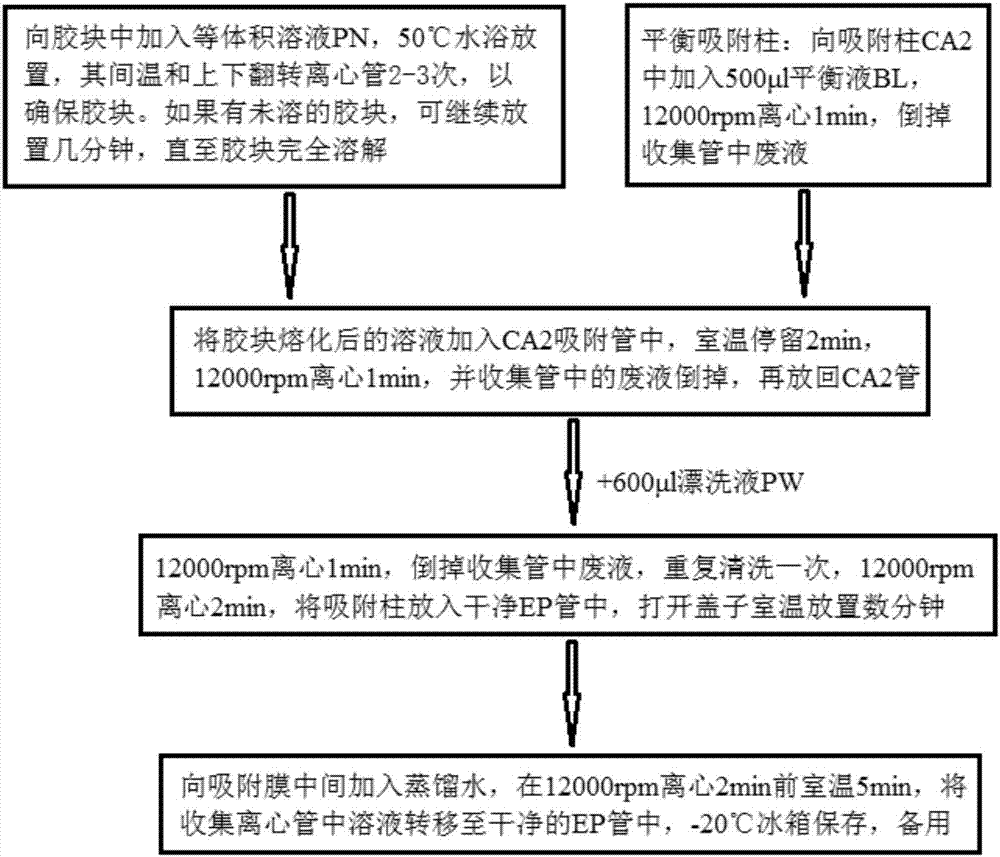
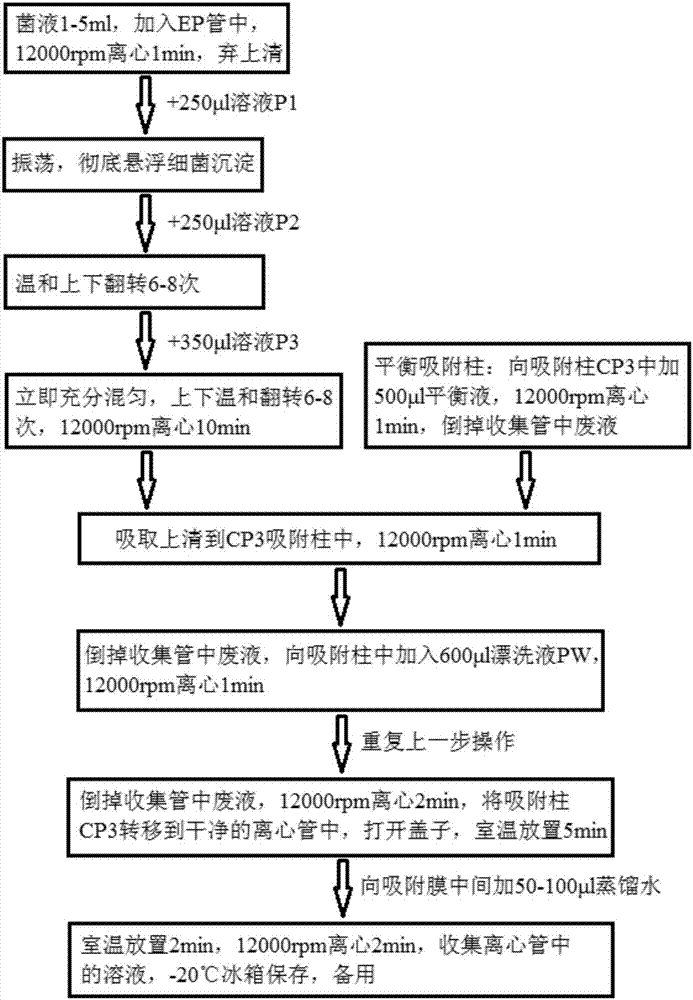
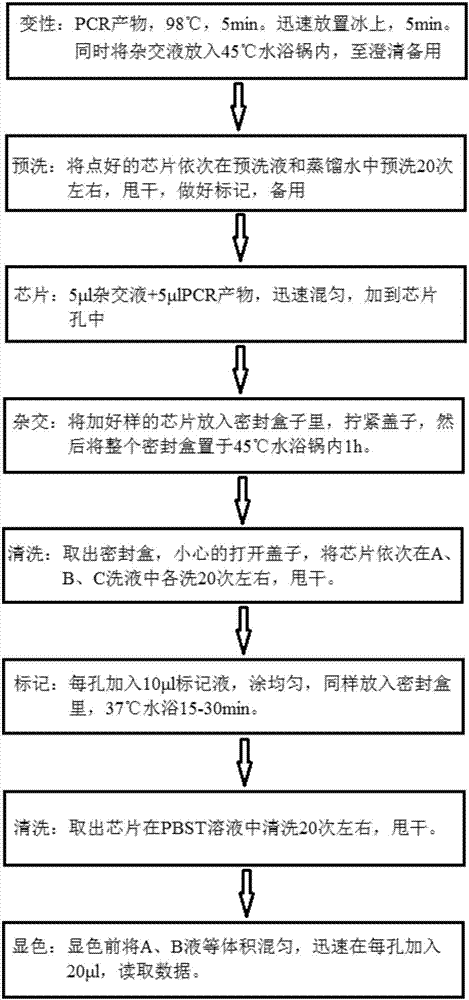
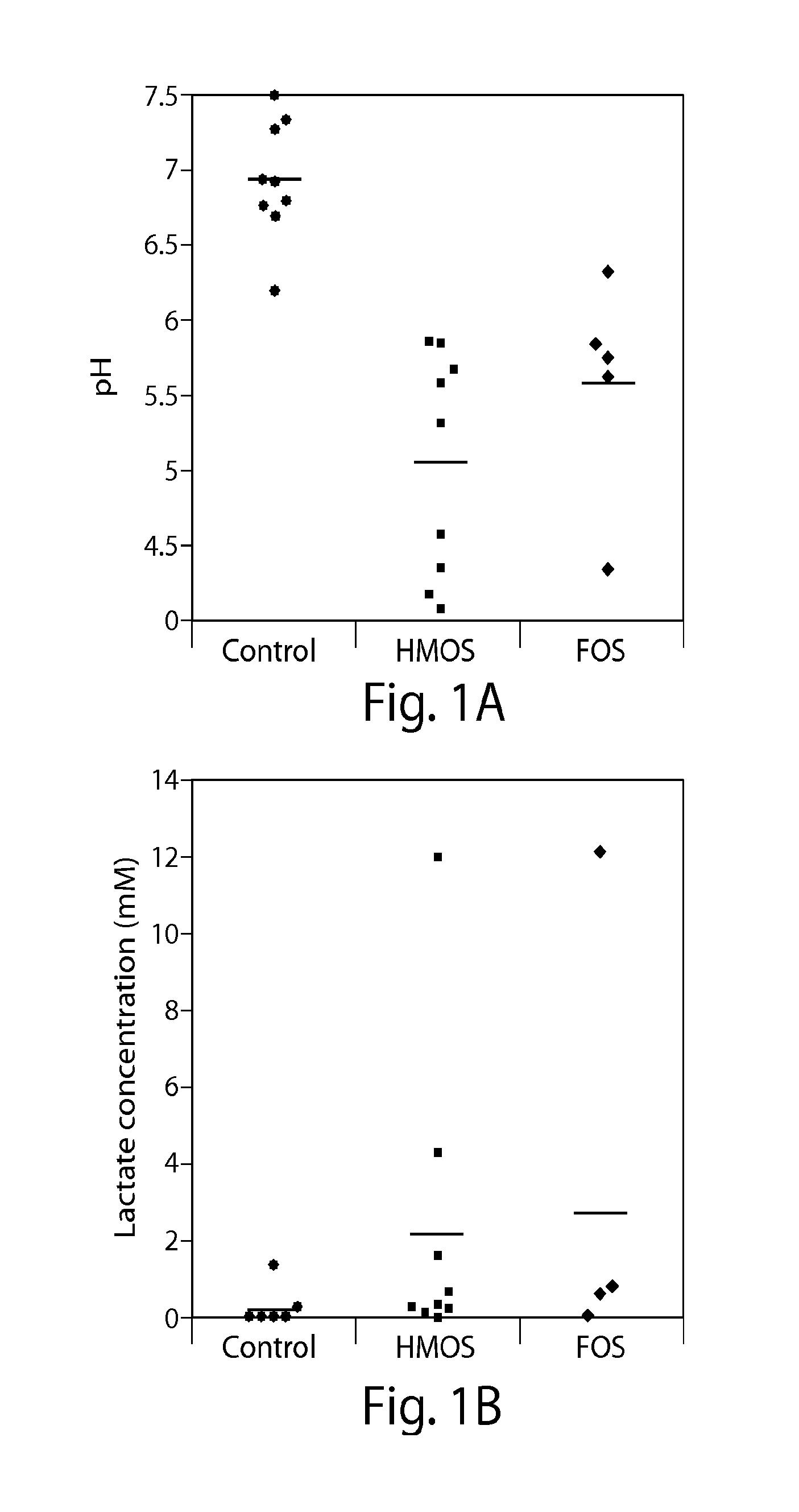
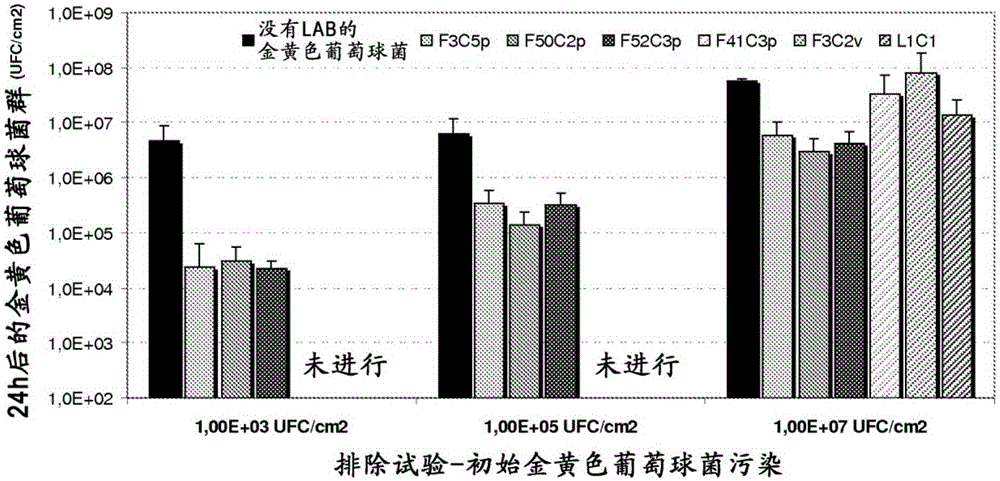
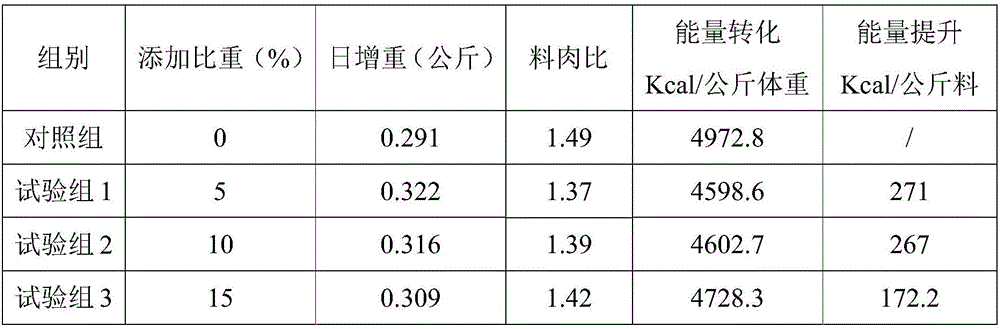
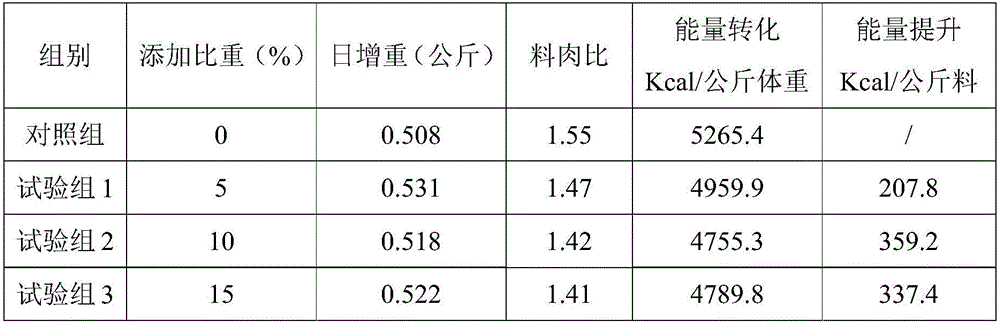
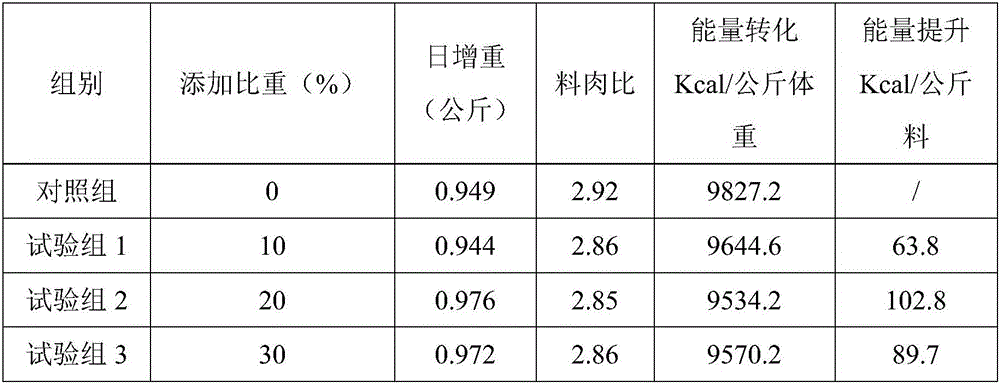
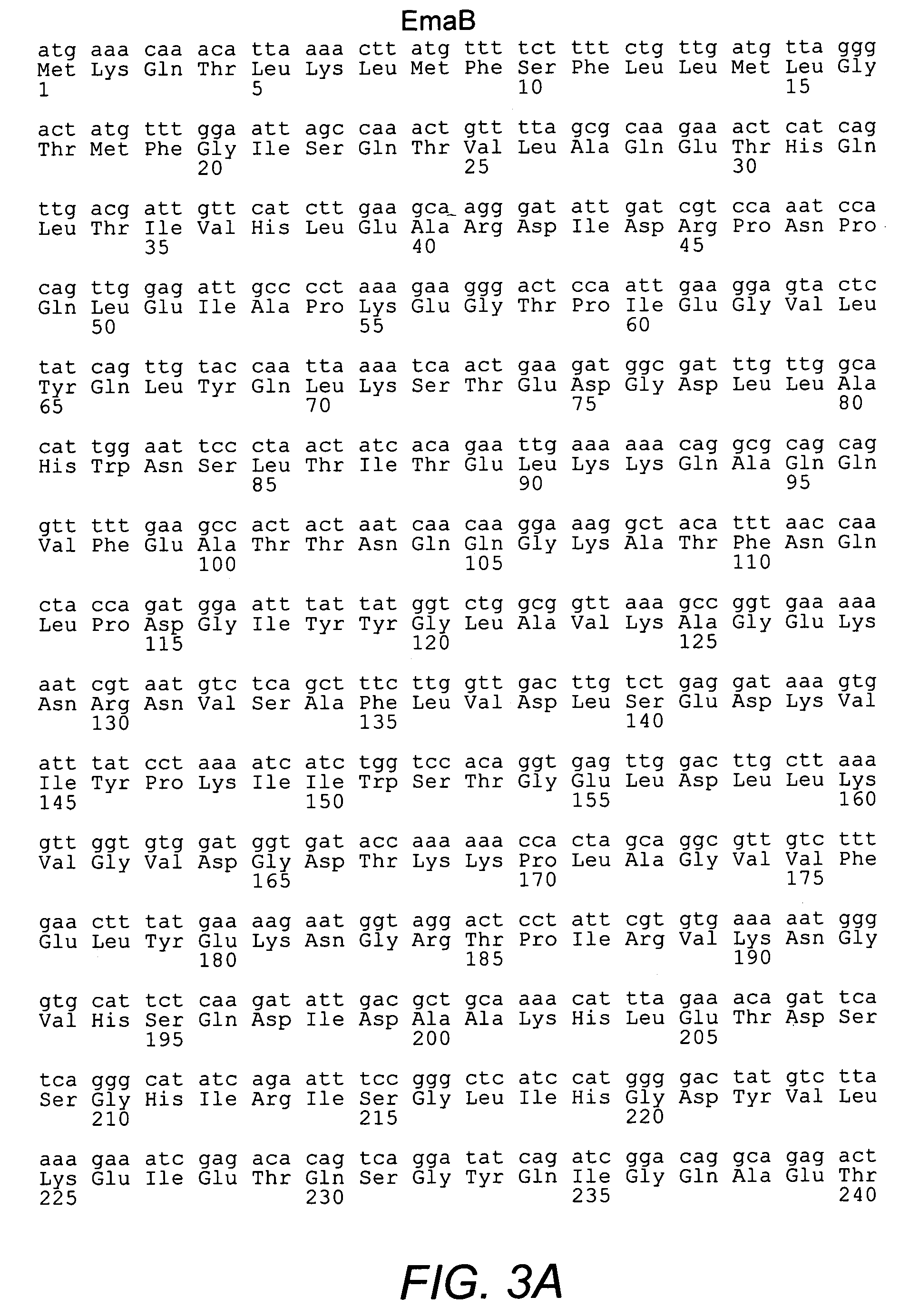Patents
Literature
540 results about "Enterococcus faecalis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
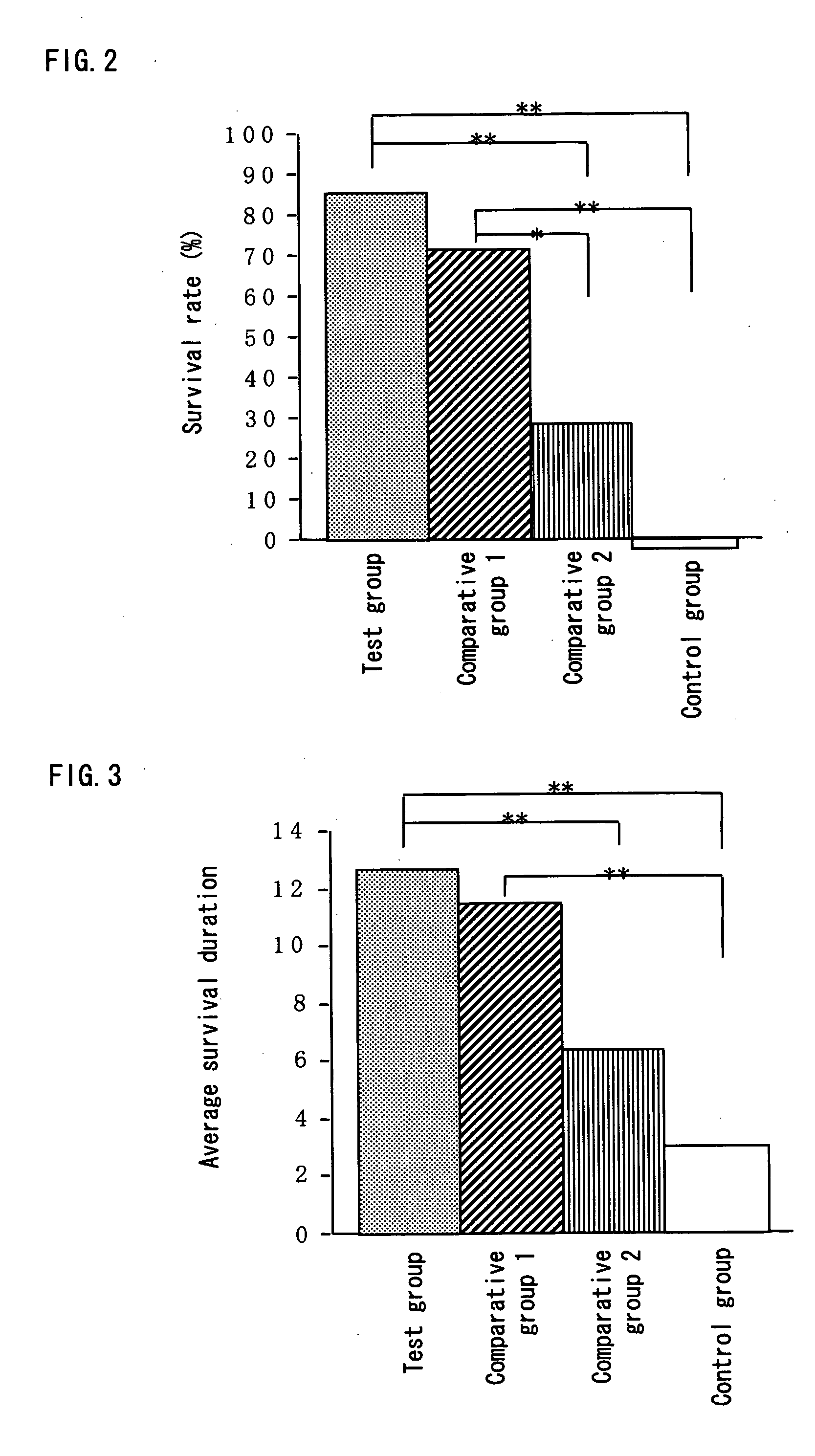
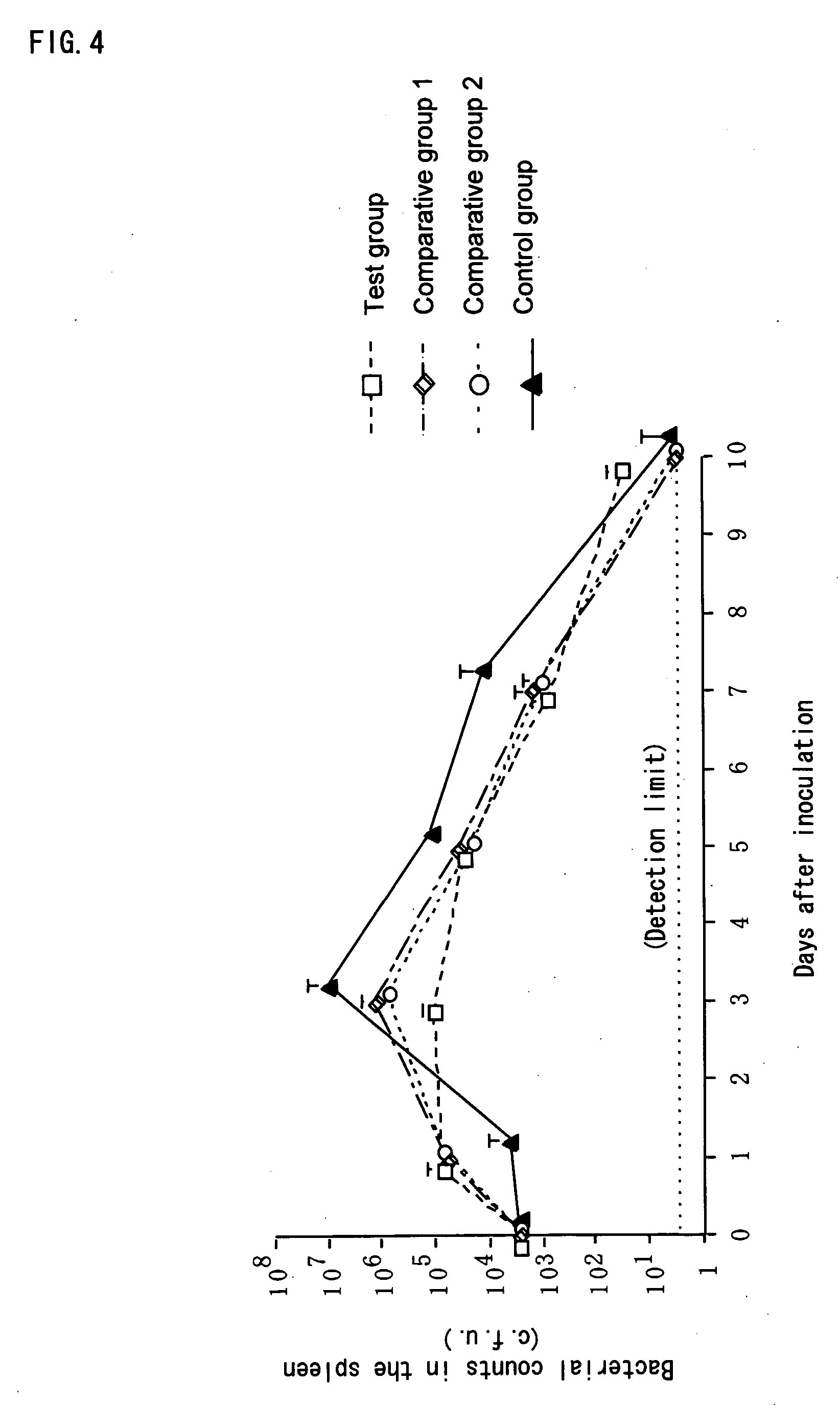
Enterococcus faecalis – formerly classified as part of the group D Streptococcus system – is a Gram-positive, commensal bacterium inhabiting the gastrointestinal tracts of humans and other mammals. Like other species in the genus Enterococcus, E. faecalis is found in healthy humans, but can cause life-threatening infections, especially in the nosocomial (hospital) environment, where the naturally high levels of antibiotic resistance found in E. faecalis contribute to its pathogenicity. E. faecalis has been frequently found in reinfected, root canal-treated teeth in prevalence values ranging from 30% to 90% of the cases. Re-infected root canal-treated teeth are about nine times more likely to harbor E. faecalis than cases of primary infections.
