Culture method of halotolerant bacteria capable of removing nitrate in high-salinity solution and application thereof
A cultivation method and technology for salt-tolerant bacteria, applied in chemical instruments and methods, bacteria, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of harsh survival conditions, inactivation of bacterial species, high salinity, etc., and achieve abundant living conditions and cultivation time. Short, small footprint effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] A method for cultivating salt-tolerant bacteria capable of removing nitrate in high-salt solutions, comprising the following steps:
[0027] 1) Add sodium chloride solution in the stirring tank with waste liquid, stir and carry out micro-aeration, control the concentration of sodium chloride at 25g / L;
[0028] 2) Continue to add nitrification sludge to the mixing tank, then add glucose to control the COD content to 1800mg / L, cultivate for 2 days, add potassium nitrate to control NO 3- The concentration is 400mg / L. After 60 hours of reaction, the water sample is emptied and the living sludge is left to obtain the salt-tolerant bacteria.
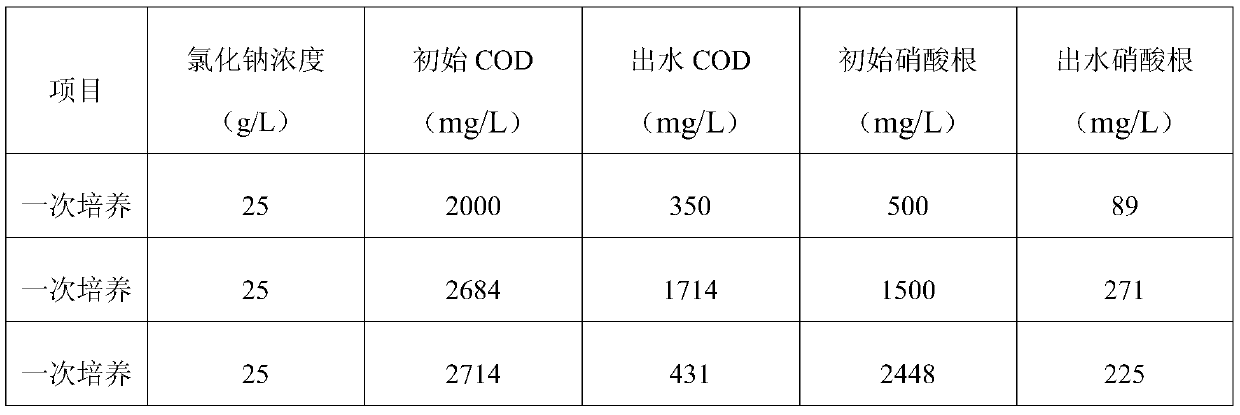
[0029] The salt-tolerant bacteria obtained in this example were cultured once, and were used in waste liquids of different concentrations (drinking water was treated with magnetic resin to absorb nitrate). The specific results are shown in Table 1 below.
[0030] The performance of the salt-tolerant bacteria once cultivated in table 1 ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] A method for cultivating salt-tolerant bacteria capable of removing nitrate in high-salt solutions, comprising the following steps:
[0035] 1) Add sodium chloride solution into the stirring tank with waste liquid, stir and carry out micro-aeration, and control the concentration of sodium chloride at 30g / L;
