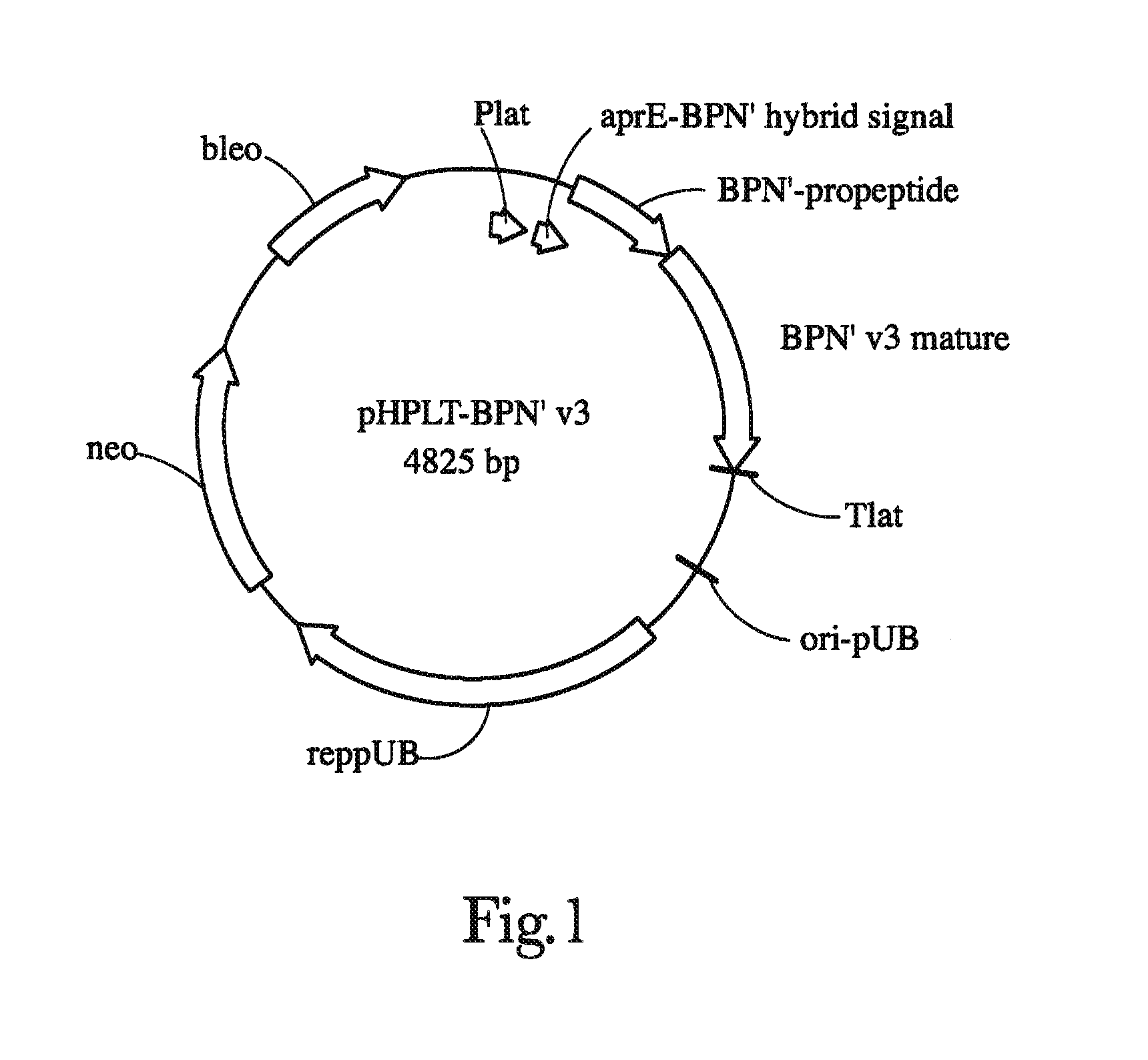
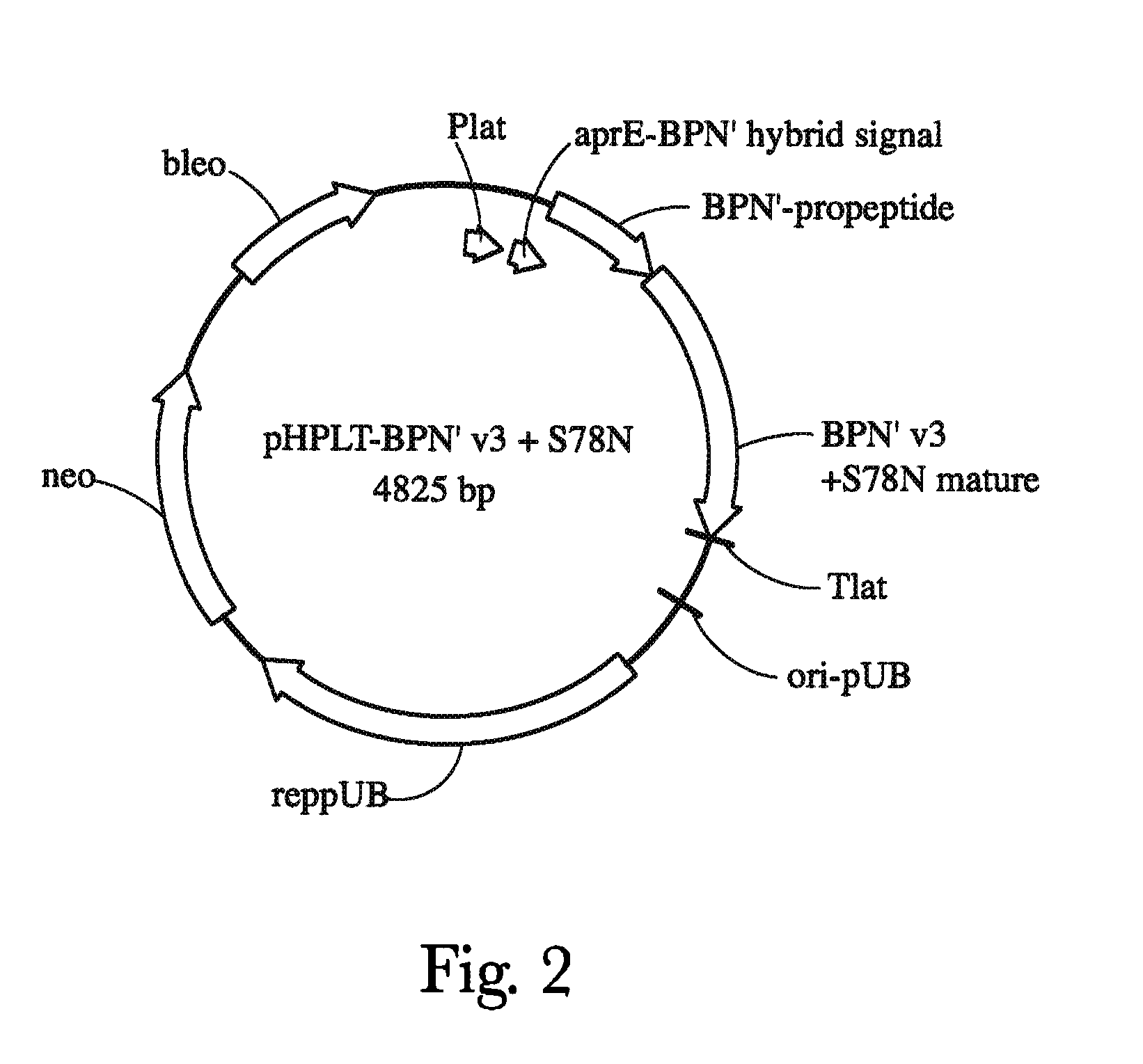
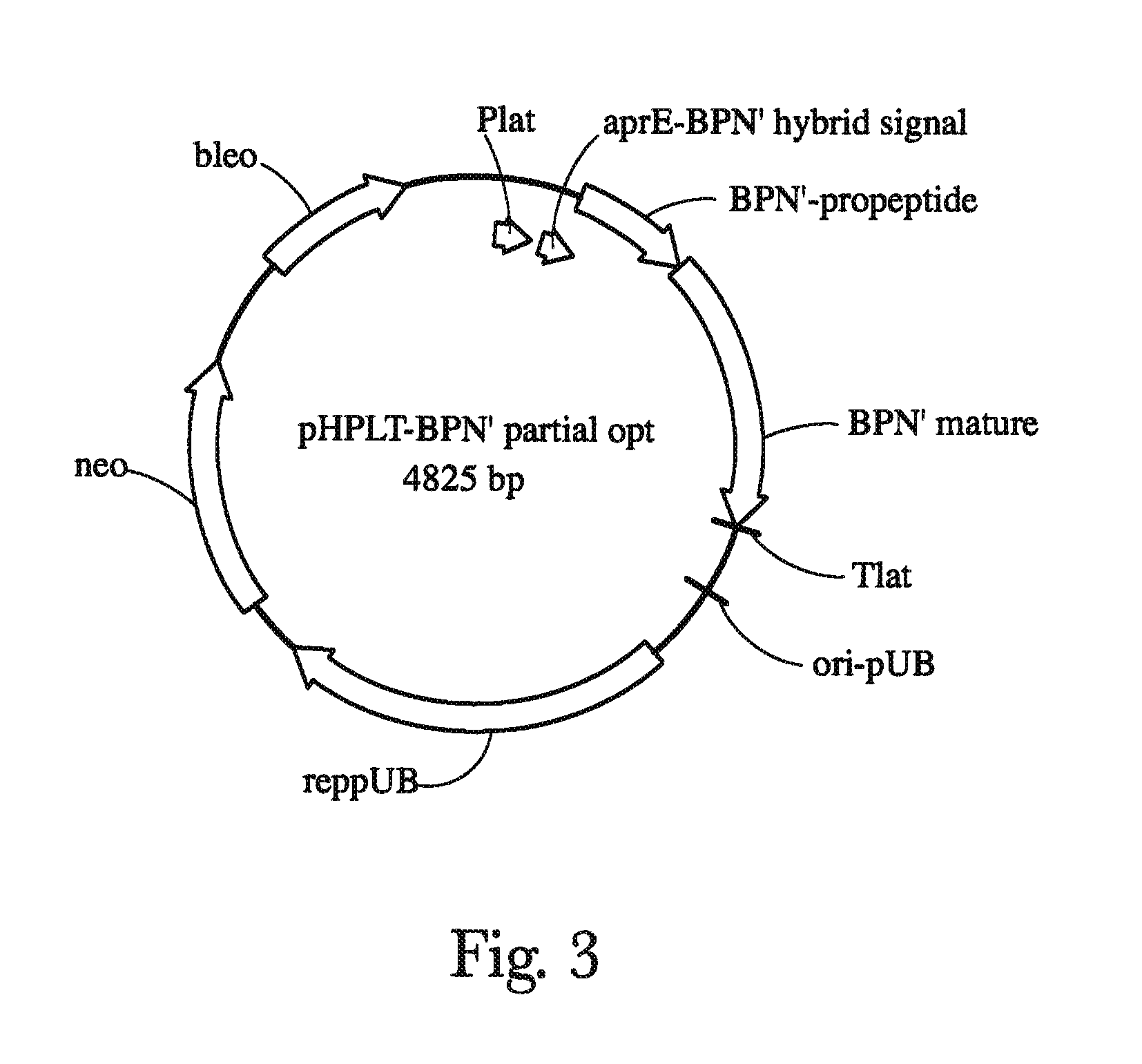
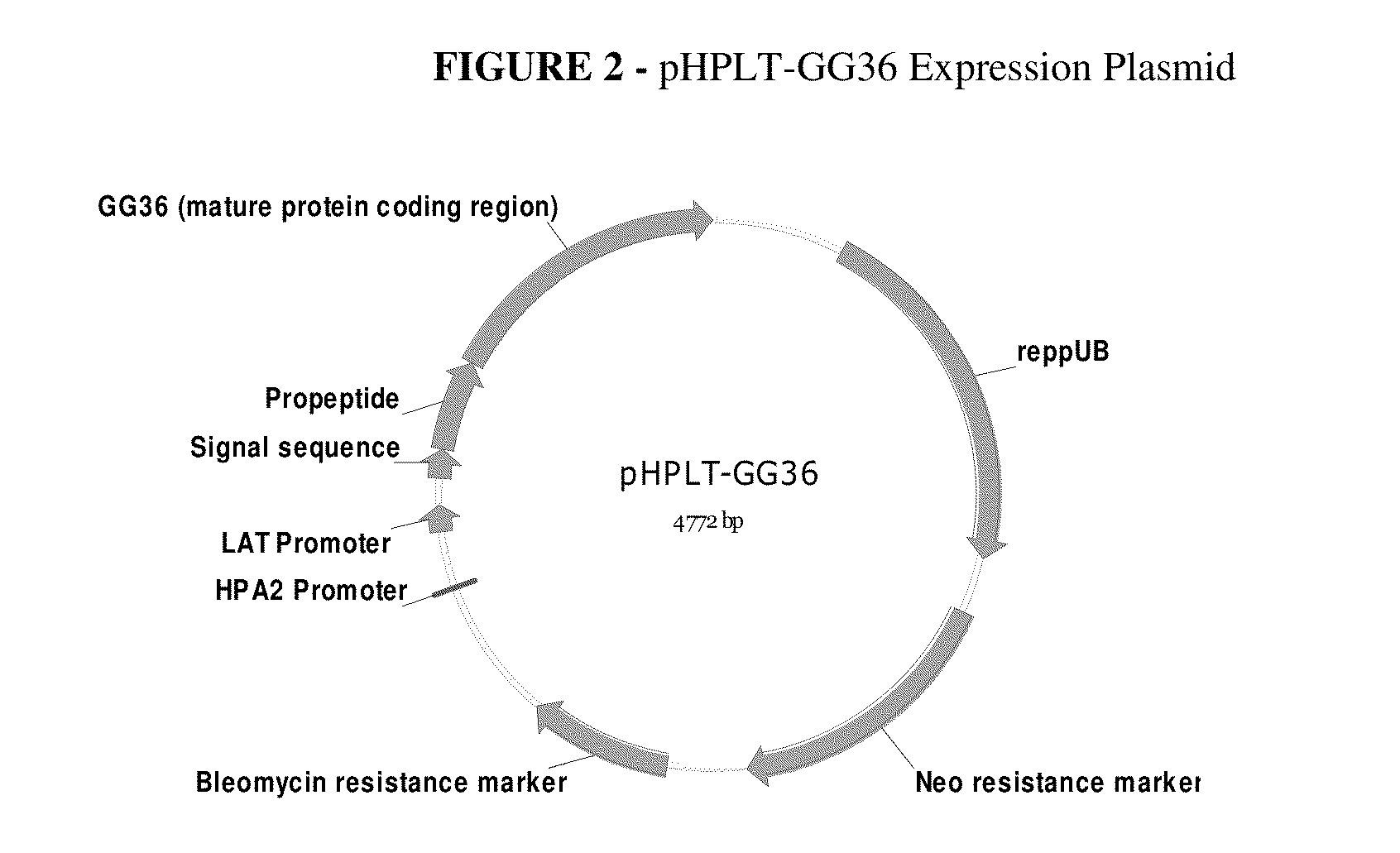
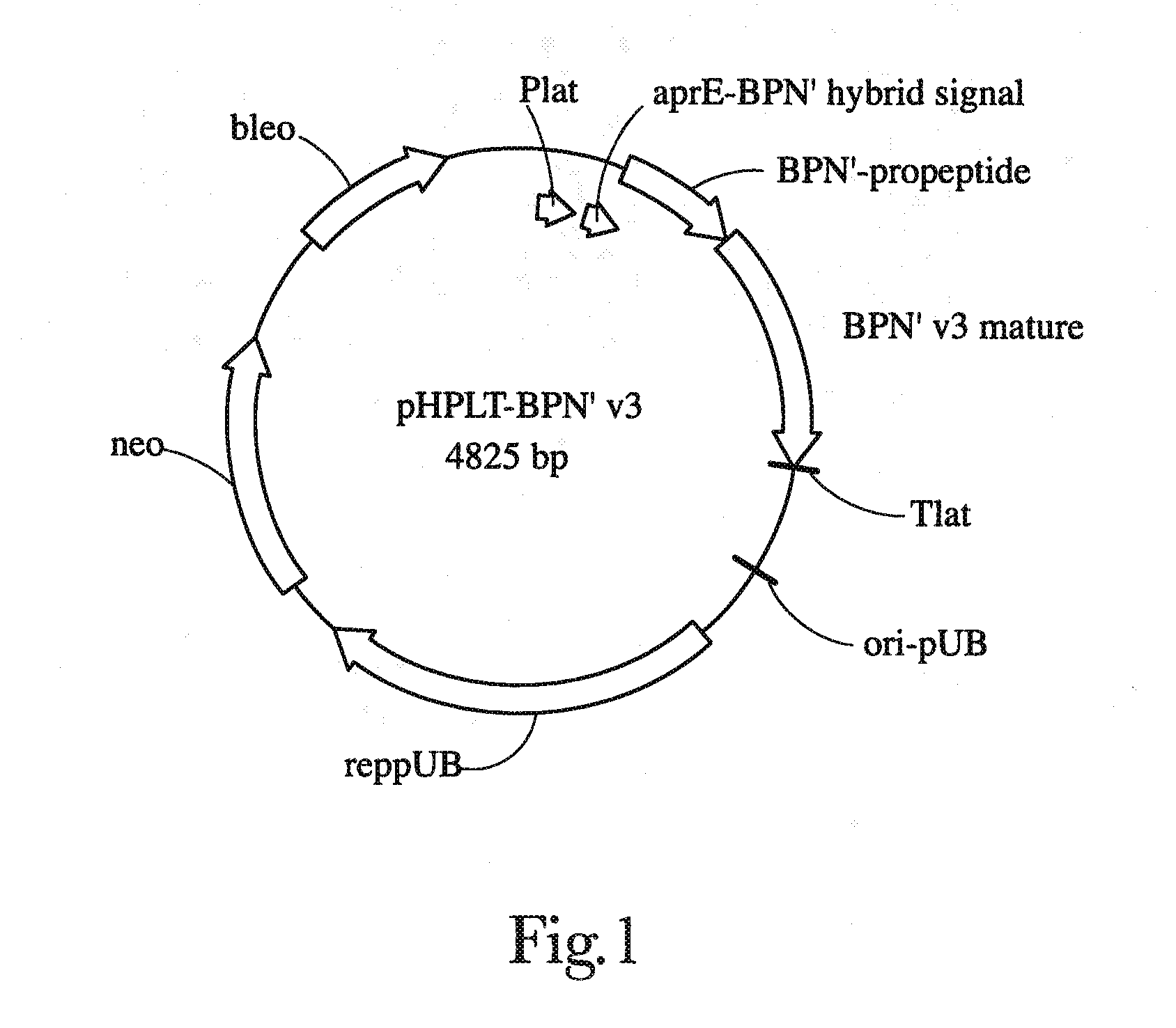
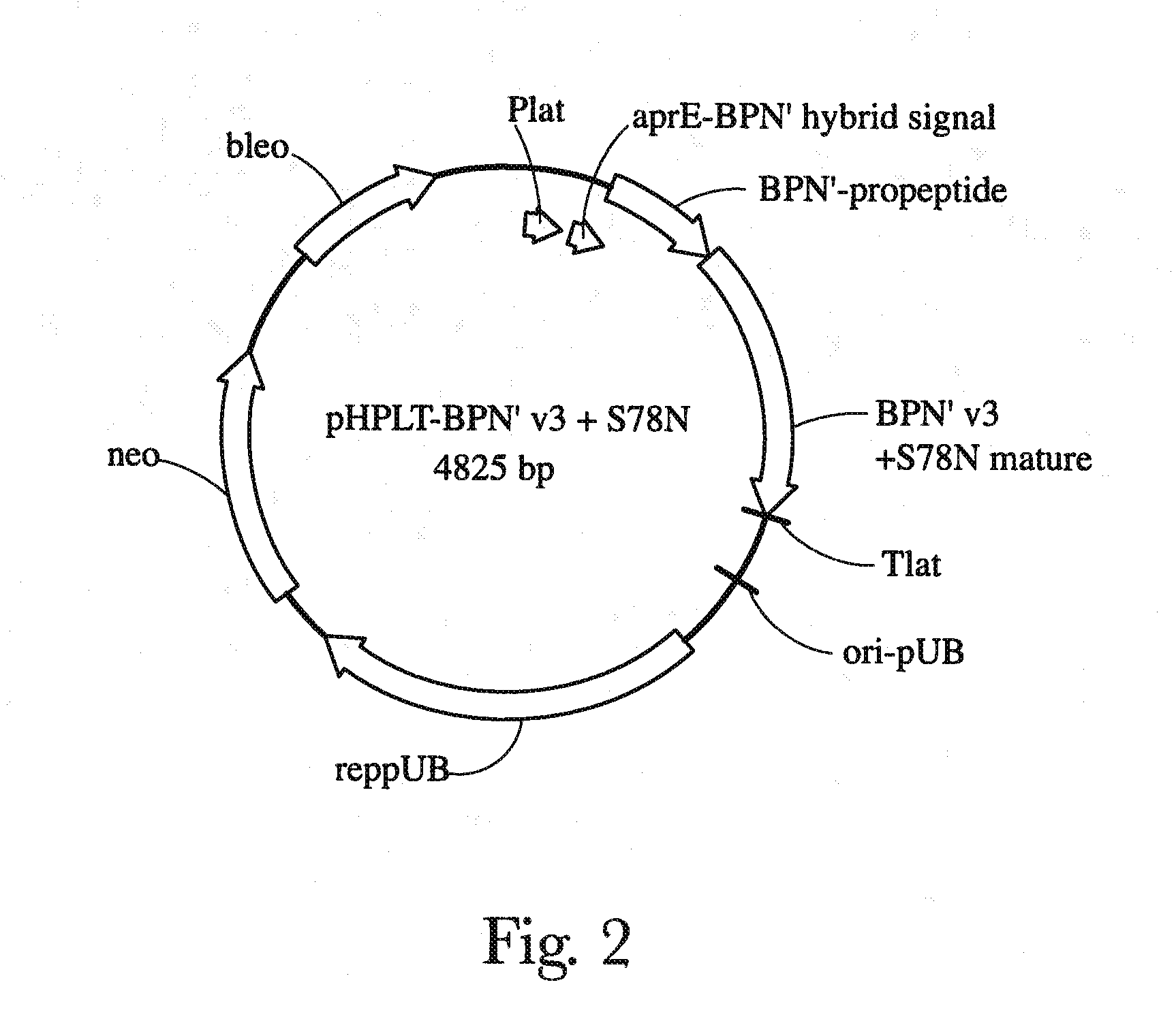
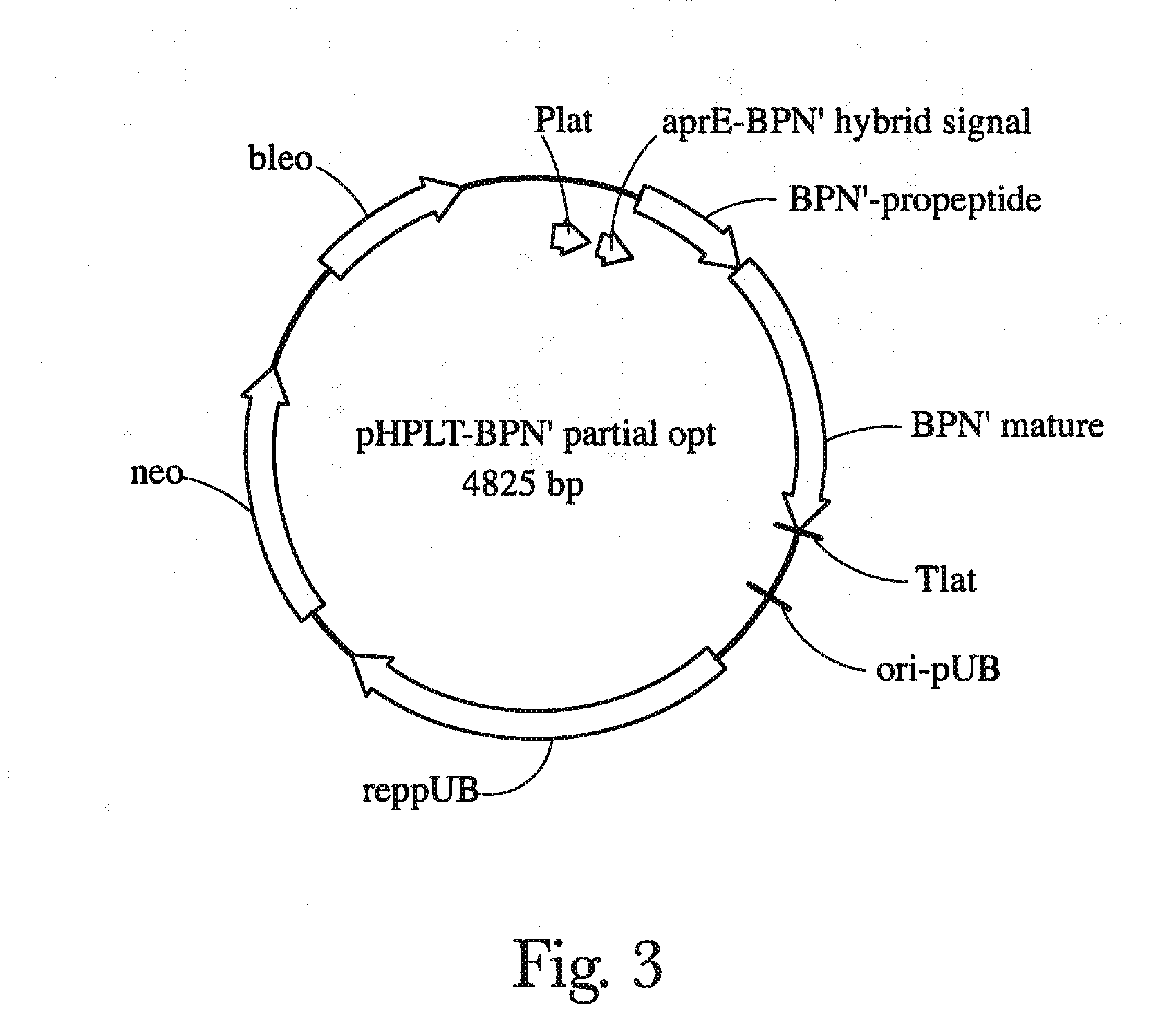
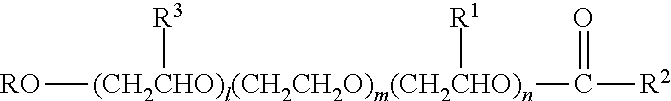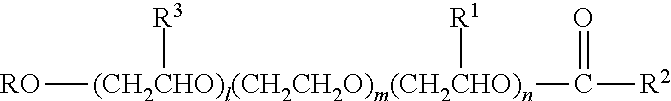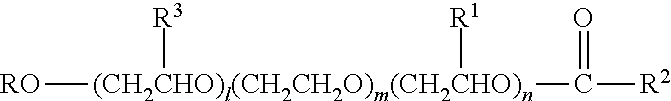Patents
Literature
54 results about "Bacillus lentus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
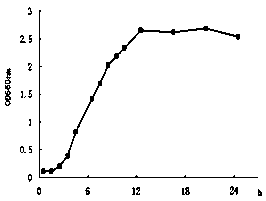
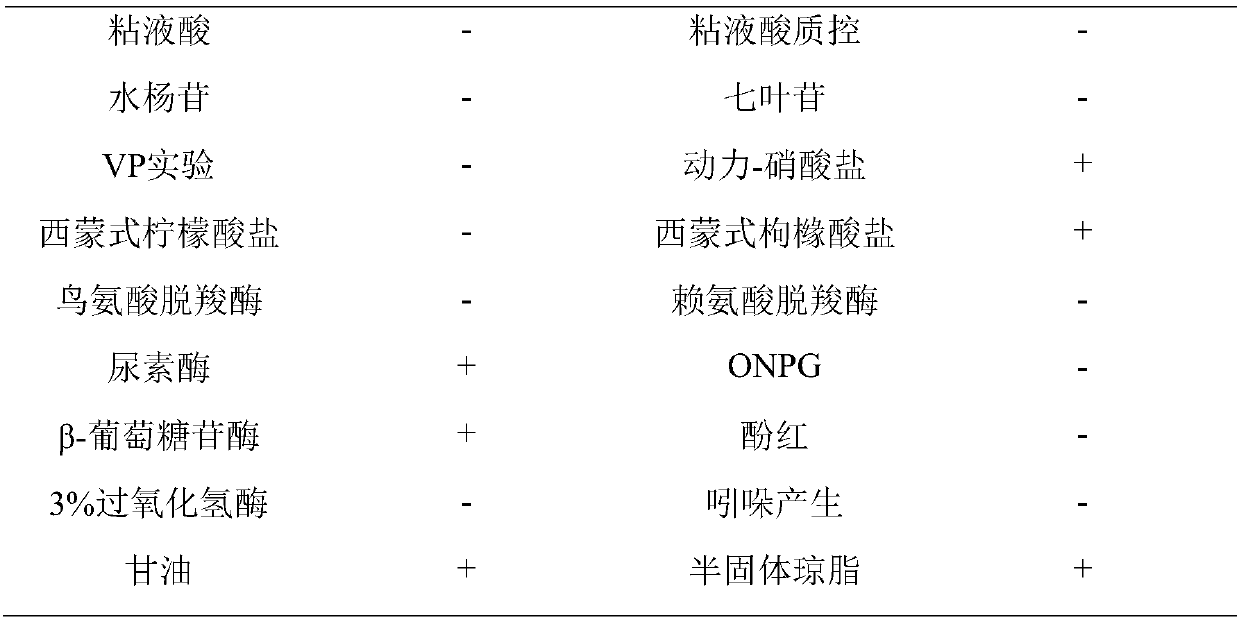
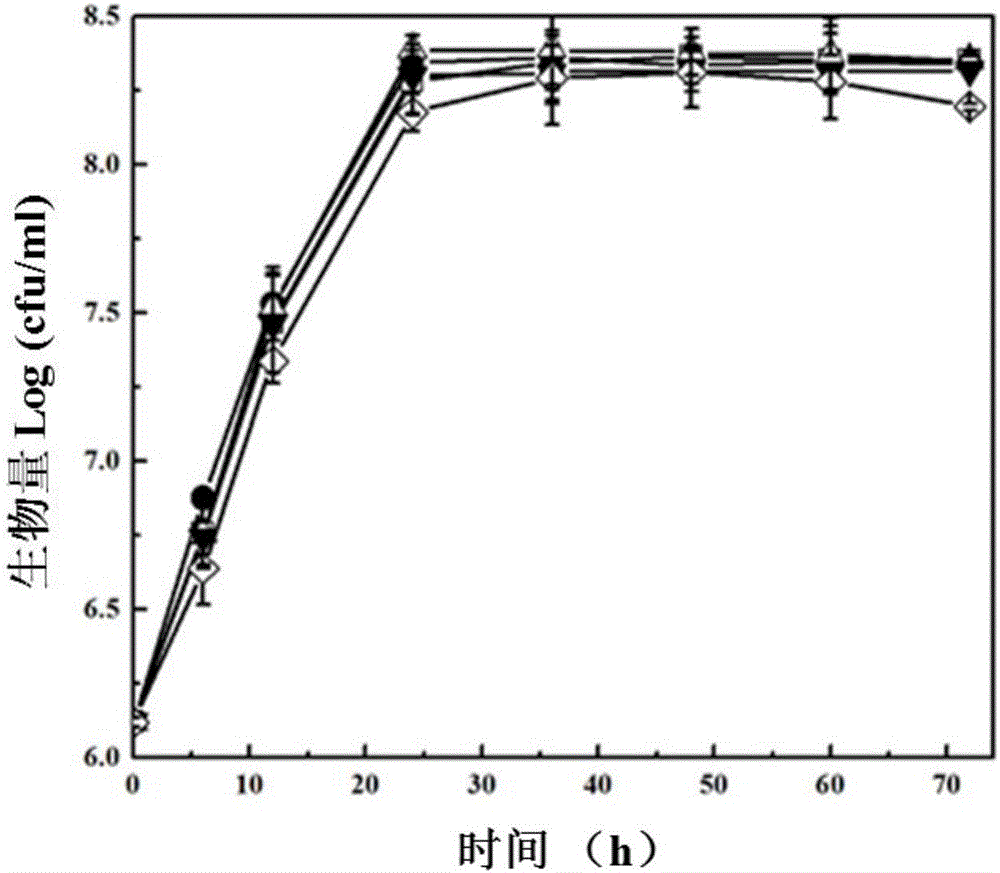
A species of strictly aerobic Gram-positive, rod shaped bacteria assigned to the phylum Firmicutes. This species is motile, spore forming, catalase positive, urease positive, indole negative, produces hydrogen sulfide, reduces nitrate, and hydrolyzes starch and esculin but not casein or gelatin. B lentus is found in soil, marine waters and sediments and is resistant to nalidixic acid and streptomycin and utilized in the biotechnology industry as a sources of alkaline proteases.
Fabric and home care products
ActiveUS20110237487A1Improve freshnessHydrolasesNon-surface-active detergent compositionsMedicineBacillus lentus
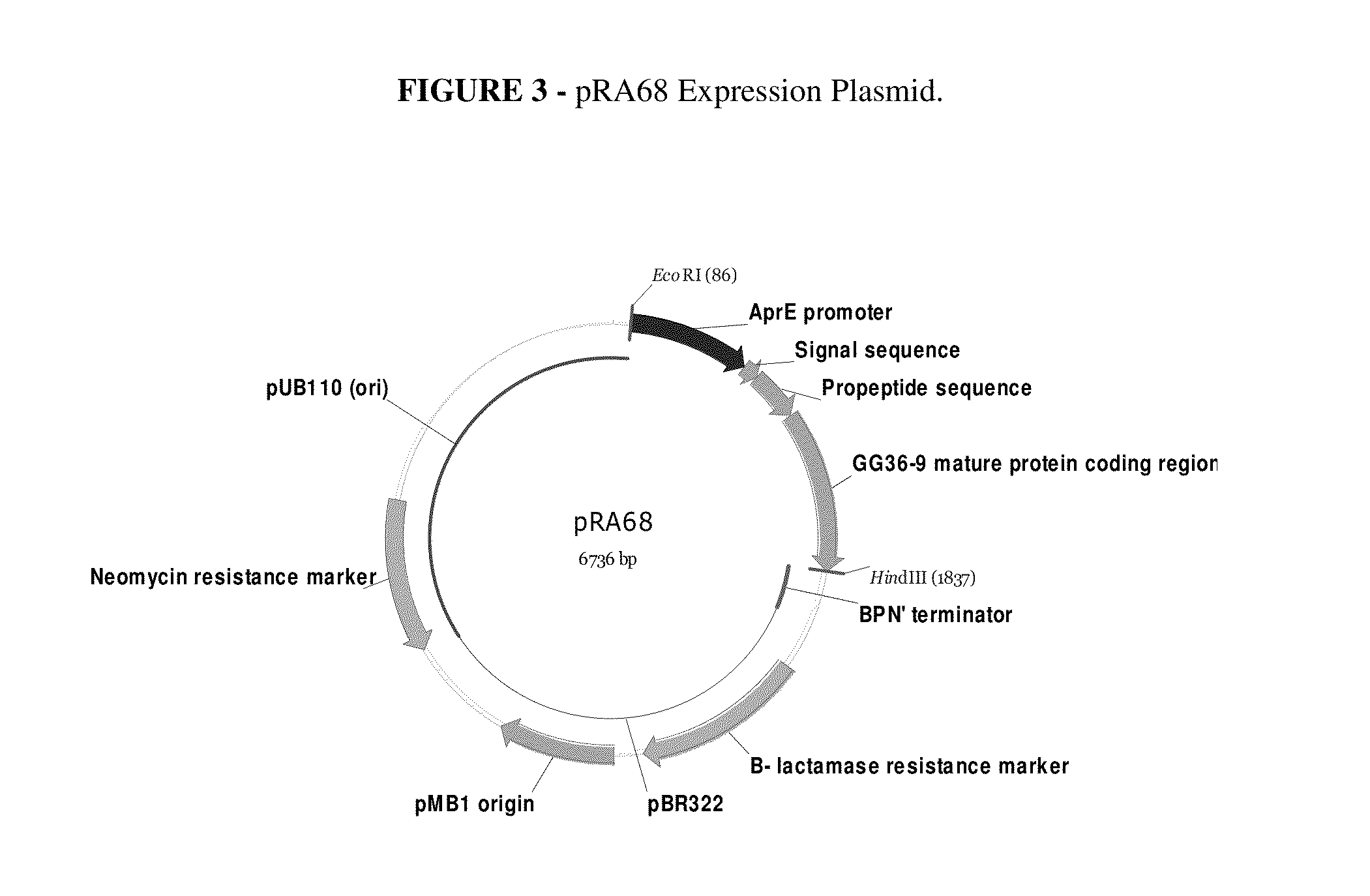
This invention relates to fabric and home care products comprising one or more cold water proteases and processes for making and using such products. Such compositions provide improved cleaning and freshness. Such cold water proteases may be derived from parent enzymes, including BPN′ subtilisin and subtilisin derived from Bacillus lentus, by substitution, insertion and / or deletion of one or more of the parent enzymes' amino acids.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Consumer products
InactiveUS20130123162A1Non-surface-active detergent compositionsDetergent materialsBacillus lentusProteinoid
This invention relates to consumer products comprising proteases, particularly cold water proteases and processes for making and using such products. Such consumer products provide improved cleaning, whiteness and / or freshness. Such proteases are derived from a parent enzyme, for example Bacillus lentus, by substitution, insertion and / or deletion of one or more of the parent enzymes' amino acids.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
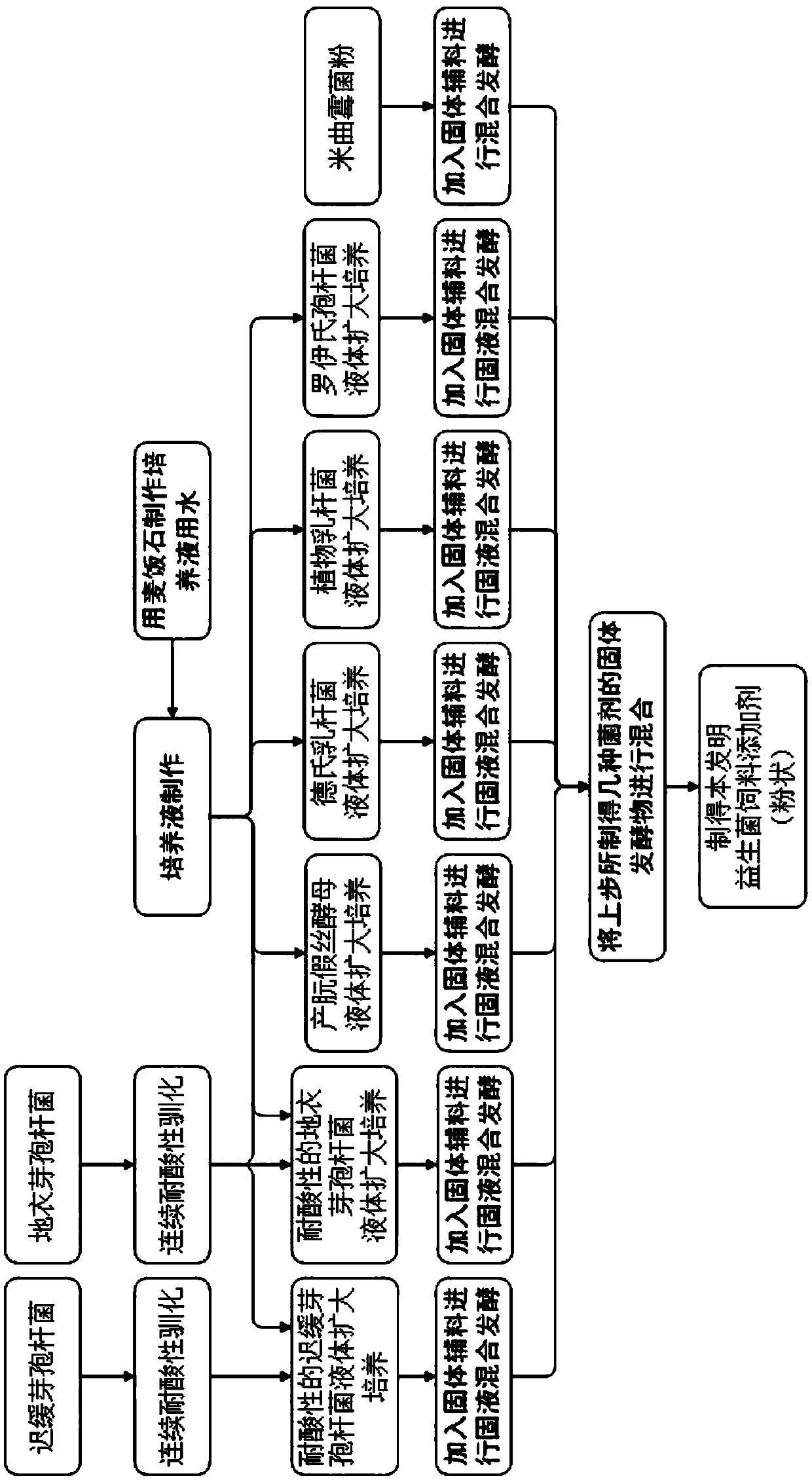
