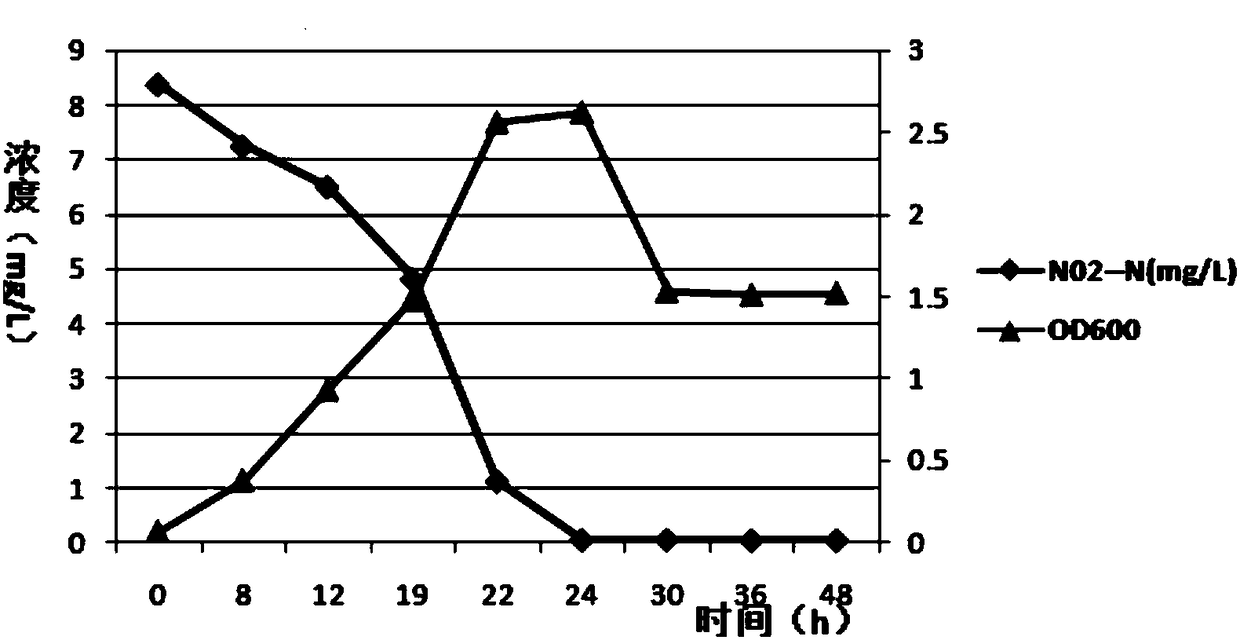
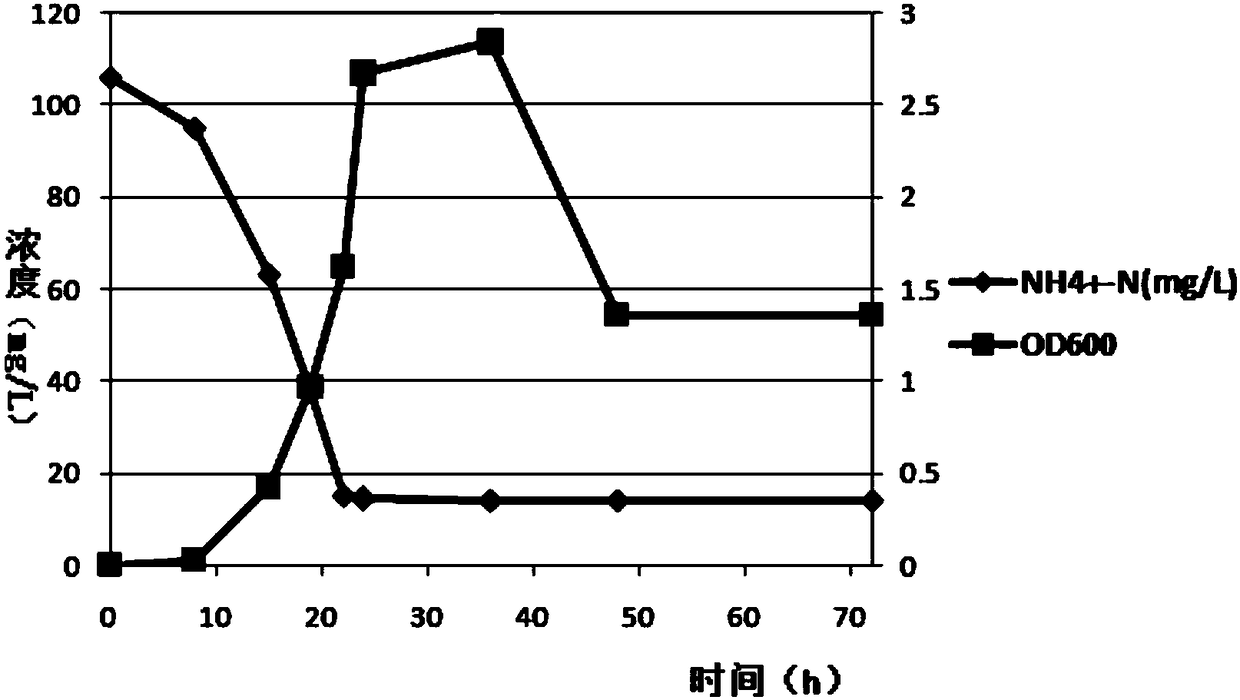
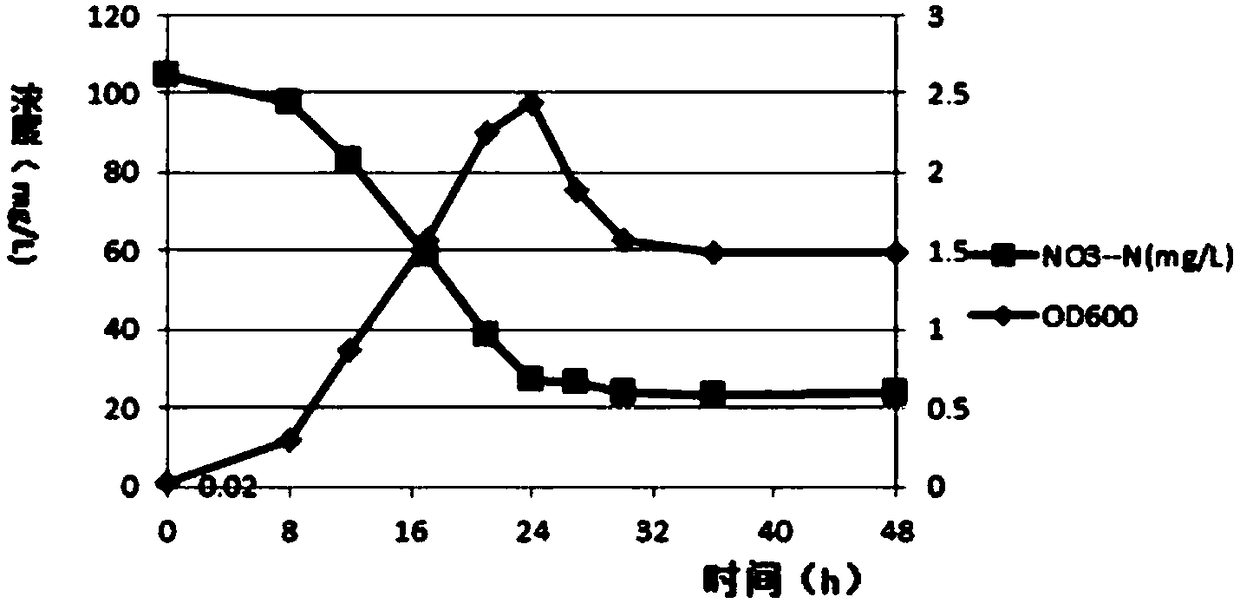
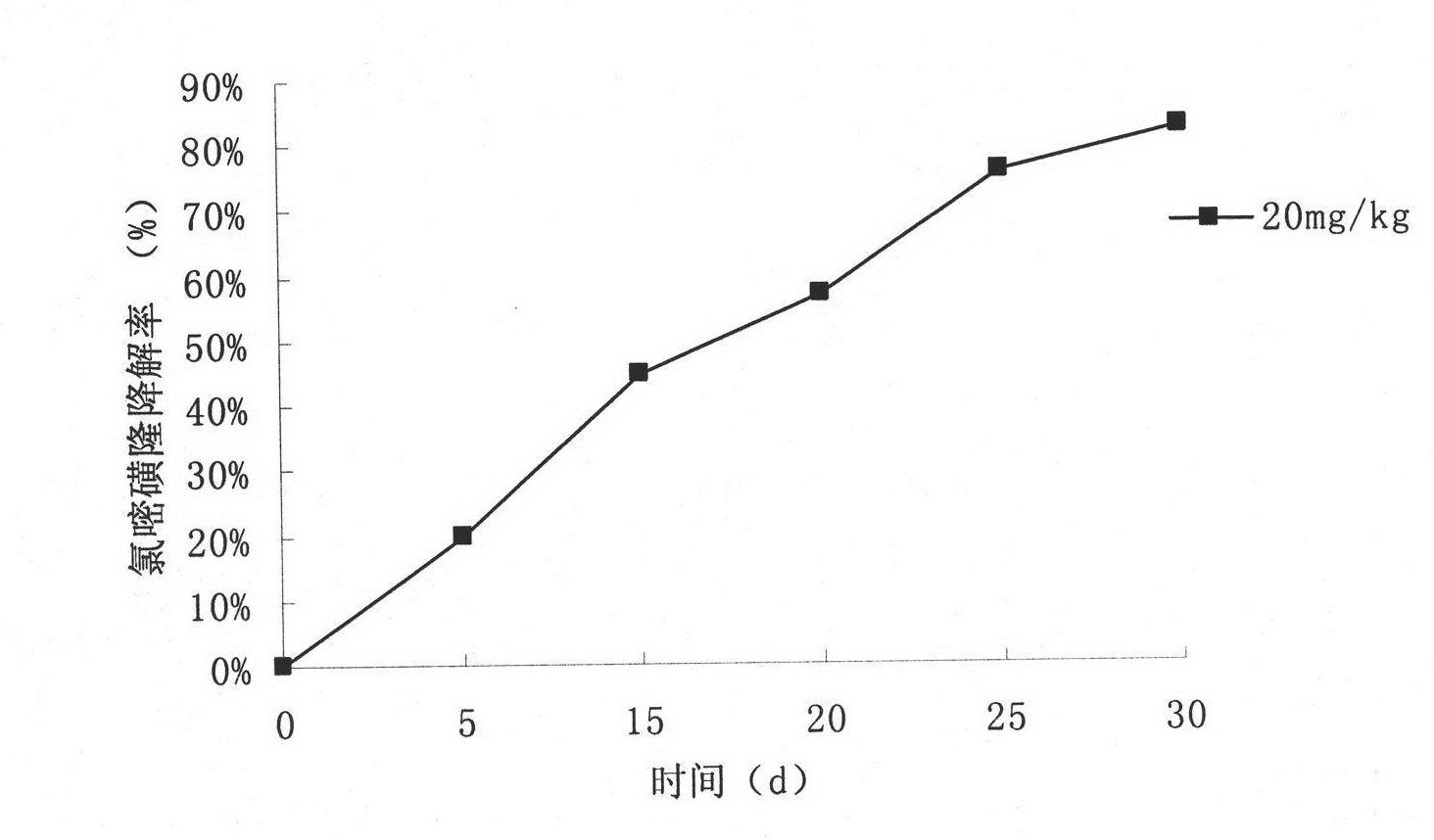
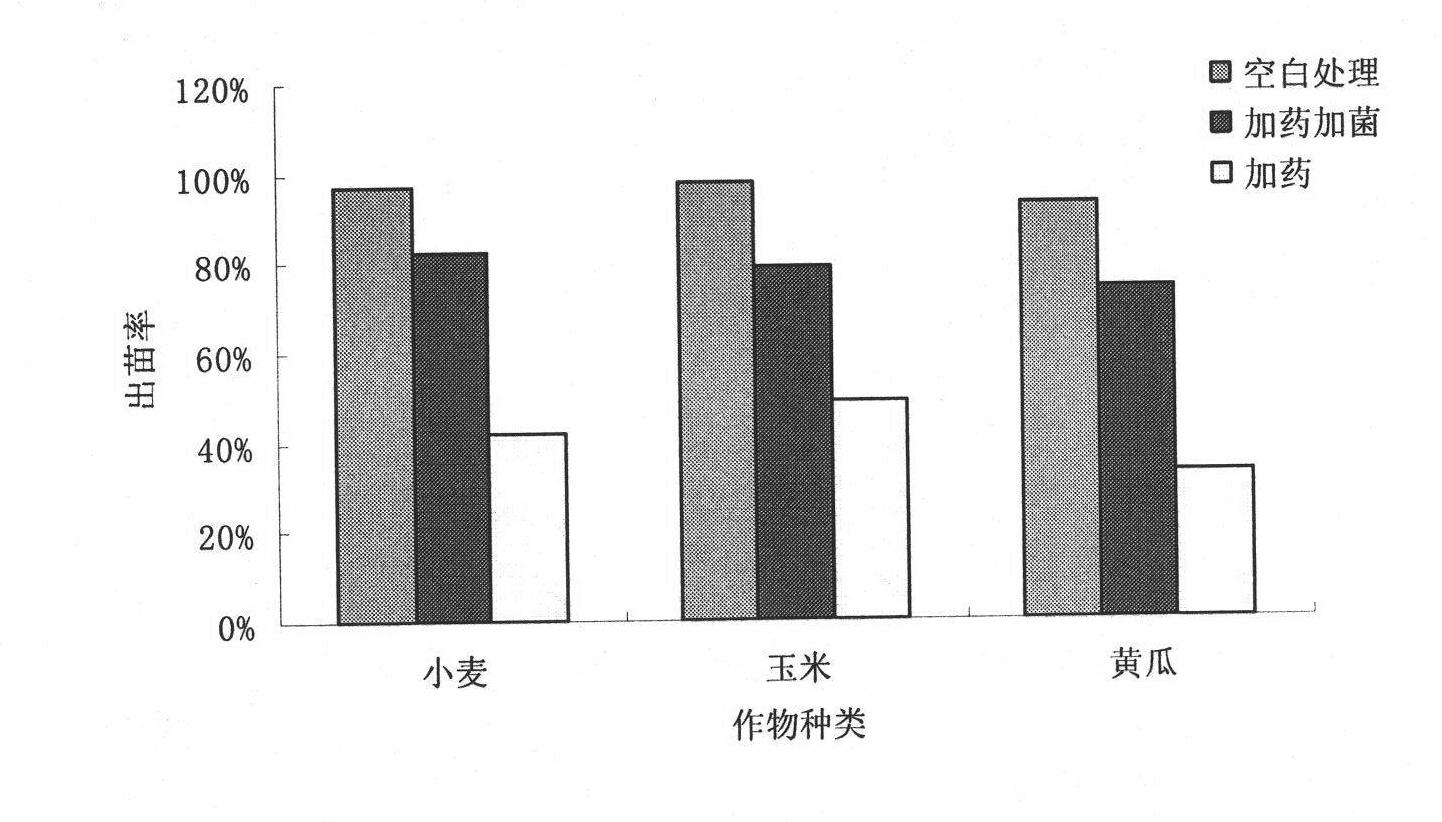
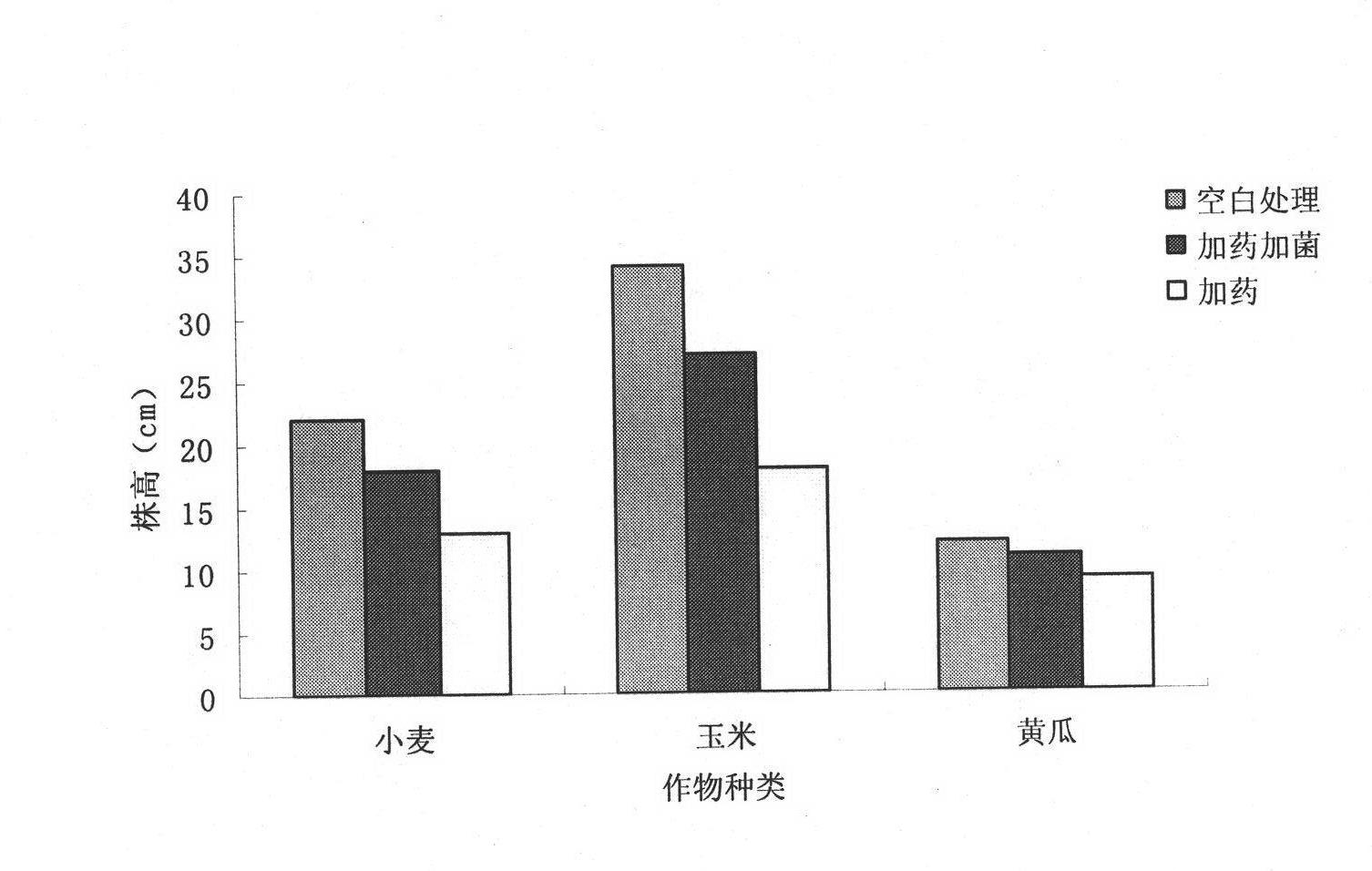
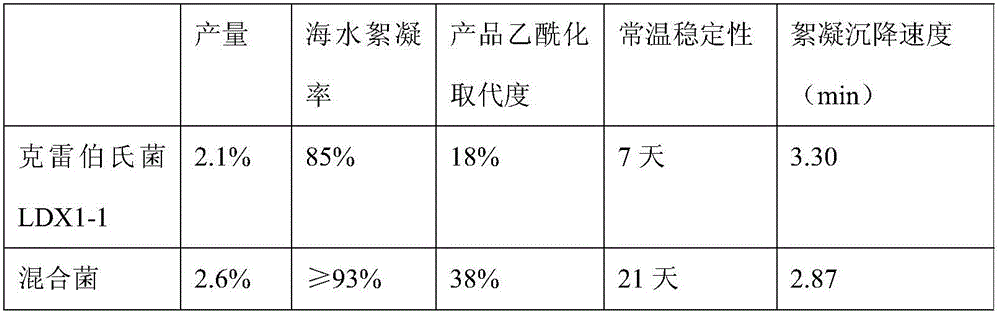
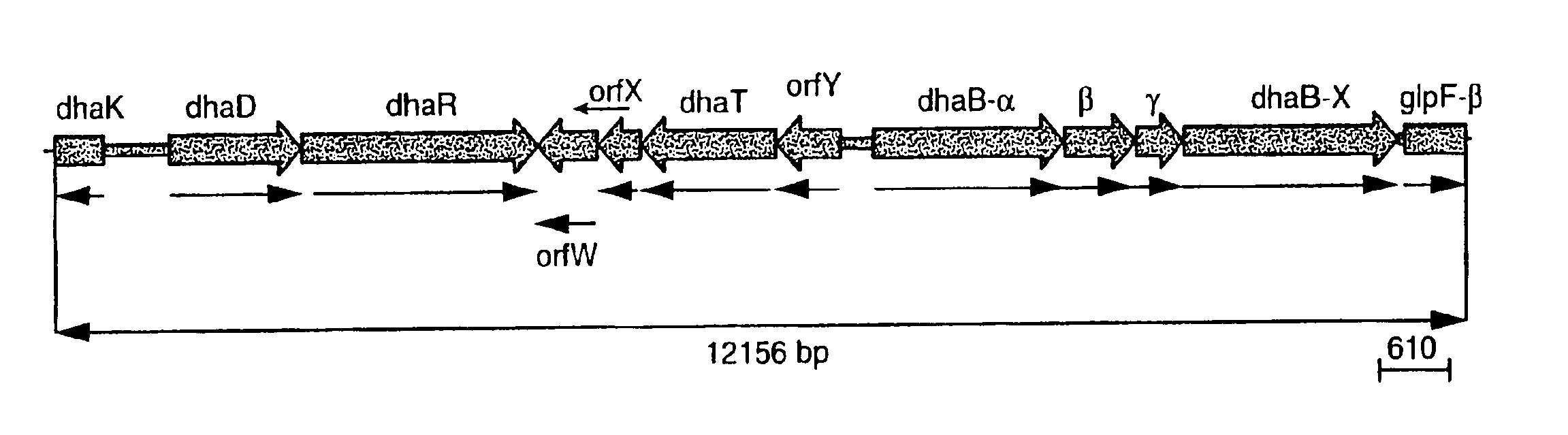
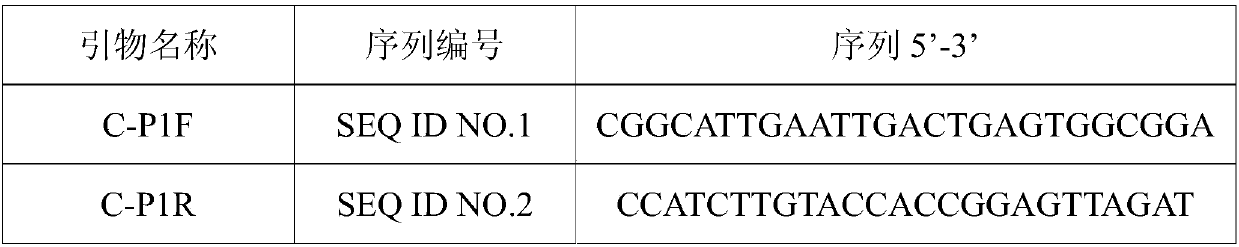
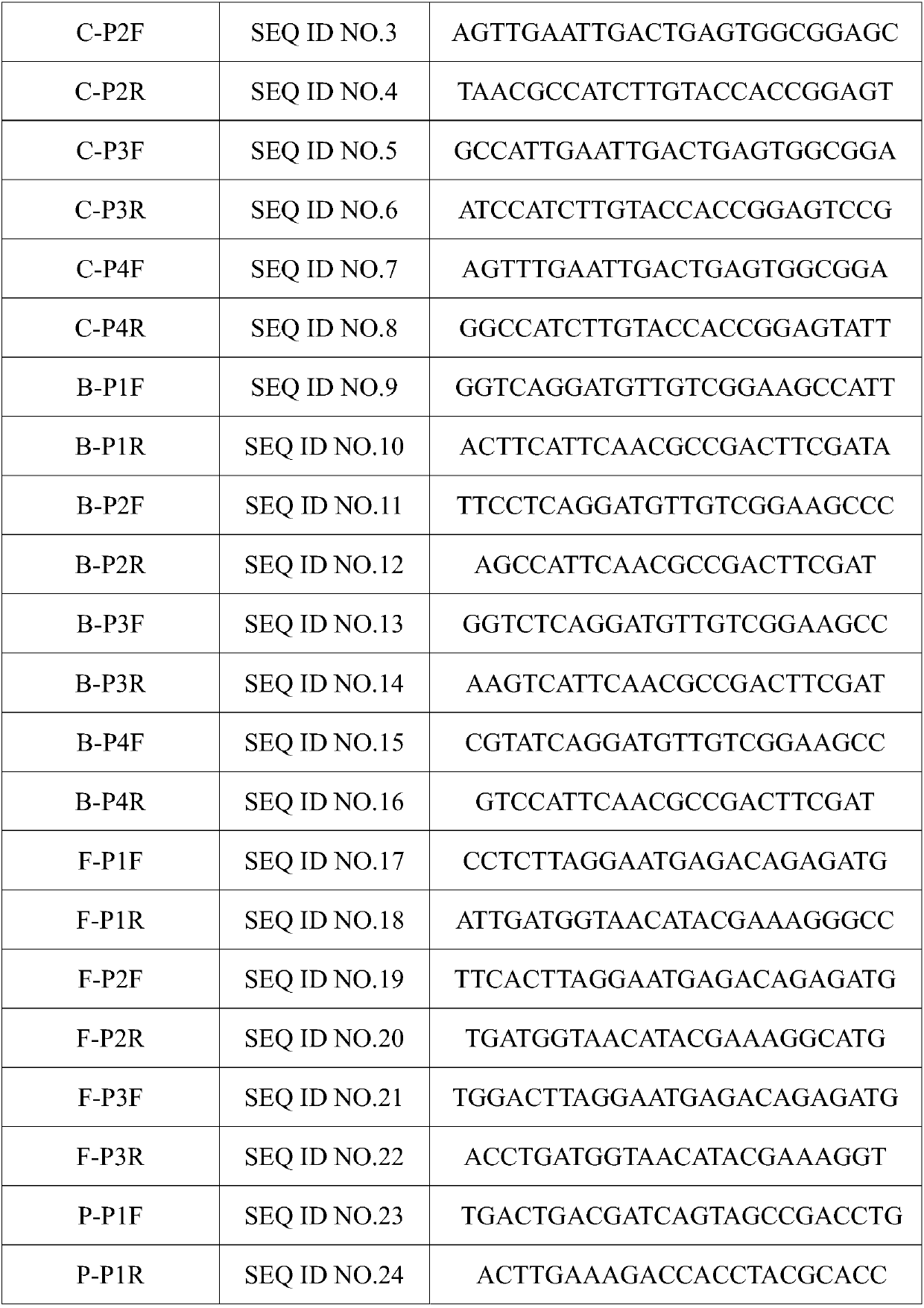
