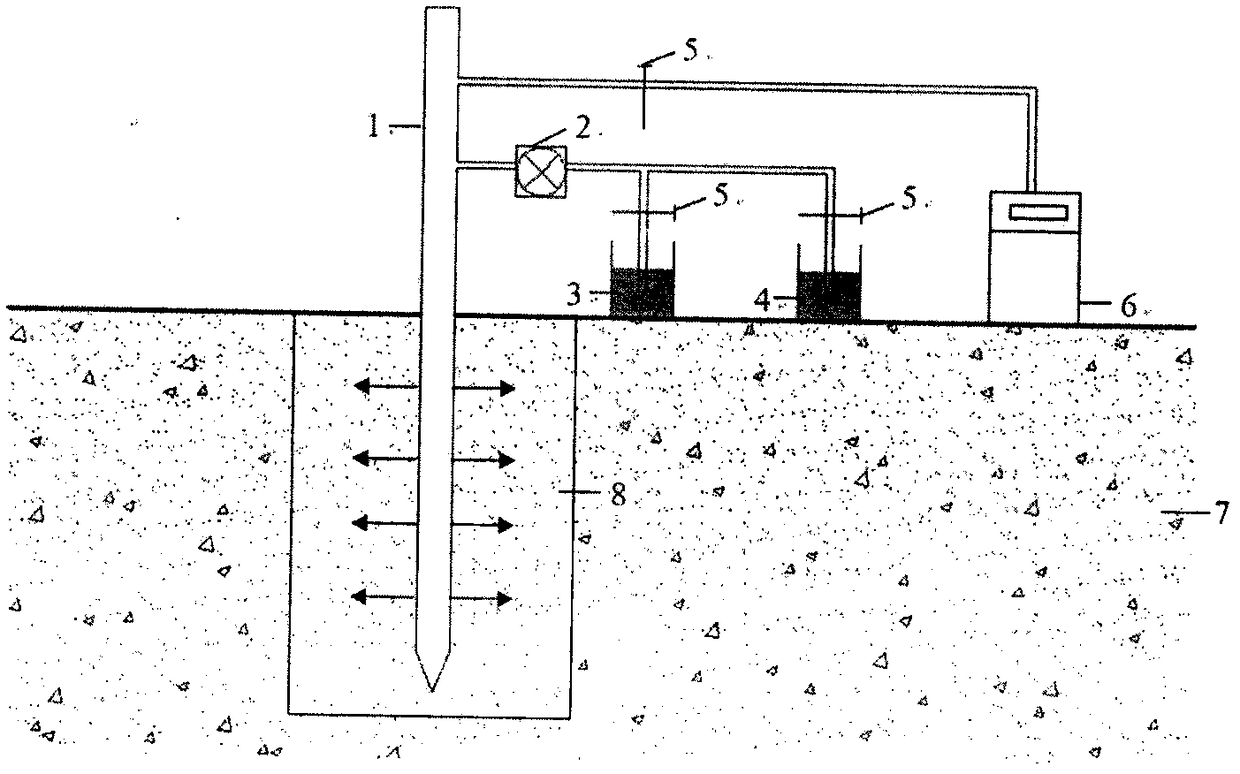
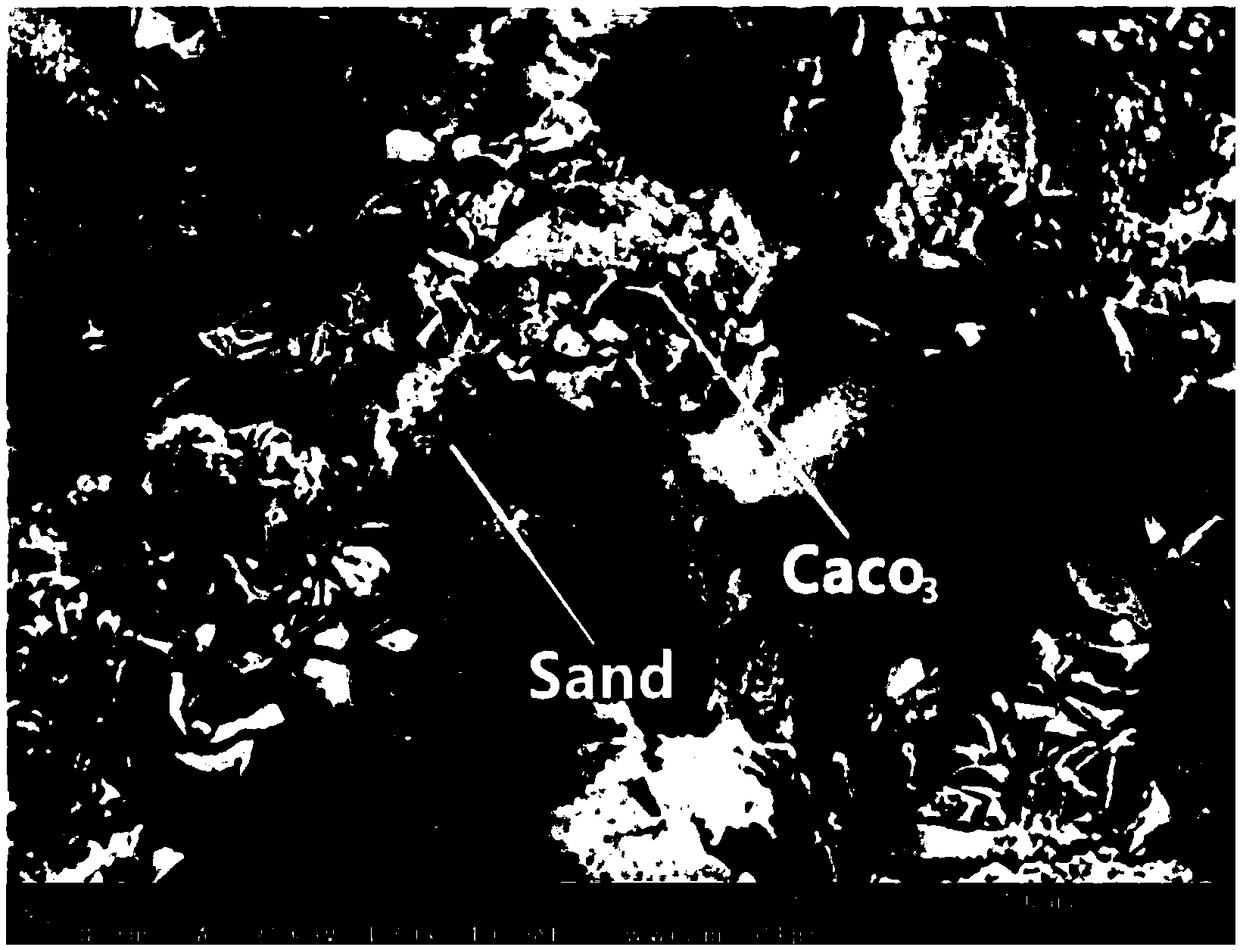
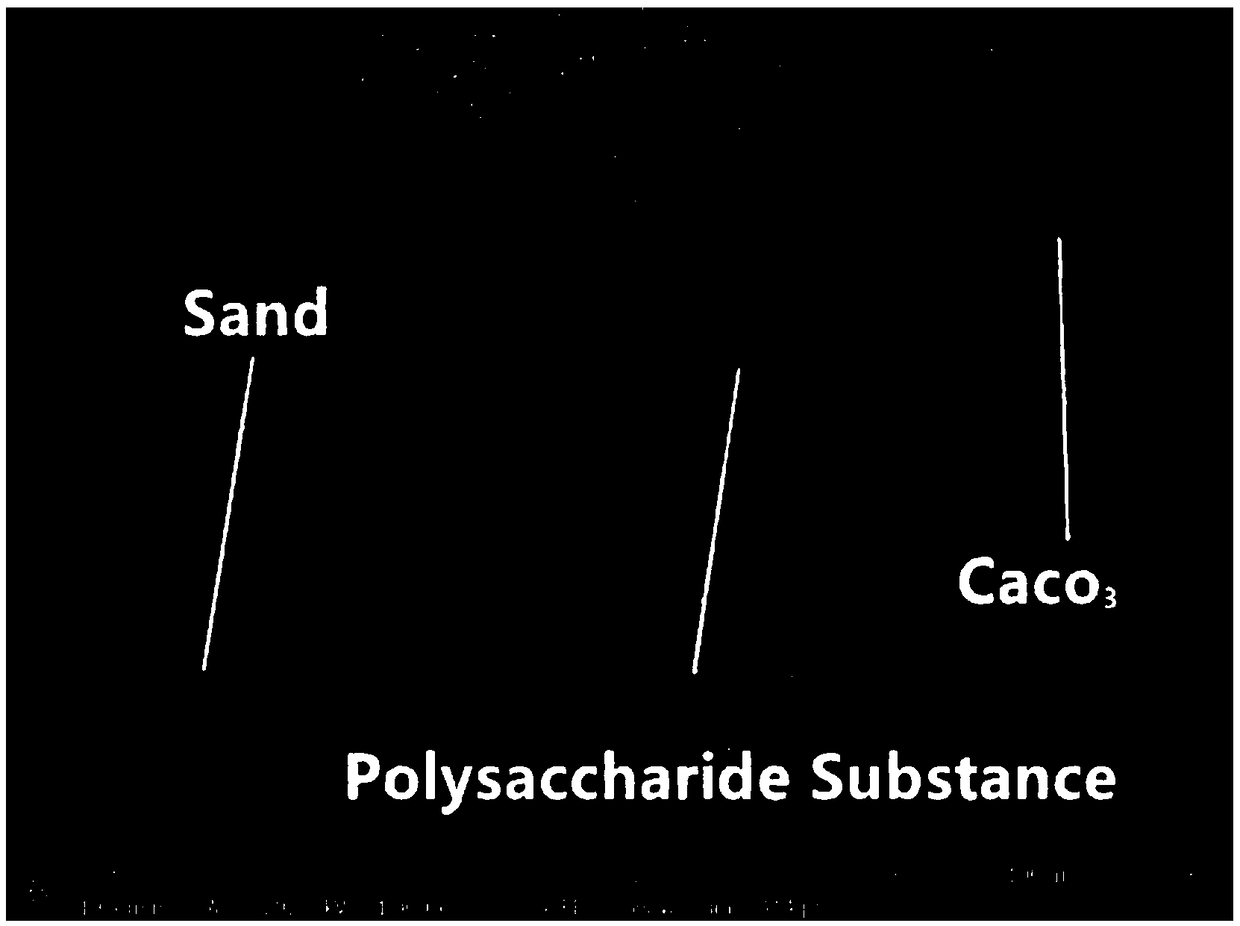
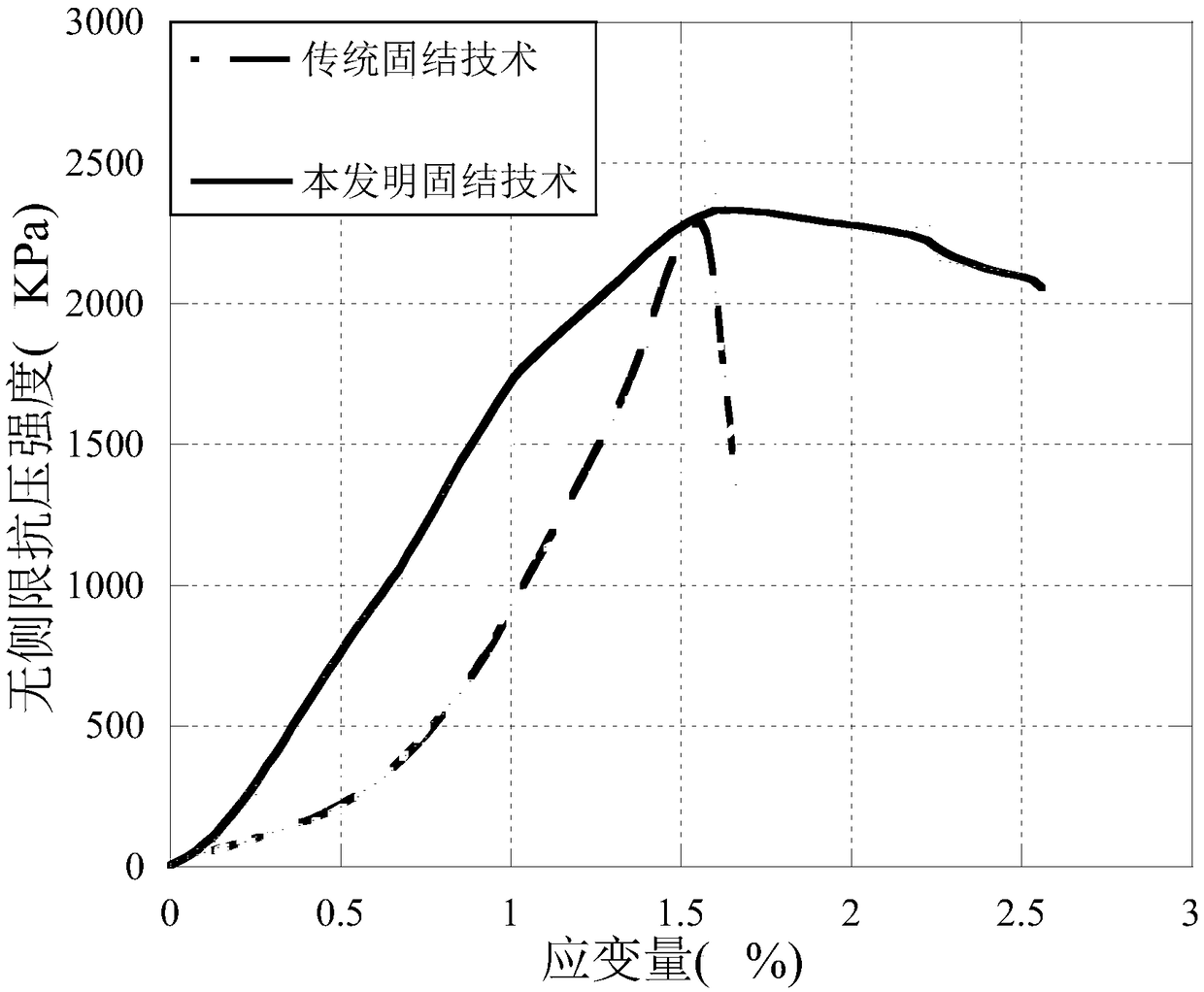
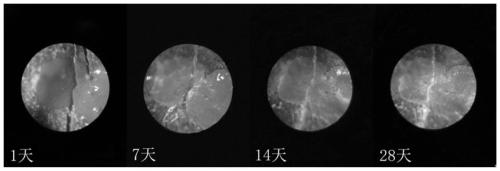
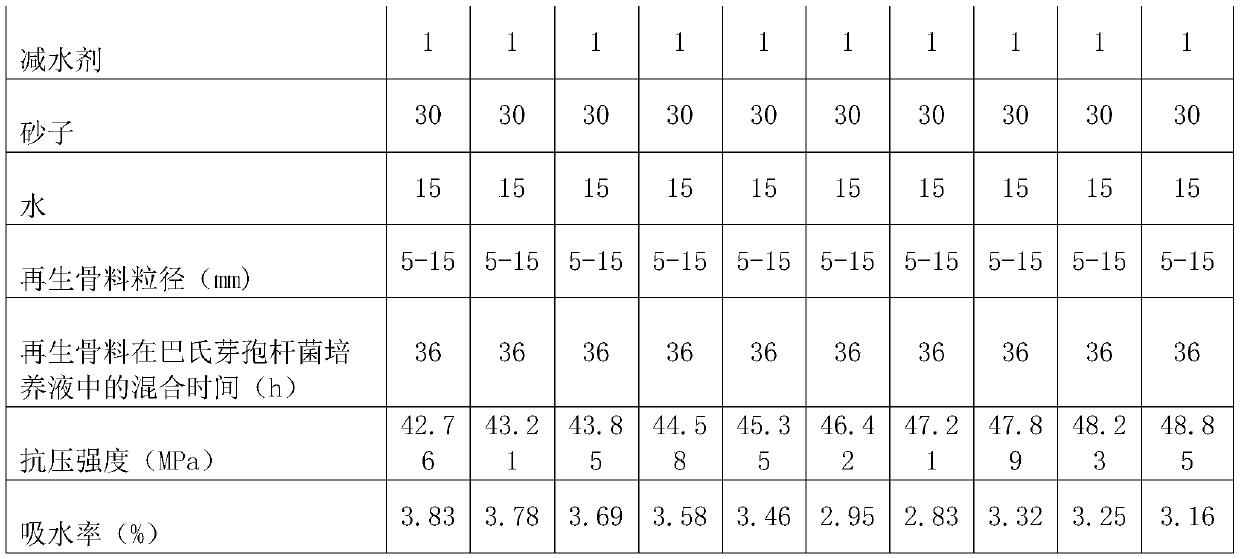
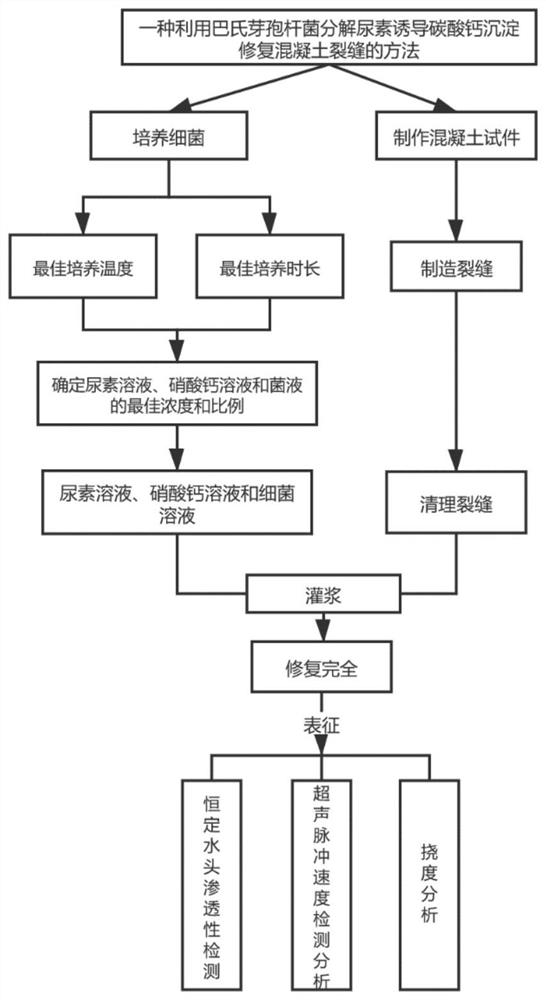
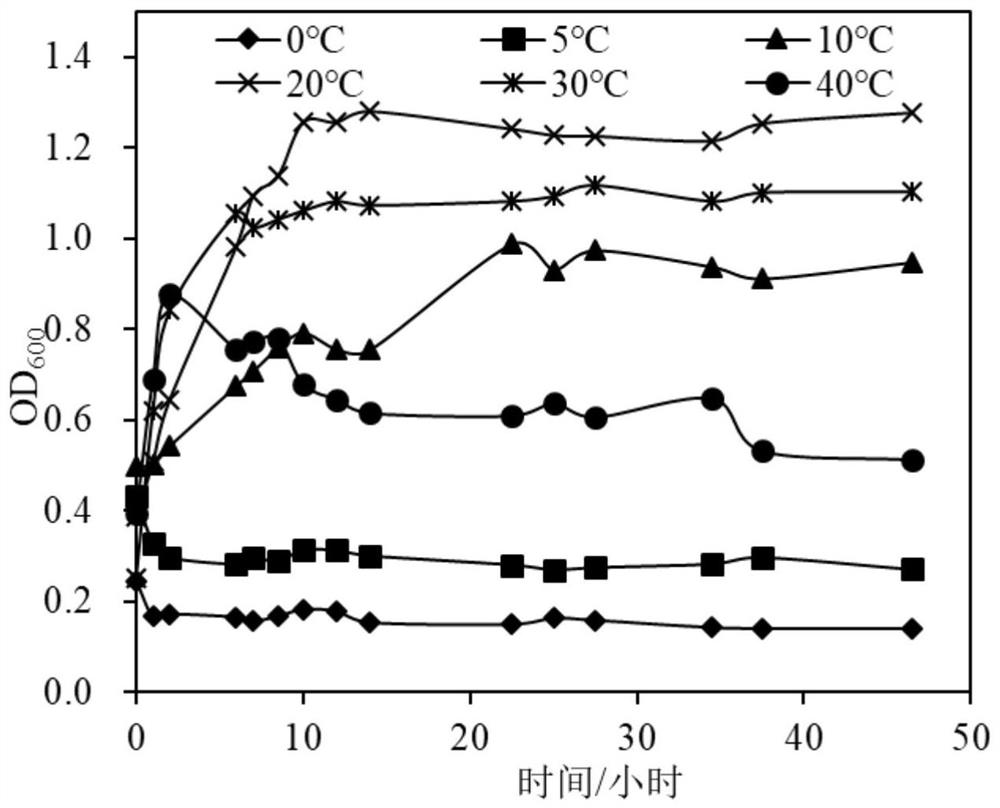
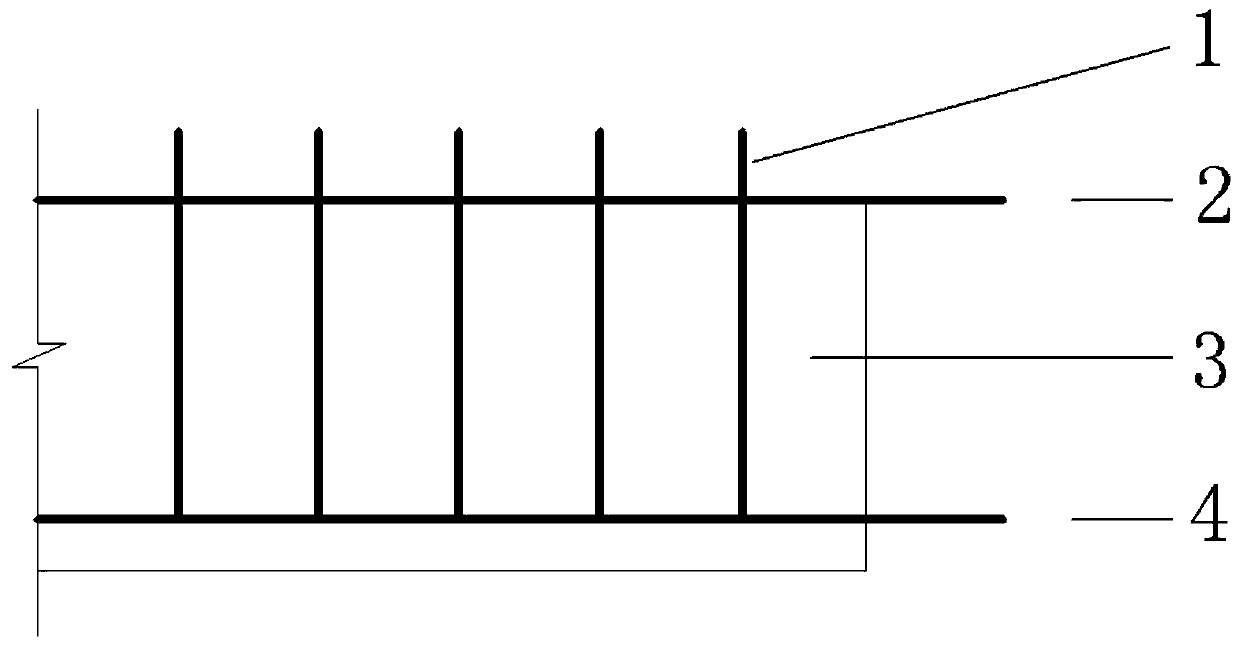
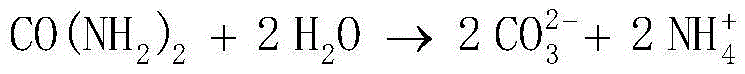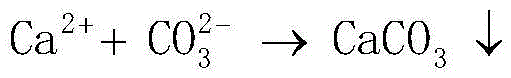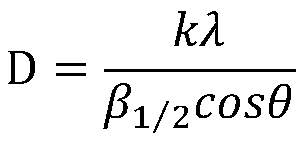Patents
Literature
102 results about "Sporosarcina pasteurii" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
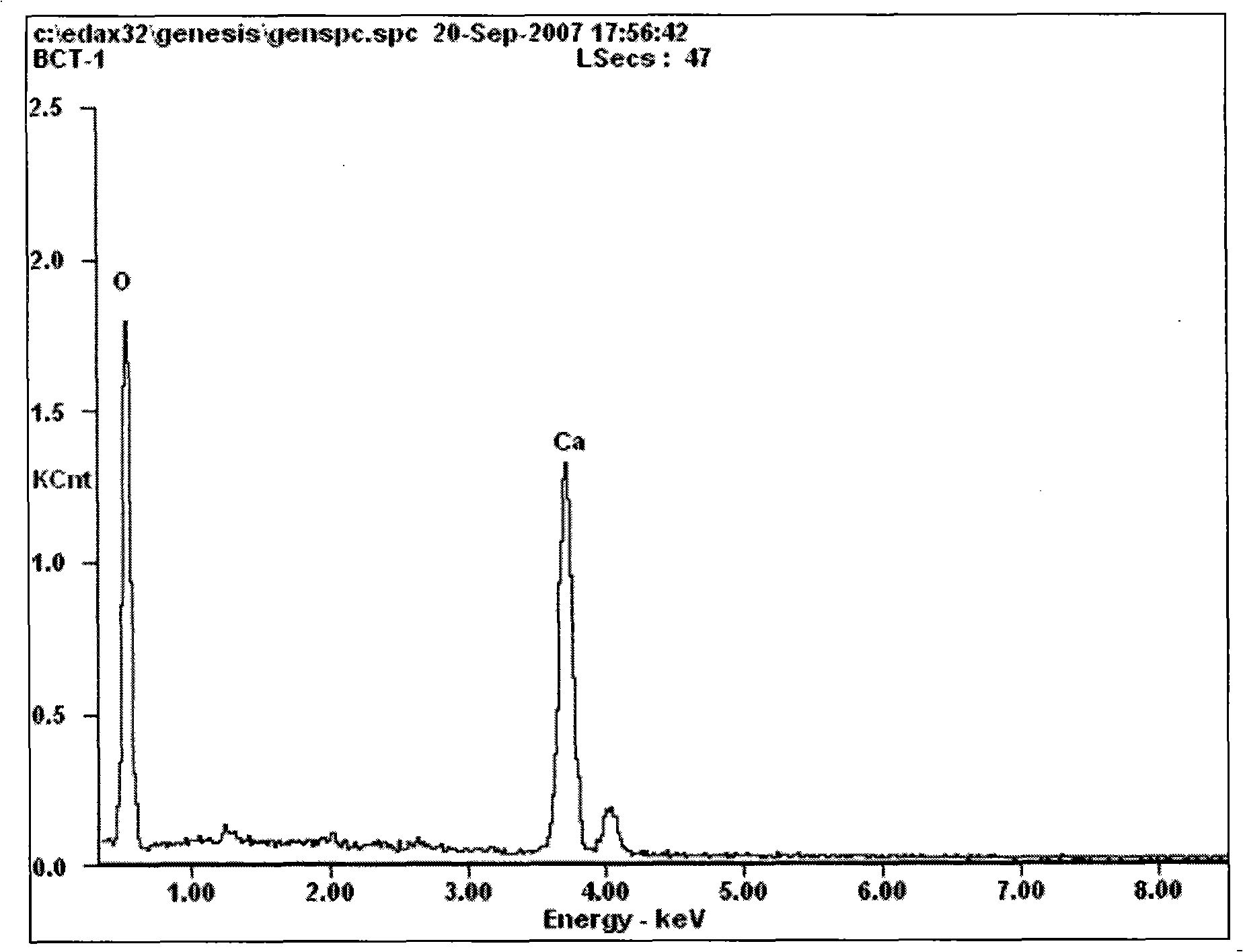
