Patents
Literature
61 results about "Yeast genome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Site-directed mutation method for genomes of saccharomyces cerevisiae
InactiveCN105624187AEfficient mutationRapid implementation of mutationsFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismRepair site
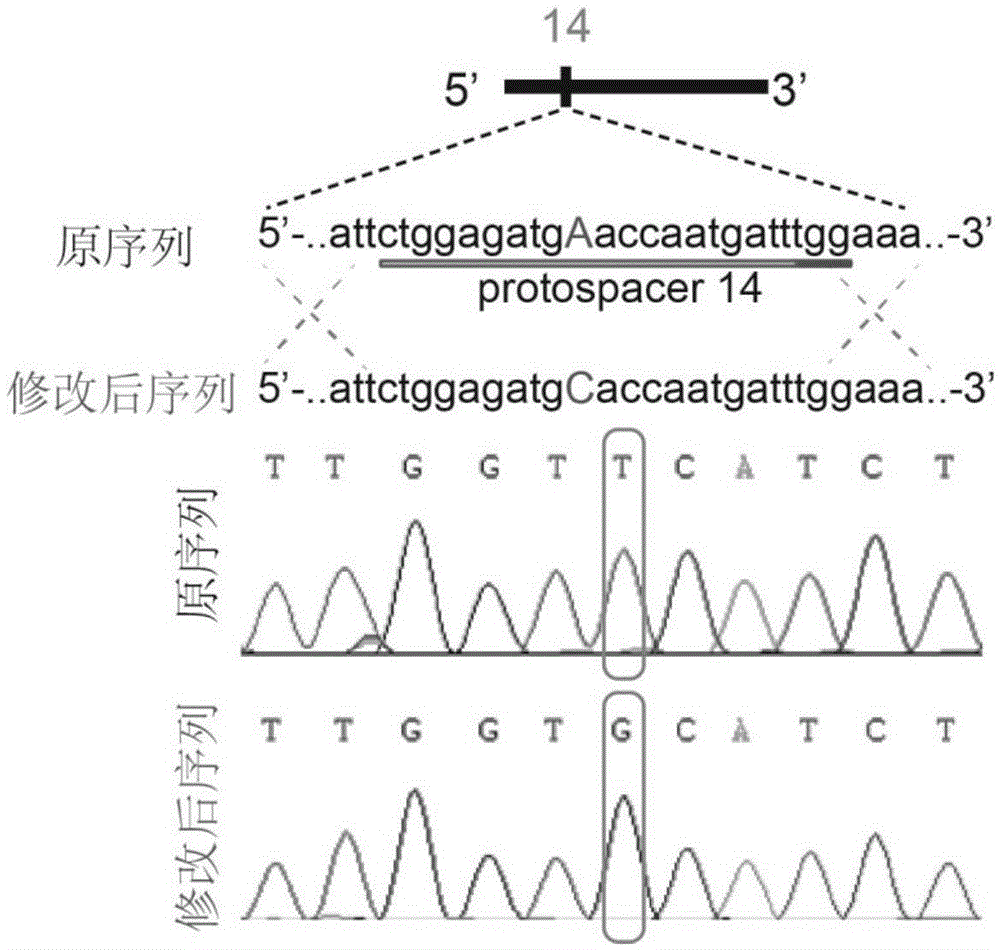
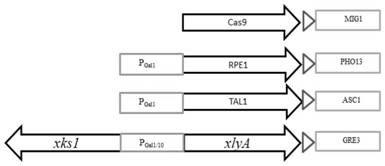
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, in particular to a site-directed mutation method for genomes of saccharomyces cerevisiae. To-be-repaired single-base mutation sites on the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be repaired by the aid of CRISPR / Cas9 technologies. Effects can be realized near the to-be-repaired sites by Cas9 proteins under the guidance actions of guide RNA (ribonucleic acid) if the mutation sites are positioned in PAM sequences (NGG) or front 11bp of the PAM sequences, and the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be subjected to double-strand break at cut positions, so that donor DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) can be efficiently recombined. Compared with existing results, the site-directed mutation method has the advantages that the sites of the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be efficiently and quickly mutated, and screening markers do not need to be integrated for the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Eukaryotic gene editing method based on gene cas7-3 in I type CRISPR-Cas system
PendingCN107557378AEasy gene editingGene editing fastStable introduction of DNAVector-based foreign material introductionEukaryotic geneEucoenogenes
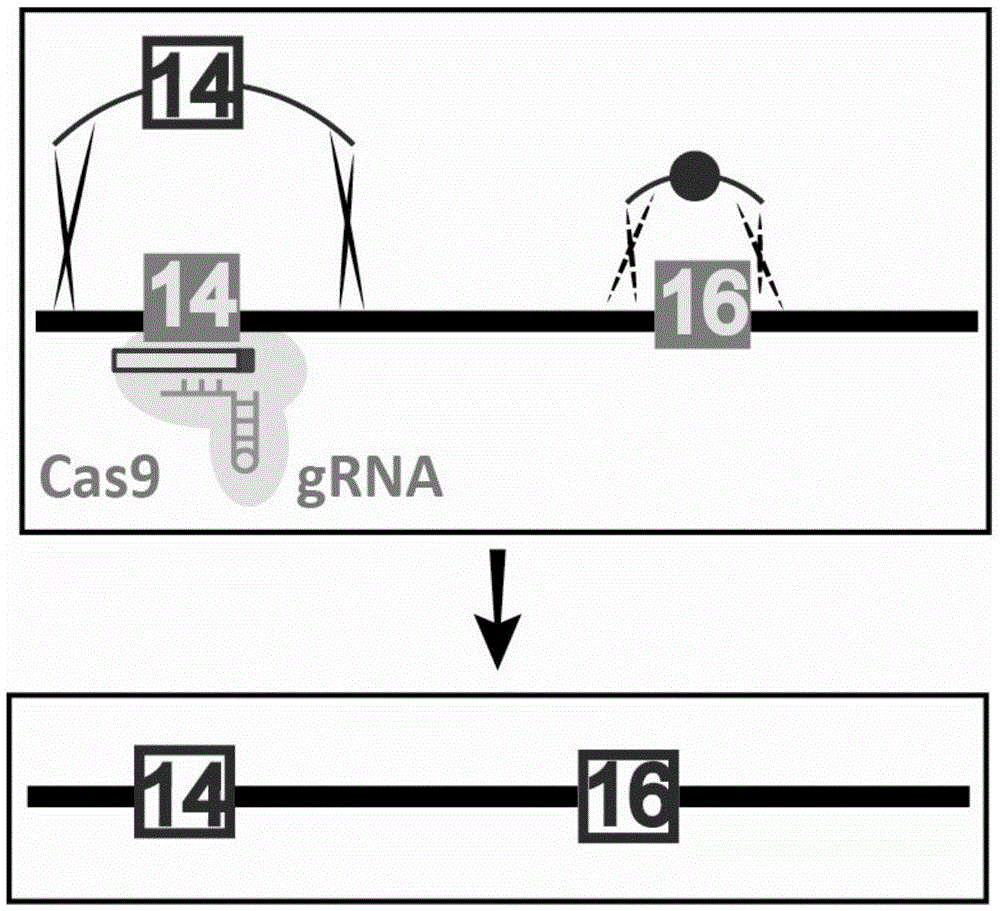
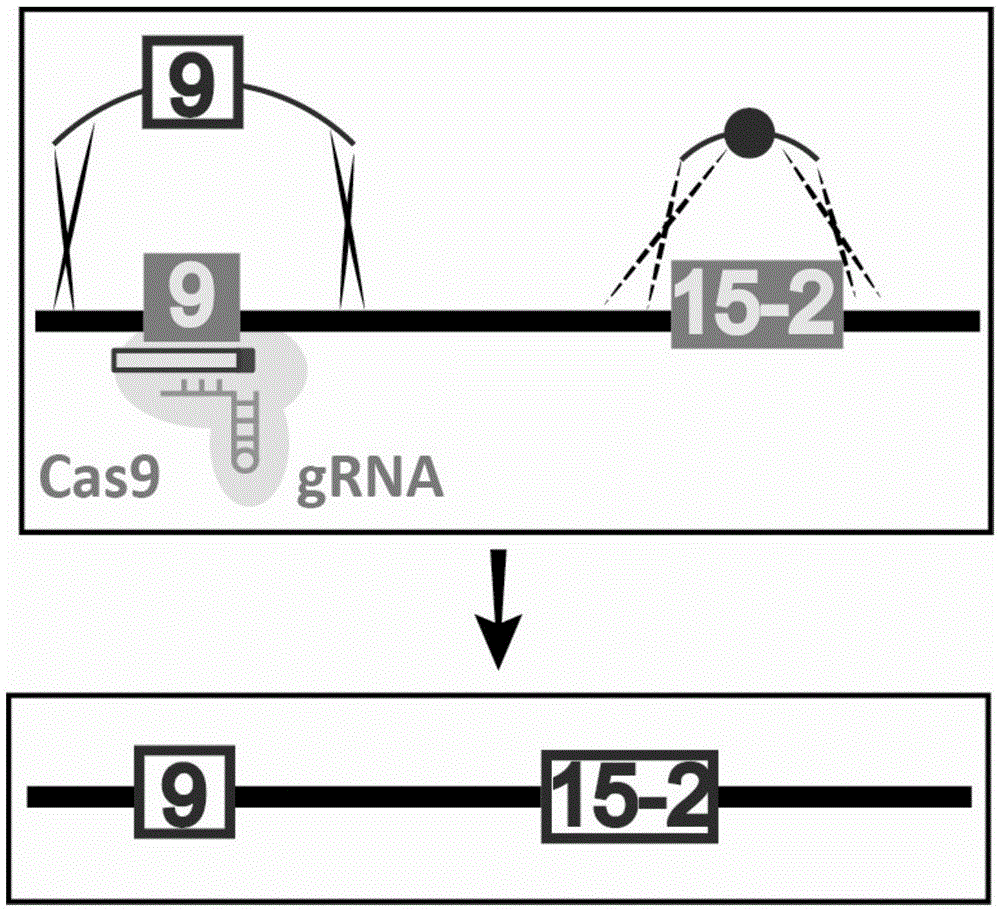
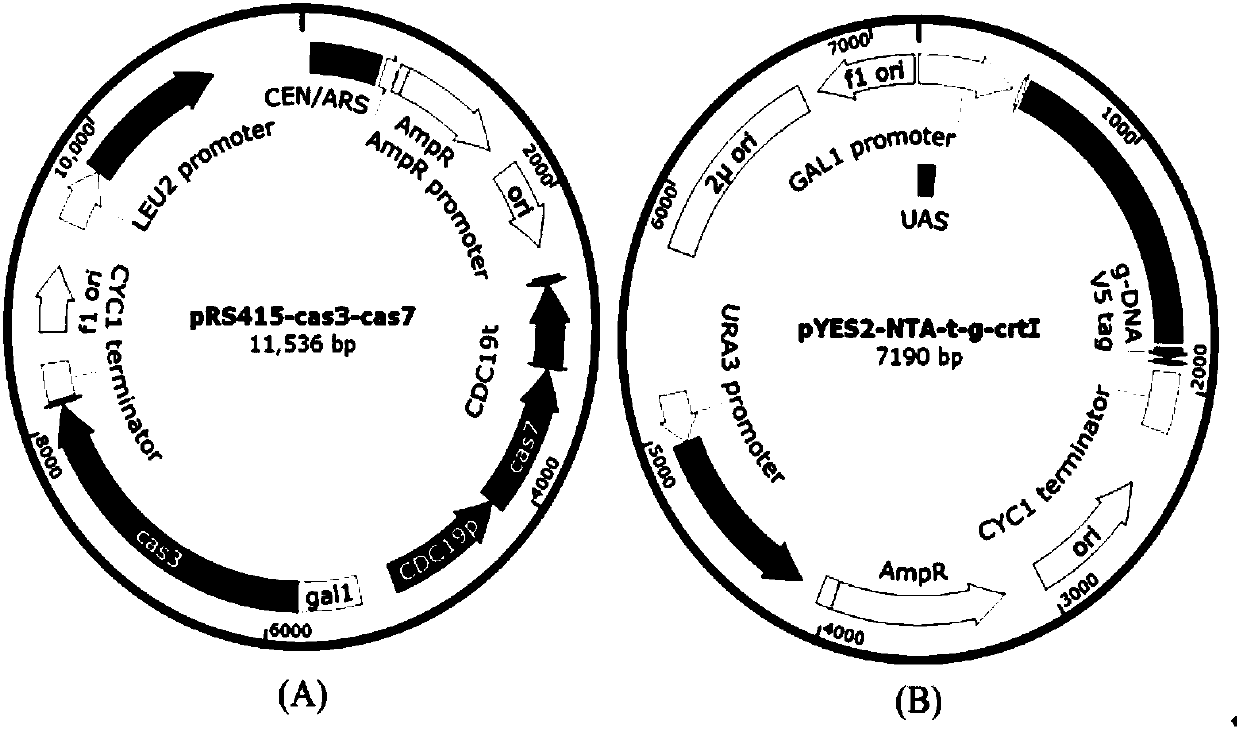
The invention discloses gene knockout and gene insertion on eukaryotic genomes carried out by two Cas proteins (Cas7 and Cas3) in a 1 class I type CRISPR-Cas system for the first time. The developmentof the method breaks the limitation of dependence on single-gene cas9 and cpf1, and provides a new perspective for performing gene editing on the eukaryotes by multi-gene. By applying the system, thegene editing can be conveniently, rapidly and effectively carried out on eukaryote brewer's yeast genomes. The optimized tool is expected to be widely used in the gene editing of other eukaryotes.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Recombinant yeast strain, and construction method and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and discloses a recombinant yeast strain, and a construction method and an application thereof. The recombinant yeast strain is obtained through the following steps: knocking out gal1, gal7, gal10 and ypl062w genes, integrating three gene fragments a genome through yeast homologous recombination, further knocking out an rox1 gene, and further integrating two gene fragments to the yeast genome. The gene knockout yeast strain constructed in the invention provides optimized host cells for production of lycopene; and combined functional genes crtE, crtB and crtI having specific sources and used for synthesizing the lycopene and specific yeast endogenous genes are selected and are integrated to the gene knockout strain genome through modular designing, so the brand new recombinant strain for highly yielding lycopene is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Recombinant yeast strain, construction method and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and discloses a recombinant yeast strain, a construction method thereof and the application thereof. In the recombinant yeast strain, gal1, gal7, gal10 and ypl062w genes are knocked out, and the recombinant yeast strain comprises 6 gene segments which are integrated to the genome through yeast homologous recombination. On the above basis, the recombinant yeast strain is further integrated onto one gene segment of a yeast genome, so that a better recombinant yeast is obtained. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the yeast strain is constructed based on gene knock-out, and an optimized host cell for producing lycopene is provided. Meanwhile, functional genes crtE crtB and crtI of a specific source combination and used for the synthesis of lycopene, specific yeast endogenous genes and specific exogenous genes are selected. The above selected genes are integrated to the gene knock-out genome of the yeast strain, and then a brand-new recombinant strain capable of producing high-yield lycopene is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
