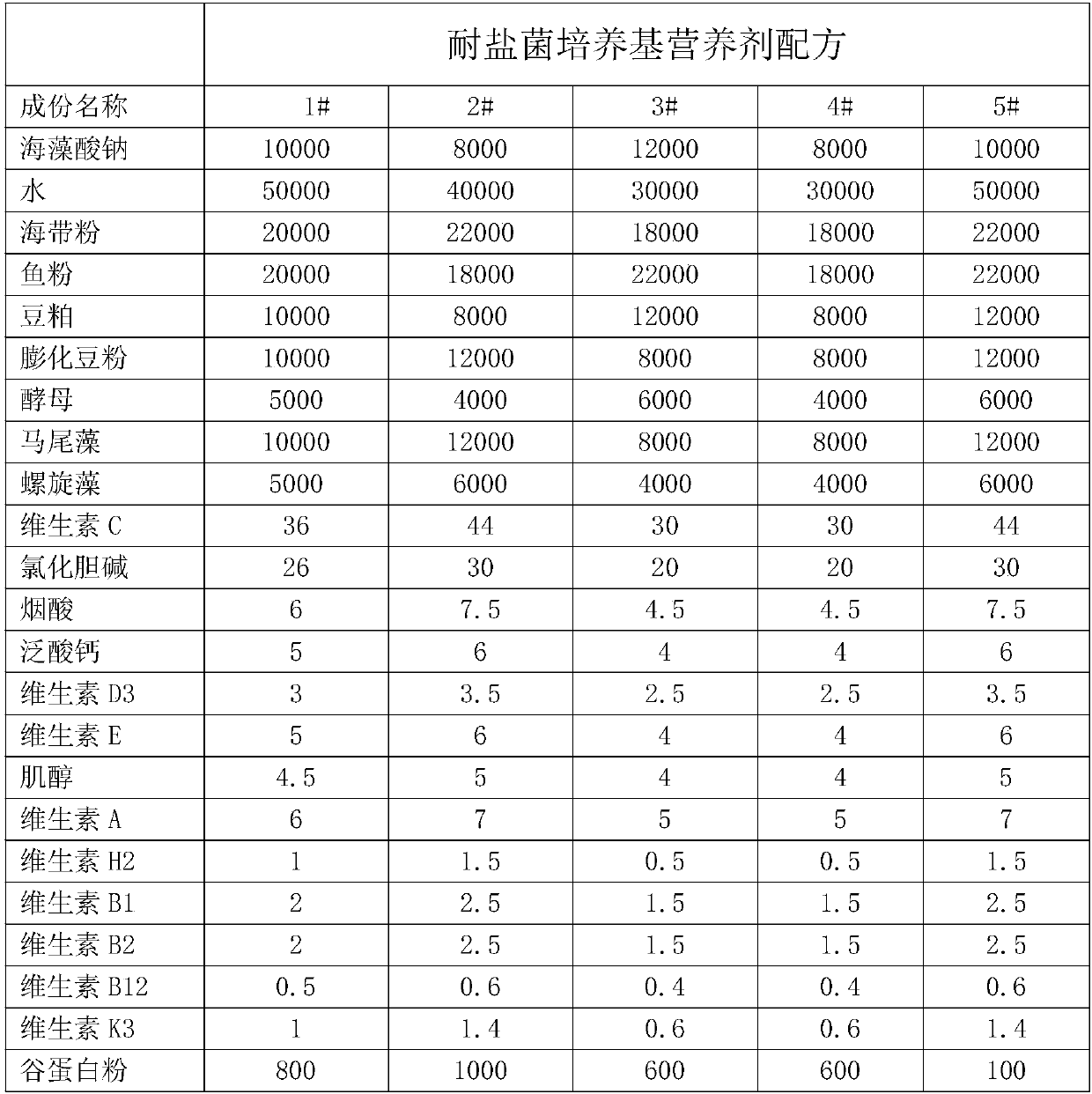
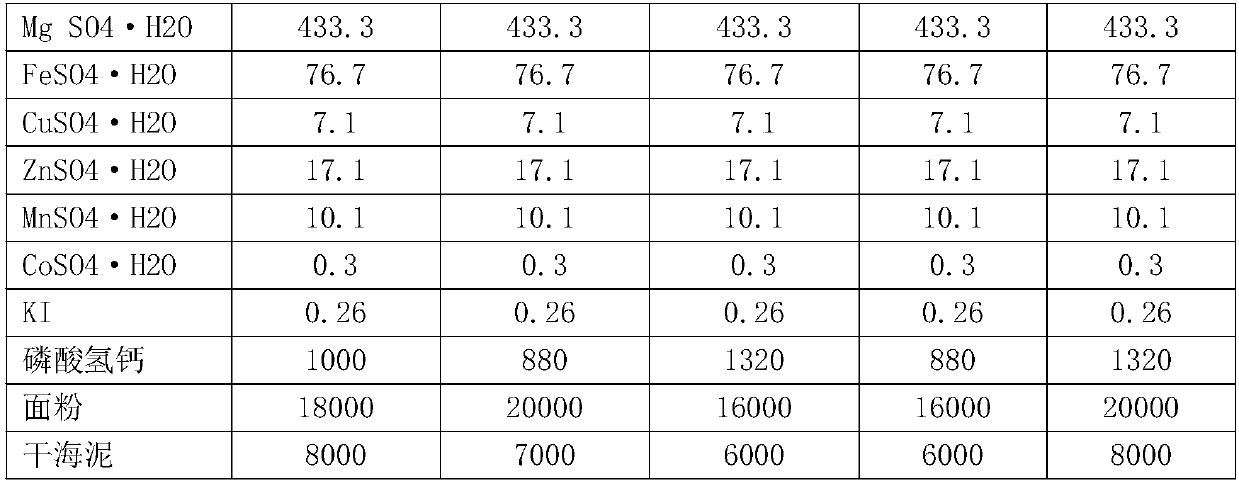
The invention discloses a halotolerant bacteria culture medium nutrient, a preparation method, a domestication method and an application thereof. The halotolerant bacteria culture medium nutrient contains the following components in parts by weight: water, sodium alginate, kelp powder, fish meal, bean pulp, expanded bean flour, yeast, gulfweed, spirulina, vitamin C, choline chloride, nicotinic acid, calcium pantothenate, 3 parts of vitamin D, vitamin E, inositol, vitamin A, vitamin H2, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B12, vitamin K3, bone protein powder, calcium hydrophosphate, flour, dry seamud and mineral substance microelement metal salt compound. The halotolerant bacteria culture medium nutrient can be used for domesticating various halotolerant bacteria, so that the treatment requirement of high salinity wastewater complex environment can be met and a better purifying effect and higher stability can be achieved.
Owner:钟华
Composite microbial agent, preparation method thereof and salty sewage treatment method
InactiveCN103740617AEasy to handleWide range of conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial agentSewage
The invention discloses a composite microbial agent, a preparation method thereof and a salty sewage treatment method. The composite microbial agent comprises halophilic archaea, halophilic bacteria and halotolerant bacteria. The preparation method comprises the following steps of performing liquid culturing on each component under different salinities respectively, and mixing bacterium solutions to obtain the composite microbial agent when each bacterium solution contains a certain amount of bacteria. The composite microbial agent can be added into salty sewage to treat the salty sewage. Different strains in the composite microbial agent are in different growth states under different salty conditions, and advantages in the growth of the strains within high, medium and low major salty ranges are achieved, so that the microbial agent can be used for treating organic sewage with different salinities, and is wide in application range.