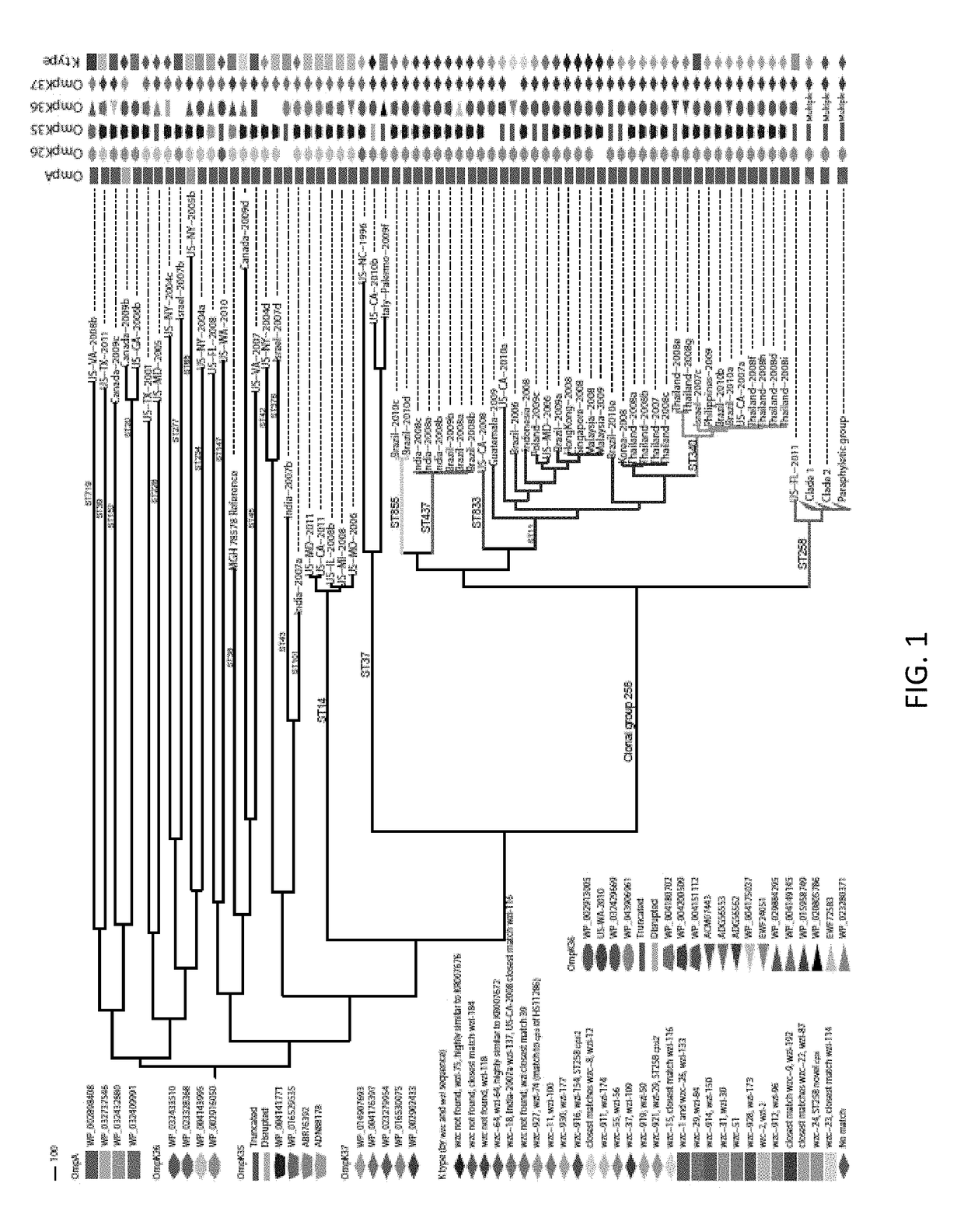
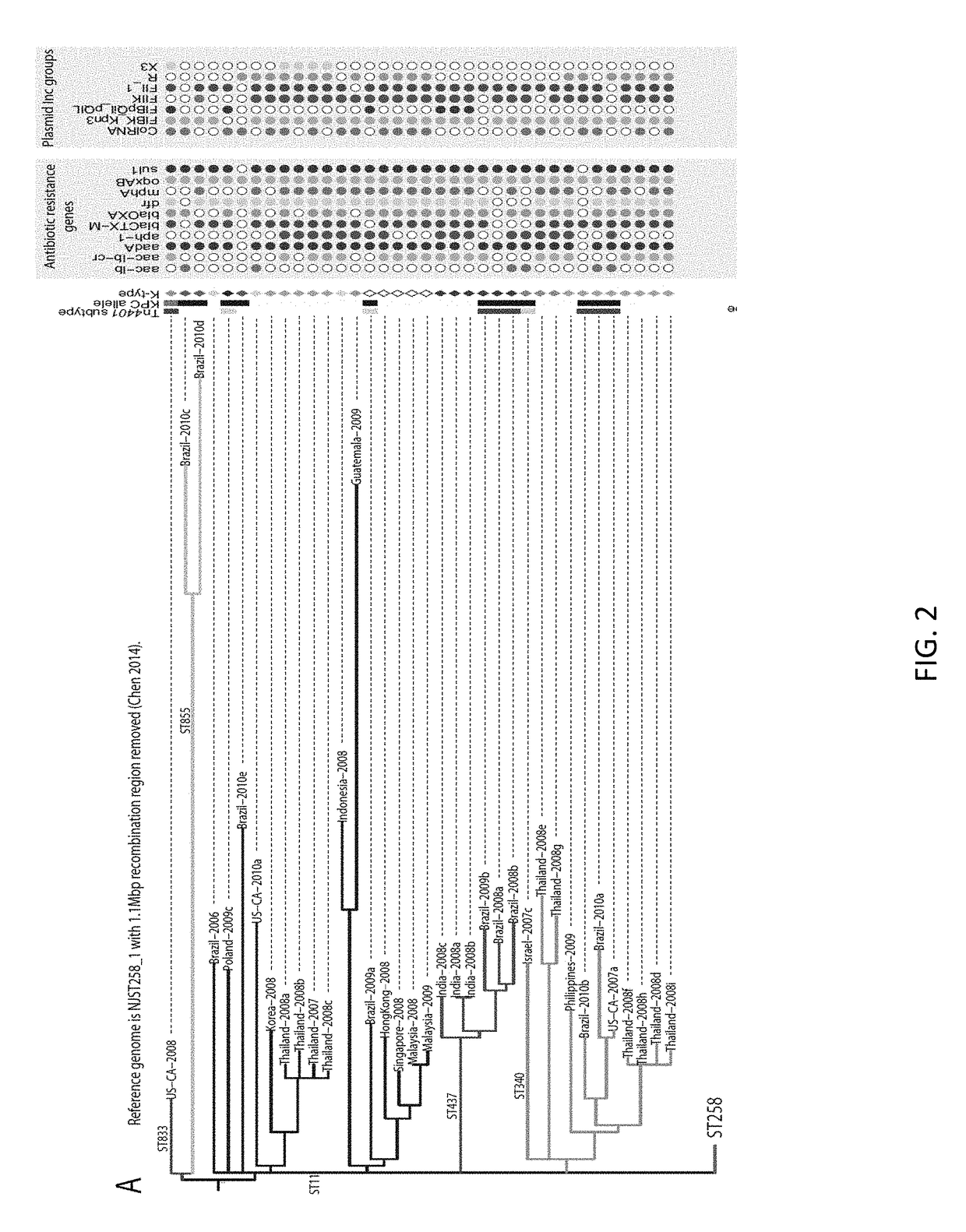
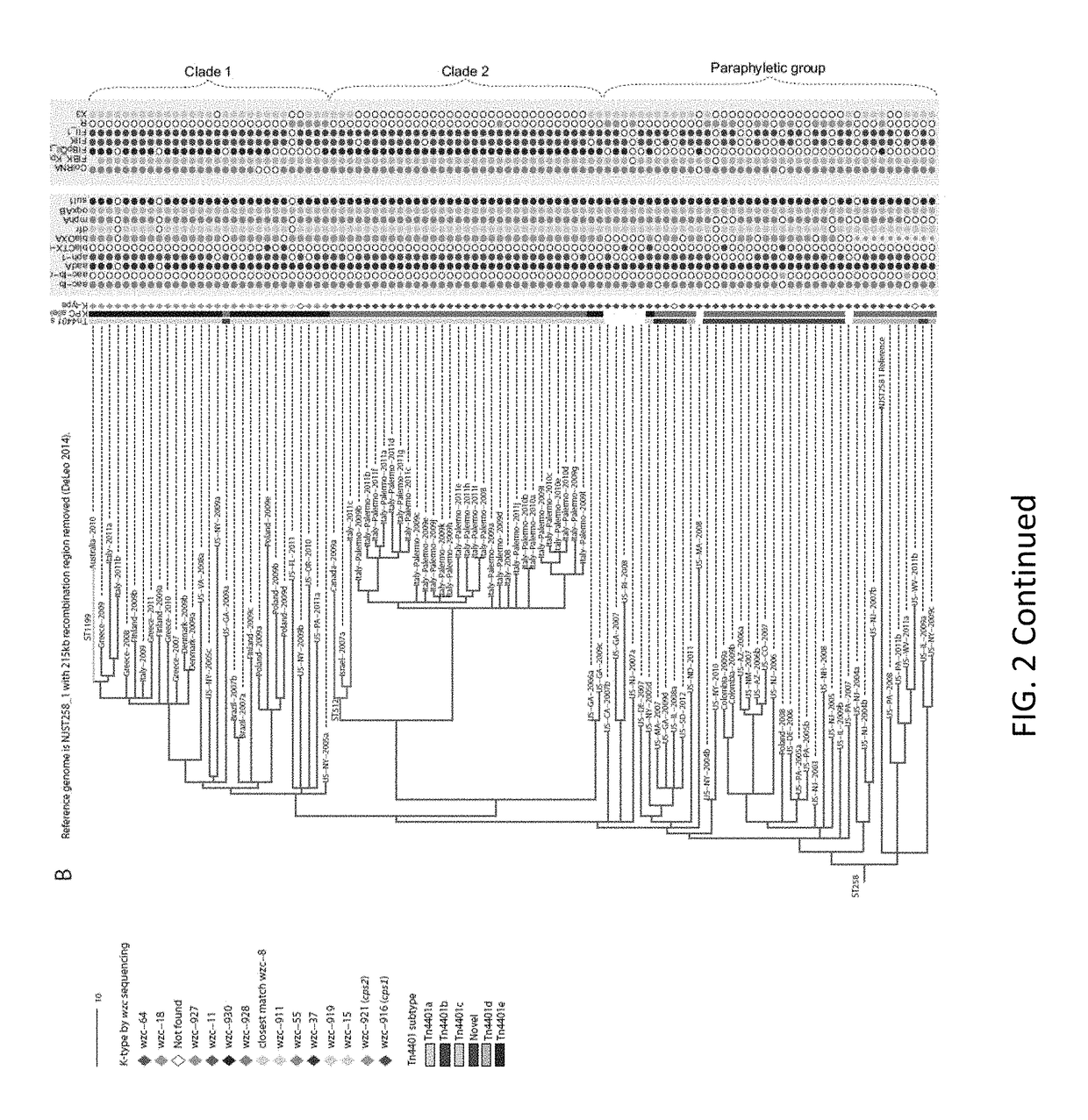
Patents
Literature
132 results about "Klebsiella species" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Klebsiella is a genus of nonmotile, Gram-negative, oxidase-negative, rod-shaped bacteria with a prominent polysaccharide-based capsule. Klebsiella species are found everywhere in nature.