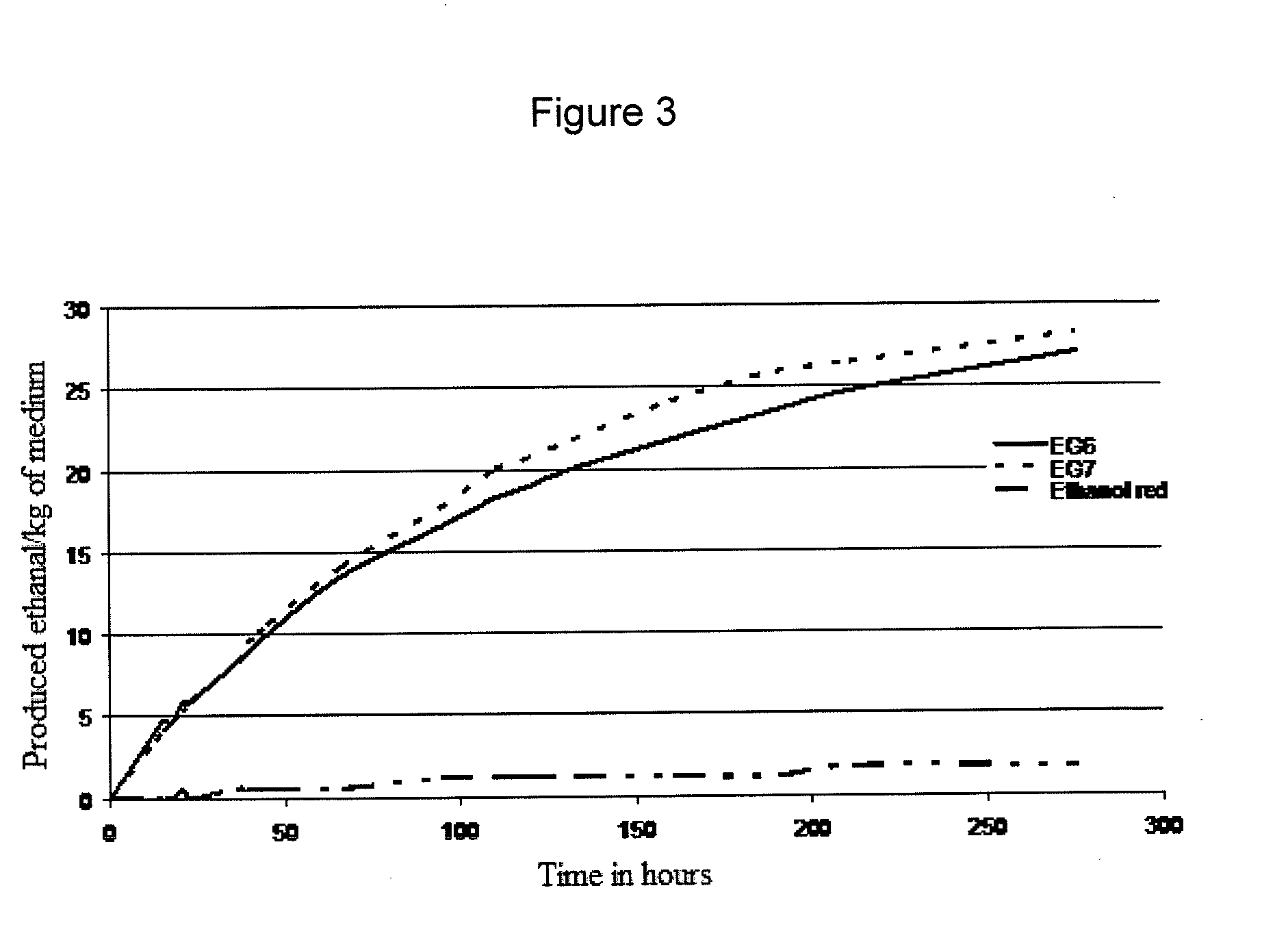
Method for preparing an industrial yeast, industrial yeast, and application to the production of ethanol from at least one pentose
The present invention relates to the field of the methods for obtaining yeast strains producing ethanol, of the thereby produced strains, and of the industrial production of ethanol from said strains.More particularly, the present invention describes in its most general aspect, a method for preparing yeasts from Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains by integration into the genome of the yeast of at least one gene coding for xylose isomerase and of at least one gene coding for xylitol dehydrogenase.The strain of the invention is useful for producing ethanol from a medium comprising at least one pentose, preferably xylose or a xylose and arabinose mixture.
Owner:LESAFFRE & CIE
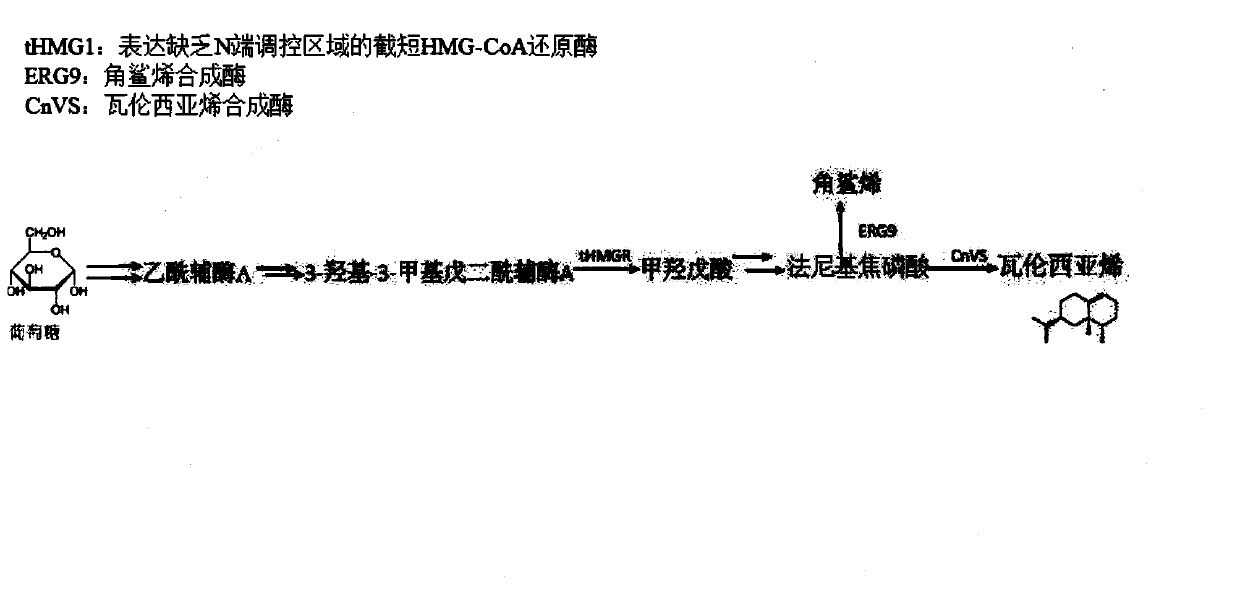
Brewer's yeast engineering bacterium for producing valencene and construction method and application of brewer's yeast engineering bacterim
ActiveCN110117551AEfficient productionIncrease production capacityFungiTransferasesBiotechnologyHMG-CoA reductase
The invention discloses a brewer's yeast engineering bacterium for producing valencene and a construction method and application of the brewer's yeast engineering bacterium. Overall inhibiting factorgenes in a yeast genome are subjected to knockout, a squalene synthetase gene is subjected to down reduction of expression, valencene synthetase is expressed, HMG-CoA reductase is overexpressed, the promoter of the valencene synthetase is optimized, and therefore the valencene is obtained. The key gene in the metabolic pathway is overexpressed through a free vector, the metabolic flux of the valencene in the synthetic route is increased, and the yeast cell factory is optimized; in combination with the suitability research of the promoter of the valencene synthetase, the brewer's yeast engineering bacterium obtained through culture optimization achieves efficient production of the valencene, and the dry cell weight yield of the valencene can reach 124.40 mg / g; the brewer's yeast engineeringbacterium has a wide industrial application prospect and positive economic and social development significance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Fusion protein having antibiotic function and uses thereof
InactiveCN101182360AStrong antibacterial activitySolve the problem of cumulative excessAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseBacteroides
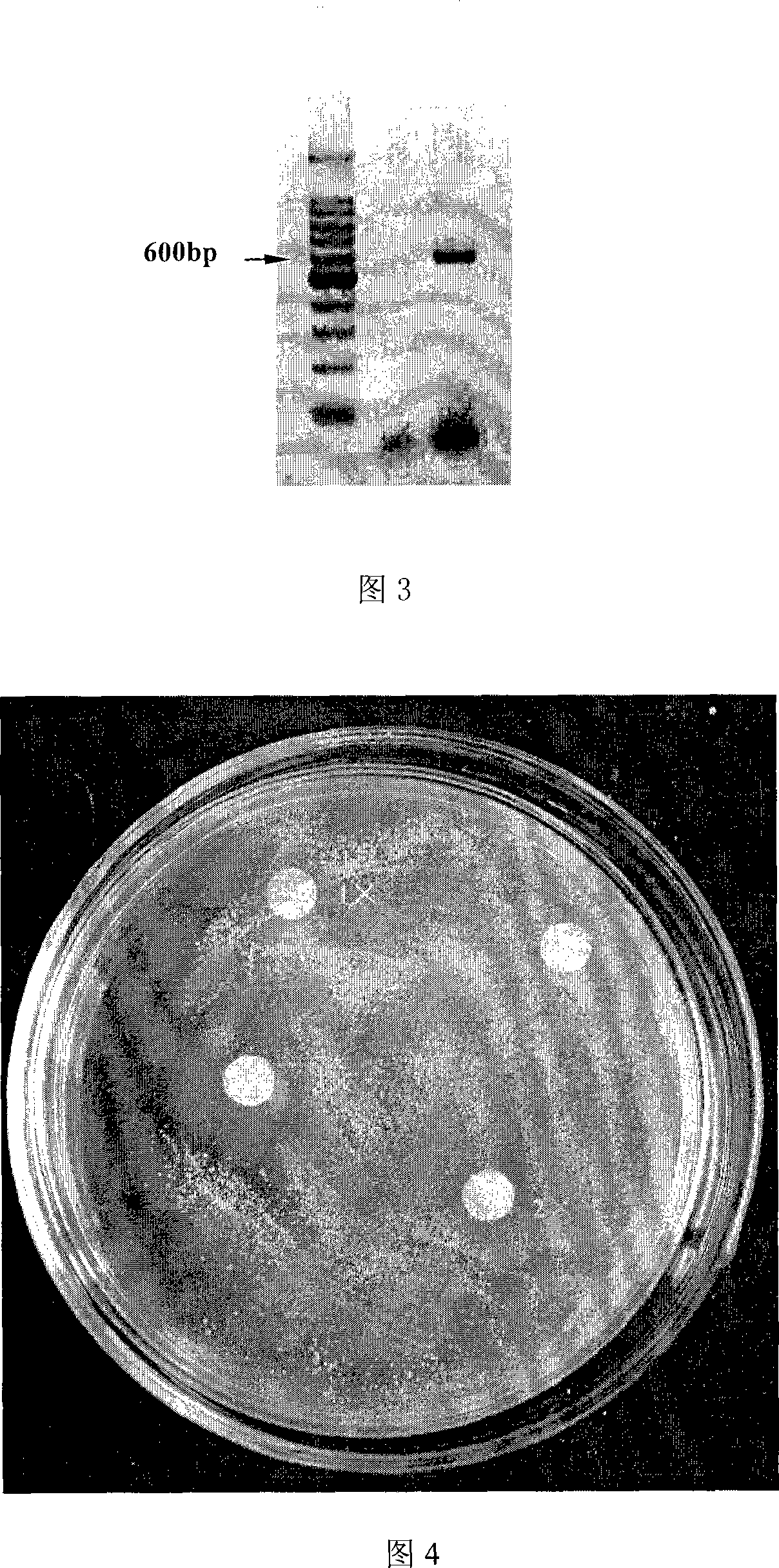
The invention discloses a fusion protein with antibacterial function and its application. The fusion protein gene sequence consists of a cloned hepcidinl precursor antimicrobial peptide gene and an artificially synthesized magainin antimicrobial peptide gene, which are composed of a novel fusion protein cDNA and integrated into the yeast genome by genetic engineering means, and induced The fusion protein cDNA is expressed in yeast, and then a large amount of fusion protein is obtained through yeast fermentation. The fusion protein of the present invention has obvious antibacterial activity after testing, and can be used for the prevention and treatment of bacterial diseases of aquatic organisms and farmed animals, or the purified fusion protein can be directly used as medicine to replace antibiotics for diseases caused by bacteria or even viruses Treatment.