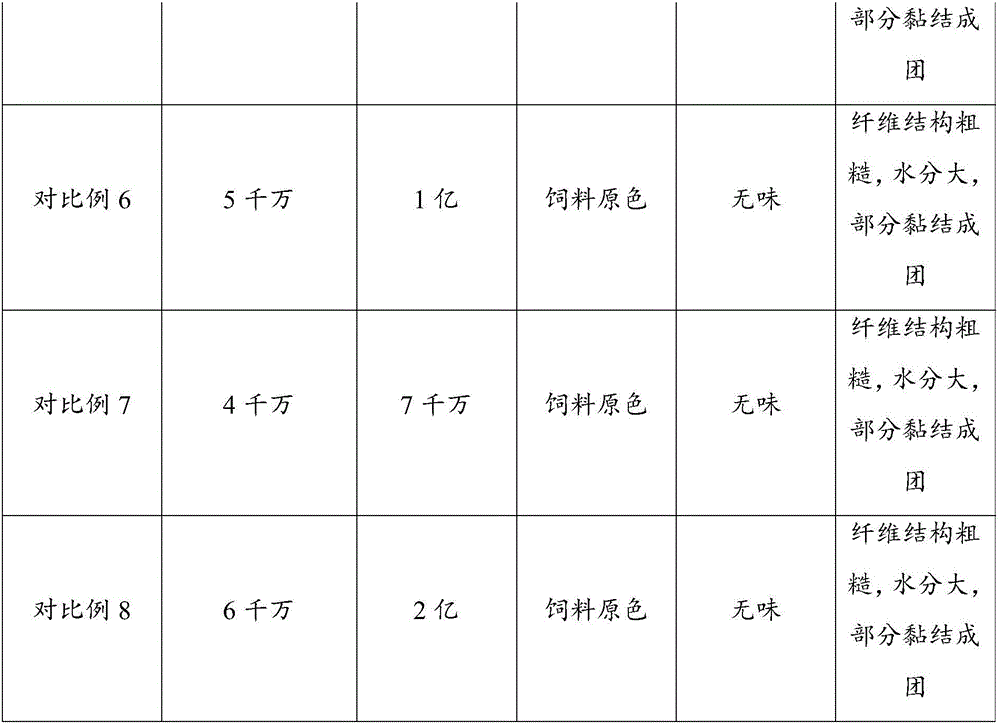
Compound microbial agent for degrading antibiotic and pesticide residues as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN106434430AEliminate pollutionAchieve biodegradableFungiBacteriaEcological environmentBacillus megaterium
The invention relates to a compound microbial agent for degrading antibiotic and pesticide residues as well as preparation and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biotechnology and environmental protection. Multi-thallus compound microbial powder is prepared from the compound microbial agent according to the weight percentage of living microbes to the total amount of compound microbial powder as follows: 10%-15% of bacillus subtilis, 10%-15% of aspergillus niger, 10%-15% of bacillus mucilaginosus, 10%-15% of enterococcus faecalis, 8%-12% of bacillus licheniformis, 8%-12% of bacillus megaterium, 8%-12% of pseudomonas fluorescens, 5%-8% of lactobacillus plantarum, 5%-8% of bacillus polymyxin and 6%-8% of streptococcus thermophiles. The compound microbial agent has the effects of degrading antibiotic and pesticide residues, fermenting and composting organic matter, acting as functional fertilizer and repairing the environment, and can solve the problems of secondary pollution caused by antibiotic residues in culture feces and resource utilization of organic waste and realizes biodegradation of the antibiotic and pesticide residues in soil when applied to the agricultural ecological environment, thereby being of great value and practical significance in restoration of agricultural ecological environment and protection of human health.
Owner:中山市润泽生物科技有限公司
Micro-ecological preparation and application thereof
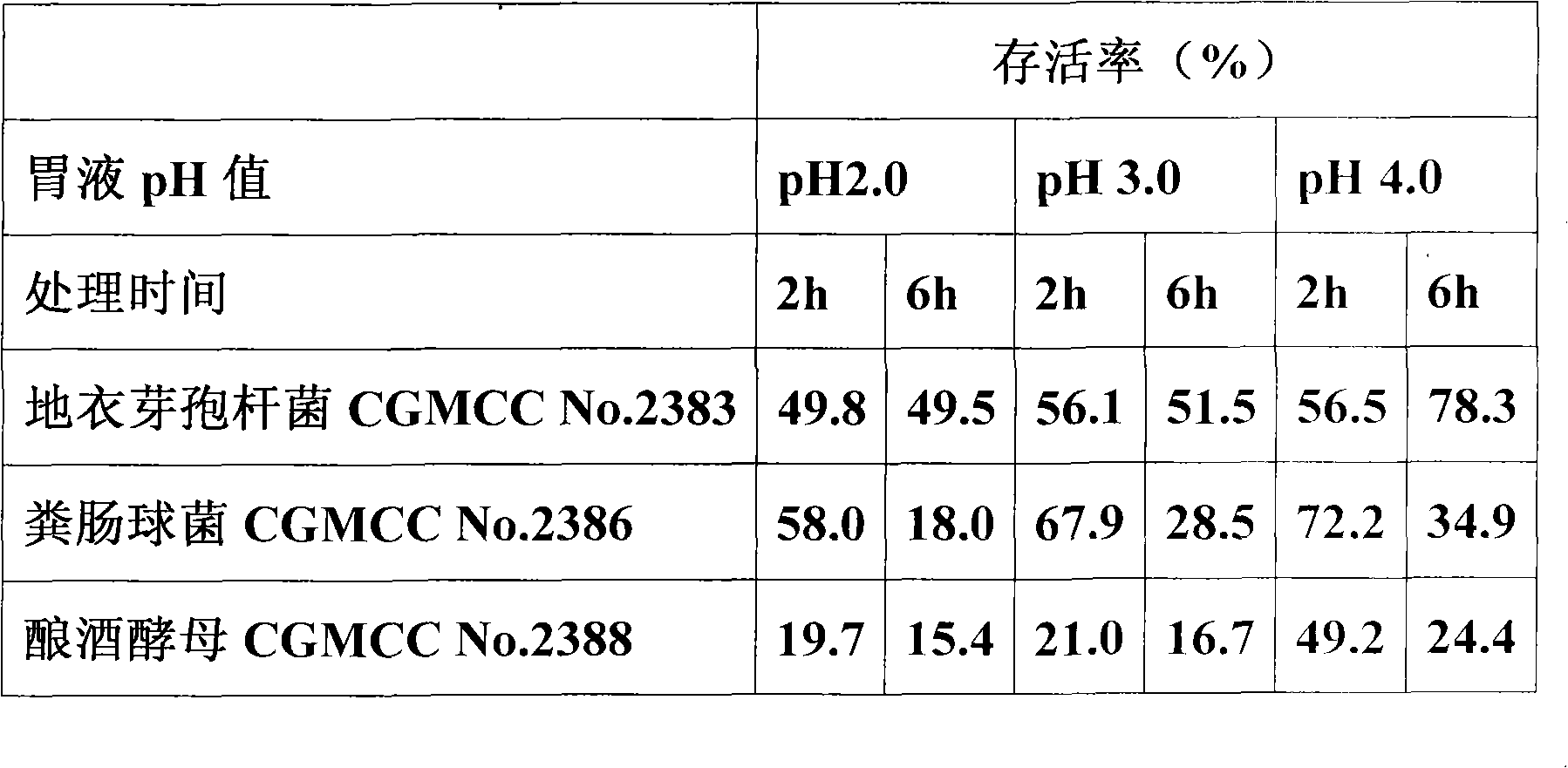
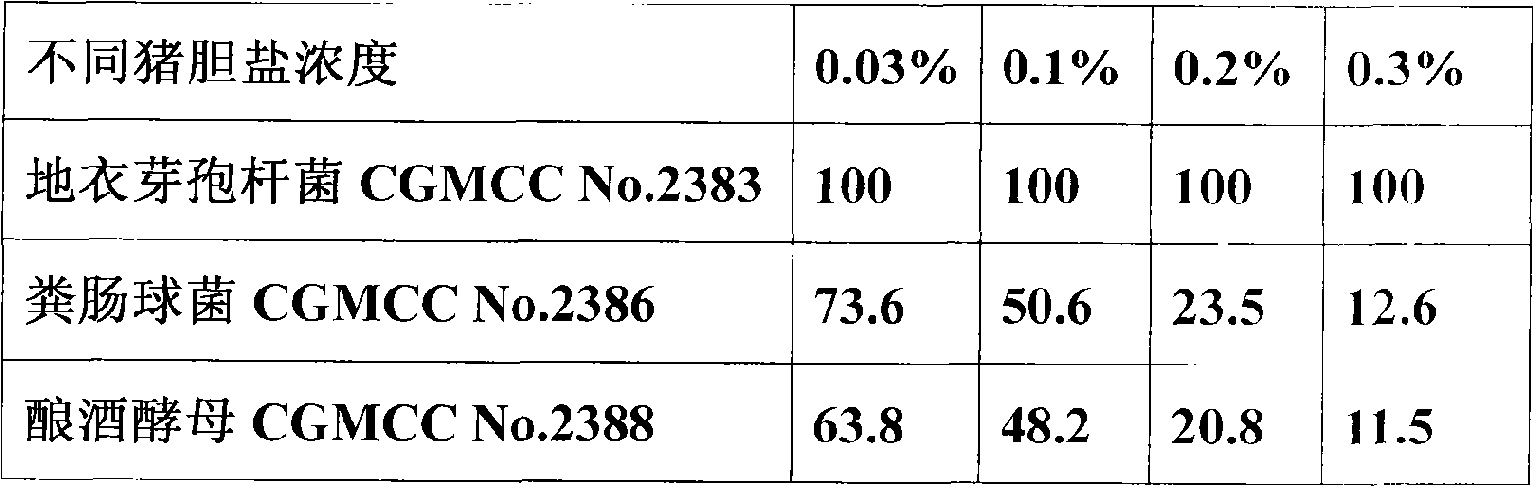
The invention relates to a micro-ecological preparation and the application thereof, in particular to a micro-ecological preparation containing a variety of probiotics and the application thereof. The micro-ecological preparation contains any three or four of the components including CGMCC No. 2383 bacillus licheniformis powder, bacillus subtilis powder, CGMCC No. 2386 enterococcus faecalis powder, lactobacillus acidophilus powder, and CGMCC No. 2388 saccharomyces cerevisiae. The micro-ecological preparation has content of live bacteria, has the adversity resistance such as gastric acid resistance, bile salt resistance, high-temperature resistance, common antibiotic resistance, and the like and the probiotic functions of producing acid and enzyme and resisting pathogenic bacteria. The variety and the proportion of the probiotics and carrier can be determined according to different kinds of animals and different animal growth phase. The micro-ecological preparation can improve the feed utilization efficiency, increase the yield of meat, eggs and milk, promote the growth of the animal, improve the immunity and the disease resistance of the animal, replace the antibiotic and improve the quality of the animal product.