[0036] 2) Continue to add nitrification sludge to the mixing tank, then add glucose to control the COD content to 2000mg / L, cultivate for 3 days, add potassium nitrate to control NO 3- The concentration is 500mg / L, after 70 hours of reaction, the water sample is emptied, and the viable sludge is retained to obtain salt-tolerant bacteria once;
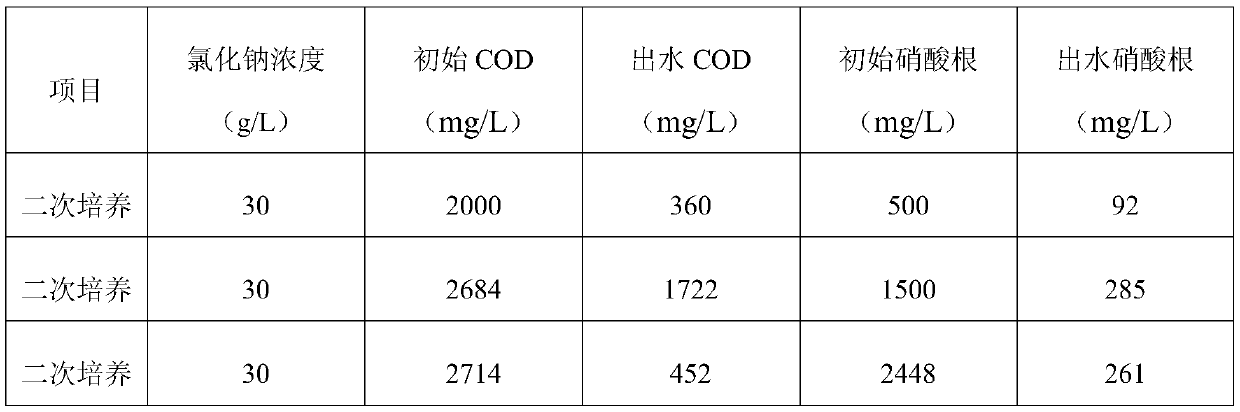
[0037] 3) In order to verify whether the performance of the salt-tolerant bacteria is stable, continue to add 30g / L NaCl solution to the activated sludge retained in step 2), and control the COD content to be 2500mg / L, NO 3- The concentration is 1400mg / L, and the reaction is 20 hours, the COD content is 1700mg / L, NO 3- The...
Embodiment 3
[0043] A method for cultivating salt-tolerant bacteria capable of removing nitrate in high-salt solutions, comprising the following steps:
[0044] 1) Add sodium chloride solution into the stirring tank with waste liquid, stir and carry out micro-aeration, and control the concentration of sodium chloride at 30g / L;
[0045] 2) Continue to add nitrification sludge to the mixing tank, then add glucose to control the COD content to 2000mg / L, cultivate for 3 days, add potassium nitrate to control NO 3- The concentration is 500mg / L, after 72 hours of reaction, the water sample is emptied, and the viable sludge is retained to obtain salt-tolerant bacteria once;
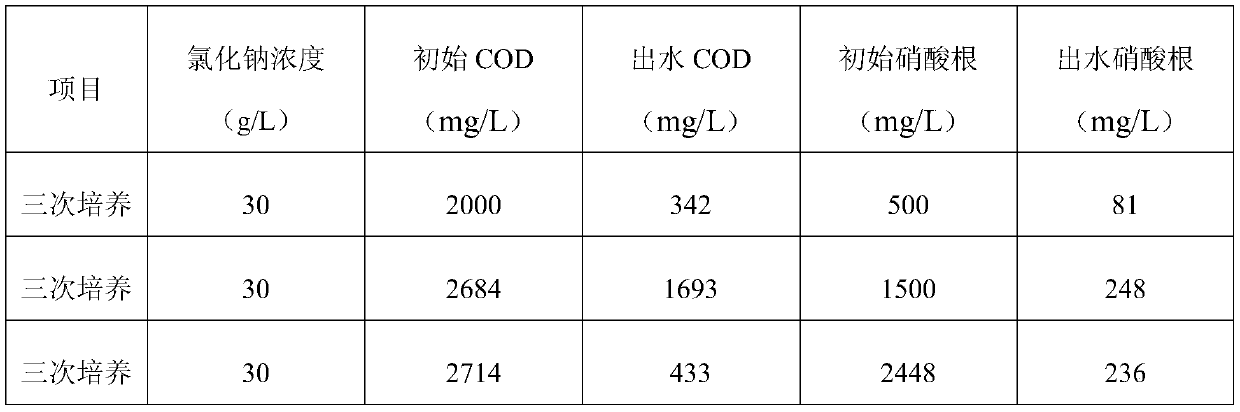
[0046] 3) In order to verify whether the performance of the salt-tolerant bacteria is stable, add 30g / L NaCl solution to the activated sludge retained in step 2), control the COD content to be 2600mg / L, and the NO 3- The concentration is 1500mg / L, and the reaction is 25 hours, the COD content is 1700mg / L, NO 3- The content...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com