Method for the production of 1,3-propanediol by recombinant organisms comprising genes for coenzyme B12 synthesis
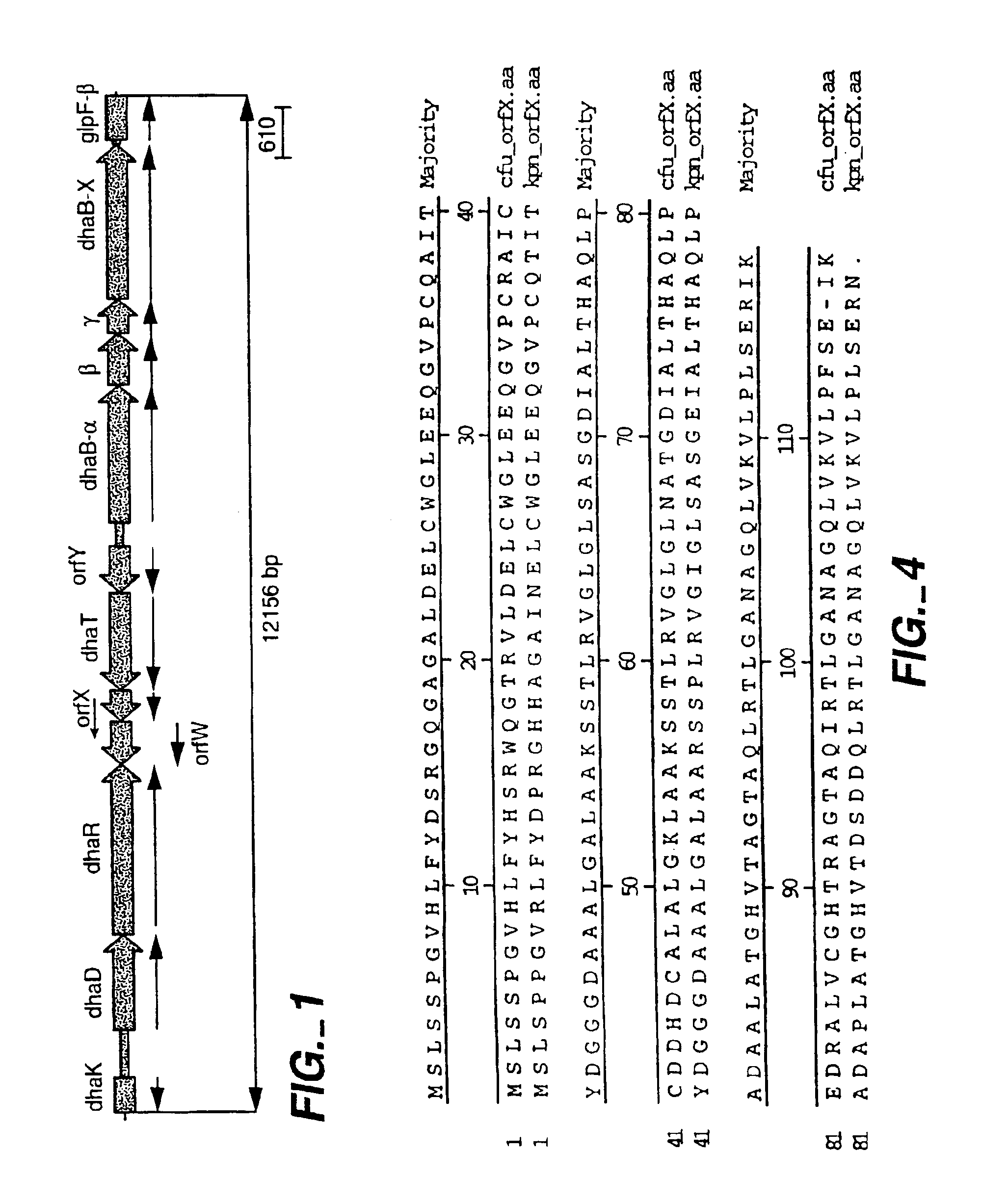
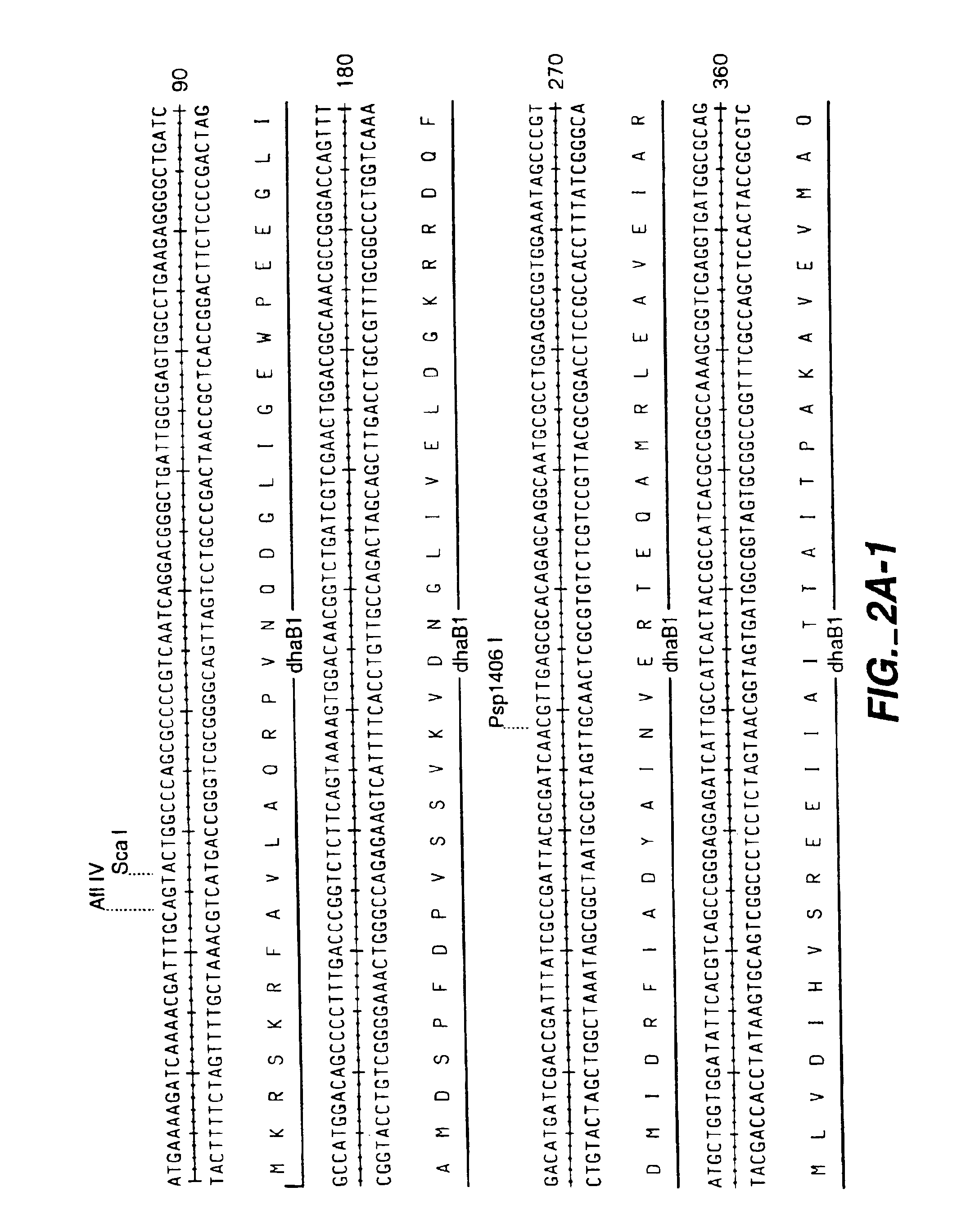
Recombinant organisms are provided comprising genes encoding aquacobalamin reductase, cob(II)alamin reductase, cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase, glycerol dehydratase and 1,3-propanediol oxidoreductase activities useful for the production of 1,3-propanediol from a variety of carbon substrates. More specifically the following nucleotide sequences are provided: btuR, encoding the E. coli cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase enzyme; cobA, encoding the Salmonella typhimurium cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase enzyme; cobO, encoding the Pseudomonas denitrificans cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase enzyme; dhaB1, encoding the α subunit of the Klebsiella glycerol dehydratase enzyme; dhaB2, encoding the β subunit of the Klebsiella glycerol dehydratase enzyme; dhaB3, encoding the γ subunit of the Klebsiella glycerol dehydratase enzyme; dhaT, encoding Klebsiella oxidoreductase enzyme; the yciK gene isolated from E. coli; the glucose isomerase promoter sequence from Streptomyces; and the N-terminal amino acid sequence for cob(II)alamin reductase from Pseudomonas denitrificans.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
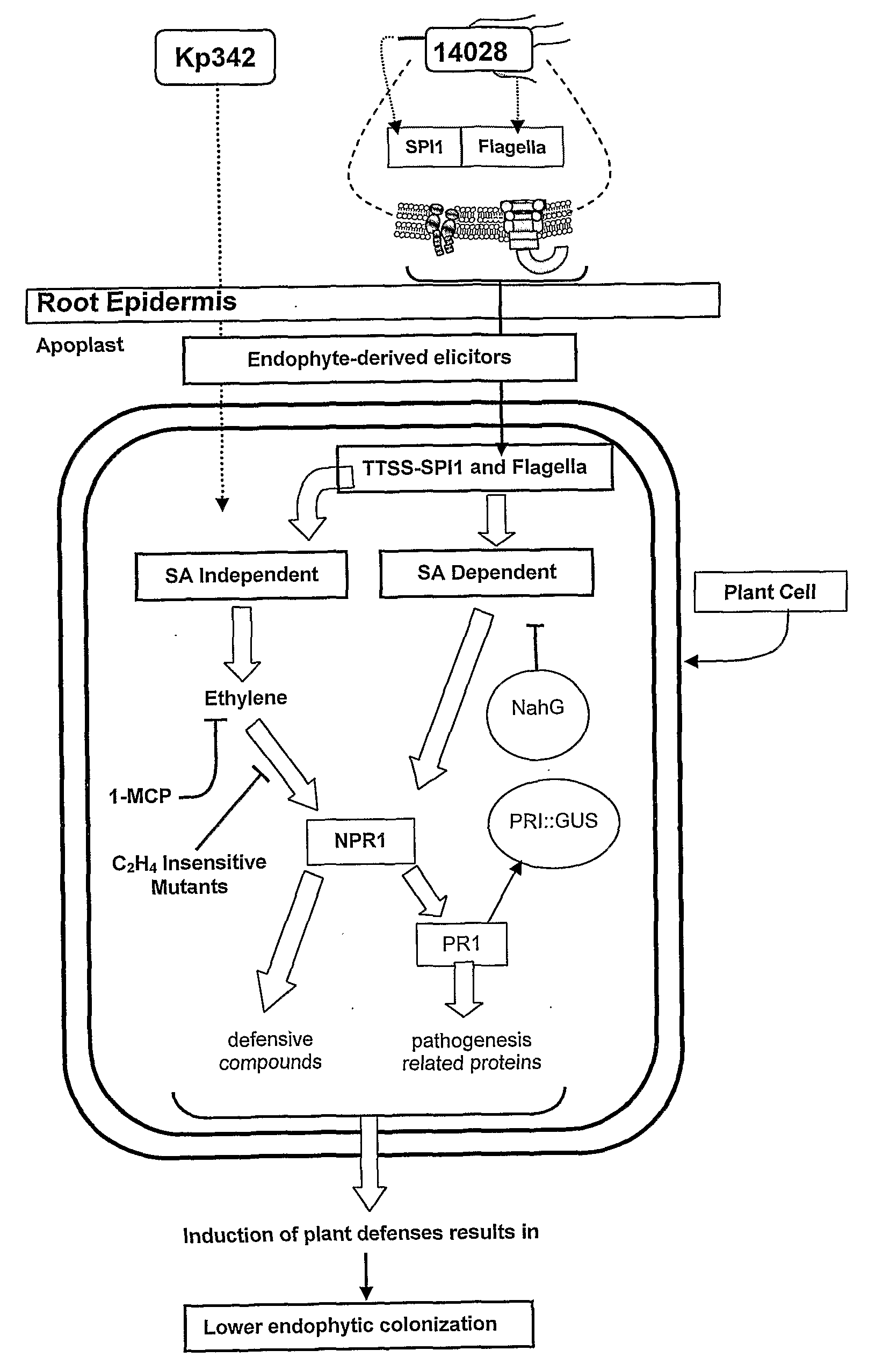
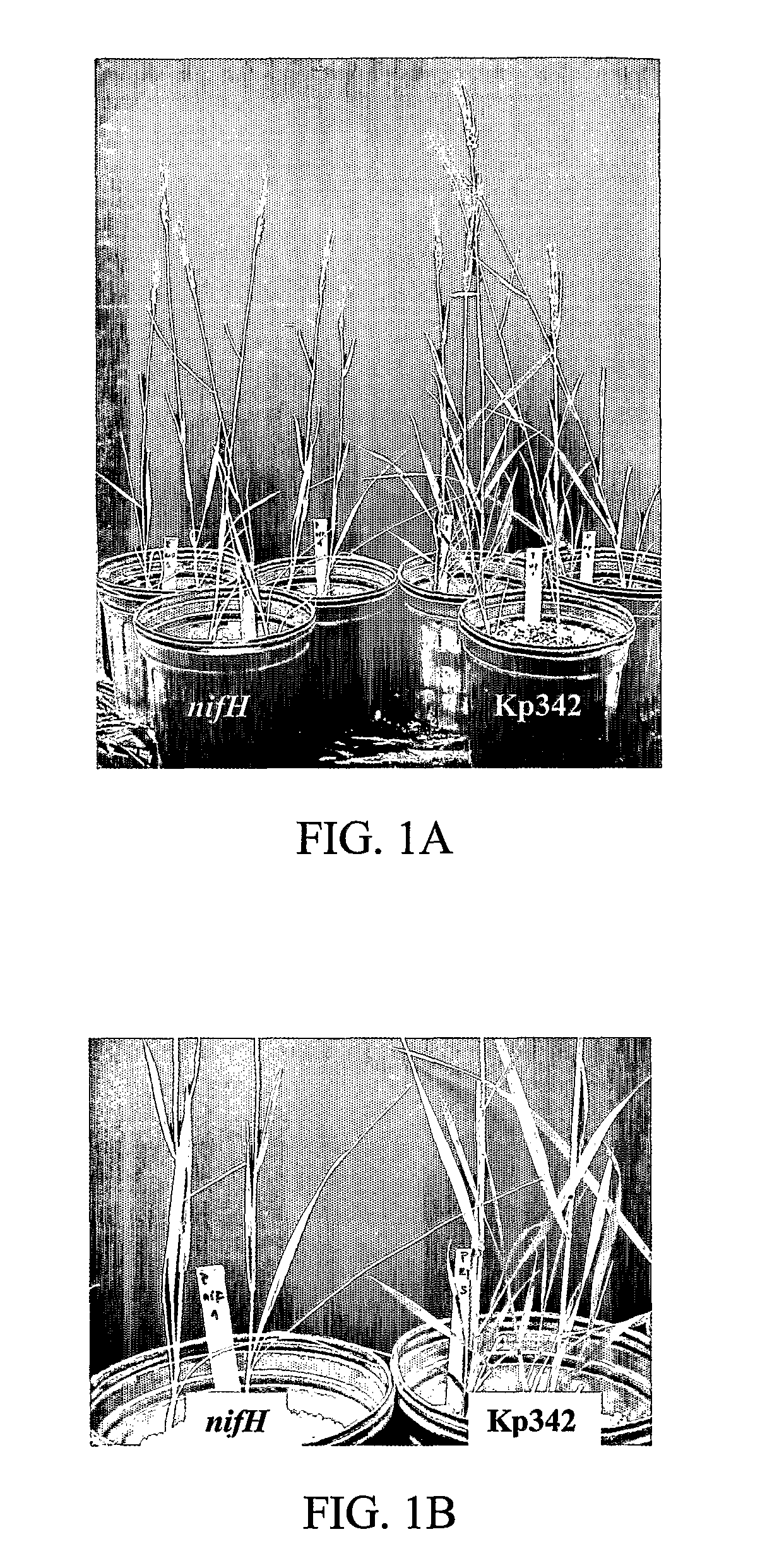
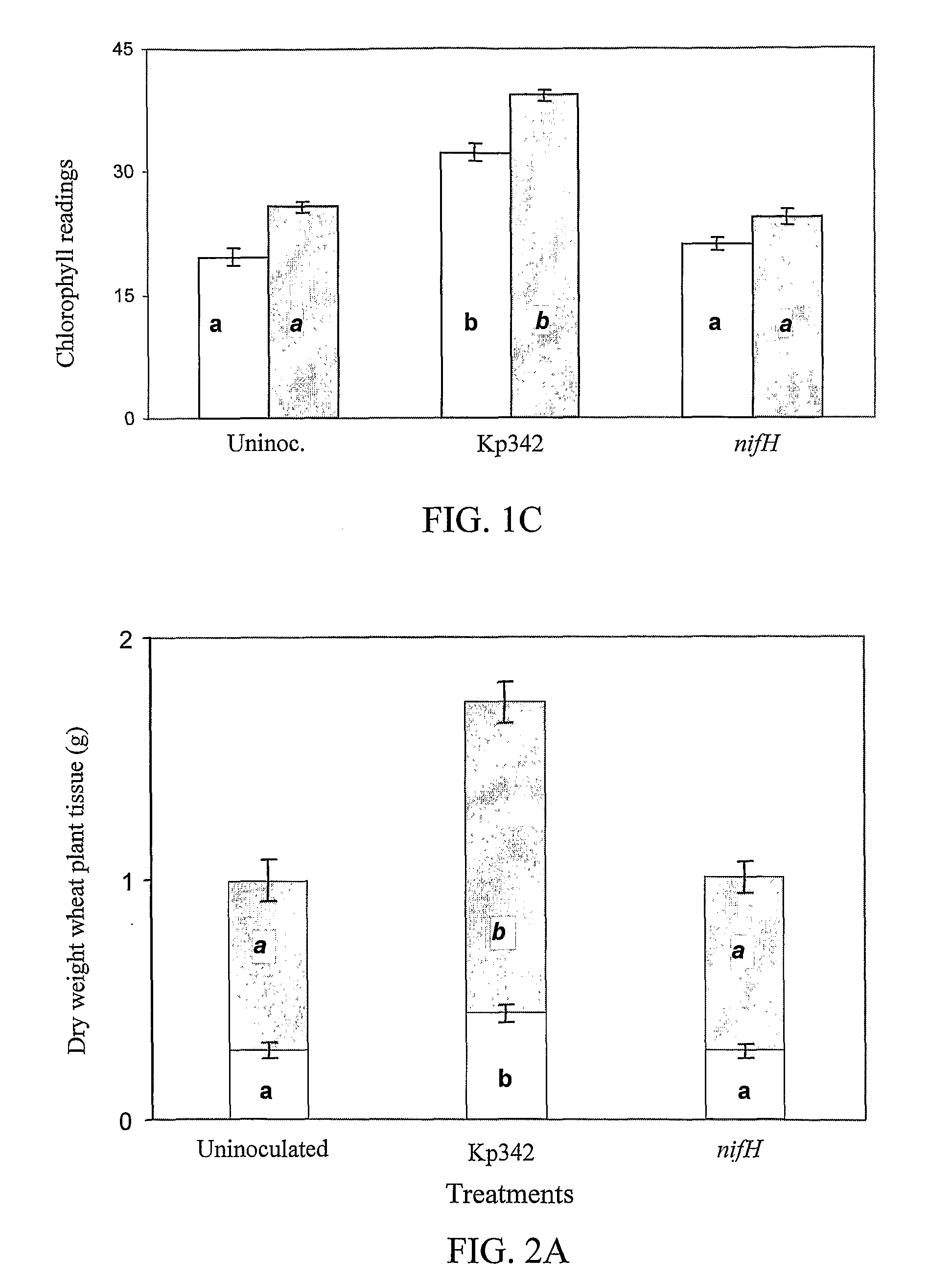
Materials and methods for enhancing nitrogen fixation in plants
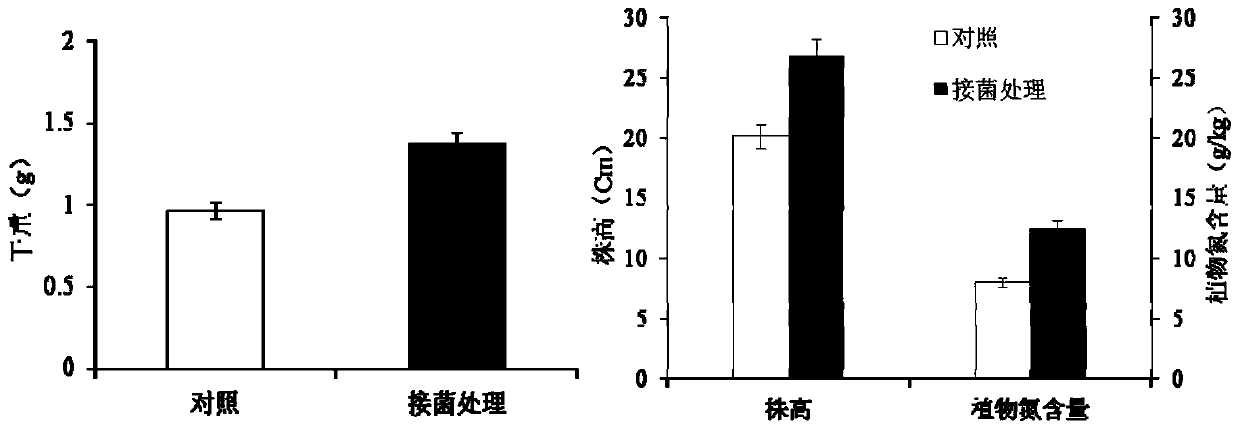
The subject invention concerns materials and methods for providing or enhancing nitrogen fixation in plants. The invention provides for the use of nitrogen fixing bacteria that are isolated from nitrogen efficient plants. Plants for which enhanced nitrogen fixation is desired are inoculated with an effective amount of nitrogen firing bacteria of the invention. In an exemplified embodiment, the bacteria is Klebsiella Kp342. The subject invention also concerns means to increase the number of free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria in plants. Mutants of beneficial endophytic bacteria that are resistant to plant defense responses can be used to colonize a plant in numbers higher than a wild type or a non-mutated bacteria can colonize a plant. The higher number of bacteria colonizing the plant provide for more nitrogen fixation for the plant. The subject invention concerns methods for producing non-leguminous plants that are capable e of utilizing atmospheric nitrogen by colonization with a nitrogen fixing endophyic bacteria that is resistant to plant defense responses. The subject invention also concerns the plants produced by the subject method. The subject invention also concerns methods for producing the mutant endophytic bacteria. The subject invention also concerns the mutant endophytic bacteria produced using the subject methods.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Detection of bacterium by utilizing dnaj gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101558168AMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyBacteroidesStaphylococcus species
Disclosed is a method for detecting the species of a bacterium in a simple manner. Specifically disclosed is a method for detecting the species of a bacterium, which can detect at least one bacterial species selected from Staphylococcus species, Streptococcus species, Klebsiella species, Escherichia species, Mycobacterium species, Legionella species, Vibrio species, Bacillus species, Neisseria species, Campylobacter species, Chlamydia species, Chlamydophila species, Mycoplasma species, Listeria species, Salmonella species and Yersinia species, and which comprises the steps of: a) contacting a sample suspected to contain a nucleic acid derived from the bacterium species to be detected with a nucleic acid molecule capable of hybridizing with at least a part of a DnaJ gene derived from the bacterial species; and b) detecting the presence or absence of the hybridization between the nucleic acid molecule and the nucleic acid contained in the sample.
Owner:GIFU UNIVERSITY +1
Processes for the bioconversion of a fermentable carbon source to 1,3-propanediol by a single microorganism
A process is provided for the bioconversion of a carbon substrate to 1,3-propanediol by a single organism utilizing microorganisms, such as, Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Clostridium, Klebsiella, Aerobacter, Lactobacillus, Aspergillus, Saccharomyces, Zygosaccharomyces, Pichia, Kluyveromyces, Candida, Hansenula, Debaryomyces, Mucor, Torulopsis, Methylobacter, Escherichia, Salmonella, Bacillus, Streptomyces and Pseudomonas, containing the genes encoding for an active glycerol or diol dehydratase enzyme by contacting these organisms with a carbon substrate under the appropriate fermentation conditions. Specifically, Citrobacter and, Klebsiella provide the source of exogenous genes for such active dehydratase enzyme.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Air purifier
InactiveCN1806886AImprove antibacterial propertiesImprove purification effectTransportable electrostatic unitsFiltration circuitsEngineeringSilver particles
The invention relates an air cleaner, solving the problem that the current air cleaners isn't disclosed the date of removing pneumococcus klebsiella and staphylococcus epidermidis and the date of effective degerming life, and the cleaning effect of current air cleaners is not good. The invention adopts the technical project that the silver particles below 100 nanometer are fixed on the surface of carrier to solve the problem.
