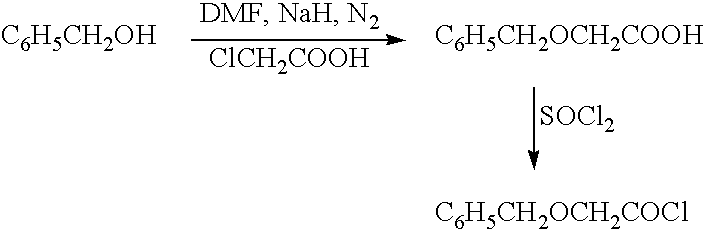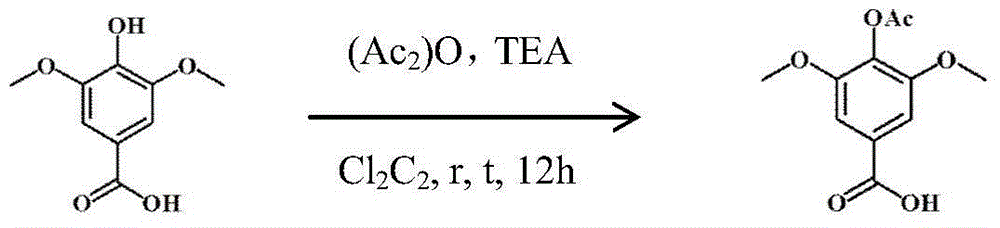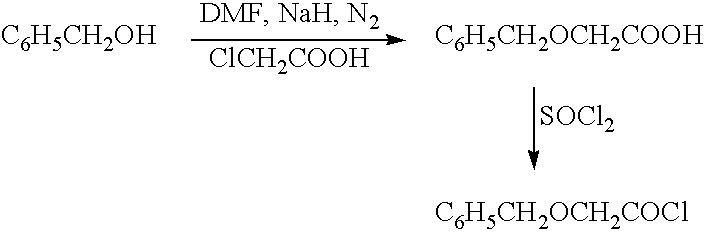Patents
Literature
90 results about "Syringic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
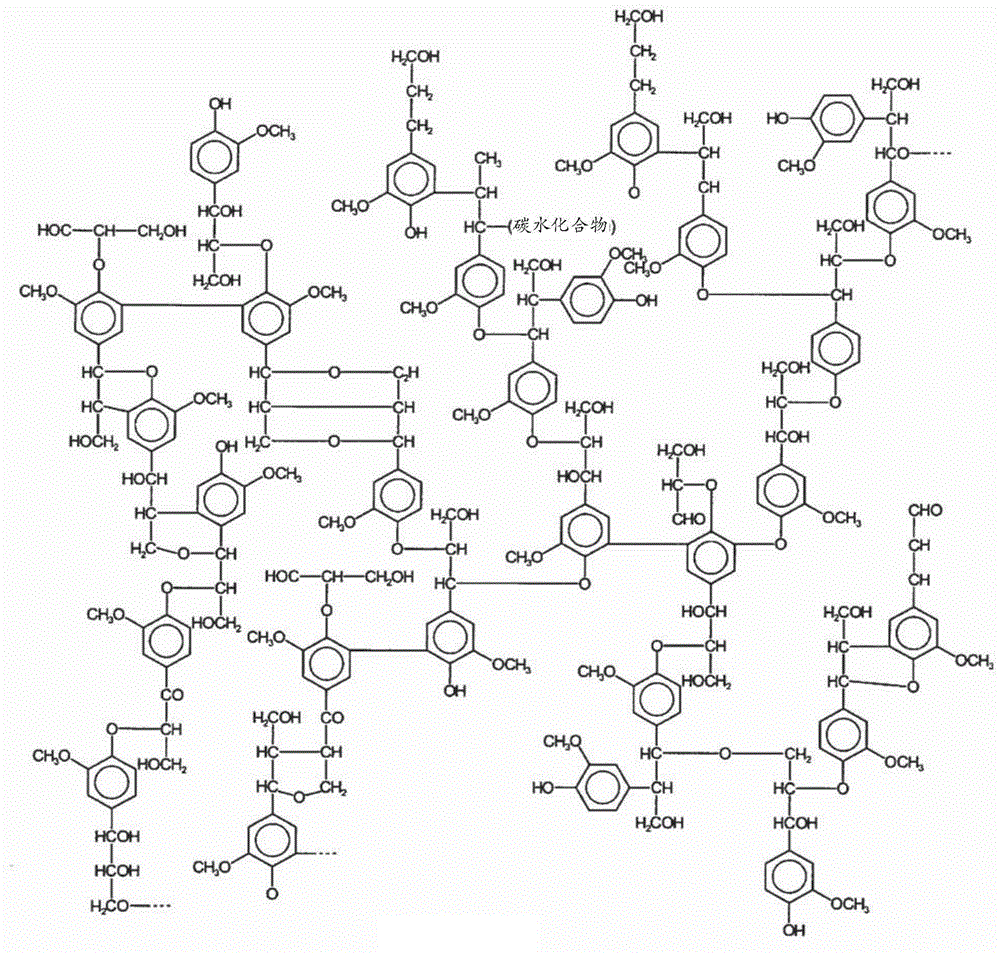
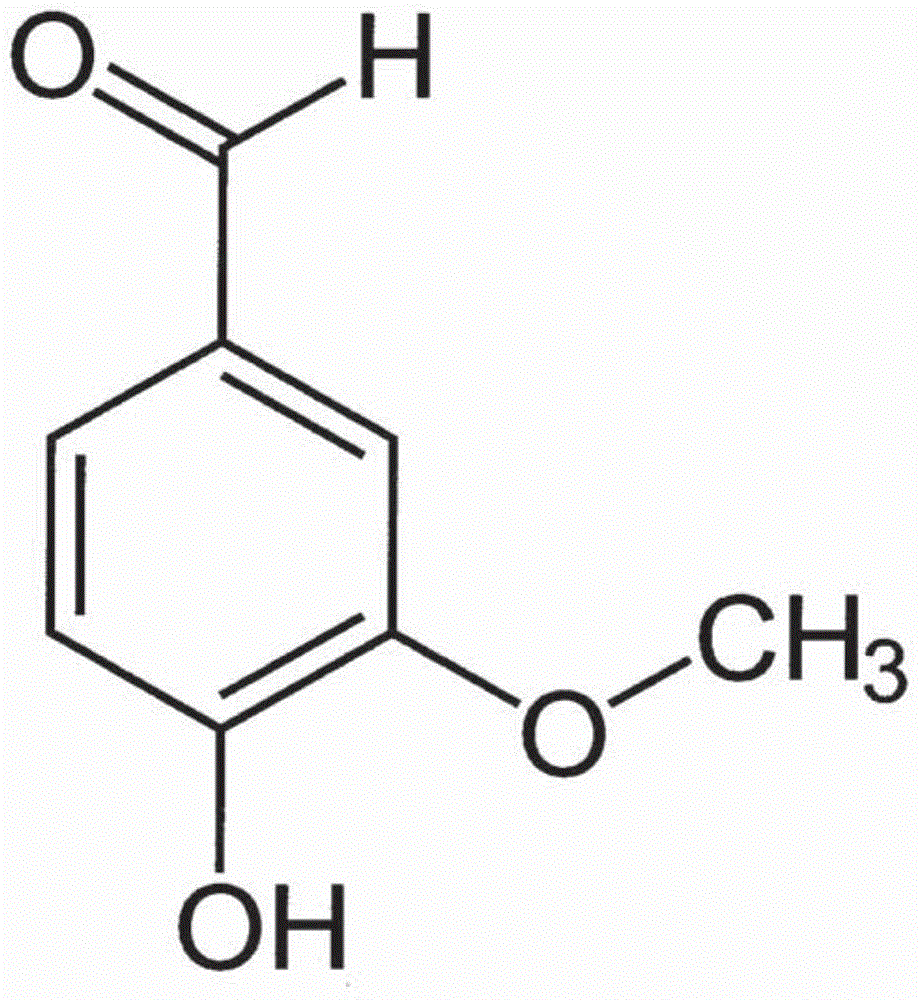
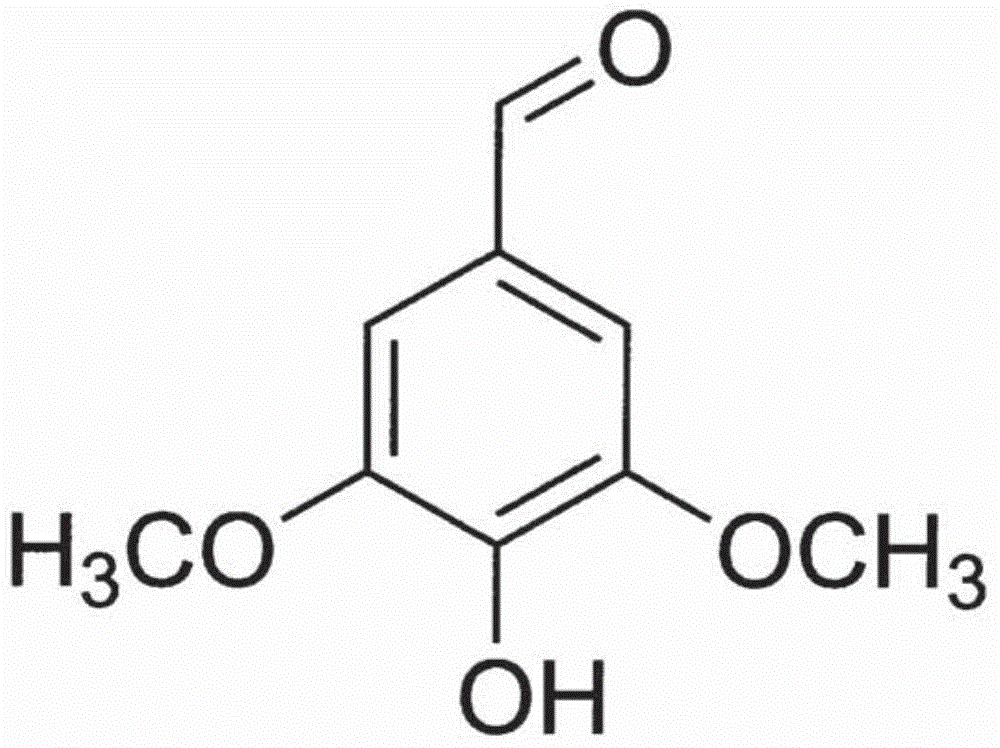
Syringic acid is a naturally occurring O-methylated trihydroxybenzoic acid, a type of chemical compound.
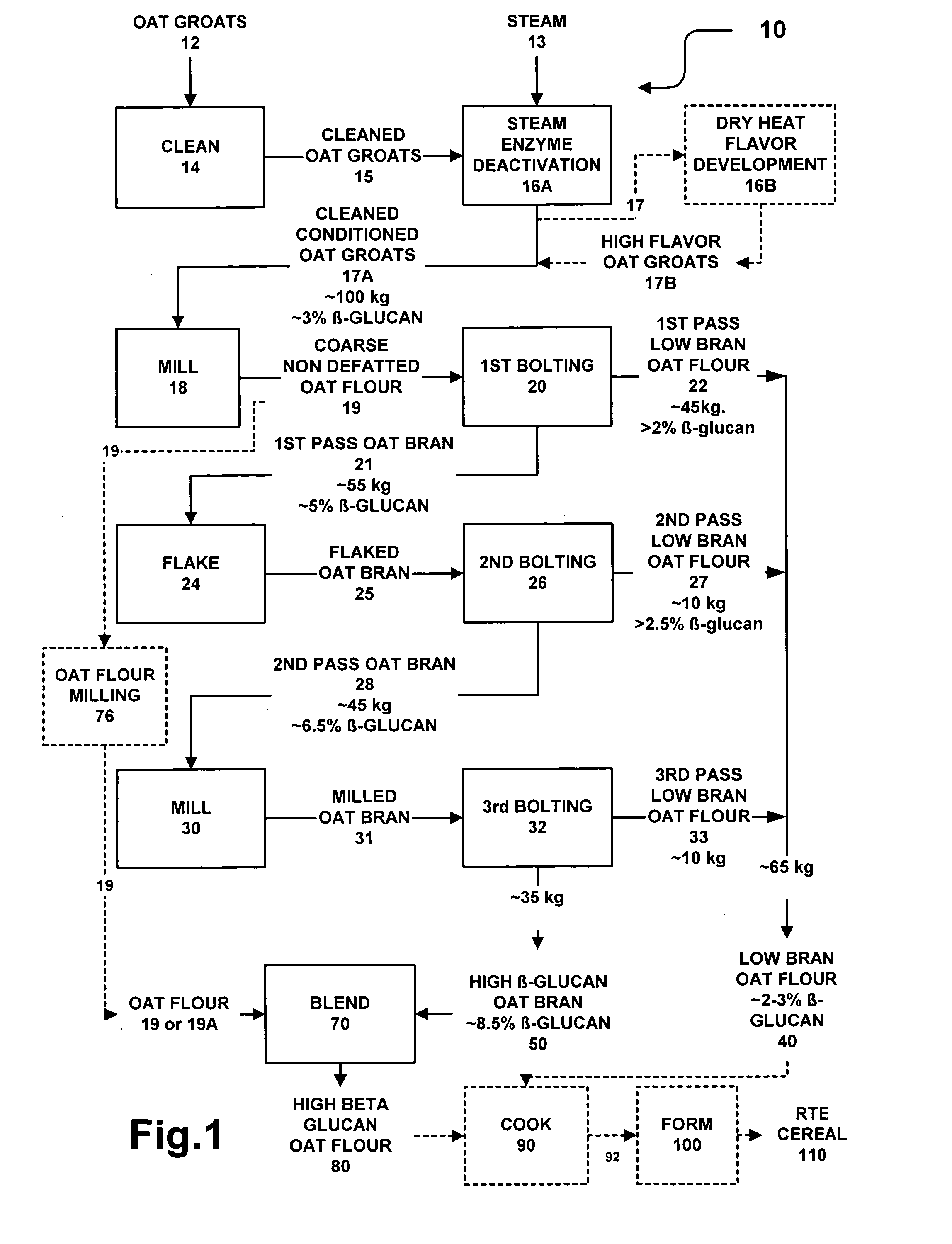
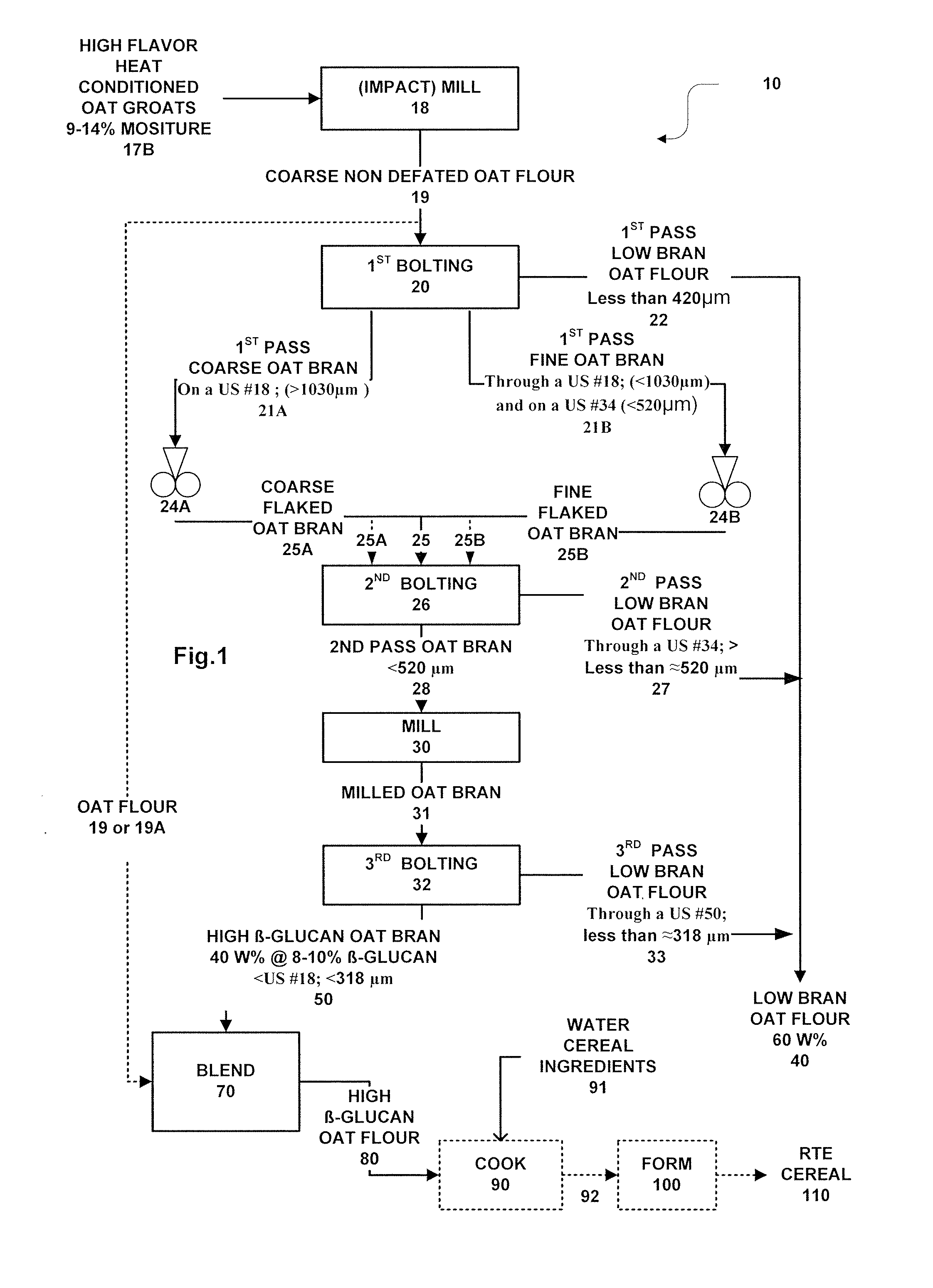
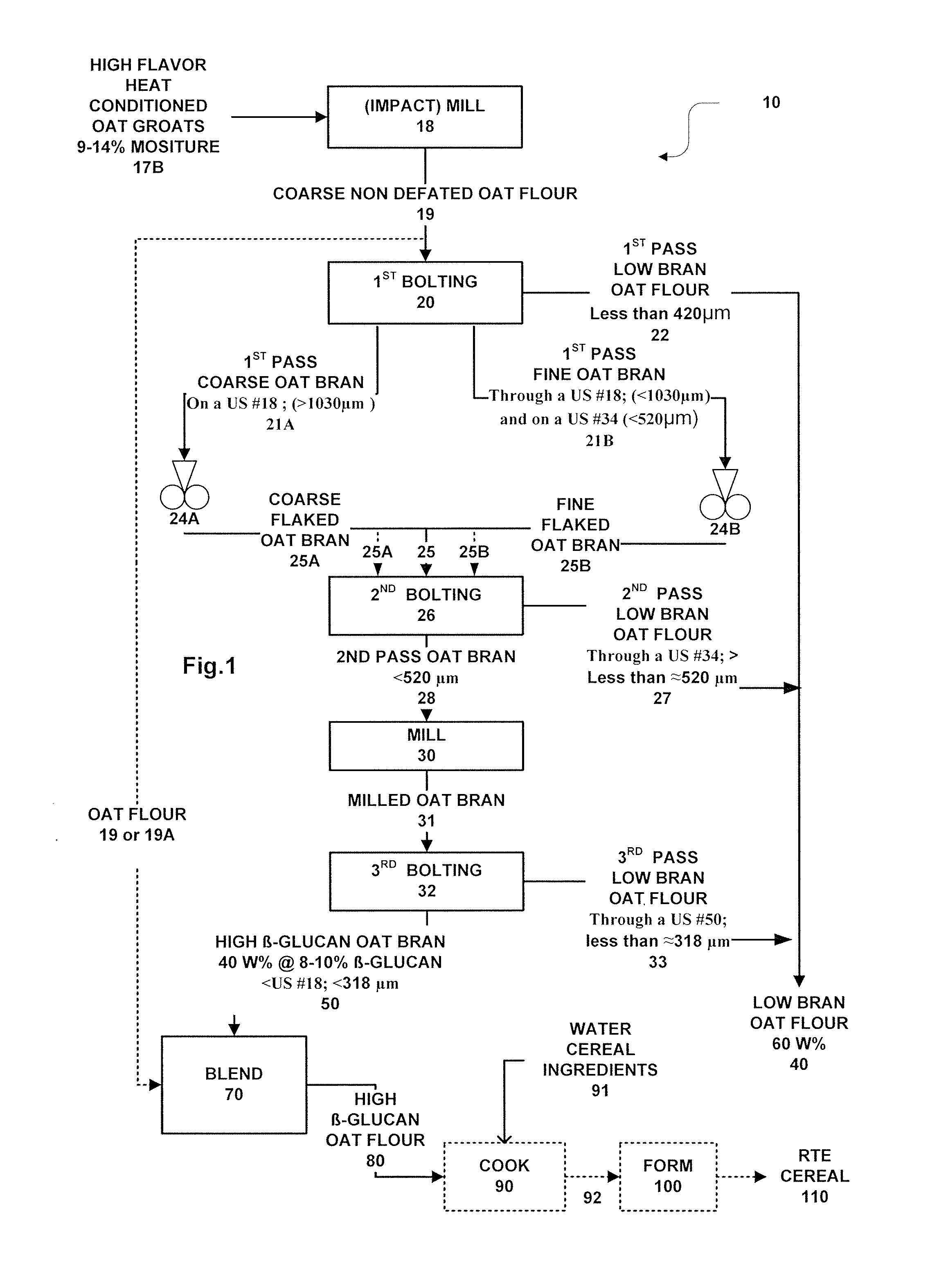
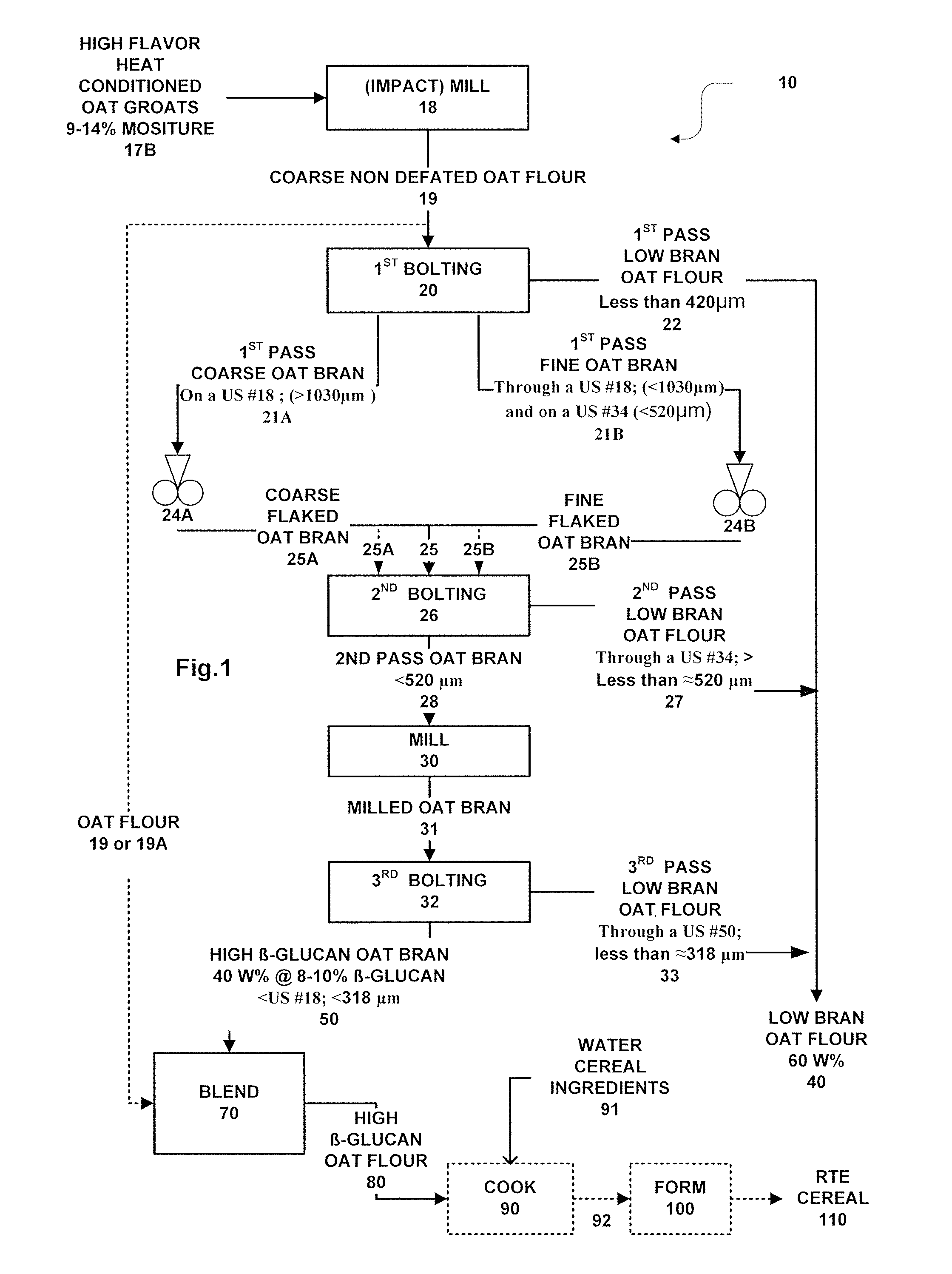
Methods for preparing oat bran enriched in beta-glucan and oat products prepared therefrom
ActiveUS20050153044A1Add flavorEnhance cooking characteristicsDough treatmentBaking mixturesFood flavorCereal grain
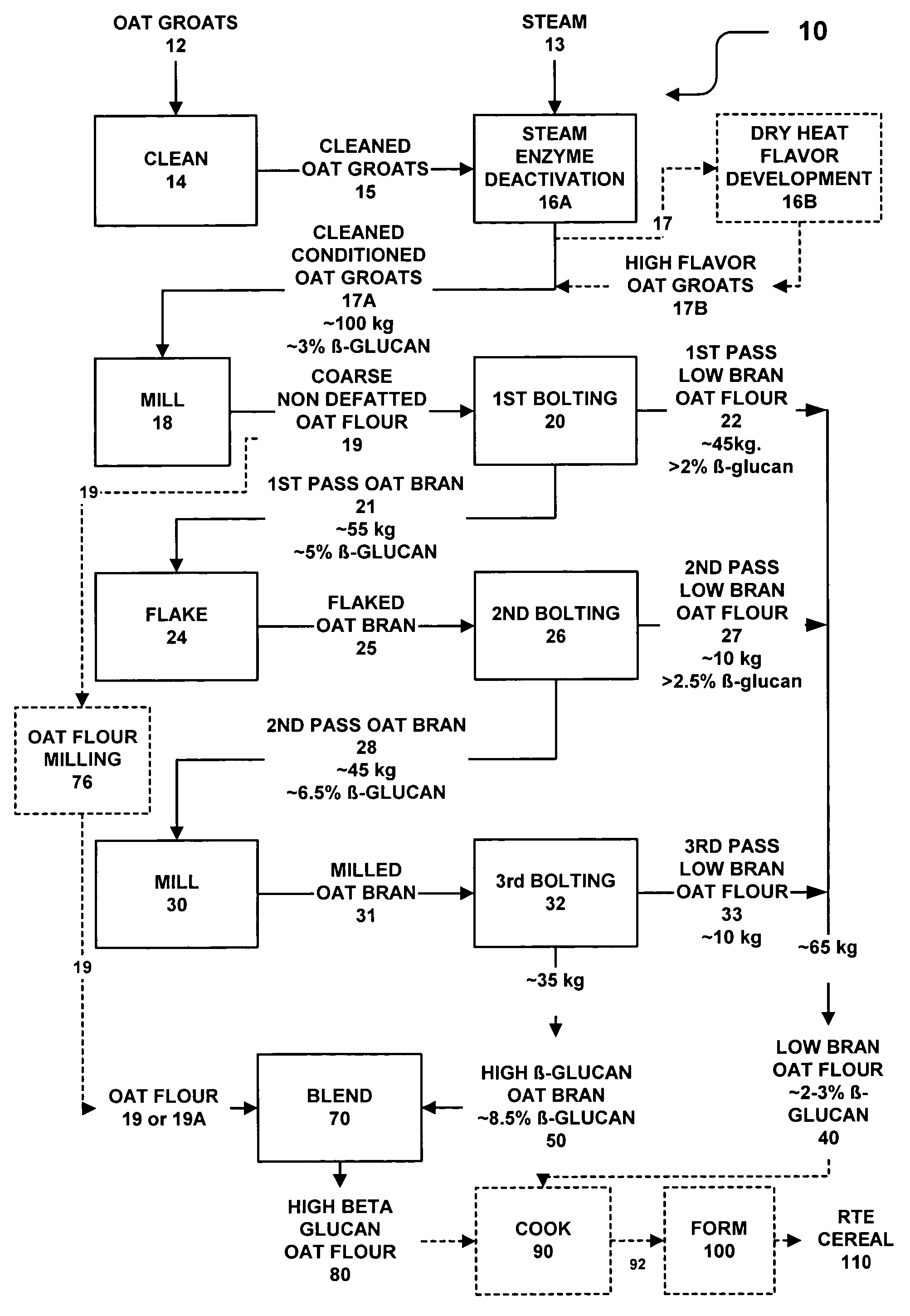
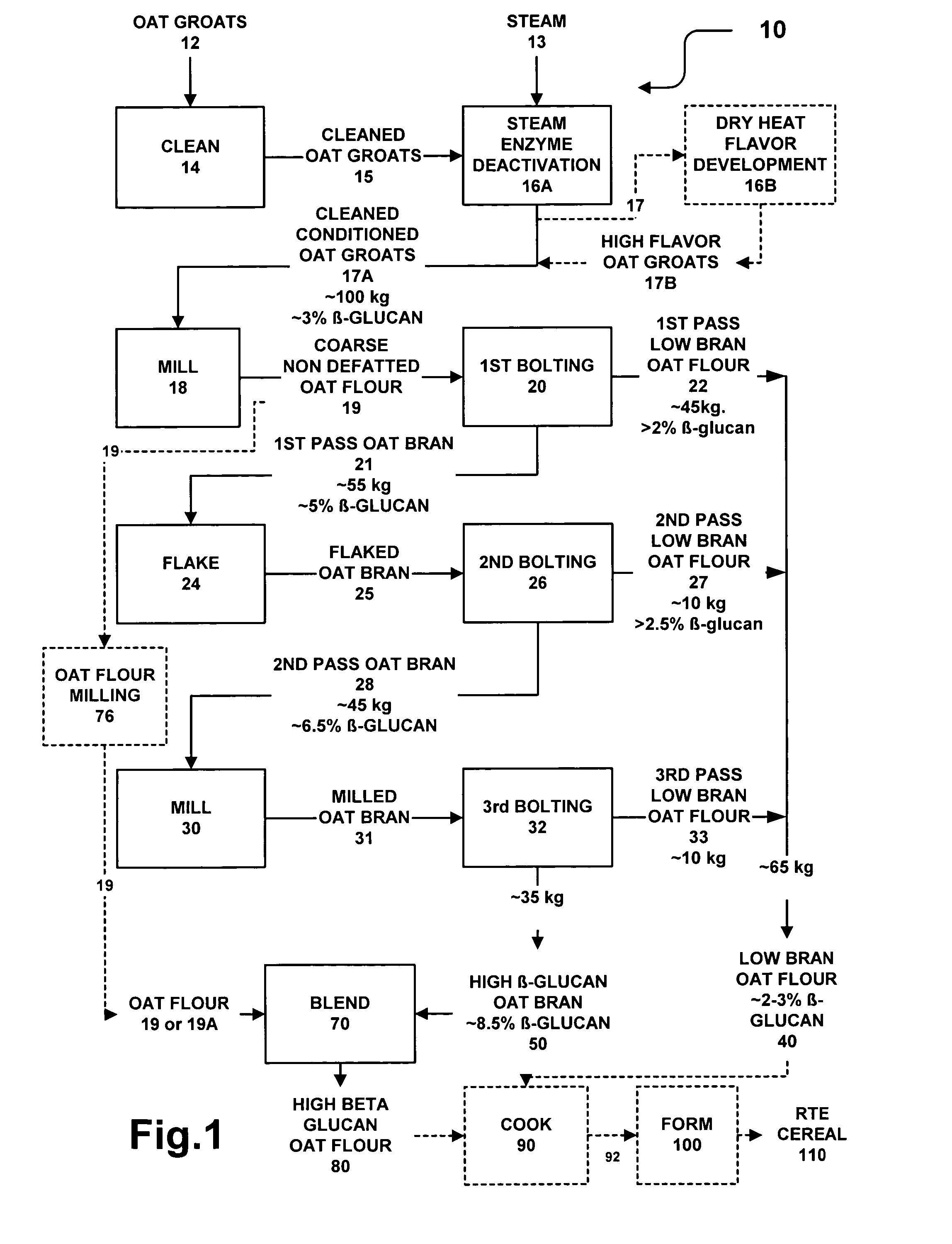
Dry milling methods for preparing oat products enriched in the content of β-glucan and methods for preparing foodstuffs incorporating such an enriched oat product especially ready-to-eat cereals are provided. Heat conditioned dehulled oats are dry milled to form a coarse whole non defatted oat flour and then, without a preceding removal of fat, dry fractionated into coarser bran and finer oat flour fractions at multiple stages. The coarse oat flour is first dry classified to separate or form a coarser fraction oat bran containing more concentrated β-glucan and a finer oat flour or starch containing or endosperm containing fraction. The oat bran is subjected to second and third rounds of milling and classification to form a high β-glucan content (>7-9%) oat bran and a low β-glucan content (3%) oat flour. The methods are low cost and commercially practical. Preferably, the high β-glucan content oat bran and oat flour fractions can have a syringic acid to ferulic acid ratio of at least 2.5:1 indicating improved flavor. Preferably, the oat bran and oat flour have a Farinograph value of 5 to 20 minutes indicated partial gelatinization. The oat bran and oat flours can be used to prepare foodstuffs such as ready-to-eat cereals.
