Microbes capable of degrading phenol and cyanogen in coking waste water and method for treating coking waste water by using same
A technology for microbial treatment and coking wastewater, applied in microorganism-based methods, sustainable biological treatment, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in removal and effluent failure to meet national first-level discharge standards
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
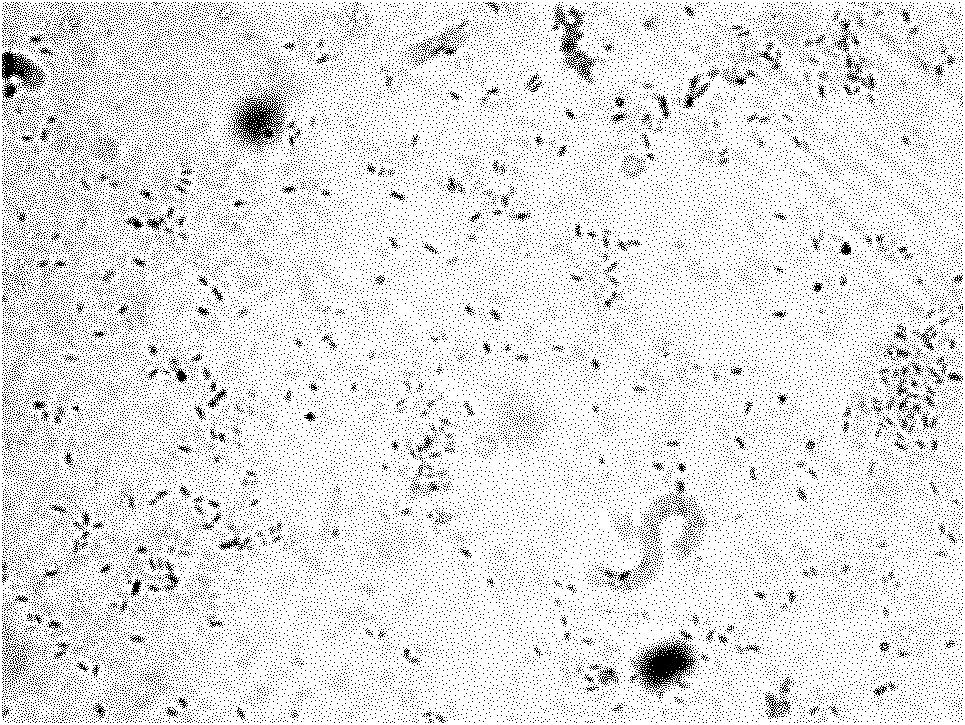
[0021] Specific embodiment 1: One of the microorganisms that can degrade phenol and cyanide in coking wastewater in this embodiment is Bacillus subtilis BHf3-4, which is preserved in the General Microbiology Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. .4046.
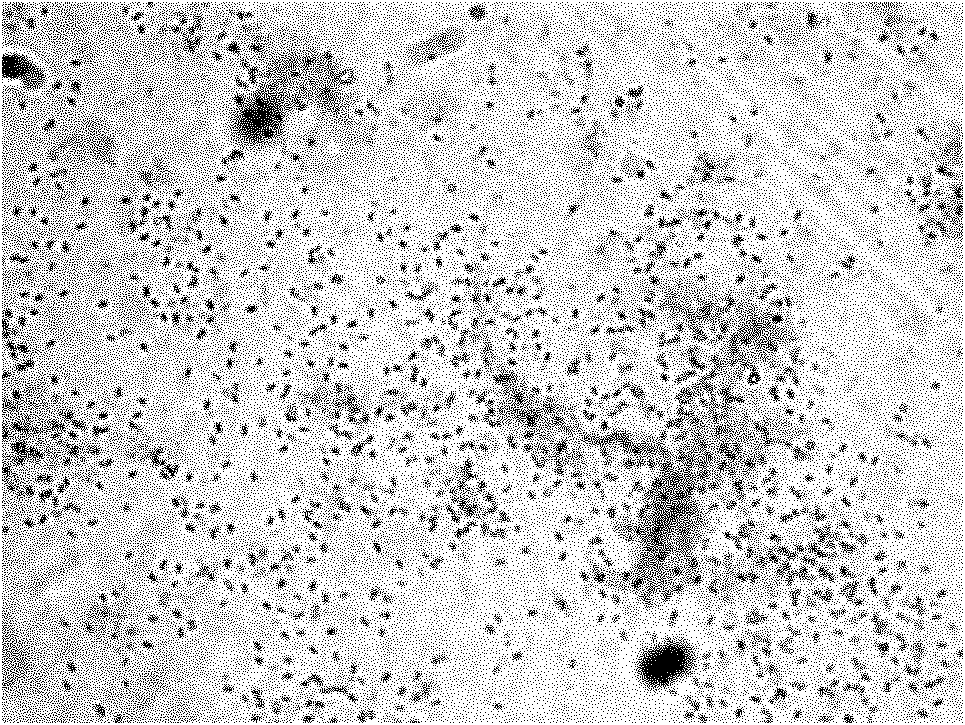
[0022] The physiological and biochemical characteristics of Bacillus subtilis BHf3-4 are shown in Table 1, and the photomicrograph of Bacillus subtilis BHf3-4 is shown in Table 1. figure 1 shown.
