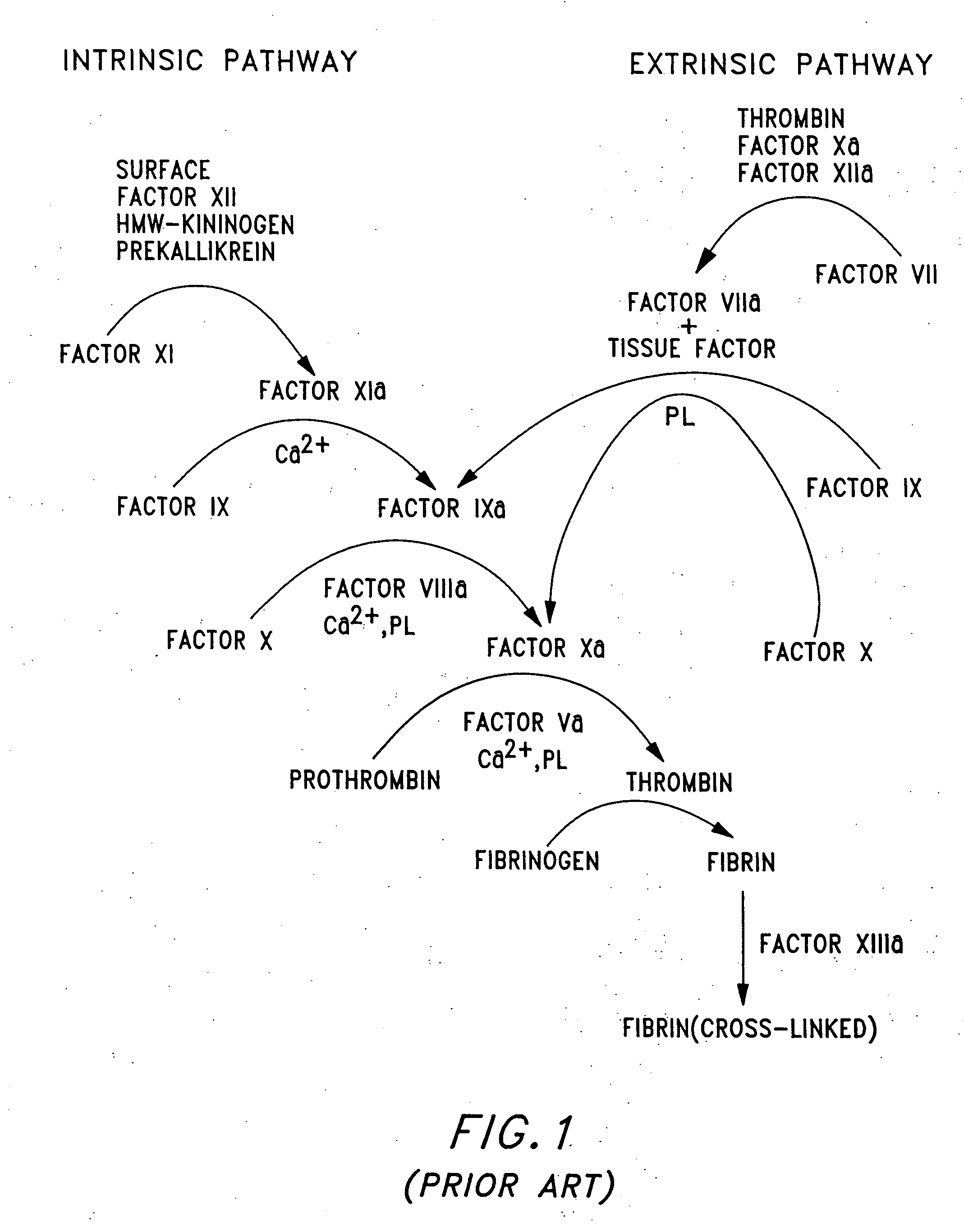
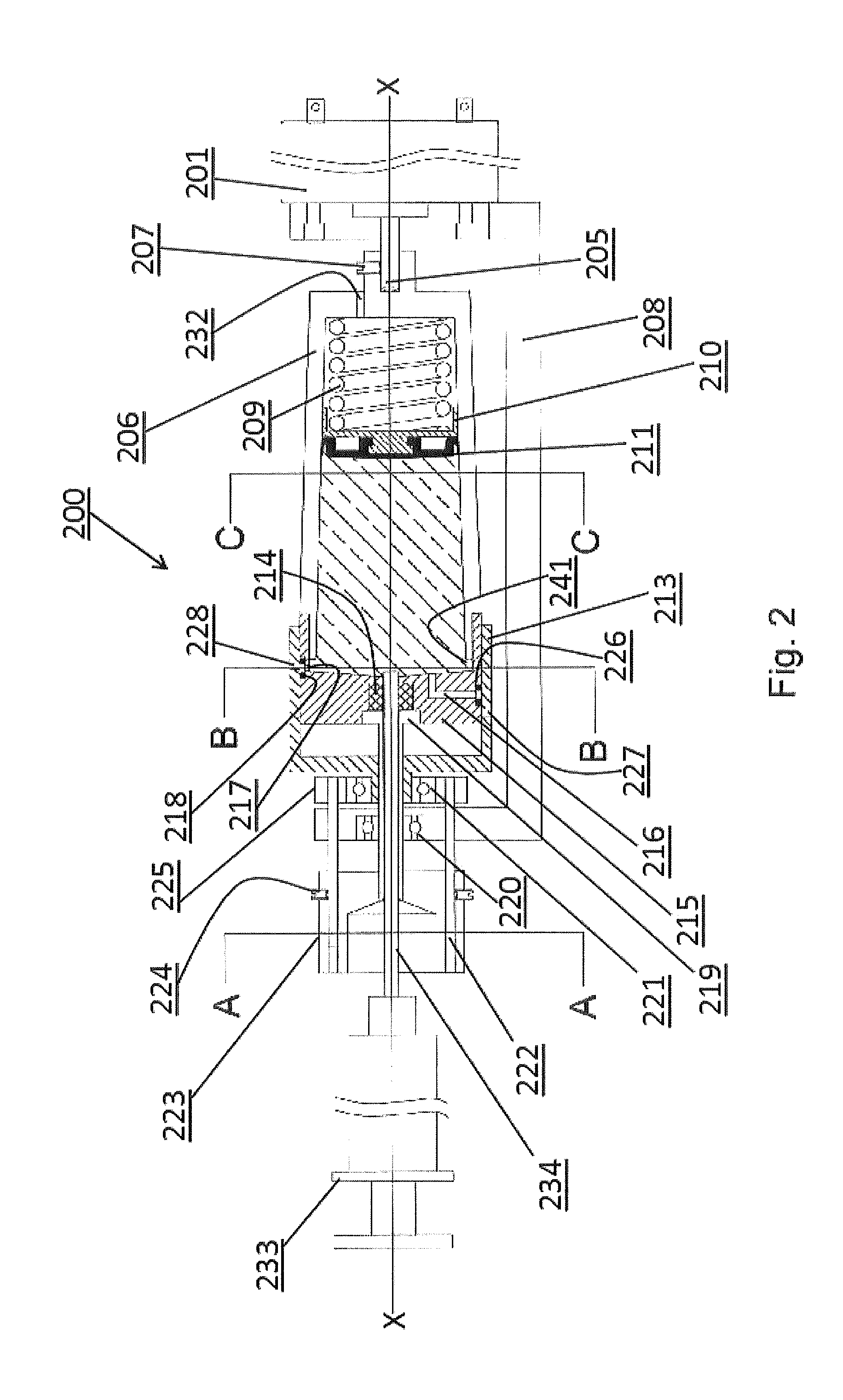
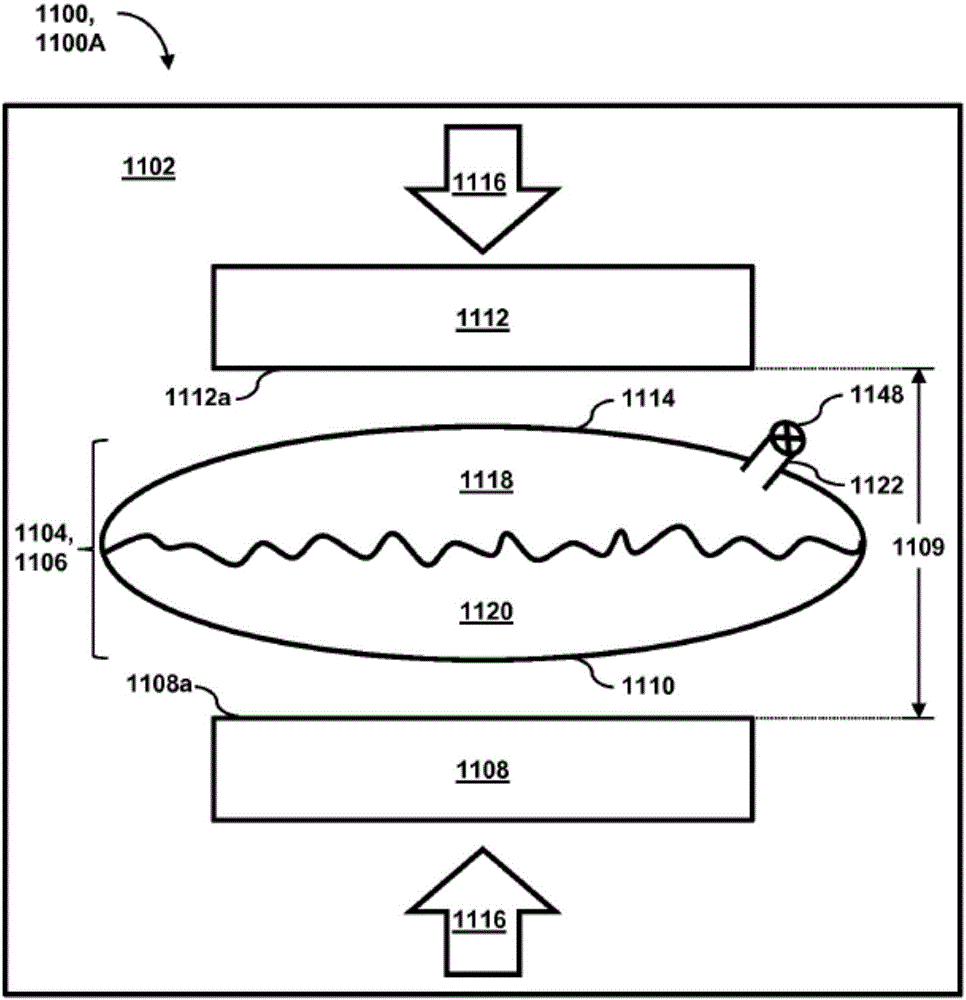
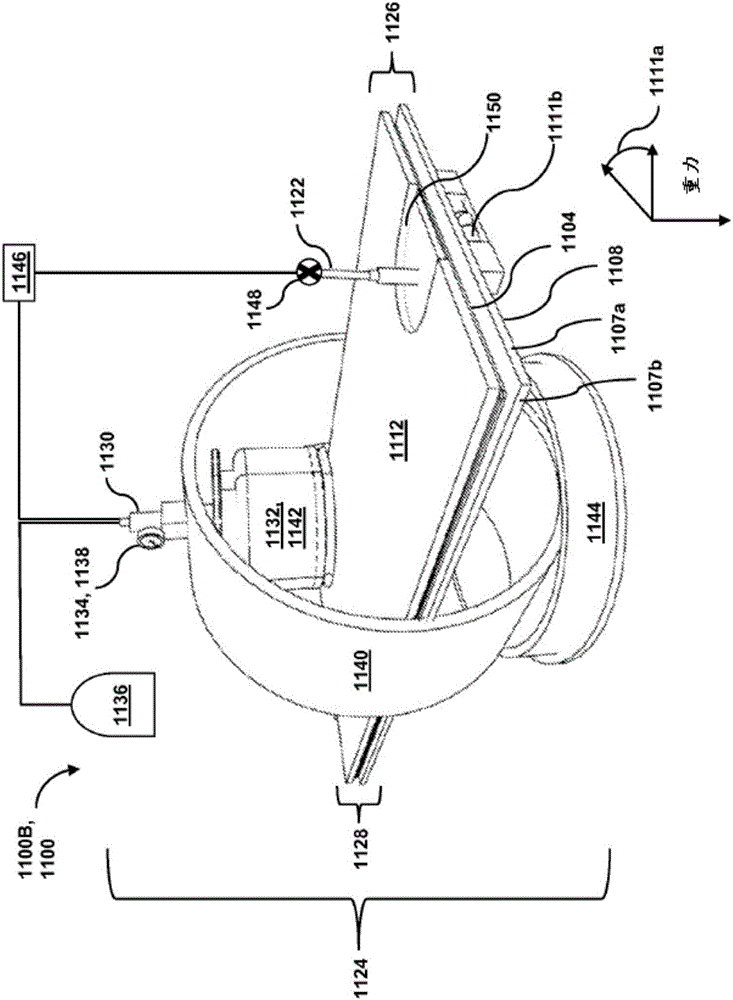
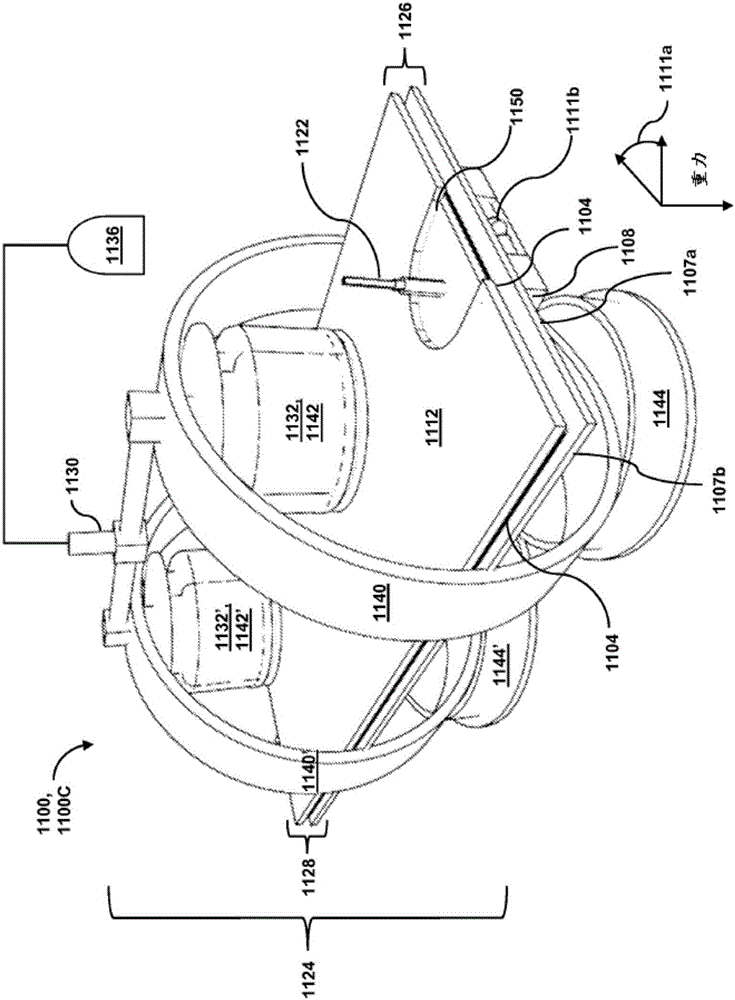
Patents
Literature
65 results about "Platelet-poor plasma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
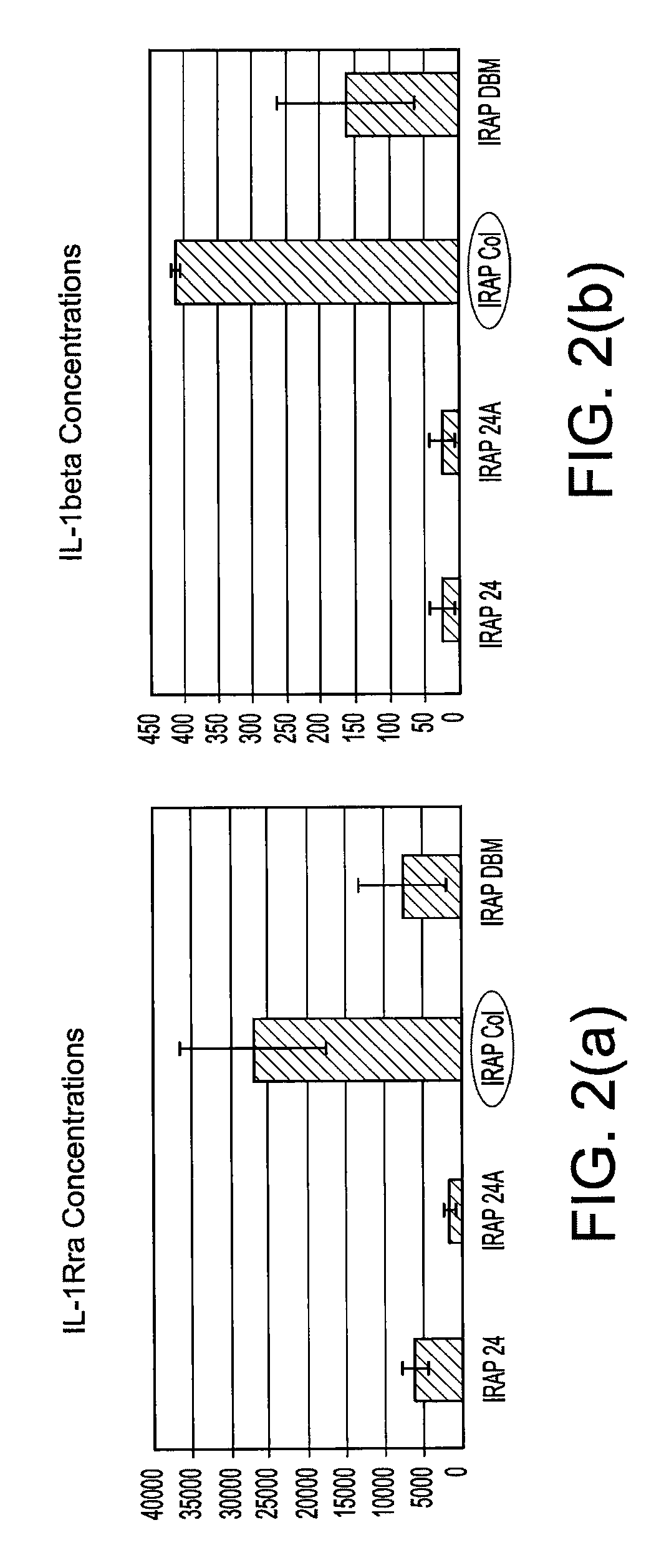
Platelet-Poor Plasma (PPP) is blood plasma with very low number of platelets (< 10 X 10³/μL). Traditionally, PPP was recommended for use in platelet aggregation studies to both adjust the Platelet-rich plasma concentration, and to serve as a control. PPP may have elevated levels of fibrinogen, which has the ability to form a fibrin-rich clot once activated. Wound healing requires cell migration and attachment, which is facilitated by this fibrin clot.