Owner:GENERAL MILLS INC
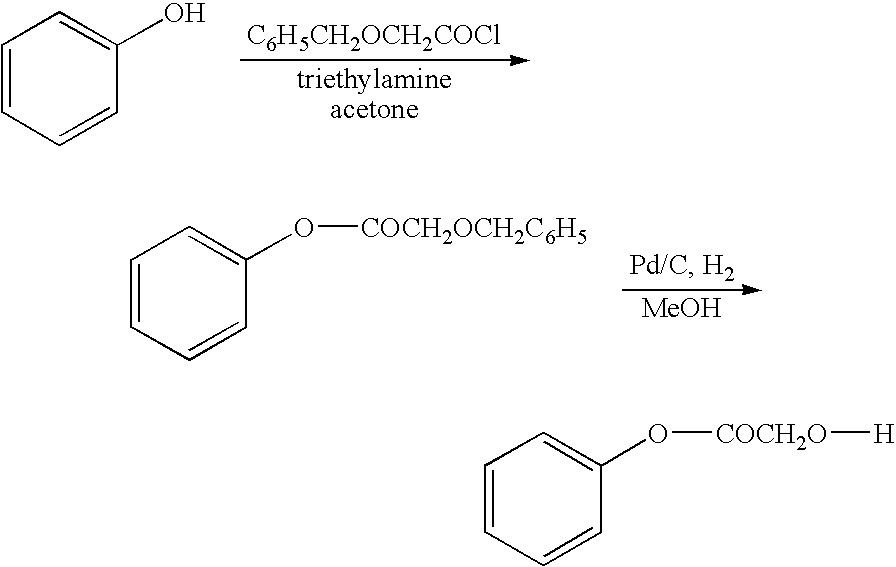
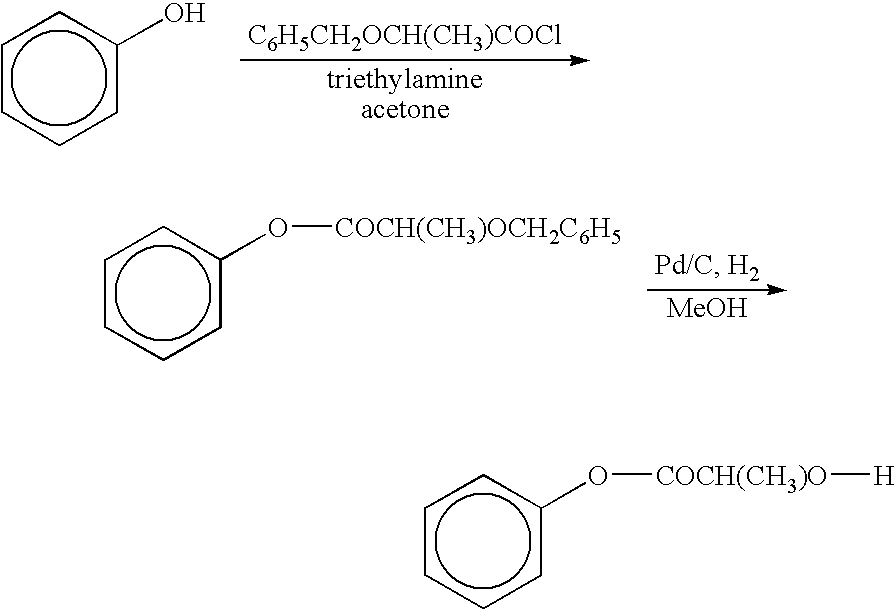
Functionalized phenolic esters and amides and polymers therefrom
InactiveUS20060173065A1Alter efficacyAlter valueBiocideOrganic chemistryBenzoic acidPhenylacetic acid
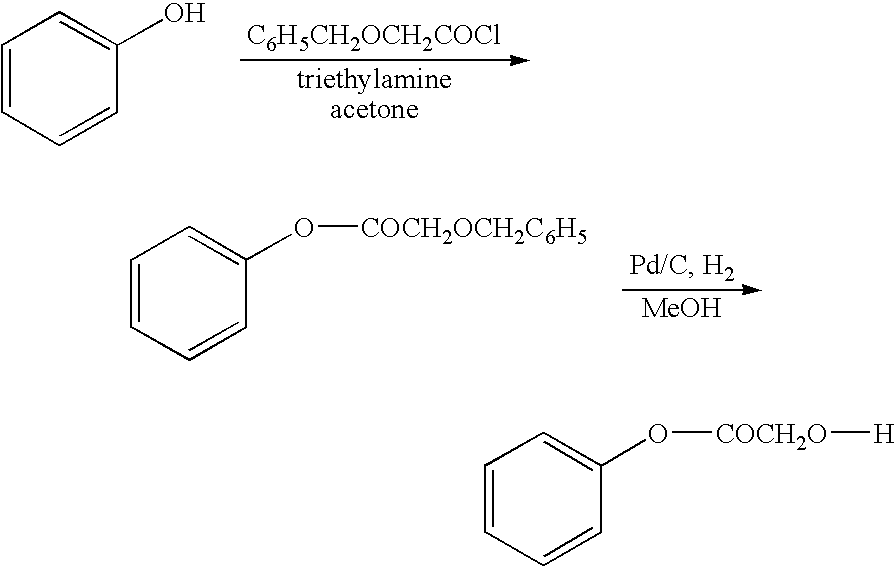
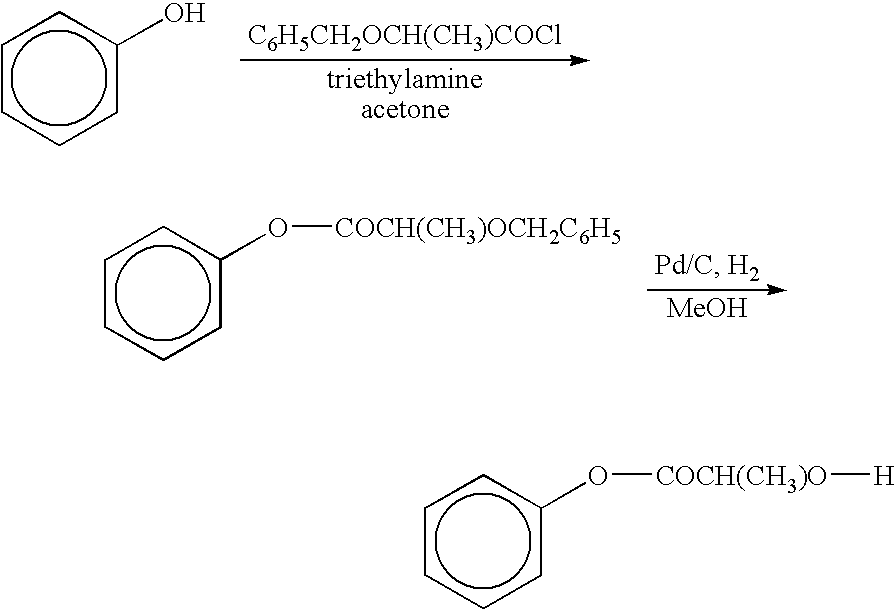
The present invention relates to a compound of the formula: R-AR—O—Y—R′Wherein R represents one or more members selected from H, alkoxy, benzyloxy, aldehyde, halogen, carboxylic acid, —NO2, —NH2, —NHCOCH3, and —NH—Y—R′, which is attached directly to AR or attached through an aliphatic chain. The carboxylic acid moiety in R includes but is not limited to the following carboxylic acids: benzoic acids, cinnamic acids, ferulic acid, caffeic acid, syringic acid, salicylic acid, vanillic acid, phenylacetic acids, phenylpropionic acids, and sinapinic acid. -AR—O— is a biologically active phenolic moiety comprising 1 to 6 substituted or unsubstituted aryl rings that are directly bonded to each other, fused together, or joined through a linking group. Y represents a member selected from: —COCH2O— (glycolic ester moiety) —COCH(CH3)O— (lactic ester moiety) —COCH2OCH2CH2O— (dioxanone ester moiety) —COCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2O— (caprolactone ester moiety) —CO(CH2)mO— where m is an integer between 2-4 and 6-24 inclusive —COCH2O(CH2CH2O)n— where n is an integer between 2 and 24, inclusive; and R′ is either hydrogen or a benzyl or an alkyl group, the alkyl group being either straight-chained or branched. The resultant functionalized phenolic compounds, used singly or in combinations, and their polymers have controllable degradation profiles, releasing the active component over a desired time range. The polymers are useful for biomaterials and biomedical devices, wherein said biologically active phenolic moiety is a residue of a phenolic compound.
Owner:BEZWADA BIOMEDICAL LLC
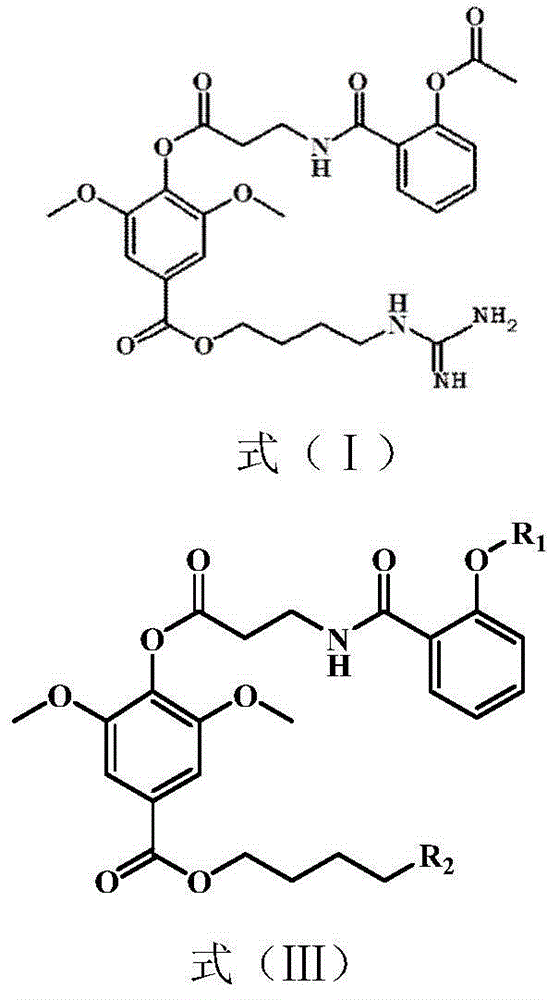
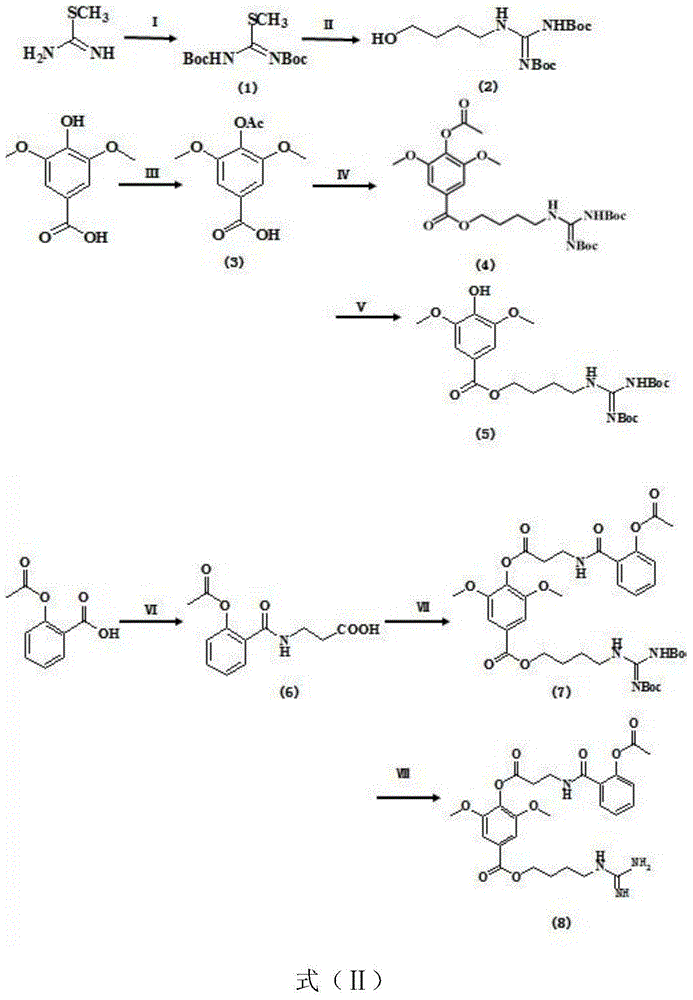
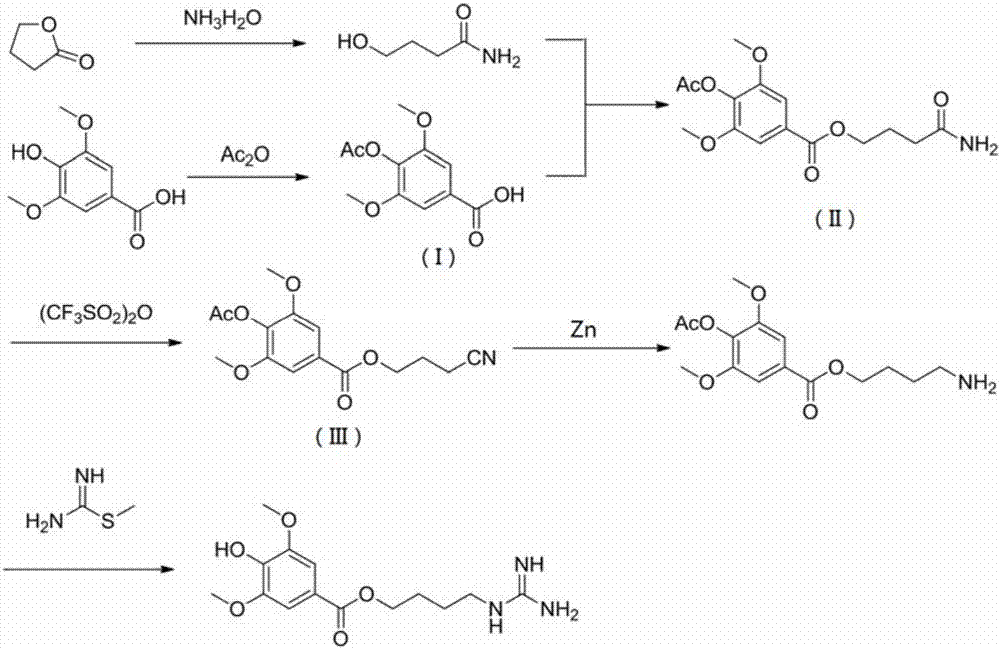
Method for synthesizing leonurine
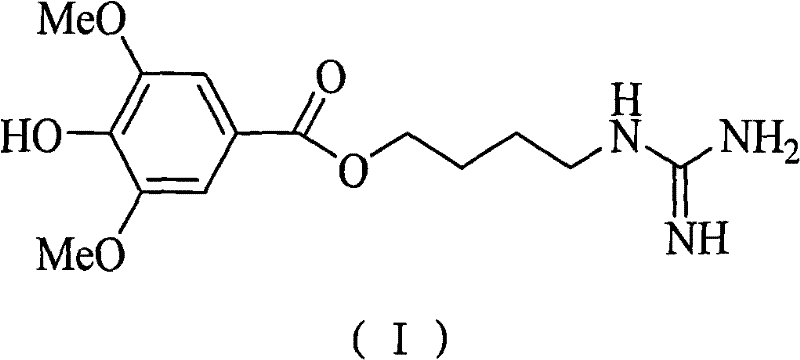
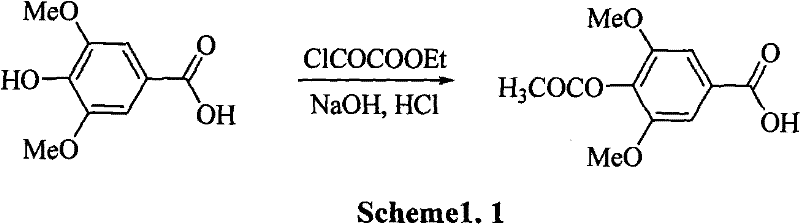
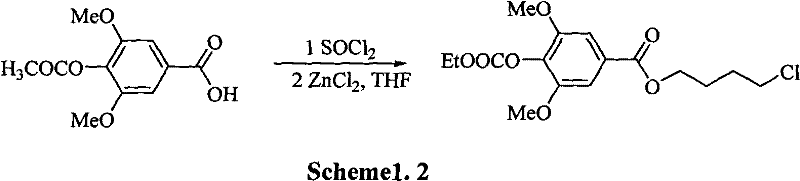
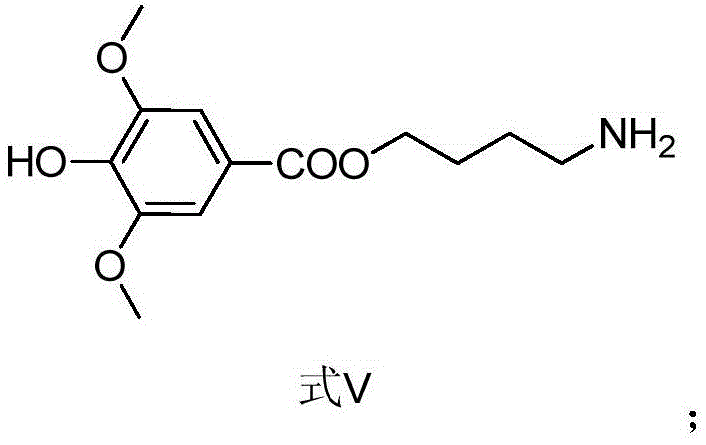
A process for synthesizing the leonurine from syringic acid as initial raw material includes such steps as carbonylation reaction, acylchlorination reaction, esterification reaction, ammonification reaction to obtain leonuriamine, and reacting with methylisothiourea. Its advantages are simple operation, easy control, high output rate, and high purity (99.8%).
