Application of phenolic acid compounds in preparation of bleeding stopping and stasis eliminating medicaments
A technology for hemostasis and blood stasis, compound, applied in the direction of active ingredients of hydroxyl compounds, drug combinations, blood diseases, etc., can solve problems that have not yet been involved in procoagulation, no raw materials used alone or in combination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
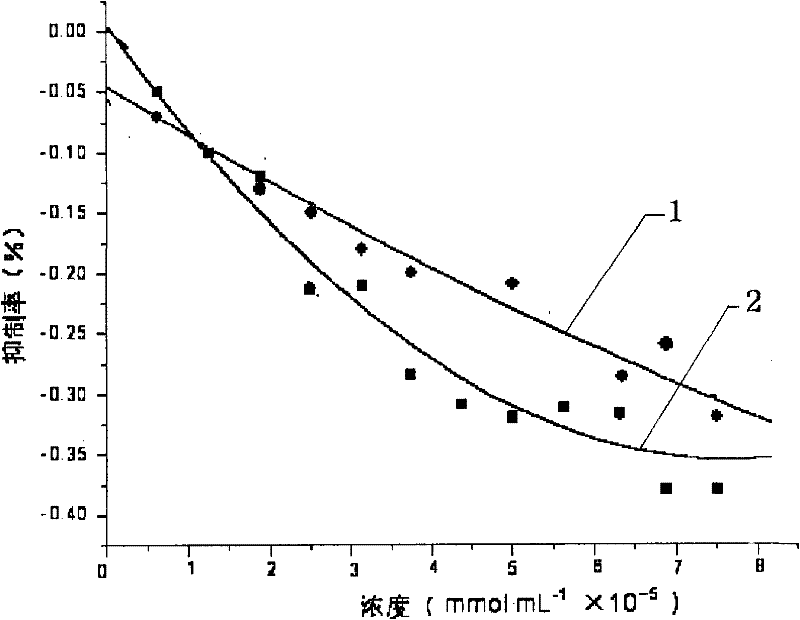
[0021] Example One Chlorogenic Acid, Determination of Bleeding Time (CT) in Mice with p-coumaric Acid
[0022] A group of healthy Kunming mice weighing 18±2g were used for both sexes. Chlorogenic acid and p-coumaric acid were dissolved in distilled water. The experimental mice were divided into 4 groups, 8 mice in each group, administered by intragastric administration for three consecutive days, and the dose was 0.1ml / 10g. The control group was replaced by normal saline, and the positive control group was replaced by Zhixuemin (0.25g / kg). One hour after the last administration, blood was taken from the venous plexus of the mouse medial canthus with a glass capillary (1×12 cm). When the blood filled the capillary, a drop of blood with a diameter of about 5 mm was dropped on the glass slide, and two stopwatches were used to start immediately. timing. After 30s, use the needle to stir slightly from the edge of the blood, carefully observe whether there are blood streaks stirr...
