Site-directed mutation method for genomes of saccharomyces cerevisiae
A genome-specific, Saccharomyces cerevisiae technology, applied in the field of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome site-directed mutation, can solve the problems of long time, limited success rate, high cost, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
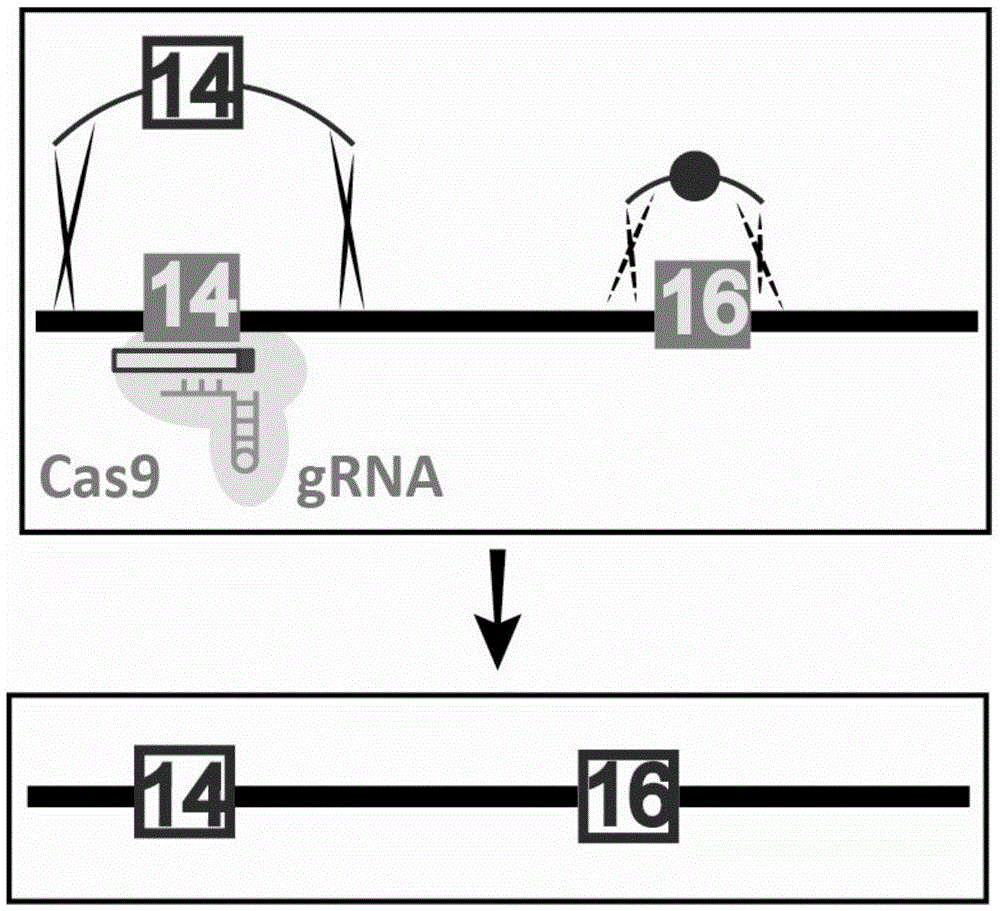
[0041] Using CRISPR / Cas9 technology, a single point mutation was introduced into sites 14 and 16 on chromosome V of S. figure 1 ), including the following steps:
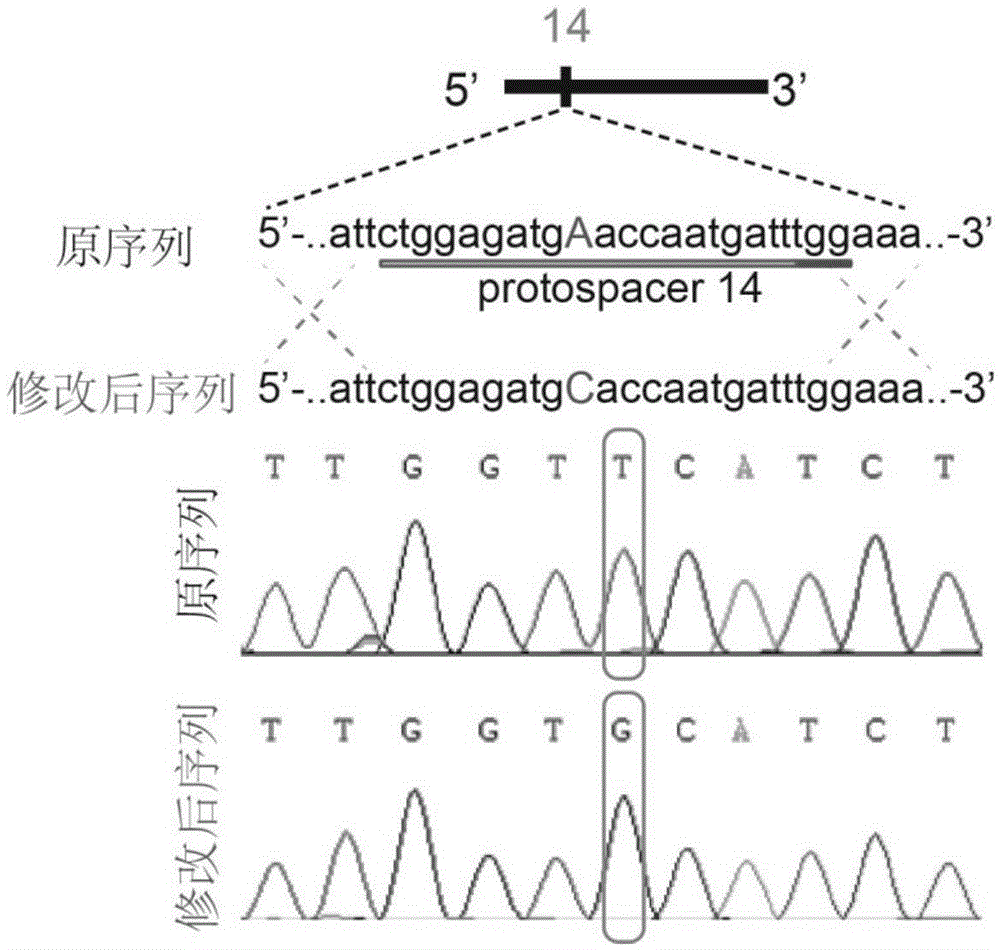
[0042] 1. The sequence at position 14 is "ctggagatgAaccaatgattTGG" (as shown in SEQIDNo.1), wherein TGG is a PAM sequence, and A is the site to be mutated; the sequence after introducing a single point mutation is "ctggagatgCaccaatgattTGG" (as shown in SEQIDNo.2 Shown), wherein TGG is the PAM sequence, and C is the site after mutation. The sequence at position 16 is "ttagctagcaaAcccttagaac" (as shown in SEQIDNo.3), where A is the site with a mutation, and the sequence after introducing a single point mutation is "ttagctagcaaCcccttagaac" (as shown in SEQIDNo.4), where C is the mutation post site. Site 14 was selected as the Cas9 cleavage target site, and site 16 was selected as the co-transformation mutation site.
