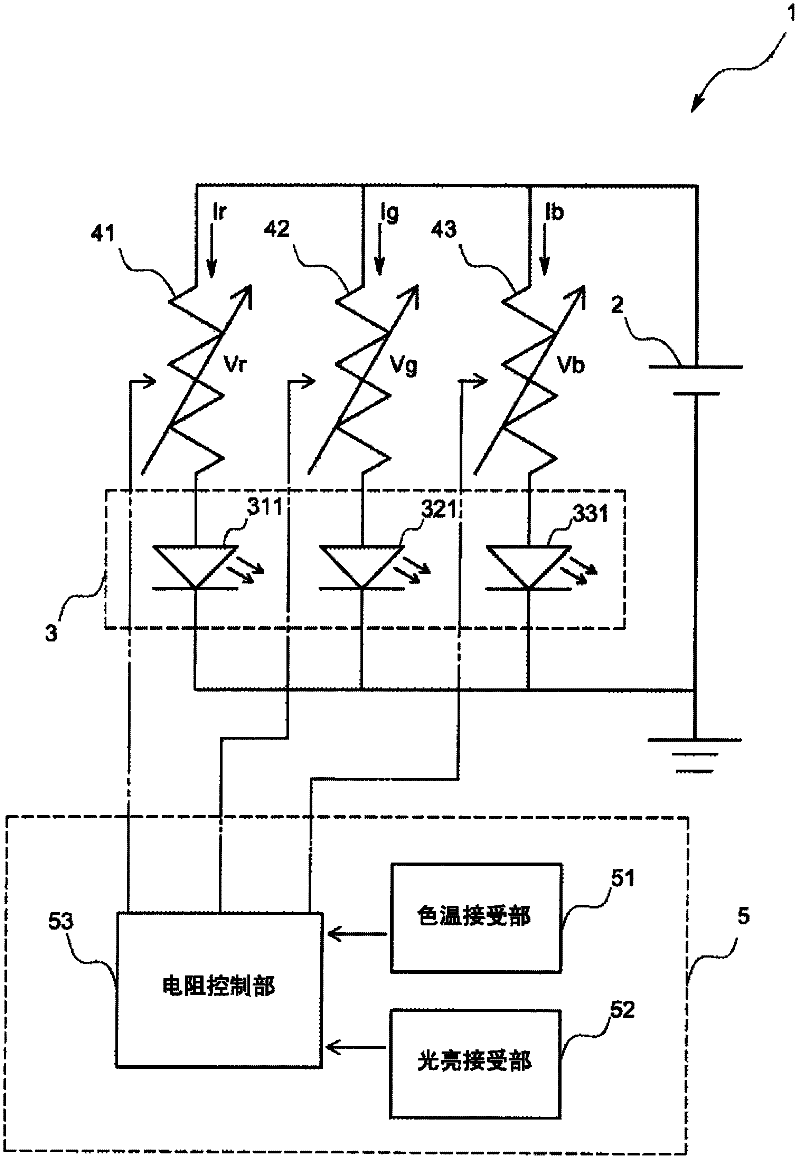
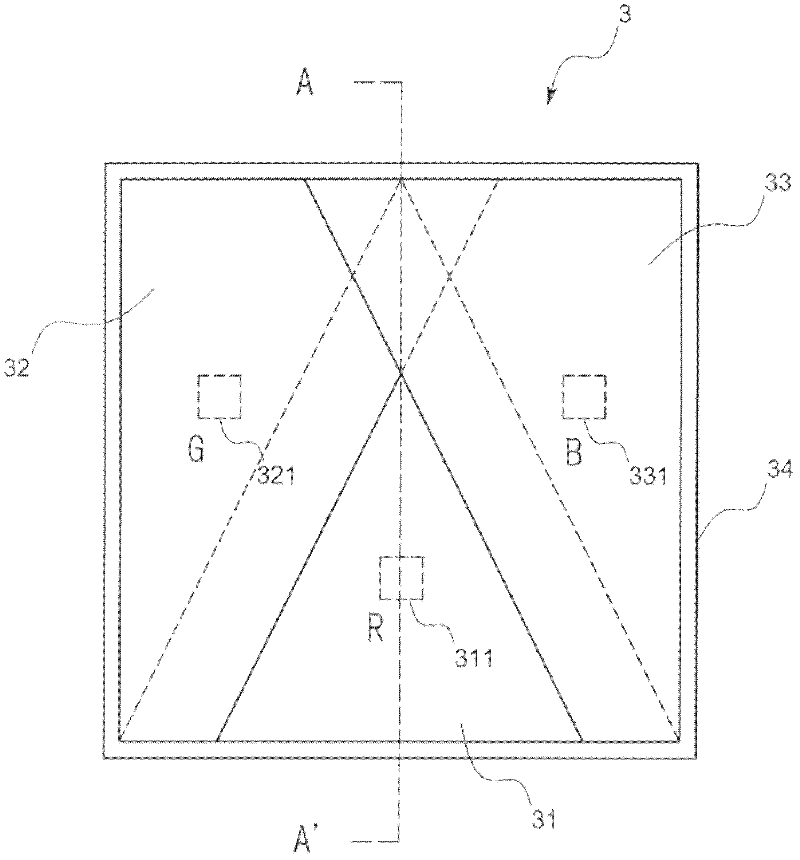
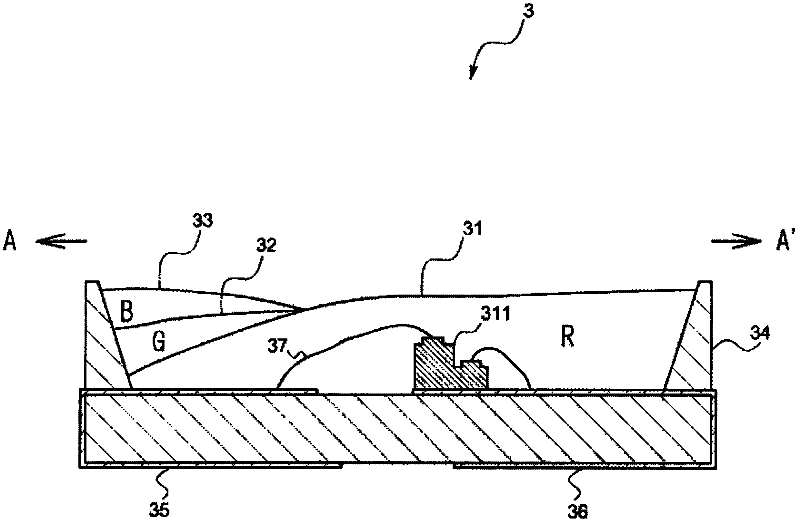
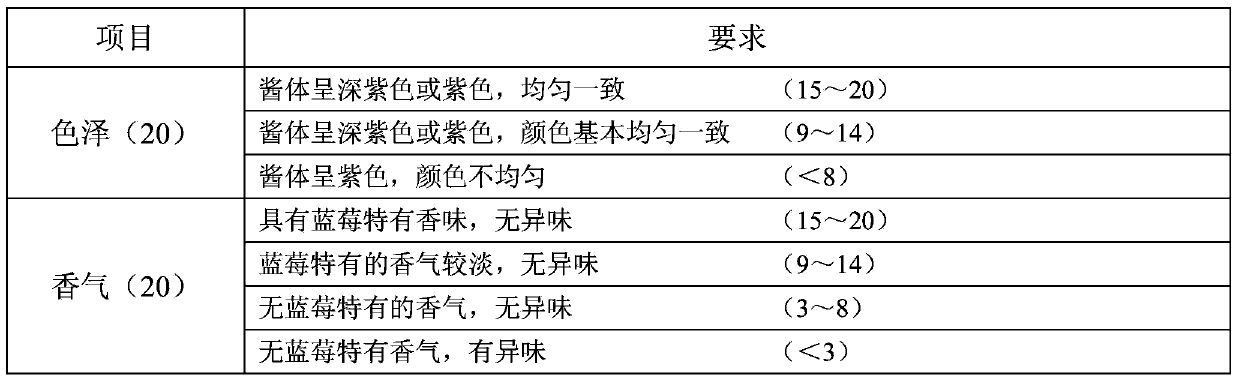
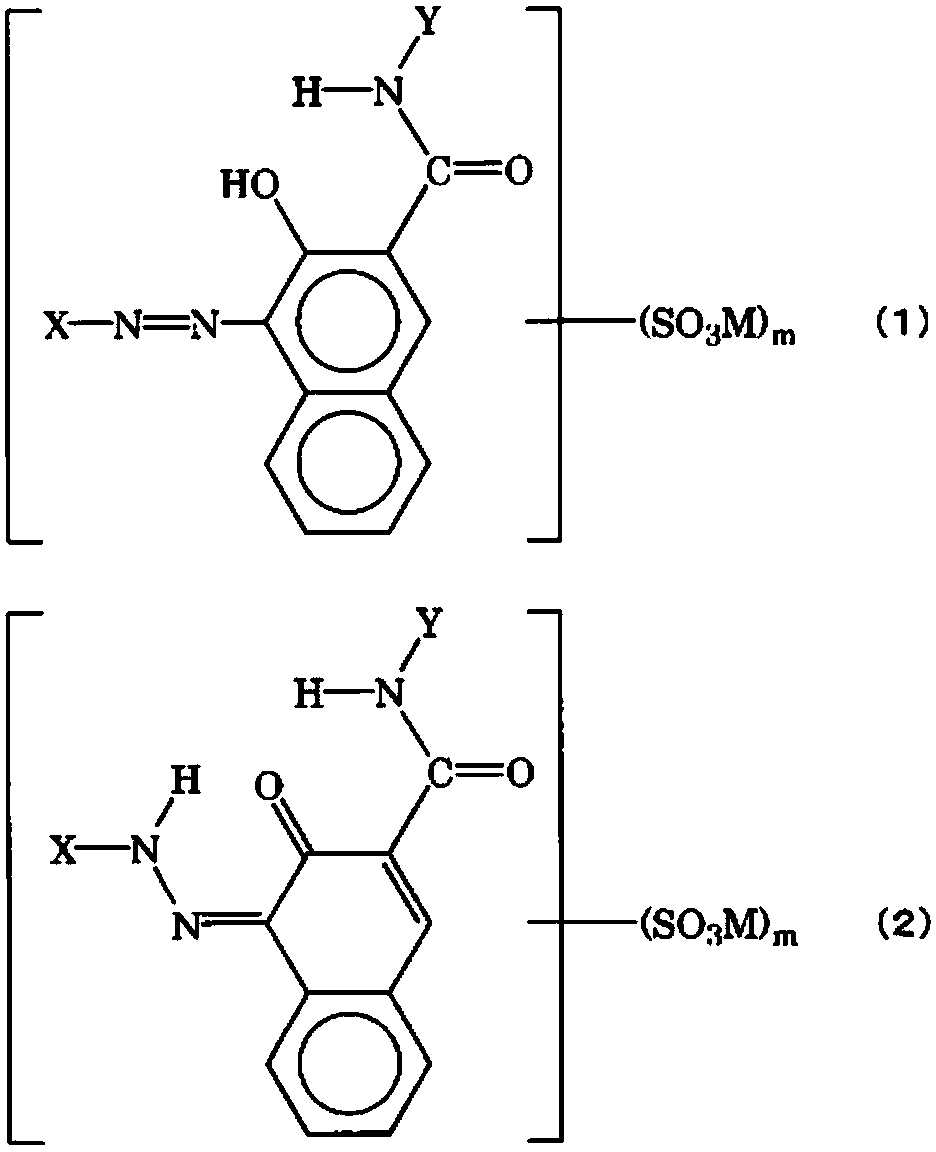
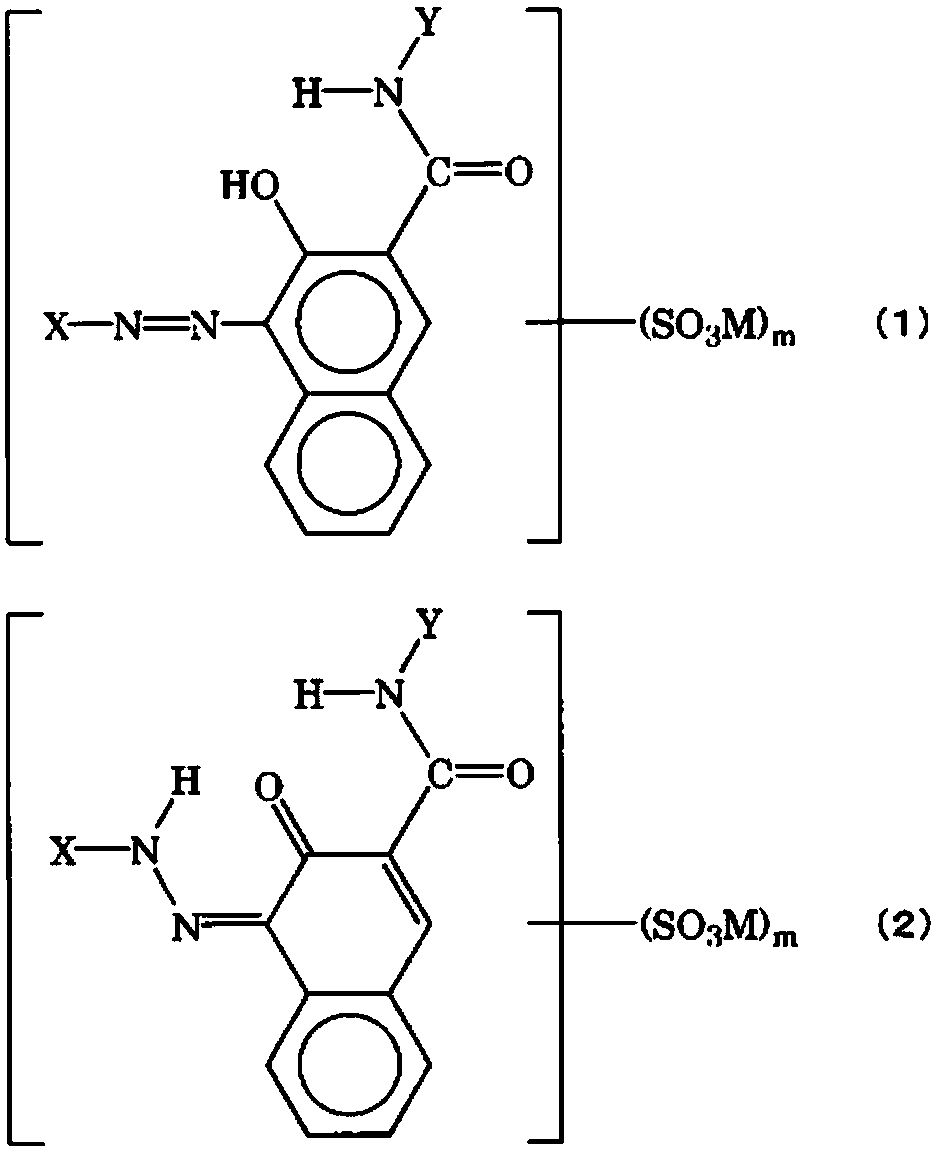
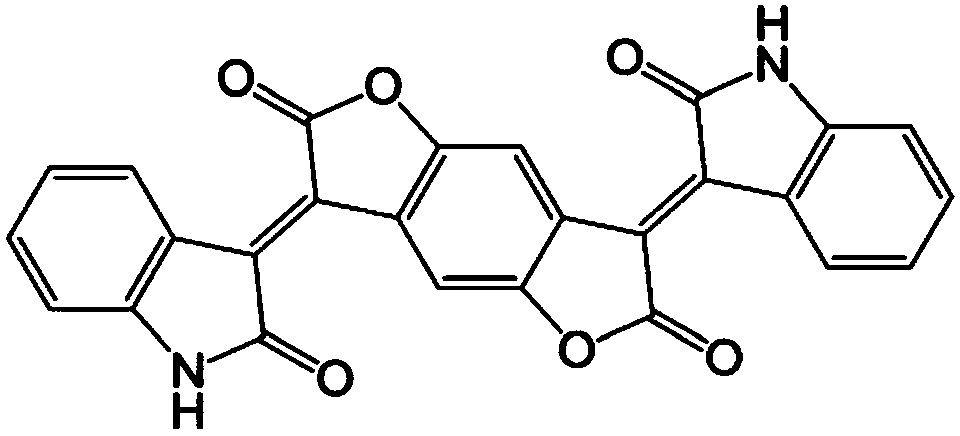
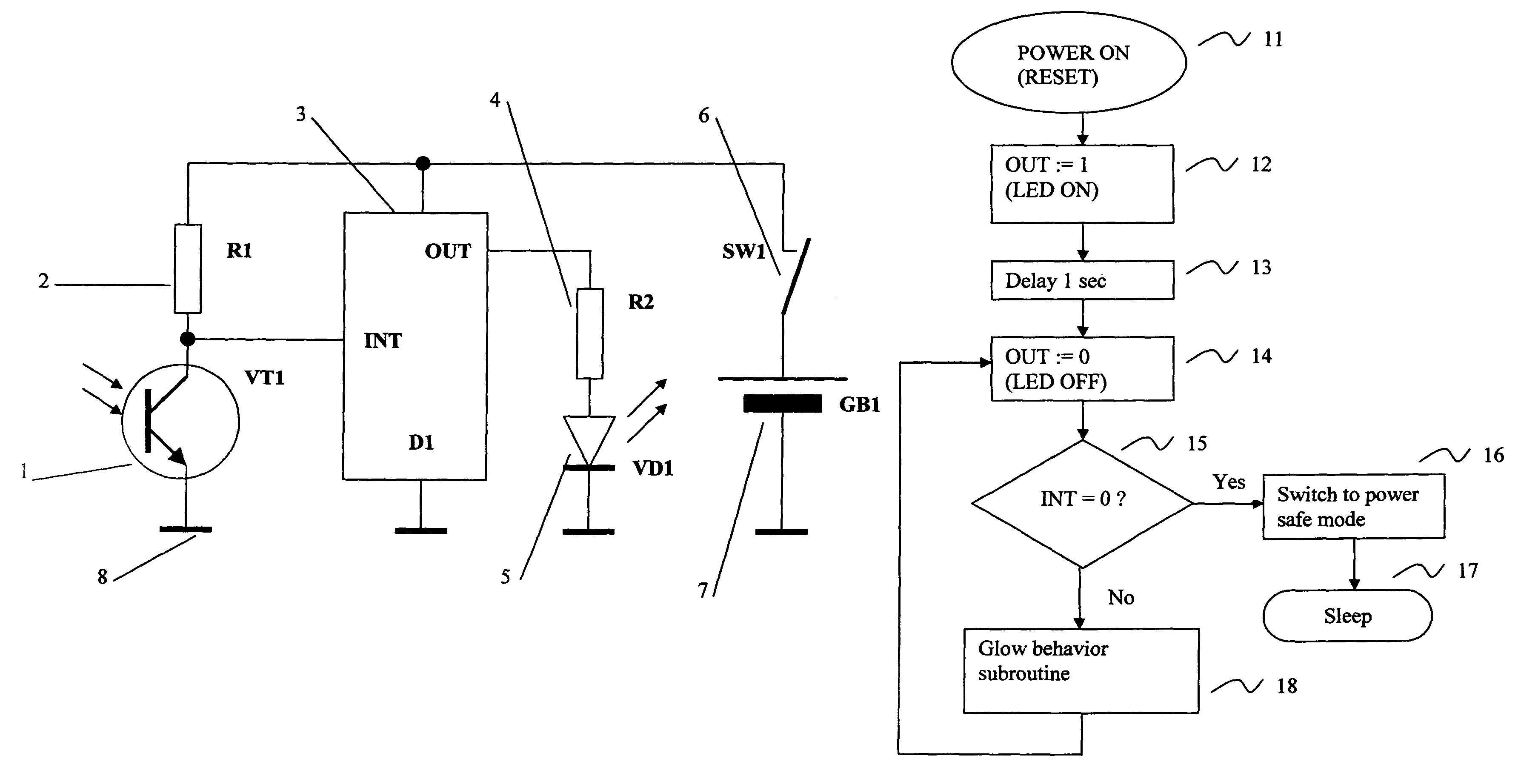
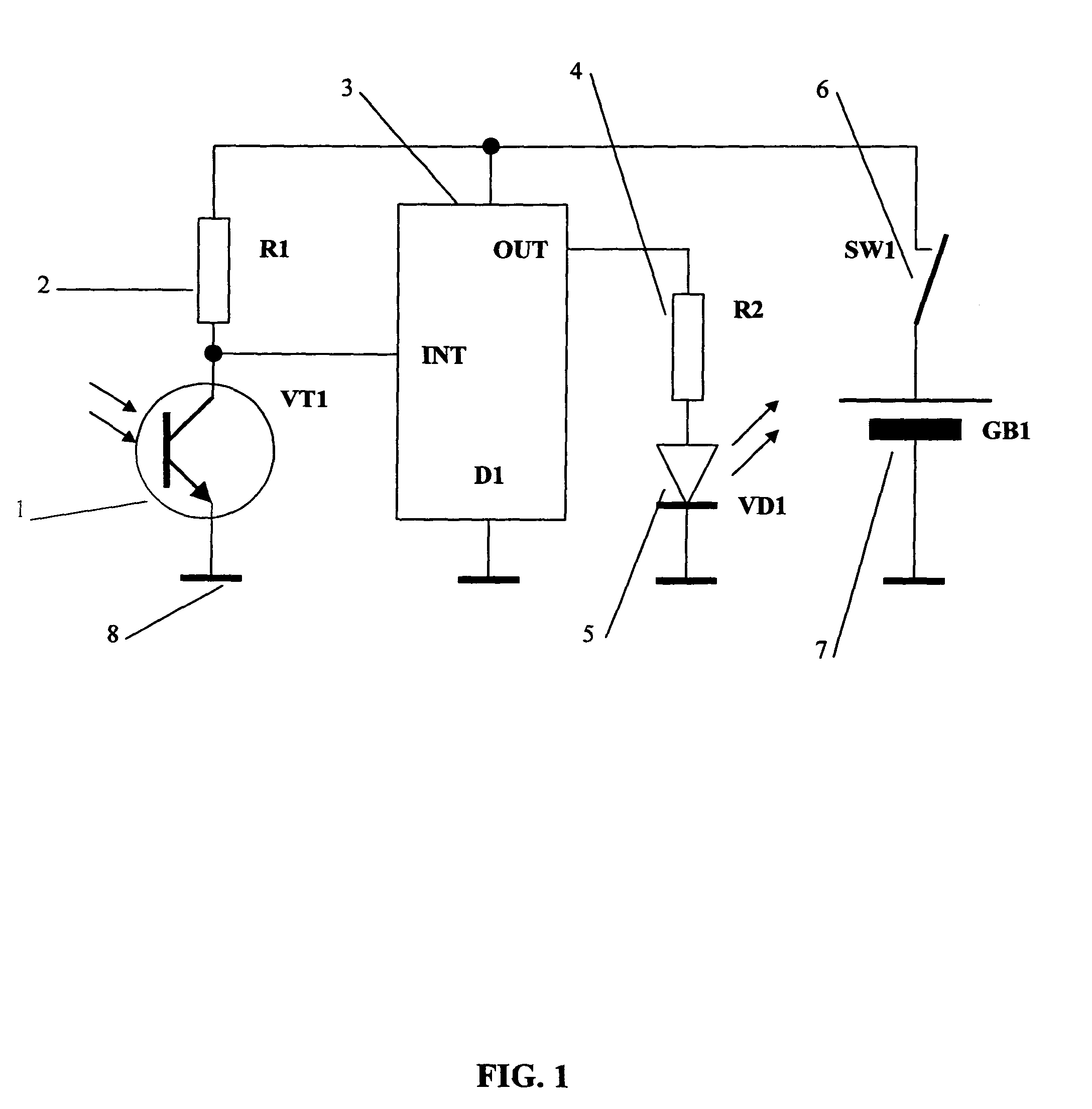
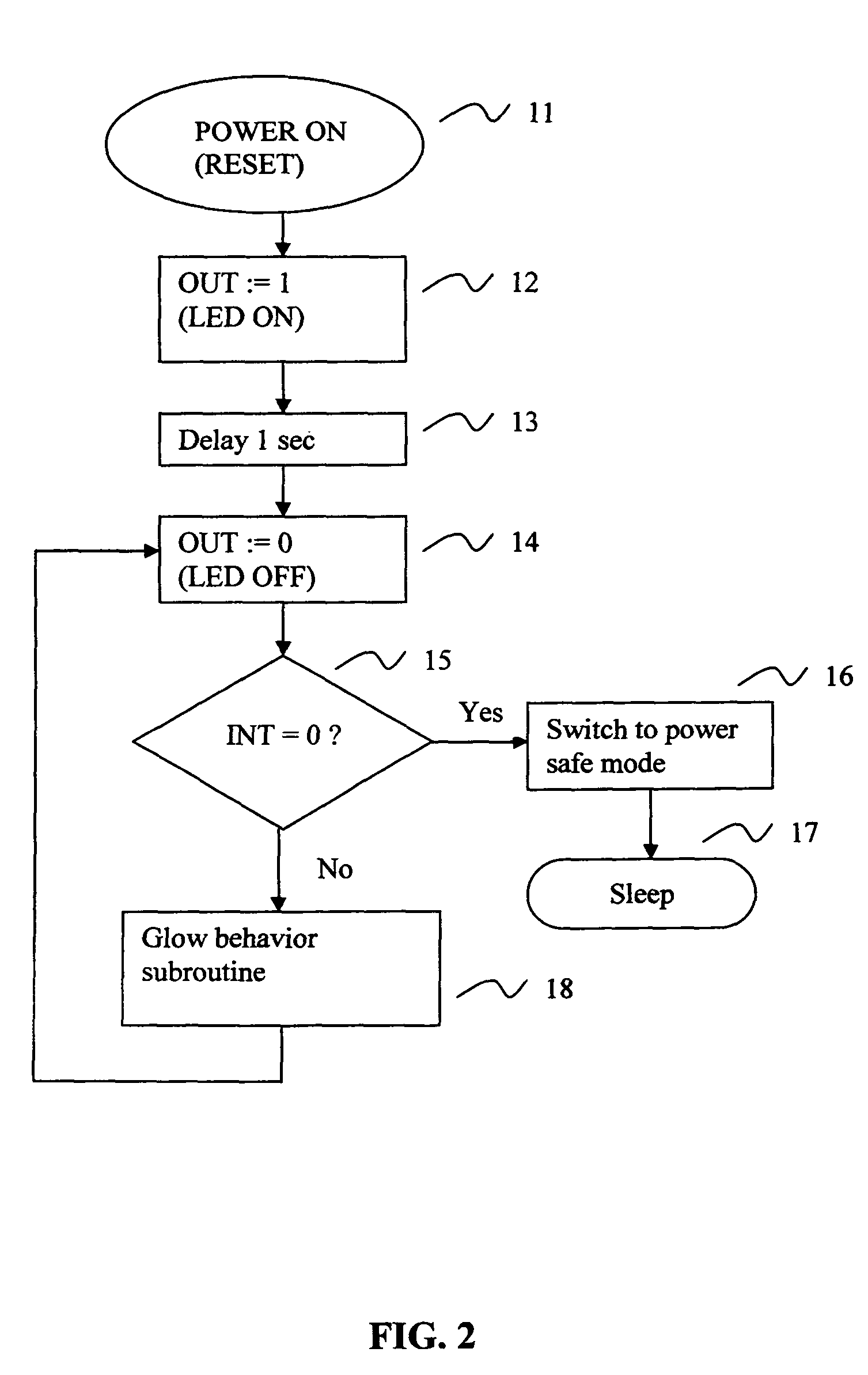
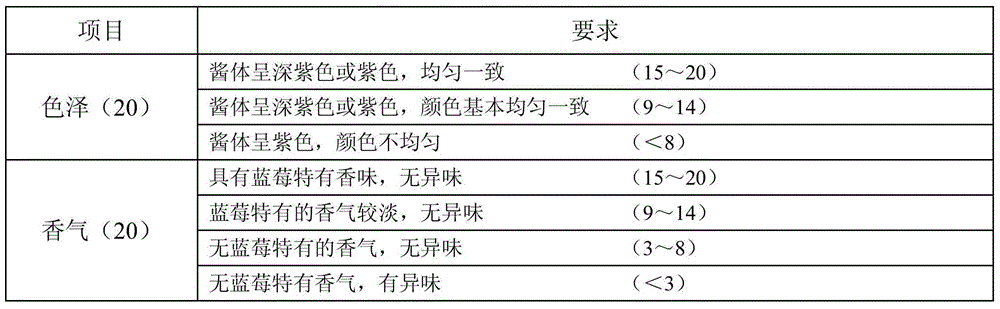
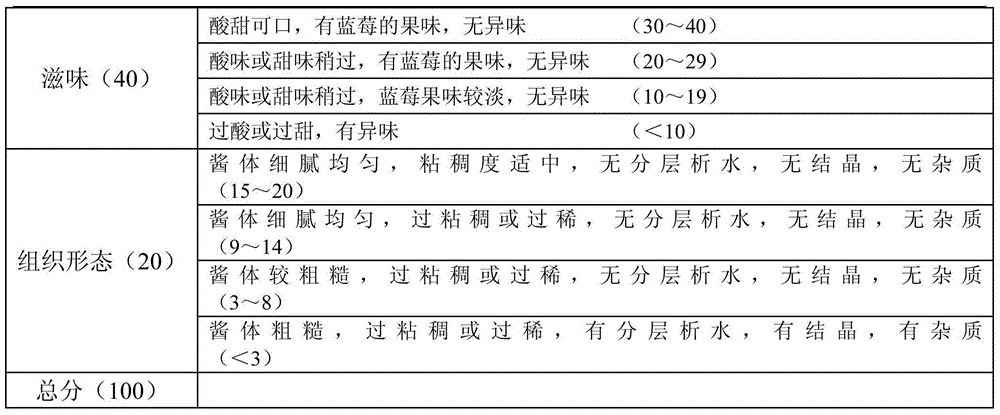
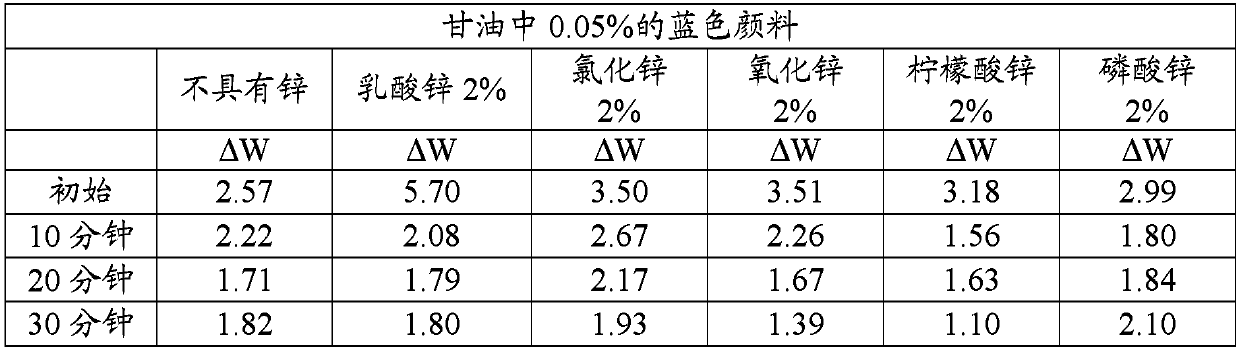
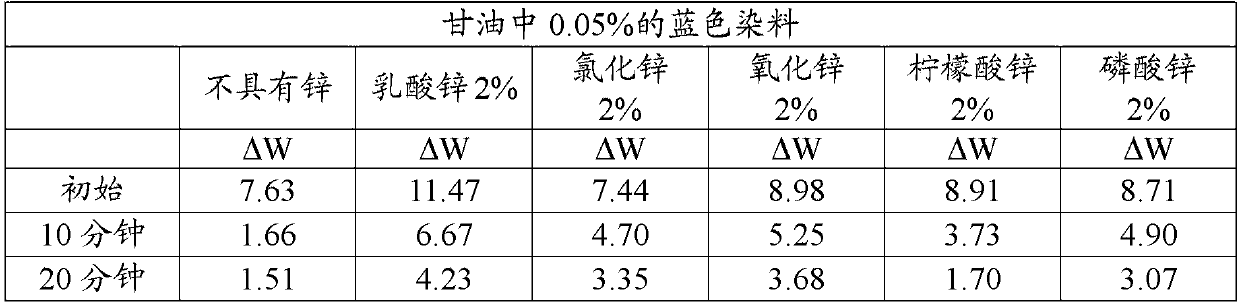
