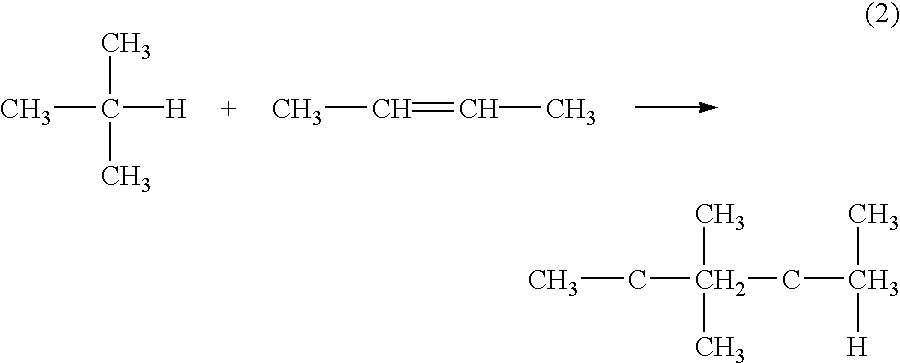Patents
Literature
212 results about "Near critical" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
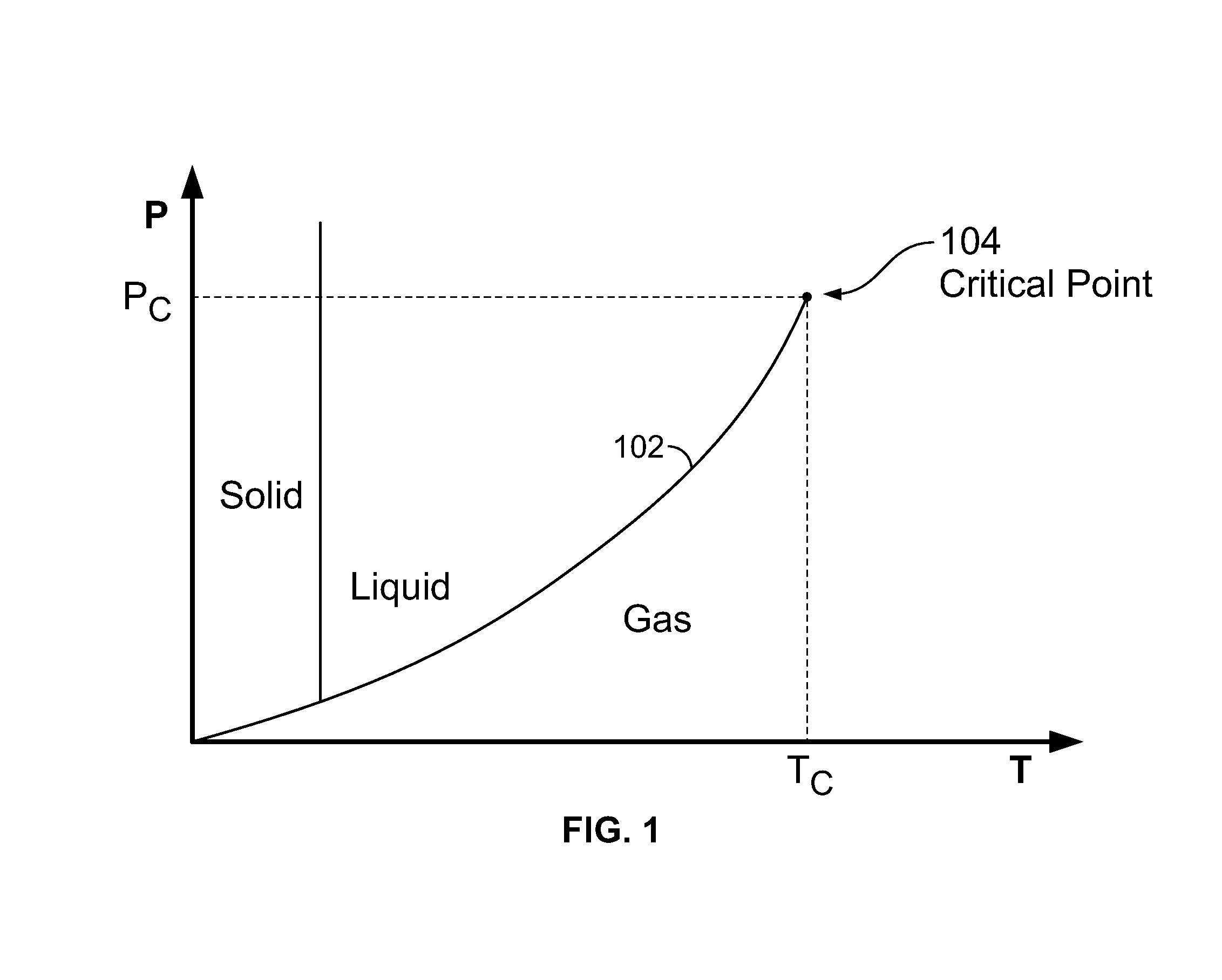
Critical fluid antimicrobial compositions and their use and generation
The present invention relates to antimicrobial compositions including a critical, near critical, or supercritical (densified) fluid and an antimicrobial agent, to methods of forming these compositions, and to methods employing these compositions. An antimicrobial agent can be generated in the presence of a densified fluid, for example, by reacting an oxidizing agent with a precursor to the antimicrobial agent.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
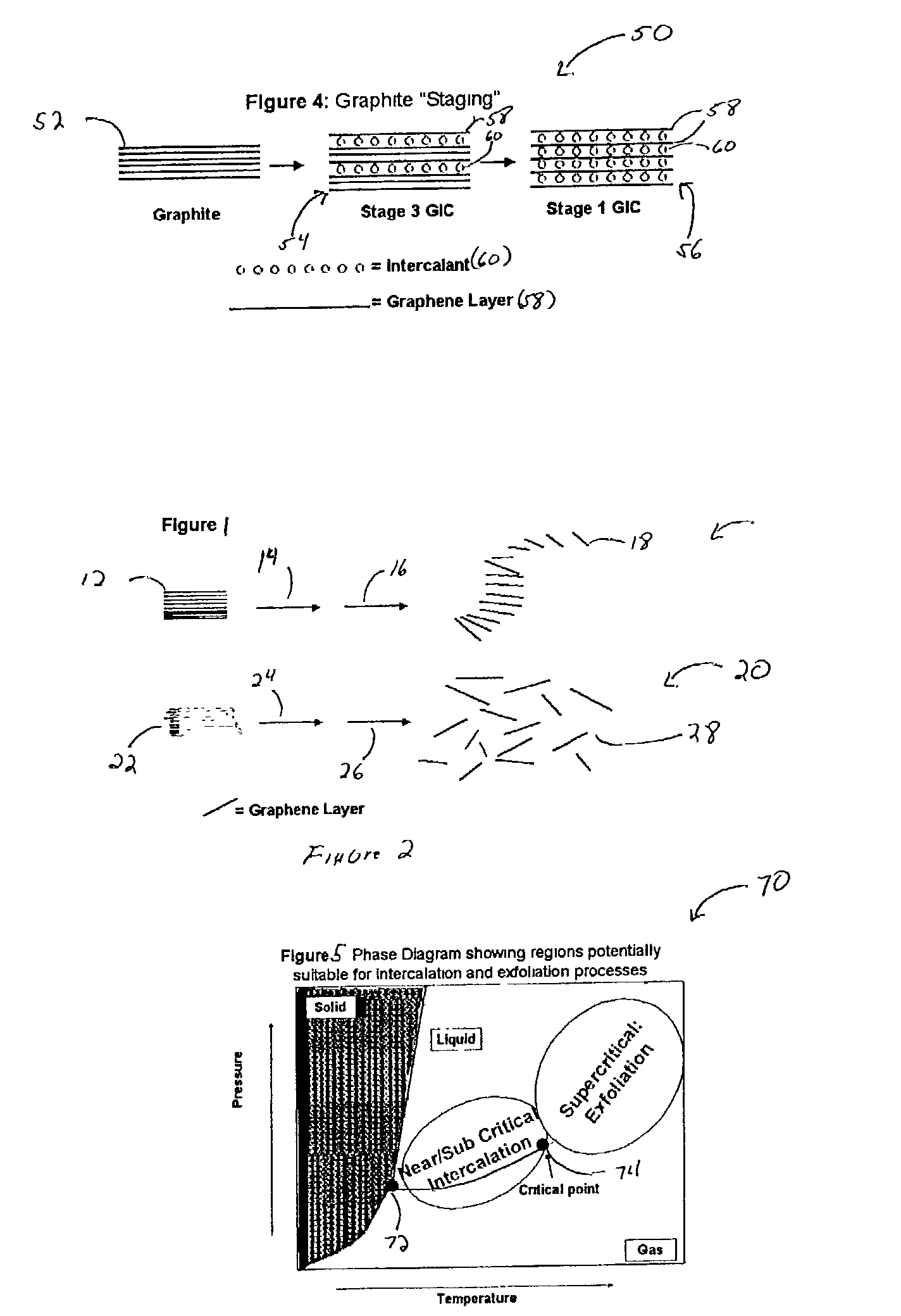
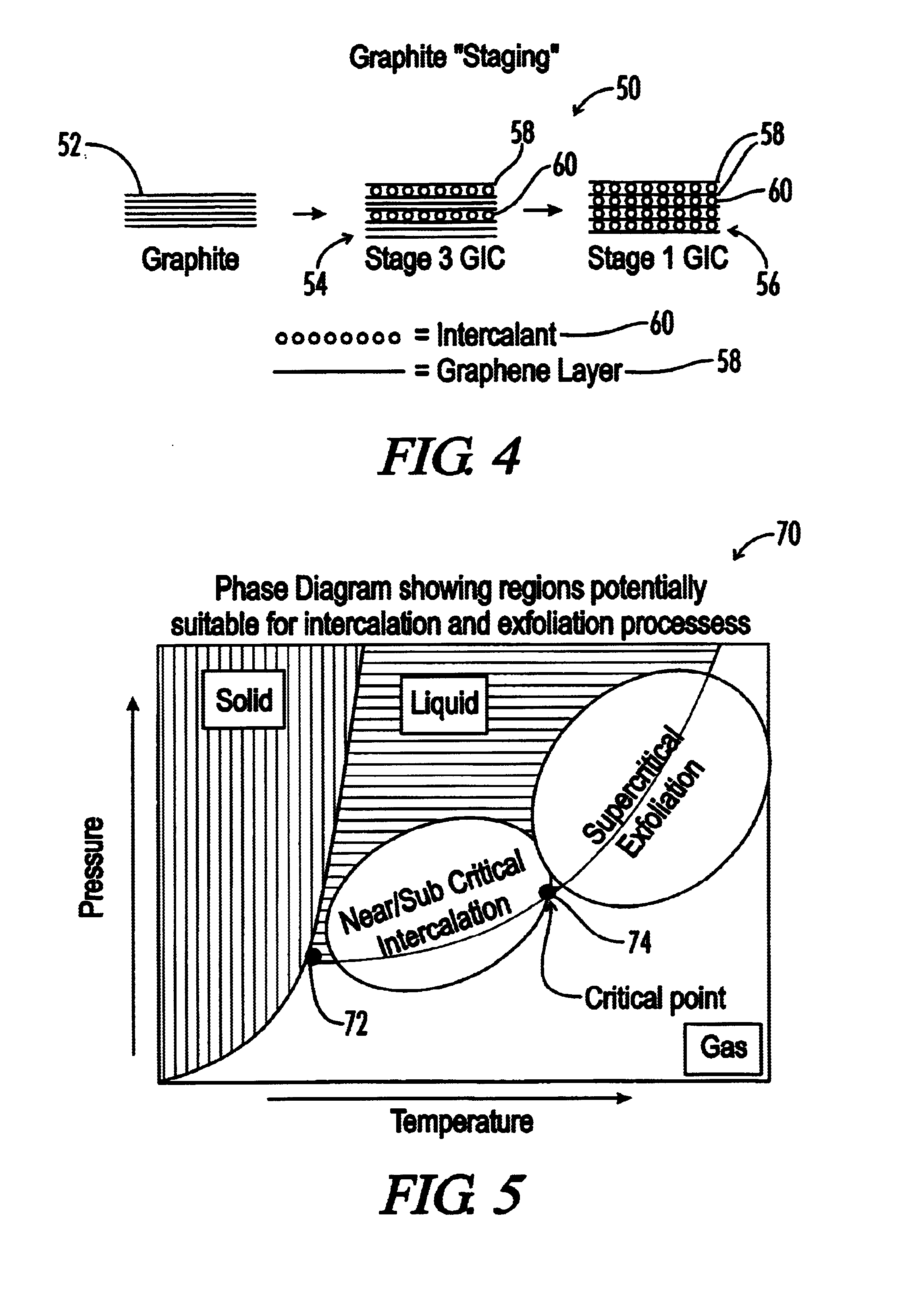
Graphite intercalation and exfoliation process
InactiveUS7105108B2Improve volume expansionReduce needMaterial nanotechnologyGraphiteConductive polymerGraphite particle
The invention relates to expanded graphite and methods of making the graphite and products that can be made from the graphite made from the inventive process. The invention includes the step of introducing a fluid into at least one of a plurality of interstices of graphite flake, wherein the fluid comprises at least one of a sub-critical point fluid, a near critical point fluid, or a supercritical fluid. The graphite flake is also intercalated with an intercalant and optionally an oxidizing agent. The invention may further include novel techniques of exfoliating the graphite. The invention may be practiced to make nano-sized graphite particles and also graphite composites. Preferred composites which may be made in accordance with the invention include conductive polymeric composites (thermally or electrically), paint composites, battery composites, capacitor composites, and pollution abatement catalyst support composites.
Owner:GRAFTECH INT HLDG INC
Methods of oxidizing multiwalled carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20050002850A1Good electrochemical propertiesSpecificMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolytic capacitorsMultiwalled carbonChlorine dioxide
Methods of oxidizing multiwalled carbon nanotubes are provided. The multiwalled carbon nanotubes are oxidized by contacting the carbon nanotubes with gas-phase oxidizing agents such as CO2, O2, steam, N2O, NO, NO2, O3, and ClO2. Near critical and supercritical water can also be used as oxidizing agents. The multiwalled carbon nanotubes oxidized according to methods of the invention can be used to prepare rigid porous structures which can be utilized to form electrodes for fabrication of improved electrochemical capacitors.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Depth profile metrology using grazing incidence X-ray fluorescence
InactiveUS6173036B1X-ray spectral distribution measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansMetrologyMicro-X-ray fluorescence
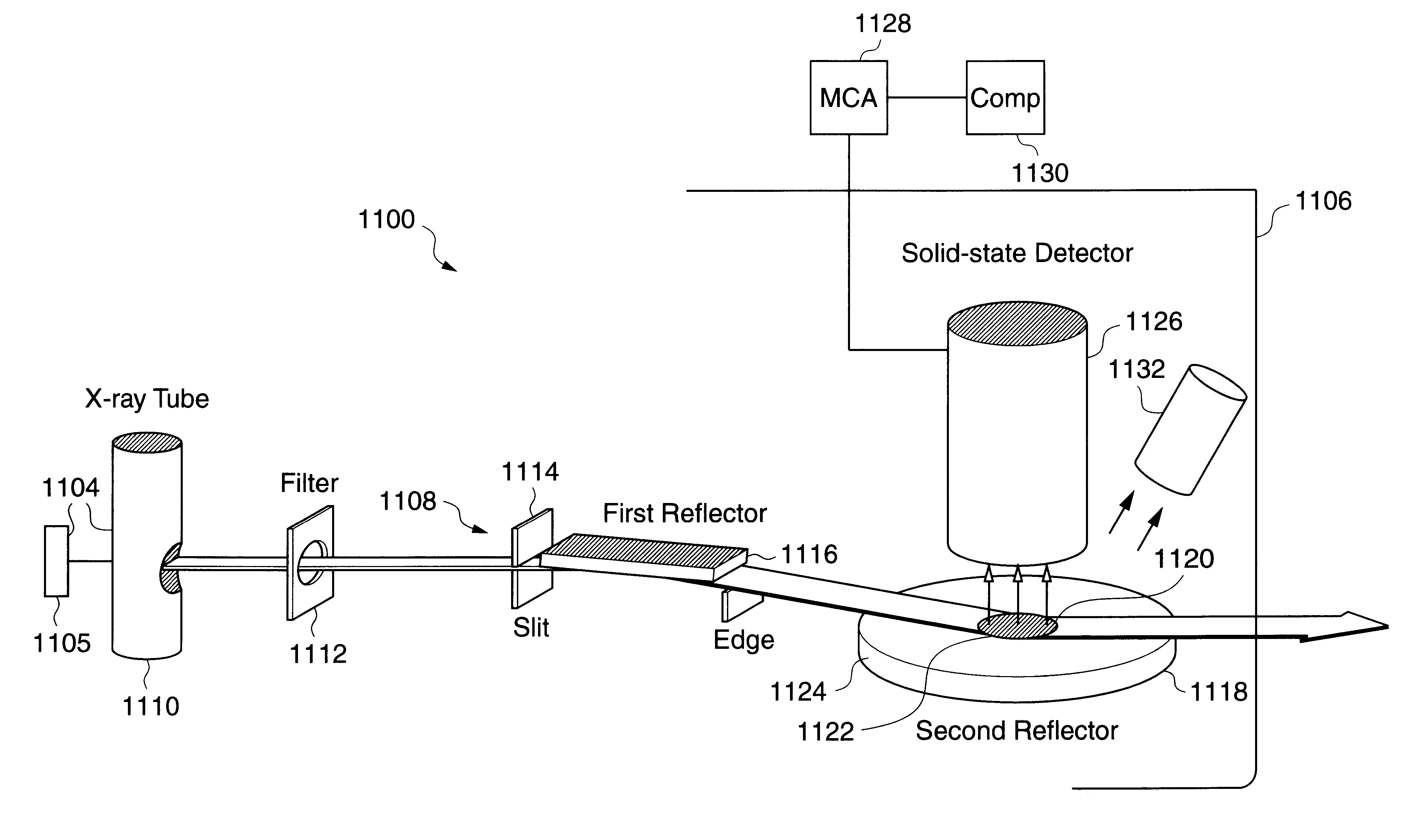
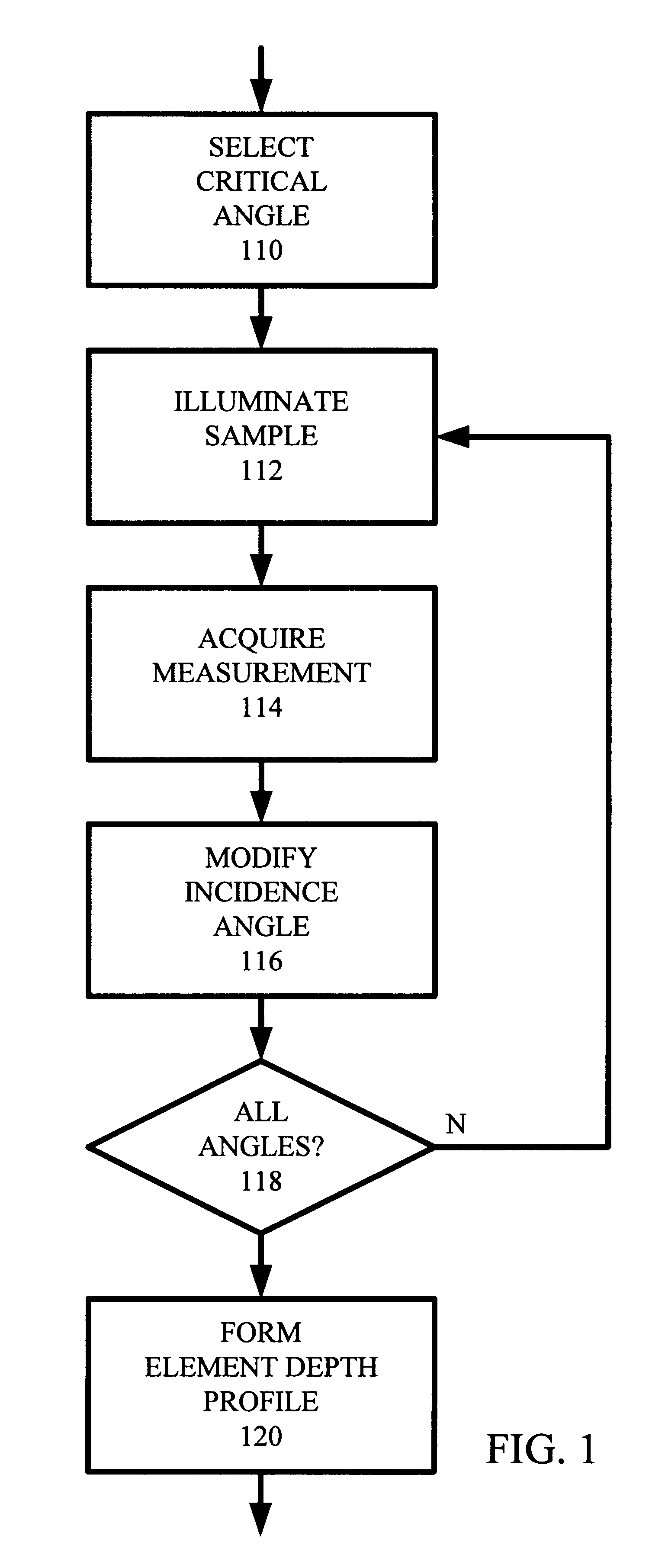
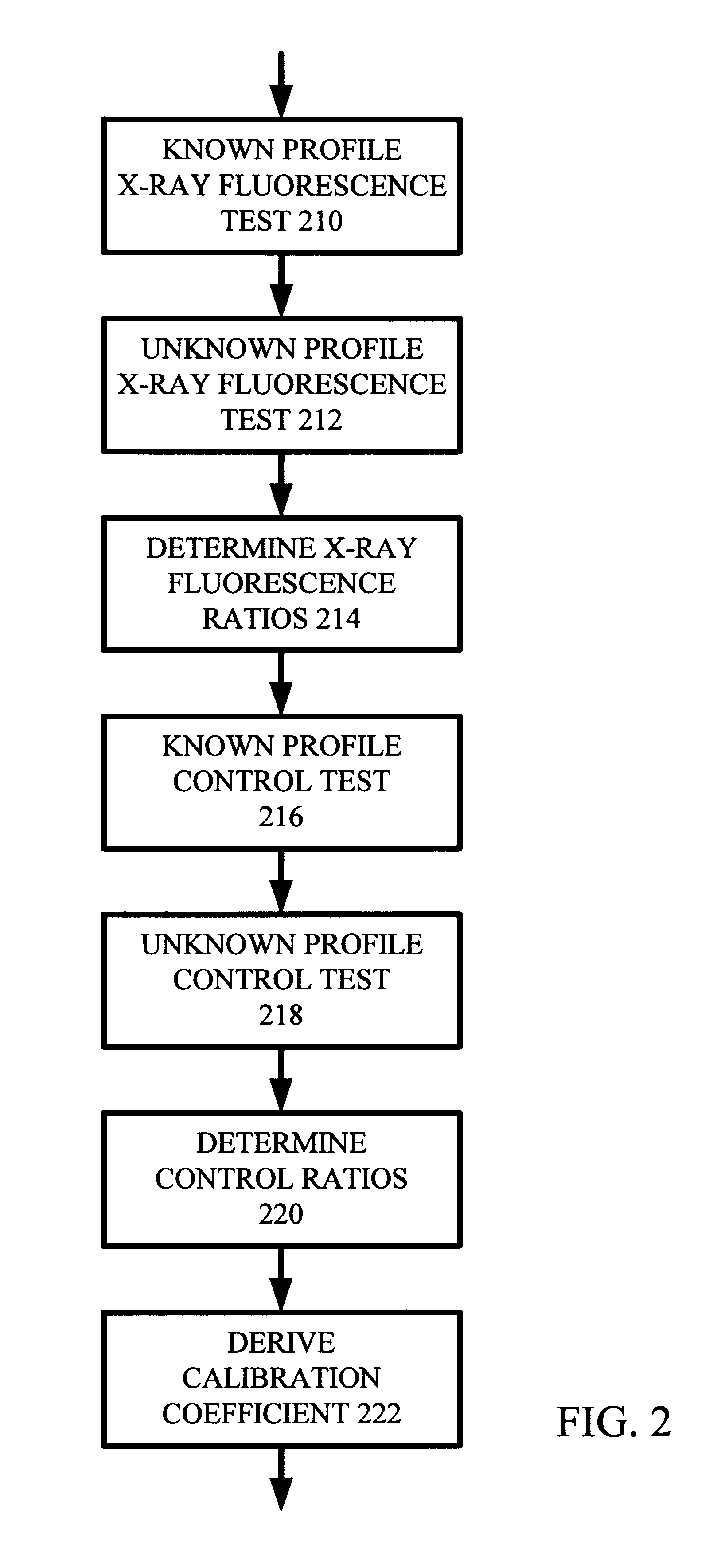
For small angles that are near critical angle, a primary incident X-ray beam has excellent depth resolution. A series of X-ray fluorescence measurements are performed at varying small angles and analyzed for depth profiling of elements within a substrate. One highly useful application of the X-ray fluorescence measurements is depth profiling of a dopant used in semiconductor manufacturing such as arsenic, phosphorus, and boron. In one example, angles are be varied from 0.01° to 0.20° and measurements made to profile arsenic distribution within a semiconductor wafer. In one embodiment, measurements are acquired using a total reflection X-ray fluorescence (TXRF) type system for both known and unknown profile distribution samples. The fluorescence measurements are denominated in counts / second terms and formed as ratios comparing the known and unknown sample results. The count ratios are compared to ratios of known to unknown samples that are acquired using a control analytical measurement technique. In one example the control technique is secondary ion mass spectroscopy (SIMS) so that the count ratios from the TXRF-type measurements are compared to ratios of integrals of SIMS profiles. In another example, the TXRF-type measurement ratios are compared to simulation profiles of known samples. Integrals of the SIMS profile that vary as a function of depth into the substrate correspond to the grazing incidence angles of the TXRF-like measurement and respective count rates.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Graphite composites and methods of making such composites
InactiveUS6927250B2Improve volume expansionReduce needSpecial tyresBulk chemical productionConductive polymerPolymer composites
The invention may be practiced to make graphite composites. Preferred composites which may be made in accordance with the invention include conductive polymeric composites (thermally or electrically), paint composites, battery composites, capacitor composites, and pollution abatement catalyst support composites. One method of making the graphite aforementioned composites includes introducing an intercalant into at least one interstice of at least one flake of natural graphite. The method also includes introducing a fluid into the at least one interstices of the flake. Preferably, the fluid comprises at least one of a sub-critical fluid, near critical point fluid, or a supercritical fluid. Furthermore the method includes blending the flake with a polymer, thereby forming a graphite-polymeric composite.