Owner:徐州煤炭工业环保设备工程公司
Device and process for processing high-salt non-biodegradable toxic industrial waste water
ActiveCN102173539ALow biological toxicityReduce inhibitionSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningWater/sewage treatmentWater qualityToxic material
Owner:浙江环科环境研究院有限公司
Method for brewing soybean sauce by adding halotolerant bacteria to reduce content of free tyrosine in sauce mash
ActiveCN111423988AAvoid the risk of white spotsReduce contentFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyColony morphology
The invention provides a method for brewing soybean sauce by adding halotolerant bacteria to reduce the content of free tyrosine in sauce mash, and in particular relates to a method for screening andseparating halotolerant bacteria consuming tyrosine. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) detecting the tyrosine content of sauce mash in different high-salt dilute fermentation tanks, selecting sauce mash of which the content of free tyrosine is most obviously reduced than the content of tyrosine in the initial fermentation stage, separating out a strain from the sauce mash, and culturing the strain by using a high-salt culture medium to obtain a halotolerant bacterium original strain; (2) observing the colony form and the thallus microscopic form of the halotolerant bacteria; (3) performing expanding culture on the halotolerant bacteria original strain to obtain a halotolerant bacterium solution; and (4) inoculating the halotolerant bacterium solution into sauce mash containing high free tyrosine for constant-temperature fermentation, and screening out sauce mash with the free tyrosine content less than 100mg / 100g, wherein halotolerant bacteria corresponding to the used bacterium solution are halotolerant bacteria capable of consuming tyrosine. According to the invention, the tyrosine-consuming halotolerant bacteria are separated out for the soybeanpaste brewing process, so that the amount of tyrosine in the later fermentation stage can be reduced, and the risk of white spots generated in the soybean paste can be reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEIWEIXIAN FLAVORING & FOOD
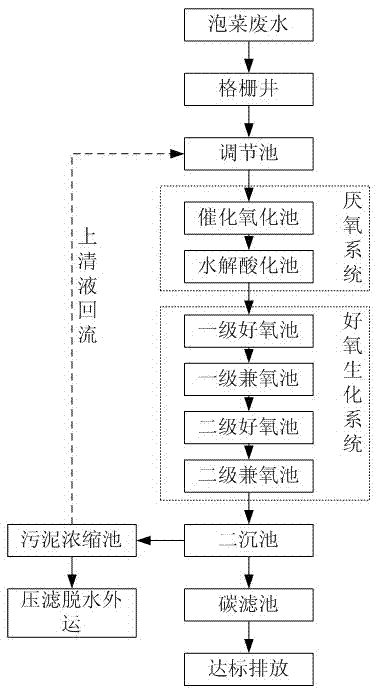
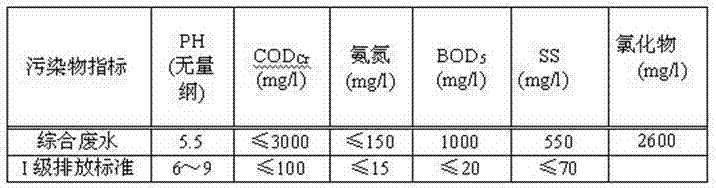
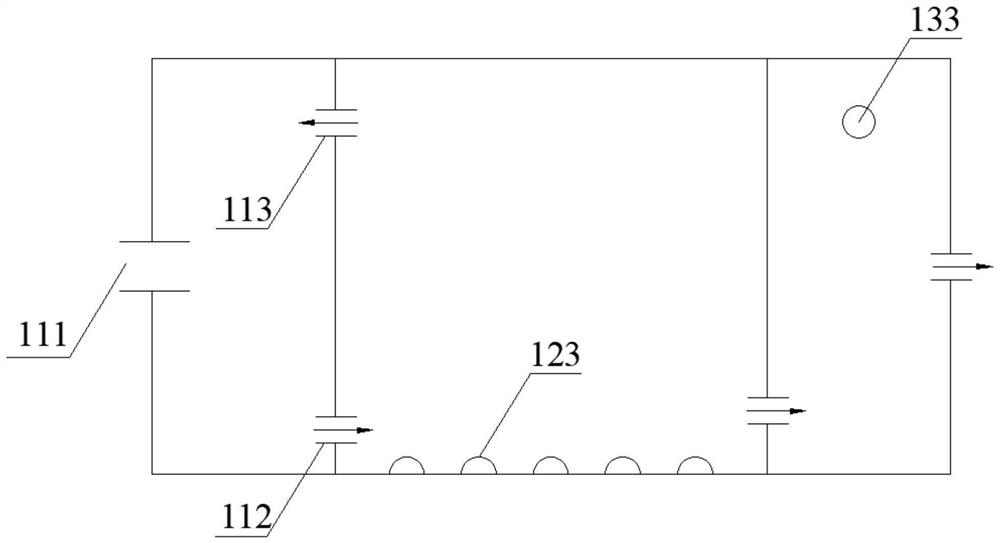
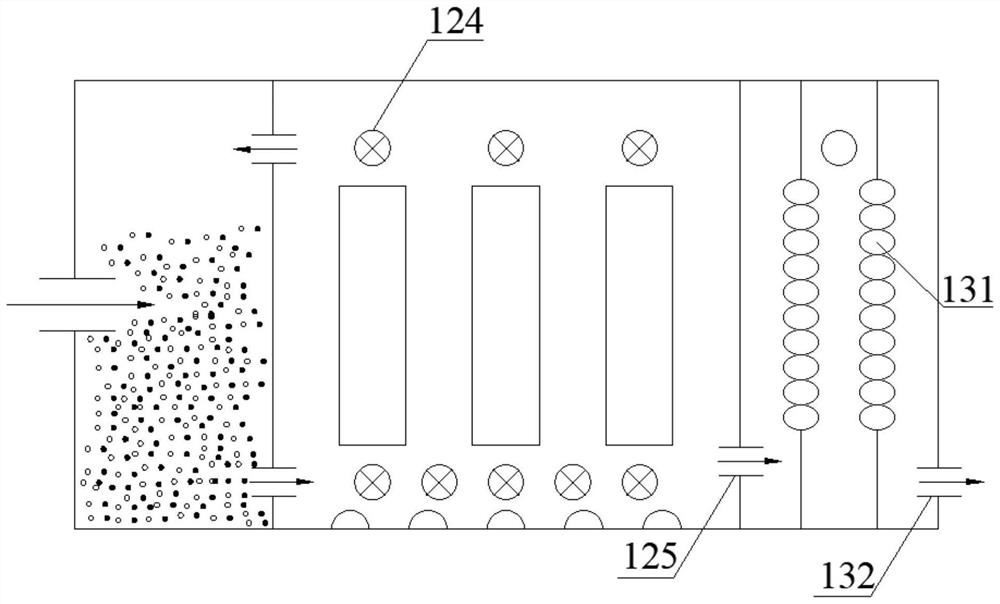
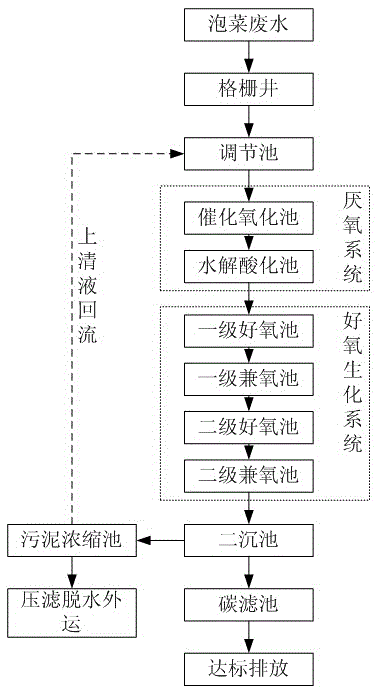
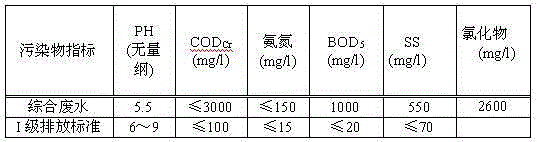
Method for treating pickle wastewater
ActiveCN103613250AEasy to handleCompact layoutMultistage water/sewage treatmentWaste water treatment from food industrySludgeWater quality
The invention discloses a method for treating pickle wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: (1) cultivating and domesticating special halotolerant bacteria; (2) feeding the pickle wastewater into a grid well to primarily eliminate suspended solids; (3) conveying the wastewater inside the grid well into a conditioning pond for physical sedimentation, and stirring so as to ensure that the water quality is balanced; (4) feeding the wastewater into an anaerobic system to be treated so as to degrade and decompose organisms; (5) feeding the wastewater into an aerobiotic biochemical system for secondary aerobic anoxic treatment, further decomposing the residual organisms by using aerobic halotolerant bacteria and anoxic halotolerant bacteria respectively, and balancing the water quality; (6) performing solid-liquid separation in a secondary sedimentation tank to settle down sludge, and performing filtering treatment in a carbon filtering tank so as to ensure that the effluent is clear in quality. The method is compact in arrangement, the land is saved, impurities such as suspended solids and organisms in the pickle wastewater are sequentially eliminated, the effect of final sewage treatment is greatly improved, and a great deal of expense for extra treatment is saved for companies.