Owner:雷景华
L-glutamic acid producing bacterium and a method for producing l-glutamic acid
ActiveUS20090215131A1Efficient productionImprove fermentation yieldBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacteroidesEnterobacter
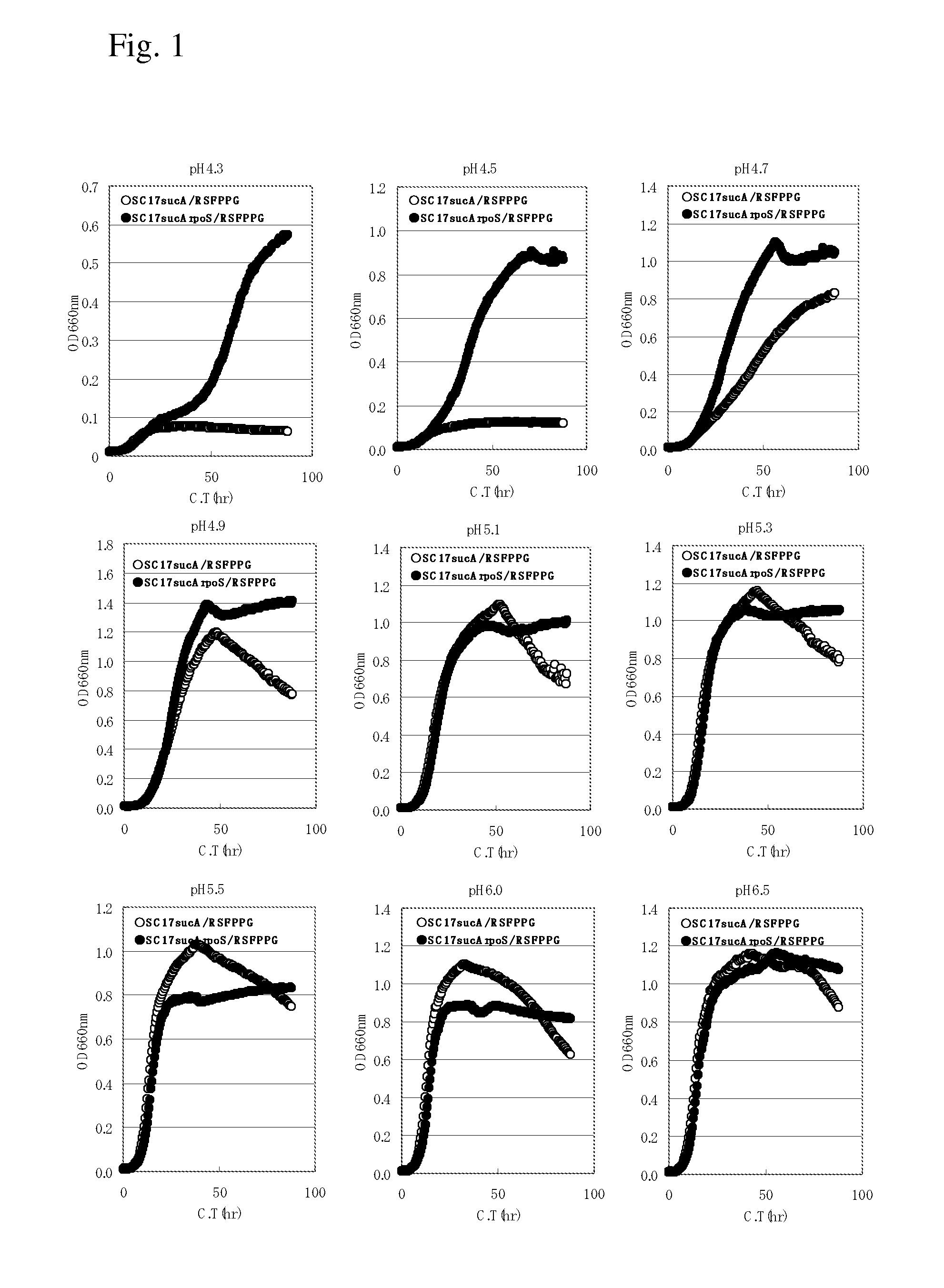
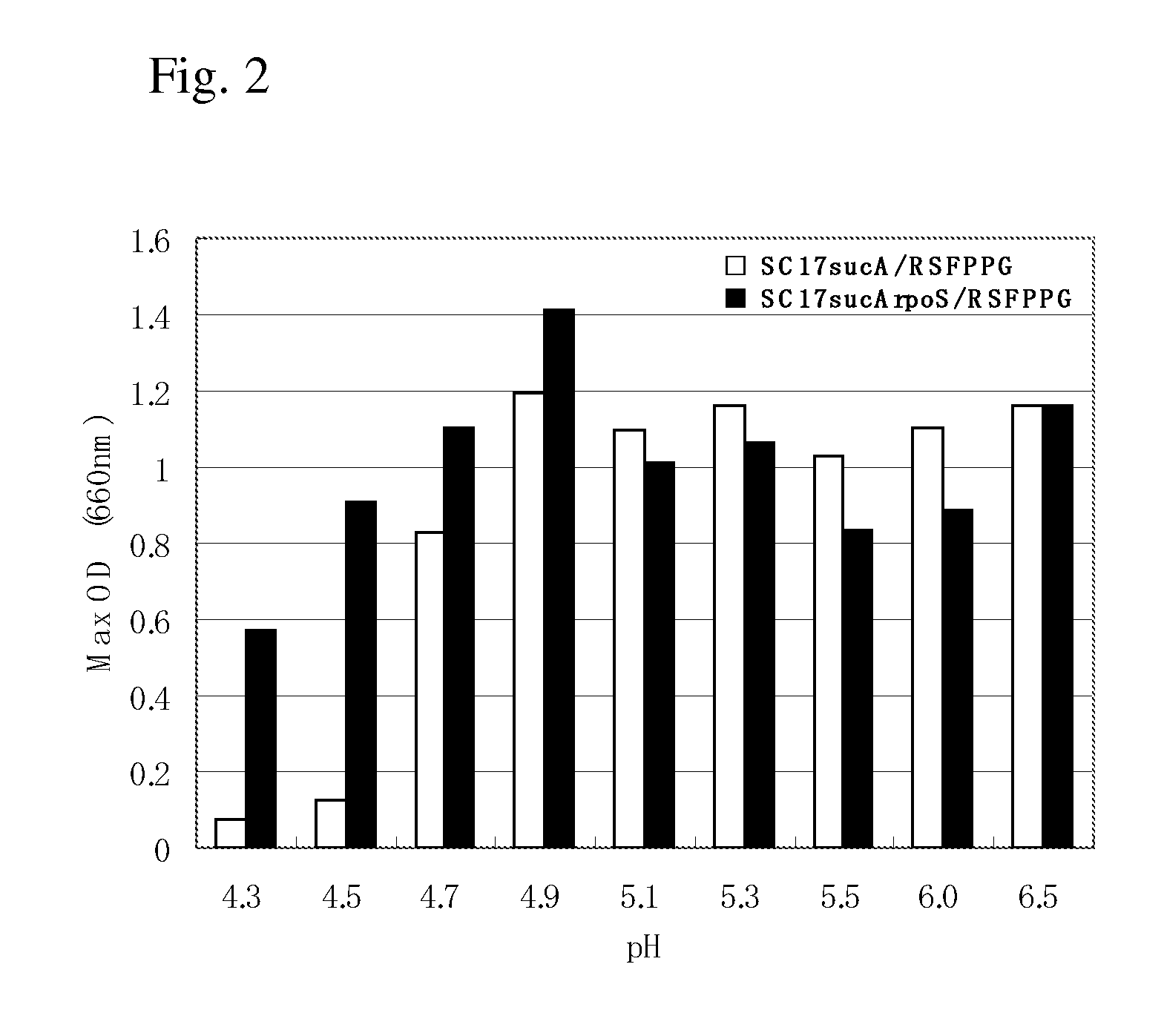
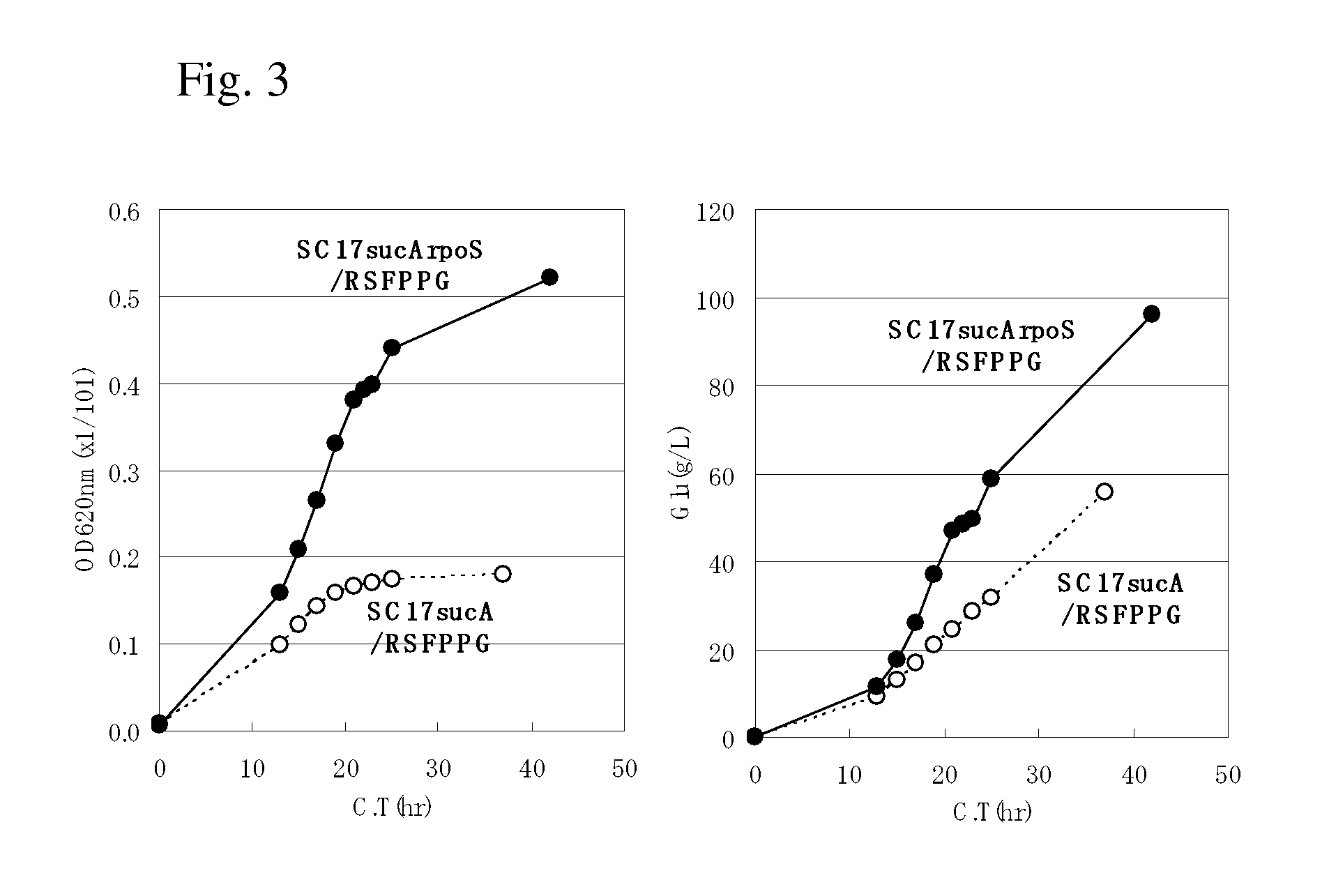
The present invention describes an L-glutamic acid-producing bacterium which belongs to the genus Pantoea, Enterobacter, Klebsiella or Erwinia, wherein the bacterium has been modified by gene recombination to inactivate the rpoS gene. A method is also described for culturing the bacterium in a medium to cause accumulation of L-glutamic acid in the medium, and collecting L-glutamic acid from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Acid-producing Klebsiella bacterium and uses thereof
InactiveCN101063095AReduce outputIncrease profitBacteriaMicroorganism based processesUltravioletKlebsiella species
The invention discloses a generating acid klebsiella and appliance, which is characterized by the following: setting the preserved number at CCTCC NO: M 207023; adopting ultraviolet and diethyl sulfate; composite-treating strain CCTCC NO: M 207023; seeding on selective solid medium with bromide of sodium and sodium bromate; culturing; sorting single bacterial colony; yeasting; preparing 2, 3-butylene glycol. This invention possesses simple operation, low cost, high efficiency and short period, which can increase receiving ratio of 2, 3-butylene glycol.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing an organic acid
InactiveUS20100297716A1Improve production efficiencyImprove production yieldSugar derivativesGenetic engineeringOrganic acidEnterobacter
An organic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, which has an ability to produce an organic acid and has been modified so that the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity is enhanced, which is selected from Enterobacter, Pantoea, Erwinia, Klebsiella and Raoultella bacteria, or a product obtained by processing the bacterium, to act on an organic raw material in a reaction mixture containing carbonate ions, bicarbonate ions, or carbon dioxide gas to produce the organic acid, and collecting the organic acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Microorganism water treatment agent in culturing water and preparation technique thereof
InactiveCN101624234APromote degradationNo reboundBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnvironmental resistanceWater quality
The invention relates to a microorganism water treatment agent in culturing water and a preparation technique thereof, belonging to the technical field of animal farming. The microorganism water treatment agent comprises (Klebsiella) AN-4, bacillus subtilis, Rhodospirillum, and Lactobacillus plantarum. Bean cake powder and molasses are used as raw materials and deeply fermented to produce water treatment agent which has lots of living bacterial and can effectively purify water quality. The product has low cost and environmental protection, overcomes problems that the current water quality purifying agent has poor stability and weak stress resistance and the like, can be used for large-scale industrial production and provides a new microorganism preparation for aquaculture water body.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Complex microbial inoculant for promoting wheat growth and application thereof
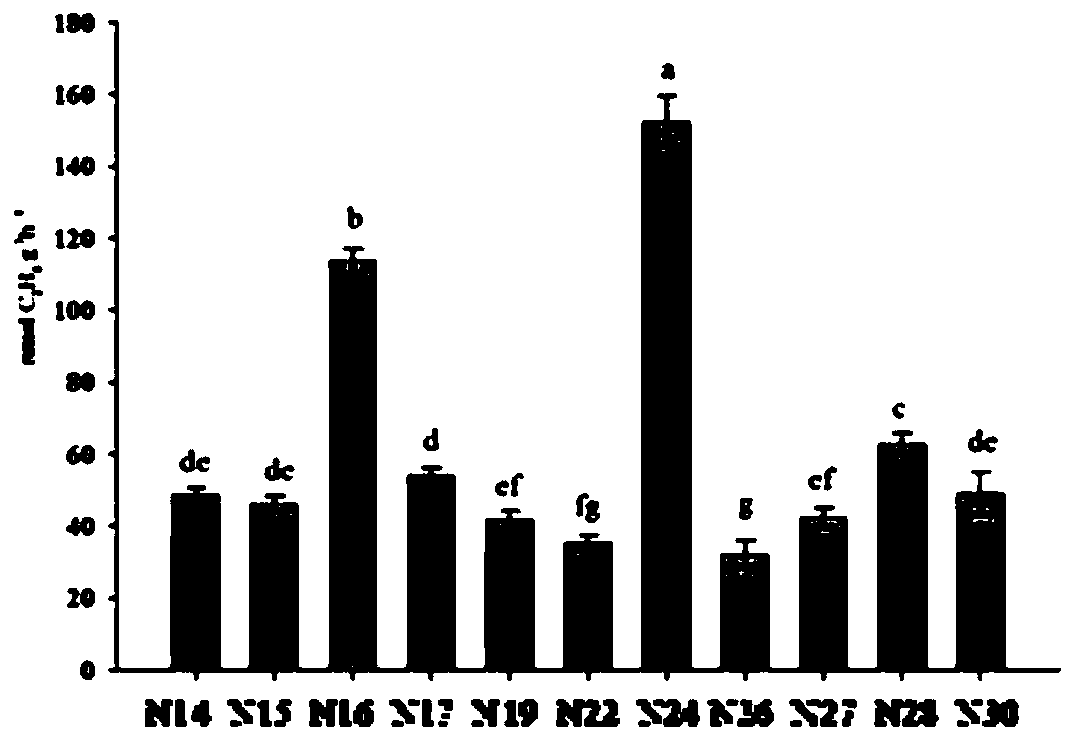
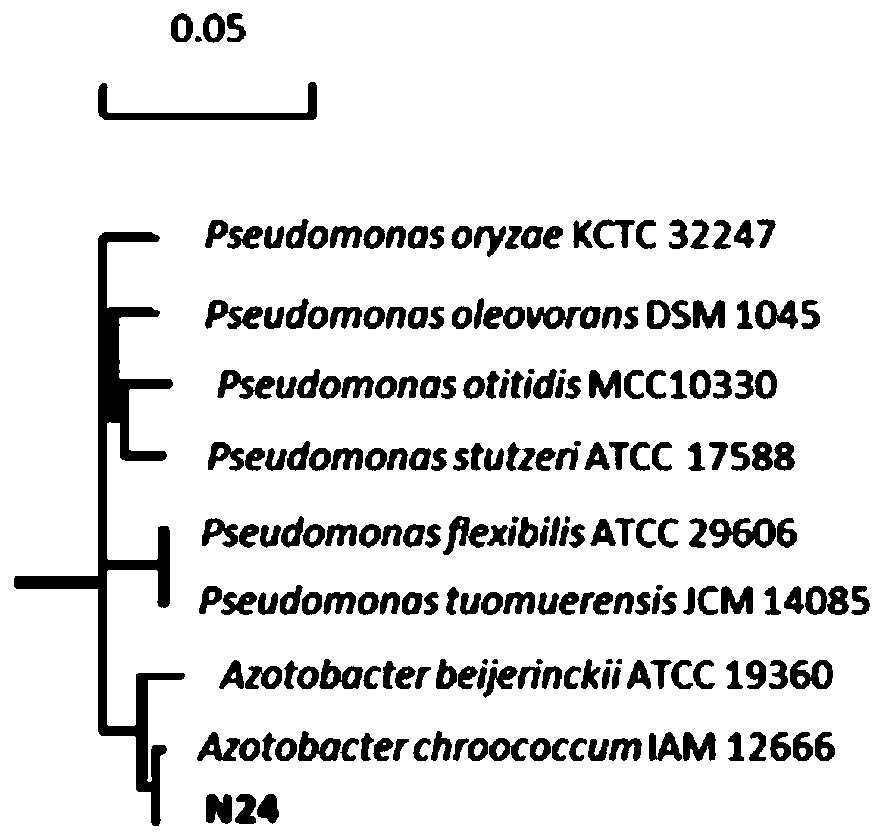
ActiveCN110564637AImprove adaptabilityPromote growthPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyAzotobacter chroococcum
The invention discloses a complex microbial inoculant for promoting wheat growth and an application thereof. The complex microbial inoculant is prepared by mixing and fermenting an Azotobacter chroococcum N24 bacterial solution, a rhizobium radiobacter J16 bacterial solution and a Klebsiella quassicola P5 bacterial solution. According to the invention, nitrogen-fixing bacteria N24, potassium bacteria J16 and phosphate solubilizing bacteria P5 are separated from rhizosphere soil of wheat, the complex microbial inoculant prepared by mixing and fermenting the three bacterial solutions simultaneously has the functions of nitrogen fixation, phosphorus dissolution and potassium dissolution, the contents of available nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium in soil can be greatly increased, the plant height, the fresh weight, the dry weight, the nitrogen content, the phosphorus content and the potassium content of plants are remarkably increased, the plant growth is promoted, the use amount of chemical fertilizers is reduced, the crop yield is increased, and the method has important significance in agricultural production.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Application of elsholtzia volatile oil in sterilizing and/or anti-bacteria and antibiotic resistant bacteria and preparation method thereof
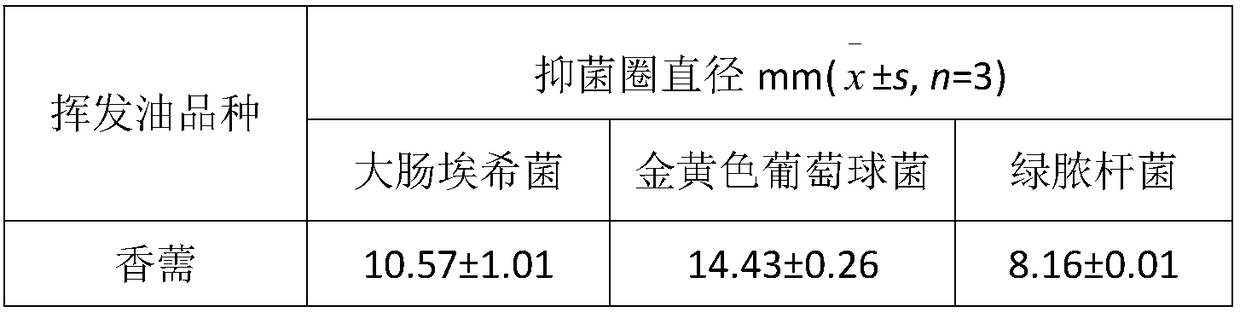
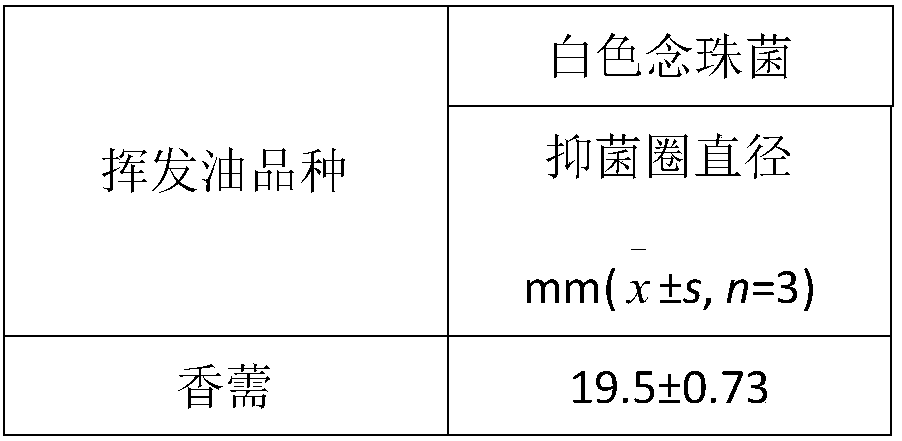
