Construction and application of heat-resistant yeast engineering bacteria capable of producing glycerine under high temperature aerobiotic condition
A technology of heat-resistant yeast and engineering bacteria, which is applied in the field of construction of heat-resistant yeast engineering bacteria, and can solve problems such as safety and cost of industrial production with limited application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
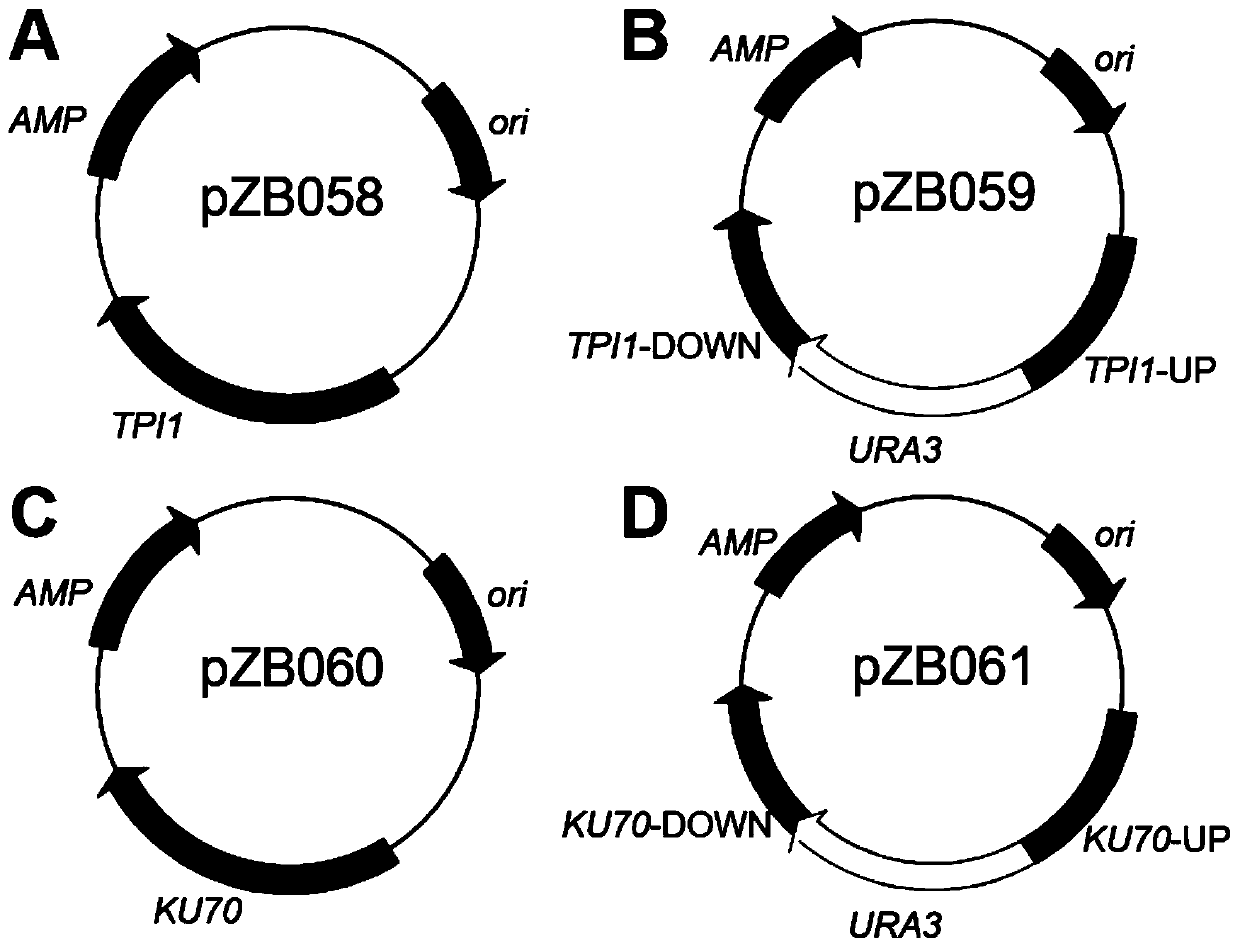
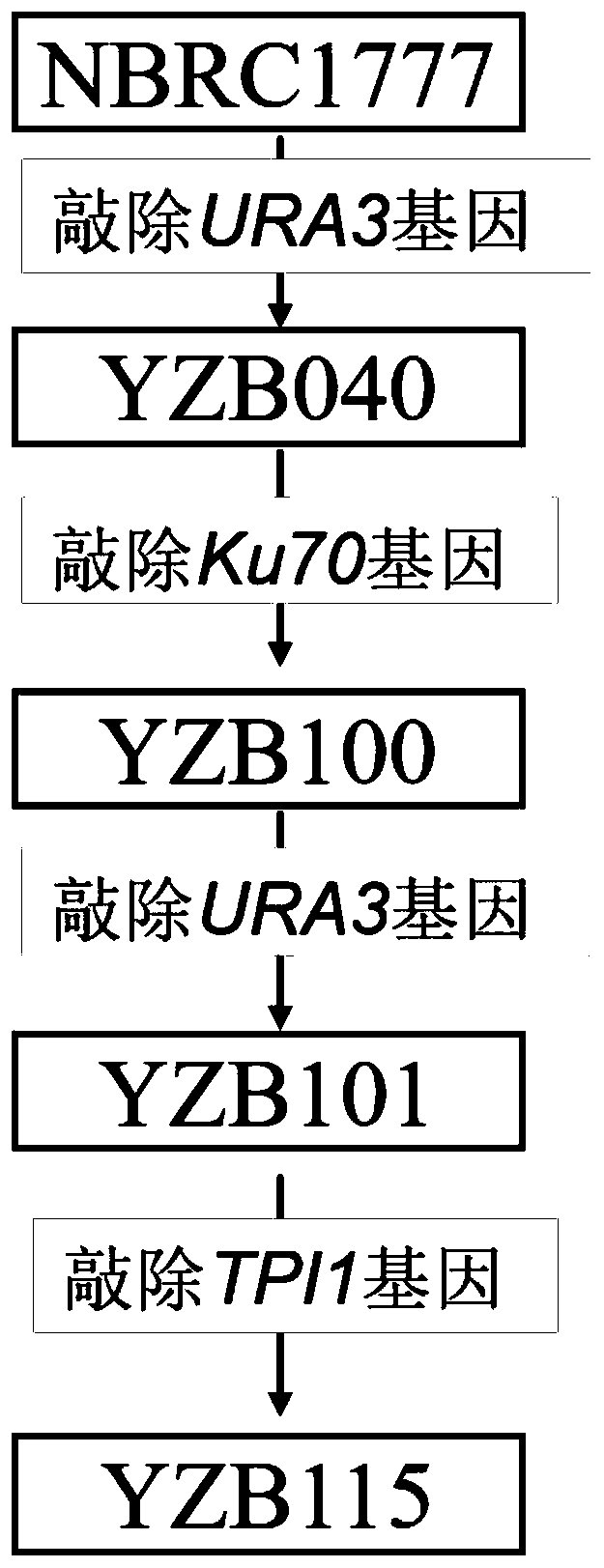
[0044] Embodiment 1: the preparation of bacterial strain
[0045] 1. The specific steps for extracting the yeast genome are as follows:
[0046] ①Pick a single clone, insert it into 5mL liquid YPD, culture at 37°C, 250rpm, for 24h.
[0047] ② Centrifuge at 12000rpm at room temperature for 5sec to collect the bacteria, and discard the supernatant.
[0048] ③ Resuspend the bacteria in 500 μL of distilled water, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 5 sec to collect the bacteria, and discard the supernatant.
[0049] ④Take 200 μL of 1x breaking buffer prepared by the laboratory (TritonX-100 (2% (w / v)), SDS (1% (w / v)), NaCl (100mM), Tris-Cl (10mM, pH8.0 ), EDTA (1mM)) to resuspend the bacteria, and transfer the bacteria solution into an EP tube containing 0.3g glass beads (425-600um, sigma, USA).
[0050] ⑤ After adding 200 μL of phenol-chloroform solution, shake at high speed for 3 minutes, add 200 μL of 1x TE (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 1 mM EDTA), and shake slightly.
[0051] ⑥Centrifu...