Owner:CHENGDU SHUANGDI ENVIRONMENT ENG
Method suitable for rapid enrichment culture of halophilic and halotolerant bacteria
The invention provides a method suitable for the rapid enrichment culture of halophilic and halotolerant bacteria. The method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out 10 times dilution on filtered, decolored and deoiled wastewater by using distilled water; 2, preparing a culturing medium composed of 3-6g of hydrolyzed casein, 5-10g of a beef extract, 5-10g of tryptone, 0.5-1g of KHPO4, 0.5-1g of K2HPO4, 2-5g of KCl, 0.05g of MgSO4.7H2O, 0.05g of CaCl2 and 0.05g of FeSO4.7H2O; 3, dissolving components composing the culturing medium in 1L of the diluted wastewater solution obtained in step 1, adding 10g of NaCl, and adjusting the pH value to 7.0-8.0 by using NaOH; and 4, placing a solution obtained in step 3 on a shaking bed, culturing at 125rpm at a temperature of 30DEG C, adding 11g of NaCl and 100ml of the culturing medium obtained in step 2 every 14h, and culturing for 70h to obtain a halophilic and halotolerant bacterium mixture.
Owner:XINJIANG DELAND
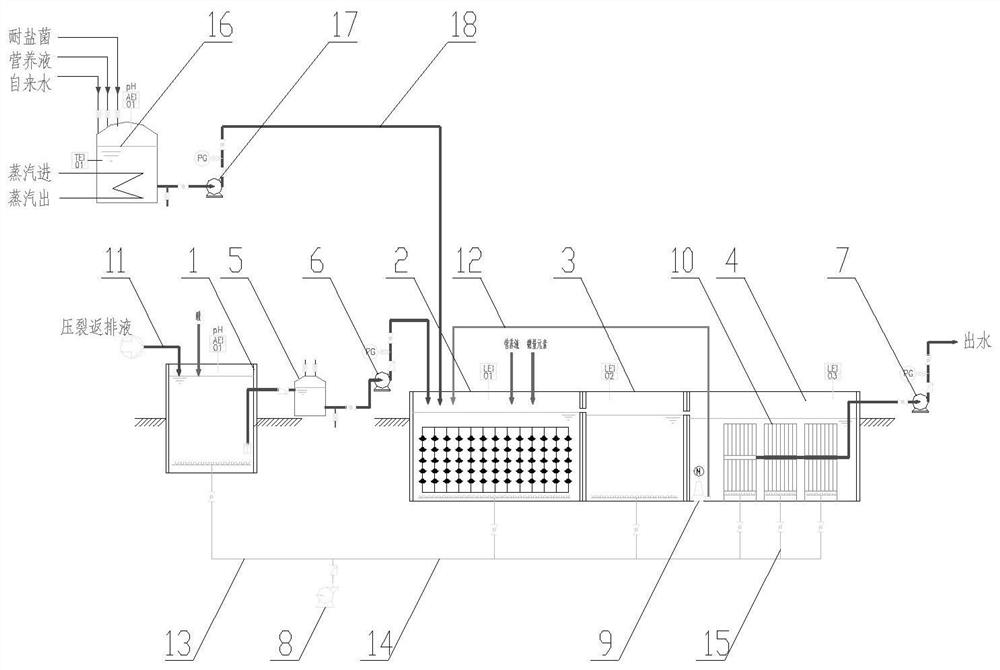
Treatment system and method for degrading organic matters in fracturing flow-back fluid by using halotolerant bacteria
PendingCN111943361ALow running costSmall footprintWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsWater productionIndustrial water
The invention belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment, and particularly relates to a treatment system and method for biochemically degrading organic matters in high-salt fracturing flow-back fluid by using halotolerant bacteria. The treatment system comprises a wastewater regulating tank (1), a contact oxidation tank (2), an aerobic aeration tank (3) and an MBR membrane tank (4) which are sequentially connected by pipelines, wherein a self-priming tank (5) and a delivery pump (6) are sequentially arranged between the wastewater regulating tank (1) and the contact oxidation tank(2); the contact oxidation tank (2), the aerobic aeration tank (3) and the MBR membrane tank (4) are sequentially connected to form an integrated reaction device; and the integrated reaction device conveys treated water reaching the standard to a water collection tank through a self-priming water production pump (7) to serve as industrial water. According to the invention, organic matters in shalegas flowback fluid are effectively removed at low cost through a biochemical method, stable effluent quality is ensured, and the problems that operation cost is high and removal effect is not stablewhen the organic matters are removed through a fracturing flowback fluid pure oxidation method of a high-salt system are solved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
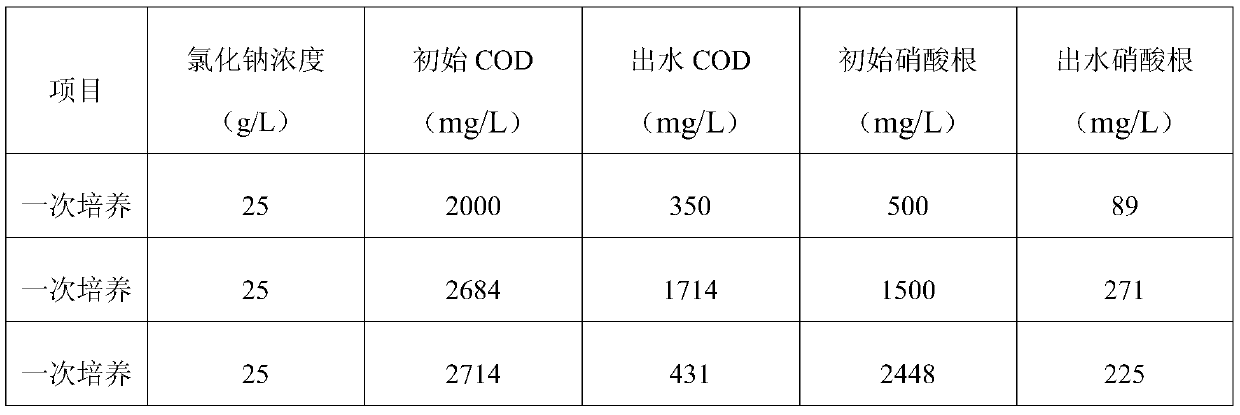
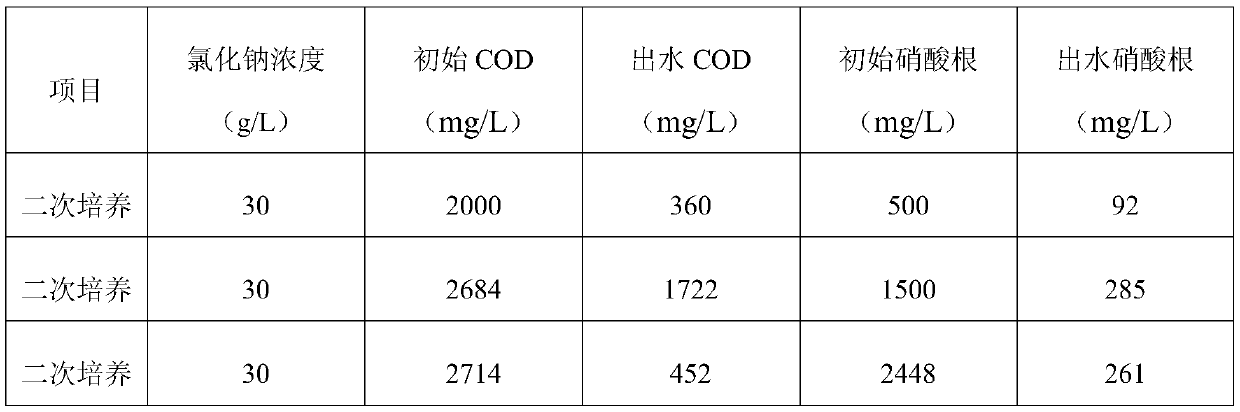
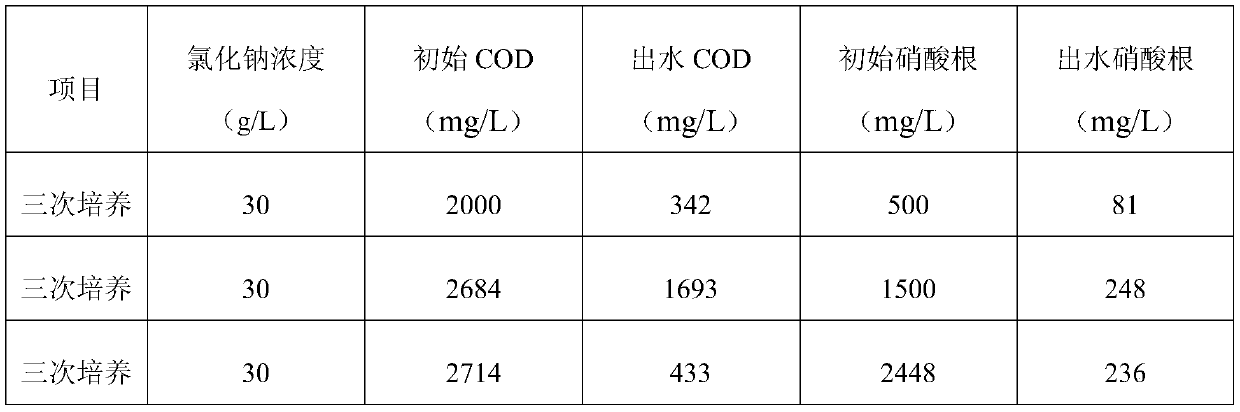
Culture method of halotolerant bacteria capable of removing nitrate in high-salinity solution and application thereof
The invention discloses a culture method of halotolerant bacteria capable of removing nitrate in a high-salinity solution, which comprises the following steps: 1) adding a sodium chloride solution into a stirring tank filled with a waste liquid, stirring and carrying out trace aeration, and controlling the concentration of sodium chloride to be 25-35g / L; and 2) continuously adding nitrified sludgeinto the stirring tank, adding glucose to control the COD content to be 1800-2200mg / L, culturing for 2-4 days, adding potassium nitrate, controlling the NO3<-> concentration to be 400-600mg / L, reacting for 60-84 hours, emptying a water sample, and retaining