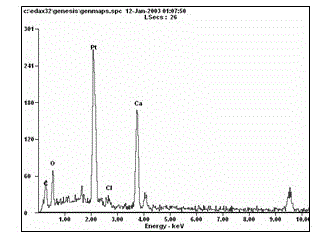
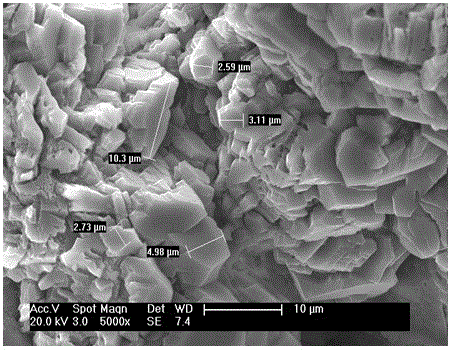
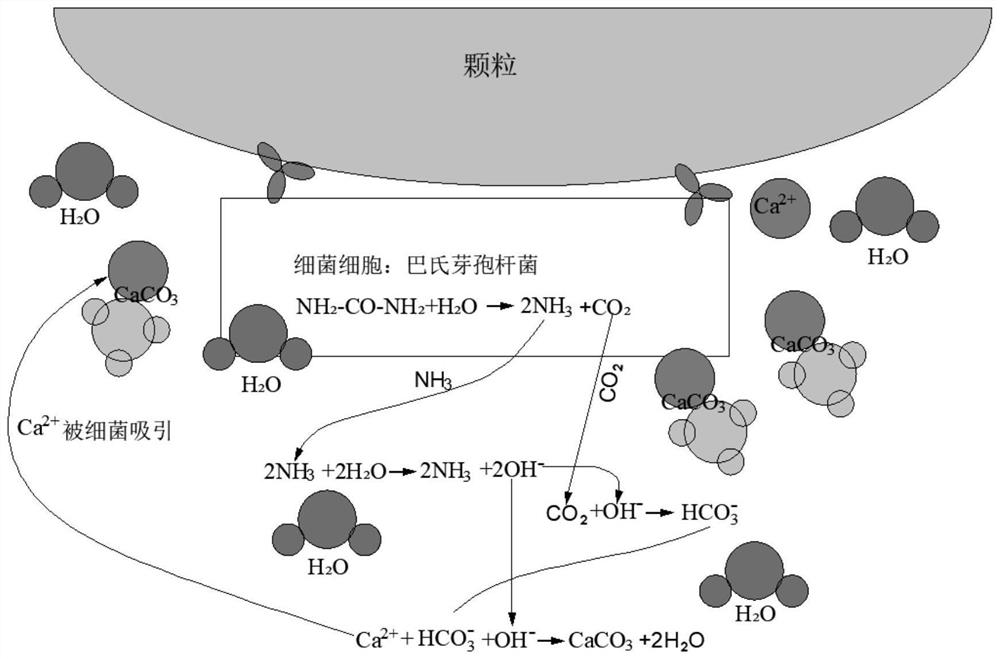
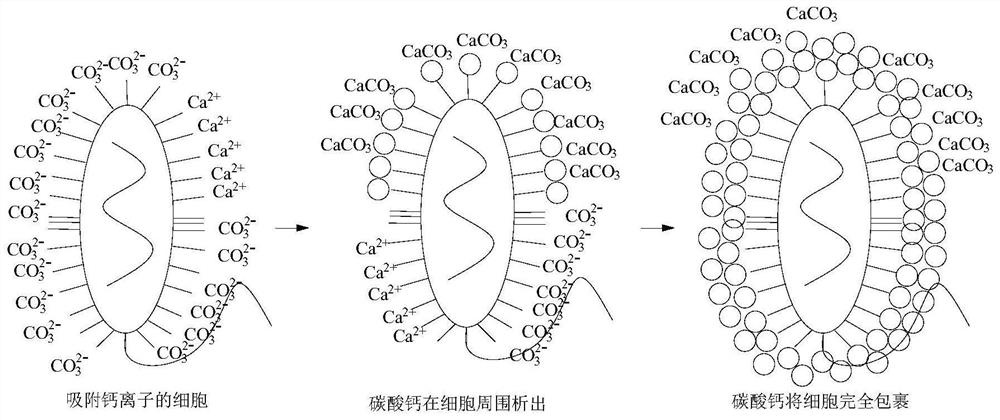
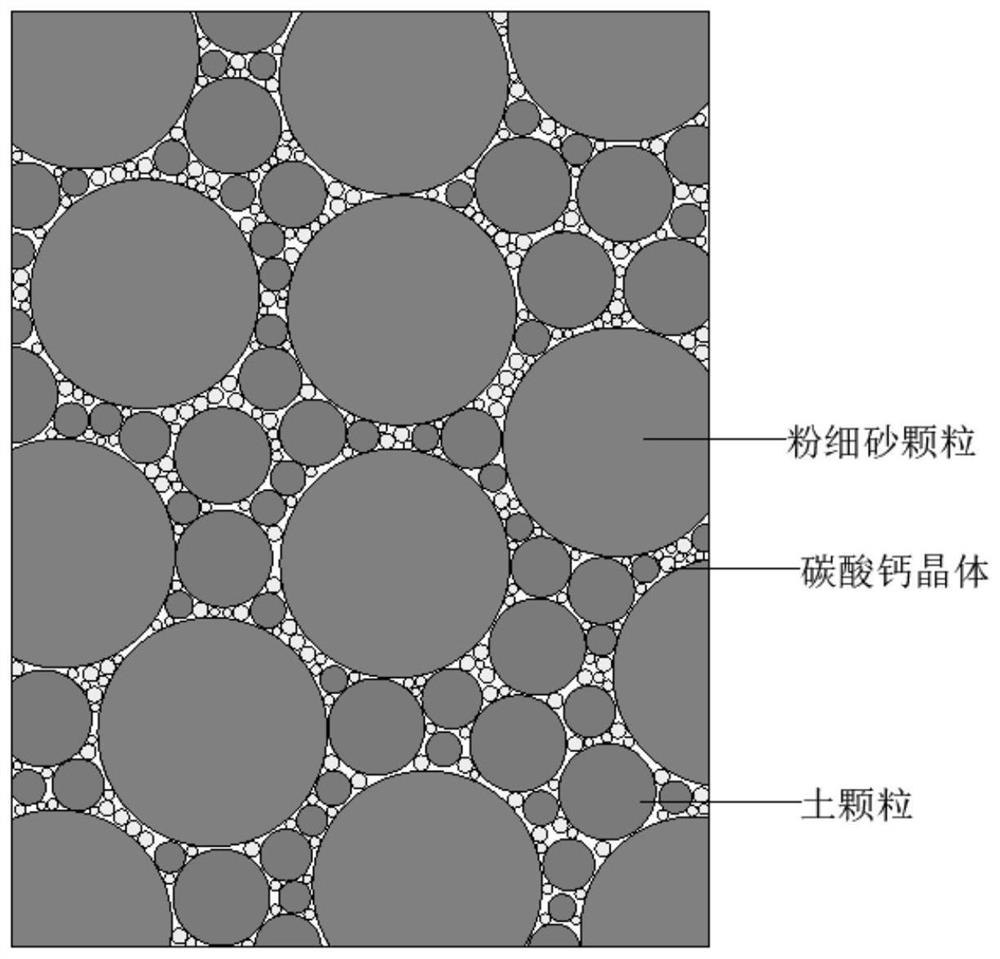
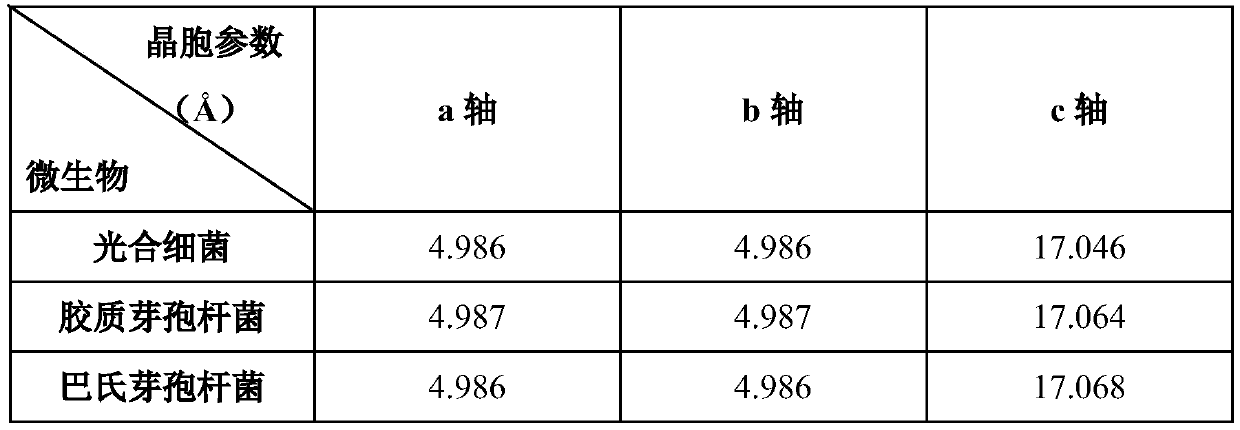
Sporosarcina pasteurii formerly known as Bacillus pasteurii from older taxonomies, is a bacterium with the ability to precipitate calcite and solidify sand given a calcium source and urea, through the process of microbiologically induced calcite precipitation or biological cementation. S. pasteurii has been proposed to be used as an ecologically sound biological construction material.
