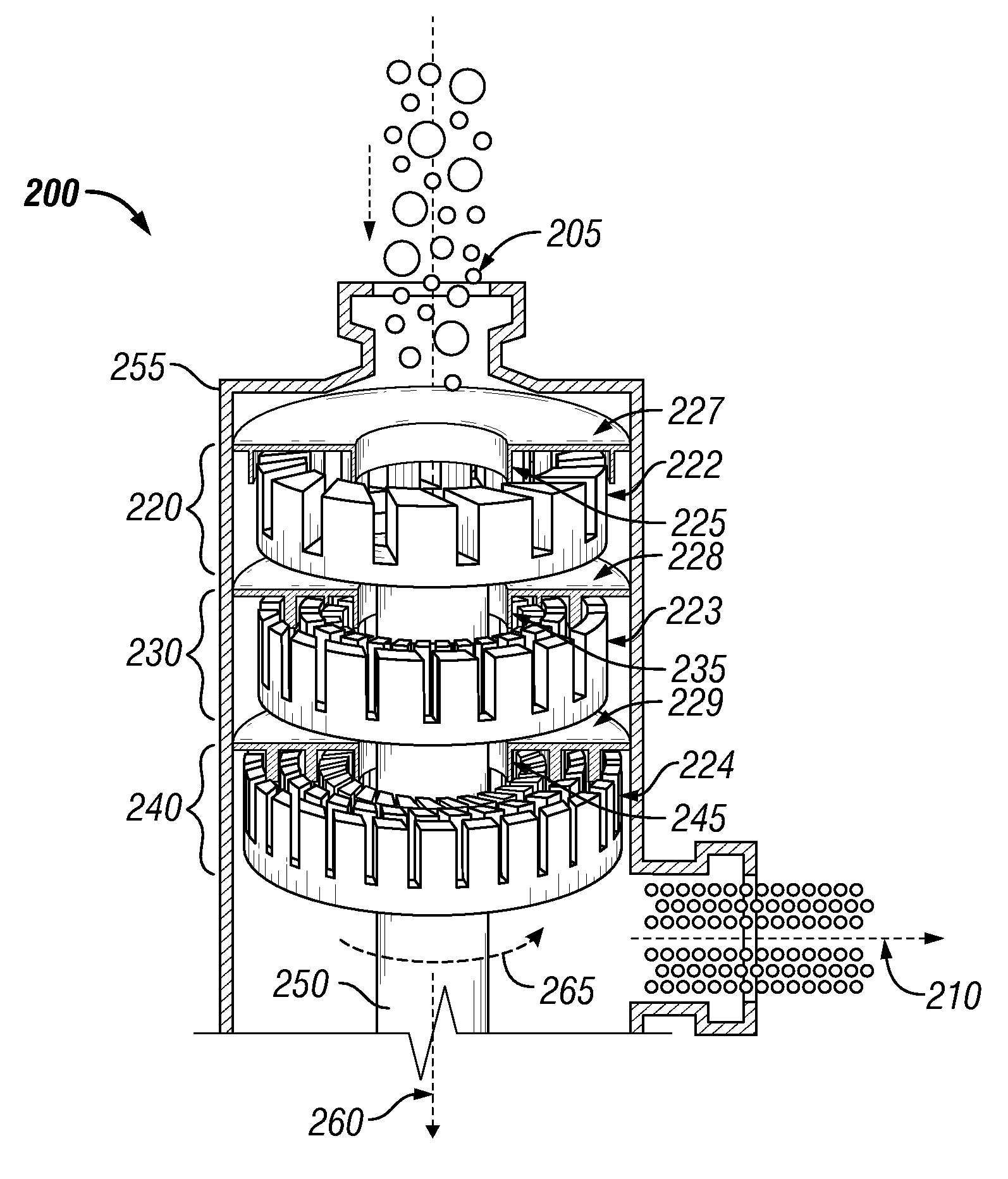
Patents
Literature
284results about How to "Increase shear" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
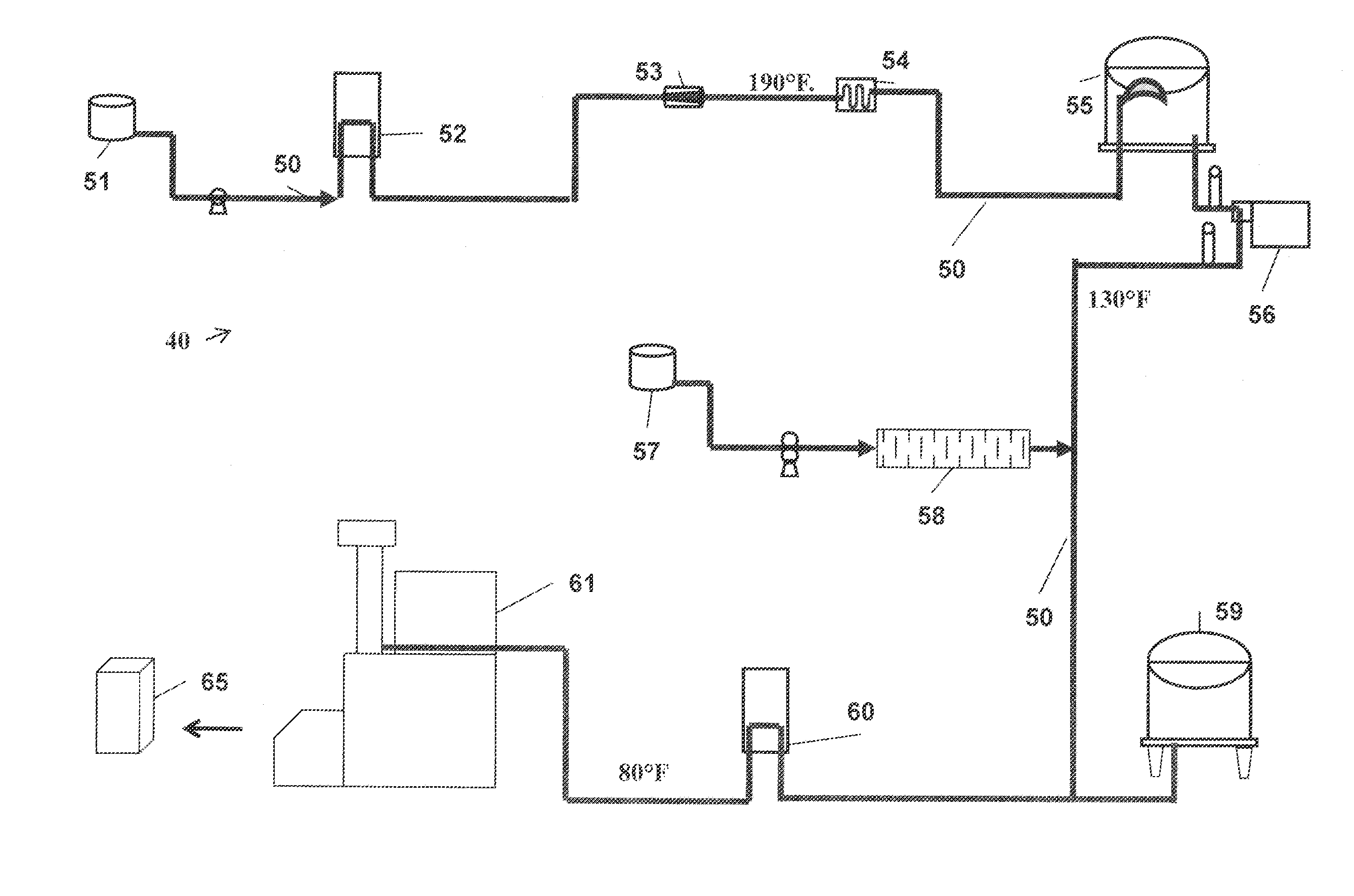
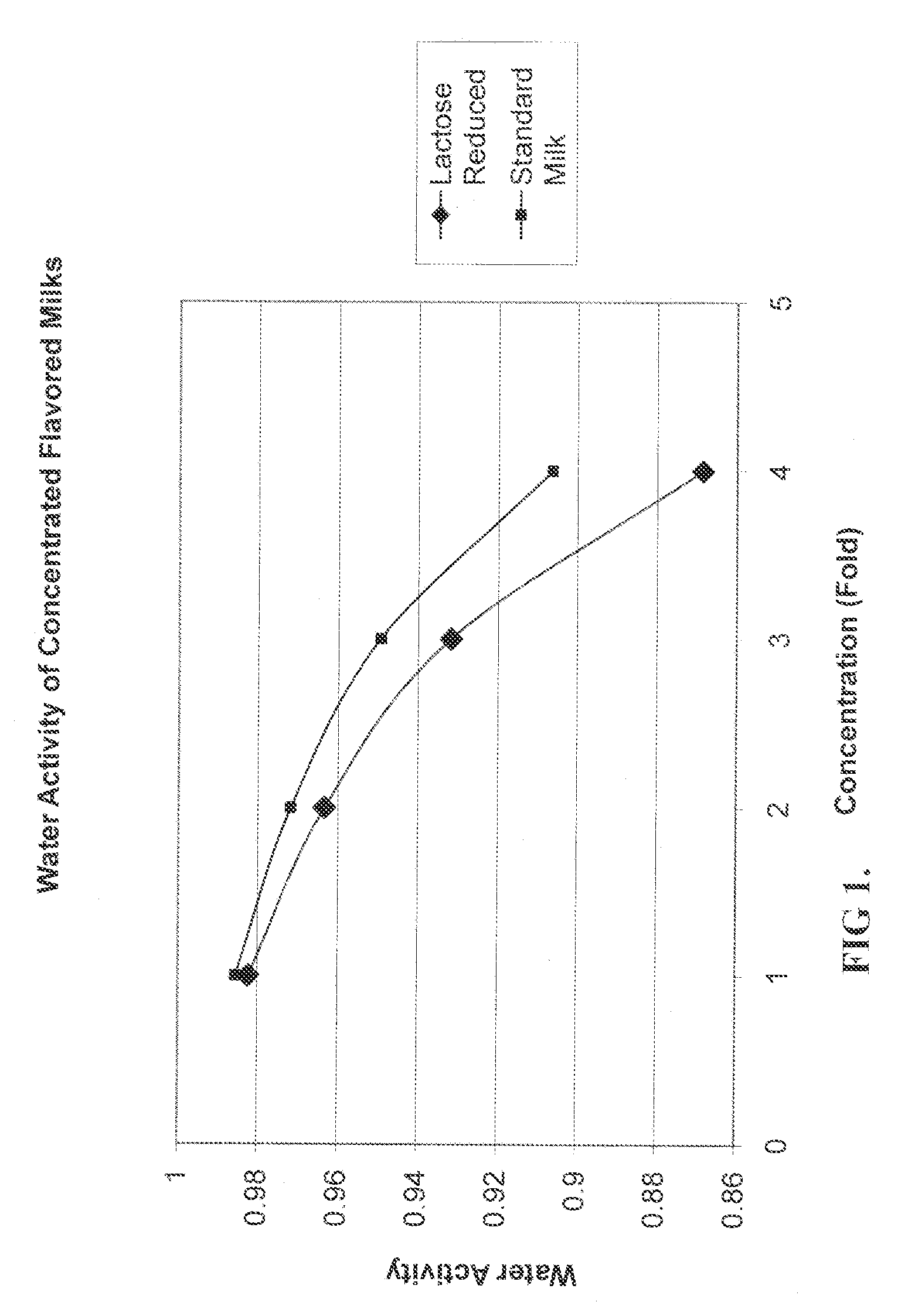
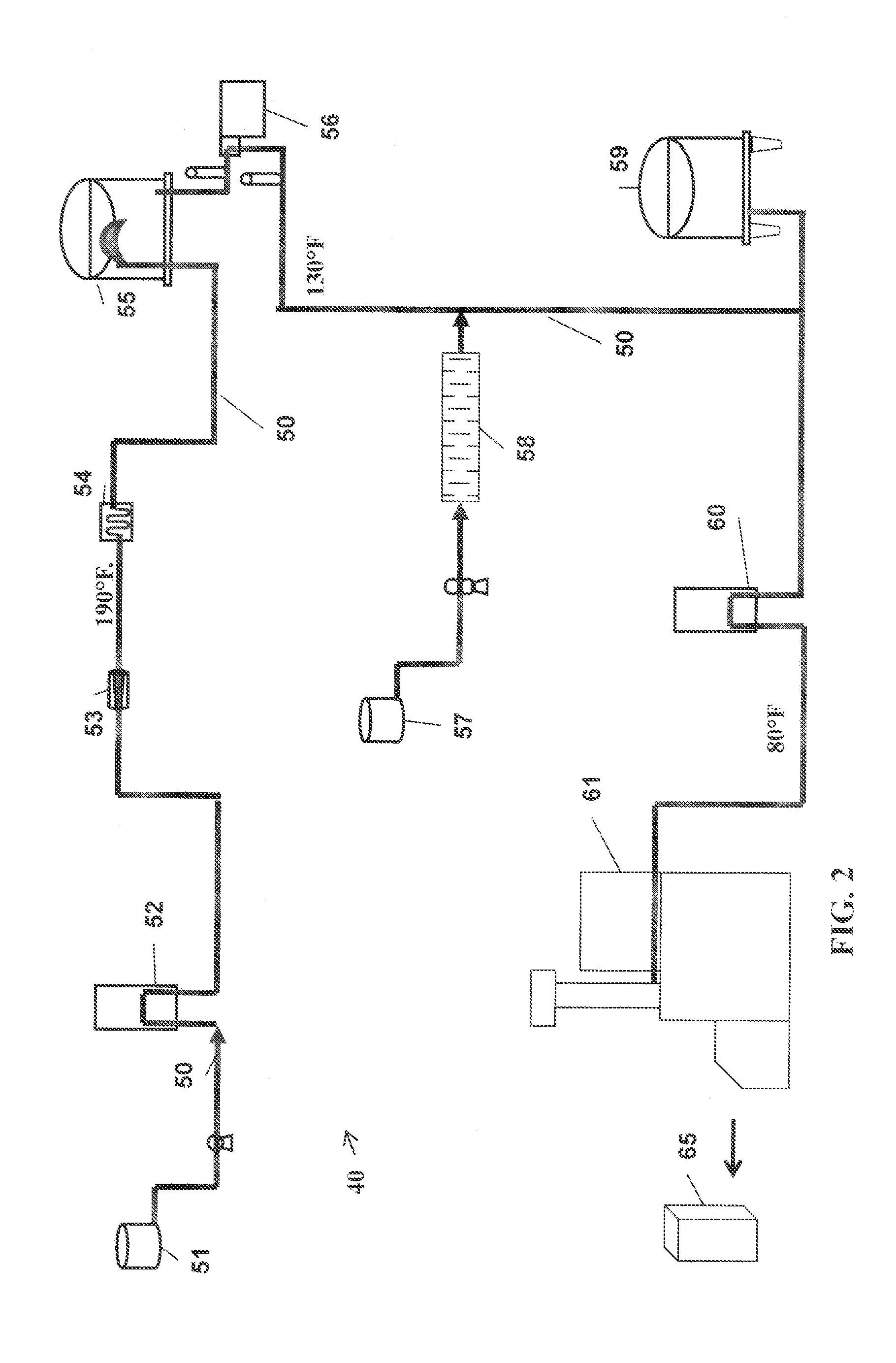
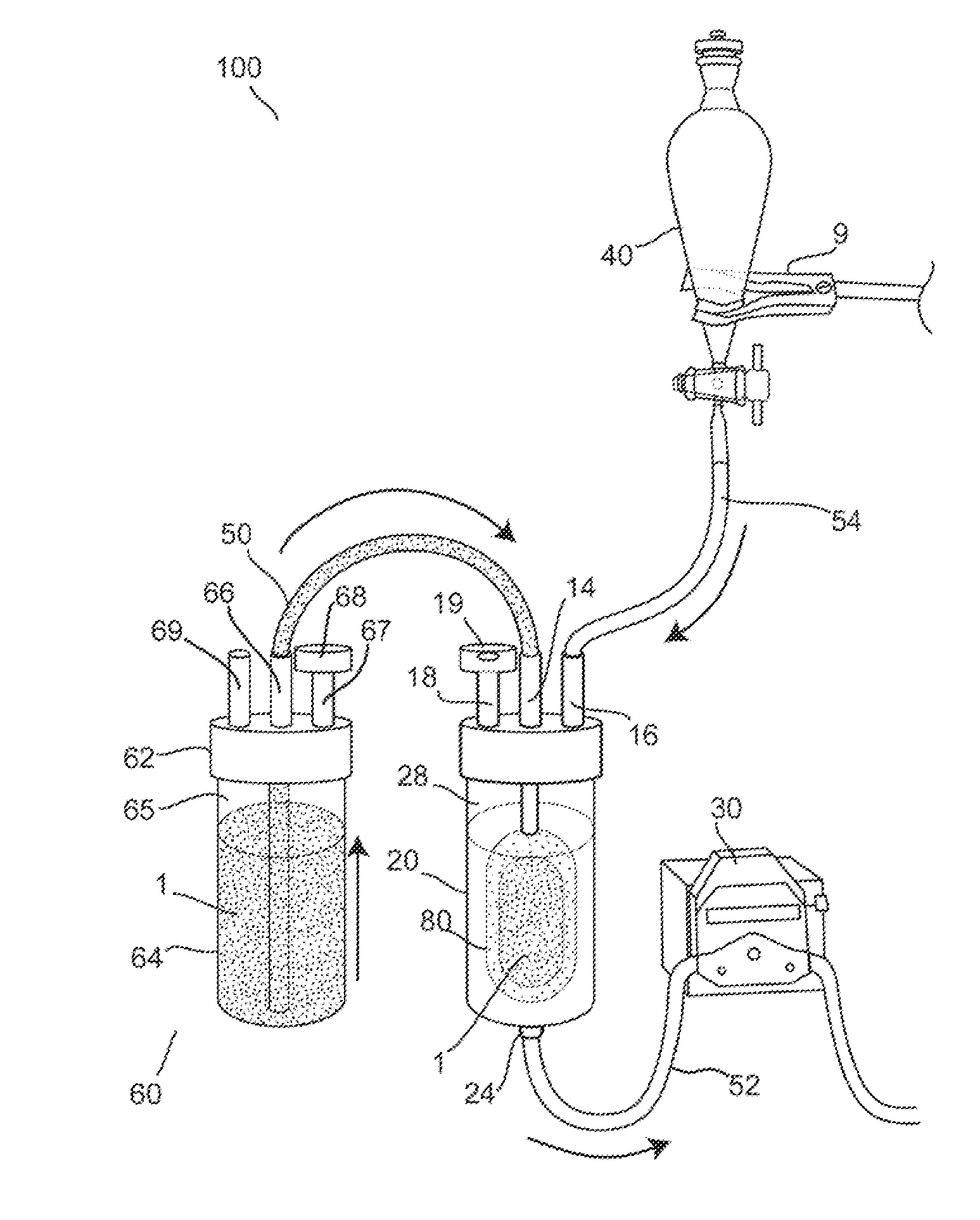
Process For Making A Shelf-Stable Milk Based Beverage Concentrate
InactiveUS20090317514A1Minimizes thermal exposureLower water activityMilk preparationMilk preservationLactaseWater activity
A concentrate, system and low-temperature process for preparing a shelf-stable milk concentrate that does not require ultra-high temperature thermal processing for control of the microbiology of the product is disclosed herein. The method preferably incorporates aseptic technology and the enzymatic reduction of lactose to control water activity. The method preferably includes the enzymatic conversion of the lactose in the milk to its component sugars glucose and galactose, which preferably changes the colligative properties of the concentrate, decreases the amount of free water, and reduces the osmolarity.
Owner:DAIRYVATIVE TECH
Surface sampler for bioterrorism particle detection
ActiveUS8677840B2Determine effectivenessFocusWithdrawing sample devicesMicroorganismBiological particles
Novel rapid, efficient sample collection systems, devices and methods are disclosed which remove and capture particles, and especially potential bioterrorism particles from surfaces into a liquid sample. The devices were developed primarily for obtaining samples of biological contamination from environmental surfaces. Biological particles, as described here, include bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms, and other particles of biological origin including nucleic acids, proteins, and toxins.
Owner:INNOVAPREP
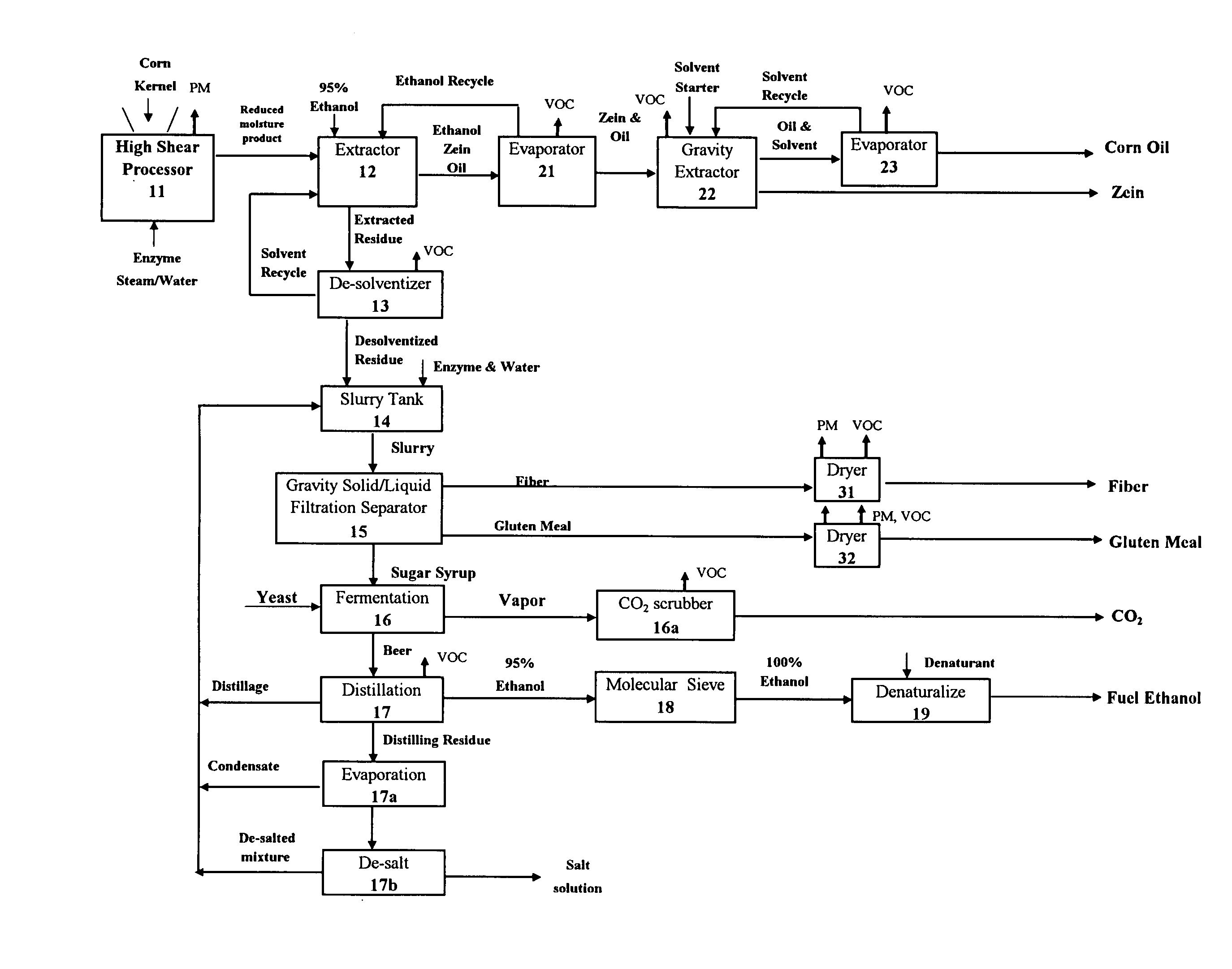
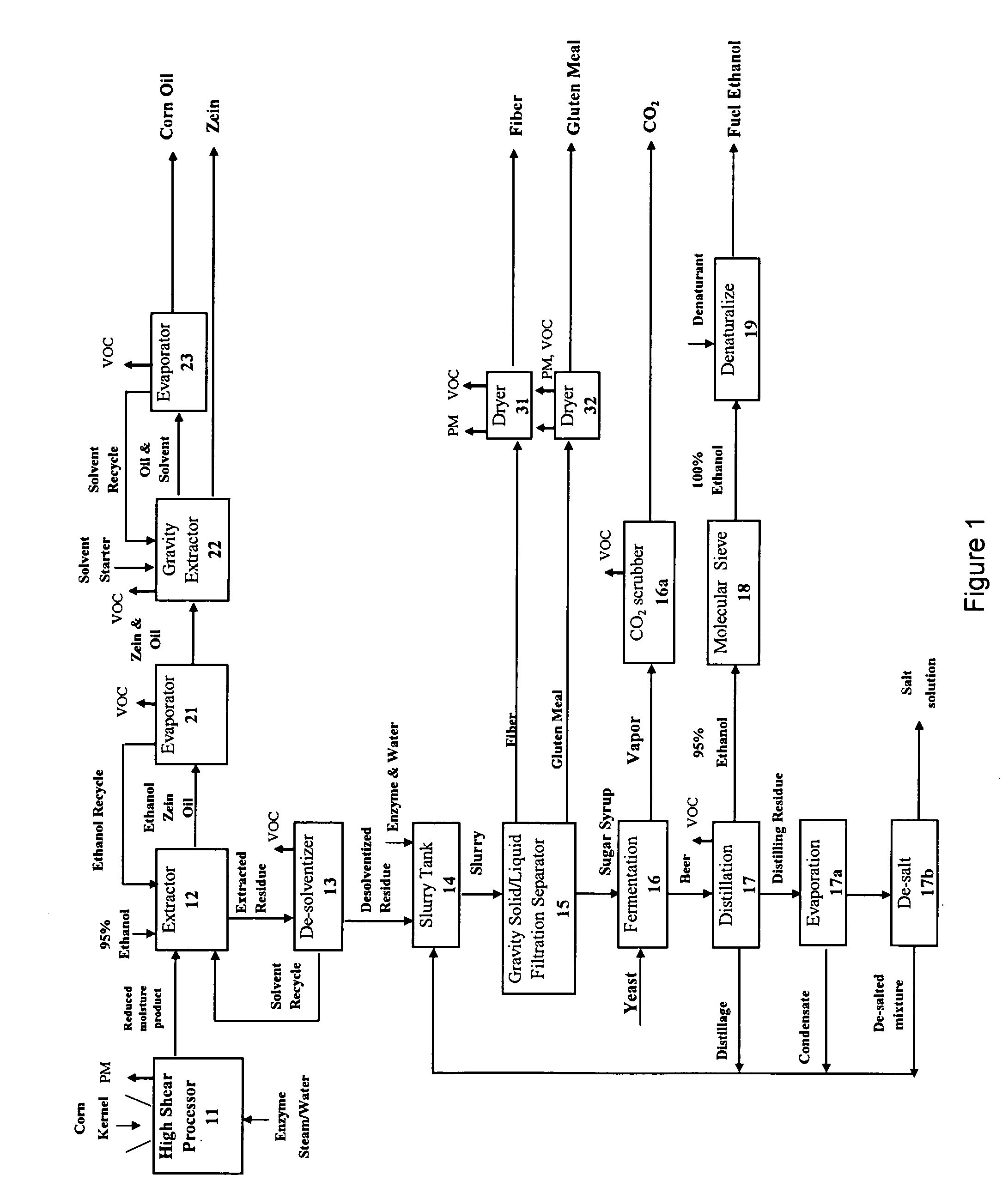
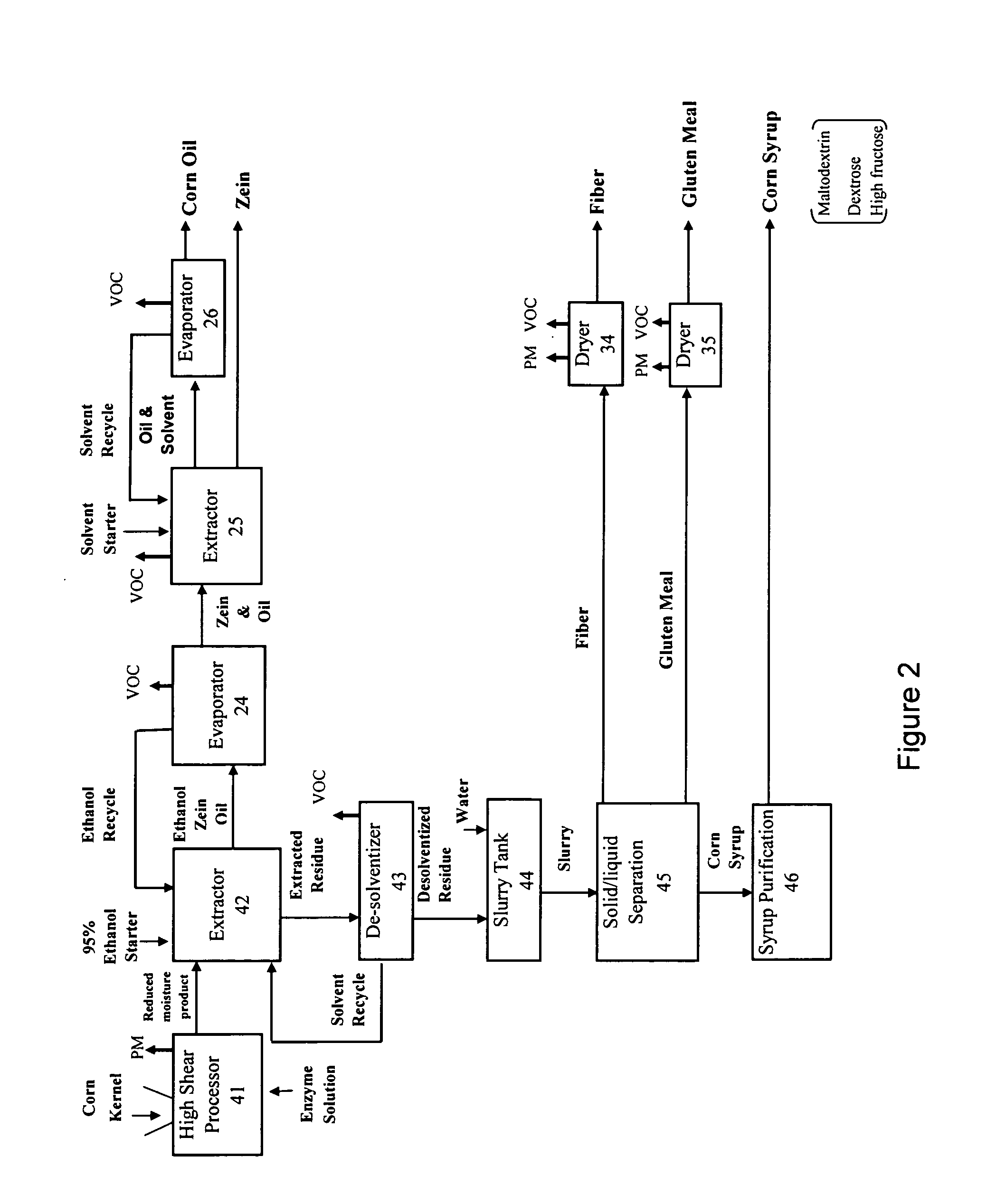