Bacillus lentus and method for generating by inducing bacillus lentus for reinforcing foundation
InactiveCN103266070AShort duration of intensityGood effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus lentusTwo step
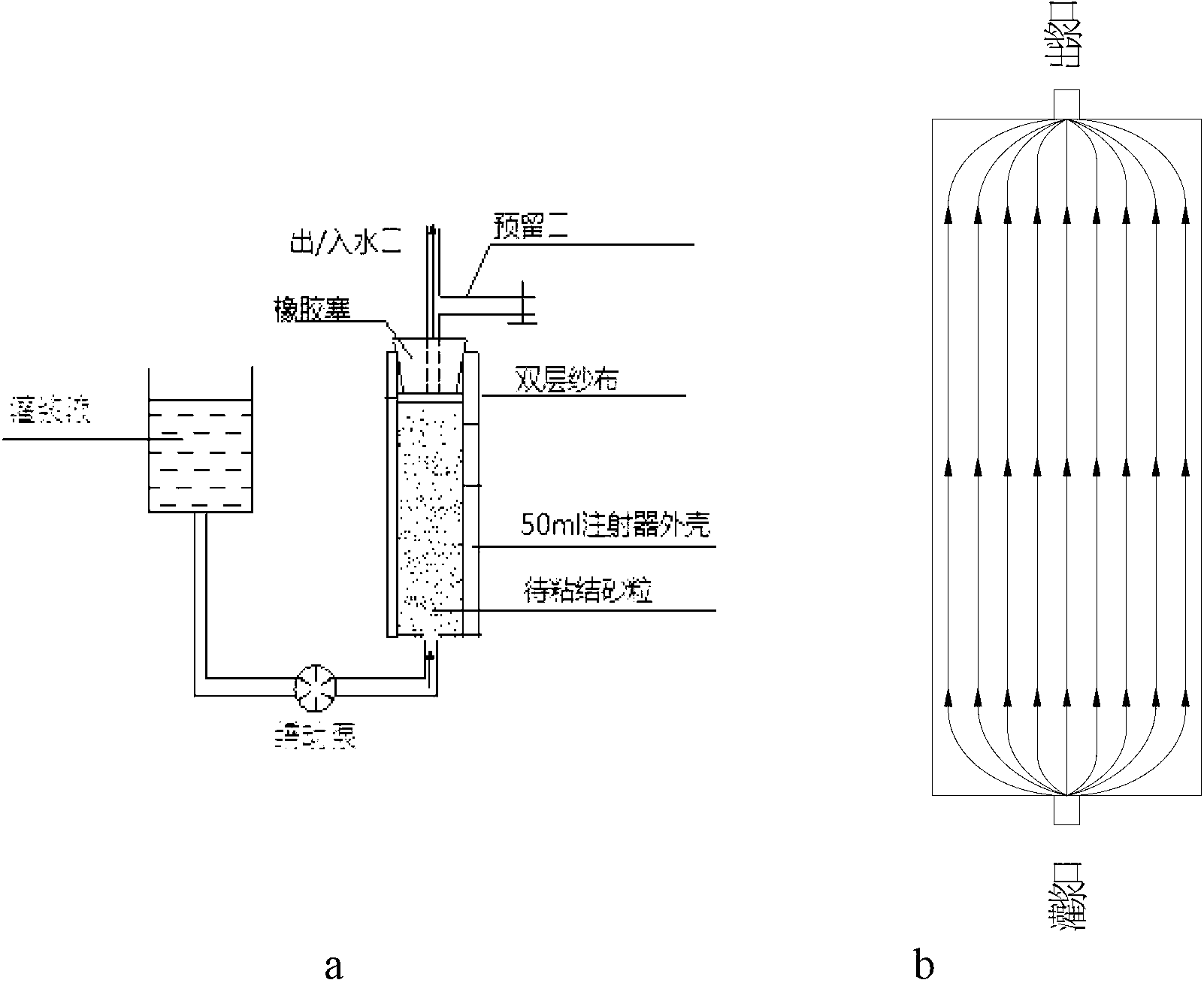
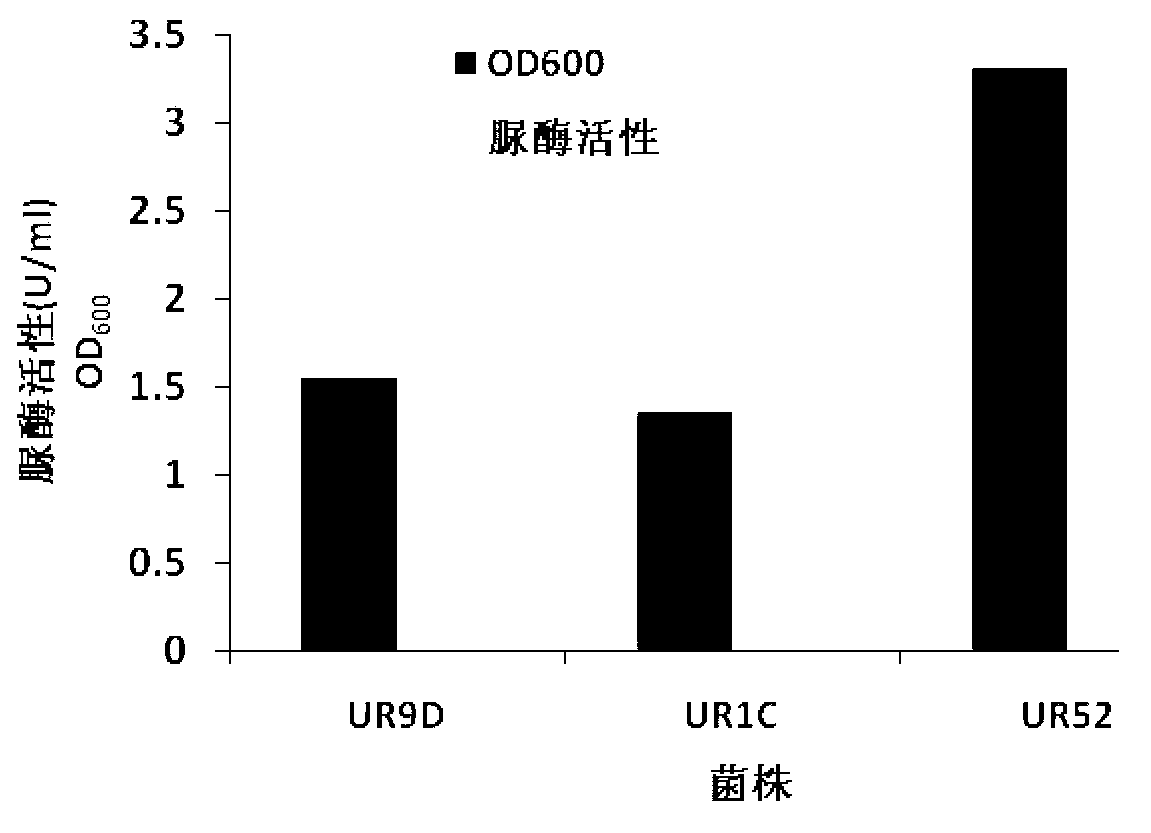
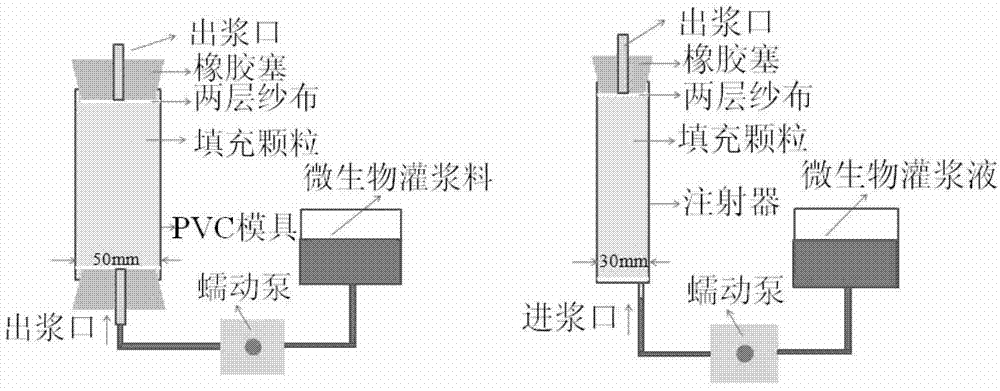
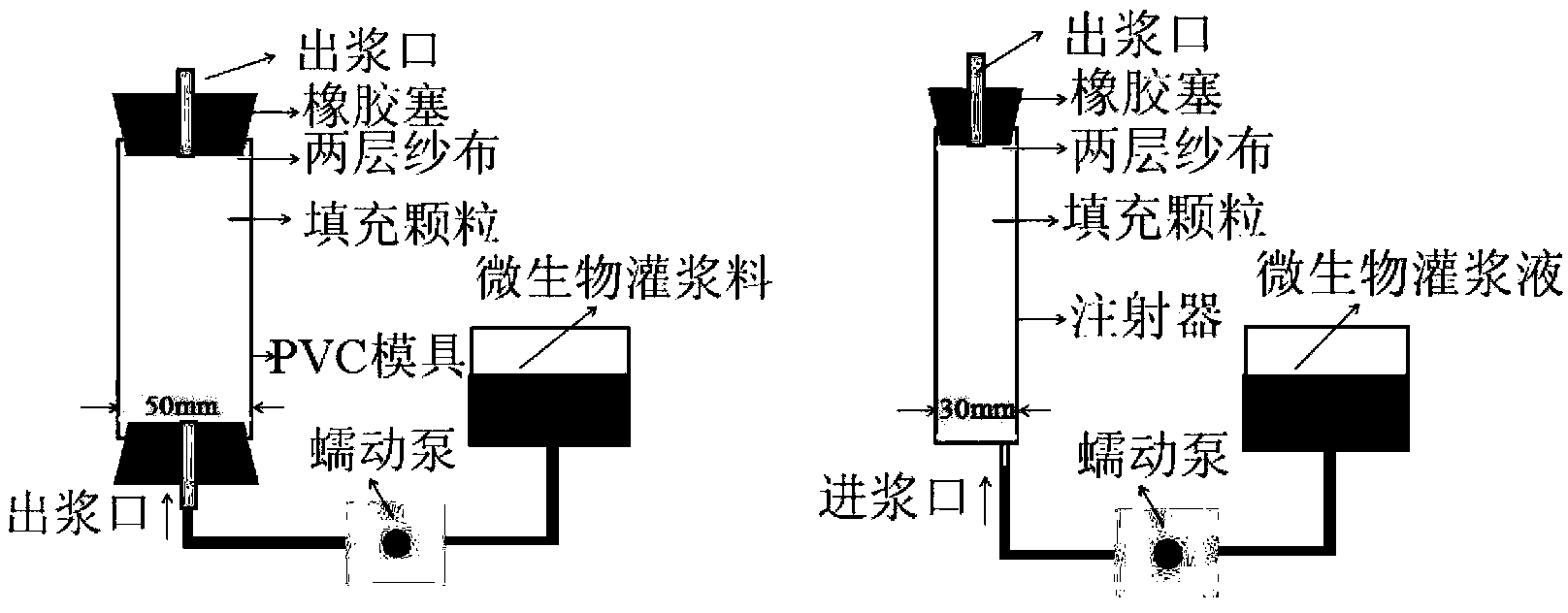
The invention provides bacillus lentus and a method for generating by inducing bacillus lentus for reinforcing foundation, the bacillus lentus URIC, the bacillus lentus UR9D, and the bacillus lentus UR52 are preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on August 29, 2012; the method comprises: firstly, respectively fermenting and culturing a single bacterium colony of bacillus lentus in a fermentation medium, then grouting in two steps, filling bacteria liquid into a sand column pumped with deionized water, and filling a mixed solution of reaction solution calcium chloride and urea, to form a microbe-calcium carbonate-sand grains consolidating body in a sand grain-solution system, and furthermore to enhance bonding degree and intensity of the sand grains. The bacillus lentus and the method of the invention has advantages of short solidification time, good effect and low cost, and will not cause pollution on environment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Deodorant special for livestock and poultry farms and application thereof
ActiveCN104307012AReduce releaseImprove deodorization efficiencyCosmetic preparationsFungiBacillus lentusCandida rugosa
The invention discloses a deodorant special for livestock and poultry farms and application thereof, wherein the deodorant is composed of the following strains: 106-108 lactobacillus acidophilus per milliliter, 107-109 lactobacillus reuteri per milliliter, 104-106 bacillus polymyxa per milliliter, 106-108 bacillus lentus per milliliter, 106-109 bacillus coagulans per milliliter, 104-106 enterococcus faecalis per milliliter, 107-109 enterococcus faecium per milliliter, 104-107 candida rugosa per milliliter, 104-107 candida valida per milliliter, 104-106 pseudomonas farinofermentans per milliliter, 106-108 rhodopseudomonas palustris per milliliter, 104-106 geotrichum suaveolens per milliliter, 106-108 aspergillus clavatus per milliliter, 106-108 rough spore aspergillus per milliliter and 106-109 streptomyces globisporus per milliliter. According to the invention, excrements