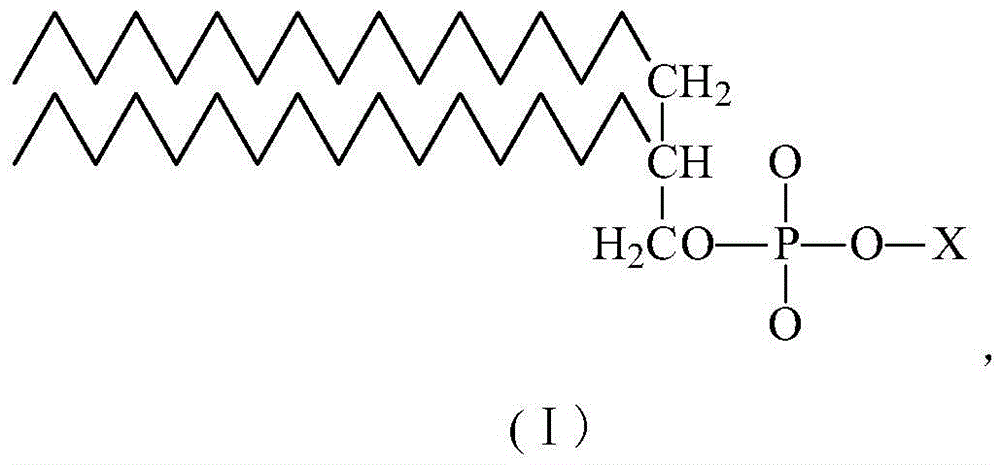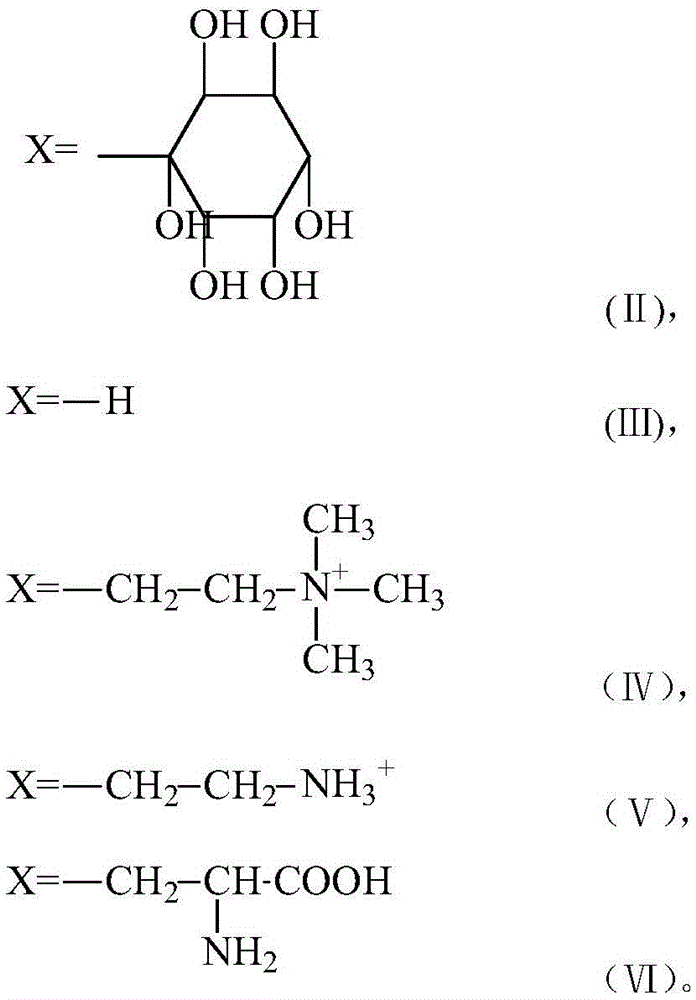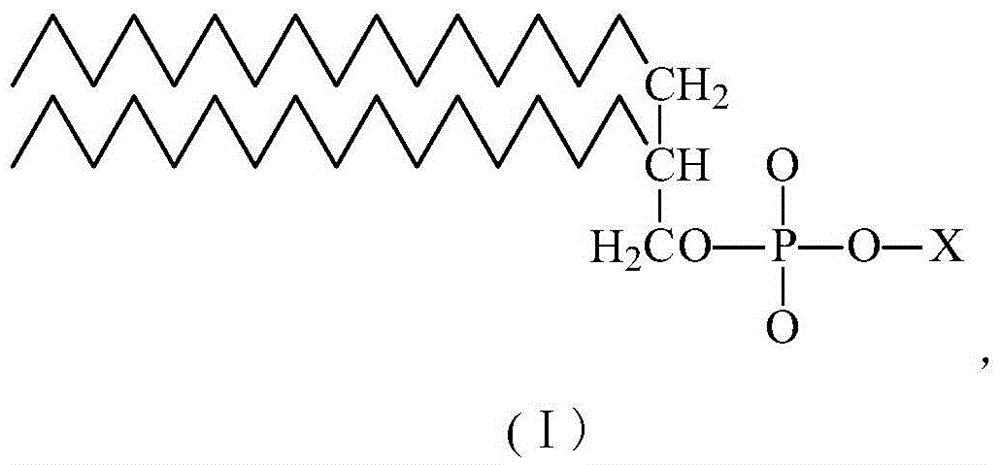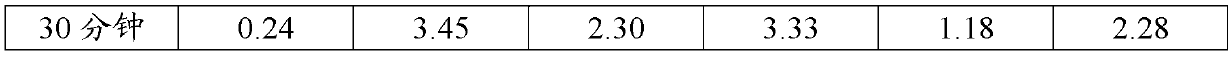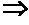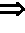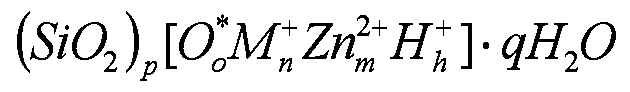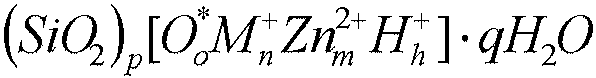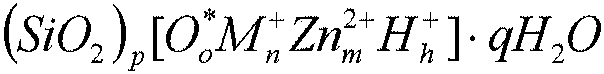Patents
Literature
49 results about "Violet color" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Violet is the color at the end of the visible spectrum of light between blue and the invisible ultraviolet. Violet color has a dominant wavelength of approximately 380-450 nanometers. Light with a shorter wavelength than violet but longer than X-rays and gamma rays is called ultraviolet.
