Method of monitoring positioning of polymer stents
a technology of stent positioning and monitoring method, which is applied in the field of monitoring positioning of polymer stents, can solve the problems of increasing thrombosis, and achieve the effects of increasing or decreasing the diameter of the stent, increasing blood flow turbidity, and increasing thrombosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019]It will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that although the following Detailed Description will proceed with reference being made to preferred embodiments, the present invention is not intended to be limited to these embodiments.
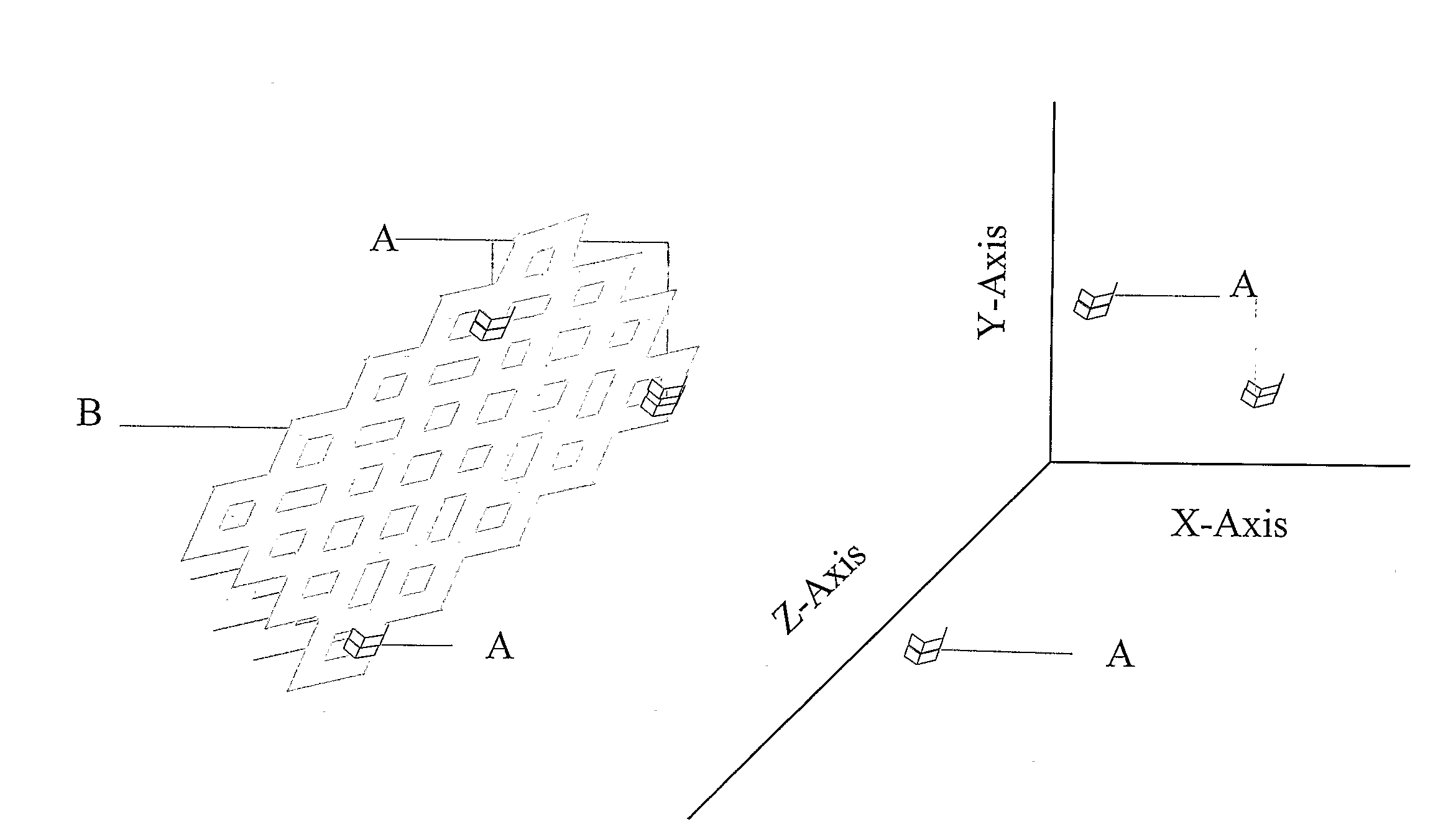
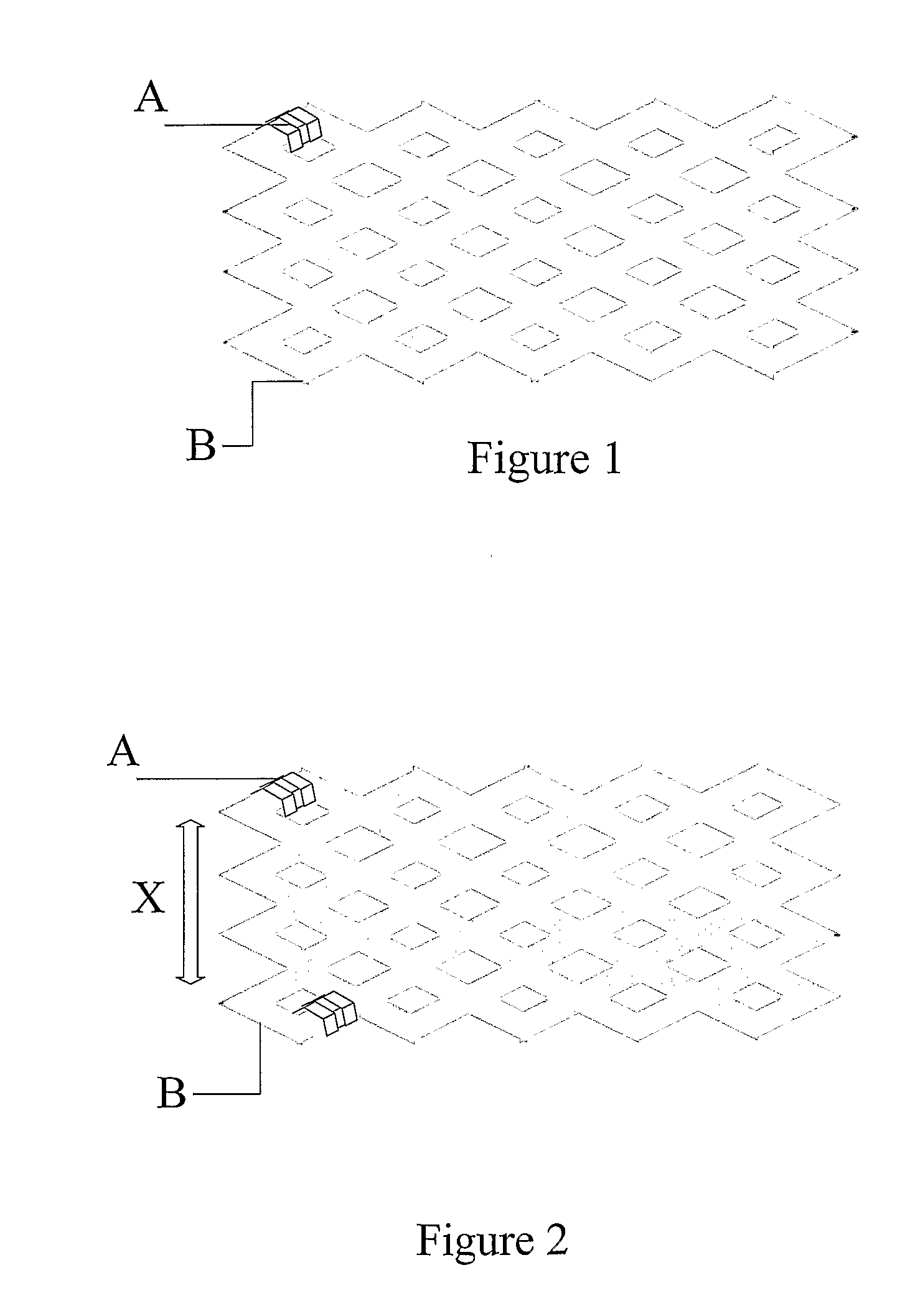
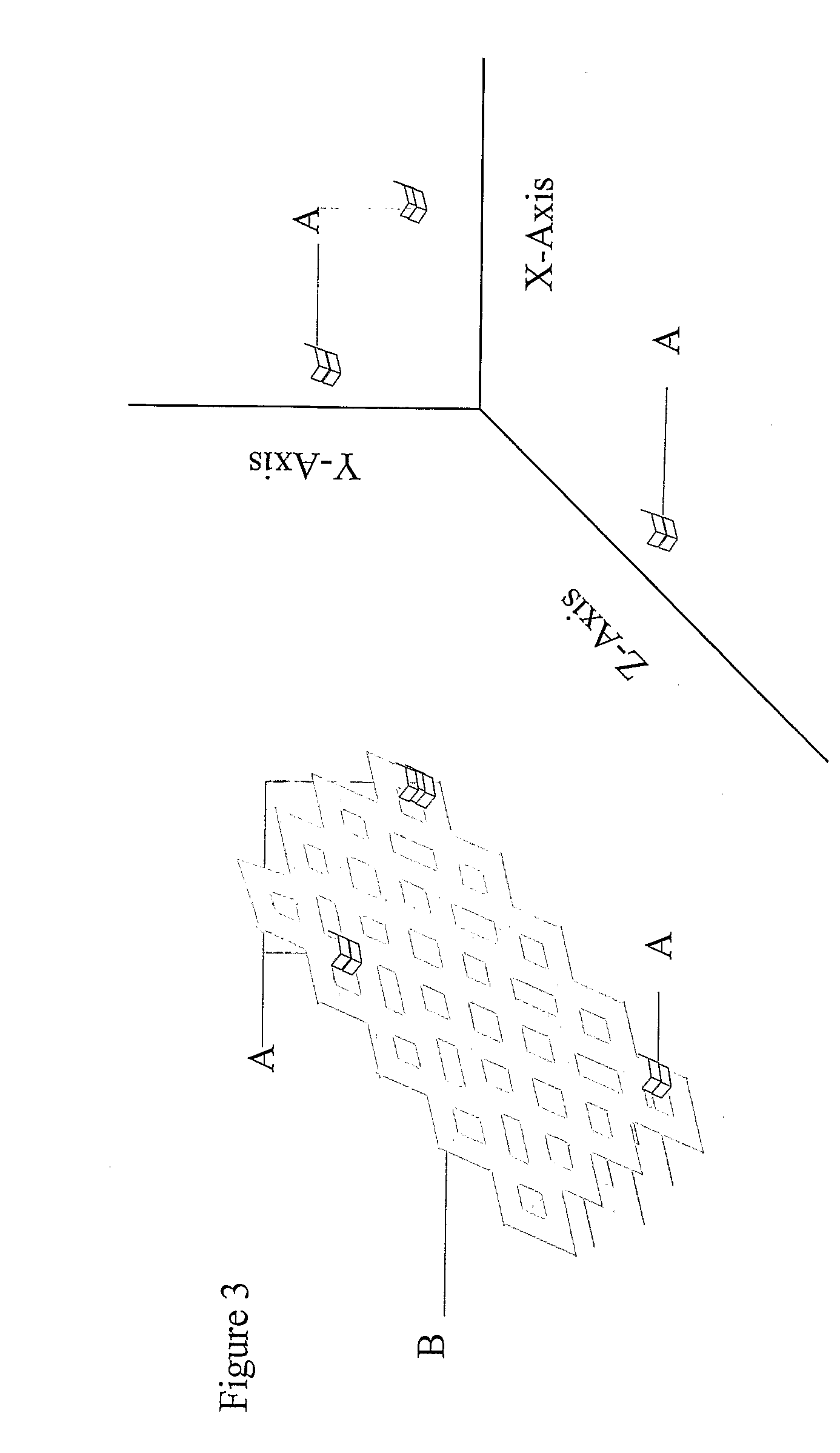
[0020]In one embodiment, the present invention is directed to a polymer stent that comprises at least one marker, where the marker is provided to track the stent during its placement within the body. The stent of the present invention can have virtually any configuration that is compatible with the body lumen in which it is implanted for the purpose of repairing the same. Typically, stents are composed of an intricate geometric pattern of circumferential and longitudinally extending members. These elements are commonly referred to as struts.
I. Detectable Marker
[0021]The markers can be made of any material that may be detected external to the body. The only limitation on the type of marker used is that it be visible by external means and may be...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com