Method and composition for creating and/or activating a platelet-rich gel by contact with a porous particulate material, for use in wound care, tissue adhesion, or as a matrix for delivery of therapeutic components
A composition, method, and use of microporous particles such as polysaccharide hemostat particle gels activates platelet rich plasma (PRP) or other platelet-containing substances. The composition may contain microporous polysaccharaide hemostats (MPH) mixed with platelet-rich plasma, platelet-poor plasma, blood, or the like. The method may contain mixing the MPH with platelet-rich plasma or other platelet-containing substance either by hand, in a device, or by applying the MPH directly to the wound before or after application of the platelet-containing substance. Alternatively, MPH can by applied directly to the bleeding wound, using the blood as a source of platelets.
Owner:MEDAFOR
Autologous fibrin sealant and method for making the same
InactiveUS20050152886A1Eliminate riskBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBlood plasmaPlasma rich platelet
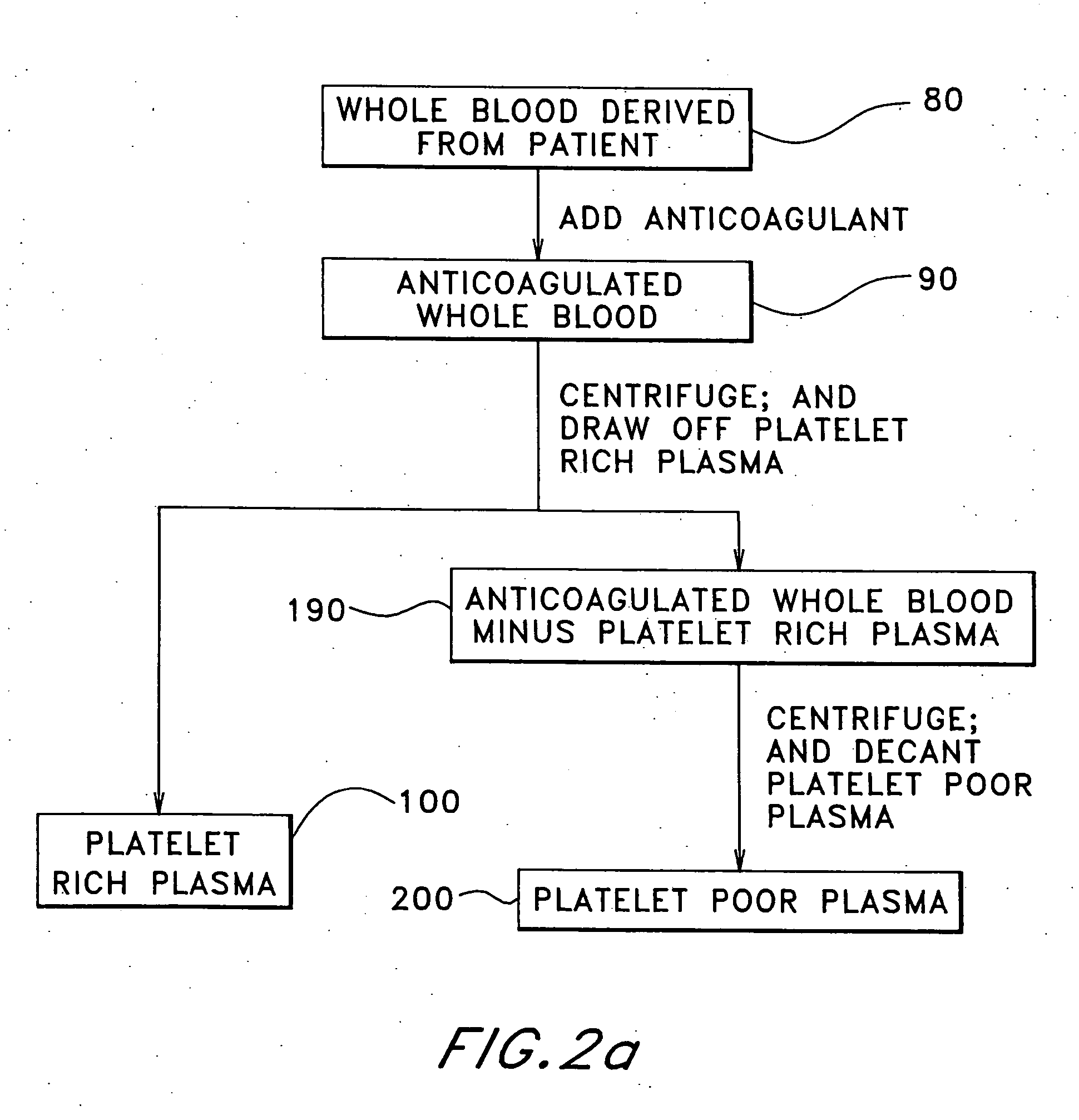
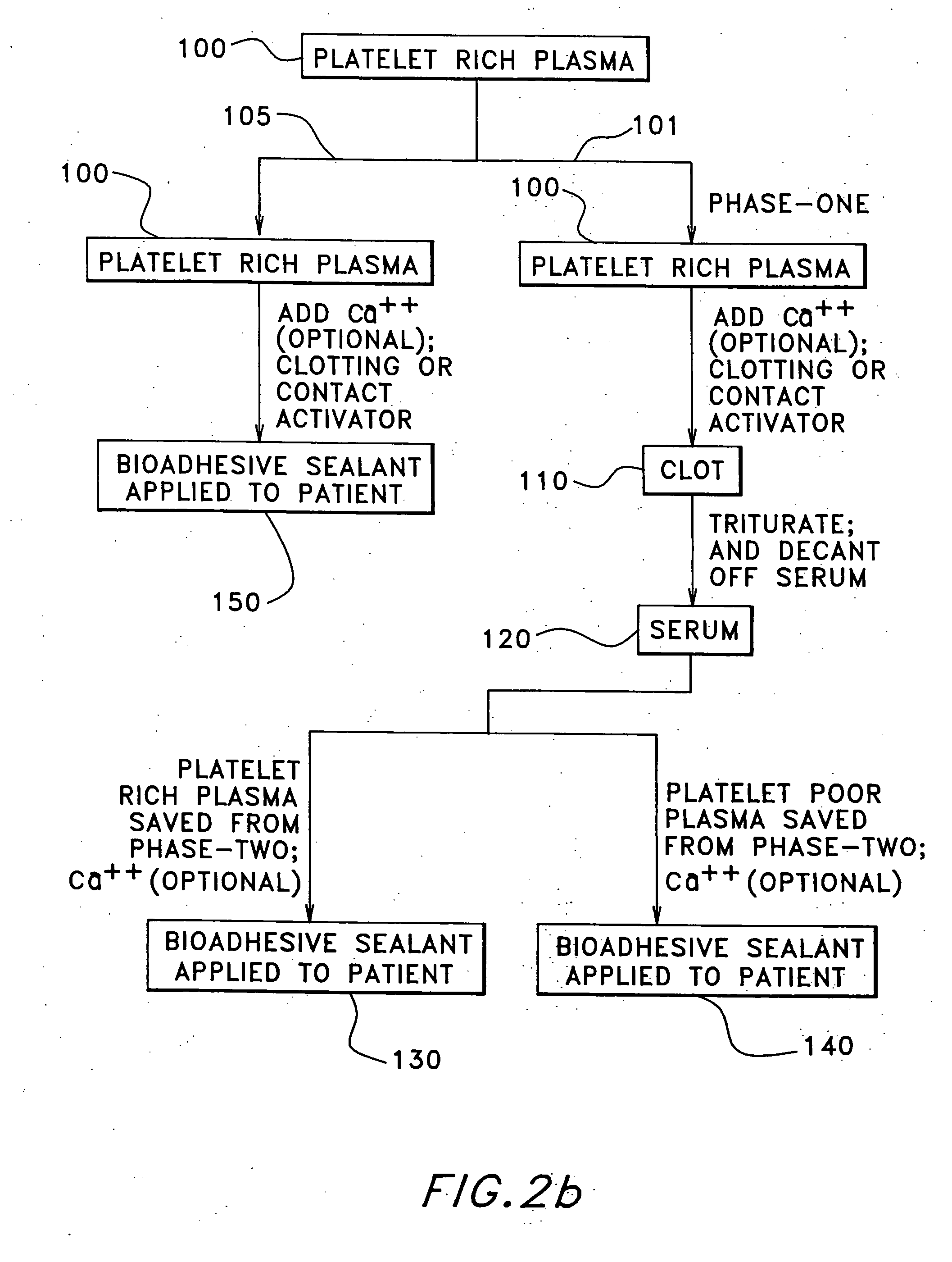
The present relates to an autologous bioadhesive sealant composition or fibrin glue prepared by a two-phase method, wherein all of the blood components for the bioadhesive sealant are derived from a patient to whom the bioadhesive sealant will be applied. A platelet rich plasma and a platelet poor plasma are formed by centrifuging a quantity of anticoagulated whole blood that was previously drawn from the patient. In one embodiment, the platelet rich plasma is divided into two portions. In phase one, a compound that reverses the effect of the anticoagulant is added to the first portion and a clot is allowed to form. The clot is then triturated, and the resulting serum containing autologous thrombin is collected. In phase two, the serum obtained from phase one is mixed with the second portion of the platelet rich plasma to form the bioadhesive sealant of the present invention.