Owner:BEIJING DABEINONG TECH GRP CO LTD +1
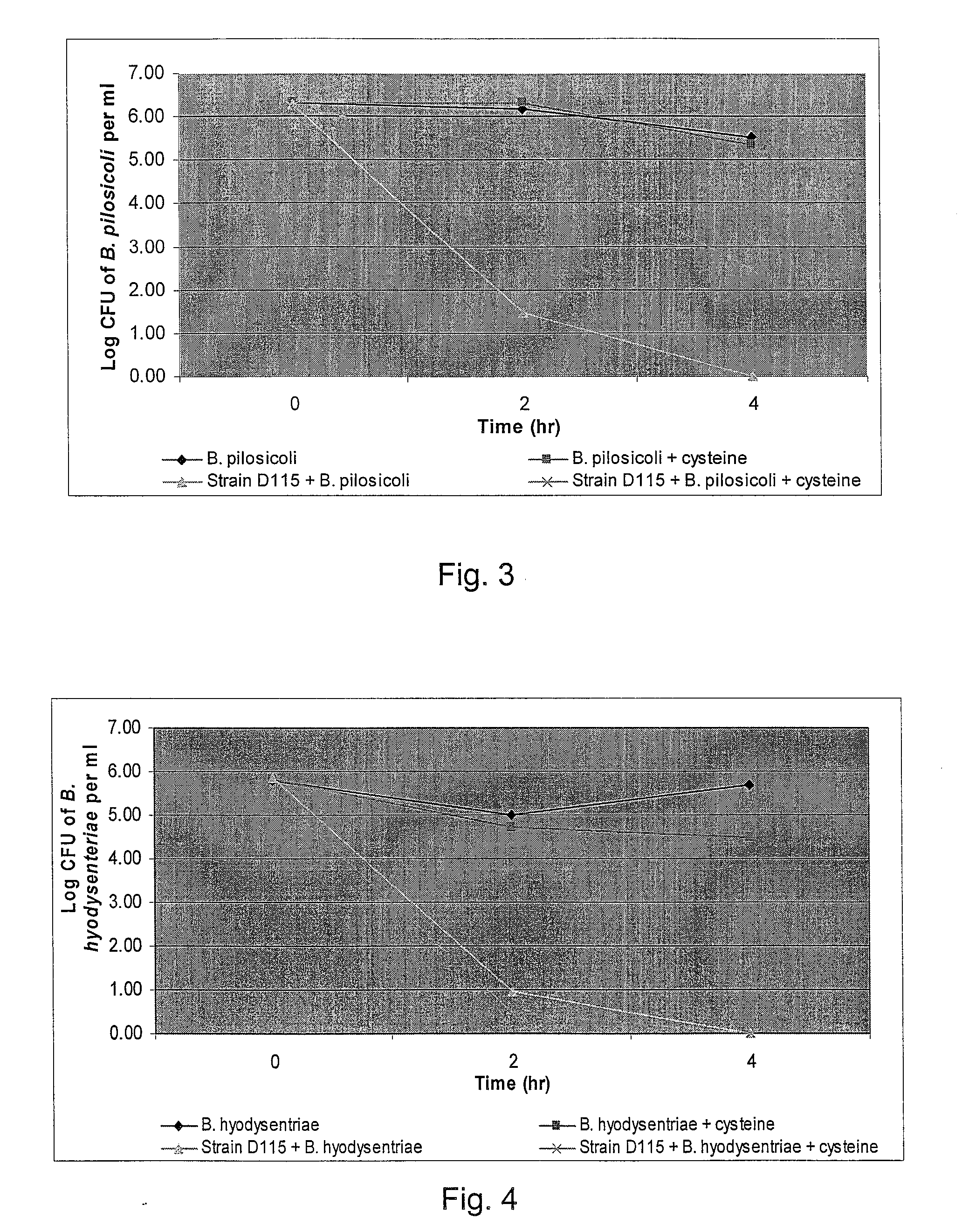
Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Lactobacillus Johnsonii D115
The present invention demonstrated the potential use of Lactobacillus johnsonii D115 as a probiotic, as a prophylactic agent or as a surface treatment of materials against human and animal pathogens such as Brachyspira pilosicoli, Brachyspira hyodysenteriae, Shigella sonnei, Vibrio cholera, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Campylobacter jejuni, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, Clostridium perfringens, Yersinia enterocolitica, Escherichia coli, Klebbsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella spp., Bacillus cereus, Aspergillus niger and Fusarium chlamydosporum. The proteineous antimicrobial compound was partially characterized and found to be heat tolerant up to 121° C. for 15 min, and acid tolerant up to pH1 for 30 min at 40° C. The compound is also stable to enzymatic digestion, being able to retain more than 60% antimicrobial activity when treated with pepsin and trypsin.
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
Feed fermenting agent, fermented feed and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a feed fermenting agent, fermented feed and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of animal product cultivation. The feed fermenting agent is mainly prepared from lactobacillus plantarum, enterococcus faecalis, bacillus subtilis, saccharomyces cerevisiae, lactobacillus cellobiosas, a complex enzyme preparation and the like. The fermented feed is prepared from the feed fermenting agent and fermentation raw materials by using a preparation method of carrying out fermentation in a device which is in one-way exhaust. According to the feed fermenting agent and the fermented feed, disclosed by the invention, the problems of high livestock cultivation cost caused by poor nutritive value, low animal digestion and absorption rate and abuse of antibiotic drugs during cultivation, long fermentation time and slow fermentation starting of existing livestock breeding feed are solved, and high absorption and conversion rate of nutrient contents of the fermented feed are achieved; the fermented feed contains a large amount of probiotics for protecting intestine health of animals, so that the organism immunity of the animals is increased, and the use of antibiotics during livestock cultivation is reduced.
Owner:湖南赛福资源饲料科技有限公司
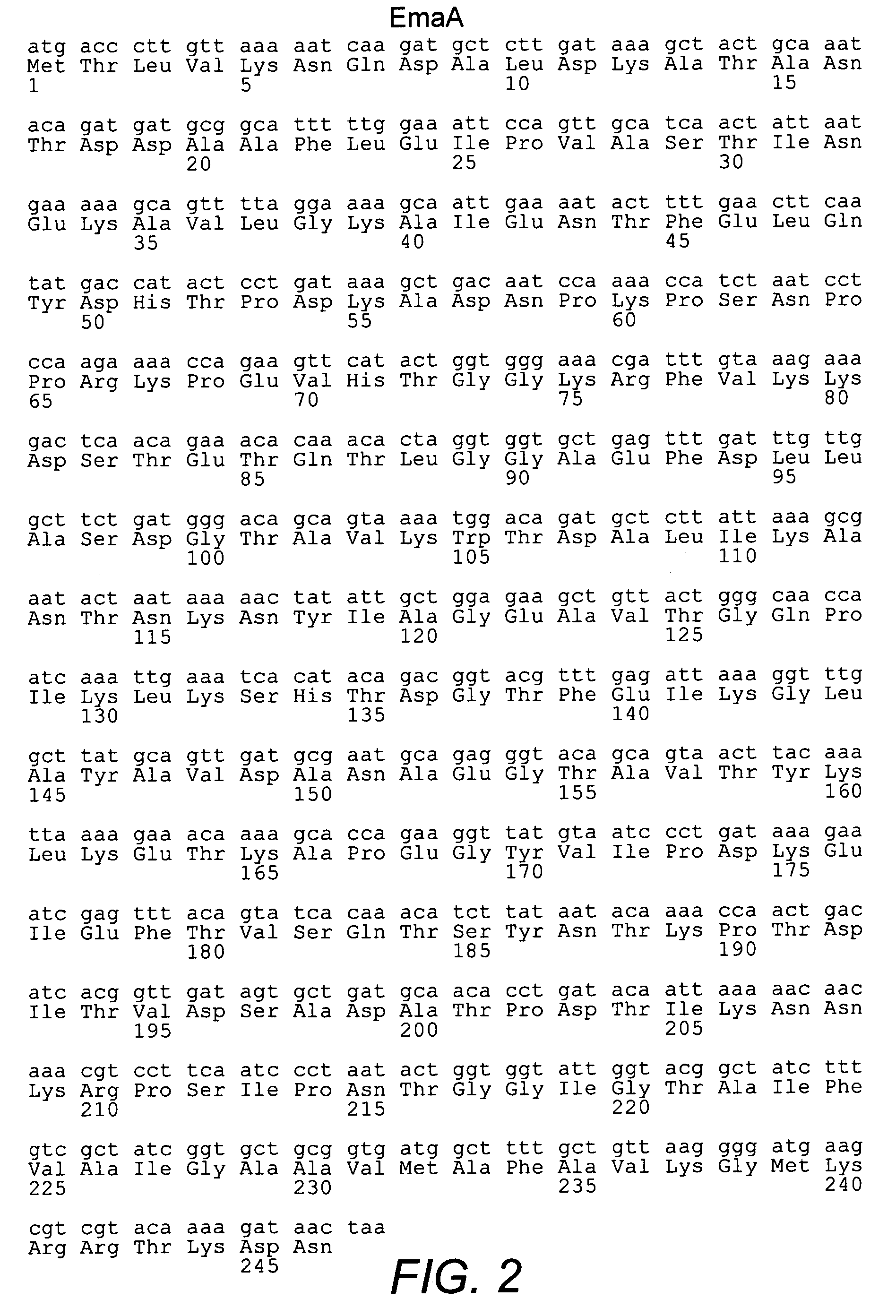
Group B streptococcus polypeptides nucleic acids and therapeutic compositions and vaccines thereof
InactiveUS7128919B2Modulate activityAvoid infectionBacteriaWhole-cell/virus/DNA/RNA ingredientsBacteroidesMutant
This invention provides isolated nucleic acids encoding polypeptides comprising amino acid sequences of streptococcal matrix adhesion (Ema) polypeptides. The invention provides nucleic acids encoding Group B streptococcal Ema polypeptides EmaA, EmaB, EmaC, EmaD and EmaE. The present invention provides isolated polypeptides comprising amino acid sequences of Group B streptococcal polypeptides EmaA, EmaB, EmaC, EmaD and EmaE, including analogs, variants, mutants, derivatives and fragments thereof. Ema homologous polypeptides from additional bacterial species, including S. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes, E. faecalis and C. diptheriae are also provided. Antibodies to the Ema polypeptides and immunogenic fragments thereof are also provided. The present invention relates to the identification and prevention of infections by virulent forms of streptococci. This invention provides pharmaceutical compositions, immunogenic compositions, vaccines, and diagnostic and therapeutic methods of use of the isolated polypeptides, antibodies thereto, and nucleic acids. Assays for compounds which modulate the polypeptides of the present invention for use in therapy are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND +1
Composite microorganism preparation and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a composite microorganism preparation including the active components as follows: at least two of enterococcus faecalis, saccharomyces cerevisiae and bacillus subtilis, and as well as zymosan and corn starch. The preparation is composed of, by weight, 0.1-15 parts of powder of the enterococcus faecalis, 0.1-15 parts of powder of the saccharomyces cerevisiae, 0.1-10 parts of powder of the bacillus subtilis, 0.1 parts of the zymosan and 59.9-74.9 parts of the corn starch. Compared with the prior art, the enterococcus faecalis, saccharomyces cerevisiae and bacillus subtilis are organically combined so that advantages of the bacteria can be achieved completely. The preparation can adapt different hosts and conditions, can partially, even completely replace antibiotics, and can regulate ecologic balance in gastrointestinal tracts, promote growth, increase conversion rate of feeds and enhance immunity. The preparation can improve enteric microorganism environment in animals, inhibit growth of harmful bacteria and promote reproduction of beneficial bacteria, improves animal immunity and enhances disease resistance, supplies nutrients to animals, improves utilization rate of feed and promotes growth of the animals.