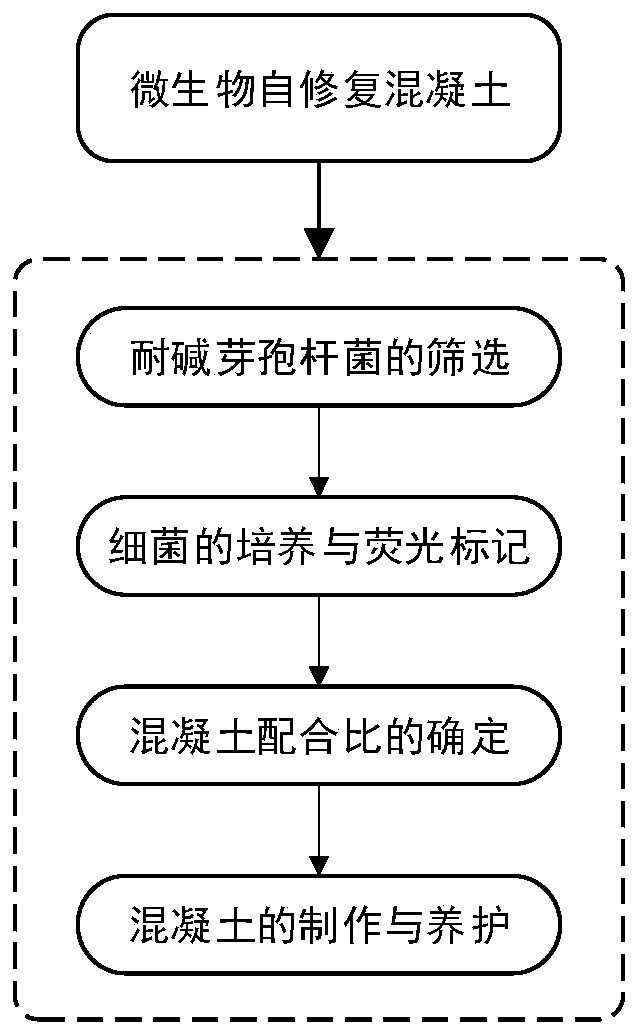
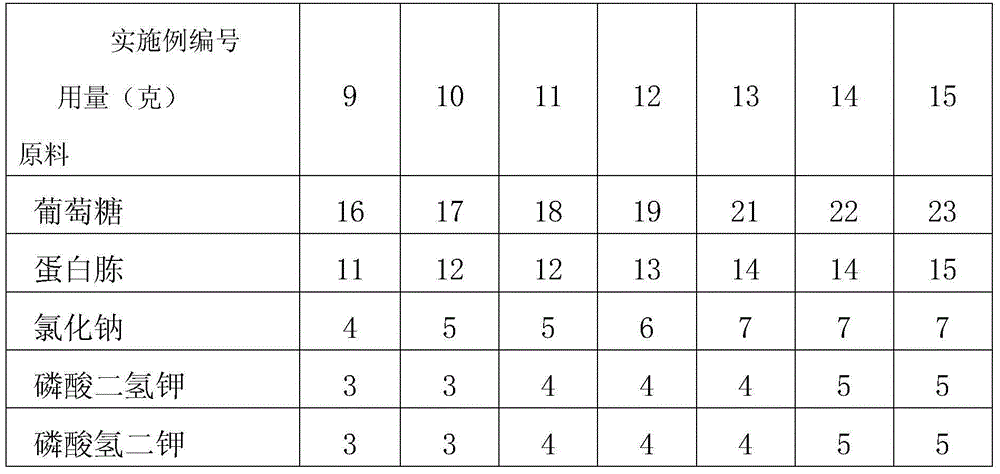
Microorganism cause concrete or concrete, producing method and application thereof
InactiveCN101270369ADoes not hinder precipitationApplicable treatmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismEnvironmental hazard
The invention discloses a microbiogenic cement and concrete and a production method thereof, which mainly mixes the Bacillus pasteurii solution for producing urease and an admixture of containing urea and mineral calcium salt and obtains the microbiogenic cement after reacting in a certain condition; adds admixture such as sand etc. into the mixture of mixing the bacterial solution and the mixture and reacts to generate the microbiogenic concrete. The microbiogenic cement or concrete of the invention can be used on protection and restoration of masonry ancient architectures and repair of cracks on concrete building or treatment of liquescent sandy soil. The invention provides a permanent method of safety, effectiveness and without environmental hazard for repair and strengthening technology of large quantity of civil architecture and structure; the invention has the advantages of the good effects, the good weatherability, the good permeability of gas and the good permeability of water and being especially suitable for treatment of the sandy soil; the invention is safe and environmental-friendly, and belongs to the environmental-friendly restoring material.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for solidifying sand by utilizing halotolerant bacteria
The invention relates to a method for solidifying sand by utilizing halotolerant bacteria. The method selects Sporosarcina pasteurii as bacteria, the strain comes from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC), and the collection number is ATCC 11859. The method comprises the following steps: putting the strain in a nutrient broth medium to obtain a bacterial solution after domestication and enrichment; putting the bacterial solution in desert underground brine containing urea, calcium ions and salinity, and culturing to obtain a bacterial solution with an induced solidification effect; spraying the bacterial solution on the surface of sand soil; putting the sand soil of which the surface is sprayed with the bacterial solution in the natural drying environment for culturing; and naturally air-drying, so that the bacteria can utilize the desert underground brine to cement and solidify sand grains on the surface of the sand soil through the solidification effect so as to prevent the sand soil on the surface layer from migrating under the wind effect. The method is environment-friendly, is low in cost, and can be widely used for solidifying mobile and semi-mobile dunes.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ECOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tailing sand biological prefabricated product and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a new method for solidification treatment of tailing sand accumulated in an ore field, in particular to a tailing sand biological prefabricated product and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the cross scientific and technical field of microbiology and building materials. The method is characterized in that the cementing mechanism is realized by using microorganisms to induce the generation of calcium carbonate to conduct solidification treatment, so as compared with other using methods for the tailing sand, the method is environment-friendly and free of environmental pollution, and the calcium carbonate formed by microbial mineralization has the cementing property that cannot be obtained from chemical preparation. The prefabricated product comprises the following raw materials: the tailing sand from an iron ore field, bacillus pasteurii, casein, soy protein and anhydrous calcium chloride, which are shaped in a cementing mode according to a definite cementing process. The prefabricated product can be used for cementing prefabricated bricks as well as for the reinforcement of tailing sand ore dams. The new interdisciplinary method provided by the invention has the biggest characteristics of environment protection, no pollution, recycling of discarded tailing sand, and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for preparing high-strength microbial mortar by using urease-producing microbes