Owner:李晓祥
Synthesis method of bioactive derivative bagasse xylan syringic acid ester-g-AM
ActiveCN107540789AImprove poor water solubilityImprove biological activitySolubilitySynthesis methods
The invention discloses a synthesis method of bioactive derivative bagasse xylan syringic acid ester-g-AM. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: by taking bagasse xylan as a starting rawmaterial, taking ammonium persulfate as an initiator, taking N,N'-methylene bisacrylamide as a crosslinking agent, preparing bagasse xylan-g-AM in a water-phase solution; then by taking the bagasse xylan-g-AM as a raw material, taking syringic acid as an esterifying agent and taking the ammonium persulfate as a catalyst, preparing the bagasse xylan syringic acid ester-g-AM in a solvent N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMA). A product prepared through the synthesis method is esterified on the basis of grafting, and a finally synthesized product, namely the bagasse xylan syringic acid ester-g-AM, improves the problem of low water solubility of the bagasse xylan and also expands the application field of the bagasse xylan. Meanwhile, by the introduction of active groups of acrylamide (AM) and the syringic acid, the bioactivity of the bagasse xylan is further improved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Lignin degradation product removing method
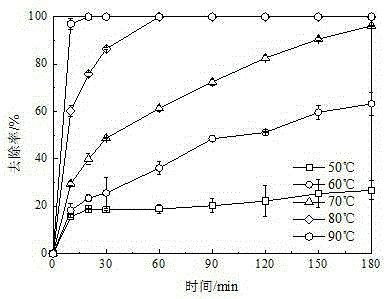
The present invention discloses a lignin degradation product removing method. According to the method, the lignin degradation products are adopted as the substrate, and the way that the persulfate is activated to generate the sulfate free radical is used to carry out oxidation removal on the lignin degradation products, wherein the activating way selects the thermal activating, and the persulfate selects ammonium persulfate as the oxidant. According to the present invention, the thermal activating way is used to activate the ammonium persulfate so as to perform the oxidation removal of the lignin degradation products, and the results show that the removal rates of vanillin, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, vanillic acid, 4-hydroxy benzoic acid and syringic acid achieve 100% within 1 h, and the syringic aldehyde removal rate achieves 100% within 2 h.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
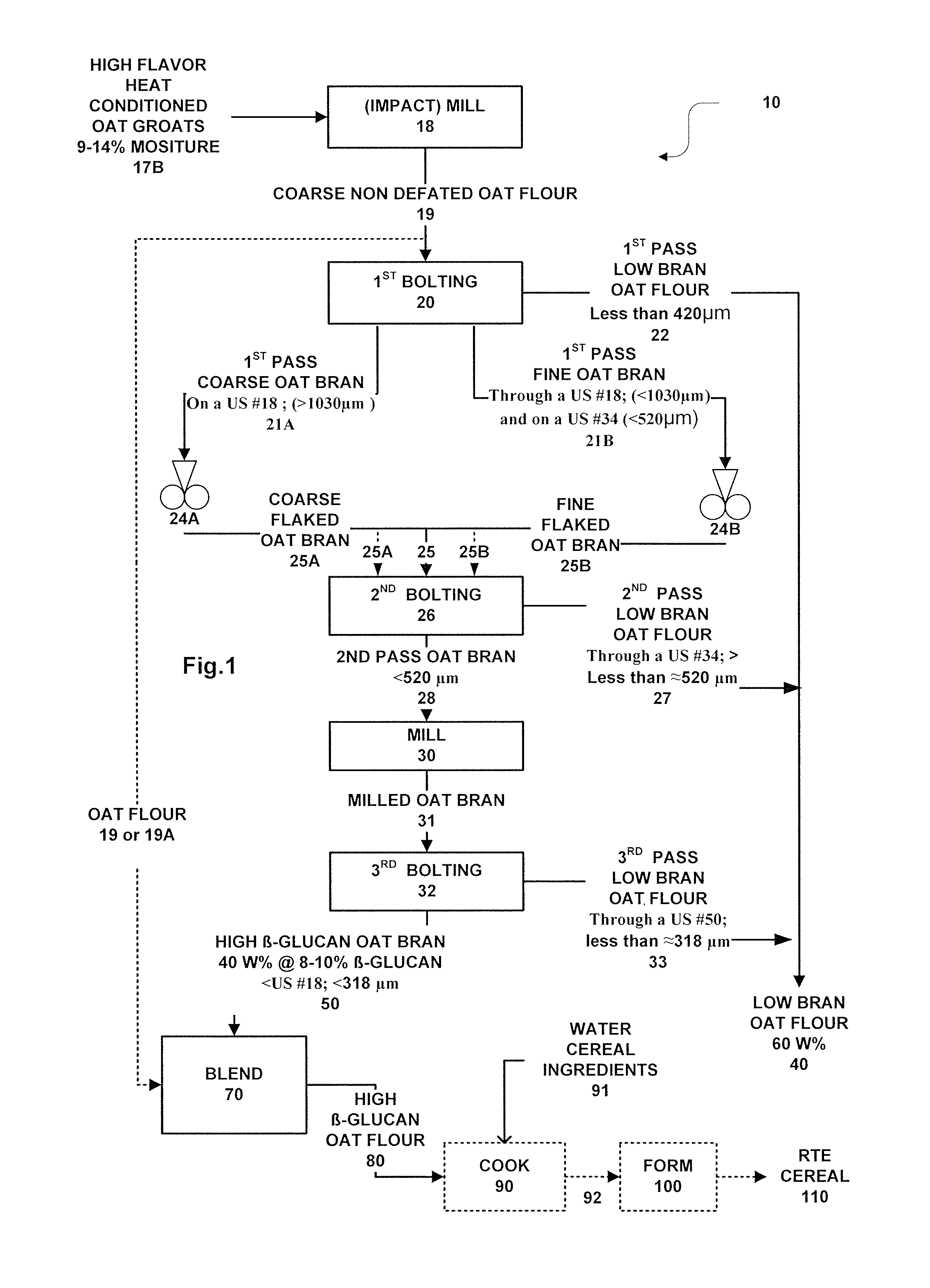
Methods for preparing oat bran enriched in beta-glucan and oat products prepared therefrom
ActiveUS7494683B2Increase contentImprove flavor profileDough treatmentBaking mixturesCereal grainBeta-Glycan
Dry milling methods for preparing oat products enriched in the content of β-glucan and methods for preparing foodstuffs incorporating such an enriched oat product especially ready-to-eat cereals are provided. Heat conditioned dehulled oats are dry milled to form a coarse whole non defatted oat flour and then, without a preceding removal of fat, dry fractionated into coarser bran and finer oat flour fractions at multiple stages. The coarse oat flour is first dry classified to separate or form a coarser fraction oat bran containing more concentrated β-glucan and a finer oat flour or starch containing or endosperm containing fraction. The oat bran is subjected to second and third rounds of milling and classification to form a high β-glucan content (>7-9%) oat bran and a low β-glucan content (3%) oat flour. The methods are low cost and commercially practical. Preferably, the high β-glucan content oat bran and oat flour fractions can have a syringic acid to ferulic acid ratio of at least 2.5:1 indicating improved flavor. Preferably, the oat bran and oat flour have a Farinograph value of 5 to 20 minutes indicated partial gelatinization. The oat bran and oat flours can be used to prepare foodstuffs such as ready-to-eat cereals.
Owner:GENERAL MILLS INC
A kind of method for preparing motherwort
InactiveCN102260198AAvoid makingSolve the defect of separation difficultyOrganic compound preparationAmino-hyroxy compound preparationPharmaceutical medicineSodium hydroxide
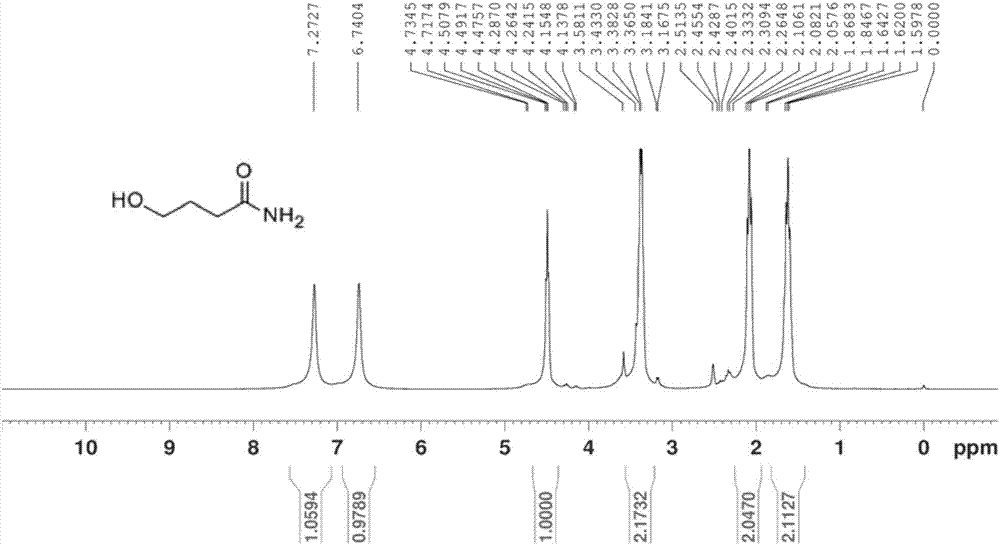
The invention belongs to the field of traditional Chinese medicine pharmacy, and relates to a method for preparing motherurine, comprising: selecting cheap aminobutyric acid as a raw material, through amino group protection and reduction reaction, conveniently synthesizing protected aminobutanol, using benzyl as p-clove The protective group of the acid phenolic hydroxyl group is crystallized after reflux in ethanol-sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, and the benzyl-protected penic acid is synthesized. The benzyl-protected syringic acid is condensed with aminobutanol by using CDI or DCC, and the protected motherwort is in Under the catalytic condition of 10% palladium hydroxide, the motherwort is obtained by hydrogen reduction, and finally the motherwort is synthesized. The method avoids the Gabriel amine-forming method in the prior art to prepare the motherwort, overcomes the separation difficulty, and reduces the use of environment-polluting reagents. The method has the advantages of less separation process, simple operation, mild reaction, easy control, and easy-to-obtain raw materials, and can synthesize the motherwortine in large quantities. The purity of the product is 99.8%, and the structure is consistent with the natural motherwortine.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Manchurian walnut bark extract and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an extractive from juglans mandshurica maxim bark, which mainly has the following active components: 8-hydroxide radical-9, 10- anthraquinone-1- carboxylic acid, regiolone, 4, 5, 8-trihydroxy-alpha-naphthalenone-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, 4, 5, 8-trihydroxy-alpha-naphthalenone-3-O-(6'-O-galloyl-group)-beta-D-glucopyranoside, 1-(4'-hydroxyphenyl)-7-(3'- methoxy-4'-hydroxyphenyl) heptane-3- ethanol, 4- hydroxide radical-2, 6- syringol-1-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, 4- hydroxide radical-2, 6- syringol-1-O-(6'-O-galloyl group)-beta-D-glucopyranoside, vanillic acid-4-O-(6'-O-galloyl group)-beta-D- glucopyranoside, vanillic aldehyde, vanillic acid, gallic acid, syringic acid, kaempferol and quercetin. The extractive from the juglans mandshurica maxim bark has good effects of treating hepatopathy and inhibiting the tumor growth and particularly has direct killing effect on liver cancer cells.
Owner:DANDONG MEDICINE GROUP
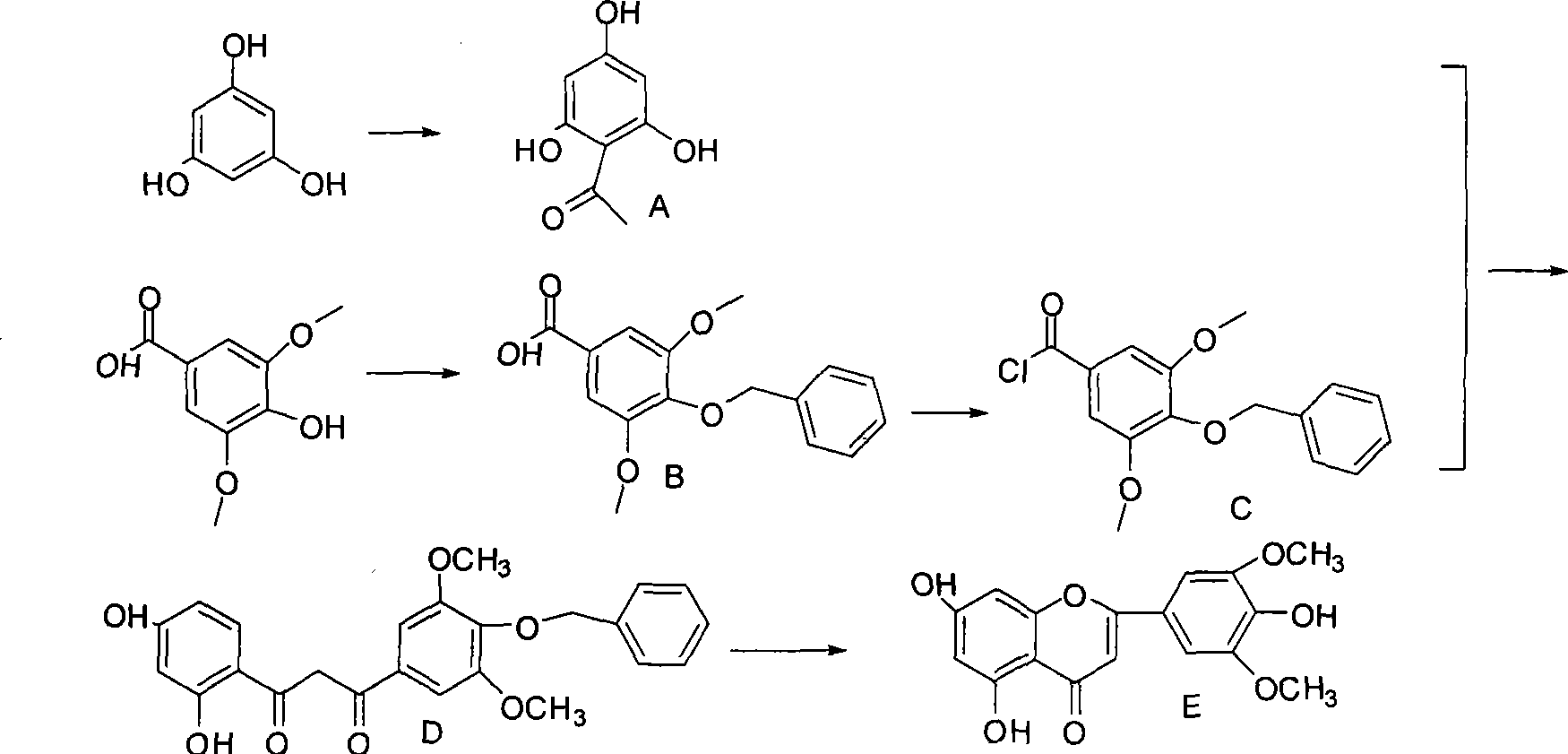
Synthesis method and application of 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-3',5'-dimethoxyflavone
InactiveCN101239960AInhibit growthInhibition of germinationBiocideOrganic chemistryChemical synthesisSpore germination
The invention relates to a synthesis method of 5, 7, 4'-trihydroxy-3', 5'-dimethoxyflavone and application thereof, particularly to a chemical synthesis method of allelochemicals, 5, 7, 4'-trihydroxy-3', 5'-dimethoxyflavone, by separating from allelochemical rice, Oryza sativa L.(PI312777). Syringic acid and phloroglucinol are used as the raw materials, the object products are synthesized by four steps. The products are protected by benzyl, and benzyl is synchronously removed with glacial acetic acid heating and ring closing in the final reaction step, thereby reducing the reaction steps. Compared with the method of removing benzyl by Pd / C charging hydrogen, the method of the invention is more simple, economical, and safe. The invention is capable of effectively stopping growth of garnyardgrass, cyperus iria linn and cyperus difformis linn seeds in rice, restraining paddyfield weed, improving rice yield, stopping spore germination of pyricularia oryzae and rhizoctonia solan so as to avoid the problems due to pesticide application and promote sustainable development of agriculture.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
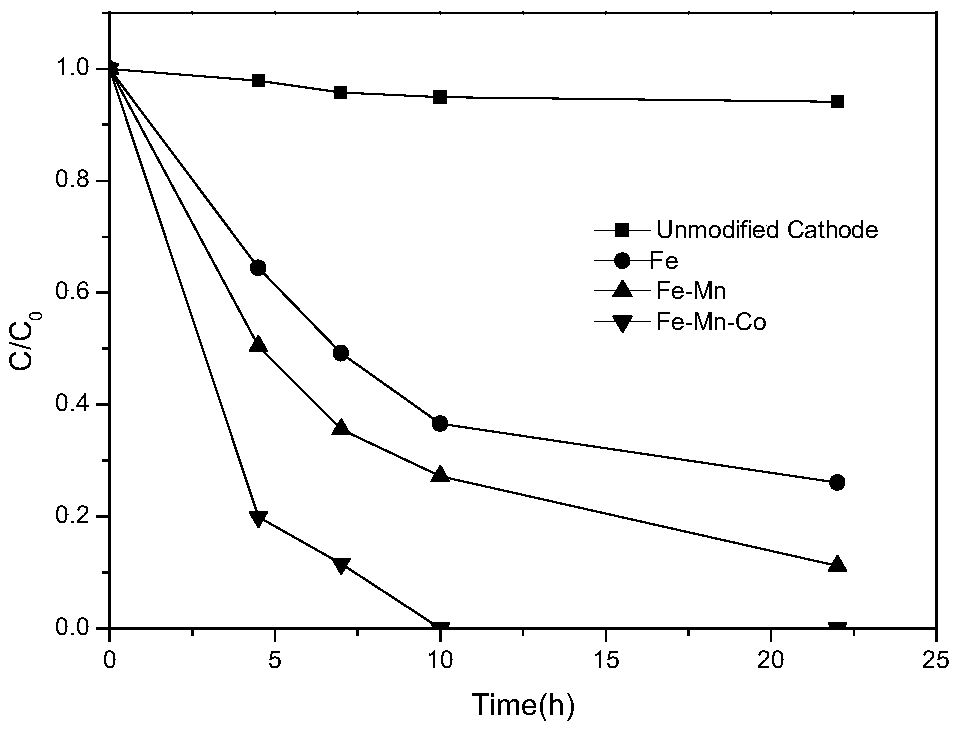
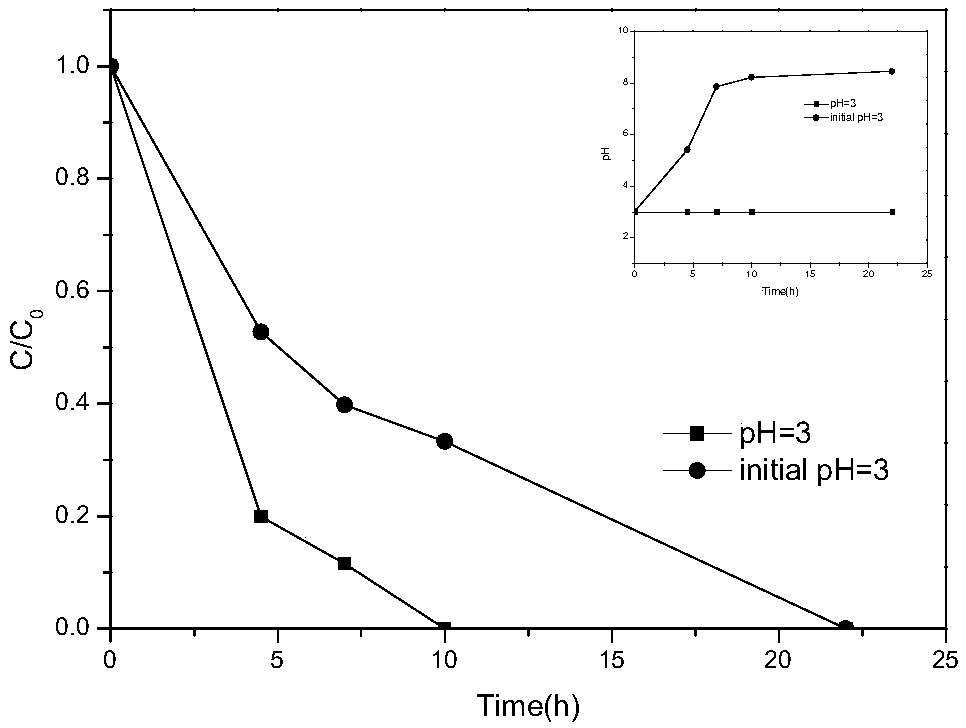
Composite cathode and preparation method thereof as well as application of composite cathode in biological electro-Fenton method
InactiveCN109160595AWide range of pH adaptationIncrease reaction rateTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater treatment compoundsComposite cathodeNanoparticle
The invention discloses a composite cathode and a preparation method thereof as well as application of the composite cathode in a biological electro-Fenton method, and belongs to the fields of preparation of environmental electrochemical materials and wastewater treatment by an advanced oxidation technology. The method comprises the following steps: soaking a clean carbon felt subjected to surfaceoxidation modification into a mixed salt solution of iron, manganese and cobalt; then adding a reducing agent and reducing the surface of the carbon felt to obtain nanoparticles, namely the compositecathode; the molar ratio of the iron to the manganese to the cobalt in the mixed salt solution is (1-4):1:1. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple; the obtained electrode has good recycling performance; the constructed bio-electric Fenton system has wide pH adaptation range and can significantly improve the degradation rate of syringic acid.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Methods for preparing oat bran enriched in beta-glucan and oat products prepared therefrom
ActiveUS20090078802A1Increase contentImprove flavor profileGrain huskingGrain polishingAmyrisFood flavor
Dry milling methods for preparing oat products enriched in the content of β-glucan and methods for preparing foodstuffs incorporating such an enriched oat product especially ready-to-eat cereals are provided. Heat conditioned dehulled oats are dry milled to form a coarse whole non defatted oat flour and then, without a preceding removal of fat, dry fractionated into coarser bran and finer oat flour fractions at multiple stages. The coarse oat flour is first dry classified to separate or form a coarser fraction oat bran containing more concentrated β-glucan and a finer oat flour or starch containing or endosperm containing fraction. The oat bran is fractionated into a coarse and fine oat bran sub-streams. The oat bran sub-streams are each is subjected to second roller milling step and then bolted. The second bolting of oat bran is then subjected to a third round of milling and classification to form a high β-glucan content (>7-9%) oat bran and a low β-glucan content (3%) oat flour. The methods are low cost and commercially practical. Preferably, the high β-glucan content oat bran and oat flour fractions can have a syringic acid to ferulic acid ratio of at least 2.5:1 indicating improved flavor. Preferably, the oat bran and oat flour have a Farinograph value of 5 to 20 minutes indicated partial gelatinization. The oat bran and oat flours can be used to prepare foodstuffs such as ready-to-eat cereals.