Starchy material processed to produce one or more products comprising starch, ethanol, sugar syrup, oil, protein, fiber, gluten meal, and mixtures thereof
InactiveUS20070014905A1Reduce processIncrease shearProtein composition from eggsConfectioneryFiberFood grade
The invention provides a method and system of processing a starchy material that can advantageously produce ethanol, sugar syrup, or starch as the chief products along with food-grade co-products such as, but not limited to oil, protein, fiber, and gluten meal. The invention can apply such a force to a starchy material that is at a superambient temperature with a high shear processor to mill, mix, and gelatinize some of the starch. A liquefaction enzyme can be introduced into the high shear processor to liquefy the processed product. The moisture content of the processed starchy material can be reduced, which preferably occurs in the high shear processor. Some of the co-products such as the oil, protein, fiber and gluten meal can be separated prior to the sugar syrup purification or ethanol fermentation steps.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Cationic Surfactant Systems Comprising Microfibrous Cellulose
ActiveUS20080146485A1Increase shearEnhanced mixing processCosmetic preparationsCationic surface-active compoundsParticulatesCellulose
Cationic surfactant systems, using microfibrous cellulose to suspend particulates therein, are described. Methods of making these systems are also described.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
A 3D printing polymer material and a preparing method thereof
ActiveCN105524399AGood dimensional stabilityGood bridgingAdditive manufacturing apparatusAntioxidantTactile sensation