Owner:THE FIRST INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY SOA
Method for information mining of genome metabolic network preliminary model
InactiveCN103399948AEasy to compareLabor savingSpecial data processing applicationsGenome scaleInformation mining
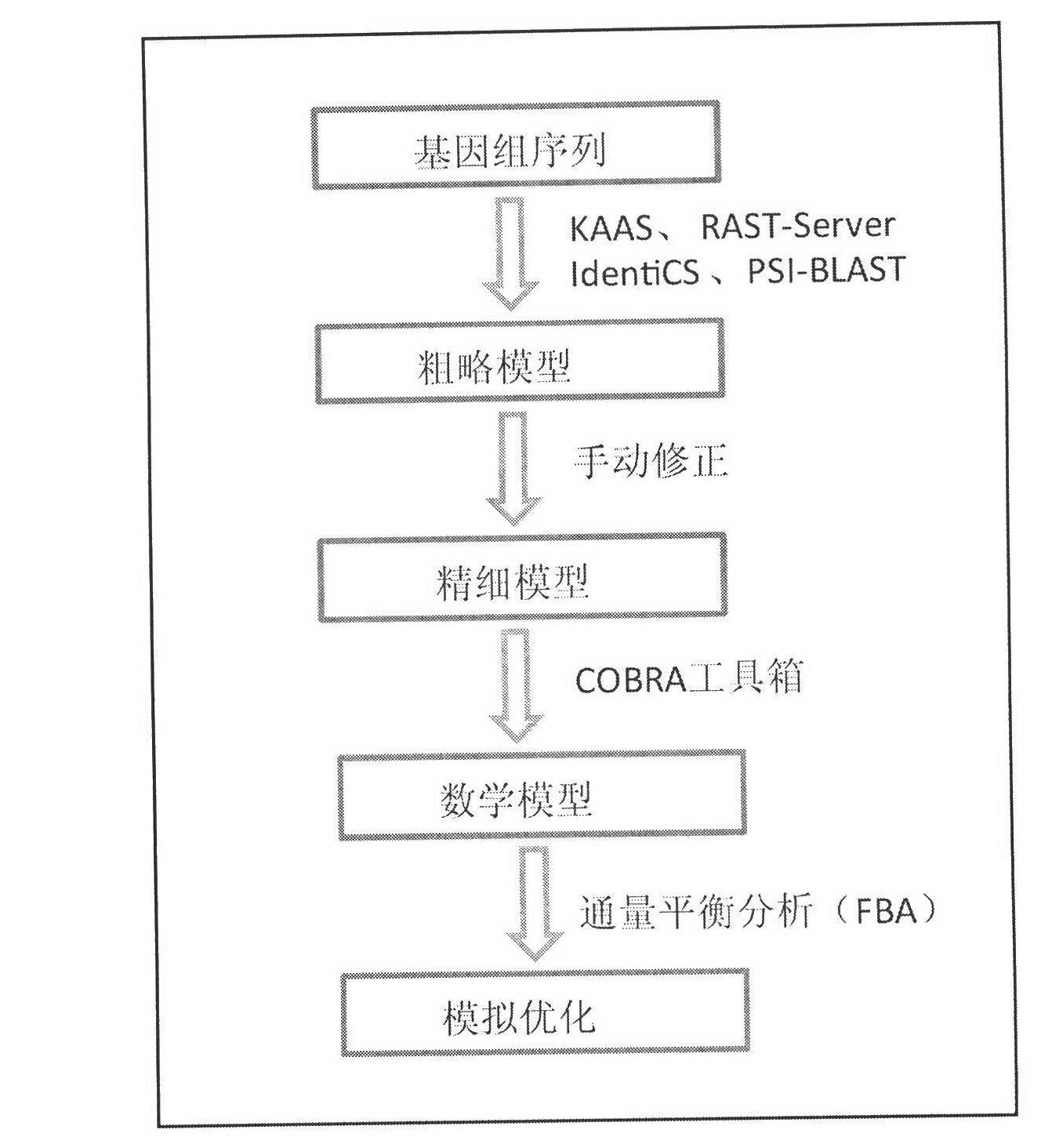
The invention provides a method for information mining of a genome metabolic network preliminary model. The method comprises the steps as follows: as for the KEGG website, extracting a corresponding relation among gene, protein and reaction, that is, determining the GPR relation by adopting a website script semantic analysis technology on the basis of webpage key content priori position information, and establishing an excel table to show the GPR relation information, so as to obtain the genome metabolic network preliminary model. The model constructed by adopting the method unifies the reaction form, and is convenient in comparison with other models and convenient in reference. The method has been applied to construction of a scheffersomyces stipitis CBS6054 genome-scale metabolic network, and compared with the construction of a traditional network preliminary model based on the KEGG database, a great amount of labor and time are saved, and the construction efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Screening method for genes of brewing yeast
InactiveUS20070042410A1Increase productivityQuality improvementFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementAlcoholScreening method
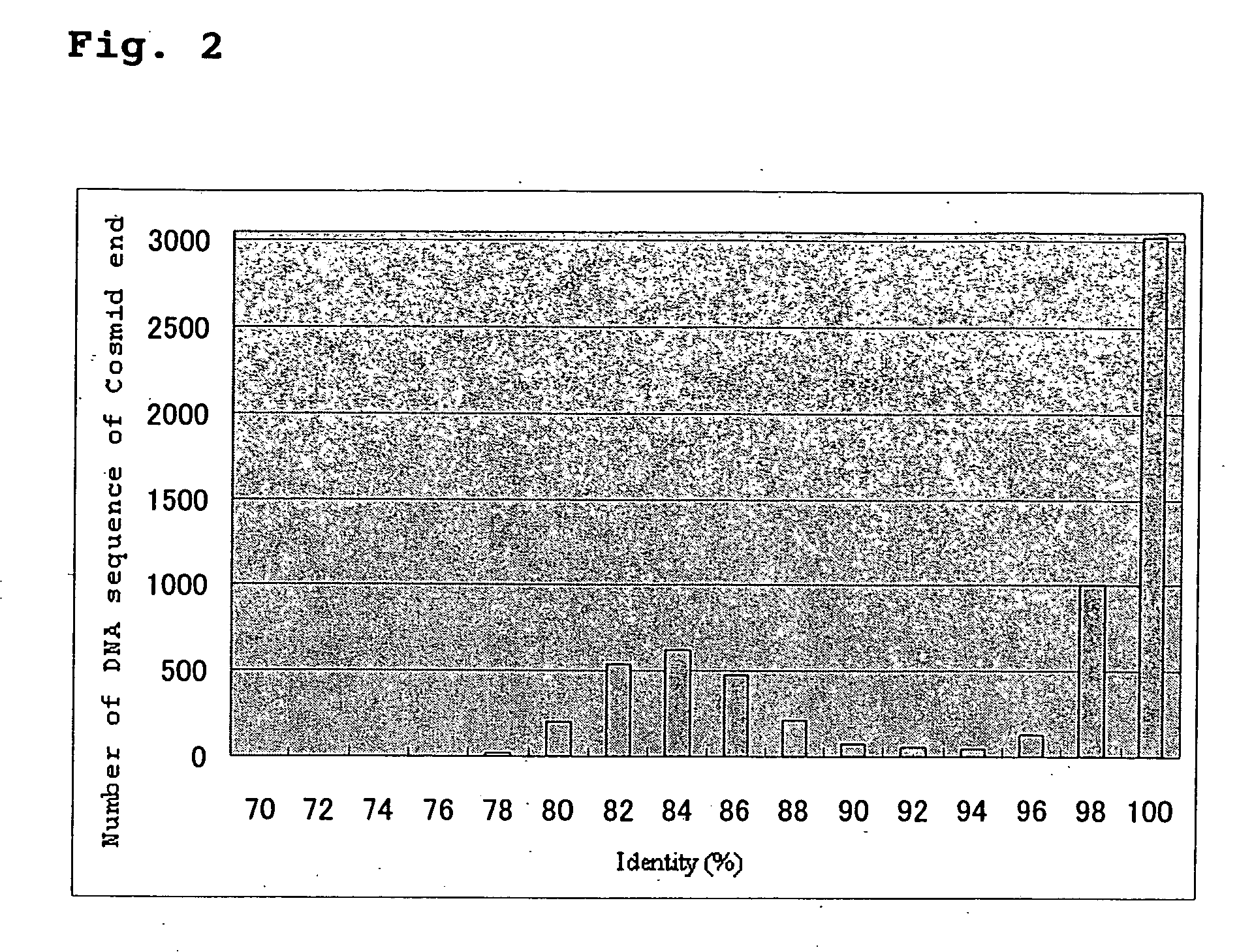
Provided herein are a method for selecting a gene participating in the desired brewing character and compiling a database of the whole genome sequence of industrial yeast; identifying a gene participating in a brewing characteristic from the database; functional analysis of the gene; and a DNA array of the whole genome sequences of an industrial yeast. Also provided are a method for yeast breeding; a method of producing an alcoholic beverage with improved quality; and a screening method to identify genes that increase productivity and / or improve flavor in the production of an alcohol or an alcoholic beverage by (A) analyzing a whole industrial yeast genome sequence, (B) comparing the genome sequence with the genome sequence of S. cerevisiae, (C) selecting a gene of the industrial yeast encoding having 70 to 97% identity to an amino acid sequence of S. cerevisiae; and (D) analyzing the selected gene.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
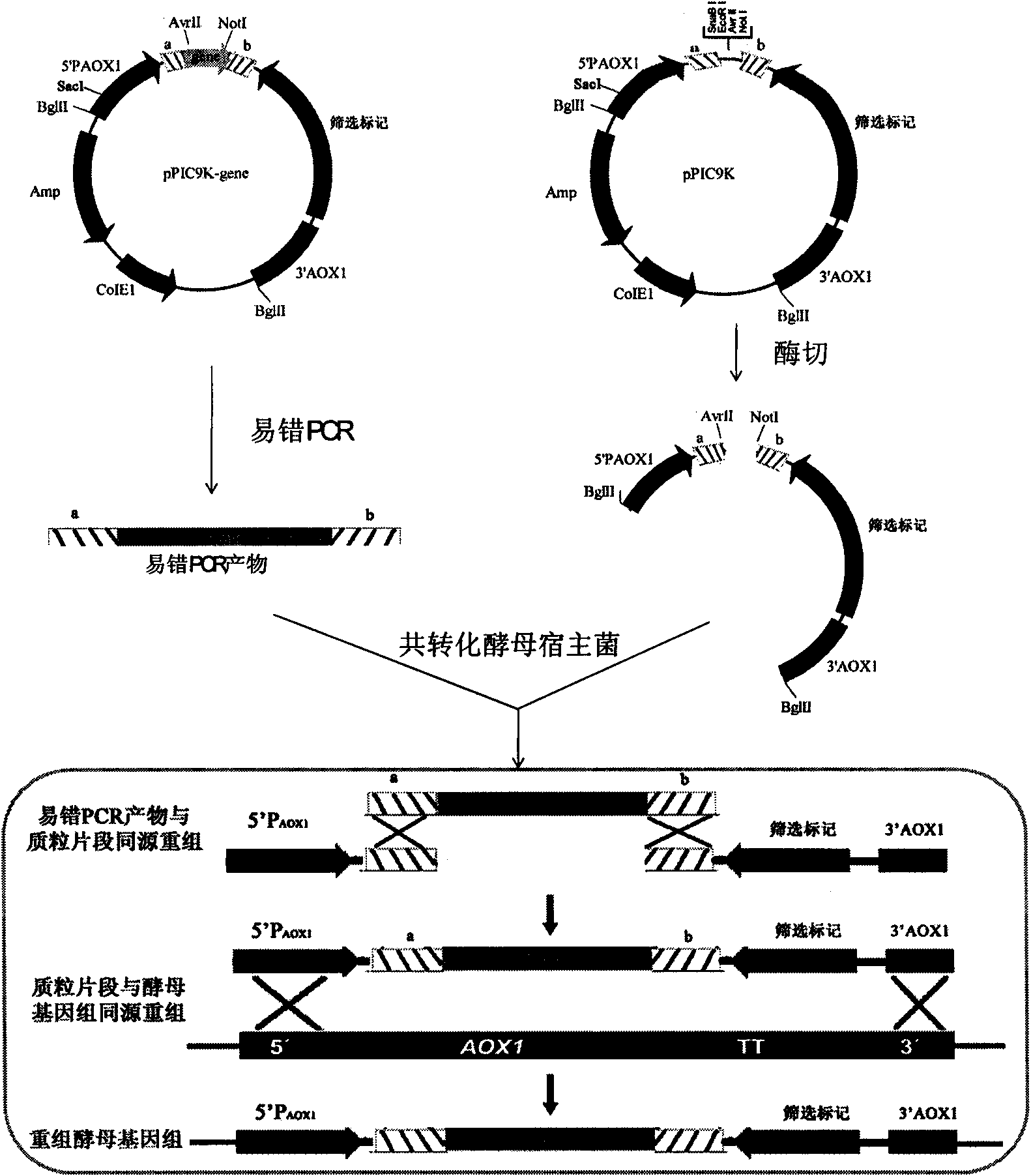
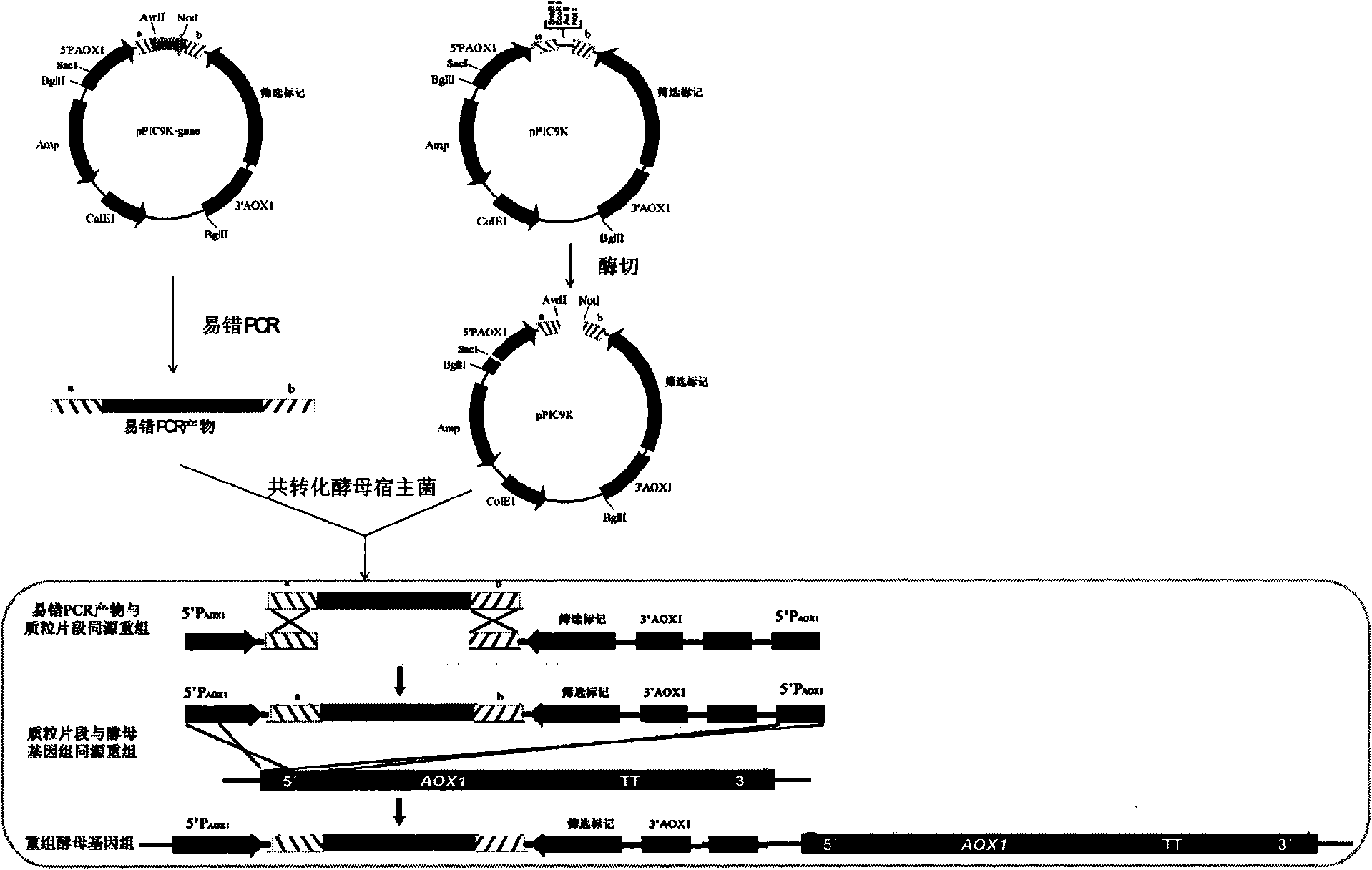
Method for establishing saccharomyces integrated gene mutation library based on in vivo homologous recombination
ActiveCN101550605AImprove efficiencyEasy to operateStable introduction of DNAMicroorganism based processesIn vivoProtein engineering
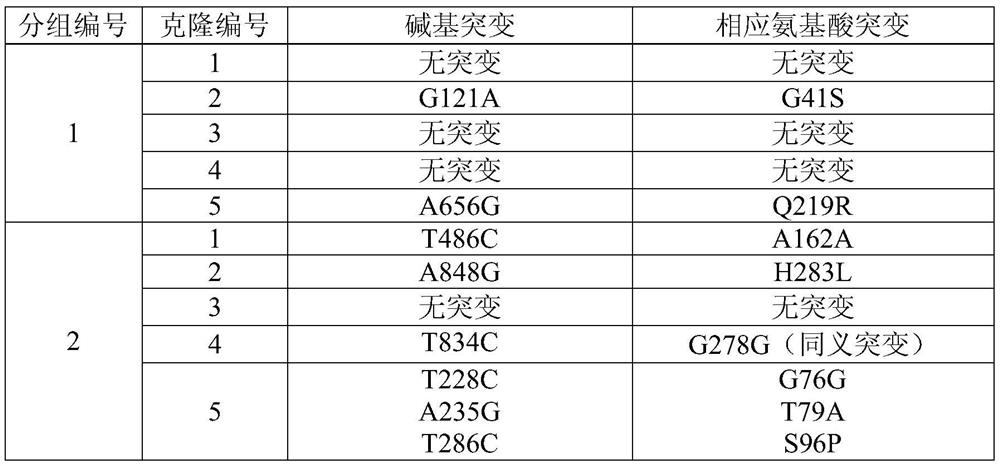
A method for establishing a saccharomyces integrated gene mutation library based on in vivo homologous recombination belongs to the fields of protein engineering, molecular biology technology and genetic engineering. The method comprises the steps of establishing the recombination expression plasmid of the target gene, designing long primer fragment by taking the recombination expression plasmid as a template, amplifying error-prone PCR to obtain the mutated gene with the expression carrier 20-70bp homologous sequence at two ends, respectively carrying out the enzyme tangential linearization to the homologous region of two ends of the mutated gene of the expression carrier and the homologous region of the gene group, mixing the error-prone PCR amplified outcome and the linearized expression carrier by a definite molar ratio and carrying out electro-transformation of the saccharomyces, and integrating the exogenous mutation target gene into the saccharomyces gene group, thus obtaining gene mutation library. The method has high efficiency and convenient operation, shortens the library establishment period from 1-2 weeks to 3 days, needs any sub-cloning steps for library establishment, reduces the loss of content and richness of the gene mutation, has generalization and can be used for various target genes capable of being expressed in the saccharomyces.