in a poultry house and excrements for accumulative fermentation are treated through a spraying manner, so as to effectively reduce the release amount of malodorous gases, and provide a technical support for the effective treatment of malodor in the livestock and poultry farms and the environmental protection. Besides, the deodorant special for livestock and poultry farms can also be sprayed to the livestock and poultry body surfaces, to keep the livestock and poultry body surfaces clean and sanitary, and be conducive to the growth of livestock and poultry.
Owner:TWINS GRP
Fabric and home care products
This invention relates to fabric and home care products comprising one or more cold water proteases and processes for making and using such products. Such compositions provide improved cleaning and freshness. Such cold water proteases may be derived from parent enzymes, including BPN′ subtilisin and subtilisin derived from Bacillus lentus, by substitution, insertion and / or deletion of one or more of the parent enzymes' amino acids.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Feed micro-ecological preparation, anti-nutritional substance-free feed and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105767507AImprove digestion utilizationPromote growth and developmentAnimal feeding stuffBacillus licheniformisBiotechnology
The present invention discloses a feed micro-ecological preparation, an anti-nutritional substance-free feed and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of feed. The feed micro-ecological preparation is prepared by fermenting the following raw materials in parts by weight: 1.0-1.2 parts of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, 0.2-0.6 part of Enterococcus faecalis, 1.5-2.0 parts of Bacillus subtilis, 0.2-0.6 part of Bacillus coagulans, 0.1-0.15 part of Bacillus licheniformis, 0.1-0.3 part of Bacillus lentus, 0.2-0.5 part of Clostridium butyricum and 993.05-995.15 parts of liquid medium. After the feed micro-ecological preparation is mixed with feed raw materials, enzymes produced in the process of microbial strain fermentation can decompose anti-nutritional substances in feed and increase the feed utilization rate; at the same time, microbial strains also have effects in improving animal intestinal environment, maintaining intestinal flora balance, inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria, and improving animal immunity.