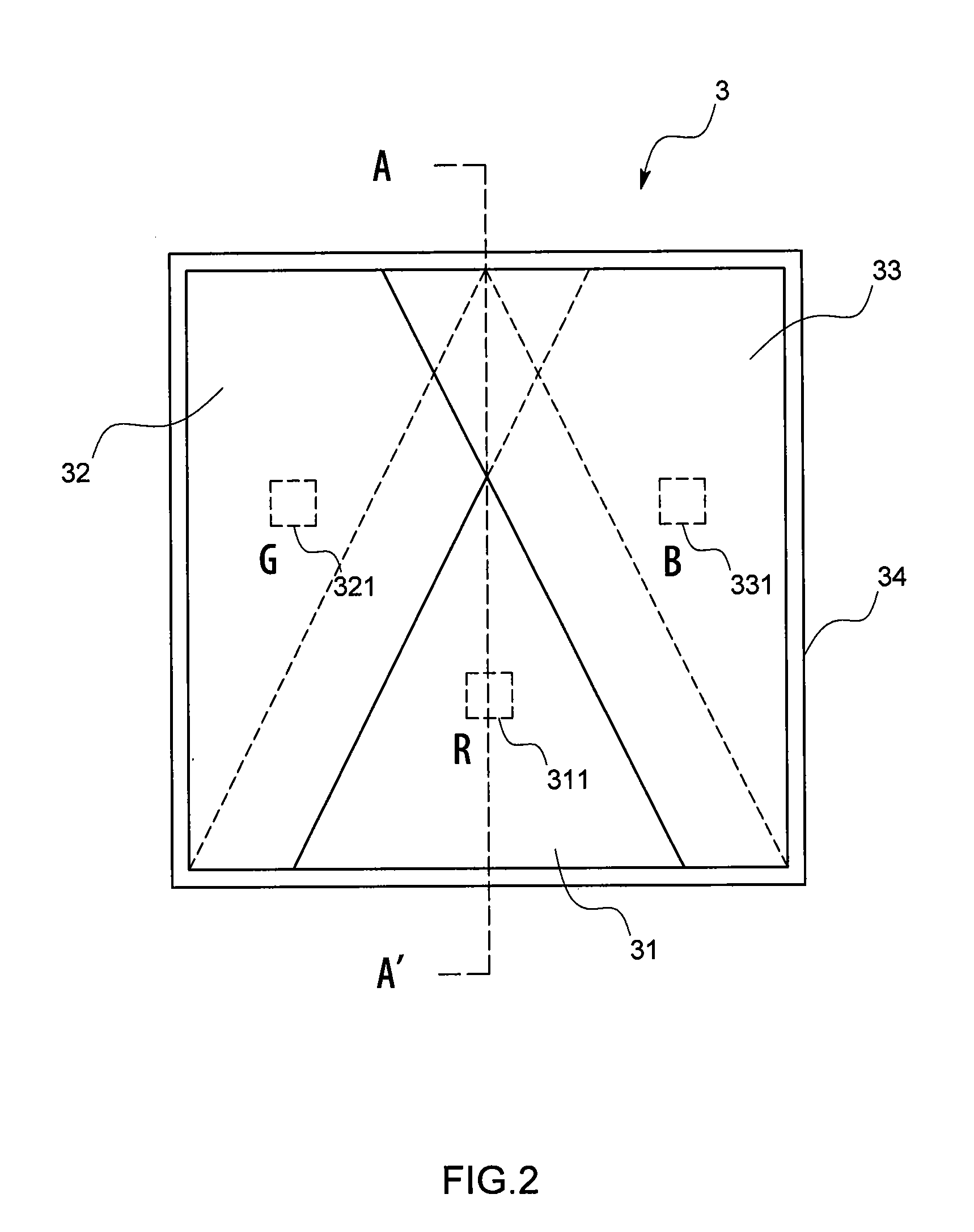
Optical information processing equipment and semiconductor light emitting device suitable therefor
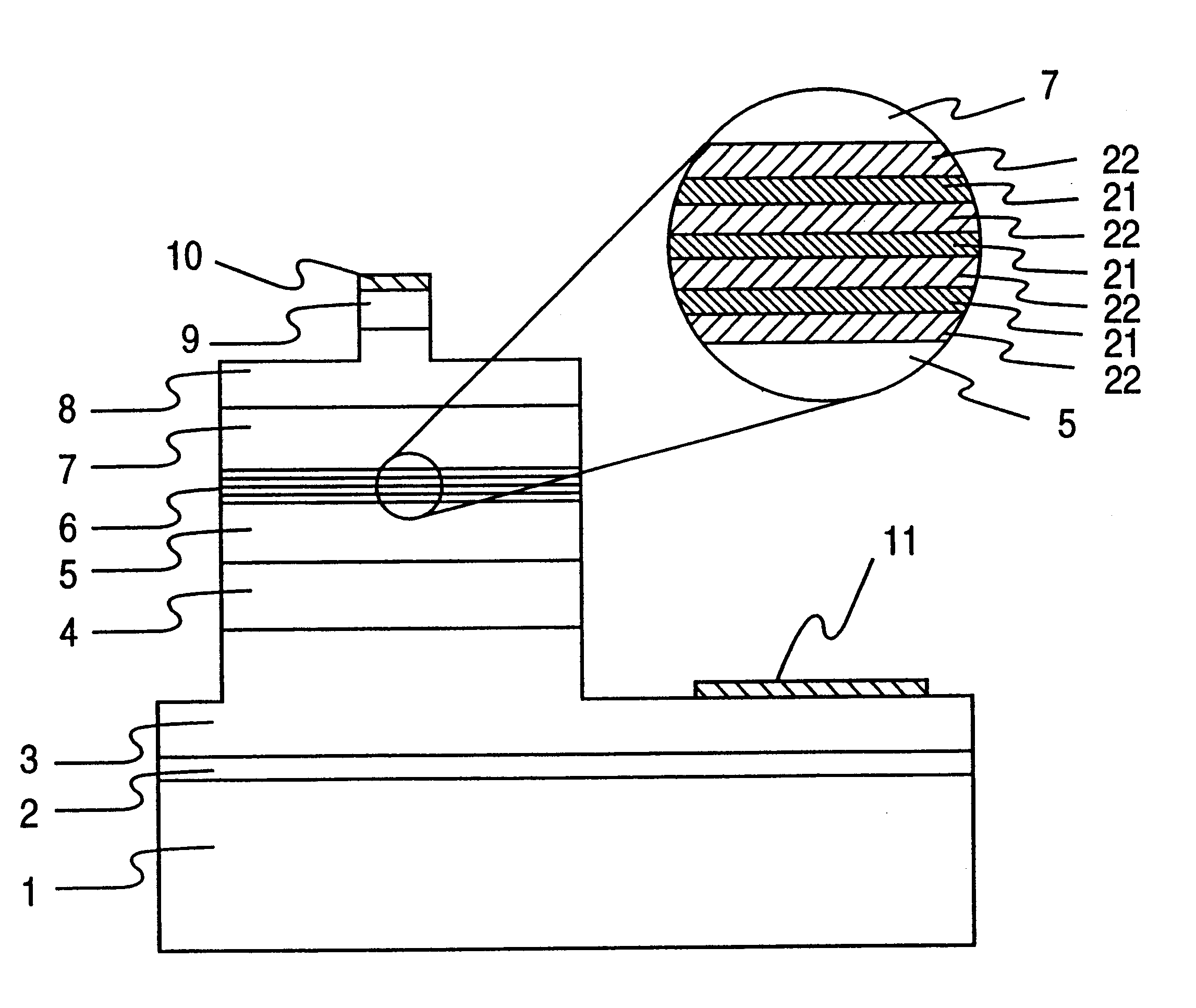
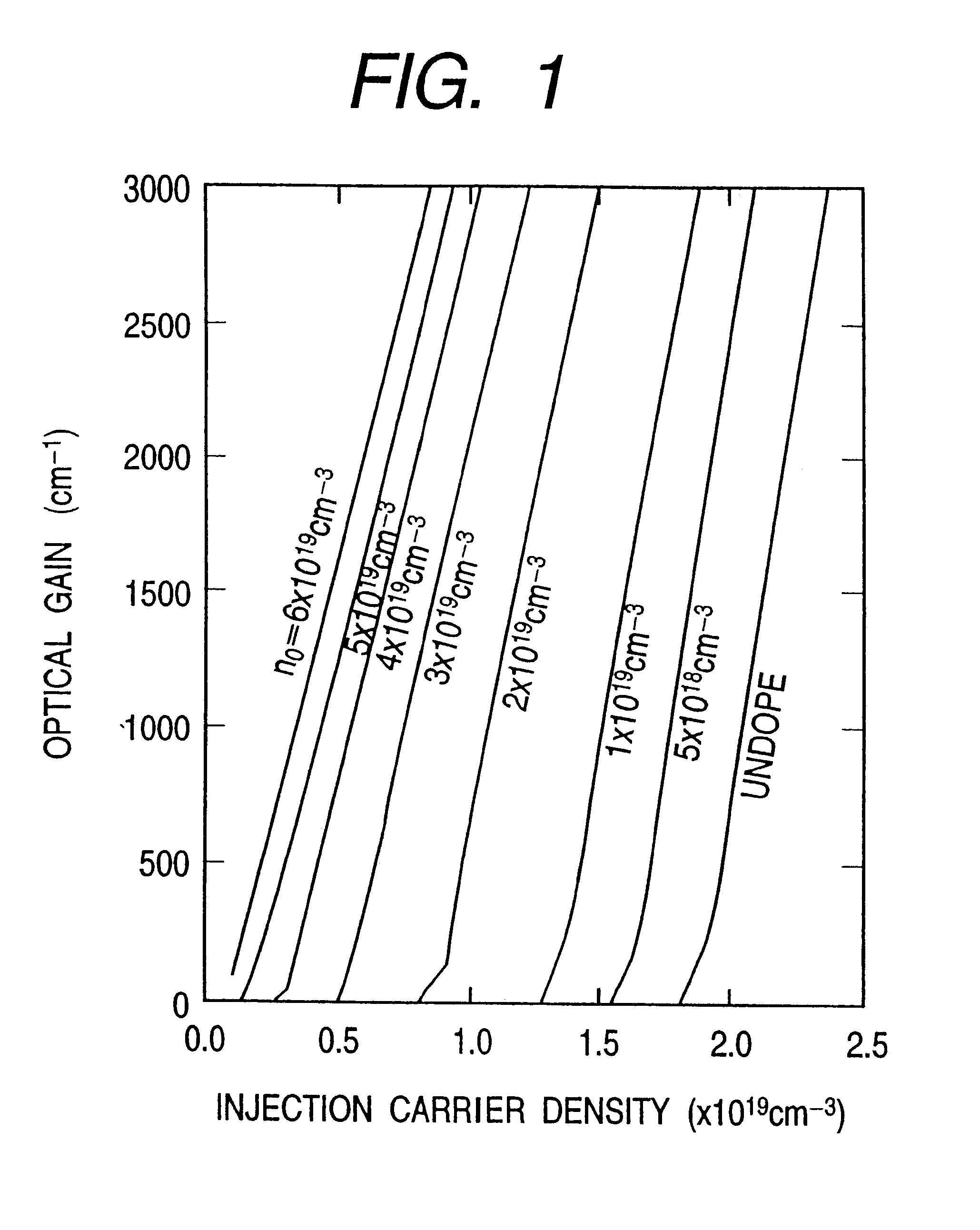
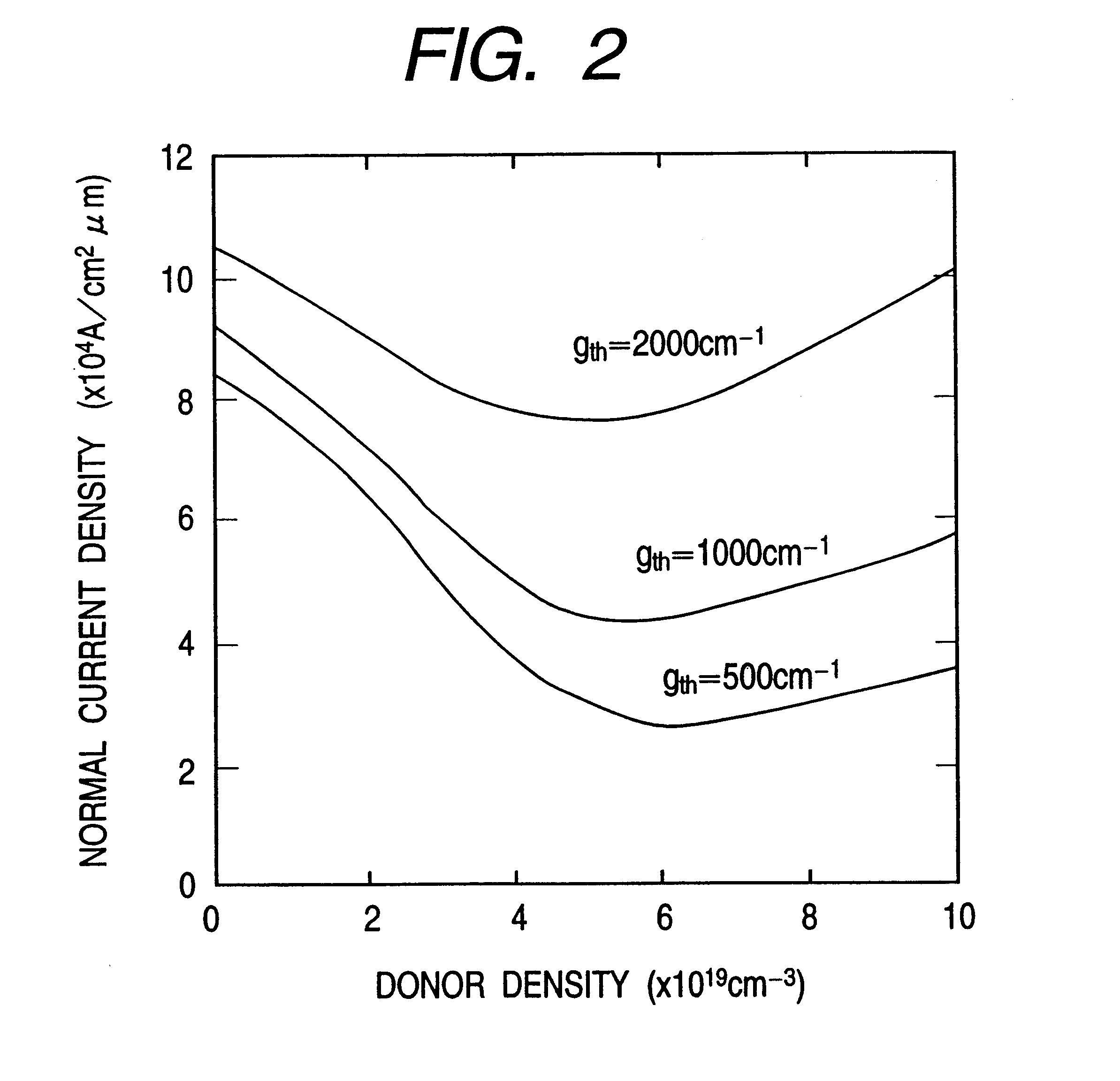
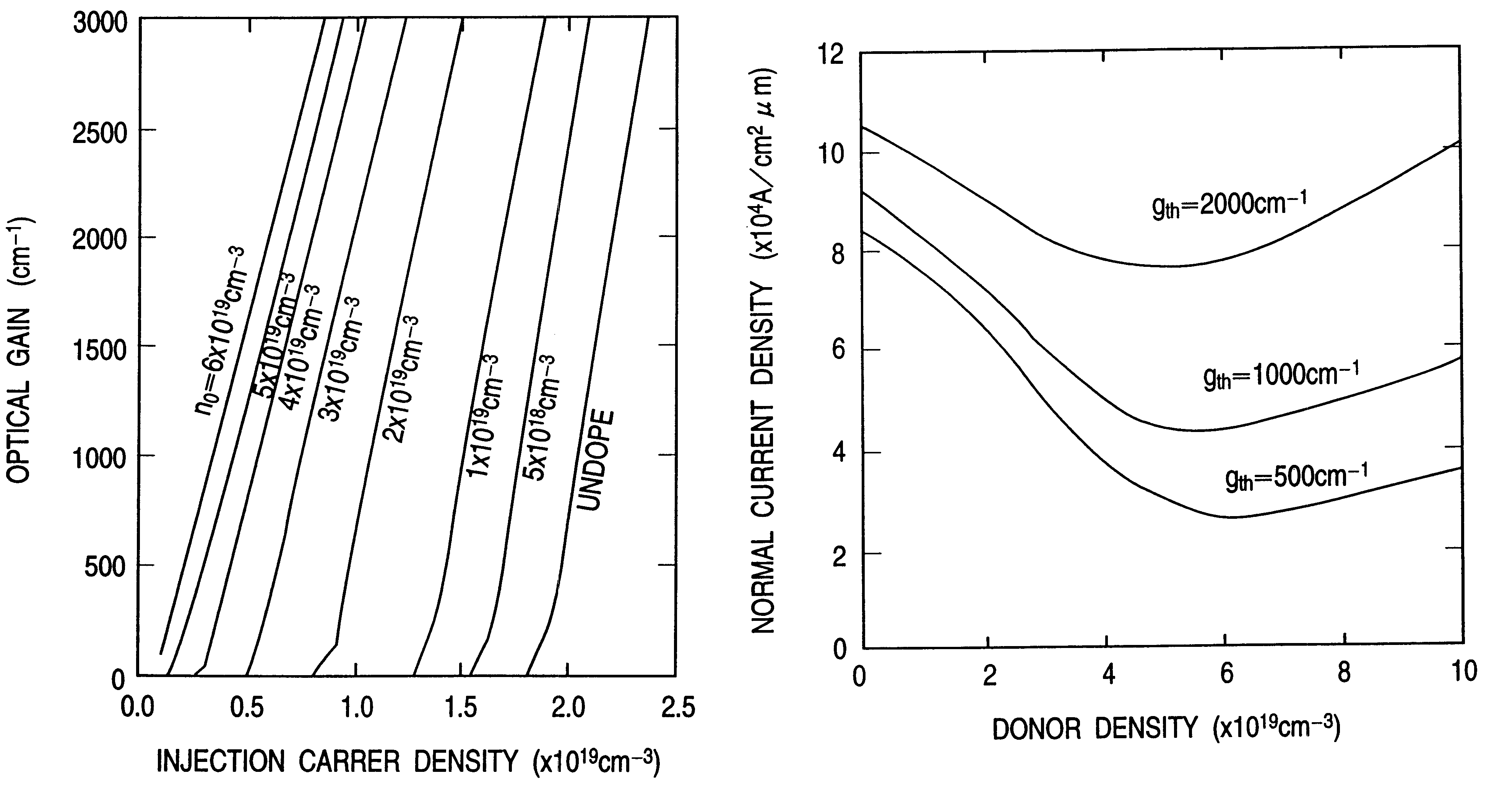
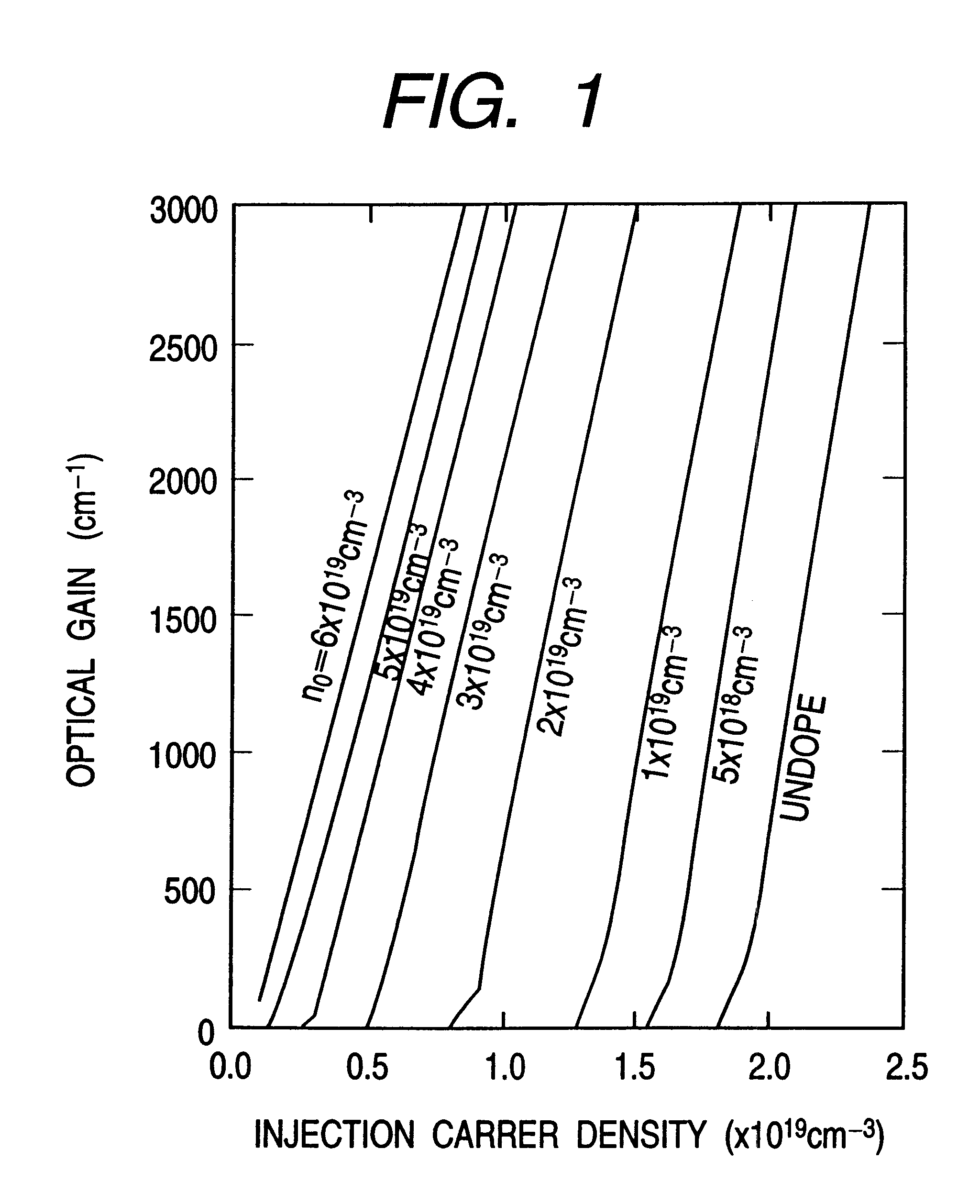
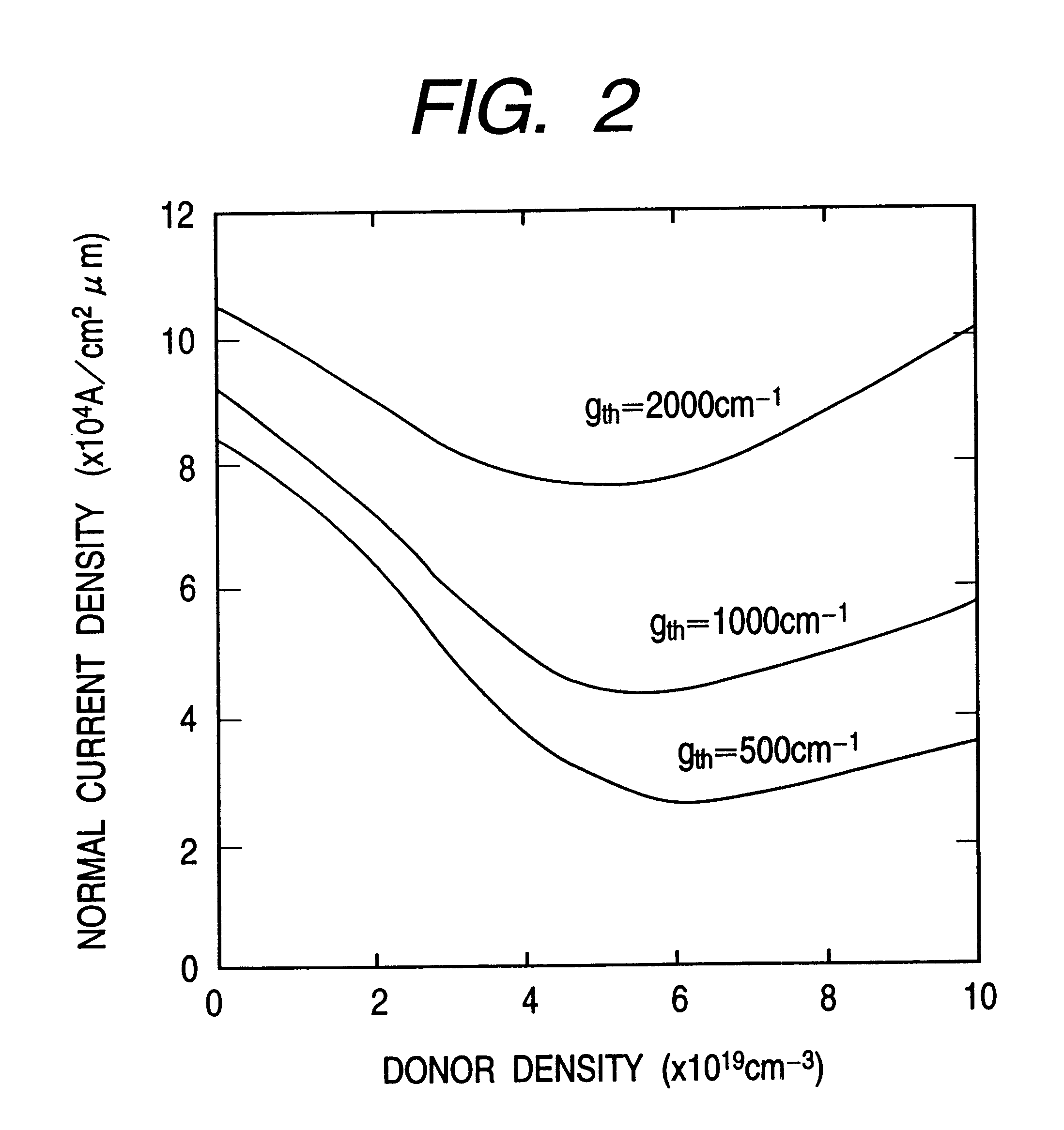
An information processor of a high reliability and a high recording density, and a blue color, blue-violet color and violet color based semiconductor light emitting device operable at a low threshold current density, used for the same, are provided. An optical information processor of a high reliability and a high recording density enables a moving picture, such as a high-definition television picture, to be recorded and reproduced satisfactorily. A barrier layer in a quantum-well active layer of a semiconductor light emitting device is doped with n-type impurities at a high density. Alternatively, the face orientation of a quantum-well active layer of a semiconductor light emitting device is a plane inclined from the (0001) plane, whereby the threshold current value of the semiconductor light emitting device can be decreased. The semiconductor light emitting device is typified by a gallium nitride based compound semiconductor laser device.
Owner:USHIO OPTO SEMICON
Optical information processor and semiconductor light emitting device suitable for the same
InactiveUS6542526B1Negligible effectLaser detailsLaser active region structureHigh definition tvRecording density