Owner:GRAFTECH INT HLDG INC
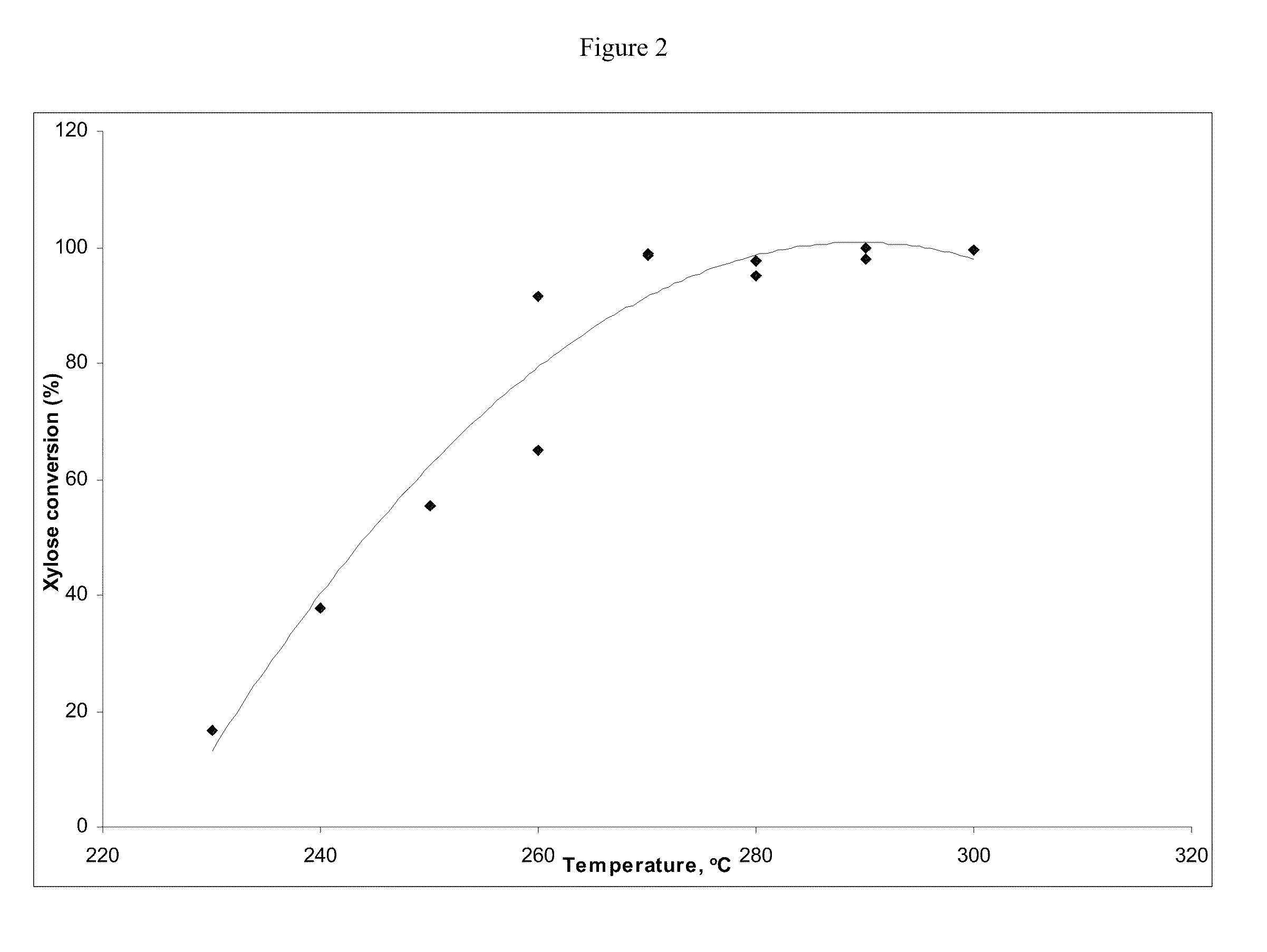
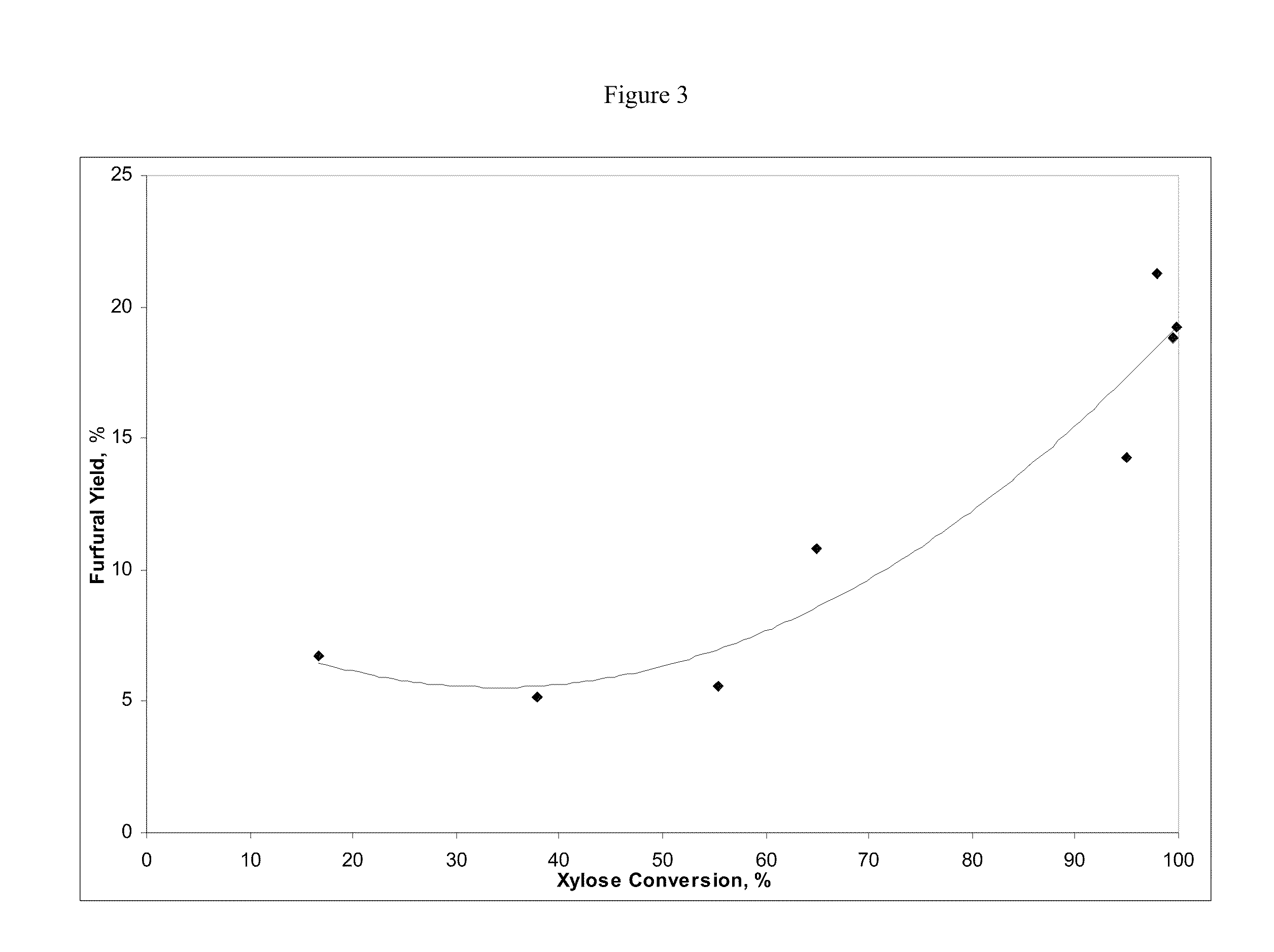
Solvo-thermal hydrolysis of xylose
ActiveUS20100048924A1Rapid coolingOrganic chemistryChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesSolventFurfural
The invention relates to a process for producing furfural from xylose comprising: (a) mixing an aqueous xylose solution containing xylose oligosaccharides with sub-critical or near-critical water to form a mixture at a first temperature and a first pressure; (b) maintaining the mixture at the first temperature and the first pressure for a first time period; and (c) rapidly cooling the mixture to a second temperature and a second pressure, wherein furfural is produced by the process (d) process can also be carried out with or without mixing of carbon dioxide with aqueous xylose solution before it is mixed with sub-critical or near-critical water to form a mixture at a first temperature and pressure.
Owner:RENMATIX INC
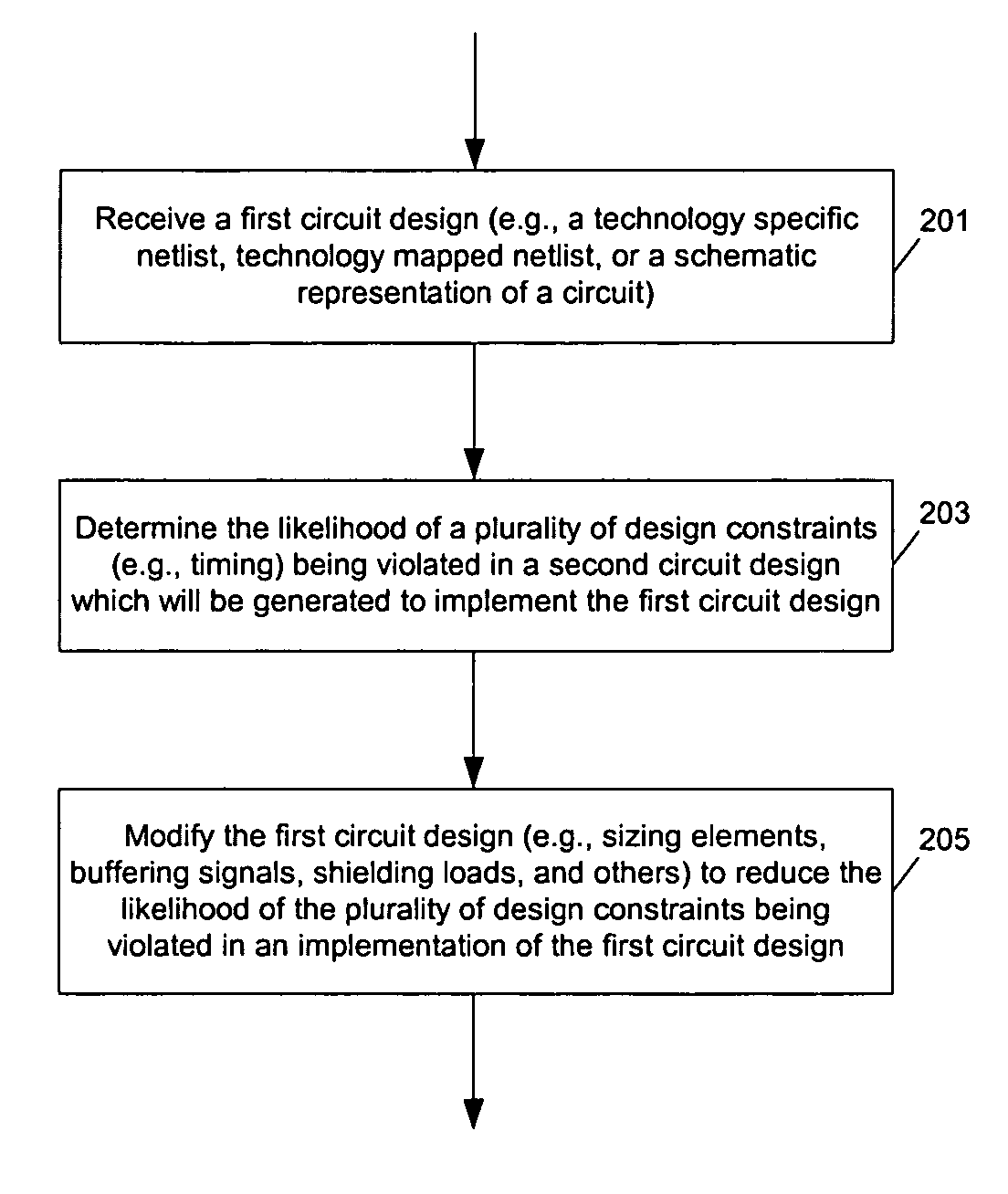
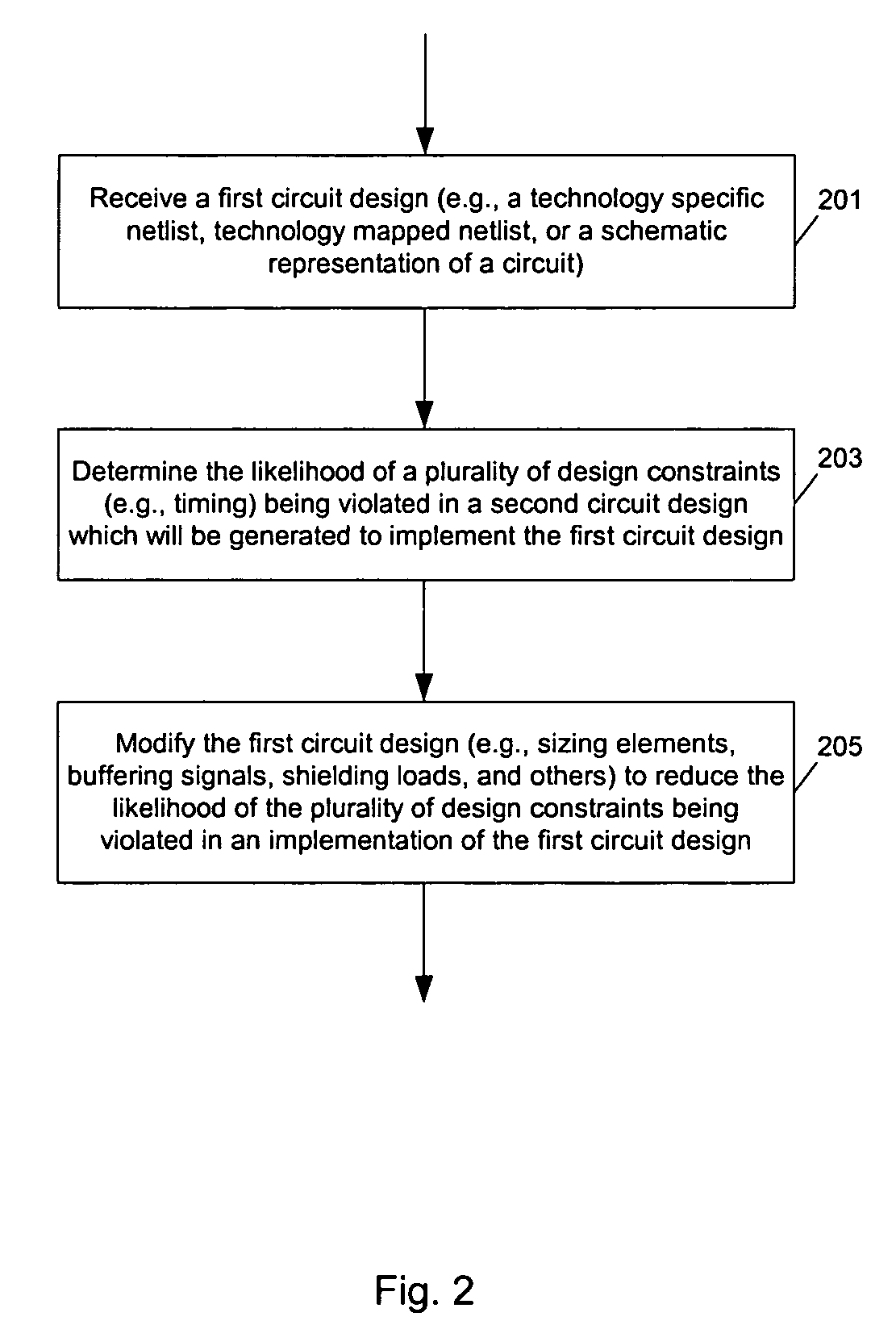
Method and apparatus for automated circuit design
ActiveUS7251800B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCritical path methodCircuit design
Methods and apparatuses to automatically modify a circuit design according to the possible deviation in the subsequent implementation of the circuit. In one aspect, a method to design a circuit includes: determining whether a design constraint is likely to be violated during a subsequent routing implementation of a design of the circuit; and, modifying the design of the circuit to reduce likelihood of the design constraint being violated during a subsequent implementation. For example, a route for a net with a number of fanout larger than two and on a timing critical or near-critical path may be considered sensitive to route topology such that an alternative routing path may lead to a violation in timing constraint; to reduce the possibility of a timing problem in a subsequent routing solution, a transformation can be selectively applied to the circuit design to an extent not worsening a cost function.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
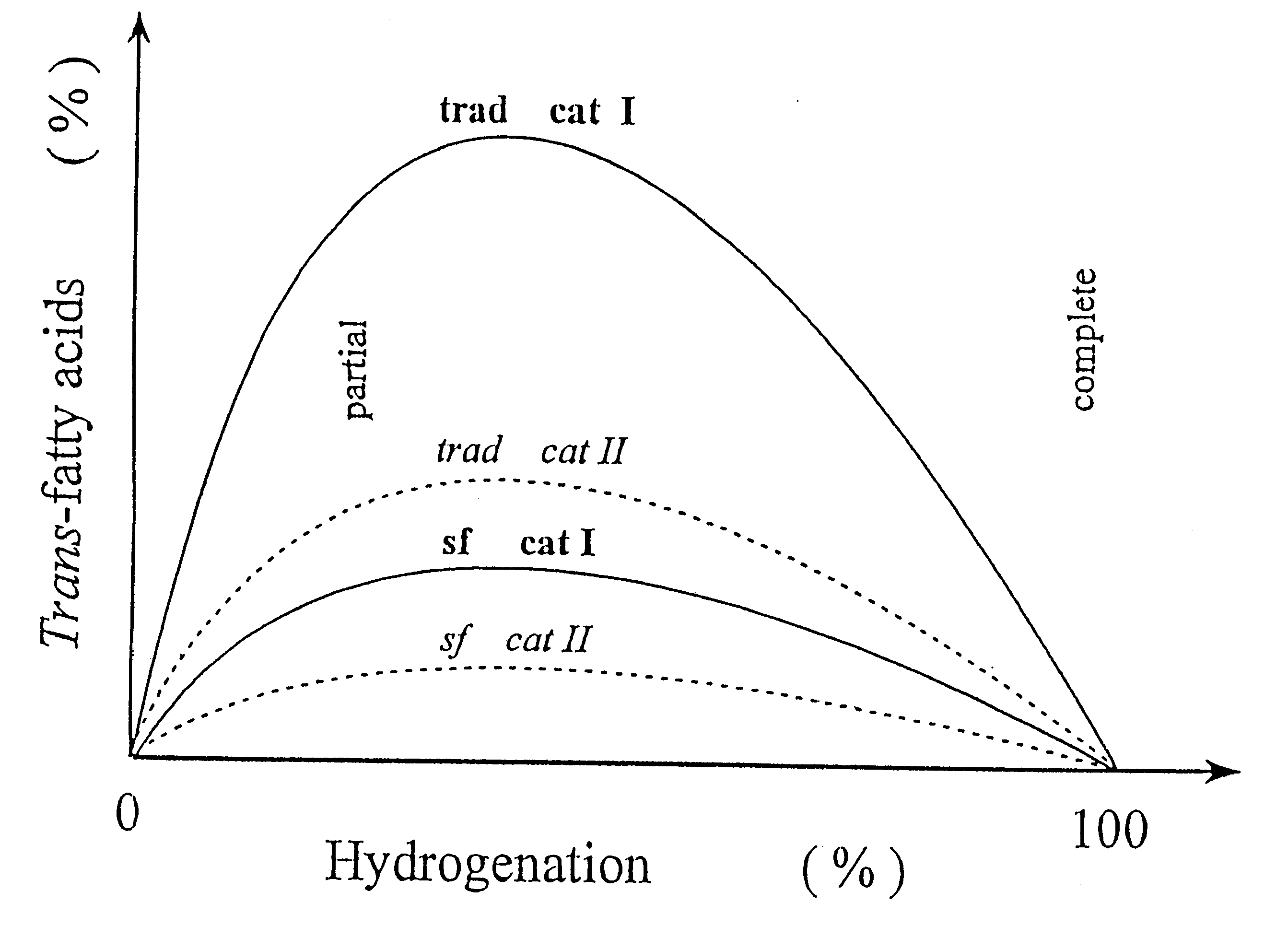
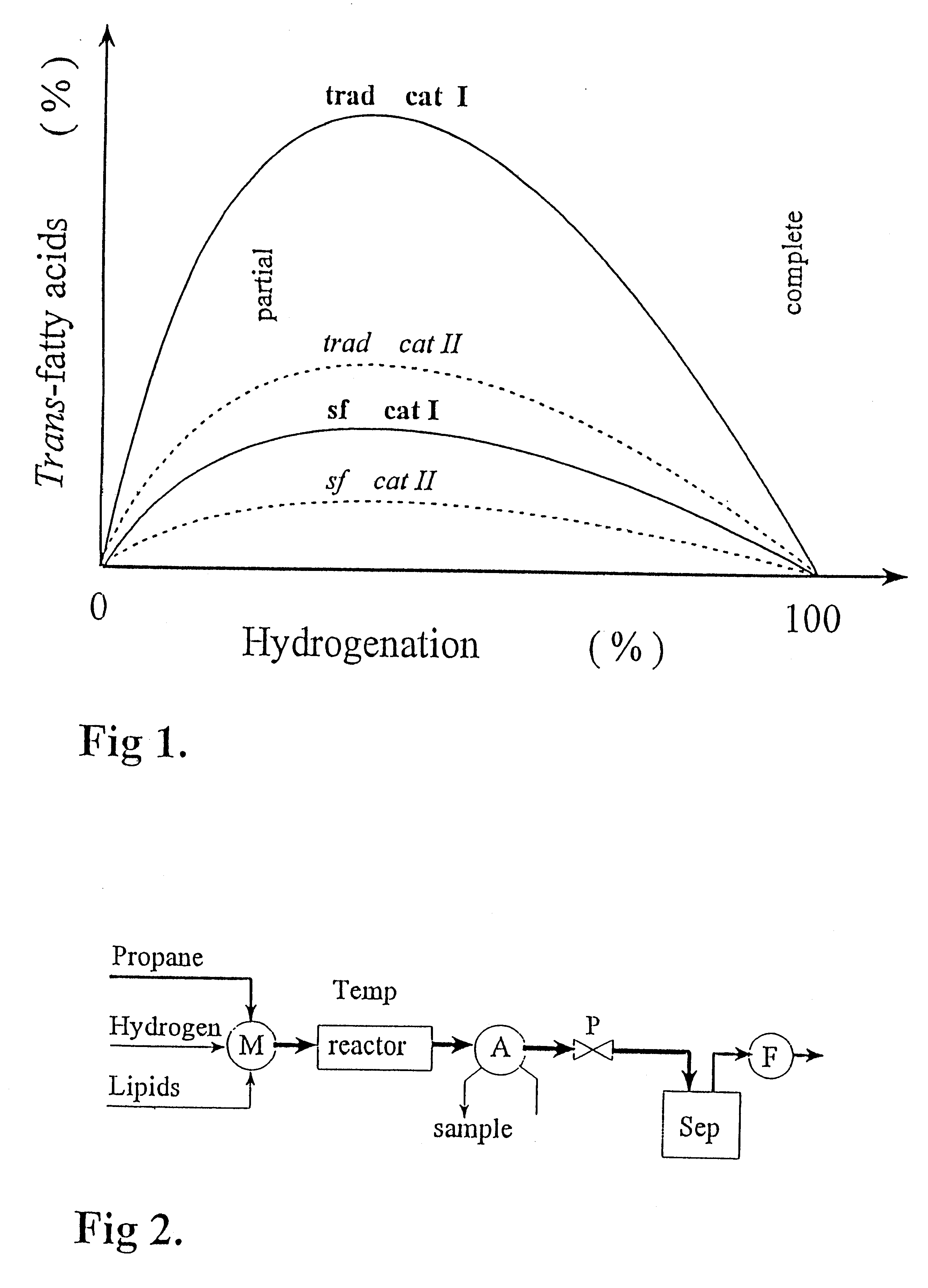
Partially hydrogenated fatty substances with a low content of trans fatty acids
A partially hydrogenated fatty substance produced by partial hydrogenation of a substrate, such as vegetable, animal or marine oil, said partially hydrogenated substance having a low content of trans fatty acids. When the hydrogenation degree is below 30% the trans-fatty acid concentration can be expressed in the following way: trans<=0.3x(initial IV-IV) in %. of the total amount of fatty acids, wherein IV refers to iodine value. When the hydrogenation degree is between 30 and 70% the trans-fatty acid concentration can be expressed with: trans<=0.09xinitial IV in % of the total amount of fatty acids. The partial hydrogenation is performed by a process in which the substrate, hydrogen gas and a solvent are mixed, and the whole mixture is brought into a supercritical or near-critical state. This substantially homogeneous super-critical or near-critical solution is led over the catalyst, whereby the reaction products formed, i.e. the hydrogenated substrates, will also be a part of the substantially homogeneous super-critical or near-critical solution.
