Anaerobic built-in zero-valent iron reactor
An anaerobic reactor and zero-valent iron technology, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve problems such as long start-up time, treatment failure, and slow sludge granulation, and achieve the effect of good working performance, small design and stable operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
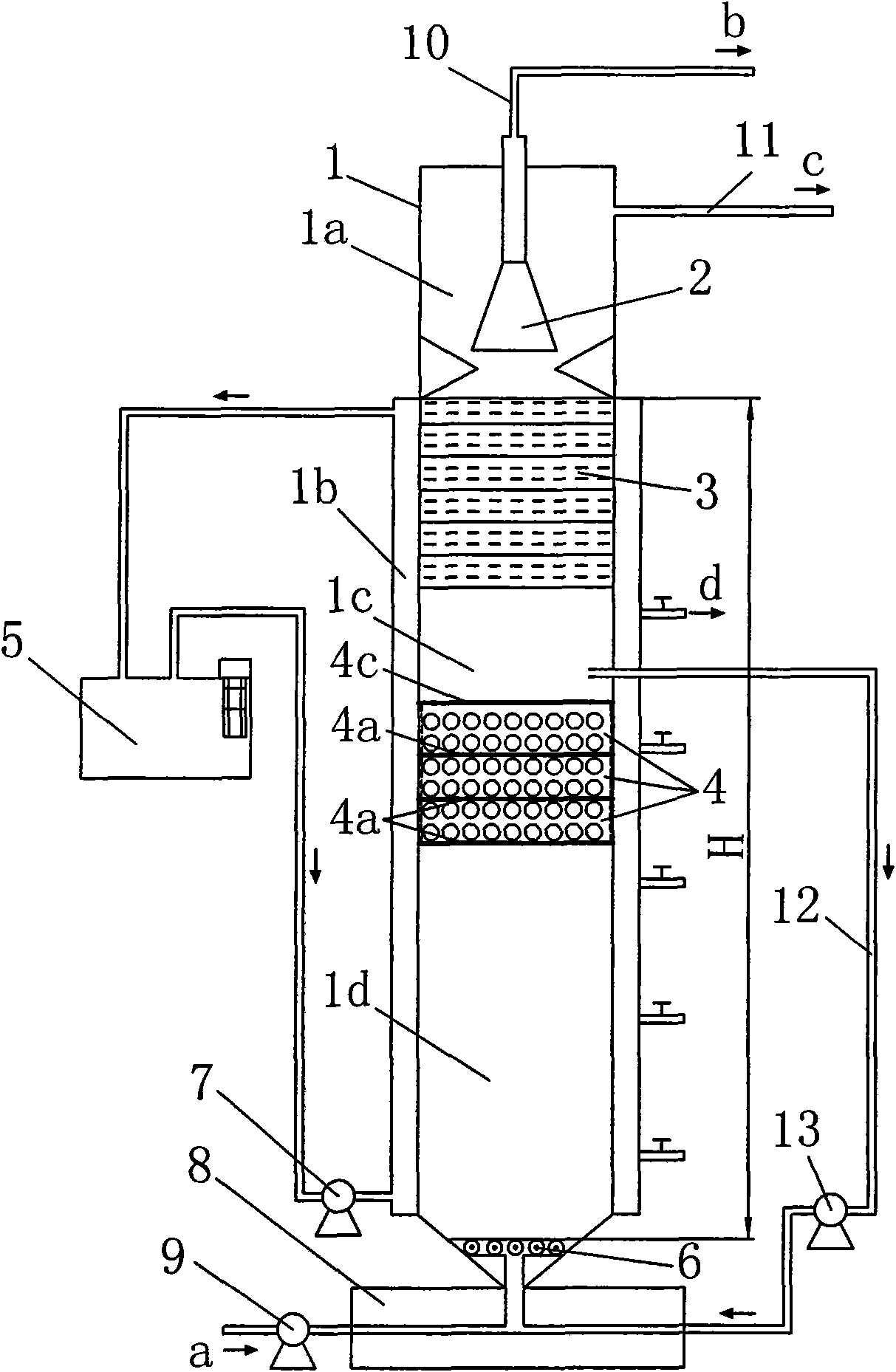
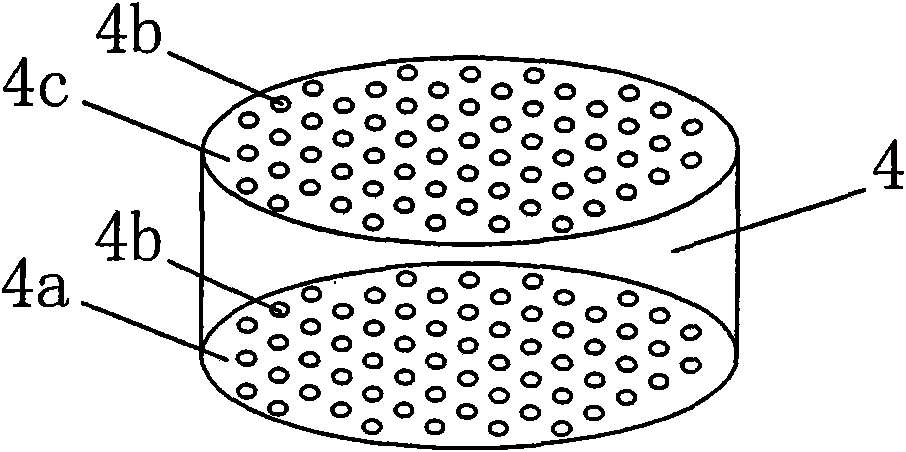
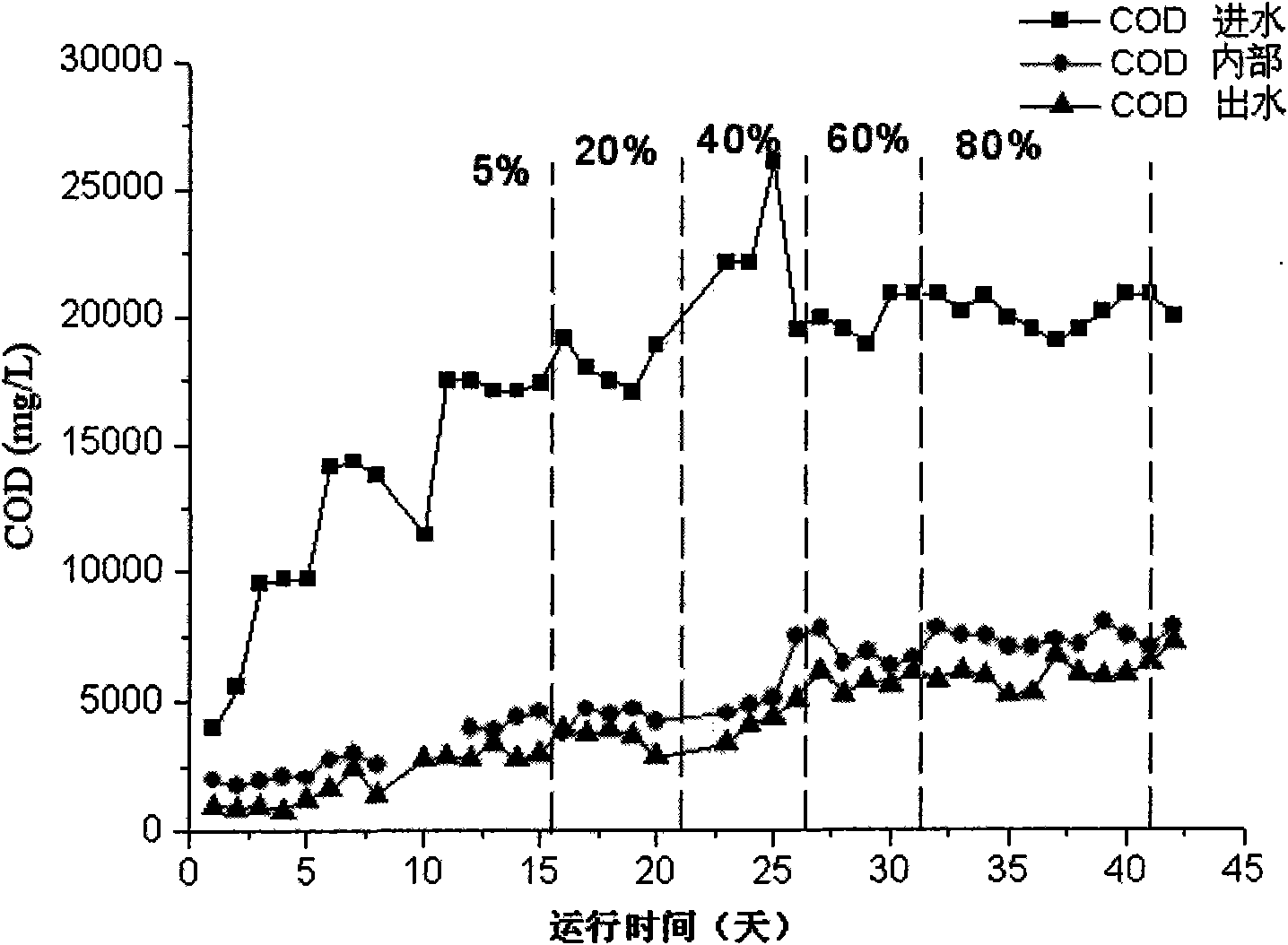
[0021] figure 1 A schematic structural diagram of an anaerobic built-in zero-valent iron reactor is shown. The device mainly includes a cylindrical anaerobic reactor 1. In the anaerobic reactor 1, a water distributor 6, three zero-valent iron filling layers 4, a biological filter layer 3 and a The three-phase separator 2 divides the inner cavity of the anaerobic reactor 1 into a gas-liquid solid separation zone 1a located above the biological filter material layer 3, a suspension zone located between the biological filter material layer 3 and the zero-valent iron filling layer 4 A sludge zone 1c and a sludge expansion zone 1d between the zero-valent iron filling layer 4 and the water distributor 6 . The shell of the anaerobic reactor 1 is made of plexiglass or FRP, with an inner diameter of 90 cm, a height of 120 cm, and an effective volume of 6.36 L. The height of the biological filter material layer 3 and the three-phase separator 2 is 10% of the effective height of the an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com