Owner:GENERAL MILLS INC
Preparation method of leonurine and aspirin conjugate
InactiveCN106146355AHigh yieldSave raw materialsUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparation4-toluenesulfonic acidO-acetylsalicylic acid
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry, and relates to a synthesizing method of leonurine and aspirin conjugate. The method comprises the steps that syringic acid, S-methylisothiourea and aspirin serve as starting materials, reactions of acetylation, BOC protection, amidation, deacetylation and the like are conducted, and corresponding structure segments are obtained; dilauryl hydrogen phosphite, 4-dimethylaminopyridine and 4-toluenesulfonic acid are used together to serve as a condensation catalyst to connect the three segments, de-BOC protection is conducted on trifluoroacetic acid, and a target compound is obtained. The synthesizing method of the leonurine and aspirin conjugate is easy and convenient to operate, mild in condition, simple in post treatment and capable of increasing the yield of the intermediate leonurine product; the total yield of the prepared leonurine and aspirin conjugate is 25.27%, a pharmacological activity test is conducted, it is shown through the result that very good antioxidant and anti-apoptosis effects at a cellular level are achieved, and the effect on protecting myocardial cells is exact.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Application of phenolic acid compounds in preparation of bleeding stopping and stasis eliminating medicaments
InactiveCN102210667AHas the effect of stopping bleeding and removing blood stasisInhibit aggregationHydroxy compound active ingredientsSexual disorderGallic acid esterChlorogenic acid
The invention discloses application of a phenolic acid compounds in preparation of bleeding stopping and stasis eliminating medicaments. The phenolic acid compounds mainly comprise chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, coumaricacid, vanillic acid, cinnamic acid, syringic acid, protocatechuric acid, gallic acid, ferulic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, hydroquinone or pyrocatechol and medicinal salts thereof. Experiments show that the phenolic acid compounds have the functions of stopping blood and eliminating stasis; one or more of the active ingredients is applied to preparing the bleeding stopping and stasis eliminating medicaments which are used for preventing and treating menorrhagia, artificial abortion, postpartum hemorrhage and dysfunctional uterine bleeding of women.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for extracting, separating and purifying chemical components of walnut green seedcases and application of chemical components
InactiveCN109734758AStrong growth inhibitory activitySugar derivativesSteroidsBenzoic acidBeta-Carotene
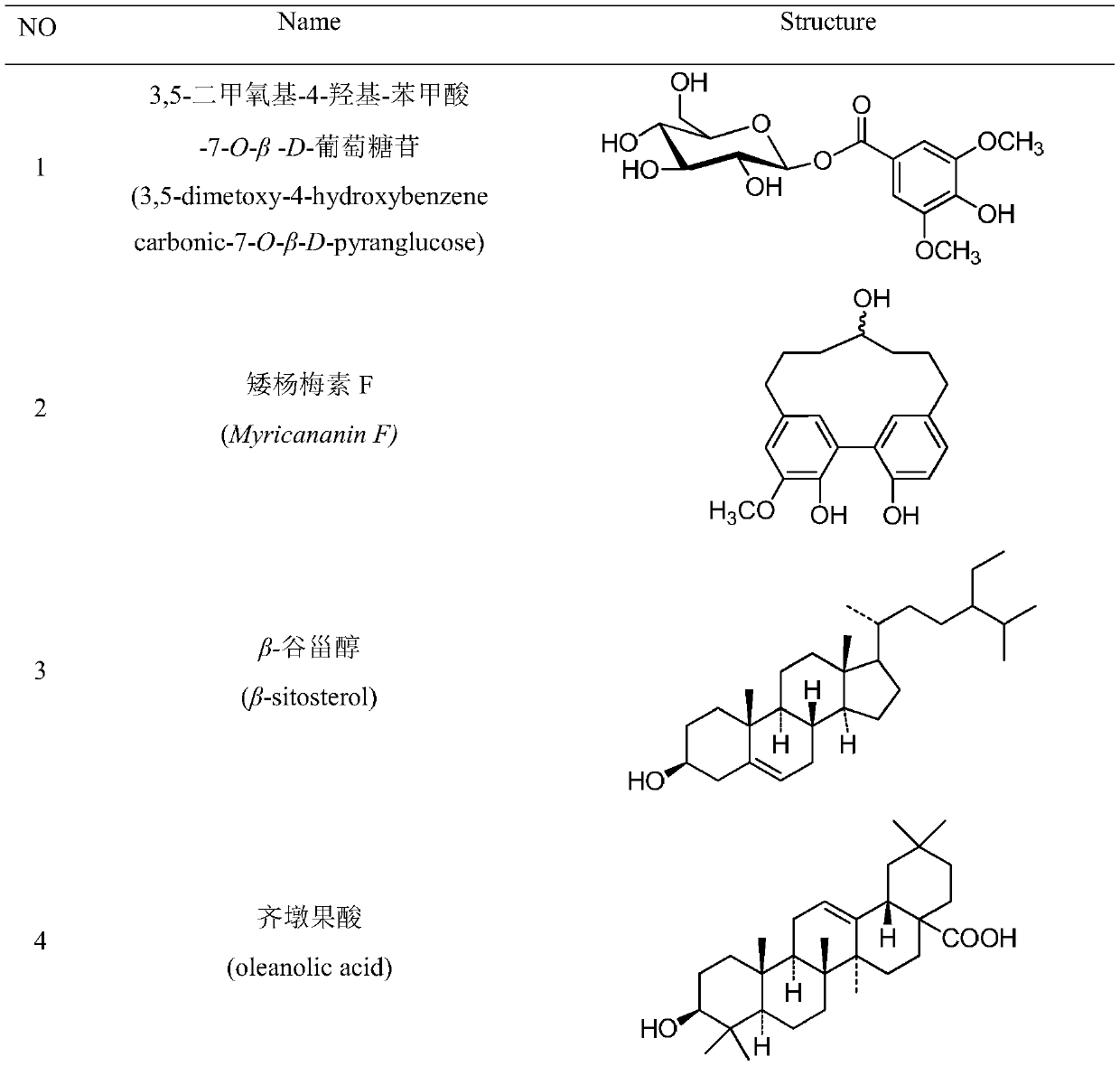
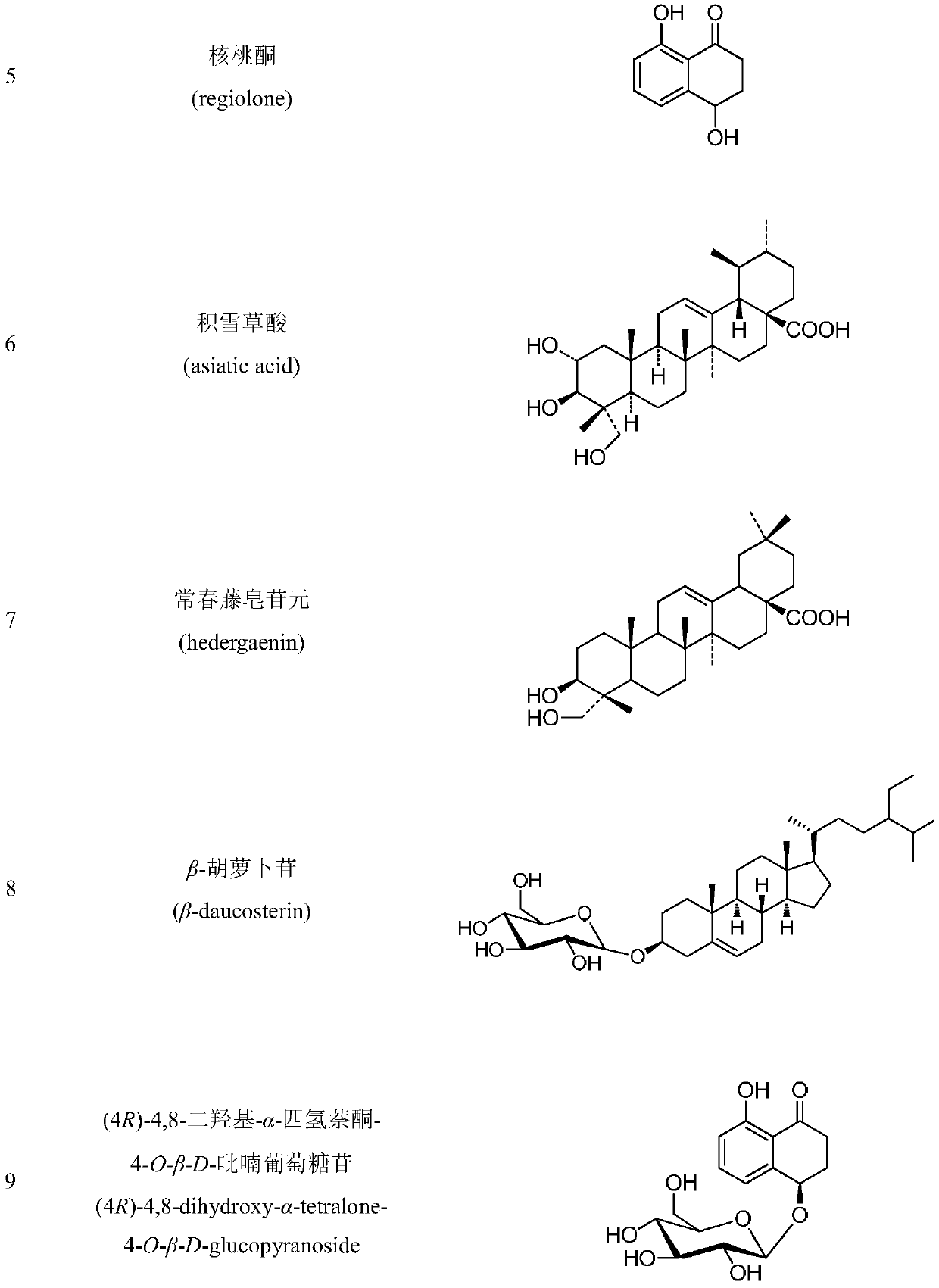
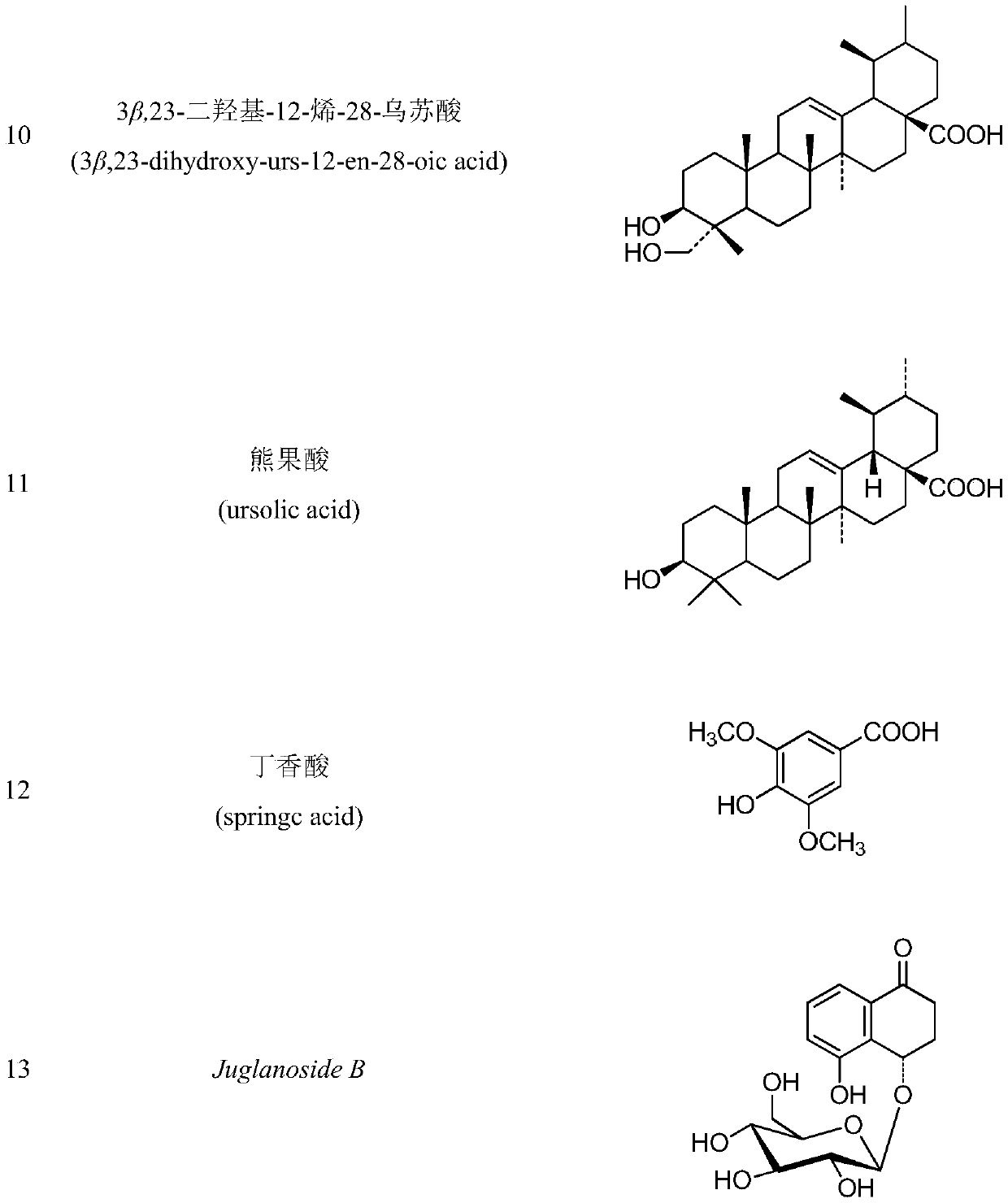
The invention discloses a method for extracting, separating and purifying chemical components of walnut green seedcases and application of the chemical components. According to the method, 13 compounds are separated from the walnut green seedcases and respectively identified as 3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxy-benzoic acid-7-O-beta-D-glucoside (1), myricananin F (2), beta-sitosterol (3), oleanolic acid (4), walnut ketone (5), asiatic acid (6), hederagenin (7), beta-carotene (8), (4R)-4,8-dihydroxy-alpha-tetralone-4-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (9), 3beta,23-dihydroxy-12-olefin-28-ursolic acid (10), ursolicacid (11), syringic acid (12) and Juglanoside B (13). After screening of anti-tumor activity in vitro, it is found that some compounds have certain growth inhibitory activity against cancer cells andcan be further used for preparing anticancer drugs.