Owner:金湖县农副产品营销协会
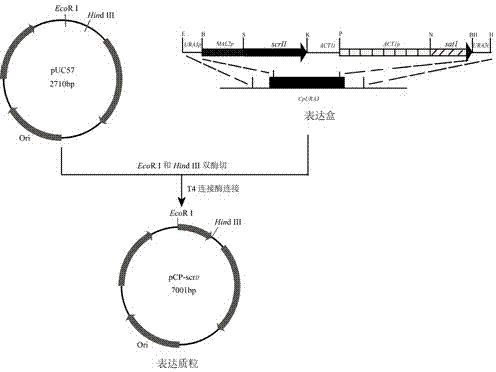
Method for using recombinant candida parapsilosis strain to efficiently prepare (S)-phenyl glycol
InactiveCN104774778AHelps understand the effect of stereoselectivityFungiMicroorganism based processesPhenyl glycolDrug biotransformation
The invention provides a method for using a recombinant candida parapsilosis strain to efficiently prepare (S)-phenyl glycol and belongs to the technical field of biological catalytic asymmetric transformation. The invention provides the recombinant candida parapsilosis strain Candida parapsilosis pCP-scrII preserved at the typical culture preservation center in China and marked with a preservation CCTCC NO: M2015107. According to the method, an expression plasmid of exogenous protein in candida parapsilosis is established, S-carbonyl reductase II is integrated to a candida parapsilosis genome to obtain the pCP-scrII, the candida parapsilosis is converted through electric shock to obtain the recombinant candida parapsilosis strain. By optimizing biotransformation reaction conditions, catalytic conversion is conducted on 2-hydroxyacetophenone through the recombinant strain to obtain the product S-phenyl glycol, the optical purity and yield of the product are up to 99.9%, an effective way is provided for efficient and low-cost preparation of the S-phenyl glycol, and a solid foundation is laid for industrial application of biological catalysis of chiral alcohol.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
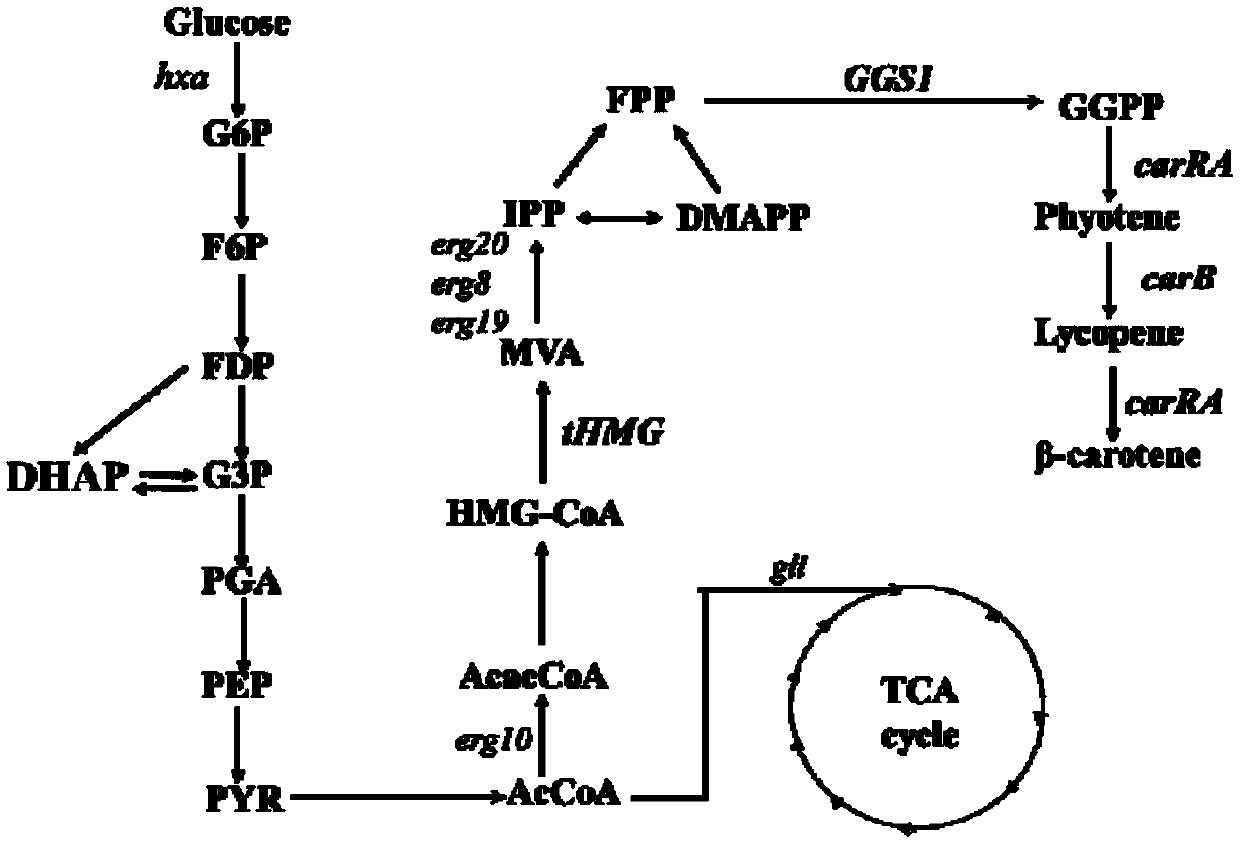
Recombinant bacteria used for producing beta-carotene and construction method utilizing Crispr-Cas9 technology
PendingCN109666596AIncrease the efficiency of homologous recombinationImprove stabilityFungiStable introduction of DNABeta-CaroteneKu70
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria used for producing beta-carotene and a construction method utilizing a Crispr-Cas9 technology. A Ku70 gene is subjected to knockout from yarrowia lipolytica, and then phytoene synthase / lycopene cyclase (carRA), phytoene desaturase (carB), geranyl pyrophosphate synthetase (GGS1) and a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase (tHMG) gene take snfas a target point and are integrated in a yarrowia lipolytica gene set after knockout of the ku70 gene, wherein the phytoene synthase / lycopene cyclase (carRA) and phytoene desaturase (carB) are from blakeslea trispora, and the geranyl pyrophosphate synthetase (GGS1) and the 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase (tHMG) gene are from the yarrowia lipolytica; the Crispr-Cas9 technology isutilized for regulating the copy number of the carRA, the carRA, the GGS1 and the tHMG, and the recombinant bacteria capable of producing the high-yield beta-carotene is constructed. After the recombinant bacteria is fermented, cultured, extracted and separated, the content of the beta-carotene can reach the dry cell weight of 35 mg / g, and the bacterial strain stability is high.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Artificially modified glucose oxidase gene and expression application thereof
The invention relates to an artificially modified glucose oxidase gene and expression application thereof, belonging to the fields of protein or enzyme preparation modification engineering and glucose oxidase production. The artificially modified glucose oxidase gene aims to further enhance enzyme activity on the basis of the existing glucose oxidase. An irrational means DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) shuffling technique in protein or enzyme preparation modification engineering is utilized to modify a glucose oxidase gene derived from Aspergillus niger Z-25; and a gene segment subjected to DNaseI random cutting is subjected to the DNA shuffling technique to recombine the segment into a complete variant gene, and the complete variant gene is connected with a shuttling expression plasmid and integrated into the yeast genome. The strain with obviously higher enzyme activity is screened from the mutant library, and the variant sequence is disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. In a 3L scale-up experiment of yeast, the end enzyme activity of the glucose oxidase reaches the higher level. Finally, in the aspect of enzyme activity and genes, the obtained high-enzyme-activity expression strain has favorable hereditary.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Saccharomyces cerevisiae, construction method thereof and application thereof in fermenting preparation of lycopene
ActiveCN108373980AEfficient synthesisEnhanced metabolic fluxFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLycopene
The invention discloses a construction method of saccharomyces cerevisiae and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae in fermenting preparation of lycopene. The invention has the beneficial effects that 1, the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium which recombines a plurality of gene expression boxes to different sites of a yeast genome through a powerful homologous recombination system of yeast is more stable in expression inheritance; 2, the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium is an optimized host cell for producing lycopene and the strain intensifies the metabolic flux of an isoprenoid synthesizing path, and can be used as a chassis host cell for producing other terpenoid compositions; and 3, the path of synthesizing lycopene by the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium is controlled by a constitute promoter, and no inducers are added in the fermenting process, so that the fermentation cost is saved, and the fermenting operation is simpler.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
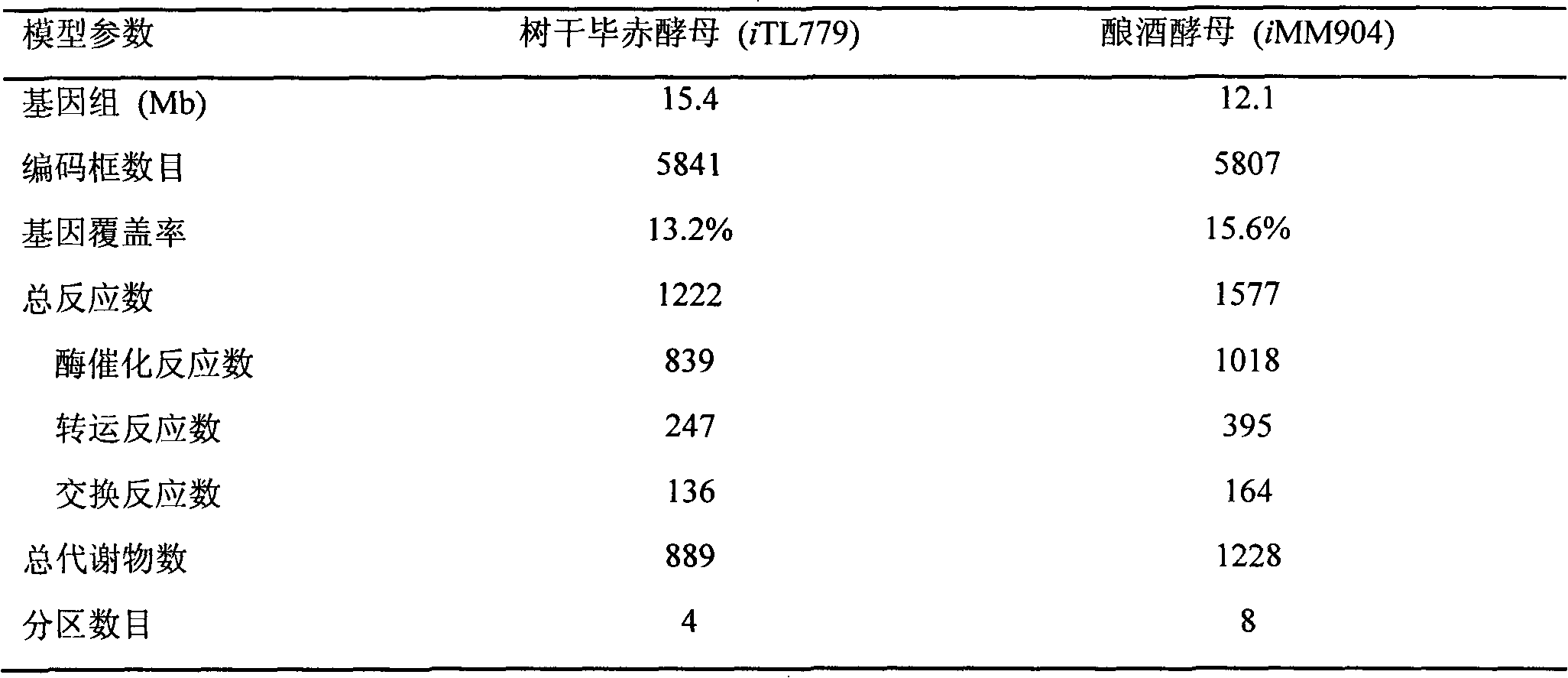
Pichia stipitis genome-scale metabolic network model construction and analysis method
The present invention describes an integrated genome-scale metabolic network model construction and analysis method with Pichia stipitis as an example, belonging to the system biology field. Based on the method, a constructed and obtained Pichia stipitis genome-scale metabolic network model is subjected to cell growth simulation of a system level and identification of a minimal gene and reaction set, and an important platform is provided for comprehensive understanding of metabolic characteristics and mechanism of the Pichia stipitis is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Screening method for genes of brewing yeast
InactiveUS7365164B2Increase productivityQuality improvementFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyAlcohol
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
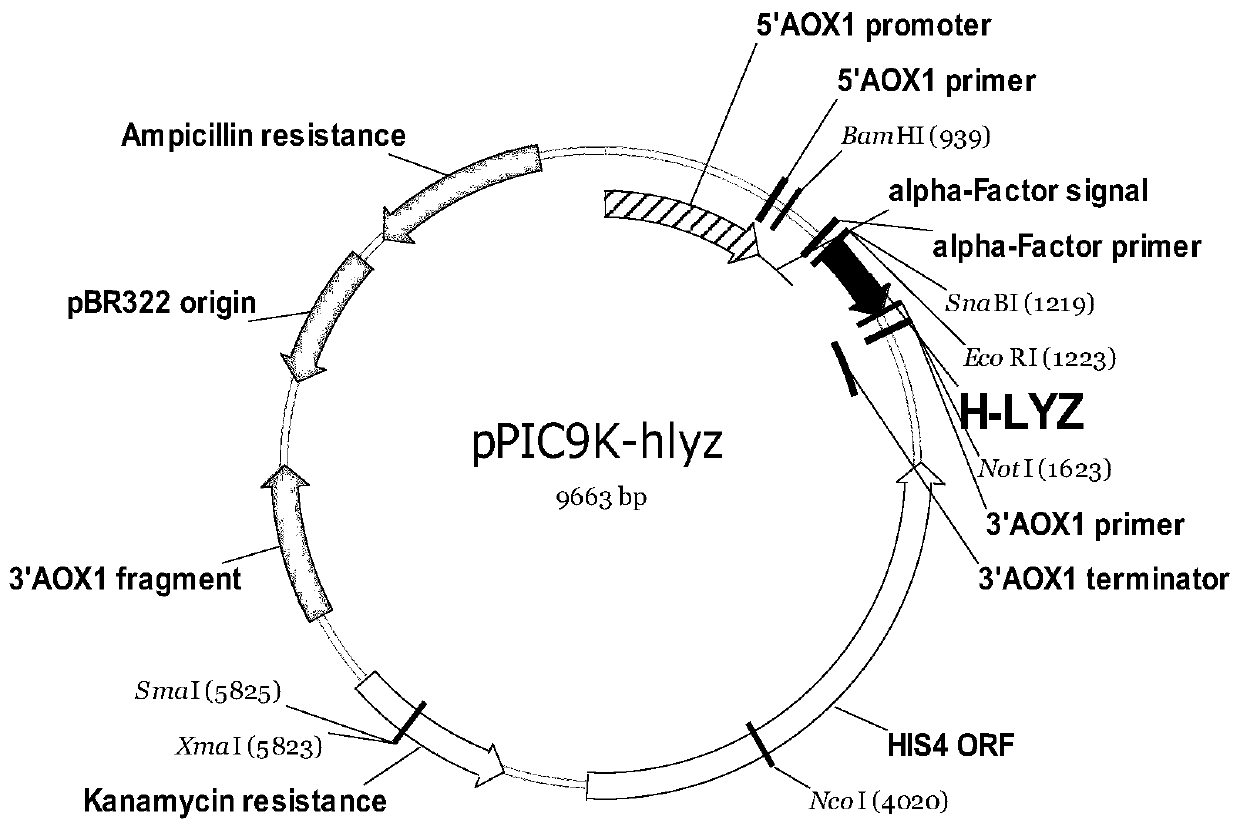
Recombinant pichia pastoris engineering bacterium containing high-copy-number humanized lysozyme gene and application thereof
InactiveCN110903991AIncrease enzyme activityFood safetyFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisMicrobiology
The invention discloses a recombinant pichia pastoris engineering bacterium containing a high-copy-number humanized lysozyme gene and application thereof. The recombinant pichia pastoris engineering bacterium is obtained by integrating a lysozyme gene shown in SEQ ID NO.1 with a pichia pastoris genome with a high copy number. According to the invention, a two-plasmid-mediated recombinant bacteriumconstruction method is adopted to obtain a recombinant bacterium with a copy number of 15; and the lysozyme produced by the recombinant bacterium has high enzyme activity, and the fermentation enzymeactivity is 180-220 KU / mL within 120-140h.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SILVER ELEPHANT BIO ENG +1
Method for rapidly constructing protein mutant pichia pastoris expression library and application thereof
ActiveCN112921029AReduce processing workImplement the buildMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesGenes mutationSodium acetate
The invention relates to a method for rapidly constructing a protein mutant pichia pastoris expression library and application thereof, which can effectively solve the problems of rapidly constructing the protein mutant pichia pastoris expression library and realizing directional selection of required property optimization enzyme, and the method comprises the following steps: constructing a target gene into a pichia pastoris vector pGAPZalpha series vector to construct plasmids, carrying out a polymerase chain reaction to obtain a PCR product, adding saturated sodium acetate and ethanol into the PCR product, carrying out centrifugation, carrying out precipitation and drying at room temperature, adding sterile deionized water for dissolving, electrically transforming the PCR product into pichia pastoris GS115 competent cells according to a yeast transformation method, coating a YPDS culture medium plate containing bleomycin with the cells to screen positive clones, extracting yeast genome DNA, then sequencing the PCR product, calculating the base mutation rate and gene mutation rate, and realizing the rapid construction of protein mutant Pichia pastoris expression library. The method has the advantages that the method is easy to operate, the time and labor are saved, the working efficiency is high, the application range is wide, and the economic and social benefits are huge.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY LIABILITY +1
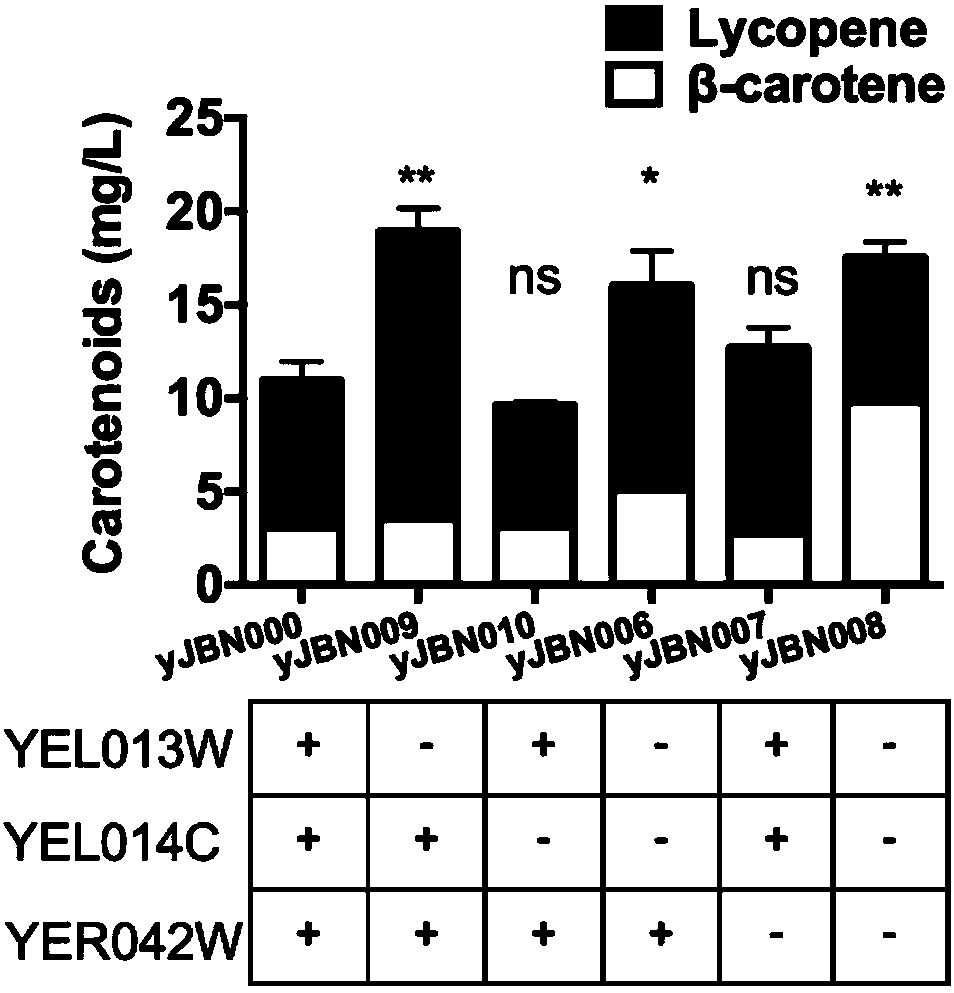
Application of gene YEL013W and gene YER042W
ActiveCN108359616AIncrease productionIdentify gene targetsFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGene targets
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and particularly discloses a novel application of gene YEL013W and gene YER042W in a yeast genome. Yield of a yeast strain for producing carotenoids can be increased remarkably by knock out the two genes, and a specific gene target is provided for modification of microbial engineering bacteria.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Yeast engineering bacterial strain capable of producing glutathione and application thereof to production of glutathione