Owner:ARTERIOCYTE MEDICAL SYST
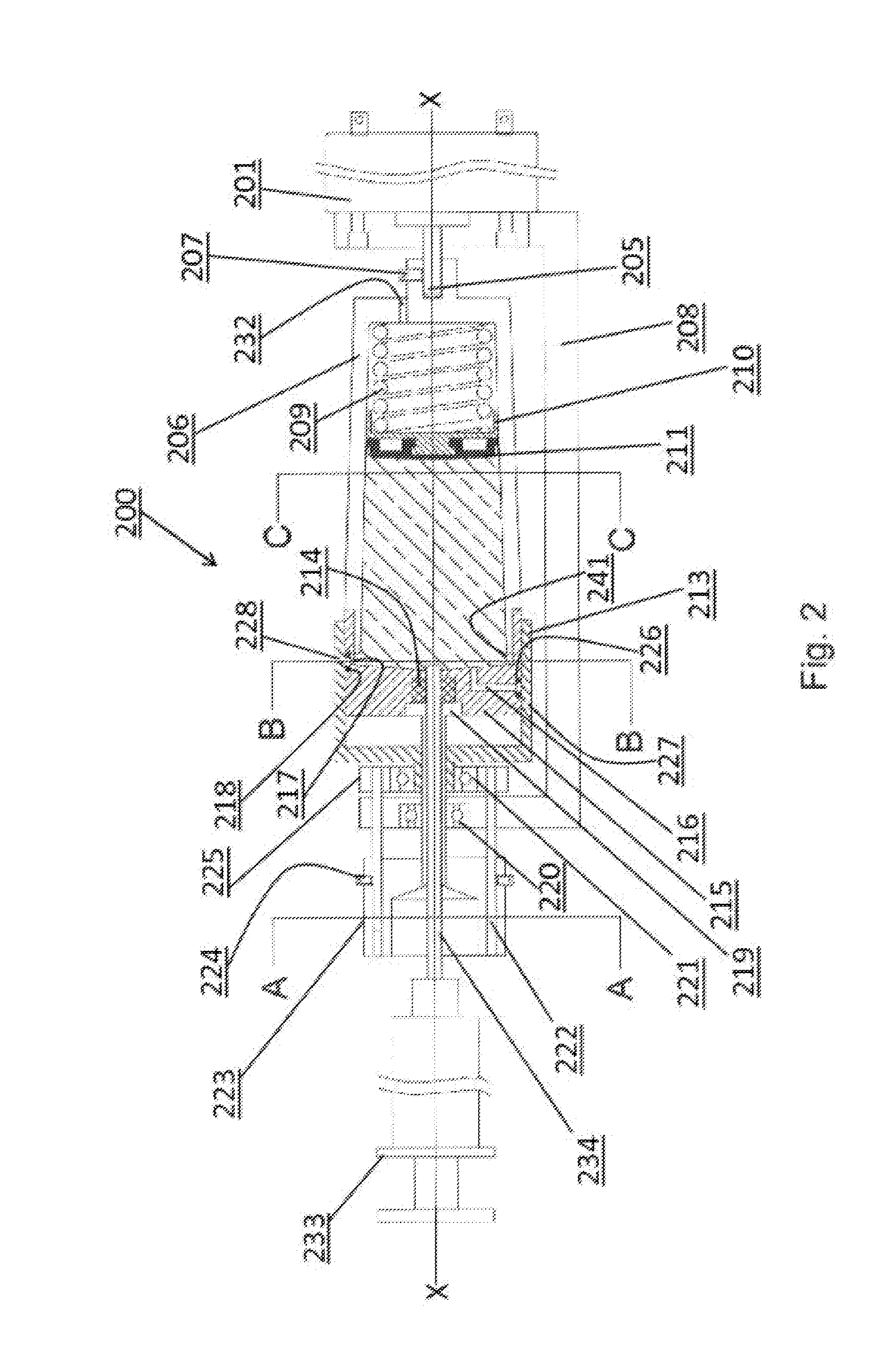
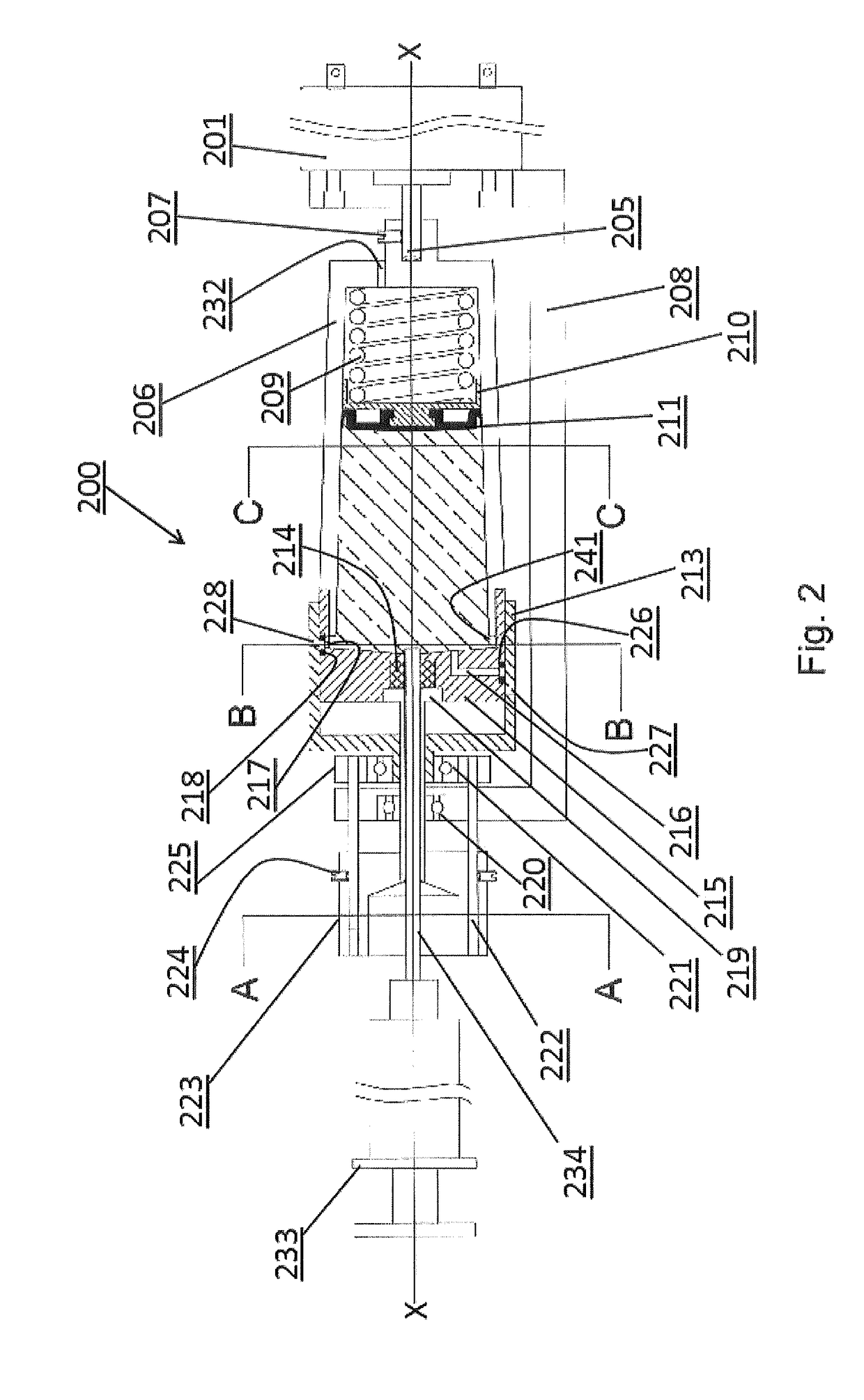
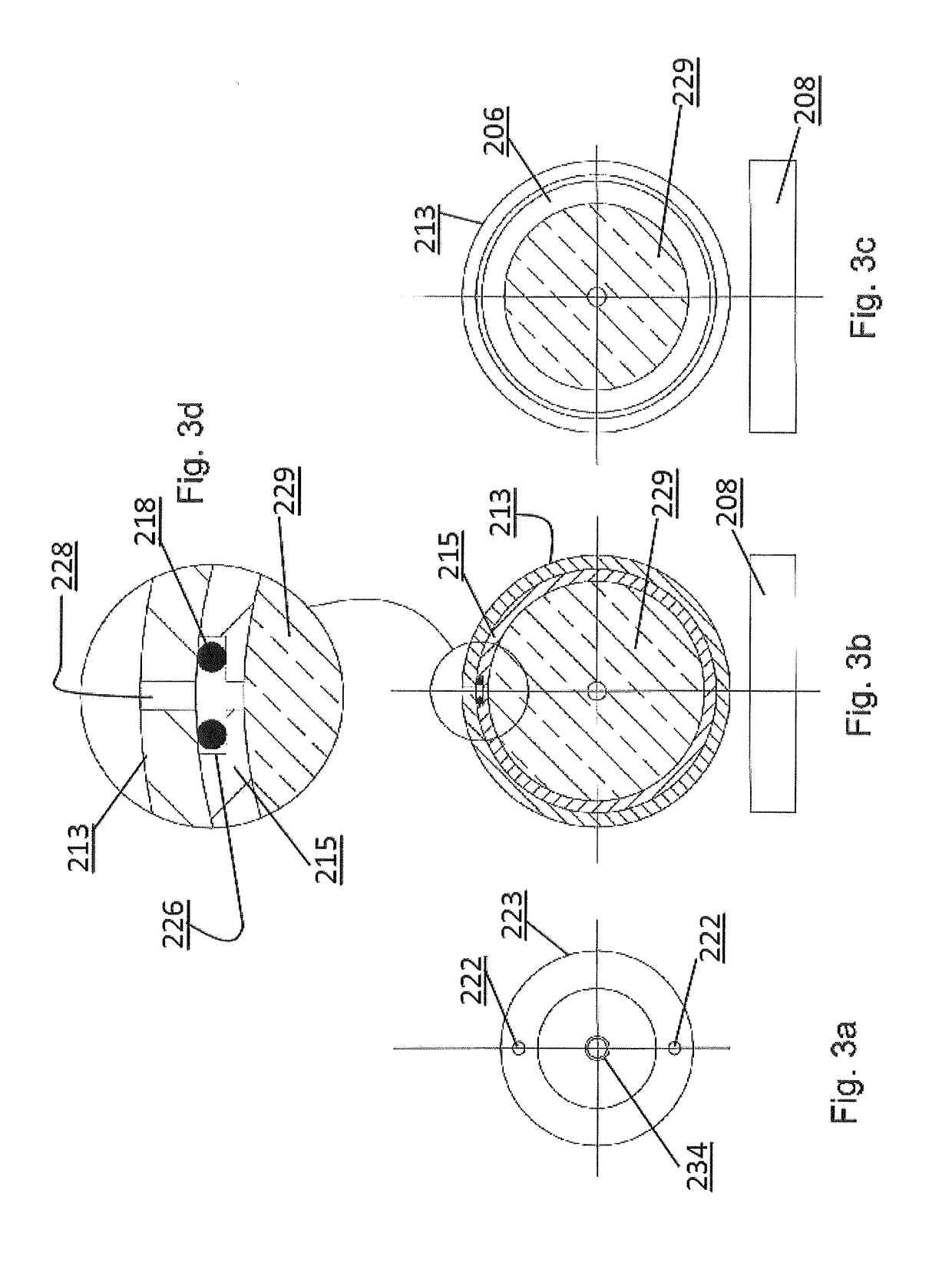
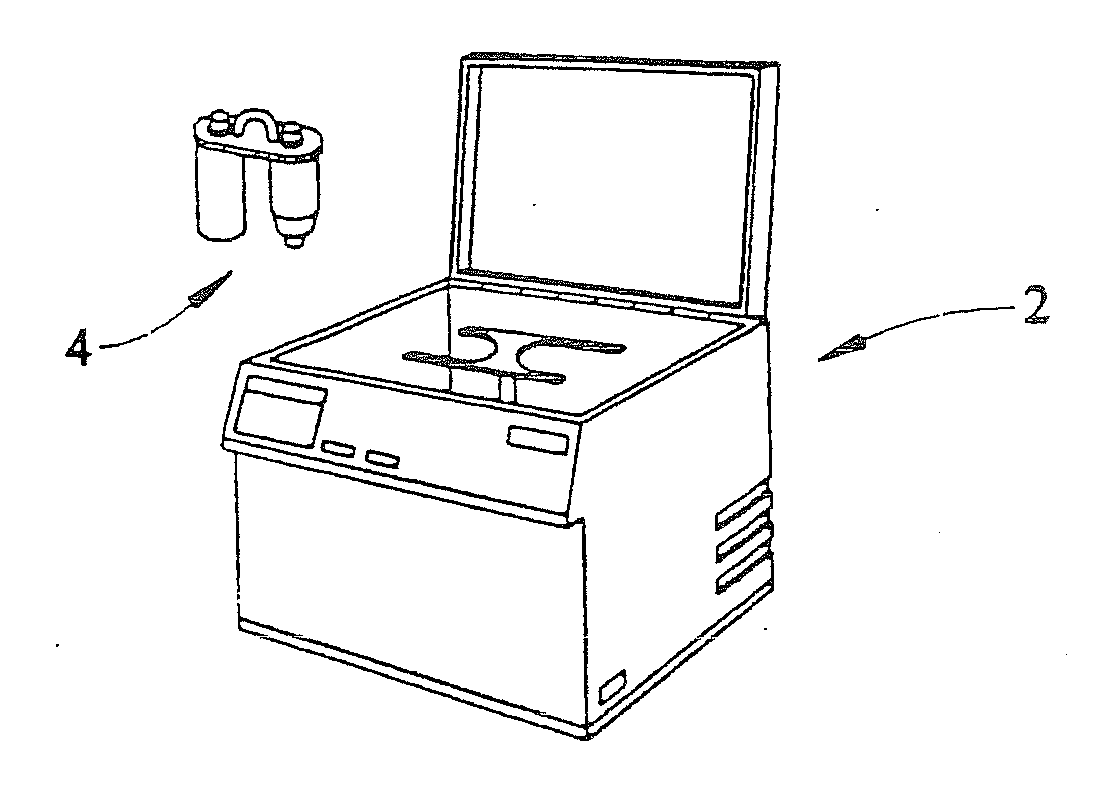
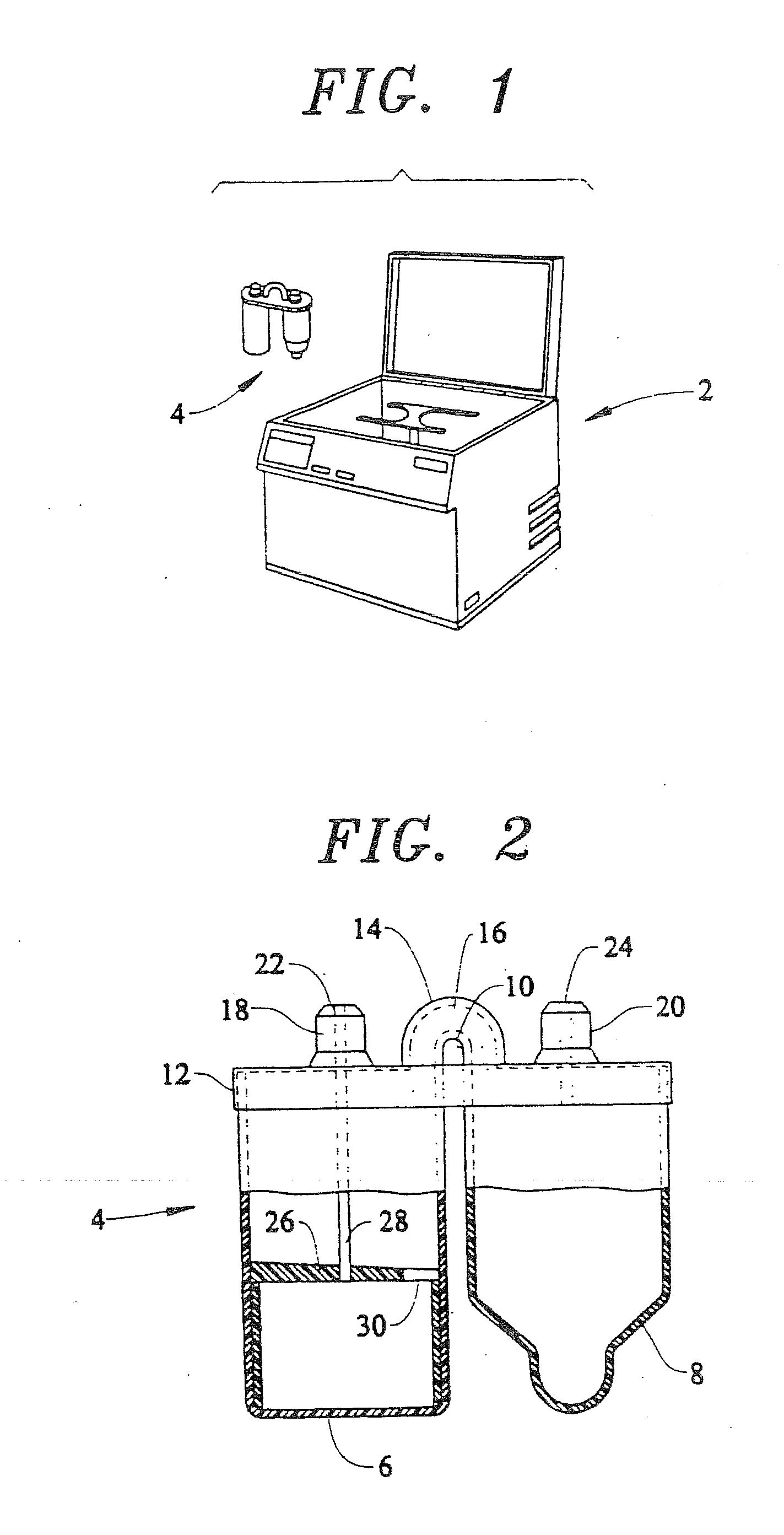
Centrifuge
ActiveUS20120129675A1Quick and reliable platelet concentrationEasy to useDispersed particle separationRotary centrifugesSlurryEngineering
Centrifuges are useful to, among other things, remove red blood cells from whole blood and retain platelets and other factors in a reduced volume of plasma. Platelet rich plasma (PRP) and or platelet poor plasma (PPP) can be obtained rapidly and is ready for immediate injection into the host. Embodiments may include valves, operated manually or automatically, to open ports that discharge the excess red blood cells and the excess plasma into separate receivers while retaining the platelets and other factors in the centrifuge chamber. High speeds used allow simple and small embodiments to be used at the patient's side during surgical procedures. The embodiments can also be used for the separation of liquids or slurries in other fields such as, for example, the separation of pigments or lubricants.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Centrifuge
ActiveUS20120252650A1Convenient for clinical operationEasy to useDispersed particle separationRotary centrifugesRed blood cellEngineering
Centrifuges are useful to, among other things, remove red blood cells from whole blood and retain platelets and other factors in a reduced volume of plasma. Platelet rich plasma (PRP) and or platelet poor plasma (PPP) can be obtained rapidly and is ready for immediate injection into the host. Embodiments may include valves, operated manually or automatically, to open ports that discharge the excess red blood cells and the excess plasma into separate receivers while retaining the platelets and other factors in the centrifuge chamber. High speeds used allow simple and small embodiments to be used at the patient's side during surgical procedures. The embodiments can also be used for the separation of liquids or slurries in other fields such as, for example, the separation of pigments or lubricants.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Method and device for testing platelet aggregation
ActiveCN101881737AFast testFully automatedInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsTransmissivity measurementsTurbidimetryBlood plasma
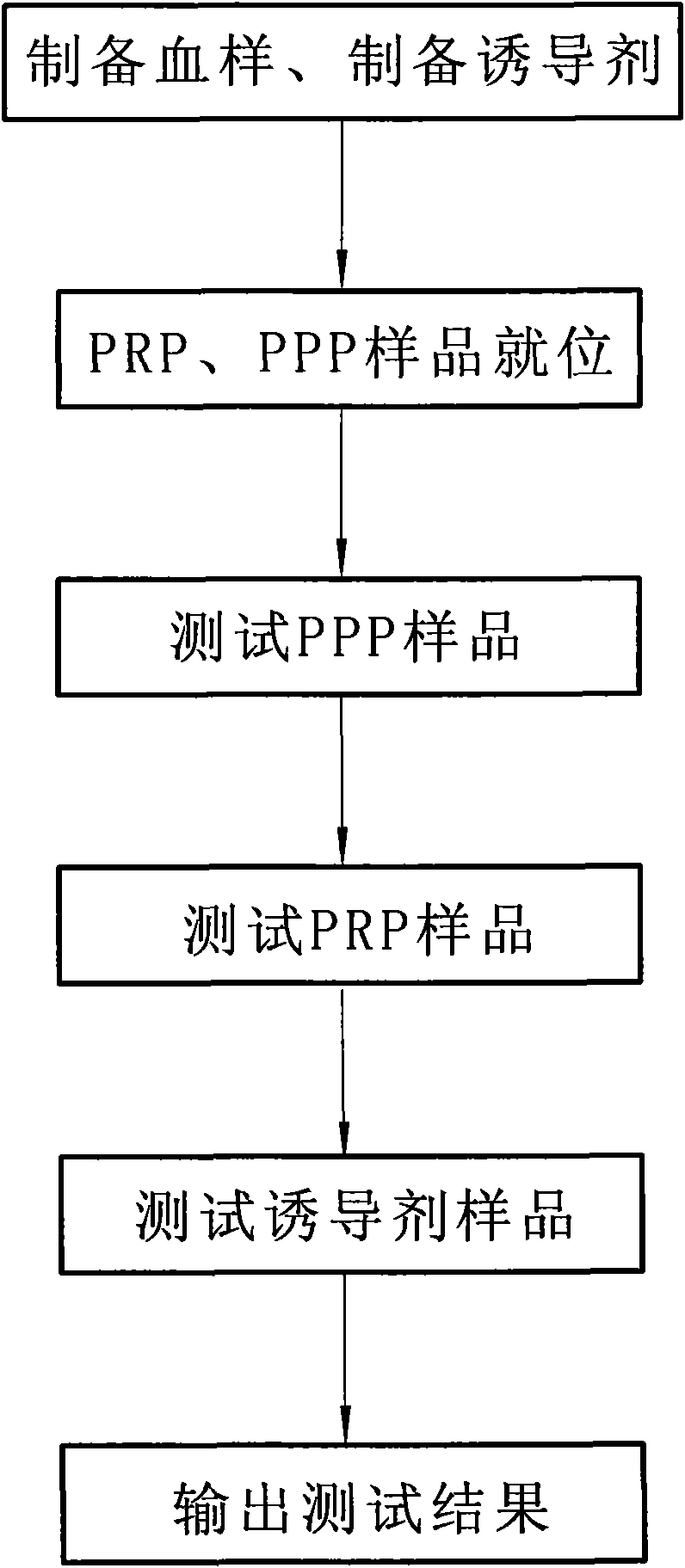
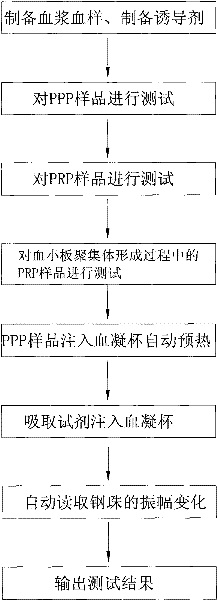
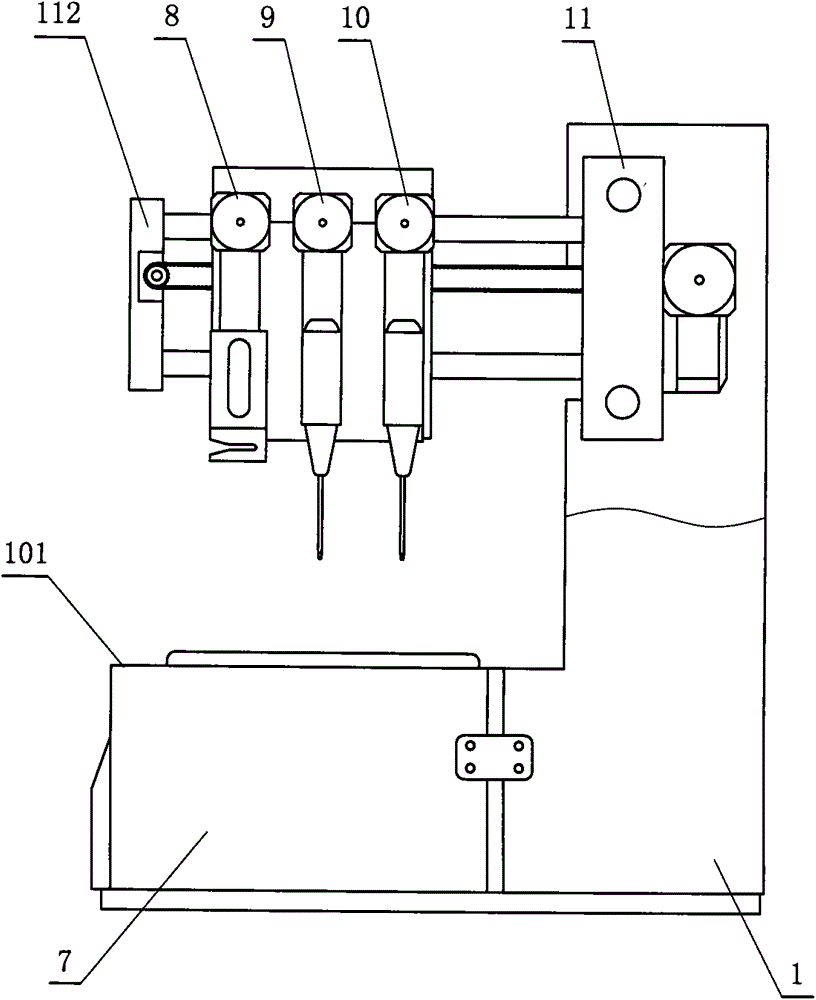
