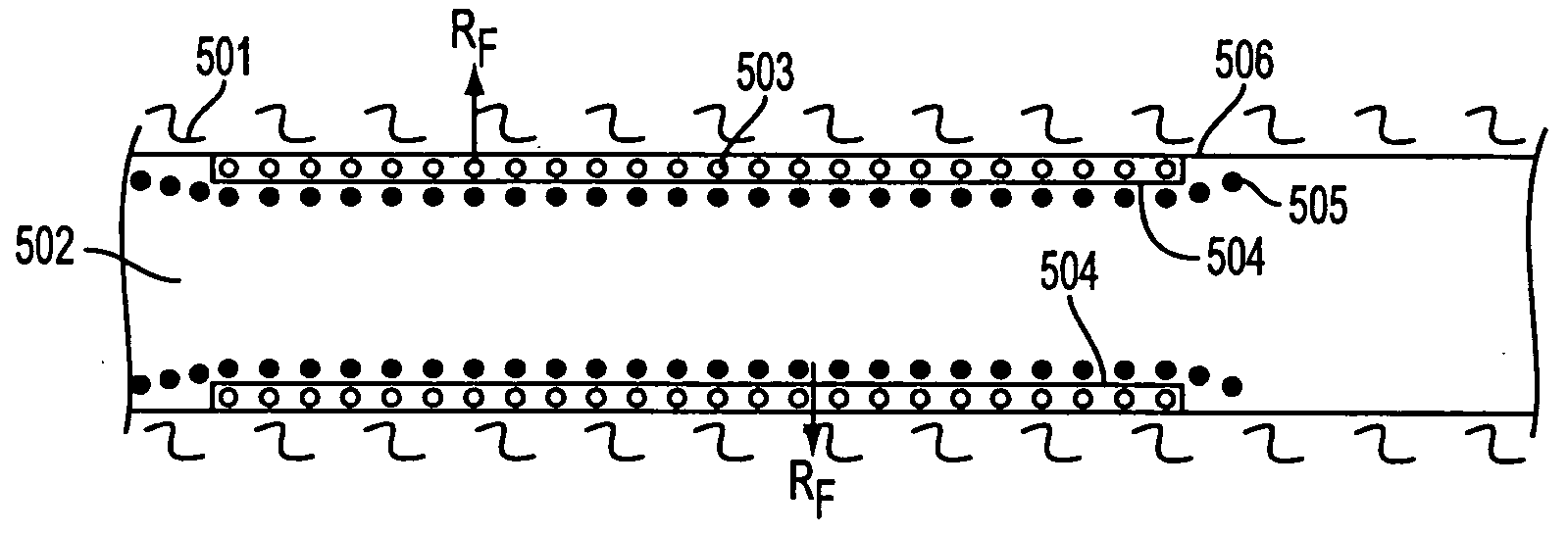
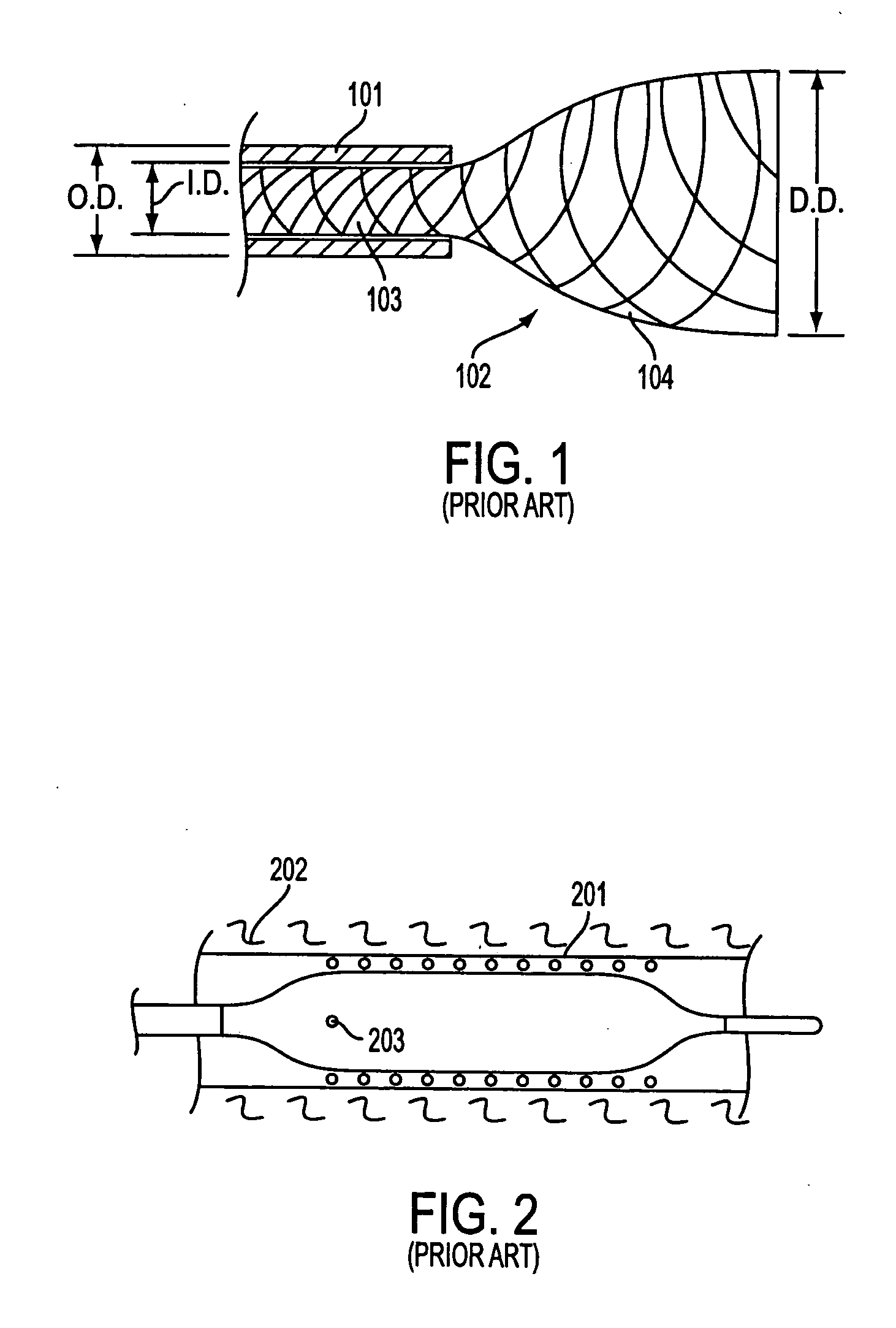
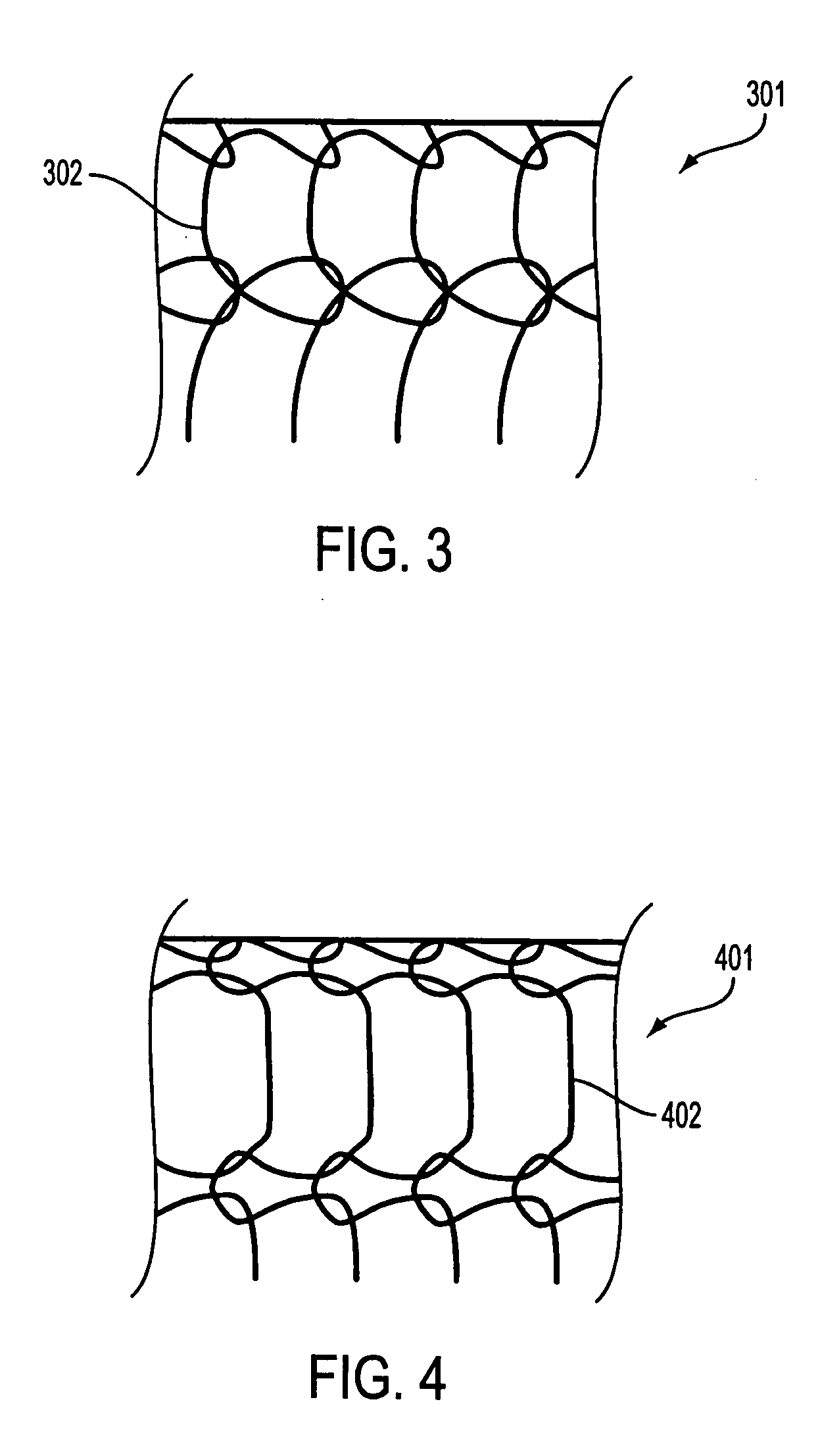
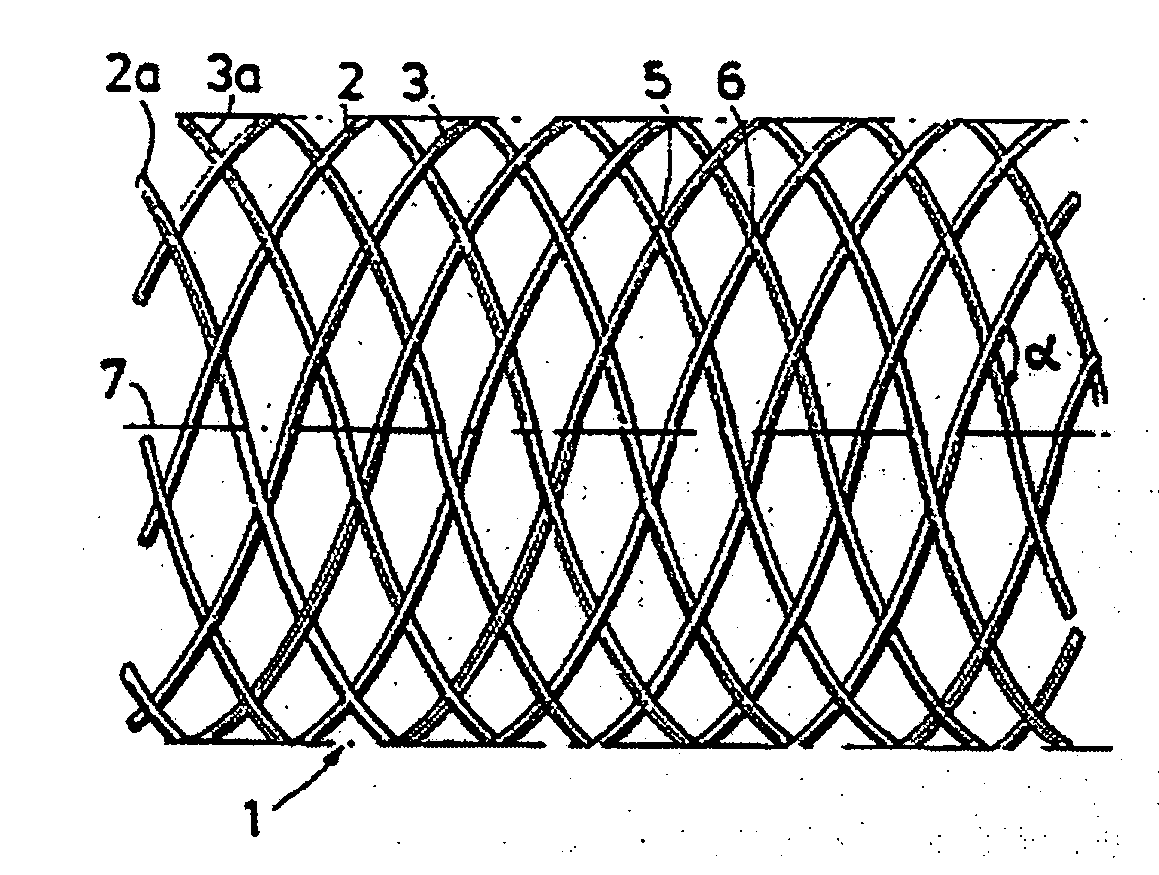
Patents
Literature
75 results about "Bioabsorbable stent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
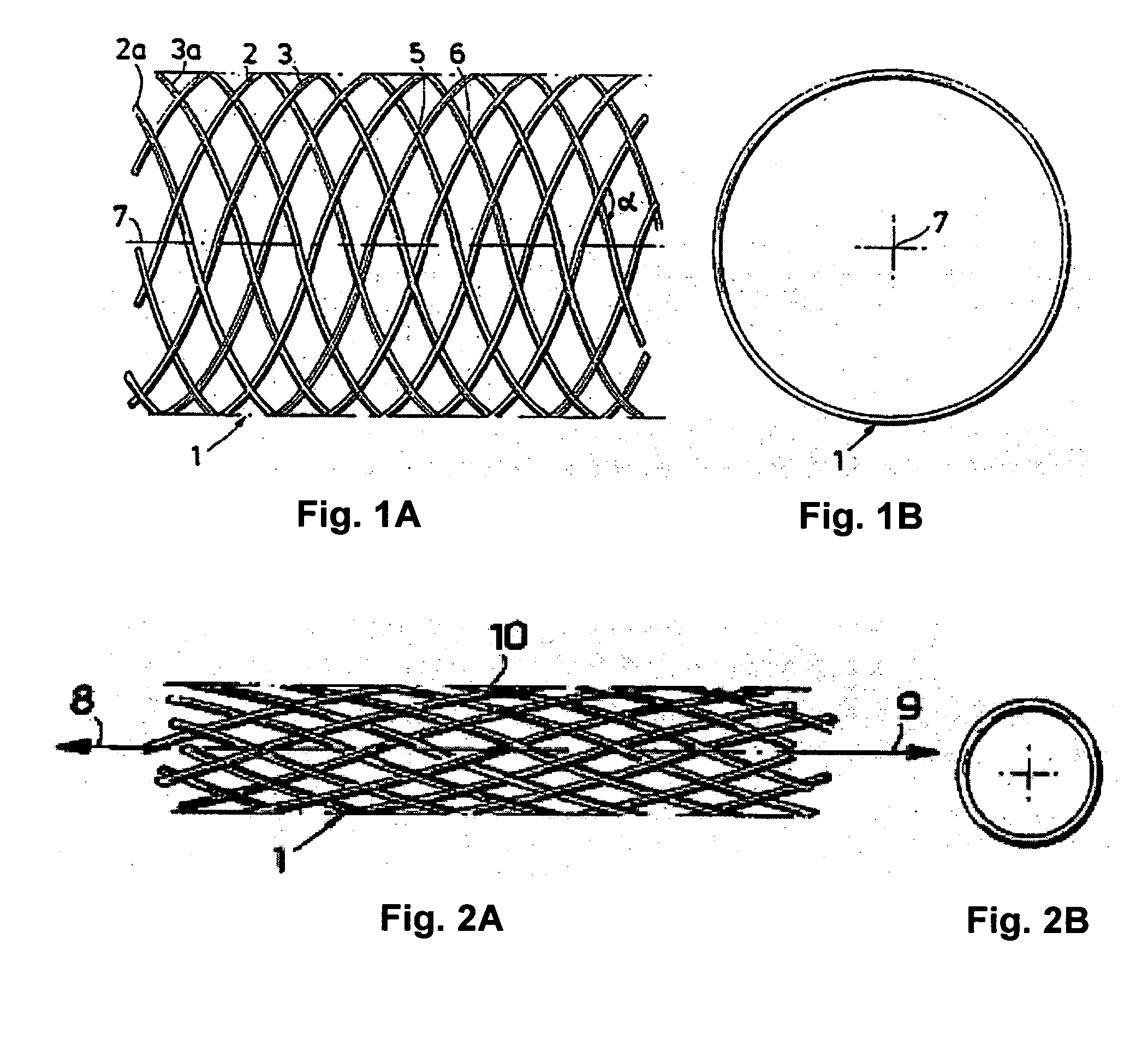
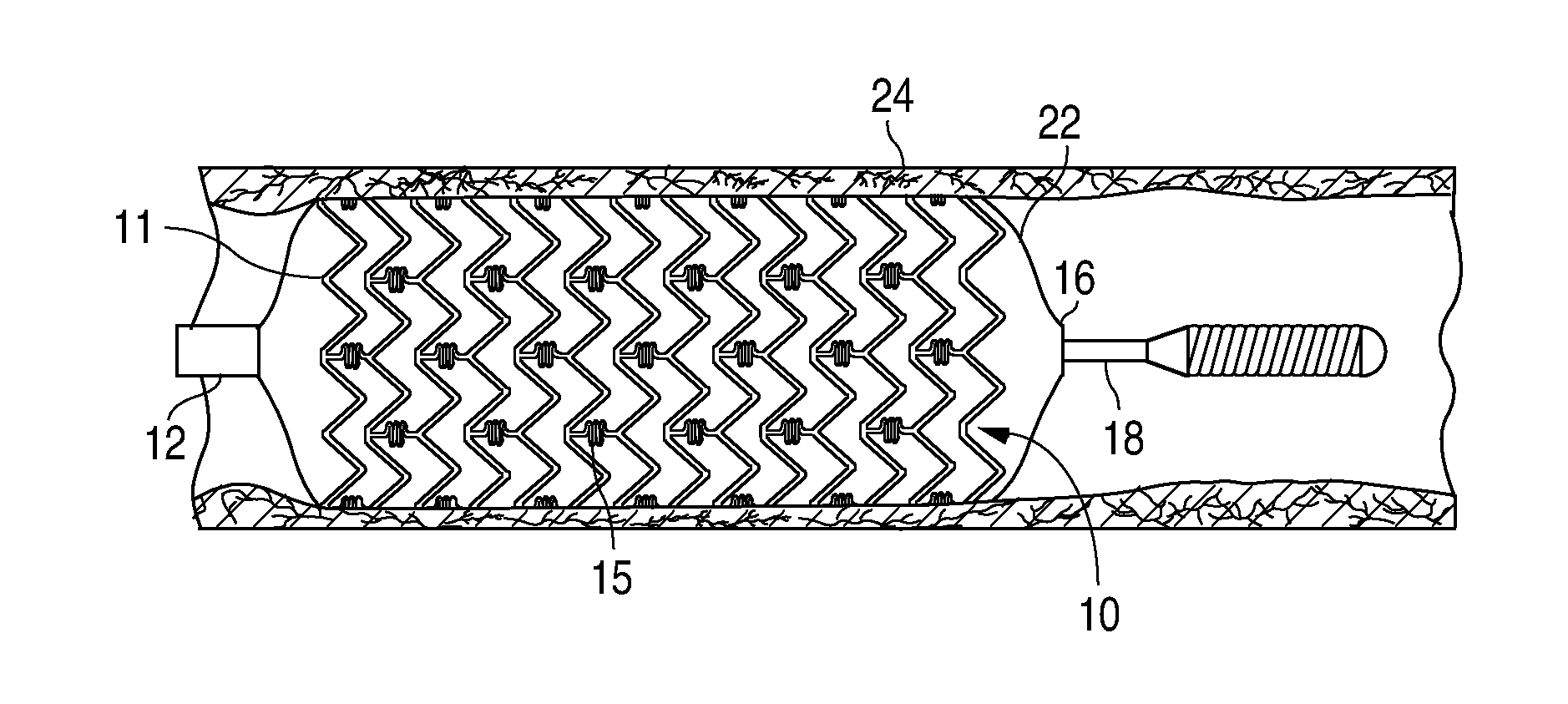
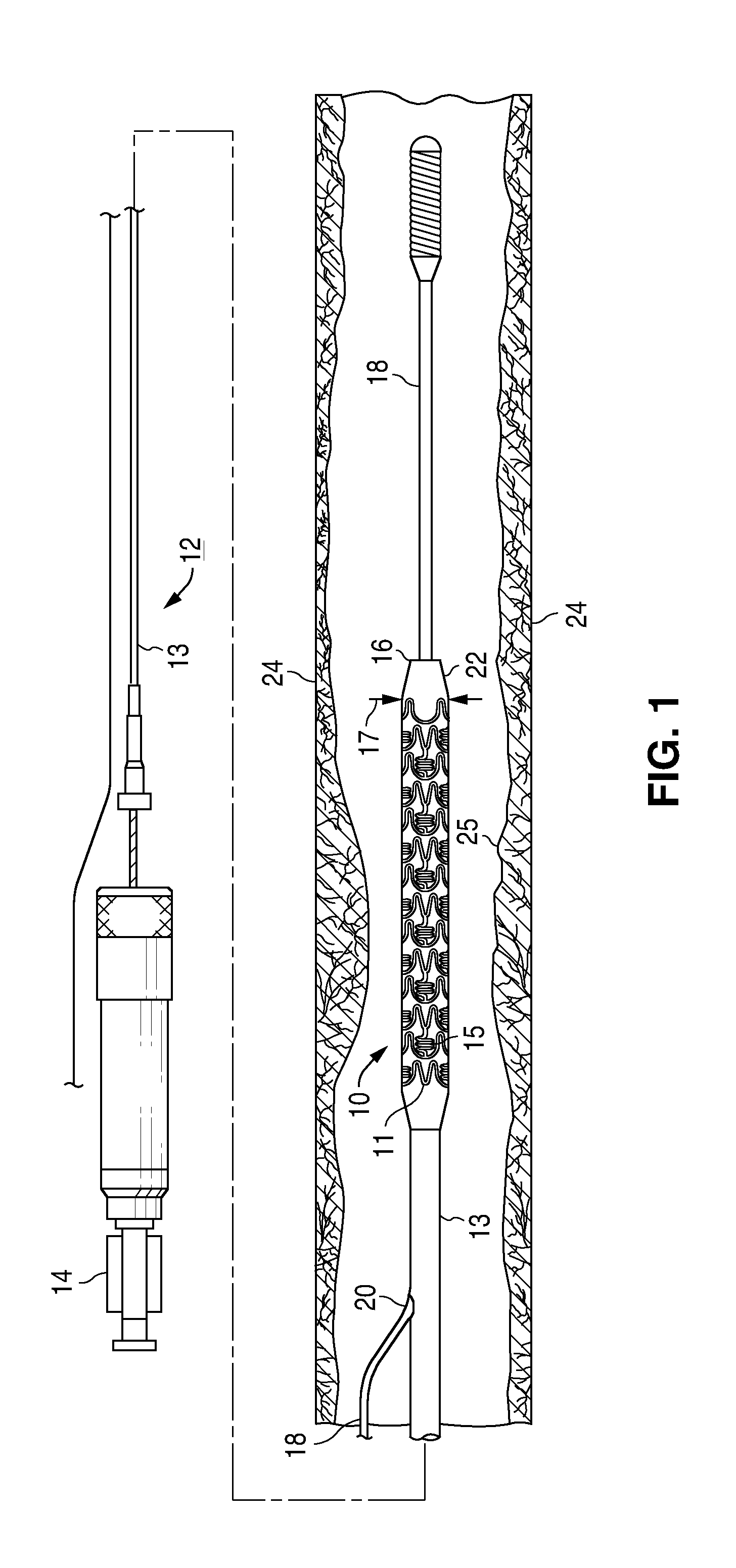
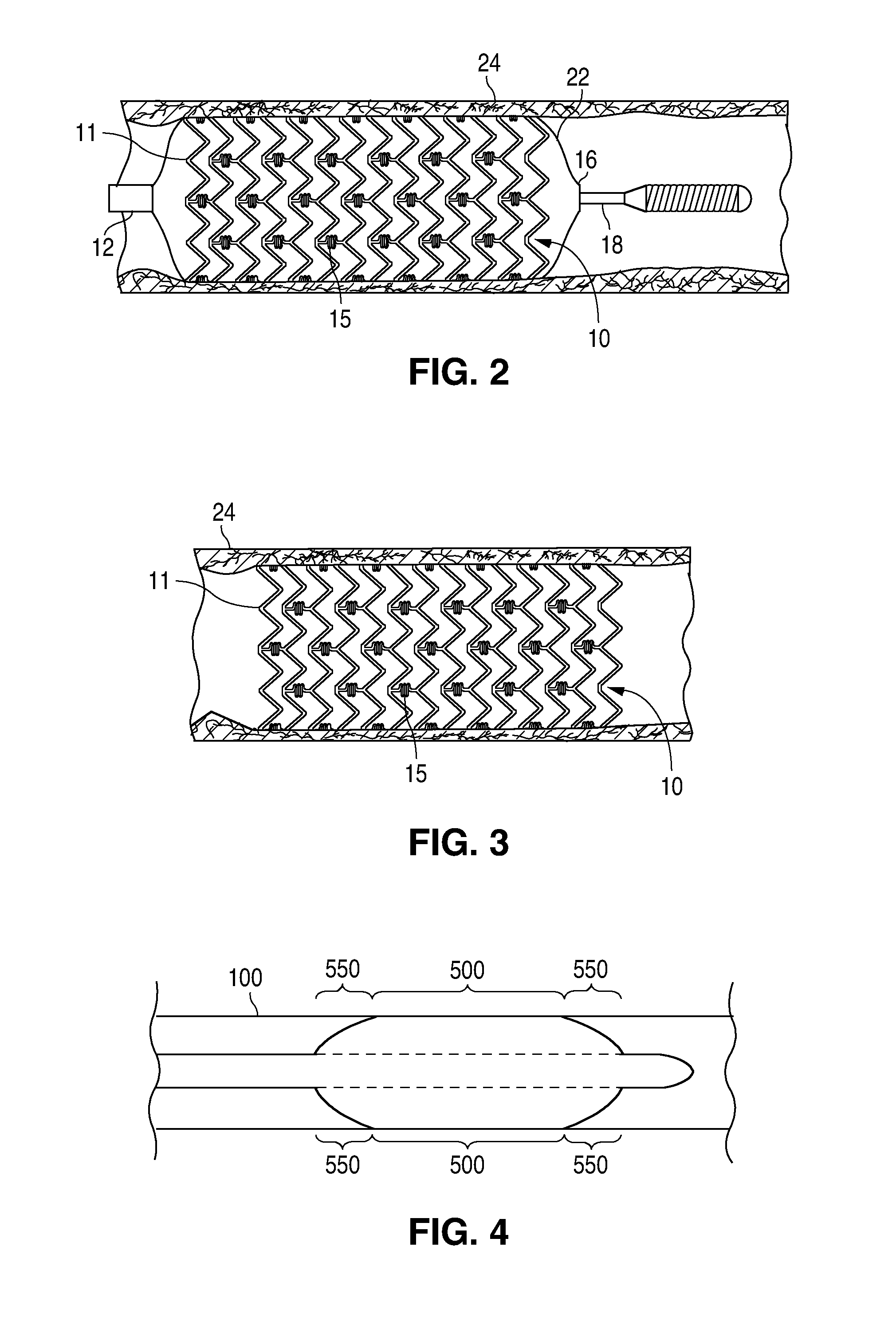
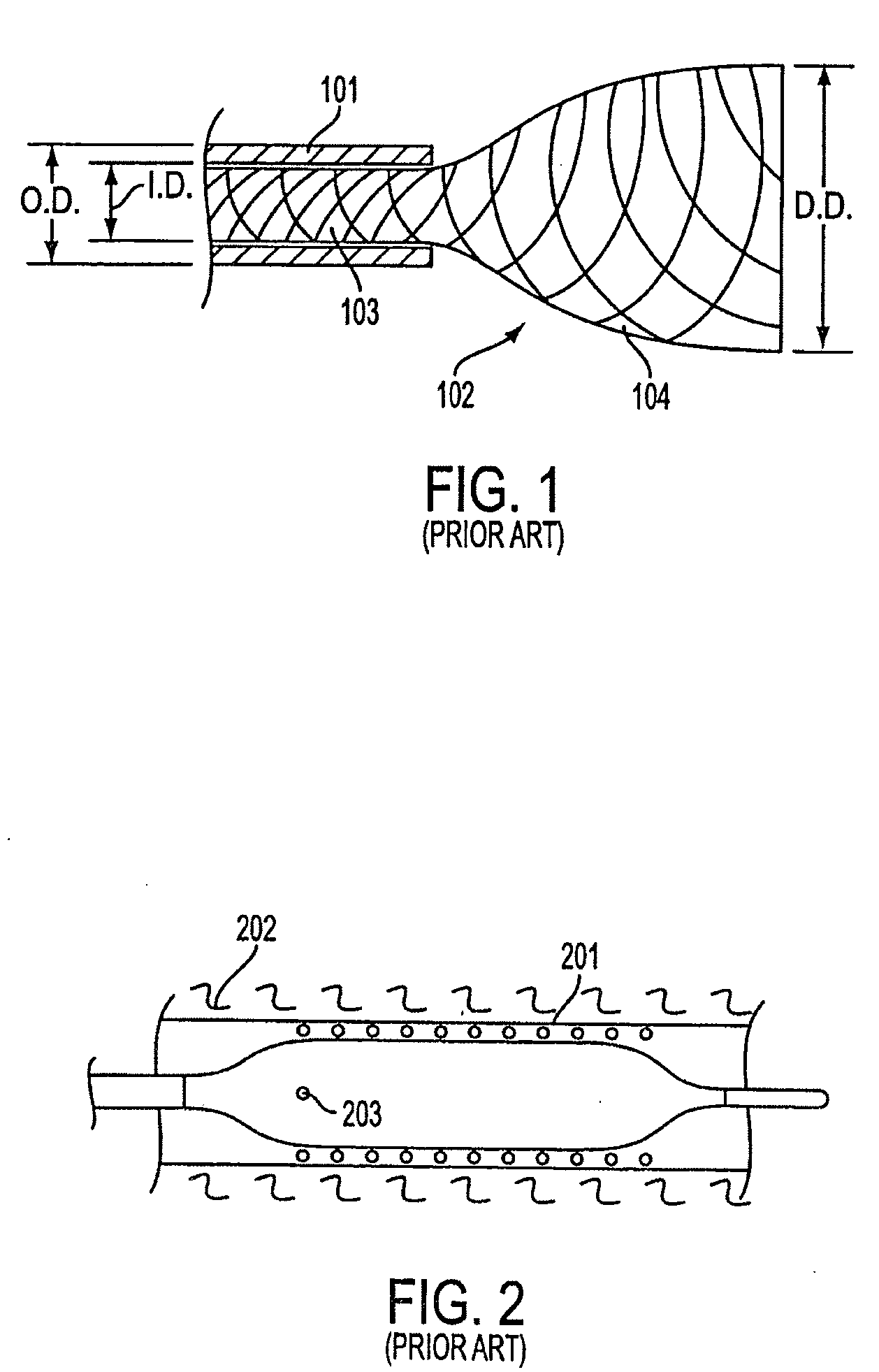
A bioresorbable stent, (also called biodegradable, or naturally-dissolving) serves the same purpose, but is manufactured from a material that may dissolve or be absorbed in the body. ... This is much short of the three-to-six month window desired for bioabsorbable stents.
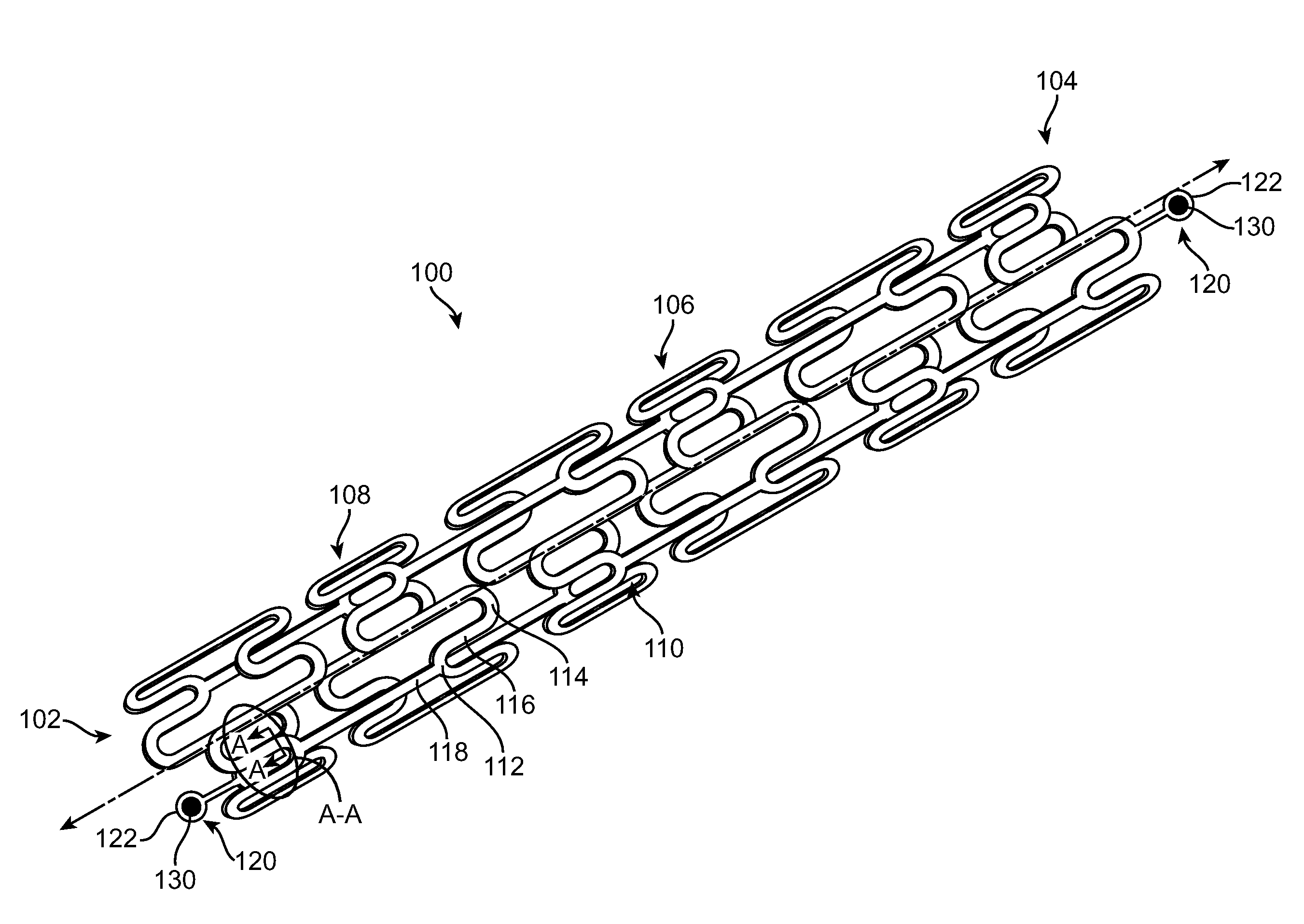
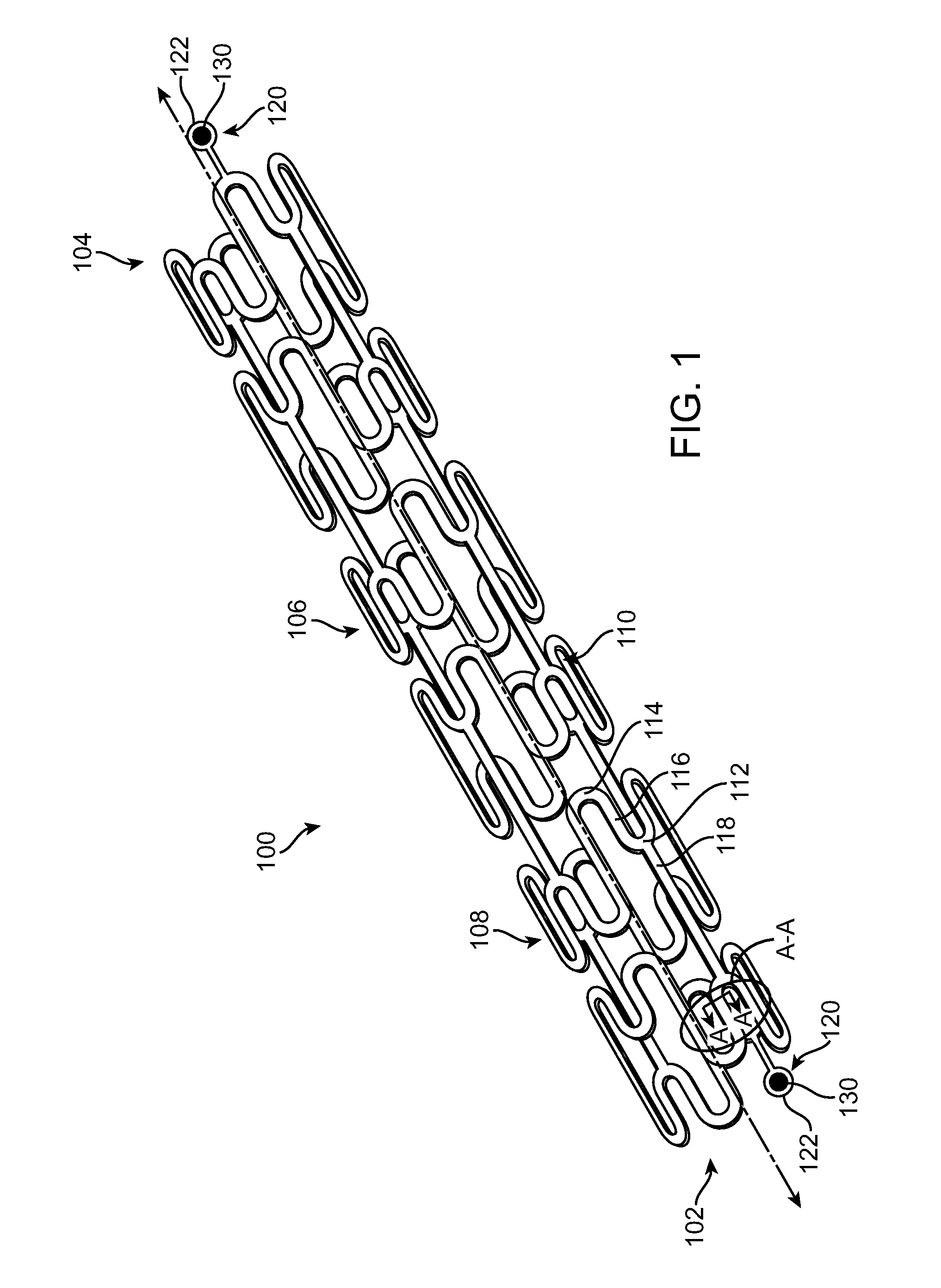
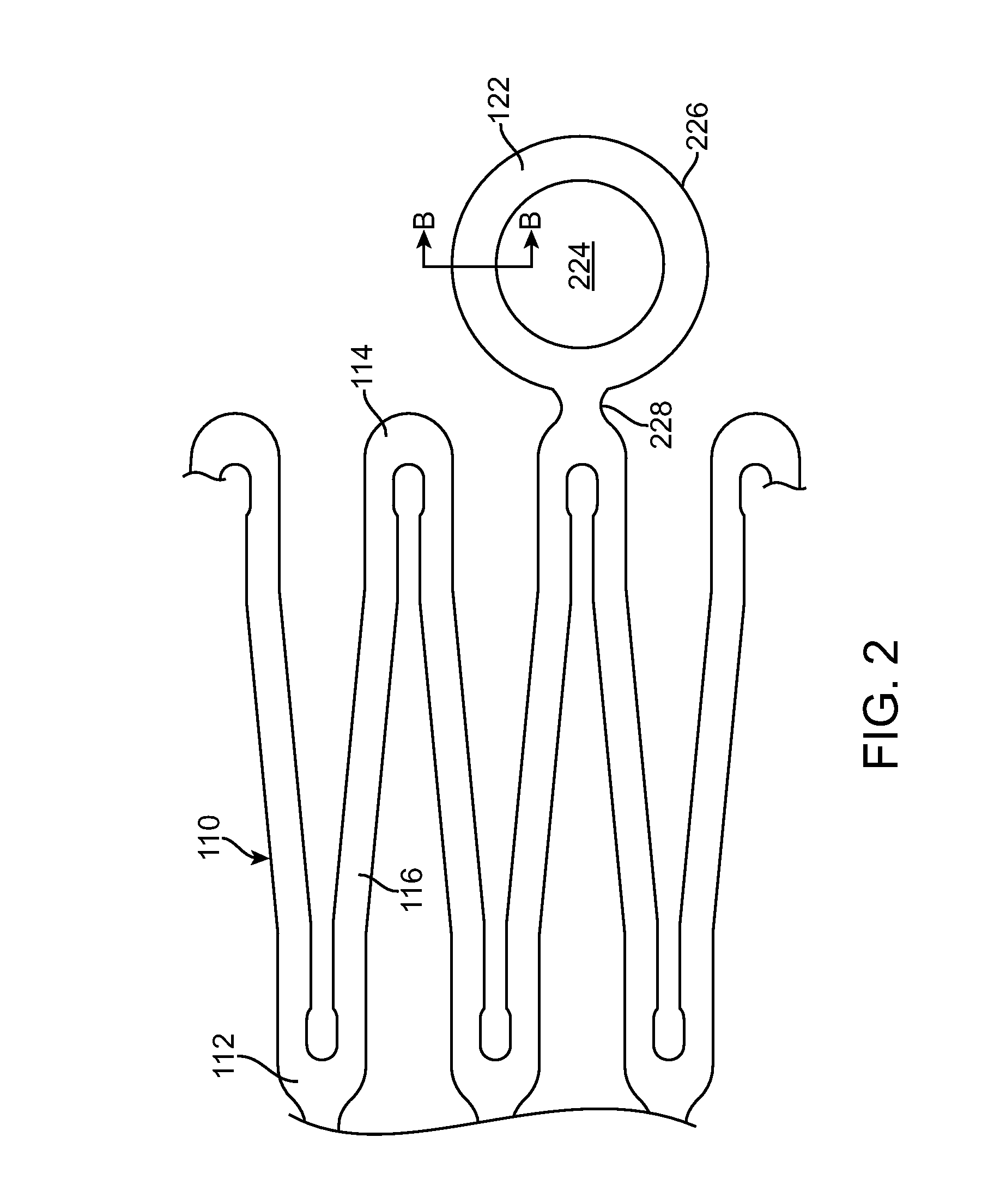