activated sludge, thereby obtaining the halotolerant bacteria. According to the method, the high-salt-tolerance microorganisms can be cultured, and the nitrate removal effect is good. According to the culture method of the halotolerant bacteria, the high-salt-tolerance microorganisms can be cultured, the culture time is short, the cost islow, the occupied area is small, the living conditions of the microorganisms are wide, temperature and pH changes (except for rapid changes) can be borne, and the effect of removing nitrate in the high-salinity solution is good.
Owner:JIANGSU YONGGUAN WATER & WASTERWATER EQUIP CO LTD +1
Method for enhancing biochemical treatment of high-salt organic wastewater by removing high-salt toxicity on microorganisms
InactiveCN111717982AImprove biological activityHelps Osmotic BalanceWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsDrug biological activityOsmoprotectant
The invention discloses a method for enhancing biochemical treatment of high-salt organic wastewater by removing high-salt toxicity on microorganisms. The method is characterized by being mainly realized by coupling pressurization and addition of compatible solutes. By removing the salt toxicity on microorganisms in the salt-containing wastewater, the activity of non-salt-tolerant flora in an original system is maintained, so that the pollutant degradation performance of the flora in the high-salt wastewater is effectively improved. The technical problem of the invention is solved by simultaneously adding a compatible solute and pressurizing in a reactor for the first time; the compatible solutes are glycine betaine, glycerol, sugar alcohol, amino acid and the like, Tween 80 can also be used as an osmotic protective agent, and the substances can contribute to osmotic balance of bacteria and are also effective to halotolerant bacteria and non-halotolerant bacteria; besides, the reactoris pressurized, the pressurization pressure is controlled to be 0.1-0.5 MPa, and due to the fact that proper pressurization is beneficial to improving the biological activity of microorganisms, bacteria can adapt to a severe environment, and the salt resistance of the bacteria can be improved to a certain extent.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Liquefied gas alkali dreg wastewater treatment method
ActiveCN108341551ASimple processLow running costFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesWater treatment compoundsLiquid wasteElectrolysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment, and discloses a liquefied gas alkali dreg wastewater treatment method. The main technology adopts a microelectrolysis reactor andan efficient bioreactor. The method comprises the following steps that 1, liquefied gas alkali dreg wastewater is pumped into a skimming tank; 2, the microelectrolysis reactor provided with a plate electrode is turned on, under the electrochemical effect, pretreated wastewater is introduced into the microelectrolysis reactor to be treated, and treated wastewater is obtained; 3, electrolysis effluent is diluted until the salinity is about 20,000 mg / L, and then phosphoric acid is used for adjusting the pH of wastewater to 10-11; 4, neutralized alkaline residues are pumped into the bioreactor, and after efficient halotolerant bacteria biochemical treatment, treated wastewater is obtained. According to the efficient and energy-saving alkali dreg wastewater treatment method, the whole process is executed under normal temperature and pressure, the technology is simple, and the integrated equipment is obtained. According to the method, the COD of the liquefied gas alkali dreg wastewater is lowered to 1,000 mg / L.