ActiveCN102559529AIncrease productionHigh yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMolecular level
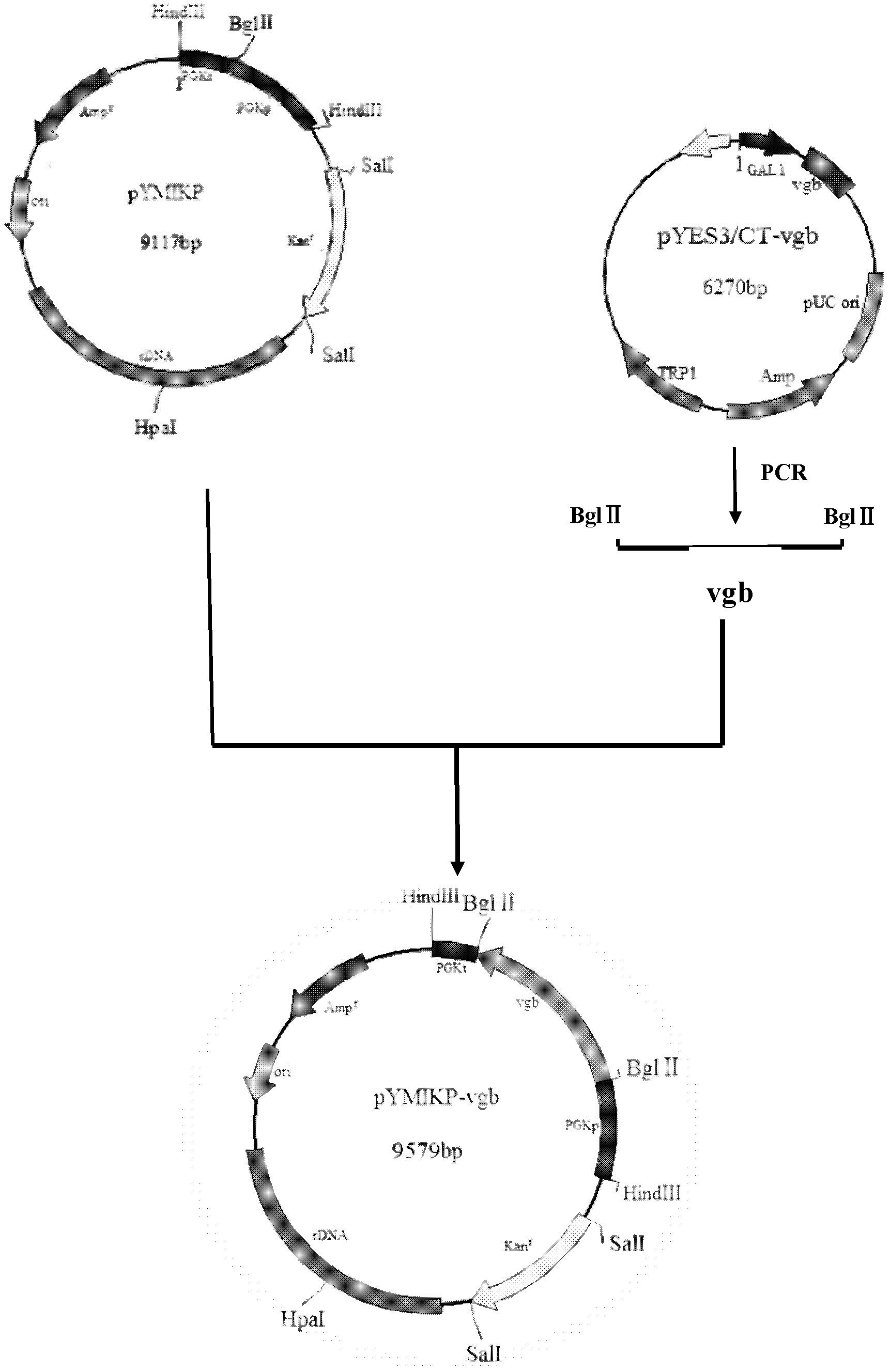
The invention discloses a yeast engineering bacterial strain capable of producing glutathione, which has the bacterial strain name of 101-V and the classification name of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on February 15, 2012, with the collection number of CGMCC NO. 5758. The invention also discloses a method for establishing an engineering bacterial strain capable of producing glutathione at a high yield. The method comprises the following steps: integrating a Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgb into a yeast genome capable of producing glutathione, and screening to obtain a recombinant yeast capable of expressing transparent Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene. Therefore, the oxygen utilizing capability of the hemoglobin gene recombinant strainis improved in a molecular level, the contradiction between supply and demand of oxygen in the microbiological fermenting process is solved, the consumption of oxygen and energy is lowered, and the yield of glutathione is increased.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
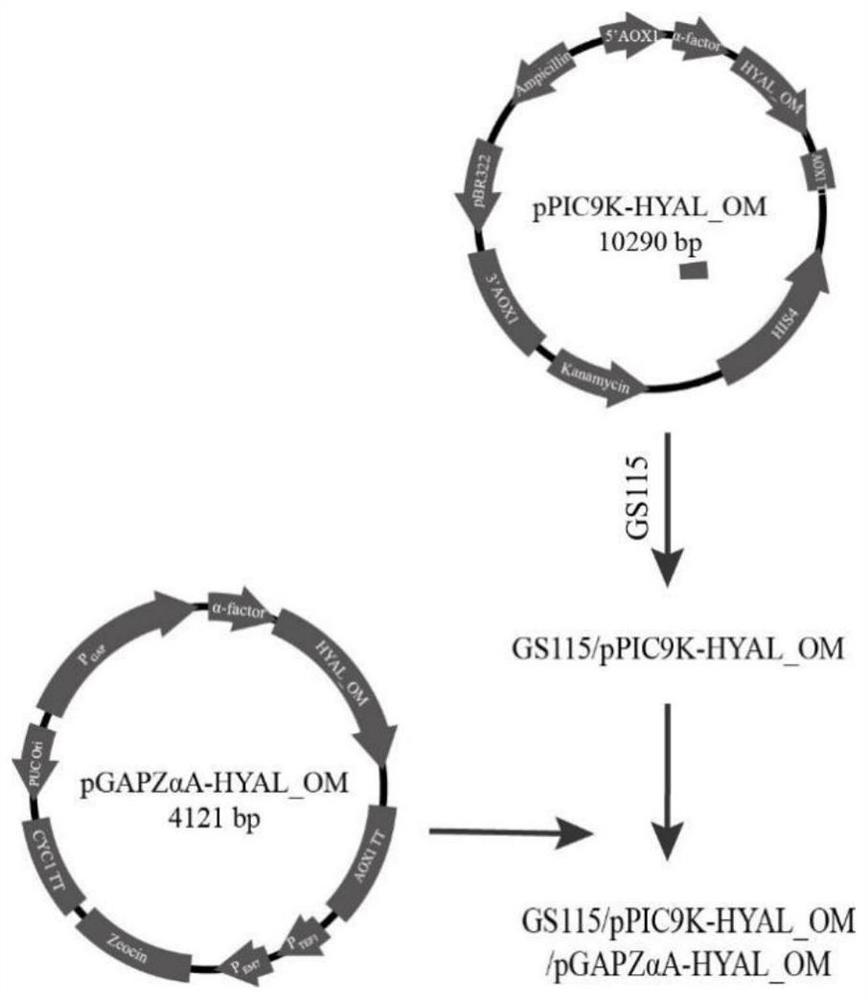
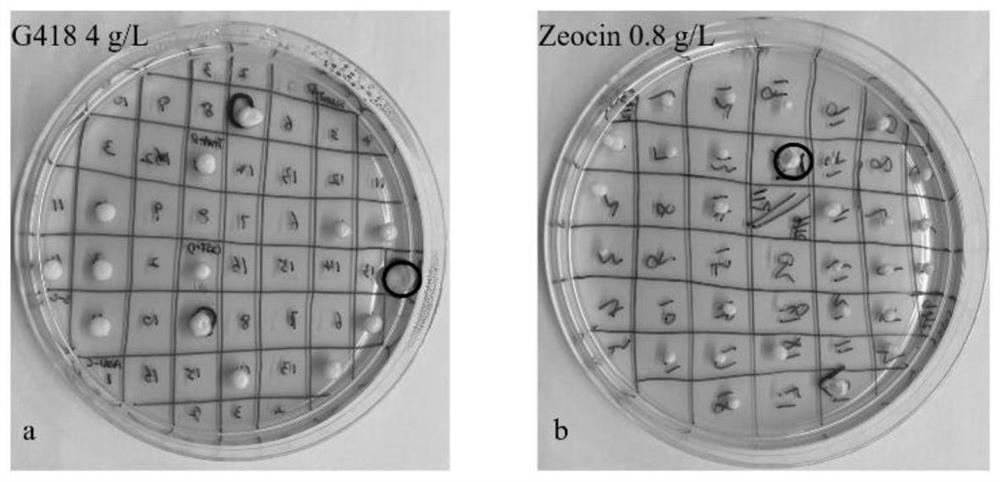
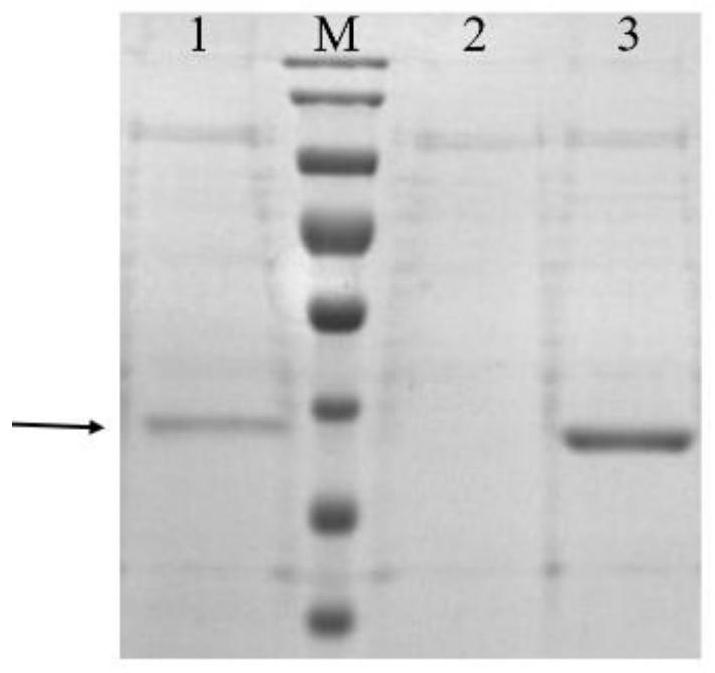
Engineering yeast strain with high yield of hyaluronidase and application of engineering yeast strain
The invention provides an engineering yeast strain for high yield of hyaluronidase. The engineering yeast strain is obtained by respectively integrating hyaluronidase genes as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 into any two sites of a yeast genome by adopting a genome integrated vector. An engineering yeast strain for producing hyaluronidase at high yield is constructed through an integrated plasmid mediated recombinant strain construction method, the highest enzyme activity of the engineering yeast strain in a culture medium taking methanol as a carbon source is 5.9 * 10 < 5 > U / mL, and the highest enzyme activity of the engineering yeast strain in a culture medium taking glycerol as a carbon source is 3.6 * 10 < 5 > U / mL. Therefore, the method is beneficial to further reducing the cost of industrial production of the Hongyonia macrophylla hyaluronidase, so that the application range of the hyaluronidase in the fields of medicine, chemical industry and food is expanded.
Owner:BLOOMAGE BIOTECHNOLOGY CORP LTD
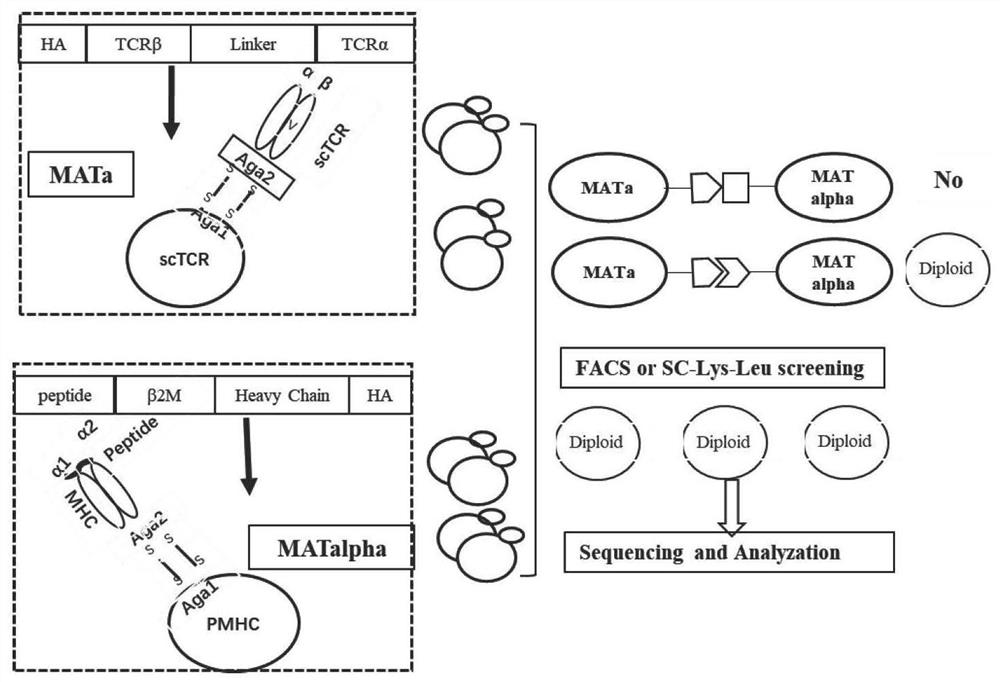
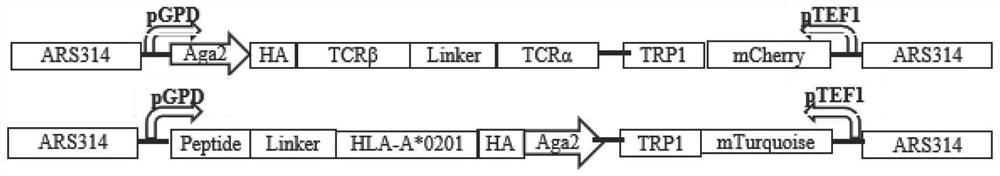
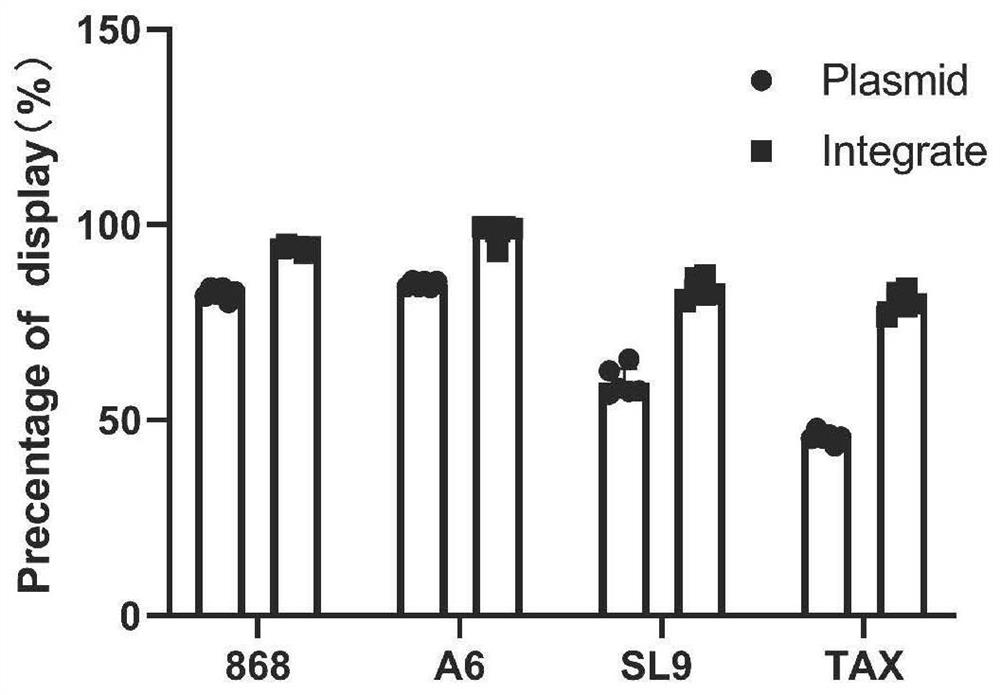
Method for rapidly identifying high-affinity TCR antigenic cross-reaction activity
ActiveCN112501269ADemonstration of increased kurtosisSimplify follow-up proceduresFungiImmunoglobulin superfamilyA-DNAPromoter
The invention relates to a method for rapidly identifying high-affinity TCR antigenic cross-reaction activity. According to the invention, TCR and pMHC sequences are adjusted into constitutive promoter for inducible expression, and the element is integrated into into a yeast genome to be expressed. The method comprises the following steps: displaying TCR and pMHC proteins on the surfaces of yeastsof different mating types; carrying out a yeast mating experiment by utilizing TCR and pMHC-integrated yeasts of different mating type ; and carrying out diploid screening and next generation sequencing. According to the method for rapidly identifying high-affinity TCR antigenic cross-reaction activity provided by the invention, pure protein is not needed, only a DNA sequence needs to be synthesized, and a more complete antigen mutation library can be obtained within one week by using a Golden-gate cloning method, thus being convenient and efficient; and the limitation of screening on the cellular level is broken through by means of a yeast mating system, operation steps are simplified, an antigen sequence interacting with a specific TCR can be obtained in a short time, and experimental results are reliable.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria for producing campesterol and construction method
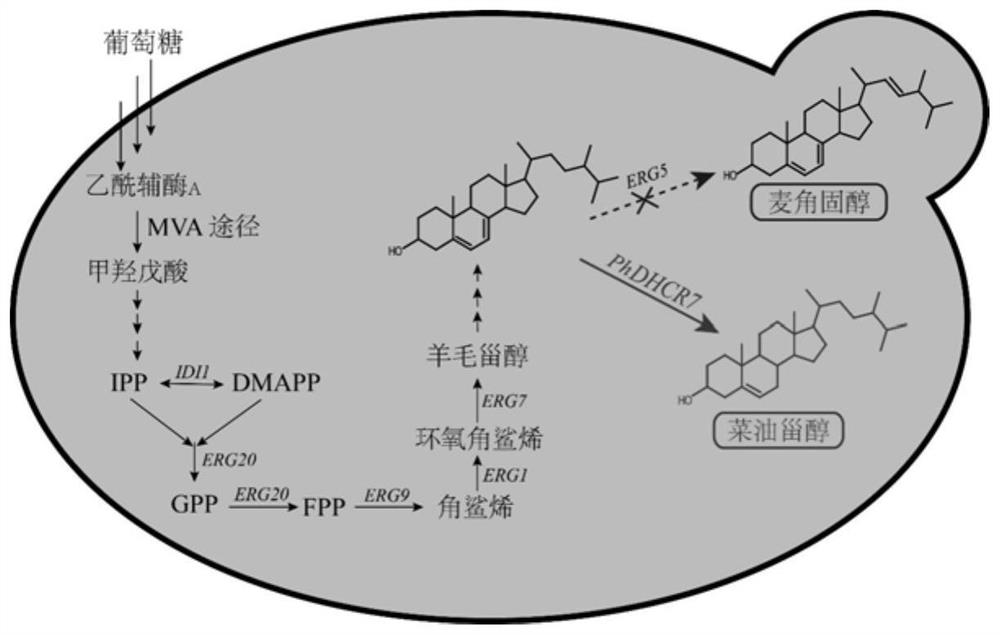