The invention discloses a method for testing platelet aggregation. A fully automatic platelet aggregometer is used for testing according to photoelectric turbidimetry. The method comprises the following test steps of: preparing a platelet aggregation inducer, putting prepared platelet rich plasma and platelet poor plasma into a sample disk device, instructing a sample adding needle to absorb the platelet poor plasma, injecting the platelet poor plasma into a test cup of a test core device and reading the transmittance data of a of a platelet poor plasma sample; instructing the sample adding needle to absorb the platelet rich plasma, injecting the platelet rich plasma into the test cup of the test core device and reading the transmittance data of a platelet poor plasma sample; instructing the sample adding needle to absorb the platelet aggregation inducer, injecting the platelet aggregation inducer into the test cup of the test core device and reading the transmittance data of an inductor sample; and calculating the maximum platelet aggregation rate of a tested blood sample and generating a test report according to input patient information.
Owner:山东泰利信医疗科技有限公司
Methods and compositions for treating respiratory conditions using platelet enriched plasma
InactiveUS20120087988A1Increase platelet concentrationImprove concentrationOrganic active ingredientsSurgeryDiseaseRespiratory disease
Described herein are methods and compositions for the treatment of respiratory diseases such as, for example, exercise induced pulmonary hemorrhage. The methods include the use of compositions comprising platelet enriched plasma, for example, platelet rich plasma and / or platelet poor plasma, for treatment of respiratory diseases in humans and animals, in particular, equines, by administration to the respiratory system.
Owner:VETGEL TECH
A kind of assay method and equipment for platelet aggregation and coagulation factor
ActiveCN102262090AFast testProtect your healthMaterial analysis by optical meansPlatelet aggregation ratioTurbidimetry
The invention relates to a method for measuring the platelet aggregation and a blood coagulation factor. In the method, a full-automatic coagulate blood analytical instrument is used, the platelet aggregation is measured by using photoelectric turbidimetry and the blood coagulation factor is measured by using a double magnetic circuit and bead method. The method comprises the following measuring steps of: preparing a platelet aggregation inductive agent, platelet rich plasma and platelet poor plasma; respectively reading light transmittance data of a platelet poor plasma sample and light transmittance data of a platelet rich plasma sample as well as light transmittance data of the platelet rich plasma during the forming process of the platelet aggregation within the specified time; calculating the platelet aggregation rate of the measured blood sample; absorbing the platelet poor plasma and injecting the platelet poor plasma in a hemagglutination cup; absorbing the selected reagent according to a test program and injecting the selected reagent into the hemagglutination cup; automatically monitoring the amplitude of a steel bead; and generating a test report by using measuring results of the platelet aggregation and the blood coagulation factor according to input information of patients.