The invention relates to the technical field of resin composition preparation and particularly relates to a 3D printing polymer material with special beautifying effects and a preparing method thereof. The polymer material comprises following raw materials by weight: 60-90 parts of matrix resin, 4.0-10 parts of a compatilizer, 0-30 parts of an inorganic filler, 0.3-2.0 parts of white oil, 0.4-0.6 part of an antioxidant, 0.5-1.0 part of a processing auxiliary agent and 1.0-5 parts of a toner. The polymer material is good in dimension stability, good in bridging effect and excellent in draping performance. The appearance of the polymer material is strong in metallic tactile sensation and pearl effects. The polymer material has one or a plurality of effects selected from heat discoloration, photochromic effects, effects of color changing when sensing water, and the like, and is of great significance for promoting material diversification and functionalization of 3D printing. The preparing method is simple, improves shearing and dispersion for the inorganic filler and the toner to the utmost, and improves properties of the polymer material.
Owner:SILVER AGE ENG PLASTICS DONGGUAN
Methods and Devices for Improved Aeration From Vertically-Orientated Submerged Membranes
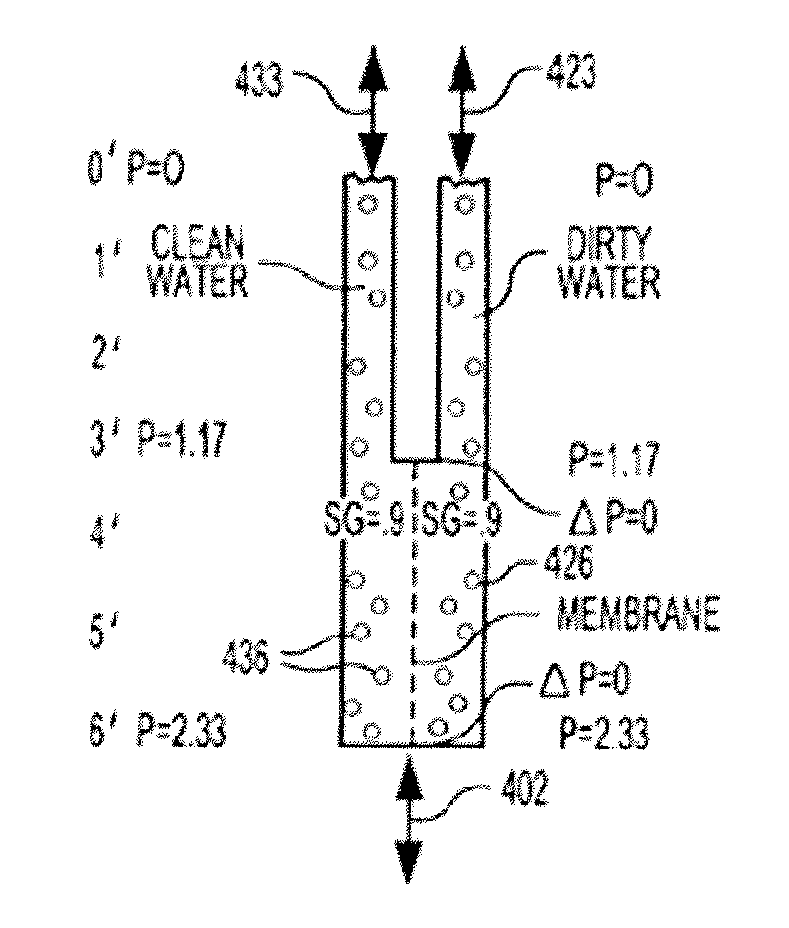
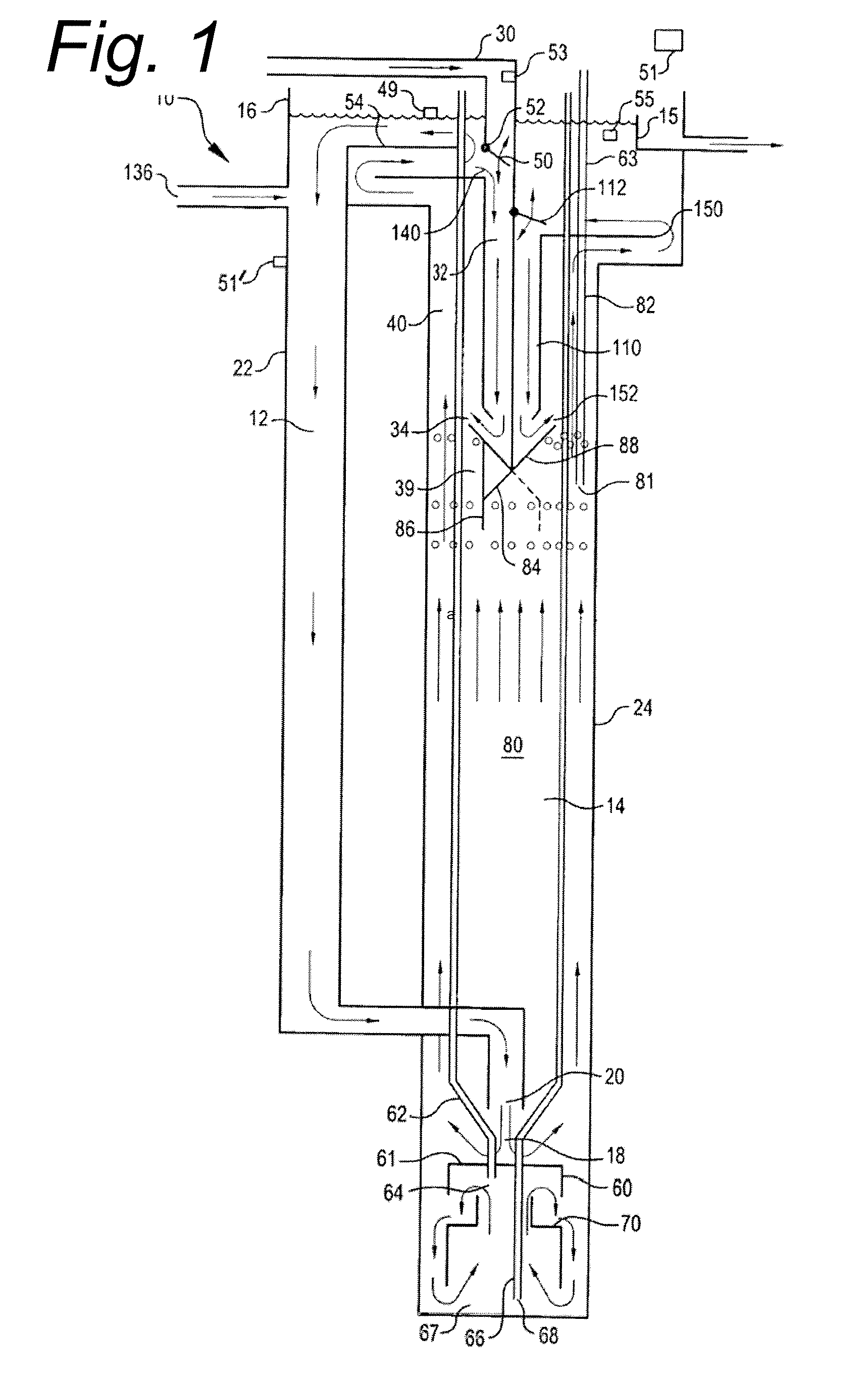
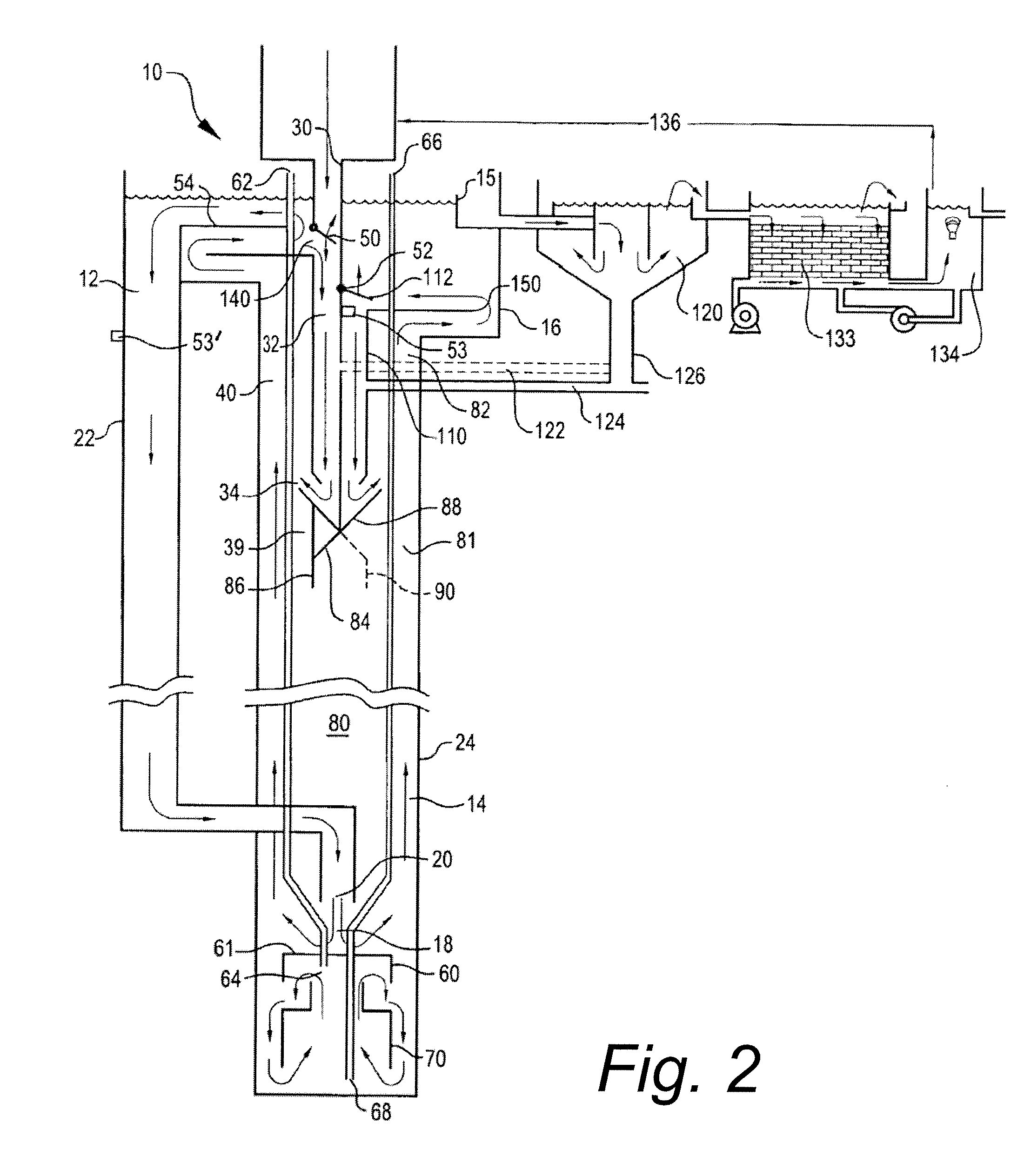
InactiveUS20080017558A1Increase aerationImprove clippingSludge treatmentUltrafiltrationAeration rateMembrane fouling
Submerged gas diffuser assemblies configured to aerate liquid suspensions in reservoirs or deep shafts with enhanced aeration contact patterns and adjustable aeration rates. Aeration contact patterns and rates are varied by the adjusting the spatial configuration of gas permeable membranes, altering the fluid flow patterns around the membranes, manipulating trans-membrane pressures across membranes, varying the sequence of aeration of liquid within the fluid flow patterns, expanding the membrane surface area, and / or by selectively occluding certain portions of membrane surface area of the membrane assemblies. The membrane assemblies are designed to prevent, control, or mitigate membrane fouling and hydro lockup.