Provided are highly reliable information processing equipment enabling a high recording density, and a blue color, blue-violet color and violet color based semiconductor light emitting device operable at a low threshold current density, which device is suitable for the information processing equipment. According to the present invention, there can be realized highly reliable optical information processing equipment enabling high recording density, which is capable of sufficiently recording or reproducing a dynamic image in or from a high-definition TV.An n-type impurity is doped in a barrier layer of a quantum-well active layer of a semiconductor light emitting device at a high density. Alternatively, the oriented plane of a quantum-well active layer of a semiconductor light emitting device is inclined from the (0001) plane, whereby the threshold current value of the semiconductor light emitting device can be reduced. The semiconductor light emitting device is represented by a gallium nitride based compound semiconductor laser device.
Owner:USHIO OPTO SEMICON
Optical devices having reflection mode wavelength material
InactiveUS8575642B1Easy to implementImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhosphorUltraviolet
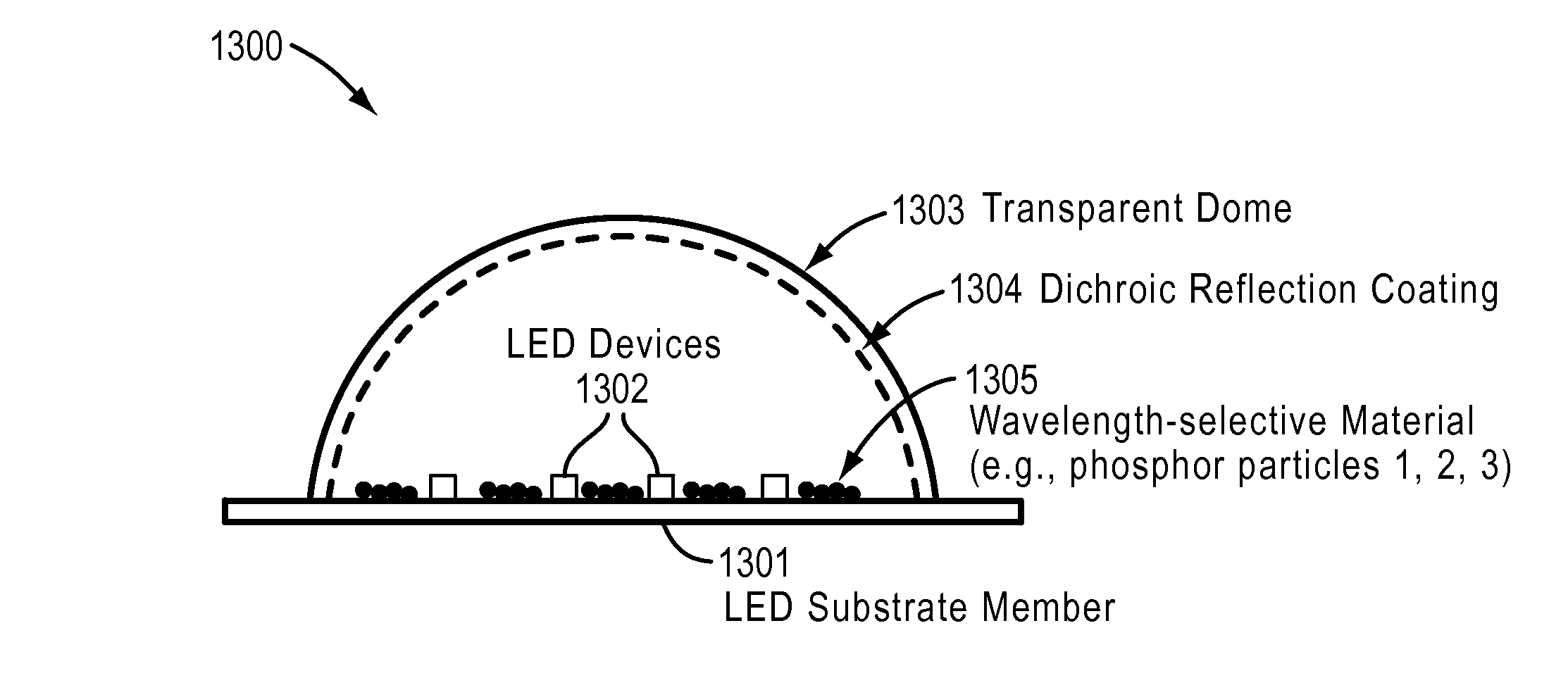
Techniques are disclosed for transmitting electromagnetic radiation such as ultra-violet, violet, blue, blue and yellow, and / or blue and green electromagnetic radiation, from LED devices fabricated on bulk semipolar or nonpolar materials and using phosphors. The substrate may include polar gallium nitride.
