Methods for the synthesis of lactic acid using crabtree-negative yeast transformed with the lactate dehydrogenase gene
a technology of lactate dehydrogenase and crabtree-negative yeast, which is applied in the field of methods and materials involved in the production of organic products, can solve the problems of limited use of living bacteria as factories, difficult and expensive, and reduced pyruvate decarboxylase activity or alcohol dehydrogenase activity of cells, so as to achieve rapid growth and produce an organic product efficiently, and ph is neutral. , the effect of good synthesis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
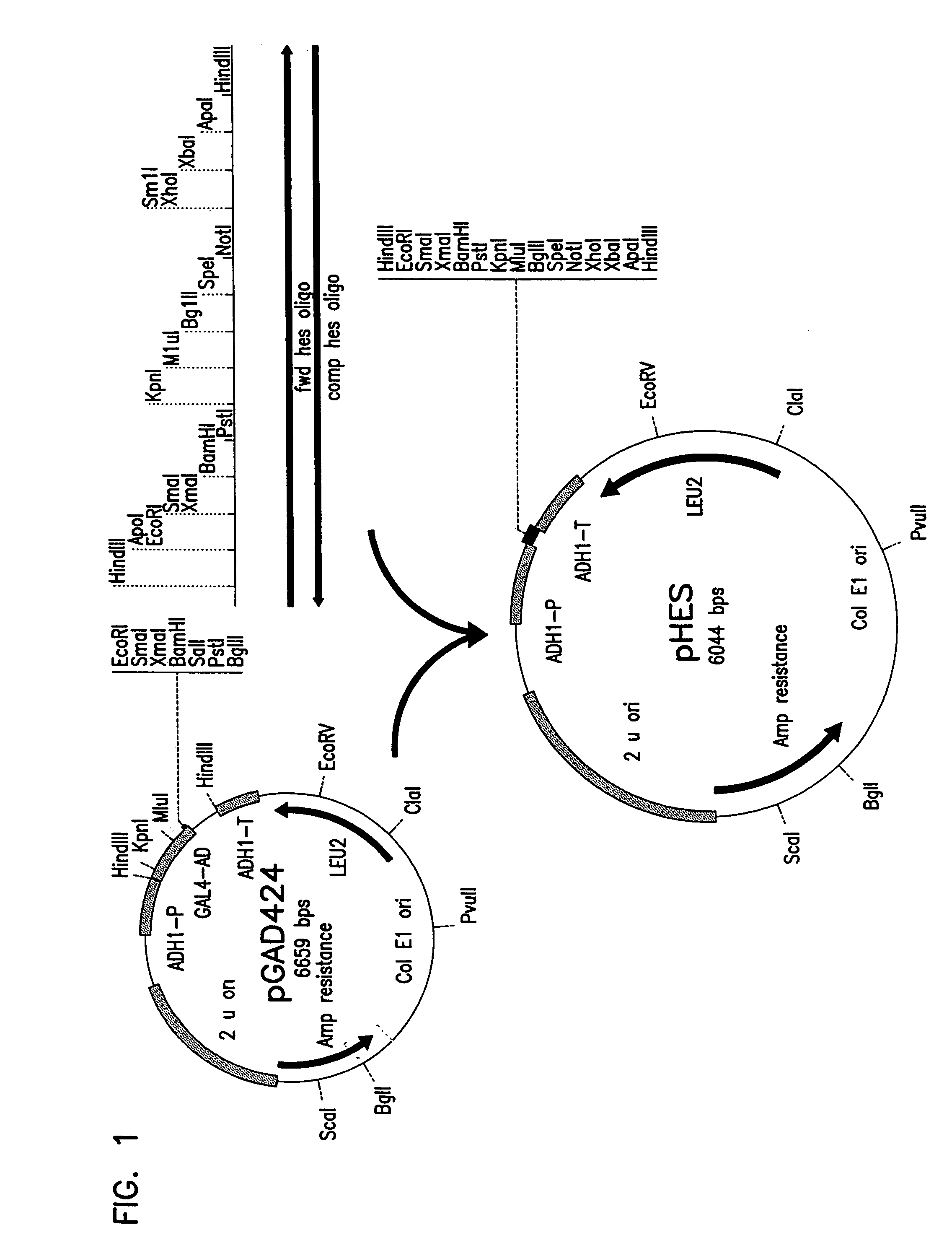
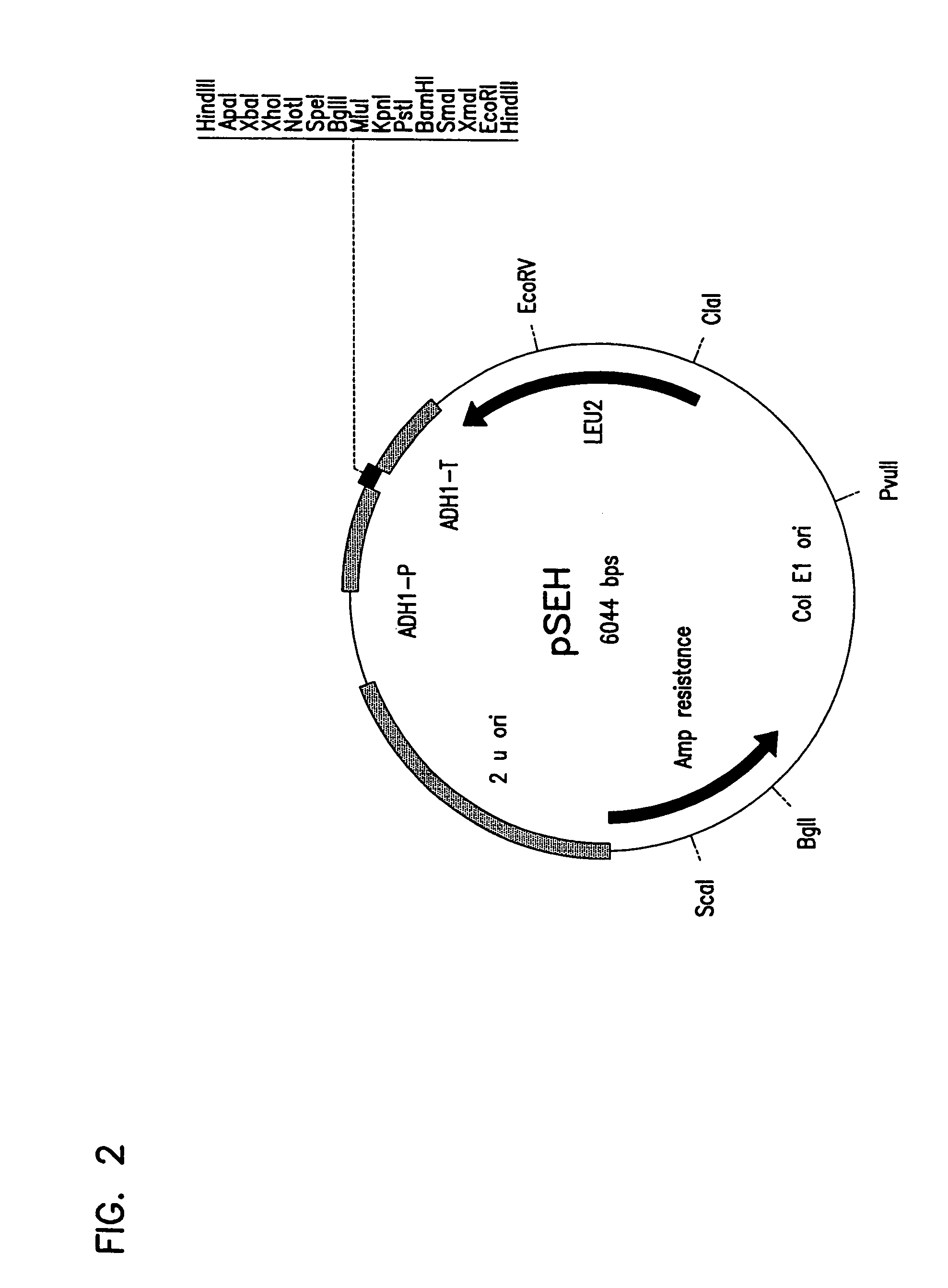
Recombinant Plasmid pHES / pSEH
[0147]0.5 μg of plasmid pGAD424 described by Chien et al. (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 88(21):9578-9582 (1991)) was digested with the restriction enzyme HindIII. The digested mixture was separated by gel electrophoresis on a 0.8% agarose gel using TBE buffer. A 5.9 kbp fragment was then purified from the gel as described in Sambrook et al., (Molecular Cloning, second edition, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Plainview, N.Y. (1989)) . A complementary pair of 92 bp synthetic oligomers with multiple restriction enzyme recognition sites was designed. The first was designated fwd hes oligo and has the sequence identified as SEQ ID NO: 1. The second was designated camp hes oligo and has the sequence identified as SEQ ID NO: 2. 500 nmoles of the two complementary oligomers were annealed to each other by boiling for ten minutes and cooling gradually to room temperature. The double stranded 92 bp DNA was digested with HindIII and ligated to the HindIII digested 5.9 kbp...
example 2
PCR Amplification of Nucleic Acid Encoding Lactate Dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus helveticus and Pediococcus acidilactici
[0148]Genomic DNA was isolated from overnight cultures of Lactobacillus helveticus (ATCC 10797) and Pediococcus acidilactici (ATCC 25741) using PUREGENE® genomic DNA isolation kit (Gentra systems, Minneapolis, Minn.). PCR primers were designed to isolate lactate dehydrogenase-encoding nucleic acid from L. helveticus (lh-ldh oligos) and P. acidilactici (pa-ldh oligos) genomic DNA. These primers were designed based on the available gene sequences for lactate dehydrogenases in the Genbank databases, and have the sequences identified as SEQ ID NO 3, SEQ ID NO: 4, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 6. The primers were optimized using Primer Designer software obtained from Sci-ed software (Durham, N.C.). One μmole of the genomic DNA was used along with 100 nmoles of primers. Pfu DNA polymerase (New England Biolabs) was used to PCR amplify lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) nucleic...