Owner:SUIPING GUANGYUAN FEED TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing high-strength microbial mortar by using urease-producing microbes
ActiveCN103173376AStrong ability to produce ureaseHigh in calcium carbonateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEpoxy
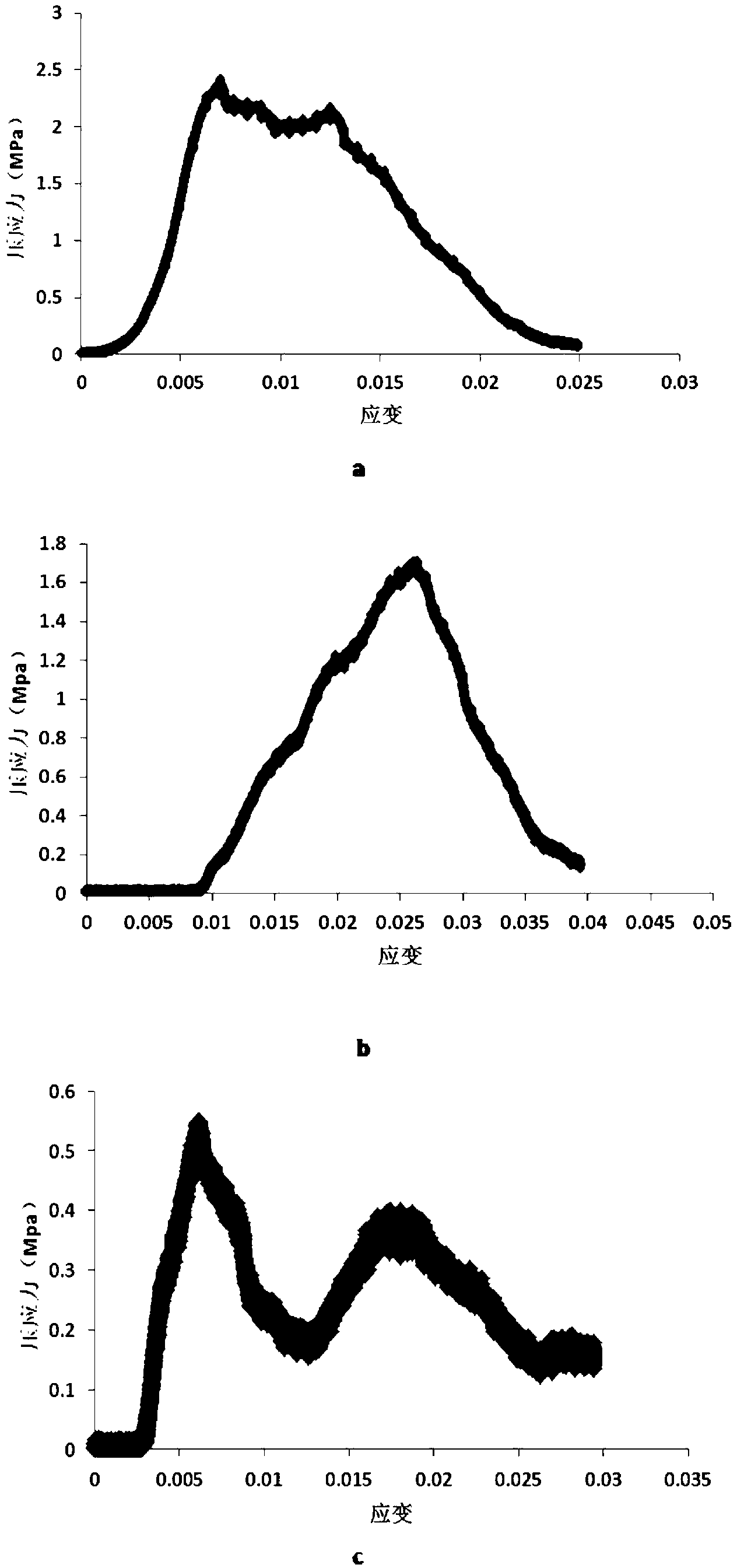
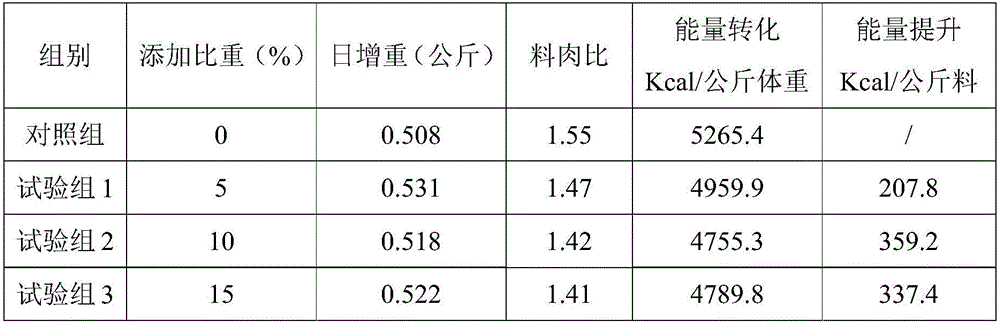
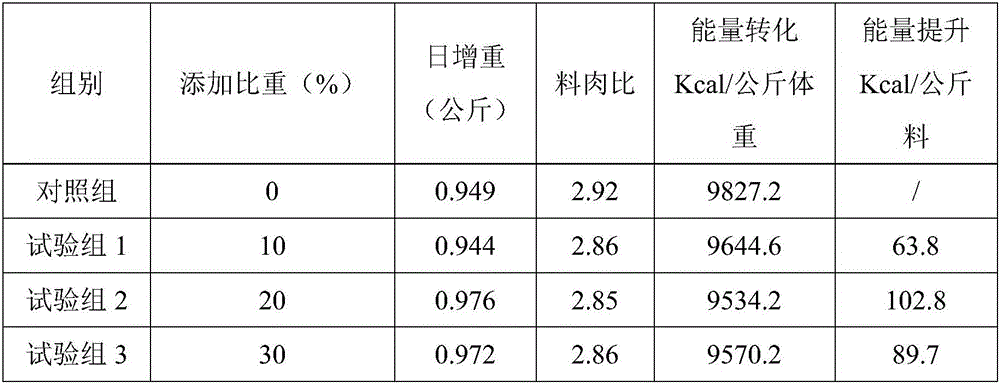
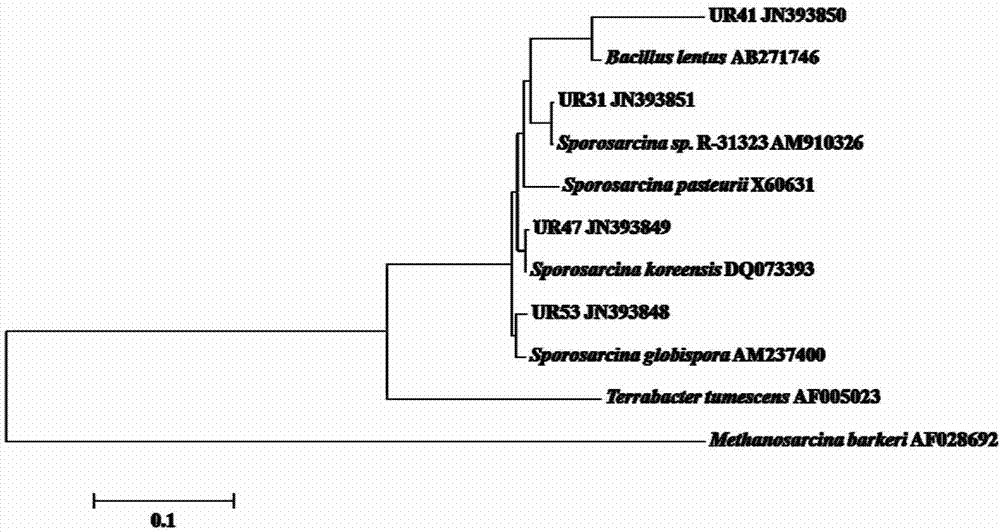
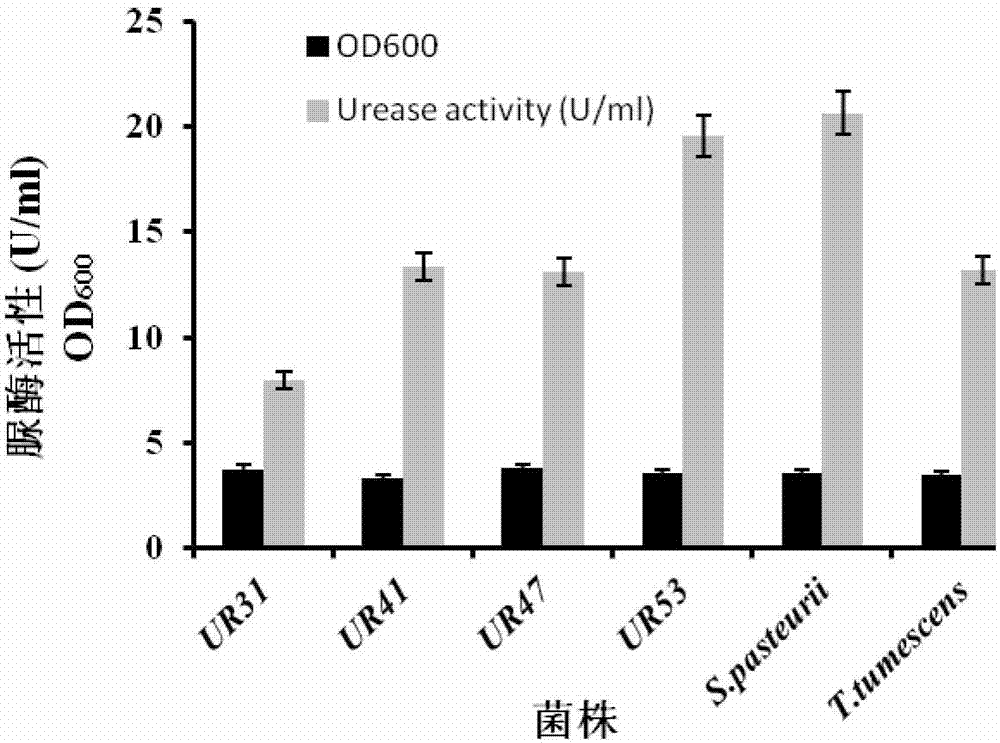
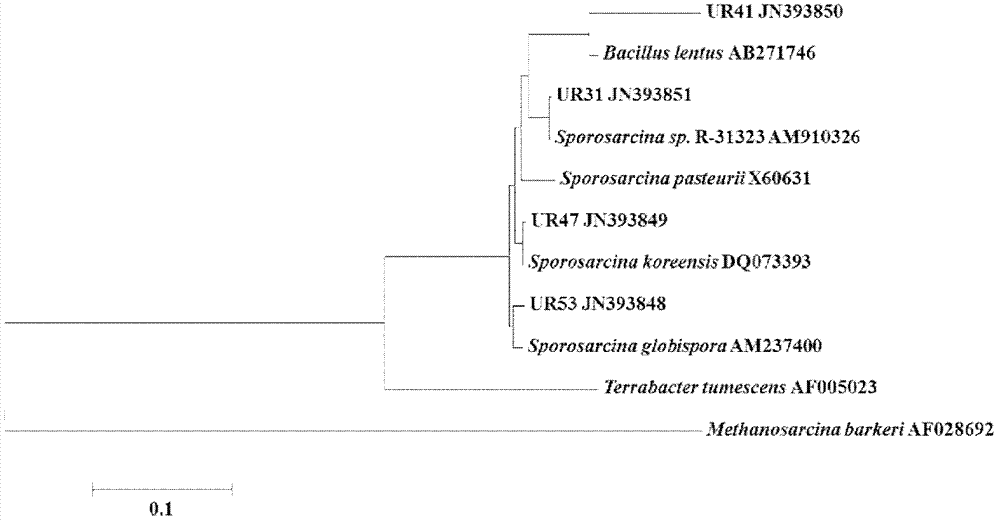
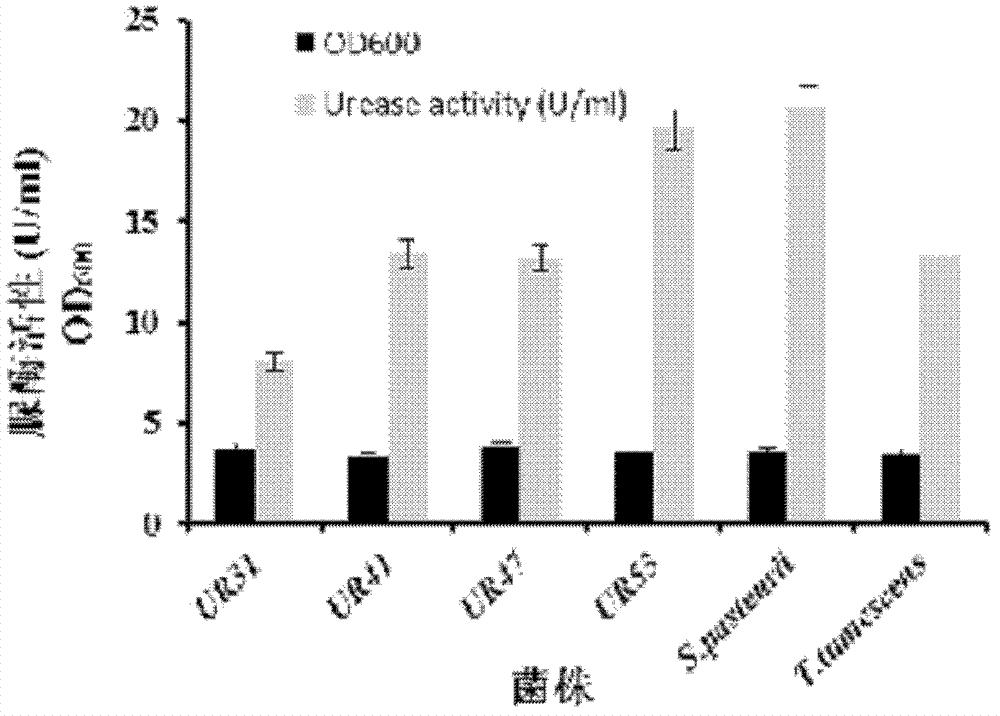
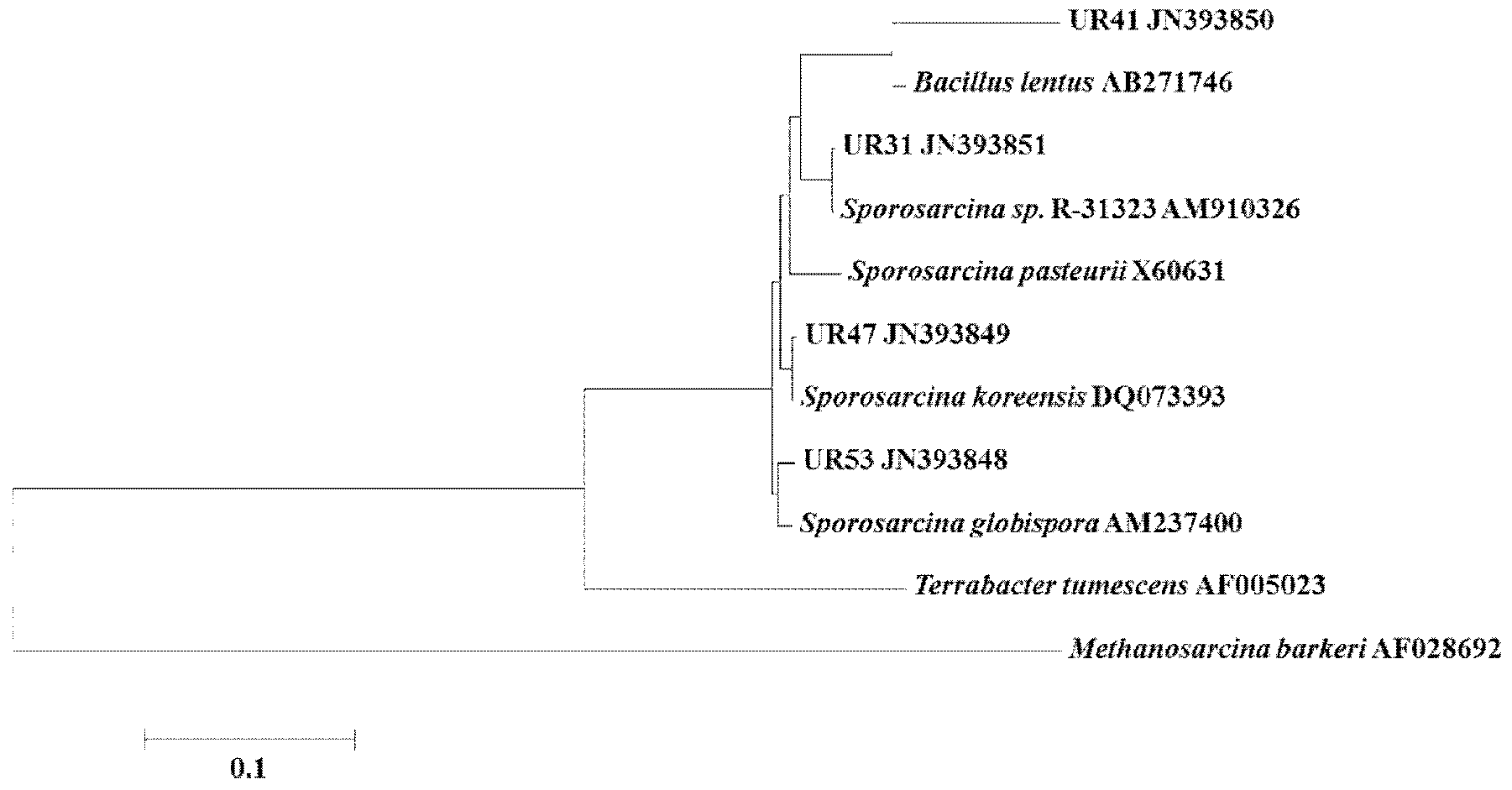
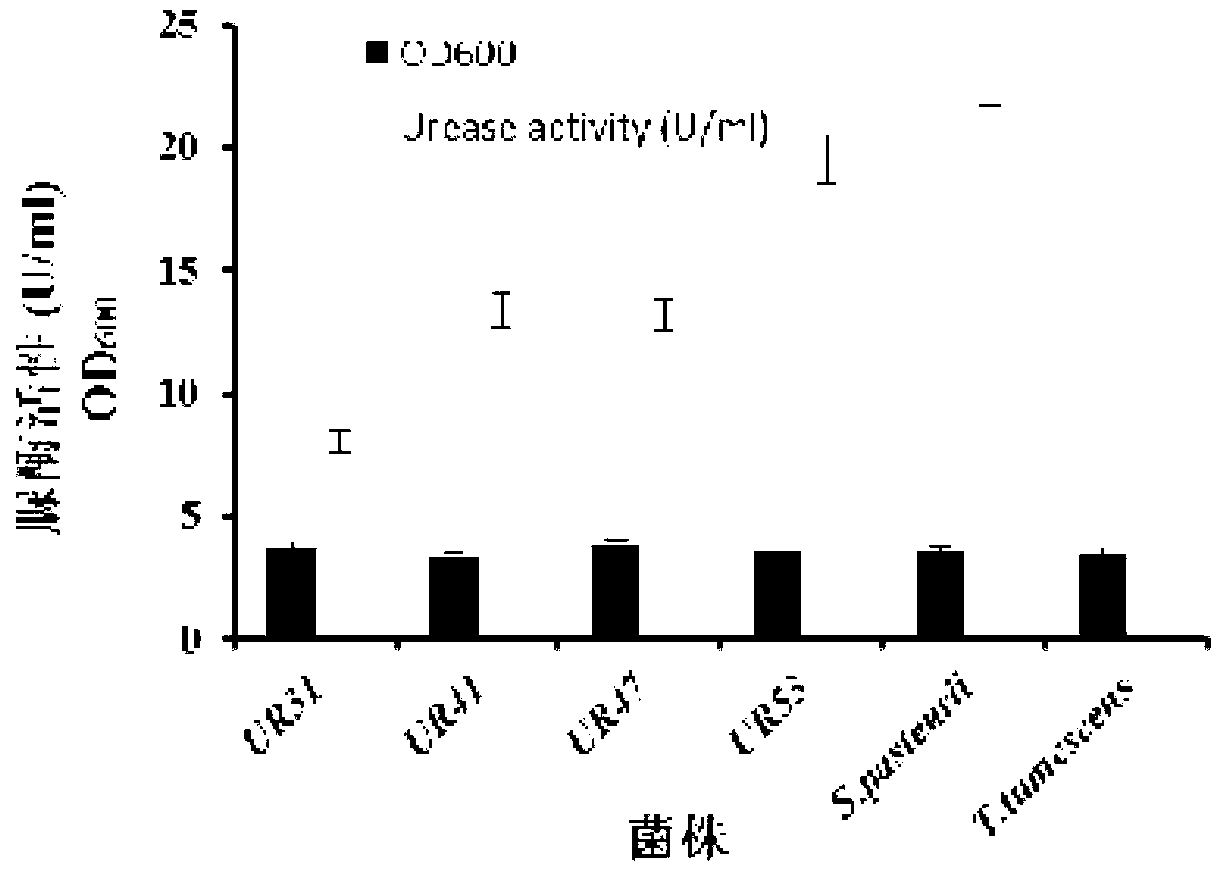
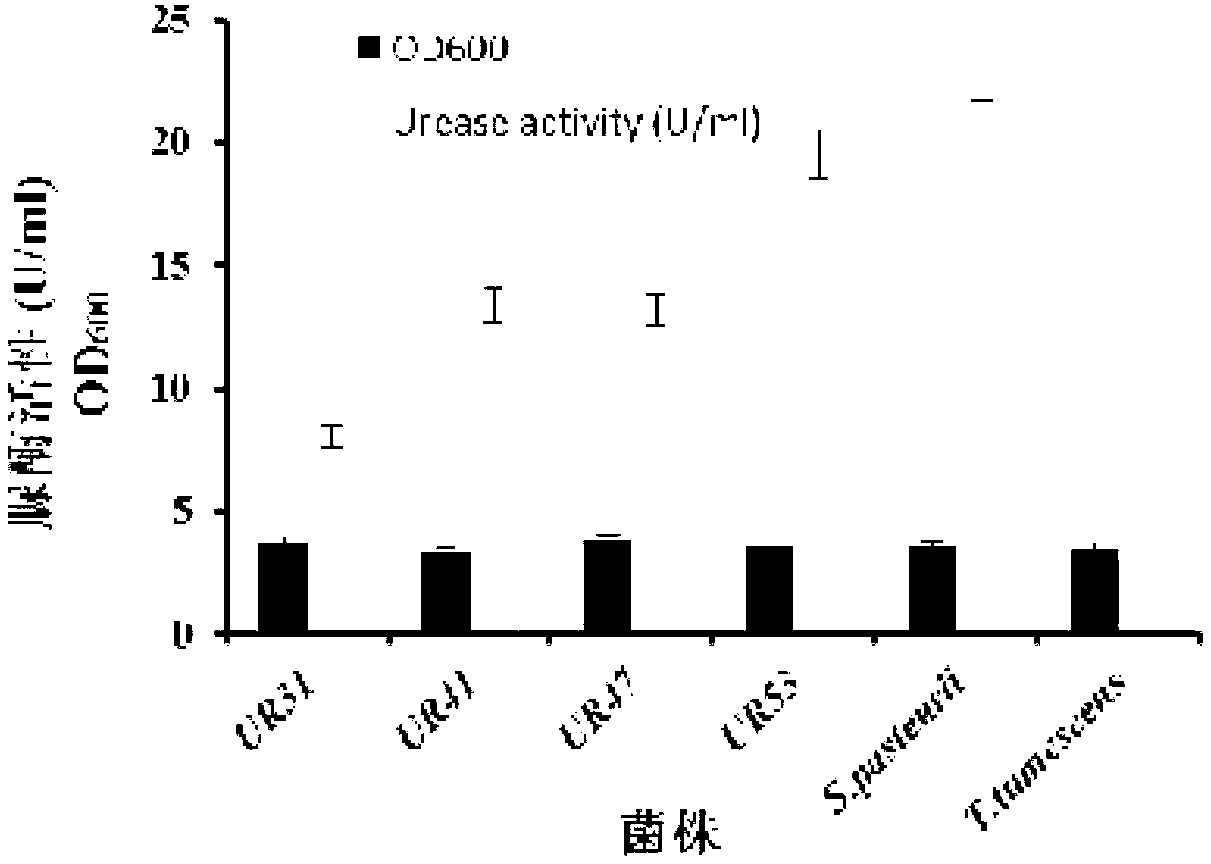
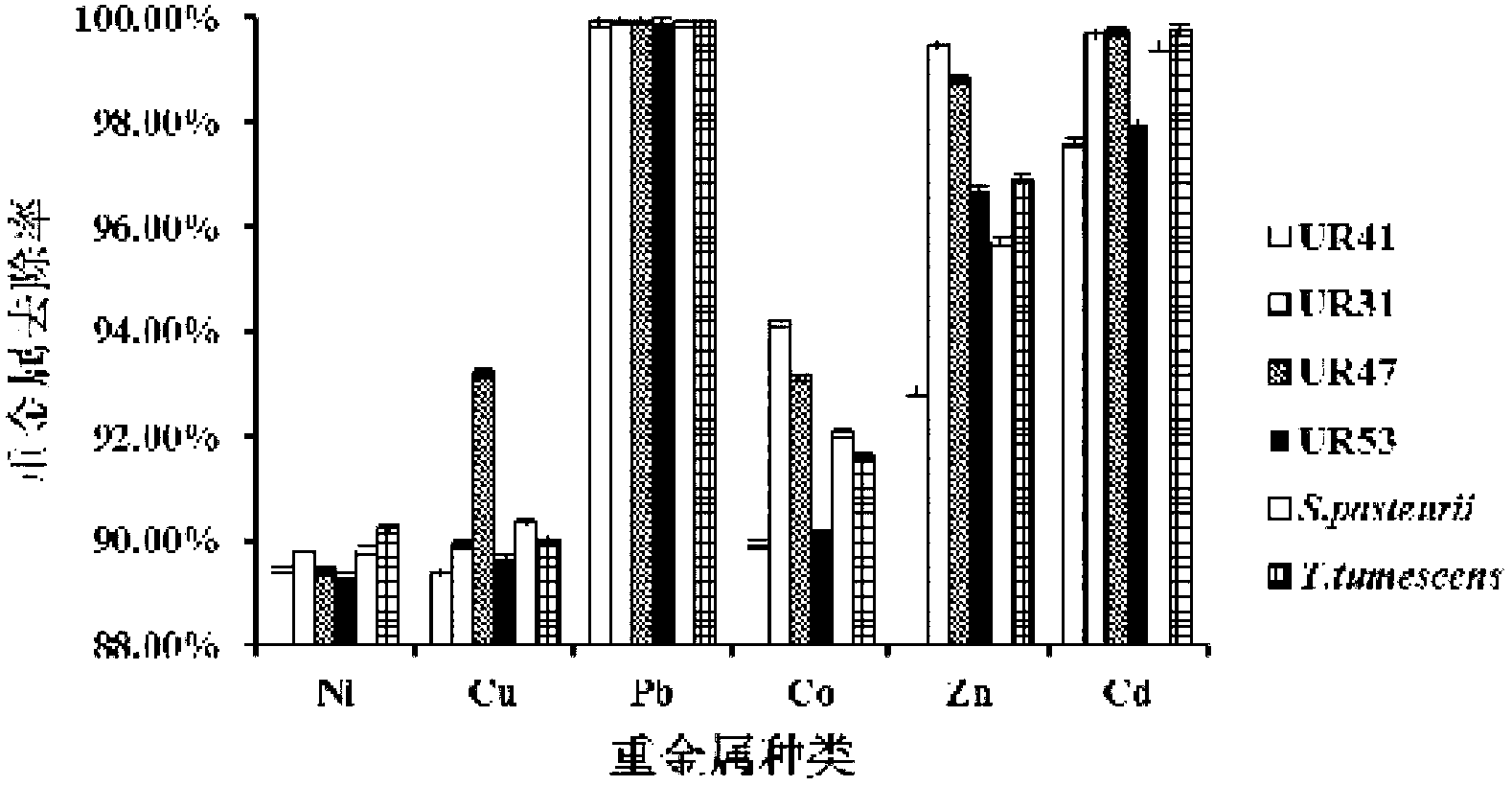
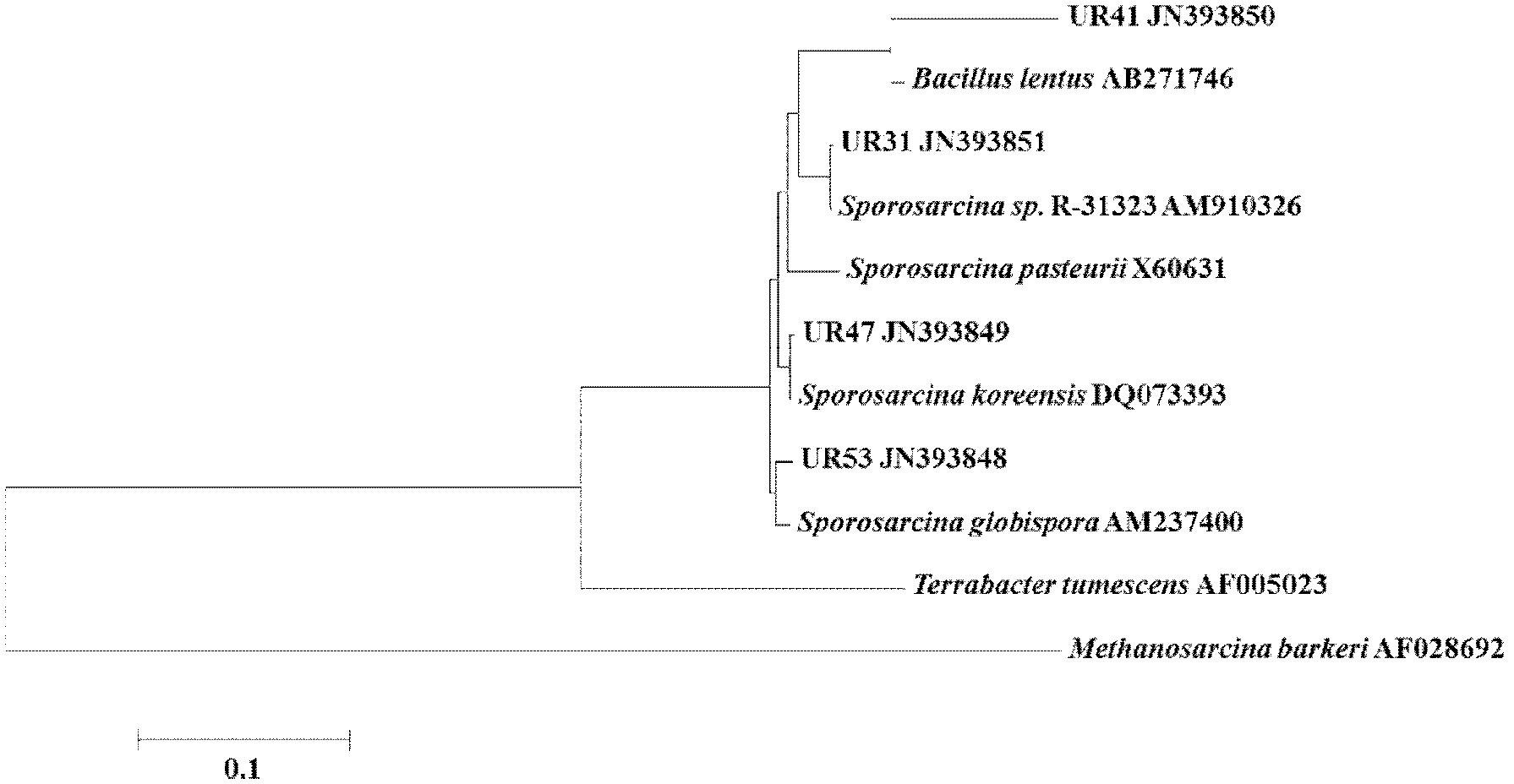
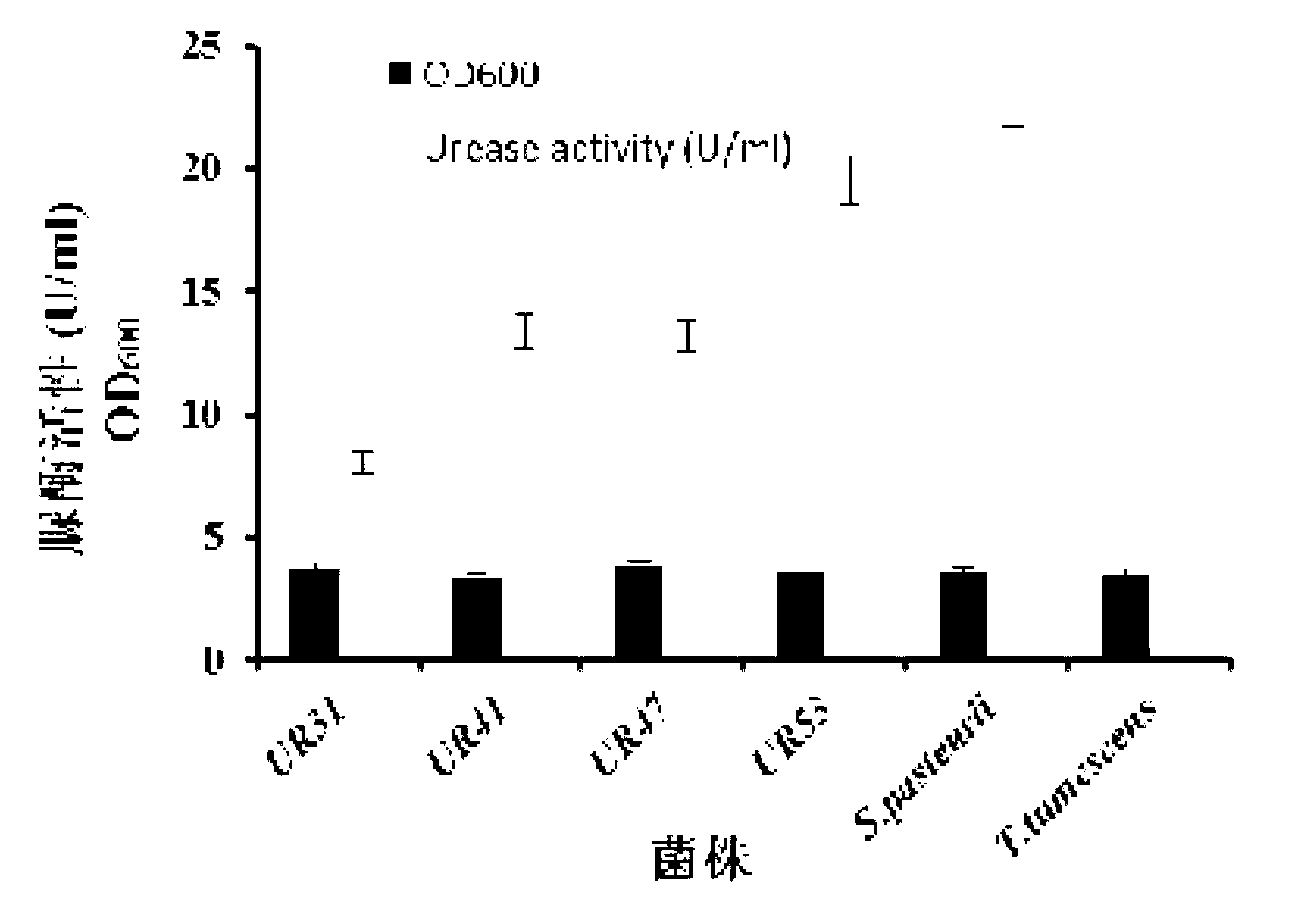
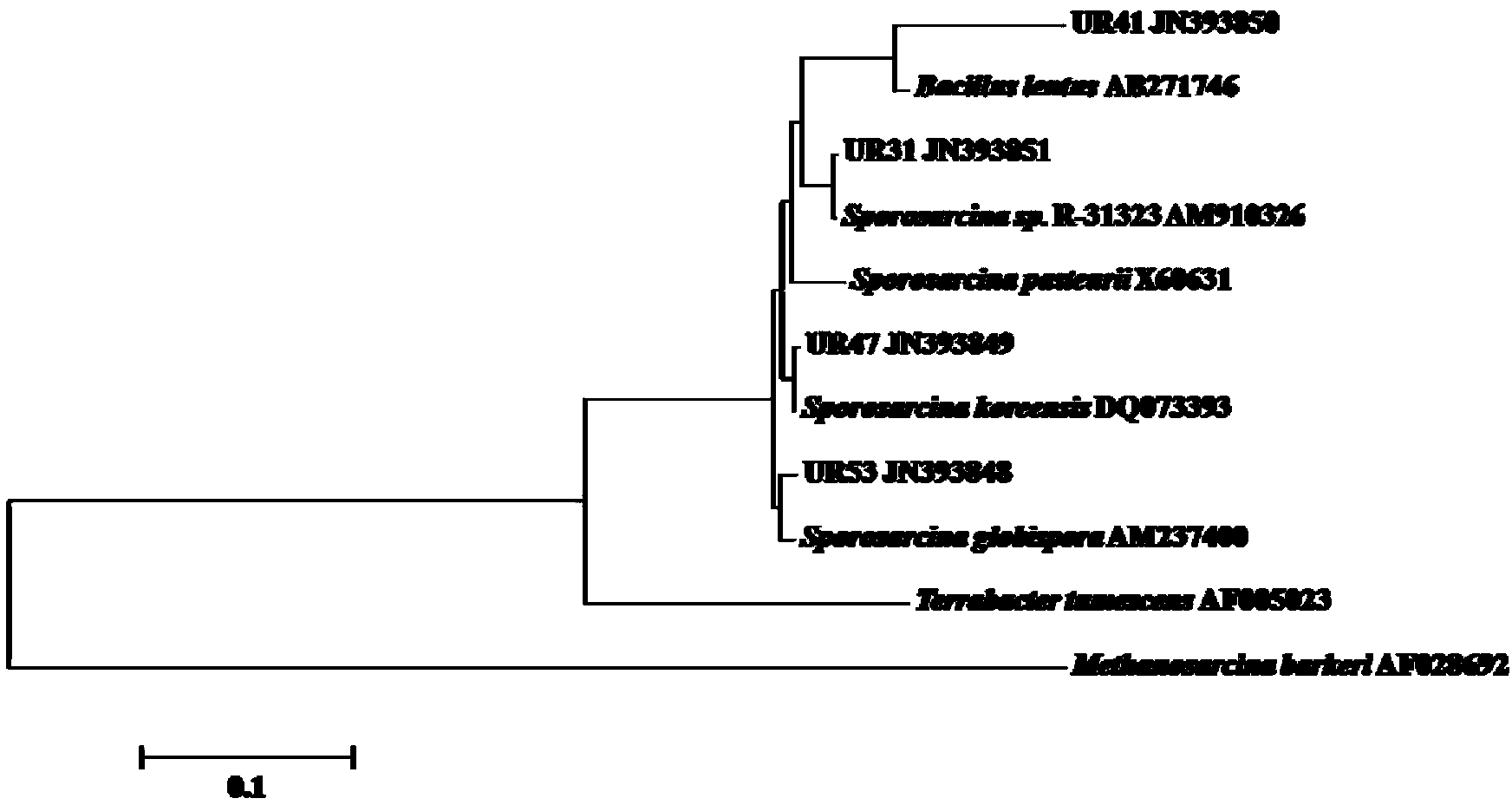
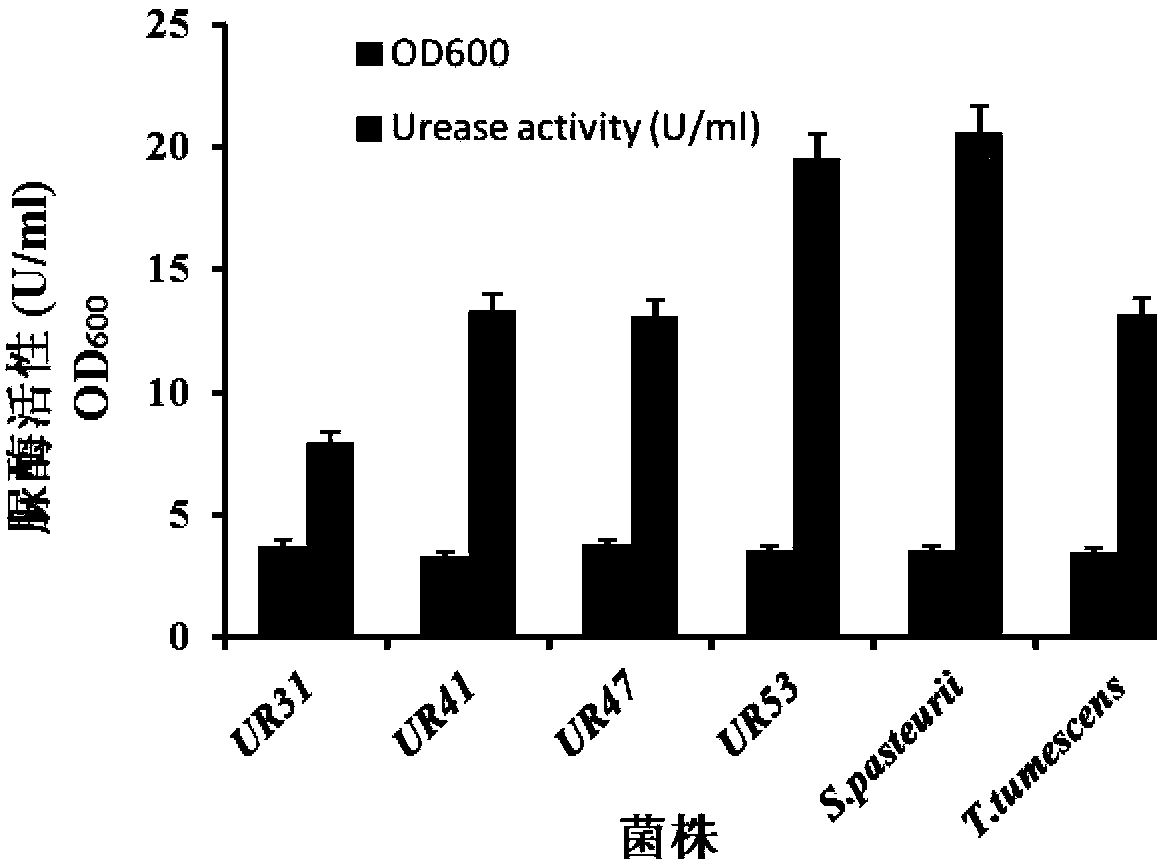
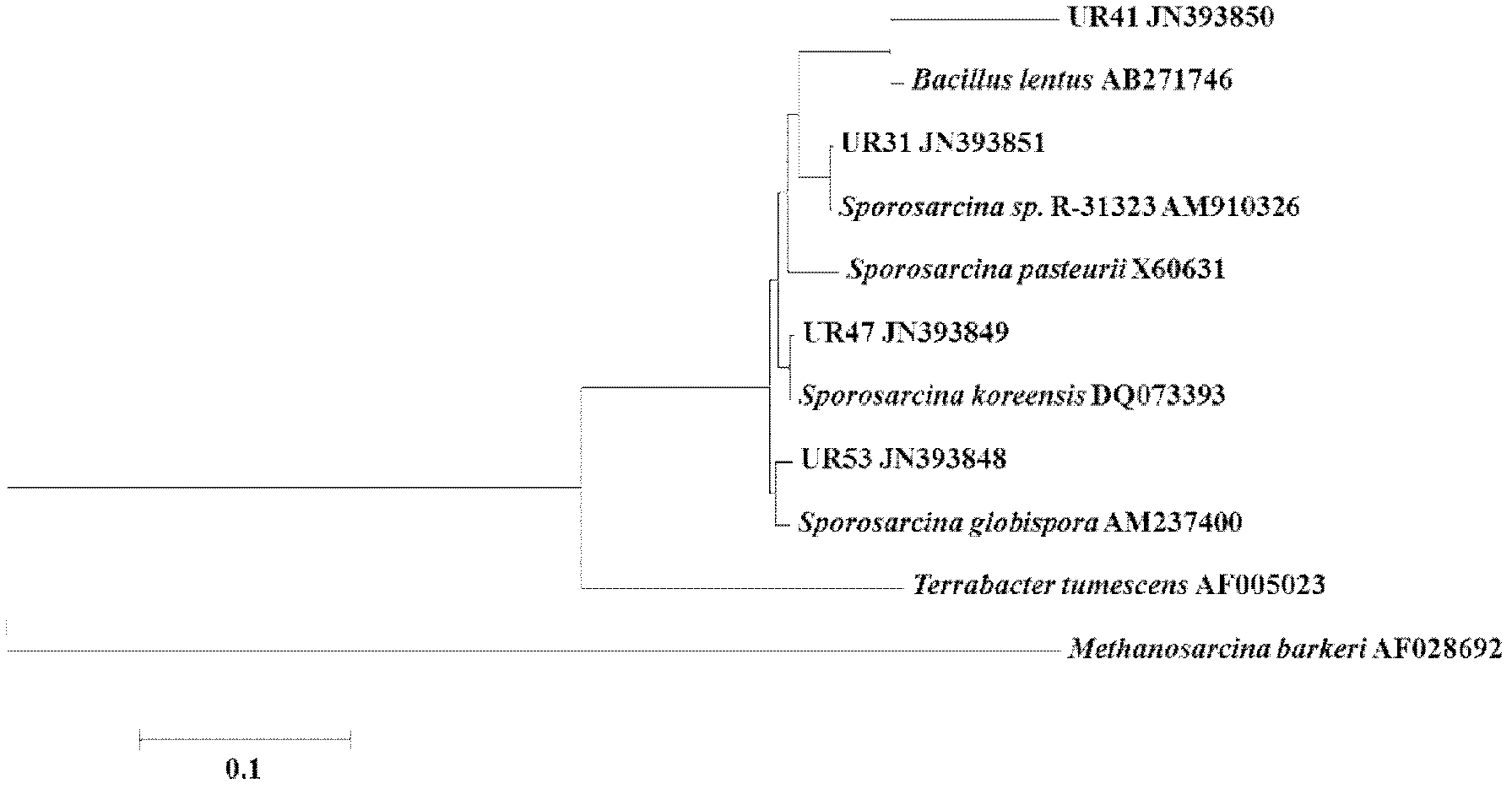
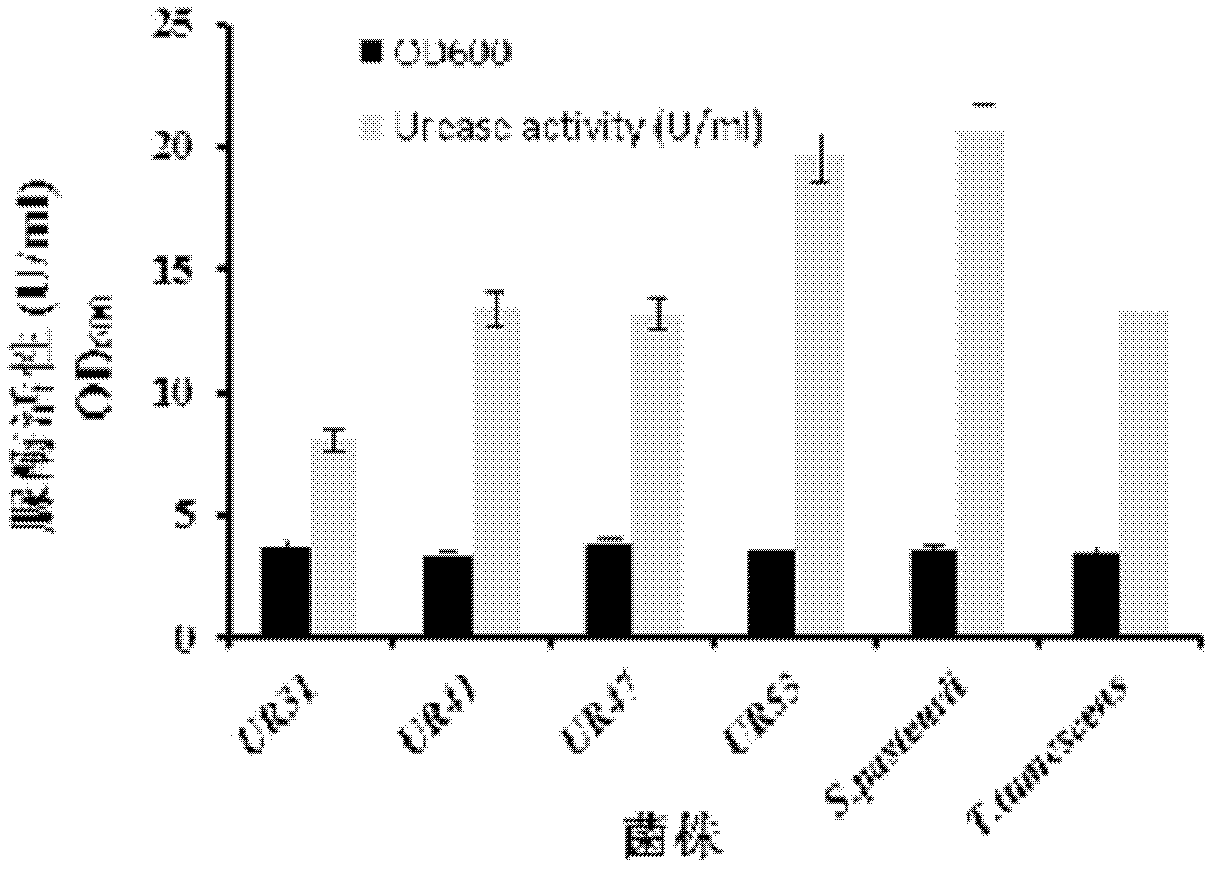
Urease-producing microbes including Sporosarcina antarctica U R 5 3, Sporosarcina koreensis UR47, Sporosarcina sp. UR31 and Bacillus lentus UR41 were preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on March 16, 2012, with the preservation numbers of CGMCC No.5916, CGMCC No.5915, CGMCC No.5913 and CGMCC No.5914 respectively. The method for preparing high-strength microbial mortar by using the urease-producing microbes comprises the following steps of: carrying out fermentation culture on the above four microbes and microbes including Sporosarcina pasteurii and Terrabacter tumescens in a fermentation culture medium to obtain a bacterial solution; and filling the bacterial solution, a fixative solution and a gelling solution into a sand particle system in batches to form microbial mortar of which the highest strength can reach 55MPa. The mechanical properties of the microbial mortar are superior to those of a cement base material; compared with a cement lime material with equivalent strength, the microbial mortar is higher in splitting tensile strength; the rigidity of the microbial mortar is similar to that of cement lime mixed mortar but far smaller than that of concrete; the fatigue load tolerance and cyclic loading capacity of the microbial mortar are higher than those of the cement base material; and an artificial sandstone is an inorganic material, and is not easy to age like organic materials including epoxy resin and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Urease-producing microorganisms and method for solidifying heavy metals in foundation using same
ActiveCN102703341AShorten the timeGood effectBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationWater insolubleBacillus lentus
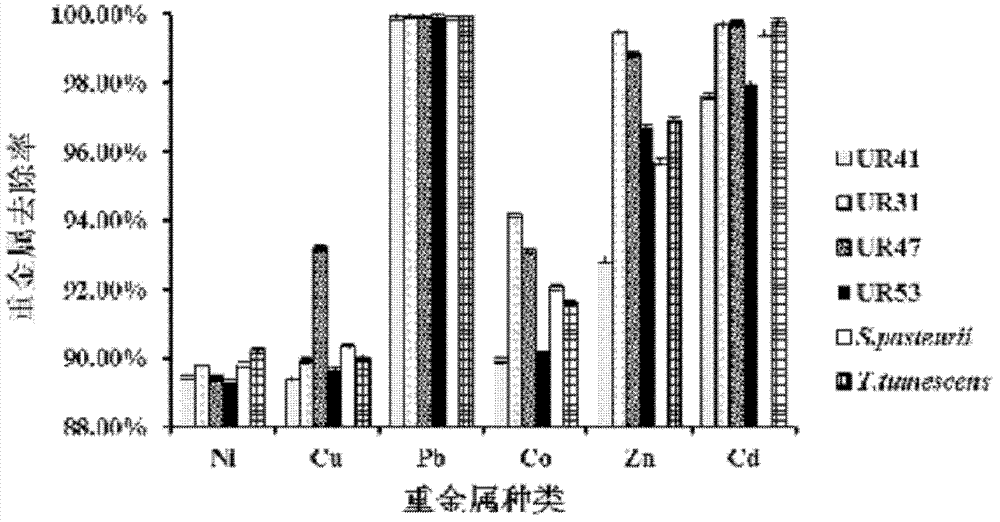
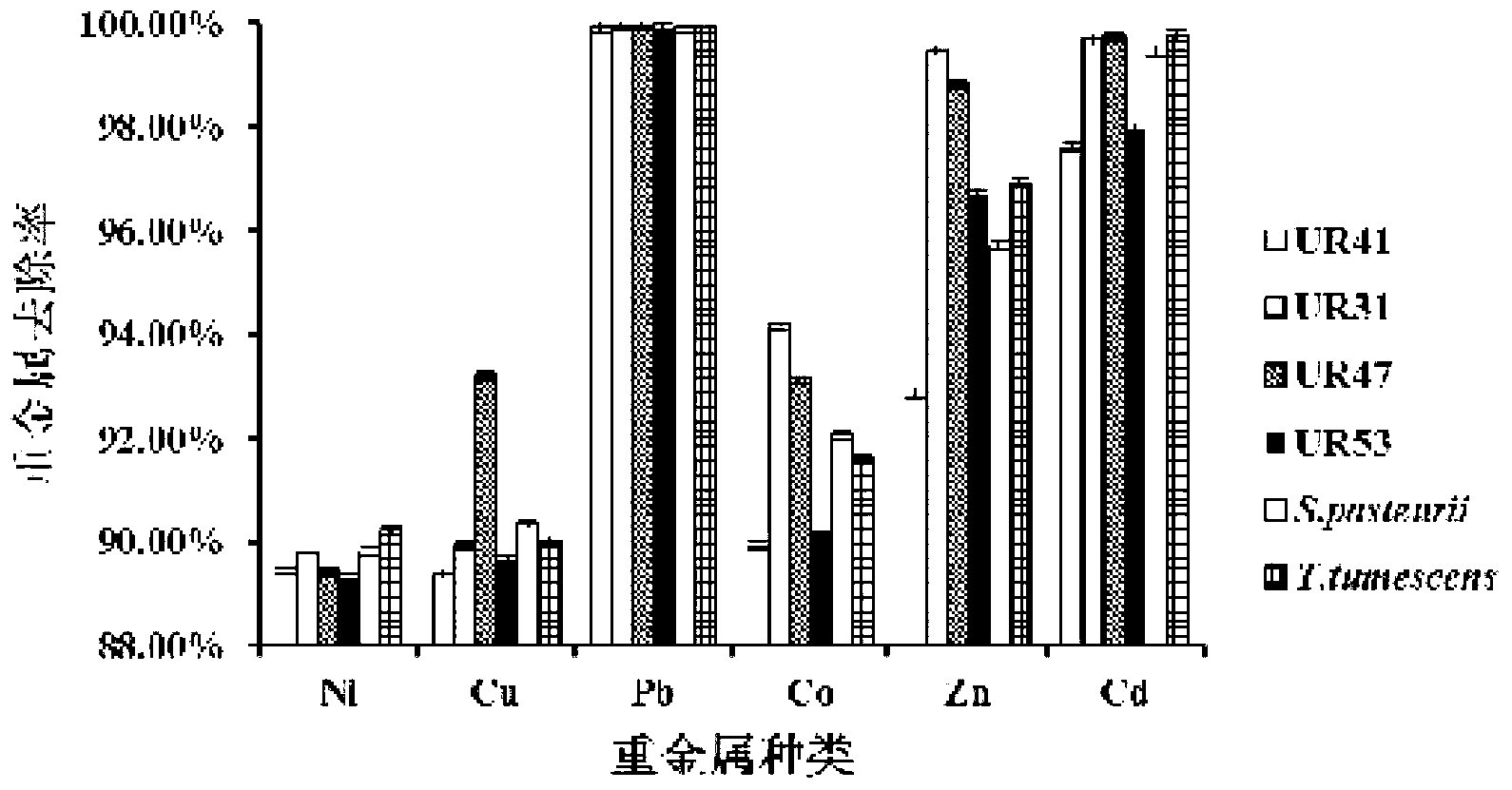
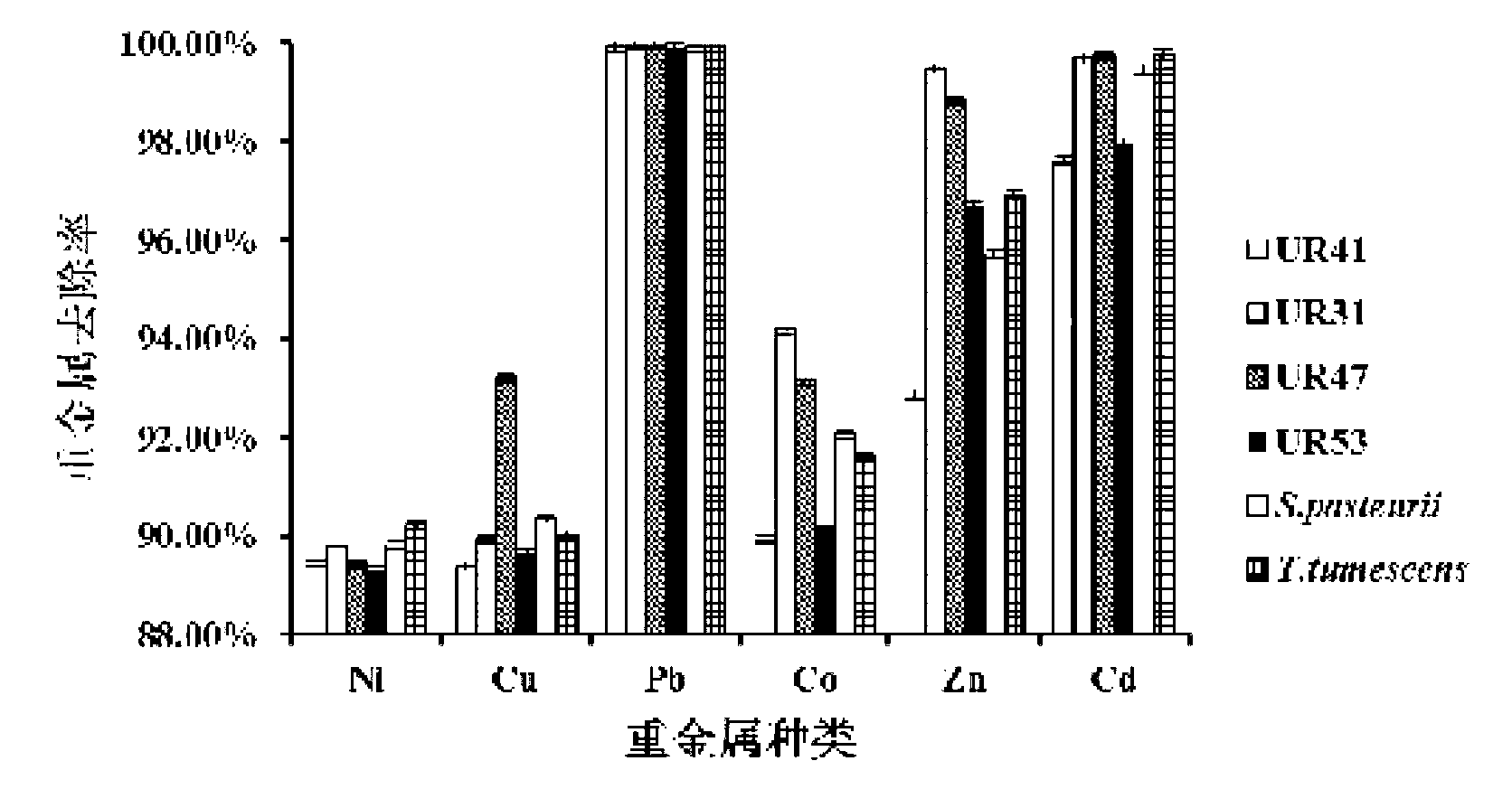
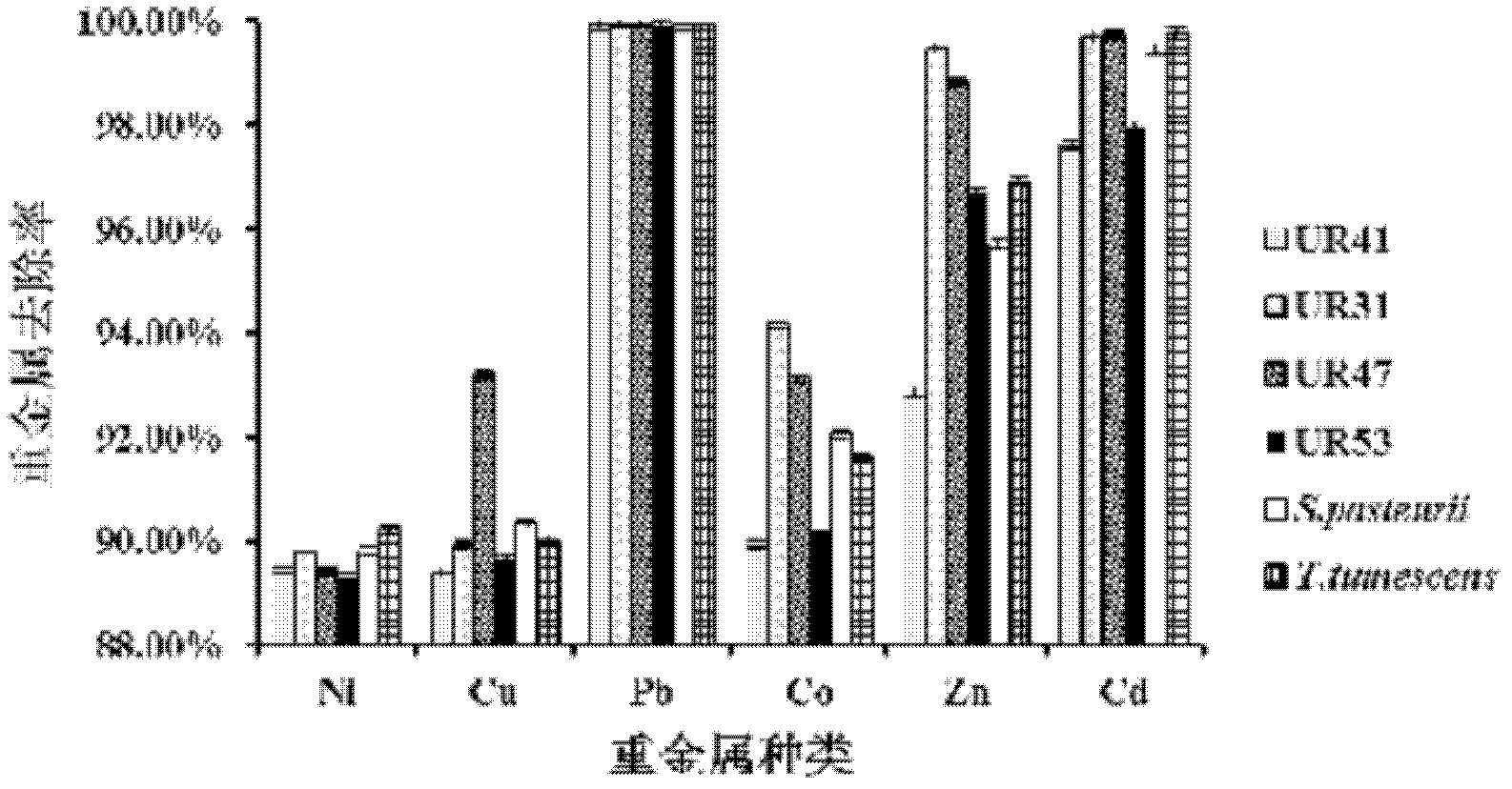
Urease-producing microorganisms of Sporosarcina antarctica UR53, Sporosarcina koreensis UR47, Sporosarcina sp. UR31 and Bacillus lentus UR41 were preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on March 16, 2012 with the preservation numbers of CGMCC NO.5916, CGMCC NO.5915, CGMCC NO.5913 and CGMCC NO.5914, respectively. The method for solidifying heavy metals in the foundation by using the urease-producing microorganisms comprises the steps of: carrying out fermentation culture on the four microorganisms and microorganisms of Sporosarcina pasteuril and Terrabacter tumescens in a fermentation culture medium to obtain microorganism liquid, adding reaction liquid urea to the microorganism liquid, and then adding to the solution containing heavy metals to form a mixed solution, so that microorganism-heavy metal flocculates are formed in the mixed solution and then water-insoluble heavy metal carbonates are further formed. The method for solidifying the heavy metals in the foundation by using the microorganisms has the advantages of short solidifying time, good effect, low cost and no secondary pollution to environment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Urease-producing microorganisms and method for solidifying heavy metals in subgrade by using same