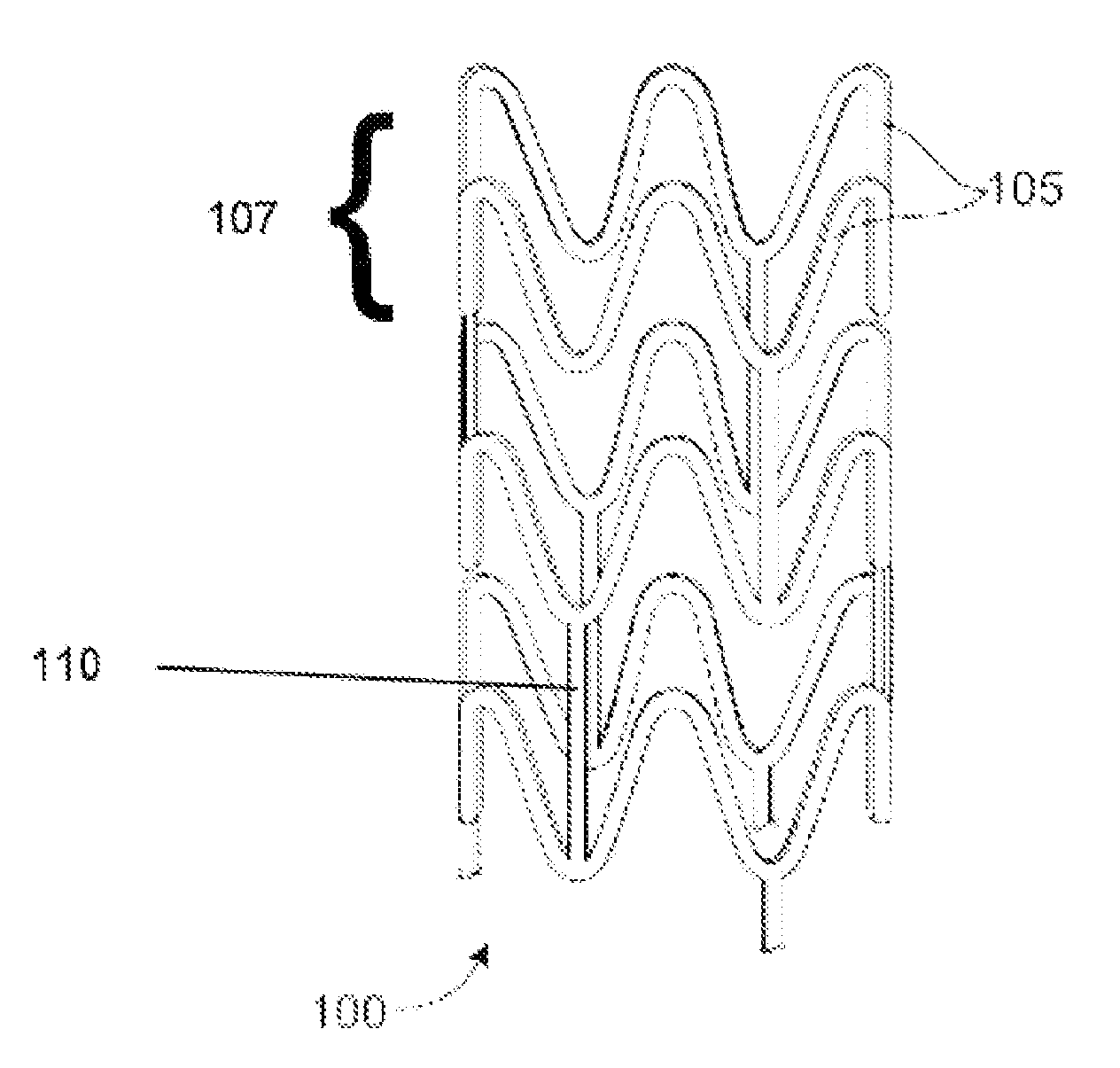
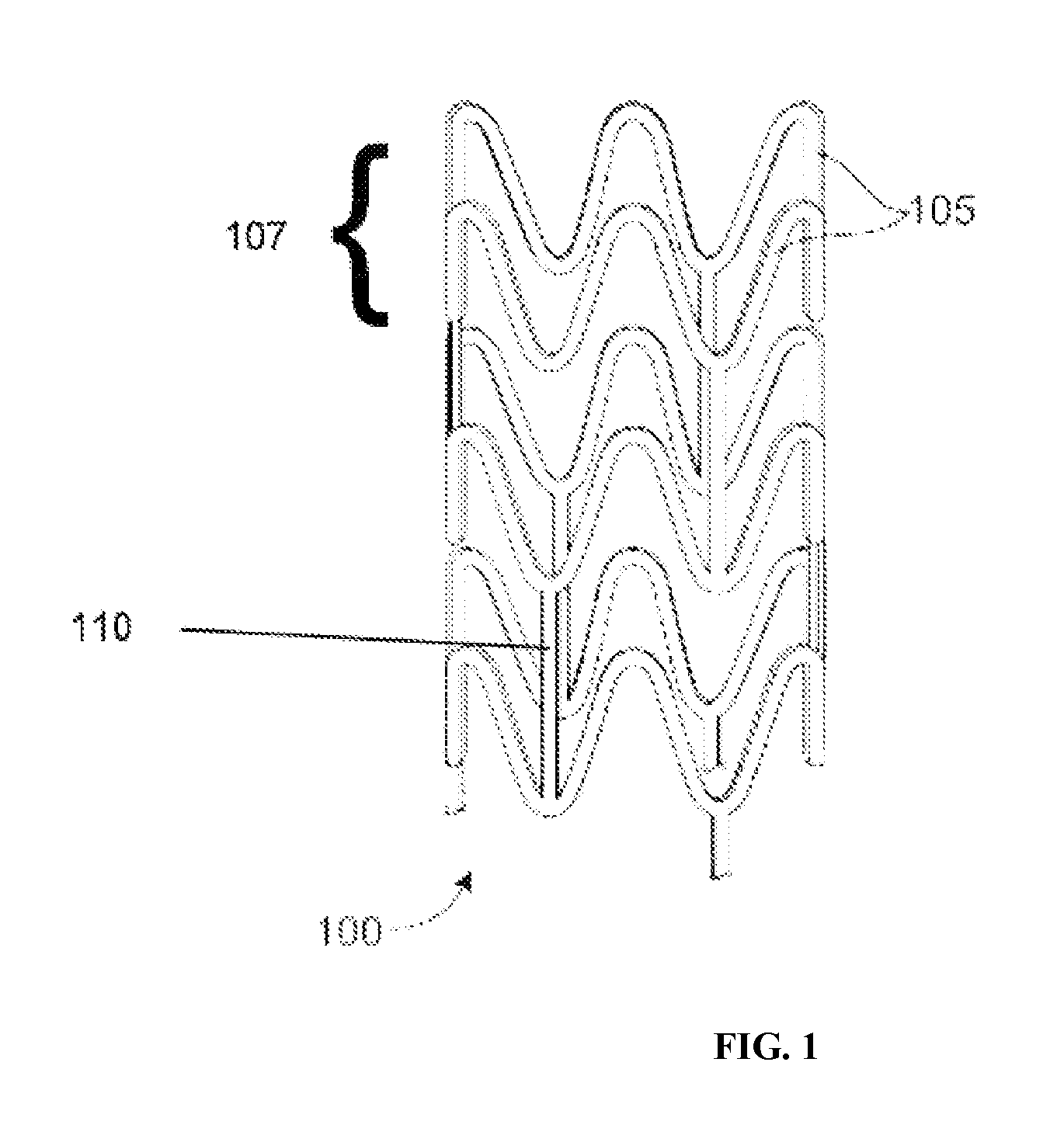
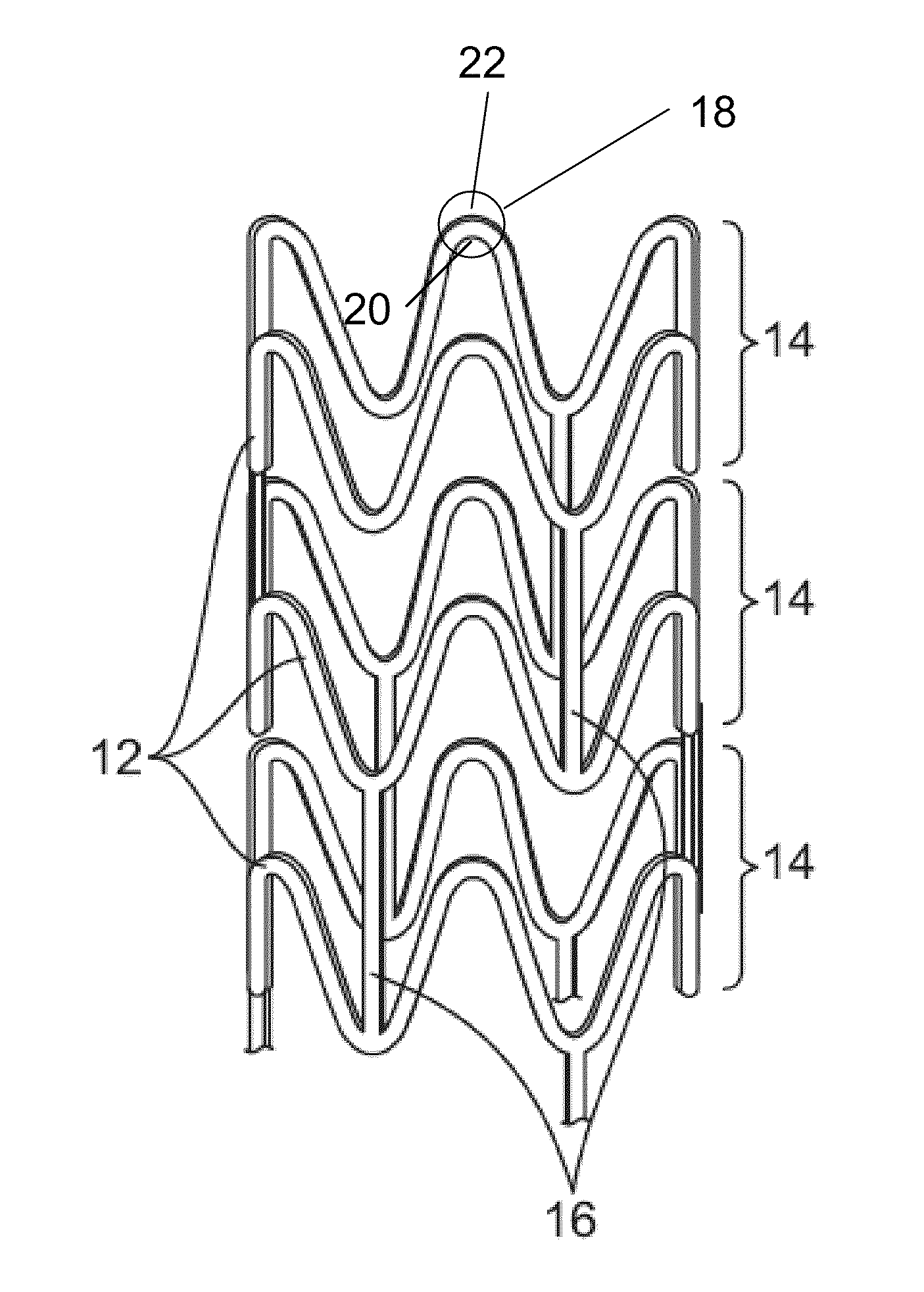
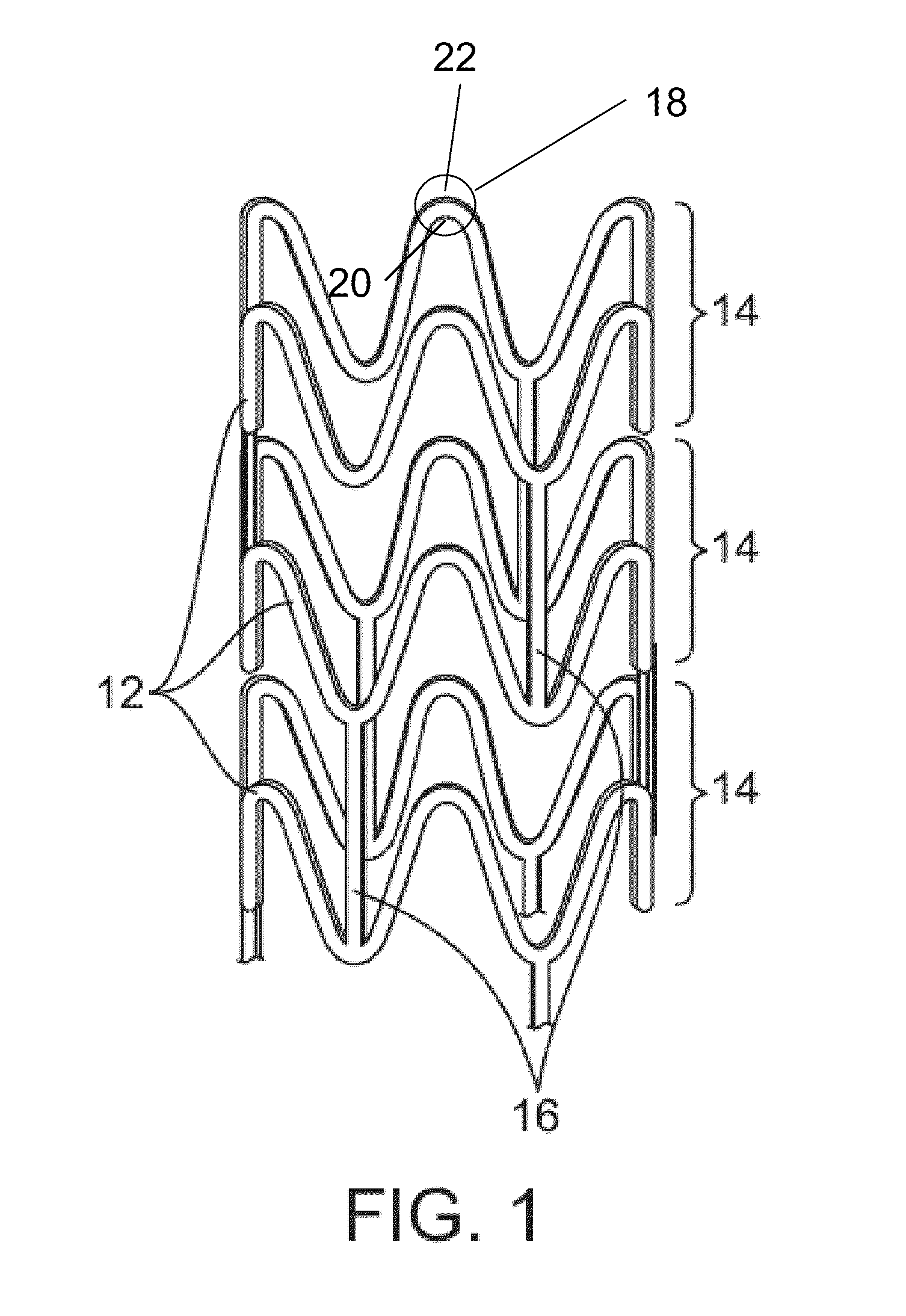
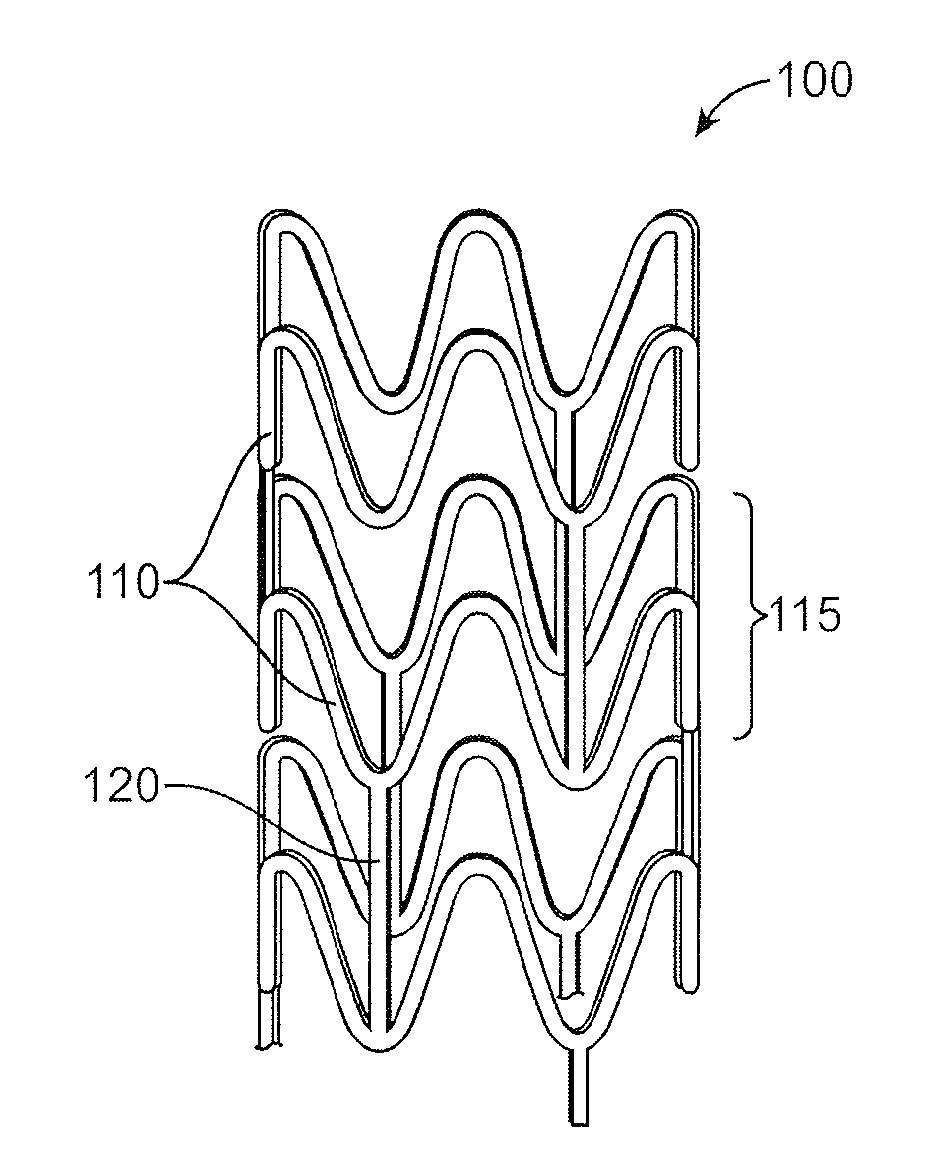
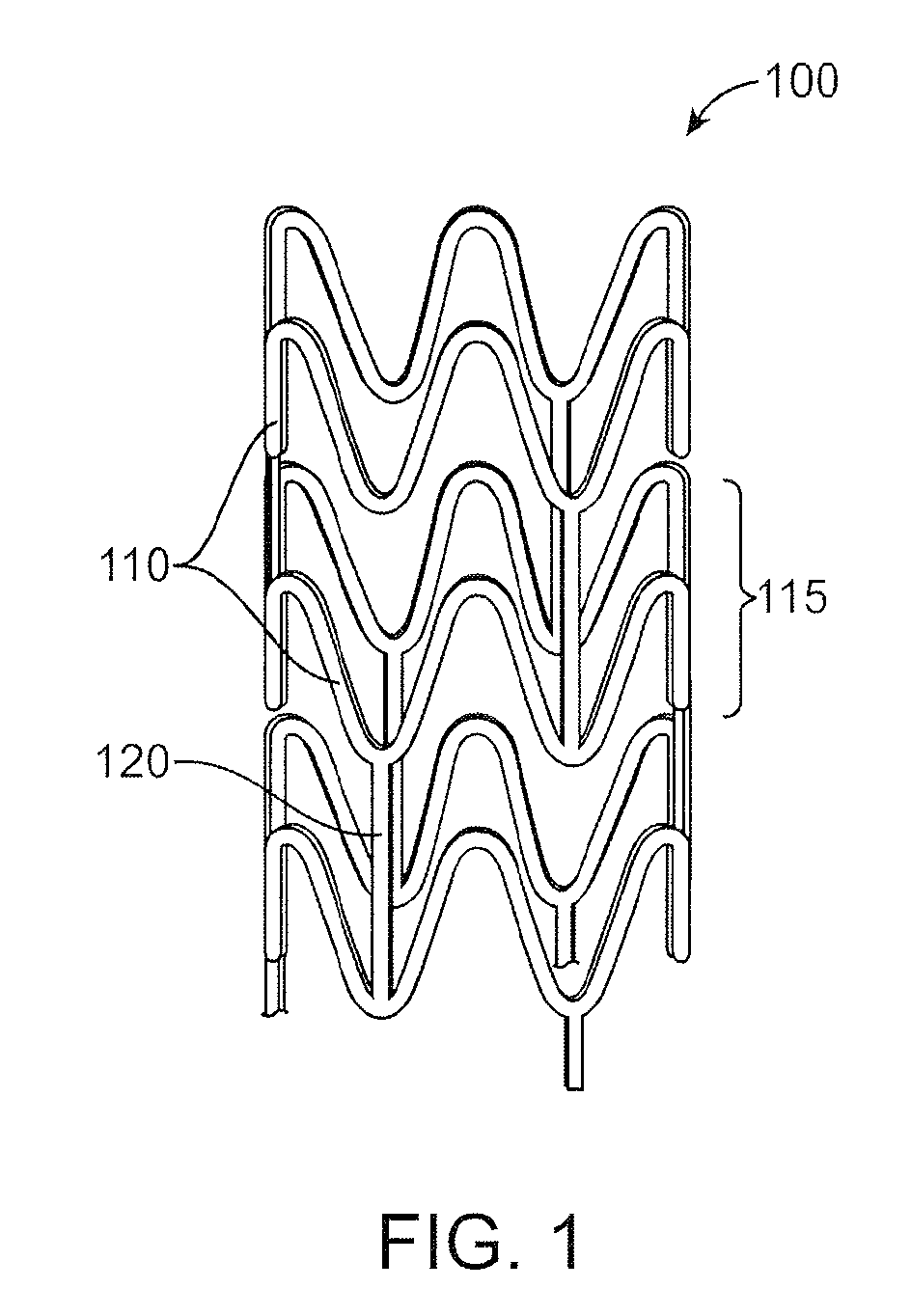
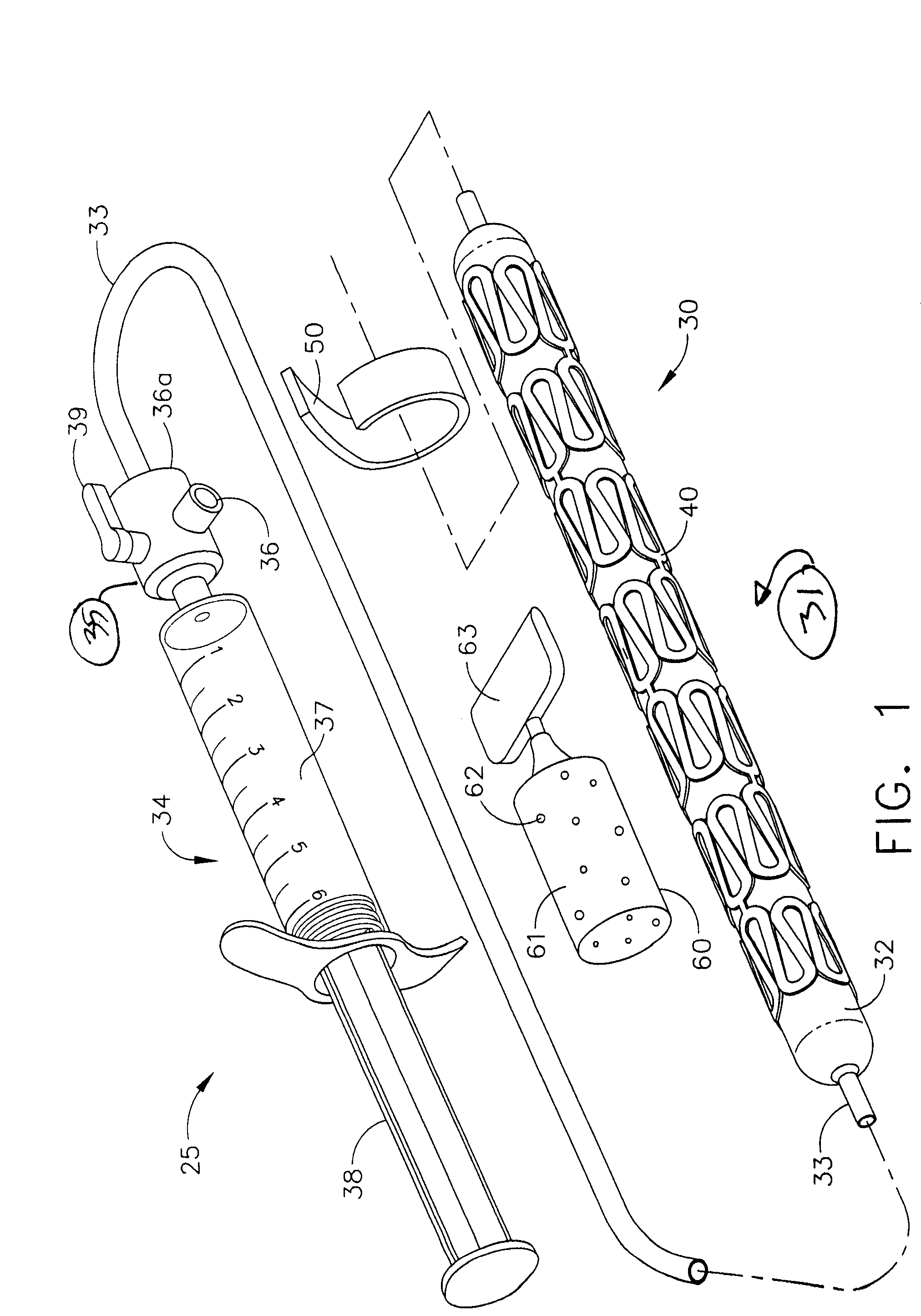
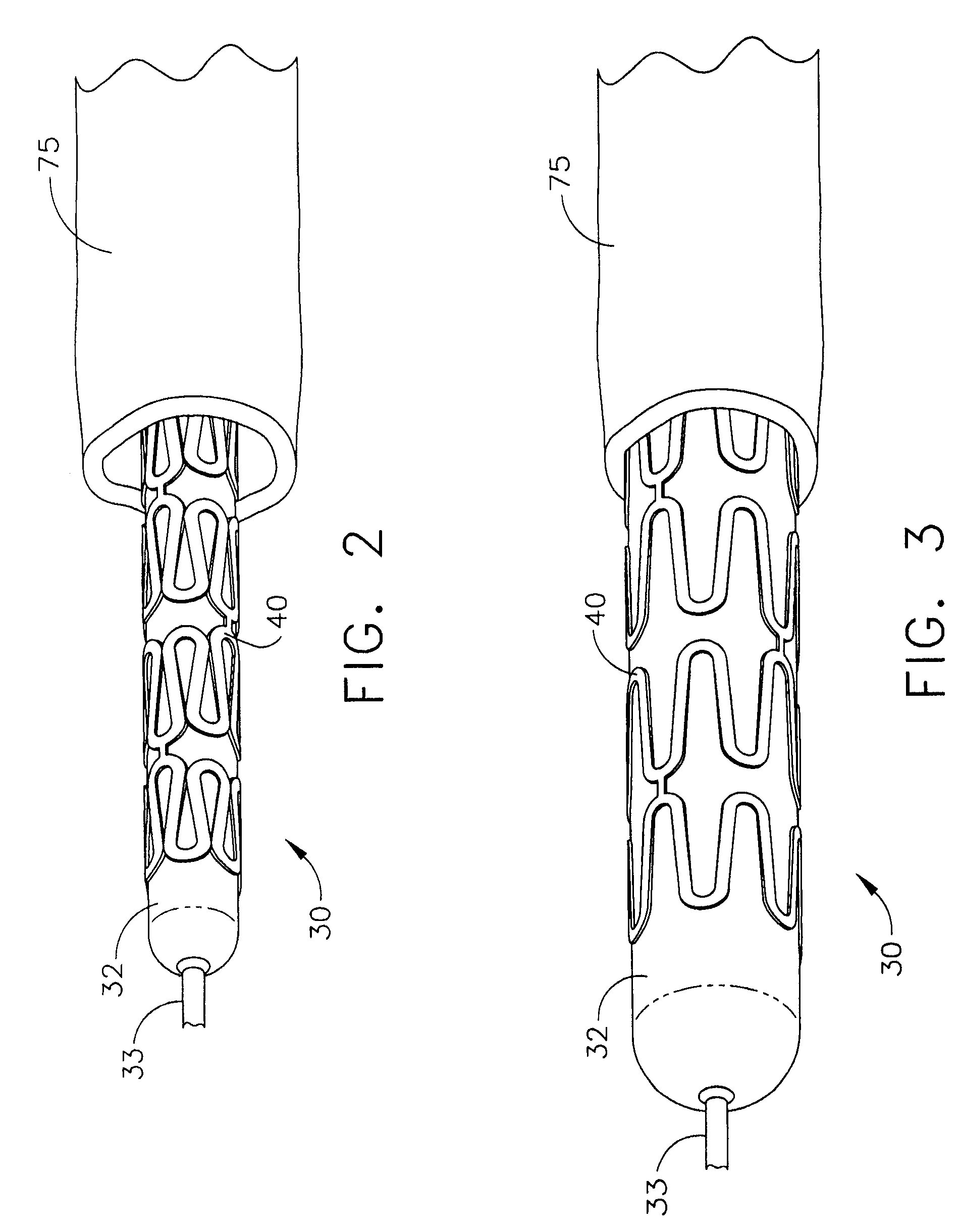
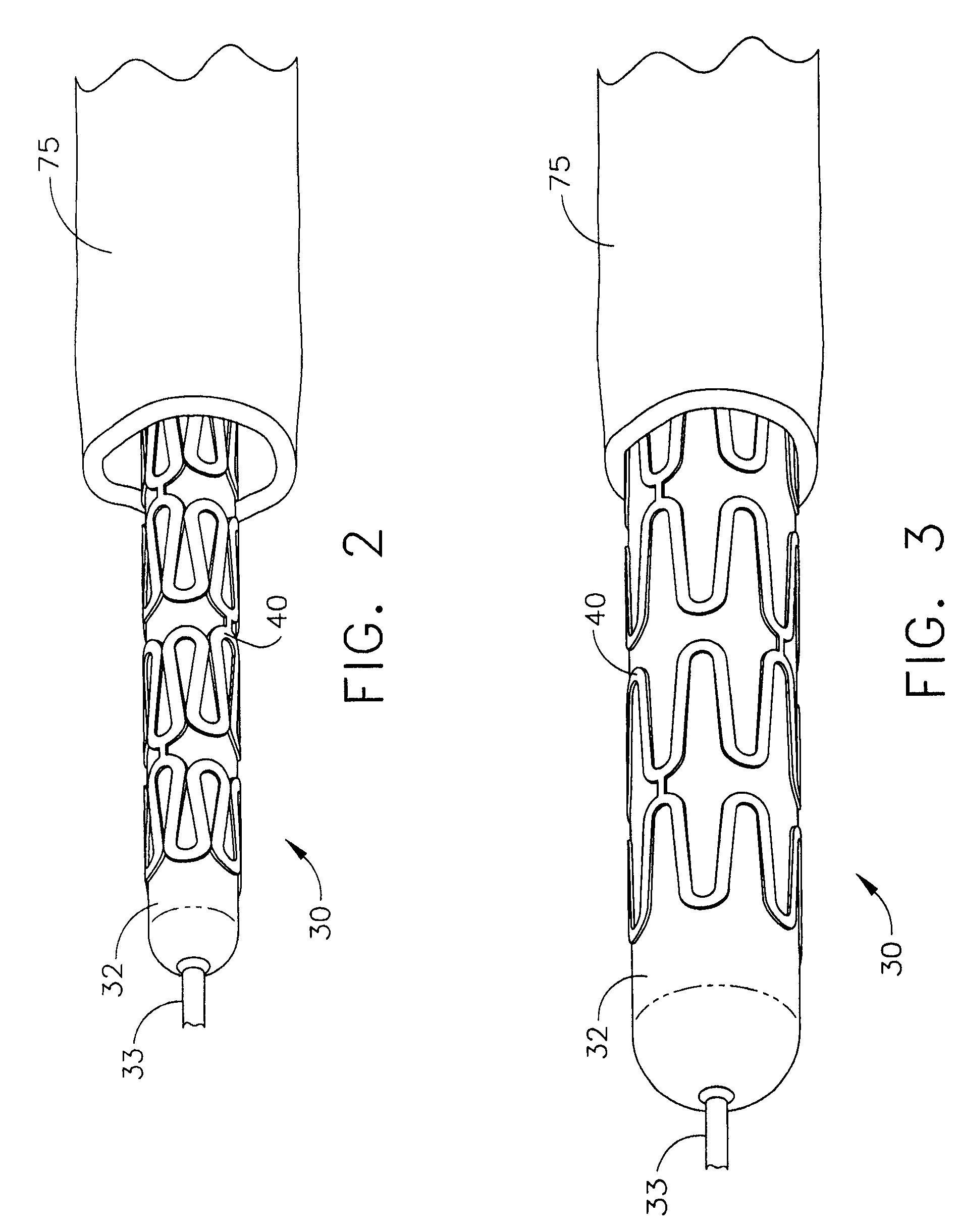
Bioabsorbable Stent Having a Radiopaque Marker
InactiveUS20090204203A1Reduce riskPrevented from dislodging and embolizingStentsBlood vesselsBioabsorbable stentSufficient time
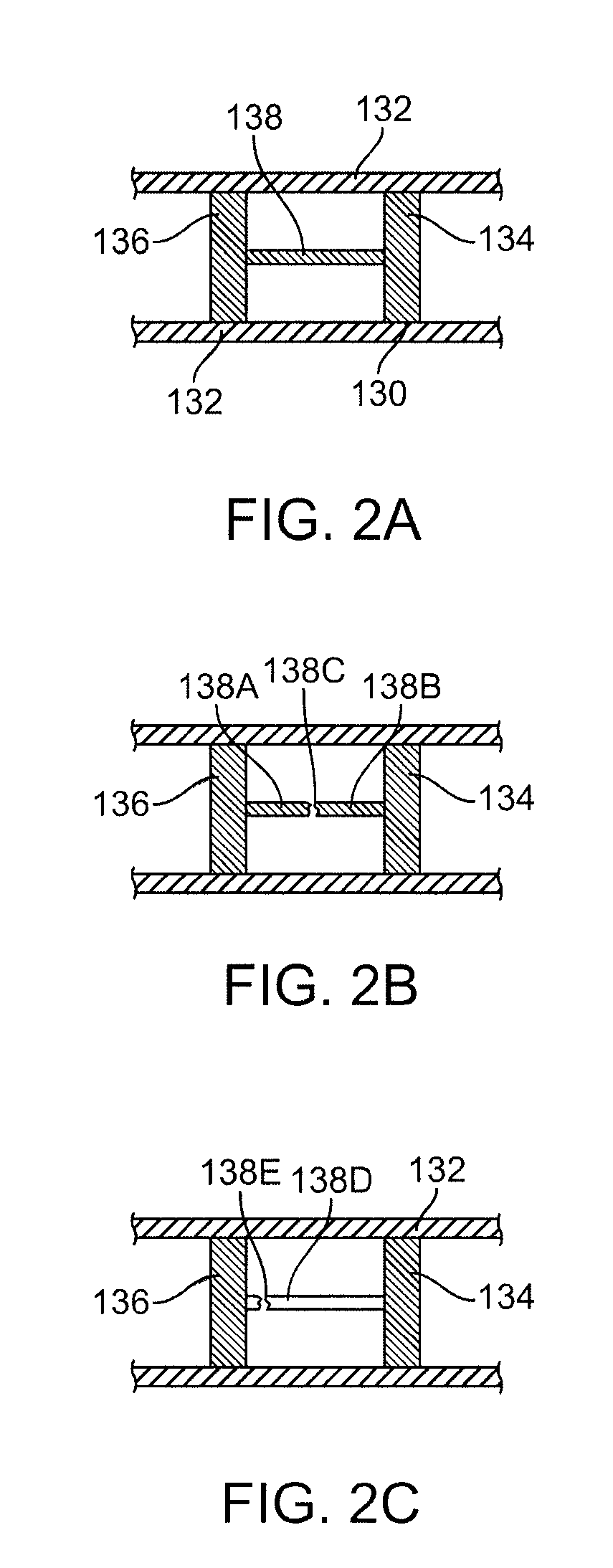
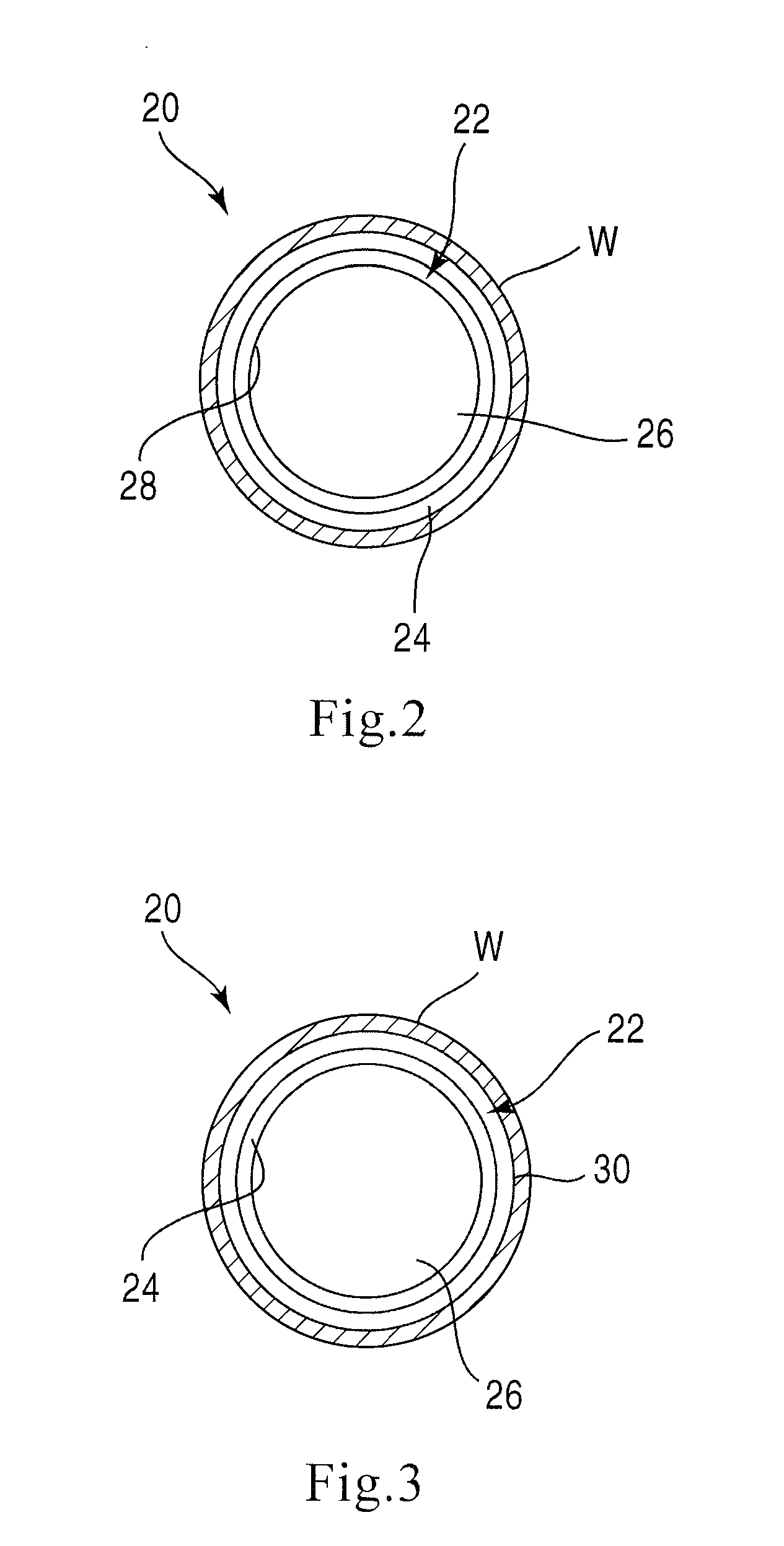
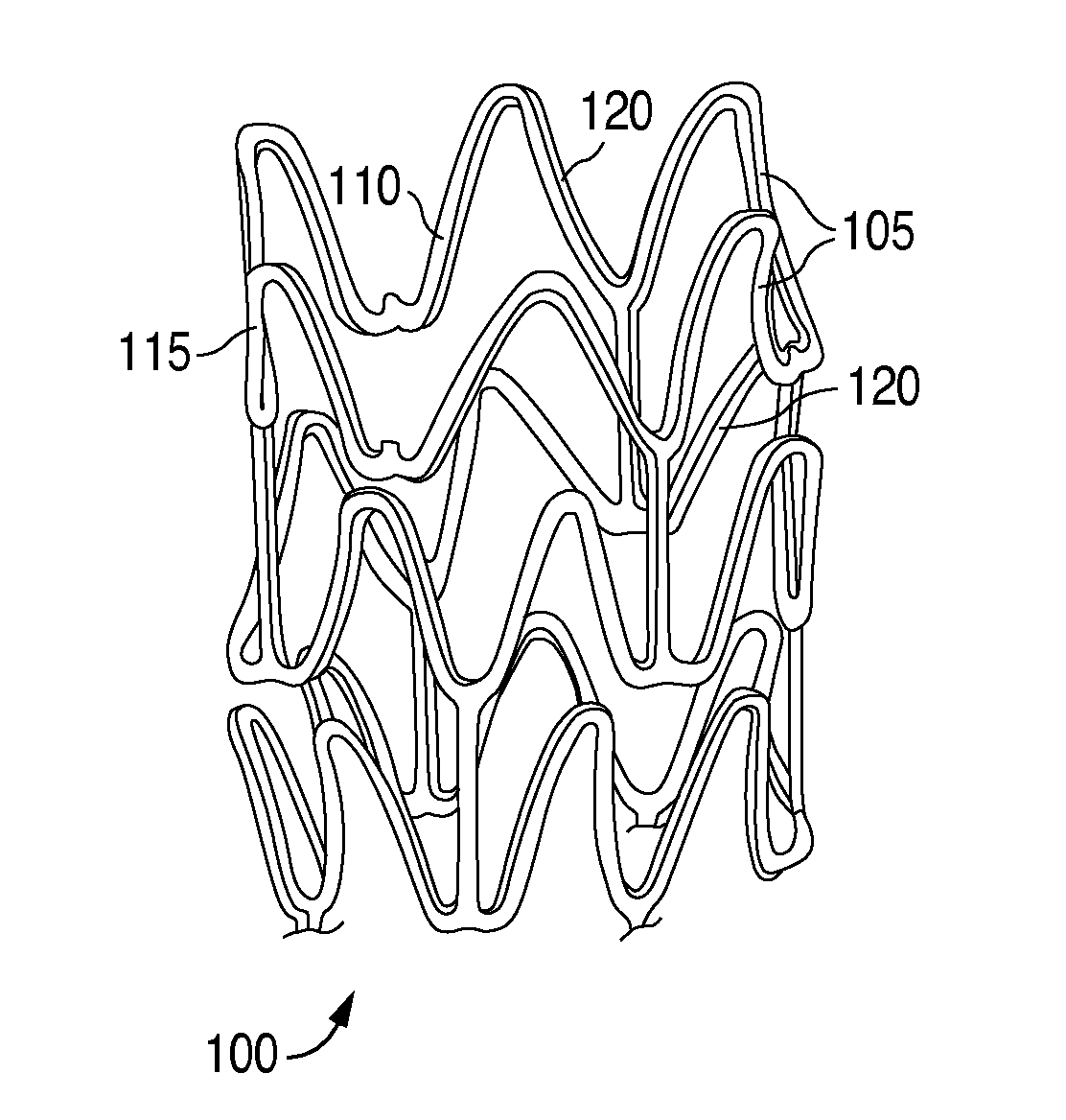
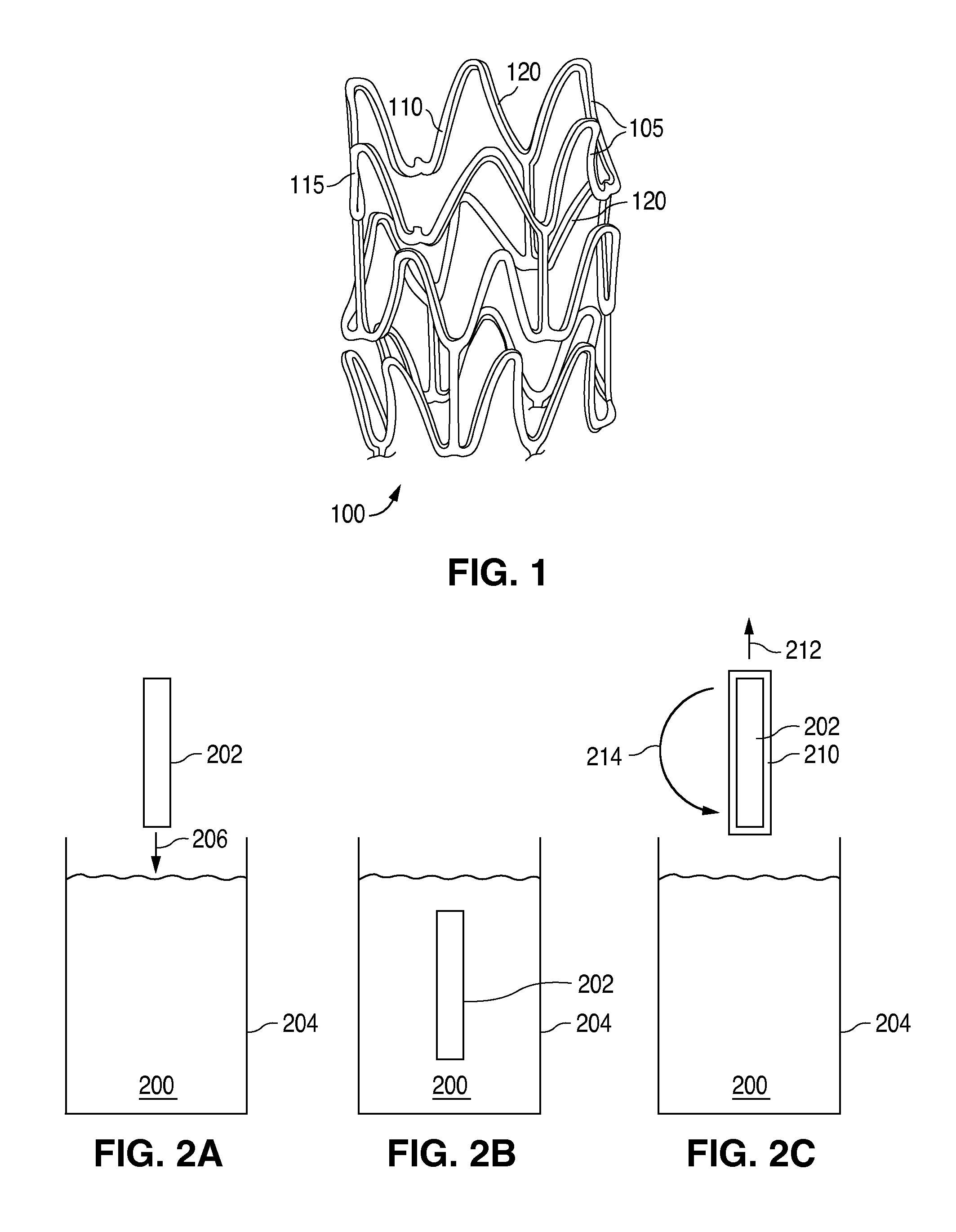
A bioabsorbable stent includes one or more radiopaque markers. The stent body may include a generally cylindrical body portion and a marker support for receiving the one or more marker(s). The marker support may be connected to an end of the body portion, or may be an integral portion of the body portion. By selectively controlling dissolution of the biodegradable material of the marker support, the marker support will remain intact for a sufficient time to allow for the marker to endothelialize and therefore prevent the marker from dislodging and embolizing. The controlled dissolution may be accomplished via one or more of the following mechanisms, including increasing the cross-sectional thickness of the marker support, passivating or oxidizing the marker support, utilizing a different, slower absorbing material for the marker support, utilizing a bioabsorbable polymeric coating on the marker support, or protecting the marker support with a sacrificial anode.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Method of monitoring positioning of polymer stents
The invention is directed to a polymer stent with one or more markers such that when the stent is placed within a lumen, the markers can be detected external to the body. The markers can also be used to monitor the stent position after placement and absorption of bioabsorbable stents. Further, the stent may comprise two markers used to determine the diameter of the stent in real time. It is also contemplated that the stent may comprise at least three markers. The use of at least three markers enables the three dimensional orientation of the stent to be determined at any time. The stent may also comprise markers such that the markers are located in regions with different in vivo lifetimes. It is also contemplated that the pattern and material type of markers on the stent may be used to determine the type of stent within a lumen or box.