[0023] Table 1
[0024] Catalase
specific Embodiment approach 2
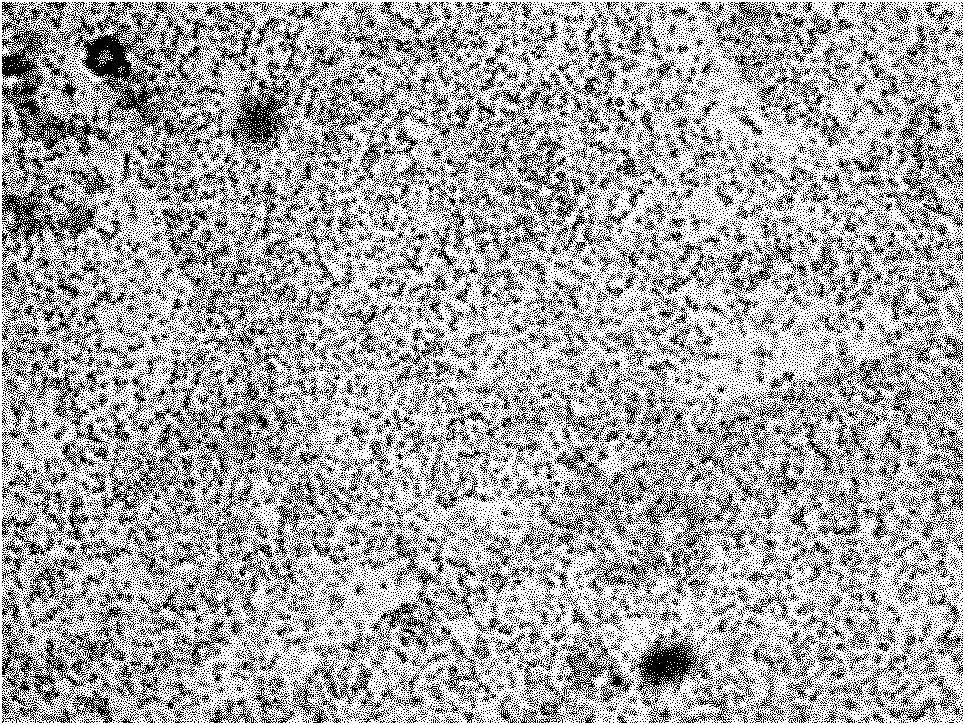
[0025] Specific implementation mode 2: The second type of microorganism that can degrade phenol and cyanide in coking wastewater in this embodiment is Bacillus sp. JhqK9-1, which is preserved in the General Microbiology Center of China Committee for the Collection of Microbial Cultures, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. .4047.
[0026] The physiological and biochemical characteristics of Bacillus JhqK9-1 are shown in Table 2, and the photomicrograph of Bacillus JhqK9-1 is shown in Table 2. figure 2 shown.
[0027] Table 2
[0028] Catalase
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0029] Specific embodiment three: The third of the microorganisms that can degrade phenol and cyanide in coking wastewater in this embodiment is Klebsiella oxytoca (Klebsiella oxytoca) JhqM8. CGMCC No. 4048.
[0030] The physiological and biochemical characteristics of Klebsiella oxytoca JhqM8 are shown in Table 3, and the photomicrograph of Klebsiella oxytoca JhqM8 is shown in Table 3. image 3 shown.
[0031] table 3
[0032] Catalase
[0033] sucrose
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com