The invention discloses saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria for producing campesterol and a construction method, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and bioengineering. An expression cassette element of 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase is introduced into a yeast cell body, and is integrated into a yeast genome by utilizing a CRISPR / Cas9 gene operating system, C-22 sterol desaturase is knocked out, competition of an ergosterol branch path is relieved, and yeast synthesis from glucose to campesterol is realized. The method is simple in process, green and environment-friendly, and can be used for producing campesterol through fermentation. The yield of campesterol prepared by adopting the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain BY4742-delta erg5-TEF1p-dhcr7-ADH1t provided BY the invention can reach 253.35mg / L in a shake flask stage, and the horizontal yield of a fermentation tank can reach 916.88mg / L, which is increased by 2.6 times compared with the yield of campesterol in the shake flask stage of the strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Construction method and application of yarrowia lipolytica with reduced fermentation foam production capacity
PendingCN113801896AImprove effective utilizationLow costFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyDefoaming Agents
The invention discloses a construction method of yarrowia lipolytica with reduced fermentation foam production capacity and a method for synthesizing erythritol by using the yarrowia lipolytica. According to the construction, yarrowia lipolytica for synthesizing erythritol is adopted as a base microorganism, and a yeast genome is mutated through a metabolic engineering improvement means to obtain a mutant strain. The obtained mutant strain remarkably reduces the foam production capacity in the fermentation process. In the fermentation process, the dosage of a defoaming agent is obviously reduced compared with that of a control strain, and even the defoaming agent is not added any more. Glucose with the initial fermentation concentration of 50-350 g / L and the like are used as a carbon source, a nitrogen source with the initial fermentation concentration of 5-30 g / L and inorganic salt are used as raw materials, the obtained yarrowia lipolytica mutant strain is inoculated after sterilization and cooling, and fermentation is conducted under the aerobic condition. And after the fermentation is finished, the erythritol is purified from the fermentation liquid.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
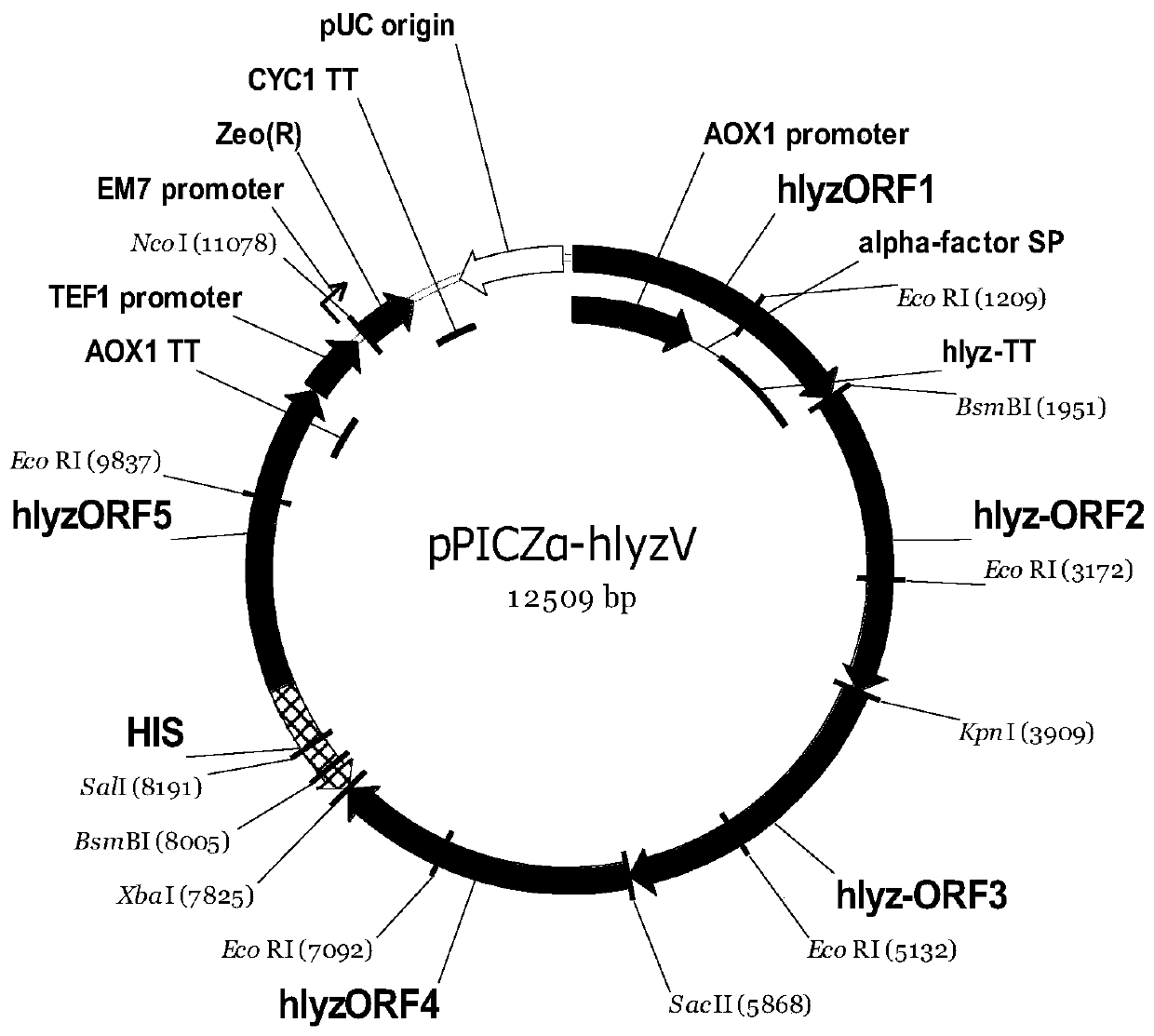
Recombinant pichia pastoris engineering bacterium containing high-copy-number egg white lysozyme gene and application thereof
InactiveCN111019851AIncrease enzyme activityFood safetyFungiMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneMicrobiology
The invention discloses a recombinant pichia pastoris engineering bacterium containing a high-copy-number egg white lysozyme gene and application thereof. The pichia pastoris engineering bacterium isobtained by integrating the lysozyme gene shown in SEQ ID NO.1 into a pichia pastoris genome at a high copy number. According to the invention, two plasmid mediated recombinant bacterium constructionmethods are adopted to obtain a recombinant bacterium with a copy number of 13; the lysozyme produced by the recombinant bacteria has high enzyme activity, and the fermentation enzyme activity is 45-50KU / mL within 120-140h.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SILVER ELEPHANT BIO ENG +1
Preparation and application of oral recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for expressing porcine epidemic diarrhea virus S protein
PendingCN113736676AImprove securityLow costFungiSsRNA viruses positive-senseEpidemic diarrheaYeast genome
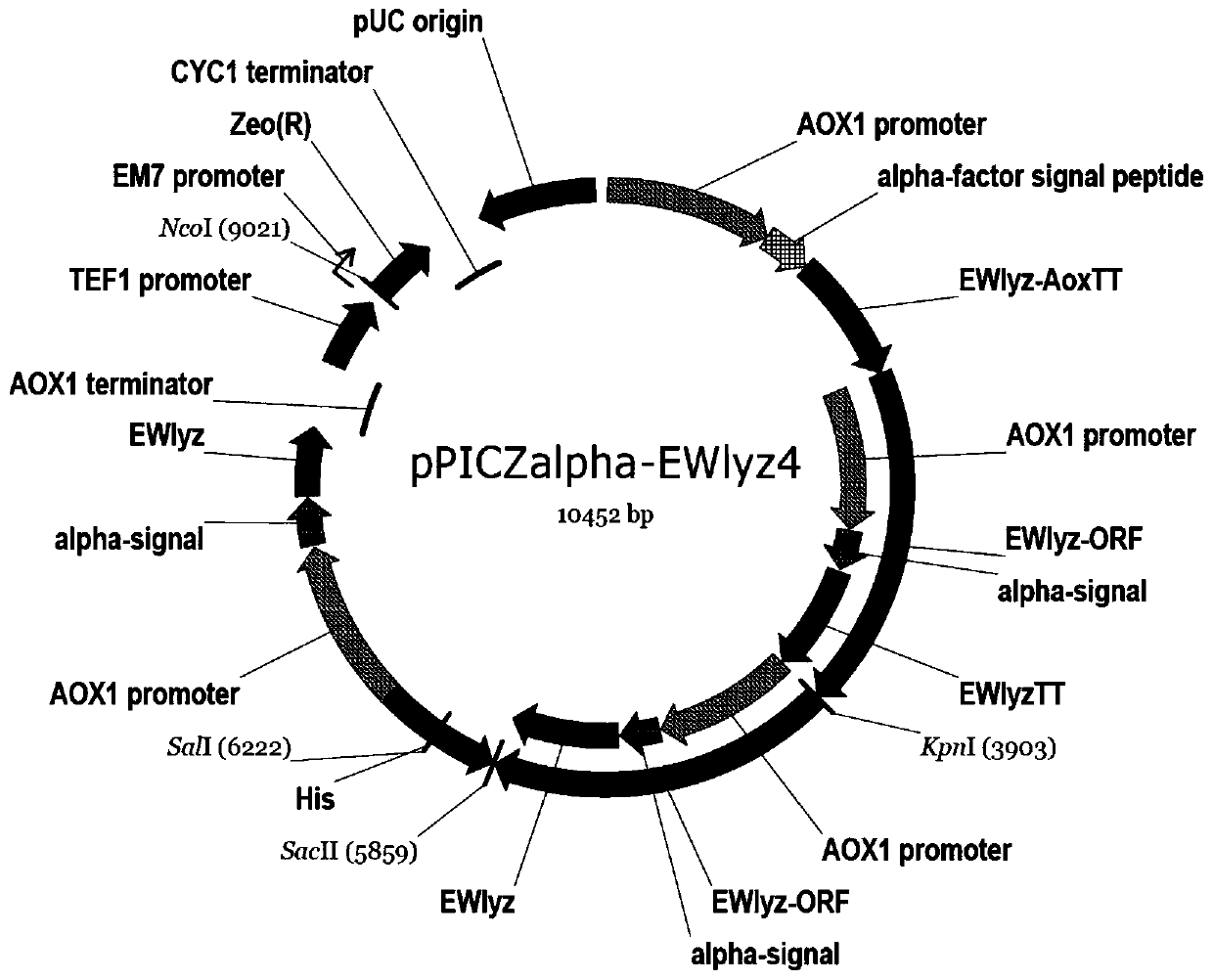
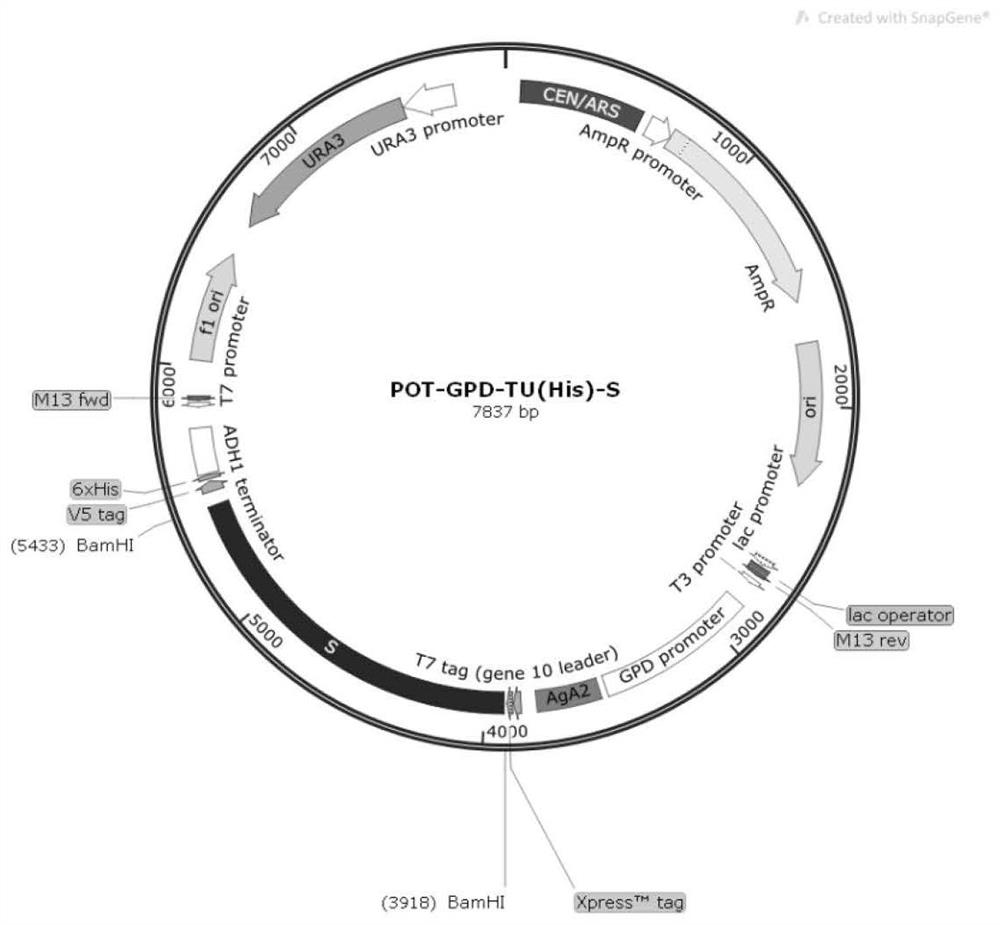
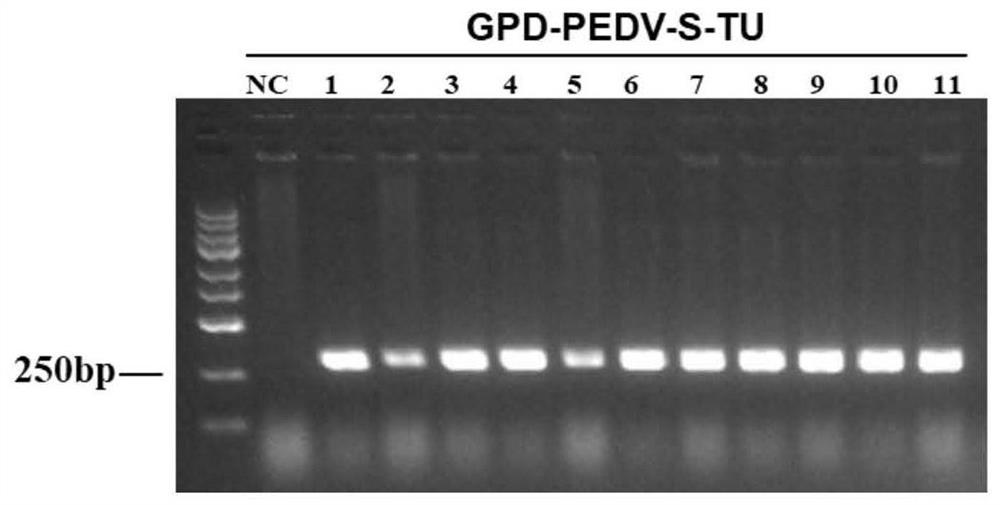
The invention discloses preparation and application of oral recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for expressing porcine epidemic diarrhea virus S protein. The oral recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae comprises S1 structural domains from 234 site to 633<rd> site of the S protein and partial S2 structural domains from 640 site to 736 site. An S protein truncated body complete transcription unit GPD-PEDV-S-TU constructed in vitro is integrated into a yeast genome through homologous recombination; the S protein truncated body is displayed on the surface of a yeast cell by utilizing an Aga1-Aga2 surface display system to obtain an S protein surface display type recombinant yeast strain ST1814G-PEDV-S; and the oral recombinant yeast is prepared by utilizing the obtained strain. The oral recombinant yeast disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low cost, safety in production and utilization, simplicity and convenience for operation, safety and effectiveness, and has an immune protection effect; and a choice is provided for prevention and control of porcine epidemic diarrhea.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
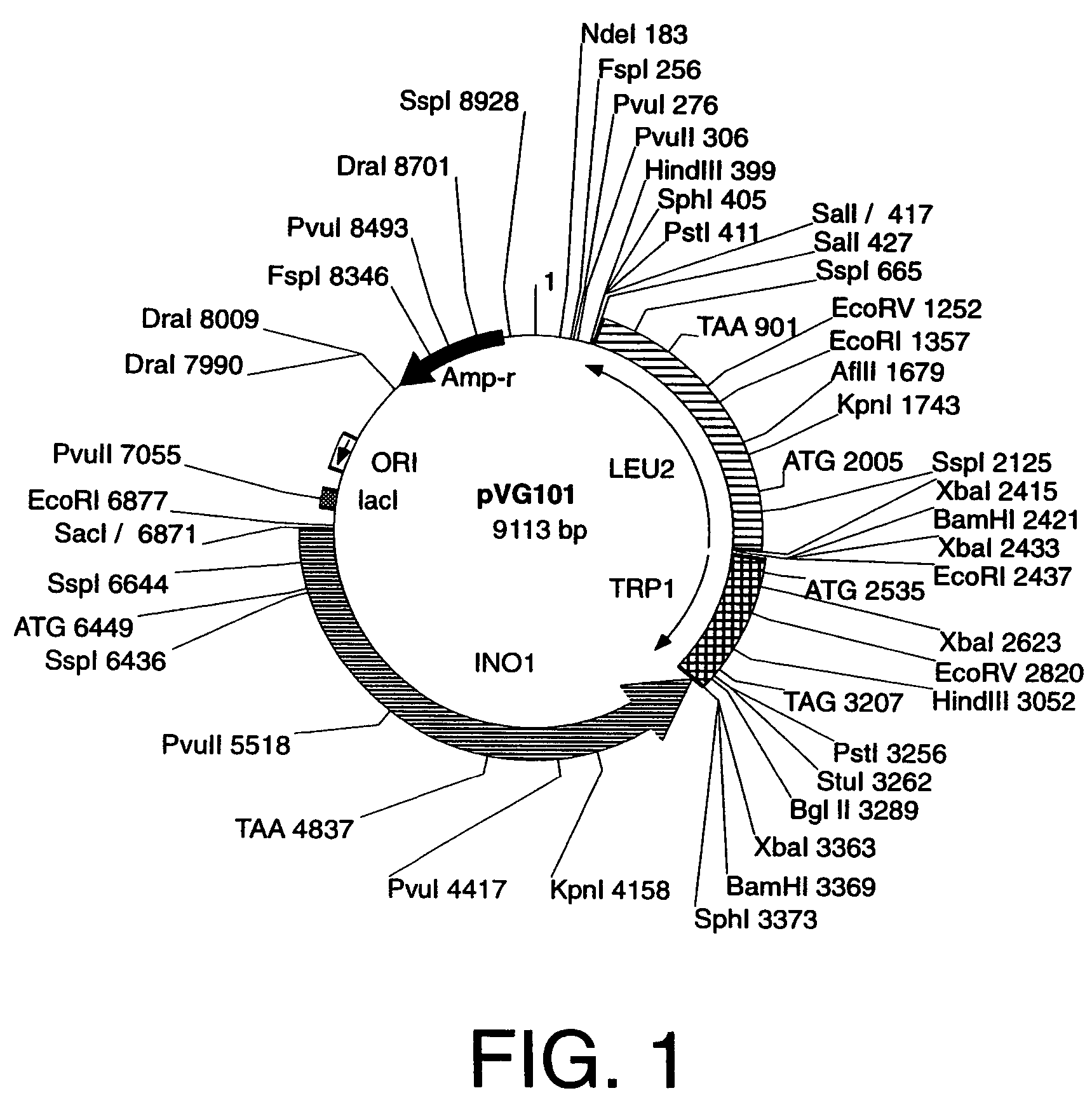
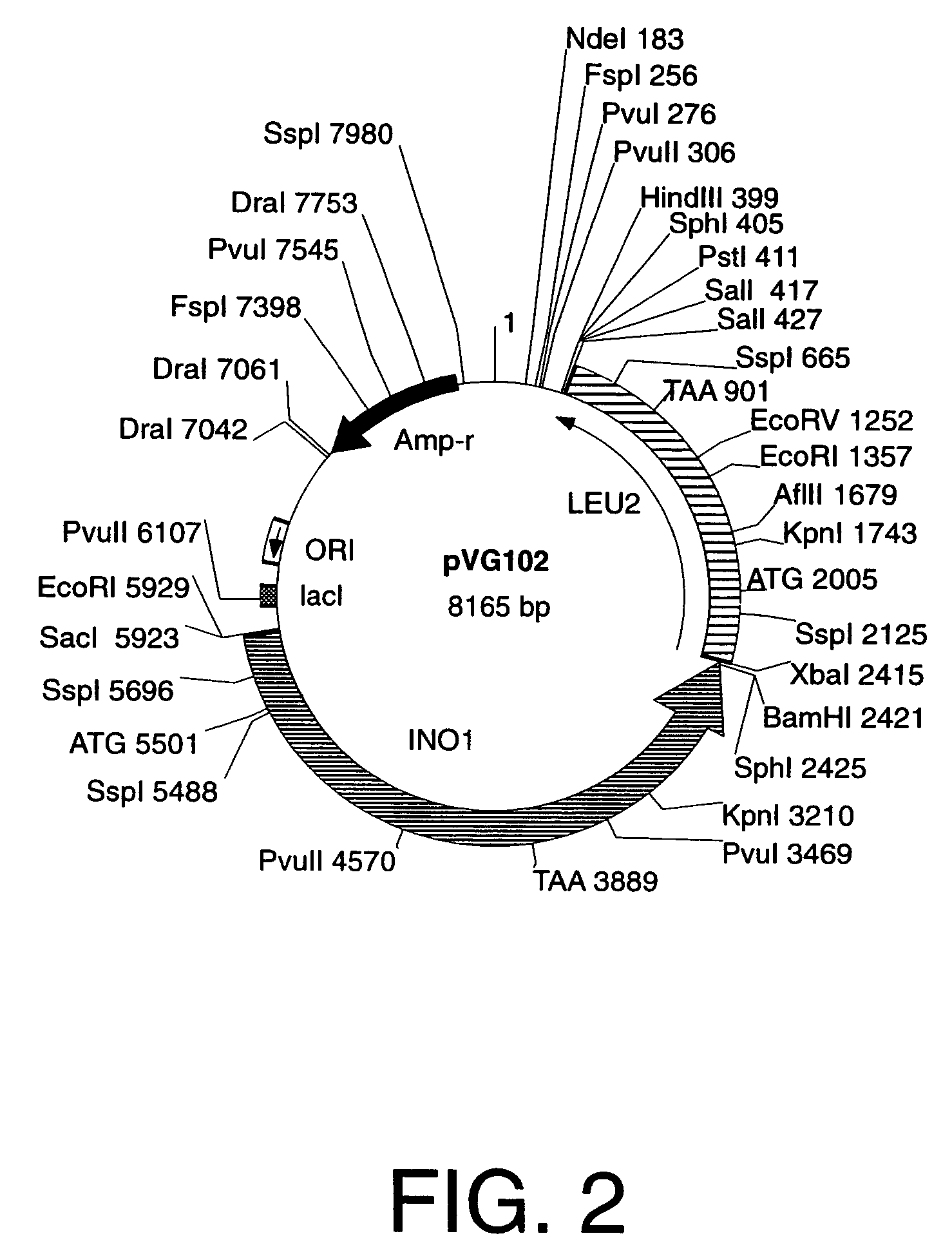
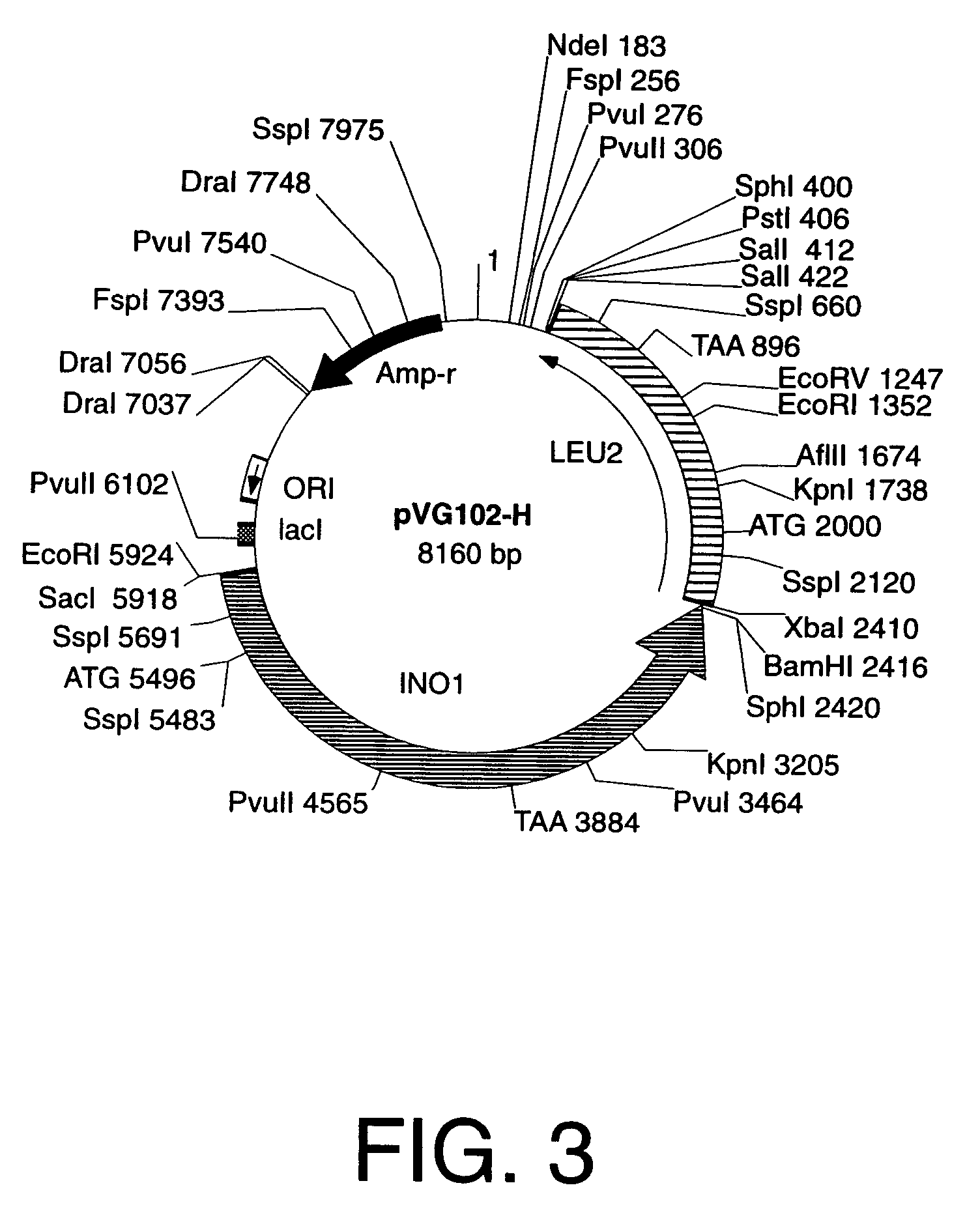
Cells engineered to contain genes of interest