Owner:大连理工环境工程设计研究院有限公司
Method for rapidly removing organic pollutants in coal gas wastewater
ActiveCN108658243ARapid separation and removalWater contaminantsBiological water/sewage treatmentMicroparticleAdsorption effect
The invention discloses a method for rapidly removing organic pollutants in coal gas wastewater. The method basically comprises the following steps: (1) selecting strains or mixed flora of halophilic / halotolerant bacteria capable of generating compatible solutes to carry out osmosis-resistant culture under a high-salt environment; (2) centrifugally collecting thalli, putting the thalli into the coal gas wastewater, and carrying out standing until floccules in the wastewater are completely settled to finish the removal of the organic pollutants. According to the method, the pollutants are rapidly separated and removed due to an adsorption effect between the compatible solutes extracellularly released by the thalli and molecules of the organic pollutants (mainly comprising a polycyclic aromatic compound, a heterocyclic compound and petroleum hydrocarbon) and by virtue of the rapid flocculation and sedimentation of the thalli serving as particle frameworks, and the method has the advantages of high speed, high efficiency and no pollution.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Resourceful treatment system and treatment method for sodium carboxymethyl cellulose production wastewater
InactiveCN110510827AEasy to handleLow running costWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesCarboxymethyl celluloseCatalytic oxidation
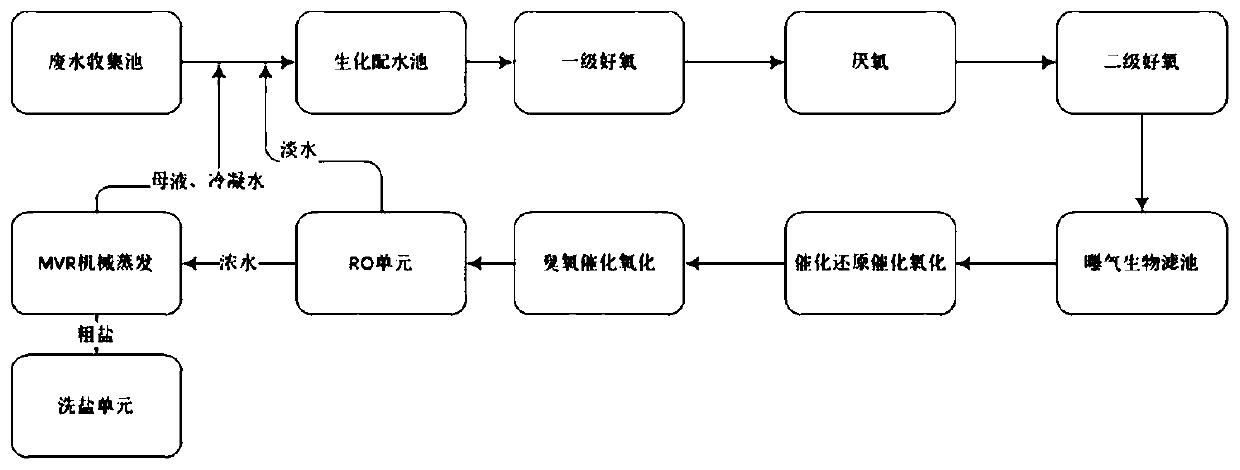
Belonging to the field of water treatment, the invention discloses a resourceful treatment system and treatment method for sodium carboxymethyl cellulose production wastewater. The system sequentiallycomprises a halotolerant bacteria biochemical system, a catalytic reduction catalytic oxidation unit, a catalytic ozonation unit, an RO unit, an MVR mechanical evaporation unit and a crude salt refining unit. The halotolerant bacteria biochemical system comprises a halotolerant bacteria primary aerobic device, a halotolerant bacteria anaerobic device, a halotolerant bacteria secondary aerobic device and a halotolerant bacteria biological aerated filter in order. The system and method provided by the invention combine the halotolerant bacteria biochemical system, catalytic reduction catalyticoxidation, membrane concentration and MVR evaporation technologies, the operation is simple, high efficiency composite halotolerant bacteria are employed for biochemical treatment of wastewater, large-multiple dilution of wastewater is not needed, the treatment water amount and the operation cost are reduced, and reclamation of salt and water is achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU LASON CHEM ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Method for treating epichlorohydrin wastewater
InactiveCN106630174AEfficient removalImprove processing efficiencyBacteriaWater contaminantsBiochemical ProcessMicrobiological culture
The invention relates to a method for treating epichlorohydrin wastewater. The epichlorohydrin wastewater is treated by a biochemical process, in a treatment process, a mode of increasing the concentrations of COD and calcium ions in water step by step is adopted, and meanwhile, halotolerant bacteria are fed, are Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, and have been deposited in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the accession number of CGMCC No. 10940. The specific halotolerant bacteria are fed in the a biochemical treatment process of the epichlorohydrin wastewater, a treatment system can bear environments with high salinity and high calcium, and COD in the wastewater can be removed effectively. The method has the characteristics of simple process, high treatment efficiency, low treatment cost and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Low-density water-retention insect-resistant saline-alkali soil conditioner and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114456814AActivate the microbiotaRestore vitalityAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesAlkali soilNitrification inhibitors
The invention discloses a low-density water-retention insect-resistant saline-alkali soil conditioner and a preparation method thereof. The density of a low-density organic bacterial fertilizer is 0.7-1.0 g / cm < 3 >; the organic fertilizer is prepared from 0.5%-1% of medium and trace nutrient elements, 2%-5% of fly ash, 1%-1.8% of ammonium sulfate, 0.1%-0.15% of ferrous sulfate, 0.1%-0.25% of diaminoferric xanthohumate, 1%-1.5% of immobilized beauveria bassiana culture, 1%-1.5% of immobilized metarhizium anisopliae culture, 0.2%-0.5% of a chelating agent, 0.05%-0.1% of a nitrification inhibitor, 0.15%-0.35% of aluminum sulfate and the balance fermented organic matter. The preparation method comprises the steps of mushroom residue treatment, high-temperature fermentation, halotolerant bacteria fermentation, material mixing and the like. The low-density water-retaining insect-resistant saline-alkali soil conditioner has multiple effects of retaining water, inhibiting plant diseases and insect pests, improving the granular structure of saline-alkali soil and the like.
Owner:聊城金余肥业有限公司
Biochemical treatment method of epoxy chloropropane waste water
ActiveCN106630173AEfficient removalImprove processing efficiencyNature of treatment waterBiological water/sewage treatmentEpoxyCalcium EDTA
The invention relates to a biochemical treatment method of epoxy chloropropane waste water. According to the biochemical treatment method of epoxy chloropropane waste water, COD and calcium ion concentration of injected water are increased gradually, a halotolerant bacteria is added, wherein the halotolerant bacteria is microbacterium kitamiense FSTB-4, is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on 1th, June, 2015, and preservation number is CGMCC No.10939. The specific halotolerant bacteria is added in biochemical treatment process of epoxy chloropropane waste water, the treatment system is capable of tolerating high salinity and high calcium environment, high efficiency removing of COD in waste water is realized, technology is simple, treatment efficiency is high, and treatment cost is low.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A resource treatment system and treatment method for high-salt and high-organic chemical wastewater
ActiveCN106495396BEasy to operateReduce dosageWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesElectricityUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a recycling treatment system of high-salinity high-organic-matter chemical wastewater. The recycling treatment system comprises an electrocatalytic oxidation device, a halotolerant bacteria biochemical system, an MBR aerobic device, an electroosmosis unit, an ultrafilter and an RO unit, the halotolerant bacteria biochemical system comprises a halotolerant bacteria anaerobic device, a halotolerant bacteria aerobic device and a halotolerant biological aerated filter. The invention further discloses a treatment method of the high-salinity high-organic-matter chemical wastewater. By the recycling treatment system and the treatment method, the problem of recycling treatment of the high-salinity high-organic-matter chemical wastewater is solved effectively, recycling rate of water and salt is high, no wastewater is discharged basically, no solid waste is generated, generated water is high in quality, generated salt is high in purity, and water resources and salt in the high-salinity high-organic-matter chemical wastewater are recycled to greatest extent; zero discharging of wastewater in the process of enterprise production is realized, and the recycling treatment system and the treatment method have important environment benefit.