ActiveCN103289919AShorten the timeGood effectBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationWater insolubleBacillus lentus
The provided urease-producing microorganisms comprise: Sporosarcina antarctica UR53, Sporosarcina koreensis UR47, Sporosarcina sp. UR31, and Bacillus lentus UR41, wherein all the above microorganisms have been deposited with the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on March 16, 2012, and assigned respectively the accession numbers: CGMCC NO.5916, CGMCC NO.5915, CGMCC NO.5914, and CGMCC NO.5913. The provided method for solidifying heavy metals in subgrade using the urease-producing microorganisms comprises steps of: putting the above four microorganisms, Sporosarcina pasteurii and Terrabacter tumescens in a fermentation medium to obtain a bacterial solution by fermenting; adding a urea reaction solution into the bacterial solution; and adding the solution of the above step into a solution containing heavy metals to form a mixed solution, so that floccules of microorganism-heavy-metal are formed in the mixed solution and water-insoluble heavy-metal-carbonates are formed further. The method for solidifying heavy metals in subgrade using the microorganisms provided by the invention has the advantages of short solidifying time, good effect, low cost, and no secondary pollution to environment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Urease-producing microbes and curing method for heavy metals in foundation
ActiveCN103289921AEfficient governanceShorten the timeBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationWater insolubleBacillus lentus
Urease-producing microbes comprise sporosarcina antarctica UR53, sporosarcina koreensis UR47, sporosarcina sp. UR31 and bacillus lentus UR41 which have been preserved in China General Microbiology Center of Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms since 16th March, 2012, and respectively have the preservation numbers of CGMCC No.5916, CGMCC No. 5915, CGMCC No. 5913 and CGMCC No. 5914. A curing method for heavy metals in a foundation by using the urease-producing microbes comprises: placing the four microbes, and microbes of sporosarcina pasteurii and terrabacter tumescens in a fermentation medium to carry out fermentation culture to obtain a bacterial liquid, adding a reaction solution urea into the bacterial liquid, then adding the bacterial liquid into a heavy-metal-containing solution to form a mixed solution and to form a microbe-heavy-metal floccule in the mixed solution, and further to obtain water-insoluble heavy metal carbonates. The curing method for heavy metals in the foundation by using the urease-producing microbes has the advantages of short curing time, good effect, low cost and no secondary pollution to environment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for combined strengthening of soil body with plant mucilage-microorganism
InactiveCN109518678AHigh strengthImproved brittle deformation propertiesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismPlant Mucilage