Owner:POUL MOLLER LEDELSES OG INGENIORRADGIVNING APS
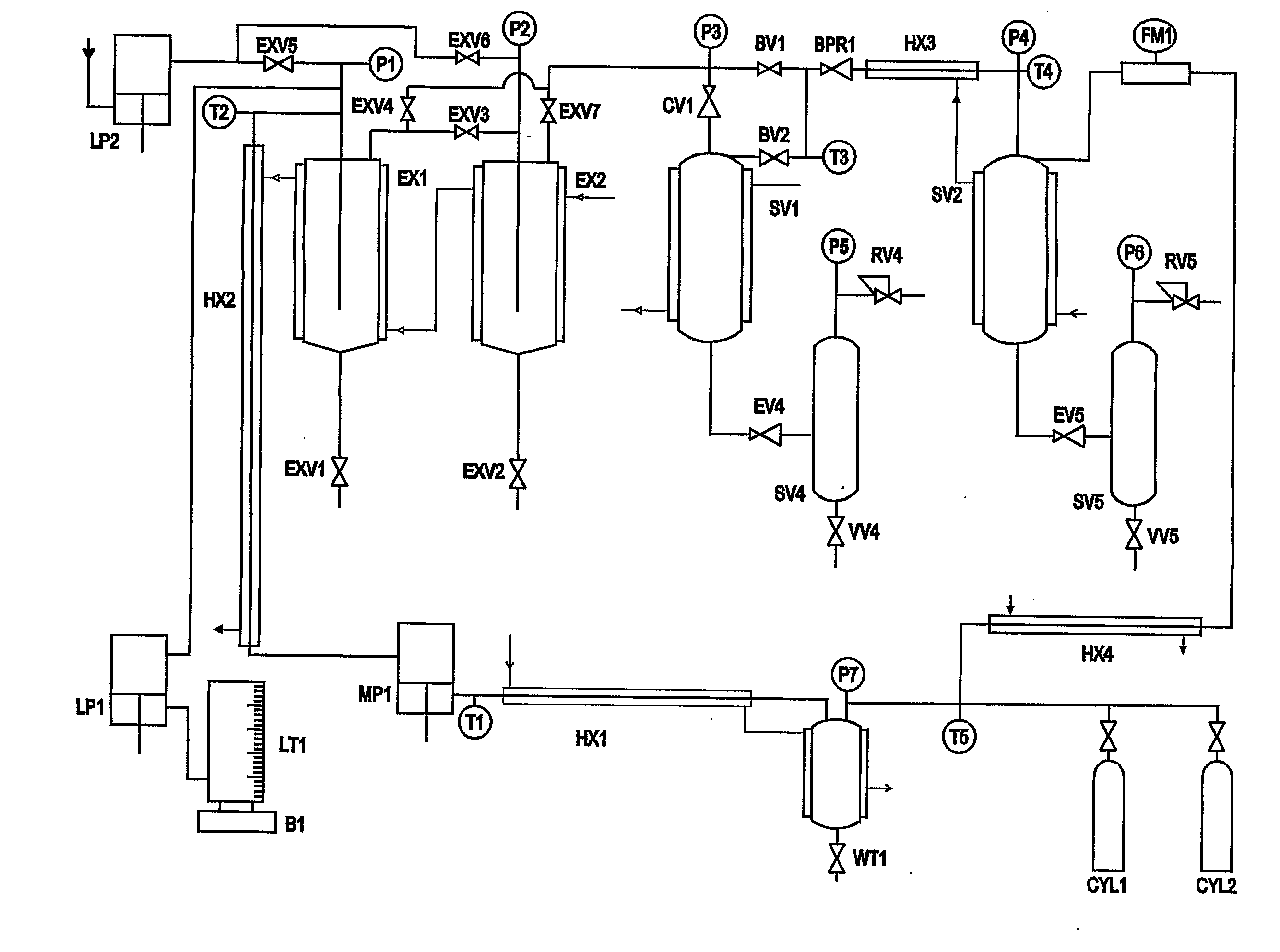
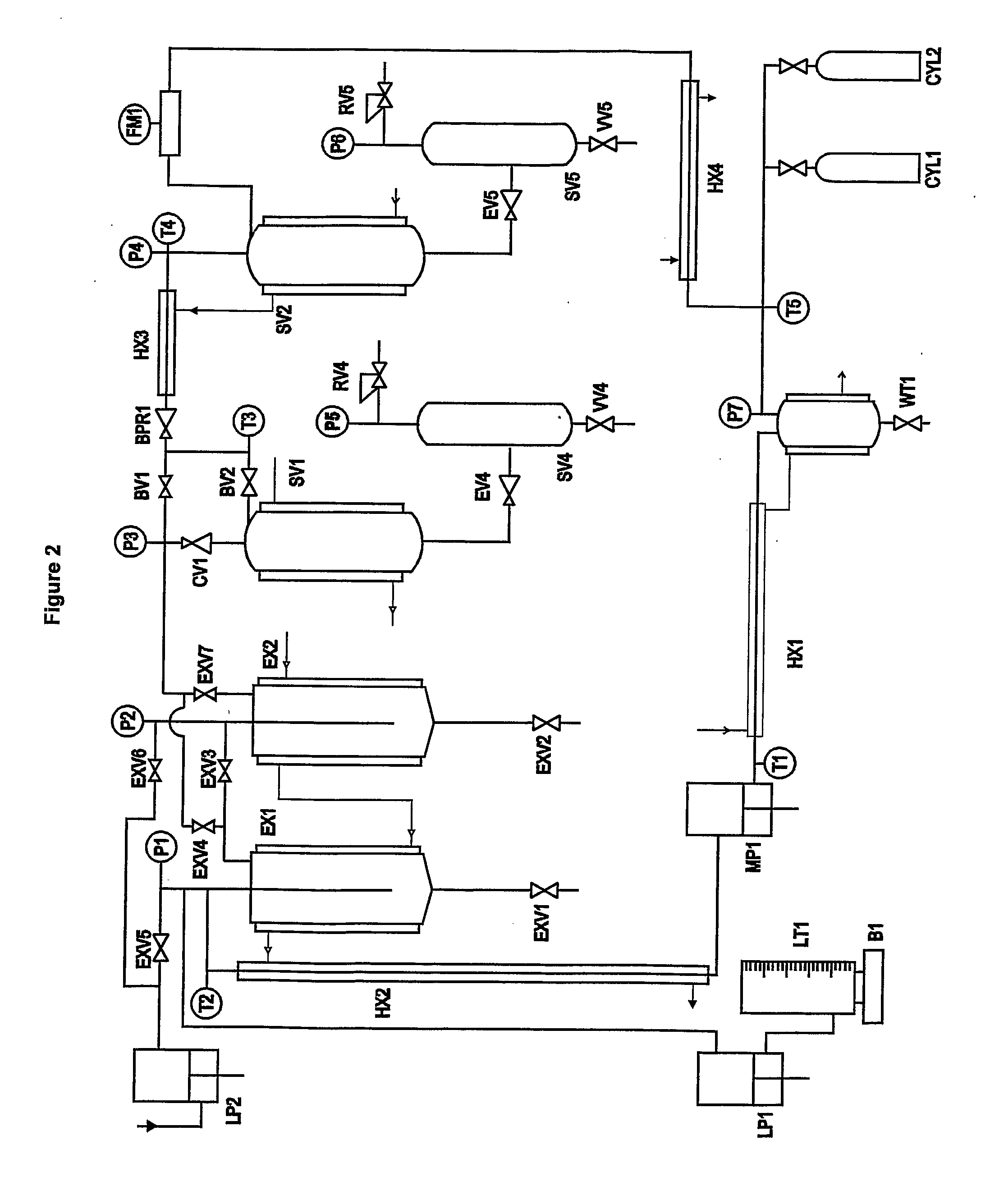
Methods and apparatus for particle formation
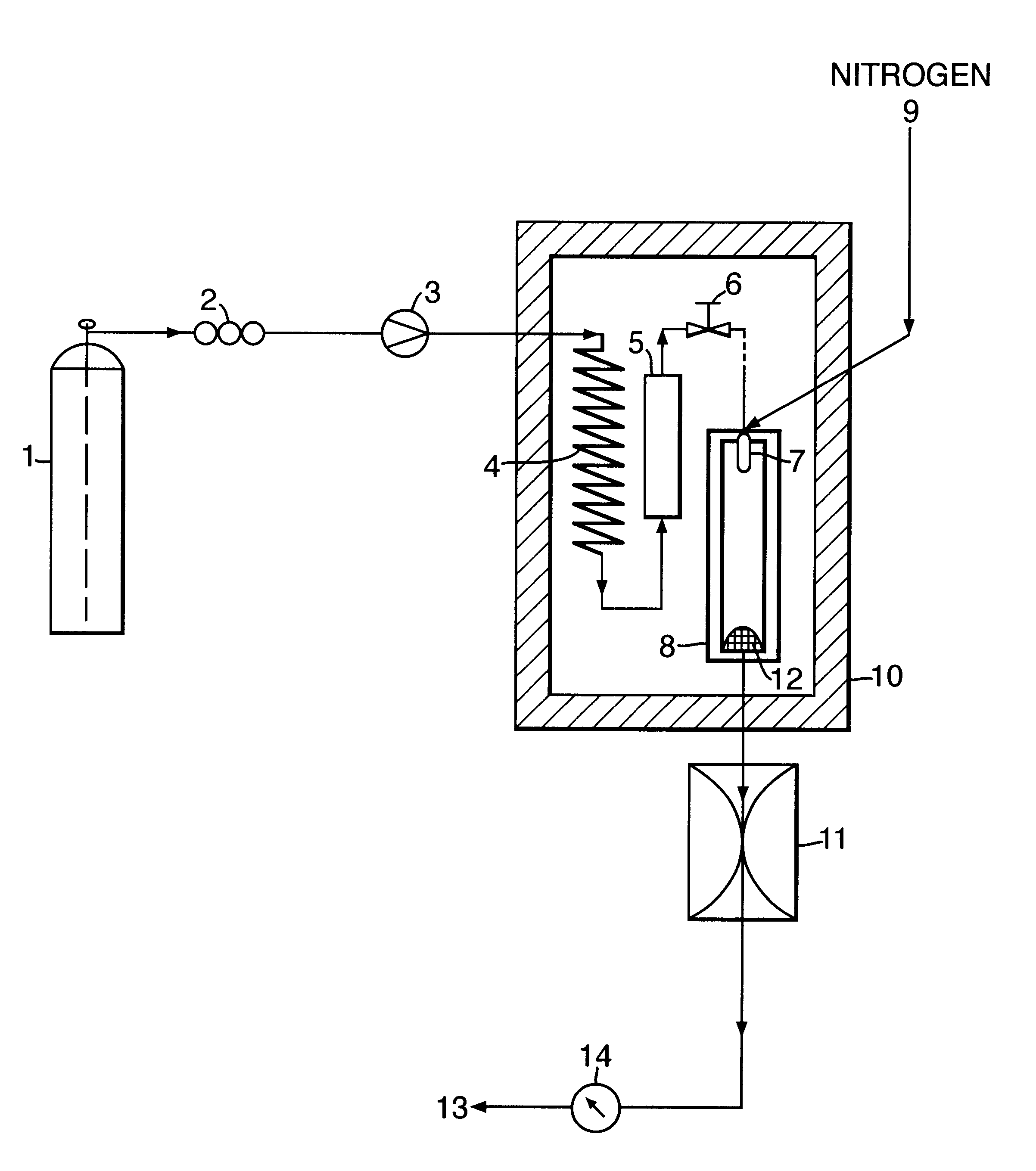
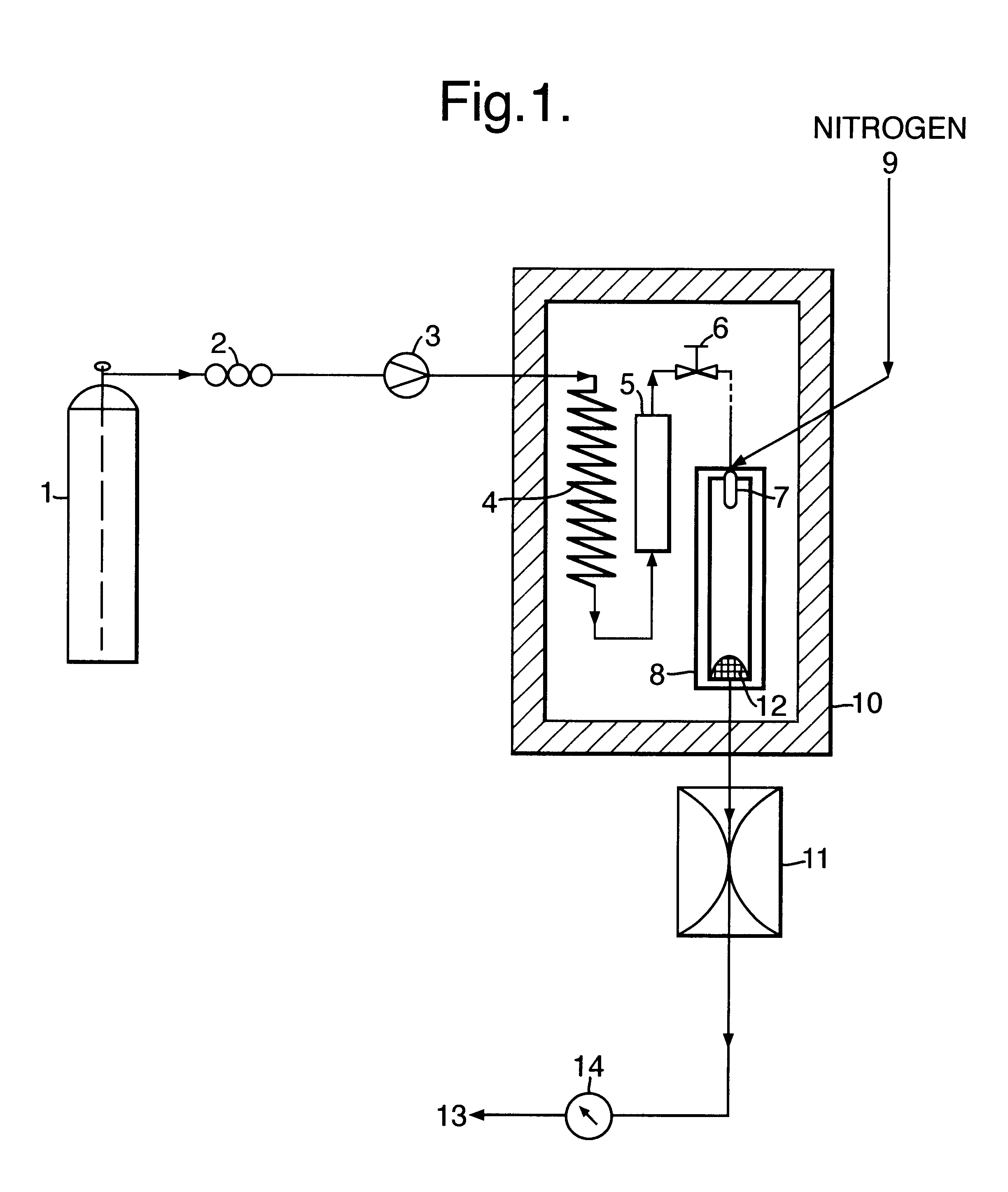
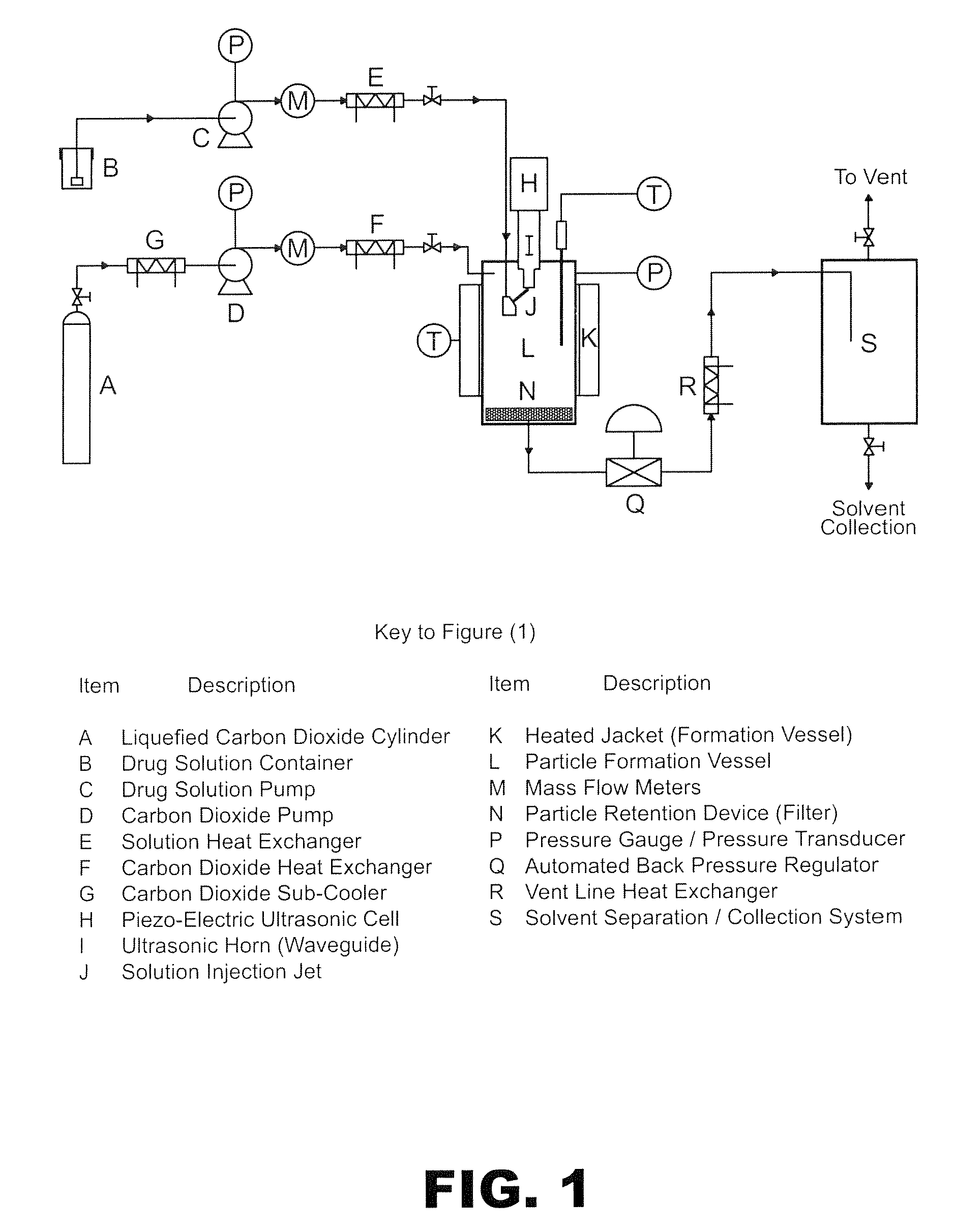
The invention provides a method for forming particles of a target substance (26), involving: (a) preparing a solution or suspension of the substance in a vehicle (21) which is or includes either a near-critical fluid (21) or a first supercritical fluid; (b) introducing the solution or suspension into a particle formation vessel (32); and (c) contacting the solution or suspension, in the particle formation vessel, with a second super-critical fluid, under conditions which allow the second supercritical fluid to cause precipitation of particles of the target substance from the solution or suspension; wherein the second supercritical fluid is miscible or substantially miscible with the vehicle and is a fluid in which the target substance is insoluble or substantially insoluble. Also provided is apparatus for use in carrying out an embodiment of the method, including a particle formation vessel and means for controlling the temperature and pressure inside it; a fluid mixing vessel and means for controlling the temperature and pressure inside it; first fluid inlet means for introducing into the fluid mixing vessel a vehicle and a solution of a target substance in a primary solvent, so as to form in the fluid mixing vessel a solution of the substance and the primary solvent in the vehicle; and second fluid inlet means for introducing the solution thus formed, preferably together with a second supercritical fluid, into the particle formation vessel. The invention also provides a particulate product formed using the method.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for underground in-situ extraction of hydrocarbon compound in oil shale
The invention relates to a method for the underground in-situ extraction of a hydrocarbon compound in an oil shale, which comprises the following steps: arranging at least one working well and one production well in an enclosed working region where the hydrocarbon compound in the oil shale is extracted, communicating the bottoms among the working wells by directional drilling after a drilling well enters an oil shale ore layer, injecting water and inert gas water vapor into the working well to form a near-critical water microenvironment, cracking the oil shale into organic compounds with different chain lengths to form an oil-water mixture, lifting the oil-water mixture to the ground through the production well, and obtaining the hydrocarbon compound through an oil-water separating system. The heat utilization ratio is improved through a multi-well integrated heat circulating system, the extraction ratio of hydrocarbon substances is greatly improved through repeated oil-water separating and circulating processes, and the technical process is shortened. A water micro-pool is formed after an oil shale layer is overflowed by water, the cracking of the oil shale can be realized within3 to 5 hours after a near-critical state is reached, and more energy sources and time are saved than an underground dry distillation method.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method of particle formation