Owner:新乡医学院三全学院
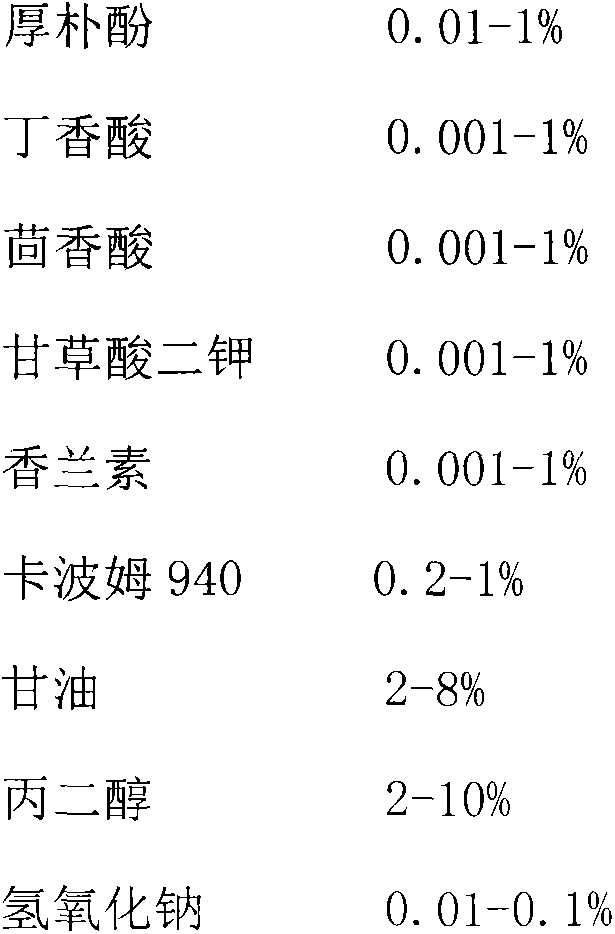
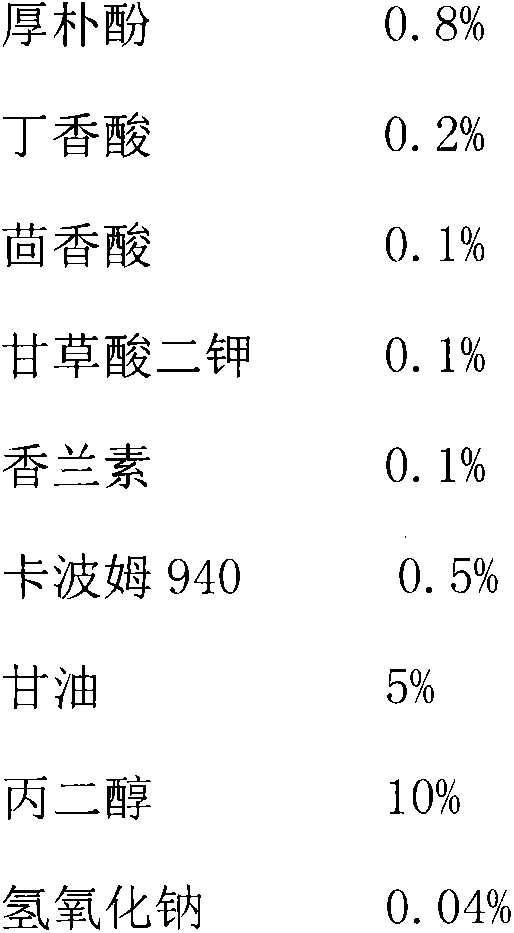
Novel medical disinfection and sterilization ultrasonic coupling agent
InactiveCN105983107ALow cytotoxicityEasy to prepareBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsUltrasonographyAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a novel medical disinfection and sterilization ultrasonic coupling agent. According to the coupling agent, disinfection and sterilization active ingredients, which are extracted from medicinal and dietary plants, are adopted, magnolol is used as a major ingredient for rapid disinfection and sterilization, and syringic acid, anisic acid, dipotassium glycyrrhizinate and vanillin are used as synergistic action ingredients. Through a compound prescription, the efficiency of disinfection and sterilization is improved when conducting ultrasonic detection and the like, and cytotoxicity, skin irritation and sensitization of a medical ultrasonic coupling agent are reduced; each piece of the coupling agent disclosed by the invention is applied to each person each time, so that such problems as cross infection and the like in clinical examination by virtue of ultrasonic instrument are avoided; meanwhile, effects on protecting mucosa skin, moistening the skin and the like can be achieved; and moreover, the medical ultrasonic coupling agent, which is applicable to complete skin, incomplete skin and mucosa, has an important significance. In addition, the novel medical disinfection and sterilization ultrasonic coupling agent disclosed by the invention is simple in preparation method and production process, low in cost and convenient for popularization and industrial production.
Owner:佛山市康伲爱伦生物技术有限公司
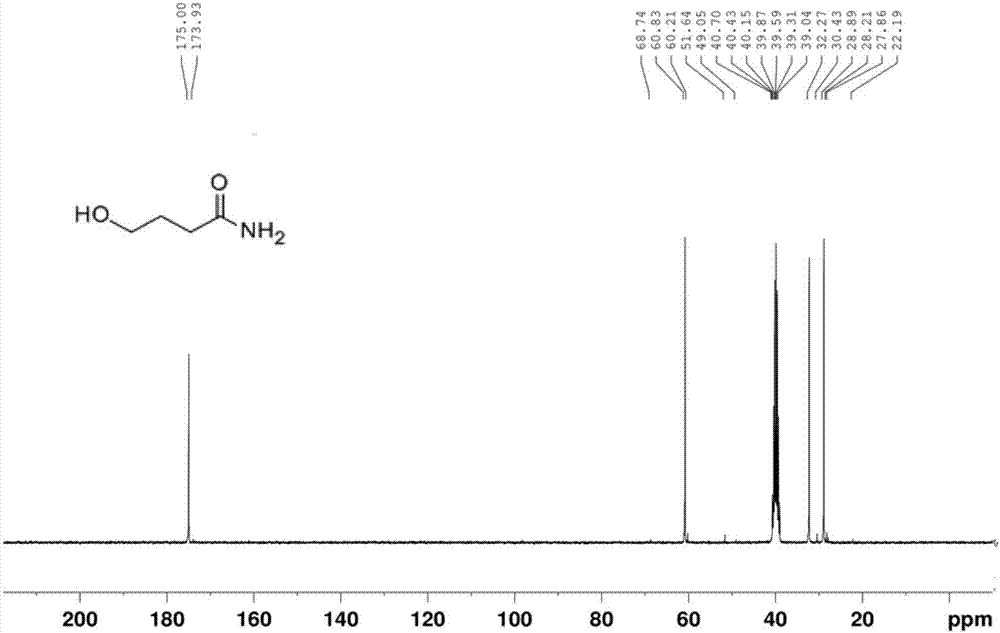
Synthetic method for leonurine
ActiveCN106866464AMild reaction conditionsEasy to controlOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSulfateLeonurine
The invention relates to the technical field of organic chemistry, in particular to a synthetic method for leonurine. Gamma-butyrolactone is used as a starting material to be subjected to ammonolysis to obtain gamma-hydroxybutyric acid amide; the gamma-hydroxybutyric acid amide and acetyl syringic acid are subjected to a condensation reaction; a dehydration reaction and a reduction reaction are carried out to obtain leonurus amine; and the leonurus amine and S-methyl isothiourea sulfate are subjected to a reaction to obtain the leonurine. The target product leonurine is synthetized from the cheap industrial raw materials of the gamma-butyrolactone and the syringic acid used as the starting materials through reactions of ammonolysis, esterification, dehydration, reduction and the like. The reaction conditions are mild and easy to control; the yield is up to 65%; the product purity is 98% or above; and the synthetic method for leonutine provides the production with an excellent synthetic route and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:绵阳市润土农业科技开发有限公司
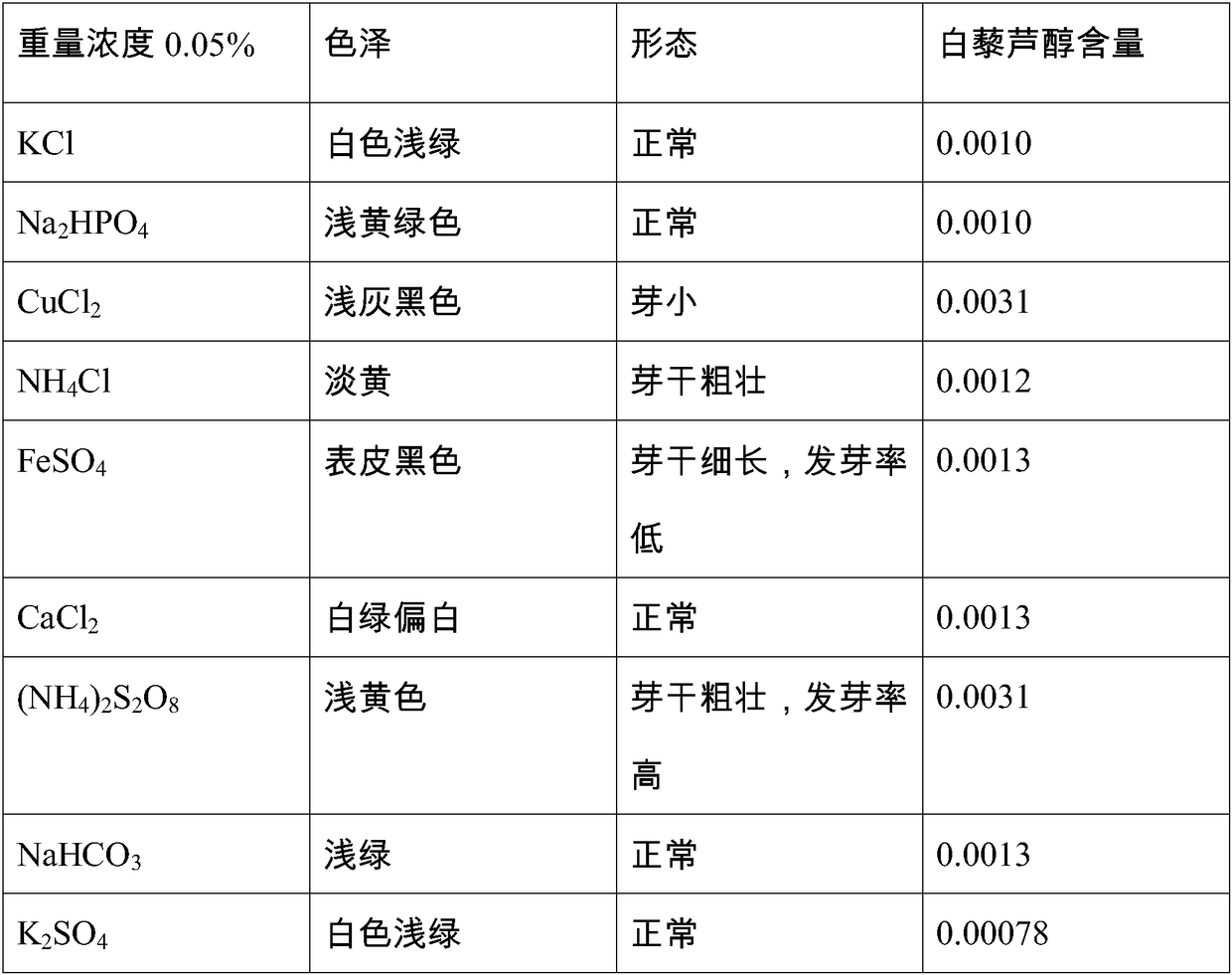
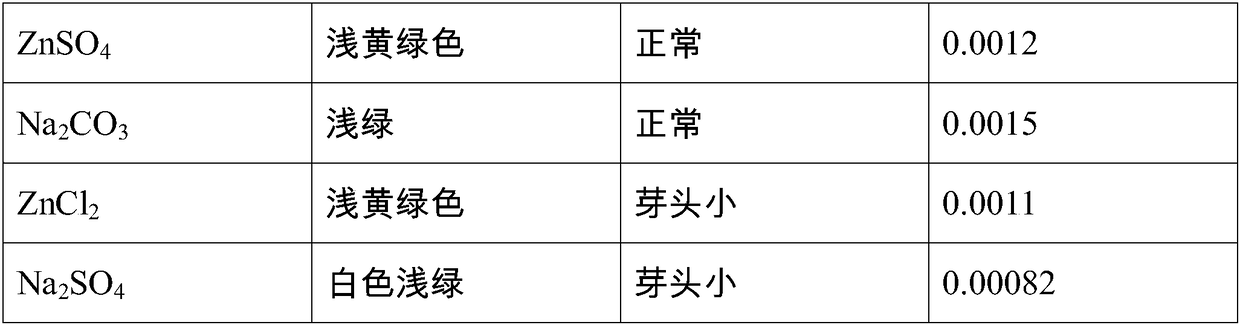
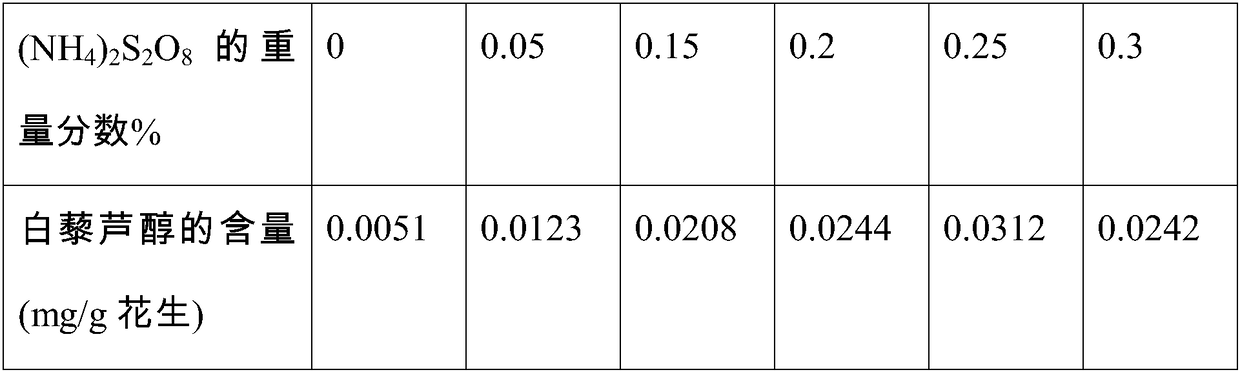
Method for increasing content of resveratrol in peanut sprouts
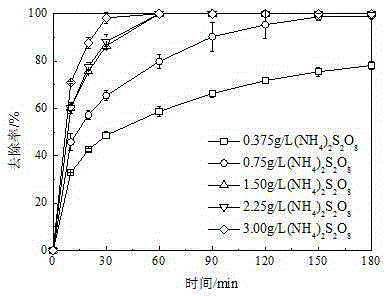
ActiveCN108174775AFast growthPromote proliferationGrowth substratesCulture mediaSalicylic acidChemistry
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a method for increasing the content of resveratrol in peanut sprouts. The method comprises the following steps of sifting peanuts which have uniform plumpness, putting the peanuts in water at the temperature of 40 DEG C to be soaked for 4 h at the constant temperature and then taking out the peanuts; proportioning a hormoneand inorganic salt tap water solution with a certain concentration to form culture liquor, putting the culture liquor in a microwave oven to be heated and sterilized for 1-2 min, taking out the culture liquor, cooling to the room temperature, adding the soaked peanuts to form peanut culture mixed liquor, laying a layer of gauze on the peanut culture mixed liquor, putting the peanut culture mixed liquor in a dark environment of which the temperature is 20-30 DEG C and the humidity is 55-60%, after the peanuts are cultured for a period, taking out the peanuts, and extracting resveratrol in the peanuts to be measured. The method is simple in technology, the culture liquor is subjected to microwave processing, can be effectively sterilized and disinfected, and is jointly proportioned by inorganic salt (NH4)2S2O8, ferulic acid, syringic acid, salicylic acid, indoleacetic acid and indolebutyric acid, the growth speed of the peanuts can be more obviously increased, the proliferation of peanutcells is promoted, and the content of resveratrol in the peanuts is obviously increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHUREN COLLEGE ZHEJIANG SHUREN UNIV
Methods for preparing oat bran enriched in beta-glucan and oat products prepared therefrom
ActiveUS7976888B2Increase contentImprove flavor profileGrain huskingGrain polishingFlavorBeta-glucan
Dry milling methods for preparing oat products enriched in the content of β-glucan and methods for preparing foodstuffs incorporating such an enriched oat product especially ready-to-eat cereals are provided. Heat conditioned dehulled oats are dry milled to form a coarse whole non defatted oat flour and then, without a preceding removal of fat, dry fractionated into coarser bran and finer oat flour fractions at multiple stages. The coarse oat flour is first dry classified to separate or form a coarser fraction oat bran containing more concentrated β-glucan and a finer oat flour or starch containing or endosperm containing fraction. The oat bran is fractionated into a coarse and fine oat bran sub-streams. The oat bran sub-streams are each is subjected to second roller milling step and then bolted. The second bolting of oat bran is then subjected to a third round of milling and classification to form a high β-glucan content (>7-9%) oat bran and a low β-glucan content (3%) oat flour. The methods are low cost and commercially practical. Preferably, the high β-glucan content oat bran and oat flour fractions can have a syringic acid to ferulic acid ratio of at least 2.5:1 indicating improved flavor. Preferably, the oat bran and oat flour have a Farinograph value of 5 to 20 minutes indicated partial gelatinization. The oat bran and oat flours can be used to prepare foodstuffs such as ready-to-eat cereals.
Owner:GENERAL MILLS INC
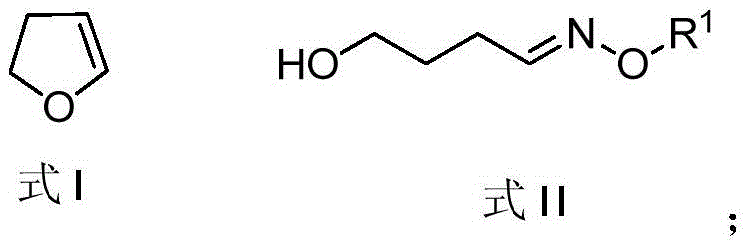
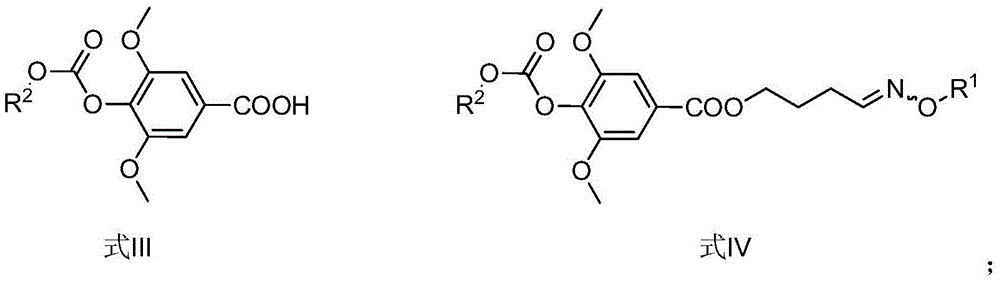
Method for synthesizing leonurine
ActiveCN105481724AHigh yieldAtom economy is highOrganic compound preparationOximes preparationS-methylisothioureaLeonurine
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing leonurine. The method is characterized in that raw material 2,3-dihydrofuran undergoes the alkoxy oxime synthesis reaction, obtained product 4-hydroxyl butyl-O-methyl oxime and carbalkoxy syringic acid undergo the esterification and oxime reduction reaction to obtain herba leonuri amine, and the herba leonuri amine reacts with S-methylisothiourea to obtain leonurine. The reaction process atom economy is good, the excessive use of a reagent is avoided, the environmental pollution is reduced, and the method is high in yield and easy to operate.
Owner:安徽省科学技术研究院
Degerming liquid medicine for insole
InactiveCN107212030ALong-term antibacterial effectLong-lasting drug releaseBiocideDead animal preservationZanthoxylum bungeanumAlcohol
The invention discloses a degerming liquid medicine for an insole. The degerming liquid medicine is prepared from the following four components in parts by mass: 20 to 35 parts of zanthoxylum bungeanum, 30 to 40 parts of borneol, 15 to 20 parts of borax and 25 to 30 parts of syringic acid, wherein the four components are ground into powder and are soaked in 600 to 800 parts by mass of ethyl alcohol for 15 days. The degerming liquid medicine is lasting-release in pharmacodynamic action; the sterilized insole can be enabled to maintain a long-acting antibacterial function; meanwhile, the degerming liquid medicine can have inhibition and killing functions on a main pathogenic bacterium breeding on the insole.