Owner:JIANGSU LASON CHEM ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
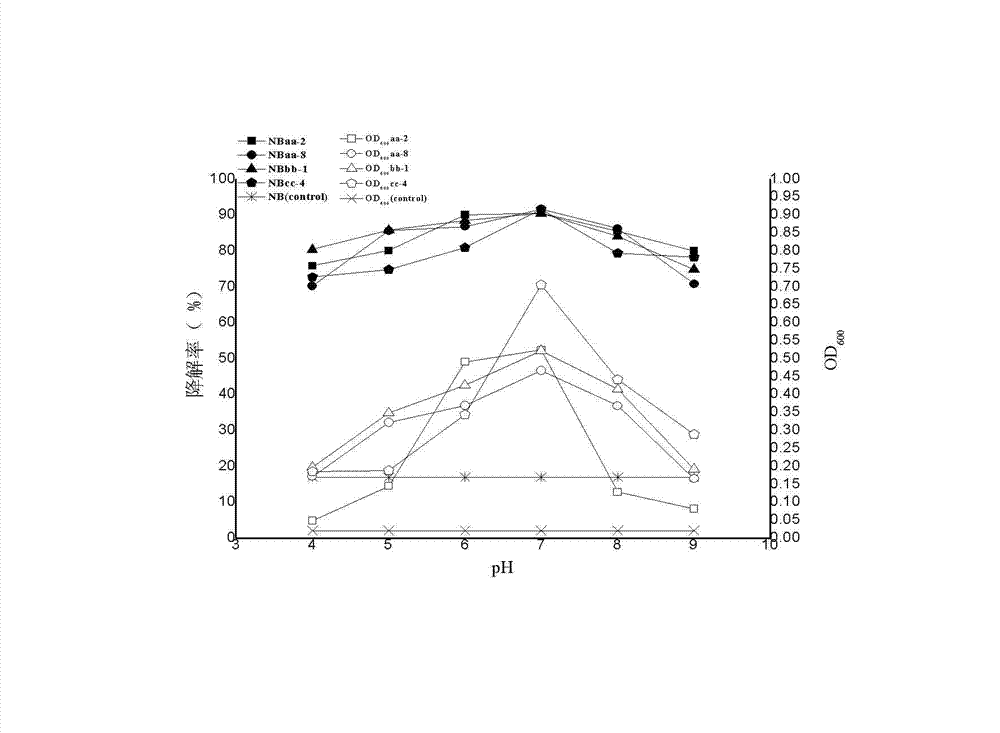
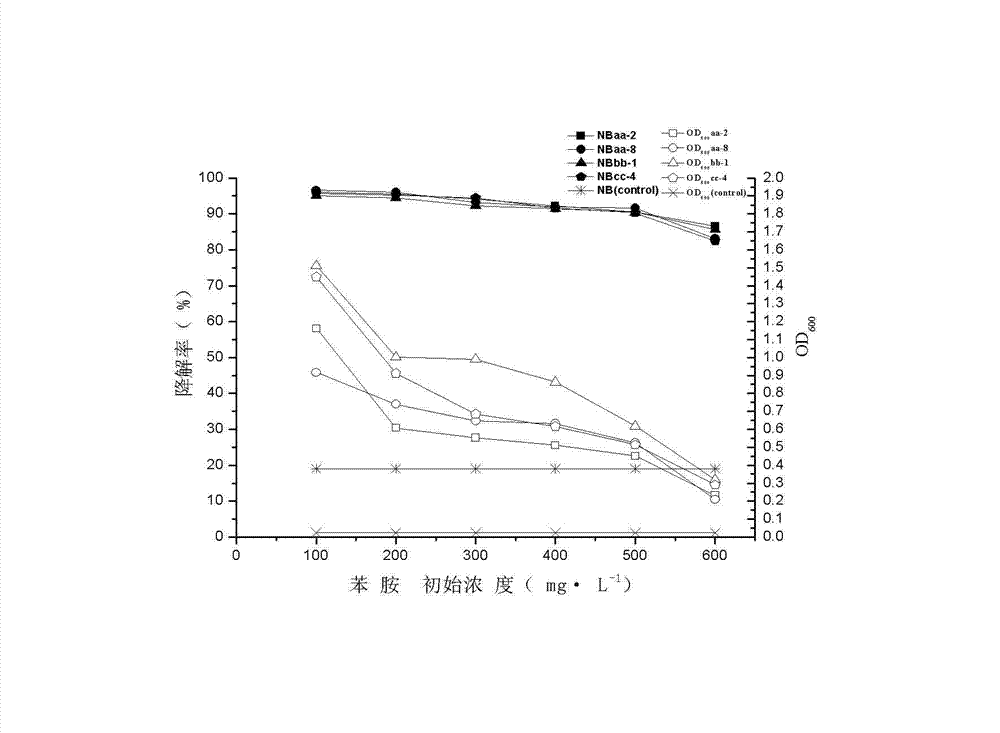
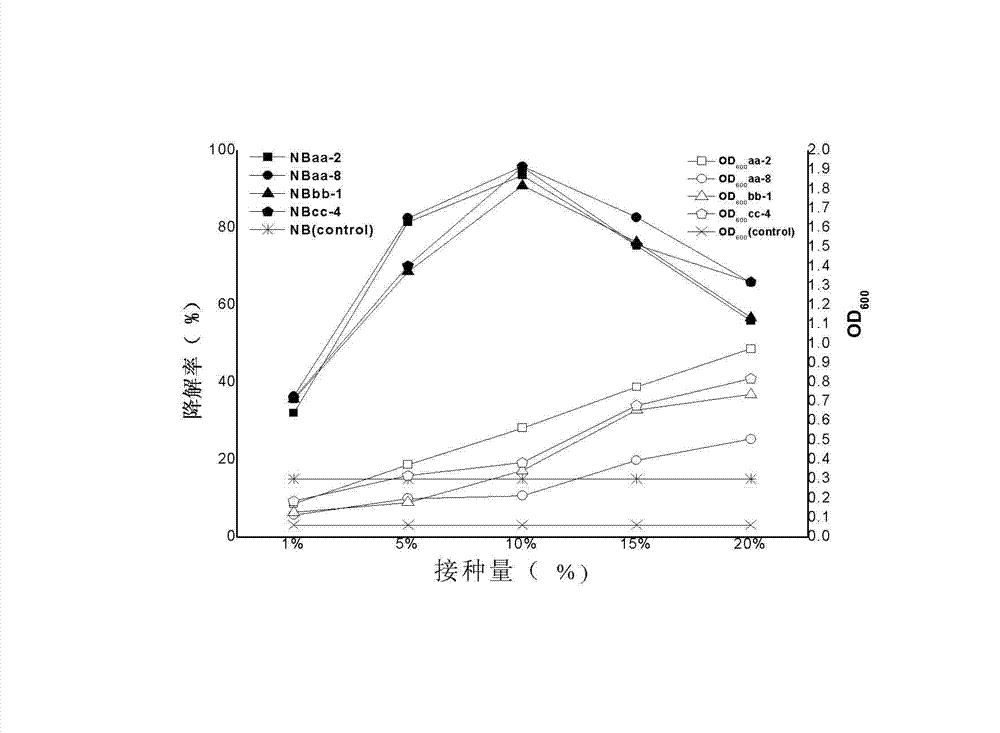
Method for degrading phenylamine in waste water
InactiveCN102730842AIncrease costCutting costsWater contaminantsBiological water/sewage treatmentEnvironmental engineeringBacterial strain
The invention relates to a method for degrading phenylamine in waste water. The method adopts the technical scheme as follows: inoculating phenylamine halotolerant bacteria in logarithm growing period into the waste water containing the phenylamine; adjusting pH value the mixing to be 4-9 to be cultivated for 48 hours under an oscillation condition. With the adoption of the method, the phenylamine can be effectively degraded under a condition of high-salt, the defects that the high-salt can restrain growth and metabolism of bacterial strains, and the degrading capacity is short can be made up, the degrading capacity of the bacterial strains on the phenylamine under the condition of the high-salt is improved, and the technology support can be provided for the phenylamine treatment under the condition of high-salt.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Microbial filler attached with halotolerant bacteria as well as preparation method and application of microbial filler
PendingCN114162976AHigh activityFlora replacementImmobilised enzymesWater treatment parameter controlBiotechnologyBiofilm
The invention relates to the technical field of wastewater treatment, and discloses a microbial filler attached with halotolerant bacteria and a preparation method and application thereof.The preparation method comprises the domestication step, in the domestication step, a biofilm-formed microbial filler is used as a domestication object, the concentration of original halotolerant bacteria on the microbial filler is larger than 0%, and the concentration of the original halotolerant bacteria on the microbial filler is larger than 0%; the method comprises the following steps: carrying out domestication by adopting salt-containing water with increased salt concentration gradient, and adding efficient halotolerant bacteria in the domestication process until in the salt-containing water with 3.0 wt% of salt concentration, the COD removal rate of the microbial filler to the water body reaches 75% or above and the MLSS on the microbial filler is greater than or equal to 5000mg / L, so as to obtain a target product; wherein the salt concentration range of the salt-containing water is 0-3.0 wt%. The halotolerant bacteria with high activity in a high-salt environment can be screened within 65 days, so that the target product can be applied to treatment of high-salt organic wastewater, and the halotolerant bacteria are high in impact resistance and stable and reliable in operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI WINNER ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
High-salt-tolerant bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN114686391AStrong salt toleranceImprove stabilityBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a strain of highly halotolerant bacteria (Halomonas nigrifans) GXNYJ-DL-1, which has been preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on July 13, 2020, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.20350. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the highly halotolerant bacteria (Halomonas nigrifans) GXNYJ-DL-1). The form of the high-halotolerant bacterium GXNYJ-DL-1 is as follows: a bacterial colony is light yellow and round, the surface is wet and opaque, and the edge is neat; the micromorphology under a microscope is as follows: thalli are rod-shaped, 0.5-0.7 [mu] m * 1.2-3.6 [mu] m, are arranged in a single or paired manner, and are gram negative. The high-salt-tolerant bacterium GXNYJ-DL-1 disclosed by the invention is excellent in salt tolerance, particularly can tolerate high sulfate, and is more suitable for removing COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) of high-salt wastewater, particularly high-sulfate wastewater compared with a high-salt-tolerant strain in the prior art.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Active sludge-membrane capacitive comprehensive treatment device and process for treating high-salt wastewater from halotolerant bacteria