Owner:VOST ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Organic recycling with metal addition
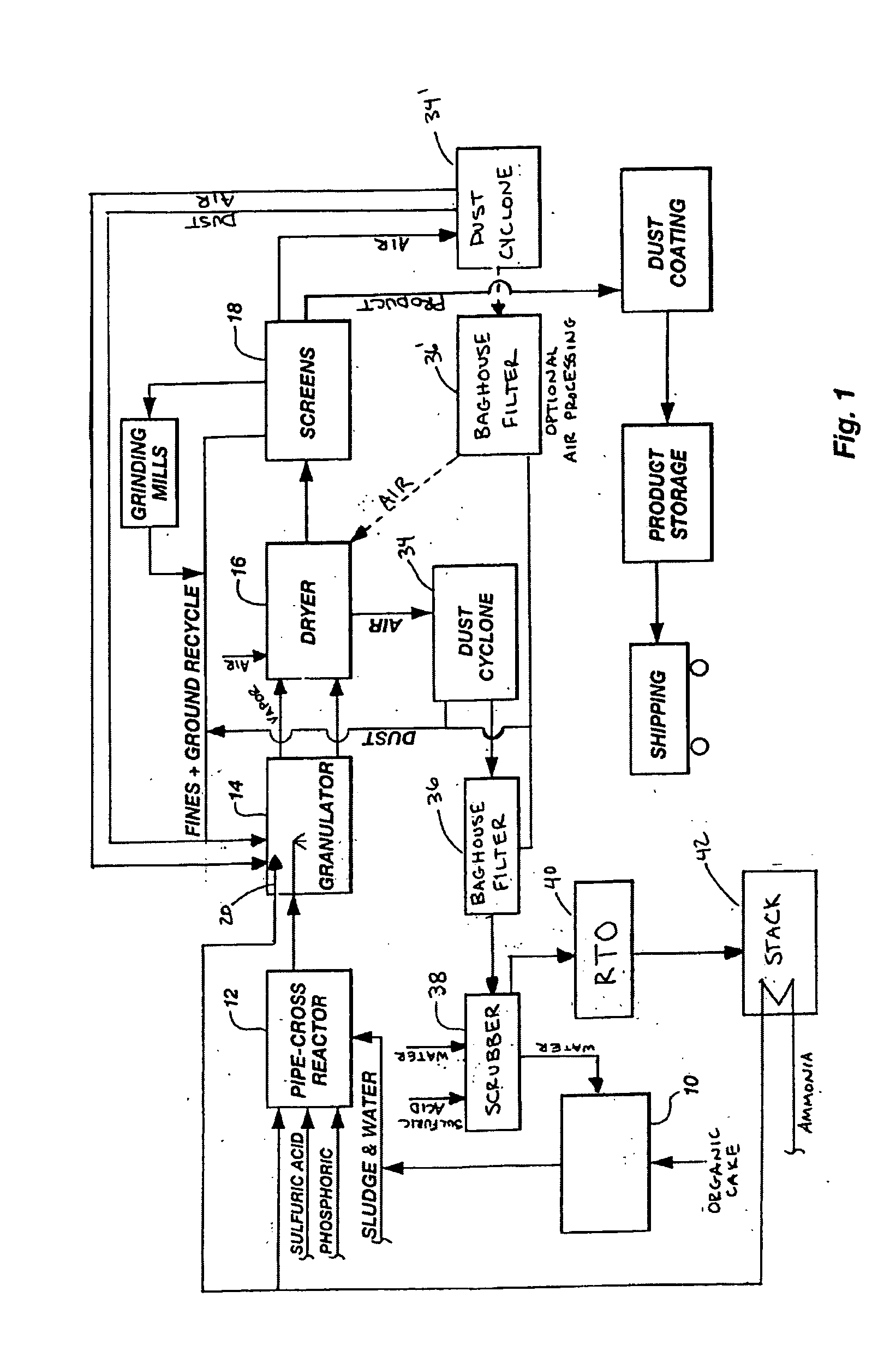
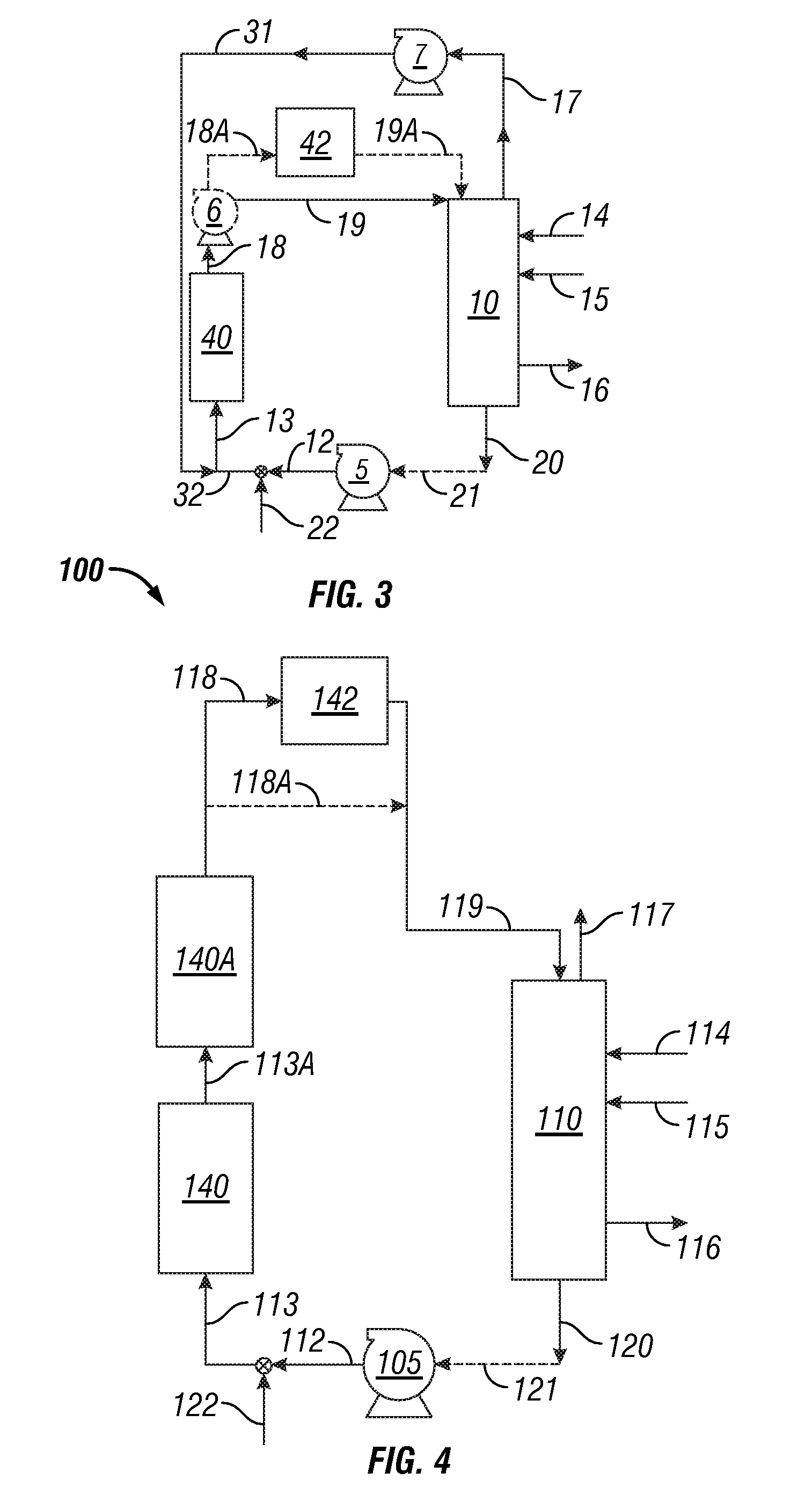
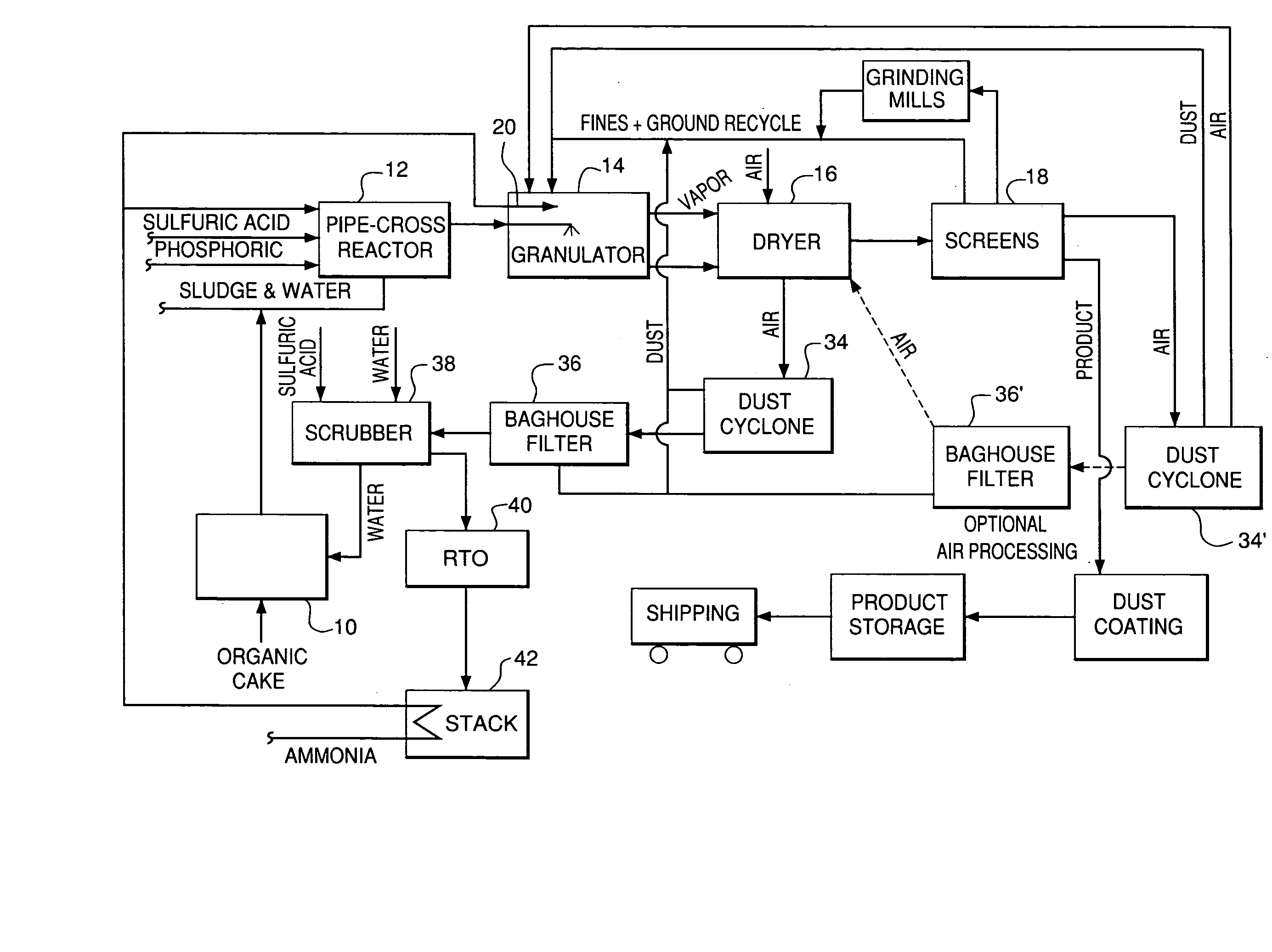
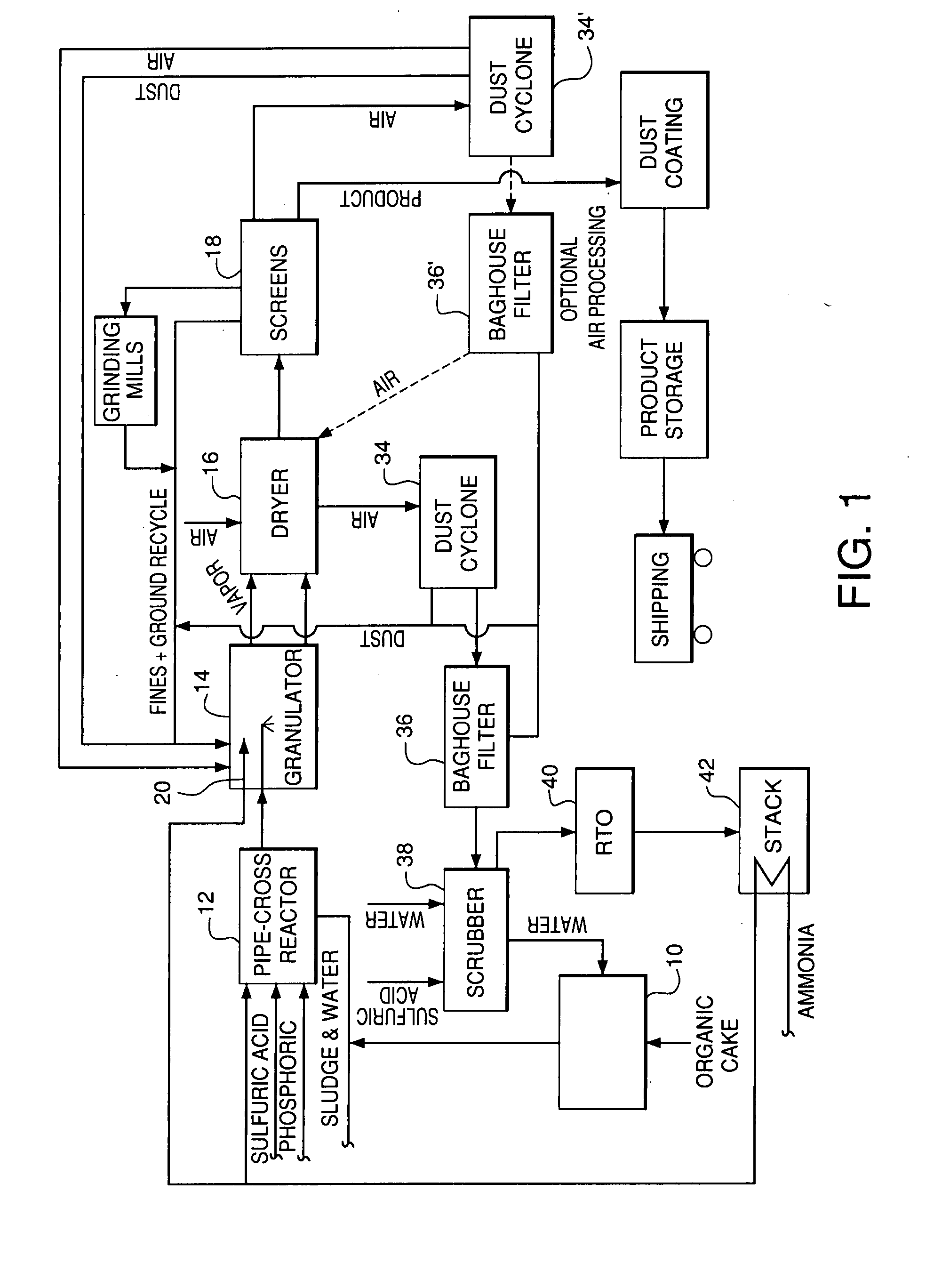
InactiveUS20050039508A1Reduce slurry viscosityAvoid flowAnimal corpse fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSolubilityIron sulfate
The invention is directed to methods for producing a granular nitrogen fertilizer from an organic material comprising adding a metallic salt to said organic material to form a slurry. Preferably the organic material comprises dewatered biosolids and contains water from a scrubber. Metallic salts that can be used comprise a salt of iron, zinc, or a mixture thereof. Preferred iron salts comprises ferric sulfate or ferric oxide, and preferred zinc salts comprises zinc sulfate or zinc oxide. Preferably, the metallic salt is mixed with an acid such as sulfuric acid to form an acidified metal salt. Slurry pH ranges from approximately 2-2.5. The acidified metal salt is added to the organic material in sufficient quantity to lower viscosity of the slurry such that the resulting fluid does not hinder fluid flow during operation. When the metallic salt comprises acidified ferric sulfate or ferrous sulfate, sufficient iron can be present to produce a fertilizer product with 0.1 weight percent to 10 weight percent iron sulfate calculated on a dry weight basis. The invention is also directed to fertilizer products made by the methods of the invention. Preferred products are granules and the metallic salt increases product hardness. Fertilizer granules preferably contain metal that is bioavailable to a plant when used as a fertilizer. Solubility of the metal of the product in water is enhanced, and the product is low staining.