Owner:陈魏魏
Juglans mandshurica husk extractive and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a juglans mandshurica husk extractive which contains the main medical active ingredients of 8-hydroxyl-9,10-anthraquinone-1-carboxylic acid, REG IOLONE, 4,5,8- trihydroxy-alpha-naphthyl ketone-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, 4,5,8- trihydroxy-alpha- naphthyl ketone-3-O-(6'-O- nutgall acyl)-beta-D- glucopyranoside, 1-(4'- hydroxyl phenyl)-7-(3''-methoxy-4''-hydroxyl phenyl) heptane-3-alcohol, 4-hydroxy-2,6- syringol-1-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, 4- hydroxyl-2,6- syringol-1-O-(6'-O- nutgall acyl)-beta-D- glucopyranoside, vanillic acid-4-O-(6'-O- nutgall acyl)-beta-D-glucopyranoside, vanillic aldehyde, vanillic acid, gallic acid, syringic acid, kaempferol, quercetin glycoside, myrica rubra and quercetin. The juglans mandshurica husk extractive has good effect in curing hepatopathy and restraining the growth of tumor and especially has the effect of directly killing the hepatocarcinoma cells.
Owner:DANDONG MEDICINE GROUP
Method for simultaneously detecting nine chemical components in quisqualis indica
ActiveCN112114079AFast separationEasy to operateComponent separationAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologyMedicinal herbs
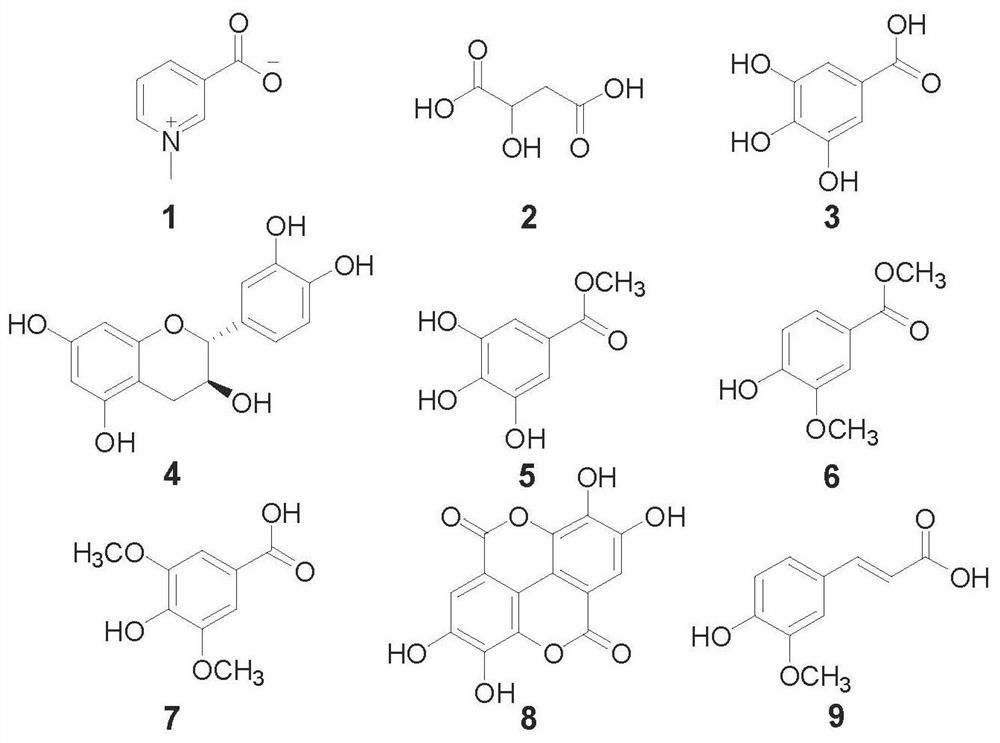
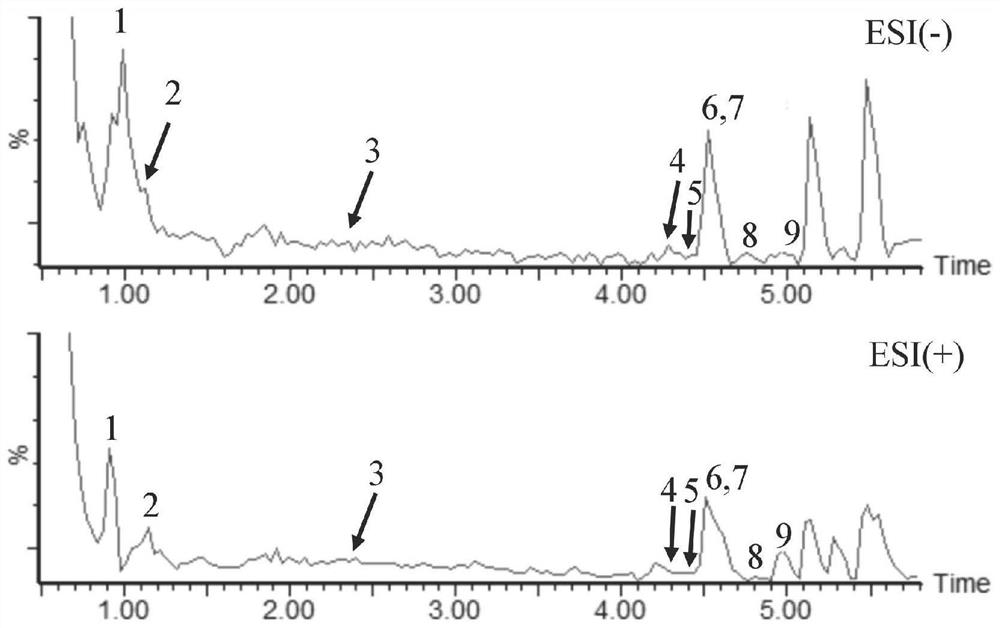
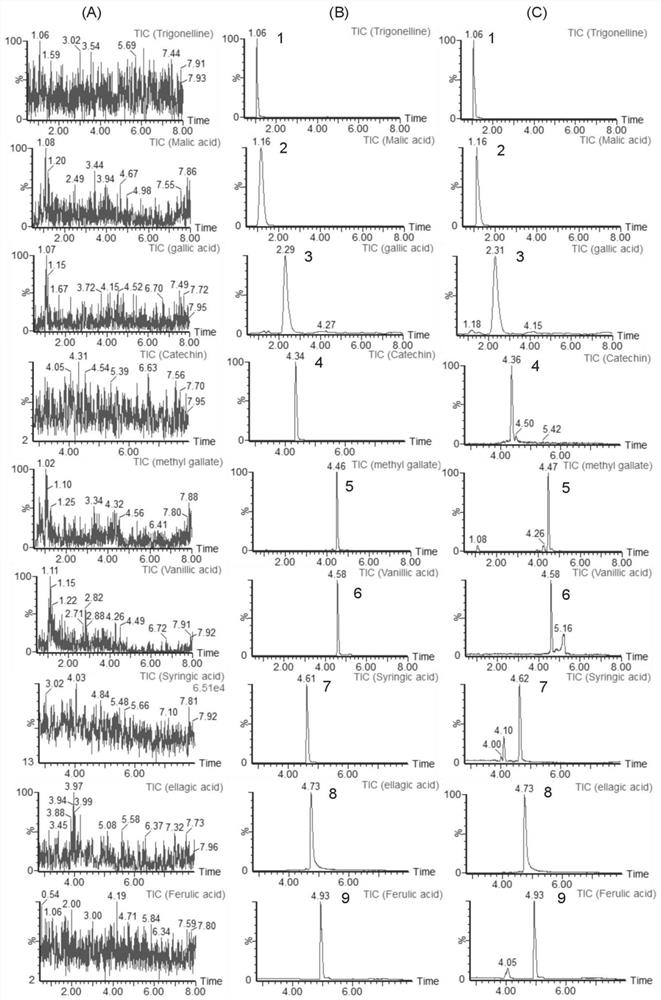
The invention provides a method for simultaneously detecting nine chemical components in quisqualis indica, and relates to the technical field of analysis and detection. The method comprises the following steps: extracting quisqualis indica by adopting an alcohol-water solution to obtain a to-be-detected sample solution; and then performing UPLC-MS / MS. According to the invention, a to-be-detectedquisqualis indica sample is pretreated through a UPLC MS / MS method, qualitative identification can be rapidly achieved while gradient elution conditions are controlled, nine chemicals (trigonelline, vanillic acid, ferulic acid, syringic acid, catechinic acid, ellagic acid, malic acid, gallic acid and methyl gallate) in the quisqualis indica medicinal material are quantitatively detected, and reliable experimental data are provided for development and utilization and quality evaluation of the quisqualis indica medicinal material. The detection method provided by the invention has the advantagesof simple operation, fast analysis time of only 8min, fast separation speed and high sensitivity, makes up the blank of nine chemical detection methods in quisqualis indica at present, and is worthyof popularization and application.
Owner:FUJIAN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Yellow rice wine flavor enhancer
InactiveCN107974388AIncrease relative volatilityAroma harmonyAlcoholic beverage preparationPhenethyl alcoholFood flavor
The invention discloses a yellow rice wine flavor enhancer, and in particular relates to the field of flavor and fragrance for wine mixing. The yellow rice wine flavor enhancer comprises the followingcomponents in parts by weight: 4 to 8 parts of phenethyl alcohol, 1 to 4 parts of syringic acid, 3 to 5 parts of mixed amino acid, 1 to 3 parts of ethyl lactate, 0.5 to 2.5 parts of ethyl acetate, 0.5 to 2.5 parts of ethyl propionate, 1 to 3 parts of citronellal, 5 to 10 parts of acetaldehyde, 40 to 60 parts of alcohol and 2 to 6 parts of other components. A main fragrant agent serves as a main material, the main fragrant agent has high volatility and the added fragrance aid and the fragrance fixing agent serve as auxiliary materials, so that the flavor enhancer has harmonious, full, strong and durable fragrance and overcomes the defects that the low-degree alcohol has flat taste and short aftertaste.
Owner:安徽香博士芳香技术研究院有限公司
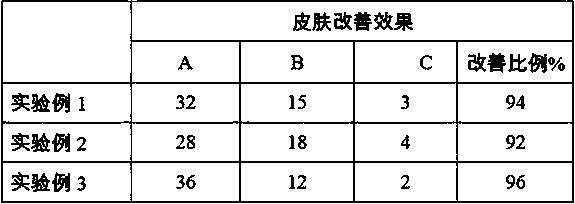
Facial cream and preparation method thereof
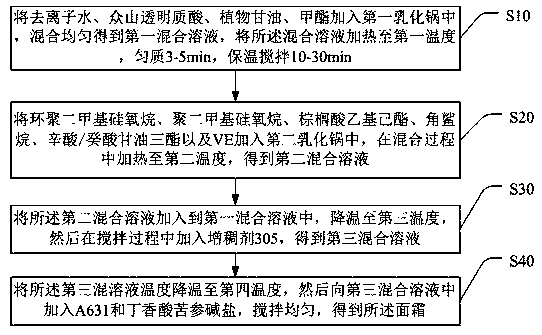
InactiveCN109528518AAntioxidantBactericidalCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSolubilityBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention discloses a facial cream and a preparation method thereof. The facial cream comprises the following components in parts by weight: 70-80 parts of deionized water, 2-5 parts of athickener 305, 6-10 parts of a moisturizer, 6-18 parts of an emollient, 0.1-0.15 part of methyl ester, 2-5 parts of VE and 0.05-0.2 part of syringic acid matrine salt. The provided facial cream uses the syringic acid matrine salt as an active ingredient, solubility of the syringic acid matrine salt is enhanced by 3 orders of magnitudes compared with solubility of syringic acid, and the syringic acid matrine salt can well lock skin moisture and prevent dry skin caused by skin moisture loss. Besides, the syringic acid matrine salt is used as a natural ionic salt, has a thermal stability reaching150 DEG C, has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and micro-organism-killing properties, and can enhance moistening and protection of skin. Therefore, the provided facial cream has a long-lasting moisturizing effect and anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects.
Owner:SHENZHEN SHINESKY BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Functionalized phenolic esters and amides and polymers therefrom
InactiveUS7858077B2Regulate the length of action of the phenolic compoundAlter efficacyBiocideOrganic chemistryBenzoic acidPhenylacetic acid
The present invention relates to a compound of the formula:R-AR—O—Y—R′Wherein R represents one or more members selected from H, alkoxy, benzyloxy, aldehyde, halogen, carboxylic acid, —NO2, —NH2, —NHCOCH3, and —NH—Y—R′, which is attached directly to AR or attached through an aliphatic chain. The carboxylic acid moiety in R includes but is not limited to the following carboxylic acids: benzoic acids, cinnamic acids, ferulic acid, caffeic acid, syringic acid, salicylic acid, vanillic acid, phenylacetic acids, phenylpropionic acids, and sinapinic acid.-AR—O— is a biologically active phenolic moiety comprising 1 to 6 substituted or unsubstituted aryl rings that are directly bonded to each other, fused together, or joined through a linking group.Y represents a member selected from:—COCH2O— (glycolic ester moiety)—COCH(CH3)O— (lactic ester moiety)—COCH2OCH2CH2O— (dioxanone ester moiety)—COCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2O— (caprolactone ester moiety)—CO(CH2)mO— where m is an integer between 2-4 and 6-24 inclusive—COCH2O(CH2CH2O)n— where n is an integer between 2 and 24, inclusive; andR′ is either hydrogen or a benzyl or an alkyl group, the alkyl group being either straight-chained or branched.The resultant functionalized phenolic compounds, used singly or in combinations, and their polymers have controllable degradation profiles, releasing the active component over a desired time range. The polymers are useful for biomaterials and biomedical devices, wherein said biologically active phenolic moiety is a residue of a phenolic compound.
Owner:BEZWADA BIOMEDICAL LLC
Catalysts for the mechanocatalytic oxidative depolymerization of polymer-containing materials and methods of making oxidized reaction products using same
InactiveCN104903283AAids in depolymerizationOrganic oxidationOrganic compound preparationNon solventVanillic acid
The presently disclosed and / or claimed inventive concept(s) relates generally to oxidative oxidized reaction products made from the mechanocatalytic oxidative depolymerization of lignin. More particularly, but without limitation, the mechanocatalytic oxidative depolymerization of lignin is performed in a non-aqueous / non-solvent based and solvent-free process, i.e., via a solid-solid mechanocatalytic oxidative reaction methodology. In one particular embodiment, the process of making such oxidative oxidized reaction products includes, without limitation, the step of mechanocatalytically reacting an oxidation catalyst with lignin or a lignin-containing material. The oxidative reaction products obtained from the process include, for example, at least one of vanillin, and syringealdehyde, vanillic acid, and syringic acid.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
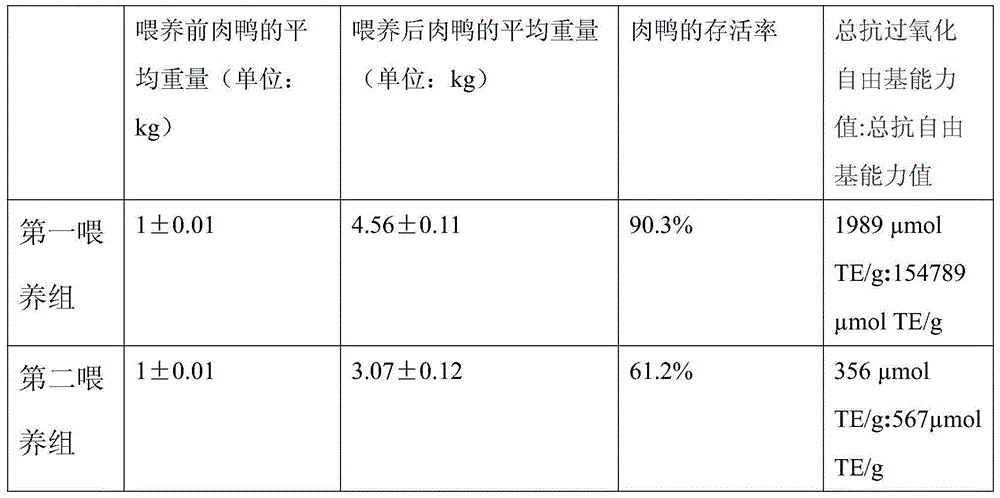
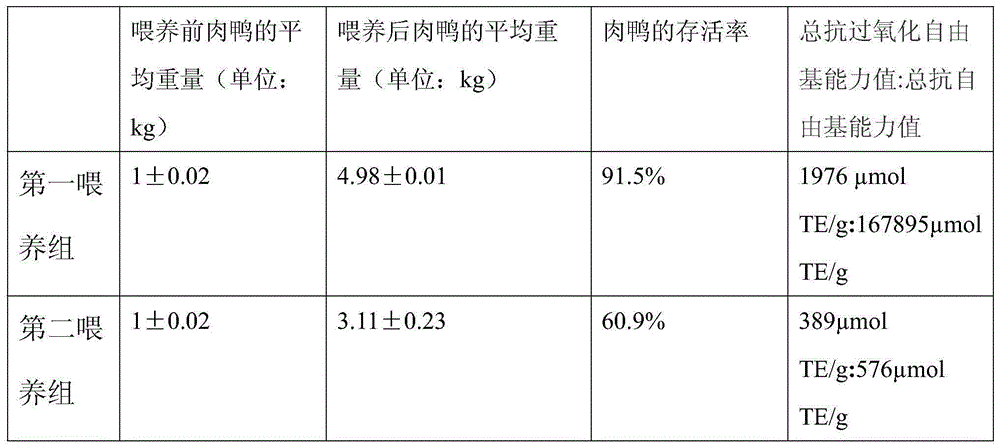
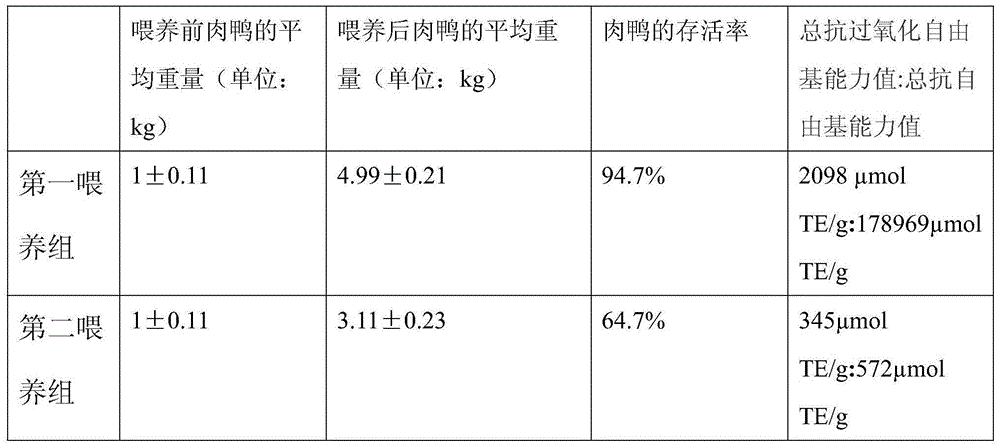
Meat duck feed with lactic acid bacteria and with function of eliminating free radicals and preparation method
The invention relates to a meat duck feed with lactic acid bacteria and with a function of eliminating free radicals and a preparation method. The meat duck feed is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 0.006-0.07 part of palmatine, 0.1-0.5 part of sodium selenite, 0.1-0.5 part of sodium selenate, 0.2-0.7 part of potassium iodide, 0.2-0.7 part of calcium iodate, 0.5-0.8 part of chlorogenic acid, 0.5-0.8 part of hydrocarbon benzoic acid. 0.5-0.8 part of ferulic acid, 0.5-0.8 part of syringic acid, 3-5 parts of fish meal, 9-16 parts of sunflower pulp, 4-6 parts of bean cakes, 15-25 parts of detoxified rapeseed meal, 15-25 parts of degossypolled cottonseed meal, 30-38 parts of high gluten flour and 2-8 parts of lactic acid bacteria. The feed combined with the preparation method of the feed can be used for avoiding the problem that the components of the meat duct feed have a high degree of contamination on soil, the immunity of the meat ducks is reduced as the individual space is reduced and the activity of the meat ducks is constrained and the immunity of the meat ducks is low as a result of internal diseases.