Owner:BEIJING PRECIL INSTR CO LTD +1
Centrifuge
ActiveUS20120275970A1Convenient for clinical operationEasy to useAnalysis using chemical indicatorsRotary centrifugesSlurryEngineering
Centrifuges are useful to, among other things, remove red blood cells from whole blood and retain platelets and other factors in a reduced volume of plasma. Platelet rich plasma (PRP) and or platelet poor plasma (PPP) can be obtained rapidly and is ready for immediate injection into the host. Embodiments may include valves, operated manually or automatically, to open ports that discharge the excess red blood cells and the excess plasma into separate receivers while retaining the platelets and other factors in the centrifuge chamber. High speeds used allow simple and small embodiments to be used at the patient's side during surgical procedures. The embodiments can also be used for the separation of liquids or slurries in other fields such as, for example, the separation of pigments or lubricants.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Centrifuge
ActiveUS20130244856A1Accurate timingMinimize disruptionRotary centrifugesSeparation devicesEngineeringSlurry
Centrifuges are useful to, among other things, remove red blood cells from whole blood and retain platelets and other factors in a reduced volume of plasma. Platelet rich plasma (PRP) and or platelet poor plasma (PPP) can be obtained rapidly and is ready for immediate injection into the host. Embodiments may include valves, operated manually or automatically, to open ports that discharge the excess red blood cells and the excess plasma into separate receivers while retaining the platelets and other factors in the centrifuge chamber. High speeds used allow simple and small embodiments to be used at the patient's side during surgical procedures. The embodiments can also be used for the separation of liquids or slurries in other fields such as, for example, the separation of pigments or lubricants.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
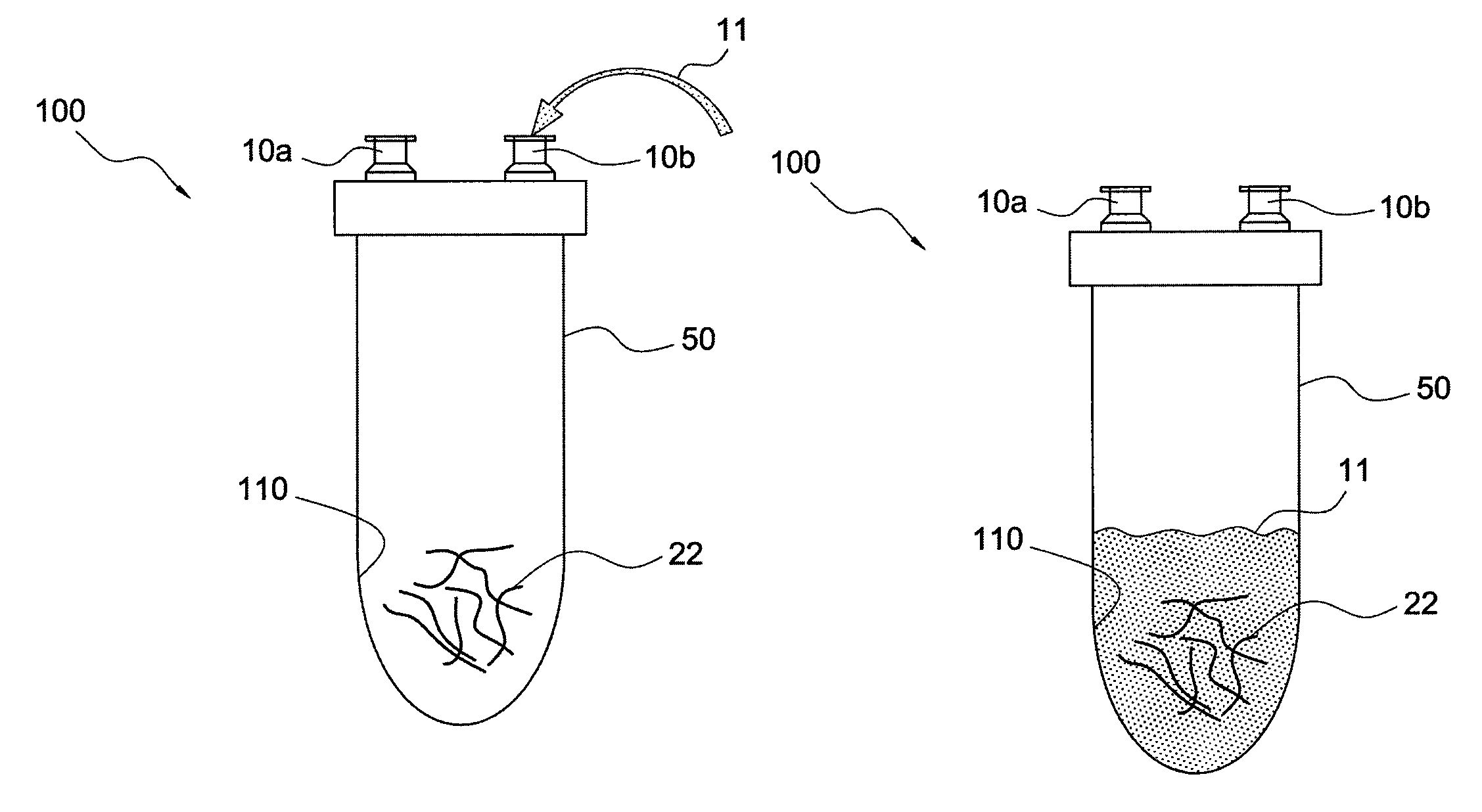
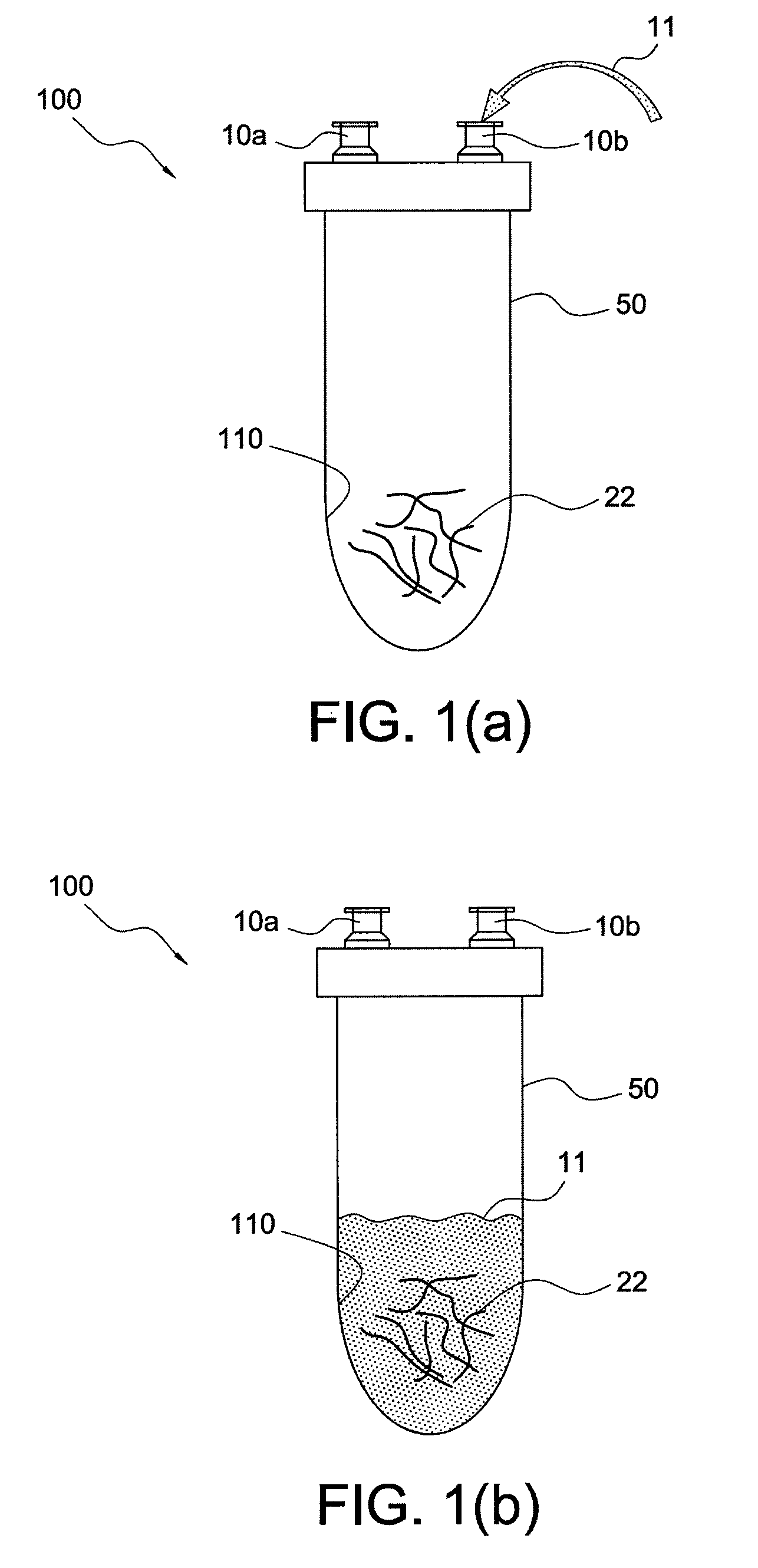
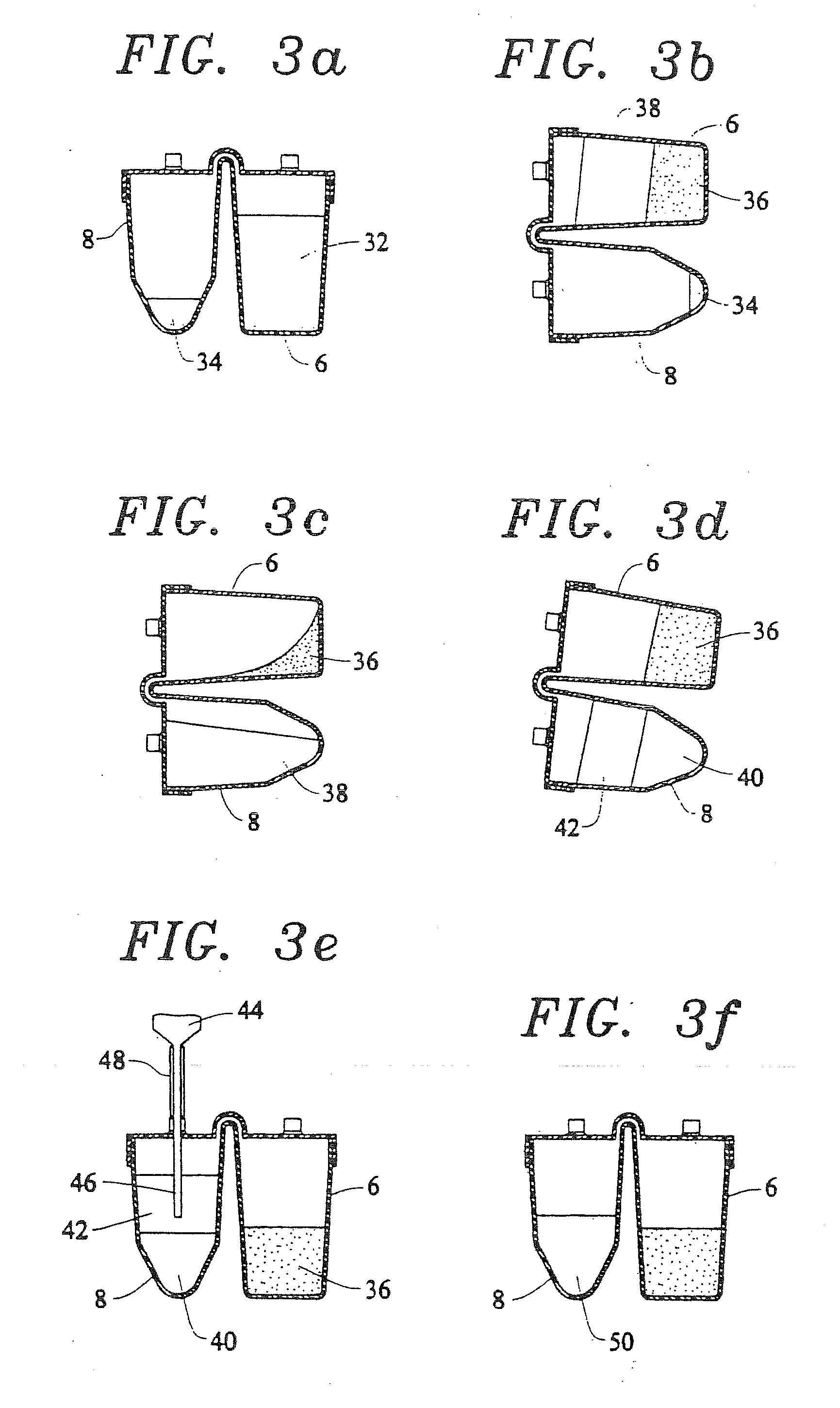
Passive separation of whole blood
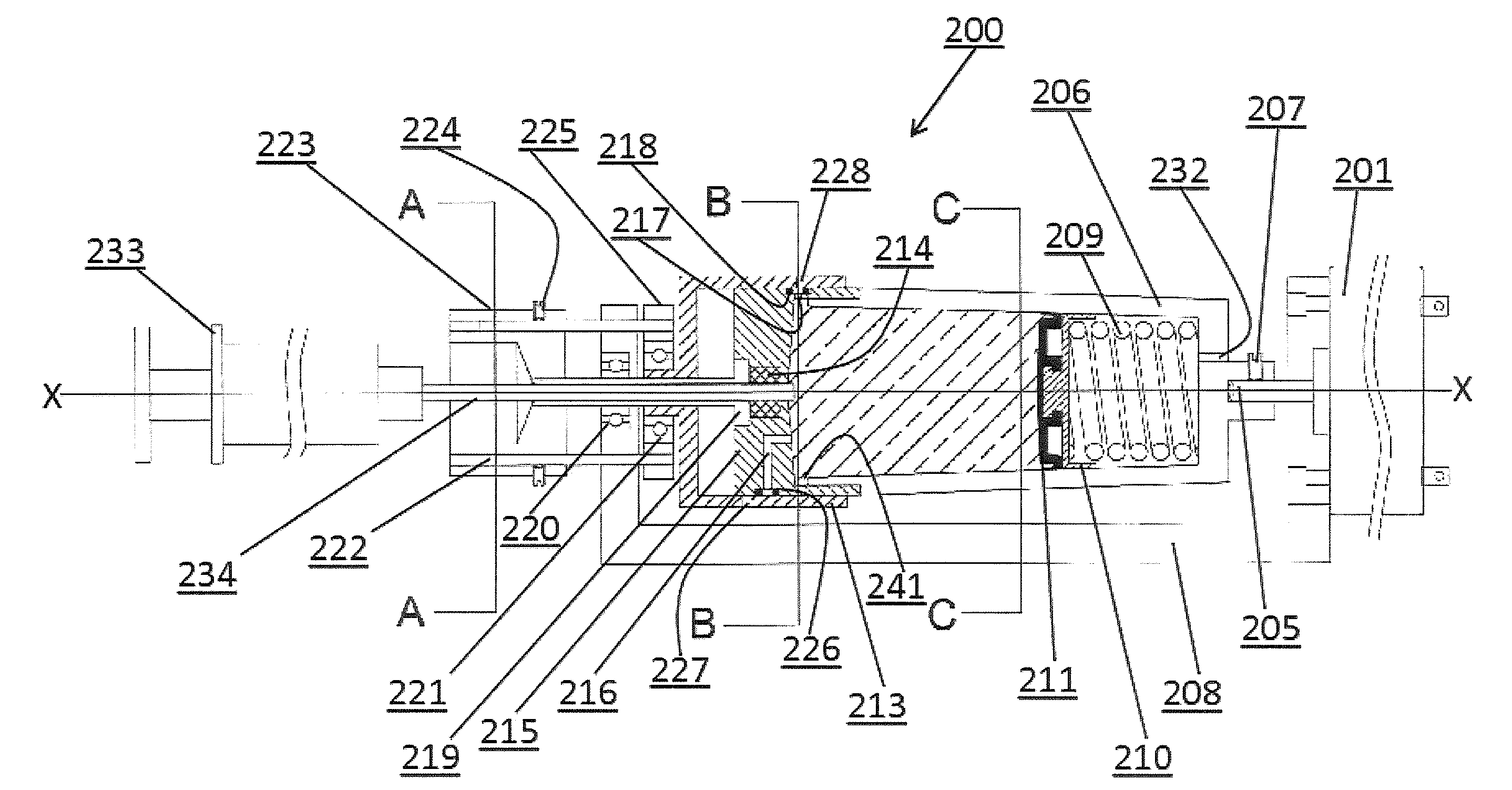
Described are systems, methods, and kits for compression sedimentation and whole blood separation. For example, a compression sedimentation system may include a compression stage configured to accept a flexible reservoir configured to contain a liquid mixture. The compression stage may include a base substrate and a compression substrate configured to apply a force to the flexible reservoir effective to create a pressure in the liquid mixture. An apparatus for whole blood separation may include a sedimentation system that separates whole blood into a supernatant including platelet rich plasma and a subnatant including red blood cells. At least one platelet-concentrating device may be included to receive the supernatant including the PRP and to separate a platelet concentrate and a platelet poor plasma from the supernatant.