ActiveCN103173376AStrong ability to produce ureaseHigh in calcium carbonateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEpoxy
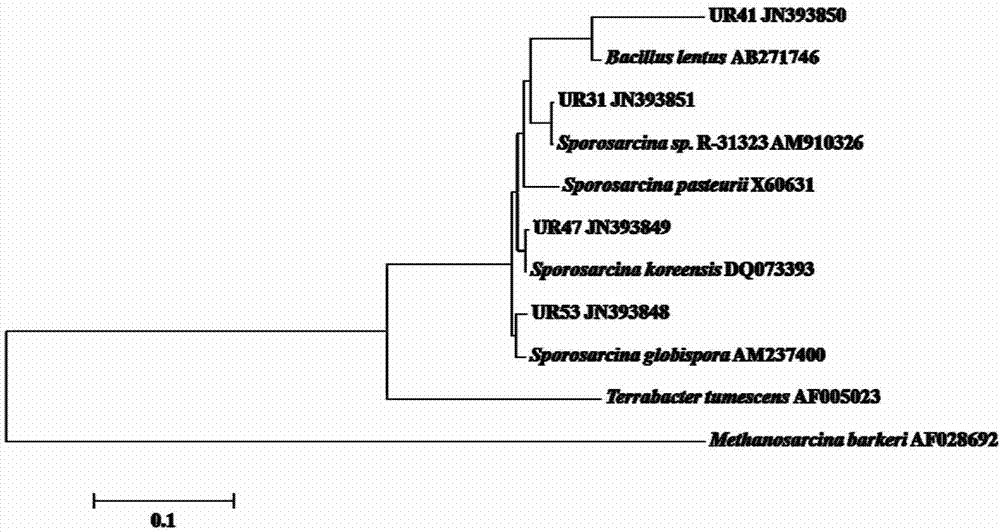
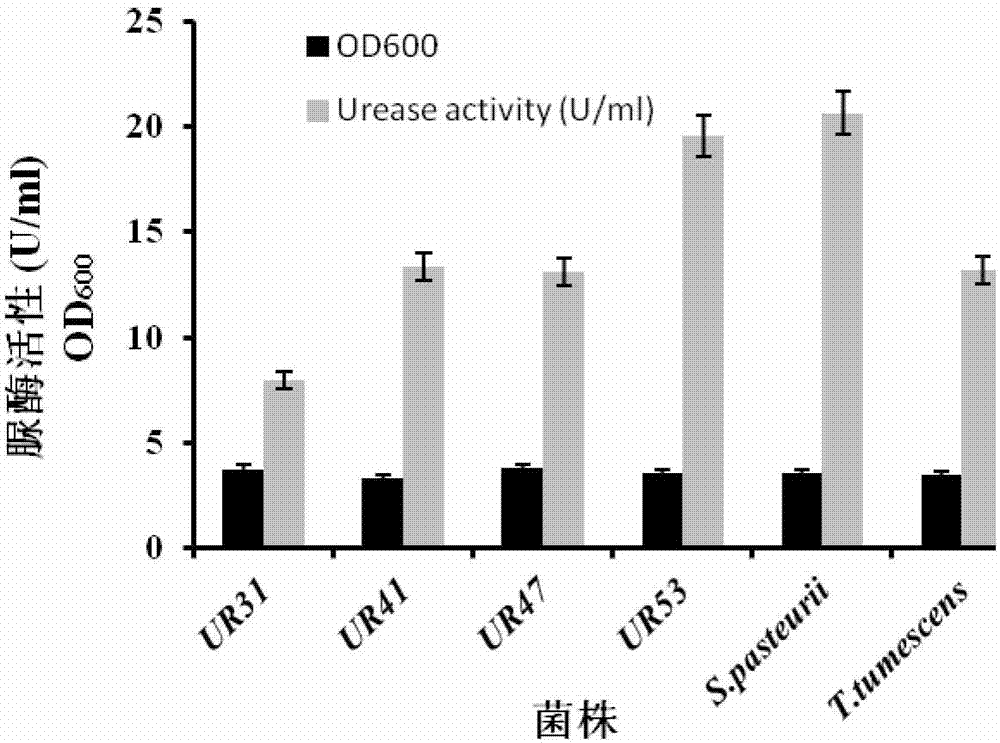
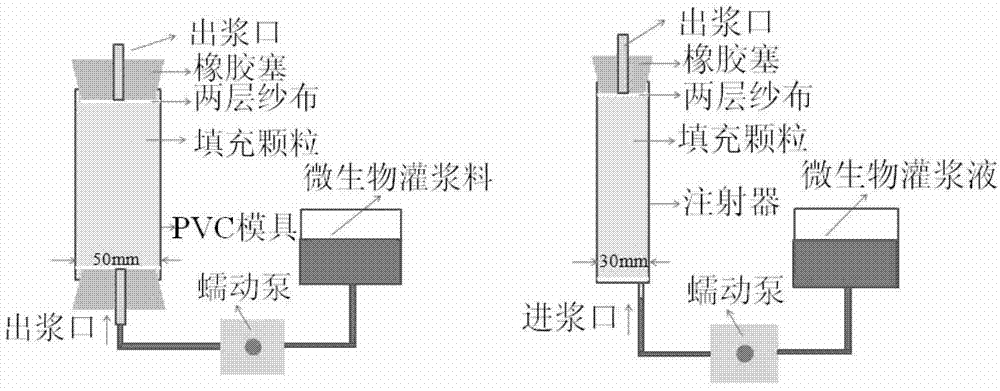
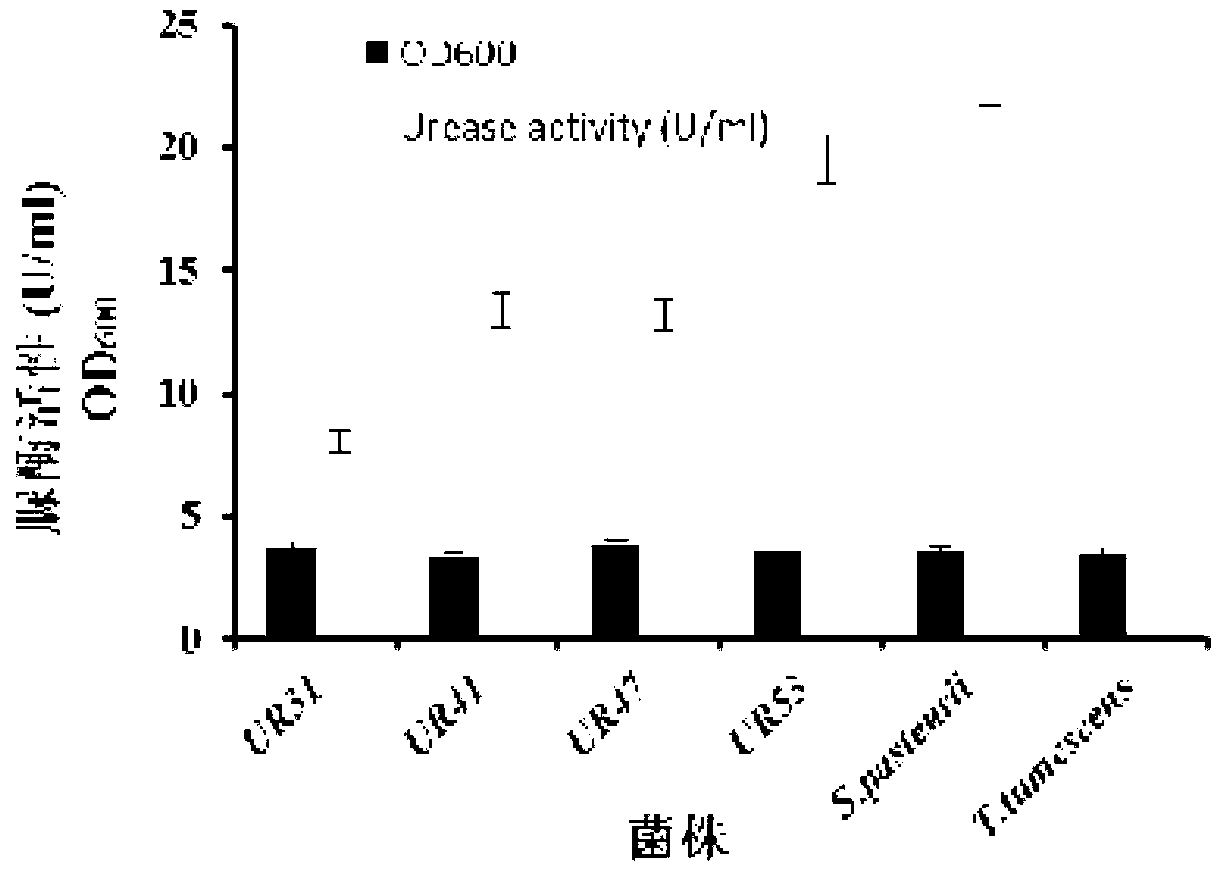
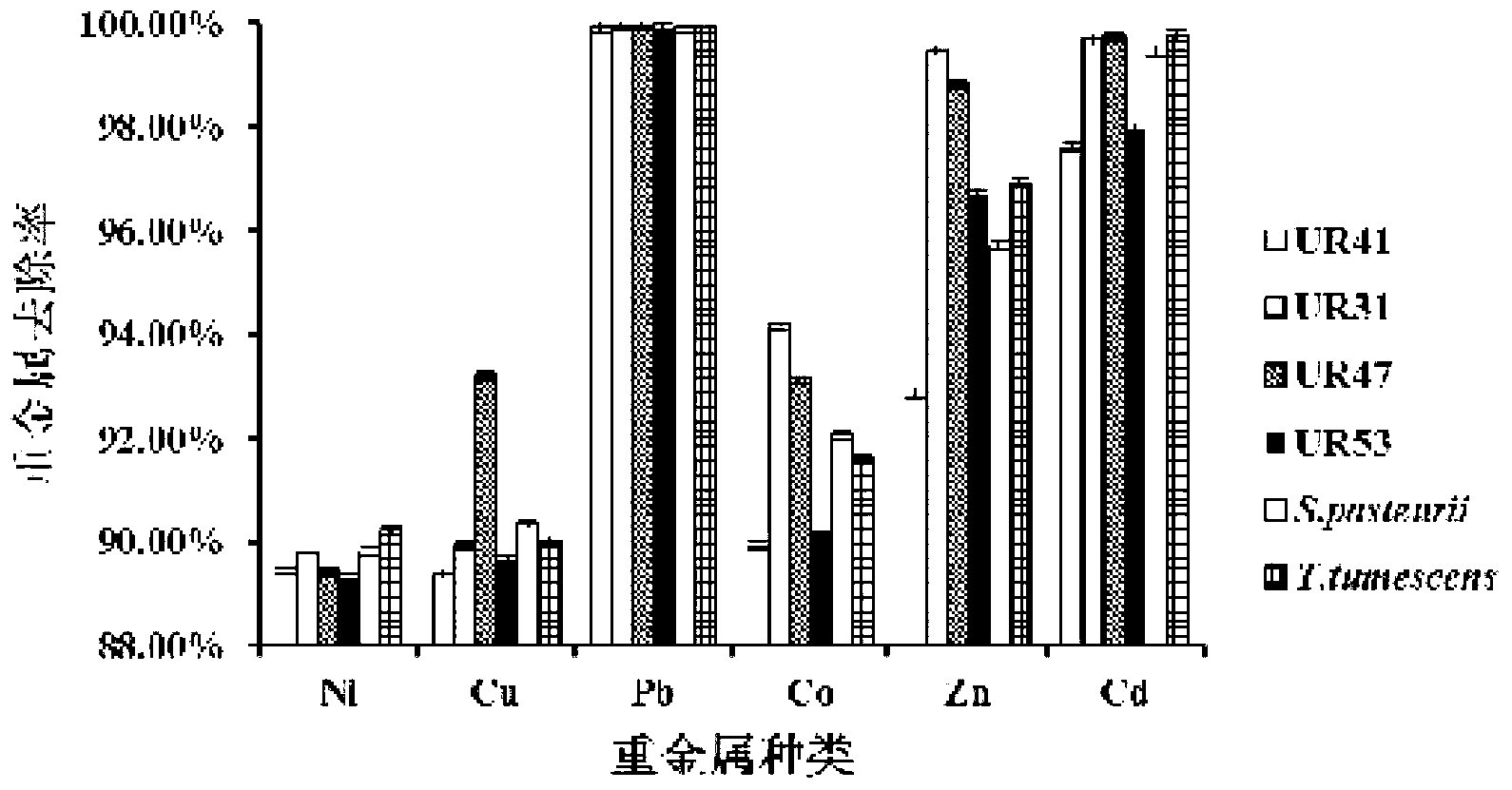
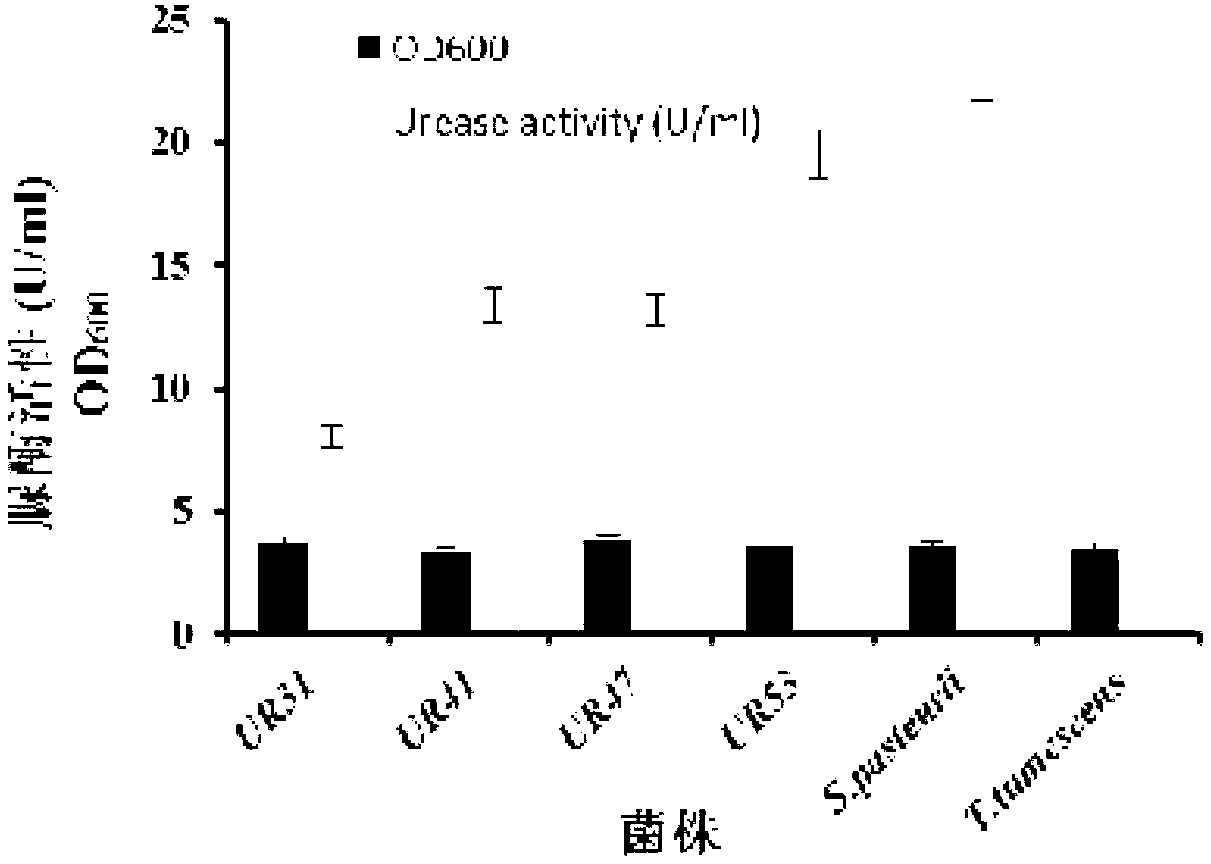
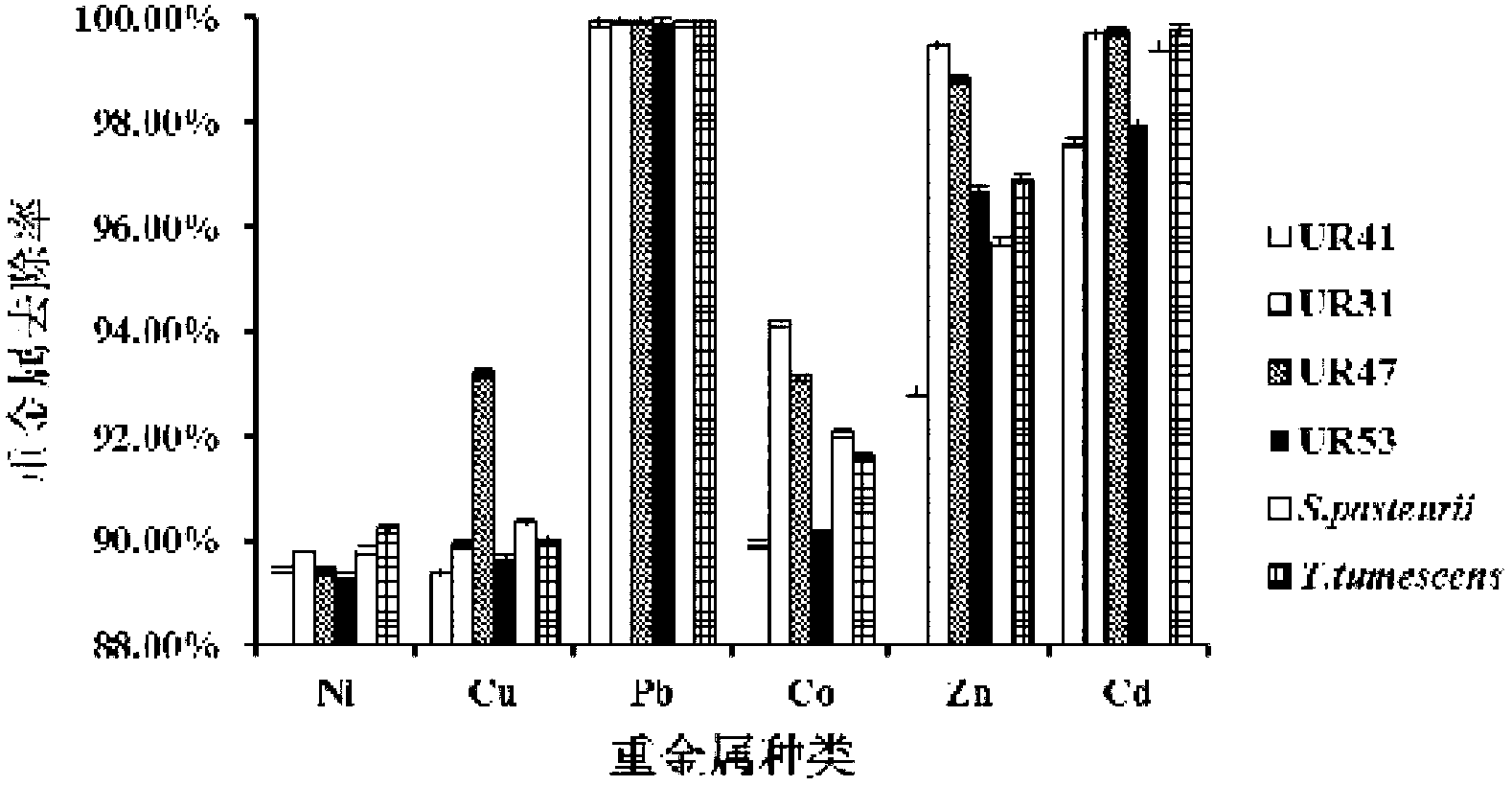
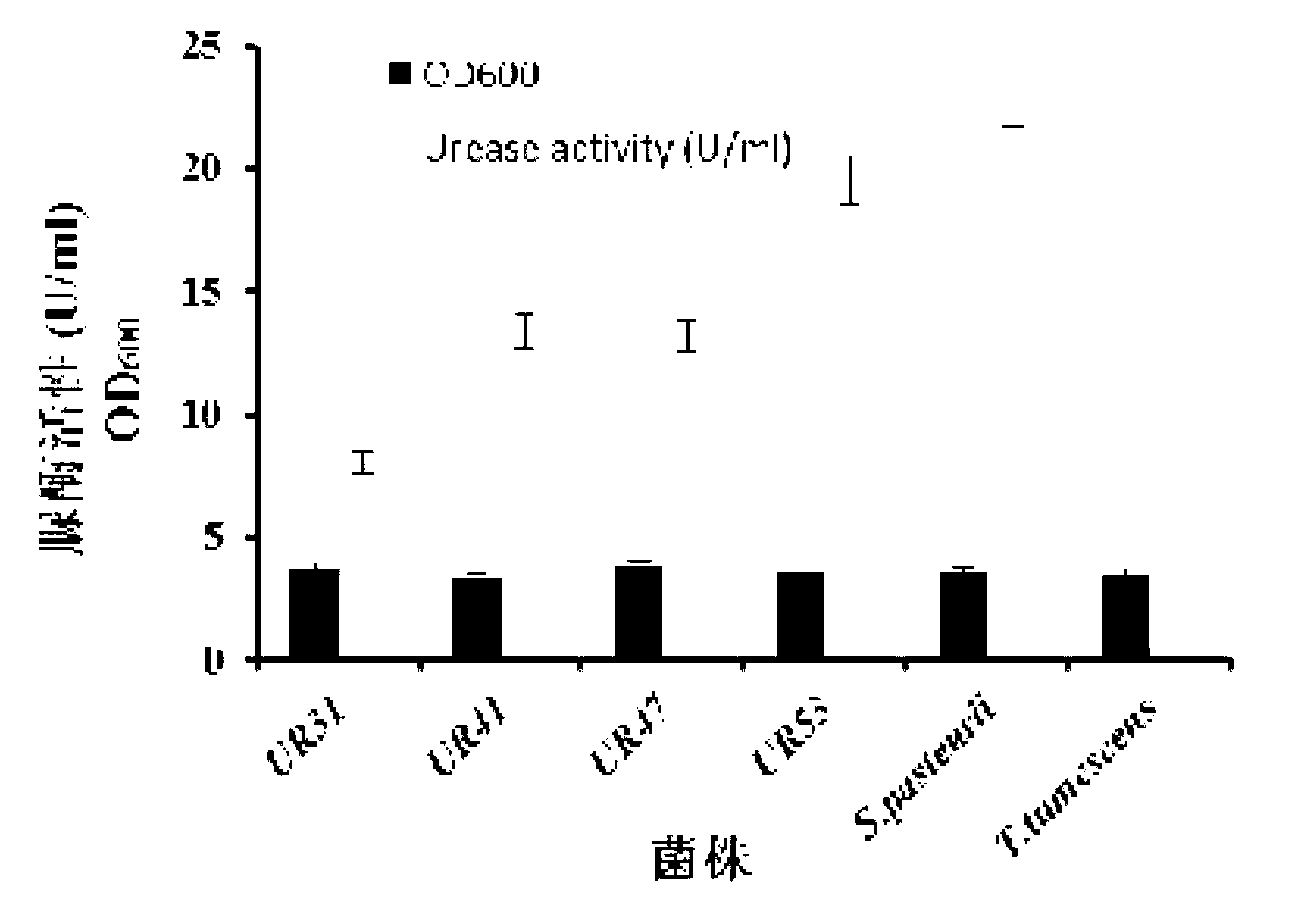
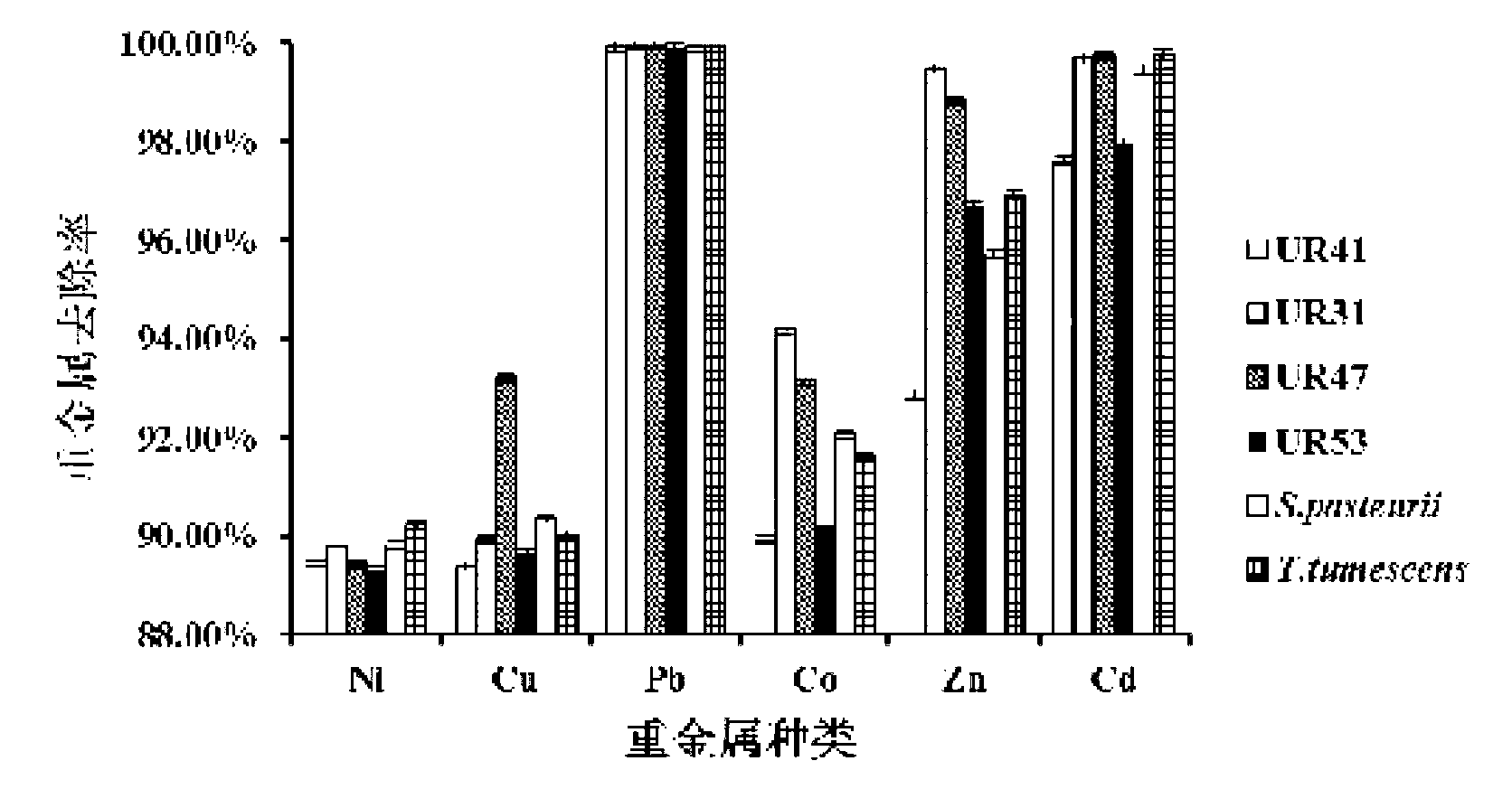
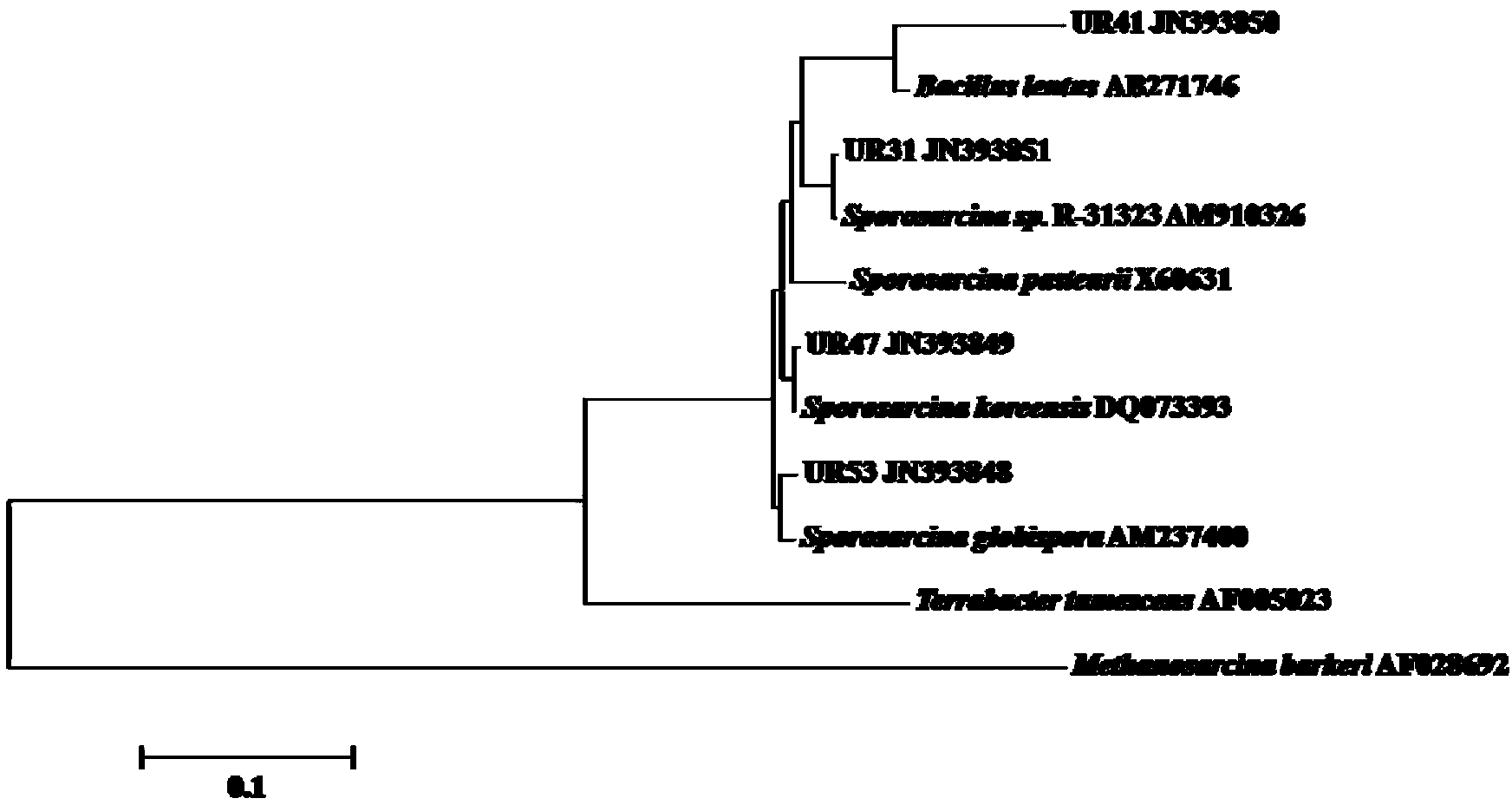
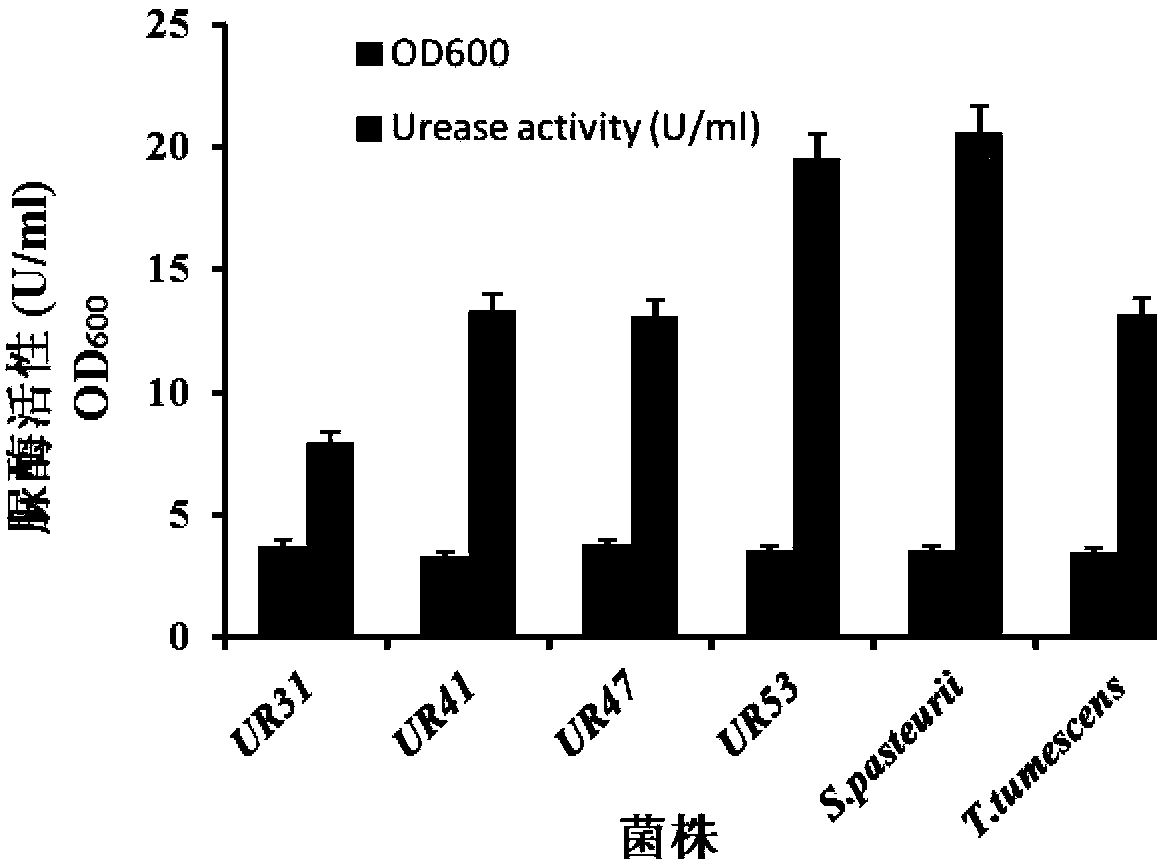
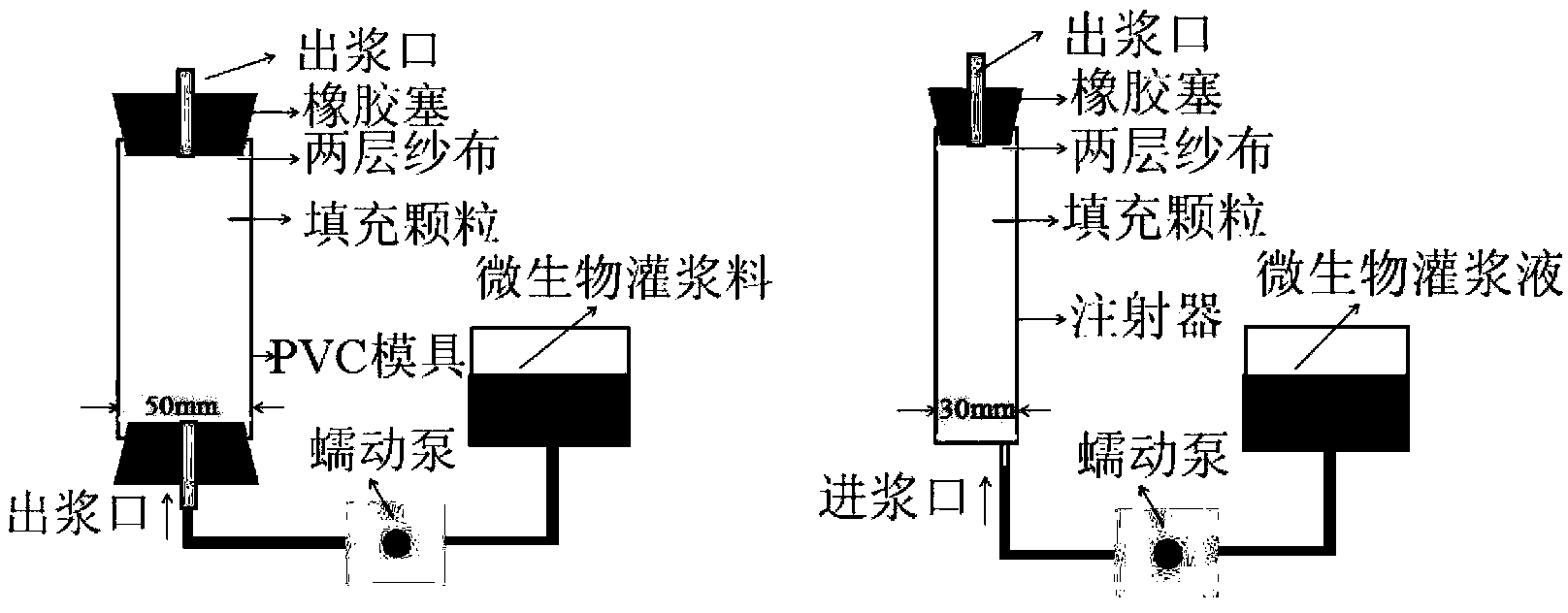
Urease-producing microbes including Sporosarcina antarctica U R 5 3, Sporosarcina koreensis UR47, Sporosarcina sp. UR31 and Bacillus lentus UR41 were preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on March 16, 2012, with the preservation numbers of CGMCC No.5916, CGMCC No.5915, CGMCC No.5913 and CGMCC No.5914 respectively. The method for preparing high-strength microbial mortar by using the urease-producing microbes comprises the following steps of: carrying out fermentation culture on the above four microbes and microbes including Sporosarcina pasteurii and Terrabacter tumescens in a fermentation culture medium to obtain a bacterial solution; and filling the bacterial solution, a fixative solution and a gelling solution into a sand particle system in batches to form microbial mortar of which the highest strength can reach 55MPa. The mechanical properties of the microbial mortar are superior to those of a cement base material; compared with a cement lime material with equivalent strength, the microbial mortar is higher in splitting tensile strength; the rigidity of the microbial mortar is similar to that of cement lime mixed mortar but far smaller than that of concrete; the fatigue load tolerance and cyclic loading capacity of the microbial mortar are higher than those of the cement base material; and an artificial sandstone is an inorganic material, and is not easy to age like organic materials including epoxy resin and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Microbial composite treatment for gold ore tailings and application method
InactiveCN108220197ANo cyanide accumulationNo secondary pollutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIonGold ore
The invention discloses a microbial composite treatment for gold ore tailings and an application method and belongs to the field of road engineering. According to the method, Bacillus pasteurii is compounded with one or more of Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus pumilus or Bacillus megaterium, so that by means of the Bacillus pasteurii, CaCO3 crystal is deposited and generated in the gaps in the gold oretailings, thus improving mechanical performance and stability and immobilizing heavy metal and noble metal ions in the gold ore tailings. The Bacillus pumilus or Bacillus megaterium can decompose thecyanides in the gold ore tailings. Through mechanical ploughing and multi-round slurry injection, the microorganisms, the gold ore tailings and a cemented liquid are fully mixed and contacted with each other, so that purposes of generating the CaCO3 crystal for reinforcing the gold ore tailings and degrading the cyanides can be achieved. The method has no secondary pollution, is low-cost, is simple and is high in resource utilization rate, and can achieve multi-channel large-scale recovery utilization of the tailings.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for preparing calcium carbonate by simultaneous mineralization of two microorganisms
InactiveCN108220380ARaise the pHNo pollution in the processMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganism resourceCalcium EDTA
