Bioabsorbable stent and preparation method thereof
A biodegradable polymer technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems that droplets cannot cover the surface of the probe at one time, cannot carry drugs at one time, and it is difficult to position or limit the coating, so as to ensure process stability Sex, avoid permanent irritation, reduce the effect of loss of solution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] The stent body 2 is made of bioabsorbable polylactic acid material (PLA), wherein the weight average molecular weight of the polylactic acid material ranges from 150,000 to 1,000,000 Daltons, and the degradable polymer of the surface coating 2 is made of poly D,L-lactide (PDLLA) material, with a weight average molecular weight ranging from 30,000 to 140,000 Daltons.
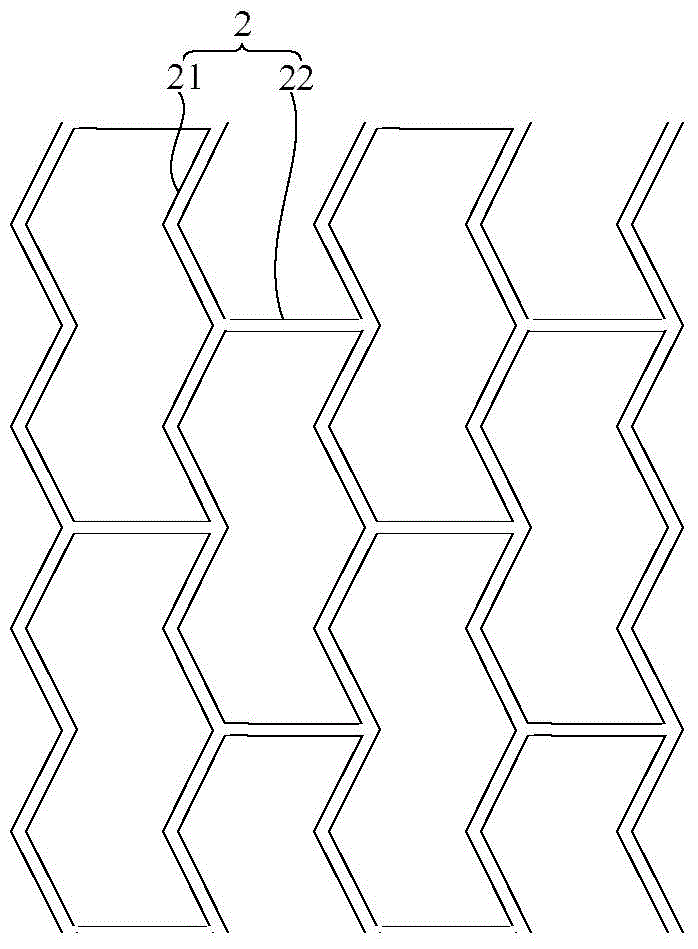
[0058] Take 0.4g of poly D,L-lactide polymer, add it into 10ml of n-propyl acetate solvent at room temperature to prepare a coating solution, after that, add 0.2g of rapamycin and mix evenly to form a coating solution, and coat the Layer solution is accurately sprayed to all parts of the outer surface of the stent body 2, and the stent structure formed refers to Figure 5 As shown, the scaffolds were left to dry at room temperature until use.
[0059] It should be noted that, according to the degradable time of the selected degradable polymer in the body and the amount of the polymer used, the poly-D, L-l...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The degradable materials used for the stent body 2 and the surface coating 3 are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0062] Take 0.2g poly D,L-lactide polymer, add it into 10ml n-propyl acetate solvent at room temperature to prepare a uniform solution, then add 0.2g rapamycin and mix uniformly to form a coating solution. The coating solution is accurately sprayed onto the outer surface of the stent body 2 except for the connecting rod 22, and the formed stent structure refers to Figure 6 As shown, the scaffolds were left to dry at room temperature until use.
[0063] Similarly, the poly-D,L-lactide polymer used in this embodiment will degrade within 2 years after completing the drug release function, and the polylactic acid stent body 3 used will degrade within 3 years.
Embodiment 3
[0065] The degradable materials used for the stent body 2 and the surface coating 3 are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0066] Take 0.2g poly D, L-lactide polymer, add it into 10ml n-propyl acetate solvent at room temperature to prepare a uniform solution, add 0.2g rapamycin and mix evenly to form a coating solution, and the coating solution is accurately Spot-coated onto the outer surface of the stent body 2, the surface coating 3 is in a discontinuous state, and the stent structure formed refers to Figure 7 As shown, the scaffolds were left to dry at room temperature until use.
[0067] Similarly, the poly-D,L-lactide used in this embodiment will degrade within 2 years after completing the drug release function, and the polylactic acid stent body 3 used will degrade within 3 years.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com