Owner:KORRUS INC
Test media and quantiative or qualitative method for identification and differentiation of biological materials in a test sample
InactiveUS20050196825A1Reduces effective shelf lifeDifficult to controlMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPink colorEscherichia coli
A test medium and method for detecting, quantifying, identifying and differentiating up to four (4) separate biological materials in a test sample. A test medium is disclosed which allows quantifying and differentiating under ambient light aggregates of biological entities producing specific enzymes, which might include general coliforms, E. coli, Aeromonas, and Salmonella in a single test medium. A new class of nonchromogenic substrates is disclosed which produce a substantially black, non-diffusible precipitate. This precipitate is not subject to interference from other chromogenic substrates present in the test medium. In one embodiment, the substrates are selected such that E. coli colonies present in the test medium show as substantially black, general coliforms colonies show in the test medium as a blue-violet color, Aeromonas colonies present in the test medium show as a generally red-pink color, and Salmonella colonies show as a generally teal-green color. Other microorganisms and color possibilities for detection and quantification thereof are also disclosed. An inhibitor and method for making a test medium incorporating the inhibitor are disclosed.
Owner:MICROLOGY INC
LED light emitting device
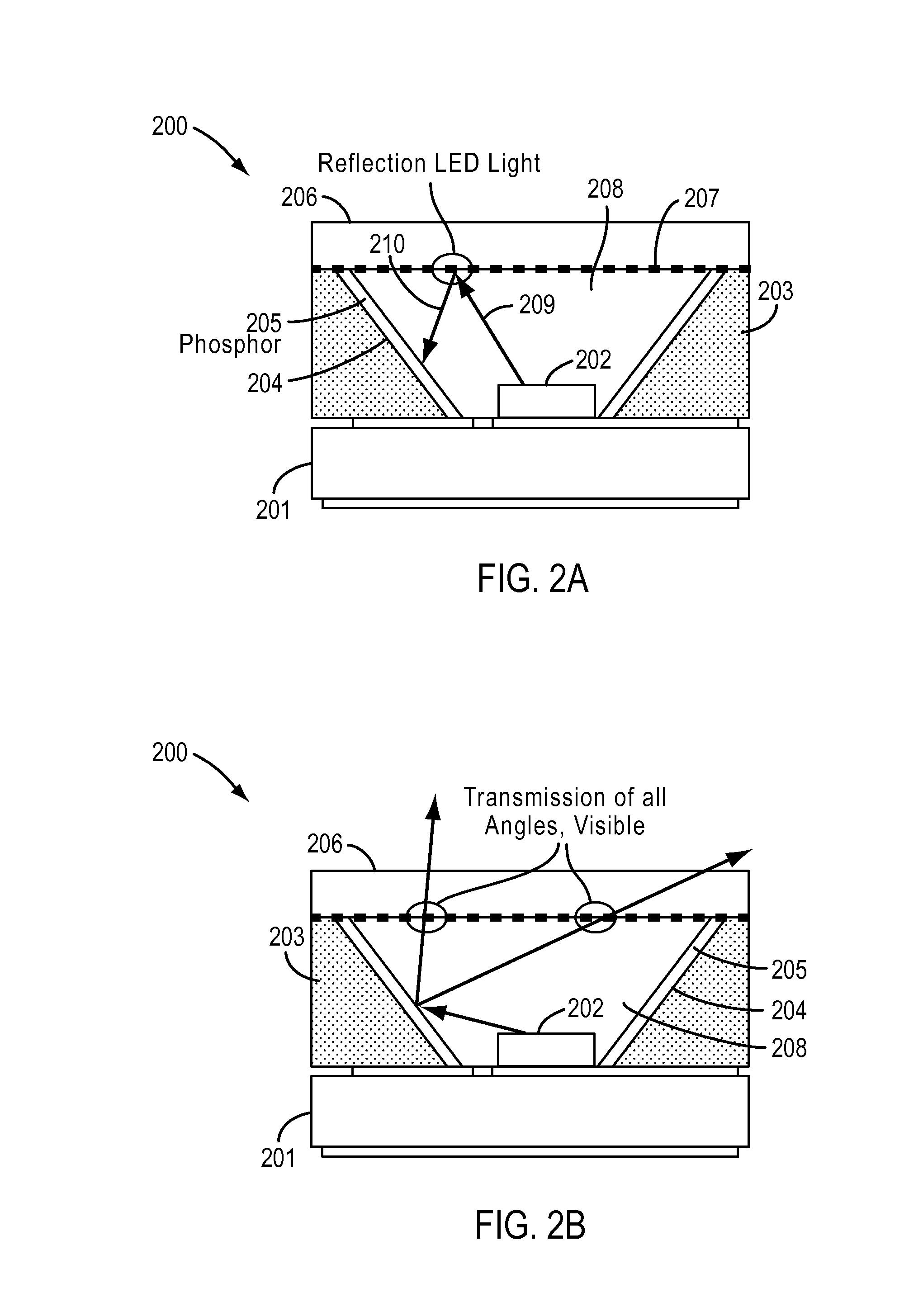
InactiveUS20110278606A1Good color controlConvenient lightingElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesPhosphorUltraviolet
In order to provide an LED light emitting device that can easily control a color temperature of white light, the LED light emitting device is provided with a plurality of types of light emitting parts that: respectively have LED elements that emit ultraviolet radiation or violet color visible light, and phosphors that absorb the ultraviolet radiation or violet color visible light to emit colored light; and emit the colored light, wherein: the colored light emitted by the plurality of types of light emitting parts become white light when all mixed with each other; the LED elements of the plurality of types of light emitting parts are all the same ones, and mounted on a single base material; and two or more light emitting parts overlap with each other in their parts.
Owner:CCS INC
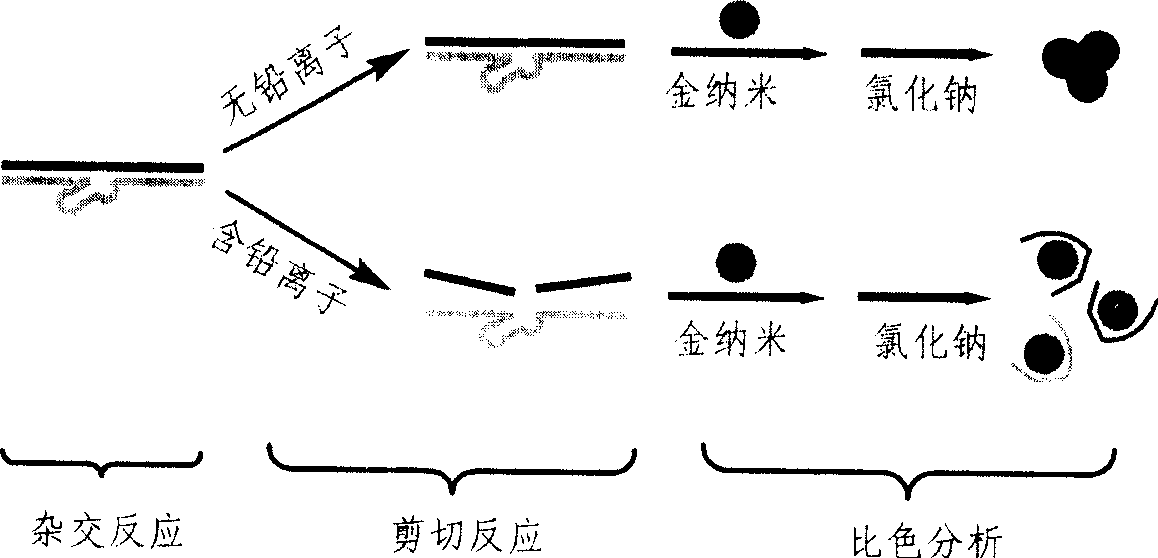
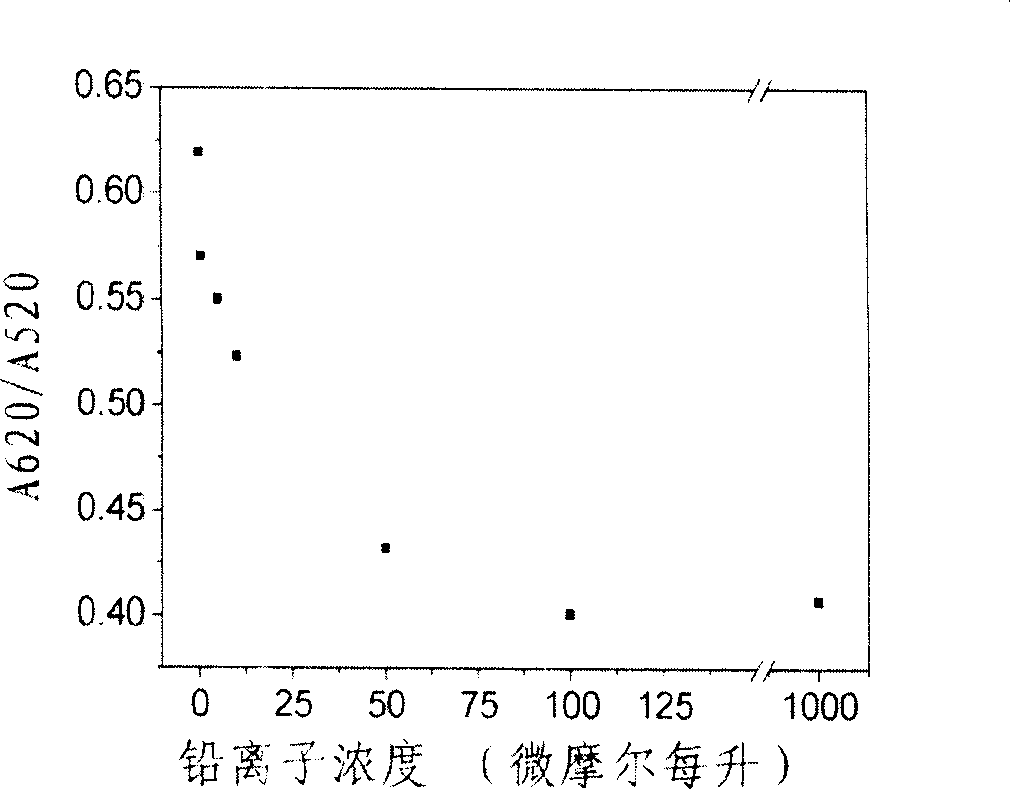
Unmarked colorimetric determination metallic lead ion method based on aurum nanometer probe and nuclease
InactiveCN101363795ASimple and sensitive colorimetric detectionEasy colorimetric detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsColor changesNuclease
The invention relates to a method for measuring metallic lead ion based on a nano-gold probe and markless color comparison of nuclease. 17E type nuclease forms a double chain structure with the substrate through hybridization. If the specimen to be tested contains lead ion, the lead ion can greatly increase the speed of catalyzing and transecting the substrate by the 17E type nuclease, after the transaction of the substrate, the double chain structure is dissociated to generate free single-chain DNA which can be adsorbed on the surface of the nano-gold probe, in order to protect the nano-gold probe from being inducted by salt and aggregated, therefore, the nano-gold probe solution is in claret red color; if the specimen to be tested does not contain lead ion, the double chain structure of the 17E type nuclease and the substrate thereof can not be damaged, reaction can not happen between the double chain structure and the nano-gold probe, therefore, the nano-gold probe can be inducted by salt and aggregated and in bluish violet color. Through the color change of the nano-gold probe, the detection of the lead ion can be realized. The detection limit to the lead ion is 500 nanomole per liter. By using the method to detect the lead ion, the selectivity is high, the sensitivity is high, the operation is simple, and complex instruments are not needed.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