InactiveCN107522353AImprove processing efficiencyLow costWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeCapacitance
The invention discloses an active sludge-membrane capacitive comprehensive treatment device and process for treating high-salt wastewater from halotolerant bacteria. The treatment process comprises the following steps: screening and cultivating of microorganisms, an active sludge treatment method and a membrane capacitive deionization method. According to the treatment process disclosed by the invention, the active sludge treatment method is combined with the membrane capacitive treatment method, and high salinity in wastewater has inhibiting and poisoning influences on microorganisms and a membrane capacitive assembly, so that treatment efficiency of the active sludge method is greatly affected; and a strain with relatively high tolerance to high salinity is screened out and is added into an active sludge treatment system, so that treatment efficiency is improved. Wastewater pretreated by the active sludge treatment method enters a membrane capacitive deionization system for being subjected to further desalination treatment. Halotolerant bacteria are added to improve treatment efficiency of the active sludge treatment method, and are combined with a membrane capacitive deionization system, so that desalination efficiency is further improved, and energy consumption and the cost are reduced.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
A method of sand-fixing by using halo-tolerant bacteria
The invention relates to a method for solidifying sand by utilizing halotolerant bacteria. The method selects Sporosarcina pasteurii as bacteria, the strain comes from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC), and the collection number is ATCC 11859. The method comprises the following steps: putting the strain in a nutrient broth medium to obtain a bacterial solution after domestication and enrichment; putting the bacterial solution in desert underground brine containing urea, calcium ions and salinity, and culturing to obtain a bacterial solution with an induced solidification effect; spraying the bacterial solution on the surface of sand soil; putting the sand soil of which the surface is sprayed with the bacterial solution in the natural drying environment for culturing; and naturally air-drying, so that the bacteria can utilize the desert underground brine to cement and solidify sand grains on the surface of the sand soil through the solidification effect so as to prevent the sand soil on the surface layer from migrating under the wind effect. The method is environment-friendly, is low in cost, and can be widely used for solidifying mobile and semi-mobile dunes.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ECOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
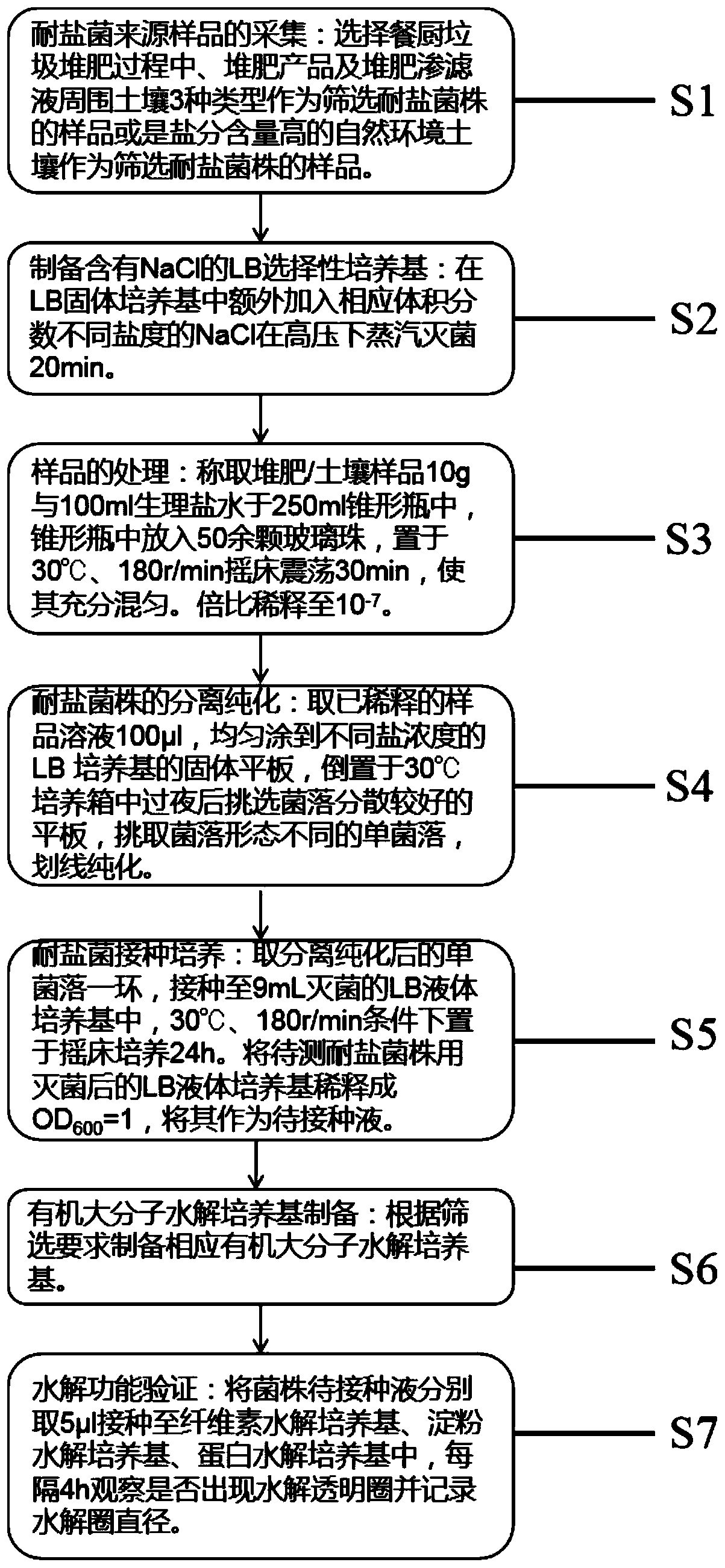
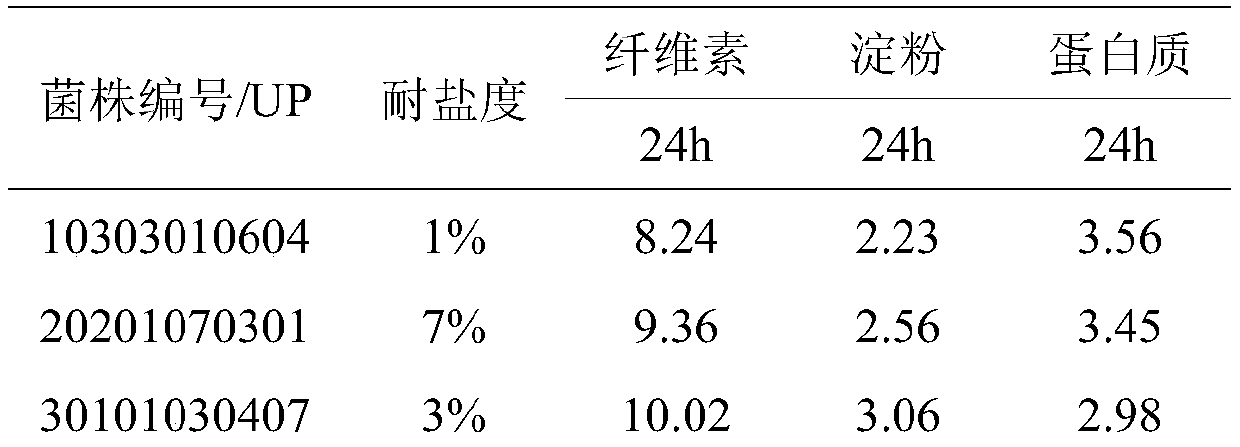
Screening method of salt-tolerant strain capable of rapidly degrading organic macromolecules
PendingCN111575191AEliminate errorsImprove screening efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism separationBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention discloses a screening method of a salt-tolerant strain capable of rapidly degrading organic macromolecules. The screening method comprises the following steps of collecting a salt-tolerant bacterium source sample; preparing an LB selective culture medium containing NaCl; treating the sample; separating and purifying a salt-tolerant strain; inoculating and culturing halotolerant bacteria; preparing an organic macromolecular hydrolysis culture medium; and carrying out hydrolysis function verification. According to the screening method, errors caused by plate hydrolysis results dueto different strain inoculum sizes are eliminated, all strains to be tested are adjusted to the same absorbance for experiments, the capacity of the strains to generate hydrolase under the same culture condition of different halotolerant bacteria is evaluated through a 'time-UP value' data relation, the screening efficiency is improved, the salt-tolerant strains capable of rapidly degrading organic macromolecules can be conveniently, rapidly and accurately screened, so that salt-tolerant strain resources are provided for subsequent research and development of kitchen waste composting inoculants.