Owner:ARTERIAL REMODELING TECH SA
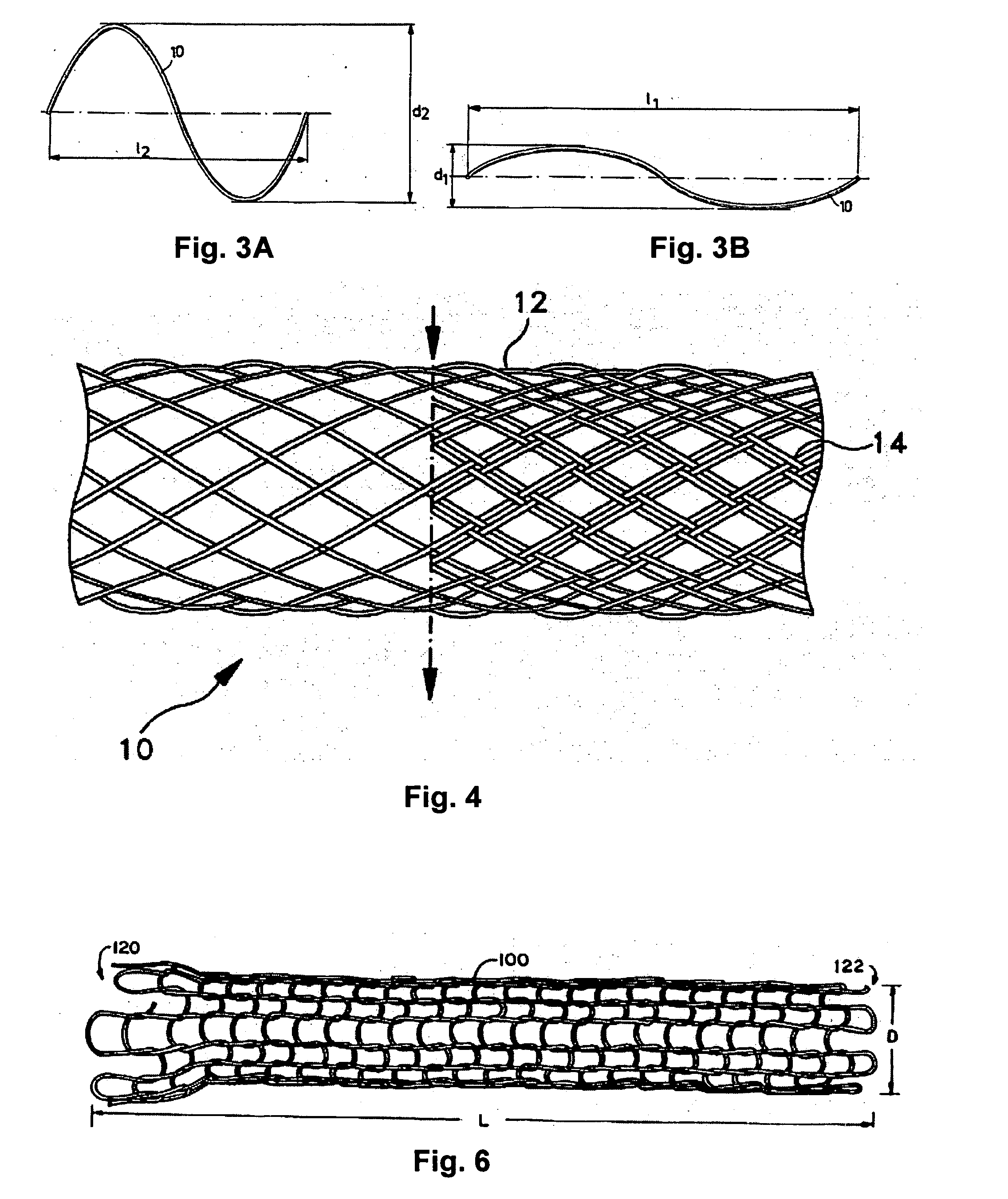
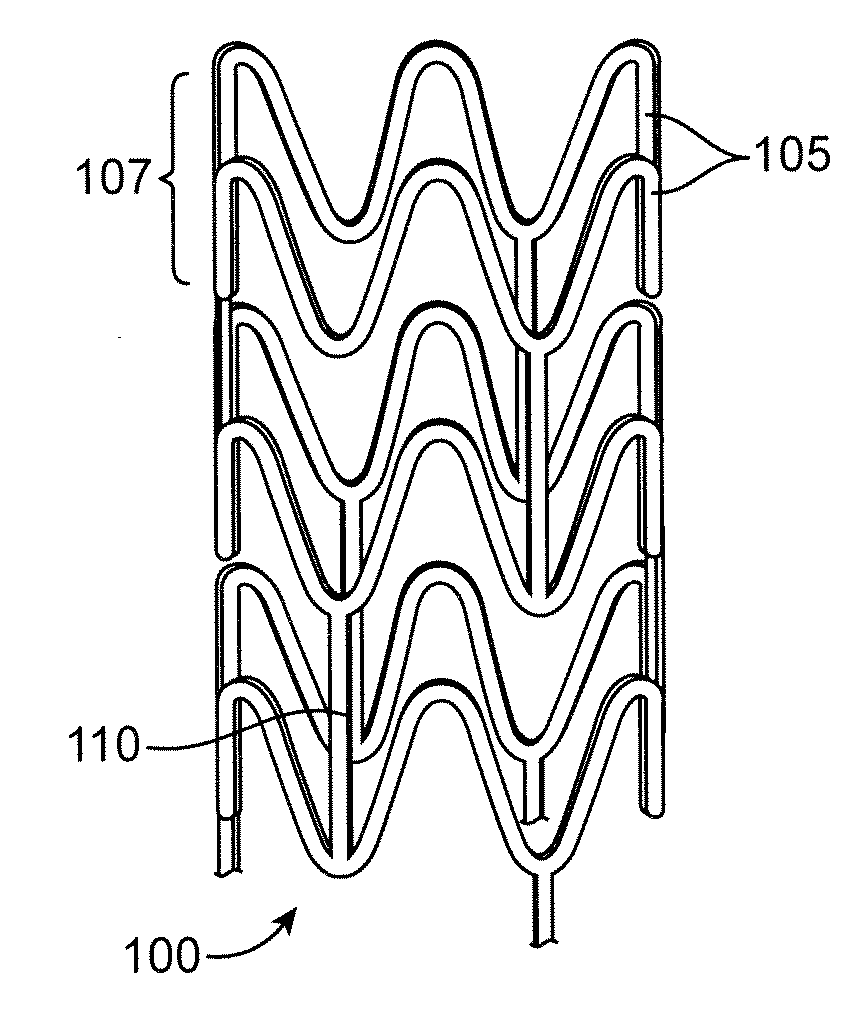
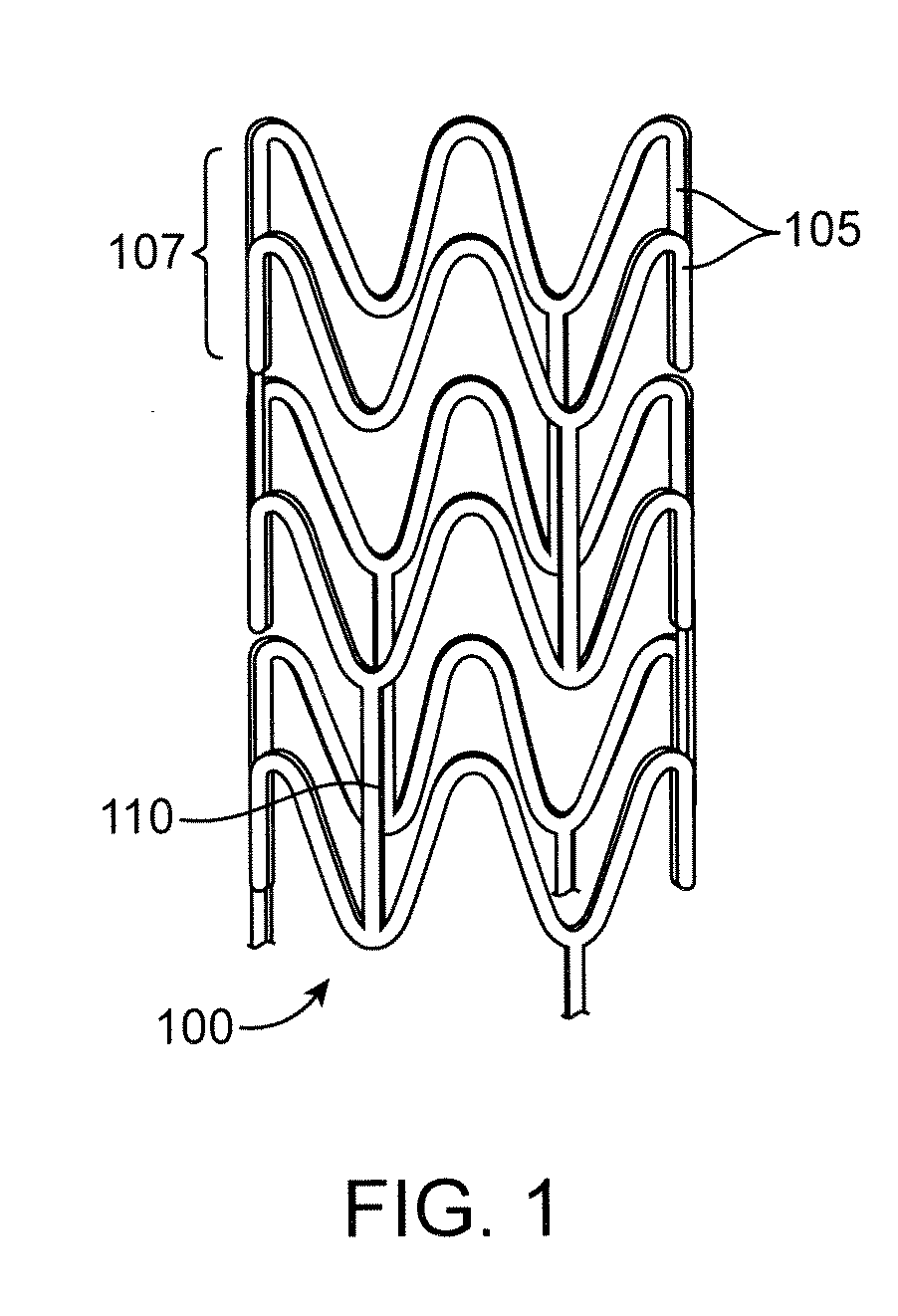
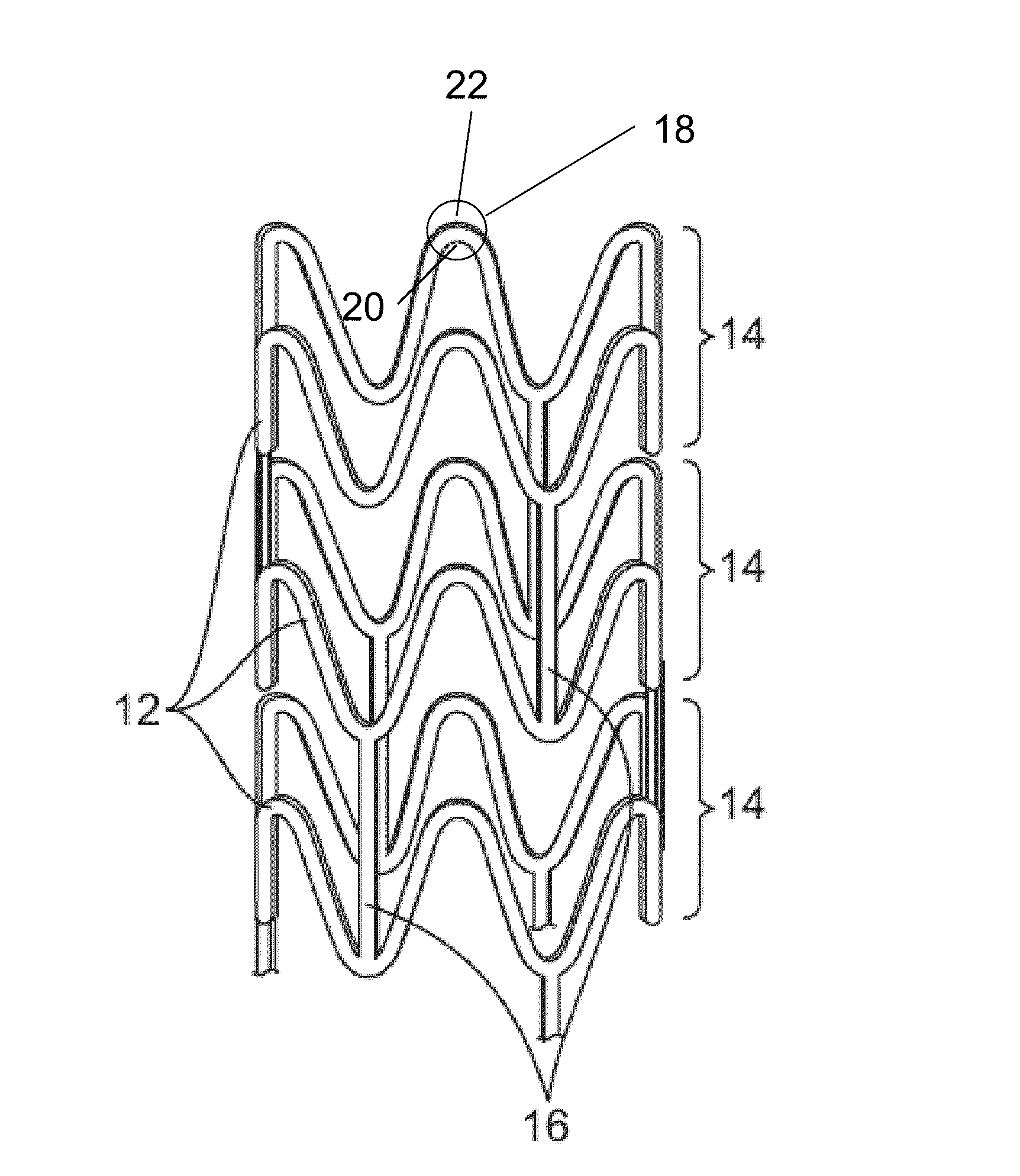
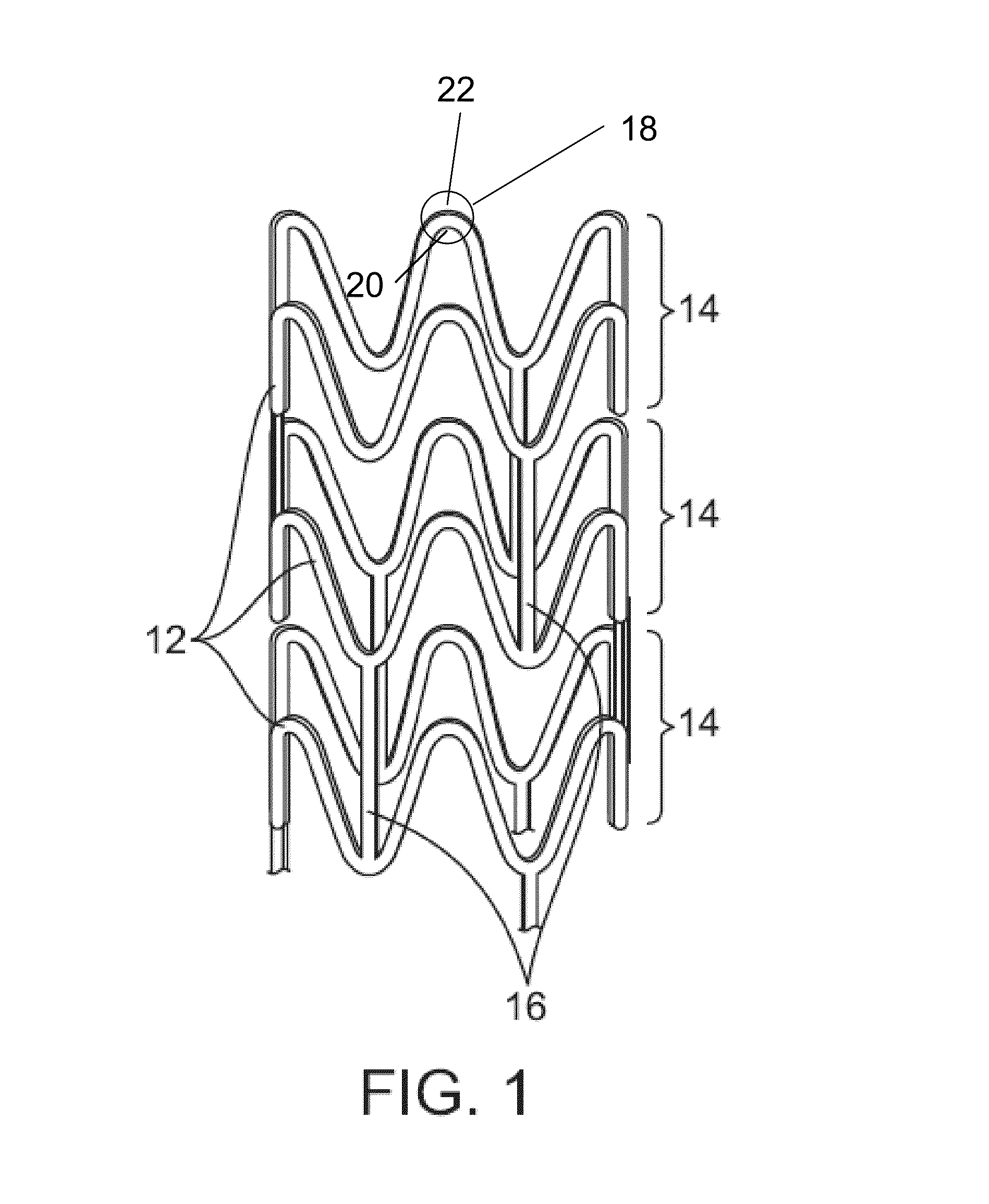
Bioabsorbable stents with reinforced filaments
ActiveUS7594928B2Improve material performanceIncrease radial forceStentsSurgeryBioabsorbable stentPolymer
According to an aspect of the present invention, a stent is provided, which contains at least one filament that has a longitudinal axis and comprises a bioabsorbable polymeric material. Polymer molecules within the bioabsorbable polymeric material are provided with a helical orientation which is aligned with respect to the longitudinal axis of the filament. The stent is at least partially bioabsorbed by a patient upon implantation or insertion of the stent into the patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Bioabsorbable stent
A medical device includes a support structure formed of a metal that is absorbable by a mammalian body. A polymer is disposed on the support structure in at least partially overlying relationship. The polymer has a thickness and a rate of absorption by a mammalian body such that said polymer is substantially completely absorbed, exposing the underlying portion of the support structure, before the underlying portion of the support structure is absorbed. In another embodiment, the medical device includes a support structure formed of a first material, the first material being absorbable by a mammalian body. An absorption inhibitor disposed on the support structure in at least partially overlying relationship and formed of a second material different from the first material. The second material being absorbable by the mammalian body. The absorption inhibitor reducing a rate of absorption of the portion of the support structure.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Composite stent with inner and outer stent elements and method of using the same
A composite stent structure includes separate and distinct stent elements or members: an outer stent element and an inner stent element removably attached to the outer stent element. The outer element may be, for example, a bioabsorbable stent typically constructed of a relatively non-resilient material such that the outer bioabsorbable stent element may not be self-expanding and subject to migration within the lumen over time. In contrast, the inner element may be, for example, a removable SEMS used to urge and maintain the outer element in position in the body lumen. The temporary inner SEMS may retain the composite structure (including the underlying inner element) in position until such time as the outer element is appropriately incorporated into the surrounding tissue or some other criteria occurs such that the removal of the SEMS is indicated. The SEMS may then be detached from the outer element and removed from the body lumen.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Bioabsorbable stents with reinforced filaments
ActiveUS20070270941A1Improve material performanceIncrease radial forceStentsSurgeryBioabsorbable stentBiomedical engineering
According to an aspect of the present invention, a stent is provided, which contains at least one filament that has a longitudinal axis and comprises a bioabsorbable polymeric material. Polymer molecules within the bioabsorbable polymeric material are provided with a helical orientation which is aligned with respect to the longitudinal axis of the filament. The stent is at least partially bioabsorbed by a patient upon implantation or insertion of the stent into the patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
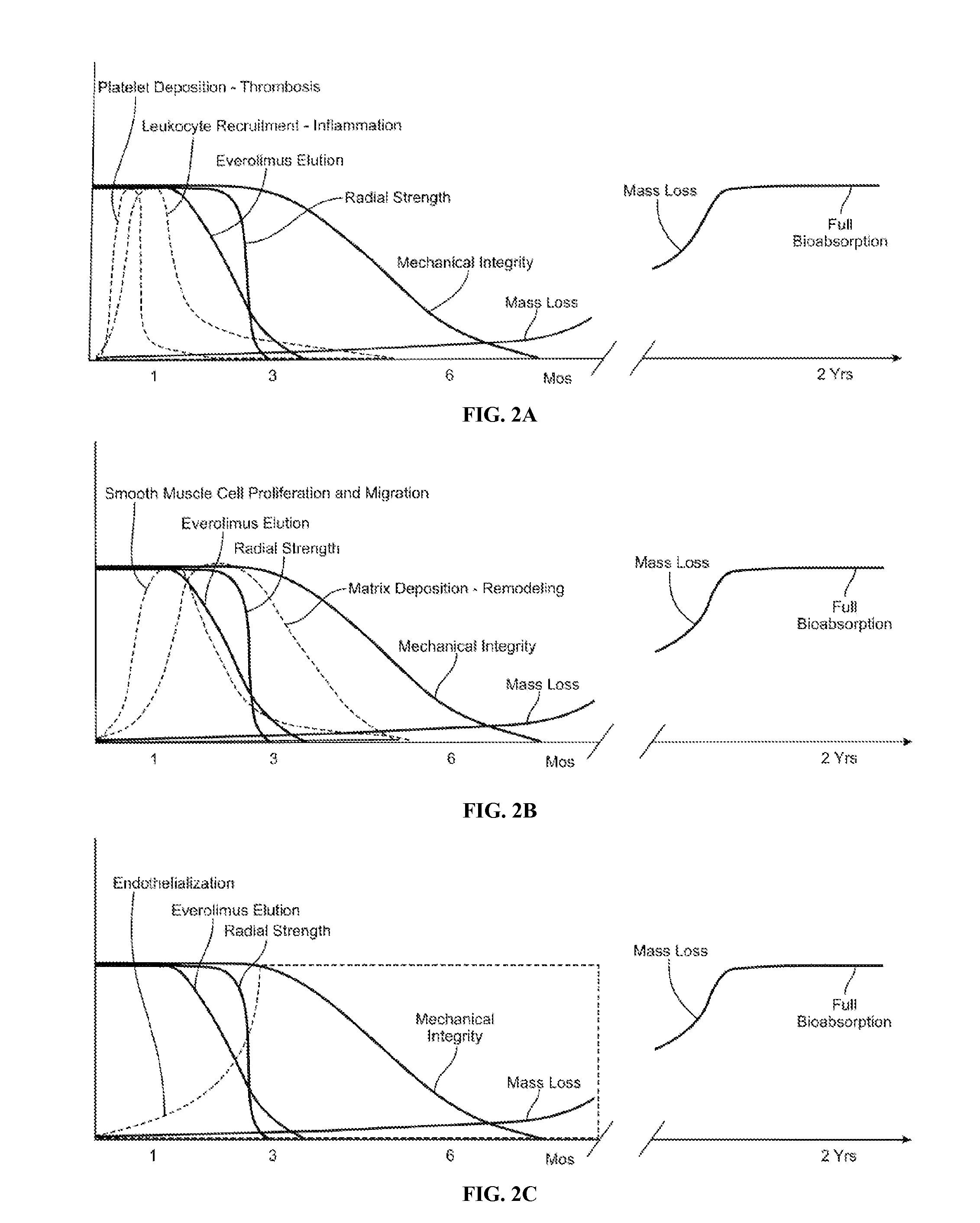
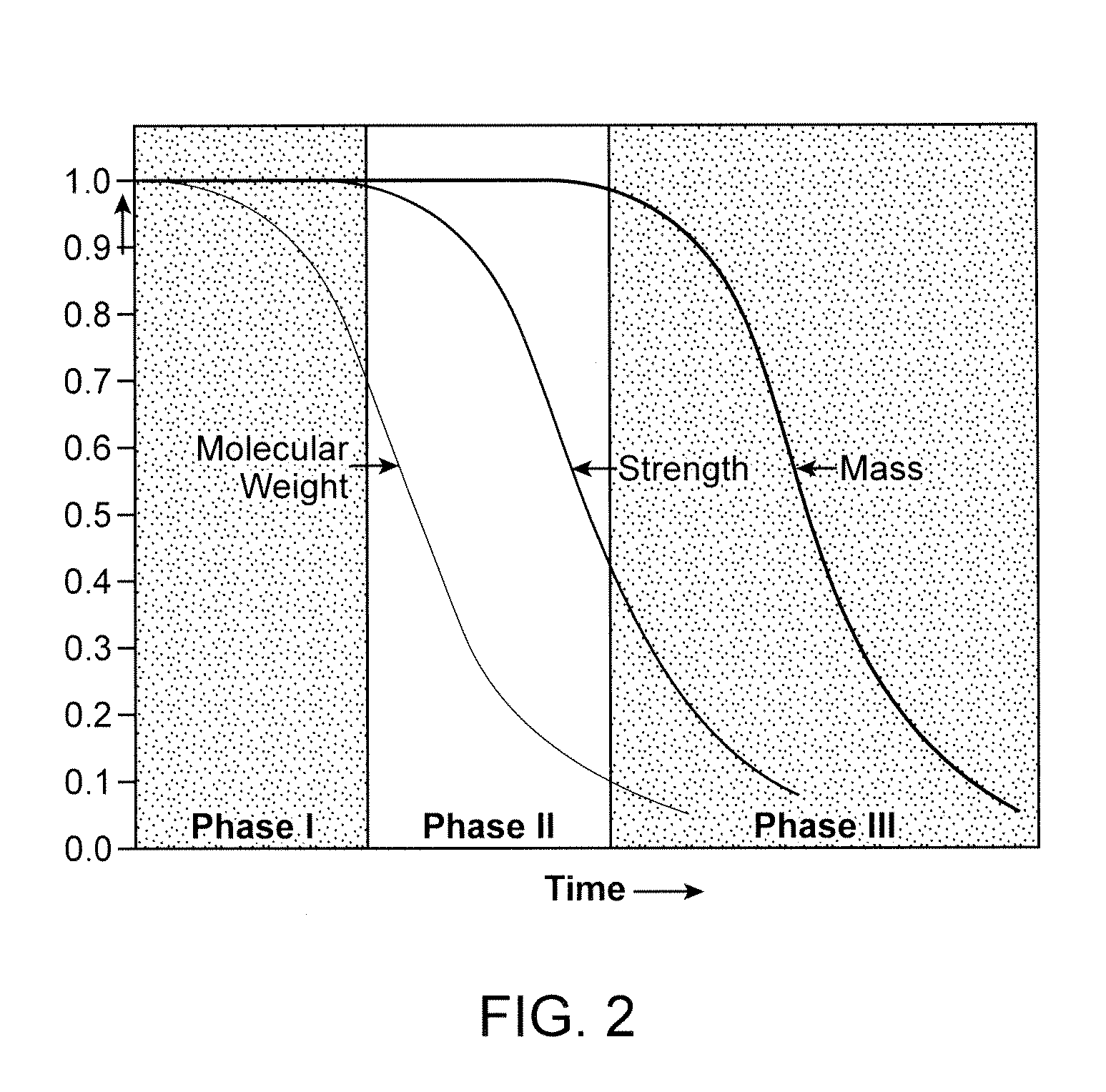
Bioabsorbable Stent With Time Dependent Structure And Properties And Regio-Selective Degradation
InactiveUS20110066225A1Promote degradationReduces tensile strength and strain to failure and fracture resistanceStentsSurgeryBioabsorbable stentRegioselectivity
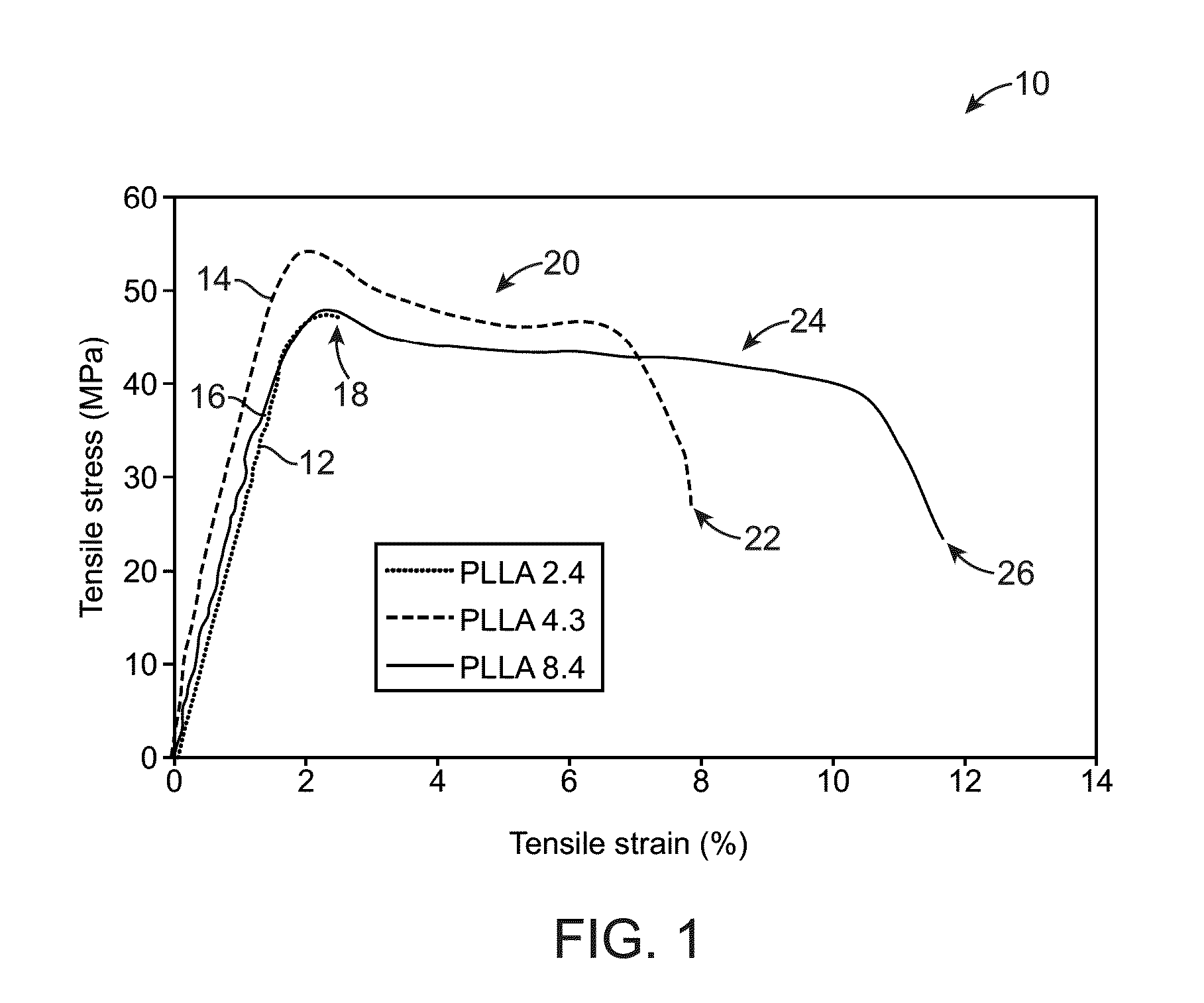
A bioabsorbable polymeric stent with time dependent structure and properties and methods of treating a diseased blood vessel with the bioabsorable polymeric stent are disclosed. The structure and properties of the stent change with time and allow the vessel to be restored to a natural unstented state. The bioabsorbable stent loses mechanical integrity in a controlled manner due to modification of selected structural elements.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Biodegradable, bioabsorbable stent anchors
Biodegradable / bioabsorbable stent anchors are provided to prevent stent migration and permit repositioning and / or removal of the stent after the anchors or portion thereof has sufficiently degraded or been absorbed.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Modification of bioabsorbable stent to reduce thrombogenecity
Bioabsorbable polymer scaffolds with coatings are disclosed that include immobilized antithrombotic agents on the scaffolds or in or on the coatings. The agents act synergistically with antiproliferative agents released from coatings by providing hemocompatibility during and without interfering with antiproliferative agent release. Methods of modifying scaffolds and coatings with the antithrombotic agents are disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