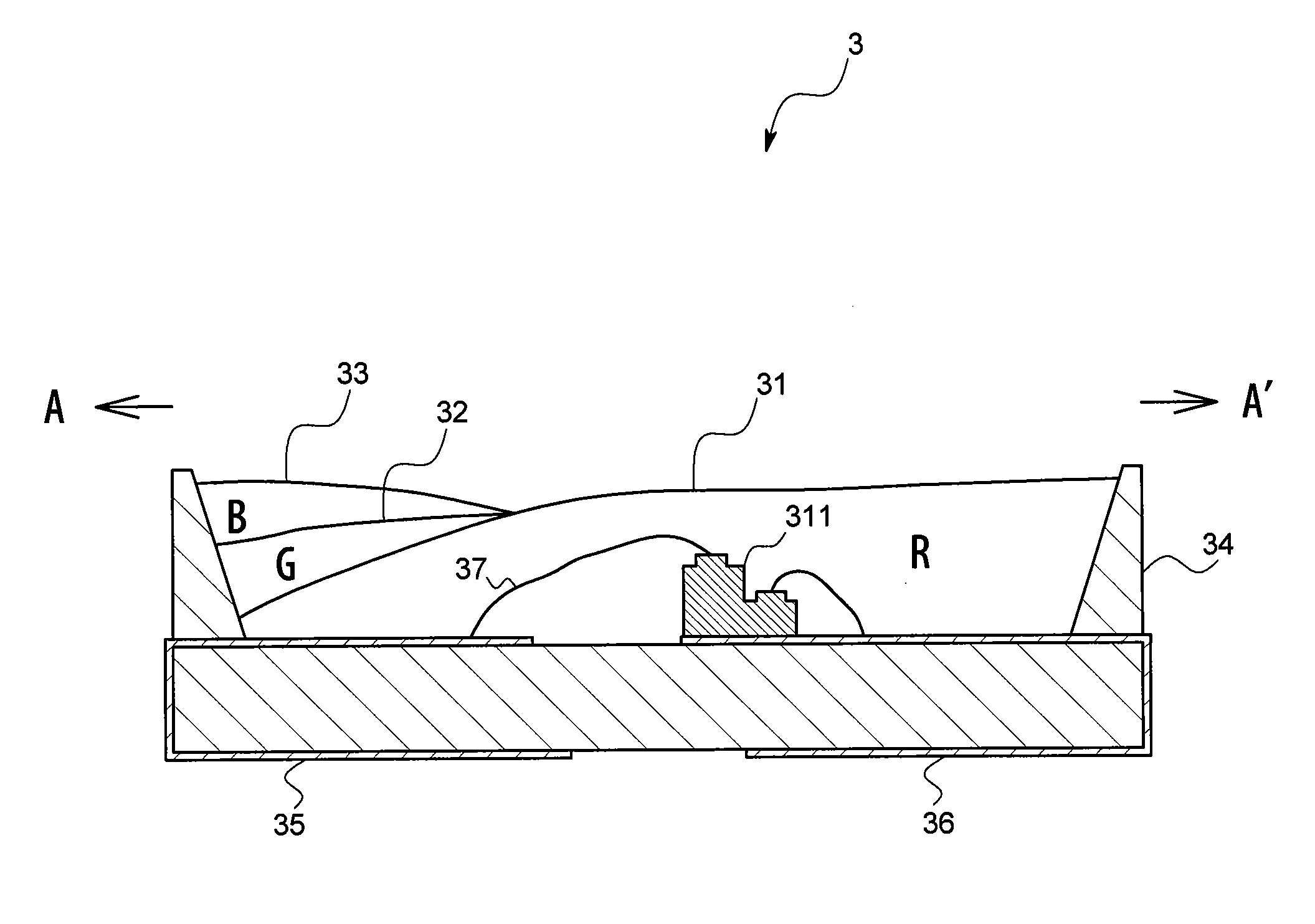
LED light-emitting device
InactiveCN102308398AEasy to identifyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesPhosphorColored light
Owner:CCS INC
Method for producing blueberry jam by using blueberry fermentation by-product
ActiveCN103355574AThe taste is moderately sweet and sourKeep the original tasteFood preparationAdditive ingredientBeta-Cyclodextrins
The invention discloses a method for producing a blueberry jam by using a blueberry fermentation by-product. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing the fermentation by-product obtained in a blueberry fermentation wine-making process, water, sugar, a thickener, and citric acid or a citrate, and concentrating to obtain the blueberry jam. The thickener consists of xanthan gum, sodium alginate, pectin and beta-cyclodextrin. By fully using the blueberry fermentation by-product, the method for producing blueberry jam by using the blueberry fermentation by-product is developed. The method is simple, low in cost, none in pollution and easy to popularize. The prepared blueberry jam has the bluish violet color of the blueberry fruit in sense, a moderate sour-sweet taste, pure fruity flavor of the blueberry, and no fermentation residual odour; and not only the original taste and flavor of the blueberry are reserved, but also the beneficial components in the blueberry are furthest reserved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
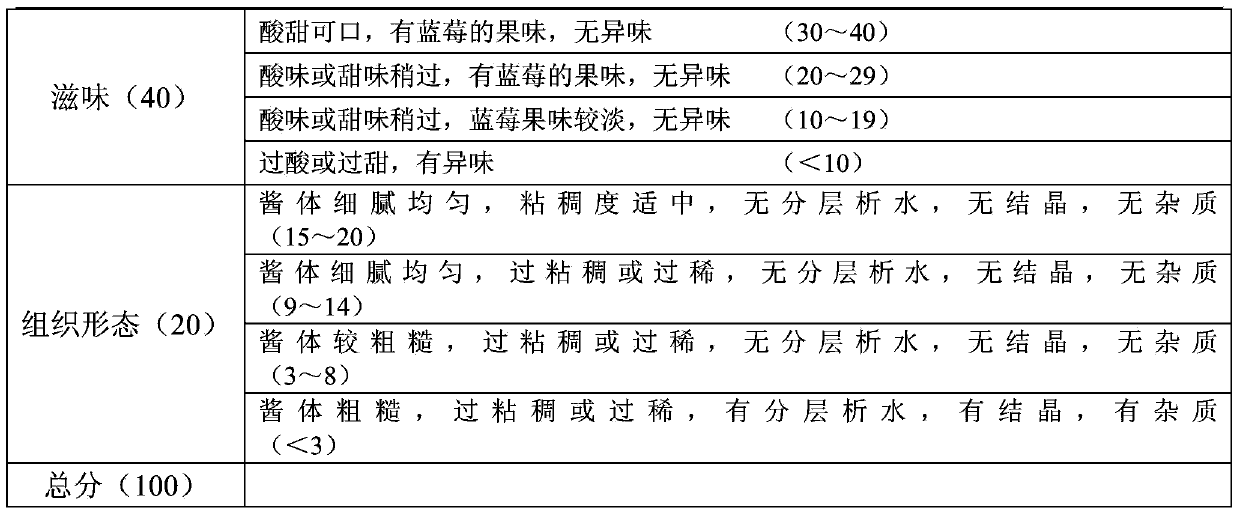
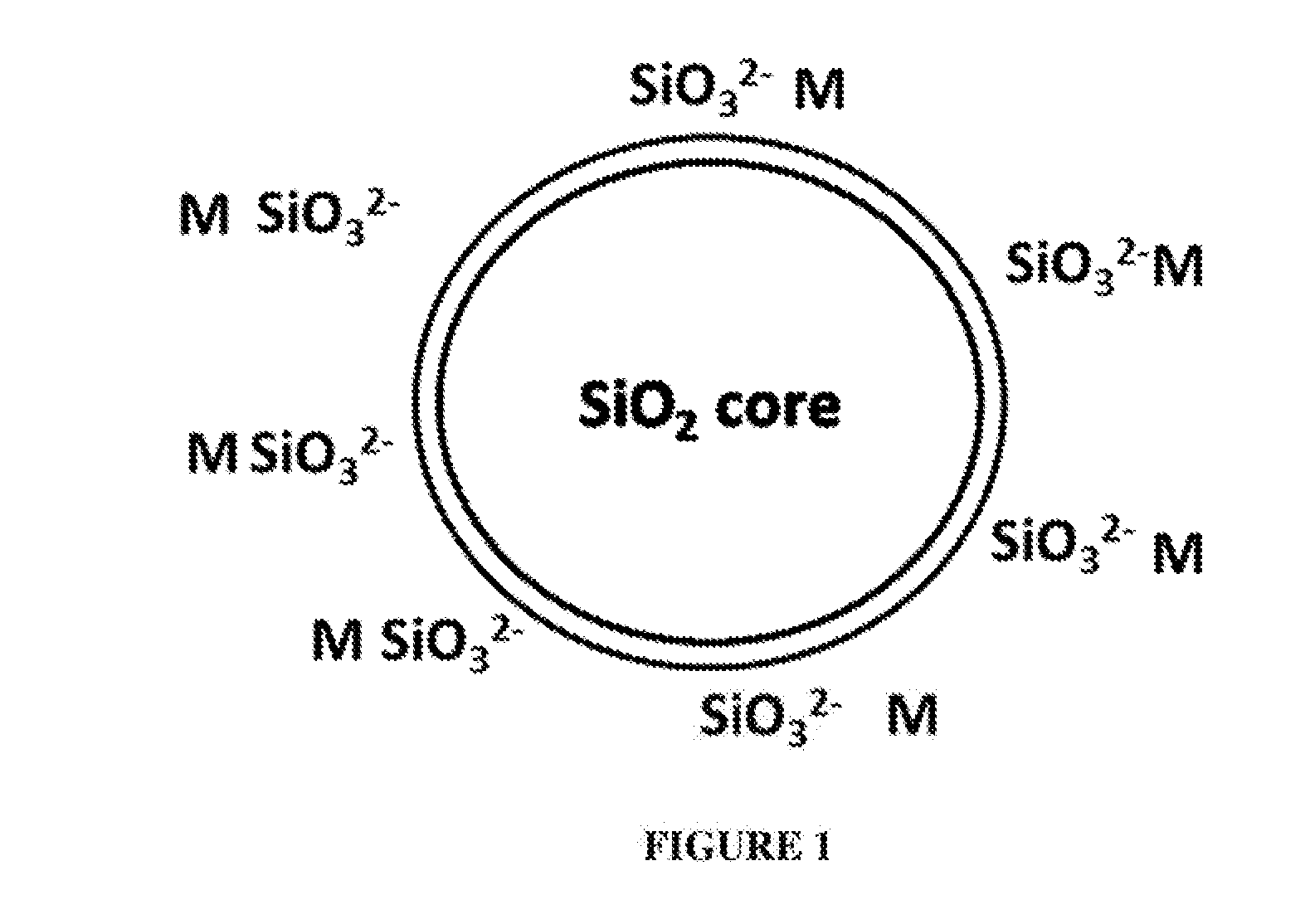
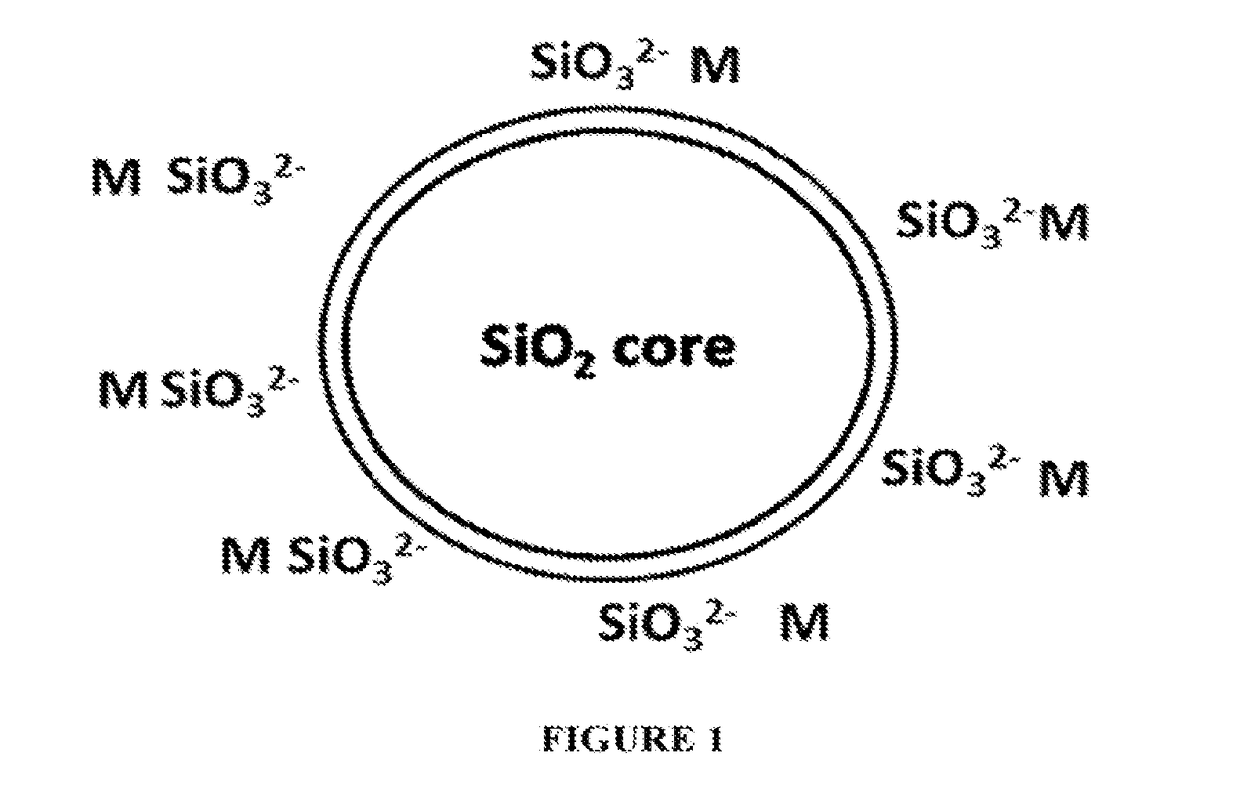
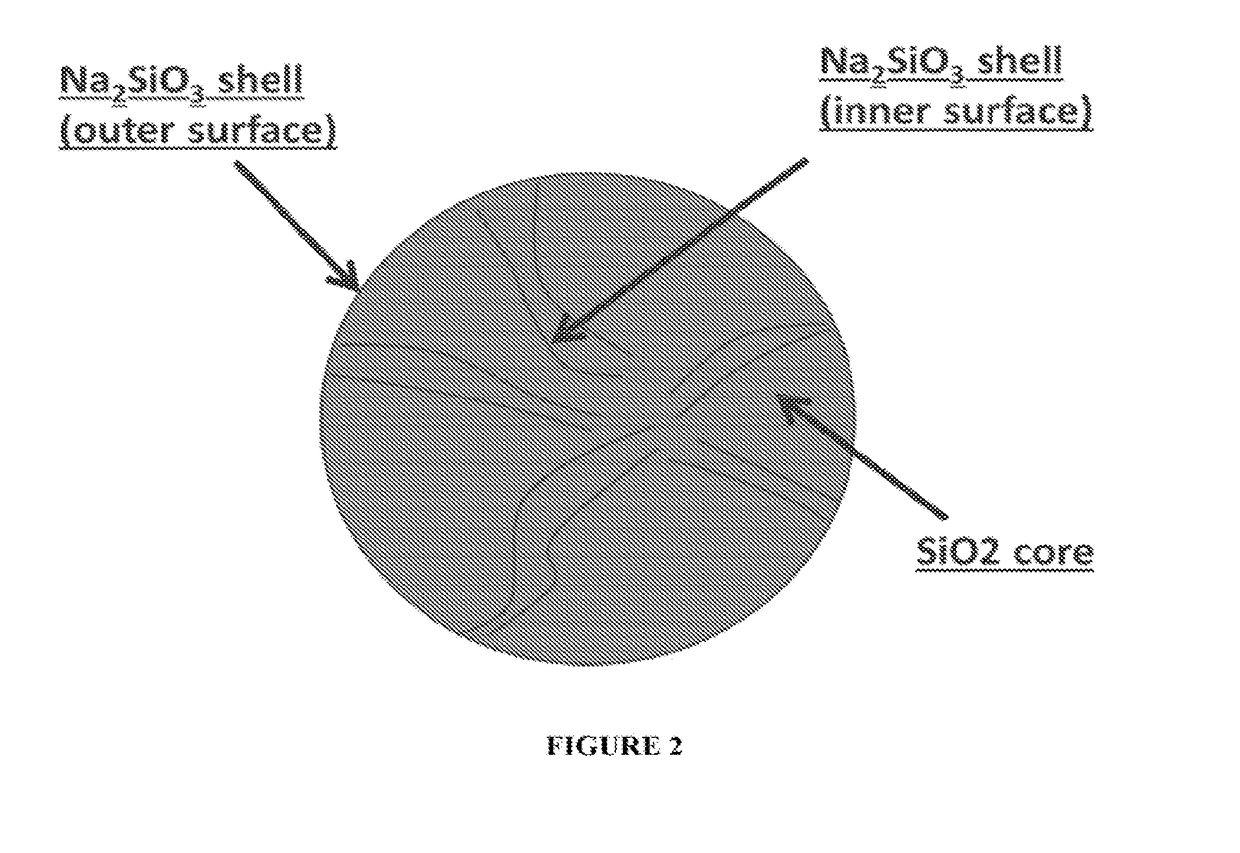
Tooth whitening oral care product with core shell silica particles
The present invention provides a tooth whitening oral care composition comprising: (i) a dye having a blue to blue-violet color with a hue angle in the CIELAB system ranging from 200 to 320 degrees; (ii) core shell silica particles, wherein each core shell silica particle comprises a silica core, and a surface of the silica core is etched with metal silicate; (iii) an orally acceptable carrier vehicle comprising a non-aqueous solvent; and wherein the composition comprises water in an amount of from 3 weight % to 30 weight %.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Composition and method for detecting and early and differentiated counting of gram-negative microorganisms
InactiveUS20030044882A1High diagnostic specificityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCitrobacter
The present invention is related with the Microbiology field and particularly with a composition and a method for early detection, identification, differentiation and count of microscopic organisms, concretely Gram-negative microorganisms. The composition described in the invention consist on a mixture of substances of protein origin with a total nitrogen content from 9 to 20% and in relationship between 2:1 to 24:1, concerning to the content of inhibitors of the Gram-positive organisms. It contains a mixture of organic and inorganic substances that facilitate the differentiation of the Gram-negative organisms, being this mixture in a relationship from 0.5:1 to 2:1 concerning to the mixture of substances of protein origin. The referred composition allows the detection and differentiated count of E. coli and other coliform organisms due to the blue-greenish color of the colonies of these microorganisms on the orange bottom of the medium; Salmonella not typhi for the red color of the centers of the colonies on rosy bottom of the medium; Salmonella typhi and Proteus for the transparency of the colonies; Citrobacter and Klebsiella for the violet color of the colonies on the pink to orange bottom of the medium and Pseudomonas aeruginosa for the orange color with darker center of the colony, taking greenish pigmentation after 24 hours and producing greenish fluorescence under low ultraviolet light.