Owner:UNIFIED ENVIRONMENTAL SERVICES GROUP +1
Systems and methods for filtration
InactiveUS20120298578A1Reduce foulingImprove water qualityMaterial nanotechnologyGeneral water supply conservationMicroorganismFiltration membrane
Filtration systems (40) utilize a pre-treatment method to cause scale formation to occur on particles (94) in the fluid stream (96) rather than on the filter surface and may also destroy microorganisms in the fluid stream. More specifically, but not limited to, a filtration device can be a filtration membrane, such as spiral wound filtration membrane (60), that utilizes an open feed spacer (80), such for example an embossed or printed pattern on the membrane, to create a thin feed spacer channel which replaces a conventional feed spacer mesh material. System (40) further utilizes a treatment device (54) to enable a pulsed power, magnetic, electro-magnetic, electro-static, or hydrodynamic fluid treatment scheme to condition particles in the fluid stream (96) such that scale forming elements precipitate (94) on to the particles in the fluid stream rather than on the filtration surfaces.
Owner:AQUA MEMBRANES +1
Expanded products with high protein content
ActiveUS20060210695A1High protein contentIncreased strengthFood shapingVegetable proteins working-upProtein isolateProtein content
High protein expanded products are produced by extrusion with unique blends of ingredients, such as wheat protein isolates, modified wheat starch, salts, gums and moisture. The mixture is extruded in a twin-screw extruder with the temperatures in the range of 50 to 140° C., screw speeds of 250 to 450 rpm and with a back pressure of 350 to 1200 psi for different recipes. A range of expanded wheat crisps and other expanded products with wheat protein contents ranging from 30 to 90% are obtained from this process. The expanded products have good cell structure with varying cell sizes when viewed under a microscope. This process can be used to develop a varied range of products such as, wheat crisps, wheat curls, wheat loops etc. The products may be used in nutritional or health bars and other comestible having a high protein and low carbohydrate content.
Owner:MGPI PROCESSING
Method for preparing graphene
InactiveCN102491314AImprove permeabilityImprove diffusion abilityGrapheneBulk chemical productionCrystal structureHigh pressure
The invention relates to a method for preparing graphene, characterized by carrying out explosion treatment for one or more times on carbonaceous materials by using fluids under supercritical state. By using the fluids under supercritical state to penetrate and dissolve the carbonaceous materials and having the aid of sudden release of high pressure hot steam, the shearing and peeling between layers of the carbonaceous materials are promoted to realize the preparation of graphene. Compared with using ball milling, mechanical peeling, high temperature and high pressure to prepare graphene in the prior art, the invention has the advantages of mild process conditions (low pressure), short process time, large area of prepared graphene, and complete preserved crystal structure. According to the invention, the content of graphene which comprises less than 5 layers is higher than 90 %, and the batch production of graphene powder products can be really realized.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
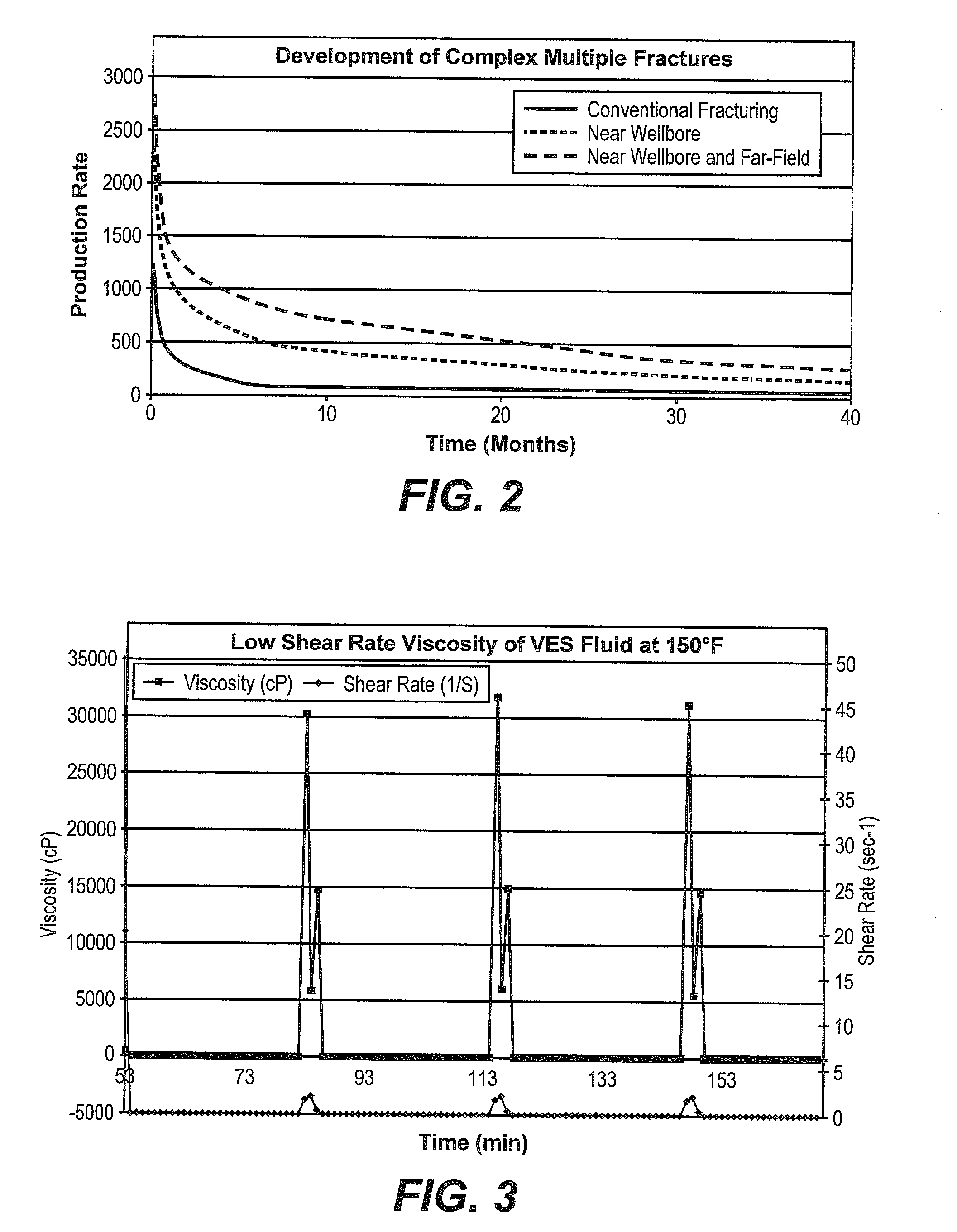
Method of Increasing the Permeability of a Subterranean Formation by Creating a Multiple Fracture Network
InactiveUS20140014338A1Wider distribution fracturing patternIncrease shearFluid removalDrilling compositionGeomorphologyFracturing fluid
The stimulated rock volume (SRV) of a subterranean formation may be increased by pumping viscous fracturing fluid into the formation in a first stage to create or enlarge a primary fracture, decreasing the pumping in order for the fluid to increase in viscosity within the primary fracture, and then continuing to pump viscous fluid into the formation in a second stage. The fluid pumped into the second stage is diverted away from the primary fracture and a secondary fracture is created. The directional orientation of the secondary fracture is distinct from the directional orientation of the primary fracture. The fluid of the first stage may contain a viscosifying polymer or viscoelastic surfactant or may be slickwater.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
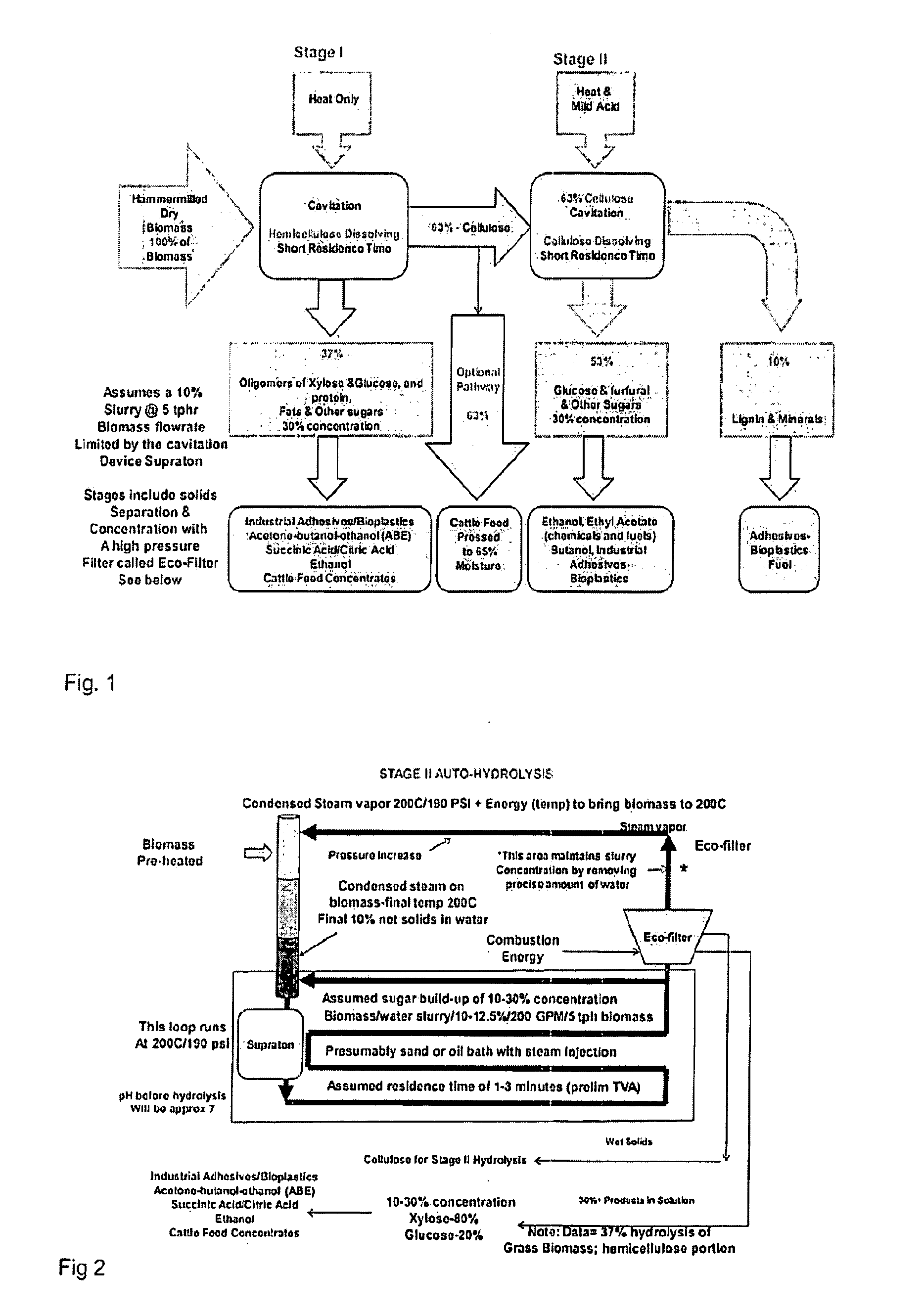
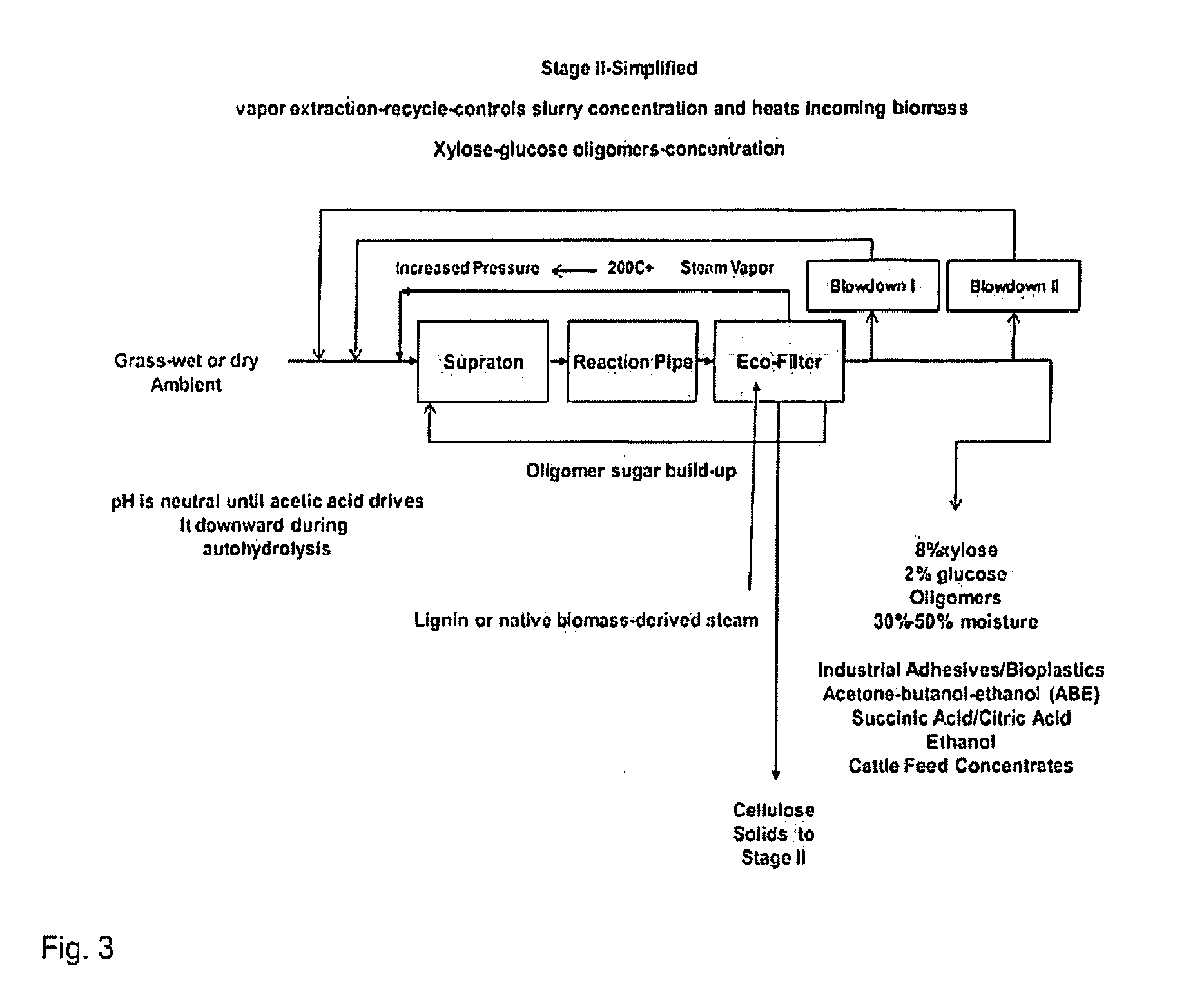
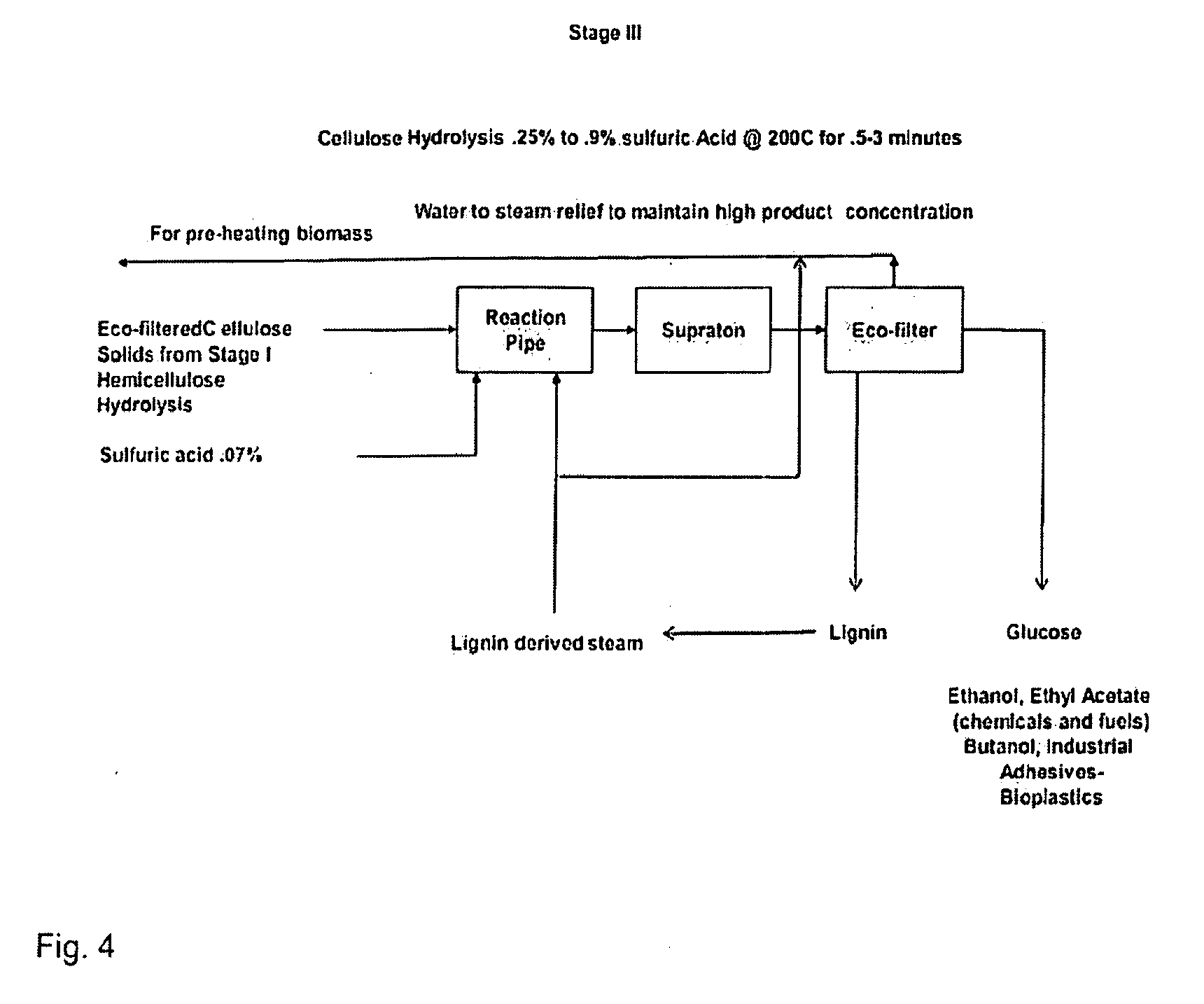
Advanced biorefinery process
The present invention is a method for refining native biomass to extremely fine and highly disrupted particles using high shear and / or cavitation in combination with high temperature and high or low pH conditions which dissolve biomass to a high percentage. The method of the present invention results in a high percentage of hydrolysis, in many cases near theoretical levels, in short residence times while minimizing inputs over other methods, using low chemical inputs, and optionally with no chemical inputs in certain stages compared to existing processes. The method of the present invention also uses minimal electrical energy inputs and conserves heat energy within the process and reduces equipment requirements while producing concentrated products.
Owner:RA ENERGY CORP
Assembly concrete new type pillar and beam structure and assembly connecting method
InactiveCN104727439AReduce in quantityReliable connection force transmissionBuilding material handlingRebarPrecast concrete
The invention relates to the field of assembly concrete buildings, in particular to an assembly concrete new type pillar and beam structure and an assembly connecting method. Assembly concrete new type pillars and an assembly concrete new type beam can serve as pillars and a beam applied to the assembly concrete buildings. The assembly concrete new type pillar and beam structure comprises a prefabricated pillar and prefabricated beam structure, and each prefabricated pillar comprises a prefabricated side pillar and a prefabricated center pillar. Grouting grooves are formed in the top and the bottom of each prefabricated pillar, and the connected grouting grooves are grouted with a grouting material to achieve equal-shearing-strength connection between the prefabricated pillars; as beam steel bar penetrating holes are reserved in the prefabricated pillars, prefabricated beam steel bars can directly penetrate through the prefabricated pillars to be connected with the prefabricated pillars; as steel poles provided with threads at the ends are pre-buried in the prefabricated beam to transmit shearing force and pull force between the prefabricated beam and post-poured concrete, and the steel poles with the threads at the ends can serve as connecting pieces for fixing a prefabricated slab to the prefabricated beam. By the adoption of the method, connection between precast concrete members is more reliable and economical.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Process and catalyst for production of low trans fat-containing triglycerides