The invention discloses a method for combined strengthening of soil body with plant mucilage-microorganism. The method for combined strengthening of the soil body with plant mucilage-microorganism comprises the following steps that 1) Bacillus pasteurii or Bacillus lentus is inoculated on a culture media; and then shake culture is conducted, supernatant is removed centrifugally, and a microorganism bacteria solution is acquired; and 2) the microorganism bacteria solution and plant mucilage are mixed and stirred uniformly, and a mixture of the bacteria solution and mucilage is acquired; and then the mixture of the bacteria solution and mucilage and a nutrient solution are added into the soil body step by step so that strengthening can be conducted. According to the method for combined strengthening of the soil body with plant mucilage-microorganism, the polysaccharide gelatinization characteristic of plant mucilage and the characteristic that calcium carbonate is generated by mineralization of microorganism are utilized so that strengthening can be conducted on the soil body; and the method is characterized in that the effect is good, the cost is low, and in addition, no pollution is caused to the environment, and the ecological equilibrium is protected.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
High-efficiency combined functional bacteria for sludge treatment
InactiveCN102234615AEmission reductionRealize ecologyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisBacillus megaterium
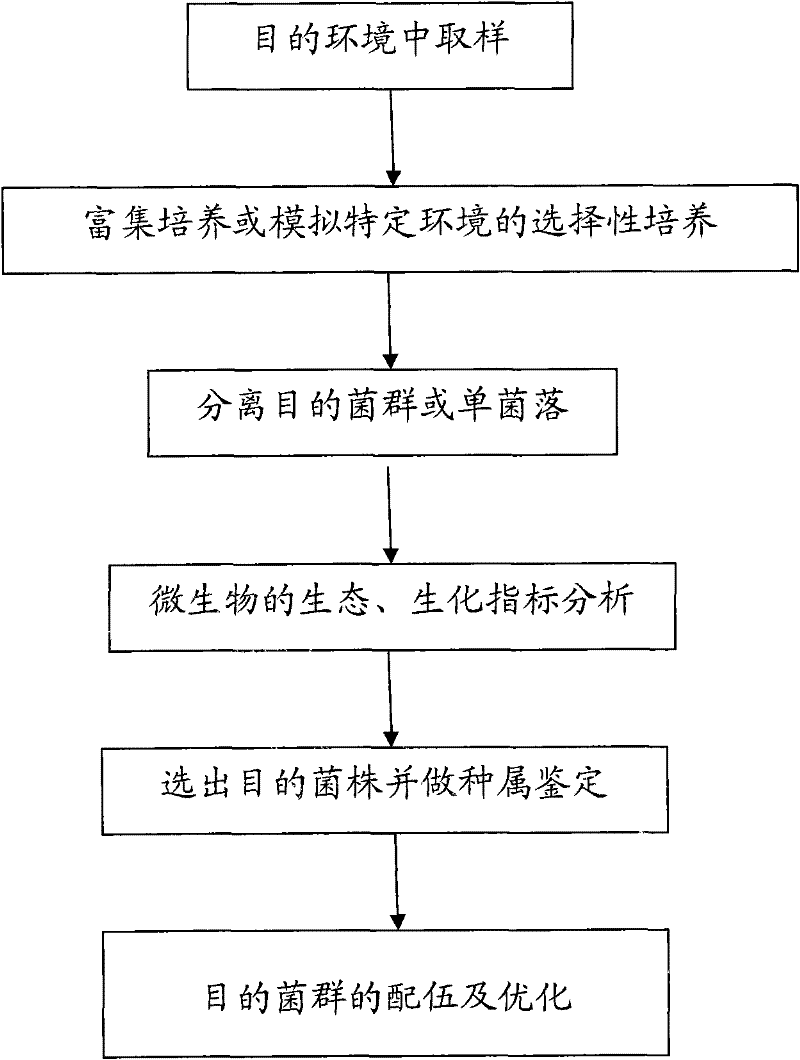
The invention discloses high-efficiency combined functional bacteria for sludge treatment. The high-efficiency combined functional bacteria comprise the following six microbes: bacillus licheniformis, bacillus subtilis, bacillus lentus, bacillus megaterium, bacillus thuringiensis and bacillus cereus. A culture method for the microbes comprises the following steps of: sampling; culturing in a culture medium; separating target strains; performing index analysis on the separated strains; identifying species; mixing; and optimizing. The functional bacteria are quick in multiplication and have obvious effect of removing phosphorus from sludge in the process of decomposing organic matters, so that the sludge treatment effect ensures that the sludge reaches the national emission standard, and the sludge discharge can be greatly reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU TONGREN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Urease-producing microbes and curing method for heavy metals in foundation
ActiveCN103289920AShorten the timeGood effectBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationWater insolubleBacillus lentus
Urease-producing microbes comprise sporosarcina antarctica UR53, sporosarcina koreensis UR47, sporosarcina sp. UR31 and bacillus lentus UR41 which have been preserved in China General Microbiology Center of Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms since 16th March, 2012, and respectively have the preservation numbers of CGMCC No.5916, CGMCC No. 5915, CGMCC No. 5913 and CGMCC No. 5914. A curing method for heavy metals in a foundation by using the urease-producing microbes comprises: placing the four microbes and microbes of sporosarcina pasteurii and terrabacter tumescens in a fermentation medium to carry out fermentation culture to obtain a bacterial liquid, adding a reaction solution urea into the bacterial liquid, then adding the bacterial liquid into a heavy-metal-containing solution to form a mixed solution so as to form a microbe-heavy-metal floccule in the mixed solution, and further to obtain water-insoluble heavy metal carbonates. The curing method for heavy metals in the foundation by using the urease-producing microbes has the advantages of short curing time, good effect, low cost and no secondary pollution to environment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Microbial fertilizer specially used for rice and for improvement of saline alkali land
