Microbial complex microbial agent for degrading lactic acid
A technology of microbial preparations and microbial strains, applied in the field of microorganisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The screening of embodiment 1 bacterial strain
[0038] During the fermentation process of Maotai-flavored liquor, a strain of lactic acid-tolerant Pichia kudriazwii was screened, and the process was as follows.
[0039] Samples of fermented grains of a Maotai-flavor liquor were collected. Weigh 10g of sample into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 90mL sterile saline, add glass beads and shake evenly. Aspirate 0.1mL supernatant into 100mL enriched medium, culture at 30°C, 200rpm for 2-4 days, observe whether the culture medium is turbid; if the culture medium is obviously turbid, absorb 0.1mL enriched culture medium In 100mL liquid screening medium, culture at 30°C and 200rpm for 2 days. After 3 to 4 times of culture, the culture solution was gradually diluted on YPD solid medium. After 3 to 4 days of culture, the single colony was the target strain with anti-lactic acid properties.
[0040] Randomly pick 7 single bacterium colonies from this plate, inoculate until adding...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The identification of embodiment 2 bacterial strains
[0042] (1) Colony characteristics and cell morphology
[0043] The colony is white, with rough surface and uniform texture, easy to pick. As a result of observing the morphology through a microscope, it was found that the isolated and screened strain cells were elliptical, and some of them were budding and dividing.
[0044] (2) Physiological and biochemical characteristics
[0045] DC-16 was inoculated in sorghum juice medium, and after 1 day of fermentation at 30°C and 200rpm, DC-16 entered a stationary phase. Such as Figure 4 As shown, when fermented for 3 days, the biomass OD of DC-16 600 Up to 4.48.
[0046] The glucose content in the sorghum juice medium is 58g·L -1 . Such as Figure 5 As shown, after 60 hours of fermentation, DC-16 can convert 58g·L of sorghum juice medium -1 The glucose is completely consumed and produces 13.06g·L -1 ethanol.
[0047] (3) Molecular biological identification
[0...
Embodiment 3
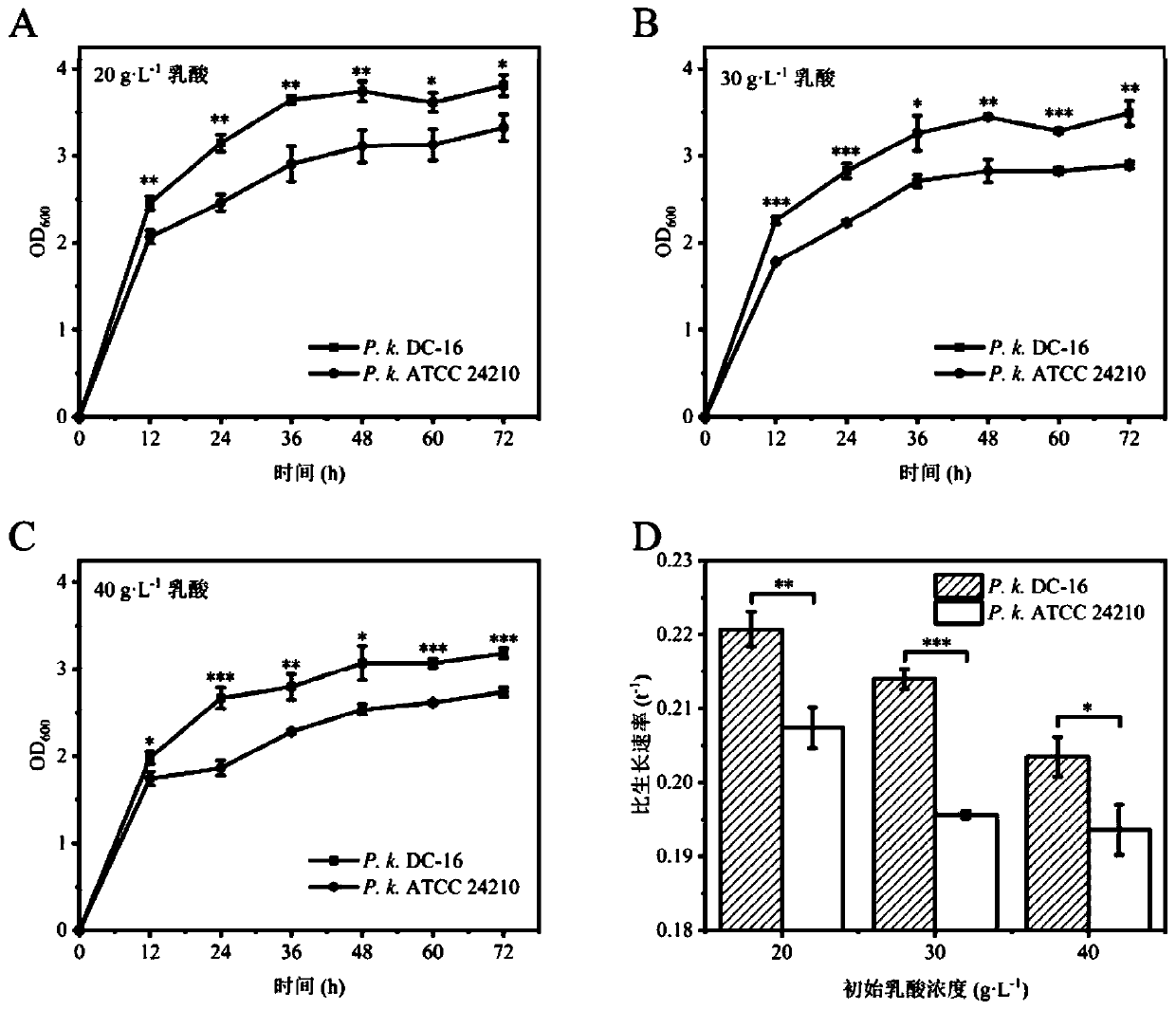