Owner:CENT NACIONAL BIOPREPARADOS
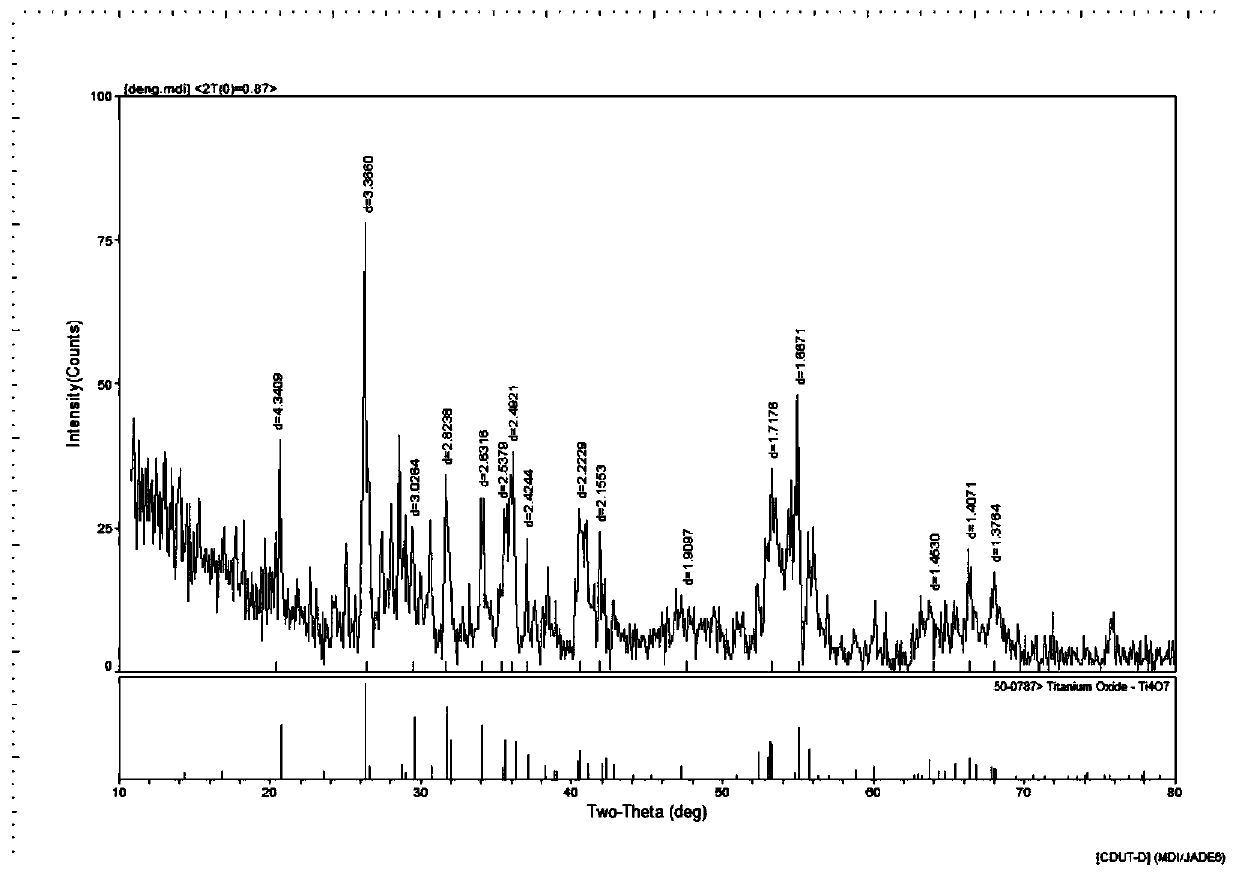
Method for preparing titanium oxide through reducing titanium-containing complexes at normal temperature
ActiveCN109879311ALow costMass productionTitanium oxides/hydroxidesTitanium oxideTitanium tetrachloride
The invention discloses a method for preparing titanium oxide through reducing titanium-containing complexes at normal temperature. The method is characterized in that reduction reaction occurs in a normal temperature liquid phase; the potential safety hazards due to mixing of reducing agents and air are eliminated; the reduction is performed in the liquid phase, the microscopic uniformity is high; the firing temperature is low; the time is short. The method has the following principle and steps that titanium sulfate or titanium tetrachloride and ammonium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide take a reaction to obtain titanic acid; the titanic acid reacts with oxalic acid or citric acid to form an oxalate oxytitanate complex-ion or oxytitanate citrate complex-ion solution; next, reaction is performed with zinc powder; the complex ions are reduced into low-valent titanium complex ions; the pH value of the solution is regulated to 12 by ammonium hydroxide; precipitates of dark brown color to dark violet color are generated; washing is performed for 3 to 5 times by 3 to 5 times of deionized water; the zin is washed away in an ion ZnO2<2-> form to obtain pure titanium hydroxide precipitates; oxalic acid is added until the pH is 0.5 to 1.5; drying is performed to 2 to 5 hours at 120 to 180 DEG C; the temperature is raised from room temperature to 820 to 950 DEG C by a muffle furnace; roasting is performed for 2 to 6 hours; titanium oxide spherical powder with the Ti4O7 content being 90 percent or higher is obtained.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Internal toning violet pigment color paste for printing and writing paper pulp with chemimechanical pulp and method for preparing violet pigment color paste
ActiveCN105672021AGood storage stabilityWon't happenPaper/cardboardColorants/pigments additionFiberPhospholipid
The invention discloses internal toning violet pigment color paste for printing and writing paper pulp with chemimechanical pulp.Color fiber problems are further worsened along with the progress of pulping technologies due to the fact that widely utilized color lake water-based pigment color paste is applied to chemimechanical pulp at present.The internal toning violet pigment color paste for the printing and writing paper pulp comprises, by weight, 20.0-22.0% of lightfast violet color lake, 8.0-10.0% of dispersing wetting agents, 2.0-3.0% of dyeing auxiliary, 10.0-15.0% of functional additives and the balance deionized water.The dyeing auxiliary is modified phospholipid with certain hydrophilicity.The internal toning violet pigment color paste has the advantages that uneven dyeing due to uneven combination speeds can be inhibited by the special dyeing auxiliary, and the color fiber problems can be thoroughly solved in procedures for manufacturing printing and writing paper with the chemimechanical pulp.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TRANSFAR WHYYON CHEM
Inorganic colour injet inks
A colour inkjet ink includes an inorganic colour pigment having a colour selected from the group consisting of cyan, magenta, yellow, blue, green, red, orange, violet, and brown; and at least 1 wt % of an inorganic colourless pigment based on the total weight of the colour inkjet ink, wherein the inorganic colourless pigment has a smaller average particle size than the inorganic colour pigment.
Owner:AGFA NV
Black pigment dispersion composition and black pigment dispersion resist composition containing the same
ActiveCN109725489AGood dispersionImprove shadingPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusPigment pastesResistTransmittance
The invention provides a black pigment dispersion composition with excellent dispersion performance, high surface resistance, high infrared transmittance and good shading performance, and a black pigment dispersion resist composition containing the same. Specifically, the black pigment dispersion composition contains a pigment A containing a to d: a. Lactam black; b. Purple pigment; c. Blue pigment and / or green pigment; and d. Carbon black.
Owner:SAKATA INX
Periodic lighting device
InactiveUS8594959B2Prevent penetrationSimplify disassemblyAnimal huntingBaitOptical radiationRadiation pulse
There is presented a detailed electronic method for simulation of a firefly, other insects, or organisms producing bioluminescence and with light radiation functions similar to a real firefly, other insects, or organisms producing bioluminescence. An illuminated artificial firefly, other insects, or organisms producing bioluminescence can be placed on trees and shrubs in landscape, or at home to produce radiation, at night time, and blinking a gradually decaying light. More particularly it relates to a decorative type of device in the form of a firefly, other insects, or organisms producing bioluminescence and with light radiation functions similar to a real firefly, other insects, or organisms producing bioluminescence. The light is simulated by an electronics program that is a part of compact device with the form of a real firefly, other insects, or organisms producing bioluminescence. Short radiation pulses of microsecond-millisecond duration time in violet and ultraviolet range of radiation wavelengths can be utilized for scaring birds or other animals from undesirable or dangerous places of human activity, such as airports, contaminated ponds, wind turbines, electorized fences and antennas.
Owner:SCHAAL HERBERT RUDOLF +1
Method for producing blueberry jam by using blueberry fermentation by-product
ActiveCN103355574BThe taste is moderately sweet and sourKeep the original tasteFood preparationAdditive ingredientBeta-Cyclodextrins
The invention discloses a method for producing a blueberry jam by using a blueberry fermentation by-product. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing the fermentation by-product obtained in a blueberry fermentation wine-making process, water, sugar, a thickener, and citric acid or a citrate, and concentrating to obtain the blueberry jam. The thickener consists of xanthan gum, sodium alginate, pectin and beta-cyclodextrin. By fully using the blueberry fermentation by-product, the method for producing blueberry jam by using the blueberry fermentation by-product is developed. The method is simple, low in cost, none in pollution and easy to popularize. The prepared blueberry jam has the bluish violet color of the blueberry fruit in sense, a moderate sour-sweet taste, pure fruity flavor of the blueberry, and no fermentation residual odour; and not only the original taste and flavor of the blueberry are reserved, but also the beneficial components in the blueberry are furthest reserved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Nutritious cake
InactiveCN105454374ASimple preparation processLow costDough treatmentBakery productsCelluloseSmoked Plum
The invention discloses a nutritious cake comprising the following raw material according to weight by parts: 60 to 80 parts of low-gluten flour, 15 to 25 parts of cream, 50 to 70 parts of egg white, 10 to 30 parts of cake flour, 10 to 20 parts of corn powder, 10 to 20 parts of butter, 20 to 40 parts of milk, 5 to 7 parts of lotus, 15 to 25 parts of honey, 30 to 50 parts of granulated sugar, 15 to 25 parts of juice, 10 to 12 parts of bean flour, 20 to 40 parts of smoked plum, 5 to 7 parts of salt and 300 to 500 parts of water. The nutritious cake can be prepared by steps of grinding, mixing and baking. The nutritious cake has bright violet color, attractive color and rich nutrients; the nutritious cake does not have macromolecular structures such as cellulose, thereby facilitating digestion and absorption for a human body; and bioavailability can be improved.
Owner:张立涛
Dentifrice including zinc and blue dye or pigment
A whitening dentifrice composition includes a blue coloring agent, a zinc salt, and an orally acceptable vehicle. The blue coloring agent is selected from the group consisting of a blue pigment and ablue dye. The blue pigment has a blue to blue-violet color with a hue angle in the CIELAB system ranging from 200 degrees to 320 degrees. The whitening dentifrice composition provides a greater whitening benefit to a tooth surface in comparison to a dentifrice composition that does not contain the zinc salt.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Test media for quantitative or qualitative identification and differentiation of general coliforms, E coli, Aeromonas spp and Salmonella spp materials in a test sample
InactiveUS7273719B2Enables identificationEnables differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEscherichia coliPink color
A test medium and method for detecting, quantifying, identifying and differentiating up to four (4) separate biological materials in a test sample. A test medium is disclosed which allows quantifying and differentiating under ambient light aggregates of biological entities producing specific enzymes, which might include general coliforms, E. coli, Aeromonas, and Salmonella in a single test medium. A new class of nonchromogenic substrates is disclosed which produce a substantially black, non-diffusible precipitate. This precipitate is not subject to interference from other chromogenic substrates present in the test medium. In one embodiment, the substrates are selected such that E. coli colonies present in the test medium show as substantially black, general coliforms colonies show in the test medium as a blue-violet color, Aeromonas colonies present in the test medium show as a generally red-pink color, and Salmonella colonies show as a generally teal-green color. Other microorganisms and color possibilities for detection and quantification thereof are also disclosed. An inhibitor and method for making a test medium incorporating the inhibitor are disclosed.
Owner:MICROLOGY INC
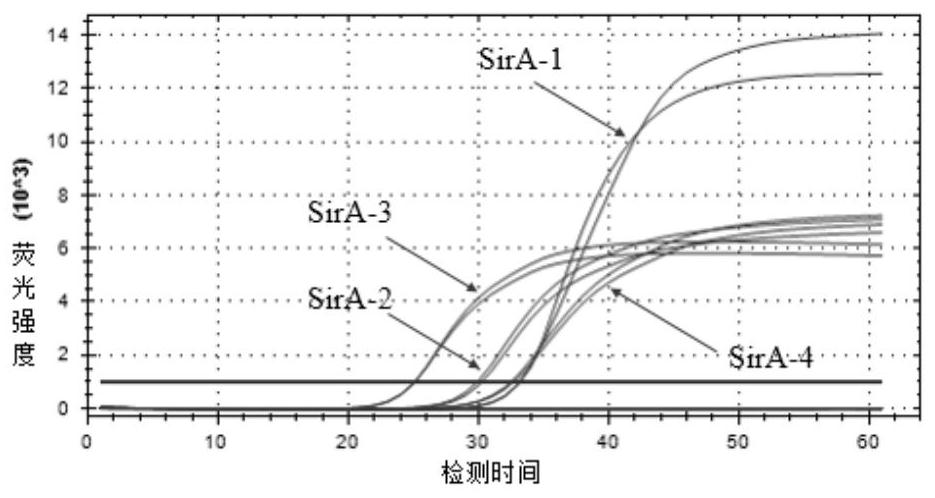
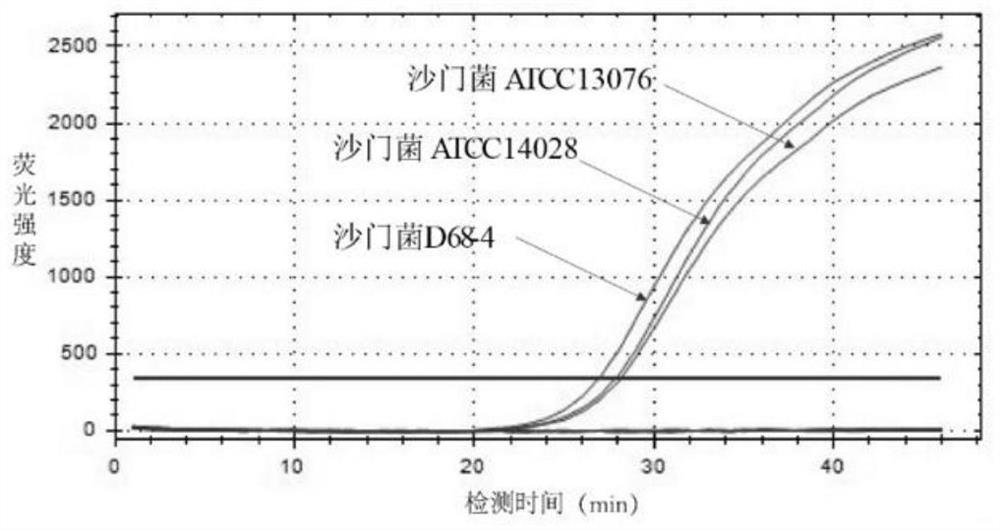
Primer group, detection method and kit for quickly detecting salmonella typhimurium by utilizing LAMP technology
ActiveCN112725480AStrong specificityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesVirulence gene expressionSalmonella diarizonae
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbiological detection, and particularly relates to a primer group, a detection method and a kit for quickly detecting salmonella typhimurium by utilizing an LAMP (Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification) technology. The salmonella virulence gene SirA (U88651.1) is selected as a main regulating gene for controlling the intestinal virogenic function of salmonella typhimurium and has the function of enhancing expression of hilA and prgH virulence genes in a salmonella pathogenic island, so that four specific primer groups capable of amplifying the gene at 62-68 DEG C are designed by selecting the salmonella virulence gene SirA as a specific target; the detection result is indicated through the HNB dye, violet (negative) is changed into sky blue (positive), and the method for detecting salmonella is good in specificity, easy to operate, free of expensive instruments and higher in sensitivity compared with conventional PCR.
Owner:武汉海关技术中心
Tooth whitening oral care product with core shell silica particles
The present invention provides a tooth whitening oral care composition comprising: (i) a dye having a blue to blue-violet color with a hue angle in the CIELAB system ranging from 200 to 320 degrees; (ii) core shell silica particles, wherein each core shell silica particle comprises a silica core, and a surface of the silica core is etched with metal silicate; (iii) an orally acceptable carrier vehicle comprising a non-aqueous solvent; and wherein the composition comprises water in an amount of from 3 weight % to 30 weight %.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Oral Care Compositions with Increased Whitening Efficacy
A dual-phase mouthwash composition for whitening teeth is disclosed. The dual-phase mouthwash composition includes an orally acceptable vehicle having a hydrophilic phase and a hydrophobic phase, a blue dye and / or blue pigment having a blue to blue-violet color with a hue angle in the CIELAB system from about 200 to about 320 degrees, and a zinc salt.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Kit and detection method for quickly detecting aluminium phosphide in edible mushroom and cereals
InactiveCN108827959ACreate pollutionEasy to commoditizeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSodium acetateBottle
The invention discloses a kit and a detection method for quickly detecting aluminium phosphide in edible mushroom and cereals. The kit comprises: a detection solution A bottle filled with a 0.2-4 mol / L sodium acetate-acetic acid buffer solution, a detection solution B bottle filled with a 0.2-5 g / L pyrocatechol violet liquid, a centrifugal tube, and a sample cup. The detection method includes thesteps of: extracting the aluminium phosphide with water to decompose the aluminium phosphide into hydrogen phosphide and Al(OH)3, wherein the Al(OH)3 can form a violet complex with the pyrocatechol violet when pH is 5.0, and according to different concentrations, the violet complex shows a red color, a purple color or a violet color in a solution; and determining whether the sample contains the aluminium phosphide or not by observing the color of the solution after the reaction. The kit for quickly detecting aluminium phosphide in edible mushroom and cereals employs low-cost and accessible consumable reagents, is free of environmental pollution, is easy and convenient to use, and has high sensitivity and intuitive results.
Owner:郑州华洲集团股份有限公司
Cordyceps sobolifera rice and preparation method thereof
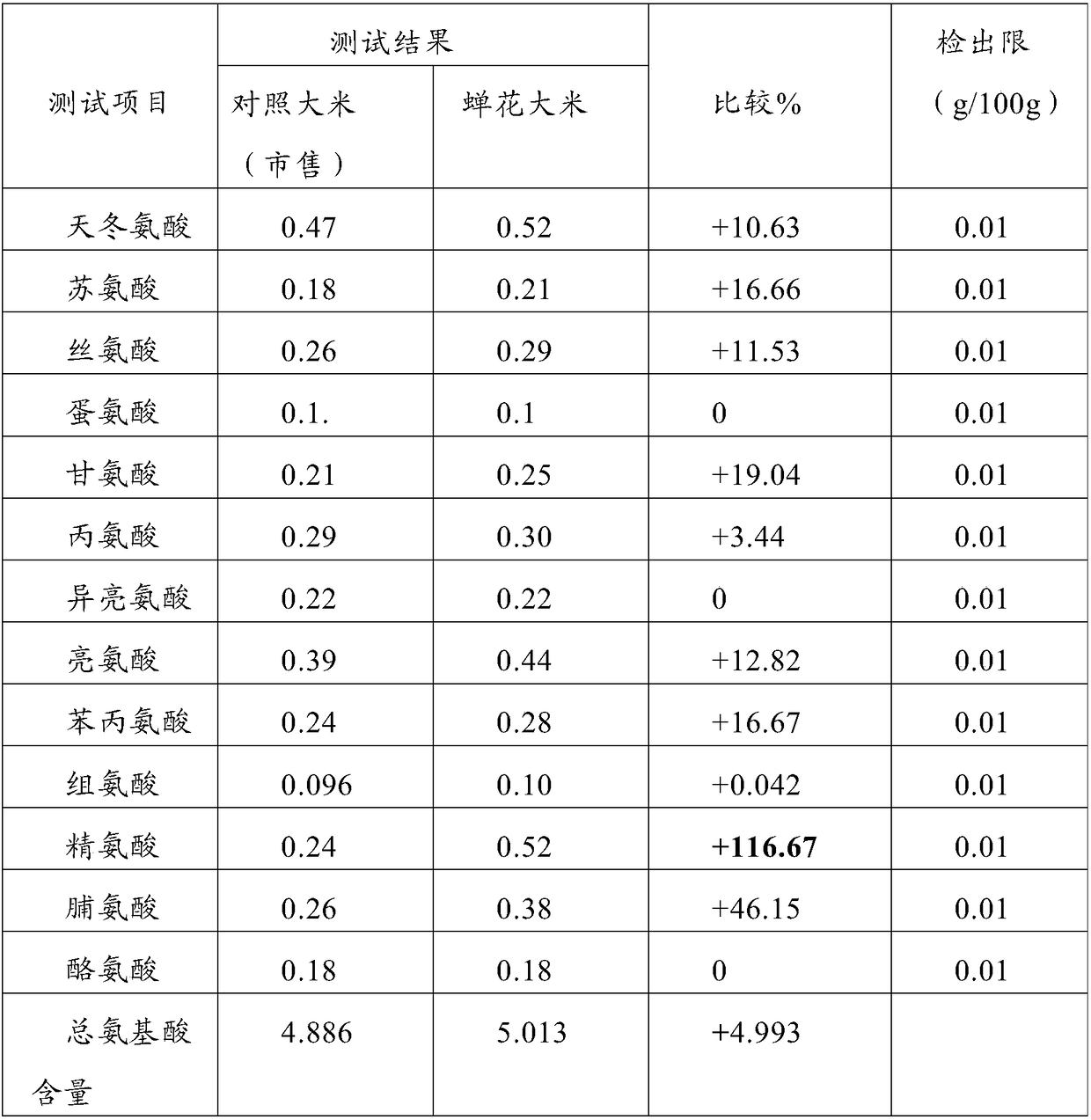
ActiveCN108371282AIncrease the content of amino acidsIncrease contentCultivating equipmentsFood ingredient functionsNutritive valuesPurplish red
The invention relates to cordyceps sobolifera rice and a preparation method thereof. The method includes inoculating liquid cultured cordyceps sobolifera strain liquid into a rice solid medium, and obtaining colorful cordyceps sobolifera rice through solid fermentation in a manner of dark culture. The prepared cordyceps sobolifera rice is in a red-violet color and has high nutritive value.