InactiveCN110423166AImprove abilityImprove salt toleranceFertilizer mixturesAlkali soilMicrobial agent
Microbial fertilizer specially used for rice and for improvement of saline alkali land belongs to the technical field of fertilizer. The fertilizer includes, by mass, the following components: 70%-80%of a microbial agent, 8%-20% of an elemental nutritional agent, 2%-10% of carbon nanotubes, and 2%-6% of 1-methylcyclopropene; and the microbial agent is obtained from fermentation of pseudomonas fluorescens, salt-tolerant Bacillus lentus, Rhizopus intermedia and lactobacillus. The microbial fertilizer specially used for the rice and for the improvement of the saline alkali land is reasonable indesign, and through intervention of exogenous functional microorganisms on a rhizosphere micro-domain of rice, the method can make the usage amount of fertilizer reduce, the improvement effect of thesaline alkali land is improved, and the salt tolerance of the rice is improved.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
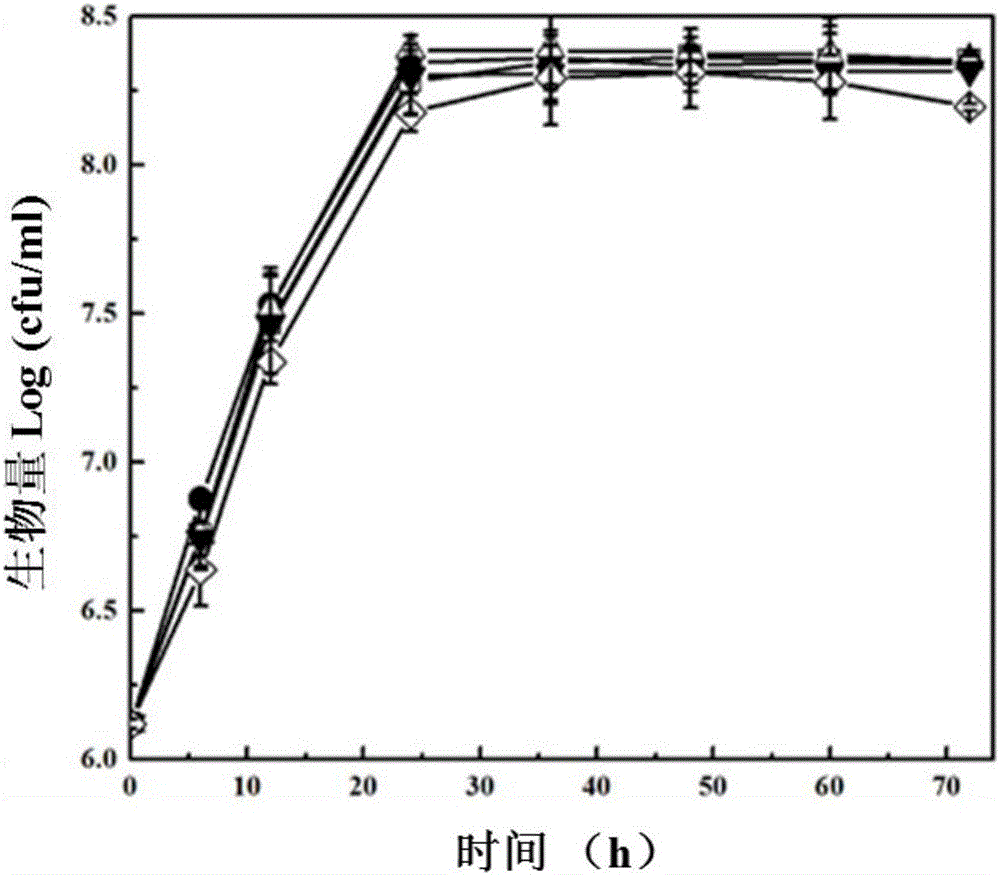
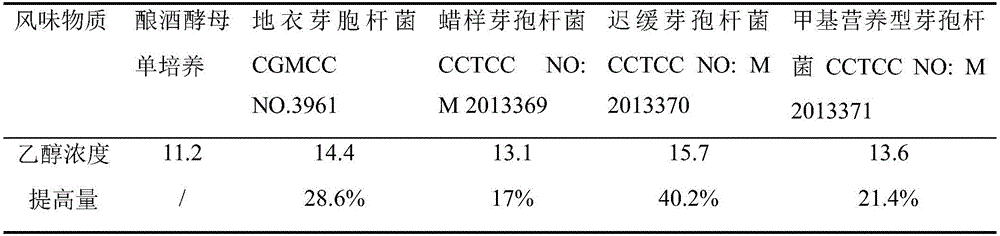
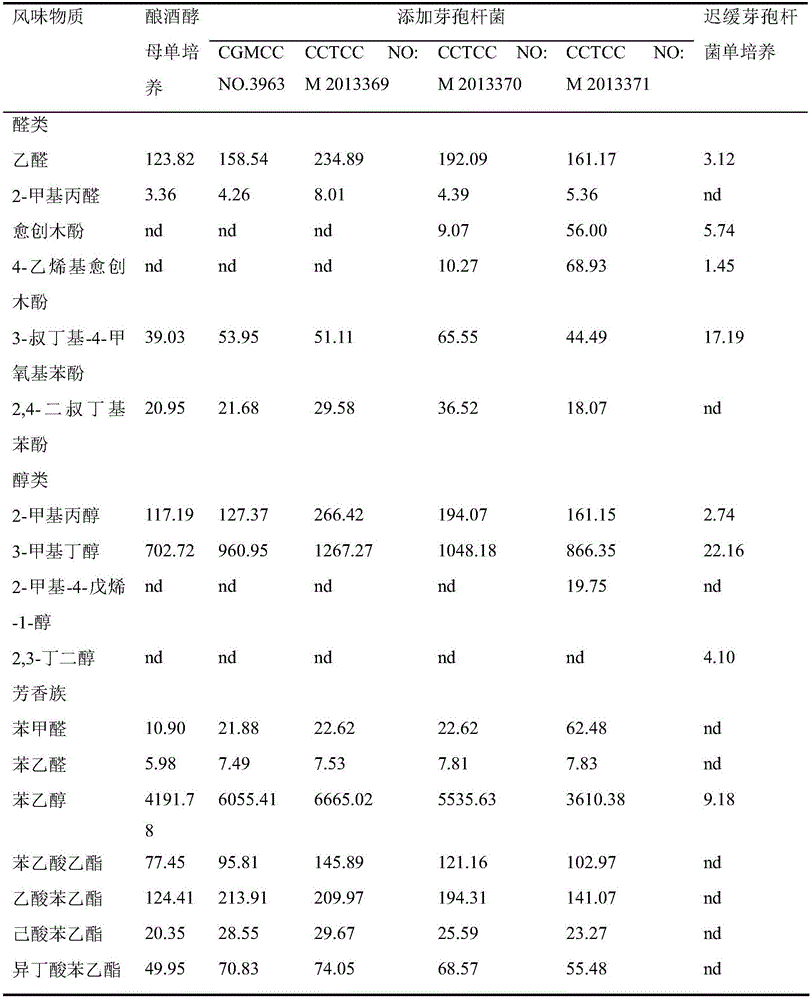
Bacillus capable of simultaneously promoting saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce ethyl alcohol and flavor substances and application of bacillus
ActiveCN104673703ATo promote metabolismEnhanced flavor metabolismBacteriaAlcoholic beverage preparationBacillus licheniformisMixed culture
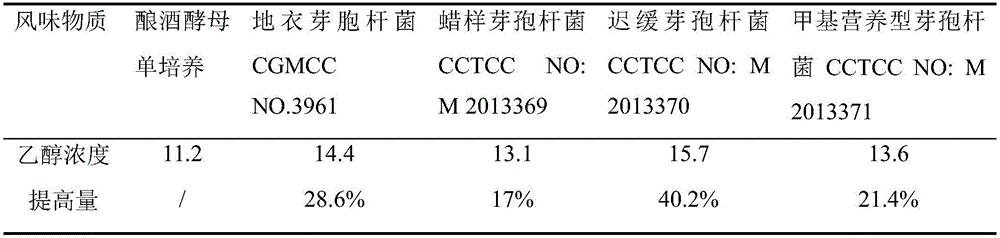
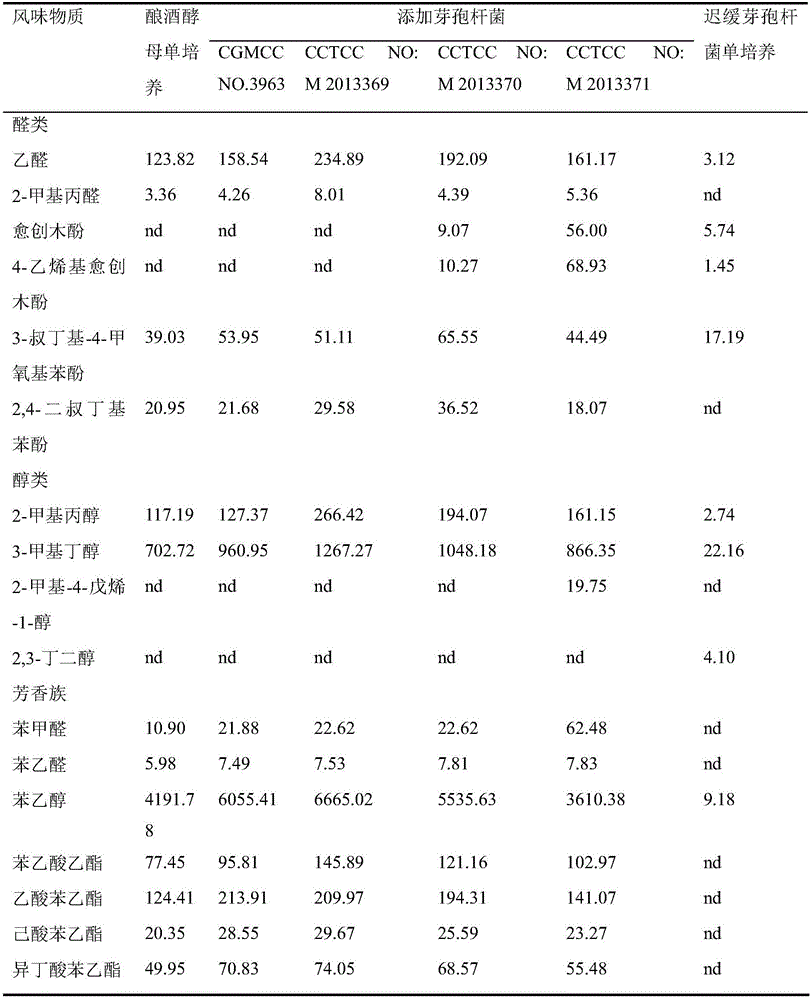
The invention relates to bacillus capable of simultaneously promoting saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce ethyl alcohol and flavor substances, and an application of the bacillus, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The bacillus provided by the invention comprises bacillus licheniformis CGMCC NO.3963, bacillus cereus CCTCC NO:M 2013369, bacillus lentus CCTCC NO:M 2013370 and bacillus methylotrophicus CCTCC NO: 2013371. After the bacillus and the saccharomyces cerevisiae are subjected to mixed culture, the yield of ethyl alcohol can be improved by over 20%; meanwhile, metabolism aldehydes, alcohols, esters, acids, and other flavor substances of the saccharomyces cerevisiae are improved; the bacillus is applied to production of fermented wine; the wine yield can be improved; and meanwhile, the flavor and the quality of the fermented wine are significantly improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Liquid biological feed additive
InactiveCN104472882AIncrease appetitePromote growthAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyBacillus pumilus
The invention belongs to the field of feed additive processing, and particularly discloses a liquid biological feed additive. The feed additive comprises the following materials by weight percentage: 10-20% of saccharomycetes, 8-15% of bacillus and 72-82% of an edible mushroom aqueous extraction concentrated solution, wherein the saccharomycetes is any one of candida utilis and candida tropicalis; the bacillus is any one or two or combination of bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, bacillus lentus, bacillus pumilus, bacillus coagulans and bacillus natto. The edible mushroom aqueous extraction concentrated solution is rich in nutritional ingredients of protein, amino acid, polyose, vitamin and the like; the nutritional value of probiotics is further improved; the liquid biological feed additive promotes metabolization of animals, improves disease resistance of bodies, enhances immunity, promotes growth of animals, and improves economic benefits finally.