[0043] 2. Construct the guide-RNA plasmid of site 14 to be repaired, and its construction steps are...
Embodiment 2
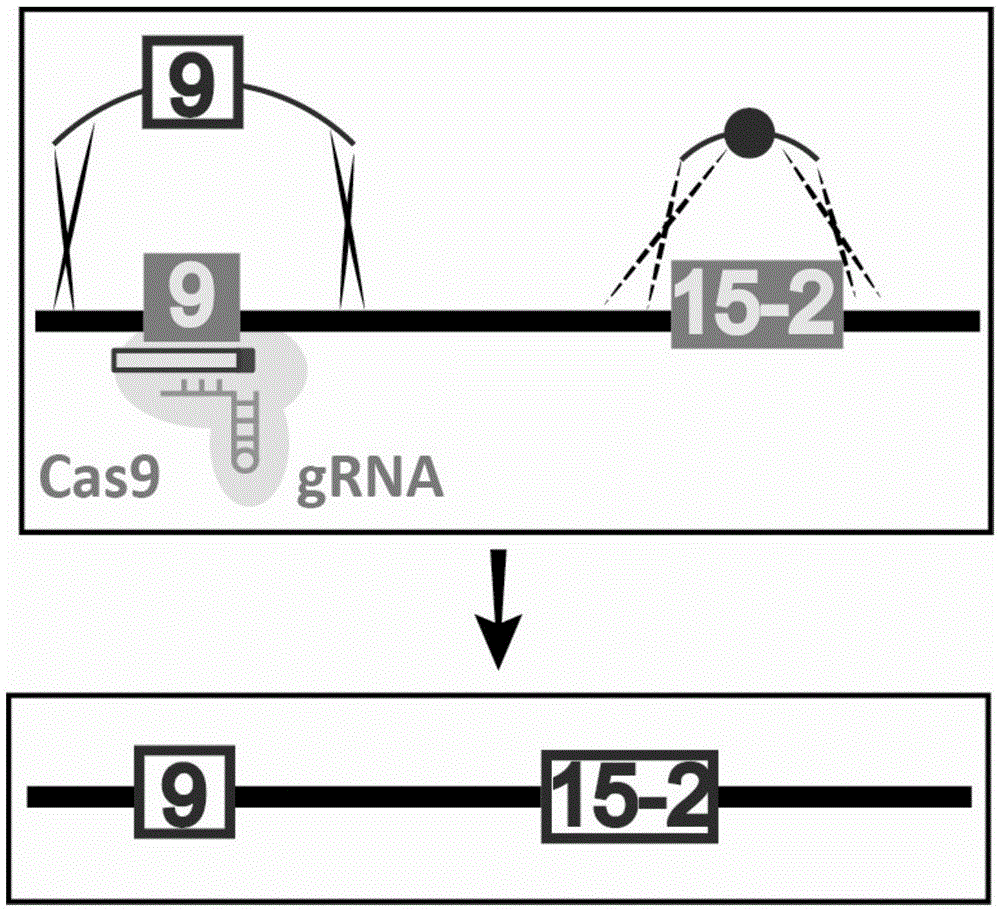
[0068] Using CRISPR / Cas9 technology, the 9 sites on chromosome V of Saccharomyces cerevisiae synthetic type ( image 3 ) introducing a single point mutation, comprising the following steps:
[0069] 1. The sequence to be introduced into the single point mutation is "aaatacgaagaacCattttgCGG" (as shown in SEQIDNo.15), wherein CGG is a PAM sequence, and C is the site to be repaired; the sequence after introducing the single point mutation is "aaatacgaagaacGattttgCGG" (as shown in SEQIDNo. .16), where CGG is the PAM sequence, and G is the repaired site. Site 9 was selected as the Cas9 cleavage target site, and site 15-2 was selected as the co-transformation mutation site.
[0070] 2. Construct the guide-RNA plasmid of site 9 to be repaired, the construction steps are as follows:
[0071] a) Select the protospacer as aaatacgaagaacCattttg;
[0072] b) synthesize primers "GCAGTGAAAGATAAATGATCaaatacgaagaacCattttgGTTTTAGGCTAGAAATAGC" (as shown in SEQ ID No. 17) and "GCTATTTCTAGCTCTA...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com