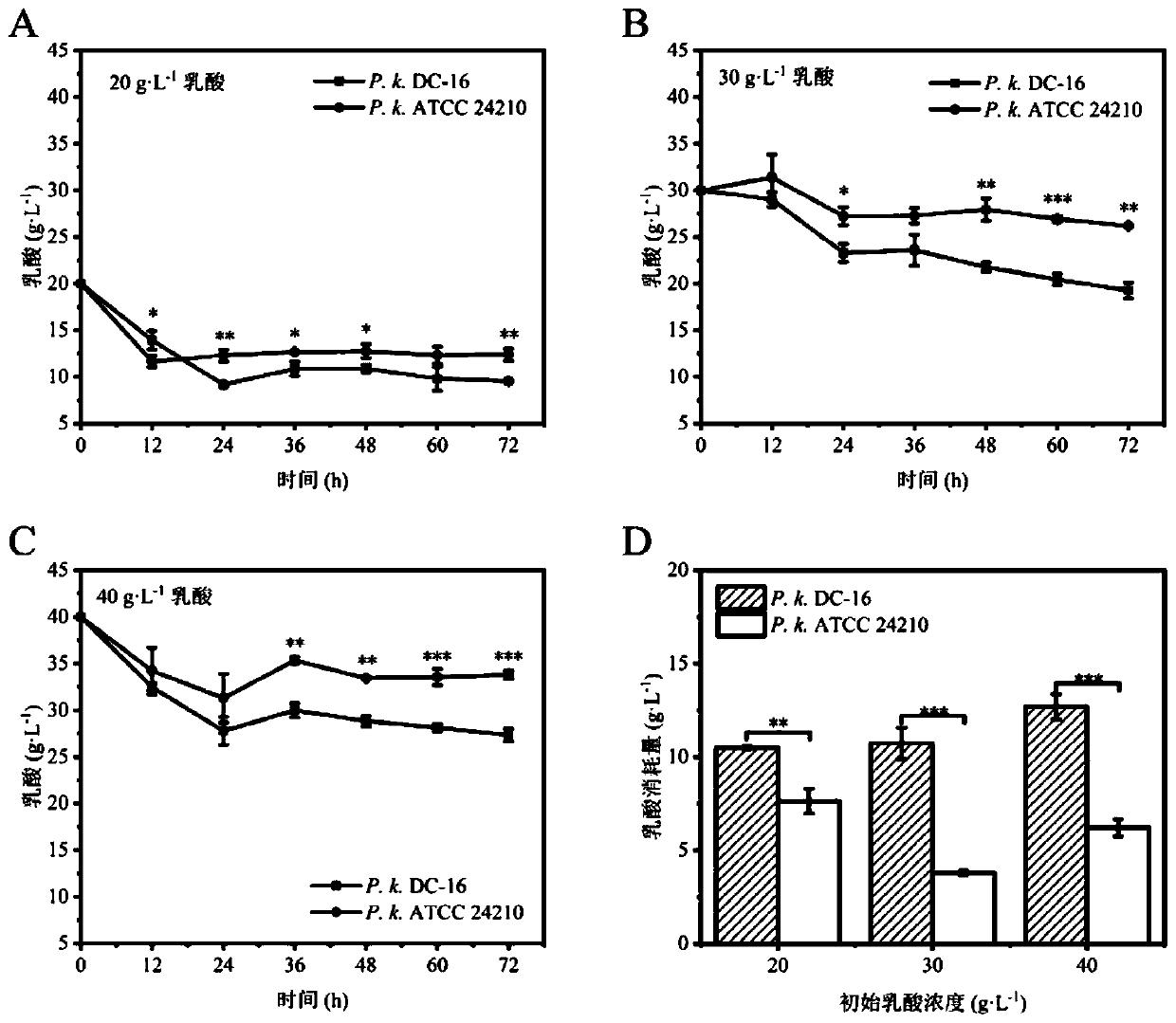
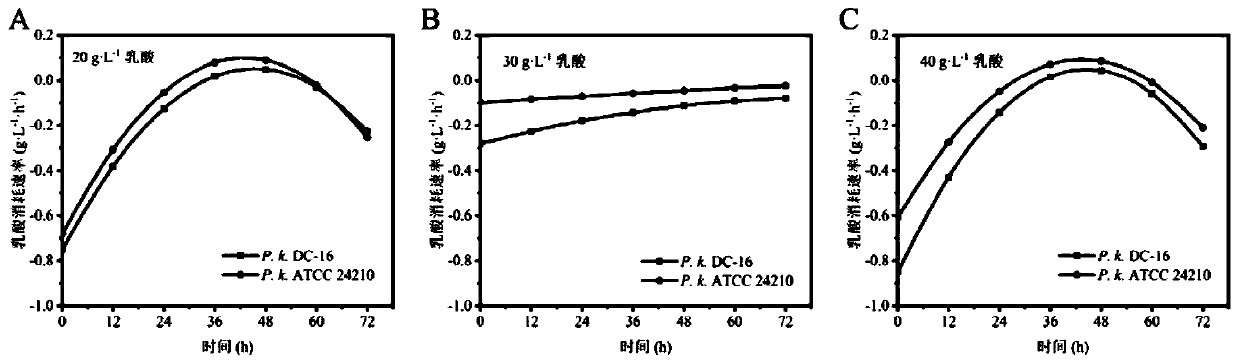
[0050] Embodiment 3 Yeast of the present invention is to the degradation situation of lactic acid
[0051] Using sorghum juice medium with different lactic acid concentrations as the fermentation medium, the experimental strain Pichia kudri Azwiya DC-16 (hereinafter referred to as P.k.DC-16) and its model strain Pichia kudri Azwiya Yeast ATCC24210 (hereinafter referred to as P.k.ATCC 24210) was used for lactic acid metabolism experiments. According to the detection results of lactic acid in fermented grains during the screening process, the addition amount of lactic acid in the metabolic experiment was designed to be 20, 30, and 40 g·L respectively. -1 .
[0052] Experimental and control group settings:
[0053] Control group 1: add 20g·L to -1 Lactic acid sorghum juice medium was inoculated with P.k.ATCC24210 at 7% inoculation volume (v:v);
[0054] Experimental group 1: add 20g·L to -1 Inoculate P.k.DC-16 in lactic acid sorghum juice medium at 7% inoculation volume (v:v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com