example 3
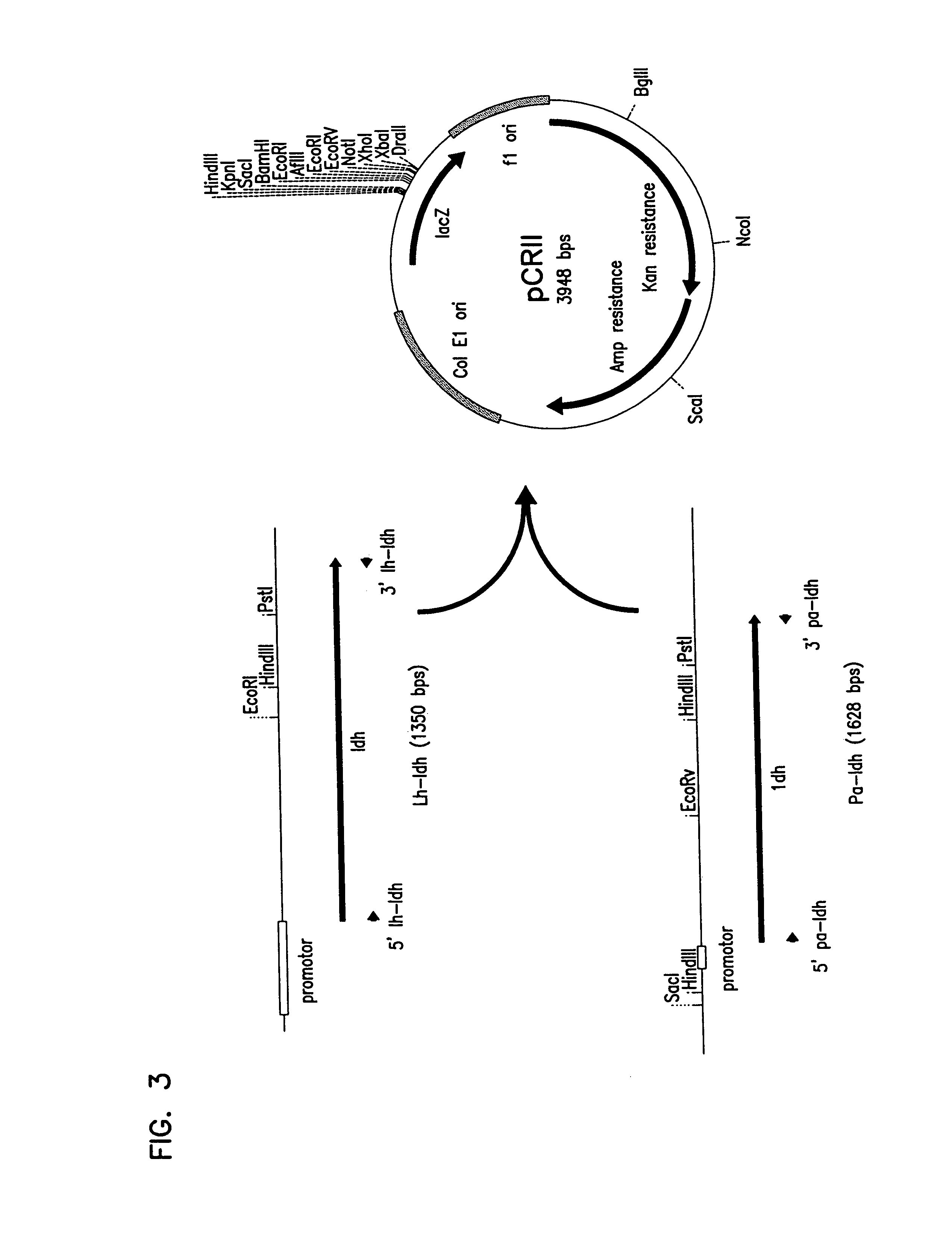
Cloning of L. helveticus and P. acidilactici into pCRII vector
[0155]PCR amplified LDH DNA products were ligated with pCRII vectors (FIGS. 3 and 4) using the TA cloning kit obtained from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, Calif.). The ligation mixture was then used to transform E. coli DR10B using methods described in Sambrook et al. (Molecular Cloning, second edition, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Plainview, N.Y. (1989)). The pCRII vectors supplied with the kit allowed for quick cloning of the PCR products according the manufacture's instructions. The pCRII vectors with the LDH genes from L. helveticus and P. acidilactici is depicted in FIG. 4.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com