Owner:HENAN HUITONGTIANXIA ANIMAL MEDICINE
Method for producing inocula for livestock and poultry by multi-thalli mixed liquid
InactiveCN101386827AReduction factorReduce ammonia nitrogenFungiBacteriaDiseaseBacillus licheniformis
The invention relates to a method for fermentation production of a poultry bacterial agent by multi-bacteria miscible liquid, wherein aerobic bacteria, namely Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, bacillus natto, beer yeast, Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus oryzae are cultured in a shaking table according to different culture mediums, so as to culture a mother seed solution; simultaneously Lactobacillus acidophilus, bifidobacteria and enterococcus faecalis are subjected to anaerobic culture by utilization of Kille flasks, and a mother bacterial solution of photosynthetic bacteria is cultured by a Kille flask under the condition of illumination; the prior stock solution is inoculated into a seed tank for anaerobic culture and fermentation according to 4 percent of the inoculum concentration, and the fermentation time is between 48 and 60 hours; and the cultured seed liquid is inoculated into a productive tank for anaerobic culture and fermentation according to 10 percent of the inoculum concentration, the fermentation time is between 60 and 72 hours, and the fermentation end point is reached when the pH value is reduced to 4.0. The method has the advantages that the microscopic examination viable count of the bacterial agent is more than 5 billion per milliliter, so that the bacterial agent is safe and nontoxic, thereby not only improving the disease resistance of poultry but also promoting the quick growth of the poultry, reducing the feed-meat ratio and improving the quality of meat, eggs and milk.
Owner:张培举
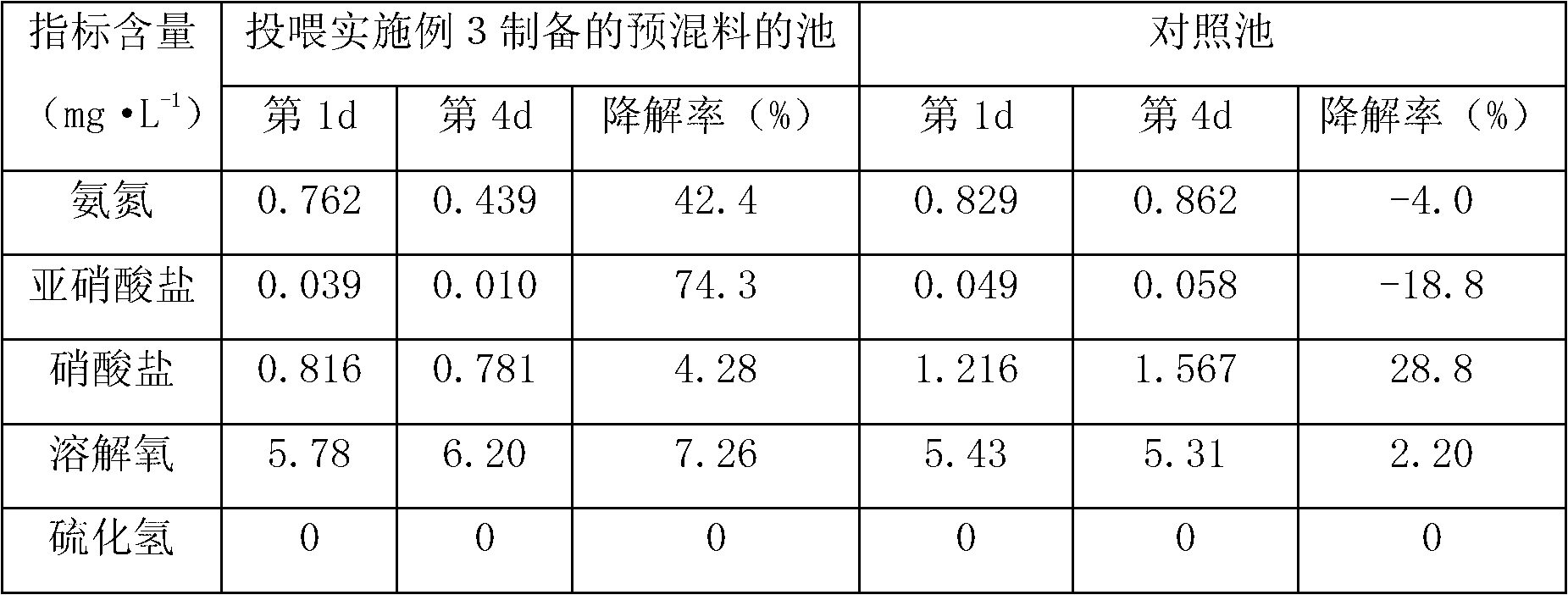
Premix compound for aquatic products, application thereof in feed additive, and batch thereof
InactiveCN102696923AHigh content of live bacteriaPromote growthAnimal feeding stuffFood additiveBacillus licheniformis
The invention discloses premix compound for aquatic products, the application thereof in feed additive and the batch thereof. In the premix compound per kilogram, vitamin B complex accounts for 80 to 140g, composite trace element accounts for 110 to 200g, taurine accounts for 100 to 300g, phytase accounts for 10 to 30g, glutamine accounts for 100 to 300g, DMPT accounts for 5 TO 20 g, composite microbial ecological agent accounts for 1 to 10g, composite traditional Chinese medicine composition accounts for 1 to 10g, and the margin is a carrier. The ingredients of the composite microbial ecological agent include fermented powder of bacillus subtilis CGMCC, No. 4628, fermented powder of bacillus licheniformis CGMCC, No. 5094 and fermented powder of enterococcus faecalis CGMCC, No. 5092. The main ingredients of the composite microbial ecological agent include three probiotics. Not only the probiotic function is achieved, but also the premix compound can be used for purification and conditioning to aquaculture water body, the environmental suitability is strong, the function is stable, and pollutants such as ammonia nitrogen, tric nitrogen, trite nitrogen, COD and the like in the water body are effectively degraded.
Owner:TIANJIN CHANGNONG TECH +1
Kit for quickly detecting 15 pneumonia pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN107338315AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesStaphylococcus aureus
The invention discloses a kit for quickly detecting 15 pneumonia pathogenic bacteria. The kit can detect streptococcus pneumoniae, staphylococcus aureus, haemophilus influenzae, mycoplasma pneumoniae, pseudomonas aeruginosa, baumanii, enterococcus faecalis, enterococcus faecium, klebsiella pneumoniae, escherichia coli, enterobacter cloacae, stenotrophomonas maltophilia, burkholderia cepacia, legionella pneumophila and chlamydia pneumoniae which cover clinically common pneumonia pathogenic bacteria difficult to culture. 16S rDNA and specific gene sequences corresponding to the pneumonia pathogenic bacteria are detected by combining gene chips with multiple asymmetric PCR reactions, and the categories of the bacteria in a to-be-detected sample are identified in genus and species. The kit makes up for the defect that current clinical detection of pneumonia pathogenic bacteria is not in time or comprehensive and a novel detection means for early diagnosis and early treatment of patients suffering from pneumonia is provided.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20050042606A9Rapid bacterial identificationShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesGenomic SegmentMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Deodorant special for livestock and poultry farms and application thereof
ActiveCN104307012AReduce releaseImprove deodorization efficiencyCosmetic preparationsFungiBacillus lentusCandida rugosa
The invention discloses a deodorant special for livestock and poultry farms and application thereof, wherein the deodorant is composed of the following strains: 106-108 lactobacillus acidophilus per milliliter, 107-109 lactobacillus reuteri per milliliter, 104-106 bacillus polymyxa per milliliter, 106-108 bacillus lentus per milliliter, 106-109 bacillus coagulans per milliliter, 104-106 enterococcus faecalis per milliliter, 107-109 enterococcus faecium per milliliter, 104-107 candida rugosa per milliliter, 104-107 candida valida per milliliter, 104-106 pseudomonas farinofermentans per milliliter, 106-108 rhodopseudomonas palustris per milliliter, 104-106 geotrichum suaveolens per milliliter, 106-108 aspergillus clavatus per milliliter, 106-108 rough spore aspergillus per milliliter and 106-109 streptomyces globisporus per milliliter. According to the invention, excrements in a poultry house and excrements for accumulative fermentation are treated through a spraying manner, so as to effectively reduce the release amount of malodorous gases, and provide a technical support for the effective treatment of malodor in the livestock and poultry farms and the environmental protection. Besides, the deodorant special for livestock and poultry farms can also be sprayed to the livestock and poultry body surfaces, to keep the livestock and poultry body surfaces clean and sanitary, and be conducive to the growth of livestock and poultry.