The invention relates to a method for preparing calcium carbonate by simultaneous mineralization of two microorganisms. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: adding a culturesolution of the two cultured microorganisms to a mixed solution of calcium salt and urea, putting a reactor in an open mode to enable the solution to be exposed to the air to be subjected to mineralization reaction, taking out the precipitate after the reaction is completed, and washing and drying the precipitate to obtain a calcium carbonate product. The two microorganisms are respectively sporosarcina pasteurii belonging to a urease high-yield strain and bacillus pumilus belonging to a carbonic anhydrase high-yield strain. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the twostrains together participate in the mineralization process, the generation efficiency of calcium carbonate is increased, simultaneously, the pollution to the environment caused by generation of ammonia gas can be reduced, CO2 in the atmosphere can also be captured, and the advantages of the two strains are complementary so as to cooperatively promote the whole mineralization process; the microorganisms utilized in the method are rich in resources, efficient and single in enzyme catalysis reaction, simple in production process and low in cost; and furthermore, the obtained calcium carbonate product is higher in purity, has better cementing action and can be widely applied to the field of civil engineering.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Urease-producing microorganisms and method for solidifying heavy metals in subgrade by using same
ActiveCN103289919AShorten the timeGood effectBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationWater insolubleBacillus lentus
The provided urease-producing microorganisms comprise: Sporosarcina antarctica UR53, Sporosarcina koreensis UR47, Sporosarcina sp. UR31, and Bacillus lentus UR41, wherein all the above microorganisms have been deposited with the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on March 16, 2012, and assigned respectively the accession numbers: CGMCC NO.5916, CGMCC NO.5915, CGMCC NO.5914, and CGMCC NO.5913. The provided method for solidifying heavy metals in subgrade using the urease-producing microorganisms comprises steps of: putting the above four microorganisms, Sporosarcina pasteurii and Terrabacter tumescens in a fermentation medium to obtain a bacterial solution by fermenting; adding a urea reaction solution into the bacterial solution; and adding the solution of the above step into a solution containing heavy metals to form a mixed solution, so that floccules of microorganism-heavy-metal are formed in the mixed solution and water-insoluble heavy-metal-carbonates are formed further. The method for solidifying heavy metals in subgrade using the microorganisms provided by the invention has the advantages of short solidifying time, good effect, low cost, and no secondary pollution to environment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Urease-producing microbes and curing method for heavy metals in foundation
ActiveCN103289921AEfficient governanceShorten the timeBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationWater insolubleBacillus lentus
Urease-producing microbes comprise sporosarcina antarctica UR53, sporosarcina koreensis UR47, sporosarcina sp. UR31 and bacillus lentus UR41 which have been preserved in China General Microbiology Center of Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms since 16th March, 2012, and respectively have the preservation numbers of CGMCC No.5916, CGMCC No. 5915, CGMCC No. 5913 and CGMCC No. 5914. A curing method for heavy metals in a foundation by using the urease-producing microbes comprises: placing the four microbes, and microbes of sporosarcina pasteurii and terrabacter tumescens in a fermentation medium to carry out fermentation culture to obtain a bacterial liquid, adding a reaction solution urea into the bacterial liquid, then adding the bacterial liquid into a heavy-metal-containing solution to form a mixed solution and to form a microbe-heavy-metal floccule in the mixed solution, and further to obtain water-insoluble heavy metal carbonates. The curing method for heavy metals in the foundation by using the urease-producing microbes has the advantages of short curing time, good effect, low cost and no secondary pollution to environment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Microorganism calcareous glue, preparation method and application thereof, sandy soil column and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108823259AIncrease contentLarge internal friction angleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCalcium in biologyCalcite