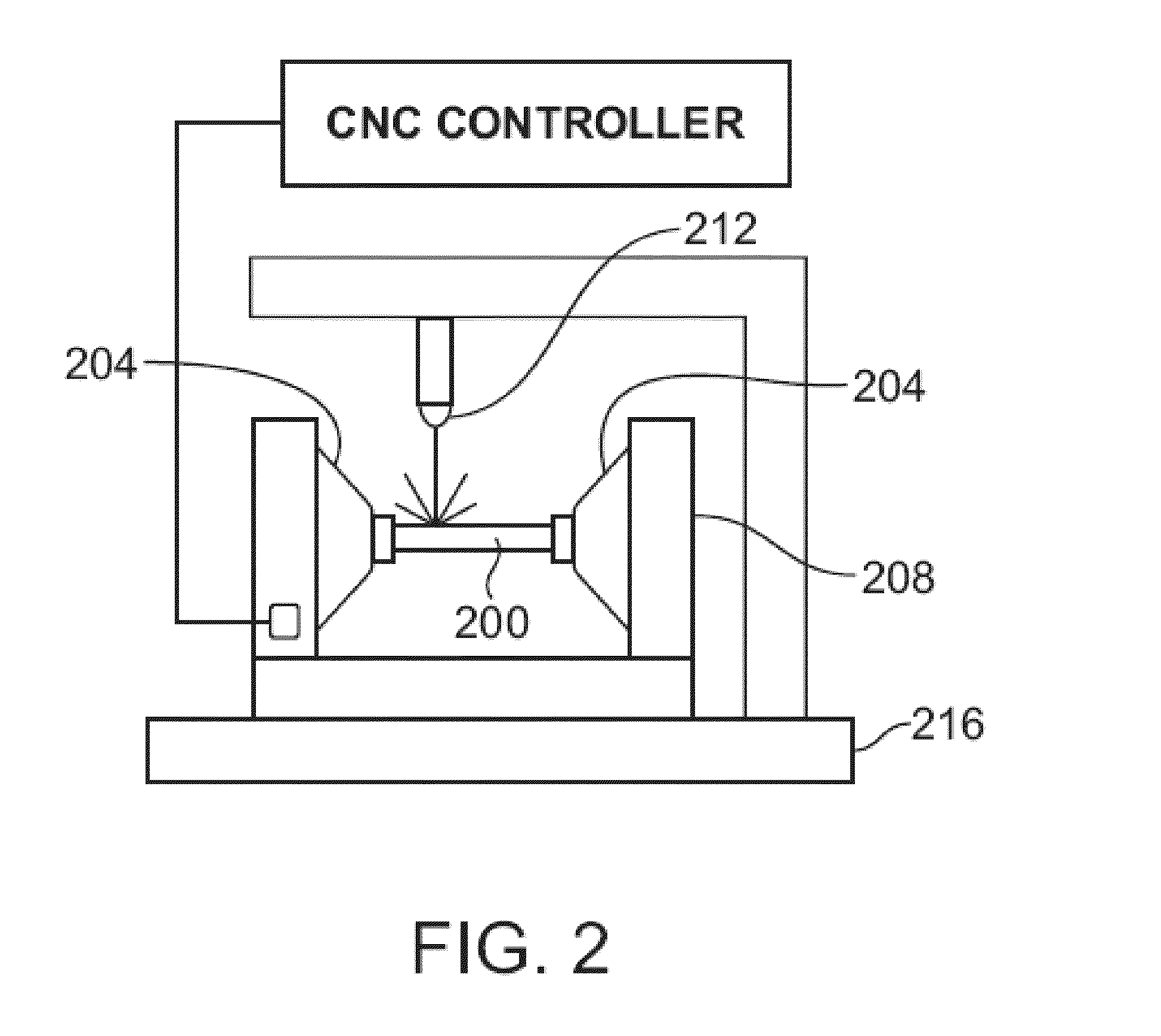
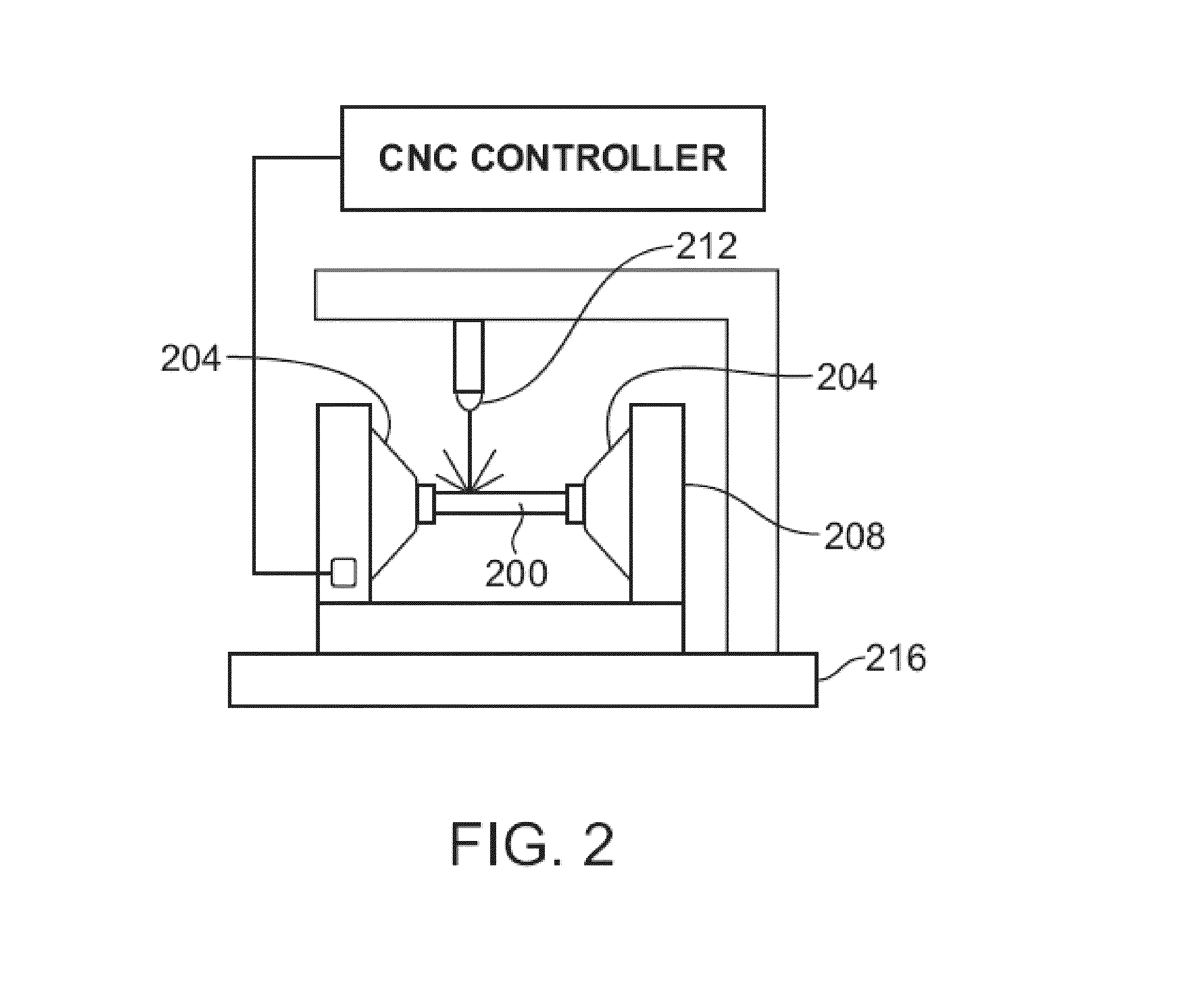
Laser System And Processing Conditions For Manufacturing Bioabsorbable Stents
The present invention involves laser machining polymer substrates to form a stent with laser parameters that minimize damage to the substrate in a surface region adjacent to the machined edge surface. The wavelength and pulse width are selected for this unique application and they can be controlled to minimize the surface modifications (such as voids, cracks which are induced by the laser-material interaction) which contribute to the variation in mechanical properties with distance from the edge surface, bulk mechanical properties, or a combination thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Control Of Degradation Profile Of Bioabsorbable Poly(L-Lactide) Scaffold
ActiveUS20120290070A1Reduce MnReduce diameterElectric discharge heatingSurgeryStrength lossEngineering
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Method of treatment with a bioabsorbable stent with time dependent structure and properties and regio-selective degradation
InactiveUS8425587B2Promote degradationReduces tensile strength and strain to failure and fracture resistanceStentsSurgeryBioabsorbable stentMechanical integrity
A bioabsorbable polymeric stent with time dependent structure and properties and methods of treating a diseased blood vessel with the bioabsorable polymeric stent are disclosed. The structure and properties of the stent change with time and allow the vessel to be restored to a natural unstented state. The bioabsorbable stent loses mechanical integrity in a controlled manner due to modification of selected structural elements.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Bioabsorbable stent with radiopaque layer and method of fabrication
Embodiments of a stent and methods of fabricating the same with a bioabsorbable radiopaque layer are disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Method of Performing An End-to-End Anastomosis Using a Stent and an Adhesive
A method and instruments used to performing an end-to-end anastomosis between two portions of intestinal tissue is disclosed. The method involves drawing a first portion of intestinal tissue over a portion of a bioabsorbable stent. The end of the first portion of intestinal tissue is everted on the stent to create a collar of exposed inner intestinal tissue. A second portion of intestinal tissue is drawn over the stent and over the exposed intestinal tissue. A bandage containing one adhesive compound selected from the group of an adhesive and an adhesive initiator is wrapped about the juncture. The other adhesive compound is applied to saturate the bandage and the combination of an adhesive and an adhesive initiator sets the adhesive to adhere the first portion and the second portion of adhesive to the bandage.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Bioabsorbable stent
A medical device includes a support structure formed of a metal that is absorbable by a mammalian body. A polymer is disposed on the support structure in at least partially overlying relationship. The polymer has a thickness and a rate of absorption by a mammalian body such that said polymer is substantially completely absorbed, exposing the underlying portion of the support structure, before the underlying portion of the support structure is absorbed. In another embodiment, the medical device includes a support structure formed of a first material, the first material being absorbable by a mammalian body. An absorption inhibitor disposed on the support structure in at least partially overlying relationship and formed of a second material different from the first material. The second material being absorbable by the mammalian body The absorption inhibitor reducing a rate of absorption of the portion of the support structure.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
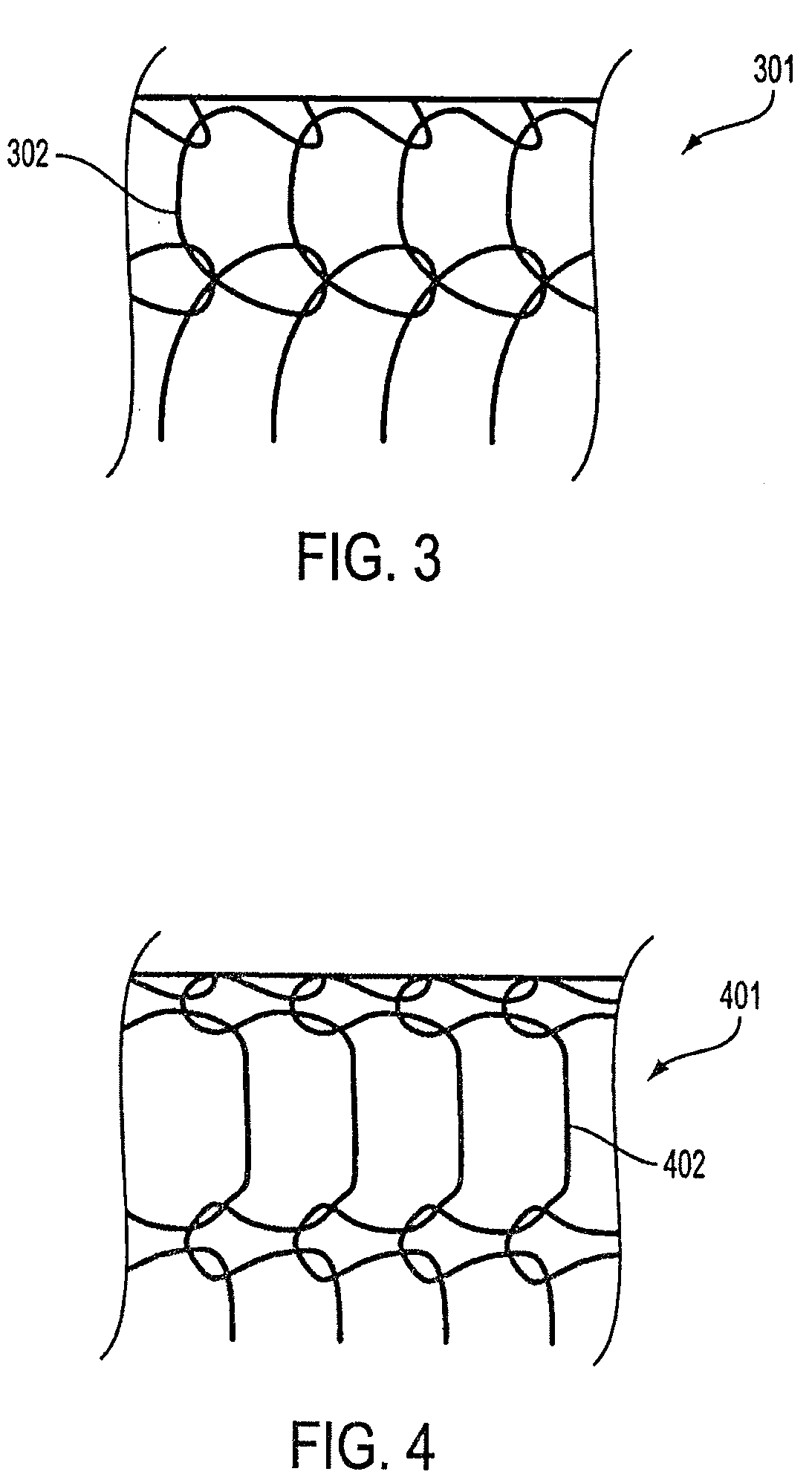
Bioabsorbable stents
InactiveUS20150342764A1Improve mechanical propertiesReduced flexibilityStentsSurgeryDelayed timeEngineering
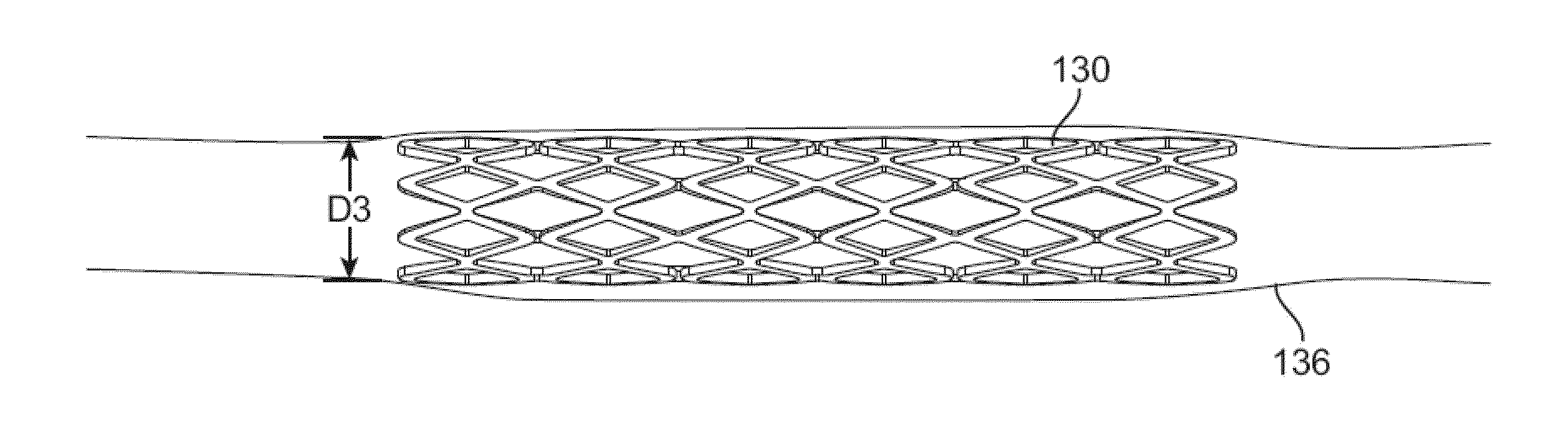
Tubular casting processes, such as dip-coating, may be used to form substrates from polymeric solutions which may be used to fabricate implantable devices such as stents. The polymeric substrates may have multiple layers which retain the inherent properties of their starting materials and which are sufficiently ductile to prevent brittle fracture. Parameters such as the number of times the mandrel is immersed, the duration of time of each immersion within the solution, as well as the delay time between each immersion or the drying or curing time between dips and withdrawal rates of the mandrel from the solution may each be controlled to result in the desired mechanical characteristics. Additional post-processing may also be utilized to further increase strength of the substrate or to alter its shape.