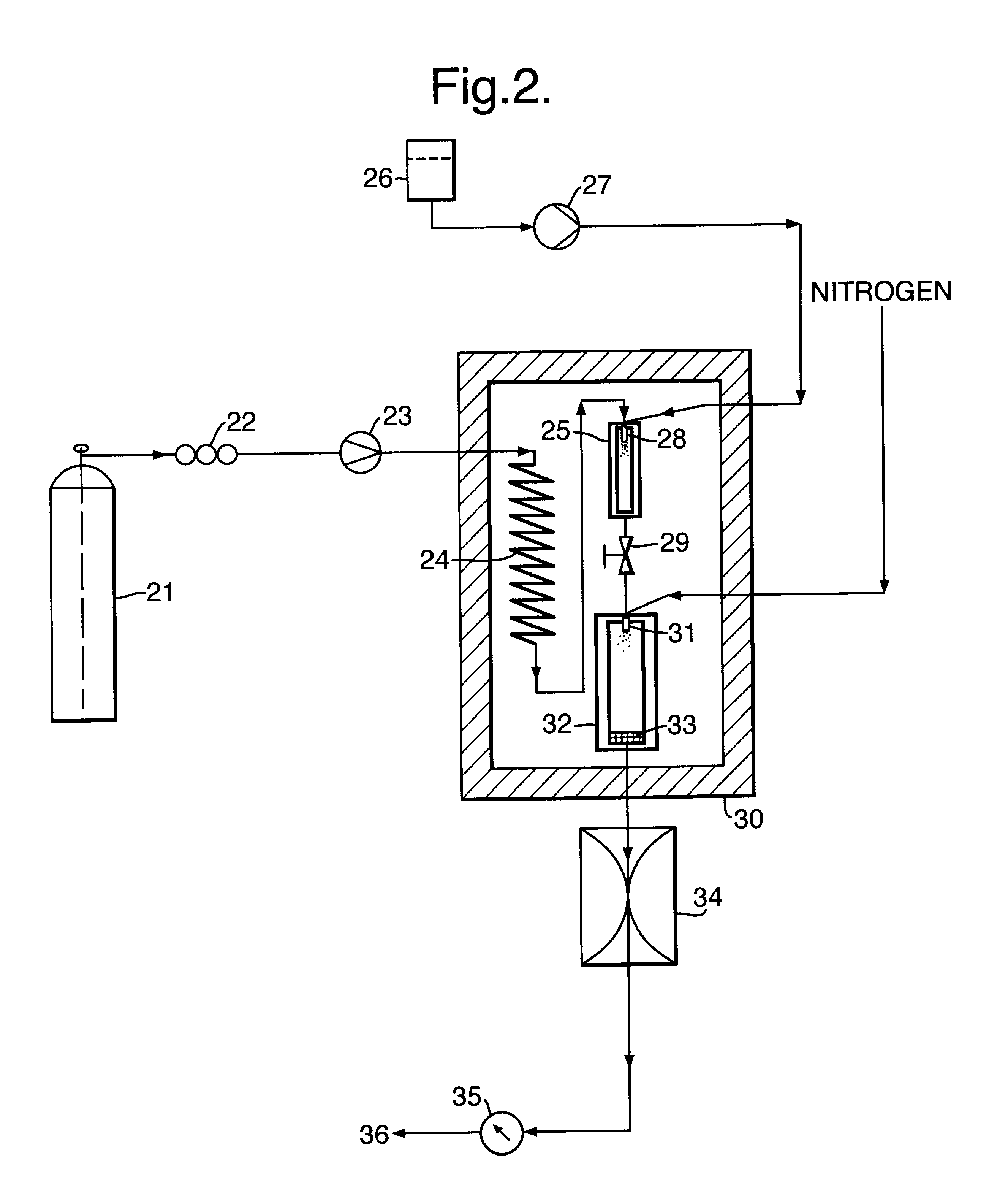
InactiveUS20050206023A1Characteristic is differentSufficient flow ratePressurized chemical processPeptide/protein ingredientsAnti solventTemperature and pressure
The invention provides a method for forming particles of a target substance, comprising (a) co-introducing into a particle formation vessel, under controlled temperature and pressure, a supercritical or near-critical anti-solvent fluid; a “target solution or suspension” of the target in a first vehicle; and a second vehicle which is soluble in the anti-solvent fluid; and (b) using the anti-solvent to disperse the target solution / suspension and the second vehicle, and to extract the vehicles, substantially simultaneously and substantially immediately on introduction of the fluids into the particle formation vessel, wherein the second vehicle is immiscible with the first, and wherein contact between the target solution / suspension and the second vehicle occurs a sufficiently short period of time before their dispersion by the anti-solvent, and with sufficient physical mixing, as to allow only insignificant, if any, phase separation to occur between the two vehicles between their contact with one another and their dispersion.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
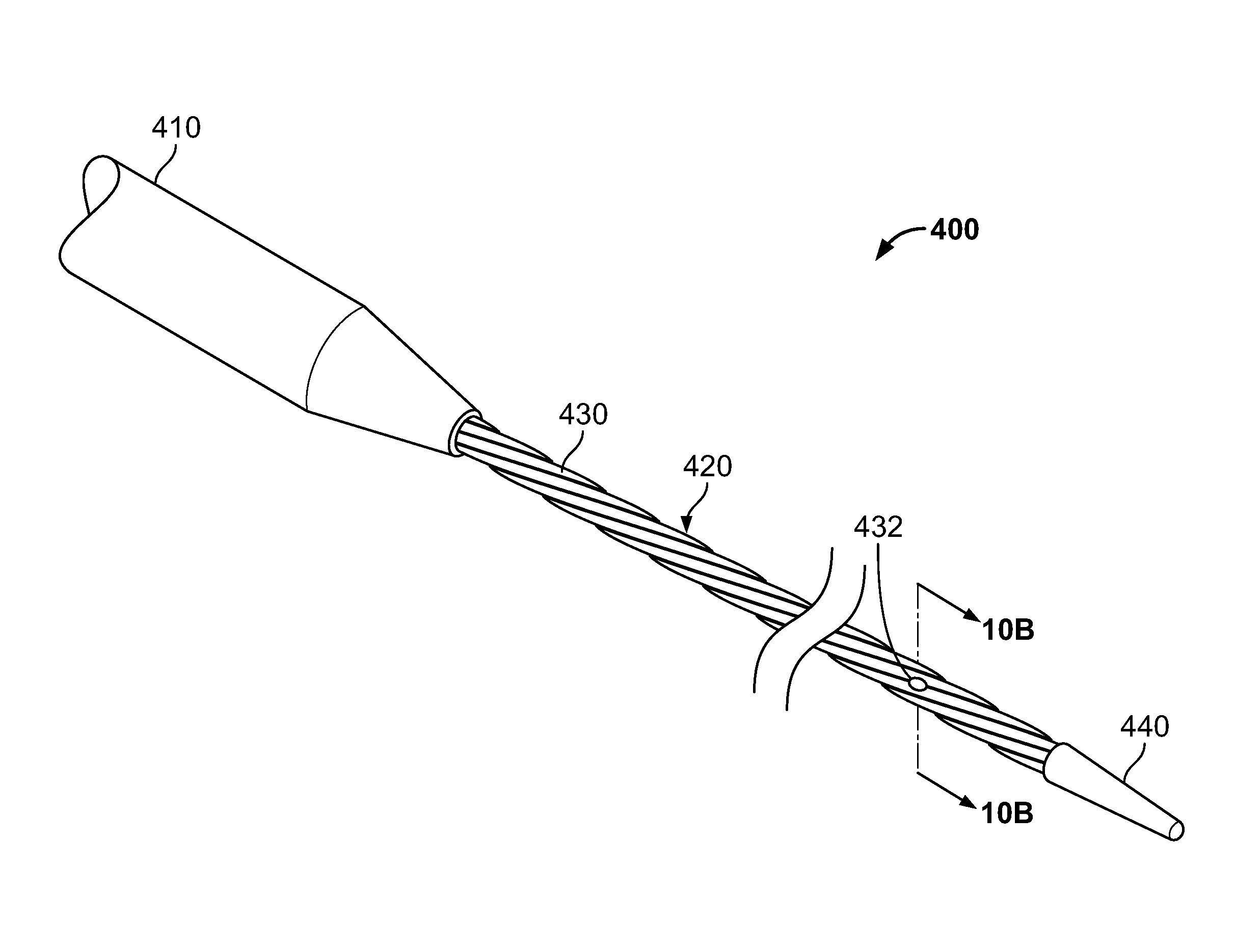
Flexible multi-tubular cryoprobe
ActiveUS20110040297A1Increase flexibilityImproved thermal managementCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingEngineeringInlet flow
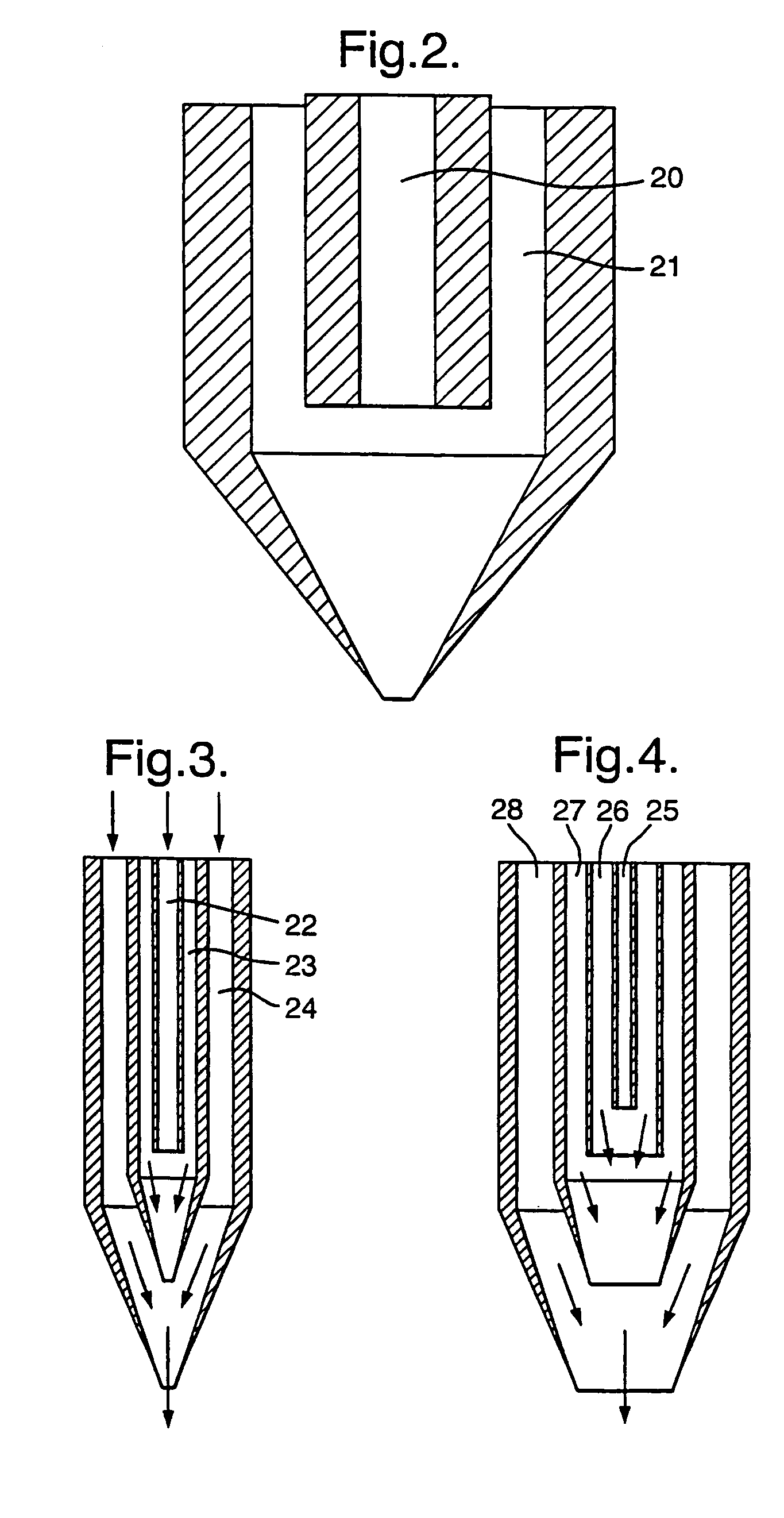
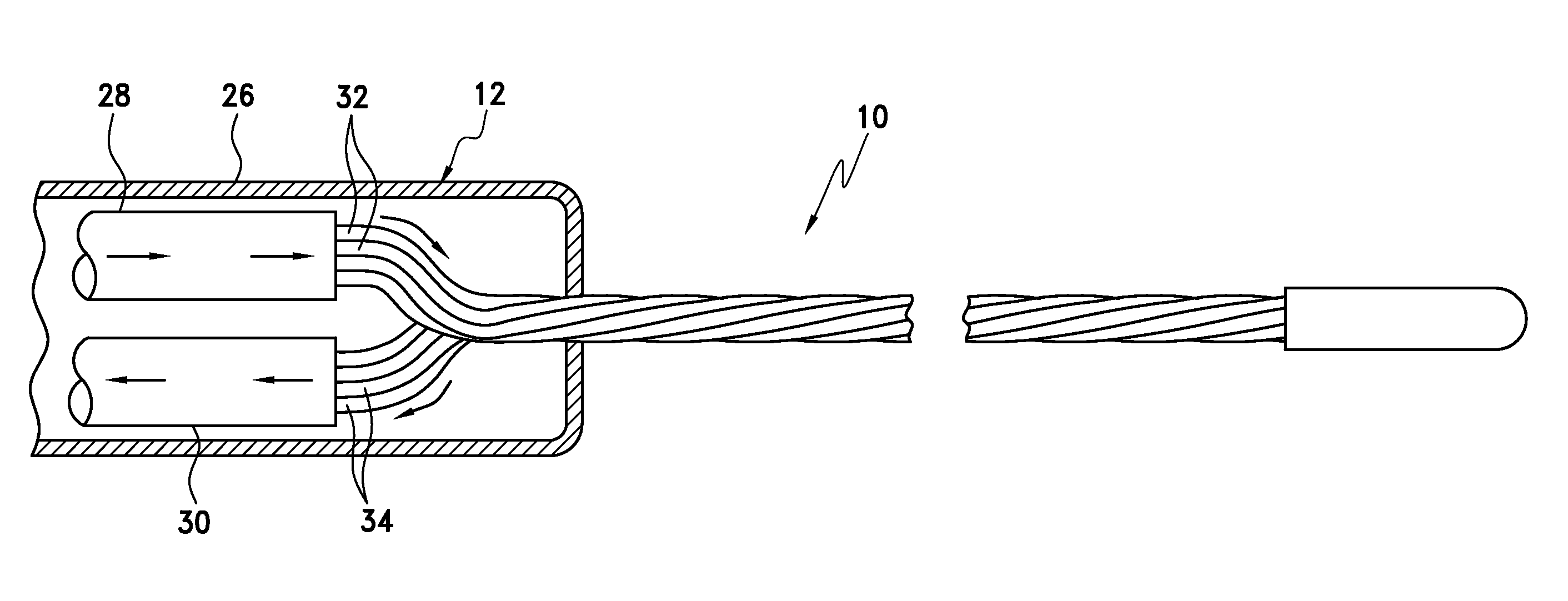
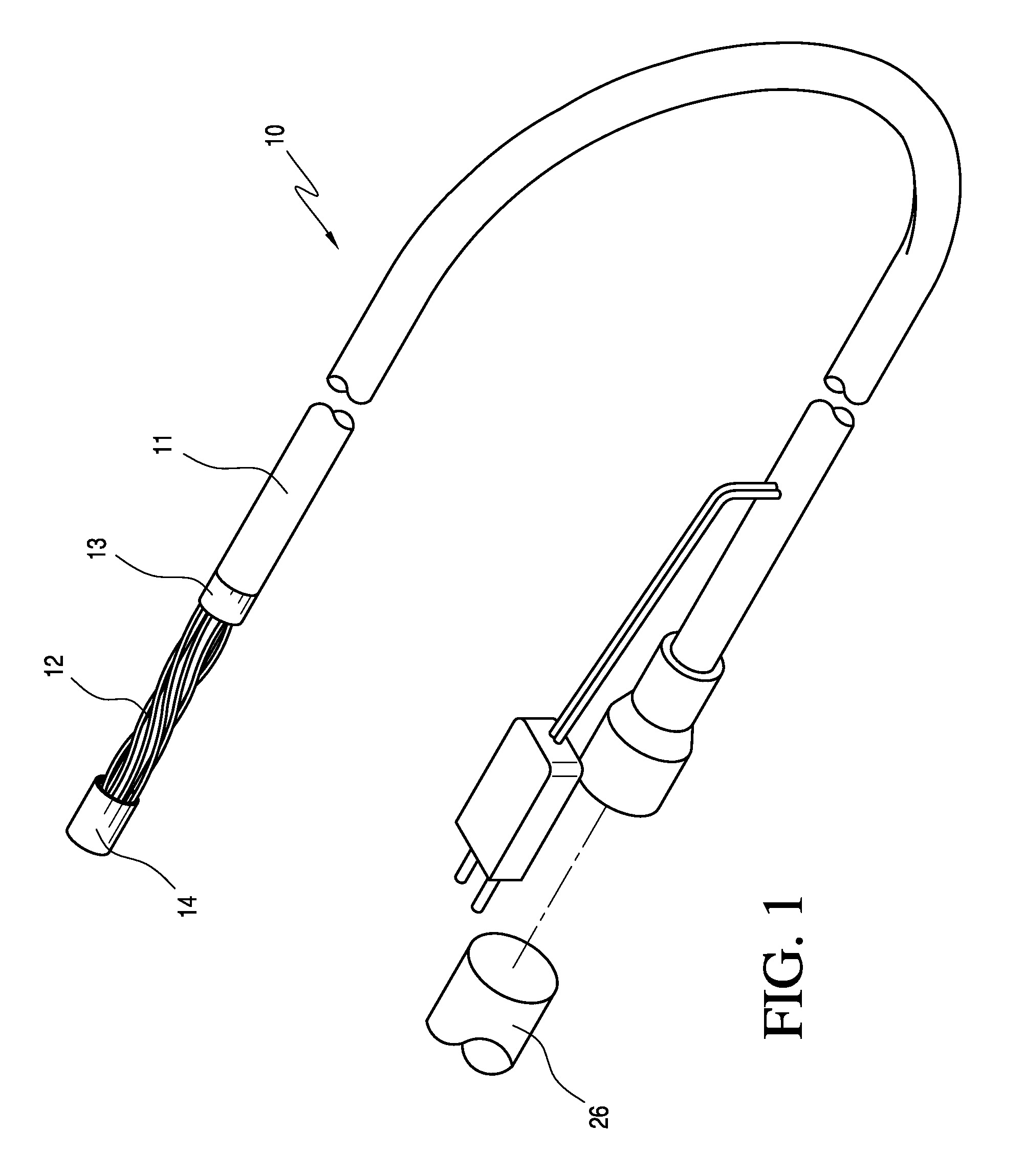
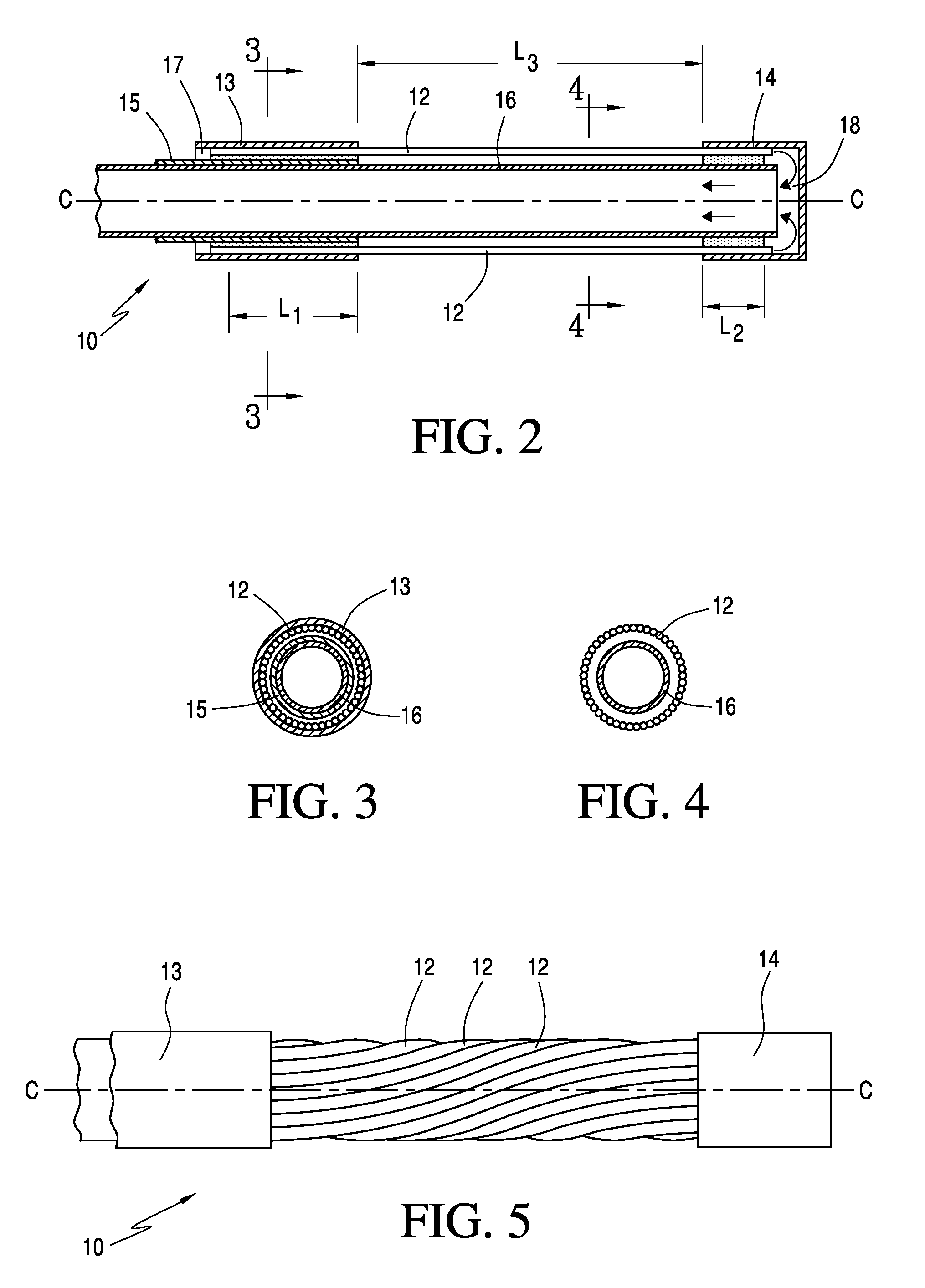
A flexible multi-tubular cryoprobe, including a housing for receiving an inlet flow of near critical cryogenic fluid from a fluid source and for discharging an outlet flow of the cryogenic fluid. A plurality of fluid transfer tubes are securely attached to the housing. This includes a set of inlet fluid transfer tubes for receiving the inlet flow from the housing; and, a set of outlet fluid transfer tubes for discharging the outlet flow to the housing. Each of the fluid transfer tubes is formed of material that maintains flexibility in a full range of temperatures from −200° C. to ambient temperature. Each fluid transfer tube has an inside diameter in a range of between about 0.10 mm and 1.0 mm and a wall thickness in a range of between about 0.01 mm and 0.30 mm. An end cap is positioned at the ends of the plurality of fluid transfer tubes to provide fluid transfer from the inlet fluid transfer tubes to the outlet fluid transfer tubes.