The invention discloses environment-friendly microorganism calcareous glue, a preparation method and application thereof, a sandy soil column and a preparation method thereof. The environment-friendlymicroorganism calcareous glue is prepared from a microorganism bacteria solution with mineralization performance, a calcium source nutrient solution and an environment-friendly colloid in a volume ratio of 1 to (10 to 100) to (0.001 to 1). In the preparation of the microorganism bacterial solution, a culture medium is inoculated with 5 percent of sporosarcina pasteurii serving as a strain for performing oscillation and propagation to obtain a bacteria solution; in preparation of the calcium source nutrient solution, the calcium source nutrient solution is prepared according to a formula, andthe preparation of the nutrient solution is finished no less than 3 hours and no more than 6 hours before spraying. The environment-friendly colloid liquid of biomacromolecule liquid with colloidalityis prepared by dissolving exopolysaccharide of cell secretion or purified polysaccharide products. By adopting the environment-friendly microorganism calcareous glue, the defect of large brittlenessof a calcite cementation sand material by only relying on microorganism induction is overcome, and the concretion result of sand is effectively improved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
Crack self-repairing concrete and preparation and repairing method thereof
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
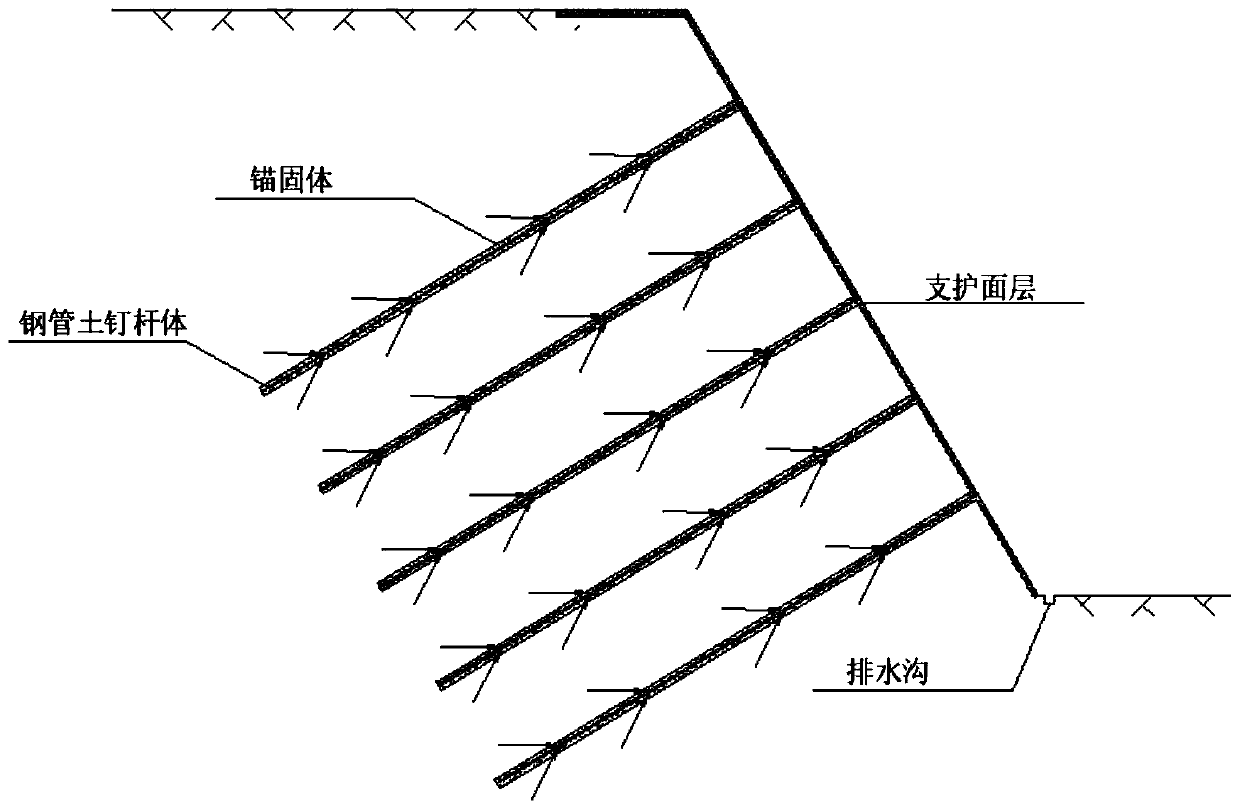
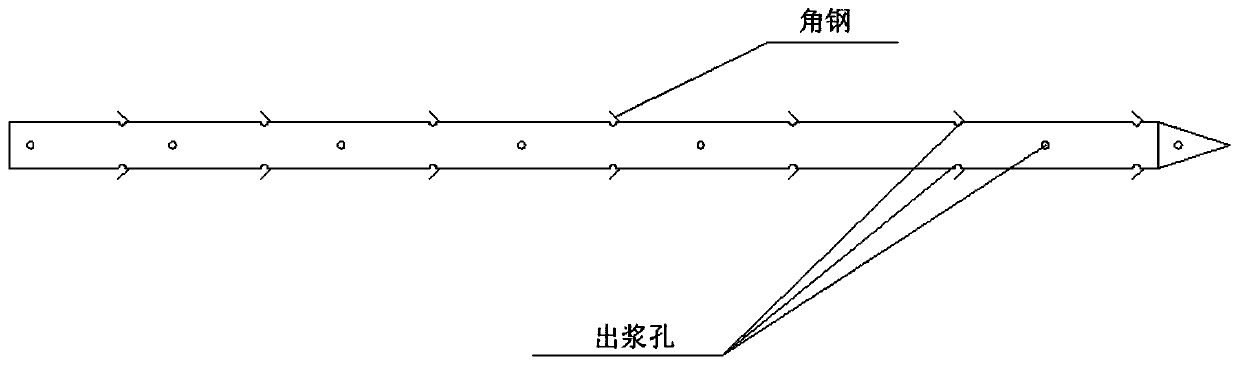
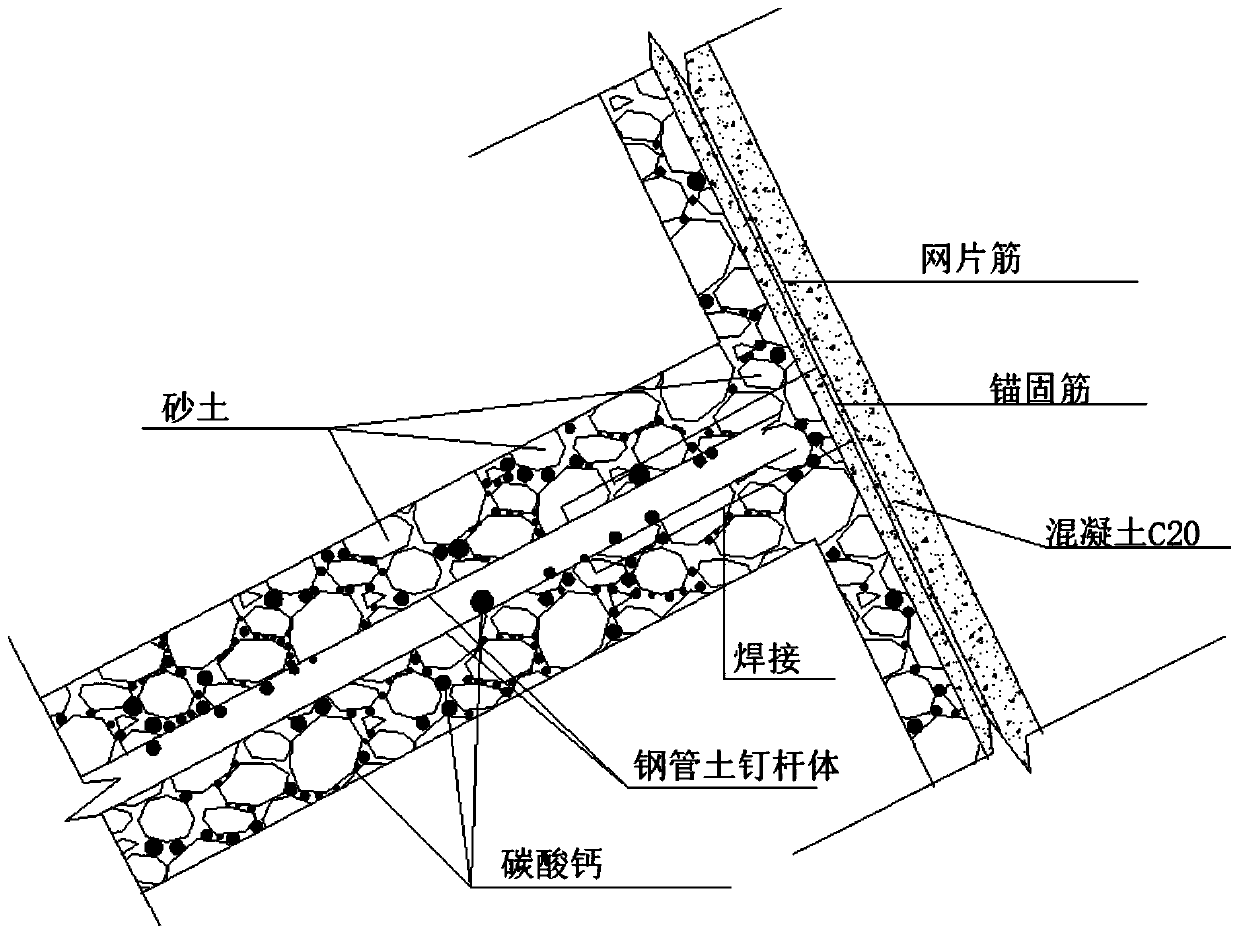
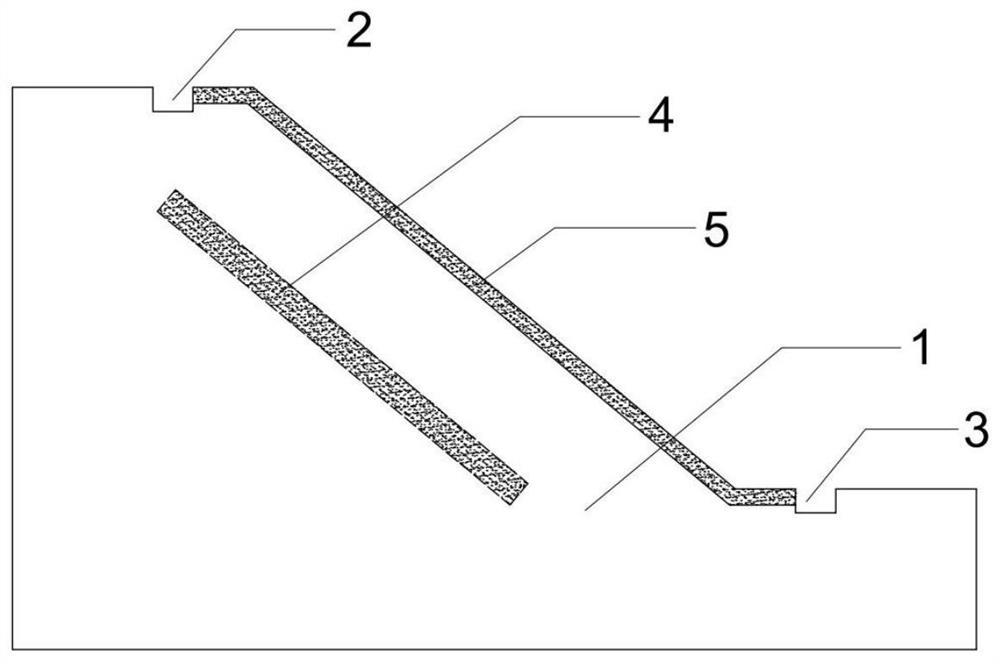
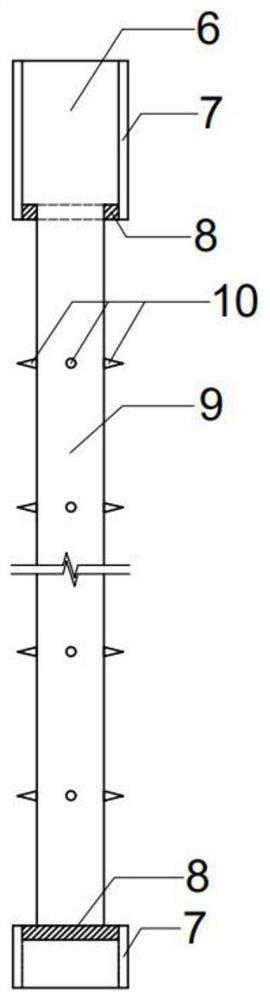
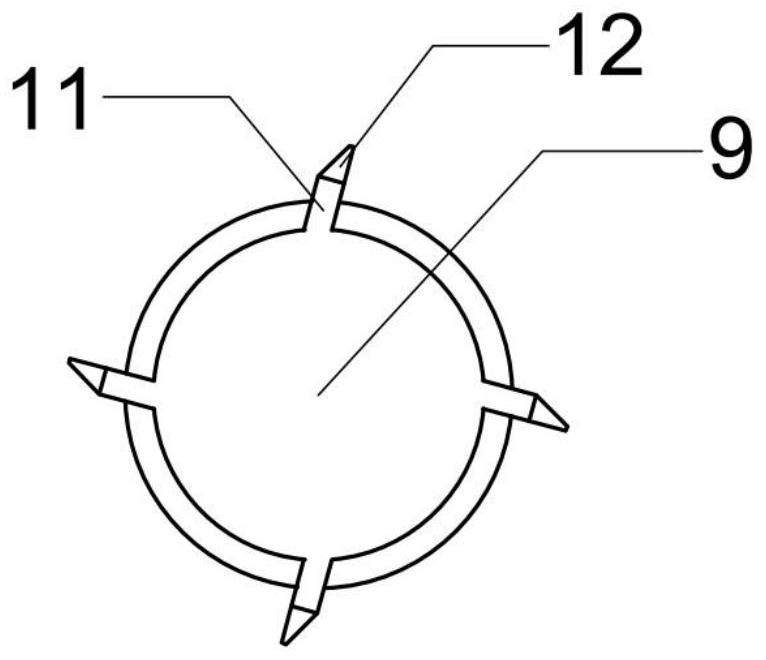
Microorganism curing striking-in type steel pipe soil nail and construction method thereof
InactiveCN110528533AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove integrityExcavationsSoil preservationSoil nailingNutrient solution
The invention discloses a microorganism curing striking-in type steel pipe soil nail and a construction method thereof. The steel pipe soil nail mainly comprises a steel pipe and angle iron. The steelpipe comprises a pipe head and a pipe body. The construction method mainly includes the steps that the steel pipe soil nail is manufactured, and the steel pipe soil nail is struck into mud through apneumatic down-the-hole hammer; sporosarcina pasteurii is activated and subjected to enlarge cultivation, and a microorganism bacterium solution is obtained; the obtained microorganism bacterium solution is injected into the soil nail through the steel pipe soil nail so that the microorganism bacterium solution can be spread in sandy soil; a composite nutrient solution is prepared and includes 0.5mol / L of urea and 0.5 mol / L of calcium salt; the composite nutrient solution is injected into the steel pipe soil nail and a slope face, and an anchoring body is formed; and the above steps are repeated till the strength of the soil nail reaches the design requirement, and the microorganism curing striking-in type steel pipe soil nail is obtained. By means of the microorganism curing striking-intype steel pipe soil nail and the construction method thereof, the sandy soil in the soil nail is cemented through a cementing effect of microorganisms, the mechanical property of a slope soil body isimproved, the integrity and self stability of the slope soil body are improved, and the slope can be more stable.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Microbial self-repairing concrete and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the field of concrete, and particularly discloses microbial self-repairing concrete, which comprises the following components in parts by weight: 860-980 parts of coarse aggregate, 630-760 parts of fine aggregate, 320-360 parts of cement, 40-55 parts of silica fume, 140-180 parts of mineral powder, 140-160 parts of water, 7-9 parts of a sodium sulfamate water reducing agent, 11-13 parts of urea, 13-15 parts of calcium chloride, and 85-100 parts of a carrier, which is loaded with a crack repairing agent and has a coated surface, wherein the crack repairing agent is anaerobic bacillus pasteurii liquid. The microbial self-repairing concrete has the advantage that the concrete can be self-repaired after cracking in an anoxic environment.