Owner:JIANGSU UNISON BIOTECH DEV
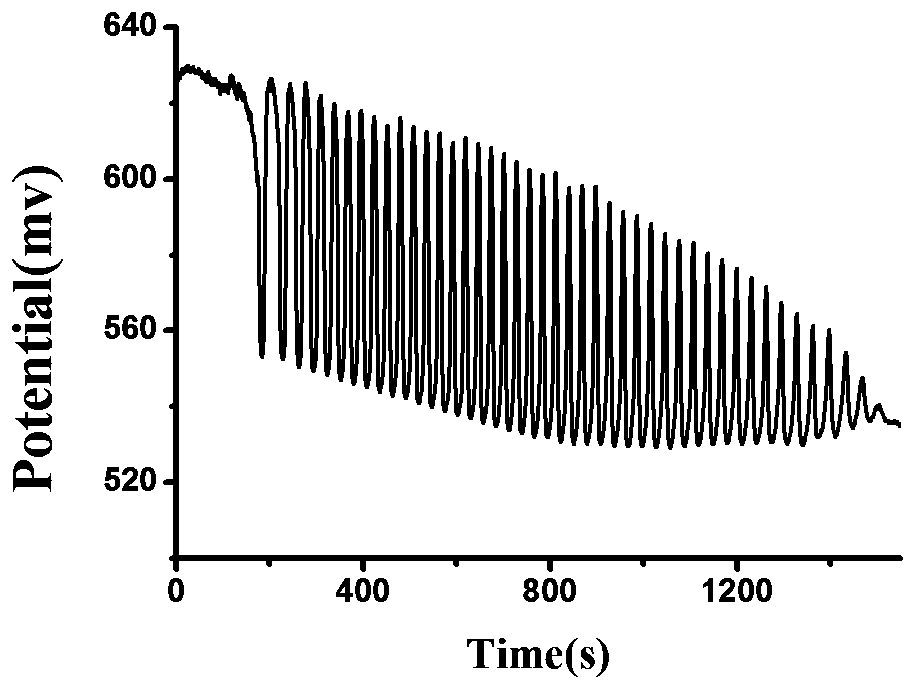
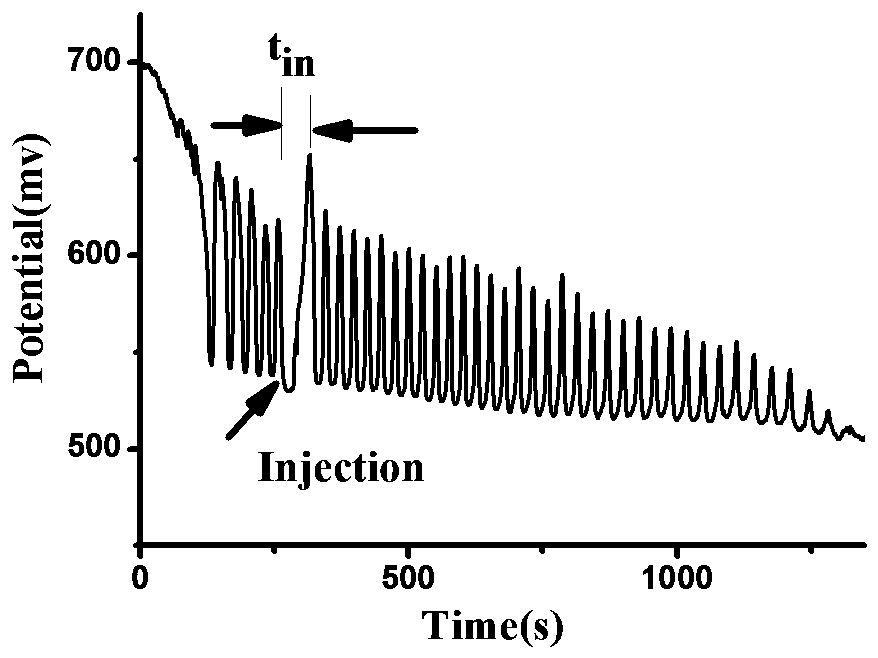
Detection method of syringic acid
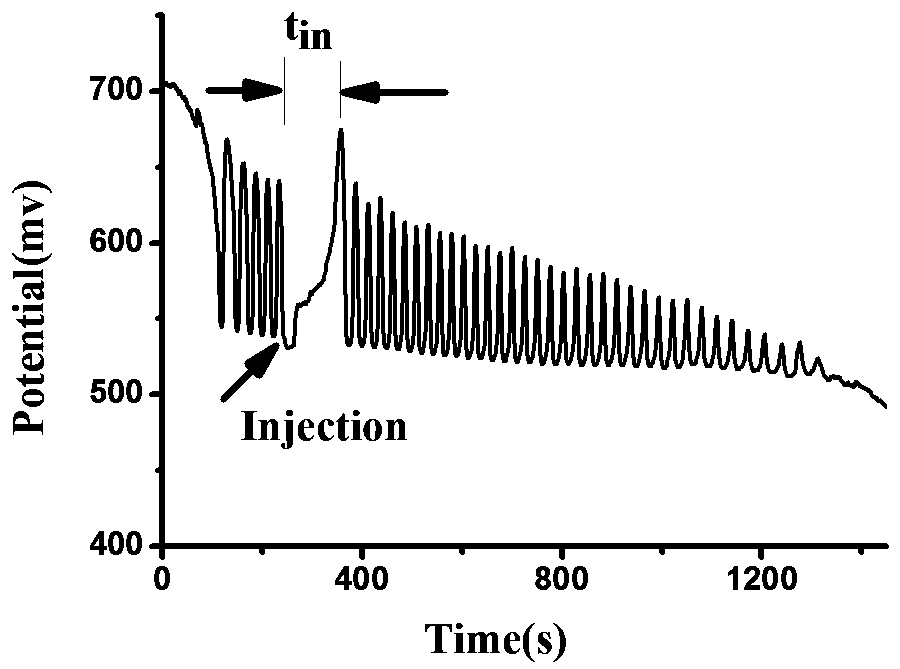
The invention discloses a method for quantitative analysis to syringic acid. The method is characterized in that H2SO4-KIO3-[NiL] (ClO4) 2-MA (malonic acid)-H2O2 nonlinear chemical oscillating systemis adopted as a detection solution, a working curve is established for oscillatory response produced by syringic acid according to the detection, and further quantitative analysis to the syringic acidis realized; in [NiL] (ClO4) 2, L is 5, 7, 7, 12, 14, 14-hexamethyl-1, 4, 8, 11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-4, 11-diene. The method has the characteristics of high accuracy, high easiness in operation,convenience and quickness.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
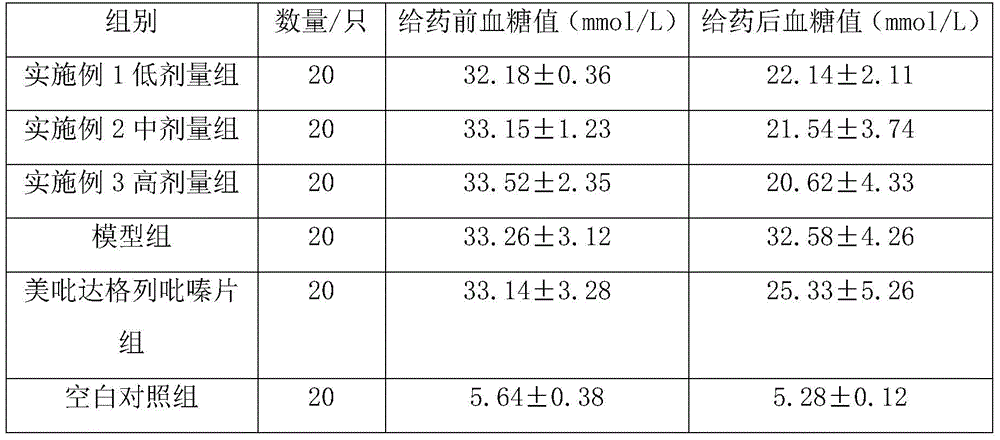
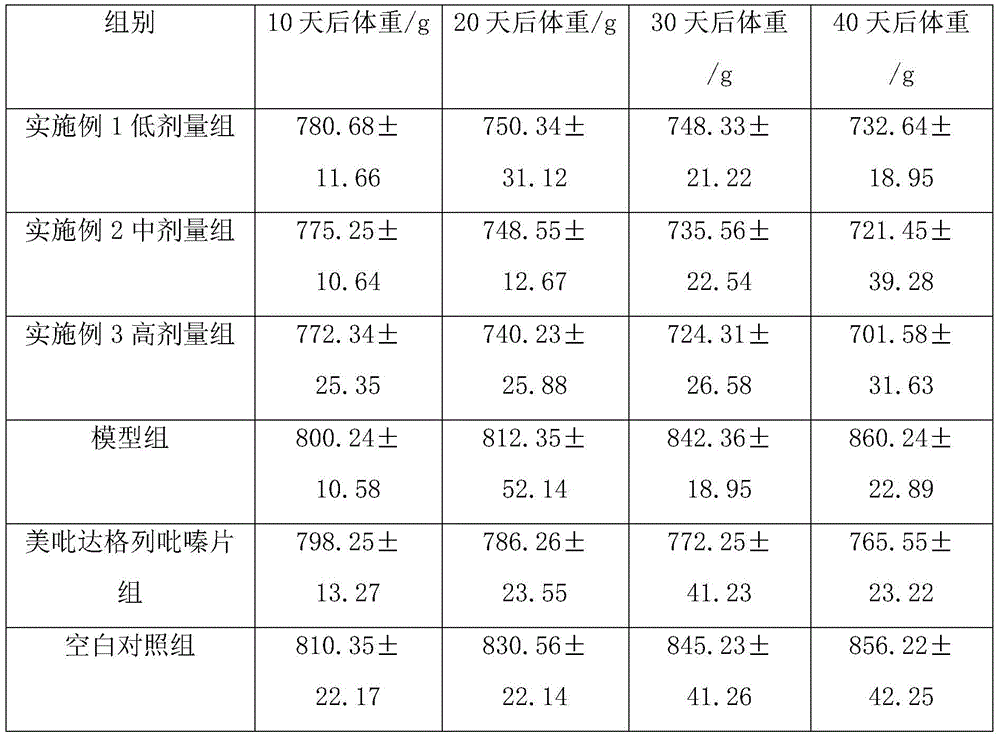
Compound nanometer preparation for treating diabetes mellitus type 2 and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105641674AInsulation absorptionPromote absorptionMetabolism disorderTripeptide ingredientsSide effectAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a compound nanometer preparation for treating the diabetes mellitus type 2 and a preparation method thereof. The compound nanometer preparation for treating the diabetes mellitus type 2 is mainly prepared from, by weight, 8-15 parts of aloe acetylation gulcomannan, 3-6 parts of Cicletanine, 1-2 parts of decanoyl acetaldehyde, 4-8 parts of syringaresinol monoglucoside, 5-20 parts of banana leaf powder, 3-7 parts of grapefruit seed extract, 1-4 parts of sodium ethylene diamine tetracetate, 0.8-2.0 parts of myristic acid, 0.1-0.5 part of syringic acid, 0.1-0.3 part of gentisic acid, 3-10 parts of lysine, 1-3 parts of carotenoid and 0.03-0.1 part of antioxidant. According to the compound nanometer preparation, blood glucose rising is controlled through interaction of various ingredients, the blood pressure and blood fat of a patient suffering from the diabetes mellitus type 2 are adjusted, sufficient nutritional ingredients can be provided for the patient suffering from the diabetes mellitus type 2, the immunity of the patient is improved, diabetes mellitus and arteriosclerosis are relieved, the effect of treating the diabetes mellitus type 2 is remarkable, and the side effect is small.
Owner:李华红
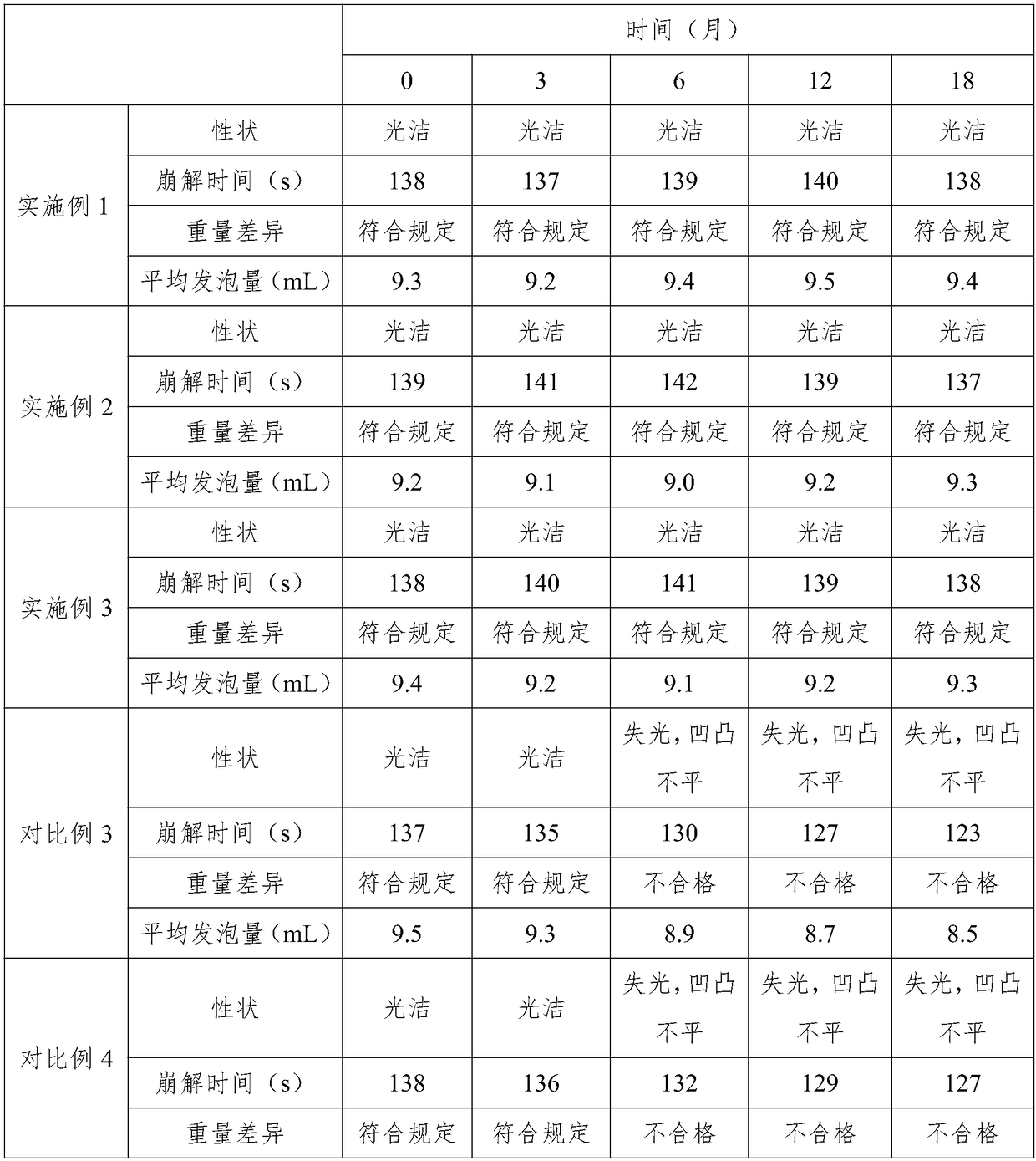
A kind of golden lotus effervescent tablet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106420656BSignificant improvementQuality improvementOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticSodium bicarbonateIdiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
A Tropaeolum majus effervescent tablet consisting of Tropaeolum majus powder, coixol, syringic acid, sorbitol, xanthan gum, sodium citrate, and sodium bicarbonate. The different components of the Tropaeolum majus effervescent tablet coordinate and achieve the effects of clearing heat, activating blood, resolving stasis, removing toxin and inflammation, and relieving pain. The present invention has treatment effects on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and reduces the suffering of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients.
Owner:GUANGDONG ROC MEDICINAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com