Owner:ZHONGNONGXINKE SUZHOU ORGANIC RECYCLING RES INST CO LTD
Preparation method of salt-tolerant biological agent and adding method thereof
InactiveCN110564617ARemain biodegradableEasy to handleMicroorganismsOn/in organic carrierTherapeutic effectSewage
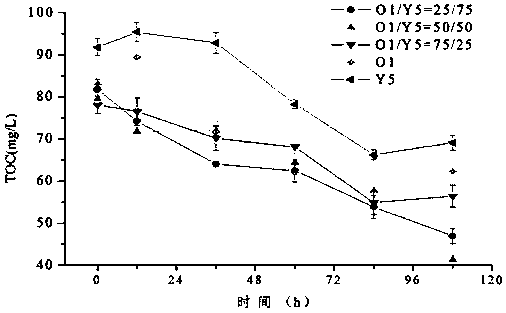
The invention relates to the field of sewage treatment, in particular to a preparation method of a salt-tolerant biological agent and an adding method thereof. The salt-tolerant biological agent comprises a salt-tolerant efficient inoculant and a salt-tolerant efficient bacteria filler, the salt-tolerant efficient inoculant is prepared by mixing and compounding halotolerant bacteria O1 and halotolerant bacteria Y5, according to the salt-tolerant efficient bacteria filler, the salt-tolerant efficient inoculant is immobilized, and loaded on a polyurethane filler. The influence of the composite efficient halotolerant bacteria in different proportions on the removal effect of organic pollutants in sewage is recorded through experiments, so that the optimal configuration proportion of the O1 efficient halotolerant bacteria and the Y5 efficient halotolerant bacteria is explored, and the treatment effect is greatly improved no matter whether the salt-tolerant efficient composite inoculant orthe salt-tolerant efficient composite microbial filler is added; and the salt-tolerant high-efficiency composite bacteria filler has an obvious effect of maintaining TOC degradation efficiency.
Owner:芜湖青弋环保科技有限责任公司
Acclimation and culture device for halotolerant bacteria in salt-containing wastewater and using method of acclimation and culture device
PendingCN114031182ATake advantage ofSimple structureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEnvironmental engineeringHalotolerant bacteria
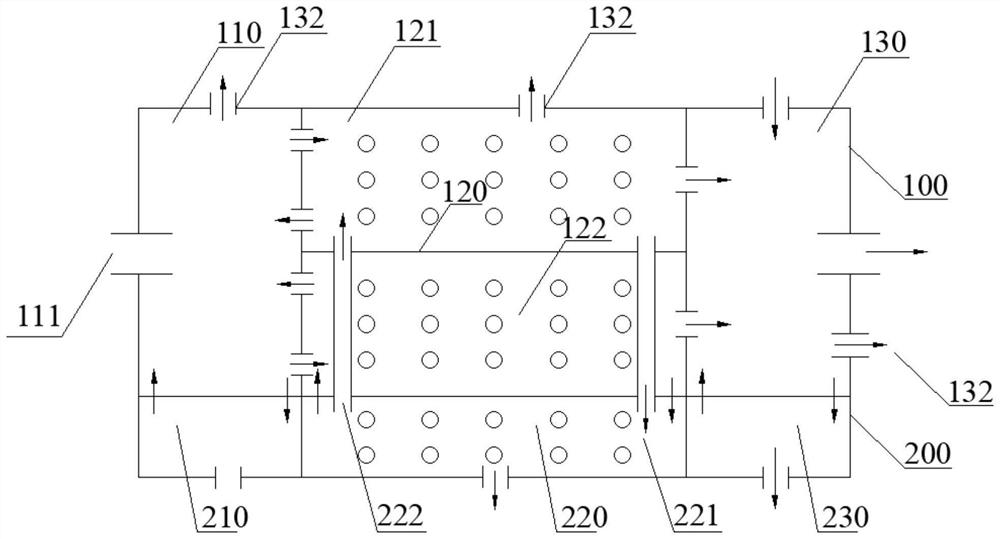
The invention discloses an acclimation and culture device for halotolerant bacteria in salt-containing wastewater and a using method of the acclimation and culture device. The device comprises an acclimation zone and a culture zone which are connected through a pipeline, wherein the acclimation zone comprises an anaerobic / anoxic zone, an aerobic zone and an anoxic zone which are communicated in sequence; the culture zone comprises an anaerobic culture zone, an aerobic culture zone and an anoxic culture zone which are not communicated with one another; the aerobic zone is internally provided with a first treatment zone and a second treatment zone which are connected in parallel; the initial end of the anaerobic / anoxic zone is connected with a water inlet pipe, and the anaerobic / anoxic zone, the aerobic zone and the anoxic zone are connected with drain pipes; a first slow-release filler is arranged in each of the first treatment zone and the second treatment zone; and a second slow-release filler is arranged in the anoxic zone. The device is not provided with a sedimentation tank, a sludge backflow device or a stirring device, and is simple in structure, low in equipment cost and operation electric charge, not prone to being damaged and easy to operate.
Owner:深圳永清水务有限责任公司
A method for quickly removing organic pollutants from coal gasification wastewater
ActiveCN108658243BRapid separation and removalWater contaminantsBiological water/sewage treatmentCoal gasification wastewaterEnvironmental engineering
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of processing method of kimchi wastewater
ActiveCN103613250BEasy to handleCompact layoutMultistage water/sewage treatmentWaste water treatment from food industrySludgeSewage treatment
The invention discloses a method for treating pickle wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: (1) cultivating and domesticating special halotolerant bacteria; (2) feeding the pickle wastewater into a grid well to primarily eliminate suspended solids; (3) conveying the wastewater inside the grid well into a conditioning pond for physical sedimentation, and stirring so as to ensure that the water quality is balanced; (4) feeding the wastewater into an anaerobic system to be treated so as to degrade and decompose organisms; (5) feeding the wastewater into an aerobiotic biochemical system for secondary aerobic anoxic treatment, further decomposing the residual organisms by using aerobic halotolerant bacteria and anoxic halotolerant bacteria respectively, and balancing the water quality; (6) performing solid-liquid separation in a secondary sedimentation tank to settle down sludge, and performing filtering treatment in a carbon filtering tank so as to ensure that the effluent is clear in quality. The method is compact in arrangement, the land is saved, impurities such as suspended solids and organisms in the pickle wastewater are sequentially eliminated, the effect of final sewage treatment is greatly improved, and a great deal of expense for extra treatment is saved for companies.
Owner:CHENGDU SHUANGDI ENVIRONMENT ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com