Owner:HALCYON BIOMEDICAL
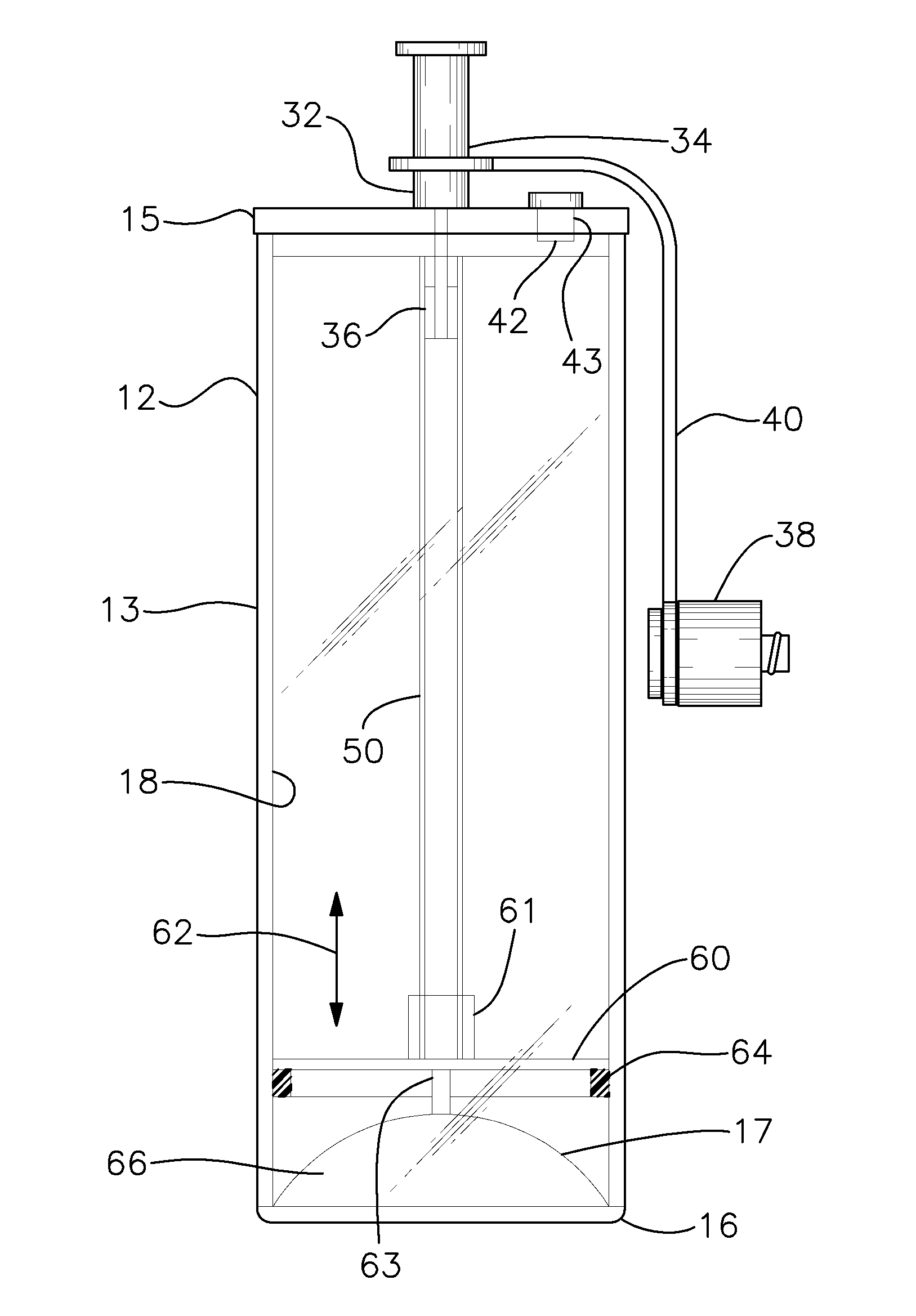
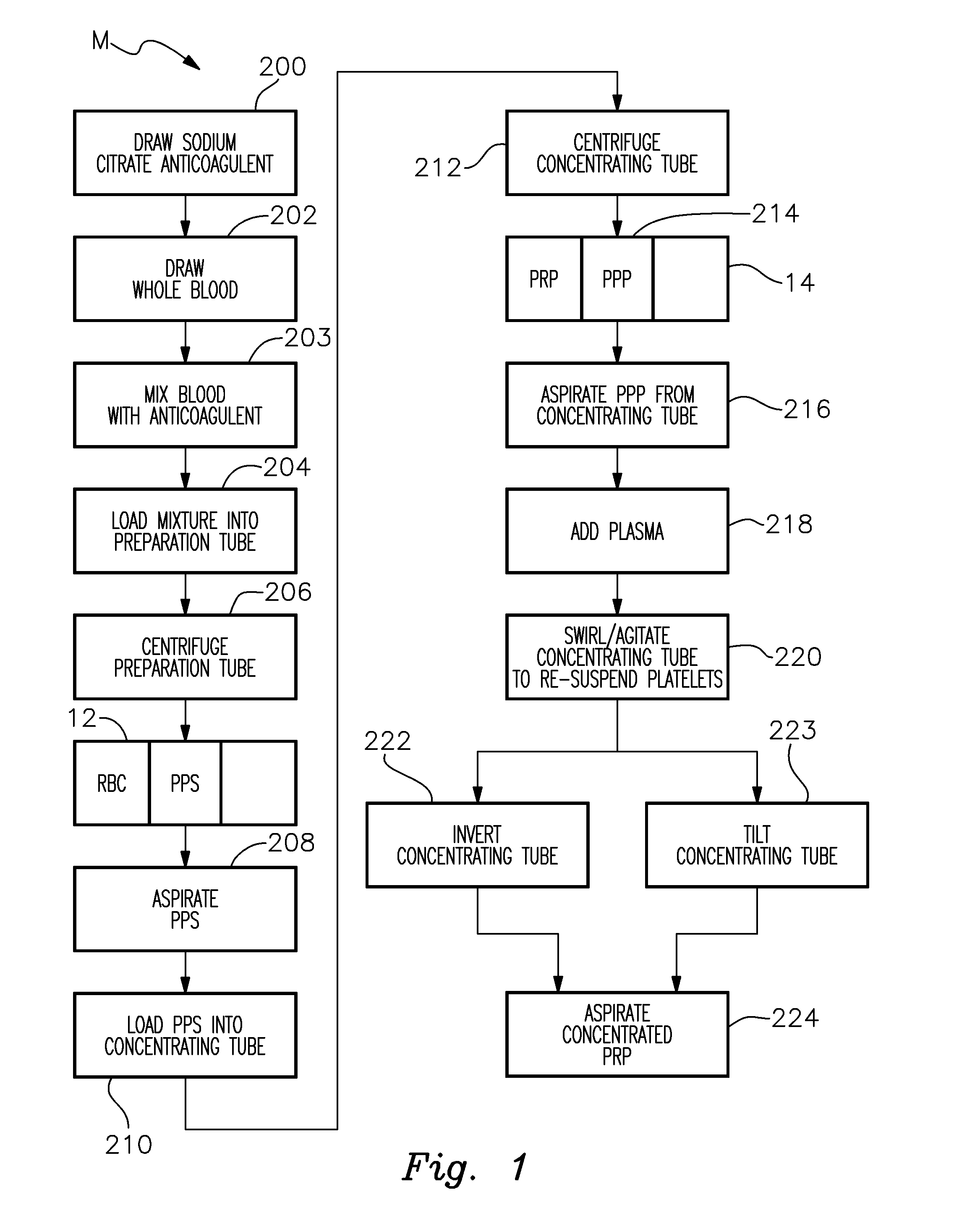
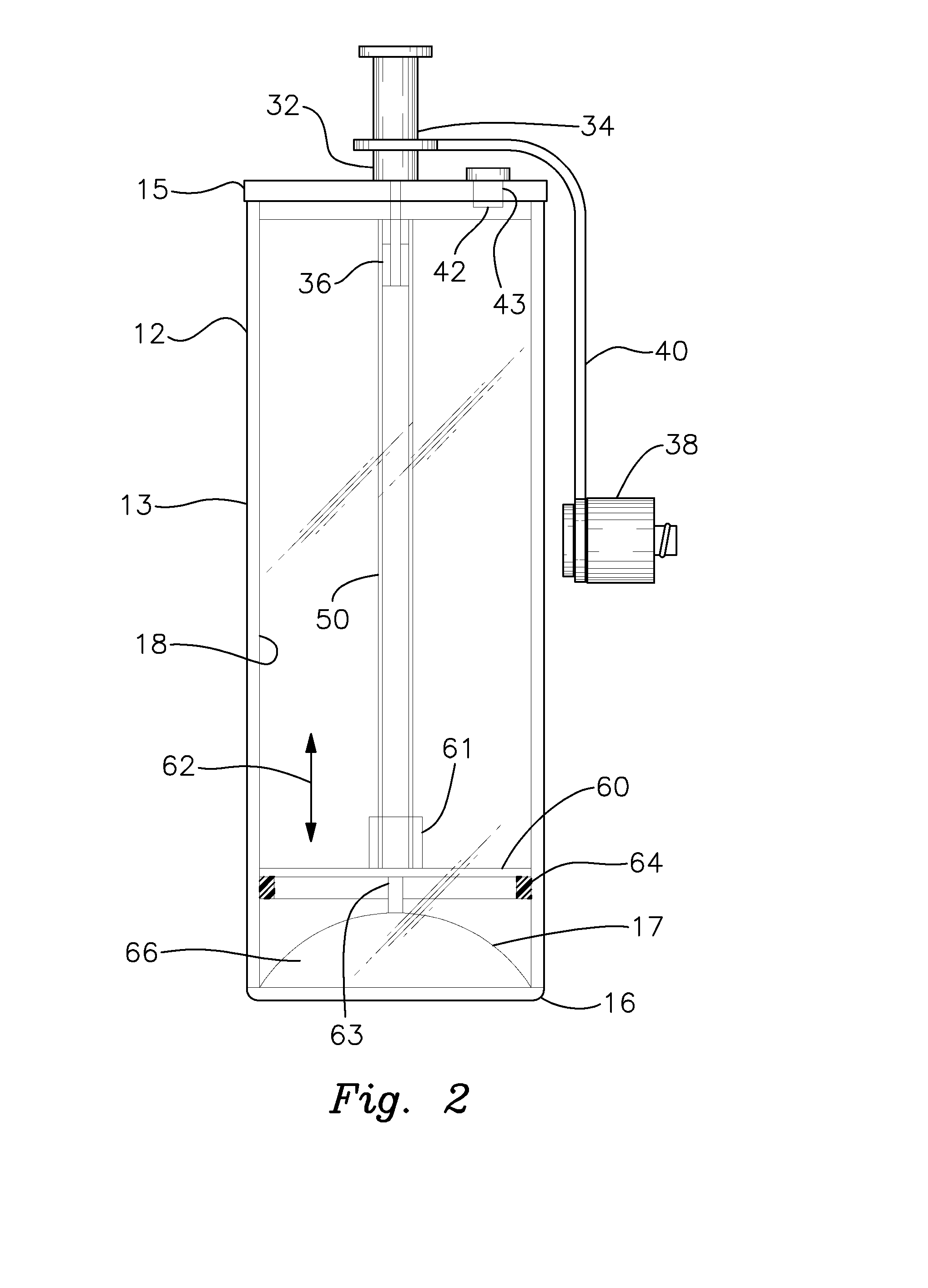
Platelet Concentrating System
InactiveUS20150367064A1Effectively and efficiently manufacturedHighly concentrated and medically effective PRP productOther blood circulation devicesDispersed particle separationMedicinePlatelets blood
A method for more effectively concentrating blood platelets for use in medical procedures includes providing preparation and concentrating tubes. Anticoagulated whole blood is added to the preparation tube, which is centrifuged to separate red blood cells from a platelet plasma suspension The platelet plasma suspension is aspirated and loaded into the concentrating tube, which is itself centrifuged to separate the platelet plasma suspension into platelet poor plasma and platelet rich plasma layers. The platelet poor plasma is aspirated through a port of the concentrating tube and the remaining concentrated PRP is aspirated through the same or a different port of the concentrating tube.
