Pretreating cellulosic biomass
a cellulosic biomass and pretreatment technology, applied in the direction of cellulose treatment using microorganisms/enzymes, pulp liquor regeneration, bulk chemical production, etc., can solve the problems of limited bioconversion of plant biomass, large amount of wood material not being used for more traditional structural uses of wood, and large amount of wood material being used for the more traditional structural use of wood. , to achieve the effect of improving the pretreatment effect of cellulosic biomass
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Biomass Raw Materials
[0067]Representative hardwood (red oak), soft wood (white pine) and waste paper (newsprint) were tested. Kiln-dried, “green” oven dried and “green” never-dried red oak and white pine shavings, cubes and chips were tested. White pine and red oak cubes were prepared by cutting kiln-dried boards with an 8″ Craftsman table saw ripped with the grain; these strips were then cross-cut with a Delta bandsaw to produce cubes which are approximately 6 mm on each side. Shavings (approximately 25 mm×6 mm×3 mm) of white pine and red oak were prepared by planting kiln-dried boards on a 6″ Delta joint-planer. “Green” never-dried white pine and red oak chips were prepared making transverse cuts across the diameter of a log from a freshly felled tree. The transverse cuts were made with a newly sharpened chain saw blade to produce thin chips approximately 10 mm×6 mm×1 mm. The “green” never-dried chips were prepared with the courtesy of Professor Robert P. Ordway, Loudon, N.H. News...
example 2
Effect of Residence Time on CBP
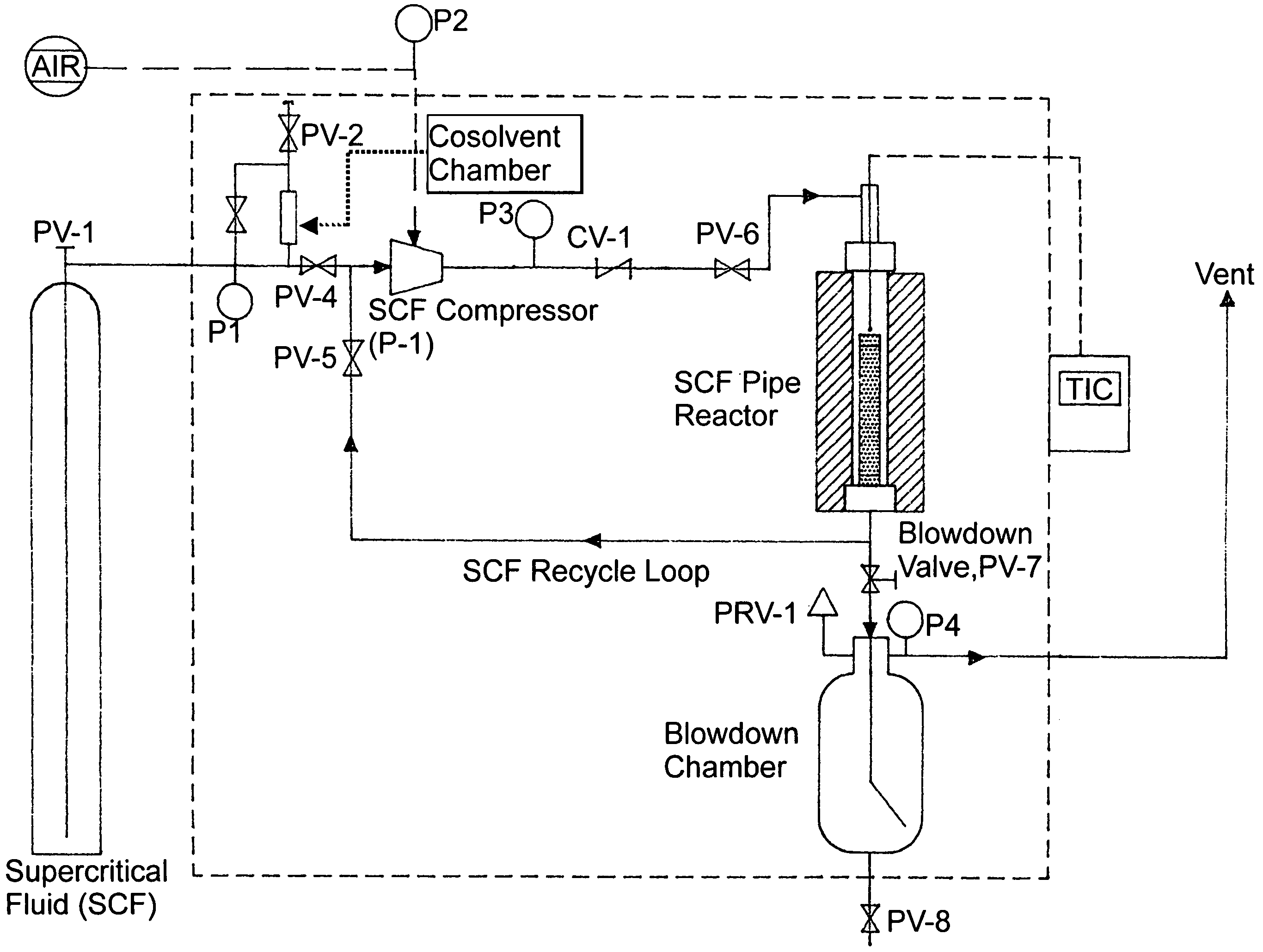
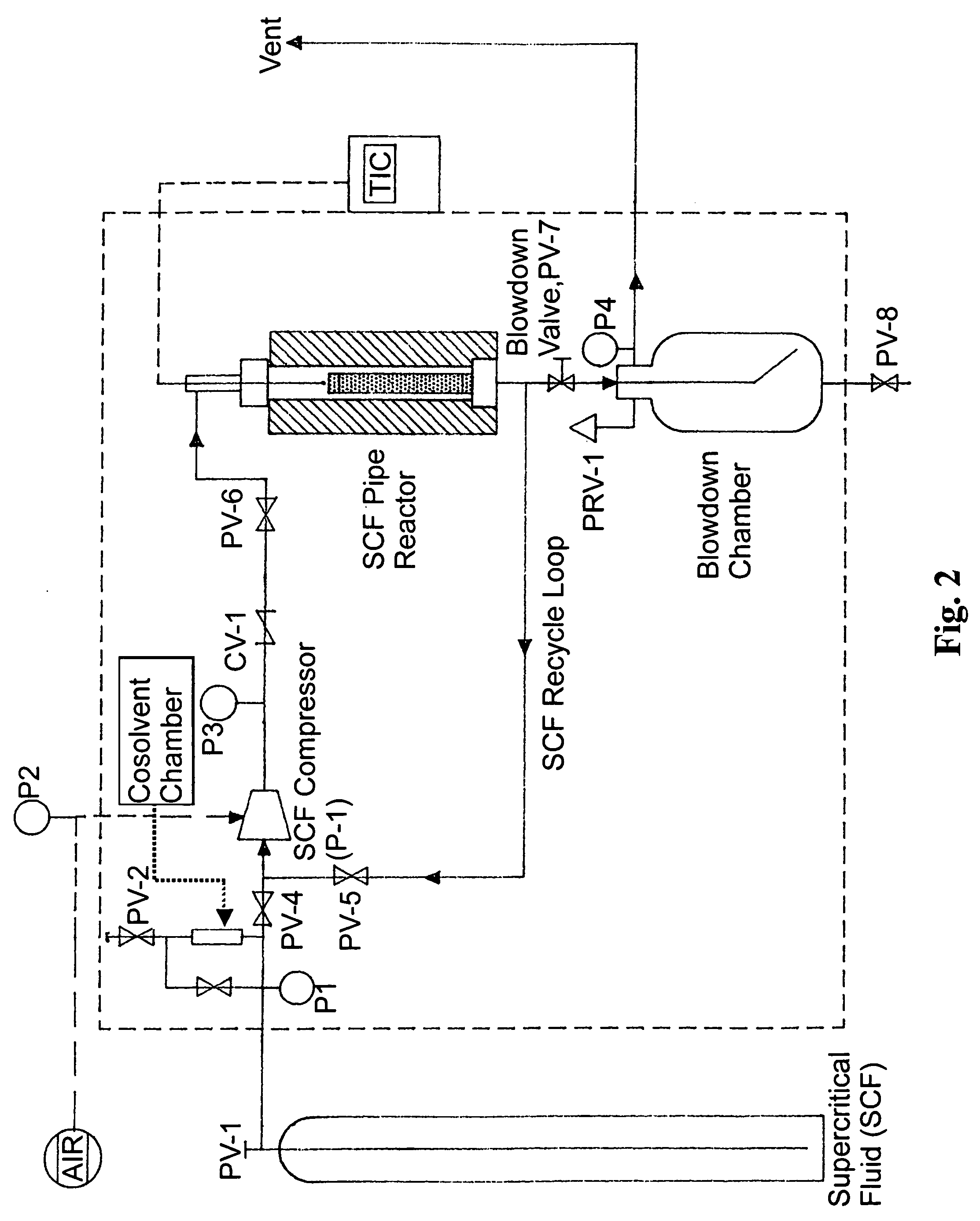
[0078]Residence time is a major operating parameter since it impacts process equipment size and process economics. The effect of residence time on the CBP of kiln-dried white pine cubes by supercritical carbon dioxide (SFS CO2) at 10,000 psig and 200° C. is shown in FIG. 7 and detailed in Table 3.