Owner:TWINS GRP
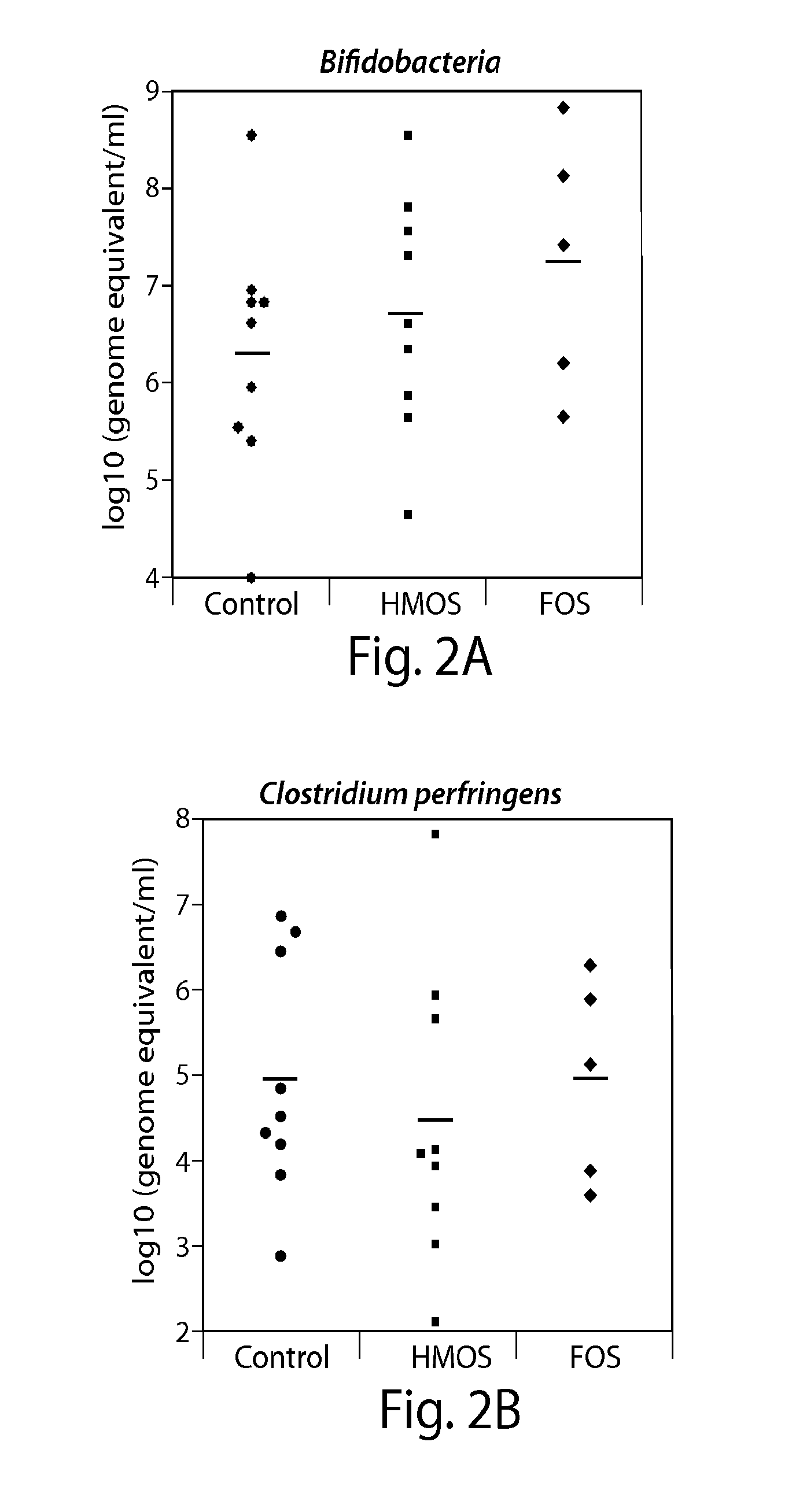
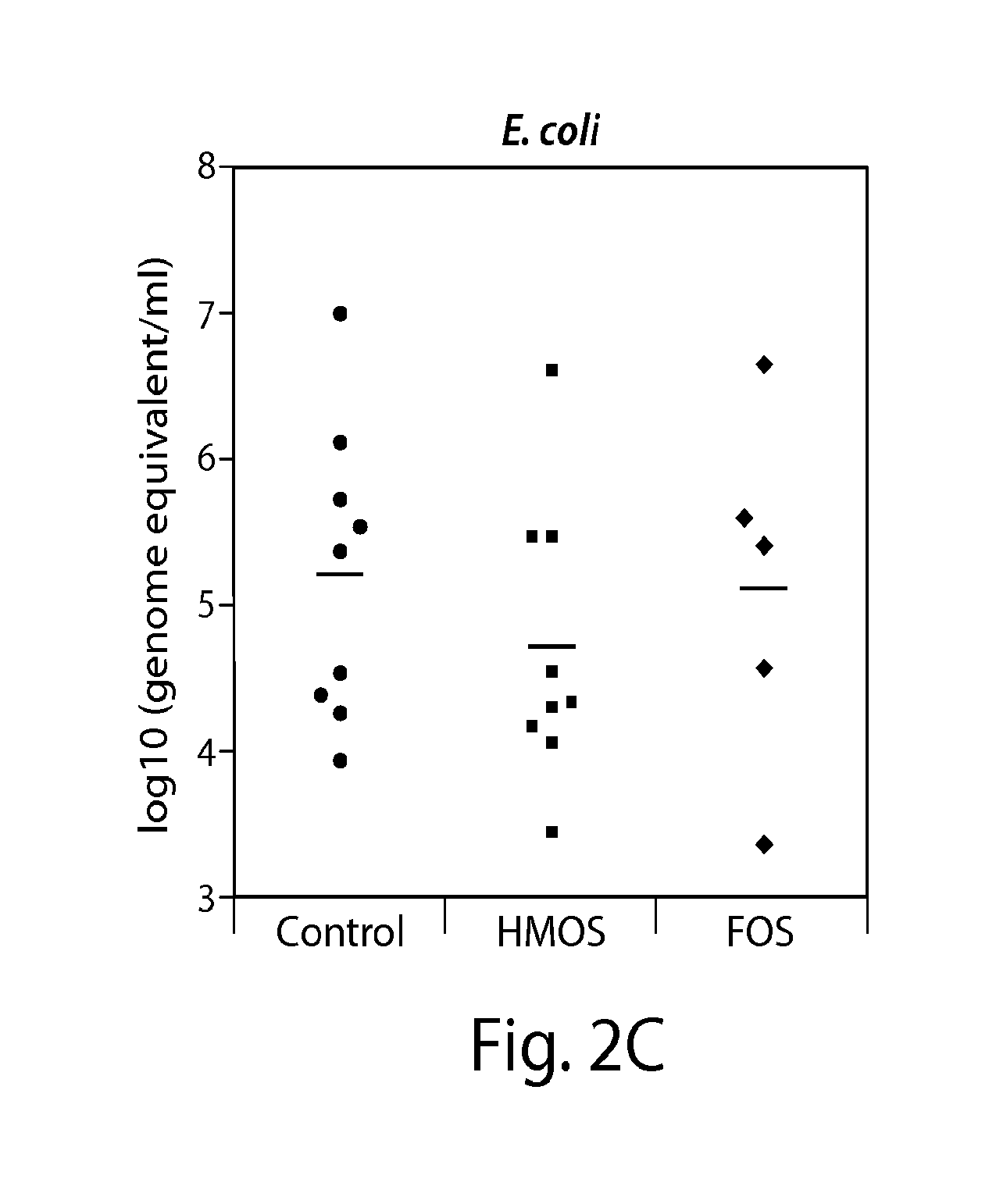
Prebiotic effect of sialyllactose
InactiveUS20150265661A1Promote growthHigh prebiotic effectBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBacteroidesOligosaccharide
Provided herein are prebiotic compositions comprising a combination of oligosaccharides such as sialyated oligosaccharides and fusocylated oligosaccharides, and uses thereof in stimulating the proliferation of beneficial intestinal micro biota, for example, of bifidobacteria, and / or in decreasing the abundance of enteric pathogens. The prebiotic compositions can further contain a probiotic, which can be a population of bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, Bacteriodes fragilis, Bacteriodes thetaiotaomicron, Enterococcus faecalis (pro biotic strains thereof), Staphylococcus epidermides, Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobacter cloacae, or related bacteria having similar functions.
Owner:BOSTON COLLEGE
FQ15 enterococcus faecalis and method for producing somatotrophic feed additive with the bacteria
The invention discloses an FQ15 enterococcus faecalis and a method of a feed additive which uses the bacteria production for promoting the growth: an MRS culture medium is taken as a seed culture medium, and the FQ15 enterococcus faecalis is cultured under the aerobic or facultative condition at 30 to 45 DEG C for 4 to 24 hours, so as to become a grade one seed; the grade one seed liquid is inoculated in a seed tank for amplification culture, the MRS culture medium is adopted as the seed culture medium, and the culture is carried out for 4 to 24 hours under the aerobic or the facultative condition at 30 to 45 DEG C to become a grade two seed; the grade two seed liquid is inoculated in a fermentation tank for fermentation culture, an improved MRS culture medium is adopted as the fermentation culture medium, and the culture is carried out for 8 to 36 hours by using timing or continuous fed-batch fermentation mode under the aerobic or the facultative condition at 30 to 45 DEG C; the obtained fermentation liquid is sub-packaged or the fermentation liquid which is obtained by step c is separated, 1 to 25 percent drying protector is added in the bacterial sludge, and the granulation at 20 - 80 DEG C, freeze-drying or spray drying are adopted. The invention has the advantages that the invention can substitute the feed antibiotics and improve the high efficient weight increase of livestock and poultry; the production process is simple; the cost is low, etc.
Owner:DALIAN SANYI ANIMAL MEDICINE CO LTD +2
Ternary compound inoculant for fermentation bed for pigs
The invention provides a ternary compound inoculant for a fermentation bed for pigs. The ternary compound inoculant is prepared from a compound inoculant I, a compound inoculant II and a compound inoculant III, wherein the compound inoculant I is a starting inoculant and consists of trichoderma koningii, bacillus licheniformis and bacillus amyloliquefaciens; the compound inoculant II is a maintaining inoculant and consists of azotobacter chroococcum, enterococcus faecalis, bacillus laterosporus, bacillus amyloliquefaciens and bacillus subtilis; the compound inoculant III is a stacking inoculant and consists of aspergillus oryzae, streptomycete, azotobacter chroococcum, trichoderma koningii and bacillus licheniformis. The ternary compound inoculant provided by the invention is an efficient conversion flora system with complementary function and complementary enzyme system; the compound inoculant I is fermented to produce heat before entering; the compound inoculant II is subjected to biological deodorization, bacteria inhibition and waste transformation in cultivation; the compound inoculant III is decayed at high temperature after being discharged; nutrients are preserved in situ. The ternary compound inoculant system is collaboratively progressive, a continuous circulating fermentation process for cultivation of the fermentation bed is achieved, and healthy and clean production of pigs is facilitated.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for preventing and/or treating infections, colonisations, or illnesses related to staphylococcus aureus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, streptococcus pyogenes, enterococcus faecium, enterobacter cloacae, proteus mirabilis, bacteroides fragilis, staphylococcus epidermidis, propionibacterium acnes, candida albicans and/or malassezia furfur
The subject matter of the present invention is a bacteria or mix of bacteria having an antagonistic activity with respect to stains of S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, Streptococcus pyogenes, Enterococcus faecium, Enterobacter cloacae, Proteus mirabilis, Bacteroides fragilis Staphylococcus epidermidis, Propionibacterium acnes, Candida albicans and / or Malassezia furfur as well as the use thereof in the treatment and / or prevention of infections or colonisations related to those pathogens. The invention pertains to care products containing one or more non-pathogenic antagonistic strains intended to prevent and / or treat infections or colonisations on skin, wounds, mucous membranes and appendages.
Owner:URGO RECH INNOVATION & DEVEMENT
Feed micro-ecological preparation, anti-nutritional substance-free feed and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105767507AImprove digestion utilizationPromote growth and developmentAnimal feeding stuffBacillus licheniformisBiotechnology
The present invention discloses a feed micro-ecological preparation, an anti-nutritional substance-free feed and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of feed. The feed micro-ecological preparation is prepared by fermenting the following raw materials in parts by weight: 1.0-1.2 parts of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, 0.2-0.6 part of Enterococcus faecalis, 1.5-2.0 parts of Bacillus subtilis, 0.2-0.6 part of Bacillus coagulans, 0.1-0.15 part of Bacillus licheniformis, 0.1-0.3 part of Bacillus lentus, 0.2-0.5 part of Clostridium butyricum and 993.05-995.15 parts of liquid medium. After the feed micro-ecological preparation is mixed with feed raw materials, enzymes produced in the process of microbial strain fermentation can decompose anti-nutritional substances in feed and increase the feed utilization rate; at the same time, microbial strains also have effects in improving animal intestinal environment, maintaining intestinal flora balance, inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria, and improving animal immunity.
Owner:SUIPING GUANGYUAN FEED TECH CO LTD
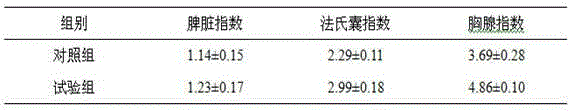
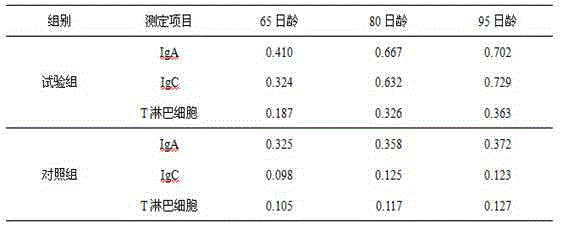
Enterococcus faecalis HEW-A131 and application thereof
ActiveCN104293696ASignificant probioticInhibition of growth and reproductionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismEconomic benefits
The invention discloses enterococcus faecalis HEW-A131 which is high in thermal resistance, wide in acid-alkali resistance range, high in stress resistance and relatively high in probiotic property. The strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on June 17th, 2014, the preservation serial number is CGMCC NO.9353, and the classification name is enterococcus faecalis. The enterococcus faecalis HEW-A131 has excellent microorganism characteristics, remarkable probiotic property and stress resistance and super high fermentation property, not only is the utilization efficiency of feed of animals increased, but also the cost is reduced, moreover the stability of the environment inside the alimentary canals of animals is greatly improved, the adsorption and utilization of nutrition are promoted, the animal growth is promoted, the production performance, immunity and breeding property of the animals are remarkably improved, the production cost is lowered, and the economic benefits are increased.
Owner:江西好实沃生物技术有限公司
Novel microbial feed additive and method of producing the same
ActiveCN101278702AIncrease payImprove qualityBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyBacterial strain
The invention relates to a novel microorganism feed additive, in particular to a microorganism feed additive which contains bacterial strain that can produce conjugated linoleic acid and a preparation method thereof, which belongs to the microorganism feed additive technical field. The preparation method of the microorganism feed additive is that plant lactobacillus and enterococcus faecalis are respectively processed by zymotic liquid which is cultured by liquid deep-layer high-density fermenting and are made into powder by a micro-capsule peridum spray drying method and a frozen-dried preparation method. The microorganism feed additive transforms linoleic acid into the conjugated linoleic acid in the intestinal tracts of poultry and livestock, which takes effects of promoting the growth performance of the poultry and the livestock, reducing fat, increasing meat factor and regulating immunity reaction, etc., and the microorganism feed additive also solves the problem of the high expense caused by adding the conjugated linoleic acid into the feed directly. The microorganism feed additive prepared by the method has the advantages of high viable bacteria content, long holding period and little microbial pollution.