Owner:ADAGIO MEDICAL
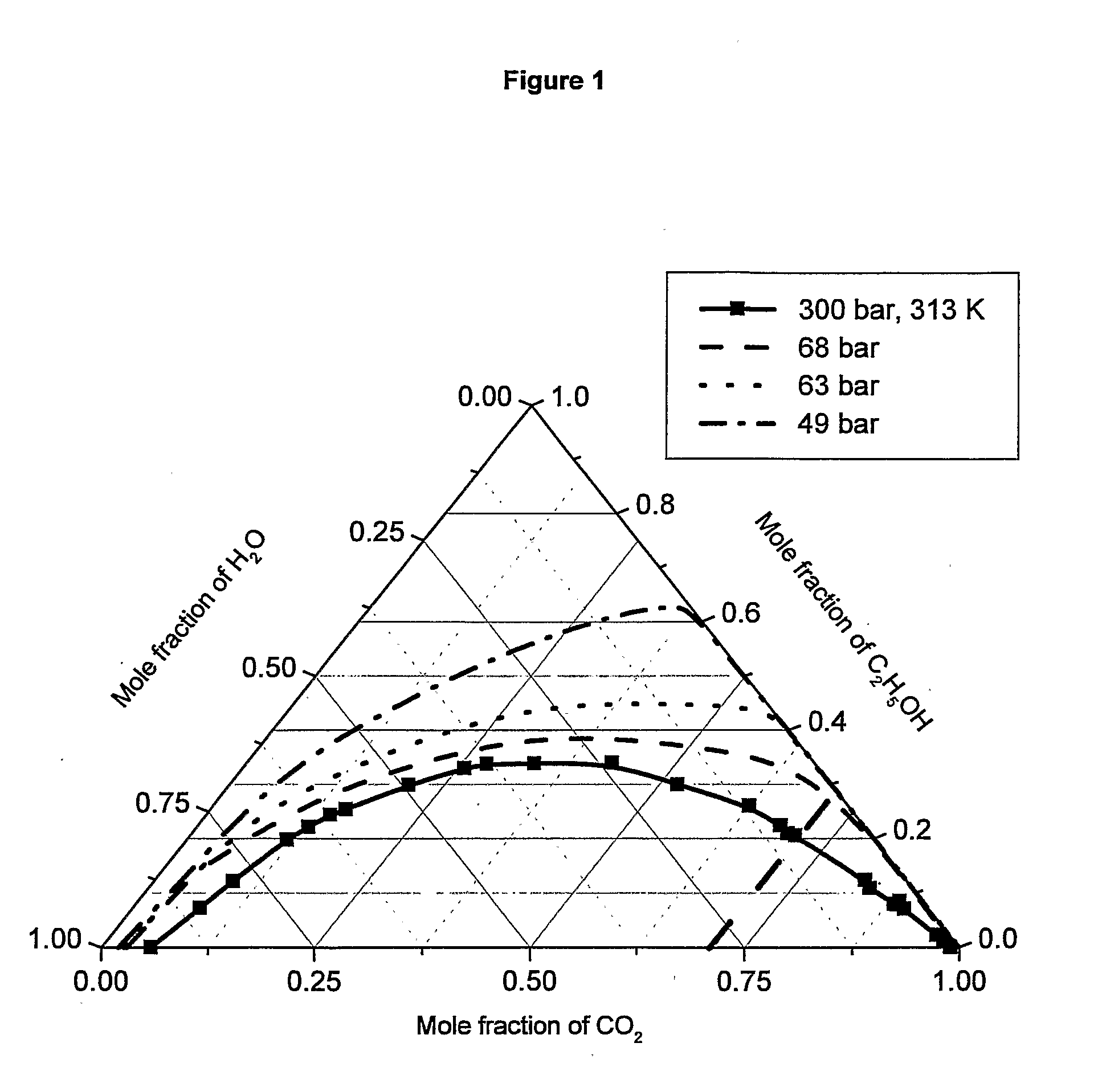
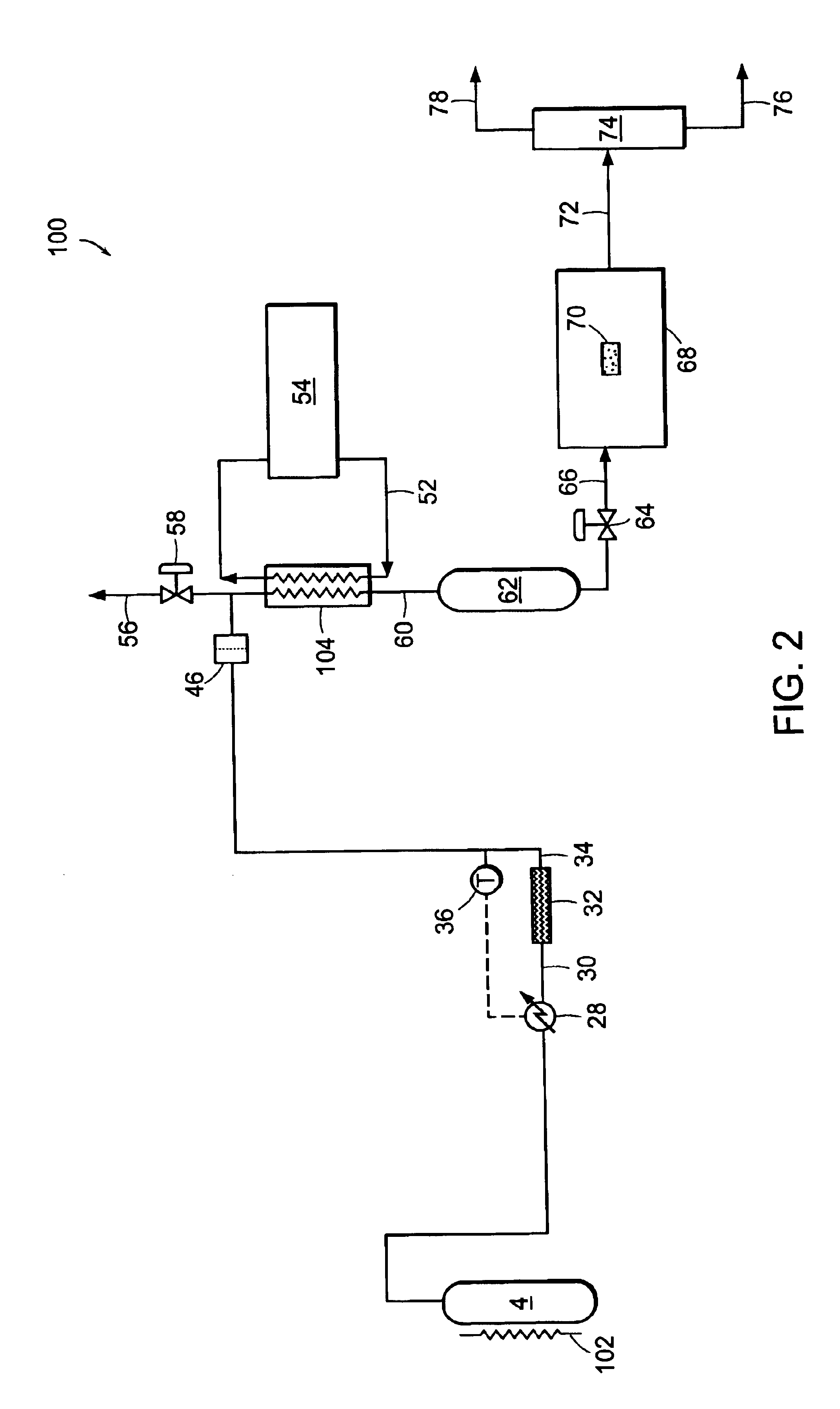
Near-critical fluid extraction process
ActiveUS20100151098A1Reduce pressureReduce the temperatureSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisFluid phaseOrganic solvent
A process for fractionating the constituents of a solution obtained by extracting plant or animal material with an aqueous-organic solvent where the aqueous-organic solvent is a mixture of water and a water-miscible organic solvent, generally including the steps of contacting the solution with a near-critical fluid to produce a raffinate phase containing high polarity constituents and water, and a near-critical fluid phase containing low to medium polarity constituents, separating the near-critical fluid phase from the raffinate phase, and recovering the low to medium polarity constituents from the near-critical fluid phase and the high polarity constituents from the raffinate phase.
Owner:CALLAGHAN INNOVATION
Expandable multi-tubular cryoprobe
ActiveUS20110009854A1Good thermal contactStay flexibleCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingWorking fluidEngineering
An expandable, flexible multi-tubular cryoprobe operational with a near critical cryogenic working fluid. The inlet fluid transfer micro-tubes utilized are formed of material that maintains flexibility in a full range of temperatures from −200° C. to ambient temperature. During operation, the cryoprobe is mechanically actuated to provide radial expansion of the inlet fluid transfer micro-tubes. Thus, enhanced thermal contact with target biological tissue to be treated is provided.
Owner:ADAGIO MEDICAL
Method for moving contaminants from gases
InactiveUS6962629B2Efficient removalLower Level RequirementsSolidificationLiquefactionCarbon dioxide exposureCatalytic oxidation
Carbon dioxide is purified through the use of catalytic oxidation. Carbon dioxide is exposed to at least one catalyst, oxidizing at least a portion of the nonvolatile organic residues to form purified carbon dioxide that is directed to an application. Carbon dioxide that is in a near-critical, critical, or supercritical phase can be exposed to the catalyst.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Method and apparatus for selective deposition of materials to surfaces and substrates
InactiveUS20060223312A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsSemiconductor chip
Methods are disclosed for depositing materials selectively and controllably from liquid, near-critical, and / or supercritical fluids to a substrate or surface controlling the location and / or thickness of material(s) deposited to the surface or substrate. In one exemplary process, metals are deposited selectively filling feature patterns (e.g., vias) of substrates. The process can be further used to control deposition of materials on sub-surfaces of composite or structured silicon wafers, e.g., for the deposition of barrier films on silicon wafer surfaces. Materials include, but are not limited to, overburden materials, metals, non-metals, layered materials, organics, polymers, and semiconductor materials. The instant invention finds application in such commercial processes as semiconductor chip manufacturing. In particular, selective deposition is envisioned to provide alternatives to, or decrease need for, such processes as Chemical Mechanical Planarization of silicon surfaces in semiconductor chip manufacturing due to selective filling and / or coating of pattern features with metals deposited from liquid, near-critical, or supercritical fluids.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Modulated temperature method of atomic layer deposition (ALD) of high dielectric constant films
ActiveUS7442415B2Uniform depositionEfficient removalSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingOxygenDielectric layer
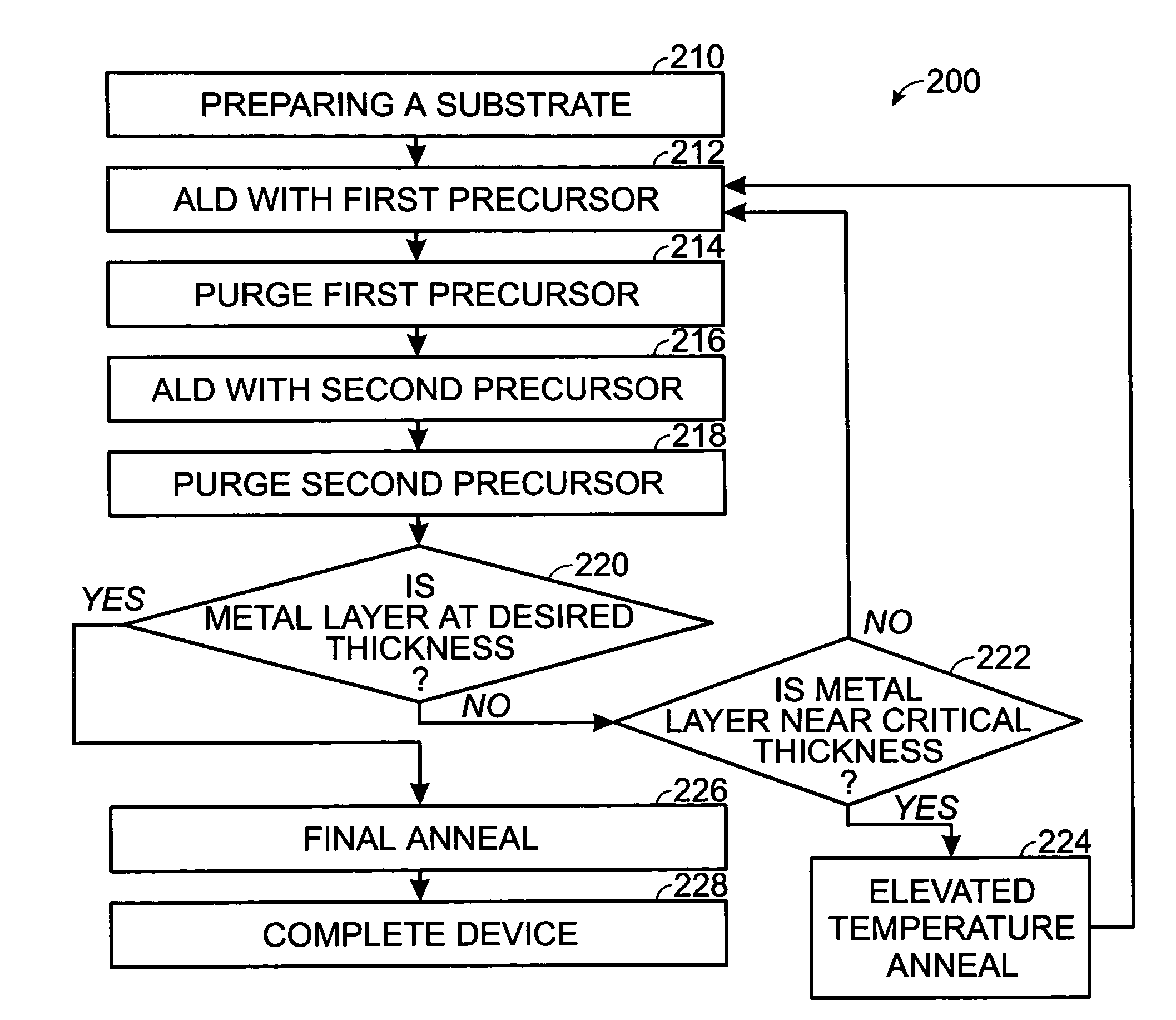
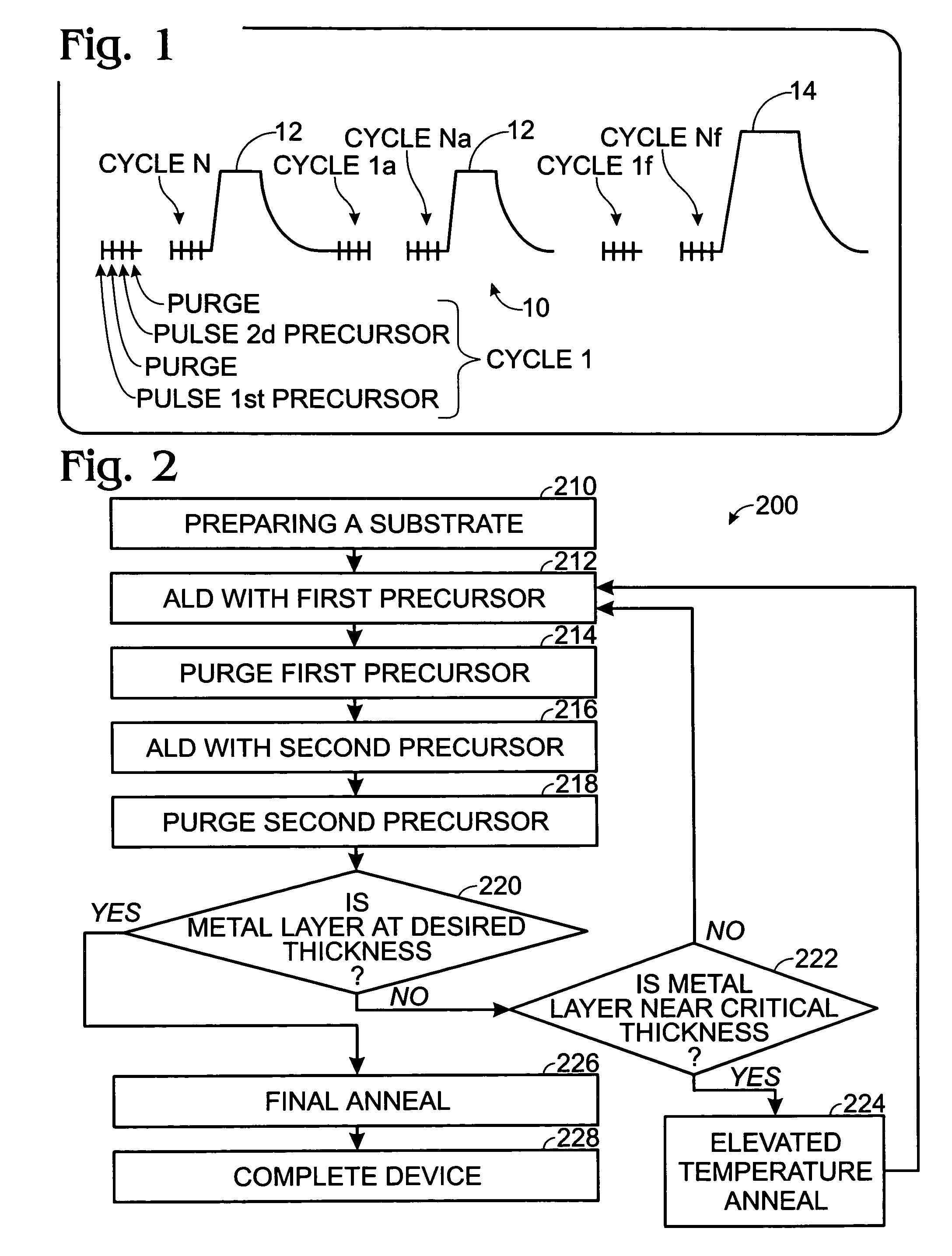
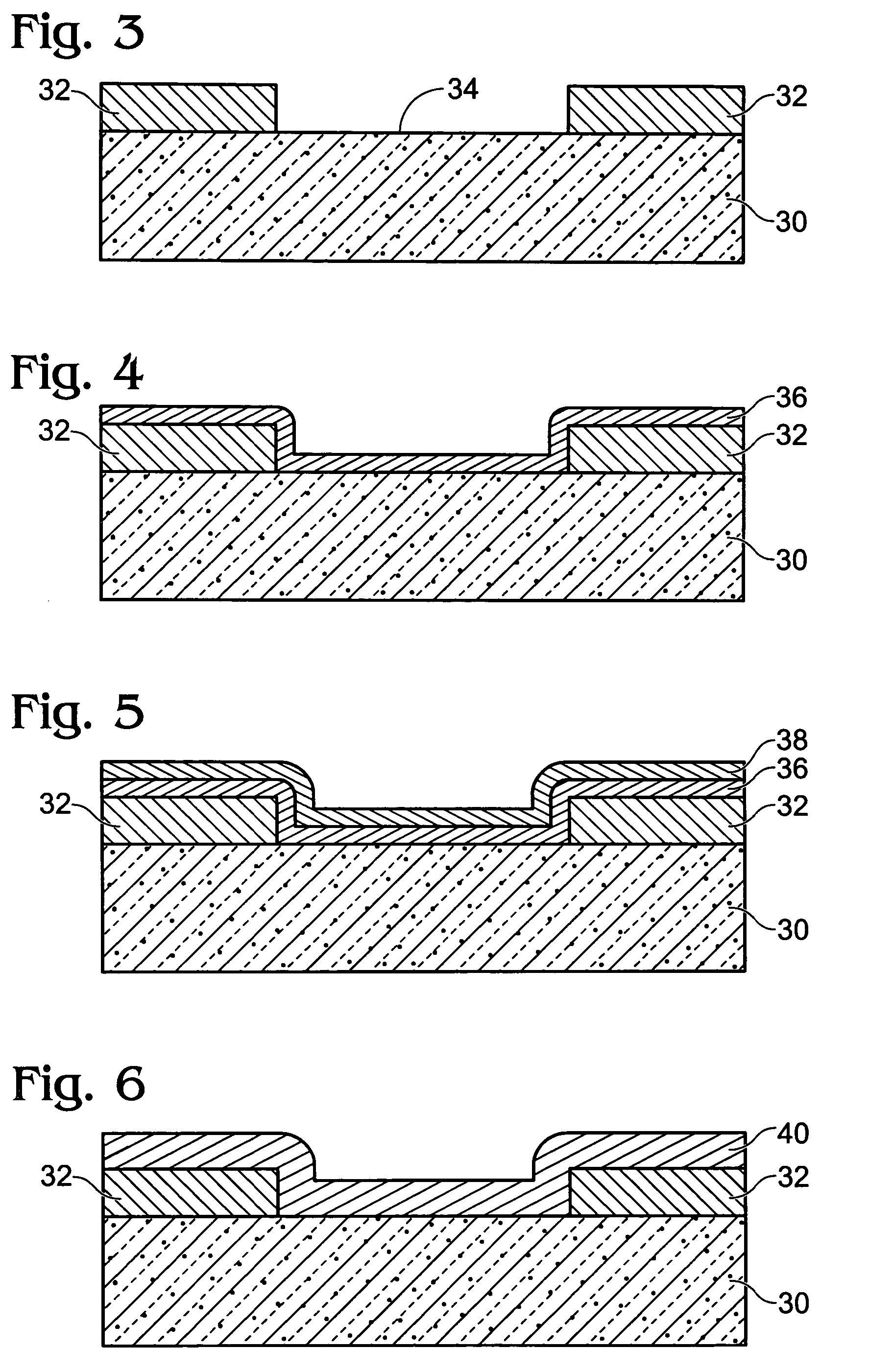
A method of forming a layer of high-k dielectric material in an integrated circuit includes preparing a silicon substrate; forming a high-k dielectric layer by a sequence of ALD cycles including: depositing a first layer of metal ligand using ALD with an oxygen-containing first precursor; and depositing a second layer of metal ligand using ALD with a second precursor; repeating the sequence of ALD cycles N times until a near-critical thickness of metal oxide is formed; annealing the substrate and metal oxide layers every N ALD cycles in an elevated temperature anneal; repeating the sequence of ALD cycles and elevated temperature anneals until a high-k dielectric layer of desired thickness is formed; annealing the substrate and the metal oxide layers in a final annealing step; and completing the integrated circuit.