The invention discloses application of elsholtzia volatile oil in anti-bacteria and antibiotic resistant bacteria. The elsholtzia volatile oil is extracted by steam distillation. The elsholtzia volatile oil has certain functions of killing and / or inhibiting growth on bacteria of staphylococcus, escherichia coli, candida, pseudomonas, enterobacter, streptococcus and the like and fungi. The elsholtzia volatile oil has certain functions of killing and / or inhibiting growth on bacteria of drug-resistant staphylococcus, drug-resistant escherichia coli, drug-resistant enterobacter, drug-resistant klebsiella, drug-resistant pseudomonas, drug-resistant acinetobacter, drug-resistant streptococcus, and drug-resistant enterococcus and the like. The elsholtzia volatile oil can be used in industries offood, medicine, health care products, cosmetics and the like and can be used for preparing various forms of products with antibacterial and antibiotic resistant bacteria functions, and belongs to thenew application field of the elsholtzia volatile oil.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Denitrifying phosphorus accumulation organism (DPAO) with function of efficiently removing nitrogen and phosphorus and application of DPAO
ActiveCN104726366ANo pollution in the processThorough denitrificationBacteriaTreatment using aerobic processesBacterial strainNitrogen gas
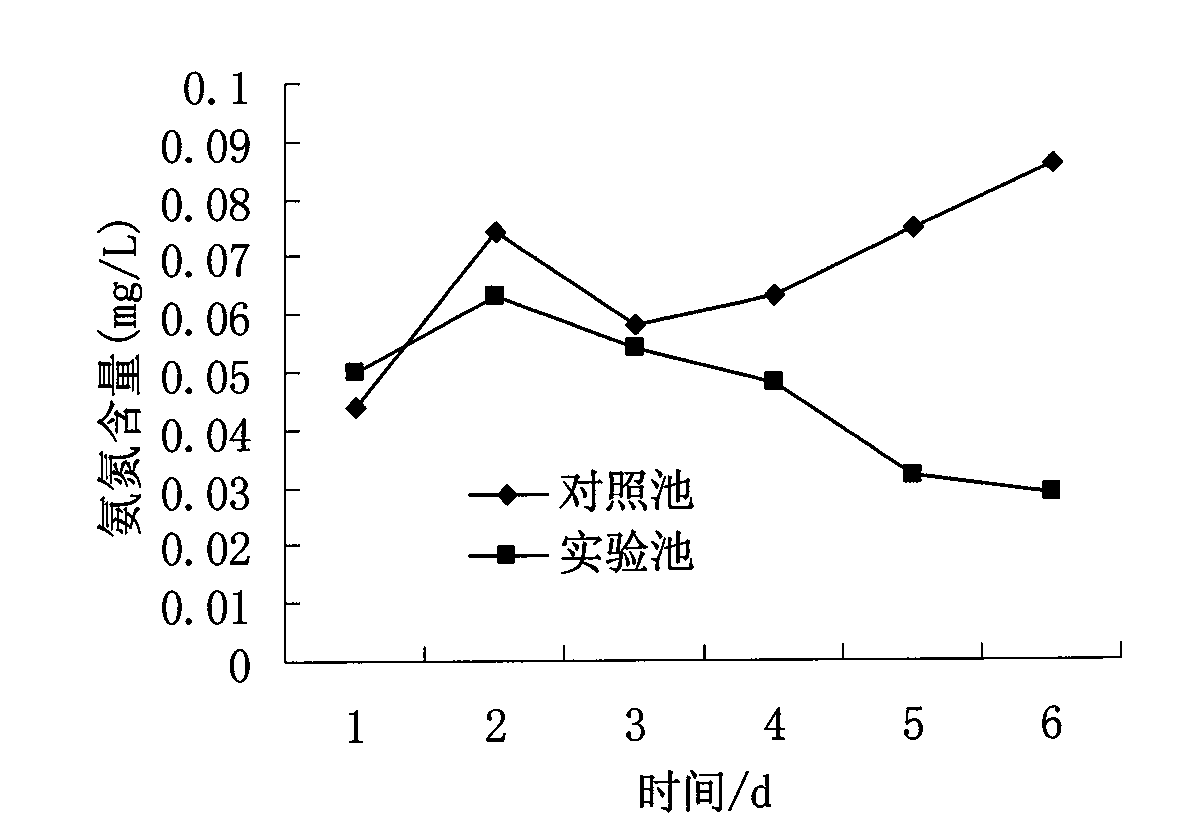
The invention relates to denitrifying phosphorus accumulation organism (DPAO) with a function of efficiently removing nitrogen and phosphorus and application of the DPAO, and belongs to the field of environmental microbiology. The bacterial strain is named Klebsiella sp. N14, belongs to Klebsiella species, and is preserved in China general microbiological culture center (CGMCC), the preservation number of the bacterial strain is CGMCC No. 10290. The bacterial strain is a Gram negative bacteria without spore and has thick capsule in a thick and short rod shape; the bacterial colony is milky white, the center of the bacteria is protruded, the edge is regular, and the surface is wet, transparent and glossy. The bacterial strain has a function of synchronously removing the nitrogen and the phosphorus, and can be applied to sewage biological sewage treatment process; after the bacterial strain is aerobically cultivated in nitrogen and phosphorus containing sewage for 24 hours, the phosphorous removal rate is 81.79%, and the nitrogen removal rate is 85.94%. The denitrifying final product of the bacteria strain is identified to be N2 with the full denitrifying capability; when the bacterial strain is used for treating the nitrogen and phosphorus containing sewage, inorganic nitrogen, such as nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen, in a water body is directly reduced to be harmless nitrogen gas to be discharged out of the water body; the effect is remarkable, the cost is low, and no secondary pollution exists.
Owner:龙岩水发环境发展有限公司
Microbes capable of degrading phenol and cyanogen in coking waste water and method for treating coking waste water by using same
InactiveCN101974459AGood removal effectBacteriaTreatment using aerobic processesMicrobial inoculationVolatile phenols
The invention discloses microbes capable of degrading phenol and cyanogen in coking waste water and a method for treating coking waste water by using the same, which relate to microbes for degrading phenol and cyanogen in coking waste water and a method for treating waste water by using the same. The invention solves the problem that micromolecule harmful substances in the coking waste water treatment process, such as volatile phenol and cyanides, are difficult to remove. The microbes capable of degrading the phenol and the cyanogen in the coking waste water comprise bacillus subtilis BHF3-4, bacillus JhqK9-1 and acid-producing klebsiella JhqM8. The method for treating the coking waste water comprises the following steps: 1. inoculating the microbes capable of degrading the phenol and the cyanogen in the coking waste water to a membrane biological reactor (MBR); 2. and treating the coking waste water. When the method is used for treating the coking waste water, the removal rate of the volatile phenol in the coking waste water can reach 99.6-99.9%, and the removal rate of cyanides can reach 99.5-99.7%, thus, the outlet water can reach the Chinese first-class emission standard.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
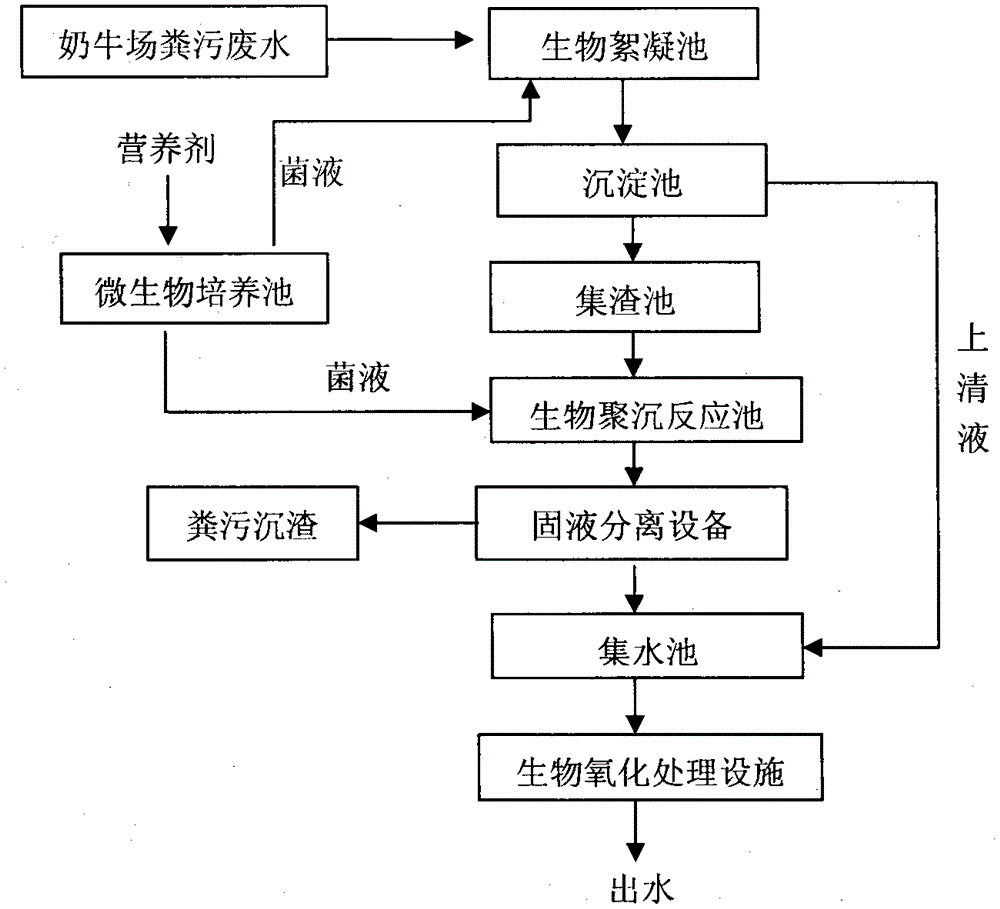
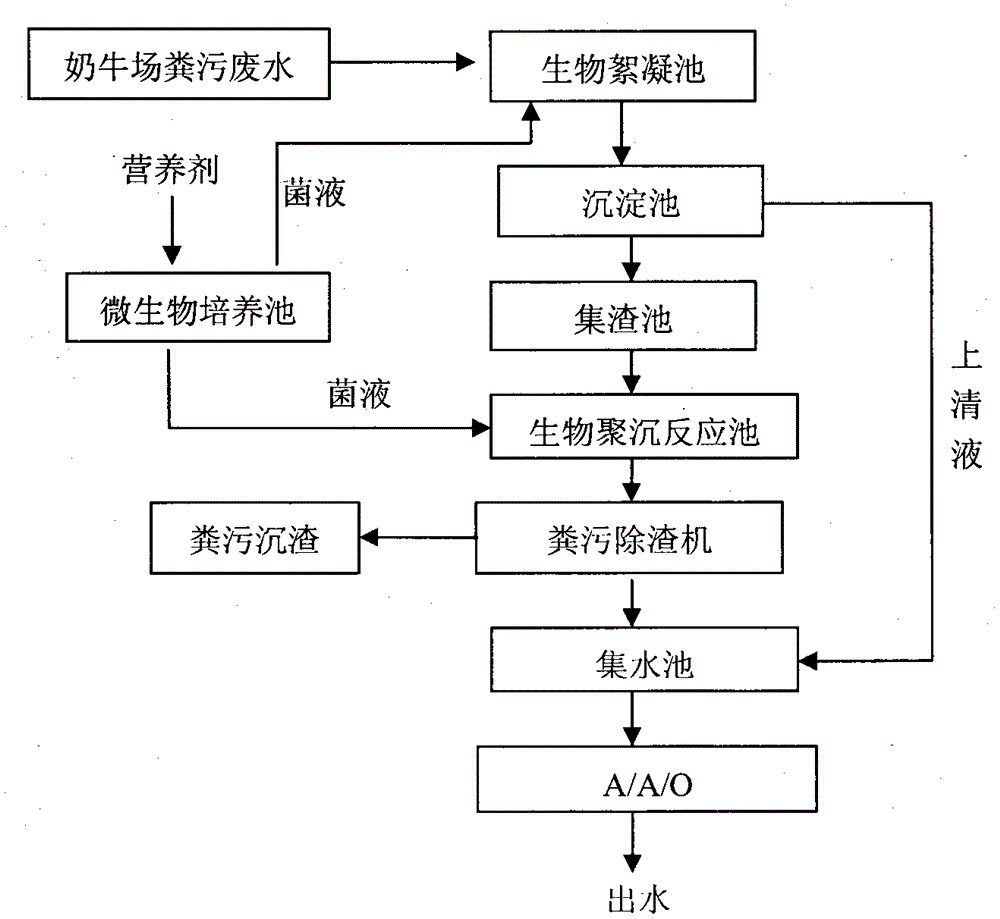
Method for quickly treating excrement wastewater in large-scale dairy farm
ActiveCN105417778AEasy to handleNo degradationWaste water treatment from animal husbandryMultistage water/sewage treatmentFlocculationSlag
The invention provides a method for quickly treating excrement wastewater in a large-scale dairy farm and particularly provides a biological coagulation oxidation technology, belonging to the technical field of environment engineering. The method mainly adopts a biological flocculation tank, a sedimentation tank, a slag collecting tank, a biological coagulation reaction tank, solid-liquid separation equipment, a microbe culture tank, a water collecting tank and a biological oxidation treatment tank. The method is characterized in that a specific microbe (heterotrophic klebsiella F1 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.3032) is used for generating a biological flocculant, the biological flocculant polymerizes with SS, COD, ammonia nitrogen and total phosphorus in the excrement wastewater in the dairy farm through the effects of absorption bridging, charge neutralization and sweeping so as to generate sediments, the solid-liquid separation equipment is further used for separating, the separated excrement sediments are used for producing organic fertilizers, and the separated wastewater is subjected to further biological oxidation treatment to realize up-to-standard discharge.