Owner:BEIJING DABEINONG TECH GRP CO LTD +2
Animal health care probiotics leavening capable of improving meat quality and application thereof
ActiveCN102356816AImprove meat qualityGood animal healthAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyBifidobacterium
The invention discloses an animal health care probiotics leavening capable of improving meat quality and application thereof. The leavening includes a component A, a component B and a component C, and a live bacteria proportion in the component A, component B and component C is 1: (0.2-5) : (0.1-5); the component A is a composition of one or two from plant lactobacillus and manure enterococcus faecalis; the component B is composition of one or two from lactobacillus acidophilus and bifidobacterium; and the component C is saccharomyces cerevisiae. The leavening of the invention can be utilizedto prepare probiotics bacteria liquid and fermented feed for animal culture in order to increase meat quality of culture animals. The technical method of the invention is capable of improving meat quality, simple and practical.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Antibiotic-free mixed feedstuff and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102318735ANo pollution in the processNo drug resistanceFood processingAnimal feeding stuffTrichoderma reeseiAspergillus niger
The invention provides an antibiotic-free mixed feedstuff and a preparation method thereof. The invention belongs to the field of animal feedstuffs. According to the invention, a mixed feedstuff containing Chinese herbal medicines is mixed with a mixed fermentation material containing various probiotics according to a certain proportion, such that the feedstuff provided by the invention is obtained. The mixed feedstuff containing Chinese herbal medicines comprises half-dried ginkgo leaves or ginkgo leaf extraction residues, Japanese honeysuckle stems, balloon flower root, soybean meal, peanutmeal, corn powder, wheat flour, calcium hydrogen phosphate, common salt, composite microelement, mulvital, and selenium-enriched yeast. The mixed fermentation material containing various probiotics comprises an enterococcus faecalis fermentation material, a bacillus licheniformis fermentation material, a saacharomyces cereisiae fermentation material, a Trichoderma reesei fermentation material, and an aspergillus niger fermentation material, which are mixed according to a certain proportion. Microbe strains are processed through targeted acclimatization, and are cultivated by using a solid fermentation medium, such that the mixed fermentation material is obtained. The antibiotic-free mixed feedstuff provided by the invention assists in promoting growth, and brings no toxic or side-effect. The feedstuff causes no antibiotic residue, no pollution, and no drug resistance. With the mixed fermentation the utilization rate of the feedstuff can be improved, healthy growth of live stocks can be promoted, and meat qualities of the live stocks can be improved.
Owner:SHANDONG YONGCHUNTANG GRP
Composition containing beta-glucan and constipation-relieving drug, immunopotentiatior, and skin moistening agent using the composition
InactiveUS20050272694A1Organic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsAureobasidiumBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention provides a composition containing β-glucan in which the physiologically active effects of β-1,3-1,6-glucan contained in a cultured composition of a bacterium belonging to the genus Aureobasidium sp. are further enhanced, and a constipation-relieving drug, preparation an immunopotentiator, and a skin moistening agent using the composition. A composition containing β-glucan, which contains a cultured composition containing β-1,3-1,6-glucan obtained by culturing a bacterium belonging to the genus Aureobasidium sp. and lactic acid bacterium cells, is obtained. This composition containing β-glucan is employed as an active ingredient of a constipation-relieving drug, an immunopotentiator, or a skin moistening agent. Aureobasidium pullulans M-1 (FERM BP-08615) is preferable as the bacterium belonging to the genus Aureobasidium sp. Moreover, Enterococcus faecalis is preferable as the lactic acid bacterium. It is still preferable that the lactic acid bacterium has been killed by heating. Furthermore, the content of the cultured composition in solid matters preferably ranges from 1 to 80% by mass in terms of β-1,3-1,6-glucan, while the content of the lactic acid bacterium cells preferably ranges from 4 to 95% by mass.
Owner:AUREO CO LTD
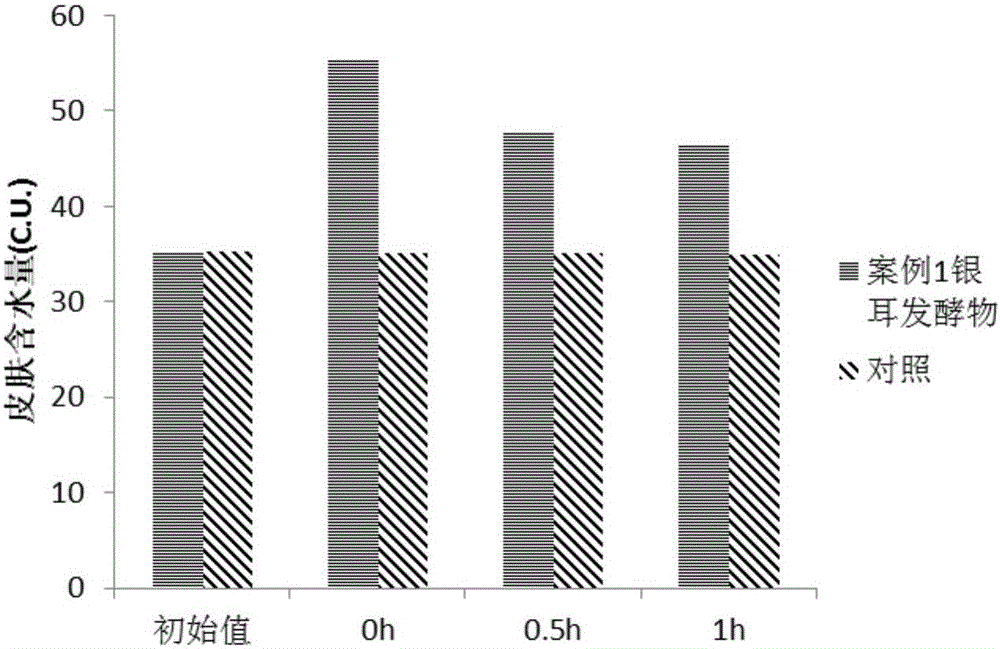
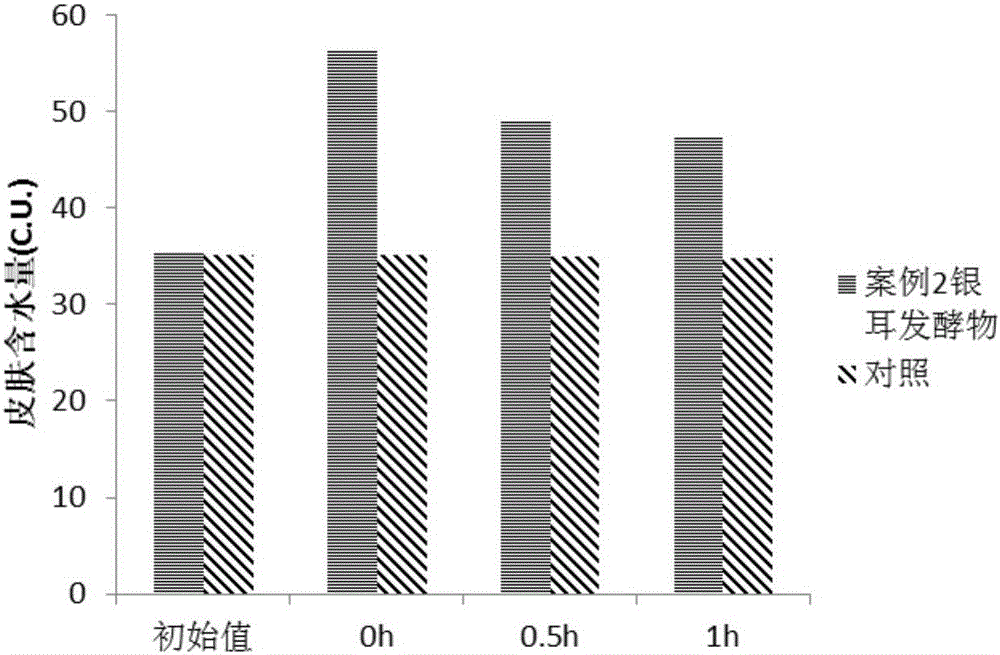
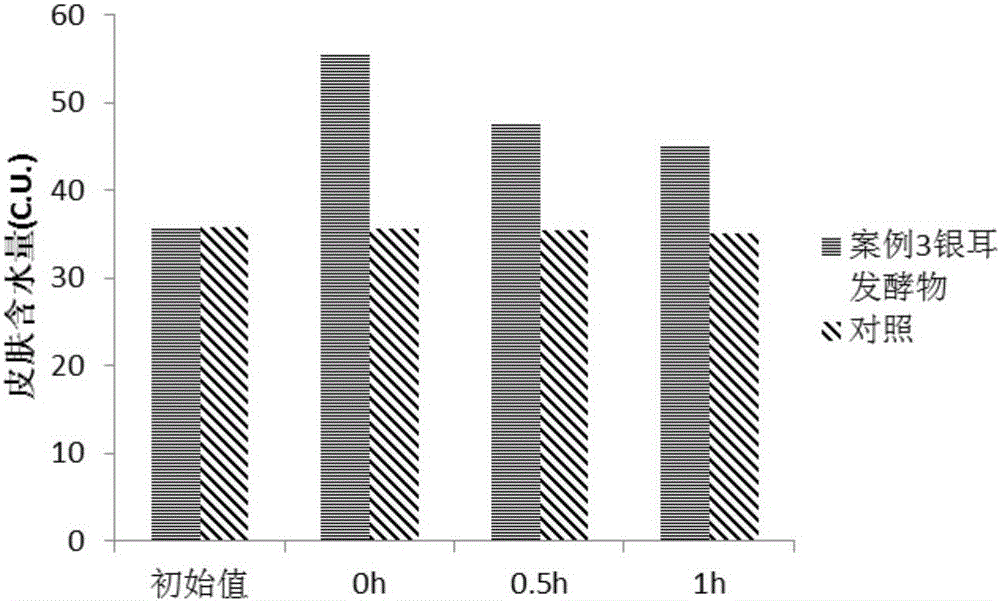
Preparation method and application of tremella fermentation extract
ActiveCN105002254AFully absorbedCause negative effectsCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsTremellaZygosaccharomyces
The invention discloses a preparation method of a tremella fermentation extract and its application. The preparation method of the tremella fermentation extract comprises the following step: tremella undergoes fermentation cultivation by the use of a strain or its culture solution or its suspension so as to obtain a fermentation product, namely the tremella fermentation extract. The strain is at least one of the following strains: zygosaccharomyces rouxii, pasteur yeast, brewer's yeast, wine yeast, acetobacter xylinum, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. Bulgaricus, Streptococcus thermophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, lactococcus lactis and enterococcus faecalis. Through experiments, it proves that the tremella fermentation extract prepared by the method contains no chemical components, can be directly used as a finished product of facial mask or essence or toner, is more natural than other existing products in the market and will not have any negative effect on the skin. In addition, smaller components can be obtained by the preparation method in comparison with a common extraction method and the extract is easier to fully absorb by the skin.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOTRULY BIOTECH CO LTD
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20070009947A1Rapid and exponential in vitro replicationQuick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesBacteroidesMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20090053702A1Rapid and exponential in vitro replicationQuick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesStreptococcus pyogenes
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
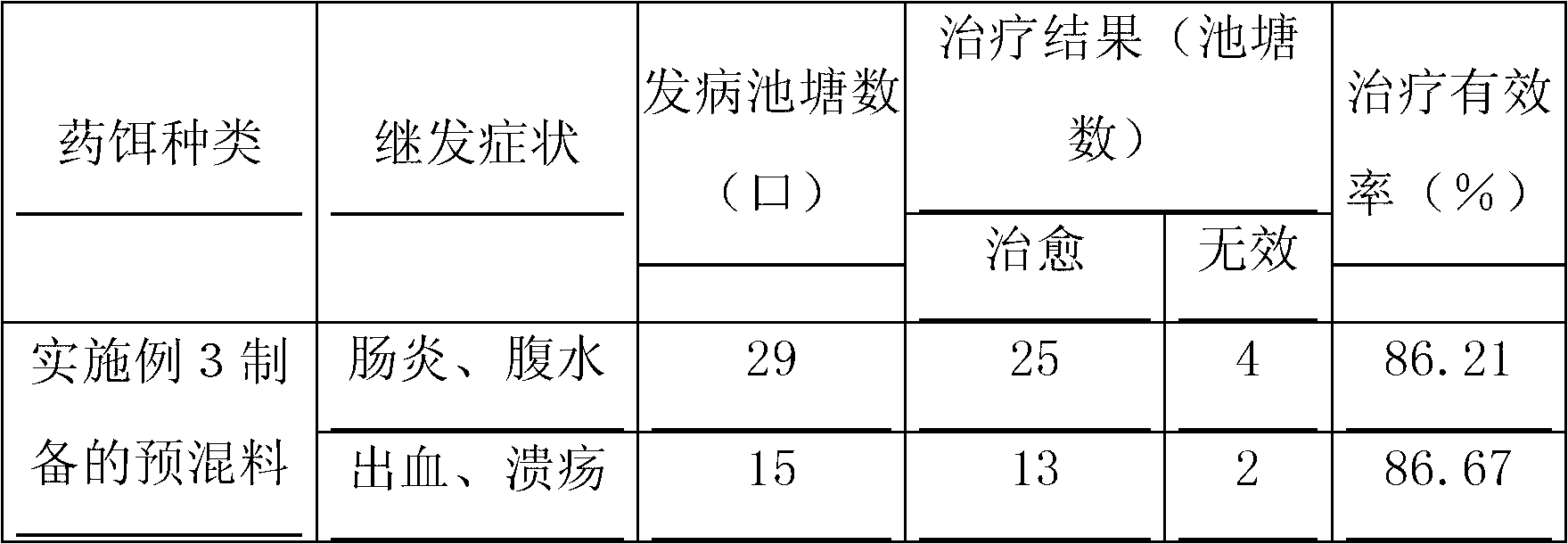
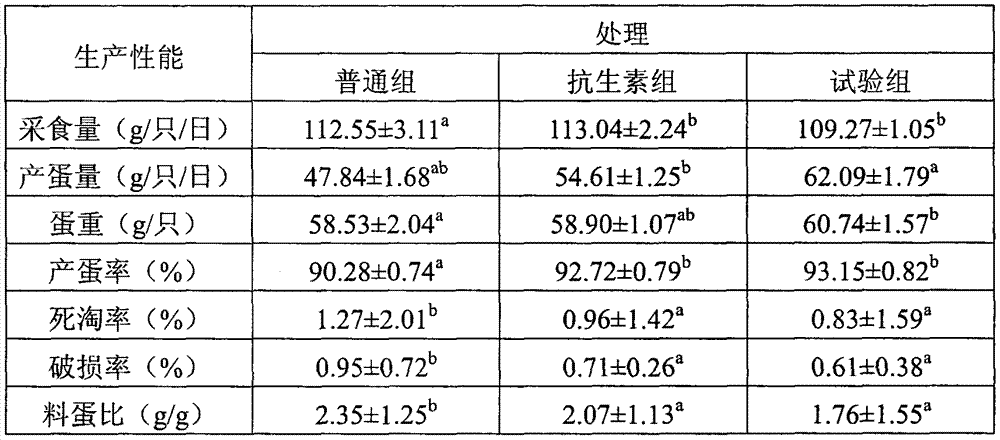
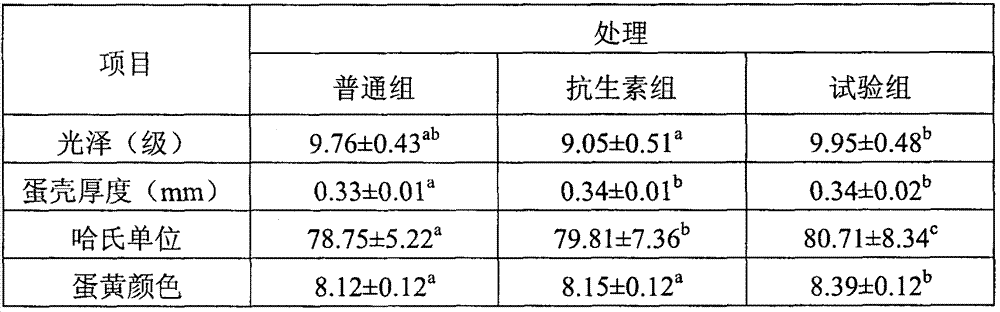
Chicken feed probiotic agent containing enterococcus faecalis and preparation method of chicken feed probiotic agent
ActiveCN104293697AImprove feed utilization efficiencyIncrease production capacityFungiBacteriaSludgeMass ratio
The invention discloses a chicken feed probiotic agent containing enterococcus faecalis and a preparation method of the chicken feed probiotic agent. The chicken feed probiotic agent is prepared by virtue of the steps of evenly mixing enterococcus faecalis HEW-A131 active bacterial sludge, bacillus subtilis active bacterial sludge, saccharomyces cerevisiae active bacterial sludge and a stabilization protective agent together in the mass ratio of (0.1-0.8): (1-2.5): (0.1-0.5): 1, and then pelletizing, drying, coating and the like; the probiotic agent is capable of improving the utilization efficiency of an animal feed and saving the cost, and also capable of greatly improving the steady state of the internal environment of the digestive tract in an animal body, promoting the absorption and utilization of nutrition and promoting the growth of the animal; as a result, the productivity, the immune performance and the reproductive performance of the animal are obviously improved, the production cost is reduced and the economic benefit is increased.