Owner:PENNIE PATRICK
Centrifuge
ActiveUS8556794B2Quick and reliable platelet concentrationEasy to useRotary centrifugesSuction devicesSlurryEngineering
Centrifuges are useful to, among other things, remove red blood cells from whole blood and retain platelets and other factors in a reduced volume of plasma. Platelet rich plasma (PRP) and or platelet poor plasma (PPP) can be obtained rapidly and is ready for immediate injection into the host. Embodiments may include valves, operated manually or automatically, to open ports that discharge the excess red blood cells and the excess plasma into separate receivers while retaining the platelets and other factors in the centrifuge chamber. High speeds used allow simple and small embodiments to be used at the patient's side during surgical procedures. The embodiments can also be used for the separation of liquids or slurries in other fields such as, for example, the separation of pigments or lubricants.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
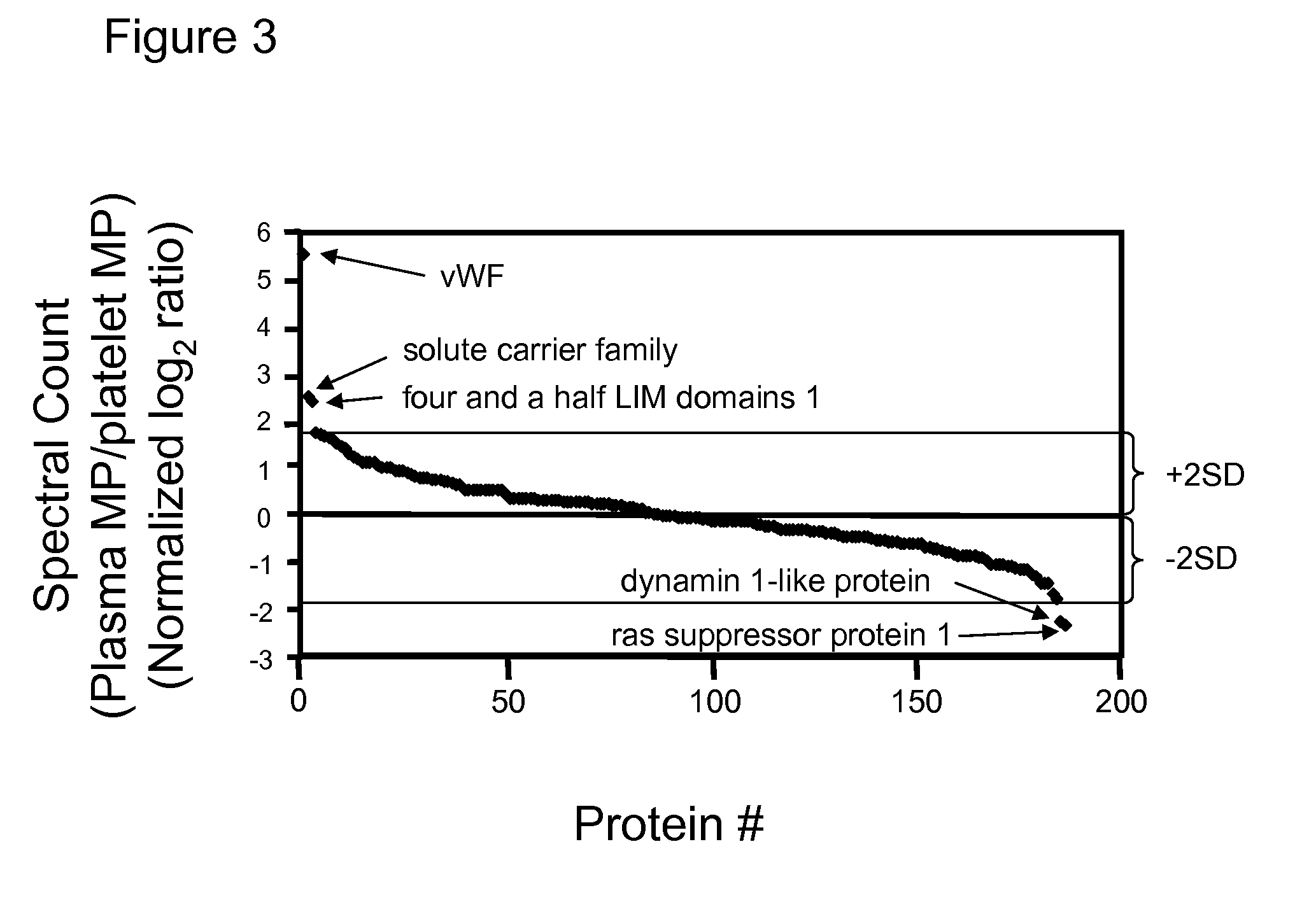
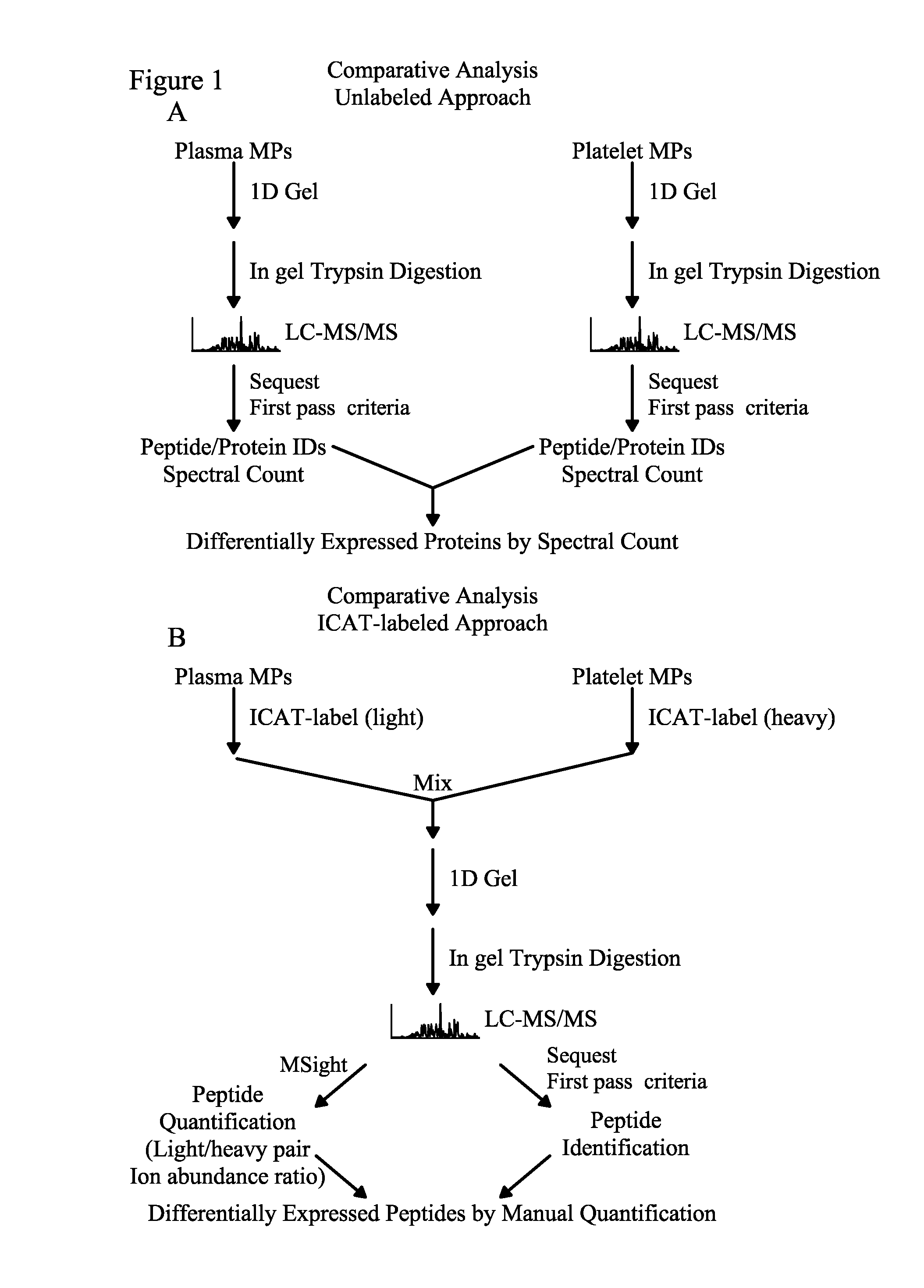
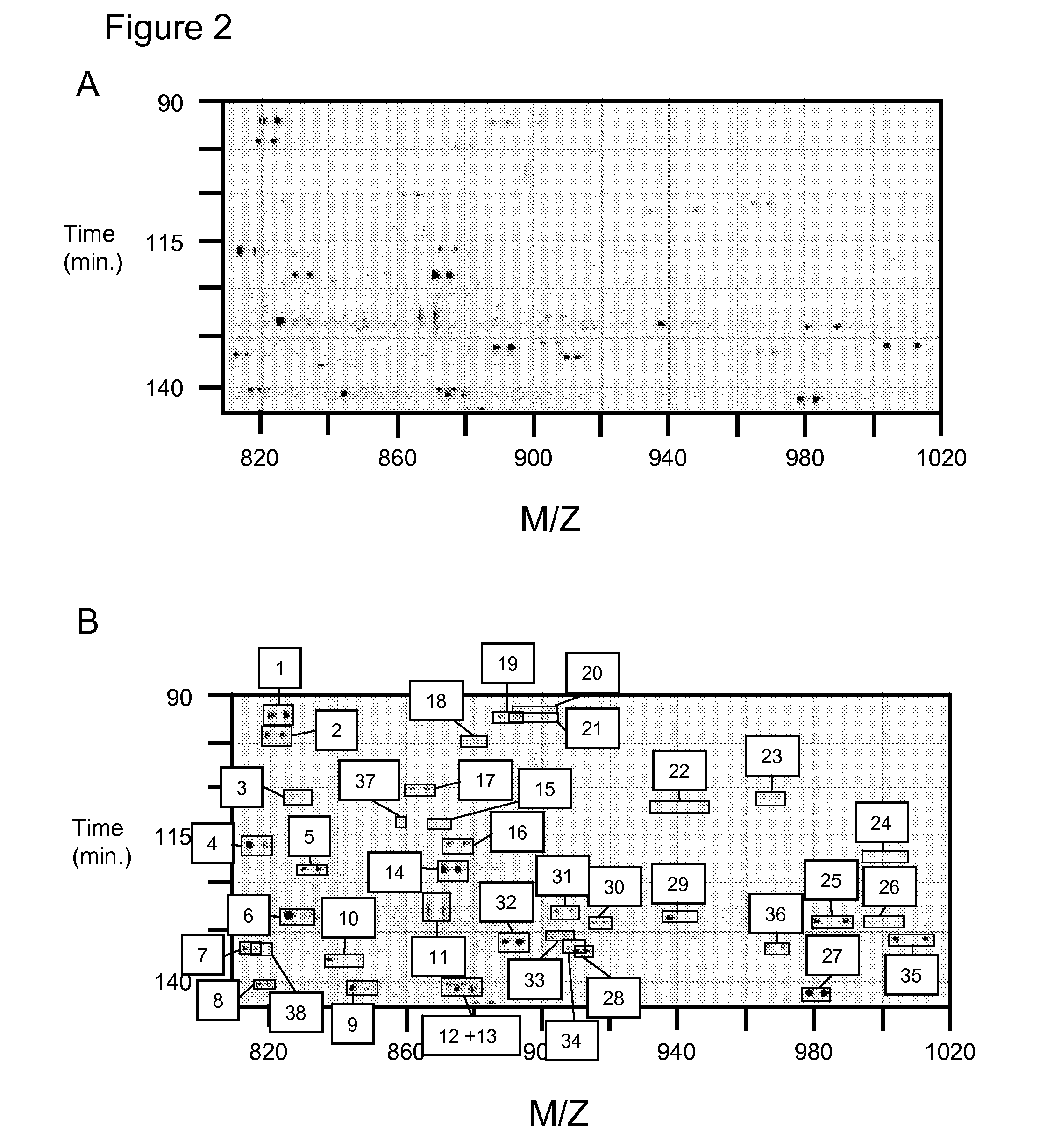
Methods for identifying and analyzing biomarkers from plasma-derived microparticles
Owner:MICROPARTICLE PROTEOMICS LLS
Inorganic Solids That Accelerate Coagulation of Blood
The present invention is a method to accelerate the coagulation of blood through the application of inorganic materials. Any solid that can be used to activate the coagulation of platelet-poor plasma in the APTT clinical test or whole blood in the ACT clinical test has been found to be effective as a coagulation accelerator in vivo. Typical materials that can be used for in-vivo clotting include diatomaceous earth, glass powder or fibers, precipitated or fumed silica, and calcium exchanged permutites. Thes materials can be used in an aqueous slurry, dry powder or dehydrated forms, and can also be bound with suitable organic or inorganic binders and / or contained in a variety of forms.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method for producing activated autologous platelet rich and platelet poor plasma and methods of use
A method and kit to produce activated autologous platelet rich and platelet poor plasma (AAPRPP) and methods of use to treat pain. The method to produce AAPRPP generally comprising (1) obtaining whole blood from patient; (2) centrifuging whole blood in a collection tube; (3) extracting platelet rich and platelet poor plasma mixture from collection tube; and (4) transferring platelet rich and platelet poor plasma mixture to an activation tube containing at least one platelet aggregator and at least one platelet activator to obtain a resulting platelet concentration. The method to treat pain generally comprising producing AAPRPP and extracting contents of activation tube into a standard syringe then injecting AAPRPP at or near the nerve group responsible for the affected anatomical area.
Owner:RELEFORD JR BILL J +2
Centrifuge
ActiveUS8394006B2Quick and reliable platelet concentrationEasy to useRotary centrifugesSuction devicesSlurryEngineering
Centrifuges are useful to, among other things, remove red blood cells from whole blood and retain platelets and other factors in a reduced volume of plasma. Platelet rich plasma (PRP) and or platelet poor plasma (PPP) can be obtained rapidly and is ready for immediate injection into the host. Embodiments may include valves, operated manually or automatically, to open ports that discharge the excess red blood cells and the excess plasma into separate receivers while retaining the platelets and other factors in the centrifuge chamber. High speeds used allow simple and small embodiments to be used at the patient's side during surgical procedures. The embodiments can also be used for the separation of liquids or slurries in other fields such as, for example, the separation of pigments or lubricants.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Systems And Methods For Therapeutic Platelet Depletion
Systems and methods are provided for depleting platelets from blood. The system includes a multi-stage blood separation chamber in which blood is separated into red blood cells and platelet-rich plasma. The platelet-rich plasma is conveyed from a first stage of the chamber to a second stage, where it is separated into platelets and platelet-poor plasma. The platelet-poor plasma is conveyed out of the chamber while the platelets are allowed to accumulate in the second stage of the chamber. When a controller of the system has determined that the maximum chamber capacity of platelets has been accumulated in the second stage of the chamber, the platelets are conveyed out of the chamber to a waste container. The cycle of separating blood into its components, accumulating platelets in the chamber, and then flushing the platelets from the chamber is repeated until a target platelet concentration of the blood is achieved.
Owner:FENWAL
Centrifuge
ActiveUS8469871B2Quick and reliable platelet concentrationEasy to useRotary centrifugesSeparation devicesSlurryEngineering
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Enhanced autologous growth factor production and delivery system
ActiveUS9205110B2Dead animal preservationMammal material medical ingredientsActive proteinBlood plasma
Systems and methods for producing enhanced blood serum with concentrated growth factors and / or prophylactically and therapeutically active proteins. An autologous blood product is obtained from a donor and then incubated into a containment device (sterile container) that includes a source of cells or tissue (for example, autologous, allogeneic, or xenographic tissue, or combinations thereof). The cells from the injected fluid (autologous blood product) interact / incubate with the source of cells or tissue inside the containment device, to produce a serum that is loaded with autologous proteins, growth factors, and cytokines. The autologous blood product may be a fluid and / or composition that includes blood, whole blood, autologous conditioned plasma, platelet-rich plasma, platelet-poor plasma, bone marrow aspirate, bone marrow concentrate and stem cells, among others, and combinations thereof.
Owner:ARTHREX
Method and apparatus for producing platelet rich plasma and/or platelet concentrate
InactiveUS20080206858A1Easy to produceSmall amount is easilyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBlood plasmaRed Cell
Platelet rich plasma and / or platelet concentrate is prepared by placing whole blood in a first chamber of a sterile processing disposable having two chambers. The processing disposable is subjected to a first centrifugation to separate red blood cells, and the resulting platelet rich plasma supernatant is decanted to the second chamber. The processing disposable is subjected to a second centrifugation to concentrate platelets. A volume of the platelet poor plasma supernatant in the second chamber is removed, and the platelets are re-suspended in the remaining plasma. The second chamber may contain anticoagulant to preclude aggregation of the platelets.
Owner:BLASETTI LOU +1
Method for detecting activated blood coagulation factor XI in human intravenous immunoglobulin
ActiveCN103185710AAvoid preactivationIndirectly reflect changes in production contentFluorescence/phosphorescenceInitiation factorFactor ii
The invention discloses a method for detecting an activated blood coagulation factor XI in human intravenous immunoglobulin. The method comprises the steps as follows: (1) mixing an IVIG (intravenous immunoglobulin) sample with specially-preprocessed platelet-poor plasma (PPP); (2) adding a thrombin specific fluorogenic substrate with a phospholipid agent into a reaction system; (3) adding an initiation factor for starting a TGT (thrombin generation test), wherein the initiation factor comprises a calcium ion source and the phospholipid agent; (4) obtaining a thrombin generation curve providing parameters by the optimized reaction system; and (5) negatively correlating the peak time of thrombin (TTP) of the detected sample with the FXIa (activated blood coagulation factor XI) level in the sample. The FXIa level in the detected sample can be indirectly obtained by comparing the TTP of the detected sample with that of an FXIa standard sample. The method is suitable for detecting residual micro FXIa in human intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) products and is used for extracorporal evaluation of thrombosis risk of related products.
Owner:BLOOD TRASFUSION INST CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Blood products with binding agent
The present invention provides a non-liquid biomaterial that may be used as a surgical sealant, a suture support, a blood flow controller, an adhesion reducing agent, an adhesion preventing agent, a tissue support, a tissue filler, a wound dressing or a combination thereof. The non-liquid biomaterial may comprise a blood derived material such as plasma, platelet poor plasma, platelet rich plasma or a material derived from blood containing tissue aspirate, such as bone marrow aspirate, a protein binding agent and a polymerizing agent. Methods for making and using the non-liquid biomaterial are also provided.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Centrifuge
ActiveUS20140094930A1Quick and reliable platelet concentrationEasy to useOther blood circulation devicesRotary centrifugesSlurryEngineering
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Methods for identifying and analyzing biomarkers from plasma-derived microparticles
InactiveUS20080171312A1Peptide/protein ingredientsElectrophoretic profilingPlasma derivedMicroparticle
Owner:MICROPARTICLE PROTEOMICS LLS
Method for improving stability of platelet aggregation index
InactiveCN104931460AEliminate background errorsImprove accuracyTransmissivity measurementsMicrocomputerTurbidimetry
The invention relates to a method for improving stability of a platelet aggregation index; the method comprises the steps: determining according to a photoelectric turbidimetry; making a patient blood sample into a platelet-rich plasma sample and a platelet-poor plasma sample; transferring the platelet-poor plasma sample into a test cup, automatically reading light transmittance data of the platelet-poor plasma sample by a detection optical path system, and storing in a microcomputer; transferring the platelet-rich plasma sample into the same test cup, automatically reading light transmittance data of the platelet-rich plasma sample by the detection optical path system, and storing in the microcomputer; injecting a platelet aggregating agent into the same test cup, automatically reading data of the light transmittance of the platelet-rich plasma sample changing along with the time in a regulated time by the detection optical path system, storing in the microcomputer, and calculating out the platelet aggregation index by the microcomputer according to a formula; and generating a test report from the determination results of the platelet aggregation index according to inputted patient information.