Owner:南京贝克特环保科技有限公司
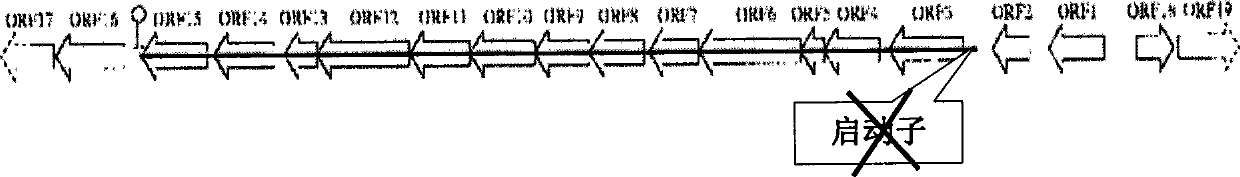
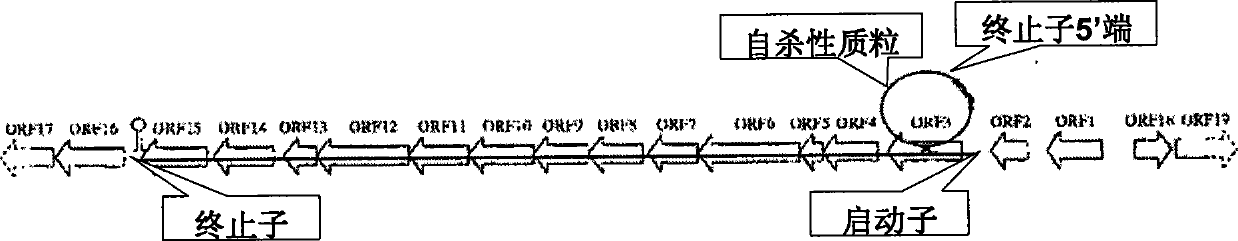
Method for constructing klebsiella with deleted capsula
ActiveCN101397547ALow viscosityReduce pathogenicityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPathogenicityViscosity
The invention discloses a method for constructing Klebsiella without capsules, pertaining to the technical field of biochemical engineering. In PDO producing bacteria, a gene knockout method is adopted to knock out the promoter of the capsule protosome or integrate a terminator behind the promoter so as to stop the transcription of the capsule protosome, thus leading the capsules of the Klebsiella to be partially or completely deleted. Therefore, the fermentation liquor viscosity of the Klebsiella is reduced, the separation and extraction difficulty of POD products is reduced, simultaneously, the thalli pathogenicity is lowered, thereby being favorable to the PDO industrial production application of the Klebsiella.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method for knocking out arcA to increase yield of Klebsiella 1,3-propylene glycol
ActiveCN106399217ADeregulation of transcriptionPromote accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlycerolBiology
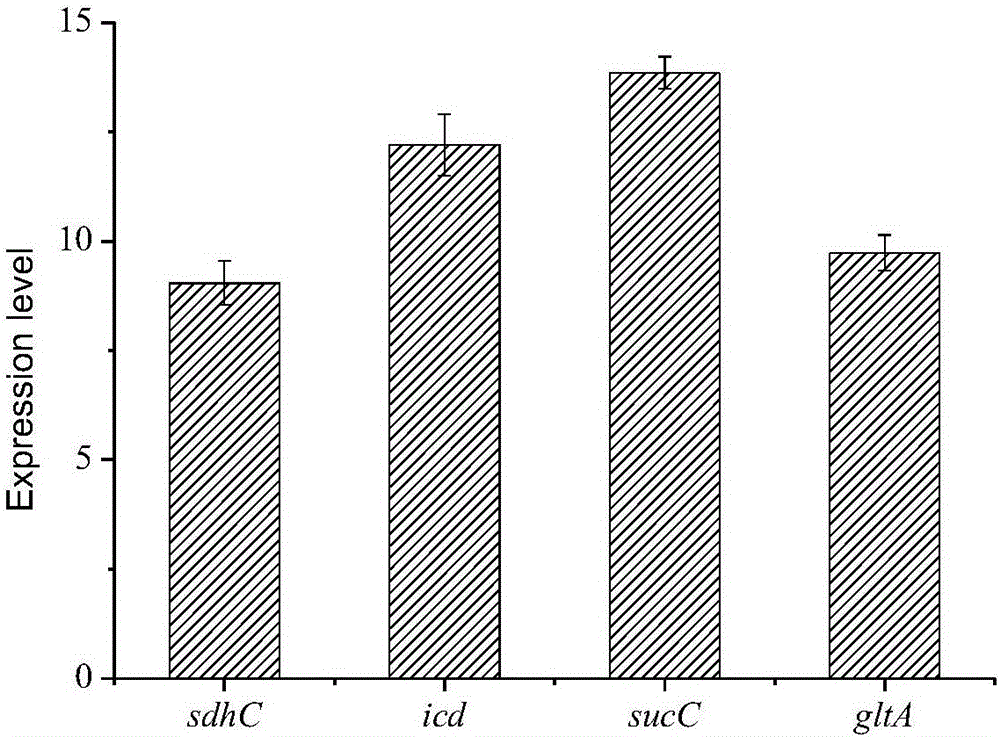
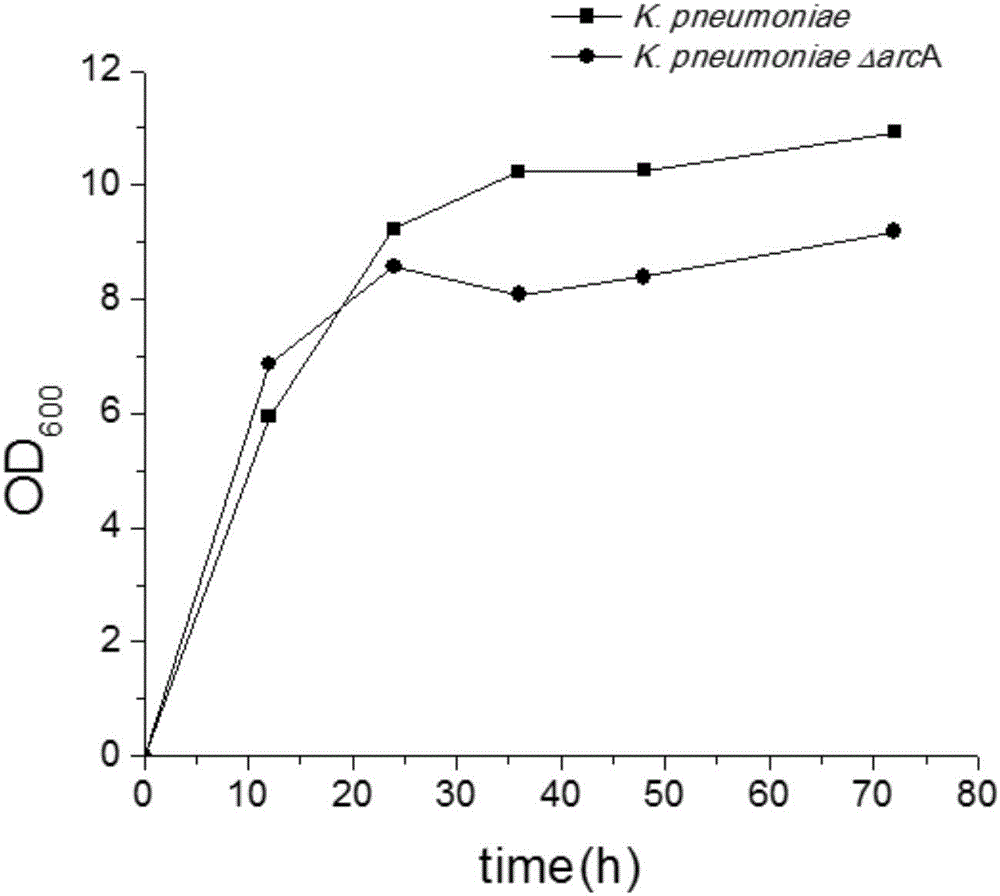
The invention discloses establishment and application of a Klebsiella arcA gene-deleted strain. In the invention, the key gene arcA inhibiting TCA cycle of 1,3-propylene glycol producing Klebsiella is knocked out by a homologous recombination method, the TCA cycle activity of cells in a micro-aerobic condition is increased, the reducing power regeneration is enhanced, and the yield of 1,3-propylene glycol is increased. The yield of 1,3-propylene glycol synthesized by fermenting glycerin with knockout bacteria K.pneumoniae (delta)arcA under micro-aerobic conditions is increased by 12.57% to 17.64g / L, indicating that the yield of 1,3-propylene glycol can be effectively increased by knocking out the arcA gene participating in TCA cycle transcription regulation.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Klebsiella strain and application thereof in river sewage and rural ammonia-containing domestic sewage
ActiveCN108342339AIncrease productionFast growth rateBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementSewageOxygen
The invention provides denitrifying strain Klebsiella sp. KSND-3 with simultaneous aerobic nitrification and denitrification performances and preparation and application thereof. The present inventionalso provides a Klebsiella strain and application thereof in river sewage and rural ammonia-containing domestic sewage. Because of fast growth rate, high cell yield and low dissolved oxygen concentration demand of the Klebsiella strain, the Klebsiella strain can be used for simultaneous nitrification and denitrification, and the denitrification process is more concise, economical and effective.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHUANGLIANG SUNDA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION CO LTD
Method for producing 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol from raw starch material
The invention discloses a method for producing 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol from raw starch materials, including the following steps: 1) Candida krusei or Hansenula Arabitolgens Fang are inoculated into a fermentation medium with the saccharifying liquid of the raw starches as a carbon source; the yeast cells are cultured on an aerobic condition until glucose-consuming-rate is significantly reduced, and then fermented anaerobically to a glucose concentration from 5 to 10 g / L; the fermentation broth is collected and filtered to remove the yeast cells in the broth, and the resultant filtrate is glycerin fermentation broth; 2) Klebsiella, Clostridium butyricum, or Clostridium pasteurianum are inoculated into a fermentation medium in which the glycerin fermentation broth obtained from step 1) serves as a carbon source; the bacteria are fermented anaerobically for 30-32 hours, and then fermented aerobically when the production rate of 1,3-propanediol decreased obviously, and the fermentation was stopped when the concentration of glycerin is reduced to a level below 10 g / L, and finally 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol are obtained. The method of the present invention can effectively reduce production cost and increase productivity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Chlorimuron-ethyl degrading bacterium, soil bioremediation agent based on same, and application thereof
InactiveCN101798564ARemoval of pesticide residuesReduce manufacturing costBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPesticide residueSludge
The invention relates to a chlorimuron-ethyl pesticide residue degrading bacterium which is named klebsiella 2N3 (Klebsiella jilinsis H.Zhang 2N3) with the storage No. of CCTCC NO: M 209248 in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), a soil bioremediation agent prepared from the chlorimuron-ethyl pesticide residue degrading bacterium, and application thereof. The chlorimuron-ethyl pesticide residue degrading bacterium is a bacterial strain which has strong degradation capacity to chlorimuron-ethyl and is obtained by carrying out enrichment culture and separation on sludge at a drainage outlet of an insecticide factory for producing chlorimuron-ethyl, the bacterial strain grows by using the chlorimuron-ethyl as the unique nitrogen source, and the activity of the bacterium in a liquid nutrient medium is increased by the induction of the chlorimuron-ethyl so as to improve the degradation capacity to the chlorimuron-ethyl. The preparation method for the bacterium is simple, low in cost and convenient to use, and can be spread in the soil, and the degradation effect in the soil can reach 82.6 percent; therefore, the chlorimuron-ethyl pesticide residue degrading bacterium has good application prospect.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Preparation method of microbial flocculant for purifying aquaculture seawater
ActiveCN106011215APromote acylationIncreased acetylationSeawater treatmentWaste water treatment from animal husbandryXanthomonas campestrisSeawater
The invention discloses a preparation method of a microbial flocculant for purifying aquaculture seawater. The preparation method is characterized by carrying out synergistic fermentation on a mixed strain of klebsiella LDX1-1 and xanthomonas campestris CICC10258 with fermentation of a high-magnesium fermentation culture medium by adopting an antagonism-free compatible shake flask, and carrying out gelation strength treatment by adopting a salt mixture after the fermentation is completed. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is fast in fermentation speed, the technology can be easily operated, the fermentation concentration is high, and the production cost is low; the produced flocculant is used for treating high-salinity high-buoyancy seawater, has the characteristics of stable structure, flocculating block compactness and fast settling speed, and has an obvious effect in purifying the aquaculture seawater.
Owner:QINGDAO YAODONG GRP
Method for the recombinant production of 1,3-propanediol
The present invention provides a microorganism for the production of 1,3-propanediol from a variety of carbon sources in an organism capable of 1,3-propanediol production and comprising a) at least one gene encoding a dehydratase activity; b) at least one gene encoding a glycerol-3-phosphatase; and c) at least one gene encoding protein X. The protein X may be derived from a Klebsiella or Citrobacter gene cluster. The recombinant microorganism may further comprise d) at least one gene encoding a protein having at least 50% similarity to a protein selected from the group consisting of protein 1 (SEQ ID NO:60 or SEQ ID NO:61), of protein 2 (SEQ ID NO:62 or SEQ ID NO:63) and of protein 3 (SEQ ID NO:64 or SEQ ID NO:65) from Klebsiella or Citrobacter.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Klebsiella for strengthening expression of citT gene and application of klebsiella in production of 1,3-propylene glycol
ActiveCN107325999AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPropylene glycol
The invention provides klebsiella for strengthening the expression of a citT gene and an application of the klebsiella in production of 1,3-propylene glycol. The klebsiella provided by the invention is specifically obtained by strengthening the expression of the citT gene in the klebsiella. By applying klebsiella provided by the invention to fermentation production of 1,3-propylene glycol, the yield of 1,3-propylene glycol can be increased.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG GLORY CHEM IND CO LTD
