Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass through removal of inhibitory compounds
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
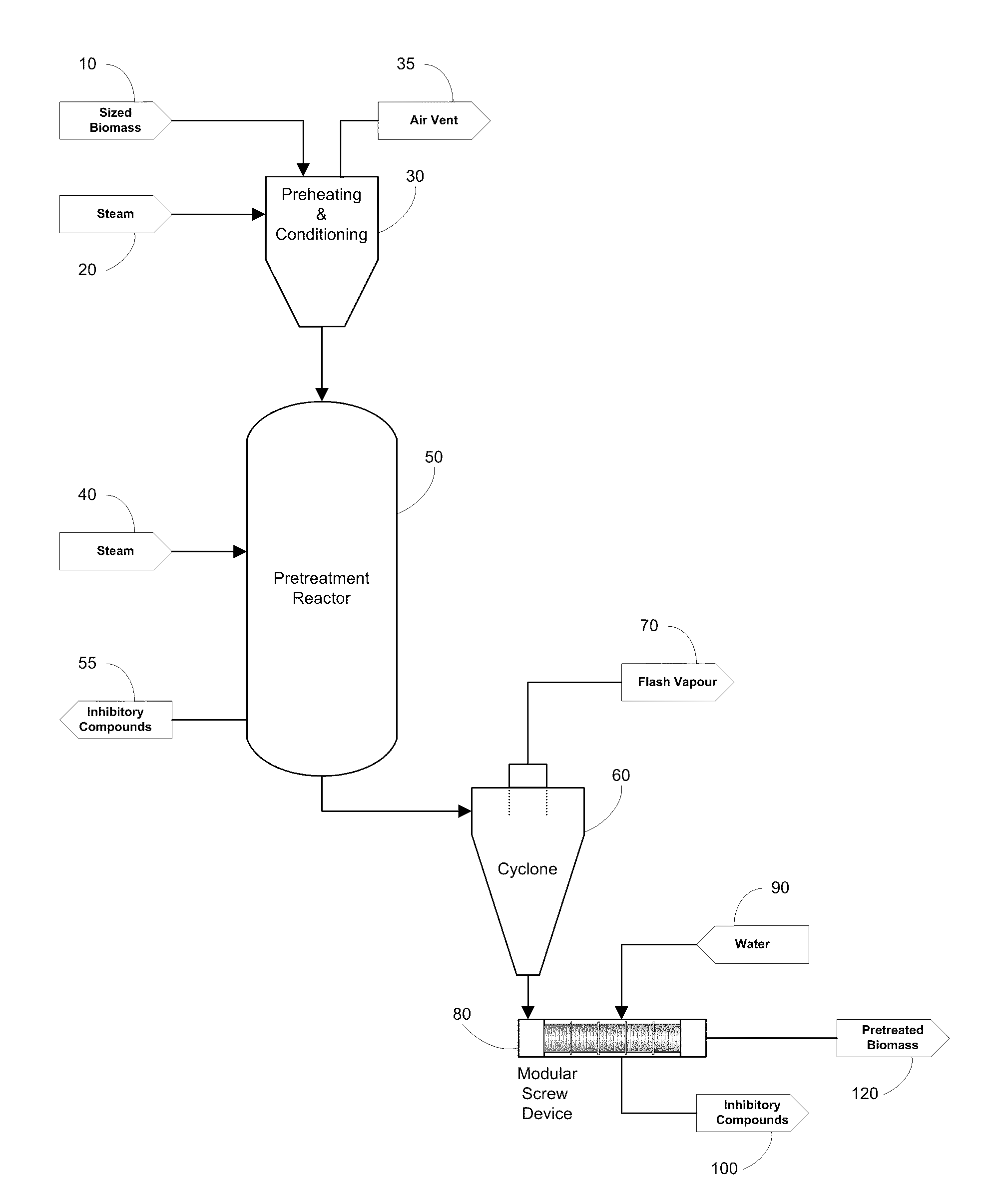
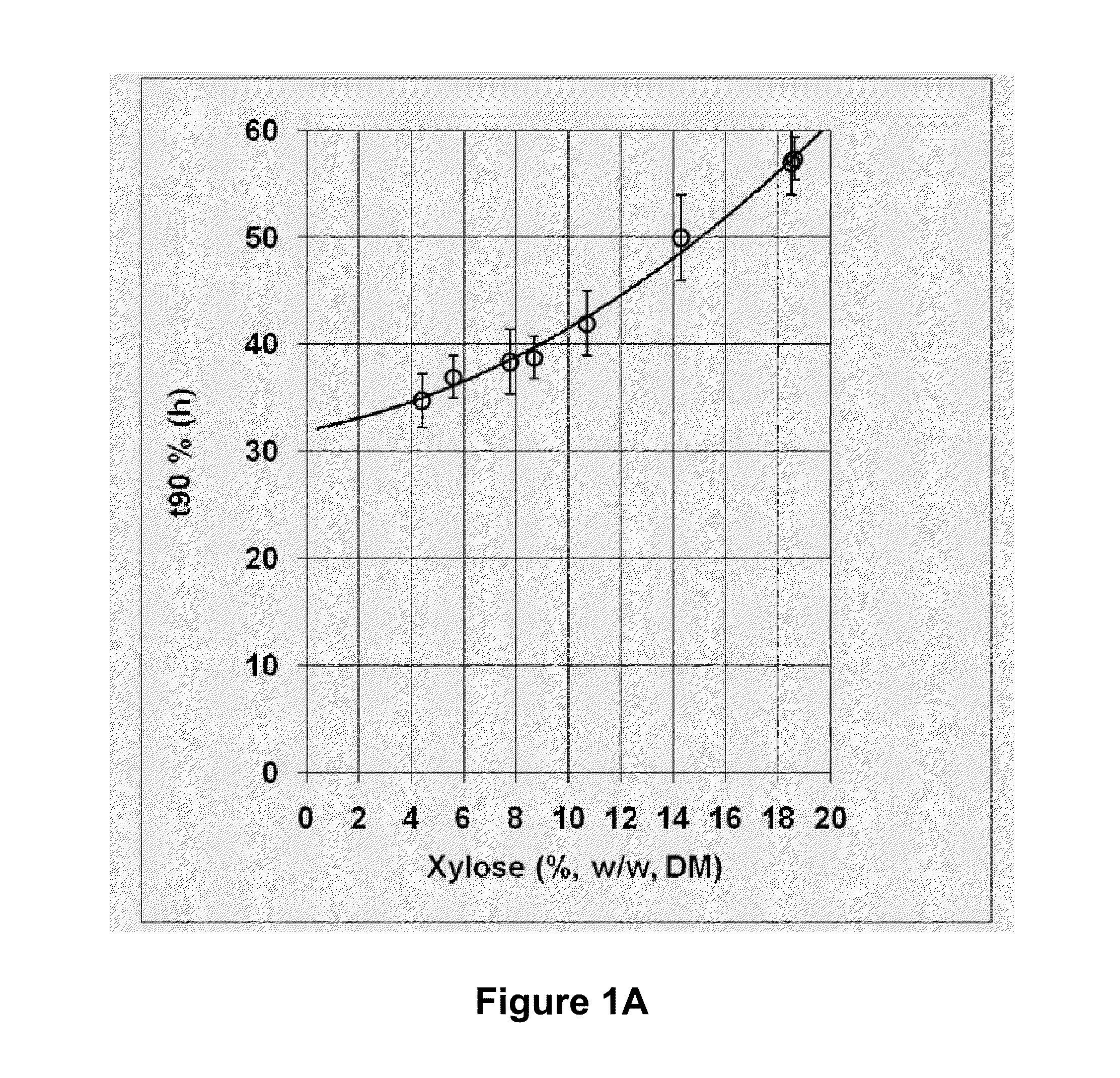
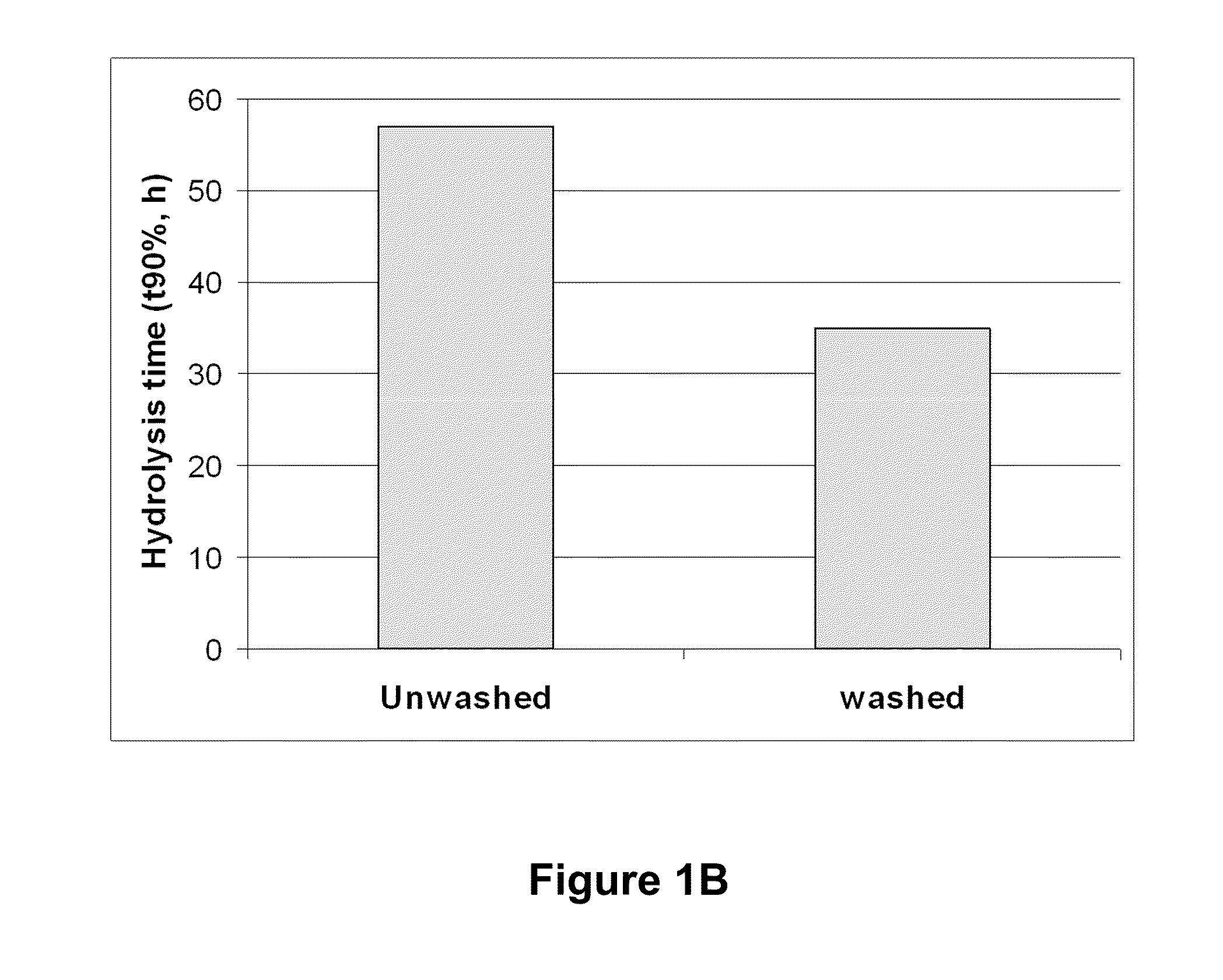
[0071]Batch steam explosion pretreatment of corncob was carried out in a steam gun (FIGS. 4A and 4B). The steam gun (50), was supplied with saturated steam from a steam storage vessel (40). Pre-steamed ground corncobs of 0.5 to 1 cm3 particle size were fed through a V shaped hopper and screw auger (from Genemco, not shown). The amount of each batch load was controlled by a weigh hopper. Batch loads of 6 kg corncob were used per steam explosion shot. Corncob weight and production rates are expressed on a dry matter basis. After filling the batch load into the steam gun (50) from above, a fill gate (not shown) was closed to seal the steam gun. Pressurized saturated steam until the desired cooking pressure was reached. Cooking pressures of 167 to 322 psig were used (12.6 to 23.2 bar). After a residence time of 3 to 10 minutes, at temperatures from 190° C. to 220° C., the pressure in the steam gun was quickly released by opening a flash purge valve (not shown) located at the bottom of t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com