Owner:BEIJING HESWOF BIOTECH CO LTD
Methods for preventing or treating infectious diseases caused by extracellular microorganisms, including antimicrobial-resistant strains thereof, using gallium compounds
InactiveUS20080241275A1Effect be exertReduce in quantityAntibacterial agentsBiocidePresent methodInfectious Disorder
The present invention relates to methods for preventing or treating infectious diseases caused by extracellular microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, by systemically administering to a patient a compound containing gallium. The extracellular microorganisms targeted by the present methods include methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE), E. coli O157:H7, fluoroquinolone-resistant Salmonella typhi, and the like. Furthermore, in the present methods, gallium compounds can be co-administered with one or more conventional antimicrobial agents to treat infectious diseases with reduced risks of creating multi-drug resistant pathogens. The methods of the present invention is also applicable to those microorganisms, such as ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, complete eradication of which so far has been difficult to achieve.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Silage additive special for paper mulberries and application
ActiveCN108041289APH dropIncrease feed intakeAnimal feeding stuffAnimal fodder preservationRetention periodZymogen
The invention provides a silage additive special for paper mulberries and an application of the silage additive. The additive comprises zymogen and complex enzymes, wherein the zymogen consists of lactobacillus plantarum (lactobacillus plantarum) plantarum ) ACCC11016 and enterococcus faecalis (enterococcus faecalis) faecalis ) CICC20440 according to the ratio of the viable count of the lactobacillus plantarum to that of the enterococcus faecalis being (1-10) to (0-1), and the complex enzymes consist of cellulase, pectinase and glucose oxidase. According to the silage additive, through synergistic effects of lactic acid bacteria, an enzyme preparation and soluble carbohydrate, the retention period of a fresh paper mulberry coarse feed is prolonged, besides, various organic acids and various nutrient substances are produced, the palatability and the digestion and utilization rate of paper mulberry branches and leaves are increased, the content of neutral washing fibers and the content of acidic washing fibers are reduced, increase of the food consumption of livestock and poultry is facilitated, and the silage additive can be used for producing an environmental-friendly biologic feed.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Microbial fermented composite antibiotic-free feed containing natural antibacterial components
ActiveCN108813098AReasonable nutritional structureLow costFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyAntibiotic Y
The present invention provides a microbial fermented composite antibiotic-free feed containing natural antibacterial components. The feed comprises a fermented product based on the united segmented fermentation of aerobic-anaerobic composite strains, composite natural antibacterial components, a non-plant source protein / polypeptide compound nutrient supplement agent, and an additive comprising atleast a soybean protein amino acid / polypeptide compound chelate. The composite strains comprises at least lactic acid bacteria, bacillus subtilis, yeast selected from candida utilis or saccharomyces cerevisiae, and enterococcus faecalis. The fermented product based on the united segmented fermentation is prepared by carrying out secondary fermentation on fermentation raw materials through the aerobic-anaerobic composite strains. The combination of the microbial fermented feed and the natural antibacterial components is beneficial to the balance of intestinal flora of animals, and can prevent the dysbacteriosis of digestive tracts, improve the immunity functions of animal organisms, reduce or replace the use of feed antibiotics, and significantly improve the digestion and absorption efficiency of the feed and the meat quality of animals.
Owner:JILIN QIAN KE LAI FEED TECH
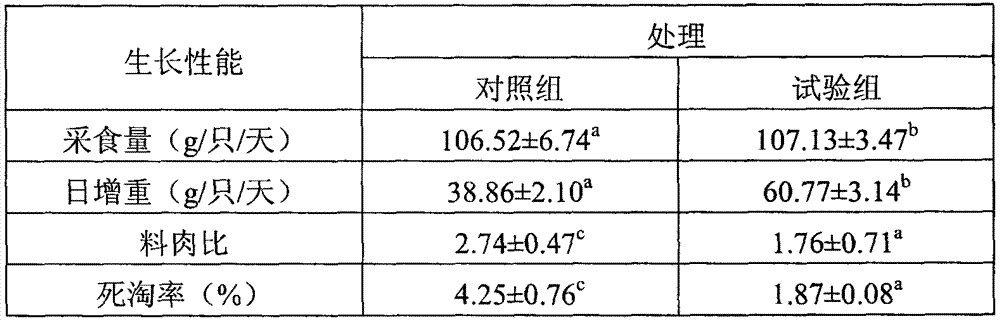
A Strain of Enterococcus Faecalis for Feed and Its Application
InactiveCN102277325AEnhanced inhibitory effectImprove the living environmentAntibacterial agentsBacteriaDiseaseOptimal growth
The invention discloses an Enterococcus faecalis strain SBD, of which the collection number is CGMCC No.4848. The strain is a Gram positive strain and is spherical according to observation with microscope, and the strain does not form spores; the strain can well grow on a Mann, Rogosa and Sharpe (MRS) agar plate and can grow into a round, smooth and raised bacterial colony like a grey white dew and with a diameter of 0.5 to 1 millimeter within 48 hours; and the strain can grow in a facultatively anaerobic environment, the growth temperature range is from 10 to 50 DEG C, the optimal growth temperature is 30 to 40 DEG C, and the growth pH value range is from 4 to 10 and the optimal pH value is 6.5. The bacterial preparation made by the strain is nontoxic and safe, can resist gastric juice and cholate, has a strong inhibition effect on various harmful bacteria and can be widely used in livestock breeding industry (by directly adding into daily ration or drinking water of animals) to increase the disease resistance in animals; and the preparation is expected to replace antibiotic for feed purpose and can obviously improve average weight of weaned piglets, reduce a feed-to-meat ratio and improve living environment of livestock and therefore has a bright prospect.
Owner:北京金泰得生物科技股份有限公司
Food and rink castoff feed processing method and culture medium and confecting method thereby
The invention discloses a method for processing the food waste to feed through adopting the microecology fermentation technology, which is characterized in that: two groups of the microecology preparation are used during treating; one group of the microecology preparation comprises yeast, lactobacillus and combined fungus of enterococcus faecalis; and the other group of the microecology preparation comprises bacillus cereus, bacillus subtilis, photosynthetic bacteria and actinomycetes. The method has the advantages that: the microecology preparation used as starter is added into the food waste, so as to remove the harmful microorganism such as pathogen through fermentation and realize full utilization and zero discharge of resources during feed processing; the consumption of energy is low; the equipment investment is low with simple and easy practice; and the produced microecology forage can replace the forage containing the antibiotic additive with green environmental protection. The invention also discloses a culture medium containing the component of seaweed, soybean sprout and sweet potato and a configuration process, the culture medium has the advantages of adapting to cultivation and proliferation of a plurality of probiotics and being beneficial to mass produce high-quality microecology preparation with low price and easy configuration.
Owner:JUNZHU DALIAN BIOLOGICAL IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com