Embodiment 2
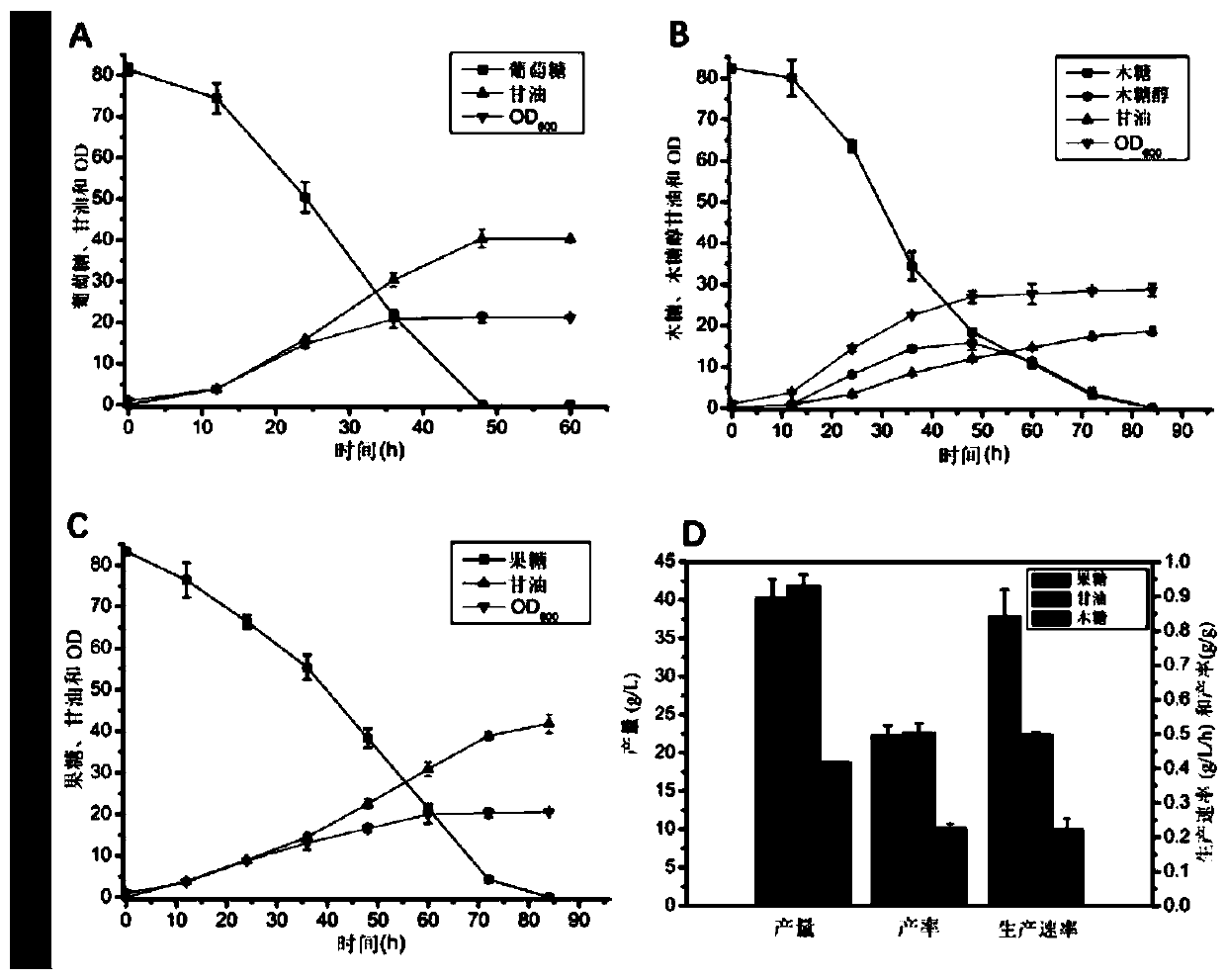
[0165] Embodiment 2: the engineering strain fermentation situation of construction
[0166] This example is used to test the effects of engineering strains on producing glycerol by fermentation of glucose, fructose and xylose. The results showed that the engineered strain obtained by transforming heat-resistant yeast could efficiently produce glycerol by aerobic fermentation at high temperature (42°C), and almost no by-products were contained in the fermentation broth after fermentation.
[0167] 1. Resuscitate strain YZB115 on a YPD medium plate and culture at 37°C for 1 day.
[0168] 2. Pick a single clone, inoculate in 5mL liquid YPE medium, 37°C, 250rpm, overnight.
[0169] 3. Seed cultivation. Transfer 5mL of liquid YPE medium to 250mLYPE, culture at 37°C, 250rpm, for 48h.
[0170] 4. Preparation 2.5 LYPD, YPF and YPX are cultured in a 5L fermenter and sterilized for use.
[0171] 5. Put 250mL seed culture medium into 2.5L fermentation medium, ferment at 42°C, rotatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com