Methods and materials are provided for stably introducing any gene into a specific locus in the genome of a microorganism such as yeast without the addition of any drug resistance genes. Specifically provided herein are new genetically engineered inositol-overproducing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains obtained by using a novel set of yeast integration plasmids that allow the safe, stable, and controlled introduction of homologous as well as heterologous genes into the host genome. In particular, specific loci of the S. cerevisiae yeast genome can be targeted with single or multiple copies of a specific gene that is desired to be expressed or a given set of specific genes that the host can use without the addition of any drug resistance genes. The principles of this new methodology can also be used for the construction of other recombinant yeast and bacterial strains as well as higher eukaryotic cells.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Yeast genome editing method based on CRISPR/Cas9
PendingCN112458092AGuaranteed editing efficiencyEfficient and convenient editingFungiHydrolasesEscherichia coliYeast genome
The invention relates to a yeast genome editing method based on CRISPR / Cas9. The method comprises the following steps of: designing a target sequence according to target sites on a saccharomyces cerevisiae genome, constructing a gRNA expression cassette by using the target sequence, and then, together transforming saccharomyces cerevisiae cells by using the gRNA expression cassette, a starting vector and donor DNA fragments, so that editing on multiple genome sites of saccharomyces cerevisiae at the same time is realized, wherein homologous arms with the same sequence as the starting vector are arranged on two sides of the gRNA expression cassette; two ends of the donor DNA fragment are provided with homologous arms which are the same as upstream and downstream sequences of a saccharomycescerevisiae genome target site; and Cas9 protein is expressed in the saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. According to the method, gRNA plasmid construction does not need to be carried out in escherichia coli or by utilizing technologies, such as Golden Gate; a gRNA vector skeleton does not need to be amplified; therefore, the experiment time is shortened; the experiment cost is reduced; and multiple genome sites can be efficiently edited at the same time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A kind of recombinant yeast strain and its construction method and application
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and discloses a recombinant yeast strain, a construction method thereof and the application thereof. In the recombinant yeast strain, gal1, gal7, gal10 and ypl062w genes are knocked out, and the recombinant yeast strain comprises 6 gene segments which are integrated to the genome through yeast homologous recombination. On the above basis, the recombinant yeast strain is further integrated onto one gene segment of a yeast genome, so that a better recombinant yeast is obtained. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the yeast strain is constructed based on gene knock-out, and an optimized host cell for producing lycopene is provided. Meanwhile, functional genes crtE crtB and crtI of a specific source combination and used for the synthesis of lycopene, specific yeast endogenous genes and specific exogenous genes are selected. The above selected genes are integrated to the gene knock-out genome of the yeast strain, and then a brand-new recombinant strain capable of producing high-yield lycopene is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
A kind of artificially modified glucose oxidase gene and its expression application
The invention relates to an artificially modified glucose oxidase gene and expression application thereof, belonging to the fields of protein or enzyme preparation modification engineering and glucose oxidase production. The artificially modified glucose oxidase gene aims to further enhance enzyme activity on the basis of the existing glucose oxidase. An irrational means DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) shuffling technique in protein or enzyme preparation modification engineering is utilized to modify a glucose oxidase gene derived from Aspergillus niger Z-25; and a gene segment subjected to DNaseI random cutting is subjected to the DNA shuffling technique to recombine the segment into a complete variant gene, and the complete variant gene is connected with a shuttling expression plasmid and integrated into the yeast genome. The strain with obviously higher enzyme activity is screened from the mutant library, and the variant sequence is disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. In a 3L scale-up experiment of yeast, the end enzyme activity of the glucose oxidase reaches the higher level. Finally, in the aspect of enzyme activity and genes, the obtained high-enzyme-activity expression strain has favorable hereditary.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com