Owner:浙江泛亚保健食品有限公司
Test media for quantitative or qualitative identification and differentiation of general coliforms, E. coli, Aeromonas spp and Salmonella spp in a test sample
InactiveUS7344854B2Reduces effective shelf lifeDifficult to controlMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPink colorEscherichia coli
Owner:MICROLOGY INC
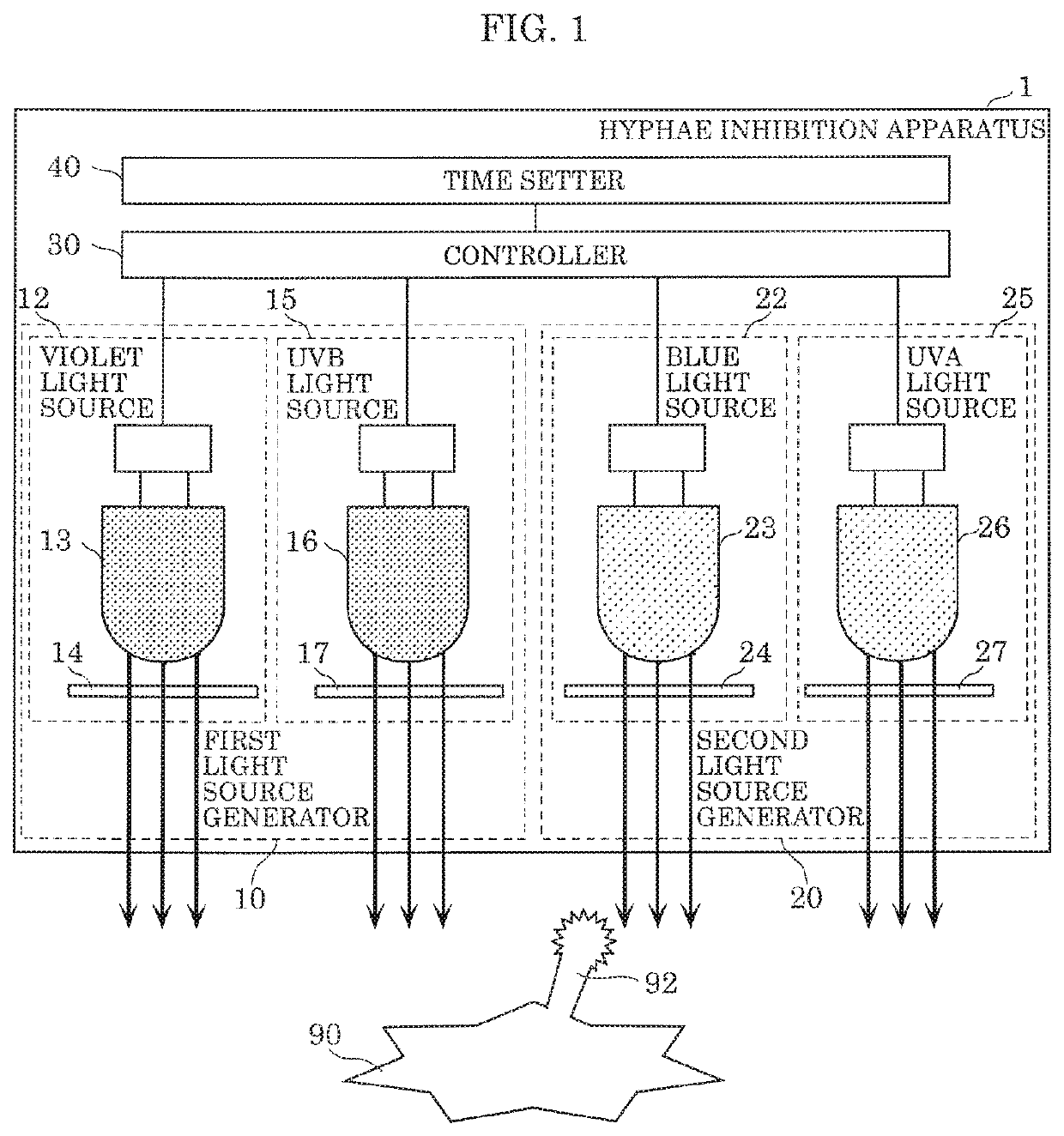
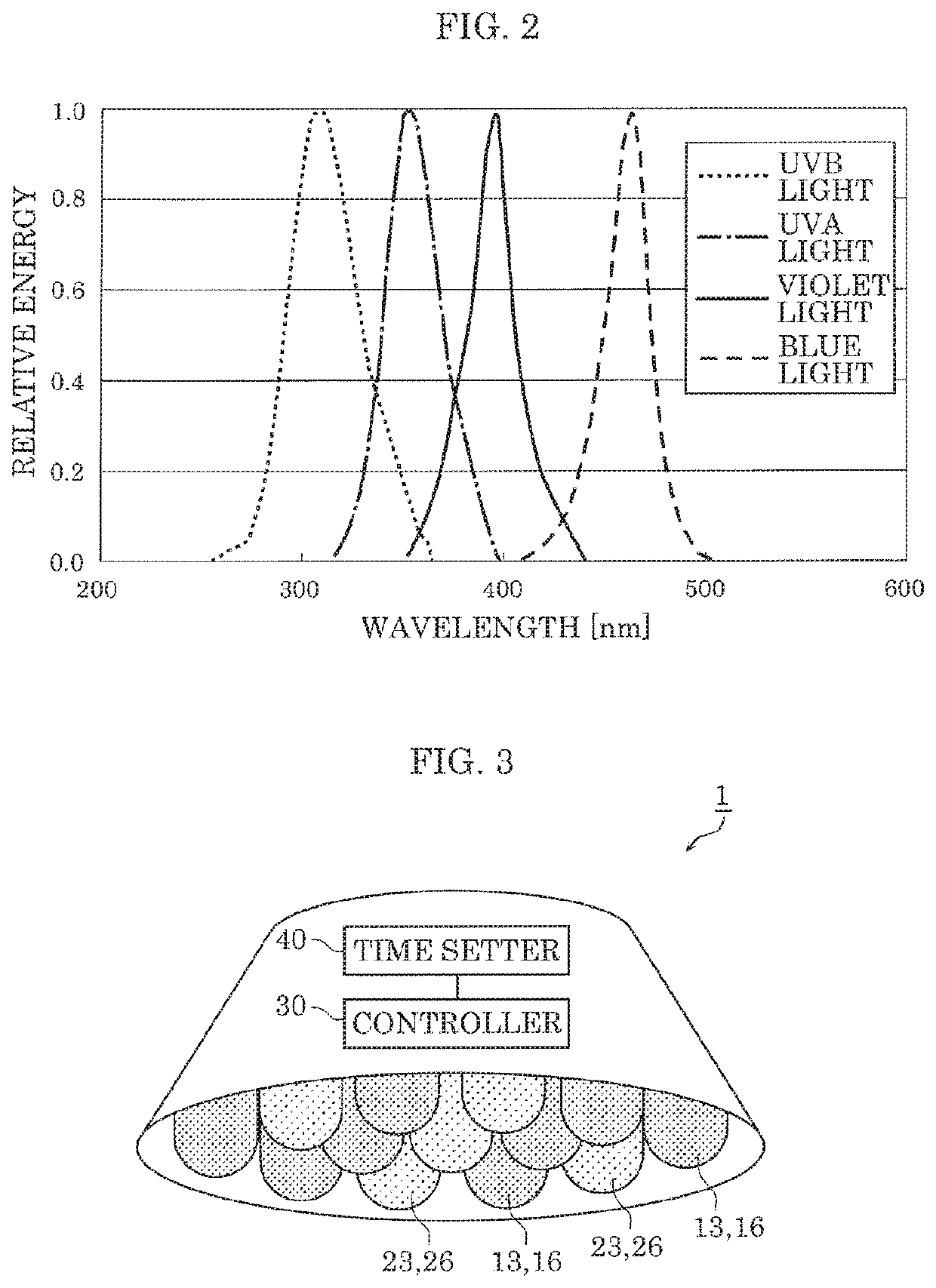
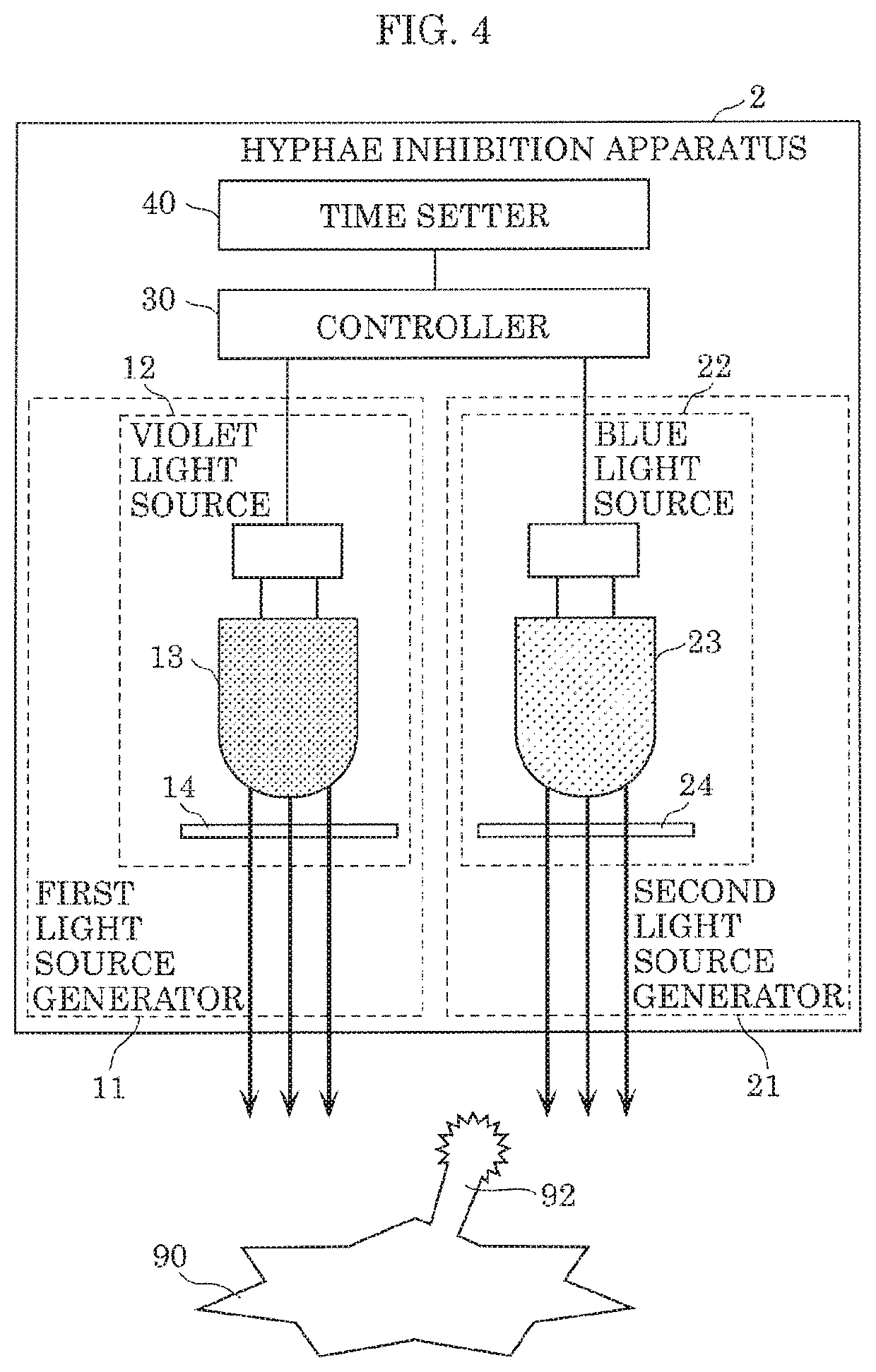
Hyphae inhibition apparatus and hyphae inhibition method
ActiveUS20200093944A1Excess proliferationPrevent proliferationElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesUva lightPhoto irradiation
A hyphae inhibition apparatus irradiates an organism having hyphae with light to inhibit growth of the hyphae. The hyphae inhibition apparatus includes a first light source generator, including at least one of a violet light source that emits light having a peak wavelength in a range of from 380 nm to 410 nm, inclusive, or a UVB light source that emits light having a peak wavelength in a range of from at least 280 nm to below 350 nm. The hyphae inhibition apparatus also includes a second light source generator, including at least one of a blue light source that emits light having a peak wavelength in a range of from at least 350 nm to below 380 nm or a UVA light source that emits light having a peak wavelength in a range of from 415 nm to 480 nm, inclusive.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Primer group, detection method and kit for rapidly detecting Staphylococcus aureus by using LAMP technology and application
PendingCN113528687AStrong specificityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyStaphyloccocus aureus
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbiological detection, and particularly relates to a primer group, a detection method and a kit for rapidly detecting Staphylococcus aureus by using an LAMP technology, and application. The Staphylococcus aureus virulence gene spA is selected as a specific target, four specific primer groups capable of amplifying the gene at 62-68 DEG C are designed, a detection result is indicated through a visual dye such that violet (negative) is changed into sky blue (positive). The method for detecting the Staphylococcus aureus is good in specificity, simple to operate, and free of expensive instruments, and the sensitivity is higher than that of conventional PCR. The kit disclosed by the invention can be used for rapidly and specifically detecting Staphylococcus aureus (within 1 hour), and the detection limit is 10<-6> ng / [mu]L. The kit is simple to operate, easy in result interpretation and suitable for import and export quarantine, food hygiene and clinical sample detection.
Owner:武汉海关技术中心
Whitening Dentifrice Compositions with Zinc Core Shell Silica Particles
InactiveUS20180168965A1Great whitening benefitImprove welfareCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWhitening AgentsHue
A whitening dentifrice composition, free from peroxide whitening agents, includes a blue coloring agent, a zinc core shell silica (Zn-CSS) particle, and an orally acceptable vehicle including a non-aqueous solvent and water. The blue coloring agent includes at least one of a blue pigment and a blue dye and has a blue to blue-violet color with a hue angle in the CIELAB system ranging from 200 degrees to 320 degrees. The Zn-CSS particle includes a silica core, and a surface of the silica core etched with a metal silicate, which is a silicate of zinc ion and optionally a monovalent metal ion.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Whitening dentifrice compositions with zinc core shell silica particles
A whitening dentifrice composition, free from peroxide whitening agents, includes a blue coloring agent, a zinc core shell silica (Zn-CSS) particle, and an orally acceptable vehicle including a non-aqueous solvent and water. The blue coloring agent includes at least one of a blue pigment and a blue dye and has a blue to blue-violet color with a hue angle in the CIELAB system ranging from 200 degrees to 320 degrees. The Zn-CSS particle includes a silica core, and a surface of the silica core etched with a metal silicate, which is a silicate of zinc ion and optionally a monovalent metal ion.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
A kind of purple pigment paste for internal coloring of cultural pulp containing chemical mechanical pulp and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105672021BStrong color renderingGood storage stabilityPaper/cardboardColorants/pigments additionFiberPigment
The invention discloses internal toning violet pigment color paste for printing and writing paper pulp with chemimechanical pulp.Color fiber problems are further worsened along with the progress of pulping technologies due to the fact that widely utilized color lake water-based pigment color paste is applied to chemimechanical pulp at present.The internal toning violet pigment color paste for the printing and writing paper pulp comprises, by weight, 20.0-22.0% of lightfast violet color lake, 8.0-10.0% of dispersing wetting agents, 2.0-3.0% of dyeing auxiliary, 10.0-15.0% of functional additives and the balance deionized water.The dyeing auxiliary is modified phospholipid with certain hydrophilicity.The internal toning violet pigment color paste has the advantages that uneven dyeing due to uneven combination speeds can be inhibited by the special dyeing auxiliary, and the color fiber problems can be thoroughly solved in procedures for manufacturing printing and writing paper with the chemimechanical pulp.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TRANSFAR WHYYON CHEM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com