Owner:SHARP KK
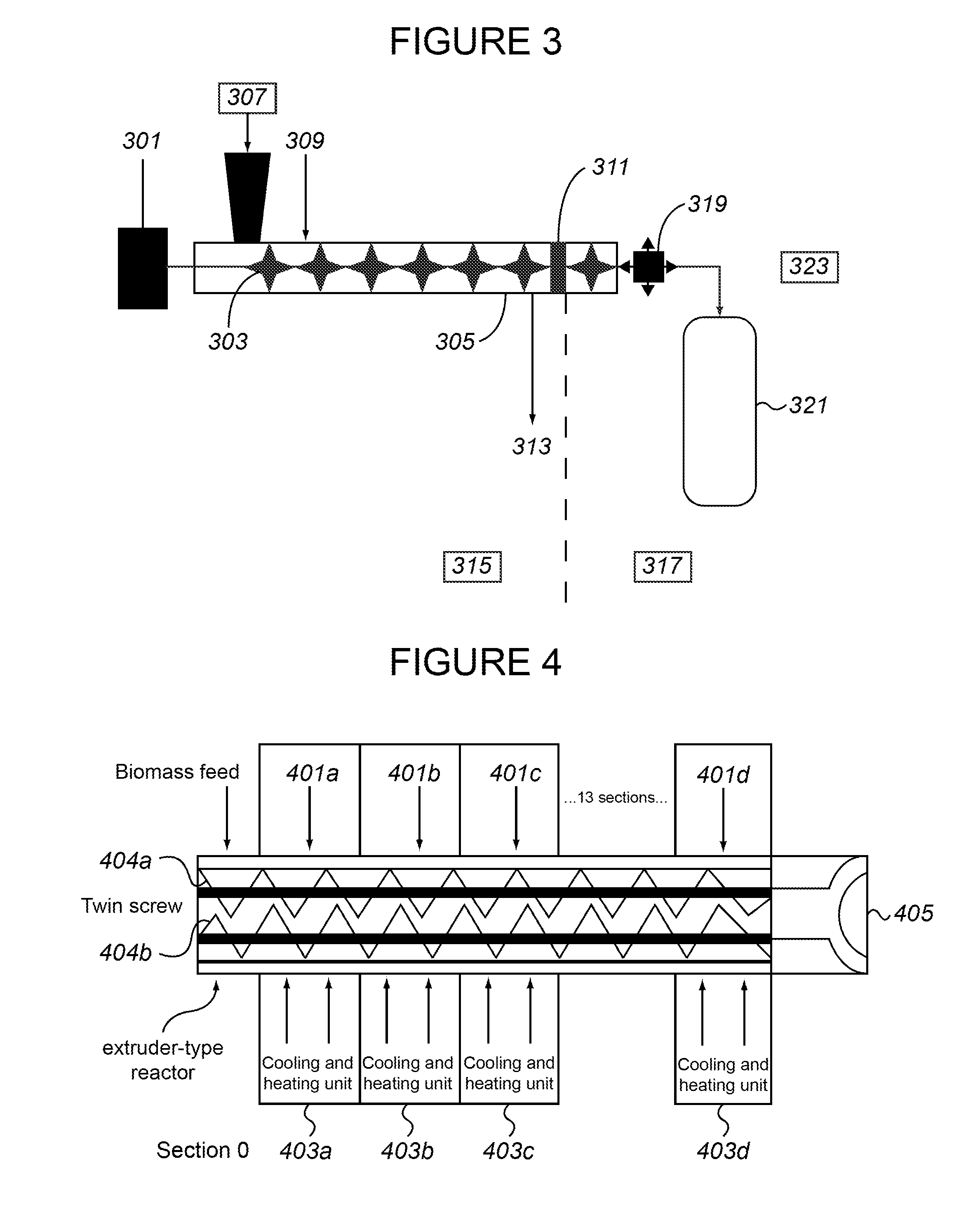
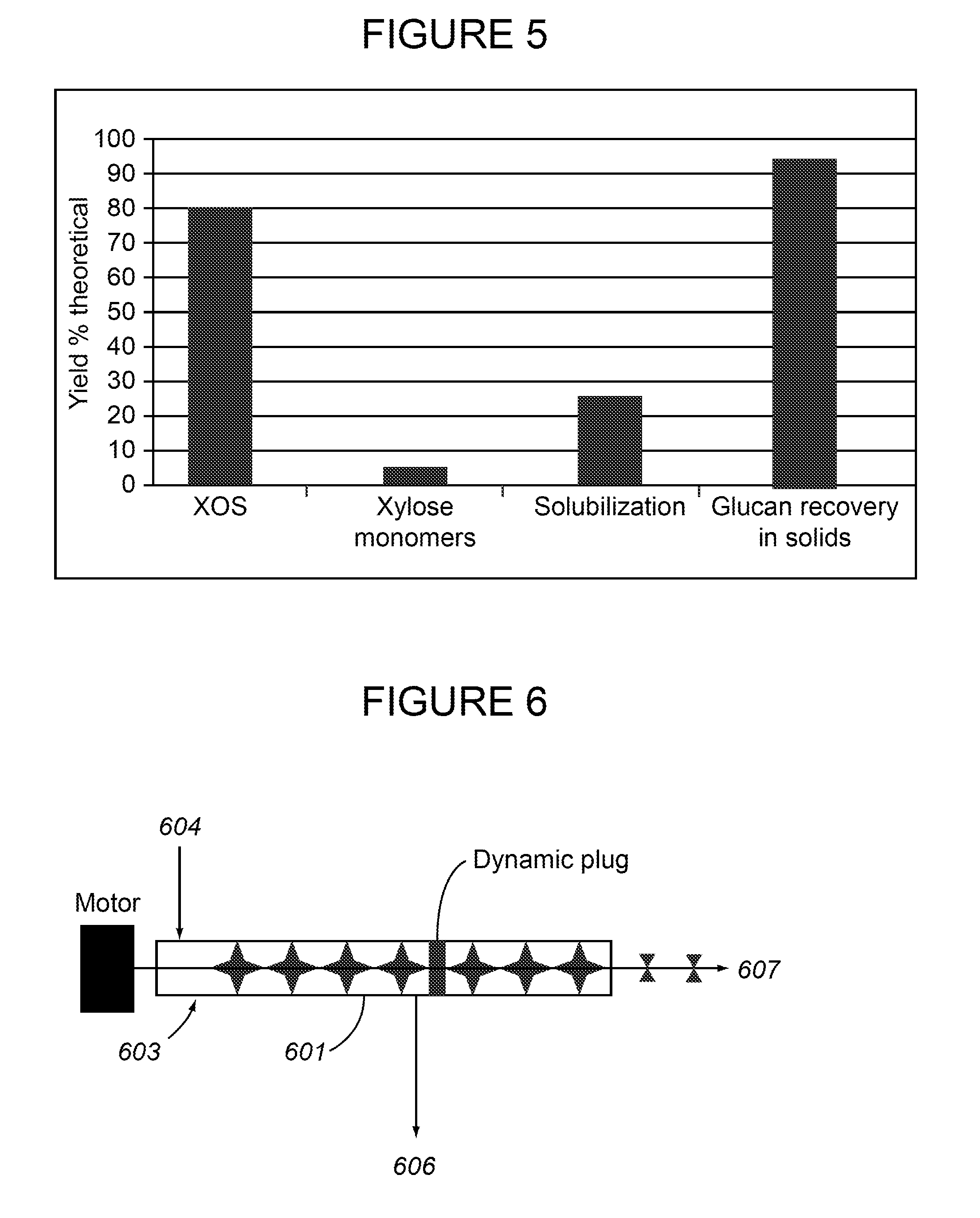
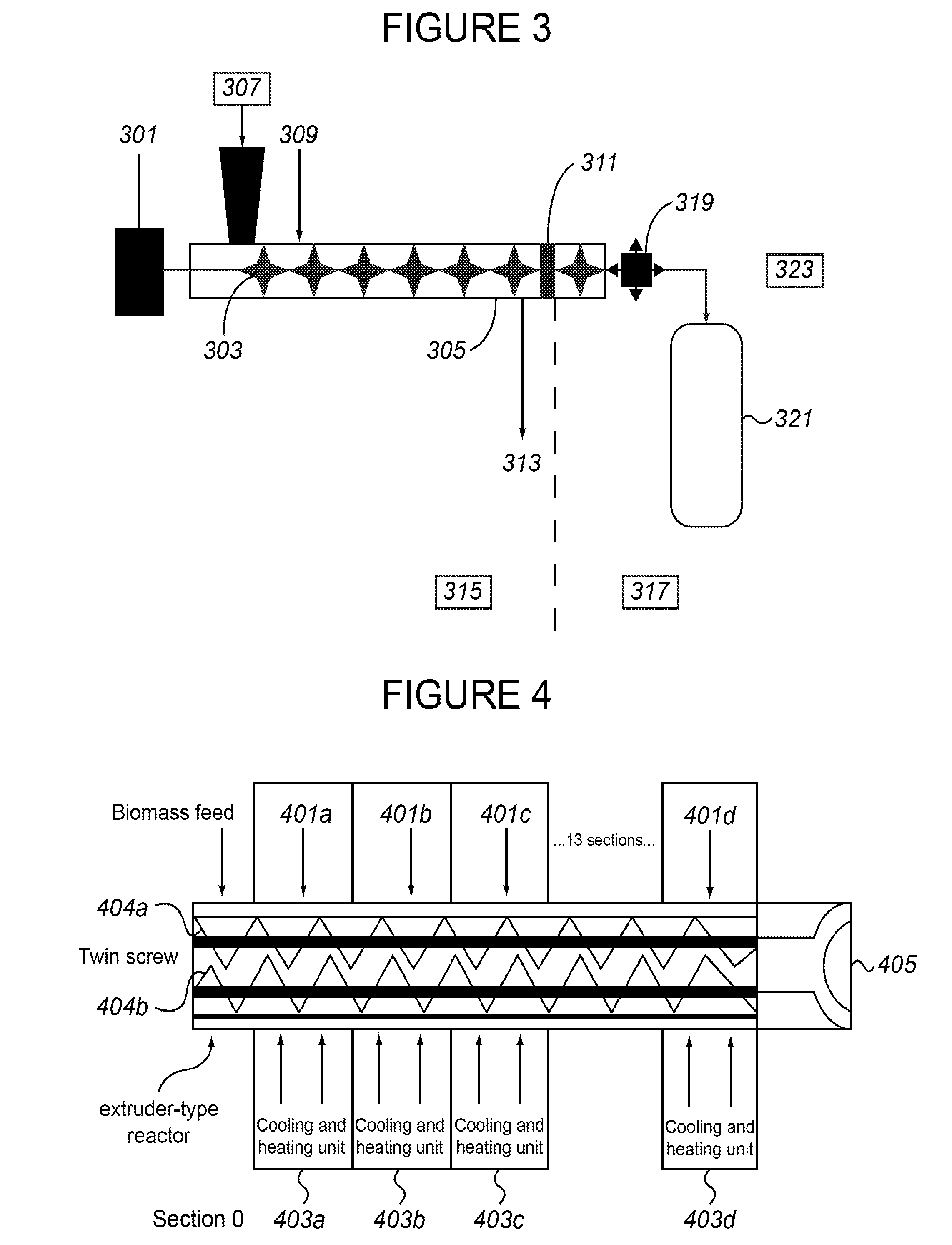
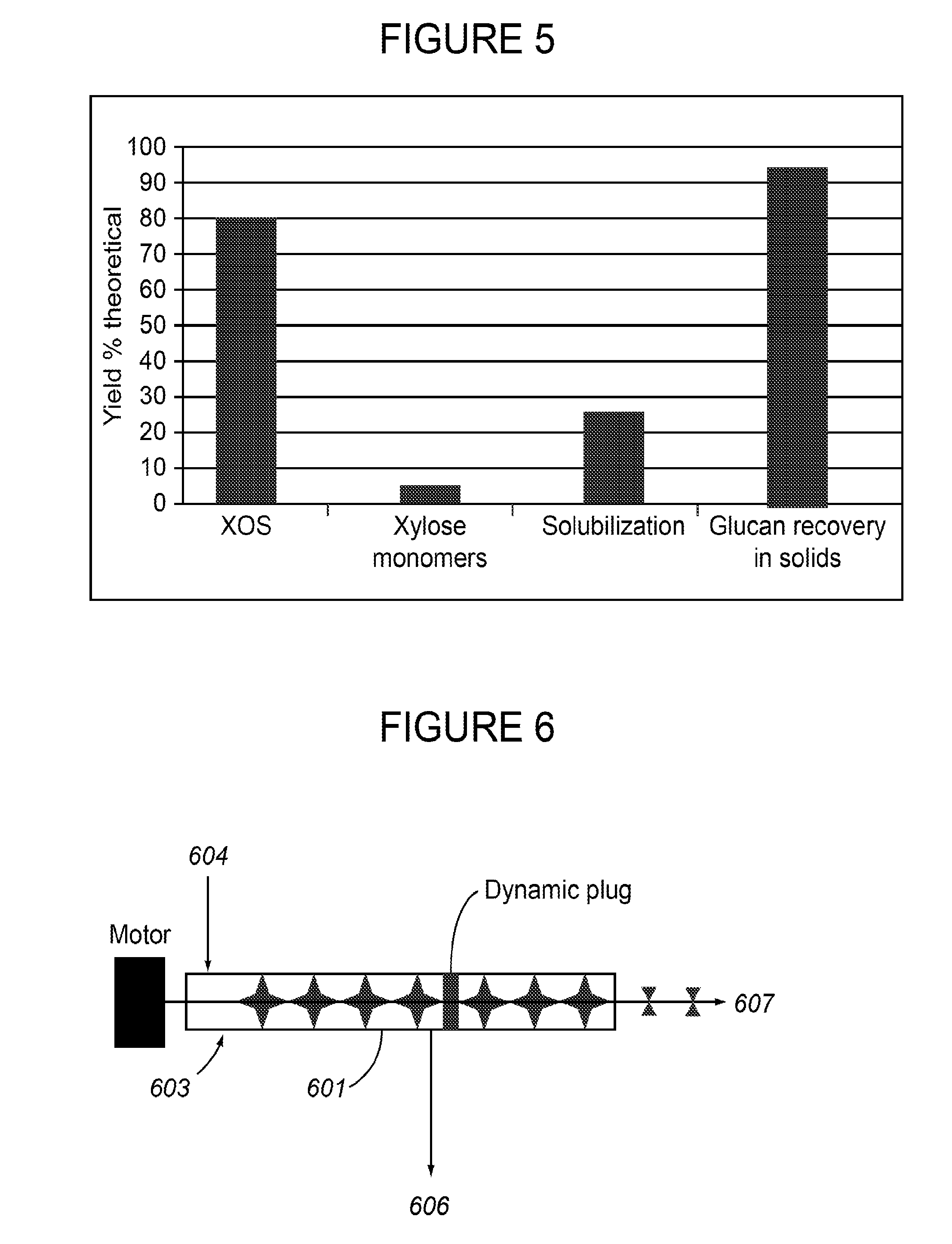
Production of fermentable sugars and lignin from biomass using supercritical fluids
Methods are disclosed for the continuous treatment of biomass comprising a pretreatment step, wherein said biomass is contacted with a first supercritical, near-critical, or sub-critical fluid to form a solid matrix and a first liquid fraction; and a hydrolysis step, wherein said solid matrix formed in said pretreatment step is contacted with a second supercritical or near-supercritical fluid to produce a second liquid fraction and a insoluble lignin-containing fraction. Also disclosed are apparatuses for the continuous conversion of biomass comprising a pretreatment reactor and a hydrolysis reactor associated with said pretreatment reactor.
Owner:RENMATIX INC
Pulse width modulation sequence generating a near critical damped step response
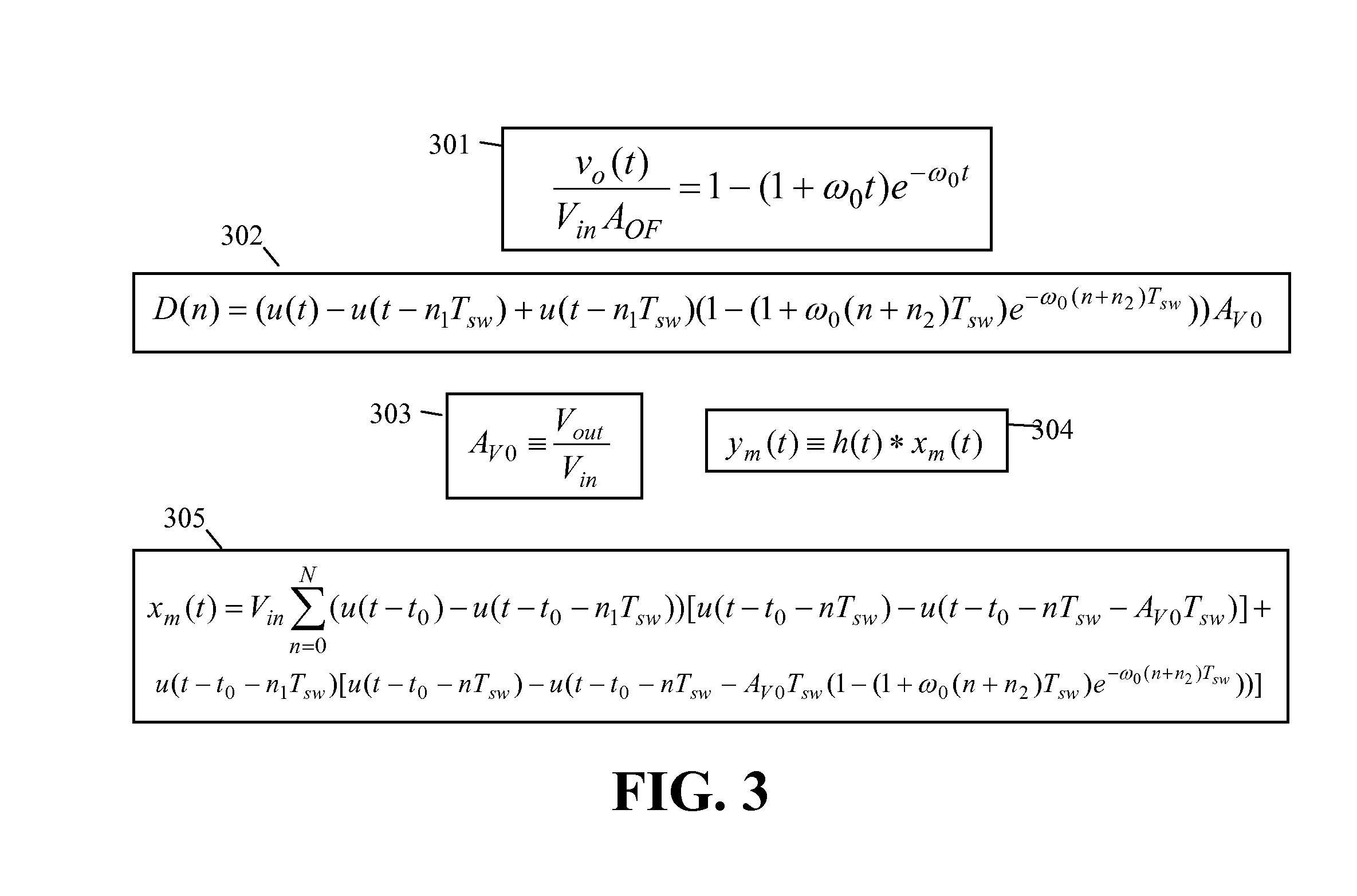
InactiveUS20080088385A1Improve powerMinimal componentEfficient power electronics conversionDigital data processing detailsSequence controlPulse sequence
A digital circuit implementing pulse width modulation controls power delivered in what one can model as a second order or higher order system. An exemplary control plant could embody a step-down switch mode power supply providing a precise sequence of voltages or currents to any of a variety of loads such as the core voltage of a semiconductor unique compared to its input / output ring voltage. An algorithm produces a specific sequence of pulses of varying width such that the voltage or current delivered to the load from the system plant closely resembles a critical damped step response. The specific pulse width modulation sequence controls a plant that provides a near critical damped step response in one embodiment without a feed-forward or feedback loop physically embodied in the control system thereby reducing the parts cost or control semiconductor production yield cost while enhancing noise immunity and long term reliability of the control system. The specific algorithm exhibits tolerance to variations of twenty percent or greater in output load or ten percent or greater in control plant element parameters thus maintaining near critical damped step response characteristics when actual parameter values deviate from initial estimates.
Owner:IPOWER HLDG
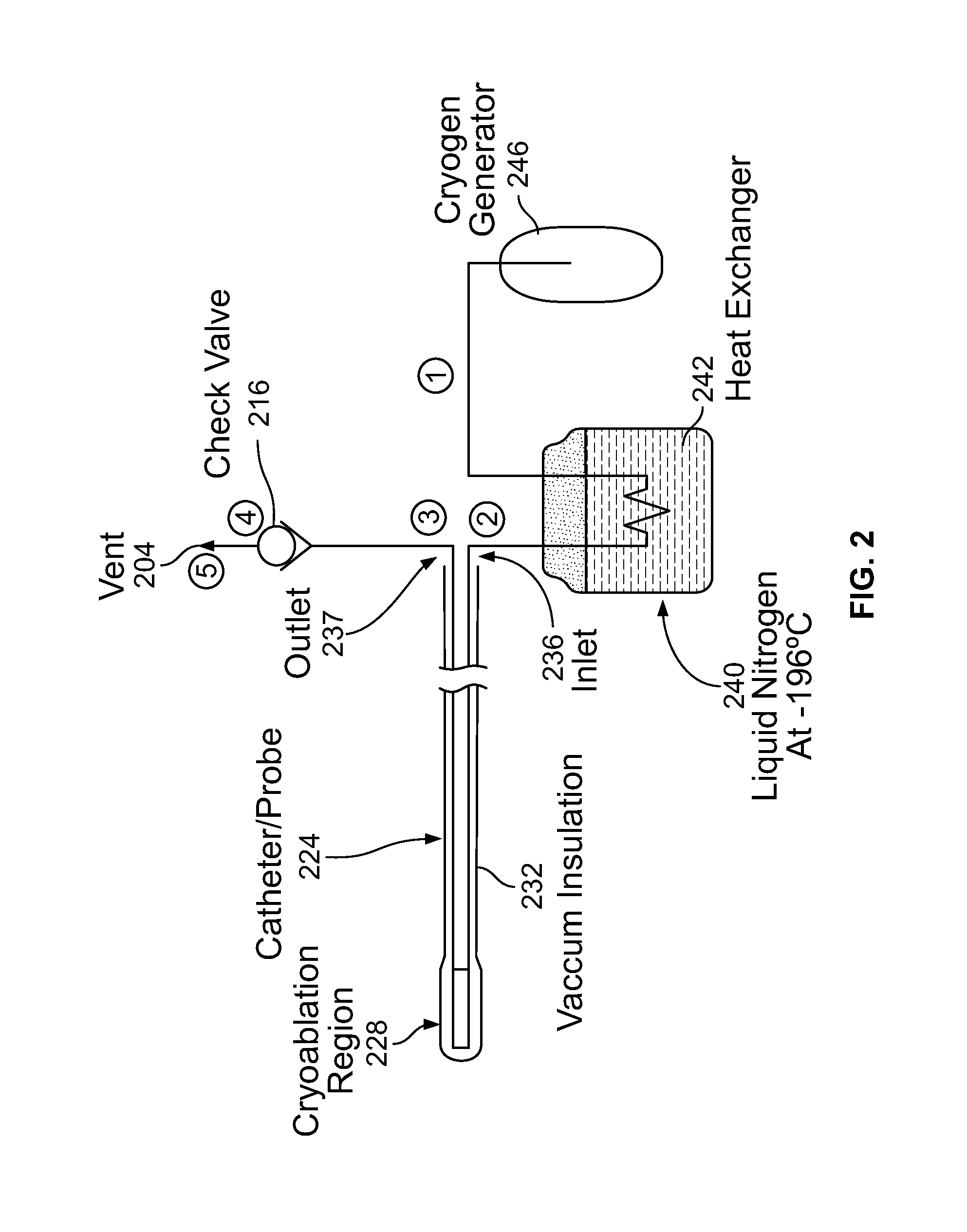
Pressure modulated cryoablation system and related methods
ActiveUS20160135864A1Reduce stressCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingMedicineBiological activation
A near critical fluid based cryoablation system comprises a cryoablation catheter for creating a lesion in tissue. A cryogenic fluid is transported under pressure through the catheter. A controller adjusts the pressure from a relatively high (e.g., near critical) pressure to a substantially lower pressure based on a condition during the catheter activation. In one configuration, the pressure is modulated based on the temperature of the catheter. When the temperature of the catheter reaches a target temperature, the pressure is reduced.
Owner:ADAGIO MEDICAL
Pretreating cellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20090288788A1Improves cellulosic biomass pretreatmentMachine wet endPulp by-products recoveryCelluloseLiquid waste
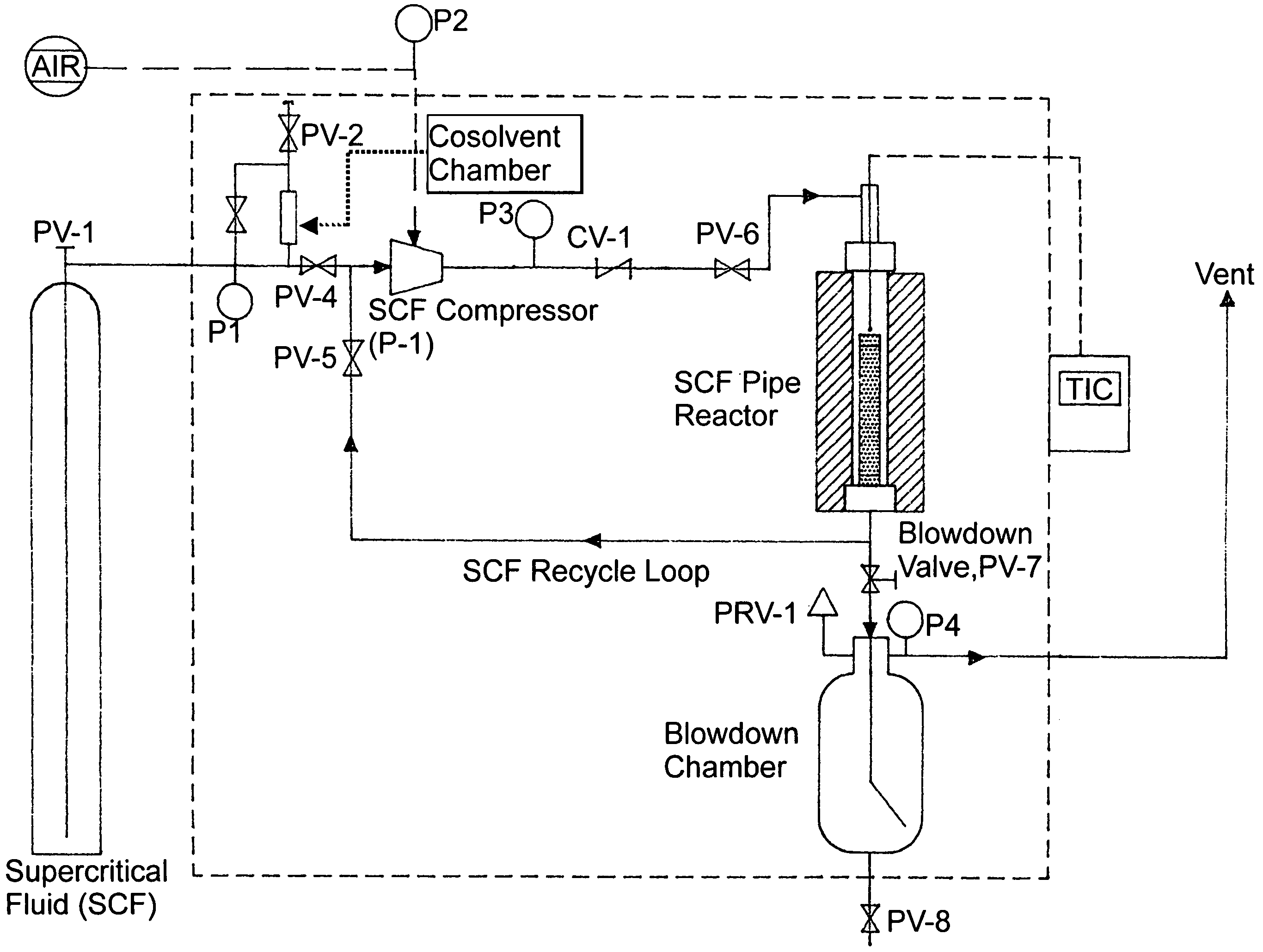
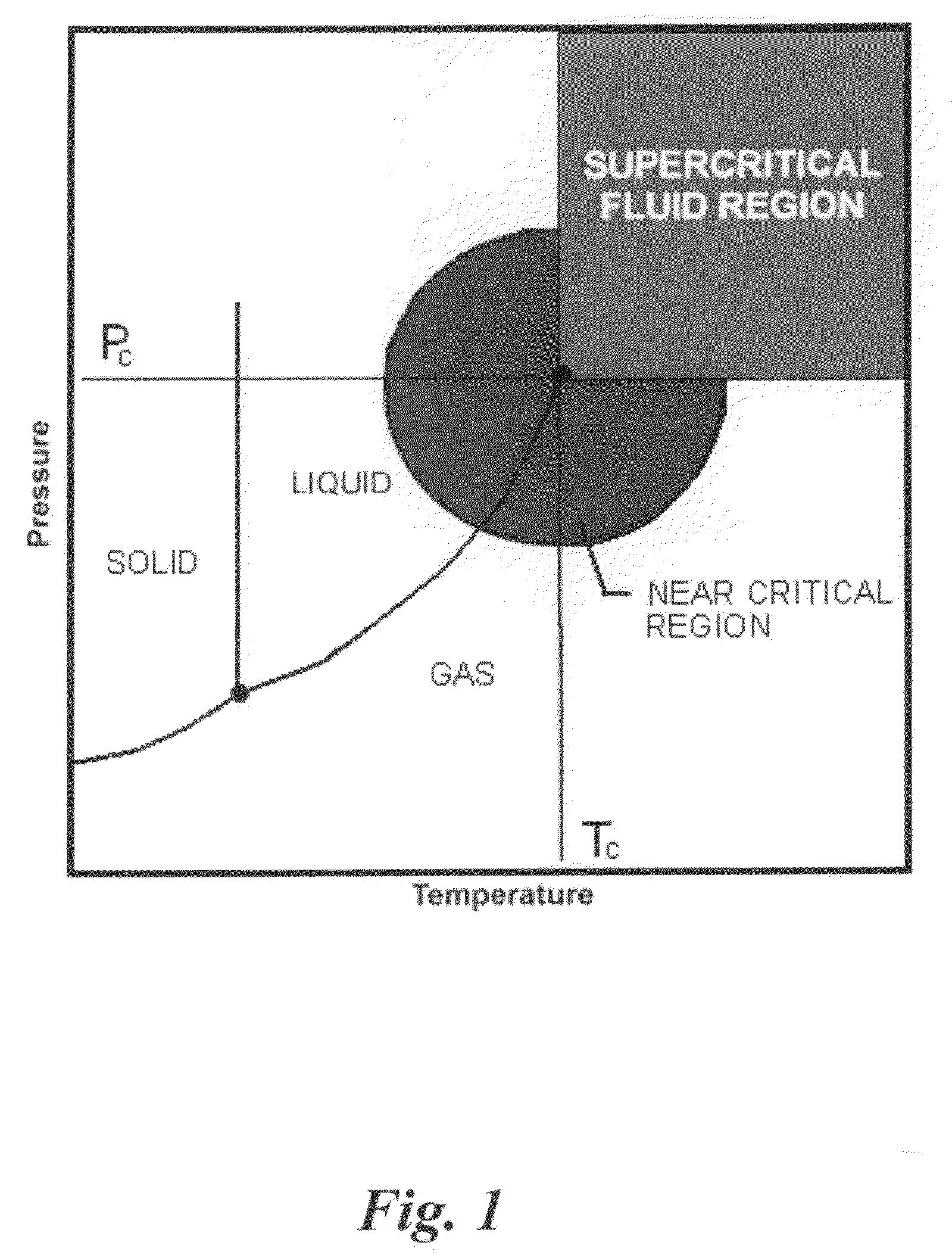
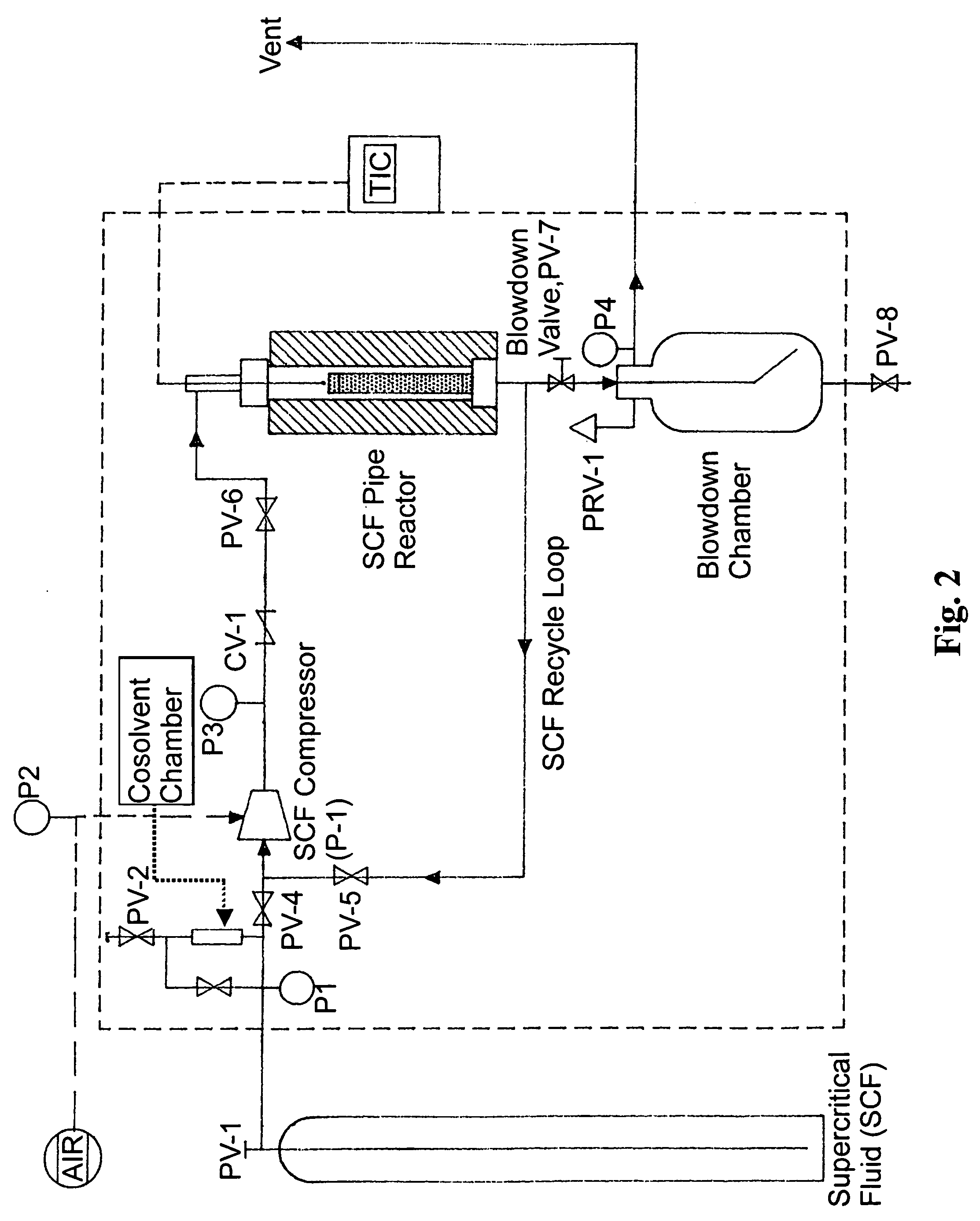
The present invention pertains to methods for pretreatment of cellulosic biomass for bioconversion into ethanol and other biofuels and wood-based chemicals, recycling of newsprint and other paper products, microfibrillation of cellulose for use as an additive in the food and cosmetic industries, manufacturing improved hardboard, and producing and improved “super” pulp while reducing chemical usage and spent liquor generation. In particular, the instant invention employs supercritical, critical or near critical fluids with and without polar cosolvents [critical fluid, SuperFluids or SFS] for the pretreatment of cellulosic biomass.