[0079]The experiments listed were conducted with the apparatus shown in FIG. 7 in a non-recycle mode. The listed temperatures and pressures are time-averaged over each run's duration. The biomass recovery efficiency or yield, Eb, is corrected for moisture content before and after ever CBP experiment (for the experiments listed in Table 3, the average moisture content was reduced from 8.87% before to 2.80% after the experiments). The enzymatic hydrolysis conversion efficiency, Ec, is based on the dry weight of biomass recovered after CBP, i.e. Ec is corrected for moisture content and biomass material loss. These qualification, unless otherwise noted, are true f...
example 3
Effect of Pressure on CBP
[0083]The effect of pressure on the pretreatment of kiln-dried white pine cubes by supercritical carbon dioxide at 200° C. for a residence time of 15 minutes is shown in FIG. 8 and detailed in Table 4.
[0084]Pressure and pressure drop are important variables in the critical fluid pretreatment process. Higher pressures are expected to drive more gases into the cells, and increase the pretreatment efficiency by increasing the PV work on decompression. Greater pressure drops on decompression should also improve defibration efficiency and enzymatic hydrolysis susceptibility.
[0085]Pressure and pressure drop were thus seen as very important variables in the CBP process and consequently, among the first to be tested to prove process feasibility. Pressure drop is also seen to be an important economic variable in that PV work can be conserved and recompression energy minimized by limiting the size of the pressure swing. From a practical standpoint, pressure drop may b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com