Owner:邳州市小河科技发展有限公司
Method for reducing heavy metal emission in livestock and poultry manure
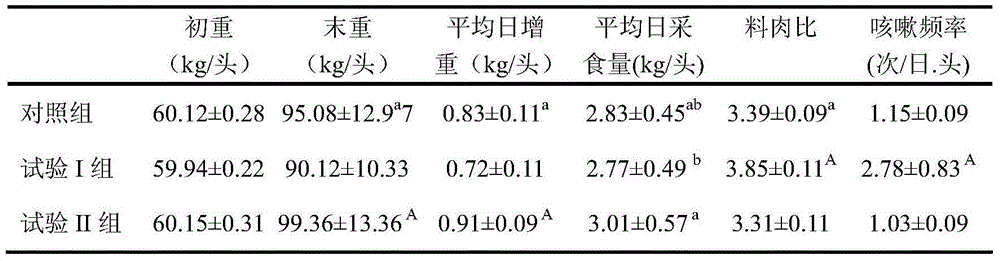
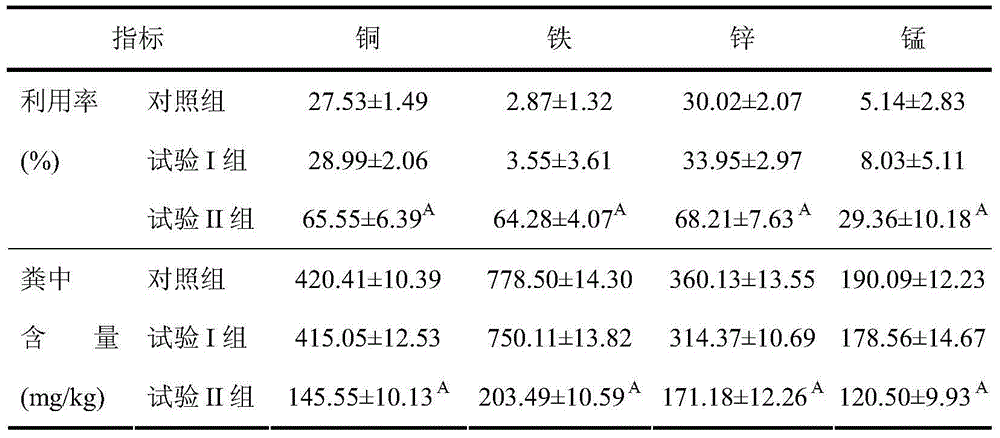
ActiveCN104957373AEmission reductionImprove palatabilityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseFeces
The invention discloses a method for reducing heavy metal emission in livestock and poultry manure. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, producing a mixed feed additive comprising microorganisms, a trace element namely zinc and a carrier, wherein the microorganisms comprise four or five of aspergillus niger, bacillus lentus, bacillus subtilis, bacillus amyloliquefaciens, and lactobacillus plantarum; mixing the mixed feed additive with crushed coarse feed raw materials of which the particle granularity is 0.4-0.7mm, crushed protein feed raw materials, crushed energy feed raw materials, vitamins and mineral elements so as to obtain a complete formula dry powder feed; adding water in the complete formula dry powder feed till the water content is 40-50%; performing anaerobic fermentation under indoor temperature for 3-5 days; and feeding the fermented feed to livestock and poultry in a wet feeding manner. Through the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, the utilization ratios of copper, iron, zinc and manganese in the feed raw materials are increased; trace elements of copper, manganese and iron do not need to be added in feeds for living pigs, so that the possibility that pigs suffer from the disease of gastric ulcer can be reduced; besides, the palatability of feeds can be improved; when the production performance of animals is improved, the heavy metal emission in manure is reduced.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY MEDICINE SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
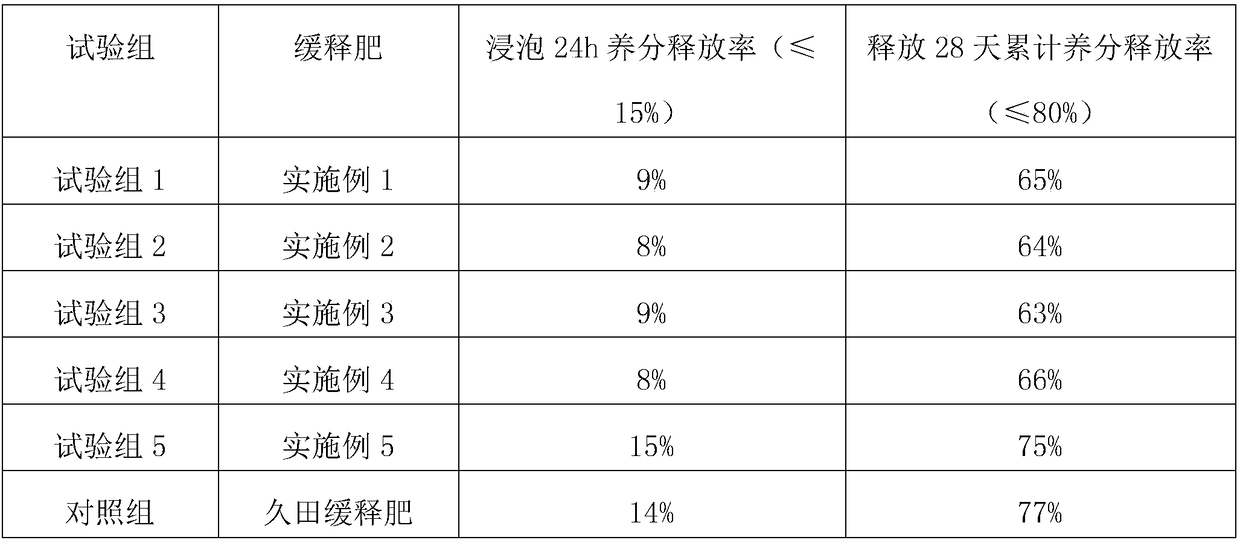
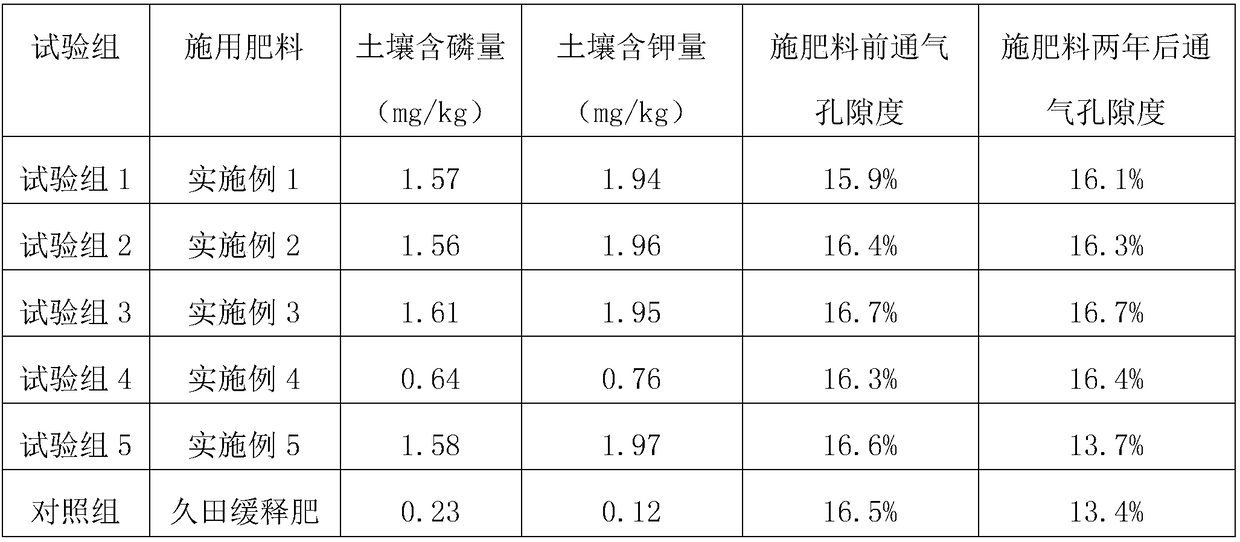
Method for producing sugarcane carbon-based slow-release fertilizer by carbonization of filter mud in sugar refinery
ActiveCN108911877AHealthy growthIncrease profitSuperphosphatesSewage/sludge fertilisersXanthomonas campestrisVegetable oil
The invention belongs to the technical field of fertilizers, and particularly relates to a method for producing a sugarcane carbon-based slow-release fertilizer by carbonization of filter mud in a sugar refinery, the sugarcane carbon-based slow-release fertilizer is mainly prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 40-50 parts of the filter mud, 45-55 parts of alcohol waste liquid, 15 to20 parts of urea, 10 to 15 parts of potassium sulfate, 8 to 12 parts of calcium superphosphate, 0.12 to 0.18 part of Azotobacter chroococcum, 0.15 to 0.35 part of Bacillus subtilis, 0.45-0.64 part ofbacillus mucilaginosus, 0.25-0.46 part of Bacillus lentus, 0.15-0.37 part of Pseudomonas caryophylli, 2-4 parts of lignin, 1-3 parts of vegetable oil, 0.2 to 0.5 part of sulfuric acid, 2 to 3 parts of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris gum and 1 to 3 parts of curdlan. The method comprises preparing of fertilizer core particles, preparing of a coating and coating. The method solves the problemsof low utilization rate of fertilizers in the prior art and difficulty in degradation of a coating agent material in slow release fertilizers.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Probiotic feed additive for realizing zero discharge of manure waste and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109527209AImprove acid resistanceArrive smoothly and play an effectFungiBacteriaBacillus licheniformisAspergillus oryzae
The invention discloses a probiotic feed additive for realizing zero discharge of manure waste. The feed additive for realizing zero discharge of manure waste is characterized by comprising Candida utilis, Bacillus lentus, Bacillus licheniformis, Lactobacillus delbrueckii, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus reuteri, and Aspergillus oryzae. The bacterial strain matching used by the probiotic feed additive of the invention has the advantages of improving animal immunity and reducing the risk of disease caused by livestock, does not use antibiotics, and is healthy and environmentally friendly.
Owner:共 放鸣
Bacillus capable of promoting production of alcohol and flavor substances from saccharomyces cerevisiae and application thereof
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A kind of dead valley bacillus and application thereof
ActiveCN103952329BHas a growth-promoting effectNon-pathogenicBiocideBacteriaMicroscopic examBacillus lentus
The present invention provides Bacillus vallismortis SZ-4, which has the preservation number of CGMCC No.8273. According to the present invention, the strain grows on a beef extract-peptone (NB) culture medium in a single cell reproduction growth manner to form bacterial colonies, and the bacterial colonies have characteristics of round shape, milk white color, slightly elevated center, and moist and transparent surface; microscopic examination results show that the Bacillus vallismortis SZ-4 has a rod shape, has flagella, has a size of 0.7-0.82*1.6-2.2 mum, presents the positive Gram staining effect, has spores, and can grow on a beef extract-peptone (NB) culture medium containing 2-5% of NaCl, wherein the beef extract-peptone (NB) culture medium comprises: 3.0 g of a beef extract, 10.0 g of peptone, 5.0 g of NaCl, 17 g of agar and 1000 ml of water, and the pH value is 6.8-7.2; and the Bacillus vallismortis SZ-4 provides significant antagonism effects for pathogenic bacteria causing ginseng root rot, blight, sclerotinia sclerotiorum and botrytis cinerea. The present invention further provides an application of the Bacillus vallismortis SZ-4 in prevention and control of plant fungal diseases or preparation of microorganism preparations for prevention and control of plant fungal diseases.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Detergent composition
InactiveUS20110143988A1Positively impactingEasy to cleanSurface-active detergent compositionsDetergent compounding agentsNumbering systemHydrogen
Automatic dishwashing detergent composition for use in the main wash of a dishwasher to provide drying wherein the detergent comprises an esterified alkyl alkoxylated surfactant of general formula (I)whereR is a branched or unbranched alkyl radical having 8 to 16 carbon atoms;R3, R1 independently of one another, are hydrogen or a branched or unbranched alkyl radical having 1 to 5 carbon atoms;R2 is an unbranched alkyl radical having 5 to 17 carbon atoms;l, n independently of one another, are a number from 1 to 5 andm is a number from 13 to 35; andan enzyme selected from:a) a protease demonstrating at least 90% identity with the wild-type enzyme from Bacillus lentus, comprising mutations in one or more, preferably two or more and more preferably three or more of the following positions, using the BPN' numbering system and amino acid abbreviations as illustrated in WO00 / 37627:68, 87, 99, 101, 103, 104, 118, 128, 129, 130, 167, 170, 194, 205 & 222 and optionally one or more insertions in the region comprising amino acids 95-103;b) an amylase exhibiting at least 95% identity with the wild-type enzyme from Bacillus sp.707 (SEQ ID NO:7 in U.S. Pat. No. 6,093,562), especially those comprising one or more of the following mutations M202, M208, S255, R172, and / or M261; andc) a mixture thereof.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method for preparing high-strength microbial mortar using urease-producing microorganisms
ActiveCN103173376BStrong ability to produce ureaseHigh urease activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEpoxyBacillus lentus
Urease-producing microbes including Sporosarcina antarctica U R 5 3, Sporosarcina koreensis UR47, Sporosarcina sp. UR31 and Bacillus lentus UR41 were preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on March 16, 2012, with the preservation numbers of CGMCC No.5916, CGMCC No.5915, CGMCC No.5913 and CGMCC No.5914 respectively. The method for preparing high-strength microbial mortar by using the urease-producing microbes comprises the following steps of: carrying out fermentation culture on the above four microbes and microbes including Sporosarcina pasteurii and Terrabacter tumescens in a fermentation culture medium to obtain a bacterial solution; and filling the bacterial solution, a fixative solution and a gelling solution into a sand particle system in batches to form microbial mortar of which the highest strength can reach 55MPa. The mechanical properties of the microbial mortar are superior to those of a cement base material; compared with a cement lime material with equivalent strength, the microbial mortar is higher in splitting tensile strength; the rigidity of the microbial mortar is similar to that of cement lime mixed mortar but far smaller than that of concrete; the fatigue load tolerance and cyclic loading capacity of the microbial mortar are higher than those of the cement base material; and an artificial sandstone is an inorganic material, and is not easy to age like organic materials including epoxy resin and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Urease-producing microorganisms and method for solidifying heavy metals in foundation using same
ActiveCN102703341BEfficient governanceShorten the timeBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationWater insolubleBacillus lentus
Urease-producing microorganisms of Sporosarcina antarctica UR53, Sporosarcina koreensis UR47, Sporosarcina sp. UR31 and Bacillus lentus UR41 were preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on March 16, 2012 with the preservation numbers of CGMCC NO.5916, CGMCC NO.5915, CGMCC NO.5913 and CGMCC NO.5914, respectively. The method for solidifying heavy metals in the foundation by using the urease-producing microorganisms comprises the steps of: carrying out fermentation culture on the four microorganisms and microorganisms of Sporosarcina pasteuril and Terrabacter tumescens in a fermentation culture medium to obtain microorganism liquid, adding reaction liquid urea to the microorganism liquid, and then adding to the solution containing heavy metals to form a mixed solution, so that microorganism-heavy metal flocculates are formed in the mixed solution and then water-insoluble heavy metal carbonates are further formed. The method for solidifying the heavy metals in the foundation by using the microorganisms has the advantages of short solidifying time, good effect, low cost and no secondary pollution to environment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Concrete crack repairing technology based on microorganisms
InactiveCN111825422AImprove repair efficiencyImprove restoration qualityBacteriaBuilding repairsBiotechnologyCALCIUM LACTOBIONATE
The invention relates to the technical field of concrete crack repairing, and further discloses a concrete crack repairing technology based on microorganisms. The technology involves the following rawmaterials by weight: 15-5 parts of calcium carbonate, 5-10 parts of bacillus sphaericus, 5-10 parts of bacillus lentus, 15-25 parts of calcium lactate, 3-9 parts of peptone, 5-12 parts of glutamate,10-18 parts of spore powder, 80-150 parts of an oxygen release agent, 6-18 parts of nutrient substance and 3-9 parts of an acid-base regulator. According to the concrete crack repairing technology based on the microorganisms, calcium carbonate deposition is driven through urea metabolism of bacillus sphaericus and bacillus lentus, and then calcium carbonate is rapidly catalyzed by the microorganisms for precipitation, so that the effect of improving the concrete crack repairing efficiency and quality is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN XINBIN ENG TECH INSPECTION
Preparation method of antibiotic-free amino acid piglet mixed feed additive
InactiveCN109170148APromote growthPromote growth hormone secretionAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsAmylaseCentella asiatica extract
The present invention relates to a preparation method of an antibiotic-free amino acid piglet mixed feed additive. A formula comprises the following raw materials in weight percentages: 2.1-3.1% of L-tyrosine, 2.3-3.3% of natural vitamin E, 1.5-2.5% of tricalcium phosphate, 2.5-3.5% of lactobacillus buchneri, 2.2-3.2% of dimethylancymidol menadione sulfite, 2.6-3.6% of bacillus lentus, 0.1-1.1% ofmanganese carbonate, 0.5-1.5% of a snake gall extract, 0.3-1.3% of a centella asiatica extract, 0.9-1.9% of enterobacter cloacae, 0.2-1.2% of Japanese cayratia herb, 1.1-2.1% of amylase, 1.9-2.9% ofrhizoma coptidis, 1.8-2.8% of indigo, 2-3% of lignosulfonate, 1.3-2.3% of niacin, 1.5-2.5% of radix scutellariae, 1.2-2.1% of radix sophorae flavescentis, 0.6-1.6% of probiotics, 0.3-1.3% of amino acids and 73.1-53.2% of water. The antibiotic-free amino acid piglet mixed feed additive has a relative good adsorption of bacterial toxin, purifies intestinal environment, promotes growth hormone secretion, promotes growth of piglets, and has a good growth-activating effect especially for the piglets.
Owner:CHANGSHA XIEHAOJI BIOENG CO LTD
Microorganism-enhanced microbial agent capable of remarkably promoting composting effect before household garbage incineration, and application thereof
ActiveCN111004748AEasy growth metabolismGrow fastBacteriaSolid waste disposalBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a microorganism-enhanced microbial agent capable of remarkably promoting the composting effect before household garbage incineration, and an application thereof. The enhanced microbial agent is prepared by mixing a plurality of composite microbial agents or mixing the composite microbial agents with a carrier, and the composite microbial agents comprise Lactobacillus pasteurii with the preservation number of CGMCC No.18391, Clostridium butyricum with the preservation number of CGMCC No.14499, Bacillus lentus with the preservation number of CGMCC No.18392, and Bacillus psychrophilus with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 18393. The microorganism-enhanced microbial agent can obviously promote the composting effect before household garbage incineration, increase thelow calorific value during garbage incineration and promote garbage dehydration, also can increase the abundance and content of functional microorganisms in garbage composting and accelerate the garbage fermentation process, and can rapidly start the composting process in cold regions to remarkably reduce the use of a combustion improver.
Owner:QINGDAO SHANGDE BIOTECH
Salt-tolerant Bacillus lentus GBW-HB1902 and application thereof
ActiveCN111004749APromote degradationSolve the problems of poor biochemical properties and low pollutant removal efficiencyBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyBacillus lentus
The invention provides a salt-tolerant Bacillus lentus GBW-HB1902 and an application thereof. The classification name of the Bacillus lentus GBW-HB1902 is Bacillus lentus with the preservation numberof CGMCC No.18392, the bacterial colony of the strain is round and faint yellow, the diameter is 1-2 [mu]m, the surface is smooth, wet and glossy, the middle of the surface is slightly convex and opaque, and the edge of the surface is neat and free of halo ring; and the optimal growth temperature is 28-32 DEG C, and the pH value is 7.2-8.5. The Bacillus lentus GBW-HB1902 has broad salt tolerance,can grow normally under a salt concentration of 2-4%, has the capacity of rapidly degrading ammonia nitrogen in sewage in a high-salt environment, can effectively improve the biological treatment effect of water containing ammonia nitrogen difficult to degrade and the operation stability of sewage treatment facilities under a high-salt extreme environment condition, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:QINGDAO SHANGDE BIOTECH
Bacillus capable of promoting production of alcohol and flavor substances from saccharomyces cerevisiae and application thereof
ActiveCN106754581ABacteriaAlcoholic beverage preparationBacillus licheniformisBrevibacterium saccharolyticum
The invention discloses bacillus capable of promoting production of alcohol and flavor substances from saccharomyces cerevisiae and an application thereof, belonging to the technical field of bioengineering. The bacillus disclosed by the invention comprises bacillus licheniformis CGMCC NO.3963, bacillus cereus CCTCC NO:M 2013369, bacillus lentus CCTCC NO:M 2013370 and bacillus methylotrophicus CCTCC NO:2013371. After mixed culture of the bacillus and saccharomyces cerevisiae, the alcohol output can be increased by over 20% while saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolism aldehydes, alcohols, esters, acids and other flavor substances are increased. By applying the bacillus to fermented liquor production, the liquor yield can be increased, and the flavor quality of the fermented liquor is remarkably improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Antimicrobial-free selenium-enrichment piglet mixed feed additive preparation method
InactiveCN109198169AMaintain integrityMaintain epithelial cell functionAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsAdditive ingredientManganese
The invention relates to an antimicrobial-free selenium-enrichment piglet mixed feed additive preparation method. A formula of the antimicrobial-free selenium-enrichment piglet mixed feed additive comprises the ingredients by weight percent: 1.8 to 2.8% of L-tyrosine, 2.3 to 3.3% of natural vitamin E, 1.2 to 2.2% of rhizoma pinelliae, 2.3 to 3.3% of lactobacillus buchneri, 1.5 to 2.5% of trisodiummonohydrogen, 2.5 to 3.5% of saw palmetto extractive, 2 to 2.8% of bacillus laterosporus, 1.3 to 2.3% of mile swertia herb, 2.6 to 3.6% of radix berberidis, 1 to 2% of enterobacter cloacae, 0.5 to 1.5% of calcium propionate, 1.2 to 2.2% of radix angelicae sinensis, 0.3 to 1.3% of dimethyl ancymidol menadione sulfite, 0.8 to 1.8% of bacillus lentus, 0.9 to 1.7% of manganese carbonate, 0.6 to 1.6%of snake gall extractive, 0.9 to 1.8% of chromium yeast, 1.2 to 2.2% of rhynchophylline, 0.9 to 1.9% of probiotic, 0.6 to 1.6% of selenium yeast and 73.6 to 54.1% of water. The antimicrobial-free selenium-enrichment piglet mixed feed additive disclosed by the invention has better functions of promoting mitosis and differentiation proliferation of lymphocyte and macrophage, increasing cell factorsand maintaining intestinal mucosa completeness and mammary epithelial cells.
Owner:CHANGSHA XIEHAOJI BIOENG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com