Owner:APHIOS
Production of Fermentable Sugars and Lignin from Biomass Using Supercritical Fluids
ActiveUS20120291774A1Improve the level ofBiofuelsPulp by-products recoveryFermentable sugarSupercritical fluid
Methods are disclosed for the continuous treatment of biomass comprising a pretreatment step, wherein said biomass is contacted with a first supercritical, near-critical, or sub-critical fluid to form a solid matrix and a first liquid fraction; and a hydrolysis step, wherein said solid matrix formed in said pretreatment step is contacted with a second supercritical or near-supercritical fluid to produce a second liquid fraction and a insoluble lignin-containing fraction. Also disclosed are apparatuses for the continuous conversion of biomass comprising a pretreatment reactor and a hydrolysis reactor associated with said pretreatment reactor.
Owner:RENMATIX INC
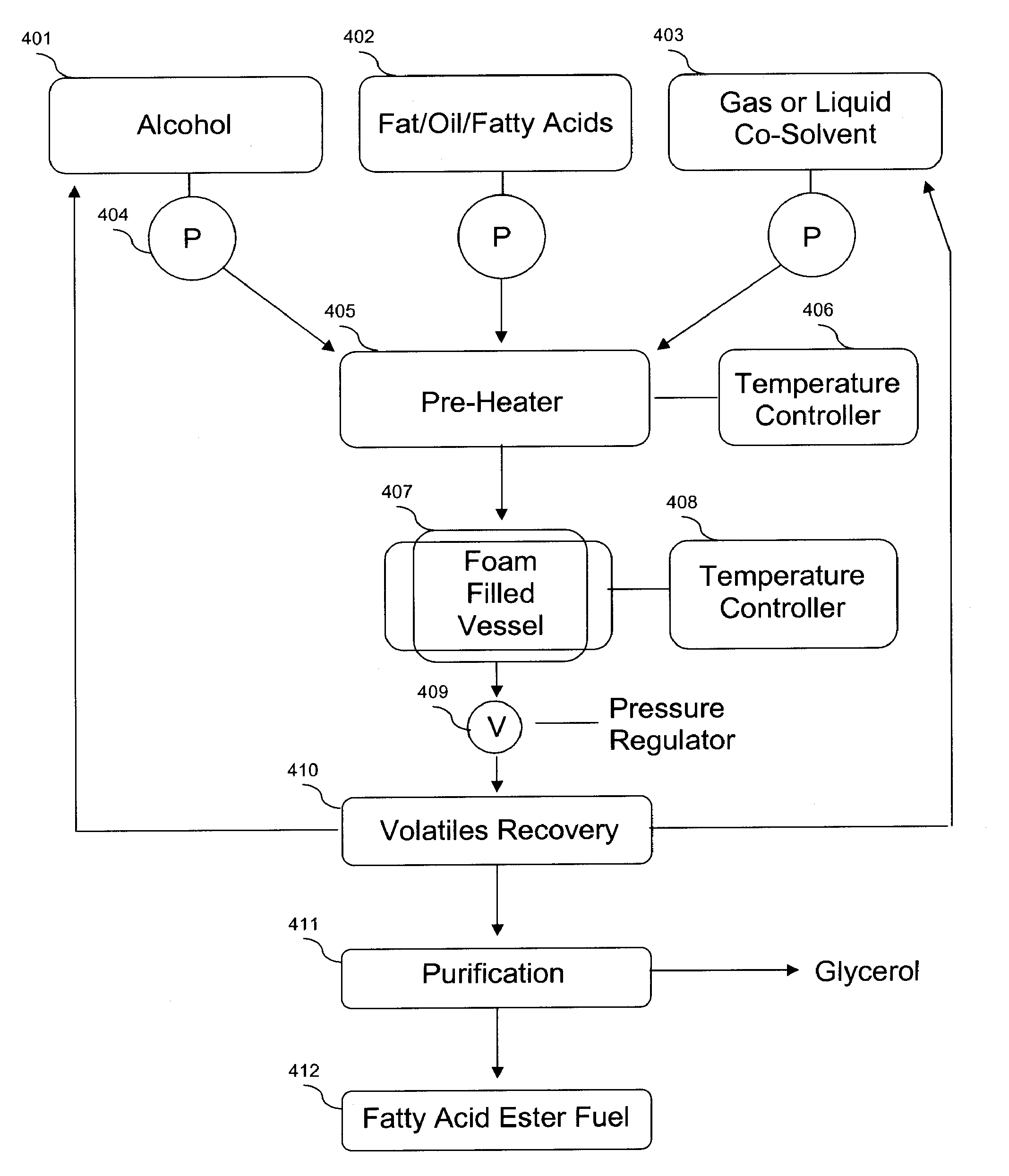
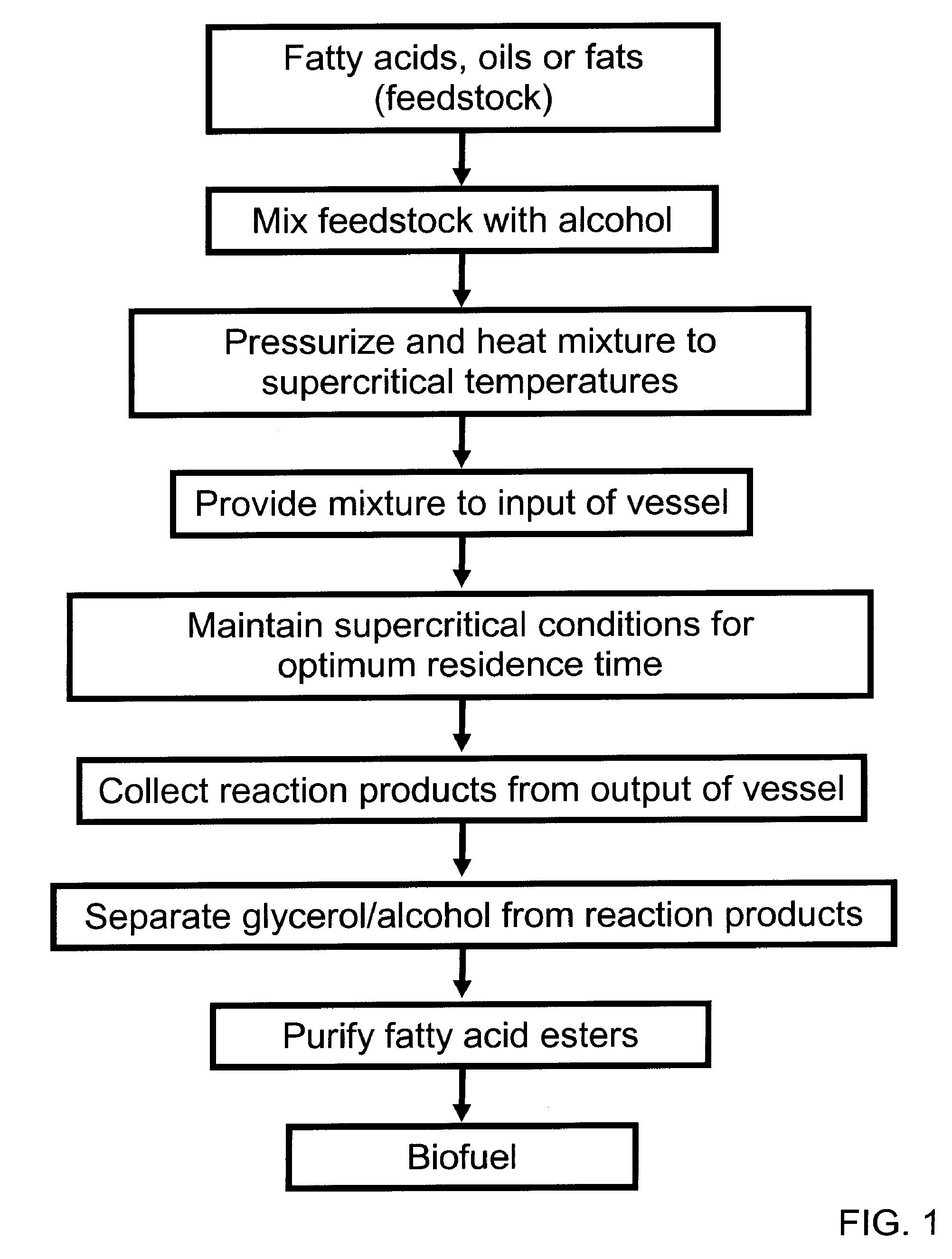
Vessels and methods for synthesis of biofuel
InactiveUS20090005582A1Fatty acid esterificationOrganic compound preparationTransesterificationBiofuel
Vessels and methods for esterification and transesterification of fatty acids under near critical or supercritical reaction conditions are disclosed herein. Alkyl esters produced in the vessel with the disclosed methods are used to create biofuel, such as biodiesel.
Owner:BIOFUELBOX
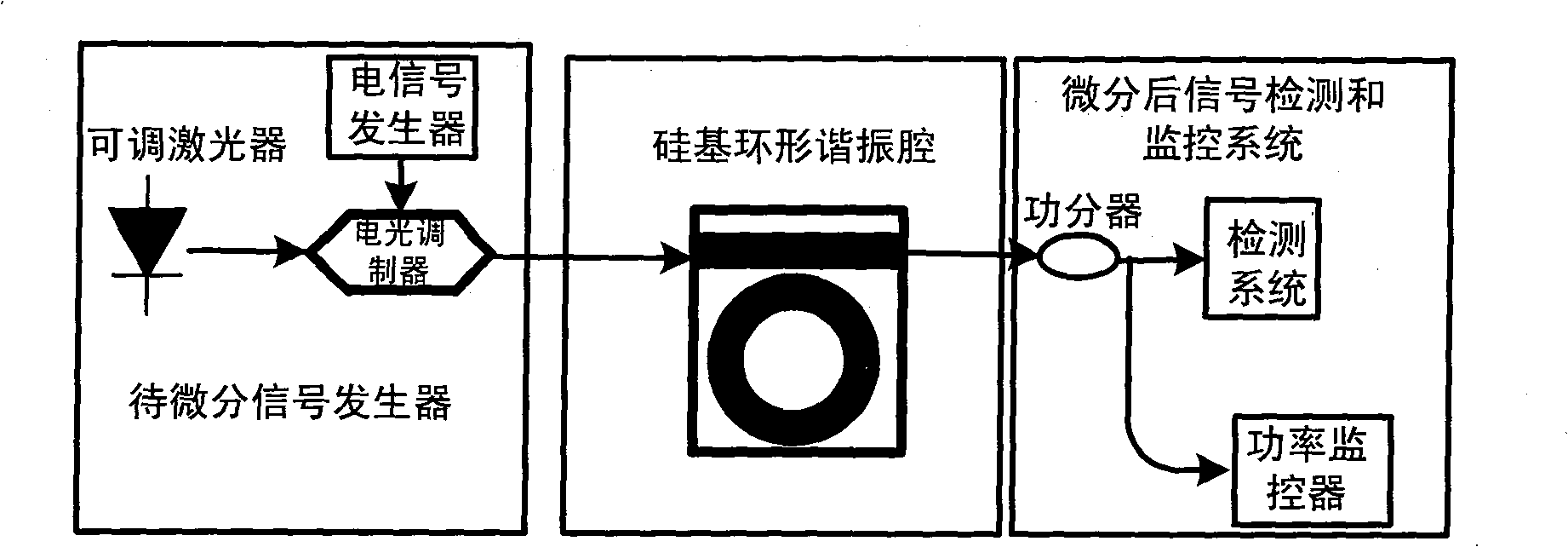
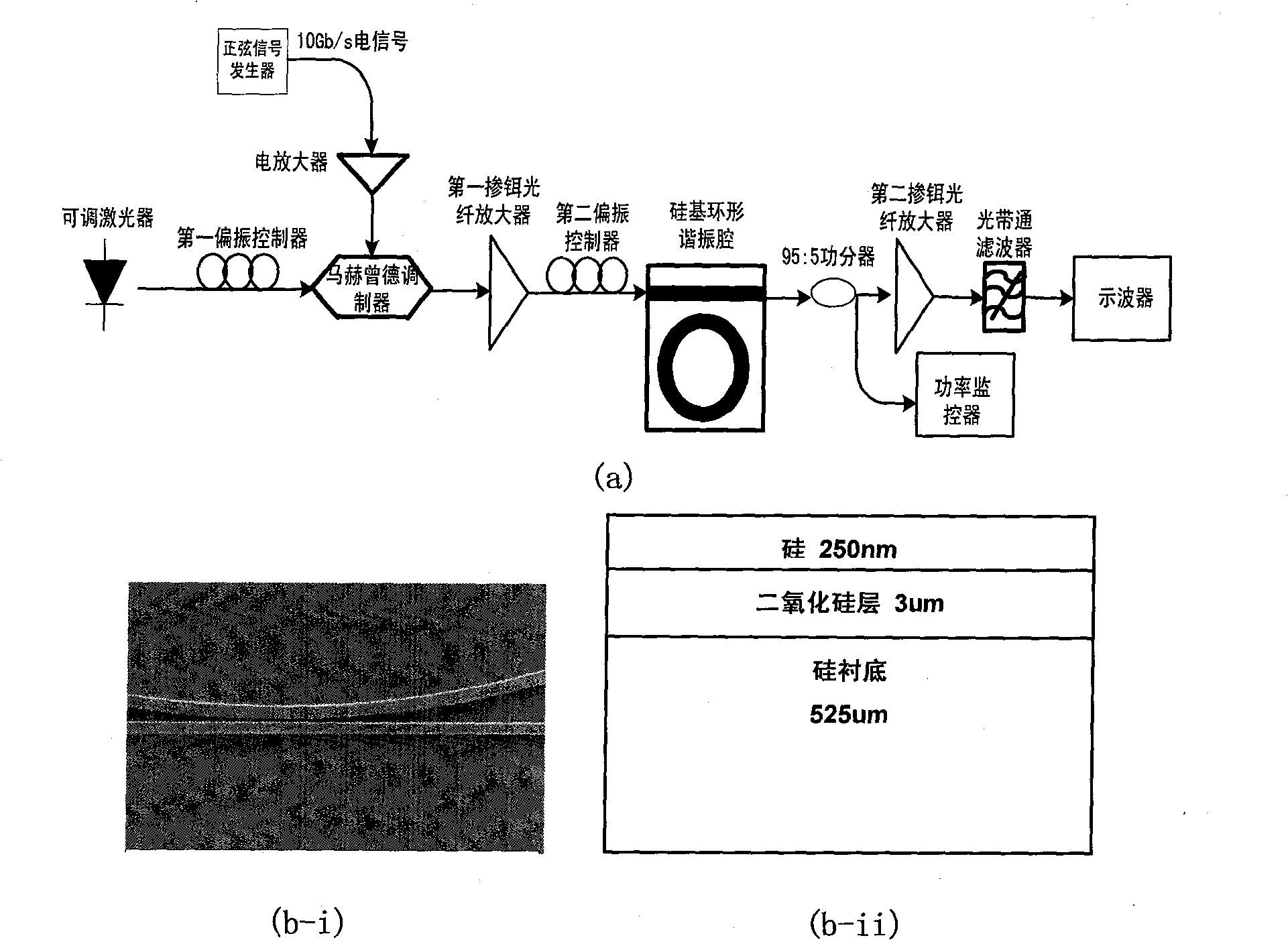
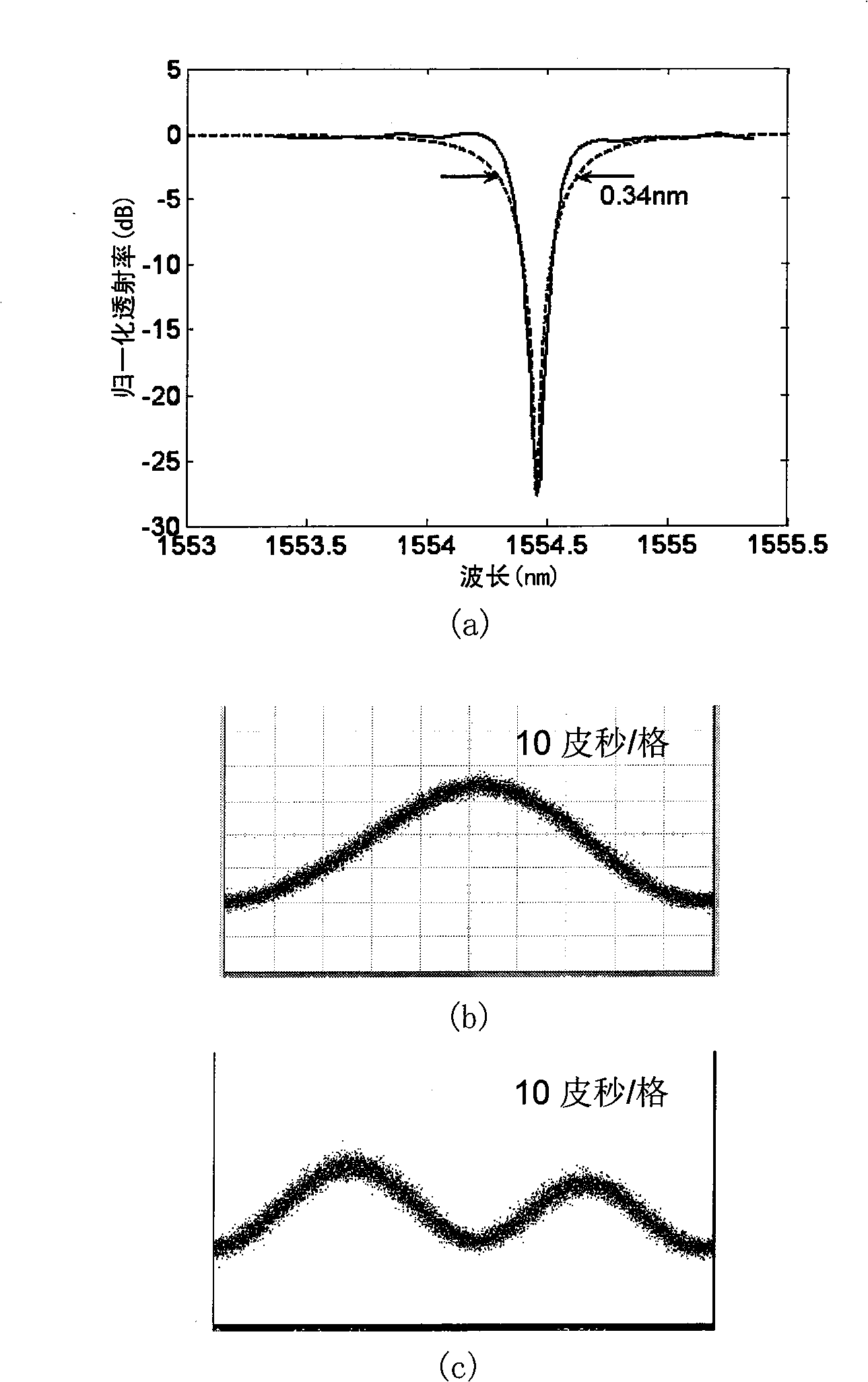
Light differentiator based on silicon based ring-shaped resonant cavity
InactiveCN101303506ASimple structureReduce volumeElectromagnetic transmissionNon-linear opticsFrequency spectrumDifferentiator
The invention discloses an optical differentiator based on a silicon-based annular cavity resonator, which belongs to the field of optical fiber communication technology. The optical differentiator comprises a to-be-differentiated signal generator, a silicon-based annular cavity resonator, and a differentiated signal detecting and monitoring system. The silicon-based annular cavity resonator consists of a silicon-based annulet and a straight waveguide and the air-gap between the annulet and the straight waveguide is from dozens to hundreds of nanometers; the spectra of the silicon-based annular cavity resonator is characterized by periodical band-stop filtering and the transmissivity at the resonant wavelength is equal to 0 or quite close to 0. The principle of the optical differentiator is that when the silicon-based annular cavity resonator meets or is close to a critical coupling state, the spectra characteristic of the silicon-based annular cavity resonator is quite similar to the differentiator within certain range with the resonant wavelength as the center. The optical differentiator manufactured by the device has simple structure, small volume and convenient integration and can be used in an integrated all-optical signal processing system.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Programmable device configuration methods adapted to account for retiming
ActiveUS8677298B1Reduce delaysOptimize circuit designCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsEmbedded systemIntegrated circuit
A method of configuring an integrated circuit device with a user logic design includes analyzing the user logic design to identify critical and near-critical cyclic logic paths within the user logic design, applying timing optimizations to the critical and near-critical cyclic logic paths, and retiming logic paths other than the critical and near-critical cyclic logic paths.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Method for preparing crystalline polyether-ether-ketone foam material
The invention belongs to the technical field of processing of high molecular material, and in particular relates to a method for preparing a crystalline polyether-ether-ketone foam material. By the method, the content of crystal in polyether-ether-ketone and the thickness and the perfection of a laminated crystal are controlled by controlling saturation temperature, saturation pressure and saturation time by using near-critical or supercritical carbon dioxide as a physical foaming agent so as to prepare the polyether-ether-ketone foam material with high performance. By the method, the defects that the gas saturation time is long, the solubility is small, the growth of a foam hole and morphology crystallized area are limited and the like are overcome, so that by controlling technological parameters, the high-performance foam material with the low-intensity and the high foaming ratio is effectively prepared, the application field of polyether-ether-ketone is widened, and the blank of a domestic high-performance crystalline polyether-ether-ketone foaming technology is made up.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for reactivating solid catalysts used in alkylation reactions
InactiveUS6579821B1Reducing and eliminating needMaintained relatively longOther chemical processesCatalyst regeneration/reactivationAlkyl transferAlkylation
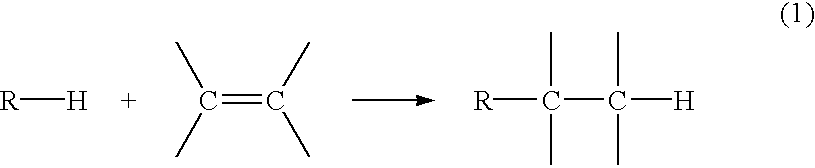
A method for reactivating a solid alkylation catalyst is provided which can be performed within a reactor that contains the alkylation catalyst or outside the reactor. Effective catalyst reactivation is achieved whether the catalyst is completely deactivated or partially deactivated. A fluid reactivating agent is employed to dissolve catalyst fouling agents and also to react with such agents and carry away the reaction products. The deactivated catalyst is contacted with the fluid reactivating agent under pressure and temperature conditions such that the fluid reactivating agent is dense enough to effectively dissolve the fouling agents and any reaction products of the fouling agents and the reactivating agent. Useful pressures and temperatures for reactivation include near-critical, critical, and supercritical pressures and temperatures for the reactivating agent. The fluid reactivating agent can include, for example, a branched paraffin containing at least one tertiary carbon atom, or a compound that can be isomerized to a molecule containing at least one tertiary carbon atom.