Owner:RAZMODICS LLC
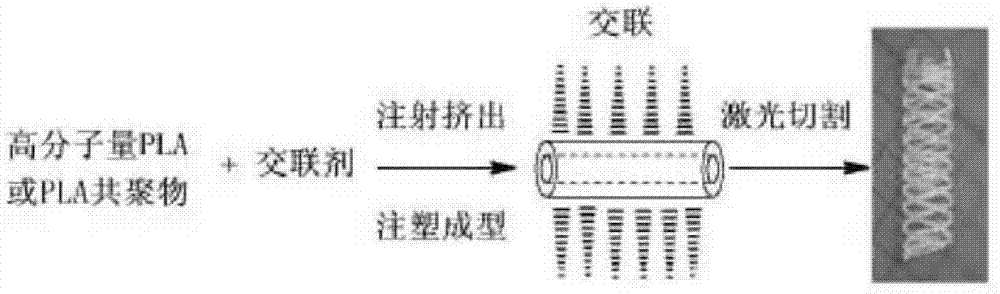
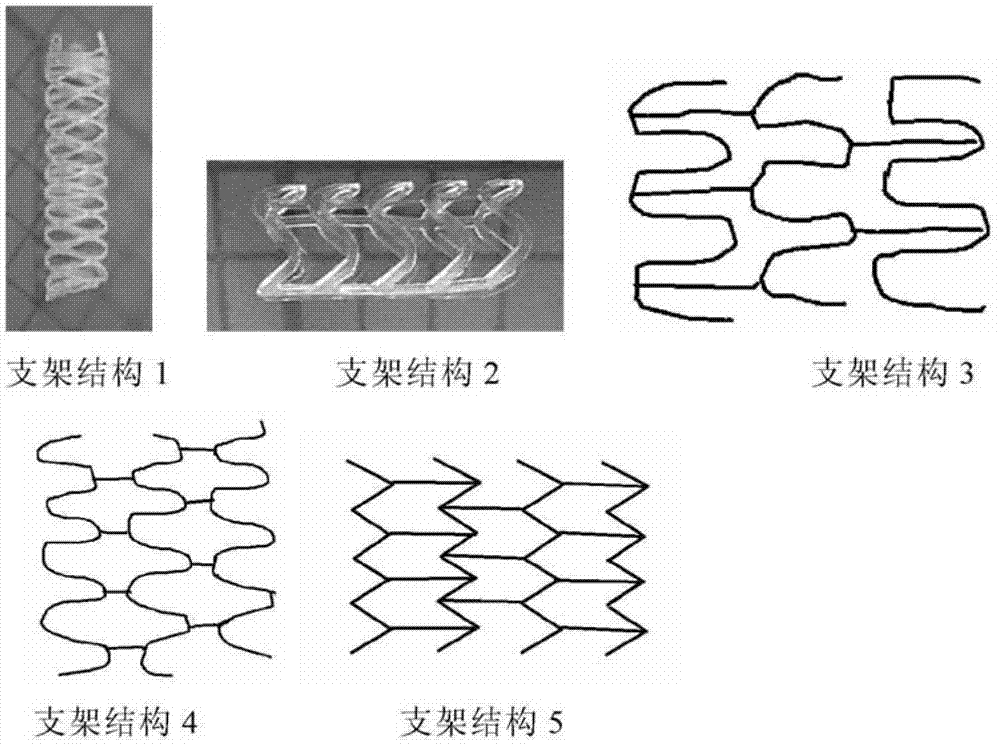
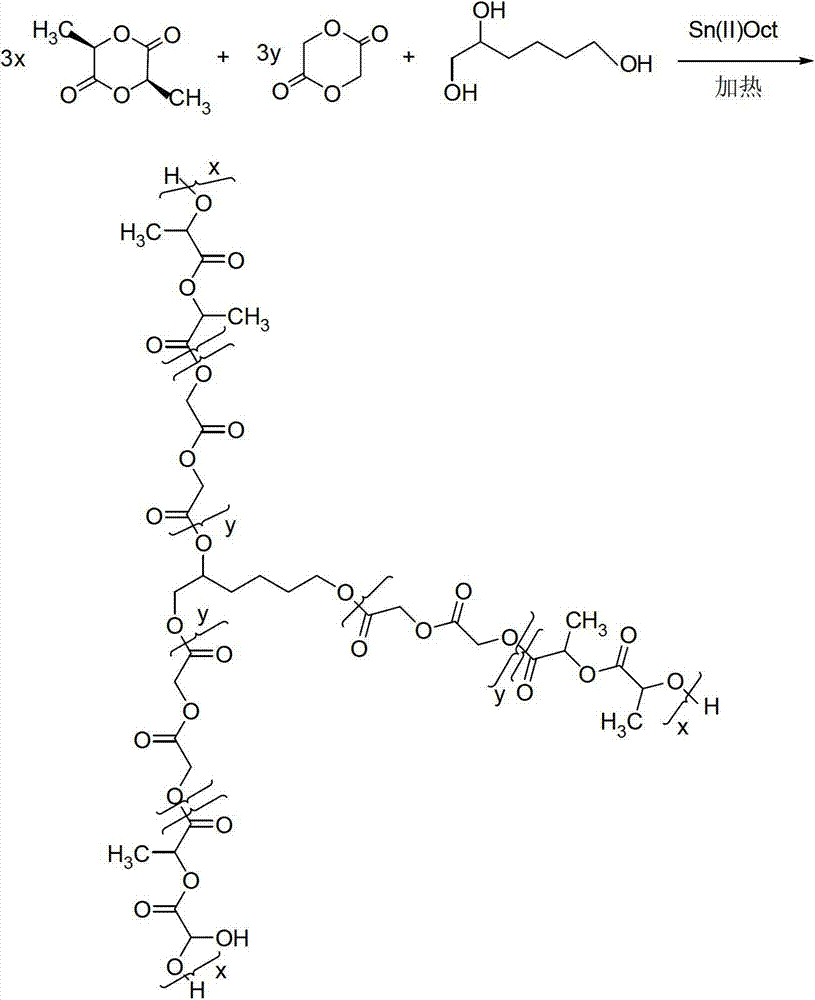
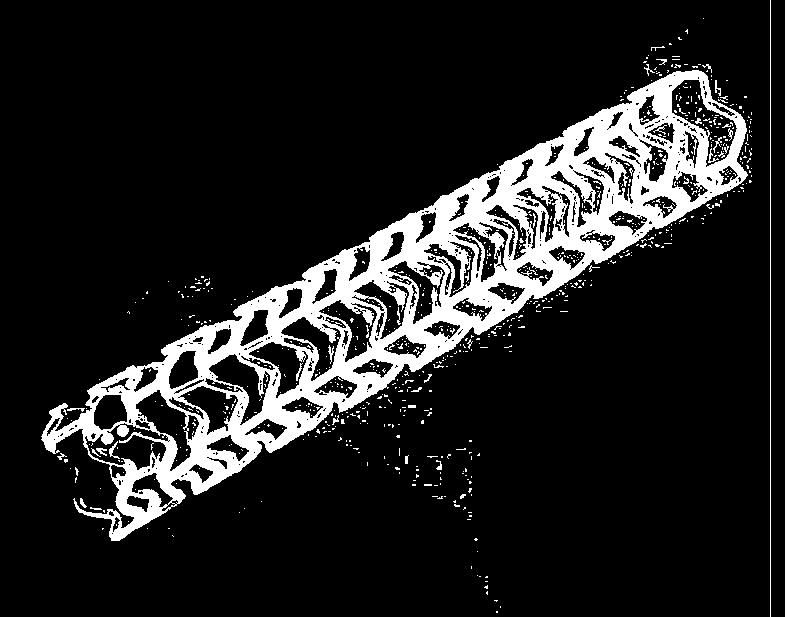
Modified polylactic acid degradable stent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103709386AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove radial supportSurgeryCross-linkPolymer science
The invention relates to the field of medical devices, and more specifically discloses a biodegradable stent based on a modified polylactic acid or a polylactic acid copolymer, and a preparation method thereof. According to the present invention, a linear polylactic acid or polylactic acid copolymer with a high molecular weight is blended with a biodegradable cross-linking agent, injection extrusion, injection molding or other processing methods are adopted to prepare a pipe material, the pipe material is subjected to a cross-linking polymerization reaction to form a semi-interpenetrating polymer network, and finally laser cutting is adopted to obtain the stent. The stent has characteristics of sufficient mechanical strength, sufficient structural stability, and improved processability.
Owner:上海发微医用材料有限公司
Biodegradable bracket and preparation method thereof
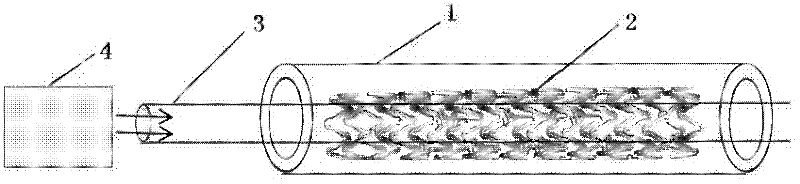
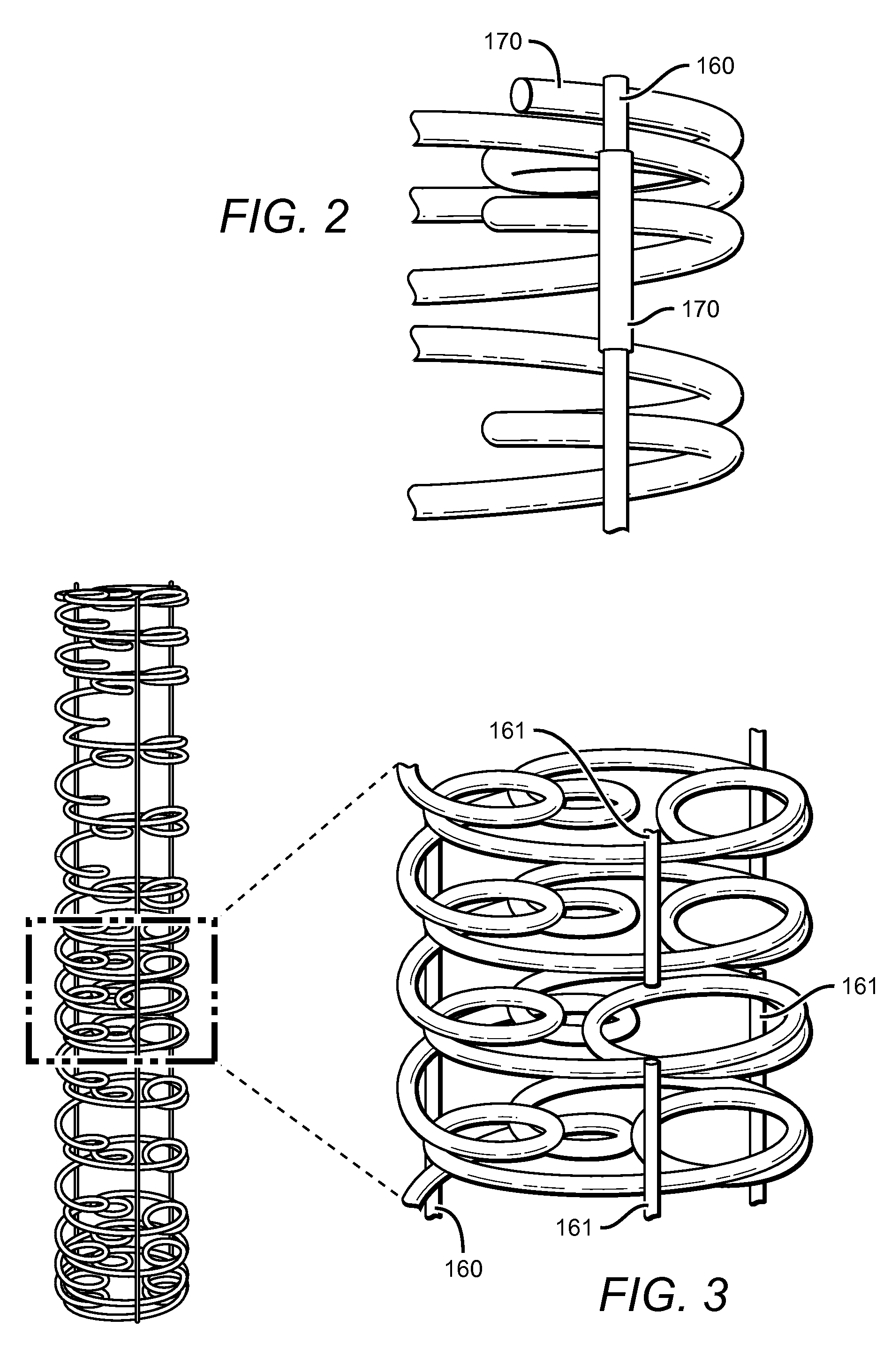
InactiveCN102697587AFacilitate successful completionShow 3D outlineStentsSurgeryWinding machineBioabsorbable stent
The invention discloses a biodegradable bracket; the bracket comprises a reticular bracket body formed by weaving degradable silky material, and further comprises a micro-spring ring formed by winding metal wires; the degradable silky material penetrates in the inner hole of the micro-spring ring and forms a whole with the micro-spring ring. A preparation method of the biodegradable bracket comprises the following steps: (1), winding metal wires into a micro-spring ring through a spring winding machine; (2), putting degradable silky material longer than the micro-spring ring through the inner hole of the micro-spring ring to form a whole; (3), winding the degradable silky material to weave the biodegradable bracket; and (4), detecting the bracket and manufacturing a finished product. The biodegradable bracket has the advantage that the visibility under development of X rays as well as the flexibility and security of the bracket are improved greatly.
Owner:湖南千山医疗器械有限公司
Bioabsorbable tracheal stent, and method of manufacturing thereof
A bioabsorbable tracheal stent is provided. The bioabsorbable stent comprises a biodegradable polymer, wherein the “ biodegradable polymer comprises about 0 to 30 wt % glycerol, polyethylene glycol, triethyl citrate, or mixture thereof. A drug is dispersed within or dissolved in the biodegradable polymer. In a second and third aspect, the invention relates to methods of manufacturing a bioabsorbable tracheal stent. The first method includes forming a solution comprising a biodegradable polymer and a drug, the biodegradable polymer comprising about 0 to 30 wt % glycerol, polyethylene glycol, triethyl citrate, or mixture thereof. The method further comprises casting the solution to form the bioabsorbable tracheal stent. The second method includes forming a polymeric stent, and dip casting the polymeric stent in a solution comprising a biodegradable polymer and a drug to form a coating on the polymeric stent, wherein the biodegradable polymer comprises about 0 to 30 wt % glycerol, polyethylene glycol, triethyl citrate, or mixture thereof.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +1
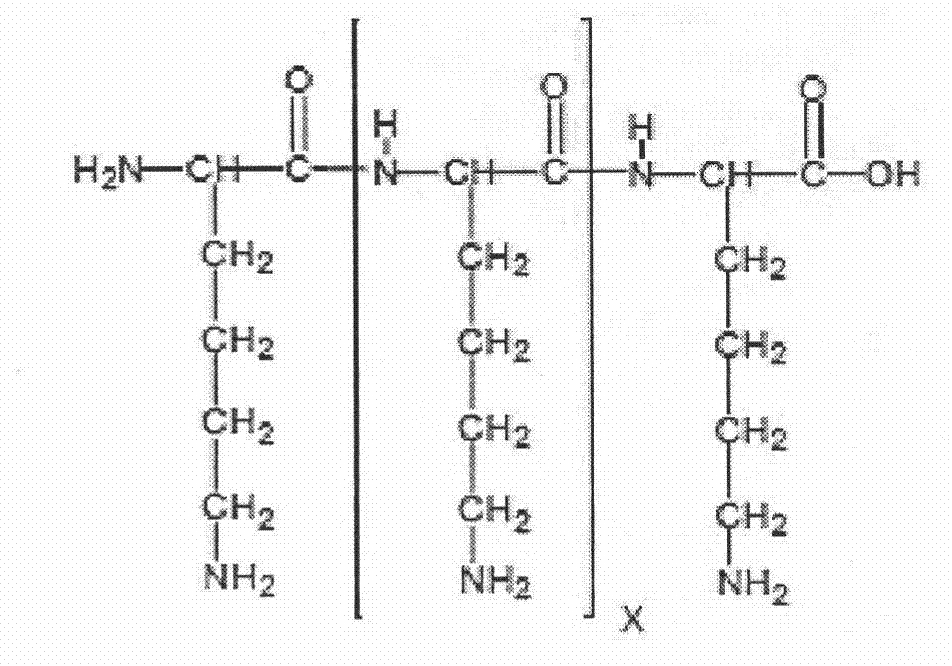
RGD peptide attached to bioabsorbable stents
InactiveUS20070293941A1Increase probabilityHigh regeneration rateStentsSurgeryBioabsorbable stentMedicine
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
New processing method of biodegradable stent
InactiveCN102371670AImprove radial supportExpand back shrinkStentsSurgeryBioabsorbable stentBiomedical engineering
The invention provides a new processing method of a biodegradable stent. The processing method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a parison of the biodegradable stent from a biodegradable material; and (2) blow-molding the parison so that a material in each wave pole of the parison is highly oriented along the forced direction at the wave pole, and finally obtaining the biodegradable stent. By adopting the processing method, the strength and toughness of the biodegradable stent can be effectively improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT MEDICAL (GROUP) CO LTD
Method of performing an end-to-end anastomosis using a stent and an adhesive
A method and instruments used to performing an end-to-end anastomosis between two portions of intestinal tissue is disclosed. The method involves drawing a first portion of intestinal tissue over a portion of a bioabsorbable stent. The end of the first portion of intestinal tissue is everted on the stent to create a collar of exposed inner intestinal tissue. A second portion of intestinal tissue is drawn over the stent and over the exposed intestinal tissue. A bandage containing one adhesive compound selected from the group of an adhesive and an adhesive initiator is wrapped about the juncture. The other adhesive compound is applied to saturate the bandage and the combination of an adhesive and an adhesive initiator sets the adhesive to adhere the first portion and the second portion of adhesive to the bandage.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Laser system and processing conditions for manufacturing bioabsorbable stents
The present invention involves laser machining polymer substrates to form a stent with laser parameters that minimize damage to the substrate in a surface region adjacent to the machined edge surface. The wavelength and pulse width are selected for this unique application and they can be controlled to minimize the surface modifications (such as voids, cracks which are induced by the laser-material interaction) which contribute to the variation in mechanical properties with distance from the edge surface, bulk mechanical properties, or a combination thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Treatment Of Diabetic Patients With A Drug Eluting Stent And A Drug Coated Balloon
Embodiments of the present invention include methods for the treatment, prevention, or amelioration of vascular disease and / or disorder in diabetic patients. The methods include implantation of a stent including a drug, and the use of a drug coated balloon. The DES may be a DES having a metal body and a coating including the drug, or a bioabsorbable stent with drug in the body of the stent, in a coating on the stent, or both in the body of the stent and in a coating on the stent.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
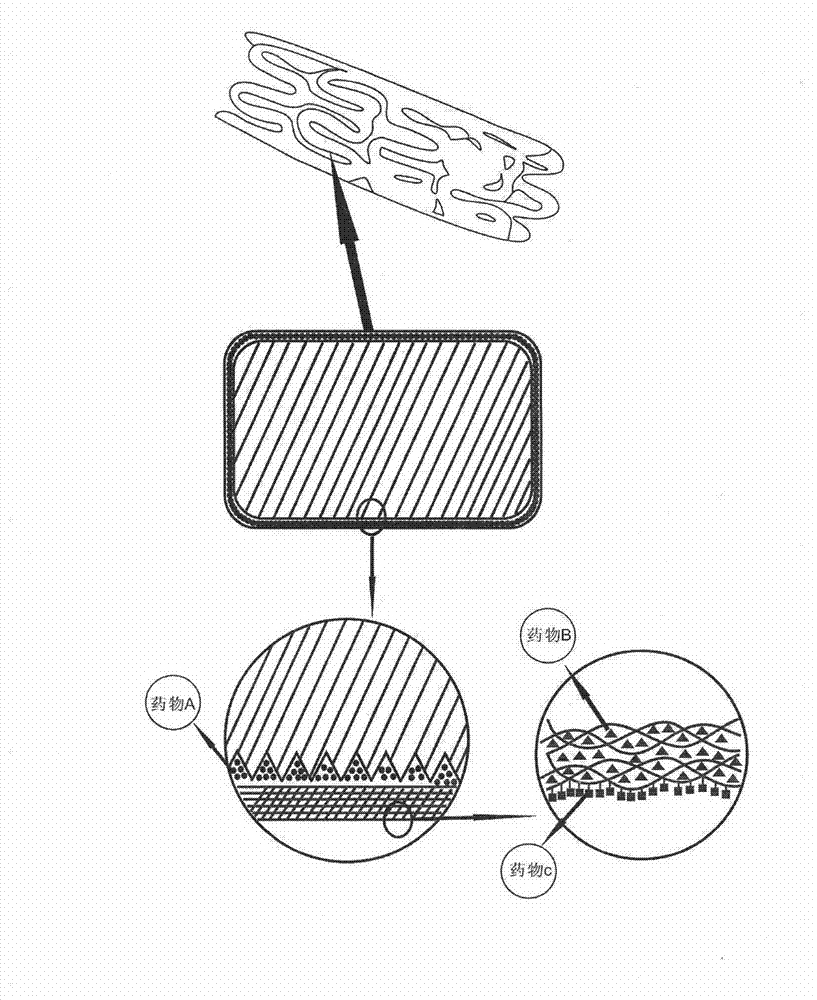
Biodegradable bracket with multiple drugs
The invention provides a biodegradable bracket with multiple drugs, belongs to the field of medical equipment and relates to a biodegradable bracket with a single coating. Besides support function, the bracket further comprises the single coating which contains anti-proliferative drugs, anti-inflammation and anti-immune drugs, drugs for promoting endothelial cells to grow and a developing agent. The bracket main body is made of biodegradable polymers of which mechanical strength is high. After implanted on a pathological position, the bracket has strong support force, so that action of supporting the pathological vessels in short time can be achieved. Because of the developing agent, doctors can accurately obverse the position and the expansion consistency of the bracket during operation, and displacement or other adverse events can be prevented; the anti-proliferative drugs can prevent the vessels from becoming narrow in short time after the bracket is implanted; and the drugs for promoting the endothelial cells to grow can promote the endothelial cells to grow on the surface of the bracket and can cover the bracket in the endothelium of the vessels, so that embolism phenomenon caused by degradation fragments of the bracket dropping in blood can be prevented.