Embodiment 2
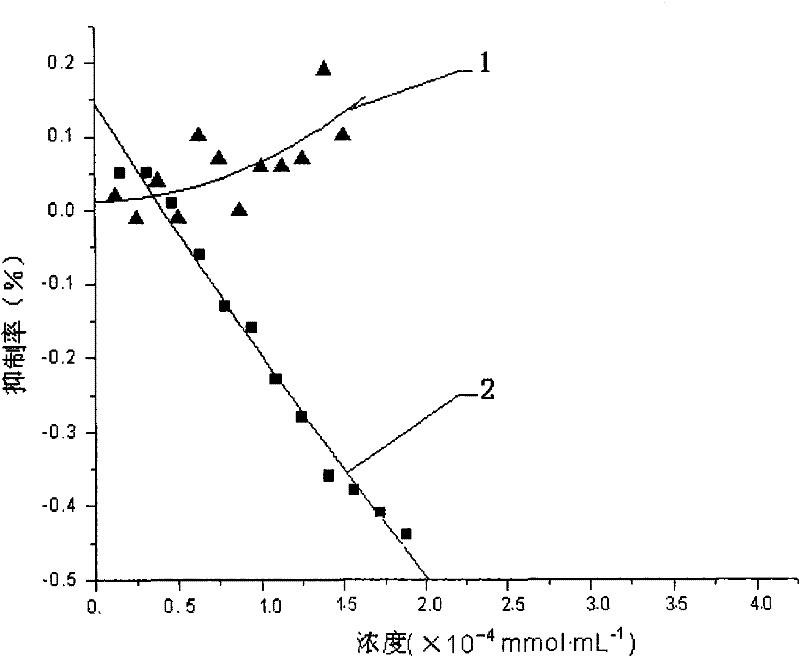
[0027] Example 2 Effects of vanillic acid, syringic acid, p-coumaric acid, and protocatechuic acid on rabbit plasma prothrombin time (PT) and partial thromboplastin time (APTT)
[0028] The experimental rabbits were divided into a treatment group and a blank control group. Vanillic acid, syringic acid, p-coumaric acid, and protocatechuic acid were orally administered three days in advance, and blood was drawn one hour after the administration on the third day. Preparation of platelet-free plasma: draw 1.8ml of venous blood, slowly inject it into a plastic test tube containing 0.2ml of 109mmol / L sodium citrate solution, mix well, and centrifuge at 3000r / min for 15min to remove platelets and separate plasma. Take another plastic test tube, add 0.1ml of plasma to be tested, and place it in a 37°C water bath to pre-warm for 3 minutes. Add 0.1ml of PT reagent preheated to 37°C, time it immediately, and keep tilting the test tube in the water bath to mix, and slowly tilt the test tu...
Embodiment 3
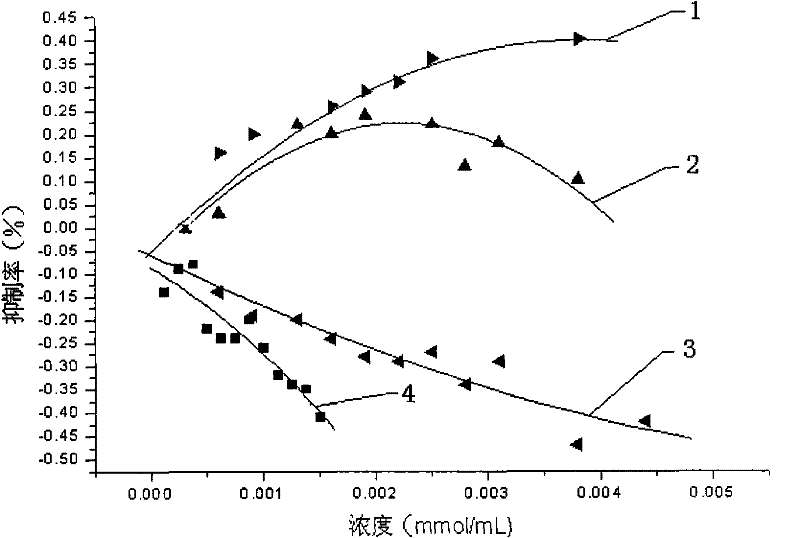
[0034] Example 3 Effects of vanillic acid, p-coumaric acid and protocatechuic acid on rabbit platelet aggregation
[0035] Preparation of platelet rich plasma (platelet rich plasma, PRP) and platelet poor plasma (platelet poor plasma, PPP): blood was collected from the carotid artery of conscious rabbits, anticoagulated with 3.8% sodium citrate, collected in plastic test tubes, and blood was mixed with Anticoagulant volume ratio 9:1. After centrifugation at room temperature for 10 minutes at 1200r / min, the obtained plasma is PRP; the remaining blood is then centrifuged at 3000r / min for 15min, and the supernatant is PPP, which is used for zero adjustment during measurement or for adjusting the number of platelets in PRP. During the test, the number of platelets in PRP was controlled at about 500,000 mm -3 .
[0036]Take the measurement tube (put 1 stirring bead in advance), add 200 μl of PPP, place the measurement tube in the preheating hole of the constant temperature body f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com