Owner:陕西恒盛混凝土有限公司
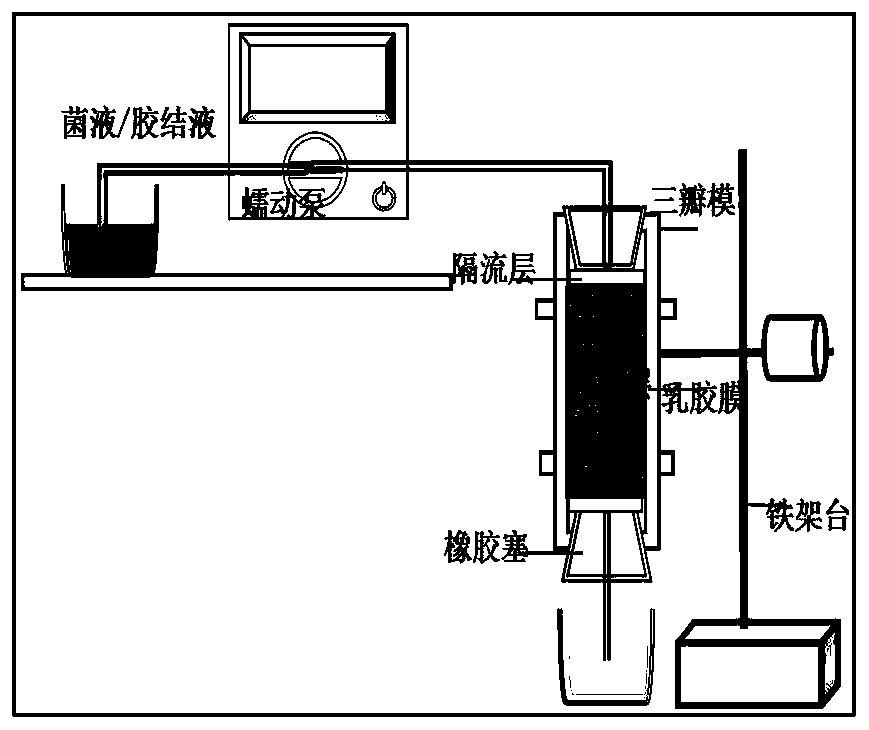
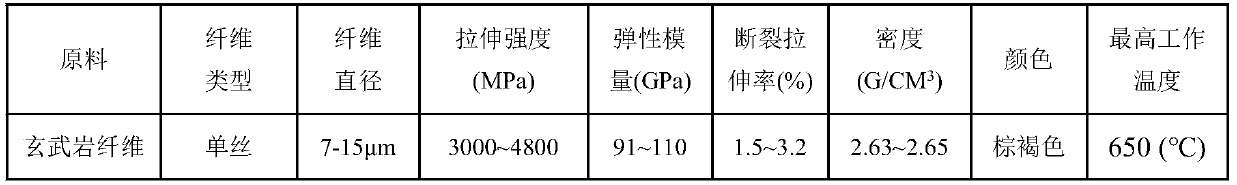
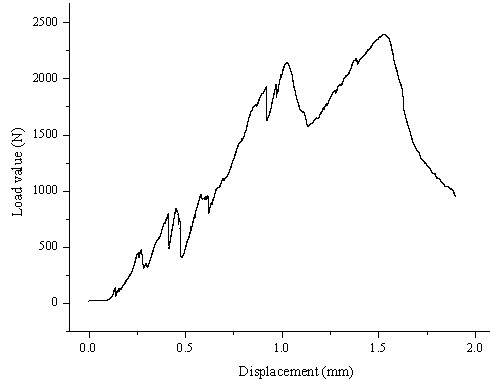
Method for improving mechanical properties of calcium sand through fiber reinforced and microbial curing
InactiveCN110685266AHigh strengthHigh tensile strengthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPeristaltic pumpMicrobiology
The invention provides a method for improving mechanical properties of calcium sand through fiber reinforced and microbial curing. The method comprises the following steps that coarse gravels are loaded at the bottom of a mold as a spacing layer, fibers and calcium sand are mixed and stirred evenly and are filled in a sample mold and tamped, then monofilament short-cut basalt fibers with the samelength are mixed with calcium sand according to the same proportion and then stirred evenly and filled in the sample mold and tamped, repeated for a plurality of times until the filling is finished, and laying up an isolating flow layer. The bacteria liquid is obtained through procedures applied to freeze-dried powder of bacillus pasteurii such as slope activation culture, glycerol tube retention,expansion culture bacillus pasteurii freeze-dried powder. In a mixture of loose fibers and sand, a peristaltic pump is used for firstly introducing bacterial liquid from the upper end of the mold andthen standing, after the bacterial liquid completely seeps, the mixed solution of urea and calcium chloride is introduced from the lower end of the mold, after the mixed solution is completely seeping out, standing is carried out for 2 hours, and repeated curing is carried out. According to the method, the unconfined compressive strength and the tensile strength of the calcium sand are improved,and the defect of brittle failure of the solidified body is solved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for bonding uranium tailing slag by using carbon-nano-material-immobilized mineralization bacterium
InactiveCN104561615AImprove adsorption capacitySolving Diffusion ProblemsProcess efficiency improvementHigh concentrationSlag
The invention discloses a method for bonding uranium tailing slag by using a carbon-nano-material-immobilized mineralization bacterium. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: culturing Sporosarcina pasteurii in a liquid culture solution to prepare a high-concentration bacterium solution with the concentration of 1-1.5*10<10> / ml; taking 100g of uranium tailing slag, spraying 5-20ml of 1mg / ml carbon nano material water solution, evenly mixing, and standing for 24 hours; adding 10-30ml of high-concentration bacterium solution, evenly mixing, standing for 2-3 hours, and sucking out the residual bacterium solution; adding 50ml of mineralization culture solution, culturing at 27-33 DEG C for 24 hours, and sucking out the mineralization culture solution to obtain the uranium tailing slag subjected to bonding treatment; repeating the process 5-10 times; and standing the uranium tailing slag after the last time for bonding treatment at 27-33 DEG C for 10-20 days, and bonding the uranium tailing slag into a block with certain permeation resistance and mechanical properties under the mineralization action of the microbe.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
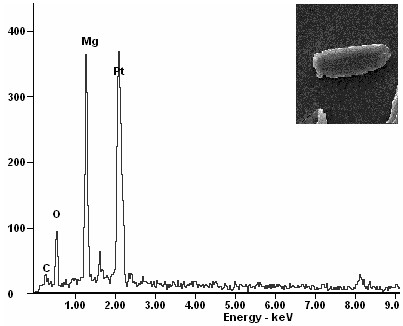
Microbial gelled material and method for forming magnesite by using same to glue sand grains
InactiveCN102531432AGood mechanical propertiesImprove performancePeristaltic pumpSporosarcina pasteurii
The invention discloses a microbial gelled material and a method for forming magnesite by using the microbial gelled material to glue sand grains. The microbial gelled material consists of basophilic microbial broth and mixed solution, wherein the volume ratio of the basophilic microbial broth and the mixed solution is 1:1, the basophilic microbial broth is Sporosarcina pasteurii broth, and the mixed solution is obtained by mixing equal volumes of urea and aqueous solution of MgCl2.6H2O. The method for forming the magnesite comprises formulating 70-90g sand in two grading of lower than 0.15mm and 0.15-0.30mm according to a Fuhlen densest packing method, placing the sand into a test mold, and alternately injecting the basophilic microbial broth in the microbial gelled material into the test mold from top to bottom by using a peristaltic pump. After continuous injection for 10-15 days, the sand grains in the test mold are glued to form the magnesite. The compressive strength of the magnesite is up to 4.0 MPa.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Microorganism repairing agent for repairing rock cracks and preparation method of microorganism repairing agent
InactiveCN112125592AReduce volumeReduce viscosityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismNutrient broth
The invention discloses a microorganism repairing agent for repairing rock cracks and a preparation method of the microorganism repairing agent. The microorganism repairing agent is prepared from thefollowing raw materials of: bacillus pasteurii and a cementing material, the cementing material is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 17-35 parts of urea, 32-64 parts of calcium chloride, 10-20 parts of nutrient broth, 1.5-2.5 parts of NaHCO3 and 9-12 parts of NH4Cl; the OD600 value of the bacillus pasteurii in the repairing agent is 0.6-1.2. The microbial remediation agent provided by the invention has the advantages of small size, low viscosity, high permeability, environmental friendliness and the like, and can quickly enter narrow rock cracks to fill and seal thecracks so as to solve the problem of rock crack leakage; the product of microbial mineralization is mainly calcite type calcium carbonate; the product has good stability and durability and is good incompatibility with a matrix material; the method that microorganisms are adopted to induce calcium carbonate precipitation is an eco-friendly technology and has the advantage of being green and environmentally friendly.
Owner:广西壮族自治区水利科学研究院
Microbial reinforcement liquid for slope reinforcement and preparation method and construction method of microbial reinforcement liquid
PendingCN112239672ANo pollution in the processMeet Green GovernancePlant growth regulatorsBiocideBacillus licheniformisNutrient broth
The invention discloses a microbial reinforcement liquid for slope reinforcement, a preparation method and a construction method thereof, and relates to a microbial reinforcement liquid. The adhesivebinder is a sodium ion solution, strains of the mineralized bacteria solution A are bacillus subtilis and bacillus licheniformis, the OD600 value is 1.0-1.5, the mineralized bacteria solution A comprises distilled water, 3-5g / L of nutrient broth, 35-45g / L of urea, 65-85g / L of calcium chloride and 10-20g / L of ammonium chloride, and strains of the mineralized bacteria solution B are sporosarcina pasteurii and rhodopseudomonas; the OD600 value ranges from 0.5 to 1.0; the mineralized bacteria nutrient solution B comprises distilled water, 4-6g / L of nutrient broth, 25-35g / L of urea, 45-65g / L of calcium chloride and 10-20g / L of ammonium chloride. The mineralization ability of bacillus subtilis and sporosarcina pasteurii is utilized to carry out ecological reinforcement on the expansive soil slope.
Owner:哈尔滨工大岩土工程技术有限公司
Urease-producing microbes and curing method for heavy metals in foundation
ActiveCN103289920AShorten the timeGood effectBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationWater insolubleBacillus lentus
Urease-producing microbes comprise sporosarcina antarctica UR53, sporosarcina koreensis UR47, sporosarcina sp. UR31 and bacillus lentus UR41 which have been preserved in China General Microbiology Center of Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms since 16th March, 2012, and respectively have the preservation numbers of CGMCC No.5916, CGMCC No. 5915, CGMCC No. 5913 and CGMCC No. 5914. A curing method for heavy metals in a foundation by using the urease-producing microbes comprises: placing the four microbes and microbes of sporosarcina pasteurii and terrabacter tumescens in a fermentation medium to carry out fermentation culture to obtain a bacterial liquid, adding a reaction solution urea into the bacterial liquid, then adding the bacterial liquid into a heavy-metal-containing solution to form a mixed solution so as to form a microbe-heavy-metal floccule in the mixed solution, and further to obtain water-insoluble heavy metal carbonates. The curing method for heavy metals in the foundation by using the urease-producing microbes has the advantages of short curing time, good effect, low cost and no secondary pollution to environment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Construction method for ecological protection of expansive soil slope by using phosphogypsum and microbial mineralization technology
PendingCN111424687ASatisfy ecological greeningReduce occupancyBacteriaHops/wine cultivationMicroorganismGrowth plant
The invention discloses a construction method for ecological protection of an expansive soil slope by utilizing phosphogypsum and a microbial mineralization technology, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) putting a bacillus pasteurianus into a culture medium to prepare a microbial solution, and mixing urea, calcium chloride and water to prepare a cementing solution; (2) mixing phosphogypsum, fly ash and soil into a mixture, then uniformly mixing and stirring the mixture, the microbial solution and the water, then adding the cementing solution and mixing with water toprepare an improved mixture slurry; and (3) spraying the improved mixture slurry to the surface of the side slope by adopting a wet spraying method, and covering a non-woven fabric and binding firmly.The method disclosed by the invention can meet the requirements of ecological greening of a slope, rainwater erosion resistance and shallow landslide prevention, can consume phosphogypsum, reduce theoccupation of cultivated land, and can promote plant growth with effective phosphorus. The low-cost culture medium is adopted for the microbial culture, so that the use cost is reduced, the microorganisms-modified phosphogypsum can solidify harmful elements, and the pollution to the environment is reduced.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Building garbage concrete-brick mixed self-repairing concrete and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses building waste concrete-brick mixed self-repairing concrete and a preparation method thereof. The preparation raw materials of the self-repairing concrete comprise a concrete and self-repairing recycled concrete-brick mixture, and the self-repairing recycled concrete-brick mixture accounts for 15%-45% of the self-repairing concrete in percentages by volume; the volume ratioof self-repairing recycled coarse aggregates to self-repairing recycled brick aggregates is 1-4: 1-3; the self-repairing recycled coarse aggregates are prepared by impregnating the recycled coarse aggregates with bacillus pasteurii liquid, and the self-repairing recycled brick aggregates are prepared by impregnating recycled brick aggregates with the bacillus pasteurii liquid; the OD value of thebacillus pasteurii liquid is 1-1.3; in terms of mass percentage, the mass content of the bacillus pasteurii liquid accounts for 0.065% of the recycled coarse aggregates, and the mass content of the bacillus pasteurii liquid accounts for 0.085% of the brick aggregates. The building waste concrete-brick mixed self-repairing concrete has the advantages of being high in repairing efficiency and beneficial to recycling application of construction wastes.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Microorganism induction silty-fine sand consolidating soft soil roadbed ecological improvement method
InactiveCN111893988AAchieving enhanced processingGood consolidationBacteriaRoadwaysMicroorganismEngineering
The invention provides a microorganism induction silty-fine sand consolidating soft soil roadbed ecological improvement method. Microorganism adopts bacillus pasteurii, the strain initially is freeze-dried powder, and bacteria activation and culture are carried out in a culture solution to obtain a concentrated solution of bacillus pasteurii; then silty-fine sand is mixed into soft soil, the mixing ratio of silty-fine sand is 10-20%, and the silty-fine sand provides large-size aggregate for a soft soil road; and the concentrated solution of bacillus pasteurii is mixed into a nutrient solutionand injected into a sandy roadbed, and then a consolidation solution is injected until the roadbed reaches an expected goal. The microorganism induction silty-fine sand consolidating soft soil roadbedecological improvement method applies interdisciplinary subjects, and biochemical technology is used for treating soft soil roadbed, so that the problems of high pollution, high energy consumption and the like of traditional physical and chemical methods for treating roadbeds are solved, the strengthen treatment on the soft soil roadbed can be realized, and the problems of environmental pollutionand energy consumption are reduced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing high-strength microbial mortar using urease-producing microorganisms
ActiveCN103173376BStrong ability to produce ureaseHigh urease activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEpoxyBacillus lentus
Urease-producing microbes including Sporosarcina antarctica U R 5 3, Sporosarcina koreensis UR47, Sporosarcina sp. UR31 and Bacillus lentus UR41 were preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on March 16, 2012, with the preservation numbers of CGMCC No.5916, CGMCC No.5915, CGMCC No.5913 and CGMCC No.5914 respectively. The method for preparing high-strength microbial mortar by using the urease-producing microbes comprises the following steps of: carrying out fermentation culture on the above four microbes and microbes including Sporosarcina pasteurii and Terrabacter tumescens in a fermentation culture medium to obtain a bacterial solution; and filling the bacterial solution, a fixative solution and a gelling solution into a sand particle system in batches to form microbial mortar of which the highest strength can reach 55MPa. The mechanical properties of the microbial mortar are superior to those of a cement base material; compared with a cement lime material with equivalent strength, the microbial mortar is higher in splitting tensile strength; the rigidity of the microbial mortar is similar to that of cement lime mixed mortar but far smaller than that of concrete; the fatigue load tolerance and cyclic loading capacity of the microbial mortar are higher than those of the cement base material; and an artificial sandstone is an inorganic material, and is not easy to age like organic materials including epoxy resin and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for regulating and controlling grain size of microbial-induced deposited calcite
InactiveCN110951816AEfficient captureStable in natureMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
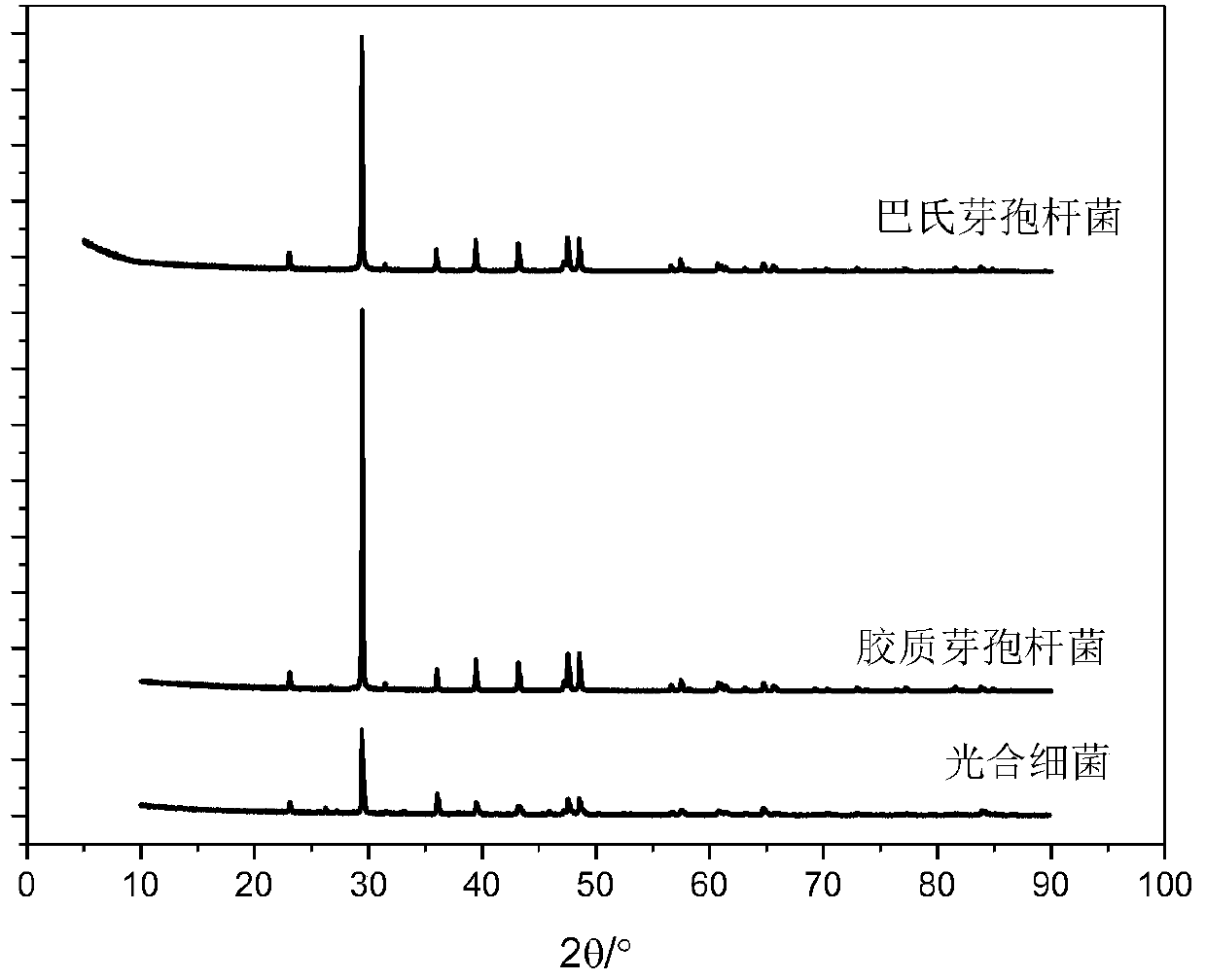
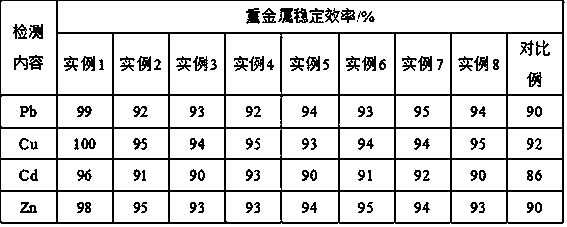
The invention provides a method for regulating and controlling the grain size of microbial-induced deposited calcite. The method includes the following steps: 1) inoculating endospores of Bacillus mucilaginosus or endospores of photosynthetic bacteria or endospores of Bacillus pasteurii to corresponding culture mediums separately so as to obtain a concentrated bacterial solution of Bacillus mucilaginosus or a concentrated bacterial solution of photosynthetic bacteria or a concentrated bacterial solution of Bacillus pasteurii separately; 2) adding a calcium source and urea to the concentrated bacterial solution of Bacillus mucilaginosus or the concentrated bacterial solution of photosynthetic bacteria or the concentrated bacterial solution of Bacillus pasteurii obtained in the step 1), andperforming still standing; and 3) after production of precipitates, washing the precipitates, performing filtration and drying, performing drying until constant weight, and then analyzing the grain size so as to prepare the calcite with a grain size of 20-60 nm. The microbial method has the characteristics of high efficiency and environmental protection, the grain size of the calcite can be adjusted according to needs, the formed calcite mineral has stable properties, and effective capture and utilization of carbon dioxide can be achieved in the process, so that the greenhouse effect is sloweddown.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Preparation method of chitosan immobilized microbial urease in-situ reinforced recycled aggregate
ActiveCN113307527AEvenly distributedDensely distributedSolid waste managementBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Composite soil passivating agent
InactiveCN108130092AReduce exchangeable heavy metal contentHarm reductionContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersSlagPhospholipid
The invention discloses a composite soil passivating agent, belonging to the technical field of heavy metal contaminated soil remediation. The composite soil passivating agent is prepared through thefollowing steps: crushing steel slag, carrying out sieving so as to obtain steel slag powder, mixing the steel slag powder and sulfuric acid with a mass ratio of 1: (30-50) under stirring, and carrying out filtering, washing and drying so as to obtain modified steel slag powder; dropwise adding octenyl succinic anhydride into an Arabic gum liquid, carrying out a reaction under stirring so as to obtain a first mixed solution, dropwise adding a sodium hydroxide solution into the first mixed solution, adjusting a pH value of the first mixed solution, carrying out heating and a reaction under stirring so as to obtain a second mixed solution, dropwise adding hydrochloric acid into the second mixed solution, and adjusting a pH value of the second mixed solution so as to obtain a modified Arabicgum liquid; and subjecting the modified steel slag powder, a Bacillus pasteurii solution, urea, the modified Arabic gum liquid, citric acid, malic acid, Carbomer, phospholipid and a protein liquid tomixing under stirring so as to obtain the composite soil passivating agent. The composite soil passivating agent provided by the invention has excellent heavy metal removal effect.