InactiveUS20080161588A1Improve product appearanceImprove textureFatty acid hydrogenationFatty acids production/refiningVegetable oilHydrogenation process
Hydrogenated vegetable oil exhibiting superior thermal stability and containing reduced levels of saturates and trans fatty acids are produced using an activated hydrogenation catalyst and / or an improved hydrogenation process incorporating high shear. The use of a high shear mechanical device incorporated into the hydrogenation process as a reactor device is shown to be capable of enabling reactions that would normally not be feasible under a given set of reaction pressure and temperature conditions. For example, the hydrogenation process described herein enables a reduction of hydrogenation time, and operation at lower temperatures than current processes. The resulting hydrogenated vegetable oil is particularly useful in frying, confectionery baking, and other applications where a product with a low trans fat content or higher thermal stability is desirable. The hydrogenated oil produced may comprise less than 10 weight % of trans fatty acids with less than 5 weight % of linolenic acid (C18:3).
Owner:HRD CORP
Organic recycling with metal addition
InactiveUS20080034822A1Reduce slurry viscosityAvoid flowAnimal corpse fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSolubilityIron sulfate
Owner:UNITY FERTILIZER LLC
Flocculation of cell material
InactiveUS6967085B1High shearImproved strengthMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesIonCell material
A process of flocculating microbial cell material from a suspending medium which contains cell material, comprising adding to the suspending medium a first polymeric material which is cationic and has intrinsic viscosity of not more than 2 dl / g, and subsequently or simultaneously adding to the suspending medium a second polymeric material which is cationic or substantially non-ionic and has intrinsic viscosity of at least 4 dl / g, and allowing the cell material to flocculate.
Owner:CIBA SPECIALTY CHEM WATER TRATMENTS
Dispensing pack and machine
Owner:GOOD HUMOR BREYERS ICE CREAM DIV OF CONOPCO
Method for preparing crystal II-type ammonium polyphosphate with distribution of high polymerization degree and narrow molecular weight
ActiveCN101597044AEliminate the effects ofTemperature controlPhosphorus compoundsSolubilityPolymerization
The invention discloses a method for preparing crystal II-type ammonium polyphosphate with distribution of high polymerization degree and narrow molecular weight. The method comprises the following steps: putting phosphorus pentoxide and diammonium phosphate which have equal molar ratio into a malaxator which can accurately control a temperature and heated by conducting oil for mixing; under the protection of inert gas, heating the materials in the malaxator to between 100 and 250 DEG C through the circulatory conducting oil; stopping introducing the inert gas; performing ammonification on the materials and heating the materials under an atmosphere of ammonia gas till the materials are totally molten down; stopping introducing the ammonia gas; after homogenization, introducing the ammonia gas again and heating the materials; throwing a surface treating agent into the malaxator; after material throwing is completed, continuously introducing the ammonia gas, keeping warm and mixing the materials; after reaction is finished, transferring the materials to a closed vessel and reducing the temperature; simultaneously, continuously introducing the ammonia gas till the temperature of the materials is below 100 DEG C; and obtaining a finished product. The method can prepare the crystal II -type ammonium polyphosphate with the distribution of the high polymerization degree and the narrow molecular weight; and the product has the characteristics of uniform granularity shape, small water-solubility, good heat resistance, high polymerization degree, narrow distribution of molecular weight and high crystal II-type purity.
Owner:GUANGDONG JUSHI CHEM CO LTD
Cationic surfactant systems comprising microfibrous cellulose
ActiveUS7888308B2Increase shearEnhanced mixing processCosmetic preparationsCationic surface-active compoundsCelluloseParticulates
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Cellular abrasive article
InactiveUS20030045213A1Quality improvementIncrease shearPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesPolymer sciencePolymer
Abrasive articles abrasive articles (e.g., abrasive wheels) comprised of abrasive agglomerate particles dispersed within cellular polymeric material, and methods of making and using the abrasive articles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Cellular abrasive article
InactiveUS6645263B2Quality improvementIncrease shearPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesPolymer sciencePolymer
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method of making alcohols
InactiveUS20090136392A1Good dispersionImprove solubilityRotary stirring mixersTransportation and packagingSolubilityMean diameter
Methods and systems for the synthesis of alcohol are described herein. The methods and systems incorporate the novel use of a high shear device to promote dispersion and solubility of olefins in water. The high shear device may allow for lower reaction temperatures and pressures and may also reduce reaction time. In an embodiment, a method of making an alcohol comprises introducing an olefin into a water stream to form a gas-liquid stream. The method further comprises flowing the gas-liquid stream through a high shear device so as to form a dispersion with gas bubbles having a mean diameter less than about 1 micron. In addition, the method comprises contacting the gas-liquid stream with a catalyst in a reactor to hydrate the olefin gas and form an alcohol.