Owner:北京泰利康信科技有限公司
Methods and compositions for treating respiratory conditions using platelet enriched plasma
InactiveUS8753882B2Increase platelet concentrationImprove concentrationOrganic active ingredientsAnimal cellsDiseaseBlood plasma
Described herein are methods and compositions for the treatment of respiratory diseases such as, for example, exercise induced pulmonary hemorrhage. The methods include the use of compositions comprising platelet enriched plasma, for example, platelet rich plasma and / or platelet poor plasma, for treatment of respiratory diseases in humans and animals, in particular, equines, by administration to the respiratory system.
Owner:VETGEL TECH
Fibrin based glue with functionalized hydrophilic polymer protein binding agent
The present invention provides a non-liquid biomaterial that may be used as a surgical sealant, a suture support, a blood flow controller, an adhesion reducing agent, an adhesion preventing agent, a tissue support, a tissue filler, a wound dressing or a combination thereof. The non-liquid biomaterial may comprise a blood derived material such as plasma, platelet poor plasma, platelet rich plasma or a material derived from blood containing tissue aspirate, such as bone marrow aspirate, a protein binding agent and a polymerizing agent. Methods for making and using the non-liquid biomaterial are also provided.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
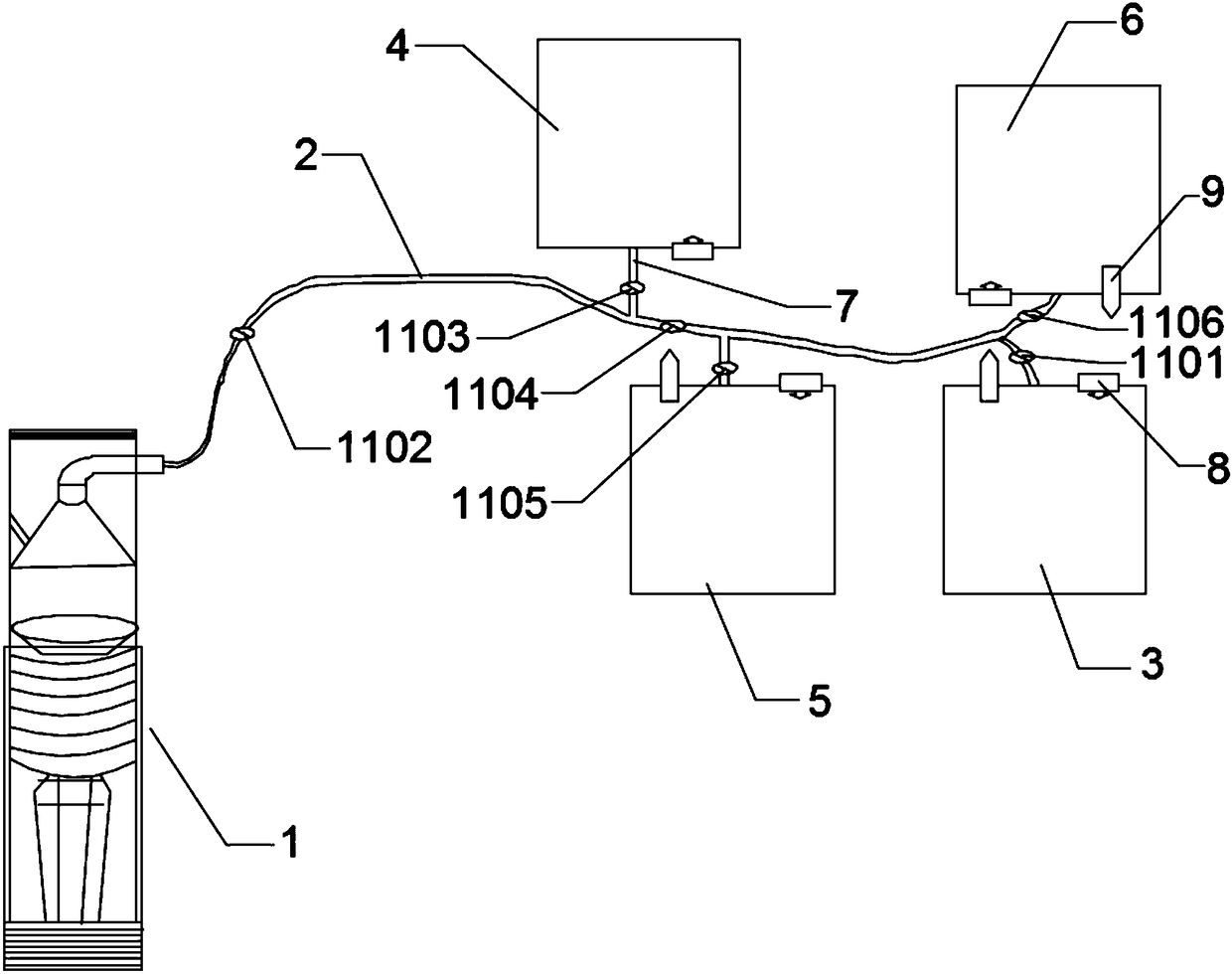
Five-port blood separation chamber and methods of using the same
Systems and methods are provided for separating blood into two or more separated blood components. The system includes a blood separation chamber with a single stage having five ports connected thereto. The five ports include a blood inlet port, a red blood cell outlet port, a platelet-rich plasma outlet port, a platelet-poor plasma outlet port, and a buffy coat outlet port. In the single stage, blood may be separated into a variety of components, such as red blood cells and platelet-rich plasma or red blood cells, platelet-poor plasma, and buffy coat. Depending on the components into which the blood is to be separated, flow out of one or more of the outlet ports may be prevented.
Owner:FENWAL
Method and apparatus for producing platelet rich plasma and/or platelet concentrate
InactiveUS20130233803A1Small amount is easilyOther blood circulation devicesDispersed particle separationBlood plasmaRed Cell
Platelet rich plasma and / or platelet concentrate is prepared by placing whole blood in a first chamber of a sterile processing disposable having two chambers. The processing disposable is subjected to a first centrifugation to separate red blood cells, and the resulting platelet rich plasma supernatant is decanted to the second chamber. The processing disposable is subjected to a second centrifugation to concentrate platelets. A volume of the platelet poor plasma supernatant in the second chamber is removed, and the platelets are re-suspended in the remaining plasma. The second chamber may contain anticoagulant to preclude aggregation of the platelets.
Owner:BLASETTI LOU +1
Sealed-type platelet rich plasma separating assembly and method
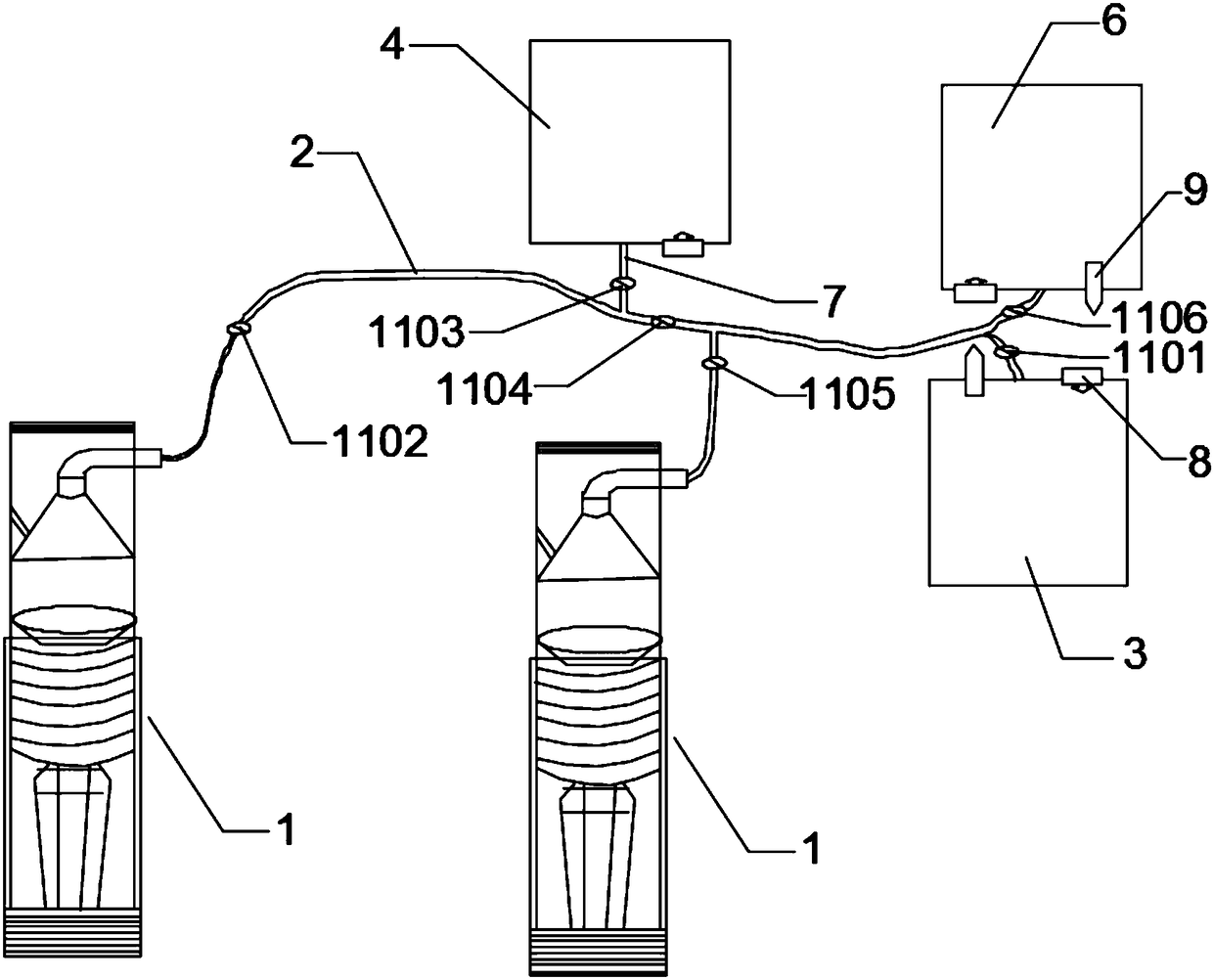
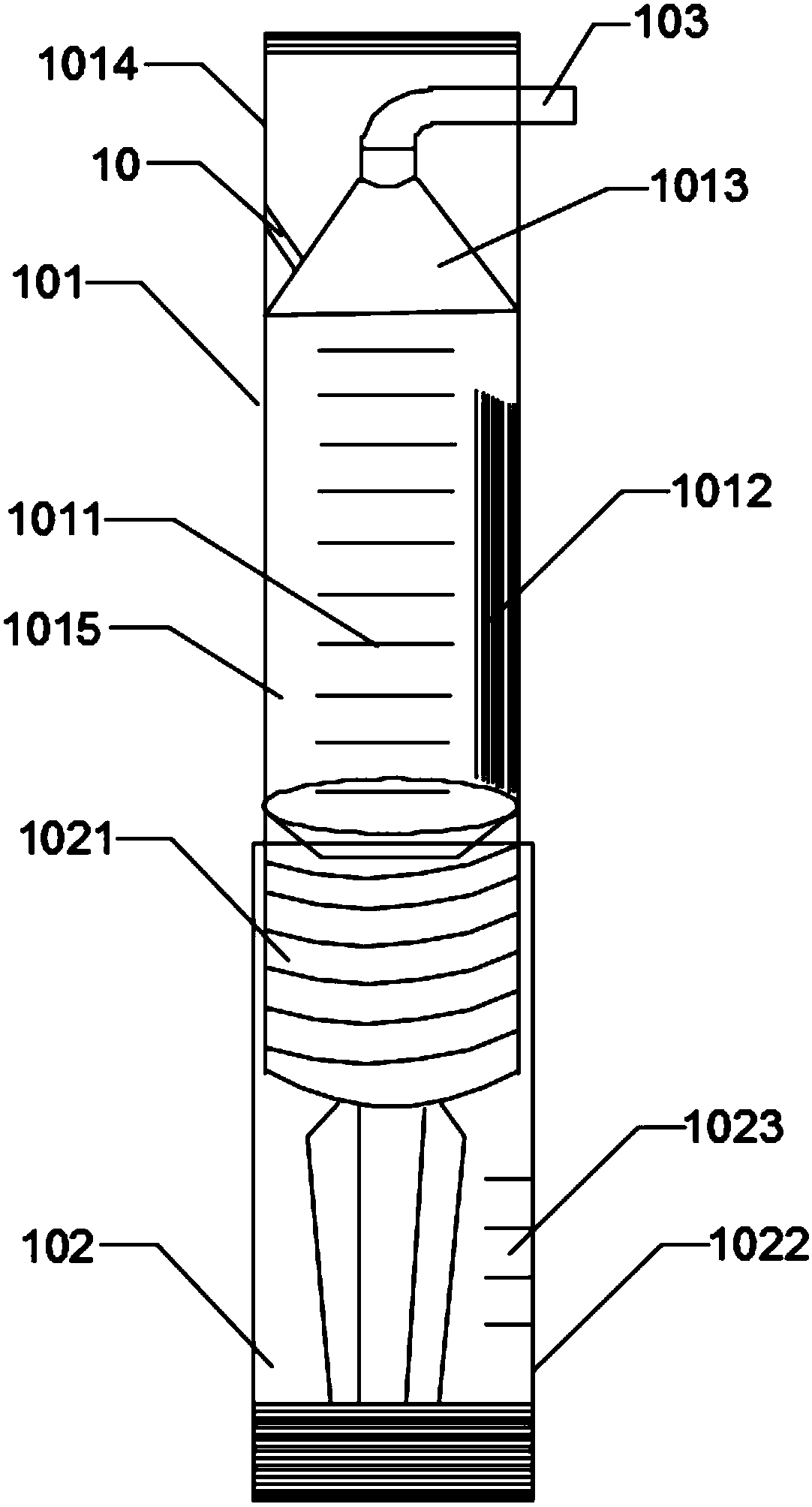
PendingCN108404241AAvoid contamination riskEasy to useOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesPlatelet-poor plasmaBlood plasma
The invention provides a sealed-type platelet rich plasma separating assembly and method. The separating method involves a separating pipe, a platelet collecting device and several collecting devices,wherein the separating pipe is connected with the platelet collecting device through a main collecting pipe; the main connecting pipe is further provided with several branch connecting pipes, and theconnecting devices are communicated with the main connecting pipe through the branch connecting pipes respectively. The separating method comprises the steps of blood drawing, first separating, erythrocyte separating, second separating, platelet poor plasma separating, and platelet rich plasma separating. By means of the sealed-type platelet rich plasma separating assembly and method, the risk that blood is exposed and contaminated in the separation and preparation process is avoided; not only is the platelet recycling rate high, but also the sealed-type platelet rich plasma separating assembly is safe and convenient to use.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GENERAL HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MILITARY COMMAND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com