Owner:郭舒洋
Protection method for improving soil slope to resist rainwater erosion through phosphogypsum and microorganisms
PendingCN111424689AReduce occupancyPromote growthBacteriaHops/wine cultivationSporosarcina pasteuriiBacilli
The invention provides a protection method for improving a soil slope to resist rainwater erosion through phosphogypsum and microorganisms. The protection method is characterized by including the steps that (1), bacillus pasteurii is put in a culture medium, a microorganism solution is prepared, urea, calcium chloride and water are mixed, and cementing liquid is prepared; (2), the mixture, the microorganism solution and water are mixed and stirred uniformly, the cementing liquid and water are added, the materials are mixed, and improved mixture slurry is prepared; and (3), a wet spraying method is adopted for spraying the improved mixture slurry onto the surface of the slope twice, then the improved mixture slurry and grass seeds are stirred uniformly, the material is sprayed to the surface of the slope at a time, the slope is covered with non-woven fabric, the non-woven fabric is firmly bound, and water is sprayed to the slope every day for maintenance. By means of the method, the protection requirements of rainwater wash resistance and slope ecological greening of the soil slope made of loess, gravelly soil and the like can be met, the phosphogypsum can be consumed, occupation ofcultivated land is reduced, and available phosphorus can promote plant growth. By means of the phosphogypsum improved with the microorganisms, harmful elements can be cured, and environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recycled concrete and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111320429AReduce crackingHigh compressive strengthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFiberMechanical crushing
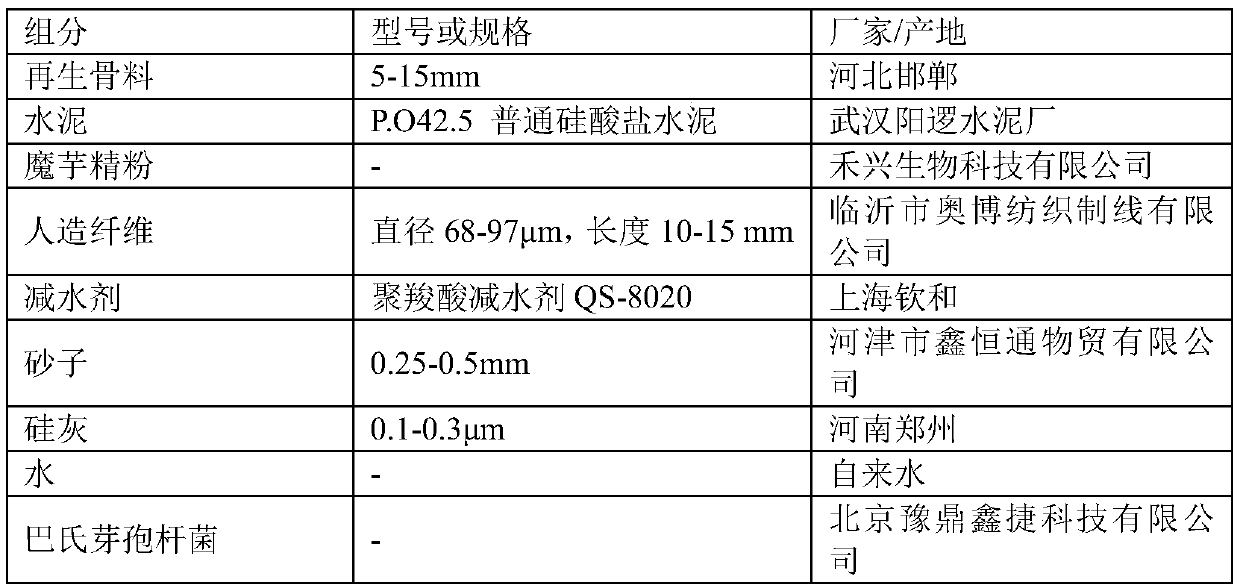
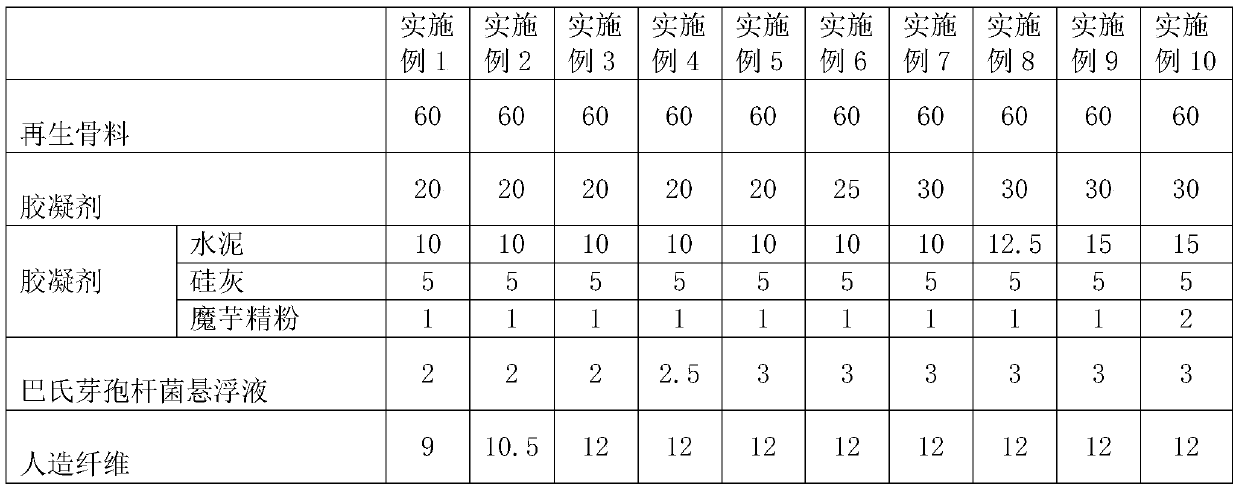
The invention discloses recycled concrete and a preparation method thereof. The recycled concrete is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by mass: 60 to 80 parts of recycled aggregate, 9to 12 parts of artificial fiber, 1 to 2 parts of water reducing agent, 15 to 20 parts of water, 30 to 35 parts of sand, 20 to 30 parts of gelatinizing agent, 1 to 2 parts of urea, 1 to 2 parts of calcium nitrate and 2 to 3 parts of bacillus pasteurii suspension with the concentration of 4 to 6 * 10 < 6 > / mL. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mechanical crushing, airflow blowing, bacillus pasteurii mineralization deposition, konjac powder coating and raw material mixing. The recycled concrete can be used for construction and has the advantages of being good in compressive strength and low in water absorption rate; in addition, the preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantage of easiness in production.
Owner:陕西百固建材有限公司
Concrete crack bioremediation method
PendingCN113530281AEasy to fixEasy to operateBuilding repairsEnvironmental engineeringSporosarcina pasteurii
The invention provides a concrete crack bioremediation method. The concrete crack bioremediation method comprises the following steps that a bacillus pasteurii solution, a urea solution and a soluble calcium salt solution are sequentially injected into a concrete crack, operation is stopped after excessive liquid seeps from the concrete crack, and the operation is repeated after 1 hour, and therefore the concrete crack is repaired. According to the method, urea is decomposed by using bacillus pasteurii, and then calcium carbonate precipitates are generated in the presence of the calcium source, so that concrete cracks are repaired. Bacteria, urea and soluble calcium salt are used as raw materials for producing calcium carbonate, and the raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain. The bacterial remediation process is simple and easy to operate, and the calcium carbonate production process is a biological process and is environmentally friendly.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Self-repairing concrete and recycled aggregate assembled reinforced concrete coupling beam, and preparation methods thereof
InactiveCN111484284APlay a resourceful roleImprove repair effectGirdersJoistsMicroorganismEarthquake resistance
The invention discloses self-repairing concrete and a recycled aggregate assembled reinforced concrete coupling beam, and preparation methods thereof; the self-repairing concrete is microorganism self-repairing concrete, and is composed of concrete ingredients, a recycled aggregate and a bacillus pasteurii liquid according to the volume percentage; the volume mixing amount of the recycled aggregate is 20-30% of the total volume of the microbial self-repairing concrete, and the volume mixing amount of the bacillus pasteurii liquid is 32-38% of the total volume of the microbial self-repairing concrete. The recycled aggregate assembled reinforced concrete coupling beam is high in repairing efficiency, high in environmental friendliness, high in overall strength, high in anti-seismic propertyand easy to operate, and achieves the effects of construction waste recycling and good structural performance.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
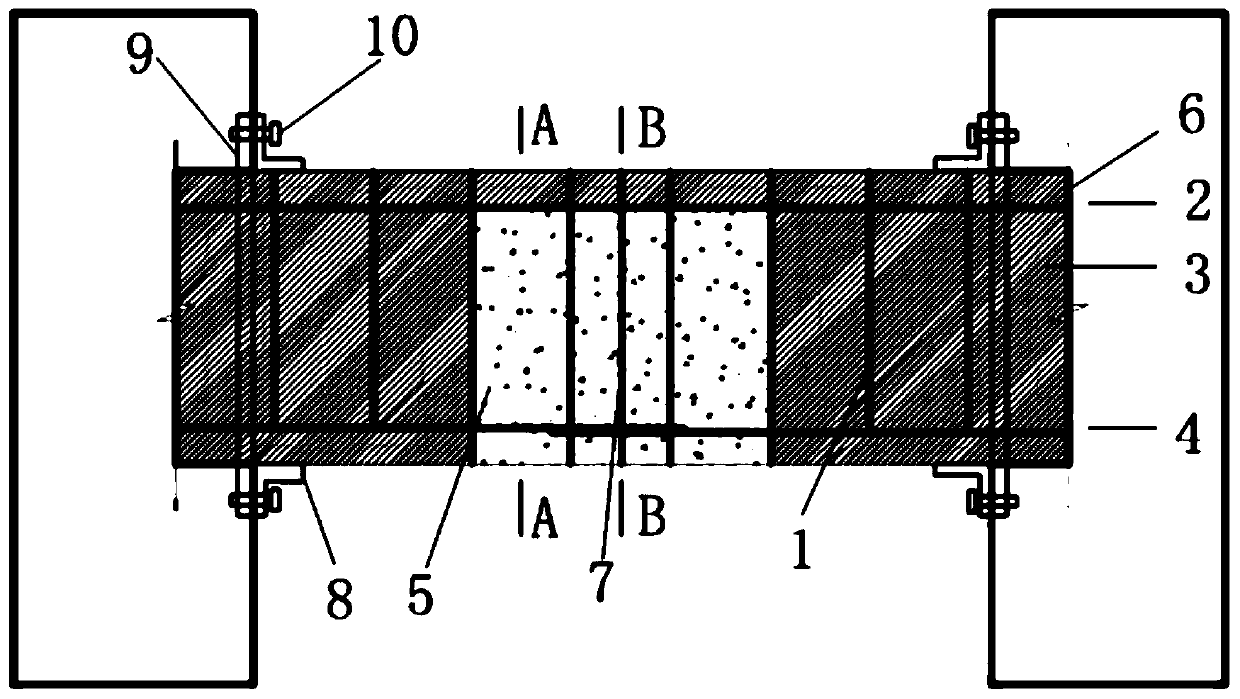
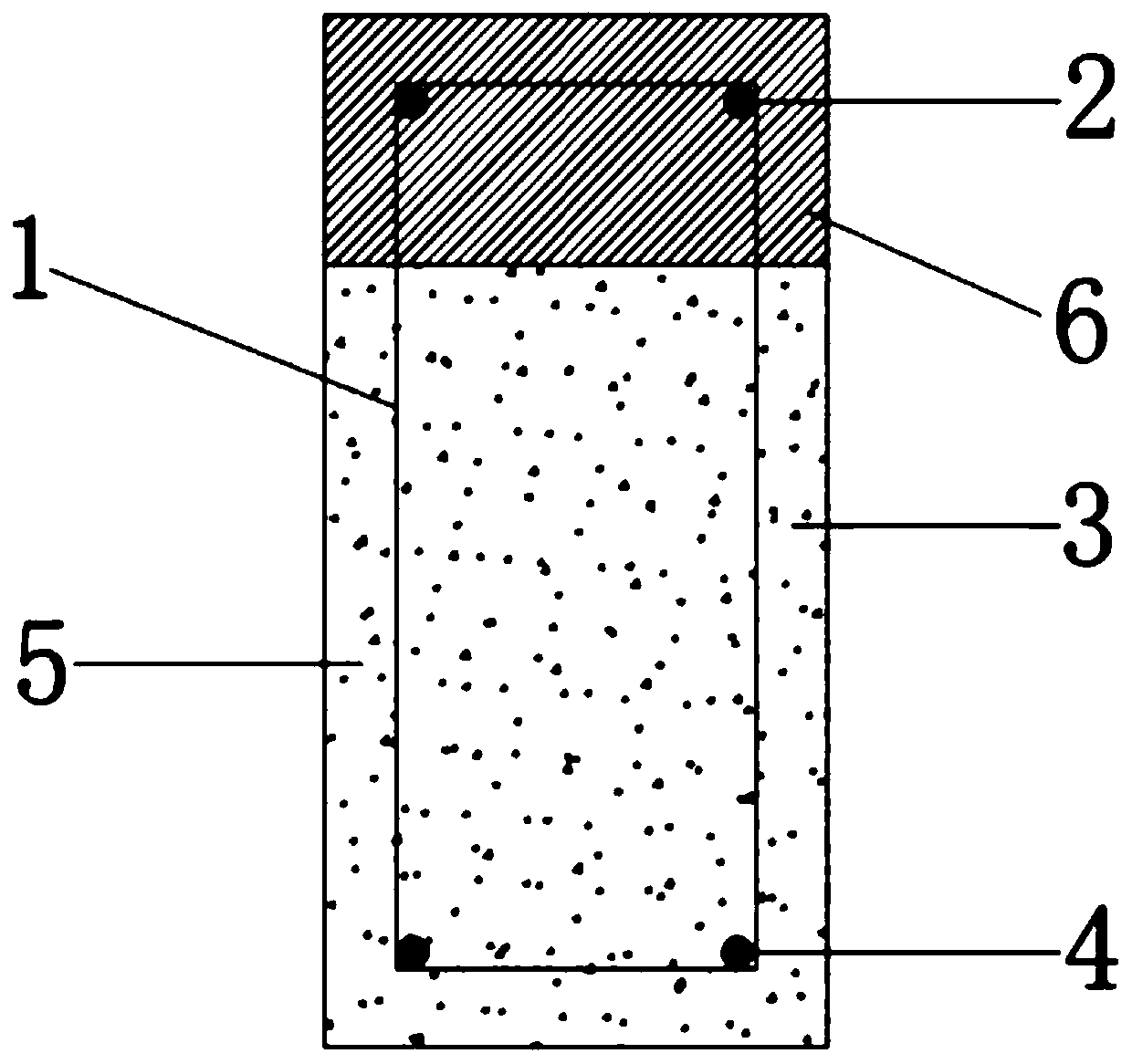
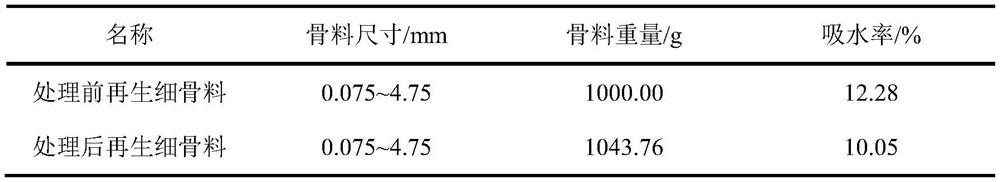
Method for reinforcing recycled fine aggregate by bacillus pasteurii DSM33
The invention provides a method for reinforcing recycled fine aggregate by using bacillus pasteurii DSM33. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a proliferation culture medium, dropwiseadding a NaOH solution and an HCl solution to regulate the pH value to 9.0-9.5, sterilizing, cooling to room temperature, inoculating bacillus pasteurii, and carrying out shake culture at 28-32 DEG Cat the rotating speed of 130 rpm to obtain a proliferated bacterial culture solution; adding dried recycled fine aggregate into the proliferated bacterial culture solution, and standing at the temperature of 28-32 DEG C for culture; taking out the soaked recycled fine aggregate, putting into a precipitation culture medium, and standing at the temperature of 28-32 DEG C for culture; completing theoperation, and drying the recycled fine aggregate to obtain primarily reinforced recycled fine aggregate; and the aggregate subjected to primary reinforcement can be repeatedly reinforced. The weightof the recycled fine aggregate prepared by the method is increased, and the water absorption rate is remarkably reduced. Recycled mortar prepared from the reinforced recycled fine aggregate has significantly improved compression strength and flexural strength, and significantly improved shrinkage performance and carbonization resistance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com