Owner:HRD CORP
Bitumen extraction and asphaltene removal from heavy crude using high shear
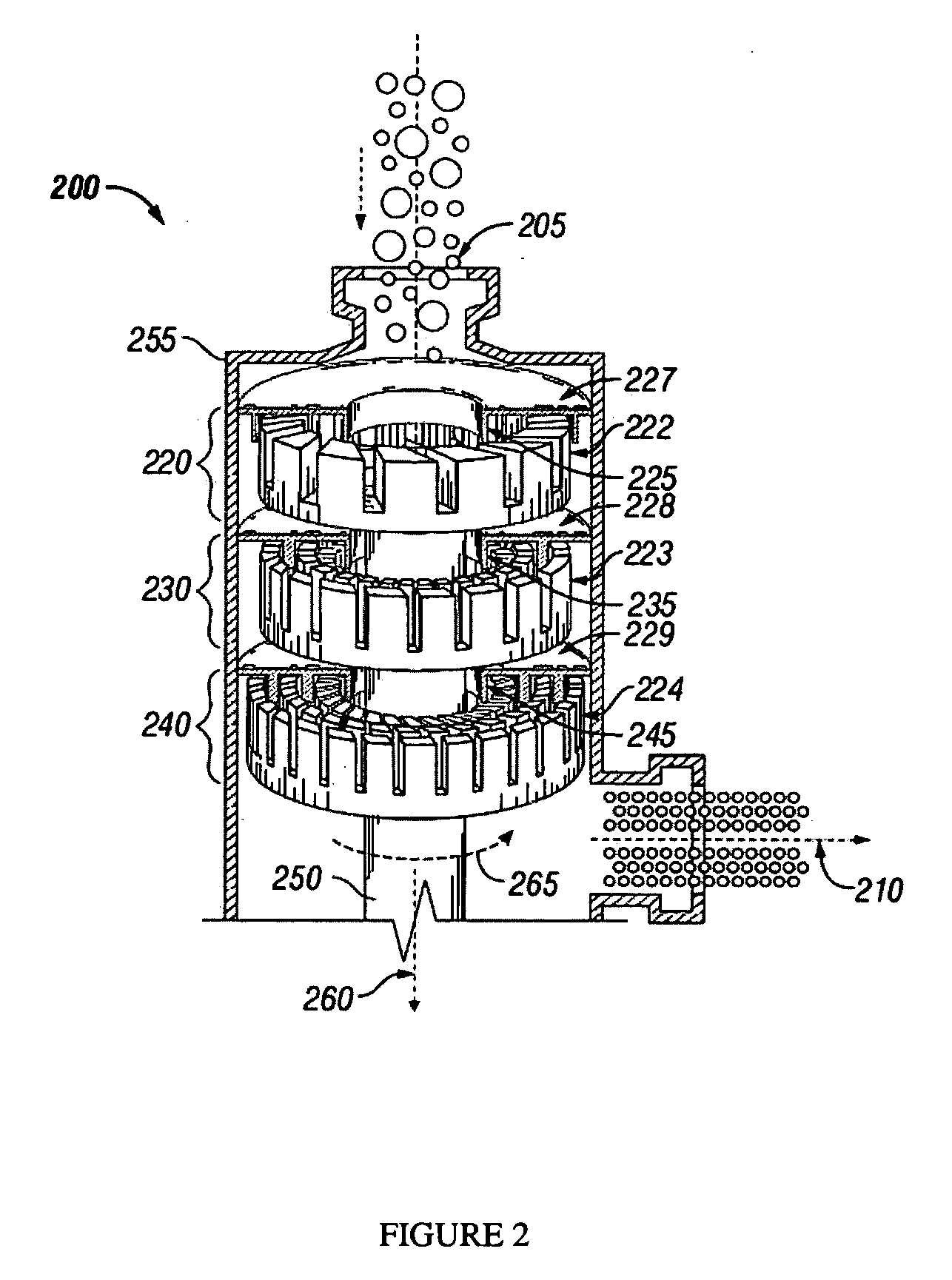
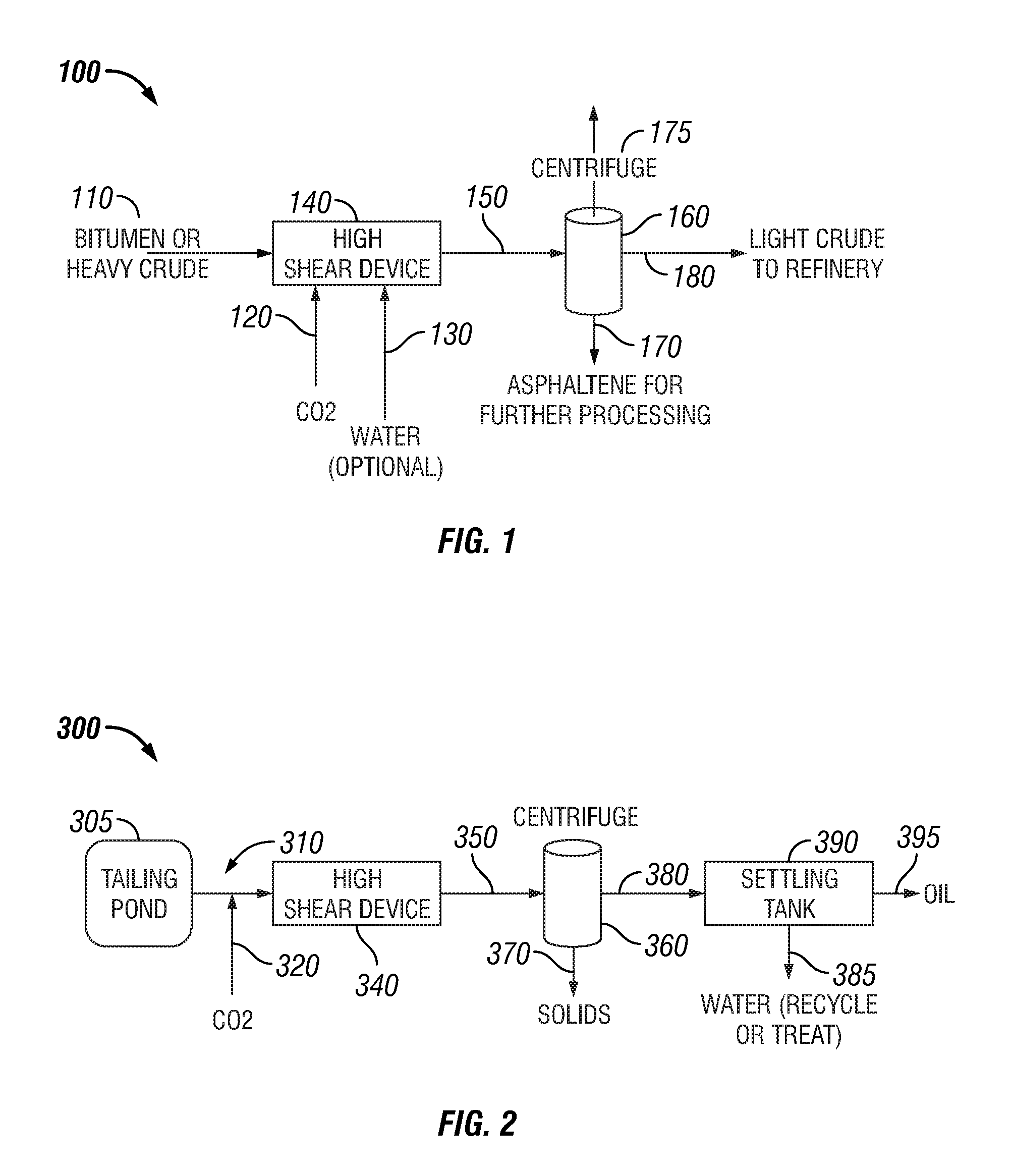
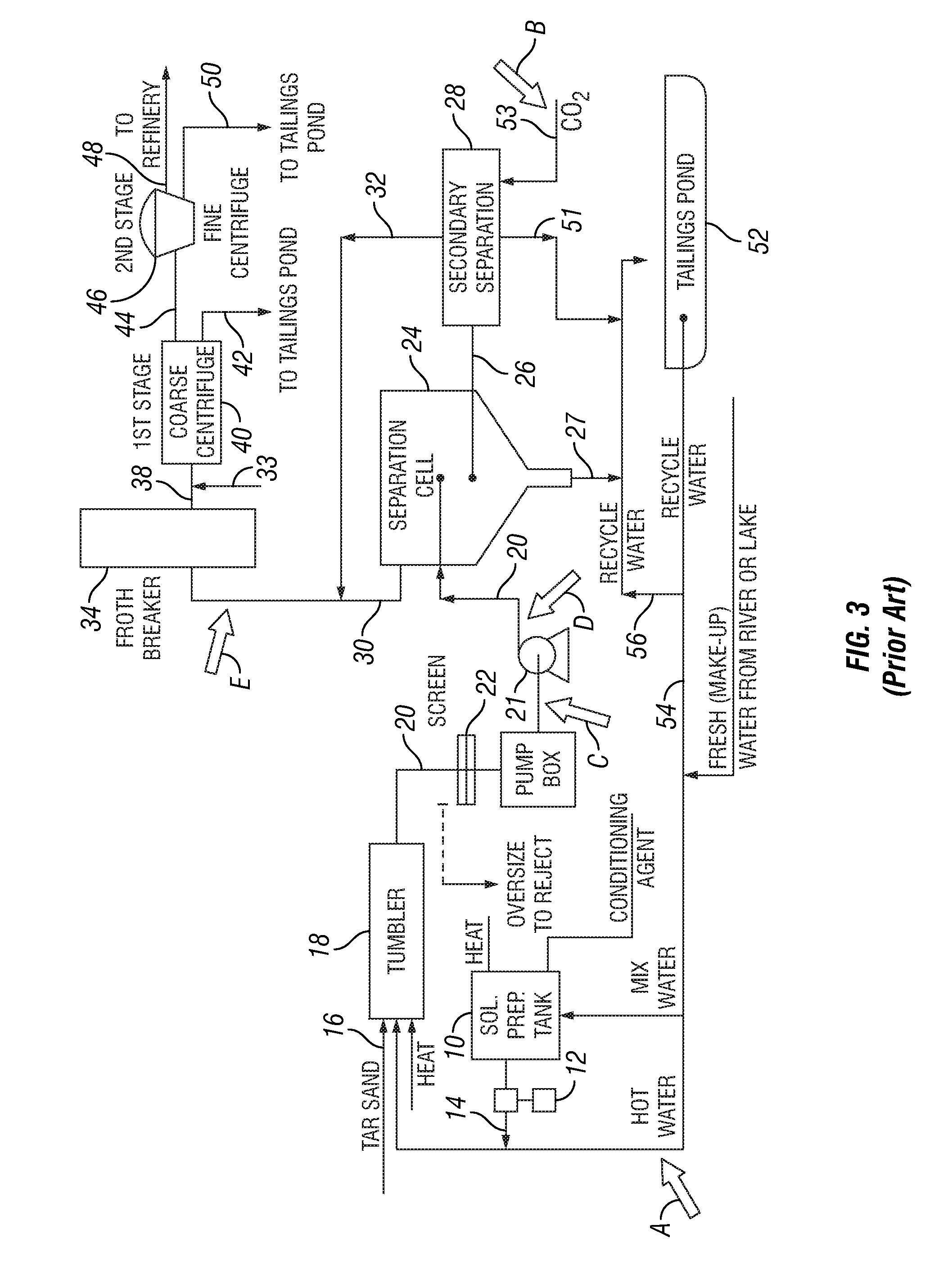
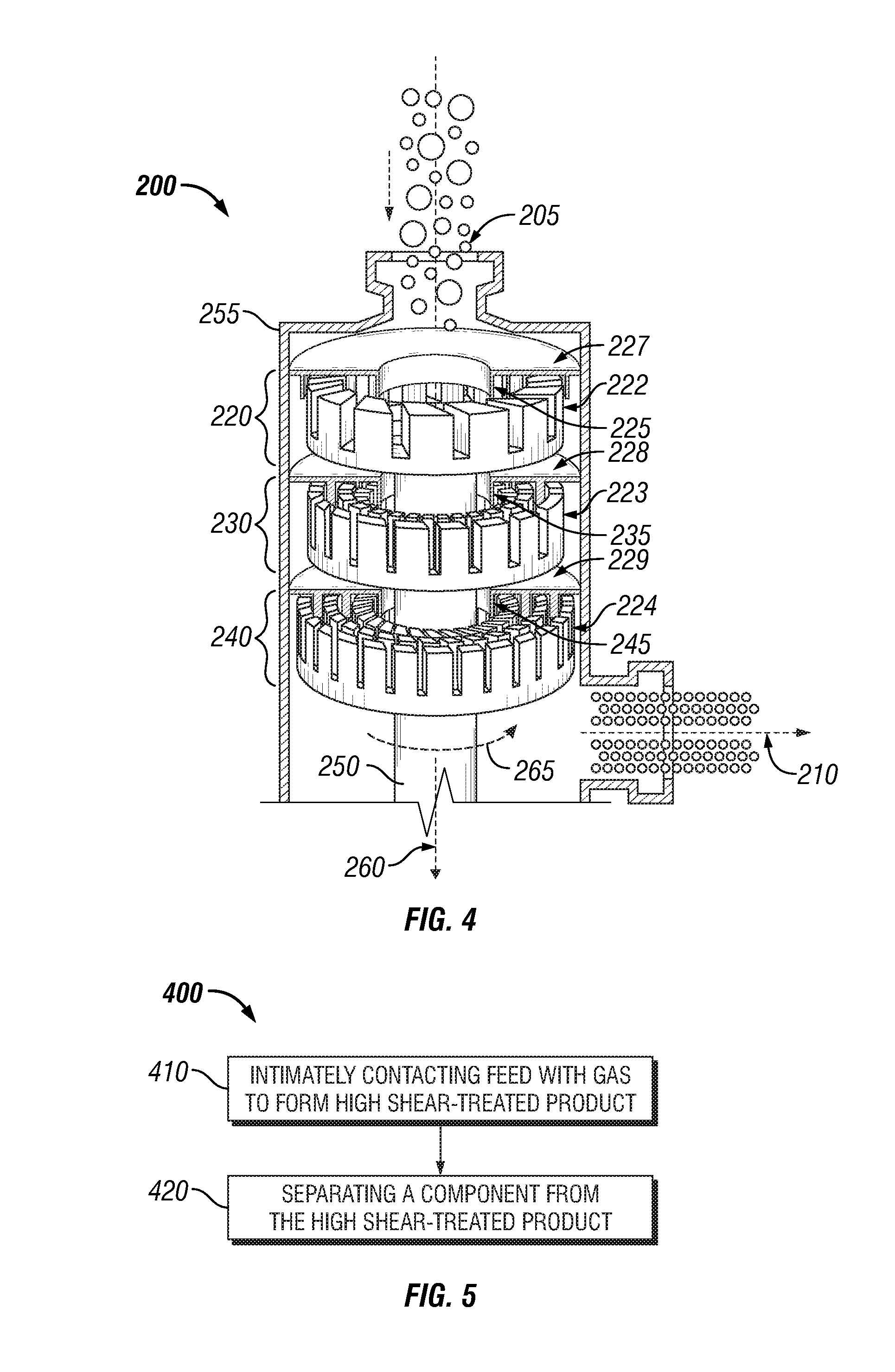
InactiveUS20110266198A1Promote recoverySimple processLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionFlotationShear rateComponents of crude oil
Herein disclosed is a method of removing at least one component from a feed by subjecting the feed to high shear in the presence of carbon dioxide to produce a high shear-treated product and separating the at least one component from the high shear-treated product to produce a component-reduced product. Also disclosed is a method of removing asphaltenes from asphaltenic oil by subjecting the asphaltenic oil to a shear rate of at least 10,000 s−1 in the presence of carbon dioxide to produce a high shear-treated product and separating asphaltenes from the high shear-treated product to produce an asphaltene-reduced product oil. Systems are also provided for carrying out the methods.