Method for producing 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol from raw starch material
ActiveUS20090081745A1Decrease seed culturing periodFermentationClostridium pasteurianumConcentrations glucose
The invention discloses a method for producing 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol from raw starch materials, including the following steps: 1) Candida krusei or Hansenula Arabitolgens Fang are inoculated into a fermentation medium with the saccharifying liquid of the raw starches as a carbon source; the yeast cells are cultured on an aerobic condition until glucose-consuming-rate is significantly reduced, and then fermented anaerobically to a glucose concentration from 5 to 10 g / L; the fermentation broth is collected and filtered to remove the yeast cells in the broth, and the resultant filtrate is glycerin fermentation broth; 2) Klebsiella, Clostridium butyricum, or Clostridium pasteurianum are inoculated into a fermentation medium in which the glycerin fermentation broth obtained from step 1) serves as a carbon source; the bacteria are fermented anaerobically for 30-32 hours, and then fermented aerobically when the production rate of 1,3-propanediol decreased obviously, and the fermentation was stopped when the concentration of glycerin is reduced to a level below 10 g / L, and finally 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol are obtained. The method of the present invention can effectively reduce production cost and increase productivity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
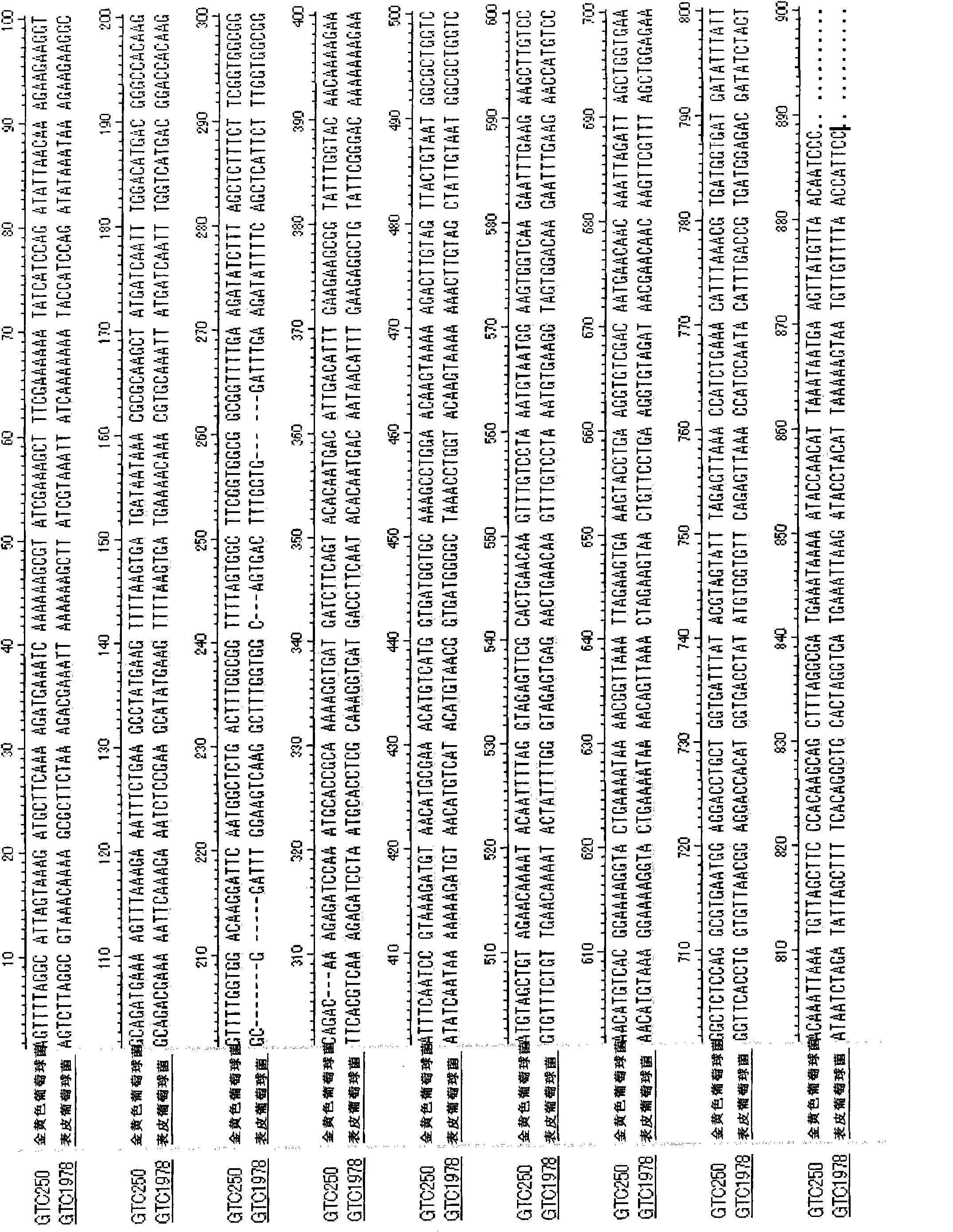
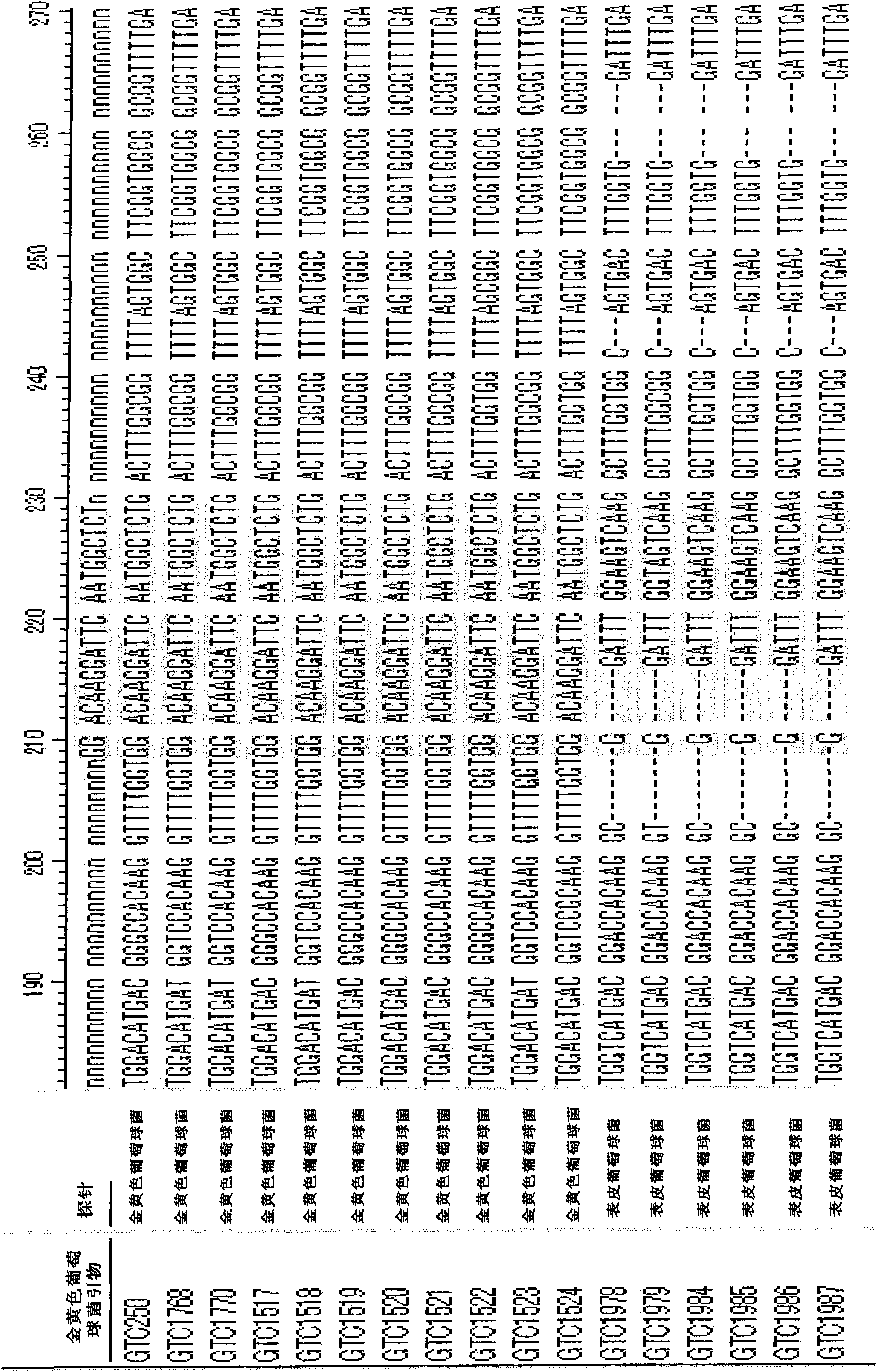
Multiplex quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer, probe, kit and detection method for corynebacterium bacteria and Klebsiella corynebacterium
ActiveCN107236793AShorten the course of the diseaseAvoid excisionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesEtiology
The invention discloses a multiplex quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer, a probe, a kit and a detection method for corynebacterium bacteria and Klebsiella corynebacterium. Aiming at corynebacterium bacterium 23S rRNA genes and Klebsiella corynebacterium 16S rRNA gene sequences, specific primers and probes are designed, whether the corynebacterium bacteria and Klebsiella corynebacterium exist in a biological sample can be identified by utilizing multiplex quantitative PCR. The primers and probes have an important guiding role in clinical targeted selective use of antibiotics. Due to reasonable usage of the antibiotics, the course of granulomatous mastitis can be effectively shortened, the condition that breast tissues are removed during the operation is avoided, physical and psychological trauma of a patient can be greatly alleviated, and an etiological basis is provided for clinical diagnosis and treatment of the granulomatous mastitis.
Owner:GUANGDONG WOMEN & CHILDREN HOSPITAL
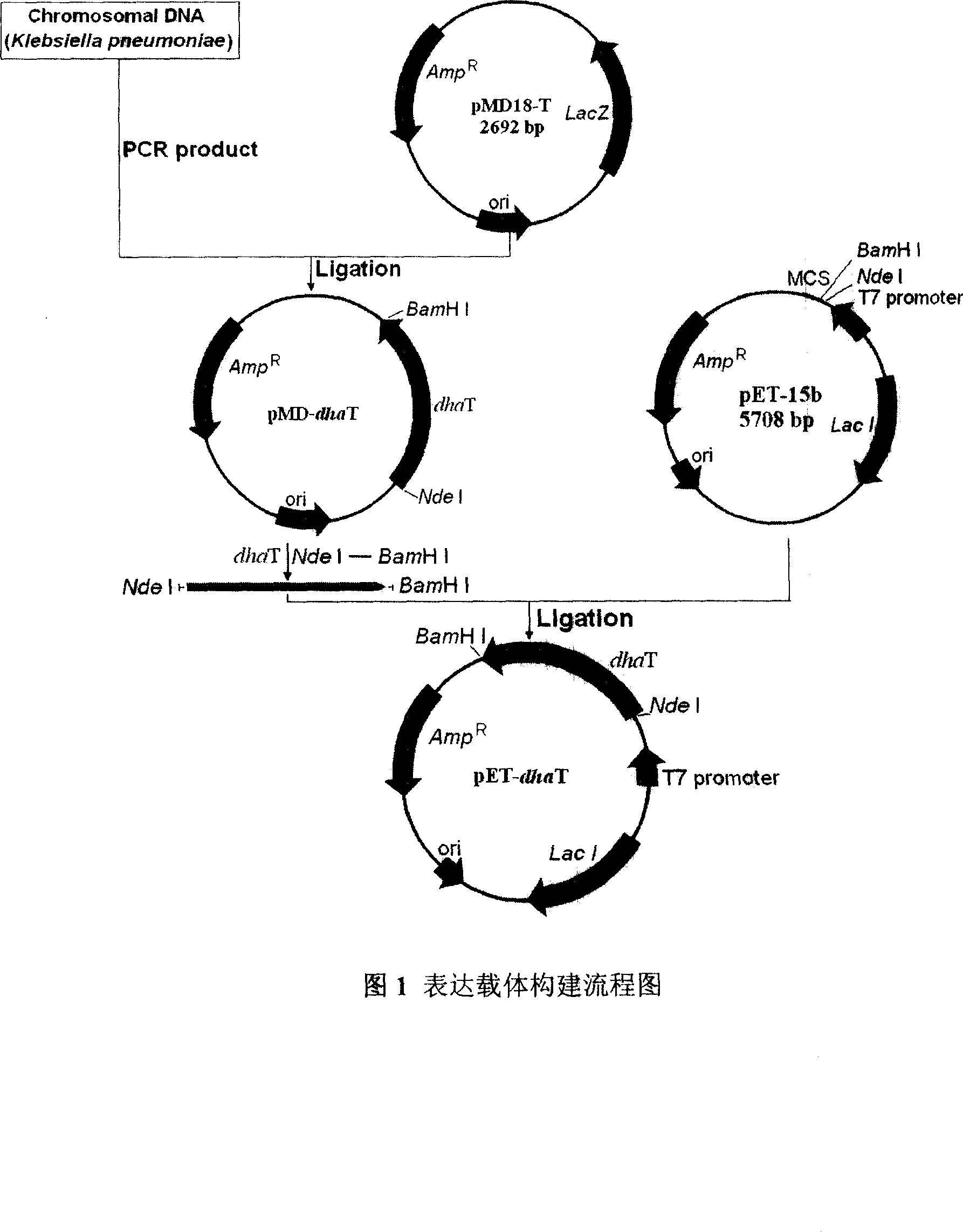
Engineering bacterium producing 1,3-methyl glycol oxidoreductase and preparation method for the enzyme
The invention discloses a preparing method of restructuring strain in biological technical domain, which comprises the following steps: adopting PCR technique; cloning dhaT gene from pneumonic klebsiella DSM 2026; constructing bacillus coli expressing carrier pET-dhaT with dhaT gene; transferring into bacillus coli DH5 alpha; proceeding plasmid reproduction; extracting recombinant plasmid; transferring to bacillus coli BL21(DE3); getting recombination gene engineering strain E. coli-pET-dhaT to express 1, 3-propanediol oxidoreductase (PDOR). This strain can get stable PDOR under the condition of non-antibiotic selective pressure.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Bacteriophage and application of same to soil remediation
ActiveCN109280650AWell developed porosityLarge specific surface areaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesBioremediation
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Primer compound for identifying intestinal microecological state and application thereof
ActiveCN109576386AEfficient and convenient identificationHigh detection specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesClostridium symbiosum
The invention provides a primer compound for identifying intestinal microecological state and an application thereof. The primer compound is a specific primer designed for intestinal bacterium 16S rRNA; the specific primer includes random basic groups; the quantity of random basic groups is 3-5; the intestinal bacterium includes any one of or combination of at least two of symbiotic clostridia, bifidobacterium adolescentis, fusobacterium nucleatum, peptostreptococcus anaerobius or klebsiella. A kit researched and developed on the basis of the primer compound provided by the invention has a specificity for detecting intestinal microecological imbalance reaching up to 92.5% and a sensitivity reaching up to 80.43%.
Owner:SUZHOU PRECISION BIOTECH CO LTD
Composition and method for detecting and early and differentiated counting of gram-negative microorganisms
InactiveUS20030044882A1High diagnostic specificityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCitrobacter
The present invention is related with the Microbiology field and particularly with a composition and a method for early detection, identification, differentiation and count of microscopic organisms, concretely Gram-negative microorganisms. The composition described in the invention consist on a mixture of substances of protein origin with a total nitrogen content from 9 to 20% and in relationship between 2:1 to 24:1, concerning to the content of inhibitors of the Gram-positive organisms. It contains a mixture of organic and inorganic substances that facilitate the differentiation of the Gram-negative organisms, being this mixture in a relationship from 0.5:1 to 2:1 concerning to the mixture of substances of protein origin. The referred composition allows the detection and differentiated count of E. coli and other coliform organisms due to the blue-greenish color of the colonies of these microorganisms on the orange bottom of the medium; Salmonella not typhi for the red color of the centers of the colonies on rosy bottom of the medium; Salmonella typhi and Proteus for the transparency of the colonies; Citrobacter and Klebsiella for the violet color of the colonies on the pink to orange bottom of the medium and Pseudomonas aeruginosa for the orange color with darker center of the colony, taking greenish pigmentation after 24 hours and producing greenish fluorescence under low ultraviolet light.
Owner:CENT NACIONAL BIOPREPARADOS
A Dissimilatory Iron-Reducing Bacteria and Its Application
InactiveCN104974964BEfficient reductionStrong restore functionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesKlebsiella oxytocaMontmorillonite
The invention belongs to the field of environmental biotechnology, and in particular relates to a dissimilating iron-reducing bacterium and its application. The dissimilating iron-reducing bacteria provided by the present invention is Klebsiella oxytoca IMFRCUG‑1, which was deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on May 27, 2015, with the preservation number CCTCC NO: M 2015332. The Klebsiella oxytoca IMFRCUG-1 of the present invention has a strong reduction function of Fe(III) reduction by dissimilation, and can efficiently reduce Fe(III) in iron citrate and montmorillonite. The invention broadens people's thinking on the application and research of Klebsiella oxytoca in its function, provides new materials for dissimilating iron-reducing bacteria in the treatment of environmental pollutants, and has strong practical application value .
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
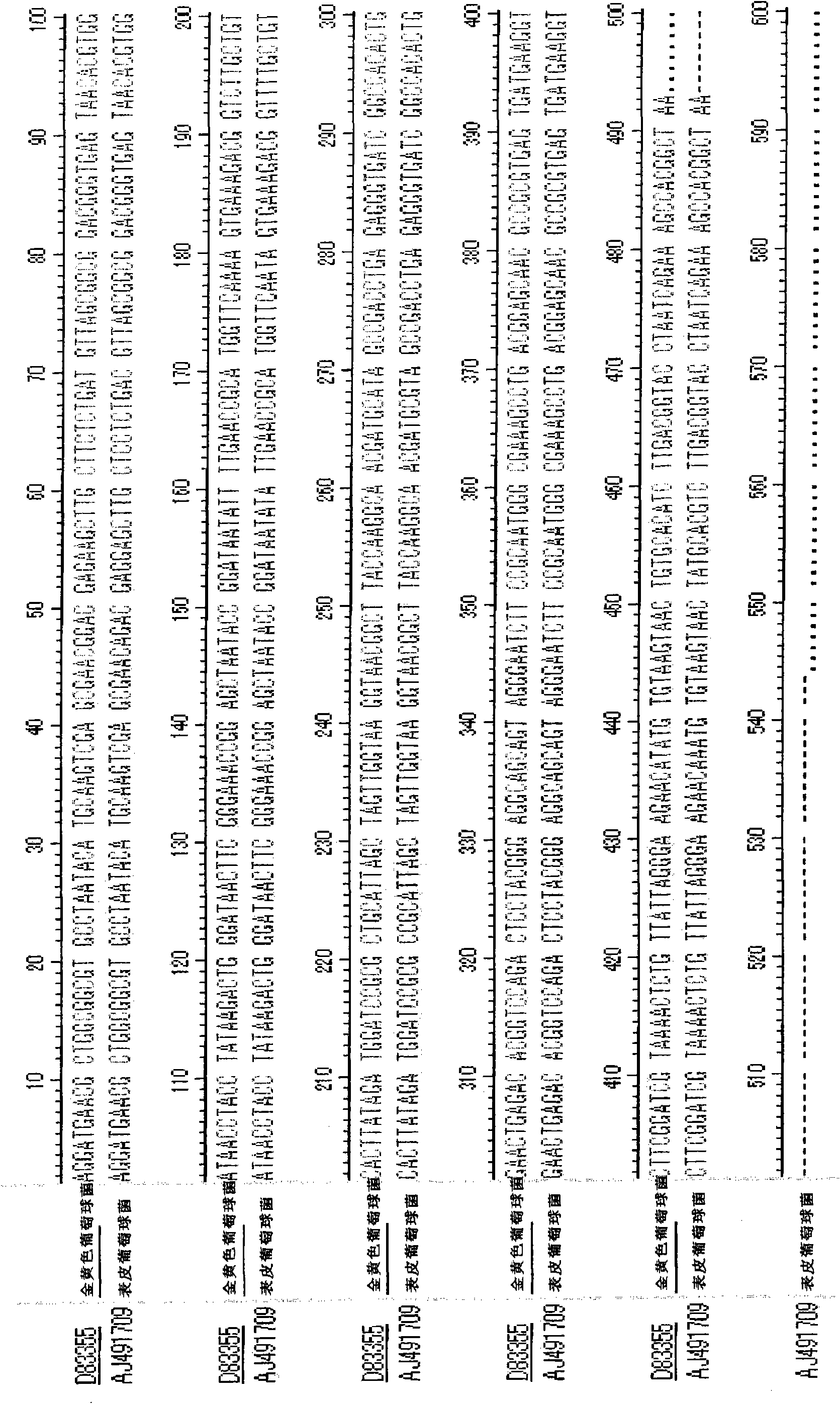
Methods and kits to identify klebsiella strains
Embodiments of the invention provide a method of detecting one or more strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae. The method may include forming a plurality of mixtures for nucleic amplification. The method can include amplification of specific sequences within the K. pneumonia genome that can provide definitive information to distinguish between one or more types or strains of K. pneumonia.
Owner:TRANSLATIONAL GENOMICS RESEARCH INSTITUTE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com