Owner:STONE RICHARD D +1
Method of creating crystalline substances
Process for preparing a cocrystal of an active substance and a cocrystal former, the process involving precipitating the active substance and the cocrystal former together from solution or suspension, in the presence of a supercritical or near-critical fluid, in particular using a GAS, SAS, SEDS or SAS-EM process. The invention also provides a cocrystal prepared using such a process, and its use as a seed crystal in a subsequent process for precipitating a cocrystal of an active substance and a cocrystal former.
Owner:THAR PHARMA
Method for extracting carotenoid and liquid biological fuel from Dunaliella sallina
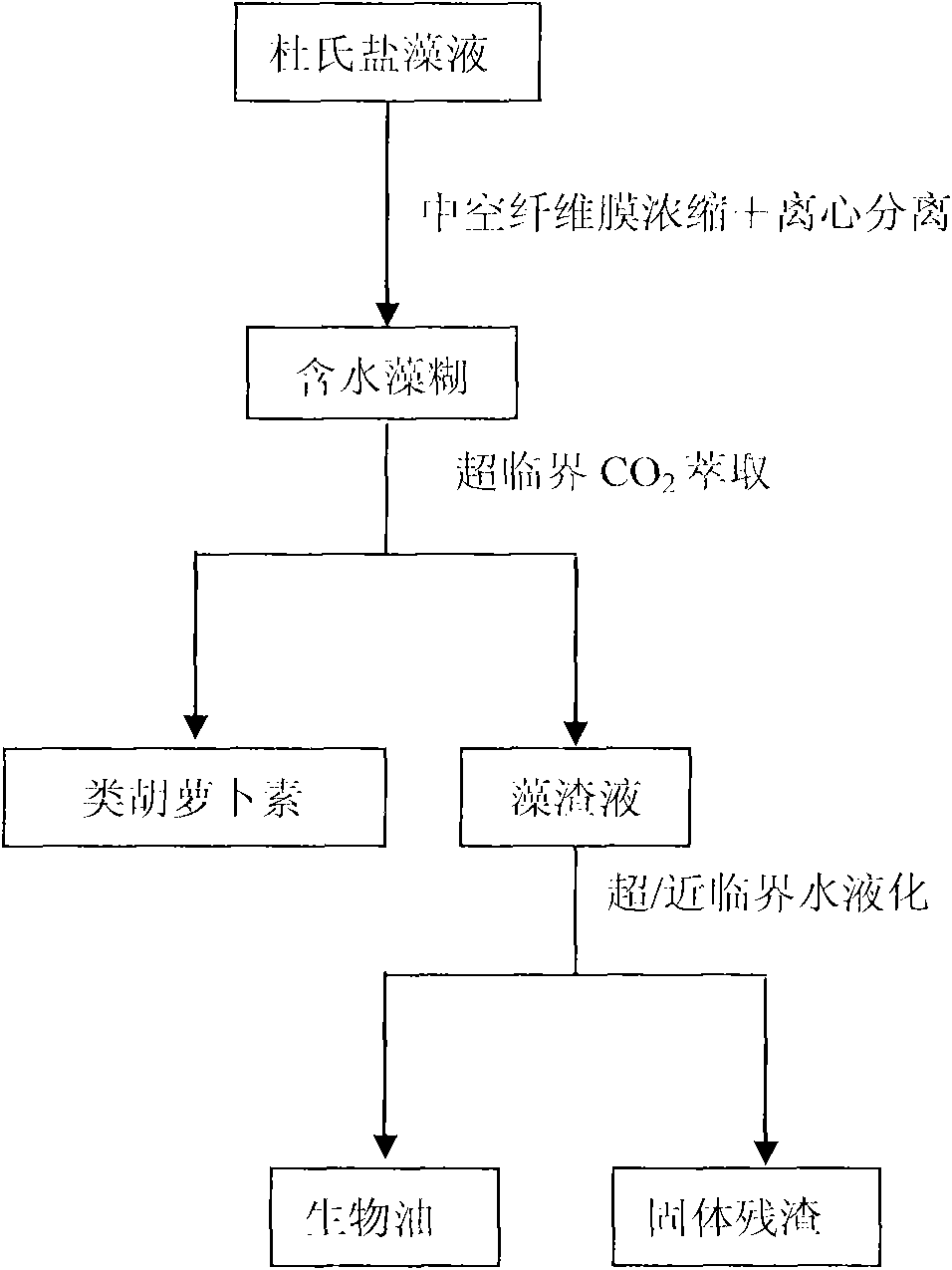
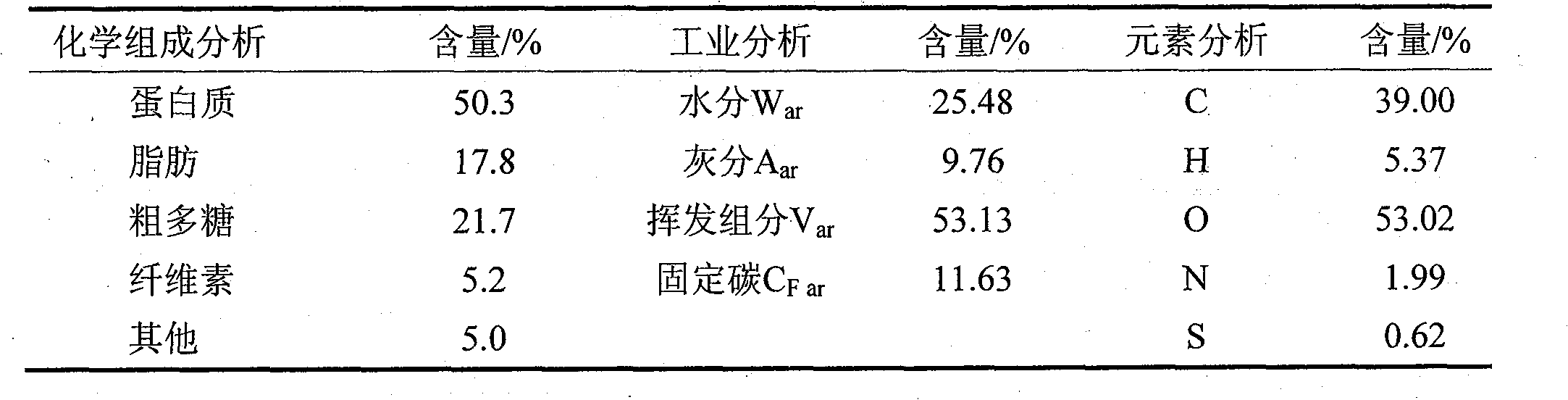
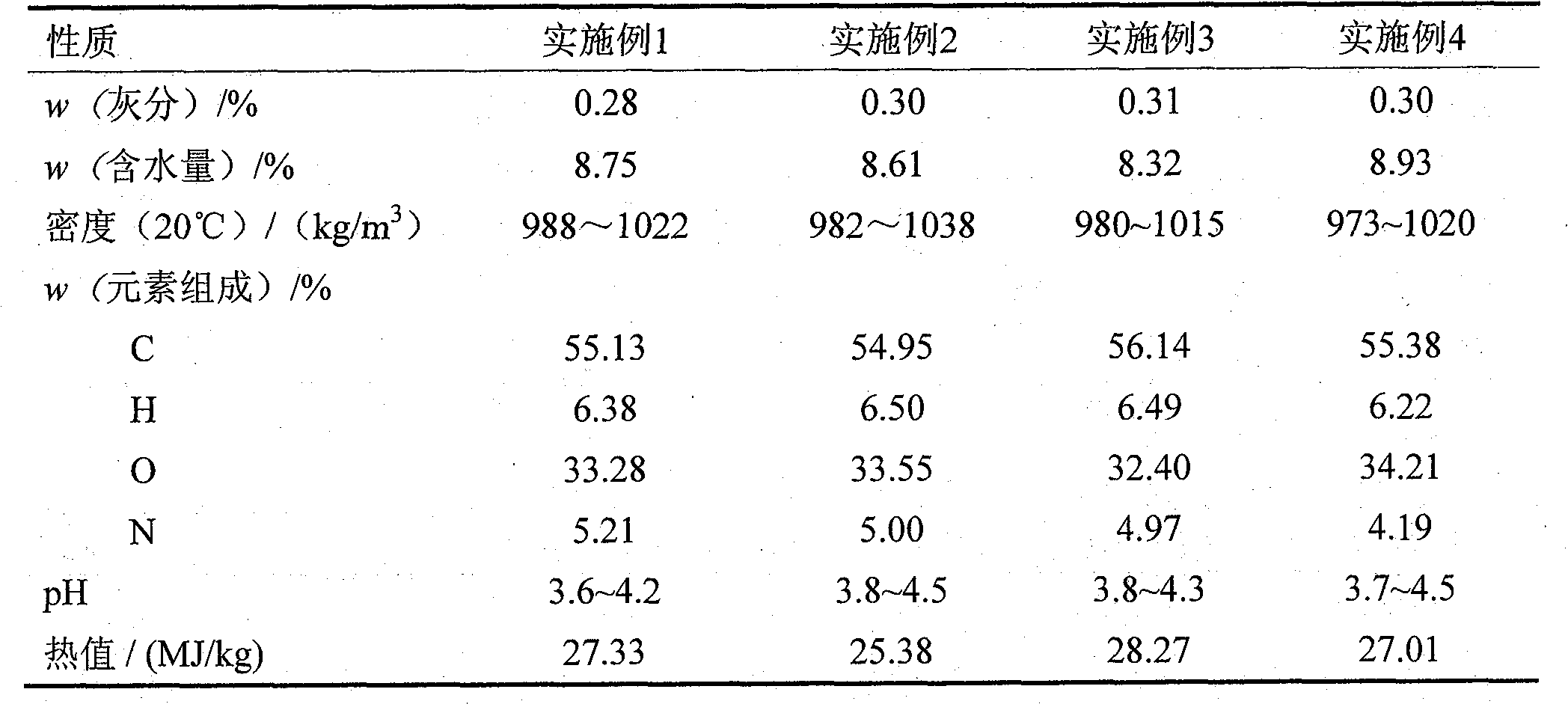
ActiveCN101774956AHigh yieldHigh calorific valueOrganic chemistryLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionFiberCarotenoid
The invention discloses a method for extracting carotenoid and liquid biological fuel from Dunaliella sallina, which belongs to the technical fields of bioactive substance extraction and biological energy. The method comprises the following steps of: concentrating a Dunalielle sallina liquid by using a hollow fiber membrane and a centrifugal separation method to obtain an aqueous sallina paste, extracting the aqueous sallina paste by using supercritical carbon dioxide to obtain a carotenoid product and a sallina residue liquid, and liquefying the sallina residue liquid by using supercritical / near-critical water to obtain the biological fuel. The invention has the advantages of no need of drying raw materials, low energy consumption, environment protection for entire process, simple technology, high utilization ratio of equipment, conduction of extraction using supercritical carbon dioxide and liquefaction using supercritical / near-critical water in the same reaction kettle, high yield of carotenoid and the biological fuel, low production cost and suitability for large-scale production.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
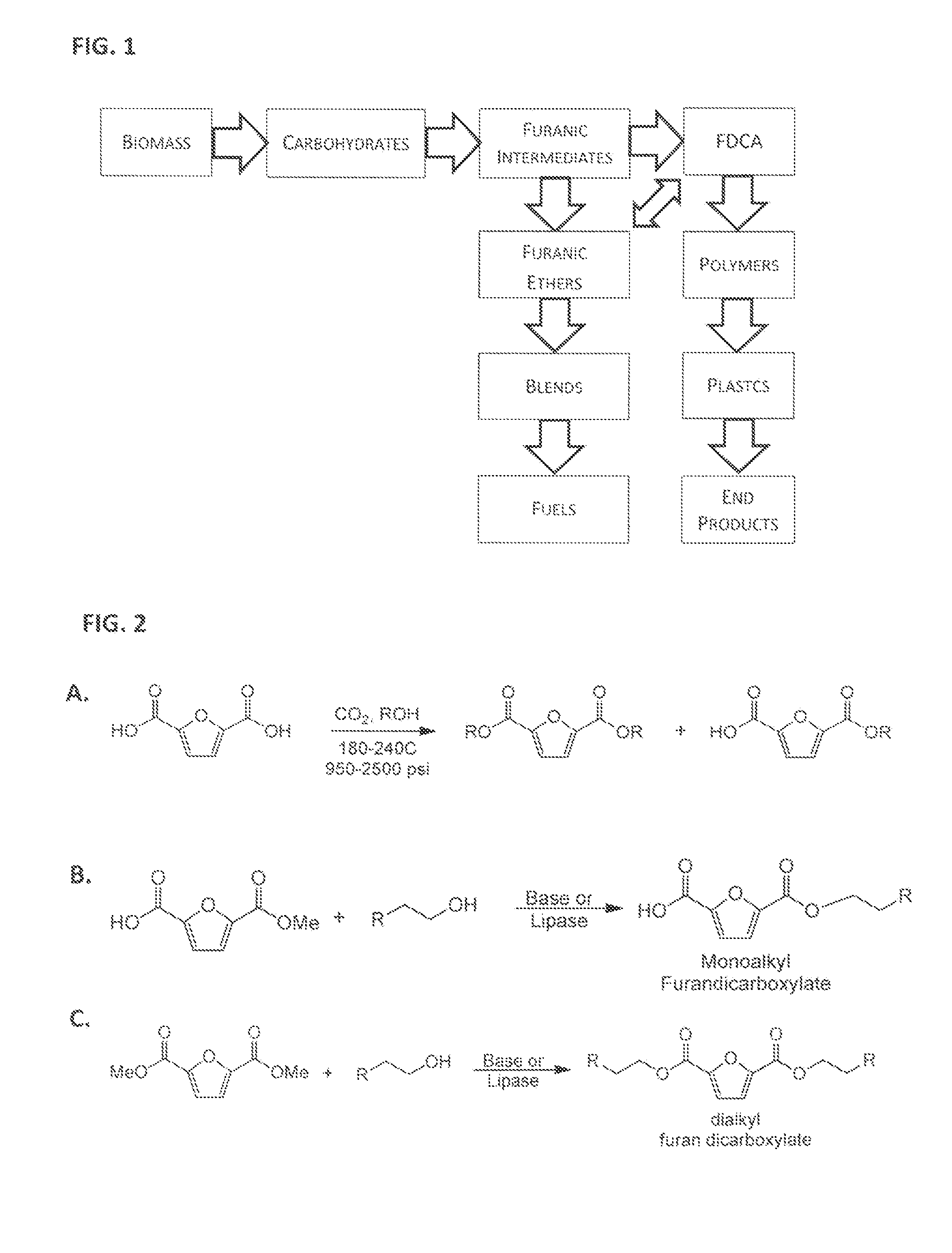
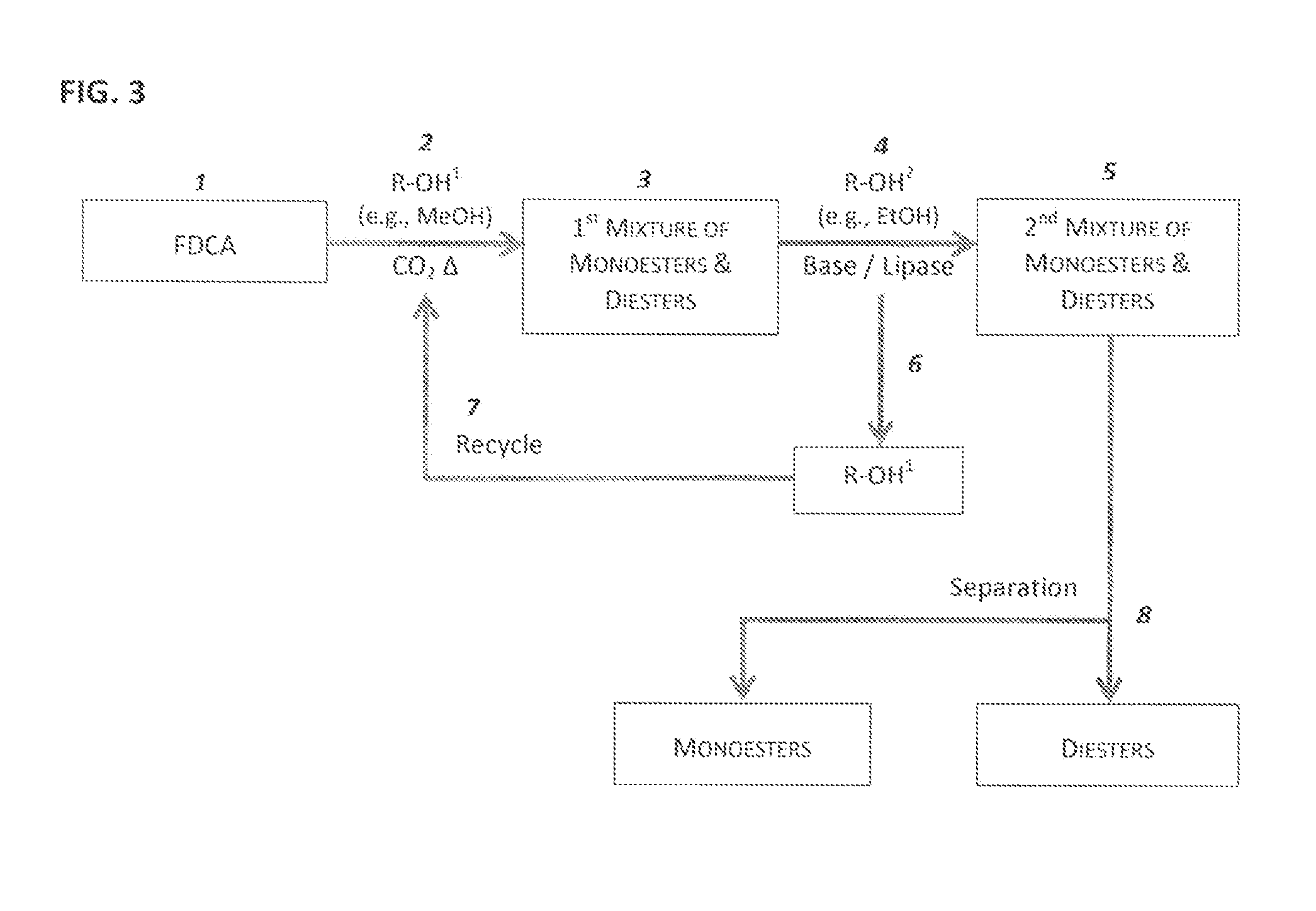
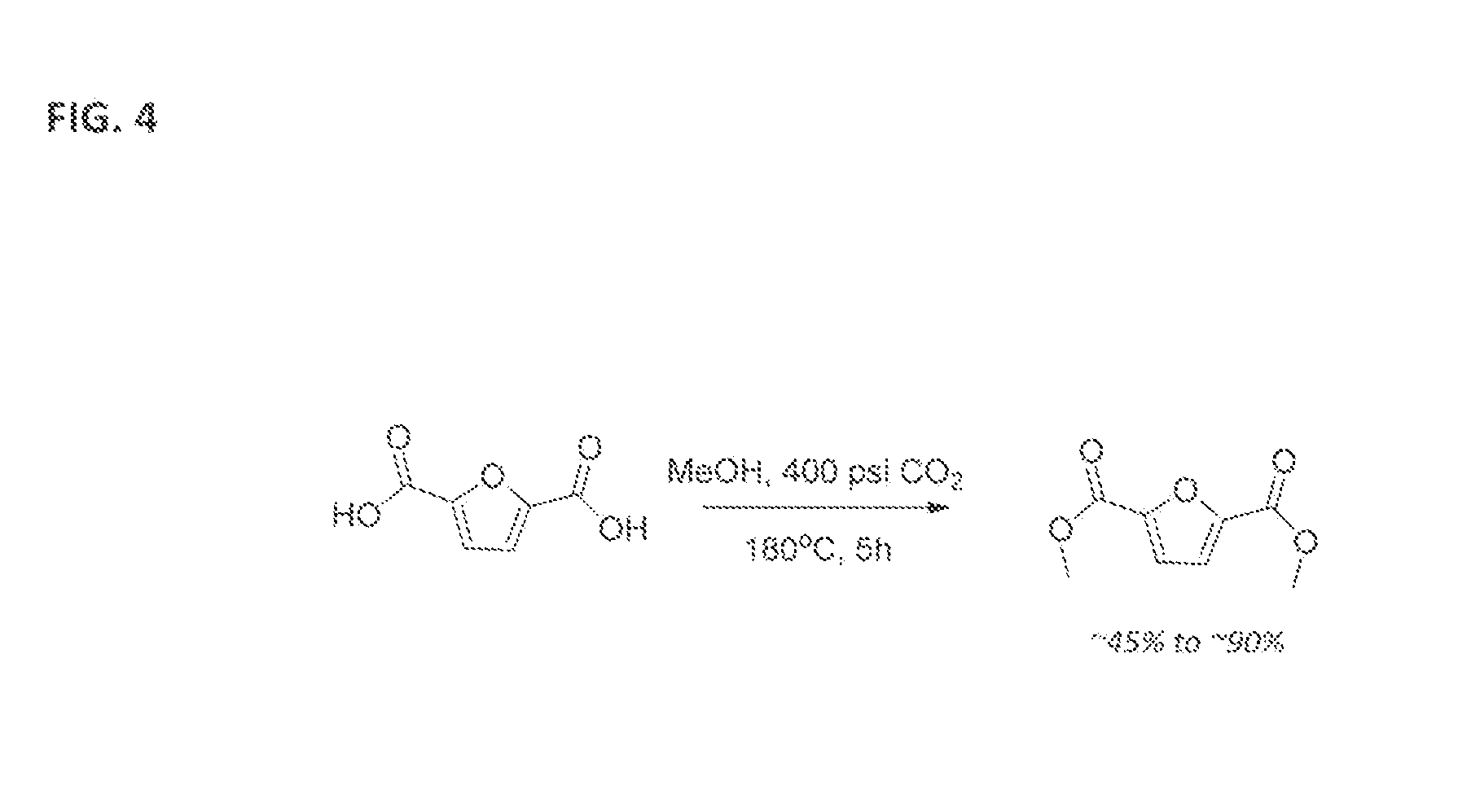
Esterification of 2,5-Furan-Dicarboxylic Acid
A method of making a furan dicarboxylate by means of reacting 2,5-furan dicarboxylic acid (FDCA) with an alcohol or mixture of alcohols in a CO2-predominant atmosphere without the presence of any other acid catalyst is described. The reaction is conducted under conditions that correspond to either supercritical, critical or near-critical temperatures and pressures for the alcohol species and / or CO2 gas.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com