Owner:HRD CORP
High shear process for aspirin production
InactiveUS20090005592A1Simple reaction conditionsIncrease ratingsOrganic compound preparationRotary stirring mixersAspirinEmulsion
Use of a high shear mechanical device in a process for production of acetyl salicylic acid, by contacting acetic anhydride with salicylic acid in a high shear device. The disclosed process makes possible a decrease in mass transfer limitations, thereby enhancing production of acetyl salicylic acid. A system for production of acetyl salicylic acid is also provided in which a reactor is configured to receive the output from a high shear device, which is configured to receive, via one or more inlets, acetic anhydride, and salicylic acid and generate a fine dispersion or emulsion of reactants.
Owner:HRD CORP
Loading system for an encapsulation device
InactiveUS9433557B2Avoid cross contaminationOvercome disadvantagesImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical batteryBiomedical engineering
The present invention provides, in at least one embodiment, a loading device, system and method that loads aggregate cells into an encapsulation device for implanting into a patient. The loading system uses negative pressure from a low pressure pump in a closed system to improve safety and cell viability while allowing for even loading of the encapsulation device.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Water and feed preservative for animal uses
InactiveUS20050170052A1Increase shearIncrease pressureMilk preservationFruit and vegetables preservationEmulsionAdditive ingredient
Composition and methods for preservation of water, feed and major feed ingredients for animal uses. A composition comprising a terpene mixture, is disclosed. The composition can be a true solution of an effective amount of effective terpene (s) and a surfactant. The composition can be a suspension or emulsion comprising of terpene (s), surfactant, and water. The composition(s) of the invention can be administered as a spray mist over feed while mixing, drop-wise as in a medicator (dosificator) in water or mix as a component of the diet. A true solution of terpene and water can be formed by mixing terpene and water at a solution-forming shear rate in the absence of a surfactant. A suspension of terpene and water can be formed by mixing terpene and water at a solution-forming shear rate in the presence of a surfactant.
Owner:ANITOX CORP
System and process for inhibitor injection
InactiveUS20090001188A1Low costIncreased fluid throughputRotary stirring mixersTransportation and packagingMean diameterMaterials science
A method for introducing inhibitor into a fluid to be treated by forming a dispersion comprising droplets, particles, or gas bubbles of the inhibitor dispersed in a continuous phase of a carrier, wherein the droplets, particles, or gas bubbles have a mean diameter of less than 5 μm, and wherein either the carrier is the fluid to be treated or the method further comprises introducing the dispersion into the fluid to be treated. A system for inhibiting an undesirable component, the system comprising at least one high shear mixing device comprising at least one generator comprising a rotor and a stator separated by a shear gap, wherein the high shear mixing device is capable of producing a tip speed of the rotor of greater than 22.9 m / s, and a pump for delivering a mixture of a carrier and an inhibitor to the high shear mixing device.
Owner:HRD CORP
Fluted ramped entryways of an orifice plate for a grinding machine
ActiveUS7461800B2Reduce widthIncrease in sizeAnimal feeding stuffAnimal fodder preservationFluteEngineering
Flutes or channels are provided at the ramped entryways of an orifice plate of a grinding machine head. Ramped entryways lead from the grinding surface of the orifice plate to one or more hard material collection passages located toward the center of the plate. Providing flutes at the ramped entryway, rather than a smooth surface, helps control the flow of hard material into the hard material collection passages by creating friction to maintain hard materials in the entryway area once collected there, and by encouraging flow of hard materials toward the collection passage.
Owner:PROVISUR TECHNOLOGIES INC
Stabilizer System For Food And Beverage Products
A stabilizer system comprising blends of cellulose, lambda-carrageenan, and guar gum. Food products and beverages, such as energy drinks, are prepared with the stabilizer blends.
Owner:PEPSICO INC
Using thermal imaging for control of a manufacturing process
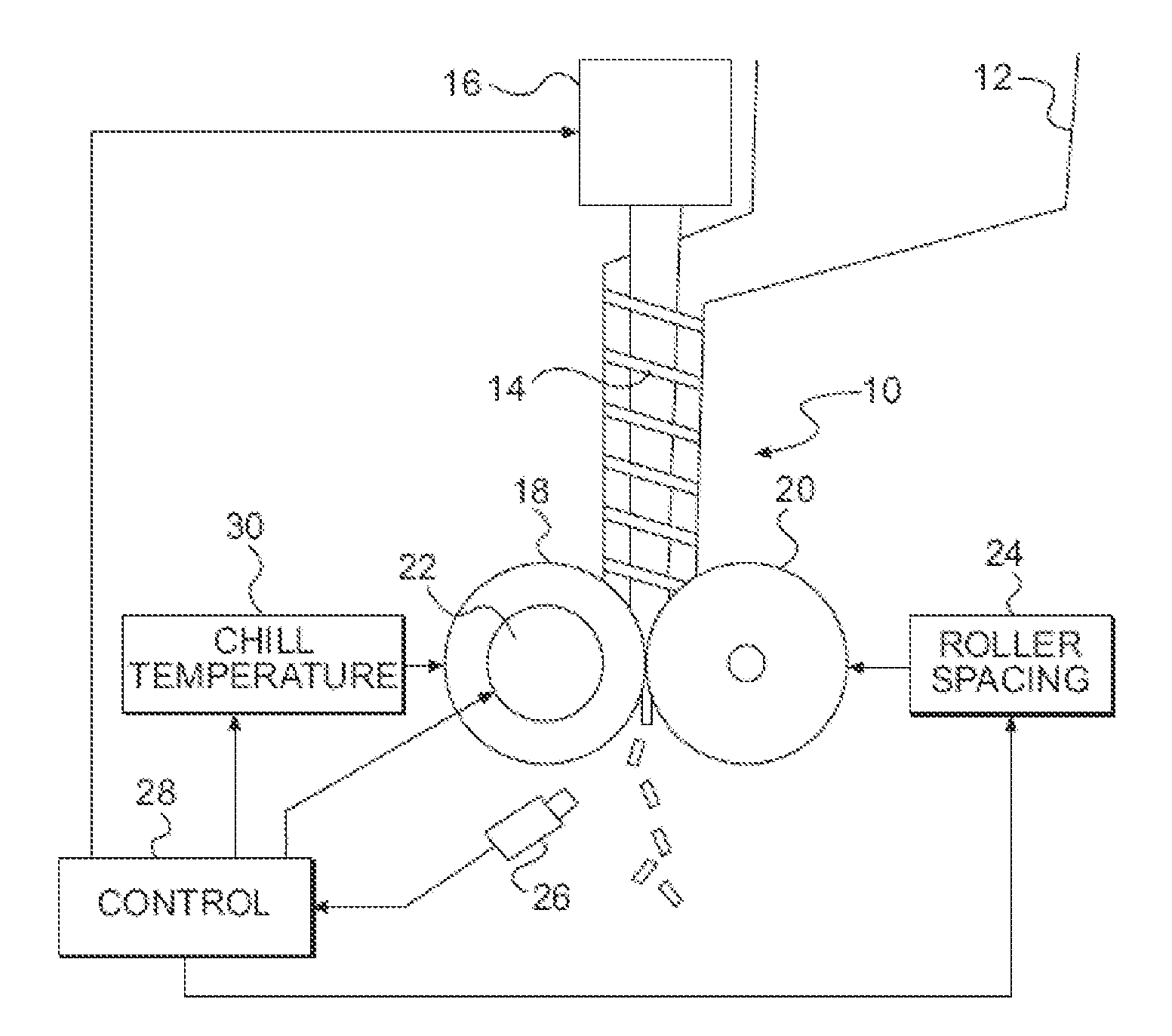
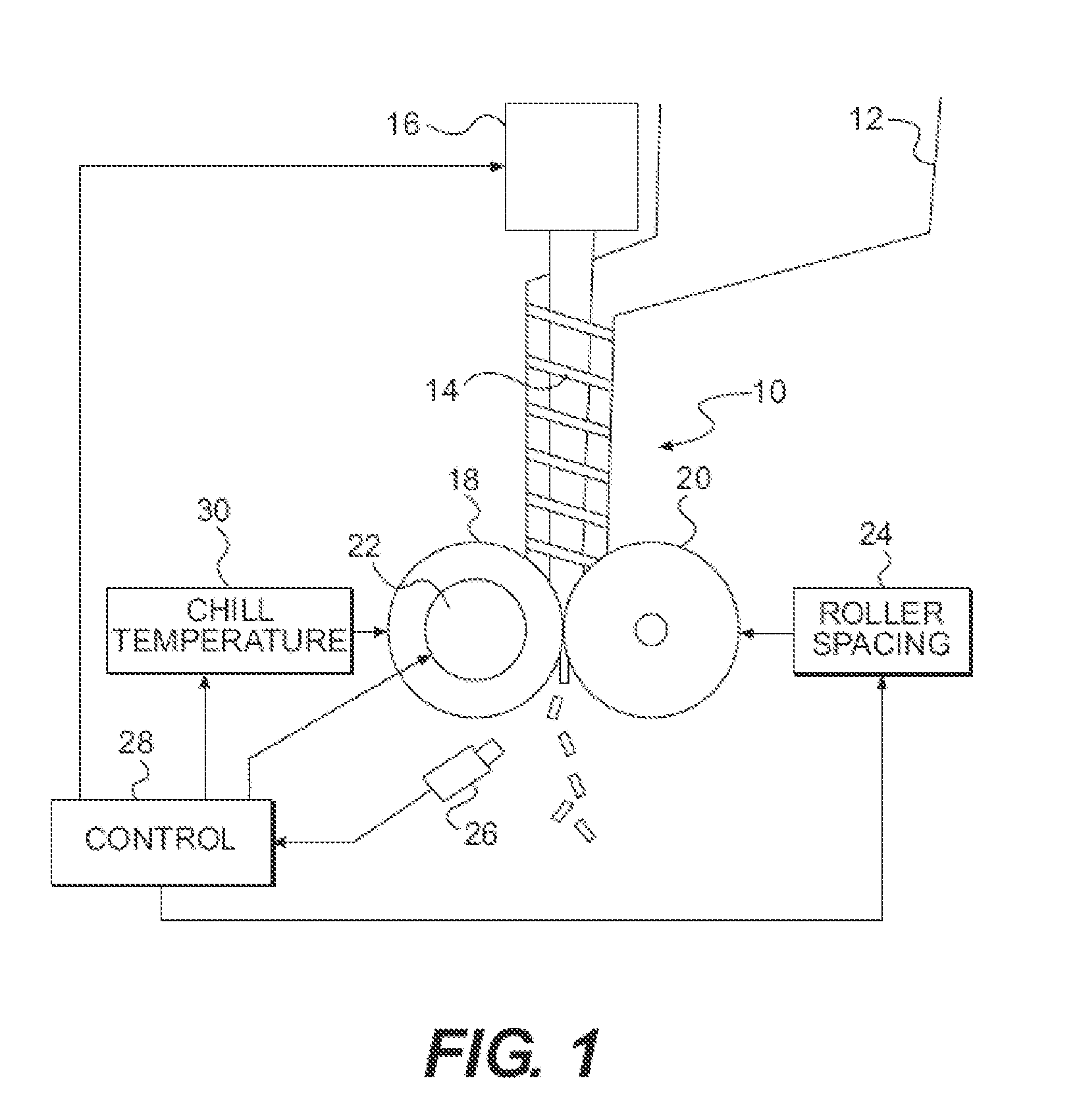
InactiveUS20120057018A1Insufficient heatingIncrease shearTelevision system detailsLiquid surface applicatorsEngineeringPrecipitation
A thermal imaging camera monitors the temperature different zones in a pharmaceutical process such as ribbon compaction, coating, spray drying, fluid bed drying, high shear wet granulation, crystallization, lyophilization, precipitation, fermentation, and low dosage dispensing of a pharmaceutically active liquid. The thermal imaging camera can be used to produce a visual display of a temperature profile, or a spray pattern. In addition, feedback from the thermal imaging camera is used to control one or more processing parameters.
Owner:GLAXO SMITHKLINE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com