Owner:深圳市昕力医疗设备开发有限公司
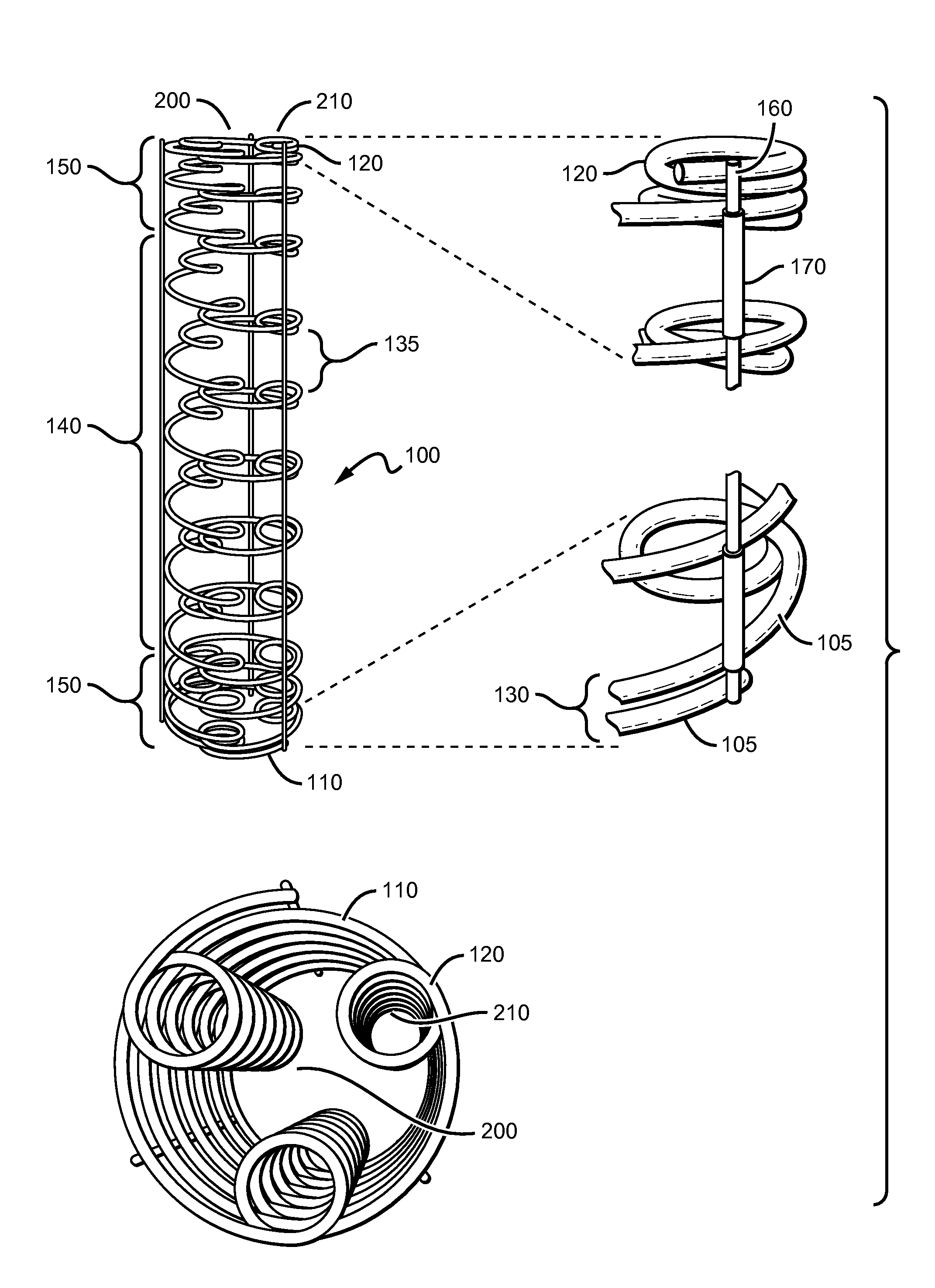
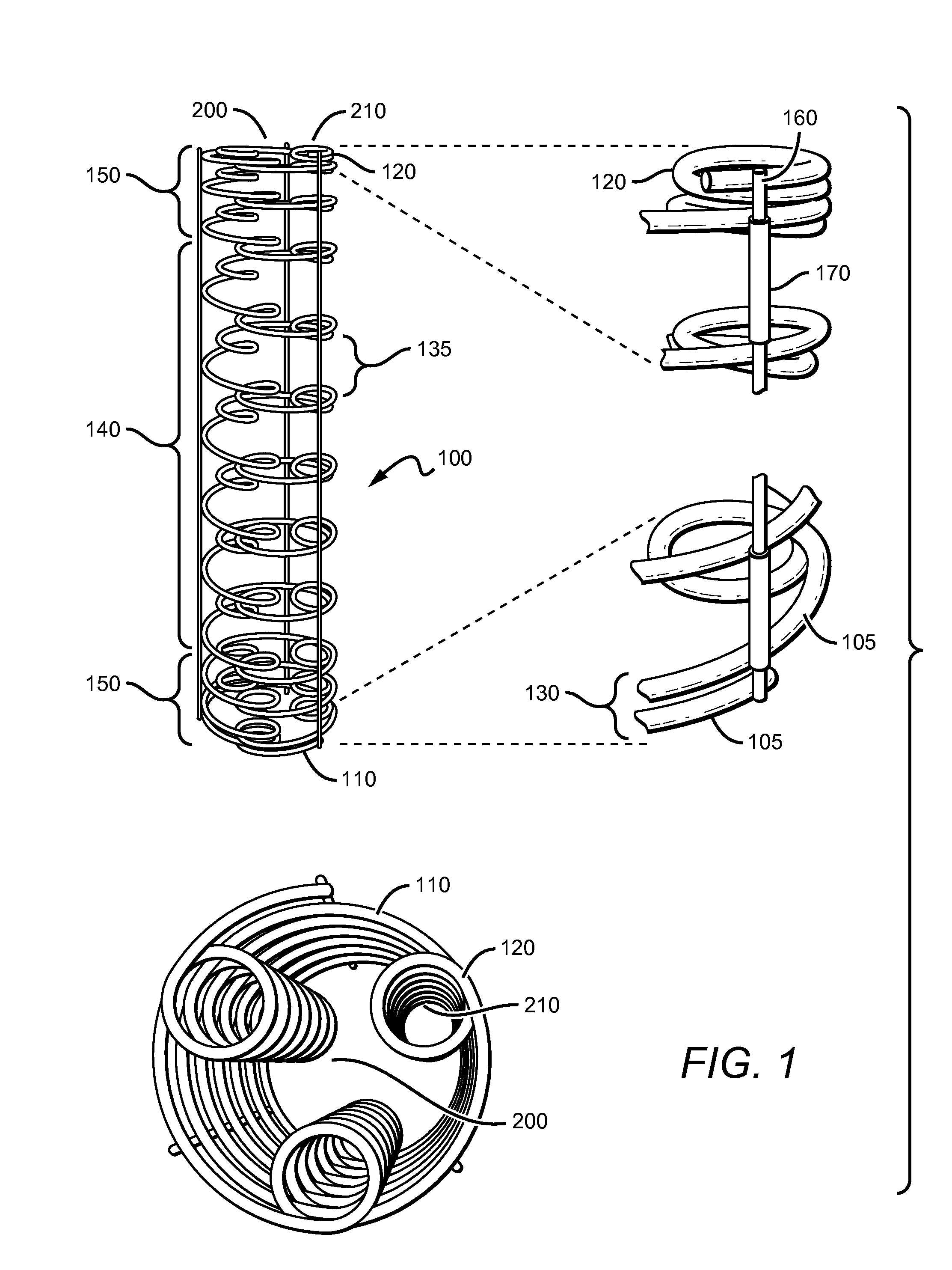
Coil Bioabsorbable Stents
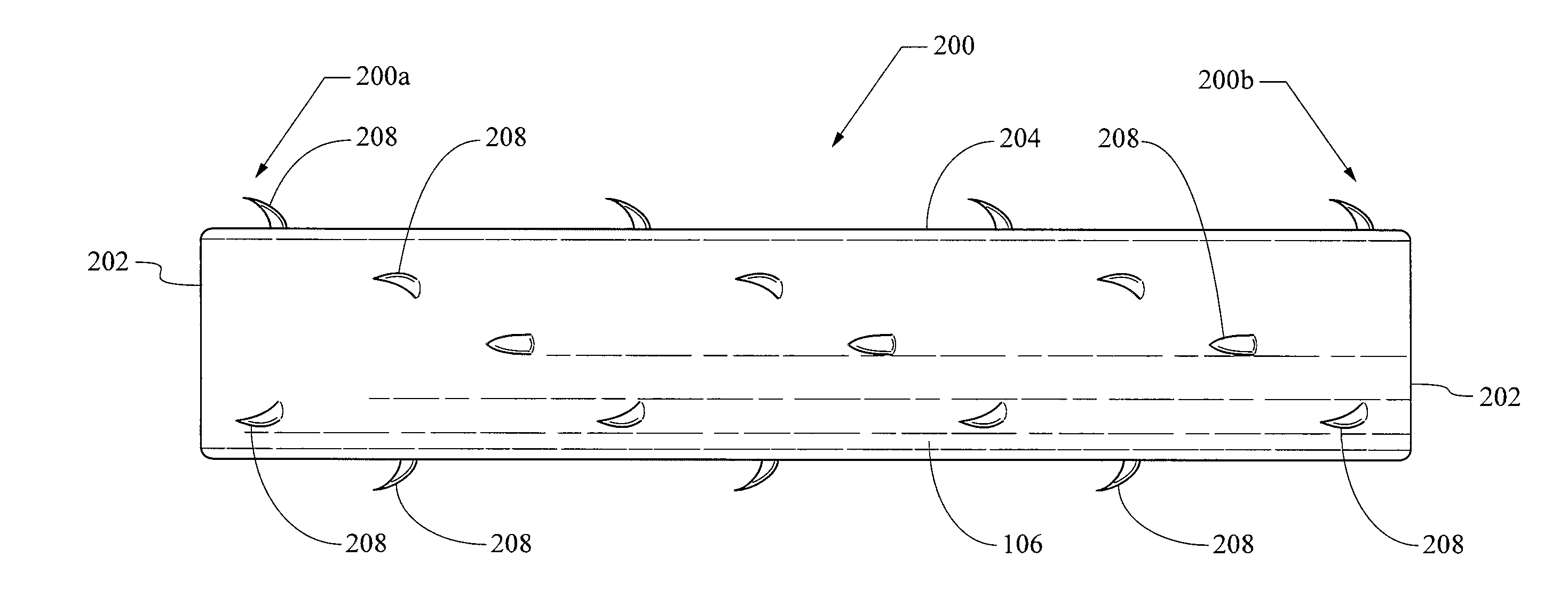
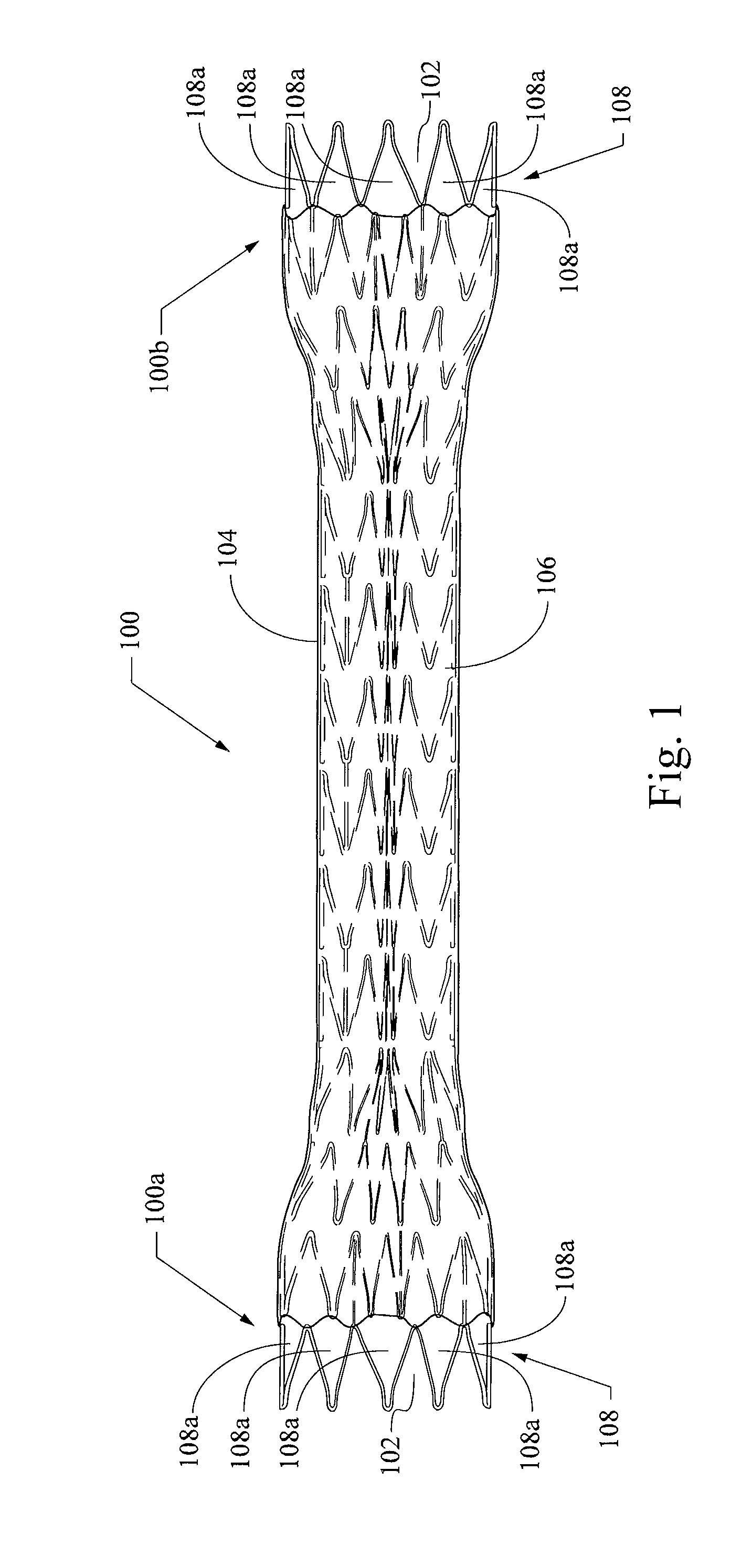
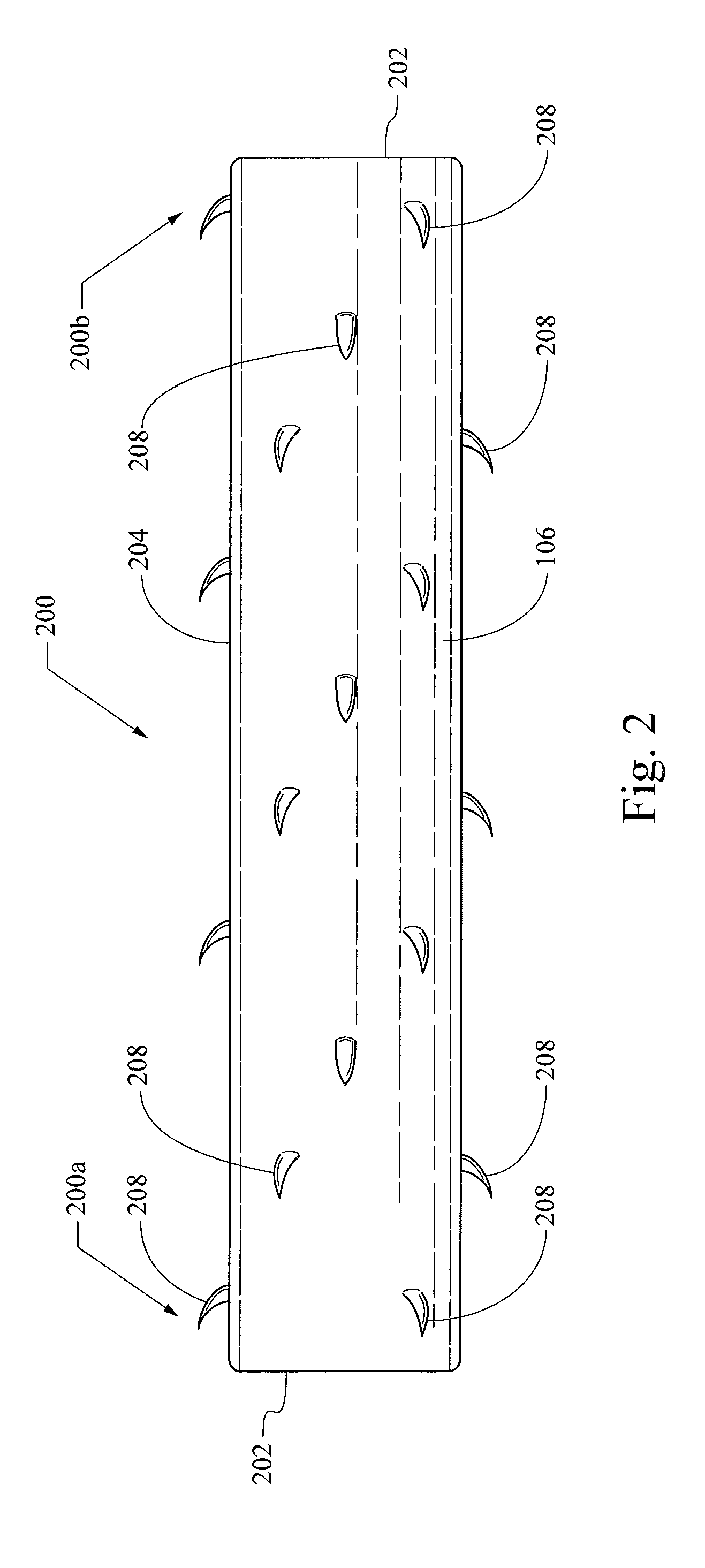
ActiveUS20130261733A1Variation in rigidityVariation in stent flexibilityStentsBlood vesselsFiberIliac Aneurysm
An expandable, bioabsorbable stent having a coiled-coil configuration is described. The stent further comprises regions of variable pitch that allow for variation in either rigidity, or variability diameter within sub-regions along the length of the deployed stent. By varying the diameter allows the stent to extend into regions such as branched vessels, or into the neck of aneurysms. In some embodiments, the stent comprises longitudinal support fibers that run substantially the length of the deployed stent to provide additional strength. In addition, the stent may also comprise regional support fibers that run less than the length of the stent, and which provide increased regional strength while permitting flexibility of the stent. The stent further comprises micro-tubes that are configured to be visible using medical imaging techniques. The stent can be manufactured from materials that are bioabsorbable and / or include the ability to release pharmacologically active substances over time.
Owner:MANLI INT
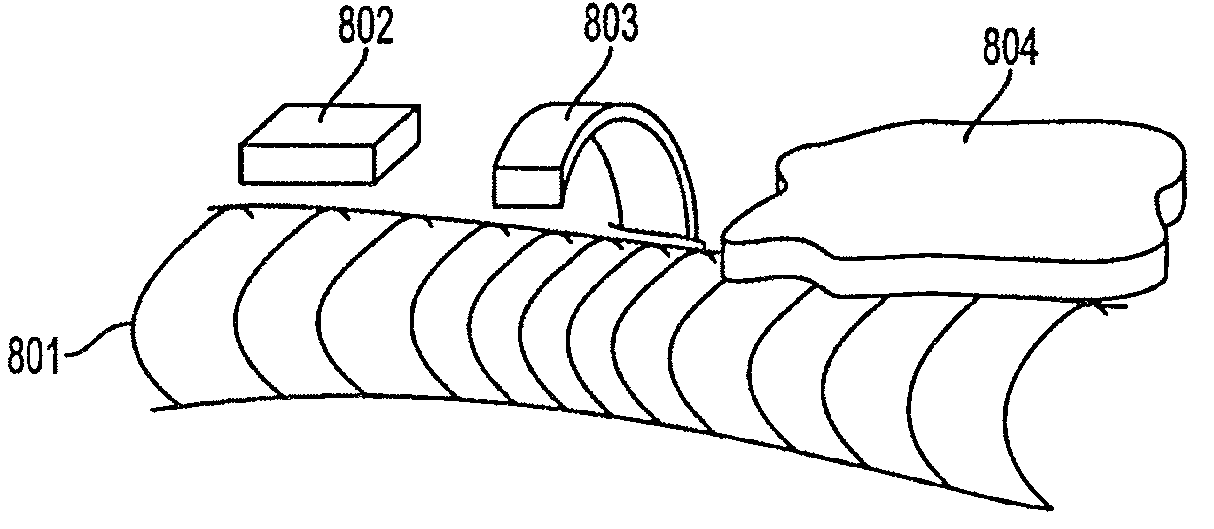
Slide fastener bioabsorbable stent and application thereof
A slide fastener bioabsorbable stent is applied as a cardiovascular system stent or a lumen stent in the disease of cardiovascular or narrow lumen. The slide fastener bioabsorbable stent includes a snap fastener stent, an edge slide fastener stent, a middle slide fastener stent, and a double fastener stent. The slide fastener bioabsorbable stent has good degradability and biocompatibility, and is more suitably used as a pediatric vascular stent, with which no late-onset stent thromboses after implanted, and thus it is not necessary to long-term take antiplatelet drugs and the subsequent surgical operation may not be affected. Also, it has a strong support, and thus can be widely used as a cardiovascular system stent or a lumen stent in the disease of cardiovascular or narrow lumen. The slide fastener bioabsorbable stent has simple production and convenient drug carrying, which can be used as a carrier of medicine or gene treatment. The stent can be matched with a delivery system, hence the difficulty of the surgery operation is reduced. Many animal experiments show that slide fastener bioabsorbable stent has high success ratio when being used, and has apparent curative effect and good clinical application prospect.
Owner:XIN HUA HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Composite stent with inner and outer stent elements and method of using the same
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
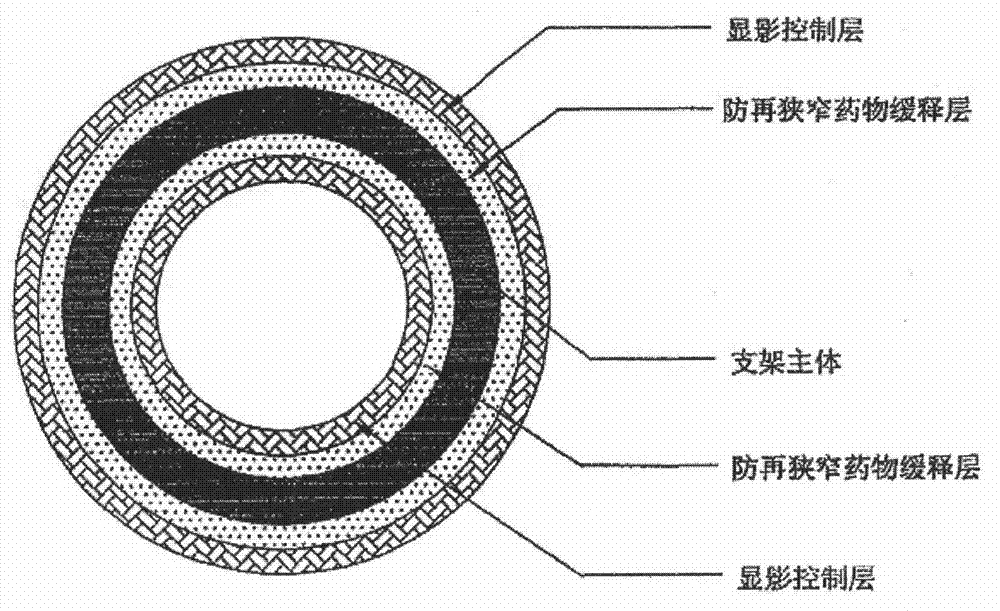
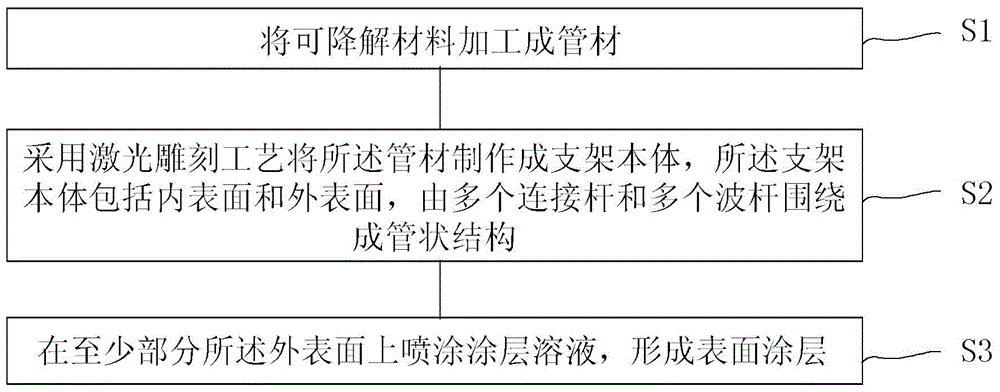
Bioabsorbable stent and preparation method thereof
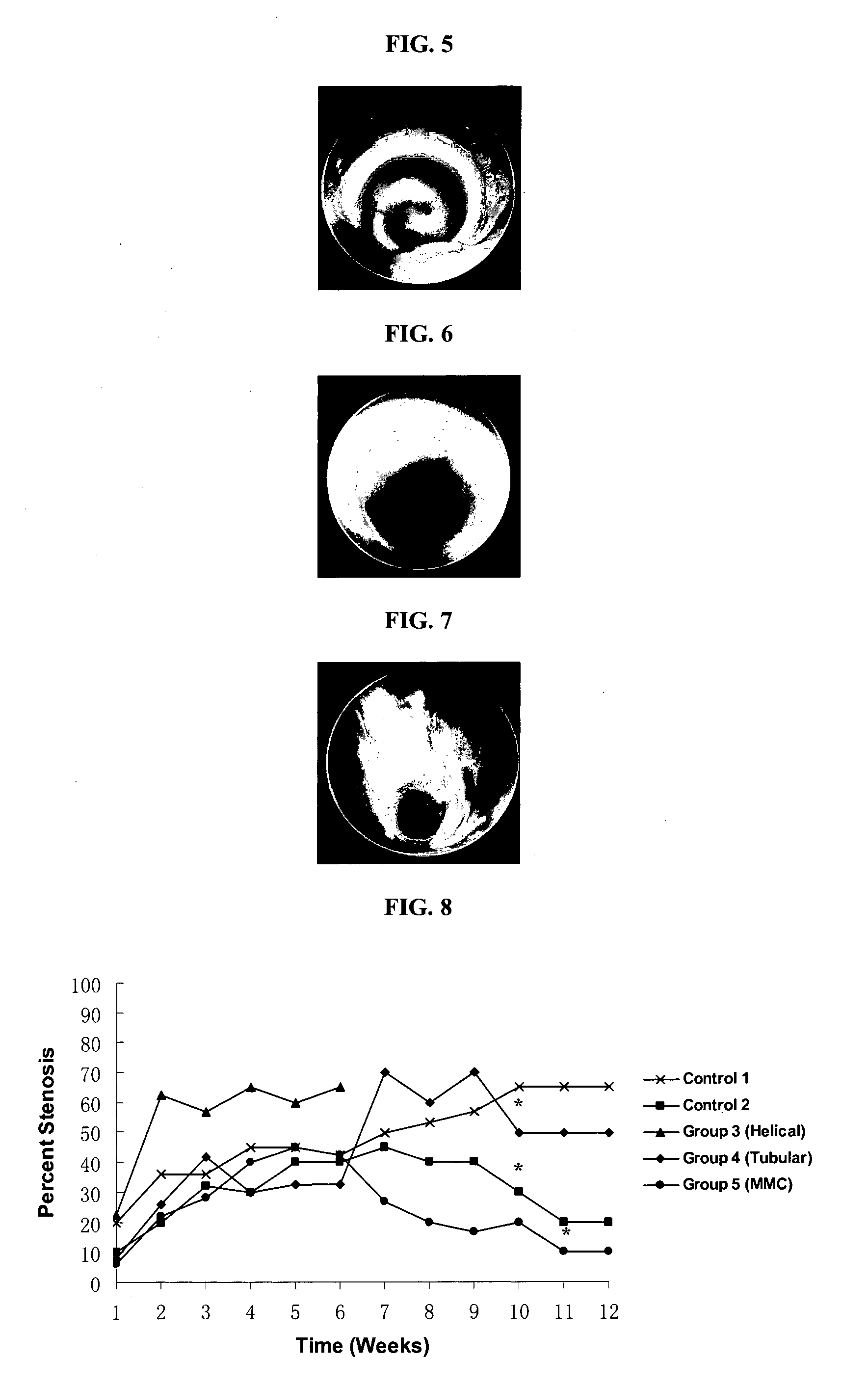
ActiveCN104644297AReduce restenosisInhibit sheddingStentsSurgeryBioabsorbable stentPercent Diameter Stenosis
The invention relates to a bioabsorbable stent and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of processing a degradable material into a tube; making the tube into a stent body by adopting a laser carving process, wherein the stent body comprises an inner surface and an outer surface and is a tubular structure formed by a plurality of connecting rods and a plurality of wavy pipes; coating solution is coated on at least part of the outer surface to form a surface coating layer. In the preparation method, the coating solution can be accurately coated at positions of the wavy rods or connecting rods on the outer surface so as to improve the utilization ratio of the solution and guarantee the process stability of the coating layer of the outer surface. Moreover, since the prepared bioabsorbable stent is prepared by using a bioabsorbable or biodegradable material, the stent can be fully degraded after medicine is released, the restenosis after stent implantation is reduced and the permanent stimulation to blood vessels is avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT MEDICAL (GROUP) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com